Page 1
General Description
The MAX6960–MAX6963 are compact cathode-row display drivers that interface microprocessors to 8 x 8 dotmatrix red, green, and yellow (R,G,Y) LED displays
through a high-speed 4-wire serial interface.
The MAX6960–MAX6963 drive two monocolor 8 x 8
matrix displays, or a single RGY 8 x 8 matrix display with
no external components. The driver can also be used
with external pass transistors to control red, green, blue
(RGB) and other displays at higher currents and voltages.
The MAX6960–MAX6963 feature open- and short-circuit
LED detection, and provide both analog and digital tile
segment current calibration to allow 8 x 8 displays from
different batches to be compensated or color matched.
A local 3-wire bus synchronizes multiple interconnected
MAX6960–MAX6963s and automatically allocates memory
map addresses to suit the user’s display-panel
architecture.
The MAX6960–MAX6963s’ 4-wire interface connects multiple drivers, with display memory mapping shared and
allocated among the drivers. A single global write operation can send a command to all MAX6960s in a panel.
The MAX6963 drives monocolor displays with two-step
intensity control. The MAX6962 drives monocolor displays
with two-step or four-step intensity control. The MAX6961
drives monocolor or RGY displays with two-step intensity
control. The MAX6960 drives monocolor or RGY displays
with two-step or four-step intensity control.
Features
♦ 2.7V to 3.6V Operation
♦ High-Speed 20MHz Serial Interface
♦ Trimmed 40mA or 20mA Peak Segment Current
♦ Directly Drives Either Two Monocolor or One RGY
Cathode-Row 8 x 8 Matrix Displays
♦ Analog Digit-by-Digit Segment Current Calibration
♦ Digital Digit-by-Digit Segment Current Calibration
♦ 256-Step Panel Intensity Control (All Drivers)
♦ Four Steps per Color Pixel-Level Intensity Control
♦ Open/Short LED Detection
♦ Burst White to Display Memory Planes
♦ Global Command Access All Devices
♦ Can Control RGB Panels or Higher
Current/Voltage Panels with External Pass
Transistors
♦ Multiple Display Data Planes Ease Animation
♦ Automatic Plane Switching from 63 Planes per
Second to One Plane Every 63s, with Interrupt
♦ Slew-Rate-Limited Segment Drivers for Lower EMI
♦ Driver Switching Timing Can Be Spread Between
Multiple Drivers to Flatten Power-Supply Peak
Demand
♦ Low-Power Shutdown with Full Data Retention
♦ -40°C to +125°C Temperature Range
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
________________________________________________________________ Maxim Integrated Products 1
Ordering Information
19-3696; Rev 0; 7/05
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim/Dallas Direct! at
1-888-629-4642, or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
Pin Configurations continued at end of data sheet.
PART
PIN-PACKAGE
PKG
CODE
M A X6 9 6 0AM H
44 MQFP —
M AX6960ATH
44 TQFN *
T4477- 3
M A X6 9 6 1AM H
44 MQFP —
M AX6961ATH
44 TQFN *
T4477-3
M A X6 9 6 2AM H
44 MQFP —
M AX6962ATH
44 TQFN *
T4477-3
M A X6 9 6 3AM H
44 MQFP —
M AX6963ATH
44 TQFN *
T4477-3
COL13
COL12
COL11
COL10
COL9
V+
COL8
COL7
COL6
COL5
COL4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1213141516171819202122
4443424140393837363534
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
GND
OSC
CS
DIN
DOUT
CLK
RST
COL1
COL2
COL3
V+
GND
RISET1
RISET0
ADDCLK
ADDIN
ADDOUTV+COL16
COL15
COL14
V+
MQFP
MAX6960-MAX6963
TOP VIEW
Pin Configurations
Applications
Message Boards Industrial Controls
Gaming Machines Audio/Video Equipment
*EP = Exposed pad.
TEMP RANGE
-40°C to +125°C
-40°C to +125°C
-40°C to +125°C
-40°C to +125°C
-40°C to +125°C
-40°C to +125°C
-40°C to +125°C
-40°C to +125°C
Page 2
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(V+ = 2.7V to 3.6V, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, typical values at V+ = 3.3V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 1)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Voltage (with respect to GND)
V+ .............................................................................-0.3V to +4V
All Other Pins................................................-0.3V to (V+ + 0.3V)
ROW1–ROW8 Sink Current ..............................................750mA
COL1–COL16 Source Current ...........................................48mA
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
A
= +70°C)
44-Pin MQFP
(derate 12.7 mW/°C over +70°C)...............................1012mW
44-Pin TQFN
(derate 27mW/°C over +70°C)...................................2162mW
Operating Temperature Range
(T
MIN
to T
MAX
) ..............................................-40°C to +125°C
Junction Temperature......................................................+150°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
UNITS
Operating Supply Voltage V+ 2.7 3.6 V
TA = +25°C
375
500Shutdown Supply Current I
SHDN
Shutdown mode, all
digital inputs at V+
or GND
T
A
= T
MIN
to T
MAX
600
µA
TA = +25°C 7.5 9
10Operating Supply Current I+
Intensity set to full,
no display load
connected
T
A
= T
MIN
to T
MAX
11
mA
Master Clock Frequency f
OSC
1 8.5
MHz
Dead-Clock Protection
Frequency
f
OSC
50
200 kHz
OSC High Time t
CH
40 ns
OSC Low Time t
CL
40 ns
TA = +25°C 384042
37 43
V
LED
= 2.3V, V+ =
3.15V to 3.6V,
current = high
T
A
= T
MIN
to T
MAX
37 44
TA = +25°C 192021
Anode Column Source Current
COL1–COL16
I
SEG
V
LED
= 2.3V, V+ =
2.7V to 3.6V, current
= low
T
A
= T
MIN
to T
MAX
22
mA
V
LED
= 2.3V, V+ = 3.15V to 3.6V,
current = high
Anode Column Source-Current
Temperature Variation
COL1–COL16
I
TC
V
LED
= 2.2V, V+ = 2.7V to 3.3V,
current = low
ppm/°C
Segment Current Slew Rate
TA = +25°C30
mA/µs
SYMBOL
MIN TYP MAX
250
TA = T
to +85°C
MIN
TA = T
to +85°C
MIN
90.5
∆I
/∆t
SEG
TA = T
to +85°C
MIN
TA = T
to +85°C 18.5 21.5
MIN
18.5
200
200
Page 3
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V+ = 2.7V to 3.6V, TA= T
MIN
to T
MAX
, typical values at V+ = 3.3V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 1)
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
LOGIC INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Input Leakage Current
DIN, CLK, CS, OSC, ADDIN,
ADDCLK, RST
I
IH
, I
IL
nA
Logic-High Input Voltage
DIN, CLK, CS, OSC, ADDIN,
ADDCLK
V
IHI
0.7 x
V+
V
Logic-Low Input Voltage
DIN, CLK, CS, OSC, ADDIN,
ADDCLK
V
ILO
0.3 x
V+
V
Logic-High Input Voltage RST V
IHR
0.95 x
V+
V
Logic-Low Input Voltage RST V
ILR
0.4 x
V+
V
t
FTDO
C
LOAD
= 100pF 10 ns
DOUT Output High Voltage V
OHDOISOURCE
= 20mA
V+ -
0.3
V
DOUT Output Low Voltage V
OLDOISINK
= 20mA 0.3 V
ADDOUT Output High Voltage
I
SOURCE
= 500µA
V+ -
0.3
V
ADDOUT Output Low Voltage
I
SINK
= 500µA 0.3 V
ADDCLK Output High Voltage
I
SOURCE
= 2.5mA
V+ -
0.3
V
ADDCLK Output Low Voltage
I
SINK
= 2.5mA 0.3 V
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
CLK Clock Period t
CP
50 ns
CLK Pulse-Width High t
CH
22 ns
CLK Pulse-Width Low t
CL
22 ns
CS Fall to CLK Rise Setup Time t
CSS
ns
CLK Rise to CS Rise Hold Time t
CSH
0ns
DIN Setup Time t
DS
ns
DIN Hold Time t
DH
10 ns
Output Data Propagation Delay t
DO
22 ns
Minimum CS Pulse High t
CSW
25 ns
Note 1: All parameters tested at TA= +25°C. Specifications over temperature are guaranteed by design.
