Page 1
General Description
The MAX7036 low-cost receiver is designed to receive
amplitude-shift-keyed (ASK) and on-off-keyed (OOK)
data in the 300MHz to 450MHz frequency range. The
receiver has an RF input signal range of -109dBm to
0dBm.
The MAX7036 requires few external components and
has a power-down pin to put it in a low-current sleep
mode, making it ideal for cost- and power-sensitive
applications. The low-noise amplifier (LNA), phaselocked loop (PLL), mixer, IF filter, received-signalstrength indicator (RSSI), and baseband sections are
all on-chip. The MAX7036 uses a very-low intermediate
frequency (VLIF) architecture. The MAX7036 integrates
the IF filter on-chip and therefore eliminates an external
ceramic filter, reducing the bill-of-materials cost. The
device also contains an on-chip automatic gain control
(AGC) that reduces the LNA gain by 30dB when the
input signal power is large. The MAX7036 operates
from either a 5V or a 3.3V power supply and draws
5.5mA (typ) of current.
The MAX7036 is available in a 20-pin thin QFN package with an exposed pad and is specified over the
AEC-Q100 Level 2 (-40°C to +105°C) temperature
range.
Applications
Low-Cost RKE
Garage Door Openers
Remote Controls
Home Automation
Sensor Networks
Security Systems
Features
o ASK/OOK Modulation
o < 250µs Enable Turn-On Time
o On-Chip PLL, VCO, Mixer, IF, Baseband
o Low IF (200kHz Nominal)
o 5.5mA DC Current
o 1µA Standby Current
o 3.3V/5V Operation
o Small 20-Pin Thin QFN Package with an Exposed
Pad
MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
________________________________________________________________
Maxim Integrated Products
1
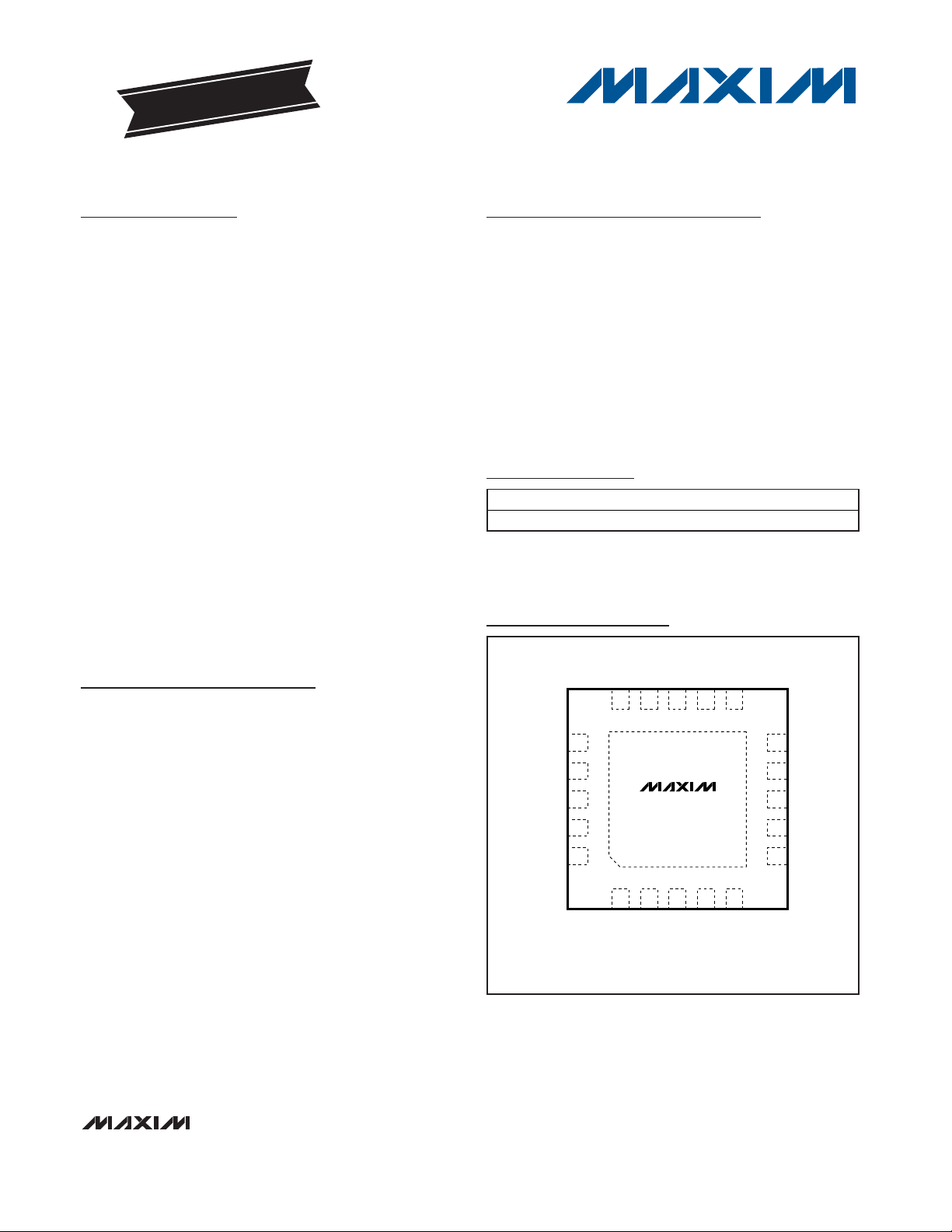
Pin Configuration
Ordering Information
19-4386; Rev 0; 3/09
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
EVALUATION KIT
AVAILABLE
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
-40°C to +105°C
20 Thin QFN-EP*
/V
Denotes an automative qualified part.
