Page 1

RCI-6900F HP
RCI-6900F TB
CHAPTER 1
SPECIFICATIONS
1.0 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.1 Transmitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.2 Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
TABLE OF
CONTENTS
PAGE
CHAPTER 2
OPERATION
2.0 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1 Control & Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.1 Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.2 Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.1.3 Frequency Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.2 Microphone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.3 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.3.1 Procedure To Receive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.3.2 Procedure To Transmit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . 7
2.4 Alternate Microphones And Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
CHAPTER 3
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
3.0 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1 PLL Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 Receiver Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Transmitter Modulation Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.4 Transmitter Amplifier Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
9
9
9
CHAPTER 4
ALIGNMENT
4.0 Required Test Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.1 Alignment Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.1 PLL Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.2 Transmitter Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.3 Receiver Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14
14
15
16
CHAPTER 5
MAINTENANCE
5.0 Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.1 Periodic Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.2 Fuse Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CHAPTER 6
DIAGRAMS AND PART LIST
6.0 PCB Layout & Part List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. 20
RCI-6900F HP
RCI-6900F TB
SPECIFICATIONS
19
CHAPTER 1
- 1 -
Page 2

1.0 GENERAL
Model RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB
Frequency Range 28.245 - 29.655MHz.
Emission Modes CW/FM/AM/SSB (A1/F3/A3/A3J)
Frequency Control Phase Lock Loop (PLL) synthesizer.
Frequency Tolerance
Frequency Stability
Operating Temperature Range
Microphone Dynamic PTT, 500 Ω
Input Voltage 13.8V DC
Current Drain: Transmit (AM full mod.) RCI-6900F HP < 5A; RCI-6900F TB < 15A.
Current Drain : Receiver (Squelched)
(Max. audio output) < 0.5A.
Antenna Connector UHF, SO239.
Dimensions : (RCI-6900F HP) 7 7/8”(W) x 10 3/4” (D) x 2 3/8”(H)
: (RCI-6900F TB) 7 7/8” (W) x 9 1/4” (D) x 3 7/8” (H)
Weight 5 lb. (RCI-6900F HP), 7lb 6 oz (RCI-6900F TB)
1.1 TRANSMITTER
AM/FM/CW ; SSB RF Power Output (RCI-6900FHP)
AM/FM/CW ; SSB RF Power Output (RCI-6900FTB)
RF Transmit Modes CW/FM/AM/SSB.
Modulation High and low level Class B, Amplitude Modulation.
Spurious Emissions -50 dB.
Carrier Suppression -35 dB.
Audio Frequency Response 300 to 2500 Hz
Antenna Impedance 50 Ohms.
Output Indicators Meter shows relative RF output power, receive signal
1.2 RECEIVER
Sensitivity For 10dB S/N (AM ; CW/SSB)
Sensitivity For 20dB S/N (FM)
IF Frequency AM: 10.695 MHz 1st IF, 455 KHz 2nd IF.
Image Rejection > 50 dB.
Adjacent Channel Selectivity > -55 dB (AM/FM) ; > -60 dB (CW/SSB)
RF Gain Control 45 dB adjustable for optimum signal reception.
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) Figure Of Merit 100 mV for 10 dB Change in Audio Output.
Squelch
Noise Blanker RF type.
Audio Output Power 2.5W @ 10% THD
Audio Frequency Response 300 to 2500 Hz.
Built-in Speaker 8 Ohms, 4 Watts.
External Speaker (Not Supplied) 8 Ohms; 4 Watts.
RCI-6900F HP
RCI-6900F TB
± 0.005 %.
± 0.001 %.
-30°C to +50°C.
≤ 0.25A.
10W ; 25W PEP
50W ; 100W PEP
and SWR. Transmit LED glows red when transmitter
is in operation.
< 0.5 µV ; < 0.25 µV.
< 0.5 µV.
Adjustable; threshold less than 0.5 µV.
(SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE)
CHAPTER 2
OPERATION
- 2 -
Page 3
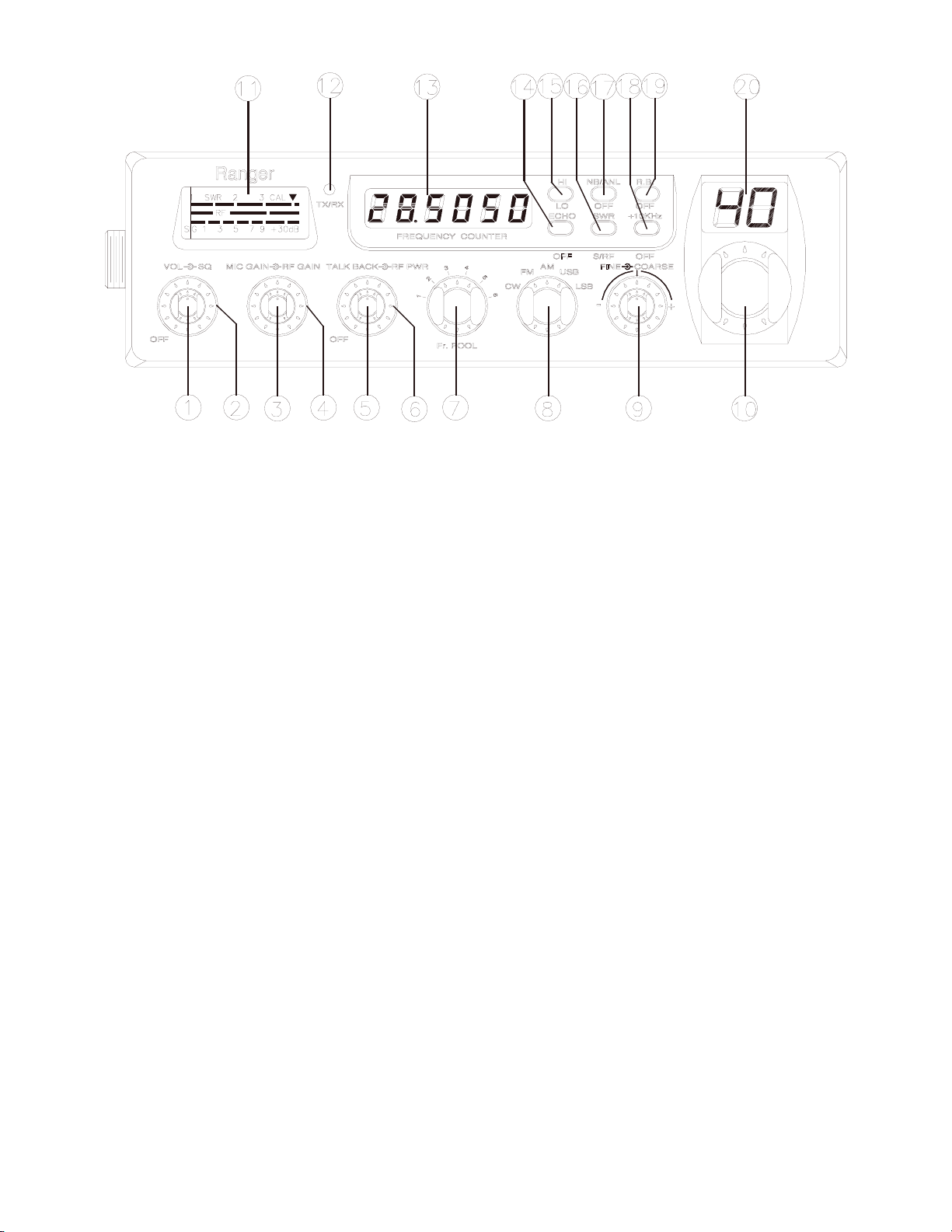
Figure 2-1 Front Panel
2.0 INTRODUCTION
This section explains the basic operating procedures for the RANGER RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB
mobile transceiver.
2.1 CONTROL AND CONNECTIONS
2.1.1 FRONT PANEL
Refer to the above Figure 2-1 for the location of the following controls.
1. ON/OFF VOLUME CONTROL
This knob controls the volume and the power to the radio. To turn the radio on, rotate the knob
clockwise. Turning the knob further will increase the volume of the receiver.
2. SQUELCH CONTROL
This switch is used to eliminate background noise being heard through the receiver which can be
disturbing when no transmissions are being received. To use this feature of your radio, gently turn the
switch fully counterclockwise, and then turn clockwise until the background noise is just eliminated.
Further clockwise rotation will increase the threshold level and only strong signals will be heard.
3. MIC GAIN CONTROL
Adjusts the microphone gain in the transmit mode. This control adjusts the gain to the extent that full
talk power is available several inches away from the microphone.
4. RF GAIN CONTROL
This control is used to reduce the gain of the RF amplifier under strong signal conditions.
5. TALKBACK CONTROL
Adjust this knob for desired volume of Talkback. This is used to monitor your own voice. For example,
you could use this feature to compare different microphones.
6. RF POWER CONTROL
This control allows the user to adjust RF power output.
- 3 -
Page 4

