
OPCOM3100
CONFIGURATION GUIDE
SOFTWARE VERSION:2.1.5
Raisecom technology Co., Ltd
(11/2005)

1
Contents
1 Overview.................................................................................................................... 3
1.1 Audience.............................................................................................................3
1.2 Organization ....................................................................................................... 3
1.3 Definitions........................................................................................................... 3
1.4 References ......................................................................................................... 3
2 Introduction................................................................................................................ 4
3 How to use command-line ......................................................................................... 5
3.1 Requirements of software and hardware............................................................5
3.2 Getting help ........................................................................................................ 5
3.3 Use history commands ....................................................................................... 5
3.4 Editing properties................................................................................................ 5
4 Configuring system commands..................................................................................7
4.1 Basic system commands and configuration........................................................7
4.2 Managing configuration files and startup files..................................................... 7
4.2.1 Configuration files.................................................................................7
4.2.2 Startup file.............................................................................................7
4.2.3 Upgrade the program file from bootrom................................................ 8
4.3 User management .............................................................................................11
5 Configuring network protocols.................................................................................. 13
5.1 Configure the mapping from IP address to physical address............................13
5.2 Configure IP address of SNMP interface..........................................................13
5.3 Configure IP routing.......................................................................................... 14
5.4 Configure SNMP COMMUNITY table............................................................... 15
5.5 Configure SNMP trap server host..................................................................... 16
6 Configure Ethernet interfaces .................................................................................. 17
7 Configure E1 interfaces ........................................................................................... 18
8 Configure cross connect .......................................................................................... 19
9 Networking............................................................................................................... 20
9.1 Point to point topology ...................................................................................... 20
9.2 Chain topology.................................................................................................. 20
9.3 Ring topology....................................................................................................21
9.4 Configuration command.................................................................................... 22
9.5 Configuration application .................................................................................. 22
9.5.1 point to point topology ........................................................................ 22
9.5.2 Chain topology.................................................................................... 23
9.5.3 Ring topology...................................................................................... 25
10 Network topology of incontinuous DCC ................................................................... 28

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
2
10.1 Configuration commands.................................................................................. 28
10.2 Examples.......................................................................................................... 28
11 Configuration applications........................................................................................ 30
11.1 Point-to-point 1+1 protection configuration ....................................................... 30
11.2 Chain topology none-protection configuration................................................... 31
11.3 Example of 2F SNC-P configuration................................................................. 33
12 Appendix: Abbreviation ............................................................................................ 38

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
3
1 Overview
1.1 Audience
This guide is for experienced network administrators who are responsible for configuring
and maintaining OPCOM3100. And it describes the device function as well as how to
configure.
1.2 Organization
There are mainly 10 chapters in this guide:
Chapter 2: INTRODUCTION
Describe the main features of OPCOM3100
Chapter 3: HOW TO USE COMMAND-LINE
Describe how to configure OPCOM3100 through command-line and application feathers.
Chapter 4: CONFIGURING SYSTEM COMMANDS
Describe system command function of OPCOM3100 and how to configure.
Chapter 5: CONFIGURING NETWORK PROTOCOLS
Describe network protocol function of OPCOM3100 and how to configure.
Chapter 6: CONFIGURING ETHERNET INTERFACES
Describe Ethernet interface function of OPCOM3100 and how to configure
Chapter 7: CONFIGURING E1 INTERFACES
Describe E1 interface function of OPCOM3100 and how to configure
Chapter 8: CONFIGURING CROSS CONNECT
Describe cross connect function of OPCOM3100 and how to configure
Chapter 9: NETWORKING
Describe how to establish network by OPCOM3100
Chapter 10: NETWORK TOPOLOGY OF INCONTINUOUS DCC
Describe how to configure incontinuous DCC
Chapter 11: CONFIGURA TION APPLICATIONS
1.3 Definitions
Describe the definitions of professional terminologies and the original words of the
alphabet abbreviations
Appendix A
1.4 References
OPCOM3100 device commands notebook

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
4
2 Introduction
OPCOM3100 is an SDH access device which supports both Ethernet services and E1
services, and is developed as an edge access device for the purpose of full use of the
resource of SDH networks. OPCOM3100 can aggregate the user data flows and
multiplex them to STM-1 data. You can access OPCOM310 0 via the device’s serial port
RS232 or network management interface: Telnet and it also provides standard SNMP
management interface and can be field upgraded.

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
5
3 How to use command-line
3.1 Requirements of software and hardware
Operation environment of hardware: platform of OPCOM3100
Computer serial interface;
Operation environment of software: WIN98/WIN2000/WINDOWS XP
3.2 Getting help
command Function description
help
Getting a brief description from help system
abbreviated-command-entry? Obtaining a list of commands that begin with a
particular character sequence
(abbreviated-command-entry)
For example:
OPCOM3100#en ?
english
enable
abbreviated-command-entry<Tab> Supplementing an unfinished command.
For example:
OPCOM3100#show mac<TAB>
OPCOM3100#show mac-address-table
?
Listing all the commands in this mode
For example:
OPCOM3100#?
command? Listing all the key words, options and brief help
information of a command.
OPCOM3100#show ?
3.3 Use history commands
There are 20 history commands in the memory of the device system by default. User can
configure the number of history commands that system can save by the command-line:
OPCOM3100> terminal history <0-20>
Use history to show commands that has been entered.
3.4 Editing properties
up arrow: last entered command
down arrow: next entered command
left arrow: move a character left
right arrow: move a character right
backspace: delete a character in front of the cursor
Ctrl+d: delete a character at the cursor

