Page 1
MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
________________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products 1
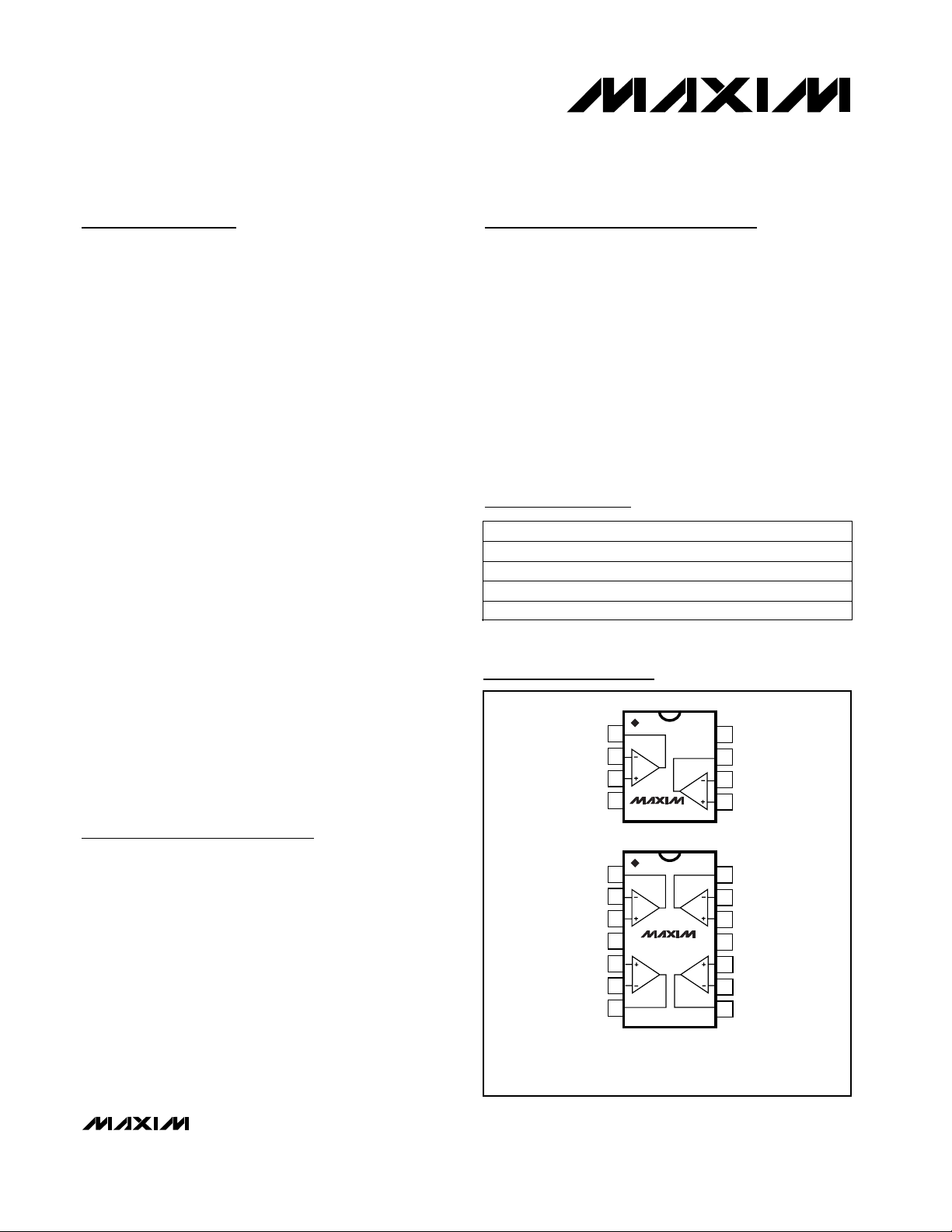
Pin Configurations
19-0129; Rev. 4; 9/01
General Description
The MAX907/MAX908/MAX909 are dual/quad/single,
high-speed, ultra-low-power voltage comparators
designed for use in systems powered from a single
+5V supply; the MAX909 also accepts dual ±5V supplies. Their 40ns propagation delay (with 5mV input
overdrive) is achieved with a power consumption of
only 3.5mW per comparator. The wide input commonmode range extends from 200mV below ground (below
the negative supply rail for the MAX909) to within 1.5V
of the positive supply rail.