DOUT Output Rise and Fall Times
V
OHADO
V
OLADO
V
OHACK
V
OLACK
-200 +20 +200
12.5
12.5
Page 4
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
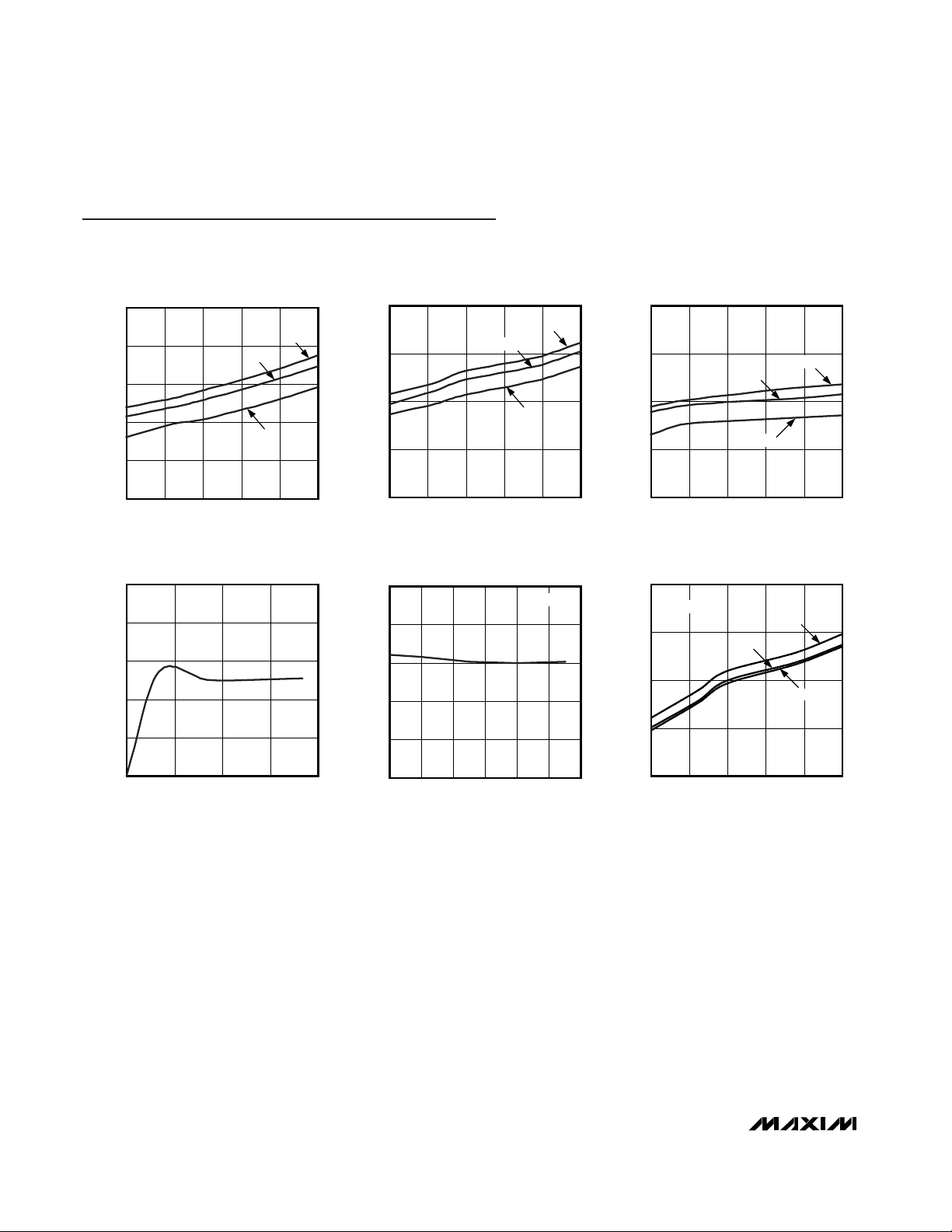
Typical Operating Characteristics
(TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
OPERATING SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX6960 toc01
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
925926-7
7.2
7.4
7.6
7.8
8.0
7.0
-40 125
3.6V
3.3V
2.7V
SHUTDOWN SUPPLY CURRENT
vs. TEMPERATURE
MAX6960 toc02
TEMPERATURE (°C)
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
925926-7
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0
-40 125
3.6V
3.3V
2.7V
DEAD-CLOCK OSCILLATOR
vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE
MAX6960 toc03
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
DEAD-CLOCK OSCILLATOR
3.383.162.942.72
85
90
95
100
80
2.50 3.60
+25°C
-40°C
+125°C
PEAK-OUTPUT SOURCE CURRENT
vs. SUPPLY VOLTAGE (HIGH-CURRENT MODE)
MAX6960 toc04
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
PEAK-OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
3.43.12.8
37
39
41
43
45
35
2.5 3.7
2.3V LED
PEAK-OUTPUT SOURCE CURRENT
vs.SUPPLY VOLTAGE (LOW-CURRENT MODE)
MAX6960 toc05
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
PEAK-OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
3.53.33.12.92.7
18
19
20
21
22
17
2.5 3.7
2.2V LED
PEAK-OUTPUT SOURCE CURRENT
vs. TEMPERATURE (HIGH-CURRENT MODE)
MAX6960 toc06
TEMPERATURE (°C)
PEAK-OUTPUT CURRENT (mA)
925926-7
39.6
40.0
40.4
40.8
39.2
-40 125
2.3V LED
3.6V
3.3V
3.15V
Typical Operating Characteristics
Page 5
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
Pin Description
PIN
NAME FUNCTION
1, 6, 11,
1, 6, 11,
GND Ground
LE D C athod e D r i ve r s. ROW 1 to RO W 8 outp uts si nk cur r ent fr om the d i sp l ay' s cathod e r ow s.
13 13 OSC Multiplex Clock Input. Drive OSC with a 1MHz to 8.5MHz CMOS clock.
14 14 CS
Chip-Select Input. Serial data is loaded into the shift register when CS is low. Data is
loaded into the data latch on CS's rising edge.
15 15 DIN
Serial-Data Input. Data from DIN loads into the internal shift register on CLK's rising edge.
16 16 DOUT Serial-Data Output. The output is tri-state.
17 17 CLK Serial-Clock Input. On CLK's rising edge data shifts into the internal shift register.
18 18 RST
Reset Input. Hold RST low until at least 50ms after all interconnected MAX6960s are
powered up.
19, 20,
21,
23–27,
29–33,
35, 36,
37
19, 20,
21,
23–27,
29–33,
35, 36,
37
LED Anode Drivers. COL1 to COL16 outputs source current into the display's anode
columns.
22, 28,
22, 28,
V+
Positive Supply Voltage. Bypass V+ to GND with a single 47µF bulk capacitor per chip
plus a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor per V+.
39 39 ADDOUT
Address-Data Output. Connect ADDOUT to ADDIN of the next MAX6960. Use ADDOUT of
the last MAX6960 as a plane change interrupt output.
40 40 ADDIN
Address-Data Input. For first MAX6960, connect ADDIN to V+. For other MAX6960s,
connect ADDIN to ADDOUT of the preceding MAX6960.
41 41 ADDCLK
Address-Clock Input/Output. Connect ADDCLK of all MAX6960 drivers together, ensuring
that only one MAX6960's ADDIN input is connected to V+.
42 42 RISET0
Digit 0 Current Setting. Connect RISET0 to GND to program all of digit 0's segment
currents to 40mA. Leave RISET0 open circuit to program all of digit 0's segment currents
to 20mA. Connect RISET0 to GND through a fixed or variable resistor to adjust all of digit
0's segment currents between 20mA and 40mA.
43 43 RISET1
Digit 1 Current Setting. Connect RISET1 to GND to program all of digit 1's segment
currents to 40mA. Leave RISET1 open circuit to program all of digit 1's segment currents
to 20mA. Connect RISET1 to GND through a fixed or variable resistor to adjust all of digit
1's segment currents between 20mA and 40mA.
— EP EP Exposed Pad on Package Underside. Connect to GND.
MQFP TQFN
12, 44
2–5, 7–10 2–5, 7–10 ROW1–ROW8
34, 38
12, 44
COL1–COL16
34, 38
Page 6
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Quick-Start Guide
Selecting the Appropriate Driver
The MAX6960–MAX6963 matrix LED drivers are available in four versions, with different levels of functionality
(Table 1). The two-part ID bits in the fault and device ID
register (Table 32) identify the driver type to the interface software. The ID bits may be of use if the same
panel software is used to drive more than one type of
display panel, because the software can automatically
detect the panel type.
This data sheet uses the generic name MAX6960 to
refer to the family of four parts MAX6960 through
MAX6963, unless there is a specific difference to
discuss.
The purpose of this quick-start guide is to provide an
overview of the capabilities of the MAX6960 so that the
driver can be easily evaluated for a particular application, without fighting through a complex data sheet.
Terminology
• Pixel: One “point” on a display. Comprises one LED
for a monocolor display, two LEDs for an RGY display, and three LEDs for an RGB display.
• Monocolor: Display has only one color, typically red
for low-cost signs or orange for traffic signs. Varying
AVAILABLE FUNCTIONS
PART
RGB 2
RGB
RGY
PIXEL
RGY
1 BIT PER
PIXEL
2 BITS PER
PIXEL
1 BIT PER
PIXEL
REGISTER LIMITATIONS
MAX6960
√√ √ √ √ √None.
MAX6961
— √ — √ — √
PI bit (bit D7) in global panel
configuration register is fixed at 0
(Table 22).
MAX6962
√√—— √√
C bit (bit D6) in global panel
configuration register is fixed at 0
(Table 21).
MAX6963
— √ —— — √
C bit (bit D6) in global panel
configuration register is fixed at 0
(Table 21).
PI bit (bit D7) in global panel
configuration register is fixed at 0
(Table 22).
Table 1. Levels of Functionality
DISPLAY CONFIGURATION MAXIMUM PIXEL COUNT
EXAMPLE MAXIMUM PANEL (PIXELS)
Monocolor 32,768 256 x 128
RGY 16,384 256 x 64
RGB
32,768 (3 buses required; see Figure 17)
128 x 85
Table 2. Maximum Display Matrix on a Single 4-Wire Interface
256 DRIVERS ON 4-WIRE INTERFACE, 50 FRAMES PER SECOND UPDATE RATE
DISPLAY-MEMORY-ACCESS METHOD
1-BIT-PER-PIXEL INTENSITY
CONTROL (Mbps)
2-BITS-PER-PIXEL INTENSITY
CONTROL (Mbps)
8-bit indirect display memory addressing
1.64 3.28
24-bit direct display memory addressing 4.92 9.83
Table 3. 4-Wire Interface Speed Requirements for Animation
*When operated per Figure 17.