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
6
Ctrl+a: move the cursor to the beginning of the command line
Ctrl+e: move the cursor to the end of the command line
Ctrl+k: delete all the characters on the right side the cursor
Ctrl+w: delete all the characters on the left side of the cursor
Ctrl+u: delete the row all
Ctrl+z: exit from other modes to privileged mode
Modes of command-line
Mode Mode description Access Prompt
User EXEC Configuring the basic
information and show
the parameters and etc.
Login the
device and
enter the
user name
and password
OPCOM3100>
Privileged
EXEC(enable)
Configuring the basic
information such as
system time and show
the parameters but not
the running information
of OPCOM3100
Form user
EXEC mode,
enter enable
command
and password
OPCOM3100#
Global
configuration
Configuring all the
running parameters of
OPCOM3100
From
privileged
EXEC mode,
enter config
command
OPCOM3100(config)#
Interface
configuration
Configuring parameters
of Ethernet network
management interface,
Ethernet service
interfaces, E1
interfaces, SDH
interfaces and DCC
interfaces.
In global
configuration
mode, enter
interface
command.
[eth/dcc
/sdh/e1/snmp]
OPCOM3100
(config-xxx/n)#
xxx refers to
eth/dcc/sdh/e1/snmp
n refers
to
number of the interface

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
7
4 Configuring system commands
Basic system configuration and user management.
4.1 Basic system commands and configuration
chinese show help information of the command in Chinese
english show help information of the command in English
clear clear the information on the screen
list show the list of all the commands in one mode
settime change the system time
4.2 Managing configuration files and startup files
4.2.1 Configuration files
¾ The present reserved configuration file name is startup_config.conf by default.
¾ Use write command to write the configuration file into the flash file system,
when the system resets next time, the reserved configuration information will be
configured again.
¾ Use erase command to delete that file
¾ The reserved configuration information file startup_config.conf can be uploaded
to the server by commands upload and download through the FTP protocol or
TFTP protocol, or downloaded to system to replace the old configuration
information.
¾ Use show startup-config command to show the reserved configuration
information.
¾ Use show running-config command to show the present configuration
information.
¾
4.2.2 Startup file
¾ Same as program file, and the file name must begin with OPCOM3100, present
program file name is: OPCOM3100-040109.Z;
¾ The program file can be uploaded to the server by commands upload and
download through the FTP protocol or TFTP protocol, or downloaded to
system.
¾ Use show version to check the version information.

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
8
4.2.3 Upgrade the program file from bootrom
There are two ways to upgrade the program file, one is using the serial port through
Xmodem protocol, and the other is using network through FTP protocol, the specific
operations are as follows:
Upgrade the grogram file by the serial port
A: The user who has management privilege can login and enter the privileged
EXEC by the serial port;
B: Enter reboot command;
C: Press the space key to enter the [raisecom] interface, enter? to show the
command list.
? show this list
h show this list
e erase Flash
i modify network manage port ip address
c choose default image file
s show network manage interface information
u update your system
m update microcode
r reboot system
D: Enter u to upgrade program file, the interface is as follows:
choose mode for updating core file.
-----------------------------------
- 1. | serial -
-----------------------------------
- 2. | network -
-----------------------------------
please input mode choose..
E: Enter 1 to choose the serial port for downloading, the interface is as follows:
choose serial baud rate for updating core file.
-----------------------------------
- 1. | 9600 -
-----------------------------------
- 2. | 14400 -
-----------------------------------
- 3. | 19200 -
-----------------------------------
- 4. | 38400 -
-----------------------------------
- 5. | 115200 -
----------------------------------please input baud rate choose...
F: After entering the chosen baud rate, the system is waiting to transmit upgrade file

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
9
through the serial port, now press the [Transfer] option in the serial port as follows:
Choose the file to transmit:
Press [Browse] option to choose the program file to be downloaded, press [Send]
then there will be the following interface:

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
10
After downloading there will be the command-line:
Do you want to update core code? <Y/N>y
Choose y and then finish the program upgrading.
Use network to upgrade the program file through FTP protocol:
A: The user who owns the management privilege can login and enter the privileges
EXEC mode by the serial port;
B: Enter reboot command;
C: Press the space key to enter the [raisecom] interface, enter ? to show the command
list.
? show this list
h show this list
e erase Flash
i modify network manage port ip address
c choose default image file
s show network manage interface information
u update your system
m update microcode
r reboot system
D: Enter u to upgrade program file, the interface is as follows:
choose mode for updating core file.
-----------------------------------
- 1. | serial -
-----------------------------------
- 2. | network -
-----------------------------------