+
Denotes a lead(Pb)-free/RoHS-compliant package.
*
EP = Exposed pad.
MAX7036GTP/V+
TOP VIEW
DSP
DSN
PDOUT
V
DATAOUT
OPP
DFFB
15 14 12 11
16
17
18
19
DD
20
+
MAX7036
13
DCOC
DVDD
EP*
IFC3
10
9
8
7
6
IFC1
IFC2
MIXIN1
MIXIN2
LNAOUT
12
XTAL2
ENABLE
THIN QFN
5mm x 5mm
45
3
AVDD
XTAL1
LNAIN
Page 2
MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
3.3V DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(
Typical Application Circuit
, 50Ω system impedance, V
AVDD
= V
DVDD
= VDD= 3.0V to 3.6V, fRF= 300MHz to 450MHz, TA= -40°C to
+105°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at V
AVDD
= V
DVDD
= VDD= 3.3V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (100%
tested at T
A
= +105°C.)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
VDDto GND...........................................................-0.3V to +6.0V
AVDD to GND........................................................-0.3V to +4.0V
DVDD to GND........................................................-0.3V to +4.0V
ENABLE to GND.........................................-0.3V to (V
DD
+ 0.3V)
LNAIN to GND .......................................................-0.3V to +1.2V
All Other Pins to GND.............................-0.3V to (V
DVDD
+ 0.3V)
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
20-Pin TQFN (derate 20.8mW/°C above +70°C) ....1666.7mW
Junction-to-Case Thermal Resistance (θ
JA
) (Note 1)
20-Pin TQFN...................................................................2°C/W
Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance (θ
JA
) (Note 1)
20-Pin TQFN.................................................................48°C/W
Operating Temperature Range .........................-40°C to +105°C
Junction Temperature......................................................+150°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
Note 1: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a single-
layer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, go to www.maxim-ic.com/thermal-tutorial
.
Supply Voltage V
Supply Current I
DIGITAL INPUT (ENABLE)
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Current I
DIGITAL OUTPUT (DATAOUT)
Output Low Voltage V
Output High Voltage V
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
IH
IL
V
AVDD
TA < +105°C
V
AVDD
V
AVDD
0 ≤ V
I
SINK
I
SOURCE
DD
IN
ENABLE
OL
OH
= V
DVDD
= V
DVDD
= V
DVDD
≤ V
ENABLE
= 100µA 0.4 V
= 100µA
= V
DD
fRF = 315MHz 5.3 6.7
fRF = 433MHz 5.8 7.3
Deep-sleep mode,
ENABLE
= 0
= V
= V
DD
V
DD
DD
3.0 3.3 3.6 V
VDD -
0.4
V
-
DD
0.4
1 2.7 µA
0.4 V
20 µA
mA
V
V
Page 3
MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
5.0V DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(
Typical Application Circuit
, 50Ω system impedance, VDD= 4.5V to 5.5V, fRF= 300MHz to 450MHz, TA= -40°C to +105°C, unless
otherwise noted. Typical values are at V
DD
= 5.0V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (100% tested at TA= +105°C.)
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(
Typical Application Circuit
, 50Ω system impedance, V
AVDD
= V
DVDD
= VDD= 3.0V to 3.6V, fRF= 300MHz to 450MHz, TA= -40°C to
+105°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at V
AVDD
= V
DVDD
= VDD= 3.3V, TA= +25°C, fRF= 315MHz, unless otherwise
noted.) (100% tested at T
A
= +105°C.)
Supply Voltage V
Supply Current I
DIGITAL INPUT (ENABLE)
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input Current I
DIGITAL OUTPUT (DATAOUT)
Output Low Voltage V
Output High Voltage V
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DD
IH
IL
TA < +105°C
V
= V
AVDD
V
AVDD
0 ≤ V
I
SINK
I
SOURCE
DVDD
= V
DVDD
≤ V
ENABLE
= 100µA 0.4 V
= 100µA
IN
ENABLE
OL
OH
4.5 5.0 5.5 V
fRF = 315MHz 5.4 6.8
fRF = 433MHz 5.9 7.4
Deep-sleep mode,
ENABLE
= 0
VDD -
0.4
V
DD
0.4
-
V
DD
mA
1 3.4 µA
V
0.4 V
20 µA
V
Receiver Input Frequency Range f
Maximum Receiver Input Level P
Sensitivity (Note 2)
Power-On Time t
AGC Hysteresis 5dB
AGC Low Gain-to-High Gain
Switching Time
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RF
RFIN
ON
fRF = 315MHz -109
= 433MHz -107
f
RF
Time for valid RSSI
output, does not
include baseband
filter settling
300 450 MHz
0 dBm
Enable power on
(V
> 3.0V)
DD
V
power on 1 ms
DD
250 µs
13 ms
dBm
Page 4
MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit
, 50Ω system impedance, V
AVDD
= V
DVDD
= VDD= 3.0V to 3.6V, fRF= 300MHz to 450MHz, TA= -40°C to
+105°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at V
AVDD
= V
DVDD
= VDD= 3.3V, TA= +25°C, fRF= 315MHz, unless otherwise
noted.) (100% tested at T
A
= +105°C.)