MONOCOLOR
BITS PER
PIXEL*
1 BIT PER
PIXEL*
2 BITS PER
MONOCOLOR
Page 7

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
the current through the LED changes the intensity of
the red.
• Bicolor: Literally means two color, and usually refers
to LEDs built with two LED dice of different colors,
typically red and green or red and orange/yellow.
• Tricolor: Literally means three color, and can refer to
LEDs built with three LED dice of different colors, typically red, green, and blue. The term is also used to
refer to a display built with bicolor LEDs, because there
are three main colors available (red, green, yellow).
• RGY: Display uses one red LED (R) and one green
LED (G) per pixel. When both red and green LEDs
are lit, the resulting color is yellow (Y). Varying the
current through the LEDs changes the intensity of the
pixel and changes the color from red through shades
of orange and yellow to green.
• RGB: Display uses one red LED (R), one green LED
(G), and one blue LED (B) per pixel. Varying the current through the LEDs changes the intensity of the
pixel and changes the color through many shades
limited by the current control resolution.
MAX6960 Applications
The MAX6960 is a multiplexed, constant-current LED
driver intended for high-efficiency indoor signage and
message boards.
The high efficiency arises because the driver operates
from a 3.3V nominal supply with minimal voltage headroom required across the driver output stages. The
problem of removing heat from even a small display is
therefore minimized.
The maximum peak LED drive current is 40mA, which
when multiplexed eight ways, provides an average current of 5mA per LED. This current drive is expected to
be adequate for indoor applications, but inadequate for
outdoor signs operating in direct sun.
The MAX6960 directly drives monocolor (typically red
or orange/yellow) or RGY (typically red/green or
red/yellow) graphic displays using LEDs with a forward
voltage drop up to 2.5V. Blue LEDs and some green
LEDs cannot be driven directly because of their high
forward voltage drop (around 3.5V to 4.5V). For these
displays, the MAX6960 can be used as a graphic controller, just as it can be used for applications requiring
higher peak segment currents, and in RGB panels
needing a higher driver voltage for the blue LEDs. In
these cases, the MAX6960 can be used with external
drive transistors to control anode-row displays, with all
driver features including pixel-level intensity control still
available (see the Applications Information section and
Figure 17).
Display Intensity Control
Five levels of intensity control are provided:
• A 256-step PWM panel intensity adjustment sets all
MAX6960s simultaneously as a global panel brightness control (Table 27). The 256-step resolution is
fine enough to allow fade-in/fade-out graphic effects,
as well as provide a means for compensating a
panel for background lighting.
• A 2-bits-per-pixel intensity control allows four brightness levels to be set independently per pixel. The
pixel-level intensity control can be set to be either
arithmetic (off, 1/3, 2/3, full) or geometric (off, 1/4,
1/2, full) for full flexibility (Table 24), and allows four
colors to be displayed on monocolor panels, or 16
colors to be displayed on RGY panels, or 64 colors
to be displayed on RGB panels.
• The LED drive current can be selected between
either a 40mA peak per segment and a lower 20mA
peak current on a digit-by-digit basis using the
R
ISET0
and R
ISET1
pins. The lower (20mA) current
may be the better choice to drive high-efficiency displays, and this setting allows the MAX6960 to operate from a supply voltage as low as 2.7V.
• The LED drive current can be adjusted between
40mA and 20mA peak current on a digit-by-digit
basis using fixed or adjustable resistors connected
from the R
ISET0
and R
ISET1
pins to GND. These controls enable analog relative adjustments in digit
intensity, typically to calibrate digits from different
batches, or to color balance RGY displays.
• The digit intensity controls allow each digit’s operating current to be scaled down in 256 steps from the
global panel intensity adjustment. The effective operating current for each digit becomes n/256th of the
panel intensity value. These controls enable digital
relative adjustments in digit intensity in addition to
the analog approach outlined above.
Display Size Limitations
The maximum display size that can be handled by a
single 4-wire serial interface is given in Table 2, which
is for the maximum 256 interconnected MAX6960s.
Larger display panels can be designed using a separate CS line for each group of (up to) 256 MAX6960s.
Each group would also have its own local 3-wire bus to
allocate the driver addresses. The 4-wire interface
speeds requirement when continuously updating display memory for high-speed animations is given in
Table 3.
Page 8
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Software Control
The hardware features are designed to simplify the
software interface and eliminate software timing dependencies:
• Two or four planes of display memory are stored,
allowing images to be preloaded into the MAX6960–
MAX6963 frame memory.
• Animation timing is built in, sequencing through the
two or four planes automatically. System software
has to update the upcoming plane(s) with new data
ahead of time, but do not be concerned about exact
timing. The frame rate is adjustable to as fast as 63
frames a second for animations, or to as slow as one
frame change every 63s for advertising sequencing.
• Multiple MAX6960s interconnect and share display
memory so that the software “sees” the display as
memory-mapped planes of contiguous RAM.
• Global commands that need to be received and
acted on by every MAX6960 in a panel do just that,
with one write.
Hardware Design
A MAX6960 normally drives an 8 x 16 LED matrix, comprising 8 cathode rows and 16 anode columns, or
8 anode rows and 16 cathode columns with external
drivers.
The MAX6960 standard wiring connection to either two
monocolor 8 x 8 digits, or to a single RGY 8 x 8 digit is
shown in Table 4. Figure 3 shows the display pin naming.
Figures 1 and 2 show example displays with the
MAX6960 drivers connecting to monocolor and RGY panels. Figure 4 shows how the display memory maps to the
physical pixels on the display panel, provided that the
MAX6960 drivers are interconnected correctly in a rasterlike manner from top left of the panel to bottom right.
Detailed Description
Overview
The MAX6960 is an LED display driver capable of driving
either two monocolor 8 x 8 cathode-row matrix digits, or a
single RGY 8 x 8 cathode-row matrix digit. The architecture of the driver is designed to allow a large graphic
DRIVER PINS ROW1–ROW8
DRIVER PINS COL1–COL8
DRIVER PINS COL9–COL16
Monocolor digit 0 (red*)
Digit 0 (red*) rows (cathodes)
R1 to R8
C8
—
Monocolor digit 1 (green*)
Digit 1 (green*) rows
(cathodes) R1 to R8
—
Digit 1 columns (anodes) C1 to
C8
RGY red/green
Red/green rows (cathodes) R1
to R8
Red columns (anodes) C1 toC8Green columns (anodes) C1 to
C8
Table 4. Standard Driver Connection to Monocolor and RGY 8 x 8 Displays
*Digit 0 of a monocolor display is called red, and digit 1 is called green in the data sheet.