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
11
please input mode choose...
E: Enter 2 to choose network for downloading, the interface is as follows:
starting config network infor ...
host ip address: 192.168.2.225
filename: OPCOM3100-040109.z
usr: wrs
passwd: wrs
Enter host IP address, file name, user name and password of FTP in turn, and then
get into the interface as follows:
starting connect host, please waiting...
choose flash disk for updating core file.
-----------------------------------
- 1. | flash: -
-----------------------------------
- 2. | CORE: -
-----------------------------------
- 3. | cancel: -
-----------------------------------
please input disk choose...
Put the new program file in flash zone or CORE zone, after confirming there will be
the following information:
start update core, please wait some minutes.....
success
Now the program upgrade has been finished.
4.3 User management
The system has a default username raisecom and the password raisecom;
Add a new user, the steps are as follows:
steps Command Description
1
user USERNAME password
{ no-encryption | md5 }
PASSWORD
z USERNAME user name;
z Password password;
z { no-encryption | md5} password not
enciphered or enciphered by MD5;

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
12
z PASSWORD password information;
2
user USERNAME privilege
[ADMINISTRANT | NORMAL |
LIMITED]
z USERNAME user name;
z Privilege key word for privilege
z [ADMINISTRANT | NORMAL
| LIMITED] user privilege
3
write
Save the configuration information
4 show user Show the user information

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
13
5 Configuring network protocols
This chapter includes the following sections:
Configure the mapping from IP address to physical address
Configure IP address of SNMP interface
Configure a static routing
Configure COMMUNITY table of SNMP
Configure SNMP trap server host
5.1 Configure the mapping from IP address to physical
address
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
arp add A.B.C.D
MACADDRESS
Add a mapping from one IP address to physical
address.
A.B.C.D the IP address of the interface;
MACADDRESS: <AA.BB.CC.DD.EE.FF>,
the port’s physical address for mapping
exit
Exit from global configuration mode to
privileged mode
show arp
Show ARP table
Using the global configuration command arp delete A.B.C.D to delete a mapping
from an IP address to a physical address.
For example: Add a mapping of a IP address 192.168.1.119 to a physical address
00:50:8d:46:fb:3
OPCOM3100# config
Configuration mode, one command input per times. End with CTRL-Z.
OPCOM3100(config)# arp add 192.168.2.11 00:50:8d:46:fb:3
Successfully add an entry from ARP table
OPCOM3100(config)# exit
OPCOM3100# show arp
LINK LEVEL ARP TABLE
destination gateway flags Refcnt Use Interface
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.2.11 00:50:8d:46:fb:3 c05 0 0 hw0
5.2 Configure IP address of SNMP interface
There is the possibility to change the IP address of network management, in this

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
14
case ip address is available.
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
interface snmp
Enter SNMP interface configuration mode
ip address A.B.C.D {A.B.C.D}
Configure IP address of network management
A.B.C.D IP address of network
management in decimal with dot.
{
A
.B.C.D} subnet mask of network
management IP address in decimal with dot.
For example: configure IP address of network management as 192.168.2.20,
subnet mask as 255.255.255.0 and serial number of network management
interface as 1.
OPCOM3100# config
Configuration mode, one command input per times. End with CTRL-Z.
OPCOM3100(config)#interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)#ip address 192.168.2.20 255.255.255.0
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# show interface snmp
Interface:snmp Status :up
5.3 Configure IP routing
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
ip route A.B.C.D A.B.C.D
A.B.C.D
Configuring the network manager’s IP address:
A.B.C.D the first parameter is the subnet or
the host IP address in decimal with dot
A.B.C.D the second parameter is the net
mask of subnet or host IP address in decimal
with dot
A.B.C.D the third parameter is the
gateway’s IP address in decimal with dot
exit
Exit from global configuration mode to
privileged mode
show ip route
Show the routing information
Use no ip route A.B.C.D A.B.C.D to delete a routing in the global configuration
mode, the A.B.C.D A.B.C.D are destination IP address and
subnet mask.
For example: configure a routing from 192.168.14.250 to the destination address
192.168.2.18:
OPCOM3100# config
Configuration mode, one command input per time. End with CTRL-Z.
OPCOM3100(config)# ip route 192.168.2.18 255.255.255.0 192.168.4.250

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
15
Successfully add a route
OPCOM3100(config)# show ip route
ROUTE NET TABLE
destination gateway proto Interface
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.2.0 192.168.4.250 static sng0
192.168.4.0 192.168.4.28 connect sng0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
ROUTE HOST TABLE
destination gateway proto Interface
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 connect lo0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
5.4 Configure SNMP COMMUNITY table
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
snmp community
COMMUNITYNAME [RO |
RW]
Add one COMMUNITY
COMMUNITYNAME name of the
COMMUNITUY
RO read only
RW both read and write
exit
Exit from global configuration made to
privileged mode
show snmp-server community
Show COMMUNITY table
Using no snmp-server community COMMUNITYNAME to delete one COMMUNITY
in global configuration mode
For example: add a COMMUNITY named raisecom that can be both read and
written
OPCOM3100# config
Configuration mode, one command input per time. End with CTRL
OPCOM3100(config)# snmp community raisecom rw
Set snmp community name successfully
OPCOM3100(config)# exit
OPCOM3100# show snmp community
ID COMMUNITYNAME RIGHT
----------------------------- 1 public ro
2 private rw
3 raisecom rw