Note 2: BER = 2 x 10-3, Manchester coded, data rate = 4kbps. IF bandwidth = 400kHz.
LNA/MIXER
LNA Input Impedance Z
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
LO Signal Feedthrough to
Antenna
Voltage Gain Reduction Low-gain mode, AGC enabled 29 dB
LNA/Mixer Voltage Gain
3dB Cutoff Frequency BW
RSSI Linearity ±0.5 dB
RSSI Dynamic Range Includes AGC 80 dB
RSSI Level
Intermediate Frequency f
Maximum Data-Filter Bandwidth BW
Maximum Data-Slicer Bandwidth BW
Maximum Peak Detector
Bandwidth
Maximum Data Rate
Crystal Frequency f
Crystal Load Capacitance C
INLNA
IF
IF
DF
DS
XTAL
LOAD
Normalized to 50Ω
High-gain LNA mode 55
Low-gain LNA mode 26
Set by capacitors on IFC1 and IFC2 (see
the Typical Application Circuit)
P
< -120dBm 1.34
RFIN
P
> 0dBm, AGC enabled 2.35
RFIN
Manchester coded 33
Nonreturn to zero (NRZ) 66
fRF = 315MHz
f
= 433MHz
RF
9.36 14.06 MHz
0.4 j5.6
0.4 j4.0
-75 dBm
400 kHz
200 kHz
50 kHz
100 kHz
50 kHz
10 pF
Ω
dB
V
kbps
Page 5

MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
Typical Operating Characteristics
(
Typical Application Circuit
, V
AVDD
= VDD= V
DVDD
= 3.3V, fRF= 315MHz, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(3.3V OPERATION)
5.5
5.4
5.3
5.2
TA = +105°C
5.1
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
5.0
4.9
4.8
3.0 3.63.5
V
AVDD
TA = +85°C
TA = +25°C
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
BIT ERROR RATE vs. PEAK RF
INPUT POWER
100
10
fRF = 315MHz
1
0.1
BIT ERROR RATE (%)
0.01
0.001
-125
PEAK RF INPUT POWER (dBm)
= V
DVDD
TA = -40°C
3.43.33.23.1
fRF = 433MHz
= V
DD
-105-110-115-120
5.45
5.40
MAX7036 toc01
5.35
5.30
5.25
5.20
5.15
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
5.10
5.05
5.00
-106.0
-106.5
MAX7036 toc04
-107.0
-107.5
-108.0
-108.5
SENSITIVITY (dBm)
-109.0
-109.5
-110.0
-110.5
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
(5.0V OPERATION)
5.0V APPLICATION CIRCUIT
TA = +105°C
4.5 5.5
TA = +85°C
°
TA = +25
TA = -40°C
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
5.35.14.94.7
SENSITIVITY vs. TEMPERATURE
BER = 0.2%
DATA RATE = 4kbps
MANCHESTER
fRF = 315MHz
-40
TEMPERATURE (°C)
fRF = 433MHz
60 85 1053510-15
MAX7036 toc02
MAX7036 toc05
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. RF FREQUENCY
7.0
6.5
6.0
5.5
5.0
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
4.5
4.0
250 500
TA = +85°C
TA = +105°C
TA = +25
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
RSSI vs. INPUT POWER
2.4
fRF = 433MHz
IF = 200kHz
2.2
2.0
1.8
RSSI (V)
1.6
1.4
1.2
-120
INPUT POWER (dBm)
°
TA = -40°C
PRF = -80dBm
MAX7036 toc03
450400350300
MAX7036 toc06
-40 -20 0-60-80-100
LNA/MIXER VOLTAGE GAIN
vs. IF FREQUENCY
60
58
56
54
52
50
48
46
LNA/MIXER VOLTAGE GAIN (dB)
44
42
40
0
PRF = -71dBm
IF FREQUENCY (kHz)
fRF = 433.92MHz
800 1000600400200
MAX7036 toc07
S11 SMITH CHART PLOT OF RFIN
(315MHz CIRCUIT)
S11 = 7.9729Ω - j0.6085Ω
= 315MHz
at f
RF
MAX7036 toc08
S11 SMITH CHART PLOT OF RFIN
(433MHz CIRCUIT)
S11 = 6.5175Ω - j5.5849Ω
= 433MHz
at f
RF
MAX7036 toc09
Page 6

MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Pin Description
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit
, V
AVDD
= VDD= V
DVDD
= 3.3V, fRF= 315MHz, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
REGULATOR VOLTAGE
vs. REGULATOR CURRENT
3.15
V
= 5V, +5V CIRCUIT
DD
3.10
TA = +105°C
TA = +85°C
3.05
REGULATOR VOLTAGE (V)
3.00
0
REGULATOR CURRENT (mA)
TA = +25°C
TA = -40°C
20 2515105
MAX7036 toc10
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
-100
-110
-120
PHASE NOISE vs. OFFSET FREQUENCY
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
0.01
OFFSET FREQUENCY (kHz)
fRF = 315MHz
100 10,0001
MAX7036 toc11
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
-100
-110
-120
PHASE NOISE vs. OFFSET FREQUENCY
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
0.01
OFFSET FREQUENCY (kHz)
fRF = 433MHz
100 10,0001
MAX7036 toc12
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1 ENABLE Enable Input. Internally pulled down to ground. Set V
2 XTAL2
3 XTAL1
Crystal Input 2. Connect an external crystal from XTAL2 to XTAL1. Can also be driven with an ACcoupled external reference oscillator (see the Crystal Oscillator section).