RED
DRIVER0
RED RED
DRIVER1
RED RED
DRIVER2
RED RED
DRIVER3
RED RED
DRIVER4
RED RED
DRIVER5
RED
RED
DRIVER6
RED RED
DRIVER7
RED RED
DRIVER8
RED RED
DRIVER9
RED RED
DRIVER10
RED RED
DRIVER11
RED
RED
DRIVER12
RED RED
DRIVER13
RED RED
DRIVER14
RED RED
DRIVER15
RED RED
DRIVER16
RED RED
DRIVER17
RED
RED
DRIVER18
RED RED
DRIVER19
RED RED
DRIVER20
RED RED
DRIVER21
RED RED
DRIVER22
RED RED
DRIVER23
RED
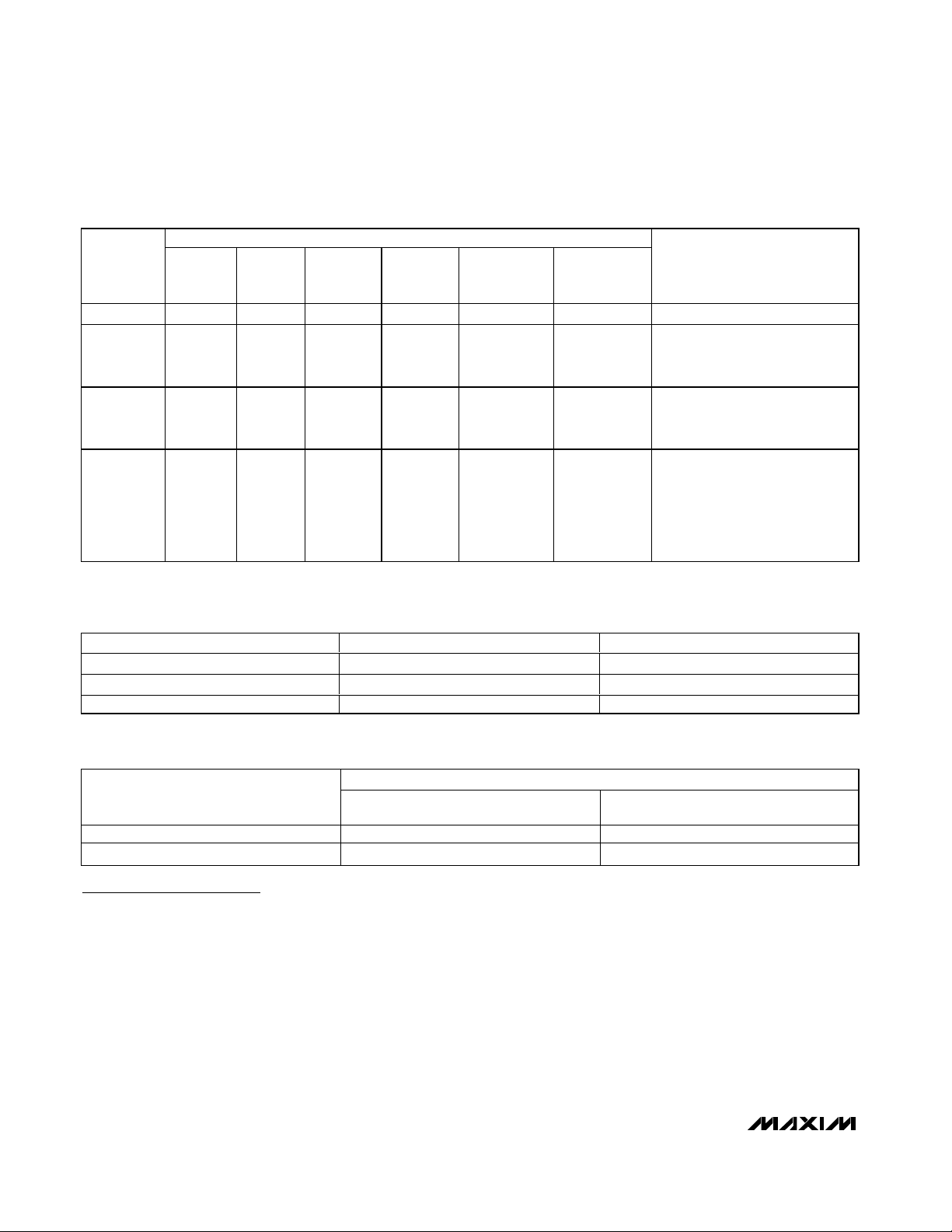
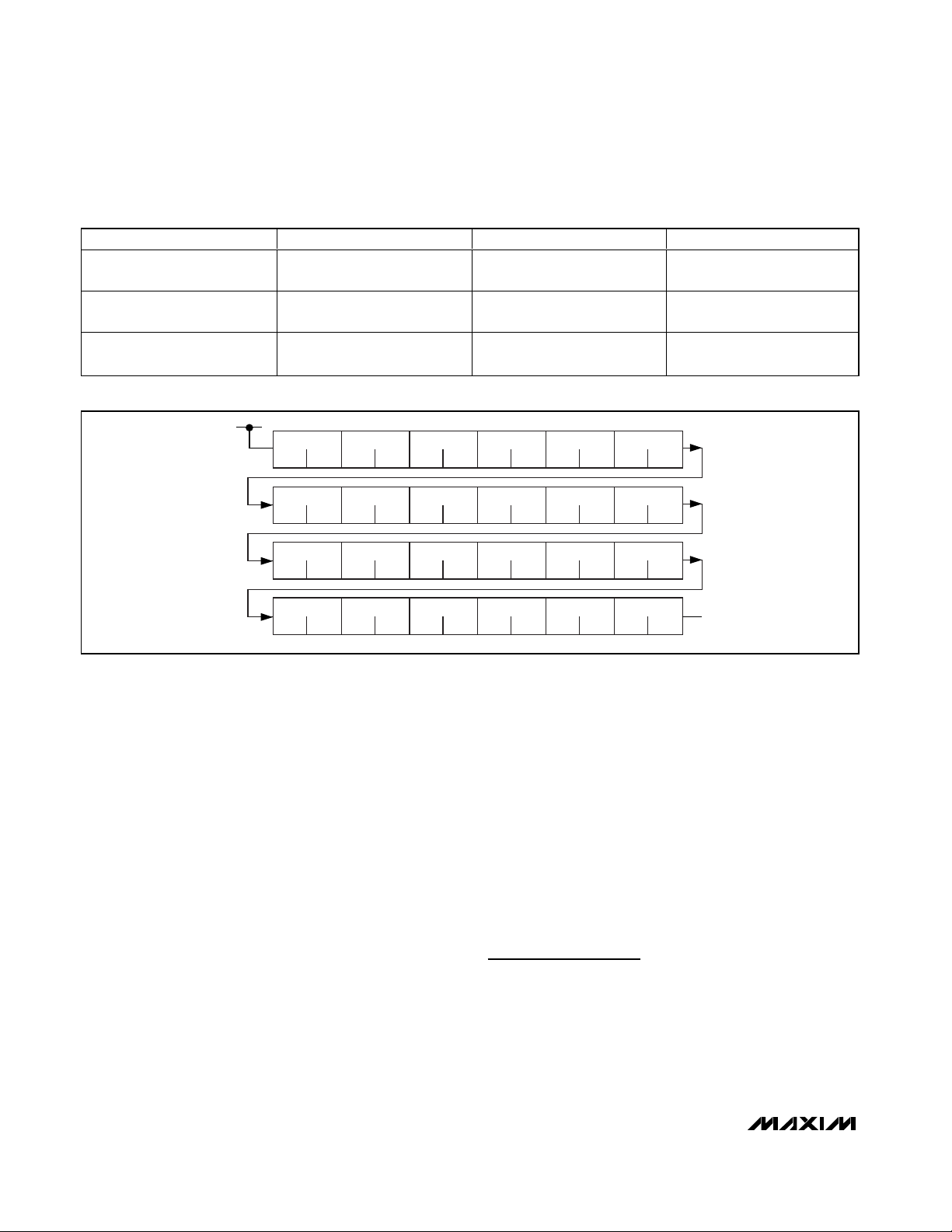
Figure 1. Monocolor 1-Bit-per-Pixel, 96-Pixel x 32-Pixel Display Example
Digit 0 columns (anodes) C1 to
Page 9
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
display panel to be driven easily and intuitively by multiple MAX6960s using 8 x 8 cathode-row matrix digits. The
MAX6960s in a display-driver design not only share the
host 4-wire interface, but they also share a local 3-wire
interface that is not connected to the host. The local 3wire interface works with the user’s driver settings to configure all the MAX6960s to appear to the host interface as
one contiguous memory-mapped driver.
The pixel level-intensity control uses frame modulation.
Pixels are enabled and disabled on a frame-by-frame
basis over a 12-frame super frame (Table 5). The effective pixel frame duty cycle within a super frame sets each
pixel’s effective intensity. The 12-frame period of a super
frame allows arithmetic and geometric intensity scales to
be mixed on the same driver. This allows the user to set
up an RGY display with a different color scale for red and
RED
DRIVER0
GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN
GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN
GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN
GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN GREEN
RED
DRIVER1
RED
DRIVER2
RED
DRIVER3
RED
DRIVER4
RED
DRIVER5
RED
DRIVER6
RED
DRIVER7
RED
DRIVER8
RED
DRIVER9
RED
DRIVER10
RED
DRIVER11
RED
DRIVER12
RED
DRIVER13
RED
DRIVER14
RED
DRIVER15
RED
DRIVER16
RED
DRIVER17
RED
DRIVER18
RED
DRIVER19
RED
DRIVER20
RED
DRIVER21
RED
DRIVER22
RED
DRIVER23
Figure 2. RGY 1-Bit-per-Pixel 48-Pixel x 32-Pixel Display Example
COLUMN 1
COLUMN 2
COLUMN 3
COLUMN 4
COLUMN 5
COLUMN 6
COLUMN 7
COLUMN 8
ROW 1
ROW 2
ROW 3
ROW 4
ROW 5
ROW 6
ROW 7
ROW 8
MONOCOLOR
COLUMN 1 (RED)
ROW 1
ROW 2
ROW 3
ROW 4
ROW 5
ROW 6
ROW 7
ROW 8
RGY
COLUMN 9 (GREEN)
Figure 3. 8 x 8 Matrix Pin Assignment
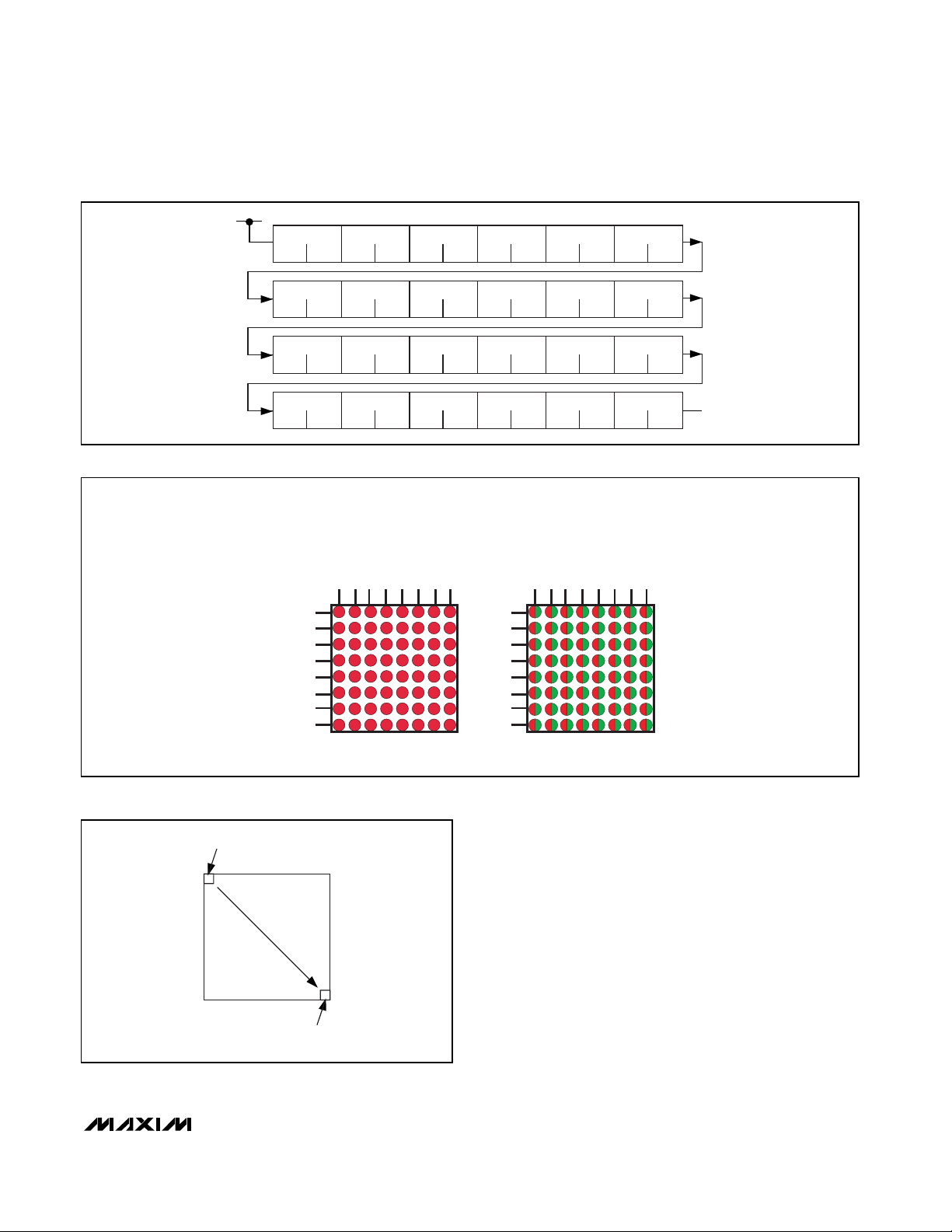
FIRST DISPLAY PIXEL
MAPS TO FIRST PLANE
LAST DISPLAY PIXEL
MAPS TO LAST PLANE
MEMORY LOCATION
Figure 4. How Plane Memory Across Multiple
MAX6960–MAX6963 Maps to Display Pixels
Page 10
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
green.The MAX6960 uses display memory planes to
store the display images. A memory plane is the exact
amount of memory required to store the display image.