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
16
5.5 Configure SNMP trap server host
The trap server host is in charge of receiving TRAP, the default interface is 162
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
snmp-server host A.B.C.D
{<1-65535>}
Configuring a SNMP trap server host
A.B.C.D the IP address of the host in
decimal with dot
{<1-65535>} interface number for trap
server
exit
Exit from the global configuration mode to
privileged mode
show snmp-server host
Show the information of the trap server host
Using no snmp-server host A.B.C.D to delete a trap server host in
global configuration mode
For example: add a trap server host which IP address is 192.168.1.16
OPCOM3100# config
Configuration mode, one command input per time. End with CTRL
OPCOM3100(config)# snmp -server host 192.168.1.16
Set trap server successfully
OPCOM3100(config)# exit
OPCOM3100# show snmp –server host
Trap server:
ADDRESS PORT
---------------------
192.168.1.16 162

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
17
6 Configure Ethernet interfaces
This chapter includes:
Configure timeslots of Ethernet interfaces
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
interface eth <1-8>
Enter Ethernet interface configuration mode
<1-8> serial number of the interface
timeslot add sdh <1-2> vc12
TSSTRING
Configure the mapping of Ethernet interface
and sdh-vc12
show interface eth <1-8>
Show the timeslots of Ethernet interface
For example: configure the timeslot of Ethernet interface 2 as {1,3,4,5,6,7,
8,9}
OPCOM3100# config
Configuration mode, one command input per time. End with CTRL-Z.
OPCOM3100(config)# interface eth 2
OPCOM3100(config-eth/2)# timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 1,3-9
Set Successfully
OPCOM3100(config-eth/2)# show interface eth 2

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
18
7 Configure E1 interfaces
This chapter includes:
Configure timeslots of E1 interfaces
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
interface e1 <1-32>
Enter E1 interface configuration mode
<1-32> range of serial number of E1
interfaces, if there is E1 sub card the range is
1-32 and otherwise the range is 1-16
timeslot add sdh <1-2> vc12
<1-63>
Configure the mapping of E1 interface and
sdh-vc12
show interface e1 1
Show the information of E1 interface
For example: configure the timeslot of E1 interface 2 as 10
OPCOM3100# config
Configuration mode, one command input per times. End with CTRL-Z.
OPCOM3100(config)# interface e1 2
OPCOM3100(config-eth/2)# timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 10
Set Successfully
OPCOM3100(config-eth/2)# show interface e1 2

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
19
8 Configure cross connect
This chapter includes: configure SDH cross connect from one timeslot to the same or
from one timeslot to another.
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 1 destination-port 2
timeslot 1
Configure a crossconnect from timeslot 1 of
optical interface 1 to timeslot 1 of optical
interface 2
show sdh crossconnect
Show all the crossconnect information

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
20
9 Networking
OPCOM3100 is available for low order cross connect of VC-12.
With bi-directional optical interfaces and tributary interfaces of Ethernet and E1,
OPCOM3100 can be configured conveniently to satisfy all the topologies of user access
networks showing as follows:
Topologies
9.1 Point to point topology
Network of point to point topology is available for LAN relay and extending or replace the
old PDH. The networking is as follows:
Topology
TM device can configure point to point none-protection network, and double TMs can
configure the linear low order VC protection of STM-1 level. When configured as 1+1
protection mode, the two optical interfaces can protect each other to enhance service
reliability.
9.2 Chain topology
Network of chain topology is available for the service flow distributed in chain form and
tributary networks in chain form. Network with OPCOM3100 is as follows:

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
21
Chain topology
TM and ADM can configure none-protection chain topology network, and double TMs
and ADM can configure the linear low order VC protection of STM-1 level.
When configured as 1+1 protection mode, service reliability will enhance but access
ability will reduce; and when configured as none-protection mode, access ability will
enhance but service reliability will reduce.
9.3 Ring topology
Network of ring topology is available for distribution of network elements in ring form.
With the feather of line interfaces self closed, service can be transmitted bi-directionally
(east and west), so the network has high reliability and self-healing ability. Showing as
follows:
Ring topology
This topology can establish 2F SNC-P.
2F SNC-P
The advantages of 2F SNC-P are high speed, flexibility and all level capacities. The
switching depends on local environment and has nothing to do with the network topology,
so 2F SNC-P is suitable for all kinds’ topologies, especially dynamic network.
The disadvantage of 2F SNC-P is that all the tributaries in the ring are all APS
architectures, that is between any two points, there are two transmission lines

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
22
transmitting the data bi-directionally, and every receiving note receives the data
bi-directionally. So the total service flow is lower than the device capacity.
2F SNC-P is suitable for access network, relay network and long distance network.,
which are concentrated, low service flow.
Configuring in-band management channel
9.4 Configuration command
Command Description Mode Limitation
hdlc channel
select
(d1d2d3|f2f3k3
|f2f3)
Configure the overhead byte of in-band
management channel, d1d2d3 are
default configuration
opcom3100(config)#
ip address
A.B.C.D
A.B.C.D
Configuring IP address of interface opcom3100(config-d
cc/X)#
ip unnumbered
Configuring the IP address of DCC
channel same as SNMP interface
opcom3100(config-d
cc/X)#
9.5 Configuration application
Point to point topology
Network of point to point topology:
9.5.1 Point-to-point topology
Configuration commands
:
OPCOM3100A:
OPCOM3100(config)# interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address 192.168.1.66