Crystal Input 1. Connect an external crystal from XTAL2 to XTAL1. Bypass to GND if XTAL2 is driven
from an AC-coupled external reference (see the Phase-Locked Loop section).
ENABLE
= VDD for normal operation.
Positive Analog Supply Voltage. Connect to DVDD. Bypass to GND with a 0.1µF capacitor as close as
4 AVDD
possible to the device (see the Typical Application Circuit). For 5.0V operation, AVDD is internally
connected to an on-chip 3.2V LDO regulator. For 3.3V operation, connect AVDD to V
5 LNAIN Low-Noise Amplifier Input. Must be AC-coupled (see the Low-Noise Amplifier section).
6 LNAOUT
7 MIXIN2
8 MIXIN1
9 IFC2
10 IFC1
11 IFC3
12 DVDD
Low-Noise Amplifier Output. Must be connected to AVDD through a parallel LC tank circuit. ACcouple to MIXIN2 (see the Low-Noise Amplifier section).
2nd Differential Mixer Input. Connect to the LNAOUT side of the LC tank filter through a 100pF
capacitor (see the Typical Application Circuit).
1st Differential Mixer Input. Connect to the AVDD side of the LC tank filter through a 100pF capacitor
(see the Typical Application Circuit).
IF Fi l ter C ap aci tor C onnecti on 2. Thi s i s fo r the S al l en- Key IF fi l ter . C onnect a cap aci tor fr om IFC 2 to GN D .
The val ue of the cap aci tor i s d eter m i ned b y the IF fi l ter b and w i d th ( see the Typical Application Circuit) .
IF Fi l ter C ap aci tor C onnecti on 1. Thi s i s fo r the S al l en- Key IF fi l ter . C onnect a cap aci tor fr om IFC 1 to IFC 3.
The val ue of the cap aci tor i s d eter m i ned b y the IF fi l ter b and w i d th ( see the Typical Application Circuit) .
IF Fi l ter C ap aci tor C onnecti on 3. Thi s i s fo r the S al l en- Key IF fi l ter . C onnect a cap aci tor fr om IFC 3 to IFC 1.
The val ue of the cap aci tor i s d eter m i ned b y the IF fi l ter b and w i d th ( see the Typical Application Circuit) .
Positive Digital Supply Voltage Input. Connect to AVDD. Bypass to GND with a 0.01µF capacitor as
close as possible to the device (see the Typical Application Circuit).
DD
.
Page 7

MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
Functional Diagram
Pin Description (continued)
PIN NAME FUNCTION
13 DCOC
14 OPP
15 DFFB
16 DSP
DC Offset Capacitor Connection. This is for the RSSI amplifier. Connect a 1µF capacitor from this pin
to ground (see the Typical Application Circuit).
Noninverting Op-Amp Input. This is for the Sallen-Key data filter. Connect a capacitor from this pin to
GND. The value of the capacitor is determined by the data-filter bandwidth.
Data-Filter Feedback Input. Input for the feedback of the Sallen-Key data filter. Connect a capacitor
from this pin to DSP. The value of the capacitor is determined by the data-filter bandwidth.
Positive Data-Slicer Input. Connect a capacitor from this pin to DFFB. The value of the capacitor is
determined by the data-filter bandwidth.
17 DSN Negative Data-Slicer Input
18 PDOUT Peak-Detector Output
Power-Supply Voltage Input. For 5.0V operation, VDD is the input to an on-chip voltage regulator
19 V
DD
whose 3.2V output drives AVDD. Bypass to ground with a 0.1µF capacitor as close as possible to the
device (see the Typical Application Circuit).
20 DATAOUT Digital Baseband Data Output
—EP
Exposed Pad. Internally connected to ground. Connect to a large ground plane using multiple vias to
maximize thermal and electrical performance.
XTAL1
XTAL2
ENABLE
V
AVDD
DVDD
LNAIN
DATAOUT DSN PDOUT DSP OPP DFFB
20 17 18 16 14 15
3
PLL
2
1
19
DD
3.2V
REGULATOR
4
12
5
687 10 9 1311
LNAOUT
MIXIN2
MIXIN1
AGC
PEAK
DETECTOR
REF
IFC1 IFC2 IFC3 DCOC
*EXPOSED PAD.
CONNECT TO GND.
MAX7036
∑
∑
REF
EP*
Page 8

MAX7036
Detailed Description
The MAX7036 CMOS RF receiver, and a few external
components, provide the complete receiver chain from
the antenna to the digital output data. Depending on
signal power and component selection, data rates as
high as 33kbps Manchester (66kbps NRZ) can be
achieved.