Because they are micropower, high-speed comparators that operate from a single +5V supply and include
built-in hysteresis, these devices replace a variety of
older comparators in a wide range of applications.
MAX907/MAX908/MAX909 outputs are TTL-compatible, requiring no external pullup circuitry. All inputs and
outputs can be continuously shorted to either supply
rail without damage. These easy-to-use comparators
incorporate internal hysteresis to ensure clean output
switching even when the devices are driven by a slowmoving input signal.
The MAX909 features complementary outputs and an
output latch. A separate supply pin for extending the
analog input range down to -5V is also provided.
The dual MAX907 and single MAX909 are available in
8-pin DIP and SO packages, and the quad MAX908 is
available in 14-pin DIP and SO packages. These comparators are ideal for single +5V-supply applications
that require the combination of high speed, precision,
and ultra-low power dissipation.
Applications
Battery-Powered Systems
High-Speed A/D Converters
High-Speed V/F Converters
Line Receivers
Threshold Detectors/Discriminators
High-Speed Sampling Circuits
Zero-Crossing Detectors
Features
♦ 40ns Propagation Delay
♦ 700µA (3.5mW) Supply Current per Comparator
♦ Single 4.5V to 5.5V Supply Operation
(or ±5V, MAX909 only)
♦ Wide Input Range Includes Ground
(or -5V, MAX909 only)
♦ Low, 500µV Offset Voltage
♦ Internal Hysteresis Provides Clean Switching
♦ TTL-Compatible Outputs
(Complementary on MAX909)
♦ Input and Output Short-Circuit Protection
♦ Internal Latch (MAX909 only)
Ordering Information
PART
TEMP. RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX907CPA
0°C to +70°C 8 Plastic DIP
MAX907CSA 0°C to +70°C 8 SO
MAX907EPA 8 Plastic DIP
MAX907ESA
-40°C to +85°C
-40°C to +85°C
8SO
Ordering Information continued at end of data sheet.
Pin Configurations continued at end of data sheet.
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim/Dallas Direct! at
1-888-629-4642, or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
TOP VIEW
OUTA
INA-
INA+
GND
OUTA
INA-
INA+
INB+
INB-
OUTB
1
2
3
4
MAX907
DIP/SO
1
2
3
4
V+
MAX908
5
6
7
DIP/SO
14
13
12
11
10
8
V+
OUTB
7
INB-
6
5
INB+
OUTD
IND-
IND+
GND
INC+
INC-
9
8
OUTC
Page 2
MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Positive Supply Voltage (V+ to GND) ........................+6V
Negative Supply Voltage (V- to GND, MAX909 only) .........-7V
Differential Input Voltage
MAX907/MAX908 ..........................-0.3V to (V+ + 0.3V)
MAX909 ..............................(V- - 0.3V) to (V+ + 0.3V)
Common-Mode Input Voltage
MAX907/MAX908 ..........................-0.3V to (V+ + 0.3V)
MAX909 ..............................(V- - 0.3V) to (V+ + 0.3V)
Latch Input Voltage (MAX909 only) .........-0.3V to (V+ + 0.3V)
Input/Output Short-Circuit Duration to V+ or GND .. . Continuous
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
8-Pin Plastic DIP (derate 9.09mW/°C above +70°C) . . .727mW
8-Pin SO (derate 5.88mW/°C above +70°C) ...........471mW
14-Pin Plastic DIP (derate 10.00mW/°C above +70°C) . .. 800mW
14-Pin SO (derate 8.33mW/°C above +70°C) ..........667mW
Operating Temperature Ranges:
MAX90_C_ _ ......................................0°C to +70°C
MAX90_E_ _ ...................................-40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range ...................-65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) ......................+300°C