7. FR. POOL SELECTOR
This switch is used to select the frequency range of operation (1 - 6).
8. MODE SWITCH
This control allows you to select one of the following operating modes: CW/FM/AM/USB/LSB.
9. FINE/COARSE CONTROL
Allows variation of the receiver operating frequency above and below the assigned frequency.
Although this control is intended primarily to tune in SSB signal, it may be used to optimize AM/FM
signals as described in the operating procedure paragraphs. Coarse operates both TX/RX, Fine operate
in RX only.
10. CHANNEL SELECTOR
This control is used to select a desired transmit and receive channel.
11. FRONT PANEL METER
The Front Panel Meter allows the user to monitor signal strength, RF output power and SWR level.
12. TX/RX LED
The red LED indicates the unit is in the transmit mode. The green LED indicates the unit is in the
receive mode.
13. FREQUENCY COUNTER
This display indicates the frequency of operations.
14. ECHO/OFF SWITCH
This control is used for echo effect.
15. HI/LO SWITCH
This switch changes tone quality in receive only. In LO position, bass is increased and in HI position,
treble is increased.
16. S-RF/SWR SWITCH
This is a two-function switch. In the S-RF position, the meter will indicate the strength of the signal
being received, as well as the relative RF output of transmission. To use the meter to measure the
standing wave ratio, turn the switch to the SWR position.
17. NB/ANL/OFF SWITCH
In the NB/ANL position, the RF Noise Blanker and the Automatic Noise Limiter in the audio circuits
are also activated. The Noise Blanker is very effective in eliminating repetitive impulse noise such as
ignition interference.
18. R.B./OFF SWITCH
In the Roger Beep position, the radio transmits an audio tone at the end of your transmission to indicate
that transmission has ended. As a courtesy to others, use the Roger Beep only when necessary.
19. +10KHz/OFF SWITCH
When the switch is pressed the frequency is shifted 10KHz up.
20. CHANNEL DISPLAY
- 4 -
Page 5
The channel display indicates the current selected channel.
2.1.2 REAR PANEL
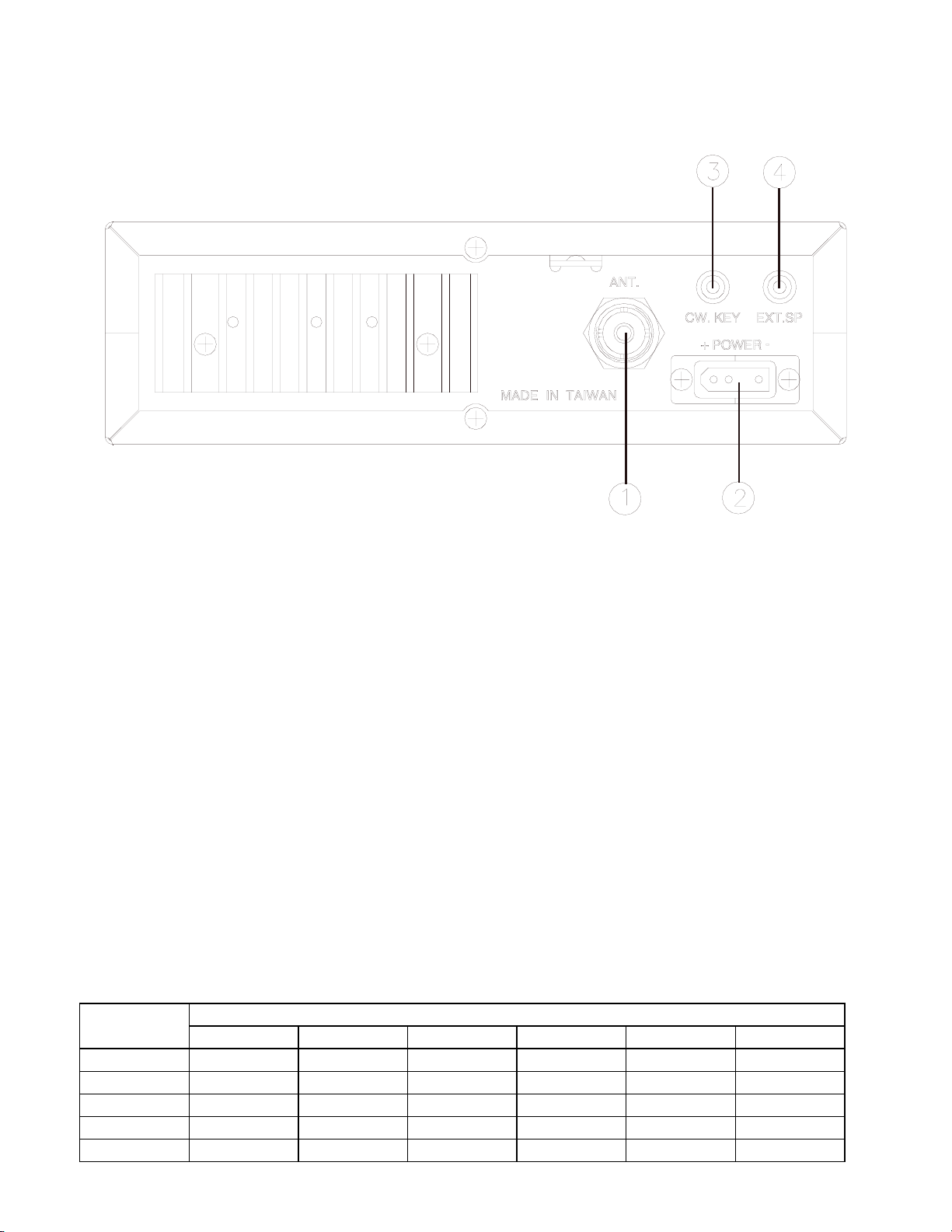
Figure 2-2 represents the location of the following connections:
Figure 2-2 Rear Panel
1. ANTENNA
This jack accepts 50 ohms coaxial cable with a PL-259 type plug.
2. POWER
This connector accepts 13.8V DC power cable with built-in fuse. The power cord provided with the
radio has a black and red wire. The black goes to negative and the red goes to positive.
3. CW. KEY
This is used for Morse Code operation. To operate this mode, connect a CW key to this jack, and place
the MODE switch in the CW position.
4. EXT. SP.
This jack accepts 4 to 8 ohms, 4 watts external speaker. When the external speaker is connected to this
jack, the built-in speaker will be disabled.
2.1.3 FREQUENCY CHART
FR. POOL
CHANNEL 1 (MHz) 2 (MHz) 3 (MHz) 4 (MHz) 5 (MHz) 6 (MHz)
1 28.245 28.695 29.145 28.315 28.765 29.215
2 28.255 28.705 29.155 28.325 28.775 29.225
3 28.265 28.715 29.165 28.335 28.785 29.235
4 28.285 28.735 29.185 28.355 28.805 29.255
5 28.295 28.745 29.195 28.365 28.815 29.265
- 5 -
Page 6
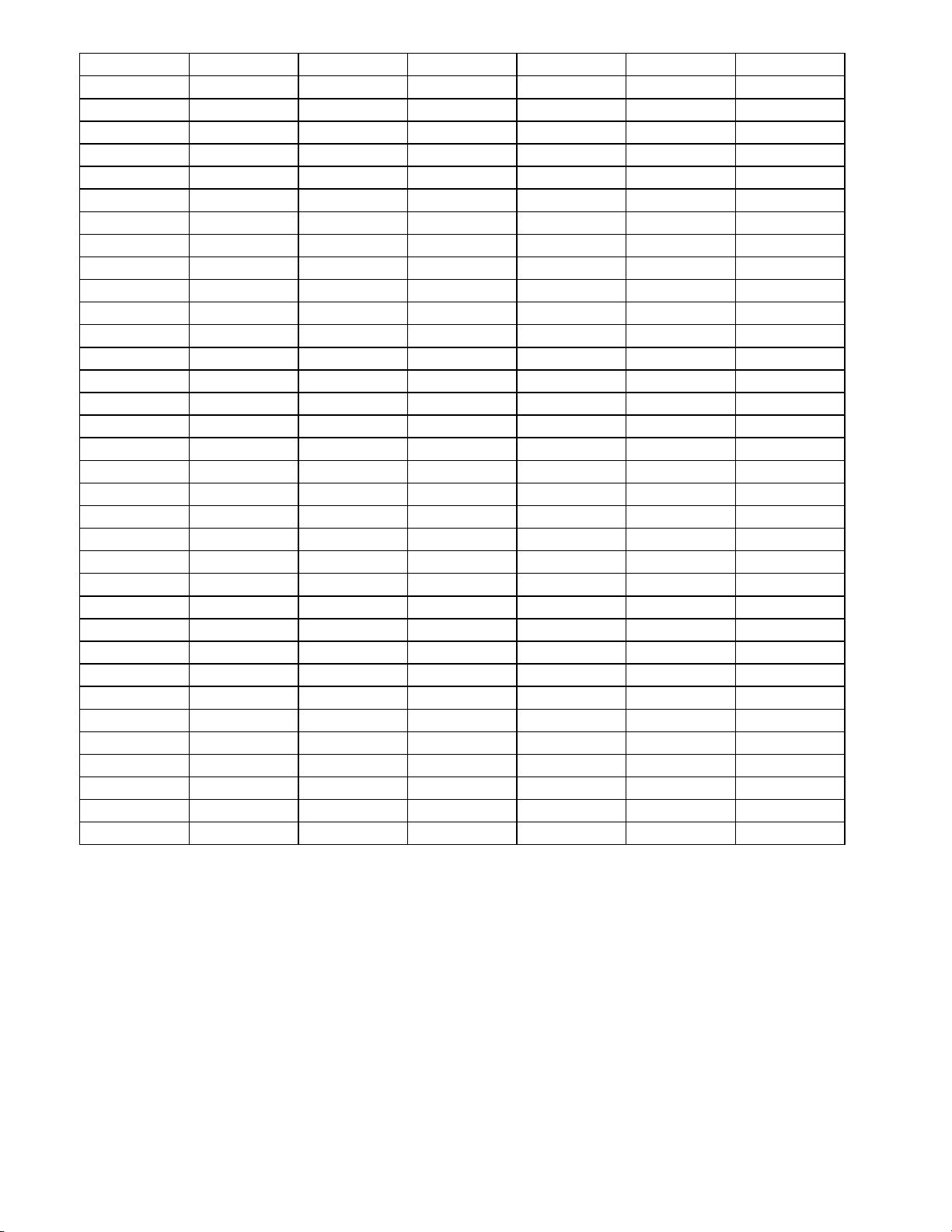
6 28.305 28.755 29.205 28.375 28.825 29.275
7 28.315 28.765 29.215 28.385 28.835 29.285
8 28.335 28.785 29.235 28.405 28.855 29.305
9 28.345 28.795 29.245 28.415 28.865 29.315
10 28.355 28.805 29.255 28.425 28.875 29.325
11 28.365 28.815 29.265 28.435 28.885 29.335
12 28.385 28.835 29.285 28.455 28.905 29.355
13 28.395 28.845 29.295 28.465 28.915 29.365
14 28.405 28.855 29.305 28.475 28.925 29.375
15 28.415 28.865 29.315 28.485 28.935 29.385
16 28.435 28.885 29.335 28.505 28.955 29.405
17 28.445 28.895 29.345 28.515 28.965 29.415
18 28.455 28.905 29.355 28.525 28.975 29.425
19 28.465 28.915 29.365 28.535 28.985 29.435
20 28.485 28.935 29.385 28.555 29.005 29.445
21 28.495 28.945 29.395 28.565 29.015 29.465
22 28.505 28.955 29.405 28.575 29.025 29.475
23 28.535 28.985 29.435 28.605 29.005 29.505
24 28.515 28.965 29.415 28.585 29.035 29.485
25 28.525 28.975 29.425 28.595 29.045 29.495
26 28.545 28.995 29.445 28.615 29.065 29.495
27 28.555 29.005 29.455 28.625 29.075 29.515
28 28.565 29.015 29.465 28.635 29.085 29.525
29 28.575 29.025 29.475 28.645 29.095 29.535
30 28.585 29.035 29.485 28.655 29.105 29.545
31 28.595 29.045 29.495 28.665 29.115 29.555
32 28.605 29.055 29.505 28.675 29.125 29.565
33 28.615 29.065 29.515 28.685 29.135 29.575
34 28.625 29.075 29.525 28.695 29.145 29.585
35 28.635 29.085 29.535 28.705 29.155 29.595
36 28.645 29.095 29.545 28.715 29.165 29.605
37 28.655 29.105 29.555 28.725 29.175 29.625
38 28.665 29.115 29.565 28.735 29.185 29.635
39 28.675 29.125 29.575 28.745 29.195 29.645
40 28.685 29.135 29.585 28.755 29.205 29.655
2.2 MICROPHONE
The receiver and transmitter are controlled by the push-to-talk switch on the microphone. Press the
switch and the transmitter is activated, release switch to receive. When transmitting, hold the
microphone two inches from the mouth and speak clearly in a normal voice. The radio comes complete
with a low impedance (500 ohm) dynamic microphone.
2.3 OPERATION
2.3.1 PROCEDURE TO RECEIVE
1. Be sure that power source, microphone and antenna are connected to the proper connectors before
going to the next step.
- 6 -
Page 7