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
23
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 1
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# ip address 192.168.2.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 2
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# ip address 192.168.3.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# work mode client
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# auto-connect
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)#
OPCOM3100B
:
OPCOM3100(config)# interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address 192.168.4.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 1
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# ip address 192.168.5.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 2
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# ip address 192.168.6.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# work mode client
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# auto-connect
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)#
If two optical interfaces are used at the same time in the network of point to point
topology, ip unnumbered command is not available, then you must configure IP address
for either interface.
9.5.2 Chain topology
Network of chain topology:

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
24
Chain topology
Configuration commands:
OPCOM3100A:
OPCOM3100(config)# interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address 192.168.2.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 1
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)#
OPCOM3100B:
OPCOM3100(config)# interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address 192.168.3.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 1
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 2
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# work mode client
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# auto-connect
Set successfully

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
25
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)#
OPCOM3100B:
OPCOM3100(config)# interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address 192.168.4.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 2
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# work mode client
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# auto-connect
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)#
9.5.3 Ring topology
Network of ring topology:
Ring topology
Configuration commands:
OPCOM3100A:
OPCOM3100(config)# interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address 192.168.1.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 1
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# ip unnumbered

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
26
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 2
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# work mode client
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# auto-connect
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)#
OPCOM3100B:
OPCOM3100(config)# interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address 192.168.2.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 1
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 2
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# work mode client
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# auto-connect
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)#
OPCOM3100C:
OPCOM3100(config)# interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address 192.168.3.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 1
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 2
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# work mode client
Set successfully

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
27
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# auto-connect
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)#
OPCOM3100D:
OPCOM3100(config)# interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# ip address 192.168.4.66
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 1
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/1)# exit
OPCOM3100(config)# interface dcc 2
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# ip unnumbered
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# work mode client
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)# auto-connect
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config-dcc/2)#

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
28
10 Network topology of incontinuous DCC
Network topology:
If the network is not only organized by OPCOM3100, DCC channel is not continuous
when there are other types of device or network, in this case we use data network to
manage and control remote OPCOM3100.
Network management configuration
10.1 Configuration commands
Command Description Mode Limitation
ip address A.B.C.D
Configure
network
management IP
OPCOM3100(config-snmp
)#
snmp community
COMMUNITYNAME
[RO|RW]
Configure SNMP
community
opcom3100(config)#
snmp-server host
A.B.C.D {<1-65535>}
Configure trap
server
opcom3100(config)#
10.2 Examples
Configure the network management IP address of OPCOM3100 as 192.168.4.28, and
network management host IP address is 192.167.4.250, ro and rw communities are
public, private.
OPCOM3100# config
Configuration mode, one command input per times. End with CTRL-Z.
OPCOM3100(config)#interface snmp
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)#ip address 192.168.4.28 255.255.255.0
OPCOM3100(config-snmp)#exit
OPCOM3100(config)# snmp-server community private rw
Set successfully
OPCOM3100(config)# snmp-server community public ro
Set successfully

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
29
OPCOM3100(config)# snmp-server host 192.168.4.250
Set successfully

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
30
11 Configuration applications
This chapter includes:
point to point 1+1 protection configuration
chain topology none-protection configuration
ring topology 2F SNC-P configuration
11.1 Point-to-point 1+1 protection configuration
Topology:
OPCOM3100-A OPCOM3100-BPort1 Port1
Port2
Port2
Point to point networking
Service requirement
There are 2 E1 services of which the timeslot is 1 and 3; one Ethernet service which
timeslots are 20 21 25 27.
Configuring timeslots
name
TM1 TM2
1,2 1,2
20,21,25,27 20,21,25,27
timeslot
STM-1
E1 1,2 E1 1,2
eth1 eth1
Configuration commands
Configure TM1
Command Description
OPCOM3100#config Enter global configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config)# sdh
Configure the work mode of the device as

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
31
device-type tm
TM
OPCOM3100(config)# sdh net-type
line
Configure the network type of device
OPCOM3100(config)#exit
OPCOM3100#write
Save the configuration
OPCOM3100#reboot
Reset device
OPCOM3100(config)#interface e1
1
Enter E1 interface 1
OPCOM3100(config-e1/1)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 1
Configure timeslot 1 to E1 interface 1
OPCOM3100(config-e1/1)#exit
Exit to global configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config)# interface e1
2
Enter E1 interface 12
OPCOM3100(config-e1/2)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 2
Configure timeslot 2 to E1 interface 2
OPCOM3100(config-e1/1)#exit
Exit to global configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config)#interface eth
1
Enter Ethernet interface 1
OPCOM3100(config-eth/1)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12
20,21,25,27
Configure Ethernet interface 1 the timeslots
21,21,25,27
Configure TM2 in the same way as TM1
11.2 Chain topology none-protection configuration
Topology:
OPCOM3100-A OPCOM3100-B OPCOM3100-C
Port1
Port1
Port2
Port1
Chain networking
Service requirement
There are 10 2M services between TM1 and ADM, 10 2M services between ADM and
TM2, and 11 2M services between TM1 and TM2
Service matrix
Name TM1(OPCOM3100-A) ADM(OPCOM3100-B) TM2(OPCOM3100-C) Total
TM1 10 11 21