The memory plane architecture allows one plane to be
used to refresh the display, while at least one other plane
is available to build up the next image. The global plane
counter register (Table 30) allows the plane used to
refresh the display to be selected either directly on command, or automatically under MAX6960 control.
Automatic plane switching can be set from 63 plane
changes a second to one plane change every 63s.
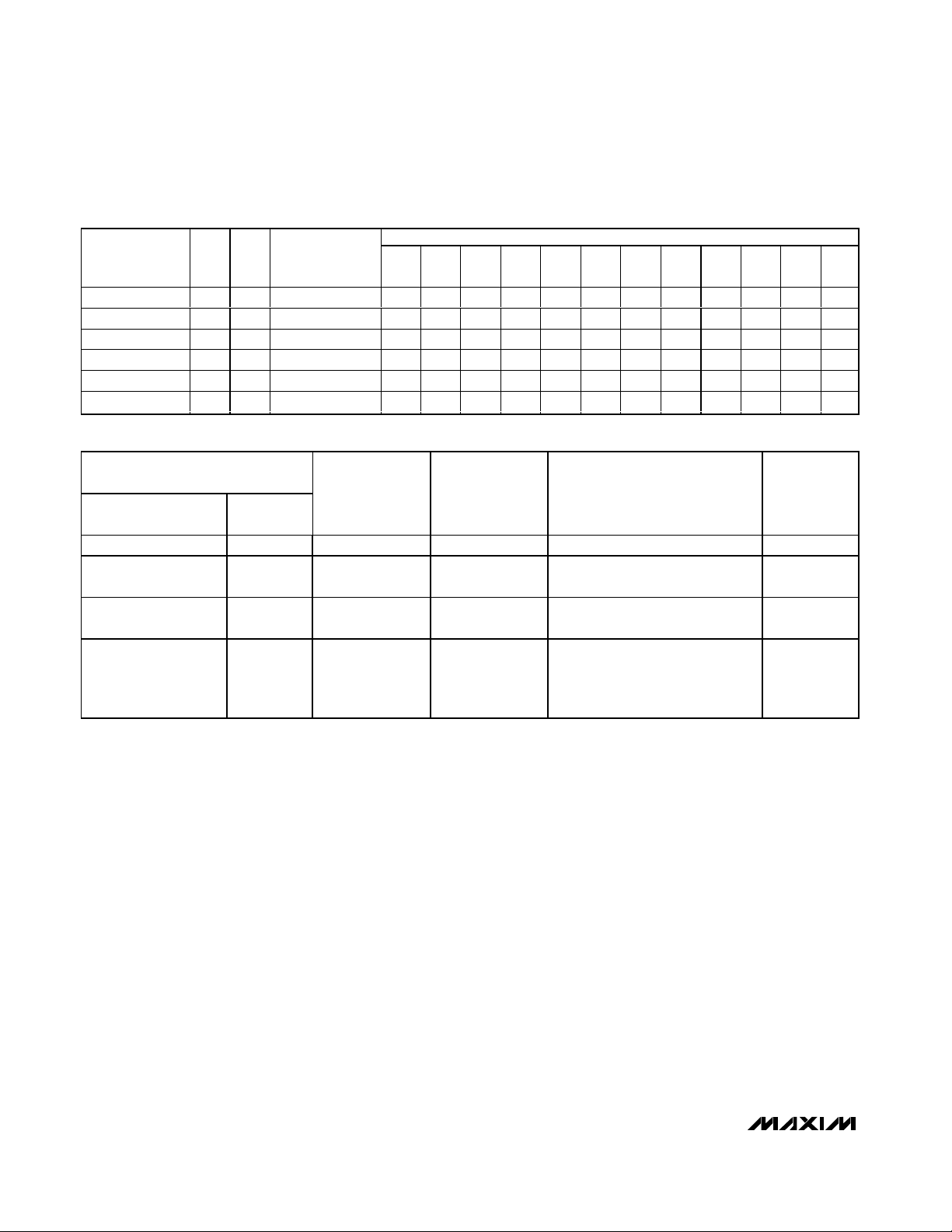
Display Memory Addressing
The MAX6960 contains 64 bytes of display mapping
memory. This display memory provides four memory
planes (of 16 bytes) when 1-bit-per-pixel intensity control is selected, or two memory planes (of 32 bytes)
when 2-bits-per-pixel intensity control is used (Table 6).
The 64 bytes of display memory in a MAX6960 could
be accessed with 6 bits of addressing on a driver-bydriver basis.
The MAX6960 uses a 14-bit addressing scheme. The
address map encompasses up to 256 MAX6960 drivers, all connected to the host through a common 4wire interface, and also interconnected through a local
3-wire interface. The purpose of the 3-wire interface is
to actively segment the 14-bit address space among
the (up to) 256 MAX6960s.
The total display memory is already partitioned among
these MAX6960 drivers in a register format. The
MAX6960s repartition these registers to appear as contiguous planes of display memory, organized by color
(red, then green) and then into planes (P0 to P4)
(Table 6).
Register Addressing Modes
The MAX6960 accepts 8-bit, 16-bit, and 24-bit transmissions. All MAX6960s sharing an interface receive
and decode all these transmissions, but the content of
a transmission determines which MAX6960s store and
use a particular transmission, and which discard it
(Table 7).