2. Turn
VOL.
knob clockwise to apply power to the radio.
3. Set the
VOL.
to a comfortable listening level.
4. Set the
MODE
switch to the desired mode.
5. Listen to the background noise from the speaker. Turn the SQ knob slowly clockwise until the noise
just disappears. The SQ is now properly adjusted. The receiver will remain quiet until a signal is
actually received. Do not advance the control too far or some of weaker signals will not be heard.
6. Set the
CHANNEL
selector switch to the desired channel.
7. Set the
RF GAIN
control fully clockwise for maximum receive gain.
8. Adjust the
FINE/COARSE
control to clarify the SSB signals or to optimize AM/FM signals.
2.3.2 PROCEDURE TO TRANSMIT
1. Select the desired channel of transmission
2. Set the
MIC GAIN
control fully clockwise.
3. If the channel is clear, depress the push-to-talk switch on the microphone and speak in a normal
voice.
2.4 ALTERNATE MICROPHONES AND INSTALLATION
For best results, the user should select a low impedance dynamic type microphone or a transistorized
microphone. Transistorized type microphones have a low output impedance characteristic. The
microphones must be provided with a four-lead cable. The audio conductor and its shielded lead
comprise two of the leads. The third lead is for transmit control and the fourth is for receiving control.
The microphone should provide the functions shown in schematic below (Figure 2-3).
4 WIRE MIC CABLE
Pin Number Mic Cable Lead
1 Audio Shield
2 Audio Lead
3 Transmit Control
- 7 -
Page 8
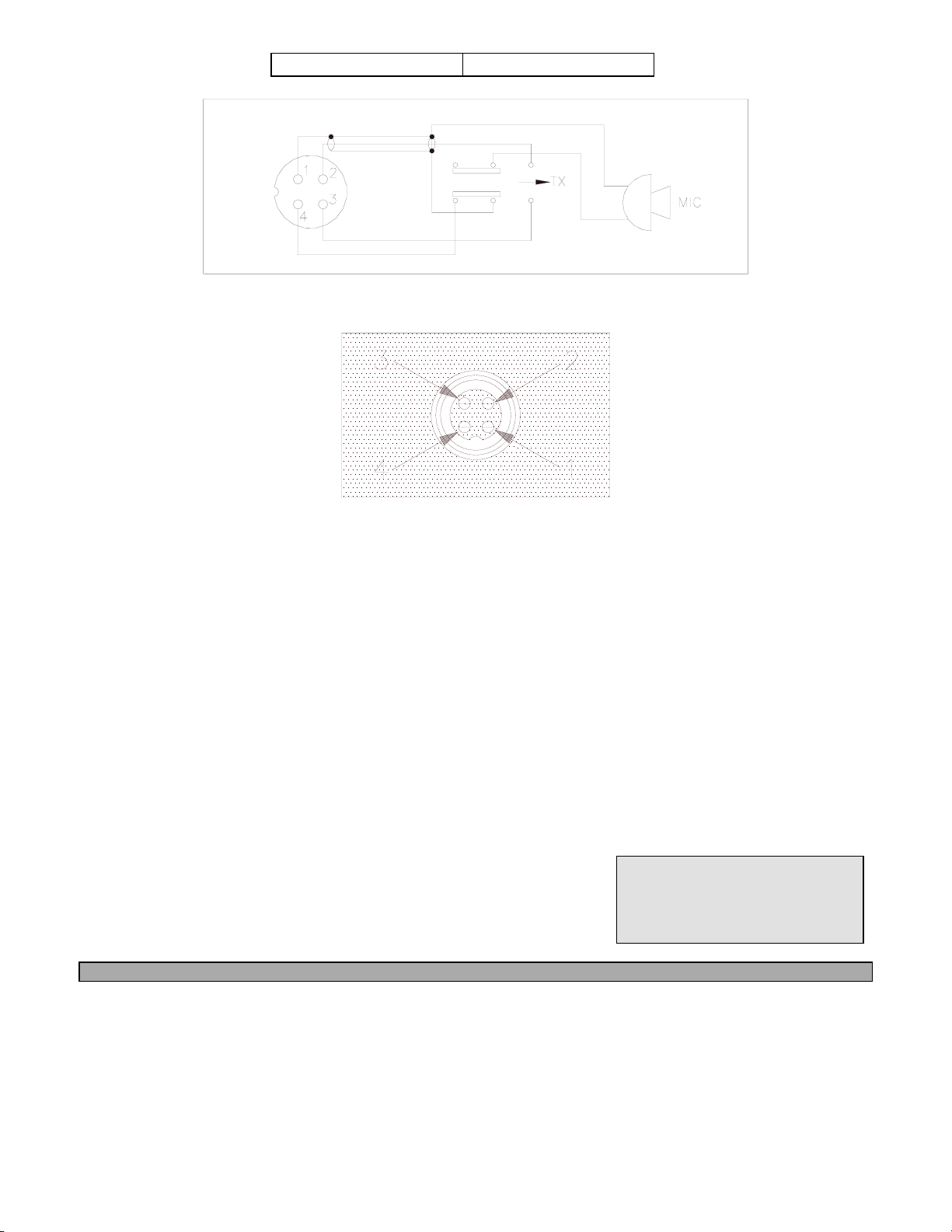
4 Receive Control
Figure 2-5 Microphone plugs pins numbers viewed from rear of pin receptacle.
RCI-6900F HP
Figure 2-3 Your Transceiver Microphone Schematic
CHAPTER 3
CIRCUIT
RCI-6900F TB
DESCRIPTION
3.0 INTRODUCTION
This section explains the technical theory of operation for the RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB mobile
transceiver.
3.1 PLL CIRCUIT
The Phase Lock Loop (PLL) circuit is responsible for developing the receiver’s first local oscillator
signal and the transmitter’s exciter signal. The PLL circuit consists primarily of IC2, IC3, IC4, IC5
- 8 -
Page 9

Q25, Q27, Q28, Q29 and Q61. The PLL circuit is programmed by the rotary channel switch GPS-0501.
The GPS-0501 communicates the correct binary data information to the programmable divider inside
of IC3. IC3 then controls the VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator), to oscillate on the correct
frequency. This signal is fed either into the receiver’s first mixer (for receive operation) or the
transmitter’s mixer (for transmit operation).
3.2 RECEIVER CIRCUIT
The incoming RF signal comes into the radio via the antenna and into the front-end pre-amp, Q17. The
RF signal is fed into the mixer circuit of the Q18 & Q19 and then into the AM IF section of the
receiver (depending on the mode of operation). The signal is then detected by either the AM detector or
product detector or then fed to the audio amplifier section of the receiver and finally out to the speaker.
3.3 TRANSMITTER MODULATION CIRCUIT
(i) The transmitter modulation circuit modulates the low-level RF signal from the PLL exciter circuit
with the user’s audio voice signal from the microphone. The audio from the microphone is then
amplified and fed into the transmit amplifier circuit.
(ii) If the transceiver is in the AM mode, the AF Power amplifier modulates the last RF amplifier,
which produces a true amplitude modulated RF signal.
3.4 TRANSMITTER AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
The transmitter takes the basic exciter signal from the TX mixer and amplifies it through a series of
amplifiers consisting of Q50, Q51, Q49, Q47, Q48 and EPA010010B (only for RCI-6900F TB) where
it is sent out to the antenna connector.
- 9 -
Page 10
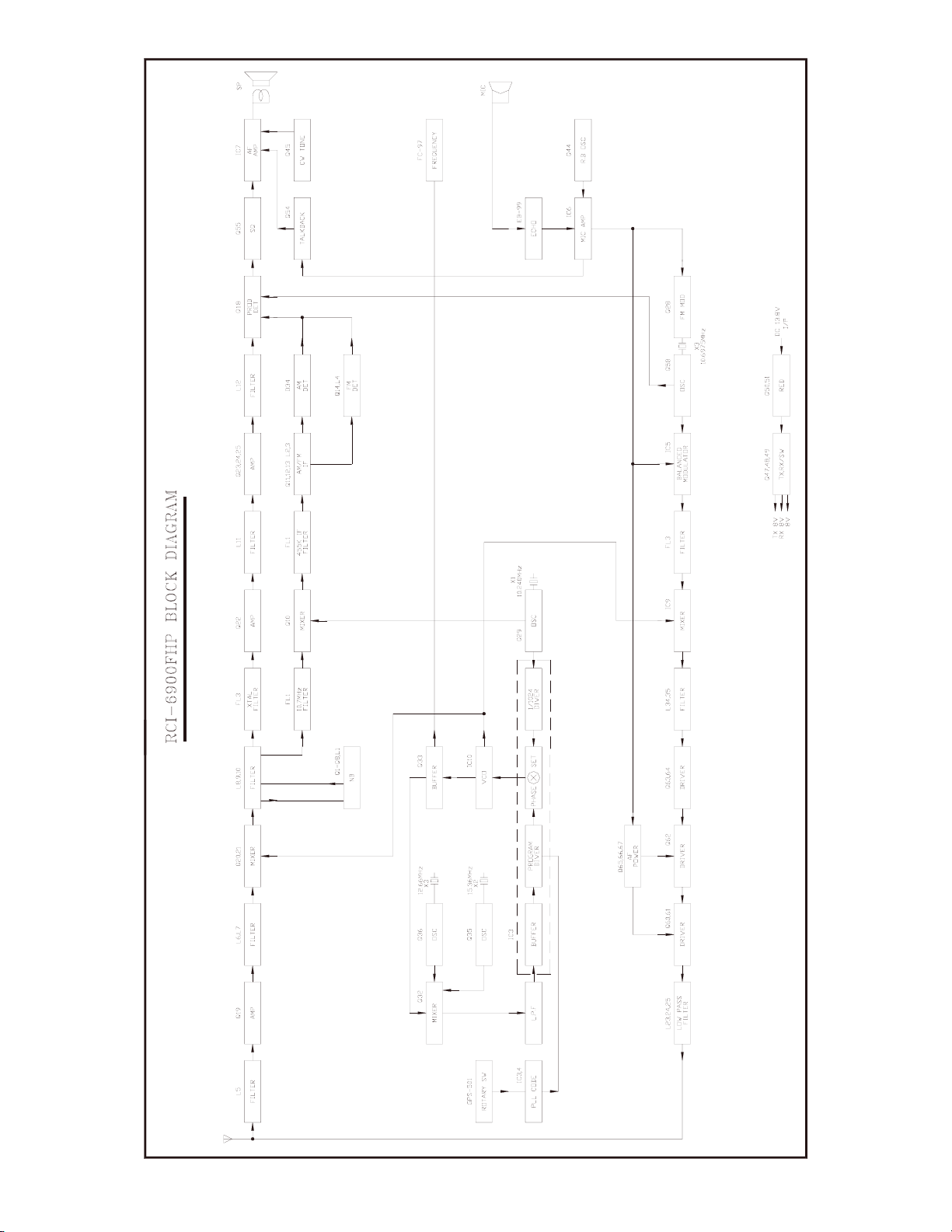
- 10 -
Page 11

- 11 -
Page 12
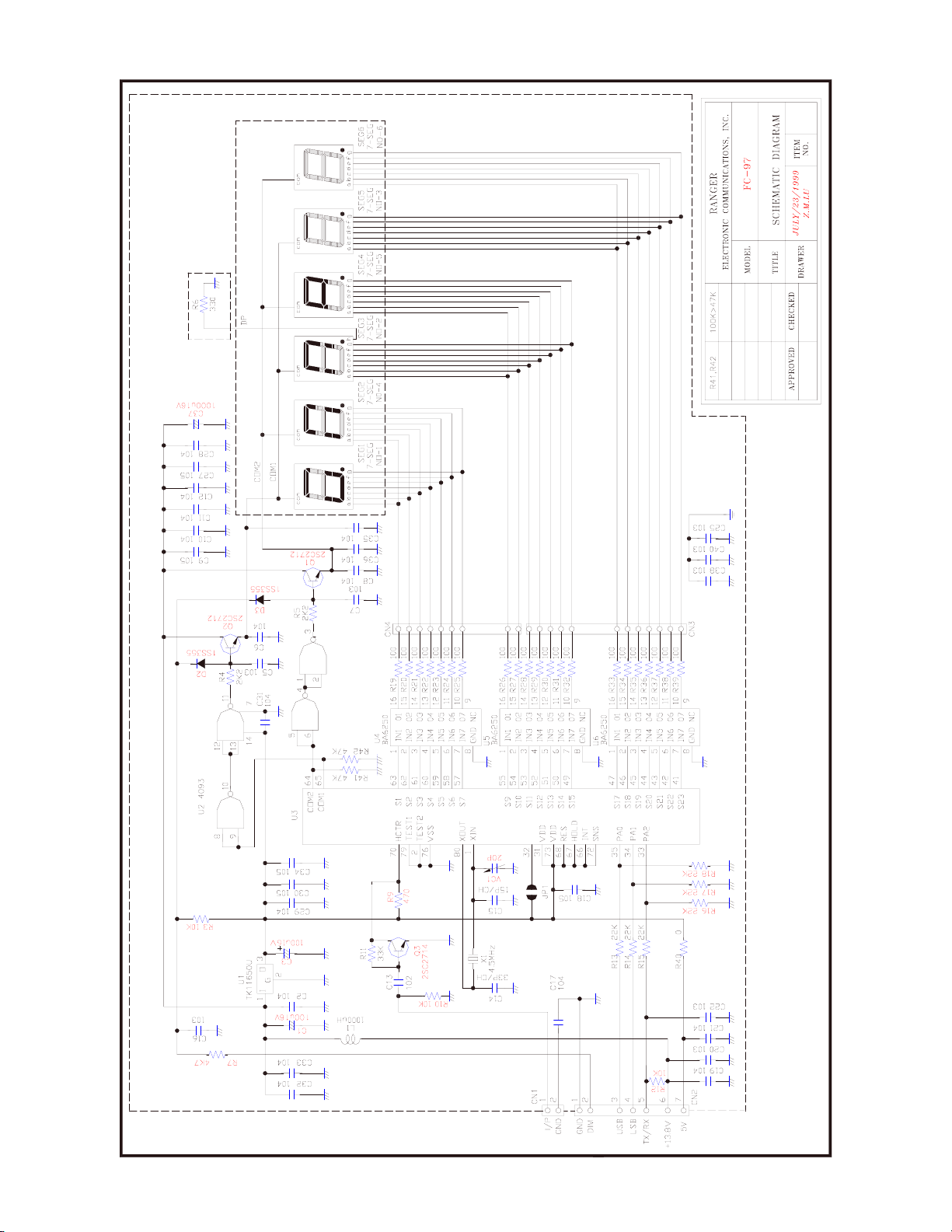
RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB FREQUENCY COUNTER CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
- 12 -
Page 13
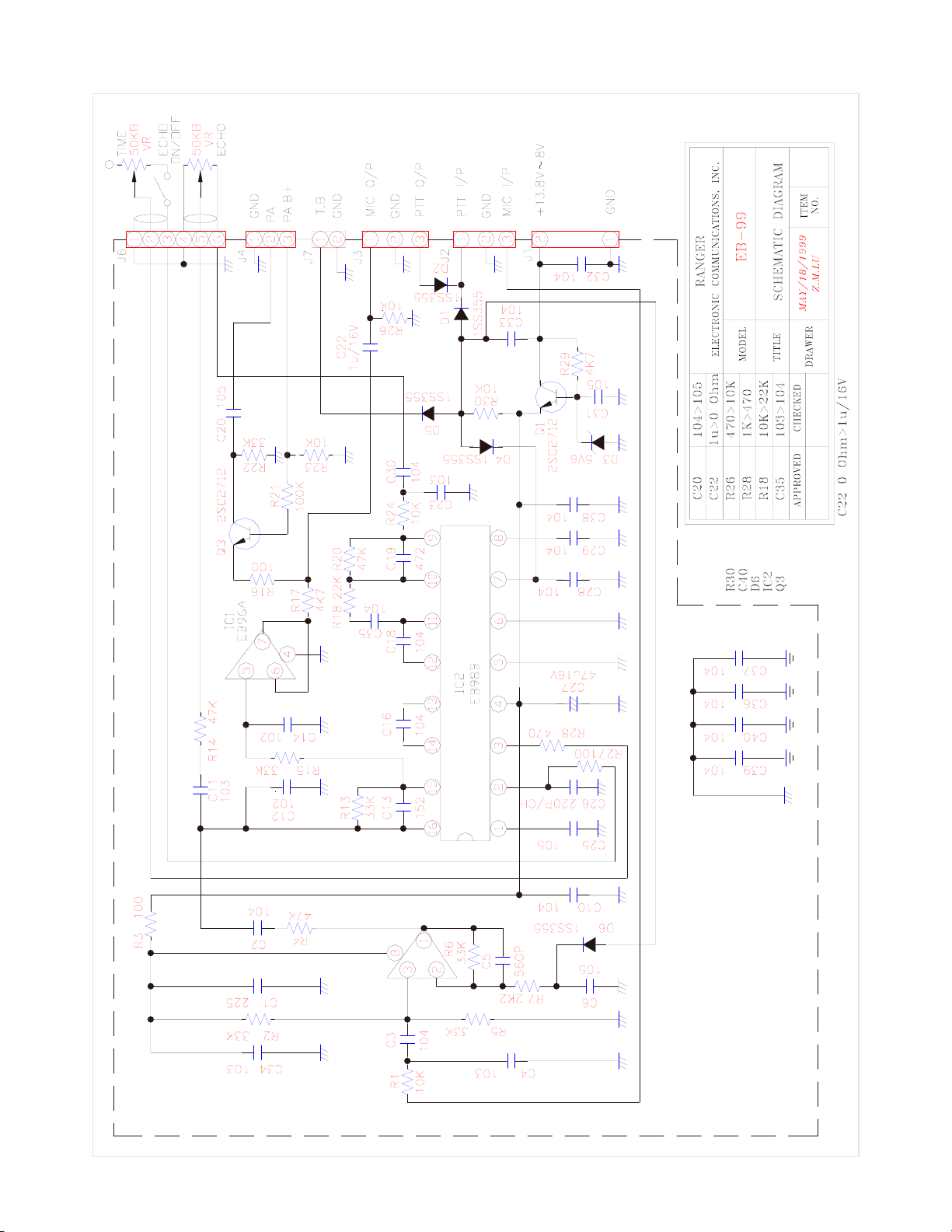
RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB ECHO BOARD (EB-99) CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
- 13 -
Page 14