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(V+ = 5V, TA= +25°C; MAX909 only: V- = 0, V
LATCH
= 0; unless otherwise noted.)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Positive Trip Point
V
TRIP+
(Note 1) 24 mV
Negative Trip Point
V
TRIP-
(Note 1) -2 -4 mV
Input Offset Voltage
V
OS
(Note 2) 0.5 2.0 mV
Input Bias Current
I
B
VCM= 0, VIN= V
OS
100 300 nA
Input Offset Current
I
OS
VCM= 0, VIN= V
OS
25 50 nA
Input Voltage Range
V
CMR
-0.2 V+ - 1.5
V
-5.2 V+ - 1.5
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR (Notes 4, 5) 50 100 µV/V
Power-Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR (Notes 4, 6) 50 100 µV/V
Output High Voltage
V
OH
I
SOURCE
= 100µA
3.0 3.5
VOutput Low Voltage
V
OL
I
SINK
= 3.2mA
0.3 0.4
I
SINK
= 8mA
0.4
Positive Supply Current per
Comparator
I+ (Note 7)
0.7 1.0
mA
1.2 1.8
Negative Supply Current I- MAX909 only: V- = -5V 60 100 µA
Power Dissipation per
Comparator
PD (Note 8)
3.5 5.5
mW
610
Output Rise Time
t
r
12 ns
Output Fall Time
t
f
6 ns
SYMBOL
MAX907/MAX908/MAX90 9
MAX907/MAX908
MAX909
MAX909
(Notes 3, 4)
MAX907/MAX908
V
OUT
= 0.4V to 2.4V, CL= 10pF
V
OUT
= 2.4V to 0.4V, CL= 10pF
V
MAX909 only: V- = -5V
Page 3
MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V+ = 5V, TA= +25°C; MAX909 only: V- = 0, V
LATCH
= 0; unless otherwise noted.)
PARAMETER
SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Propagation Delay
t
PD+,tPD-
40 50 ns
Differential Propagation Delay
∆t
PD
1 ns
Propagation Delay Skew
tPDskew
2 ns
Latch Input Voltage High
V
IH
(Note 12) 2.0 V
Latch Input Voltage Low
V
IL
(Note 12) 0.8 V
Latch Input Current
IIH, I
IL
(Note 12) 20 µA
Latch Setup Time
t
s
(Note 12) 2 ns
Latch Hold Time
t
h
(Note 12) 2 ns
VIN= 100mV, VOD= 5mV,
(Note 9)
VIN= 100mV, VOD= 5mV,
(Note 10)
MAX909 only: VIN= 100mV,
V
OD
= 5mV, (Note 11)
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(V+ = 5V, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
; MAX909 only: V- = 0, V
LATCH
= 0; unless otherwise noted.)
Positive Trip Point V
Negative Trip Point V
Input Offset Voltage V
Input Bias Current I
Input Offset Current I
Input Voltage Range V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR (Notes 4, 5) 75 200 µV/V
Power-Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR (Notes 4, 6) 75 200 µV/V
Output High Voltage V
Output Low Voltage V
Positive Supply Current per
Comparator
Negative Supply Current I- MAX909 only; V- = -5V 100 200 µV
Power Dissipation per
Comparator
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
TRIP+
TRIP-
OS
B
OS
CMR
OH
OL
I+ (Note 7)
PD (Note 8)
(Note 1) 2 5 mV
(Note 1) -2 -5 mV
(Note 2) 1 3 mV
V
= 0, V
CM
V
= 0, V
CM
C/E temp.
ranges
(Notes 3, 4)
I
SOURCE
I
SINK
= 100µA 2.8 3.5 V
= 3.2mA
IN
IN
= V
OS
= V
OS
MAX907/MAX908/MAX909 -0.2 V+ - 1.5
MAX909 only, V- = -5V -5.2 V+ - 1.5
T
= T
A
MAX
T
= 0°C 0.425
MIN
T
= -40°C 0.450
MIN
200 500 nA
50 100 nA
MAX907/MAX908 0.8 1.2
MAX909 1.2 2.0
MAX907/MAX908 4 7
MAX909 6 11
V
0.4
V
mA
mW
Page 4

MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Note 1: Trip Point is defined as the input voltage required to make the comparator output change state. The difference
between upper (V
TRIP
+) and lower (V
TRIP
-) trip points is equal to the width of the input-referred hysteresis zone (V
HYST
).