The MAX7036 is designed to receive binary ASK/OOK
data modulated in the 300MHz to 450MHz frequency
range. ASK modulation uses a difference in amplitude
of the carrier to represent digital data.
Voltage Regulator
For operation with a single 3.0V to 3.6V supply voltage,
connect AVDD, DVDD, and V
DD
to the supply voltage.
For operation with a single 4.5V to 5.5V supply voltage,
connect VDDto the supply voltage. An on-chip voltage
regulator drives the AVDD pin to approximately 3.2V.
For proper operation, connect DVDD and AVDD together. Bypass VDDand AVDD to GND with 0.1µF capacitors placed as close as possible to the device. Bypass
DVDD to GND with a 0.01µF capacitor (see the
Typical
Application Circuit
).
Low-Noise Amplifier
The LNA is an nMOS cascode amplifier. The LNA and
mixer have a combined 55dB voltage gain. The gain
and noise figures are dependent on both the antennamatching network at the LNA input and the LC tank network between the LNA output and the mixer inputs.
L2 and C1 comprise the LC tank filter connected to
LNAOUT (see the
Typical Application Circuit
). L2 also
serves as a bias inductor to LNAOUT. Bypass the
power-supply side of L2 to GND with a capacitor that
provides a low-impedance path at the RF carrier frequency (e.g., 220pF). Select L2 and C1 to resonate at
the desired RF input frequency. The resonant frequency is given by:
where L
TOTAL
= L2 + L
PARASITICS
and C
TOTAL
= C1 +
C
PARASITICS
.
L
PARASITICS
and C
PARASITICS
include inductance and
capacitance of the PCB traces, package pins, mixer
input impedance, LNA output impedance, etc. At high
frequencies, these parasitics can have a dramatic
effect on the tank filter center frequency and must not
be ignored. The total parasitic capacitance is generally
4pF to 6pF. Adjust L2 and C1 accordingly to achieve
the desired tank center frequency.
Automatic Gain Control (AGC)
The AGC circuit monitors the RSSI output. The AGC
switches to its low-gain state when the RSSI output
reaches 2.2V. The AGC gain reduction is typically
29dB, corresponding to an RSSI voltage drop of
435mV. The LNA resumes high-gain mode when the
RSSI level drops back below 1.67V for 13ms for
315MHz and 10ms for 433MHz operation. The AGC has
a hysteresis of 5dB. With this AGC function, the
MAX7036 can reliably produce an ASK output for RF
input levels up to 0dBm, with modulation depth of
30dB.
Mixer
The mixer cell is a double-balanced mixer that performs
a downconversion of the RF input to a typical IF of
200kHz from either a high-side or a low-side injected LO.
The mixer output drives the input of the on-chip IF filter.
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL)
The PLL block contains a phase detector, charge
pump, integrated loop filter, VCO, asynchronous clock
dividers, and crystal-oscillator driver. Besides the crystal, this PLL does not require any external components.
The VCO generates the LO. The relationship between
the RF, IF, and reference frequencies is given by:
where fLO= fRF±f
IF
Received-Signal-Strength Indicator (RSSI)
The RSSI circuit provides a DC output proportional to
the logarithm of the input power level. RSSI output voltage has a slope of about 14.5mV/dB (of input
power).The RSSI monotonic dynamic range exceeds
80dB. This includes the 30dB of AGC.
Applications Information
Crystal Oscillator
The crystal (XTAL) oscillator in the MAX7036 is
designed to present a capacitance of approximately
4pF between XTAL1 and XTAL2. In most cases, this
corresponds to a 6pF load capacitance applied to the
external crystal when typical PCB parasitics are added.
The MAX7036 is designed to operate with a typical
10pF load capacitance crystal. It is very important to
use a crystal with a load capacitance equal to the
capacitance of the MAX7036 crystal oscillator plus
PCB parasitics. If a crystal designed to oscillate with a
different load capacitance is used, the crystal is pulled
away from its stated operating frequency, introducing
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
f
=
RF
LC
2π
TOTAL TOTAL
1
×
f
REF
f
LO
=
32
Page 9

an error in the reference frequency. A crystal designed
to operate at a higher load capacitance than the value
specified for the oscillator is always pulled higher in frequency. Adding capacitance to increase the load
capacitance on the crystal increases the start-up time
and may prevent oscillation altogether.
In actuality, the oscillator pulls every crystal. The crystal’s natural frequency is really below its specified frequency, but when loaded with the specified load
capacitance, the crystal is pulled and oscillates at its
specified frequency. This pulling is already accounted
for in the specification of the load capacitance.
Additional pulling can be calculated if the electrical
parameters of the crystal are known. The frequency
pulling is given by:
where:
fpis the amount the crystal frequency is pulled in
ppm.
CMis the motional capacitance of the crystal.
C
CASE
is the case capacitance.
C
SPEC
is the specified load capacitance.
C
LOAD
is the actual load capacitance.
When the crystal is loaded, as specified (i.e., C
LOAD
=
C
SPEC
), the frequency pulling equals zero.
It is possible to use an external reference oscillator in
place of a crystal to drive the VCO. AC-couple the external oscillator to XTAL2 with a 1000pF capacitor. Drive
XTAL2 with a signal level of approximately -10dBm. ACcouple XTAL1 to ground with a 1000pF capacitor.