RCI-6900F HP
CHAPTER 4
RCI-6900F TB
ALIGNMENT
4.0 REQUIRED TEST EQUIPMENT
!
DC Power Supply (13.8VDC, 20A)
"
RF Wattmeter (25~60 MHz, 100W)
#
Multimeter (Digital)
$
Automatic Modulation Meter
%
Audio Signal Generator
&
Frequency Counter (100 MHz)
'
RF Signal Generator (100 MHz)
(
Automatic Distortion Meter
)
Oscilloscope (50 MHz)
*
Sinad Meter
4.1 ALIGNMENT PROCEDURES
This transceiver has been aligned at the factory and does not require any adjustments at installation.
The required test equipment listed is used for the test setup or alignment shown in Figure 4-1
Transmitter Test Setup and Figure 4-2 Receiver Test Setup. This test setup is used in part or total
during the following adjustments and refer to Figure 4-3 for adjustment location.
4.1.1 PLL ALIGNMENT
ITEM U.U.T. SETTING ADJUST
MEASUREMENT
POINT
VCO Voltage
Disconnect ‘short PCB” from TP7, TP8 and
TP9.
Set radio to Fr. Pool 6, CH 40 AM RX mode.
Set +10KHz/OFF switch to OFF position.
Connect Multimeter to TP2.
Connect Frequency Counter to TP11.
AM Frequency Set radio to Fr. Pool 1, CH 1 AM RX mode.
Set radio to Fr. Pool 6, CH 40 AM RX mode.
Connect Frequency Counter to TP3.
USB Frequency Set radio to Fr. Pool 1, CH 1 USB RX mode.
Set radio to Fr. Pool 6, CH 40 USB RX mode.
Connect Frequency Counter to TP3.
LSB Frequency Set radio to Fr. Pool 1, CH 1 LSB RX mode.
Set radio to Fr. Pool 6, CH 40 LSB RX mode.
Connect Frequency Counter to TP3.
TX Frequency Set radio to Fr. Pool 1, CH 1 AM TX mode.
Connect Frequency Counter to TP3.
AM OSC Set radio to Fr. Pool 1, CH 1 AM TX mode.
Connect Frequency Counter to TP5.
USB OSC Set radio to Fr. Pool 1, CH 1 USB TX mode.
Connect Frequency Counter to TP5.
LSB OSC Set radio to Fr. Pool 1, CH 1 LSB TX mode.
Connect Frequency Counter to TP5.
L15
VC1
L45
L41
L46
L42
L47
L43
VR8
L18
L19
L20
6.5 VDC ± 0.1
10.2400MHz ± 20Hz
17.5500MHz ± 20Hz
18.9600MHz ± 20Hz
17.5525MHz ± 20Hz
18.9625MHz ± 20Hz
17.5475MHz ± 20Hz
18.9575MHz ± 20Hz
17.5500MHz ± 20Hz
10.6950MHz ± 10Hz
10.6925MHz ± 10Hz
10.6975MHz ± 10Hz
4.1.2 TRANSMITTER ALIGNMENT
- 14 -
Page 15

ITEM U.U.T. SETTING ADJUST
MEASUREMENT
POINT
TX Power Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM TX mode.
Modulation Off.
Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 USB TX mode.
AF signal 30mV, 1 KHz to microphone.
Connect Oscilloscope to TP12.
Set RF PWR Fully Clockwise.
Set FINE/COARSE Control to 12 o’clock.
AM APC
Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM TX mode.
Connect Multimeter to TP8.
SSB APC Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 USB TX mode.
Connect Multimeter to TP8.
BIAS Current Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 USB TX mode.
Modulation Off.
Connect current meter to TP7(+) and TP9 (-)
Connect current meter to TP7 (+) and TP8 (-)
L18,L37,L35,
L34
L35,L34
VR15
Maximum Output.
Maximum Output
and Balance.
6VDC
VR18 12.5VDC
VR13
VR12 + VR11
10 mA
(50 mA + 50 mA) =
100 mA
AM TX Power Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM TX mode.
Connect ‘short PCB” to TP7, TP8 and TP9.
Set RF PWR Fully Counter Clockwise.
Connect RF Power Meter to antenna jack.
RF Power
Meter
Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM TX mode.
Set RF PWR Fully Clockwise.
VR15
VR19
10W (RCI-6900FHP)
50W (RCI-6900FTB)
2W
VR10 Adjust RF Power
meter needle until it
is in-between the
green and red bar on
TX PWR scale.
SSB ALC
SSB Carrier
Balance
Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 USB TX mode.
AF signal 30mV, 1 KHz to microphone.
Set RF PWR Fully Clockwise.
Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 USB TX mode.
AF signal 30mV, 1 KHz to microphone.
VR14 25W (RCI-6900FHP)
100W (RCI-6900F
TB)
VR7 Spurious Emission to
minimum.
Connect Oscilloscope to antenna jack.
CW TX Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 CW TX mode.
VR9 200mV (Sine Wave)
Plug in CW key.
Disconnect the Mic Jack.
Connect AC Voltmeter to EXT SP.
SWR Meter Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM TX mode.
Set SWR/S/RF switch to SWR position.
Connect 100 Ohm to antenna jack.
AM Modulation
FM Modulation
Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM TX mode.
Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 FM TX mode.
AF signal 30mV, 1 KHz to microphone.
VR1 on
SWR P.C.B
VR17 90%
Adjust SWR needle
until it is on the “2”
SWR scale.
4KHz
Set Mic Gain Fully Clockwise.
Frequency
Counter Adjust
Set radio to Fr Pool 2, CH 19 AM RX mode. VC1 on
frequency
Display should be
28.9150
counter
4.1.3 RECEIVER ALIGNMENT
- 15 -
Page 16

ITEM U.U.T. SETTING ADJUST
Set NB/ANL/OFF switch to NB/ANL
AM Sensitivity Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM RX mode.
Set RF Gain Fully Clockwise.
Set SQ Fully Counter Clockwise.
Set VOL Control at 2 o’clock.
Set NB/ANL/OFF switch to OFF position.
Connect RF SG to antenna jack
Frequency 28.915 MHz, 1uV. Mod 30%.
Set radio to Fr. Pool 6, CH 40 AM RX mode.
RF SG setting 29.655 MHz.
Set radio to Fr. Pool 1, CH 1 AM RX mode.
RF SG setting 28.245 MHz.
USB Sensitivity Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH19 USB RX mode.
Set VOL Control Fully Clockwise.
RF SG setting 28.916 MHz, 0.5uV. Mod off.
LSB Sensitivity Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH19 LSB RX mode.
Set VOL Control Fully Clockwise.
RF SG setting 28.914 MHz, 0.5uV. Mod off.
FM Distortion Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 FM RX mode.
Set MODE switch to FM mode.
RF SG setting 28.915 MHz, 1mV. Mod 3KHz.
NB Adjust Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM RX mode
RF SG setting 28.915 MHz, 100uV. Mod off.
position.
Connect Voltmeter to TP1.
AM Squelch Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM RX mode.
Set SQ Control Fully Clockwise.
RF SG setting 28.915 MHz, 1 mV. Mod 30%.
SSB Squelch Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 USB RX mode.
Set SQ Control Fully Clockwise.
RF SG setting 28.915 MHz, 1 mV. Mod off.
AM S/RF Meter
AM S-Meter
Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 AM RX mode.
Set SWR/S/RF switch to S/RF position.
RF SG setting 28.915 MHz, 100uV. Mod 30%.
SSB S-Meter
Set radio to Fr. Pool 2, CH 19 USB RX mode.
Set SWR/S/RF switch to S/RF position.
RF SG setting 28.916 MHz, 100uV. Mod off.
Figure 4-1 Transmitter test setup
MEASUREMENT
POINT
L2,3,5,6,7,8,
9,10
L5,L6
Audio output > 2V
S/N > 10 dB.
For Balance between
CH 1 and CH 40.
L5,L6
L11,L12
Audio Output > 2V
S/N > 10dB.
L11,L12
Audio Output > 2V
S/N >10db.
L4 Audio output > 3V
Distortion < 10%
L1 DC Voltage to max.
( > 2.0V )
VR4 Slowly Adjust very slowly
until squelch just
open
VR3 Slowly Adjust very slowly
until squelch just
open
VR1 Meter needle to S9
on the S scale
VR2 Meter needle to S9
on the S scale
- 16 -
Page 17

Figure 4-2 Receiver test setup
- 17 -
Page 18

Figure 4-3 Main PCB Adjustment Location
RCI-6900F HP
RCI-6900F TB
- 18 -
CHAPTER 5
MAINTENANCE
Page 19

5.0 PRECAUTIONS
The inherent quality of the solid-state components used in this transceiver will provide many years of
continuous use. Taking the following precautions will prevent damage to the transceiver.
(i) Never key the transmitter unless an antenna or suitable dummy load is connected to the antenna
receptacle.
(ii) Ensure that the input voltage does not exceed 16 VDC or fall below 11 VDC.
(iii) During alignment, do not transmit for more than 10 seconds at a time. Transmitting over long
periods can cause heat built-up and cause transmitter damage.
5.1 PERIODIC INSPECTION
This unit is aligned at the factory to deliver maximum performance. However, continued performance
cannot be expected without periodic inspection and maintenance. Important points to be checked
regularly are as follows;
Check Item Action
Whip antenna
(option)
Coaxial cable If sheath is cracked, seal with
Coaxial & power
plug connections
Battery connection If corroded, clean power
Ground terminal If corroded, clean terminal.
5.2 FUSE REPLACEMENT
To protect the equipment from serious damage, a fuse is provided on the power supply lines. The fuses
protect against over voltage / reverse polarity or internal fault of the equipment. If the fuse has blown,
first find out the cause of the trouble before replacing it. A fuse rated for more than the transceiver
requirement should not be used, since it may permanently damage the equipment. Damage due to over
fusing is not covered by the warranty.
If cracked or broken, replace it.
vinyl tape. If immersed with
water, install new coaxial cable.
If loosened, reconnect. If
corroded, clean contacts.
terminals.
RCI-6900F HP
RCI-6900F TB
- 19 -
CHAPTER 6
DIAGRAMS &
PARTS LIST
Page 20