PATTERN OF MULTIPLEX CYCLES FOR WHICH A PIXEL IS ENABLED
PIXEL
GRADUATION
BIT
BIT
PIXEL
INTENSITY
SETTING
11
Both 1 1 Full
1
Arithmetic 1 0 2/3
1
Geometric 1 0 1/2
0
Arithmetic 0 1 1/3
0
Geometric 0 1 1/4
0
Both 0 0 Off
0
Table 5. Frame Modulation with Pixel Intensity
GLOBAL PANEL CONFIGURATION
REGISTER
(PI BIT)
COLOR
(C BIT)
PIXEL-LEVEL
INTENSITY
CONTROL
DISPLAY TYPE
DISPLAY MAPPING
ADDRESSES PER PLANE
DISPLAY
PLANES
AVAILABLE
0 0 1 bit per pixel Monocolor 16 red contiguous 4
0 1 1 bit per pixel RGY
8 red contiguous,
8 green contiguous
4
10
Monocolor
16 red contiguous,
16 red contiguous
2
11
RGY
16 red
(2 noncontiguous groups of 8),
16 green
(2 noncontiguous groups of 8)
2
Table 6. Panel Configuration
012345678910
11111111111
10110110110
10101010101
01001001001
01000100010
00000000000
PLANES/INTENSITY
2 bits per pixel
2 bits per pixel
Page 11
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
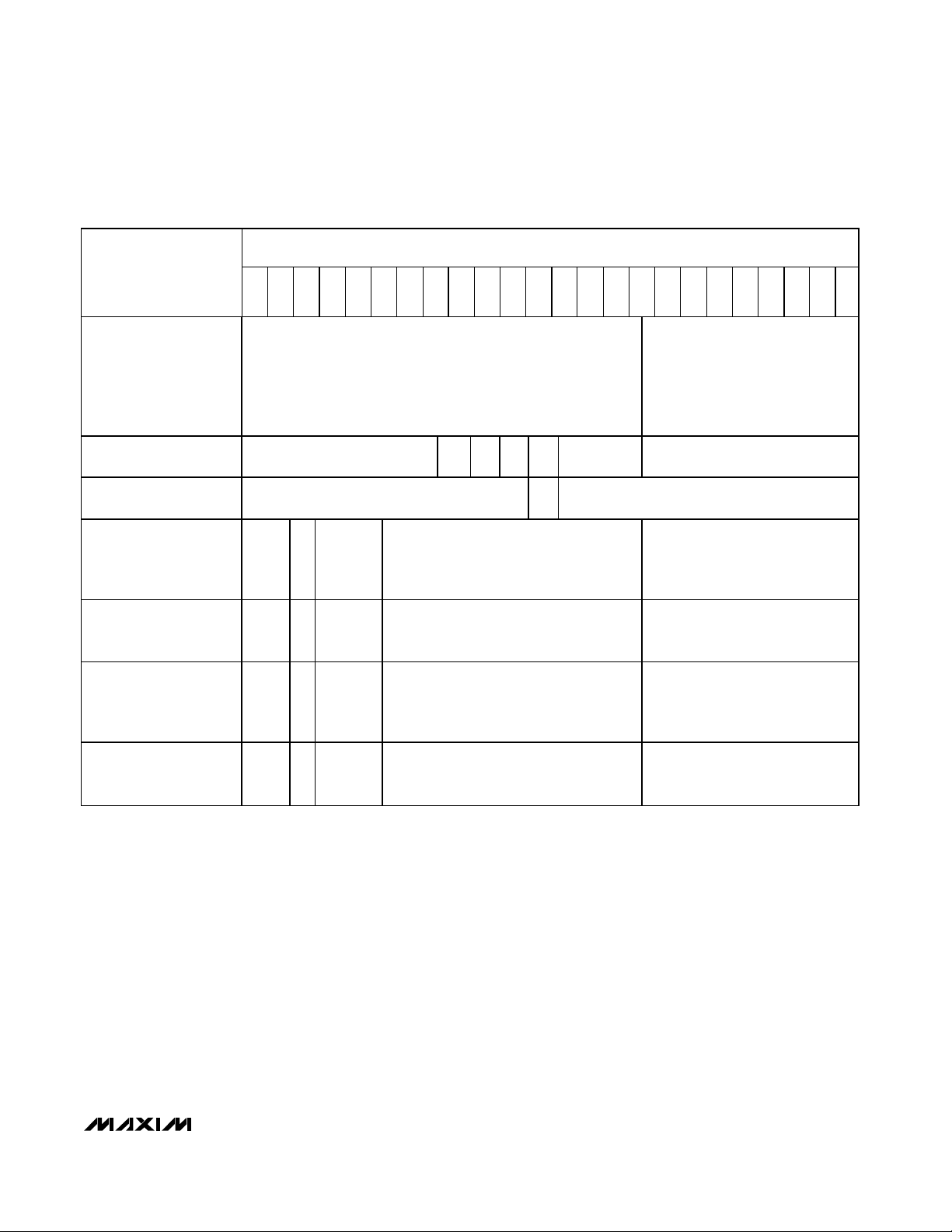
8-Bit Transmissions
Eight-bit transmissions are write-only, data-only
accesses that write data to the display memory indirected by the global display indirect address register
(Figure 6). The global display indirect address register
autoincrements after the write access. Eight-bit transmissions provide the quickest method of updating a
plane of display memory of the MAX6960. It is the most
suitable display update method if the host system
builds an image in local memory, and then dumps the
image into a display plane of the MAX6960.
16-Bit Transmissions
Sixteen-bit transmissions are read/write, commandand-data accesses to the MAX6960’s configuration
registers (Figure 7). A write can generally be global
(updates all MAX6960s on the 4-wire bus with the same
data) or specific (updates just the MAX6960 indirected
by the global driver indirect address register). Note:
The global driver indirect address register selects a
specific MAX6960. This is not the same as the global display indirect address register, which points to
display memory that could be in any MAX6960. A
16-bit read is always indirected through the global driver indirect address register to select only one
MAX6960 to respond. When a read or write is indirected through the global driver indirect address register,
the 16-bit command can choose whether the global driver indirect address is autoincremented after the command has been executed. This allows the host to set up
one or more registers in consecutive MAX6960s with
the display indirect address, autoincrementing only
when required.
8-, 16-, OR 24-BIT DATA PACKET SENT TO MAX6960
DATA FORMAT
D23
D22
D21
D20
D19
D18
D17
D16
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
8-bit indirect display
memory addressing.
Address is global display
indirect address (14 bits)
stored as {MSB, LSB} in
{register 0x0A, register
0x09}.
— 8 bits of display memory
16-bit device addressing.
—
4-bit
address
8 bits of driver register data
Factory reserved; do not
write to this address.
—
—
24-bit direct display
memory addressing
(monocolor 1 bit per
pixel).
12-bit addressing across 256 drivers,
4096 x 8 red pixels
8 bits of display memory
(1 bit per pixel)
24-bit direct display
memory addressing
(RGY 1 bit per pixel).
12-bit addressing across 256 drivers,
2048 x 8 red pixels, and
2048 x 8 green pixels
8 bits of display memory
(1 bit per pixel)
24-bit direct display
memory addressing
(monocolor 2 bits per
pixel).
0, 1
13-bit addressing across 256 drivers,
4096 x 4 red pixels
8 bits of display memory
(2 bits per pixel)
24-bit direct display
memory addressing
(RGY 2 bits per pixel).
0, 1
13-bit addressing across 256 drivers,
4096 x 4 red pixels, and
4096 x 4 green pixels
8 bits of display memory
(2 bits per pixel)
Table 7. Register Addressing Modes
R/W X
R/W X
Planes
0, 1, 2, 3
Planes
0, 1, 2, 3
R/W AI L/G 0
1
Planes
Planes
R/W X
R/W X
Page 12

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
24-Bit Transmissions
Twenty-four-bit transmissions are read/write, addressand-data accesses to the MAX6960’s display memory
(Figure 8). This is direct access to display memory
because the memory address is included in the 24-bit
transmission, compared with an 8-bit transmission,
which uses the memory address stored in the global
display indirect address register. Twenty-four-bit transmissions provide the random-access method of updating a plane of display memory of the MAX6960. It is the
most suitable display update method if the host system
builds an image directly in a display memory plane,
rather than in host local memory.
Host 4-Wire Serial Interface
Serial Addressing
The MAX6960 communicates to the host through a 4wire serial interface. The interface has three inputs:
clock (CLK), chip select (CS), and data in (DIN), and
one output, data out (DOUT). CS must be low to clock
data into the device, and DIN must be stable when
sampled on the rising edge of CLK. DOUT is used for
read access, and is stable on the rising edge of CLK.
DOUT is high impedance except during MAX6960 read
accesses. Multiple MAX6960s may be connected to the
same 4-wire interface, with all devices connected to all
four interface lines in parallel. The normal limit of paralleled MAX6960s is 256, because that is the interconnection limit for the 3-wire interface and associated
device addressing. The Applications Information section discusses some practical issues raised by driving
many devices in parallel from the same interface.
The serial interface responds to only 8-bit, 16-bit, and
24-bit commands (Table 7).
The MAX6960 ignores any transmission that is not
exactly 8 bits, 16 bits, or 24 bits between the falling
and subsequent rising edge of
CS.