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
32
ADM 10 10 20
TM2 11 10 21
Total 21 20 21 62
Timeslot table
name
TM1 TM2
timeslot
STM-1
ADM
port1 1-10 port1 1-10
port2 1-10
port1 1-10
port1 11-21
port1 11-21
E1 1-10 E1 1-10 E1 17-26
E1 11-21
E1 1-10
E1 11-21
Configuration commands
Configure TM1
Command Description
OPCOM3100#config
Enter global configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config)# sdh
device-type tm
Configure the work mode of device as TM
OPCOM3100(config)# sdh net-type
line
Configure the network topology of device
OPCOM3100(config)#sdh
protect-switch disable
Disable the protection
OPCOM3100(config)#exit
OPCOM3100#write
Save the configuration
OPCOM3100#reboot
Reset the device
OPCOM3100(config)#interface e1 1
Enter E1 interface 1
OPCOM3100(config-e1/1)# Timeslot
add sdh 1 vc12 1
Configure timeslot 1 to E1 interface 1
……
Configure E1 interfaces 2 to 21 the
timeslots 2 to 21, correspond one to one.
Configure ADM
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config)#sdh
Configure work mode of the device as ADM

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
33
device-type tm
OPCOM3100(config)# sdh
net-type line
Configure the network topology of device
OPCOM3100(config)#sdh
protect-switch disable
Disable the protection
OPCOM3100(config)#exit
OPCOM3100#write
Save the configuration
OPCOM3100#reboot
Reset the device
OPCOM3100(config-e1/1)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 1
……
Configure E1 interfaces 1 to 10 the timeslots 1
to 10 of optical interface 1, correspond one to
one.
OPCOM3100(config-e1/17)#
Timeslot add sdh 2 vc12 1
……
Configure E1 interfaces 17 to 26 the timeslots 1
to 10 of optical interface 2, correspond one to
one.
OPCOM3100(config)# sdh
crossconnect source-port 1
timeslot 11 destination-port 2
timeslot 11
Configure crossconnect of remote services,
timeslot 1 1 of optical interface 1 to timeslot 11 of
optical interface 2.
Configure timeslot 12-21 of optical interface 1 to
timeslot 12-21 of optical interface 2.
Configure TM2 in the same way as TM1
11.3 Example of 2F SNC-P configuration
The network topology is as follows:
OPCOM3100-A
OPCOM3100-B
OPCOM3100-C
OPCOM3100-D
Port2Port1
Port1
Port2
Port1
Port2
Port1
Port2
Ring networking
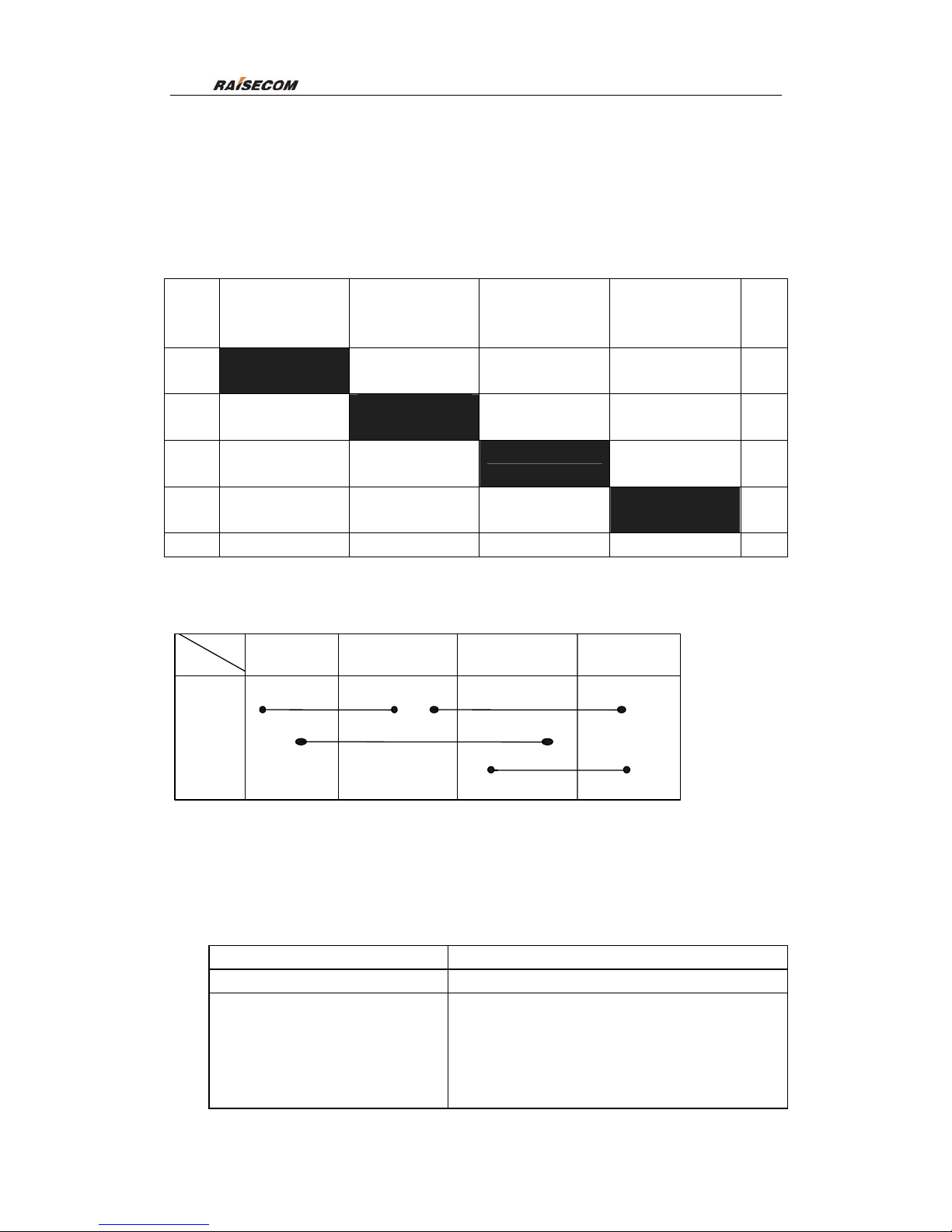
Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
34
Service requirements
There are 10 2M Ethernet services from ADM A to ADM B, 5 2M and one 10M from A to
C, 2 2M from B to D, and 5 2M from C to D.
Service matrix
Nam
e
ADM-A
(OPCOM3100-A
)
ADM-B
(OPCOM3100-B
)
ADM-C
(OPCOM3100-C
)
ADM-D
(OPCOM3100-D
)
Tota
l
ADM A 10
5+5
0 20
ADM B 10 0 2 12
ADM
C
5+5
0 5 15
ADM D 0 2 5 7
Total 20 12 15 7 54
Timeslot table
name
ADM A
ADM D
timeslot
STM-1
ADM B
1-10 1-10 21,22
11-20
11-20
ADM C
21,22
23-27 23-27
E1 1-10
E1 1-10
E1 21-22E1 21-22
E1 11-15
Eth1
E1 23-27 E1 23-27
E1 11-15
Eth1
Configuration commands
A configuring the device
Command Description
OPCOM3100#config
Enter global configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 21
destination-port 2 timeslot 21
OPCOM3100(config)#
Configure crossconnect of the service from B to
D, timeslot 21-22 of optical interface 1 to
timeslot 21-22 of optical interface 2.