6.0 GENERAL
Information on most electrical and mechanical parts is included in the parts list. The reference
designators are in alphanumeric order.
6.1 ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS
Parts orders should be referred to the parts department at:
Ranger Communications, Inc.
•
3377 Carmel Mountain Road
San Diego, CA 92121
Tel: 858-259-0287
Fax: 858-259-0437
- 20 -
Page 21

PART LIST:
RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB ROTARY SW P.C.B
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
DESCRIPTION
NUMBER
1 EPT900030Z ROTARY SW P.C.B
2 R315 RCP168214Z 820 OHM 1/16W
3 R312,R313,R314,
RCP161524Z 1.5K OHM 1/16W
R316-R324
4 J303,J304,J305,J306 WX01070705 JUMPER WIRE
5 J308 WX01070708 JUMPER WIRE
6 J301,J302,D311,D312,
WX01070710 JUMPER WIRE
D301,D314,D315,D316,
D323,D324,D325,D326
7 J307 EX07N48209 PCB CONN/S 10PIN
8 ROTARY SW EWRT32000S ROTARY SW
REMARK:
COPPER SIDE (BLUE)
- 21 -
Page 22

PART LIST:
RCI-6900F HP ANT P.C.B
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
DESCRIPTION
NUMBER
1 EPT360042Z ANT P.C.B
2 R9 RCY010004Z 0 OHM 0.1W
3 R1 RCY014714Z 470 OHM 0.1W
4 R3,R4 RCY011014Z 100 OHM 0.1W
5 R2 RCY013314Z 330 OHM 0.1W
6 R5,R11 RCY011024Z 1K OHM 0.1W
7 R10 RCY012224Z 2.2K OHM 0.1W
8 R12 RCY014724Z 4.7K OHM 0.1W
9 R7 RCY011034Z 10K OHM 0.1W
10 C5 RCY012234Z 22K OHM 0.1W
11 C7 CK1059AB1A 0.5PF 50WV
12 C6 CK1030AB1A 3PF 50WV
13 C3,C4 CK2104AB7R 0.1uF 25WV
14 C1,C2 CK1103AB7L 0.001uF 50WV
15 Q1 TY2SC2712G TR 2SC2712GR
16 D3 EDSS00355Y DIODE 1SS355
17 D1,D2 EDHM0198SY DIODE HSM198S
18 D4 EDMA0028TY DIODE MA28T
19 L1 ECRFZ10053 RF COIL C3RH0610
20 VR1 RE10300009 S/F/R 10K OHM
21 JP1 WX01070715 JUMPER WIRE
REMARK:
COPPER SIDE (BLUE)
- 22 -
Page 23

PART LIST:
RCI-6900F TB POWER P.C.B
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
DESCRIPTION
NUMBER
1 EPA010010B POWER PCB
2 R18,R19 RCM141004A 10 Ω ¼ W
3 R16 RCM141014A 100 Ω ¼ W
4 R22 RCM144714A 470 Ω 1/4W
5 R21 RCM141024A 1K Ω 1/4W
6 R15 RCP121034Z 10K Ω 1/2W
7 R14 RFP102714Z 270 Ω 1W
8 C5,C6 CC0500201A 2PF 50WV
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
- 23 -
DESCRIPTION
Page 24

NUMBER
9 C18,C19 CC0501515A 150PF 50WV
10 C13 CC0502215A 220PF 50WV
11 C9,C14 CC0505615G 560PF 50WV
12 C10,C23,C24,C25,
CC0501047L 0.1uF 50WV
C26,C27,C28,C37,
C38,C39,C40,C41,
C42,C43,C44,C45
13 C7,C8 CC5001037L .01uF 50WV
14 C34 CC5001204A 12PF 500WV
15 C32 CC5003904A 39PF 500WV
16 C31 CD5006604Z 68PF 300WV
17 C35 CD3008204Z 82PF 300WV
18 C16,C22,C33 CD3001514Z 150PF 300WV
19 C12 CE052257Z 2.2uF 50WV
20 C30 CE0254777Z 470PF 25WV
21 Q2 TDTC0114ES TR DTC114ES
22 D4,D7,D8,D9 ED1N04148Z DIODE 1N4148
23 D10 EDLT6A400Z DIODE LT6A400
24 L4,L5 ECSPG18382 SPRING COIL
25 L2 ECBAD18571 BEAD COIL
26 L3 ECBAD18572 BEAD COIL
27 L1 ECCHK16142 CHOKE COIL
28 TDK BRAND CORE ECRFZ10053 TDK BRAND CORE
29 T1 ECRFZ10184 RF COIL
30 T2 ECRFZ10185 RF COIL
31 RL1 EX05N40844 RELAY
32 J1 EX07N41226 PCB CONN/S 2PIN
33 J2 EX07N48490 PCB CONN/S 4PIN
34 B+,B- GZZZ50011Z AC 220V
35 I/P,O/P GZZZ50062Z V TYPE JACK
36 Q3,Q4 T2SC02290Z TR 2SC2290
37 Q5 T2SD02531Z TR 2SD2531
REMARK:
TOP: COMPONENT SIDE (WHITE)
BOTTOM: COPPER SIDE (WHITE)
- 24 -
Page 25

PART LIST:
RCI-6900F TB SWR P.C.B
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
DESCRIPTION
NUMBER
1 EPA010020B SWR P.C.B
2 R13,R14 RCY010004Z 0 Ω 0.1W
3 R2 RCY011014Z 100 Ω 0.1W
4 R1,R3,R4 RCY014714Z 470 Ω 0.1W
5 R5,R11 RCY011024Z 1K Ω 0.1W
6 R12 RCY014724Z 4.7K Ω 0.1W
7 R7,R8,R10 RCY011034Z 10K Ω 0.1W
8 C1,C2 CK1102AB7L 0.001uF 50WV
9 C3,C4 CK2104AB7R 0.1uF 25WV
10 D1,D2 EDHM0198SY DIODE HSM198S
11 D4 EDMA0028TY DIODE MA28T
12 VR1 RE103Y0125 10KB 3L
13 Q1 TY2SC2712G 2SC2712GR-TE85L
REMARK:
COPPER SIDE (BLUE)
- 25 -
Page 26

PART LIST:
RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB BAND P.C.B
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
DESCRIPTION REMARK
NUMBER
1 EPT690070Z BAND P.C.B
2 R1 RCP164704Z 47 OHM 1/16W
3 J1,J5,J6,J7 EX07N48223 PCB CONN/S 2PIN
4 J3 EX07W48826 PCB CONN/S 5PIN
5 J4,J12 EX07W48827 PCB CONN/S 6PIN
RCI-6900FTB
6 J8 EX07N48224 PCB CONN/S 7PIN
7 J10 EX07N48331 PCB CONN/S 6PIN
8 JP3,JP7 WX01070705 JUMPER WIRE
RCI-6900FTB
RCI-6900FHP
9 JP1 WX01070710 JUMPER WIRE
10 VOL/SQ RV50303522 VR 50KB/50KA W/SW
11 FINE/COARSE RV20303523 VR 20KB/1KB
12 MIC/RF RV10203524 VR 1KB/1KA
13 SWR CAL RV20303560 VR 20KB/5KB
14 BAND EWRT32094S ROTARY SW 6N
15 MODE EWRT32083S ROTARY SW 5N
REMARK:
COPPER SIDE (WHITE)
- 26 -
Page 27

PART LIST:
RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB MIC P.C.B
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
DESCRIPTION
NUMBER
1 EPT690050Z MIC P.C.B
2 C502, C503,C504 CC0501027L 0.001uF 50WV
3 C505,C506,C501 CC0501037L 0.01uF 50WV
4 L501 ECCHK16001 CHOKE COIL
5 L502 ECBAD18526 BEAD COIL
6 1-4 EX06N41020 MIC JACK
7 MIC-50F EX07N48903 WIRE CONN/H 3PIN
REMARK:
COPPER SIDE (BLUE)
- 27 -
Page 28

- 28 -
Page 29

PART LIST:
RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB COUNTER P.C.B
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
DESCRIPTION
NUMBER
1 EPT900040Z COUNTER P.C.B
2 R40 RCY010004Z 0 OHM 0.1W
3 R19-R39 RCY011014Z 100 OHM 0.1W
4 R6 RCY013314Z 330 OHM 0.1W
5 R9 RCY014714Z 470 OHM 0.1W
6 R4,R5 RCY012224Z 2.2K OHM 0.1W
7 R7 RCY014724Z 4.7K OHM 0.1W
8 R3,R10,R12 RCY011034Z 10K OHM 0.1W
9 R13-R18 RCY012234Z 22K OHM 0.1W
10 R11 RCY013334Z 33K OHM 0.1W
11 R41,R42 RCY014734Z 47K OHM 0.1W
12 C15 CK1150AB4A 15PF 50WV
13 C14 CK1330AB4A 33PF 50WV
14 C2,C6,C8,C10,C11,C12,
CK2104AB7R 0.1uF 25WV
C17,C19,C21,C29,C31,
C32,C33,C35,C36,C28
15 C5,7,16,20,22,25,38,40 CK1103AB6U 0.01UF 50WV
16 C13 CK1102AB7L 0.001uF 50WV
17 C9,C18,C27,C30,C34 CK5105AA7R 1uF 16WV
18 U3 YNRG0GX3SP IC LC7232N 18PIN
19 U2 YNTA04073B IC TC4093BFN 14PIN
20 U4,U5,U6 YNR006250F IC BA6250F 16PIN
21 U1 YNT011650U IC TK11650U 3PIN
22 Q3 TY25C2714Z TR 2SC2714
23 Q1,Q2 TY2SC2712G TR 2SC2712GR
24 D2,D3 EDSS00355Y DIODE 1SS355
25 L1 YCCHK16259 CHOKE COIL
26 VC1 CV038200AY TRIMMER/C 20PF
27 C1,C3 CEM161077A 100UF 16WV
28 X1 EYCAP04500 CRYSTAL 4.500MHz
29 C37 CE0161087Z 1000UF 16WV
30 COUNTER PCB x 2pc EX07N48927 PCB CONN/S 12PIN
31 CN1 EX07N48223 PCB CONN/S 2PIN
32 CN2 EX07N48224 PCB CONN/S 7PIN
REMARK:
TOP: COMPONENT SIDE (BLUE)
BOTTOM: COPPER SIDE (BLUE)
- 29 -
Page 30

PART LIST:
RCI-6900F HP/ RCI-6900F TB LED DISPLAY P.C.B
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
DESCRIPTION
NUMBER
1 EPT900022Z LED DISPLAY P.C.B
2 LED DISPLAY PCB EX03N40003 LED DISPLAY
3 1,2,3,4,5,6 EX03N40476 LED DISPLAY
4 TX/RX EX01N40004 LED RED/GREEN
5 ON,NB/ANL,R.B,S/RF,
EWPS33033X PUSH SW
SWR,+10K
6 LED DISPLAY PCB x 2pc
7 TOJ10,+10K,S/RF,
EX07N48928 PCB CONN/S 12PIN
EX07N48223 PCB CONN/S 2PIN
M-M+
8 LED DISPLAY PCB x 3pc
EX07N48350 PCB CONN/S 3PIN
9 LED DISPLAY PCB EX07N48490 PCB CONN/S 4PIN
10 RX/G/TX EX07N48947 PCB CONN/S 3PIN
REMARK:
TOP: COMPONENT SIDE (BLUE)
BOTTOM: COPPER SIDE (BLUE)
- 30 -
Page 31