Specified for an input common-mode voltage (V
CM
) of 0 (see Figure 1).
Note 2: Input Offset Voltage is defined as the center of the input-referred hysteresis zone. Specified for V
CM
= 0 (see Figure 1).
Note 3: Inferred from the CMRR test. Note that a correct logic result is obtained at the output, provided that at least one input is
within the V
CMR
limits. Note also that either or both inputs can be driven to the upper or lower absolute maximum limit with-
out damage to the part.
Note 4: Tested with V+ = 5.5V (and V- = 0 for MAX909). MAX909 also tested over the full analog input range (i.e., with
V- = -5.5V).
Note 5: Tested over the full input voltage range (V
CMR
).
Note 6: Specified over the full tolerance of operating supply voltage: MAX907/MAX908 tested with 4.5V < V+ < 5.5V. MAX909
tested with 4.5V < V+ < 5.5V and with -5.5V < V- < 0.
Note 7: Positive Supply Current specified with the worst-case condition of all outputs at logic low (MAX907/MAX908), and
with V+ = 5.5V.
Note 8: Typical power specified with V+ = 5V; maximum with V+ = 5.5V (and with V- = -5.5V for MAX909).
Note 9: Due to difficulties in measuring propagation delay with 5mV of overdrive in automatic test equipment, the
MAX907/MAX908/MAX909 are sample tested to 0.1% AQL with 100mV input overdrive. Correlation tests show that the
specification can be guaranteed if all other DC parameters are within the specified limits. V
OS
must be added to the over-
drive voltage for low values of overdrive.
Note 10: Differential Propagation Delay is specified as the difference between any two channels in the MAX907/MAX908 (both out-
puts making either a low-to-high or a high-to-low transition).
Note 11: Propagation Delay Skew is specified as the difference between any single channel’s output low-to-high transition (t
PD
+)
and high-to-low transition (t
PD
-), and also between the QOUT and QOUT transition on the MAX909.
Note 12: Latch specifications apply to MAX909 only (see Figure 2).
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V+ = 5V, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
; MAX909 only: V- = 0, V
LATCH
= 0; unless otherwise noted.)
PARAMETER
SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Propagation Delay
t
PD+,tPD-
VIN= 100mV, VOD= 5mV
(Note 9)
45 70 ns
Differential Propagation Delay
∆t
PD
VIN= 100mV, VOD= 5mV
(Note 10)
2 ns
Propagation Delay Skew
tPDskew
MAX909 only: VIN= 100mV,
V
OD
= 5mV (Note 11)
4 ns
Latch Input Voltage High
V
IH
(Note 12) 2.0 V
Latch Hold Time
t
h
(Note 12) 4 ns
Latch Input Voltage Low
V
IL
(Note 12) 0.8 V
Latch Input Current
IIH, I
IL
(Note 12) 20 µA
Latch Setup Time
t
s
(Note 12) 4 ns
Page 5

MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
_________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5
Typical Operating Characteristics
(V+ = 5V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
0.5
0.1
012
OUTPUT LOW VOLTAGE
vs. SINK CURRENT
0.2
I
SINK
(mA)
V
OL
(V)
8
0.3
2610
0.4
4
VIN = 100mV
TA = -55°C
TA = +125°C
TA = +25°C
MAX907 TOC06
2.0
0
28
MAX907
TOTAL POSITIVE SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. POSITIVE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(OUTPUTS AT V
OL
)
0.5
V
CC
(V)
TOTAL I
CC
(mA)
6
1.0
357
1.5
4
TA = -55°C
TA = +125°C
TA = +25°C
MAX907 TOC07
2.0
0
28
MAX907
TOTAL POSITIVE SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. POSITIVE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(OUTPUTS AT V
OH
)
0.5
V
CC
(V)
TOTAL I
CC
(mA)
6
1.0
357