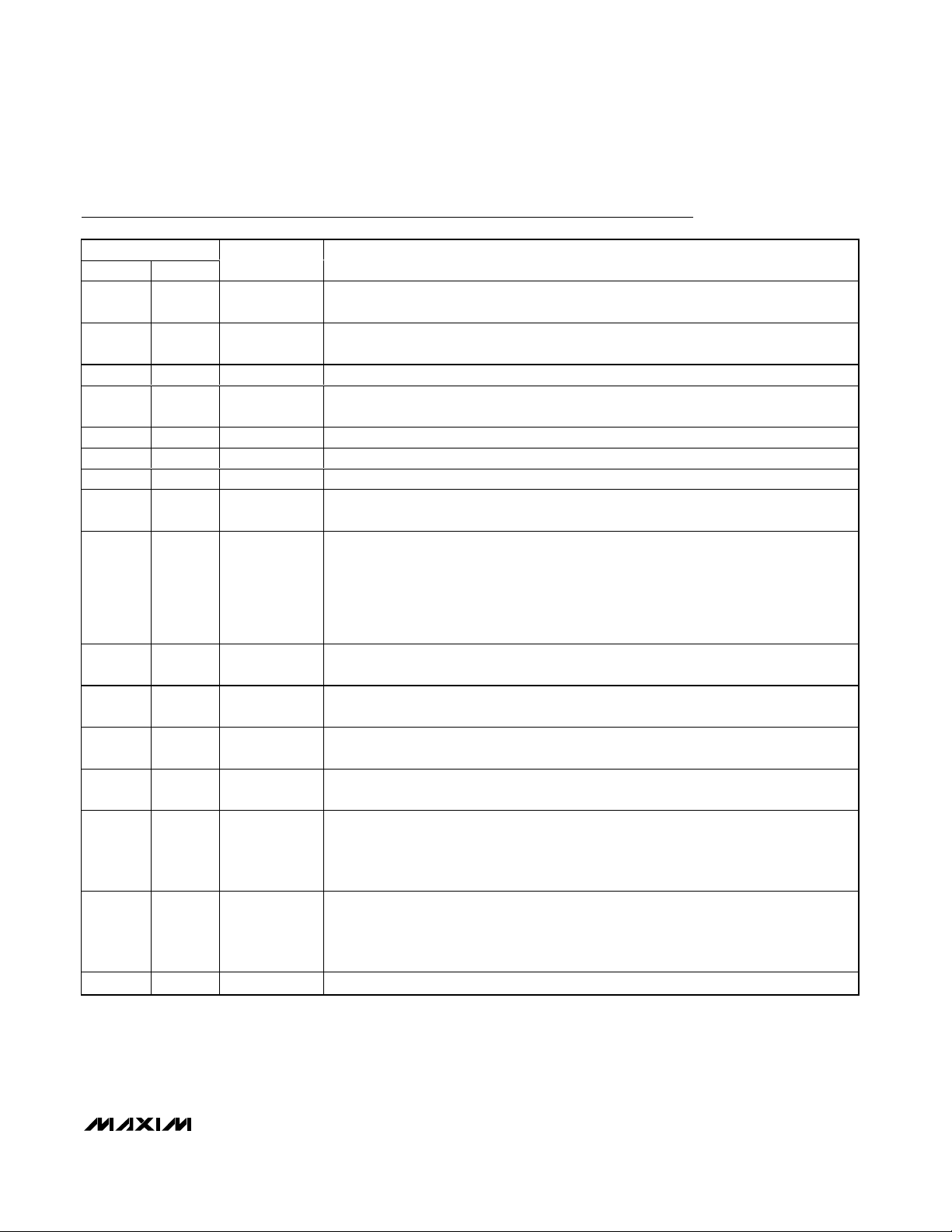
Control and Operation Using the 4-Wire Interface
Controlling the MAX6960 requires sending an 8-bit, 16bit, or 24-bit word. The last byte, D7 through D0, is
always the data byte. Eight-bit accesses are write-only
accesses; 16-bit or 24-bit accesses are read or write
accesses, as determined by the MSB of the transmission, which is set for a read access; clear for a write. A
16-bit or 24-bit read involves transmitting 16 or 24 bits
to DIN, taking CS high, and then reading back 8 bits
from DOUT. Only one MAX6960’s DOUT is enabled
from tri-state for readback. The selected MAX6960’s
DOUT normally returns to tri-state after the 8th falling
edge of CLK. However if CS falls during the read
before the 8th falling edge of CLK, then the readback is
terminated and the selected MAX6960’s DOUT returns
to tri-state.
If a number of bits other than exactly 8 bits, 16 bits, or
24 bits are clocked into the MAX6960 between taking
CS low and taking CS high again, then that transmission is ignored.
Writing Device Registers
The MAX6960 is written to using the following
sequence (Figures 3, 4, and 5):
1) Take CLK low.
2) Take CS low.
3) For an 8-bit transmission:
Clock 8 bits of data into DIN, D7 first to D0 last,
observing the setup and hold times.
For a 16-bit transmission:
Clock 16 bits of data into DIN, D15 first to D0 last,
Dn Dn-1
t
CSS
t
DS
t
DH
tCLt
CH
D1 D0
t
CP
t
CSH
t
CSW
.
t
DO
CS
CLK
DIN
DOUT
D7 D6 D1 D0
t
DO
t
DO
Figure 5. Timing Diagram
Page 13

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 13
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
CS
CLK
DIN
DOUT
TRI-STATE
Figure 6. 8-Bit Write to the MAX6960–MAX6963
D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
CS
CLK
DIN
.
DOUT
D15
= 0
TRI-STATE
Figure 7. 16-Bit Write to the MAX6960–MAX6963
D22 D21 D20 D19 D18 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
CS
CLK
DIN
DOUT
D23
= 0
TRI-STATE
.
D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8D16 D15D17
Figure 8. 24-Bit Write to the MAX6960–MAX6963
Page 14

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
14 ______________________________________________________________________________________
observing the setup and hold times. Bit D15 is low,
indicating a write command.
For a 24-bit transmission:
Clock 24 bits of data into DIN, D23 first to D0 last,
observing the setup and hold times. Bit D23 is low,
indicating a write command.
4) Take CS high (while CLK is still high after clocking
in the last data bit).
5) Take CLK low.
Reading Device Registers
Any register data within the MAX6960 may be read by
sending a logic-high to bit D15. The sequence is:
1) Take CLK low.
2) Take CS low.
3) For a 16-bit transmission:
Clock 16 bits of data into DIN, D15 first to D0 last,
observing the setup and hold times. Bit D15 is high,
indicating a read command. Bits D7 to D0 are
dummy bits, and are discarded by the MAX6960.
For a 24-bit transmission: Clock 24 bits of data into
DIN, D23 first to D0 last, observing the setup and
hold times. Bit D23 is high, indicating a read command. Bits D7 to D0 are dummy bits, and are discarded by the MAX6960.
4) Take CS high (while CLK is still high after clocking
in the last data bit).
5) Take CLK low.
6) The selected MAX6960’s DOUT is enabled from tristate for read back.
7) Clock 8 bits of data from DOUT, D7 first to D0 last,
observing the setup and hold times.
8) Take CLK low after the final (8th) data bit.
The selected MAX6960’s DOUT returns to tri-state.
Figure 10 shows a read operation when 24 bits are
transmitted and 8 bits are read back.
Local 3-Wire Serial Interface
The MAX6960 uses a 3-wire interface to bus together
up to 256 MAX6960s. The 3-wire bus enables each
device to calculate its own unique driver address
(0 to 255), and reconfigure its display memory. The
ADDOUT output also provides an interrupt at every
page change, when the plane counter is configured to
automatic (Table 30).
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
CS
CLK
DIN
DOUT
D15
= 1
TRI-STATE
D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8 D0
.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 9. 16-Bit Read from the MAX6960–MAX6963
D22 D21 D20 D19 D18 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
CS
CLK
DIN
DOUT
D23
= 1
TRI-STATE
D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8D16 D15D17 D0
.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 10. 24-Bit Read from the MAX6960–MAX6963
Page 15

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 15
3-Wire Interface Data Lines
(ADDOUT and ADDIN)
One MAX6960 is designated the master device, and
this is allocated driver address 0. The master’s ADDIN
pin is connected to V+, identifying it as the first device.
This first MAX6960 should be the driver for the topleft pixels of the display panel. The master’s
ADDOUT pin is connected to the second MAX6960’s
ADDIN pin, and that MAX6960’s ADDOUT pin is connected to the third MAX6960’s ADDIN, and so on up to
256 MAX6960s. The last MAX6960’s ADDOUT pin is left
open circuit. The last MAX6960 should be the driver
for the bottom-right pixels of the display panel. The
ADDOUT is initialized low at the start of a 3-wire interface configuration operation, and goes high (N + 1.5)
ADDCLK periods later, where n is the driver address of
the MAX6960 (0 to 255). See Figures 1 and 2 for connection examples.
3-Wire Interface Clock (ADDCLK)
The ADDCLK pins for all MAX6960s are all connected
together. ADDCLK data rate is determined by OSC / 4,
nominally 1.048576 MHz. The ADDCLK pin for the master MAX6960 (driver address 0) is always an output,
and all the other ADDCLKs are always inputs. ADDCLK
is active for exactly 256 clock cycles when a panel configuration is being performed (on power-up reset, and
after a write to the global panel configuration register).
Use of ADDOUT as Plane Change Interrupt
(IRQ)
When the plane counter is configured to automatic
mode (bit 6 of the plane counter register is set) (Table
30), ADDOUT pulses low for a time of 512/OSC (nominally 122µs) at the start of every automatic plane
change. This signal can be used as an interrupt output
from the display panel to the host to flag that the previous display plane is now unused and can be written
with a new image.
Multiplex Clock
The OSC input for all MAX6960s sharing a 3-wire interface bus (but not necessarily a 4-wire interface bus)
should be driven by a common CMOS-level clock ranging between 1MHz and 8.5MHz. It is usually necessary
to use an external clock tree to fan out multiple clock
drives when larger numbers of MAX6960s are used
because of the capacitive loads. For example, each
one of the eight outputs of a standard 74HC541 octal
buffer could drive 8 to 32 MAX6960 OSC inputs,
depending on the layout used.
The recommended setting for OSC is 4.194303MHz.
This frequency sets the slow global plane counter resolution to 1s, and the fast global plane counter resolution
to 1Hz.
Global and Local Register
Addressing
The register map (Table 8) contains three local registers and eight global registers. Global registers are
always written to in all MAX6960s (on the same 4-wire
interface) at the same time, using a 16-bit transmission.
A read from a global register also always results in a
read from driver address 0. The global nature of these
registers ensures that all drivers work together, and
there is no chance of a software miss-send causing, for
example, multiple MAX6960s to try to transmit on the 4wire DOUT line at the same time.