- 31 -
Page 32

PART LIST:
RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB ECHO P.C.B (EB-99)
ITEM REFERENCE NUMBER RANGER PART
DESCRIPTION
NUMBER
1 EPT0SSB50F ECHO P.C.B
2 R3,R16 RCY011014Z 10 OHM 0.1W
3 R28 RCY014714Z 470 OHM 0.1W
4 R27 RCY011024Z 1K OHM 0.1W
5 R7 RCY012224Z 2.2K OHM 0.1W
6 R17,R29 RCY014724Z 4.7K OHM 0.1W
7 R1,R23,R24,R30,R26 RCY011034Z 10K OHM 0.1W
8 R18 RCY012234Z 22K OHM 0.1W
9 R2,R5,R6,R13,R15,R22 RCY013334Z 33K OHM 0.1W
10 R14,R20,R4 RCY014734Z 47K OHM 0.1W
11 R21 RCY011044Z 100K OHM 0.1W
12 C26 CK1331AB5A 330PF 50WV
13 C5 CK1561AB5A 560PF 50WV
14 C12,C14 CK1102AB7L 0.001uf 50WV
15 C4,C11,C23,C34 CK2103AB7R 0.01uF 25WV
16 C2,C3,C10,C16,C28,C29,
CK2104AB7R 0.1uF 25WV
C30,C32,C33,C36,C37,
C38,C39,C40,C18,C35
17 C6,C31,C20,C22 CK5105AB7R 1uF 16WV
18 C13 CK1152AB7R 0.0015uF 50WV
19 C19 CK1472AB6U 0.0047uF 50WV
20 C25 CK5105ZZ7R 1uF 16WV
21 C1 CK5225AA7R 2.2uF 16WV
22 IC1 YNJR04558M IC NJM4558M 8PIN
23 IC2 YNES56033S IC ES56033S 16PIN
24 Q1,Q3 TY2SC2712G TR 2SC2712GR
25 D1,D2,D4,D5,D6 EDSS00355Y DIODE 1SS355
26 D3 EDZD05569Y ZENER DIODE 5.6V
27 C27 CE0164767Z 47uF 16WV
28 ECHO,TIME RE50300014 S/F/R 50K OHM
29 J3 EX07N41216 PCB CONN/S 3PIN
30 J2 EX07N41227 PCB CONN/S 3PIN
31 J1,6 EX07N48223 PCB CONN/S 2PIN
32 J1-MAIN(J7) EX07N49085 WIRE CONN/H 2PIN-2PIN
33 J3-MAIN(J12) EX07N48902 WIRE CONN/H 3PIN-3PIN
34 J6 EX07N48917 WIRE CONN/H 2PIN-2PIN
REMARK:
TOP: COMPONENT SIDE (WHITE)
BOTTOM: COPPER SIDE (BLUE)
- 32 -
Page 33

RCI-6900 HP / RCI-6900 TB MAIN PCB
REMARK:
COMPONENT SIDE (BLUE)
- 33 -
Page 34

RCI-6900F HP / RCI-6900F TB MAIN PCB.
REMARK:
SMD COMPONENT SIDE (BLUE)
- 34 -
Page 35

RCI-6900 HP / RCI-6900 TB MAIN PCB
REMARK:
COPPER SIDE (WHITE)
PART LIST RCI-6900F HP MAIN PCB
- 35 -
Page 36

REFERENCE
NUMBER
EPT990010Z MAIN P.C.B
R274,275 RCP121514Z
R270 RCP121034Z
C214 CC0501804A 18PF 50WV
C217 CC0503304A 33PF 50WV
C222 CC0504704A 47PF 50WV
C209 CC0508204A 82PF 50WV
C215 CC0501215A 120PF 50WV
C216 CC0501815A 180PF 50WV
C221,223 CC0503915G 390PF 50WV
C220 CC1001037L 0.01UF
C219 CD3005614Z 560P 300WV
C13,24,27,28,52,63,
72,128,149,168,200,
308,344
C90,188,198 CE0252267Z 22UF 25WV
C42,43,45,110,154,
183,261
C137,166,260 CE0161077Z 100UF 16WV
C161,185 CE0163377Z 330UF 16WV
C118 CE0164777Z 470UF 16WV
C269,270 CE0251087Z 1000UF 25WV
FL1 EFCFW455HT CFW-455HT
FL2 EFCFE107MX SFE10.7MX
FL3 EFX8106952 C. FILTER
X1 EYCAB10240 CRYSTAL
X2 EYCAA15360 CRYSTAL
X3 EYBAA12660 CRYSTAL
X4 EYBAE10697 CRYSTAL
IC5 ENMA00612Z AN-612 7PIN
IC9 ENSM06130Z TDA6130
Q63 T2SC02538Z TR 2SC2538
D91,92,93 ED1N04148Z DIODE
L2,3 ECIFT12002 7MC-7172ABW
L41-43,45-47 ECIFT12012 113CN-6514X
L20 ECIFT12013 113CN-6485Z
L18,19 ECIFT12016 113CN-6344Z
L1,11 ECIFT12252 I.F.T
L5 ECIFT12253 I.F.T
L38 ECIFT12255 I.F.T
L9,10 ECIFT12256 I.F.T
L12 ECIFT12257 I.F.T
L17,37 ECIFT12258 I.F.T
L15 ECIFT12263 I.F.T
L34 ECIFT12559 I.F.T
L35 ECIFT12560 I.F.T
L6 ECIFT12290 I.F.T
L7 ECIFT12440 I.F.T
L8 ECIFT12492 I.F.T
L4 ECIFT12526 I.F.T 7P
L503 ECCHK16000 CHOKE COIL
L27,28,31 ECCHK16070 CHOKE COIL
T1 ECCHK16004 CHOKE COIL
L23,24 ECSPG18003 SPRING COIL
L25 ECSPG18077 SPRING COIL
L29 ECSPG18090 SPRING COIL
L26 ECSPG18365 SPRING COIL
L14,33 ECBAD18526 BEAD COIL
L32 ECRFZ10048 RF COIL
VR8,9,13,17,19 RE10200041 S/F/R 1K
VR14,15 RE50200042 S/F/R 5K
VR1,2,7,16,18 RE10300031 S/F/R 10K
VR10 RE10400043 S/F/R 100K
VR3,4 RE50400087 S/F/R 500K
VR11,12 RE10100074
CW,EXT SP EX06N41045 EAR JACK
J12 EX07N41227 P/C/S 3P
J17 EX07N41330 P/C/S 2P
J1,11,20,21,19 EX07N48223 P/C/S 2P
J7,29,31,3 EX07N48350 P/C/S 3P
J2,9 EX07N48490 P/C/S 4P
RANGER
PART NO.
CE0251067Z 10UF 25WV
CE0254767Z 47UF 25WV
DESCRIPTION
150 Ω 1/2W
10K Ω 1/2W
100WV
10M4D
(10.695MHz)
10.240MHz
15.360MHz
12.660MHz
10.6975MHz
1N4148
S/F/R 100 Ω
J6 EX07N48222 P/C/S 5P
J10,13,15 EX07N48331 P/C/S 6P
J28 EX07N48543 P/C/S 9P
J26 EX07N48209 P/C/S 10P
J30 EX07N48244 P/C/S 3P
J27 EX07N48884 P/C/S 6P
J27,30 EX07N48151 P/C/S SHORT
TP1,2,3,5,11,12 EX07N48612 P/C/S 1 PIN
J5 EX07N49140 P/C/S 2P
TP7-9 XZZZ90006Z PCB STOPPER
L30,36 WX01070710 JUMPER WIRE
L503 WX0012015A TUBE
L504 WH0007005Z LEAD WIRE
R153,308,317,318,328
,367,307,203,C266,
C267,D118,D119,D120,
D121,D122,D123,D124
R277 RCY014794Z
R369 RCY011004Z
R293 RCY011504Z
R272,273 RCY012204Z
R246 RCY013304Z
R115,152,226,281 RCY014704Z
R125,227,231 RCY015604Z
R11,105 RCY016804Z C/F/
R3,5,8,33,36,78,81,
97,126,154,182,186,
263,286,289,360
R35,104,253,276,280 RCY011514Z
R23 RCY011814Z
R130,150,190,262,136
R32,103 RCY012714Z
R6,10,16,279,282,306
R24,176,202,250,259,
304,347,354
R292 RCY015614Z
R4,50,90,224 RCY016814Z
R74 RCY018214Z
R64,67,71,75,101,117
,118,120,123,146,147
,148,151,178,192,199
,207,213,225,233,244
,249,255,257,258,266
,267,268,269,271,287
,294,297,322,326,329
,341,344,349,351,356
,357,358,96,D126
R91,205 RCY011224Z C/F/R
R56,79,80,89,100,127
,220,221,237,260,278
,283,299
R235,247 RCY011824Z C/F/R
R27,30,70,73,95,116,
121,144,209,214,254,
288,302,310,311,320
R9,25,31 RCY012724Z C/F/R
R18,28,66,113,124,
128,184,204,230,298,
305
R52,58 RCY013924Z C/F/R
R29,38,72,86,132,206
,211,212,215,216,256
,261,175
R87,94,201,290,291 RCY015624Z C/F/R
R14,42,43,69,85,342,
352
R92,300 RCY018224Z C/F/R
R1,13,17,39,40,41,57
,65,68,83,88,128,131
,135,140,142,177,179
,188,194,217,223,228
,239-243,248,251,252
,296,301,323,324,346
,348,350,362
R191,137 RCY011234Z
R193 RCY011534Z
- 36 -
PIN
RCY010004Z
RCY011014Z
RCY012214Z
RCY013314Z
RCY014714Z
RCY011024Z
RCY011524Z C/F/R
RCY012224Z C/F/R
RCY013324Z C/F/R
RCY014724Z C/F/R
RCY016824Z C/F/R
RCY011034Z
C/F/R 0 Ω
C/F/R 4.7 Ω
C/F/R 10 Ω
C/F/R 15 Ω
C/F/R 22 Ω
C/F/R 33 Ω
C/F/R 47 Ω
C/F/R 56 Ω
R 68 Ω
C/F/R 100 Ω
C/F/R 150 Ω
C/F/R 180 Ω
C/F/R 220 Ω
C/F/R 270 Ω
C/F/R 330 Ω
C/F/R 470 Ω
C/F/R 560 Ω
C/F/R 680 Ω
C/F/R 820 Ω
C/F/R 1K Ω
1.2K Ω
1.8K Ω
1.5K Ω
2.2K Ω
2.7K Ω
3.3K Ω
3.9K Ω
4.7K Ω
5.6K Ω
6.8K Ω
8.2K Ω
C/F/R 10K Ω
C/F/R 12K Ω
C/F/R 15K Ω
Page 37