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
35
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 22
destination-port 2 timeslot 22
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 23
destination-port 2 timeslot 23
…
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 27
destination-port 2 timeslot 27
Configure crossconnect of the service from C to
D, timeslot 23-27 of optical interface 1 to
timeslot 23-27 of optical interface 2.
OPCOM3100(config)#
Interface E1 1
Enter E1 interface configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config-e1/1)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 1
……
Configure E1 interfaces 1 to 10 the timeslots 1
to 10, correspond one to one.
Same as previous
Configure E1 interfaces 11 to 15 the timeslots
11 to 15, correspond one to one.
OPCOM3100(config)#
Interface Eth 1
Enter Ethernet interface configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config-eth/1)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 16-20
Configure Ethernet interface 1 the timeslots
16-20
show sdh crossconnect
Show all the information of crossconnect
Show interface sdh 1 timeslot
Show the information of timeslot
B configure the device
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 11
destination-port 2 timeslot 11
……
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 20
destination-port 2 timeslot 20
Configure crossconnect of the service from A to
C, timeslot 11-20 of optical interface 1 to
timeslot 11-20 of optical interface 2.
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 23
destination-port 2 timeslot 23
……
Configure crossconnect of the service from C to
D, timeslot 23-27 of optical interface 1 to
timeslot 23-27of optical interface 2.

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
36
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 27
destination-port 2 timeslot 27
OPCOM3100(config)#
Interface E1 1
Enter E1 interface configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config-e1/1)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 1
……
Configure E1 interfaces 1 to 10 the timeslots 1
to 10, correspond one to one.
OPCOM3100(config-e1/21)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 21
……
Configure E1 interfaces 21 to 22 the timeslots
21 to 22, correspond one to one.
show sdh crossconnect
Show all the information of crossconnect
Show interface sdh 1 timeslot
Show the information of timeslot
C configure the device
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 1 destination-port
2 timeslot 1
……
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 10
destination-port 2 timeslot 10
Configure crossconnect of the service from A to
B, timeslot 1-10 of optical interface 1 to timeslot
1-10 of optical interface 2.
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 21
destination-port 2 timeslot 21
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 22
destination-port 2 timeslot 22
Configure crossconnect of the service from B to
D, timeslot 21-22 of optical interface 1 to
timeslot 21-22 of optical interface 2
OPCOM3100(config)#
Interface E1 11
Enter E1 interface configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config-e1/11)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 11
……
Configure E1 interfaces 11 to 15 the timeslots
11 to 15, correspond one to one.
OPCOM3100(config)#
Interface Eth 1
Enter Ethernet interface configuration mode