1.5
4
TA = -55°C
TA = +125°C
TA = +25°C
MAX907 TOC08
4.0
0
28
MAX908
TOTAL POSITIVE SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. POSITIVE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(OUTPUTS AT V
OL
)
1.0
V
CC
(V)
TOTAL I
CC
(mA)
6
2.0
357
3.0
4
TA = -55°C
TA = +125°C
TA = +25°C
MAX907 TOC09
PROPAGATION DELAY
vs. INPUT OVERDRIVE
50
RS = 10Ω
= 15pF
C
LOAD
40
30
tPD+
t
PD
-
MAX907 TOC01
80
60
40
PROPAGATION DELAY
vs. SOURCE IMPEDANCE
VOD = 5mV
= 15pF
C
LOAD
tPD+
t
PD
PROPAGATION DELAY
vs. CAPACITIVE LOAD
70
VOD = 5mV
= 10Ω
R
MAX907 TOC2
-
S
60
+
t
50
PD
MAX907 TOC03
20
PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
10
1 10 100
INPUT OVERDRIVE (mV)
PROPAGATION DELAY
vs. TEMPERATURE
70
VOD = 5mV
= 10Ω
R
S
= 15pF
C
LOAD
60
50
40
PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
30
-60 -20 60 140
-40 0 8040 120
20 100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
tPD+
t
PD
20
PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
0
10 100 10k
SOURCE IMPEDANCE (Ω)
40
PROPAGATION DELAY (ns)
1k
30
20 60 100
0 120
40
CAPACITIVE LOAD (pF)
tPD-
80
OUTPUT HIGH VOLTAGE
vs. SOURCE CURRENT
5.0
VIN = 100mV
MAX907 TOC04
-
4.5
(V)
V
4.0
OH
3.5
3.0
TA = +125°C
TA = +25°C
TA = -55°C
1 10 1000
I
SOURCE
(µA)
100
MAX907 TOC05
Page 6

MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
6 ________________________________________________________________________________________________
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V+ = 5V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
4.0
0
28
MAX908
TOTAL POSITIVE SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. POSITIVE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(OUTPUTS AT V
OH
)
1.0
V
CC
(V)
TOTAL I
CC
(mA)
6
2.0
357
3.0
4
TA = -55°C
TA = +125°C
TA = +25°C
MAX907 TOC10
0.5
-0.5
-60 -20 60 140
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE
vs. TEMPERATURE
TEMPERATURE (°C)
V
OS
(mV)
20 100
0
-40 0 8040 120
V
OUT
= 1.4V
V
CM
= 0
MAX907 TOC16
4
-4
-60 -20 60 140
TRIP POINT
vs. TEMPERATURE
-2
2
TEMPERATURE (°C)
V
OS
(mV)
20 100
0
-40 0 8040 120
VCM = 0
V
TRIP+
V
TRIP-
MAX907 TOC18
5
-1
-60 -20 60 140
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
vs. TEMPERATURE
0
4
TEMPERATURE (°C)
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE (V)
20 100-40 0 8040 120
V
CMR-
V
CMR+
MAX907 TOC13
2.0
0
23 5 8
MAX909
POSITIVE SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. POSITIVE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
V+ (V)
TOTAL I+ (mA)
46
1.0
7
V- = -5V
TA = +125°C
TA = +25°C
TA = -55°C
MAX907 TOC11
300
100
-60 -20 60 140
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
vs. TEMPERATURE
TEMPERATURE (°C)
INPUT CURRENT (nA)
20 100
200
-40 0 8040 120
VCM = 0
V
IN
= V
OS
MAX907 TOC17
60
0
-60 -20 60 140
SHORT-CIRCUIT OUTPUT CURRENT
vs. TEMPERATURE
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SHORT-CIRCUIT OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
20 100
30
-40 0 8040 120
OUTPUT
SHORTED TO
V+ (SINKING)
OUTPUT
SHORTED TO
GND (SOURCING)
MAX907 TOC15
200
0
0-1 -3 -6
MAX909
NEGATIVE SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. NEGATIVE SUPPLY VOLTAGE
V- (V)
TOTAL I- (µA)
-2 -4
100
-5 -7
V+ = +5V
T
A
= +125°C
TA = +25°C
TA = -55°C
MAX907 TOC12
5
-6
-60 -20 60 140
MAX909
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
vs. TEMPERATURE
-5
4
TEMPERATURE (°C)
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE (V)
20 100
V
CMR
+
V
CMR
-
V+ = +5V
V- = -5V
-40 40 120080