R34,93,110,133,134,
138,139,141,187,222
R122 RCY012734Z
R2,264 RCY013334Z C/
R46 RCY013934Z
R7,62,63,99,143,155157,160-165,166-173,
149,198,200,229,234,
343,345,353,355,236
R26,107,112,181 RCY016834Z
R45 RCY018234Z
R12,44,48,49,51,53,
76,77,106,109,114,
195,197,232,238,284,
285,303,295,361
R47,59,84,119,145,
210,218
R54,55,183,185,189 RCY012744Z C/F/R
R15,37,111,196,219 RCY014744Z C/F/R
R102 RCY018244Z C/F/R
R108 RCY011054Z
R208 RCY011554Z C/F/R
C236,248,249,218 CK1010AB1A 1PF 50WV
C294,288,61 CK1020AB1A 2PF 50WV
C211 CK1030AB1A 3PF 50WV
C68,69,86,88,120,253
C1,57,114,155 CK1100AB2A 10PF 50WV
C247 CK1120AB4A 12PF 50WV
C97 CK1150AB4A 15PF 50WV
C51,98 CK1180AB4A 18PF 50WV
C79 CK1220AB4A 22PF 50WV
C44 CK1270AB4A 27PF 50WV
C30,89,134,140,300 CK1330AB4A 33PF 50WV
C243 CK1470AB4A 47PF 50WV
C96,60 CK1680AB4A 68PF 50WV
C8 CK1820AB4A 82PF 50WV
C4,160,129,130,212 CK1101AB5A 100PF 50WV
C62 CK1121AB5A 120PF 50WV
C242 CK1181AB5A 180PF 50WV
C35,237 CK1221AB5A 220PF 50WV
C39 CK1271AB5A 270PF 50WV
C11,14 CK1331AB5A 330PF 50WV
C83,228 CK1471AB5A 470PF 50WV
C29,227 CK1561AB5A 560PF 50WV
C206 CK1390AB4D 39PF 50WV
C205 CK1151AB5D 150PF 50WV
C144 CK1060AB2G 6PF 50WV
C289,290,291 CK1100AB2G 10PF 50WV
C143 CK1680AB4G 68PF 50WV
C287 CK1101AB5G 100PF 50WV
C142 CK1121AB5G 120PF 50WV
C202 CK1151AB5G 150PF 50WV
C321 CK1181AB5G 180PF 50WV
C95 CK1271AB5G 270PF 50WV
C203 CK1331AB5G 330PF 50WV
C99 CK1391AB5G 390PF 50WV
C48,64,91,111,112,
122,123,131,136,141,
146,345,152,156,179,
182,210,225,229,230,
231,239,245,246,257,
263,271,275,278,279,
280,282,285,286,295,
301,302,304,307,309,
310,311,312,313,320,
326,224
C2,3,6,9,15,21,22,25
,33,34,37,59,65-67,
70,71,73,76,82,87,92
,105,115,116,126,127
,139,148,153,158,159
,175,176,177,196,197
,201,207,226,232,234
,235,238,240,250,251
,254,255,268,281,292
,297,298,303,324,325
,340,341,342,346,350
C7,31,36,47,55,58,93
,104,133,135,145,150
RCY012234Z
RCY014734Z
RCY011044Z C/F/R
RCY012244Z C/F/R
CK1050AB1A 5PF 50WV
CK2104AB7R 0.1UF 25WV
CK1103AB6U 0.01UF 50WV
CK1102AB7L 0.001UF
C/F/R 22K Ω
C/F/R 27K Ω
F/R 33K Ω
C/F/R 39K Ω
C/F/R 47K Ω
C/F/R 68K Ω
C/F/R 82K Ω
100K Ω
220K Ω
270K Ω
470K Ω
820K Ω
C/F/R 1M Ω
1.5M Ω
50WV
,178,181,190,191,192
,204,259,265,322,121
,349
C5,23,26,41,56,74,77
,78,80,81,94,101,106
,109,119,125,157,162
,170,199,258,262,272
,274,277,283,284,296
C10 CK2474AB7R 0.47UF 25WV
C38,49,165,174,193 CK1223AB6U .022UF 50V
C171 CK1153AB6U 0.015UF
C12 CK1222AB7R 0.0022UF
C40,50,53,54,172,173
,184,241,343
C186,348 CK2224AB7R 0.22UF 16WV
C169,233,264 CK5225AA7R 2.2UF 16WV
C32,84,180,194,195,
256,306,299
C124 CTY161046Z 0.1UF 16WV
C163 CTY162246Z 0.22UF 16WV
C164,167,213,351,138
C100 CTY162256Z 2.2UF 16WV
C102 CTY164746Z 0.47UF 16WV
C46,103,189,323 CTY164756Z 4.7UF 16WV
IC1 YNJR00324M NJM324M 14P
IC6 YNJR04558M NJM4558M 8P
IC3,4 YNMC14008D MC14008BDR2
IC2 YNMC45106D MC145106DW
Q19 TY2SC3356Z TR 2SC3356
Q34,47,49,67 TY2SB0798Z TR 2SB798DL
Q3,5,6,8,15,18,28,40
,43,44,45,48,50,53,
55,57,65,68,69,71,32
Q7,41 TY2SA1298Y TR 2SA1298Y
Q1,2,10,11,12,13,14,
22,23,24,25,29,33,35
,36,58,59,64
Q16,17,26,27,52,54,
56,70
Q42 TYZRN2403Z TR RN2403
Q20,21 FY2SK0302Z F.E.T
D2-10,12-17,20,23-31
,33,35-41,48,50-52,
54-63,67,69-77,80-85
,87,99-104,110,115,
116,125,128,129,130,
132,133,134,135,136,
148,149,150,152
D89,90,94,109 ED1N04148Y DIODE
D78,79,86,88,137,138
,139,140,141,142,143
,144,145,146,147,151
,153
D21,49,95,108,113,
114,127
D22,96,97,107 ED1V00231Y DIODE
D1,11,34 EDHM0198SY DIODE
D18,19,154,155 EDRS00135Y DIODE
D65,98 EDMA0028TY DIODE
D53,66 EDMA0028WY DIODE
D105,106 EDRL04004X DIODE
D64 EDZD05519Z ZENER DIODE
D68 EDZD05759Y ZENER DIODE
D112 EDZD05569Y ZENER DIODE
VC1 CV038200AY TRIMMER/C
L22,39 YCCHK16240 CHOKE COIL
L16 YCCHK16258 CHOKE COIL
L40,44 YCTLI2273C CHOKE COIL
- 37 -
CK1473AB7R 0.047UF
50WV
50WV
25WV
CK1472AB6U .0047UF
25WV
CK5105AB7R 1UF 16WV
CTY161056Z 1UF 16WV
TY2SC2712G TR2
SC2712GR
TY2SC2714Z TR 2SC2714
TYZRN1403Z TR RN1403
EDSS00355Y DIODE
1SS355
1N4148 2P
EDSS00184Y DIODE
1SS184
ED1V00217Y DIODE
1SV217-TP
1SV231
HSM1985S
RLS135
TE-11
MA28T
MA28W
RLR4004
Page 38

RCI-6900F HP MISC. PARTS
REFERENCE
NUMBER
COUNTER XZZZ90363Z PVC STAND
COUNTER JS013016WH SET SCREW
FRONT PANEL(4) JS033008MN SET SCREW
TONE(2),CH9(2),
WB/ANL(2)
SWR SW(2) JS052605MN SET SCREW
CH BRT(2),
CHASSIS(12)
SPK(4),DC SOCKET(2) JS053008MN SET SCREW
MAIN PCB(5) JS053006TN SET SCREW
SPK(4) JN263035ZS NUT WITH
Q54 XZZZ90020Z INSULATING
Q47,Q48,Q49 XZZZ90003Z INSULATING
Q47,Q48,Q49 XZZZ90358Z INSULATING
IC8 LZZZ61008Z IC SHIELD B
- ES300835SQ SPEAKER
- EX03N40005 SIGNAL
- PT9000060I FRONT PANEL
- PT9000020E CH KNOB
- PT9000040E INNER KNOB
- PT9000050E OUTER KNOB
- PT3600080A SIGNAL
- PT9000070E BAND KNOB
- PT2100031C COUNT
- PT2100041C DISPLAY
- PT7001070C PUSH KEY CR
- MT9000010X FRONT
- MT3600040S CHANNEL
- MT3600061X TOP HOUSING
- MT3600071Q BOTTOM
- MT3600030S HANDLER
- XZZZ90004Z FOAM
- XZZZ90005Z FOAM
- XZZZ90367A SPONGE
- GZZZ50000Z CLAMP
- XZZZ90098Z SOLDER
- XZZZ90021Z FOAM
- EX06T41019 ANT SOCKET
- EX06T40007 DC SOCKET
- MT3600021X SET CHASSIS
- MT3600050X DC SOCKET
- MM7878041B HEAT SINK
- JS052006MN SET SCREW
- JS052012MN SET SCREW
- JS013006MV SET SCREW
- JS013008TN SET SCREW
- JN242012ZS NUT M2x1.2t
- MT2950050X SHIELD
- MT2950060X SHIELD
RANGER
PART NO.
JS052004MN SET SCREW
JS053006MN SET SCREW
DESCRIPTION
METER
METER
HOLDER
WINDOW
WINDOW
CHASSIS
BRACKET
HOUSING
14x16x20mm
8x12x34mm
PLATE
11x30x15t
OFF
W3x16-1
M3x0.5Px8
M2x0.4Px4
M2.6x0.45x5
M3x0.5Px6
M3x0.5Px8
T3x6-2
WASHER
M3x3.5t
HOLDER
PLATE
RING
PLATE
M2x0.4Px6
M2x0.4Px12
M3x0.5Px6
T3x8-2
COVER A
- 38 -
- MT2950070X SHIELD
COVER B
COVER C
Page 39

PART LIST
RCI-6900F TB MAIN PCB
REFERENCE
NUMBER
EPT990010Z MAIN P.C.B
R274,275 RCP121514Z C/F/R
R270 RCP121034Z C/F/R
C214 CC0501804A 18PF 50WV
C217 CC0503304A 33PF 50WV
C222 CC0504704A 47PF 50WV
C209 CC0508204A 82PF 50WV
C215 CC0501215A 120PF 50WV
C216 CC0501815A 180PF 50WV
C221,223 CC0503915G 390PF 50WV
C220 CC1001037L 0.01UF
C219 CD3005614Z 560P 300WV
C13,24,27,28,52,63,
72,128,149,168,200,
308,344
C90,188,198 CEO252267Z 22UF 25WV
C42,43,45,110,154,
183,261
C137,166,260 CE0161077Z 100UF 16WV
C161,185 CE0163377Z 330UF 16WV
C118 CE0164777Z 470UF 16WV
C269,270 CE0251087Z 1000UF 25WV
FL1 EFCFW455HT C.FILTER
FL2 EFCFE107MX C.FILTER
FL3 EFX8106952 CRYSTAL
X1 EYCAB10240 CRYSTAL
X2 EYCAA15360 CRYSTAL
X3 EYBAA12660 CRYSTAL
X4 EYBAE10697 CRYSTAL
IC5 ENMA00612Z I.C AN-612
IC9 ENSM06130Z I.C 14P
Q63 T2SC02538Z TR 2SC2538
D91,92,93 ED1N04148Z DIODE
L2,3 ECIFT12002 I.F.T
L41-43,45-47 ECIFT12012 I.F.T
L20 ECIFT12013 I.F.T
L18,19 ECIFT12016 I.F.T
L1,11 ECIFT12252 I.F.T
L5 ECIFT12253 I.F.T
L38 ECIFT12255 I.F.T
L9,10 ECIFT12256 I.F.T
L12 ECIFT12257 I.F.T
L17,37 ECIFT12258 I.F.T
L15 ECIFT12263 I.F.T
L34 ECIFT12559 I.F.T
L35 ECIFT12560 I.F.T
L6 ECIFT12290 I.F.T
L7 ECIFT12440 I.F.T
L8 ECIFT12492 I.F.T
L4 ECIFT12526 I.F.T
L503 ECCHK16000 CHOKE COIL
L27,28,31 ECCHK16070 CHOKE COIL
T1 ECCHK16004 CHOKE COIL
L23,24 ECSPG18003 SPRING COIL
L25 ECSPG18077 SPRING COIL
L29 ECSPG18001 SPRING COIL
L26 ECSPG18365 SPRING COIL
L14,33 ECBAD18526 BEAD COIL
L32 ECRFZ10048 RF COIL
VR8,9,13,17,19 RE10200041 S/F/R 1K
VR14,15 RE50200042 S/F/R 5K
VR1,2,7,16,18 RE10300031 S/F/R 10K
VR10 RE10400043 S/F/R 100K
VR3,4 RE50400087 S/F/R 500K
VR11,12 RE10100074 S/F/R 100
RANGER
PART NO.
CE0251067Z 10UF 25WV
CE0254767Z 47UF 25WV
DESCRIPTION
150 Ω 1/2W
10K Ω 1/2W
100WV
10M4D
(10.695MHz)
10.240MHz
15.360MHz
12.660MHz
10.697MHz
1N4148
Ω
CW,EXT SP EX06N41045 EAR JACK
J12 EX07N41227 P/C/S 3P
J17 EX07N41330 P/C/S 2P
J1,11,20,21,19,32,35
J7,29,31,3 EX07N48350 P/C/S 3P
J2,9 EX07N48490 P/C/S 4P
J6 EX07N48222 P/C/S 5P
J10,13,15 EX07N48331 P/C/S 6P
J28 EX07N48543 P/C/S 9P
J26 EX07N48209 P/C/S 10P
J30 EX07N48244 P/C/S 3P
J27 EX07N48884 P/C/S 6P
J27,30 EX07N48151 SHORT PIN
TP1,2,3,5,11,12 EX07N48612 P/C/S 1P
J5 EX07N49140 P/C/S 2P
TP7-9 XZZZ90006Z PCB STOPPER
L30,36 WX01070710 JUMPER WIRE
L503 WX0012015A TUBE
L504 WH0007005Z LEAD WIRE
R153,308,317,318,328
,367,307,203,C266,
C267,D117,D118,D119,
D120,D121,D122,D123,
D124
R277 RCY014794Z
R369 RCY011004Z
R293 RCY011504Z
R272,273 RCY012204Z
R246 RCY013304Z
R115,152,226,281 RCY014704Z
R125,227,231 RCY015604Z
R11,105 RCY016804Z
R3,5,8,33,36,78,81,
97,126,154,182,186,
263,286,289,360
R35,104,253,276,280 RCY011514Z
R23 RCY011814Z
R130,150,190,262,136
R32,103 RCY012714Z
R6,10,16,279,282,306
R24,176,202,250,259,
304,347,354
R292 RCY015614Z
R4,50,90,224 RCY016814Z
R74 RCY018214Z
R64,67,71,75,101,117
,118,120,123,146,147
,148,151,178,192,199
,207,213,225,233,244
,249,255,257,258,266
,267,268,269,271,287
,294,297,322,326,329
,341,344,349,351,356
,357,358,96,D126
R91,205 RCY011224Z C/F/R
R56,79,80,89,100,127
,220,221,237,260,278
,283,299
R235,247 RCY011824Z C/F/R
R27,30,70,73,95,116,
121,144,209,214,254,
288,302,310,311,320
R9,25,31 RCY012724Z C/F/R
R18,28,66,113,124,
128,184,204,230,298,
305
R52,58 RCY013924Z C/F/R
R29,38,72,86,132,206
,211,212,215,216,256
,261,175
R87,94,201,290,291 RCY015624Z C/F/R
R14,42,43,69,85,342,
352
R92,300 RCY018224Z C/F/R
R1,13,17,39,40,41,57
,65,68,83,88,128,131
,135,140,142,177,179
- 39 -
EX07N48223 P/C/S 2P
RCY010004Z C/F/R 0 Ω
C/F/R 4.7 Ω
C/F/R 10 Ω
C/F/R 15 Ω
C/F/R 22 Ω
C/F/R 33 Ω
C/F/R 47 Ω
C/F/R 56 Ω
RCY011014Z
RCY012214Z
RCY013314Z
RCY014714Z
RCY011024Z
RCY011524Z C/F/R
RCY012224Z C/F/R
RCY013324Z C/F/R
RCY014724Z C/F/R
RCY016824Z C/F/R
RCY011034Z C/F/R
C/F/R 68 Ω
C/F/R 100 Ω
C/F/R 150 Ω
C/F/R 180 Ω
C/F/R 220 Ω
C/F/R 270 Ω
C/F/R 330 Ω
C/F/R 470 Ω
C/F/R 560 Ω
C/F/R 680 Ω
C/F/R 820 Ω
C/F/R 1K Ω
1.2K Ω
1.5K Ω
1.8K Ω
2.2K Ω
2.7K Ω
3.3K Ω
3.9K Ω
4.7K Ω
5.6K Ω
6.8K Ω
8.2K Ω
10K Ω
Page 40