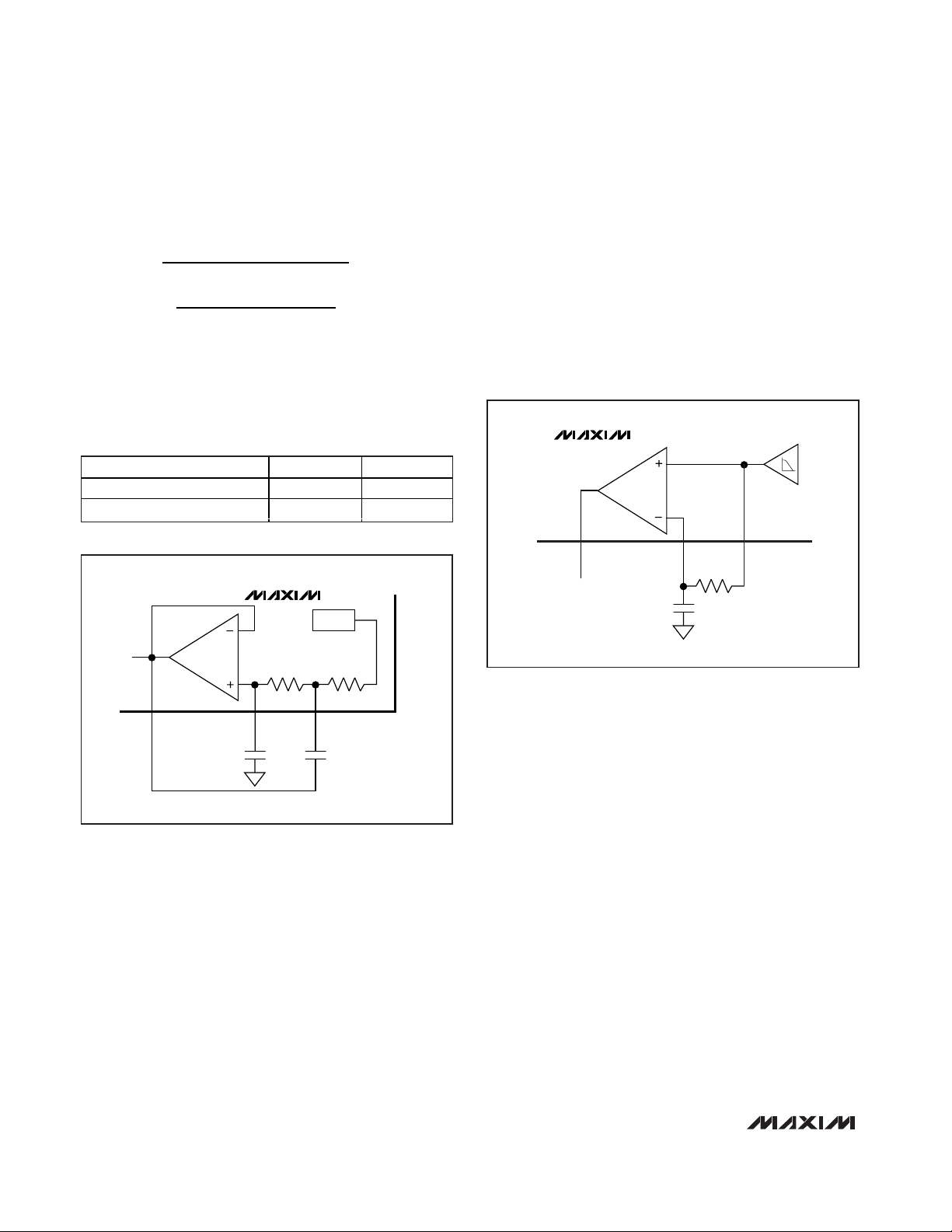
IF Filter
The IF filter is a 2nd-order Butterworth lowpass filter
preceded by a low-frequency DC block. The lowpass
filter is implemented as a Sallen-Key filter using an
internal op amp and two on-chip 22kΩ resistors. The
pole locations are set by the combination of the on-chip
resistors and two external capacitors (C9 and C10,
Figure 1). The values of these two capacitors for a 3dB
cutoff frequency of 400kHz are given below:
Because the stray shunt capacitance at each of the
pins (IFC1 and IFC2) on a typical PCB is approximately
2pF, choose the value of the external capacitors to be
approximately 2pF lower than the desired total capacitance. Therefore, the practical values for C9 and C10
are 22pF and 10pF, respectively.
Data Filter
The data filter is implemented as a 2nd-order lowpass
Sallen-Key filter. The pole locations are set by the combination of two on-chip resistors and two external capacitors. Adjusting the value of the external capacitors
changes the corner frequency to optimize for different
data rates. Set the corner frequency to approximately
1.5 times the fastest Manchester expected data rate
from the transmitter. Keeping the corner frequency near
the data rate rejects any noise at higher frequencies,
resulting in an increase in receiver sensitivity.
The configuration shown in Figure 2 can create a
Butterworth or Bessel response. The Butterworth filter
offers a very flat amplitude response in the passband
and a rolloff rate of 40dB/decade for the two-pole filter.
The Bessel filter has a linear phase response, which
works with the coefficients in Table 1.
where f
C
is the desired corner frequency.
MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
Figure 1. Sallen-Key Lowpass IF Filter
f
P
⎛
C
M
⎜
=
⎜
CC CC
2
⎝
11
+
CASE LOA D CASE SPEC
−
⎞
6
⎟
×
10
+
⎟
⎠
C
9
=
=
10
C
1
1 414
.
( )()()
2 828
( )()()
Rf
.
π
()
c
1
π
Rf
()
=
..
1 414 22 3 14 4
()()()
=
.
2 828
(
c
1
Ω
k
1
22 3 14 400
kkHz
Ω .
))( )( )( )
=
26
000
kHz
()
pF
=
13
pF
MAX7036
22kΩ22kΩ
10
IFC1
IFC2
9
C10
C9
11
IFC3
C
5
=
C
6
=
b
ak f
()()
100
π
()
c
a
kf
4 100
()()
π
()
c
Page 10
MAX7036
For example, to choose a Butterworth filter response
with a corner frequency of 6kHz:
Choosing standard capacitor values changes C5 to
390pF and C6 to 180pF, as shown in the
Typical
Application Circuit
.
Data Slicer
The data slicer takes the analog output of the data filter
and converts it to a digital signal. This is achieved by
using a comparator and comparing the analog input to
a threshold voltage. One input is supplied by the datafilter output. Both comparator inputs are accessible off
chip to allow for different methods of generating the
slicing threshold, which is applied to the second comparator input.
The suggested data-slicer configuration uses a resistor
(R1) connected between DSN and DSP with a capacitor (C4) from DSN to GND (Figure 3). This configuration
averages the analog output of the filter and sets the
threshold to approximately 50% of that amplitude. With
this configuration, the threshold automatically adjusts
as the analog signal varies, minimizing the possibility
for errors in the digital data. The values of R1 and C4
affect how fast the threshold tracks to the analog amplitude. Be sure to keep the corner frequency of the RC
circuit much lower than the lowest expected data rate.
Note that a long string of zeros or ones can cause the
threshold to drift. This configuration works best if a
coding scheme (e.g., Manchester coding, which has an
equal number of zeros and ones) is used.
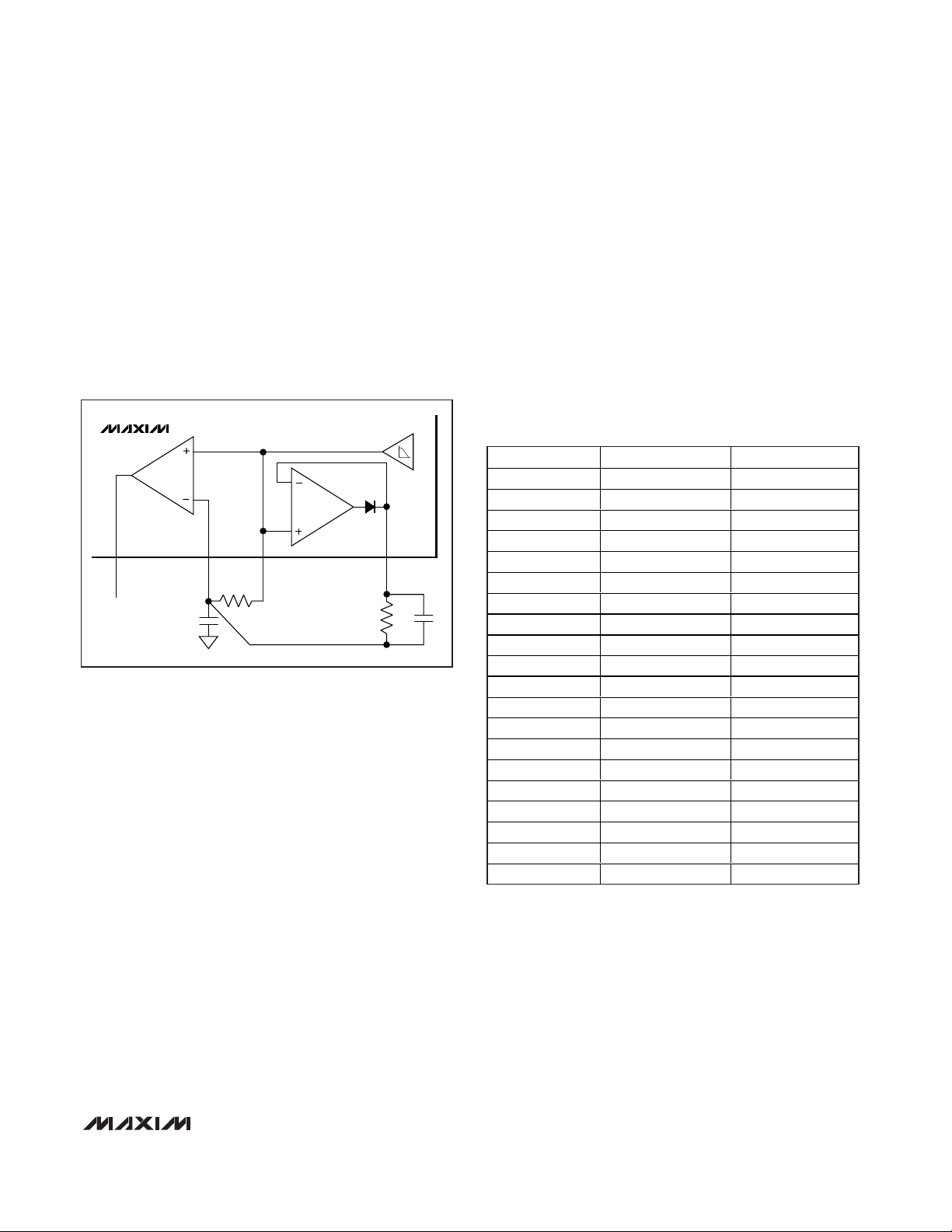
Peak Detector
The peak-detector output (PDOUT), in conjunction with
an external RC filter, creates a DC output voltage equal
to the peak value of the data signal. The resistor provides a path for the capacitor to discharge, allowing the
peak detector to dynamically follow peak changes of
the data-filter output voltage. The peak detector can be
used for at least two functions. First, it can serve as an
RSSI for ASK modulation. Second, it can be used for
faster data-slicer response by adding it to the threshold
pin (DSN) on the data-slicer comparator (Figure 4). The
two capacitors in this circuit should be equal, and the
peak detector resistor should be approximately 10
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Table 1. Coefficients to Calculate C5
and C6
16
DSP
C6
C5
R
DF2
100kΩ
R
DF1
100kΩ
RSSI
14
OPP
15
DFFB
MAX7036
Figure 2. Sallen-Key Lowpass Data Filter
20
C4
R1
17
DSN
16
DSP
MAX7036
DATA OUT
DATA
SLICER
DATA
FILTER
Figure 3. Generating Data-Slicer Threshold
C
5
=
1 414 100 3 14 6
..Ω
()( )()()
C
6
=
4 100 3 14 6
()( )( )( )