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
37
OPCOM3100(config-eth/1)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 16-20
Configure Ethernet interface 1 the timeslots
16-20
OPCOM3100(config-e1/23)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 23
……
Configure E1 interfaces 23 to 27 the timeslots
23 to 27, correspond one to one.
show sdh crossconnect
Show all the information of crossconnect
Show interface sdh 1 timeslot
Show the information of timeslot
D configure the device
Command Description
config
Enter global configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 1 destination-port
2 timeslot 1
……
OPCOM3100(config)#
sdh crossconnect source-port
1 timeslot 20
destination-port 2 timeslot 20
Configure crossconnect of the service from A to
B, timeslots 1-10 of optical interface 1 to
timeslots 1-10 of optical interface 2.
Configure crossconnect of the service from A to
C, timeslots 11-20 of optical interface 1 to
timeslots 11-20 of optical interface 2.
OPCOM3100(config)#
Interface E1 21
Enter E1 interface configuration mode
OPCOM3100(config-e1/21)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 21
……
Configure E1 interfaces 21 to 22 the timeslots
21 to 22, correspond one to one.
OPCOM3100(config-e1/23)#
Timeslot add sdh 1 vc12 23
……
Configure E1 interfaces 23 to 27 the timeslots
23 to 27, correspond one to one.
show sdh crossconnect
Show all the information of crossconnect
show interface sdh 1 timeslot
Show the information of timeslot

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
38
12 Appendix: Abbreviation
Abbreviations English
ADM Add-Drop Multiplexer
AIS Alarm Indication Signal
APS Automatic Protection Switching
AU Administrative Unit
AU-n
Administration Unit,level n
AUG Administration Unit Group
AU-PTR Administration Unit Pointer
BBE Background Block Error
BBER Background Block Error Ratio
BER Bit Error Ratio
CMI Coded Mark Inversion
C-n Container- n
CORBA Common Object Request Broker Architecture
CV Code Violation
DCC Data Communications Channel
DCE Data Circuit-terminating Equipment
DCF Data Communications Function
DCN Data Communications Network
DDN Digital Data Network
DTE Data Terminal Equipment
DXC Digital Cross Connect
ECC Embedded Control Channel
EM Element Management
EML Element Management Layer
EMS Element Management System
EOS Ethernet Over SDH
ES Error Second
ESR Error Second Ratio
ETSI European Telecommunication Standards Institute
FEBBE Far End Background Block Error
FEES Far End Error Second
FESES Far End Severely Error Second
GUI Graphical User Interface
HDLC High Digital Link Control
HPC Higher order Path Connection
IP Internet Protocol
ITU-T
International Telecommunication
Union-Telecommunication Standardization Sector
L2 Layer 2
LAN Local Area Network

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
39
LCT Local Craft Terminal
LOF Loss Of Frame
LOP Loss Of Pointer
LOS Loss Of Signal
LPC Lower order Path Connection
MAC Medium Access Control
MAN Metropolitan Area Network
MCU Micro Control Unit
MD Mediation Device
MF Mediation Function
MII Medium Independent Interface
MM Multi Mode
MS Multiplex Section

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
40
Sequel
Abbreviations English
MS-AIS Multiplex Sections - Alarm Indication Signal
MSOH Multiplex Section OverHead
MSP Multiplex Section Protection
NE Network Element
NEF Network Element Function
NEL Network Element Layer
NML Network Manager La yer
NMS Network Management System
OAM Operation, Administration and Maintenance
OFS Out of Frame Second
OOF Out of Frame
OS Operation System
OSI Open System Interconnect
PCM Pulse Code Modu lation
PDH Plesiochronou s Digital Hierarchy
PJE+ Pointer Justification Event +
PJE- Pointer Justification Event POH Path OverHead
PPP Point to Point Protocol
PRC Primary Reference Clock
RAM Random Access Memory
RDI Remote Defect Indication
REI Remote Error Indication
REG Regenerator
RFI Remote Failure Indication
RIP Router Information Protocol

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
41
Sequel
Abbreviations English
RMII Reduced Medium Independent Interface
RS Regenerator Section
RSOH Regenerator Section OverHead
SDH Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
SEC SDH Equipment Clock
SES Severely Error Second
SESR Severely Error Second Ratio
SETS Synchronous Equipment Timing Source
SM Single Mode
SNCP Subnetwork Connection Protection
SOH Section Overhead
SPRING Shared Protection Ring
SSM Synchronous State Message
STM-N Synchronous Transport Module Level-N
TCP Transport Control Protocol
TDEV Time Deviation
TDM Time Division Multiplex
TM Terminal Multiplexer
TMN Telecommunications Management Network
TU Tributary Unit
TU-m
Tributary Unit,level m
TUG-m
Tributary Unit Group,level m
UAS Unavailable Second
VC Virtual Container
VC-n
Virtual Container,level n
VLAN Virtual Local Area Network
WAN Wide Area Network

Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd
42
@2005 Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Technical information may be subject to change without prior notification.
 Loading...
Loading...