,188,194,217,223,228
,239-243,248,251,252
,296,301,323,324,346
,348,350,362
R191,137 RCY011234Z
R193 RCY011534Z
R34,93,110,133,134,
138,139,141,187,222
R122 RCY012734Z
R2,264 RCY013334Z C/F/R 33K Ω
R46 RCY013934Z
R7,62,63,99,143,155157,160-165,166-173,
149,198,200,119,134,
343,345,353,355,236
R26,107,112,181 RCY016834Z
R45 RCY018234Z
R12,44,48,49,51,53,
76,77,106,109,114,
195,197,232,238,284,
285,303,295,361
R47,59,84,119,145,
210,218
R54,55,183,185,189 RCY012744Z C/F/R
R15,37,111,196,219 RCY014744Z C/F/R
R102 RCY018244Z C/F/R
R108 RCY011054Z
R208 RCY011554Z C/F/R
C236,248,249 CK1010AB1A 1PF 50WV
C294,288,61,218 CK1020AB1A 2PF 50WV
C211 CK1030AB1A 3PF 50WV
C68,69,86,88,120,253
C1,57,11,155 CK1100AB2A 10PF 50WV
C247 CK1120AB4A 12PF 50WV
C97 CK1150AB4A 15PF 50WV
C51,98,212 CK1180AB4A 18PF 50WV
C79 CK1220AB4A 22PF 50WV
C44 CK1270AB4A 27PF 50WV
C30,89,134,140,300 CK1330AB4A 33PF 50WV
C243 CK1470AB4A 47PF 50WV
C96,60 CK1680AB4A 68PF 50WV
C8 CK1820AB4A 82PF 50WV
C4,160,129,130 CK1101AB5A 100PF 50WV
C62 CK1121AB5A 120PF 50WV
C242 CK1181AB5A 180PF 50WV
C35,237 CK1221AB5A 220PF 50WV
C39 CK1271AB5A 270PF 50WV
C11,14 CK1331AB5A 330PF 50WV
C83,228 CK1471AB5A 470PF 50WV
C29 CK1561AB5A 560PF 50WV
C227 CK1681AB5A 680PF 50WV
C206 CK1390AB4D 39PF 50WV
C205 CK1151AB5D 150PF 50WV
C144 CK1060AB2G 6PF 50WV
C289,290,291 CK1100AB2G 10PF 50WV
C143 CK1680AB4G 68PF 50 WV
C287 CK1101AB5G 100PF 50WV
C142 CK1121AB5G 120PF 50WV
C202 CK1151AB5G 150PF 50WV
C321 CK1181AB5G 180PF 50WV
C95 CK1271AB5G 270PF 50WV
C203 CK1331AB5G 330PF 50WV
C99 CK1391AB5G 390PF 50WV
C48,64,91,111,112,
122,123,131,136,141,
146,345,152,156,179,
182,210,225,229,230,
231,239,245,246,257,
263,271,275,278,279,
280,282,285,286,295,
301,302,304,307,309,
310,311,312,313,320,
326,224,345
C2,3,6,9,15,21,22,25
,33,34,37,59,65-67,
70,71,73,76,82,87,92
,105,115,116,126,127
,139,148,153,158,159
,175,176,177,196,197
RCY012234Z
RCY014734Z
RCY011044Z C/F/R
RCY012244Z C/F/R
CK1050AB1A 5PF 50WV
CK2104AB7R 0.1UF 25WV
CK1103AB6U 0.01UF 50WV
C/F/R 12K Ω
C/F/R 15K Ω
C/F/R 22K Ω
C/F/R 27K Ω
C/F/R 39K Ω
C/F/R 47K Ω
C/F/R 68K Ω
C/F/R 82K Ω
100K Ω
220K Ω
270K Ω
470K Ω
820K Ω
C/F/R 1M Ω
1.5M Ω
,201,207,226,232,234
,235,238,240,250,251
,254,255,268,281,292
,297,298,303,324,325
,340,341,342,346,350
C7,31,36,47,55,58,93
,104,133,135,145,150
,178,181,190,191,192
,204,259,265,322,349
,121
C5,23,26,41,56,74,77
,78,80,81,94,101,106
,109,119,125,157,162
,170,199,258,262,272
,274,277,283,284,296
C10 CK2474AB7R 0.47UF 25WV
C38,49,165,174,193 CK1223AB6U 0.22UF 50V
C171 CK1153AB6U 0.015UF
C12 CK1222AB7R 0.0022UF
C40,50,53,54,172,173
,184,241,343
C186,348 CK2224AB7R 0.22UF 25WV
C169,233,264 CK5225AA7R 2.2UF 16WV
C32,84,180,194,195,
256,306,299
C124 CTY161046Z 0.1UF 16WV
C163 CTY162246Z 0.22UF 16WV
C164,167,213,351,
138
C100 CTY162256Z 2.2UF 16WV
C102 CTY164746Z 0.47UF 16WV
C46,103,189,323 CTY164755Z 4.7UF 16WV
IC1 YNJR00324M NJM324M 14P
IC6 YNJR04558M NJM4558M 8P
IC3,4 YNMC14008D I.C 16P
IC2 YNMC45106D I.C 20P
Q19 TY2SC3356Z TR 2SC3356
Q34,47,49,67 TY2SB0798Z TR 2SB798DL
Q3,5,6,8,15,18,28,40
,43,44,45,48,50,53,
55,57,65,68,69,71,32
Q7,41 TY2SA1298Y TR 2SA1298Y
Q1,2,10,11,12,13,14,
22,23,24,25,29,33,35
,36,58,59,64
Q16,17,26,27,52,54,
56,70
Q42 TYZRN2403Z TR RN1403
Q20,21 FY2SK0302Z F.E.T
D2-10,12-17,20,23-31
,33,35-41,48,50-52,
54-63,67,69-77,80-85
,87,99-104,110,115,
116,125,128,129,130,
132,134,135,136,148,
149,150,152
D89,90,94,109 ED1N04148Y DIODE
D78,79,86,88,137,138
,139,140,141,142,143
,144,145,146,147,151
,153
D21,49,95,108,113,
114,127
D22,96,97,107 ED1V00231Y DIODE
D1,11,34 EDHM0198SY DIODE
D18,19,154,155 EDRS00135Y DIODE
D65,98 EDMA0028TY DIODE MA28T
D53,66 EDMA0028WY DIODE MA28W
D105,106 EDRL04004X DIODE
D64 EDZD05519Z ZENER DIODE
D68 EDZD05759Y ZENER DIODE
D112 EDZD05569Y ZENER DIODE
VC1 CV038200AY TRIMMER/C
L22,39 YCCHK16240 CHOKE COIL
L16 YCCHK16258 CHOKE COIL
L40,44 YCTLI2273C CHOKE COIL
- 40 -
CK1102AB7L 0.001UF
50WV
CK1473AB7R 0.047UF
50WV
50WV
50WV
CK1472AB6U .0047UF
50WV
CK5105AB7R 1UF 16WV
CTY161056Z 1UF 16WV
TY2SC2712G TR
2SC2712GR
TY2SC2714Z TR 2SC2714
TYZRN1403Z TR RN1403
EDSS00355Y DIODE
1SS355
1N4148
EDSS00184Y DIODE
1SS184TE85L
ED1V00231Y DIODE
1SV217-TP
1SV231
HSM198S
RLS135
RLR4004
Page 41

Q47,Q49 JS052012MN SET SCREW
IC8 JS013006MV SET SCREW
Q47,Q49 JN242012ZS NUT M2x1.2t
RCI-6900F TB MISC. PARTS
REFERENCE
NUMBER
METER STOPPER XZZZ90232Z FOAM
COUNTER XZZZ90363Z PVC STAND
COUNTER JS013016WH SET SCREW
FRONT PANEL(4) JS033008MN SET SCREW
CH BKT(2),
CHASSIS(14)
SPK(4) JS053008MN SET SCREW
MAIN PCB(5) JS053006TN SET SCREW
SPK(4) JN263035ZS NUT WITH
Q54 XZZZ90020Z INSULATING
Q47,Q49 XZZZ90003Z INSULATING
Q47,Q49 XZZZ90358Z INSULATING
IC8 LZZZ61008Z IC SHIELD B
Q37 JS052006MN SET SCREW
- WA9812300C DC CORD
- EX03N40005 SIGNAL
- EX04N40654 MIC BLACK
- PT9000060I FRONT PANEL
- PT9000020E CH KNOB
- PT9000070E BAND KNOB
- PT9000040E INNER KNOB
- PT9000050E OUTER KNOB
- PT2100041C DISPLAY
- PT3600080A SIGNAL
- PT2100031C COUNT
- PT7001070C PUSH KEY CR
- MT9000010X FRONT
- MT3600040S CHANNEL BKT
- MT3600061X TOP HPUSING
- MT3600071P BOTTOM
- MT3600030S HANDLER
- XZZZ90004Z FOAM
- XZZZ90208Z SPONGE
- GZZZ50000Z CLAMP
- LZZZ60001Z SHIELD
- XZZZ90098Z SOLDER
- XZZZ90021Z FOAM
- XZZZ90064Z INSULATING
- BA0112010P MIC PLATE
- EX06N41163 DC SOCKET
- EX06N41036 TERMINAL
- EX06T41019 ANT SOCKET
- MT3600190X SET CHASSIS
RANGER
PART NO.
JS053006MN SET SCREW
DESCRIPTION
METER
WINDOW
METER
HOLDER
WINDOW
CHASSIS
HOUSING
14x16x20mm
20x20x3t
14x14x5
CLOTH
10x88x0.3t
PLATE
11x30x15t
PLATE
13x18x0.15
OFF
W3x16-1
M3x0.5Px8
M3x0.5Px6
M3x0.5Px8
T3x6-2
WASHER
M3x3.5t
CONNECTOR
PLATE
RING
PLATE
M2x0.4Px6
- 41 -
M2x0.4Px12
M3x0.5Px6
- JS052010MN SET SCREW
M2x0.4Px10
- MT2950050X SHIELD
COVER A
- MT2950060X SHIELD
COVER B
- MT2950070X SHIELD
COVER C
 Loading...
Loading...