1 000
.
kkHz
11 414
.
kkHz
Ω
.
=
=
186
375
pF
pF
FILTER TYPE a b
Butterworth (Q = 0.707) 1.414 1.000
Bessel (Q = 0.577) 1.3617 0.618
Page 11
times larger than the resistor in the RC smoothing circuit between DSP and DSN. This circuit will provide an
instantaneous jump of one-half of the DSP increase
from “no signal” voltage to peak voltage, which then
decays with the same time constant as that of the
threshold build-up from the RC smoothing circuit. The
DC slicing voltage at DSN is slightly higher (by the ratio
of the two resistors in the circuit) than it would be without the speed-up circuit. Always provide a capacitive
path from the PDOUT pin to ground when using the
peak-detector output.
Layout Considerations
A properly designed PCB is an essential part of any
RF/microwave circuit. On high-frequency inputs and
outputs, use controlled-impedance lines and keep them
as short as possible to minimize losses and radiation.
At high frequencies, trace lengths that are λ/10 or
longer act as antennas.
Keeping the traces short also reduces parasitic inductance. Generally, 1in of a PCB trace adds about 20nH
of parasitic inductance. The parasitic inductance can
have a dramatic effect on the effective inductance of a
passive component. For example, a 0.5in trace connecting a 100nH inductor adds an extra 10nH of inductance or 10%.
To reduce the parasitic inductance, use wider traces
and a solid ground or power plane below the signal
traces. Also, use low-inductance connections to ground
on all GND pins, and place decoupling capacitors
close to all power-supply connections.
MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
Figure 4. Using PDOUT for Faster Startup
Table 2. Component Values
DATA
MAX7036
DATA
SLICER
20
DATA OUT
17
DSN
C4
16
DSP
R1
FILTER
18
PDOUT
COMPONENT fRF = 315MHz fRF = 433.92MHz
C1 4.7pF 2.7pF
C2 100pF 100pF
C3 100pF 100pF
C4 0.1µF 0.1µF
C5 390pF 390pF
C6 180pF 180pF
C7 1µF 1µF
C8 0.01µF 0.01µF
C9 22pF 22pF
C10 10pF 10pF
C11 0.1µF 0.1µF
C12 220pF 220pF
C13 10pF 10pF
C14 10pF 10pF
C15 100pF 100pF
C16 0.1µF 0.1µF
L1 100nH 47nH
L2 27nH 15nH
R1 22kΩ 22kΩ
Y1 9.8375MHz 13.55375MHz
Page 12

MAX7036
300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver
with Internal IF Filter
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
12
____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 2009 Maxim Integrated Products Maxim is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Package Information
For the latest package outline information and land patterns, go
to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.
Typical Application Circuit
Chip Information
PROCESS: CMOS
PACKAGE TYPE PACKAGE CODE DOCUMENT NO.
20 Thin QFN-EP T2055+3
21-0140
CONNECT AVDD, DVDD,
AND V
3.3V APPLICATIONS.
TOGETHER FOR
DD
C13
L1
C14
C15
C11
C16
+5V
R1
C4
DATAOUT V
ENABLE
XTAL2
Y1
XTAL1
AVDD
LNAIN
LNAOUT MIXIN2 MIXIN1 IFC1IFC2
C3
DD
PDOUT DSPDSN
MAX7036
C10
C2
DFFB
OPP
DCOC
DVDD
IFC3
C9
C5
C6
C7
C8
C1
L2
C12
 Loading...
Loading...