MAX907 TOC14
Page 7

MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
_________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(V+ = 5V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
INPUT
20mV/div
INPUT
20mV/div
OUTPUT
GND
MAX907/MAX908
PROPAGATION DELAY (t
(5mV OVERDRIVE)
tPD+
10ns/div
MAX909
PROPAGATION DELAY (t
(5mV OVERDRIVE)
tPD+
10ns/div
+)
PD
MAX907 TOC19
+)
PD
MAX907 TOC21
tPD SKEW
5mV OVERDRIVE
INPUT GND
OUTPUT
500mV/div
TTL
THRESHOLD (1.4V)
OUTPUT
GND
5mV OVERDRIVE
INPUT GND
QOUT
1V/div
1.4V
QOUT
INPUT
20mV/div
INPUT
20mV/div
OUTPUT
GND
MAX907/MAX908
PROPAGATION DELAY (t
(5mV OVERDRIVE)
tPD-
10ns/div
MAX909
PROPAGATION DELAY (t
(5mV OVERDRIVE)
tPD- tPD SKEW
10ns/div
-)
PD
MAX907 TOC20
-)
PD
MAX907 TOC22
INPUT GND
-5mV OVERDRIVE
OUTPUT
500mV/div
TTL
THRESHOLD
(1.4V)
OUTPUT
GND
INPUT GND
-5mV OVERDRIVE
QOUT
1V/div
1.4V
QOUT
RESPONSE TO 10MHz SINE WAVE
20mVp-p
10MHz SINE WAVE
INPUT
COMPARATOR
OUTPUT
50ns/div
MAX907 TOC23
1V/div
GND
Page 8

MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
_______________Detailed Description
Timing
Noise or undesired parasitic AC feedback cause most
high-speed comparators to oscillate in the linear region
(i.e., when the voltage on one input is at or near the
voltage on the other input). The MAX907/MAX908/
MAX909 eliminate this problem by incorporating internal hysteresis. When the two comparator input voltages
are equal, hysteresis effectively causes one comparator
input voltage to move quickly past the other, thus taking
the input out of the region where oscillation occurs.
Standard comparators require that hysteresis be added
through the use of external resistors. The
MAX907/MAX908/MAX909’s fixed internal hysteresis
eliminates these resistors (and the equations required
to determine appropriate values).
Adding hysteresis to a comparator creates two trip
points: one for the input voltage rising and one for the
input voltage falling (Figure 1). The difference between
these two input-referred trip points is the hysteresis.
Figure 1 illustrates the case where IN- is fixed and IN+
is varied. If the inputs were reversed, the figure would
look the same, except the output would be inverted.
The MAX909 includes an internal latch, allowing the
result of a comparison to be stored. If LE is low, the
latch is transparent (i.e., the comparator operates as
though the latch is not present). The state of the comparator output is stored when LE is high (Figure 2).
Note that the MAX909 can be operated with V- connected to ground or to a negative supply voltage. The
MAX909’s input range extends from (V- - 0.2V) to
(V+ - 1.5V).
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Pin Description
PIN
NAME FUNCTION
MAX907 MAX908 MAX909
1 1 — OUTA Comparator A Output
2 2 — INA- Comparator A Inverting Input
3 3 — INA+ Comparator A Noninverting Input
4 11 6 GND Ground
5 5 — INB+ Comparator B Noninverting Input
6 6 — INB- Comparator B Inverting Input
7 7 — OUTB Comparator B Output
8 4 1 V+ Positive Supply
— 8 — OUTC Comparator C Output
— 9 — INC- Comparator C Inverting Input
— 10 — INC+ Comparator C Noninverting Input
— 12 — IND+ Comparator D Noninverting Input
— 13 — IND- Comparator D Inverting Input
— 14 — OUTD Comparator D Output
— — 2 IN+ Noninverting Input
— — 3 IN- Inverting Input
— — 4 V- Negative Supply or Ground
— — 5 LE
— — 7 QOUT Comparator Output
— — 8
QOUT
Inverted Comparator Output
The latch is transparent when LE is low. The comparator output is
stored when LE is high.
Page 9

Applications Information
Circuit Layout
Because of the MAX907/MAX908/MAX909’s high gain
bandwidth, special precautions must be taken to realize the full high-speed capability. A printed circuit
board with a good, low-inductance ground plane is
mandatory. Place the decoupling capacitor (a 0.1µF
ceramic capacitor is a good choice) as close to V+ as
possible. Pay close attention to the decoupling capacitor’s bandwidth, keeping leads short. Short lead
lengths on the inputs and outputs are also essential to
avoid unwanted parasitic feedback around the comparators. Solder the device directly to the printed circuit
board instead of using a socket.
Overdriving the Inputs
The inputs to the MAX907/MAX908/MAX909 may be
driven beyond the voltage limits given in the Absolute
Maximum Ratings, as long as the current flowing into
the device is limited to 25mA. However, if the inputs are
overdriven, the output may be inverted. The addition of
an external diode prevents this inversion by limiting the
input voltage to 200mV to 300mV below ground
(Figure 3).
Battery-Operated Infrared Data Link
Figure 4's circuit allows reception of infrared data. The
MAX403 converts the photodiode current to a voltage,
and the MAX907 determines whether the amplifier output
is high enough to be called a “1”. The current consumption of this circuit is minimal: The MAX403 and MAX907
require typically 250µA and 700µA, respectively.
MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
Figure 1. Input and Output Waveforms, Noninverting Input
Varied
Figure 2. MAX909 Timing Diagram
V
TRIP+
V
V
HYST
V
TRIP-
COMPARATOR
OUTPUT
IN+
V
+ V
TRIP+
V
=
OS
V
= 0
IN-
TRIP-
2
V
OH
V
OL
3V
LE
1.4V
COMPARE
0
V
OUT)
V
1.4V
V
V
1.4V
V
OS
OH
OL
OH
OL
DIFFERENTIAL
INPUT
VOLTAGE
OUTPUT
(QOUT)
OUTPUT
(
Q
LATCH
t
h
t
s
V
OD
V
IN
tPD+
t
SKEW
Page 10

MAX907/MAX908/MAX909
Dual/Quad/Single, High-Speed, Ultra-Low-Power,
Single-Supply TTL Comparators
Figure 3. Schottky Clamp for Input Driven Below Ground
Figure 4. Battery-Operated Infrared Data Link Consumes Only
1mA
Pin Configurations (continued)
Ordering Information (continued)
PART TEMP. RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX908CPD
0°C to +70°C 14 Plastic DIP
MAX908CSD 0°C to +70°C14SO
MAX908EPD -40°C to +85°C 14 Plastic DIP
MAX908ESD -40°C to +85°C14SO
MAX909CPA
0°C to +70°C 8 Plastic DIP
MAX909CSA 0°C to +70°C8SO
MAX909EPA -40°C to +85°C 8 Plastic DIP
MAX909ESA -40°C to +85°C8SO
Chip Information
MAX907 TRANSISTOR COUNT: 262
MAX908 TRANSISTOR COUNT: 536
MAX909 TRANSISTOR COUNT: 140
PROCESS: Bipolar
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
10 _____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 2001 Maxim Integrated Products Printed USA is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products.
10pF
1MΩ
V
= -200mV TO -300mV
I
SRC
CLAMP
V-
1/2 MAX907
TOP VIEW
V+
IN+
IN-
1
MAX909
2
3
4
V-
8
QOUT
QOUT
7
GND
6
5
LE
DIP/SO
MAX403
SIEMENS BP-104
PHOTODIODE
100kΩ
1000pF
1000pF
2
3
47kΩ
+5V
7
4
100kΩ
0.1µF
6
+5V
+5V
8
4
0.1µF
1
DATA
MAX907
3
2
 Loading...
Loading...