The three local registers can be written to on an individual basis (updates just the MAX6960 indirected by the
global driver indirect address register), or on a global
GLOBAL PANEL CONFIGURATION
REGISTER
(PI BIT)
COLOR
(C BIT)
PIXEL-LEVEL
INTENSITY
CONTROL
DISPLAY TYPE
DISPLAY MAPPING
ADDRESSES PER PLANE
DISPLAY
PLANES
AVAILABLE
0 0 1 bit per pixel Monocolor 16 red contiguous 4
0 1 1 bit per pixel RGY
8 red contiguous,
8 green contiguous
4
10
Monocolor
16 red contiguous,
16 red contiguous
2
11
RGY
16 red
(2 noncontiguous groups of 8),
16 green
(2 noncontiguous groups of 8)
2
Table 8. Register Address Map
PLANES/INTENSITY
2 bits per pixel
2 bits per pixel
Page 16

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
16 ______________________________________________________________________________________
basis (updates all MAX6960s), according to the status
of the local/global bit (Table 9). The local/global bit is
ignored during a 16-bit read transmission, and the
MAX6960 pointed to by the global driver indirect
address register is read.
Register Address Autoincrementing
When a read or write is indirected through the global driver indirect address register, the 16-bit command can
choose whether the global driver indirect address is
autoincremented after the command has been executed.
This allows the host to set up one or more registers in
consecutive MAX6960s with the display indirect address,
autoincrementing only when required (Table 10).
Driver Address Register
Reading the driver address register (Table 11) returns
the driver address that has been assigned to a particular MAX6960. The order of the driver addresses is
determined purely by the order that the 3-wire interface
is daisy-chained through multiple MAX6960s. The register is used to detect the presence of a MAX6960 at an
address, and a binary search on the 256 possible
addresses can be used to determine the size of an
array of MAX6960s.
COMMAND ADDRESS
REGISTER
ADDRESS
CODE
(HEX)
LOCAL: Only the MAX6960 indirected by driver
indirect address is written.
0X0XXXXX
GLOBAL: All MAX6960s are written with the same
data.
0X1XXXXX
LOCAL: The MAX6960 indirected by driver indirect
address responds.
1X0XXXXX
GLOBAL: The MAX6960 configured to address 0x00
responds.
0x00 to
0x07
1X1XXXXX
GLOBAL: All MAX6960s are written with the same
data.
0XXXXXXX
GLOBAL: The MAX6960 configured to address 0x00
responds.
0x08 to
0x0F
1XXXXXXX
Table 9. Register Address Local/Global Control Bit Format
COMMAND ADDRESS
REGISTER
ADDRESS
CODE
(HEX)
Driver indirect address is not changed X 0 XXXXXX
Driver indirect address is incremented after read/write
0x00 to
0x07
X1XXXXXX
Driver indirect address is not changed
0x08 to
XXXXXXXX
Table 10. Register Address Autoincrement Control Bit Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
CODE
(HEX)
D0
Driver address 0x00
8-bit driver address 0x00 to 0xFF
LSB
Table 11. Driver Address Register Format
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
MSB
Page 17

Initial Power-Up
On power-up, all control registers are reset (Table 12),
and the MAX6960 defaults to driver address 0 within a
panel of 256 drivers, monocolor, 1-bit-per-pixel, in one
row. The 3-wire interface automatically performs a configuration on all interconnected MAX6960s after powerup, reassigning the driver address allocation according
to the 3-wire interface interconnections. After performing the driver address allocation, the MAX6960 enters
shutdown mode.
Device Configuration
The MAX6960s driving a display panel must be configured before the panel can be used to display images.
The configuration involves the global panel configuration register (Table 15–Table 22), the global driver
devices register (Table 13), and the global driver rows
register (Table 14).
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 17
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Global driver devices 0x0E
MS
8-bit global driver devices 0x00 to 0xFF
LSB
Table 13. Global Driver Devices Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Global driver rows 0x0F
8-bit global driver rows 0x00 to 0xFF
LSB
Table 14. Global Driver Rows Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER FUNCTION
ADDRESS
D0
Driver address (read only) Address 0 0x00
0
Pixel intensity scale
0x01
0
Panel intensity 128/256 intensity 0x02
0
Digit 0 intensity Full 255/256 0x03
1
Digit 1 intensity Full 255/256 0x04
1
Fault No faults 0x05
0
Global driver indirect address Address 0x00 0x08
0
Global display indirect address
LSB
0x09
0
Global display indirect address
MSB
Address 0x0000
0x0A
0
Global plane counter
0x0B
0
Global panel configuration
Shutdown mode,
ripple sync enabled,
mux flip enabled,
color is mono,
4 display planes/1 bit per
pixel
0x0D
0
Global driver devices 256 drivers interconnected 0x0E
1
Global driver rows 256 drivers in a row 0x0F
1
Table 12. Power-Up Configuration
*When reading from the global registers, only the master MAX6960 (whose driver address is 0x00) responds.
POWER-UP CONDITION
Arithmetic for red and green
Manual selection to plane 0
CODE (HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
0000000
XXXXXX0
1000000
1111111
1111111
0XXXXX0
0000000
0000000
XX00000
0000000
0011XXX
1111111
1111111
CODE (HEX)
CODE (HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
MSB
Page 18

MAX6960–MAX6963
The global driver devices register should be written
with the total number of MAX6960s interconnected on
the 3-wire interface, minus 1 (Table 13). For the four
panel examples shown in Figures 1 and 2, 24
MAX6960s are used, so the global driver devices register should be written with the value 23, or 0x17.
The global driver rows register should be written with
the number of MAX6960s per panel row, minus 1
(Table 14). For the panel examples shown in Figure 1
and Figure 2, there are six MAX6960s per row, so the
global driver rows register should be written with the
value 5.
The values stored in the global driver devices register
and the global driver rows register, together with the C
and Pl bits in the global panel configuration register
(Tables 21 and 22), are used by the 3-wire interface
configuration engine to reconfigure display memory
addressing among the interconnected MAX6960s.
Global Panel Configuration Register
The configuration register contains eight device settings (Table 15 to Table 22).
Shutdown Mode (Bit D0)
Shutdown mode is exited by clearing the S bit in the
global panel configuration register (Table 16). When
the MAX6960 is in shutdown mode, LED driver outputs
ROW1–ROW8 and COL1–COL16 are tri-stated, and
multiplexing is halted. Data in the configuration registers remains unaltered. For minimum supply current in
shutdown mode, logic inputs should be at GND or V+
potential. Shutdown mode is exited by setting the S bit
in the global panel configuration register.
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
18 ______________________________________________________________________________________
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Global panel configuration register 0x0D
CFR
S
Table 15. Global Panel Configuration Register Format
Table 16. Global Panel Configuration—Shutdown Control (S Data Bit D0) Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Logic 1 in display memory lights the appropriate
LED (normal logic)
0x0D
CFR
0S
Logic 0 in display memory lights the appropriate
LED (invert logic)
0x0D
CFR
1S
Table 17. Global Panel Configuration—Invert Pixels (IP Data Bit D1) Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Current display plane is P0 0x0D PI C F R 0 0 IP S
Current display plane is P1 0x0D PI C F R 0 1 IP S
Current display plane is P2 0x0D 0 C F R 1 0
S
Current display plane is P0 0x0D 1 C F R 1 0
S
Current display plane is P3 0x0D 0 C F R 1 1
S
Current display plane is P1 0x0D 1 C F R 1 1
S
Table 18. Global Panel Configuration—Current Plane (DP0, DP1 Data Bit D2, D3) Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Shutdown 0x0D
CFR
0
Normal operation 0x0D
CFR
1
CODE (HEX)
CODE (HEX)
CODE (HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
PI
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
PI
PI
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
DP1 DP0 IP
DP1 DP0 IP
DP1 DP0 IP
CODE (HEX)
PI
PI
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
DP1 DP0
DP1 DP0
IP
IP
IP
IP
Page 19

Invert Pixels (Bit D1)
The invert pixels (IP) bit in the global panel configuration register controls whether the display memory is
used directly or inverted (Table 17).
Current Plane Identification (Bits D2, D3)
The current plane bits in the global panel configuration
register identify which memory plane is currently being
used to control the display panel (Table 18). These bits
are read only; written data is ignored.
Ripple Sync (Bit D4)
The ripple sync feature, when enabled in the global
panel configuration register, desynchronizes the multiplex timing of all the interconnected MAX6960 drivers
on a display panel by OSC/4 (Table 19). This delay
spreads the drive transitions among the drivers to
spread power-supply peak-current demand, and ease
decoupling. The maximum delay from first driver to last
driver is 244µs with the maximum of 256 drivers used.
This is too short a time to cause visible artifacts.
Mux Flip (Bit D5)
The mux flip feature in the global panel configuration
register reverses the panel PWM timing for alternate
drivers when enabled (Table 20). Again, this spreads
power-supply peak-current demand.
Color Control (Bit D6)
The color control bit in the global panel configuration
register selects whether a monocolor or RGY display
panel is built. Select monocolor when building an RGB
panel as shown in Figure 17. This bit is fixed at zero for
the MAX6962 and MAX6963, and a write to this bit is
ignored for these parts.
Planes/Intensity Control (Bit D7)
The planes/intensity (PI) control bit in the global panel
configuration register selects whether the display memory is configured as four planes with 1-bit-per pixel per
color-intensity control, or two planes with 2-bits-per
pixel per color-intensity control. This bit is fixed at zero
for the MAX6961 and MAX6963, and a write to this bit is
ignored for these parts.
Pixel Intensity Scale Register
The pixel intensity scale register (Table 24) sets the
graduation type used when 2-bits-per-pixel intensity
control is selected by setting the PI bit (Table 22). The
pixel level-intensity control can be set to be either
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 19
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Ripple sync is disabled; all interconnected
MAX6960s on the same 4-wire bus resynchronize
together.
0x0D
CF0
IP S
Ripple sync is enabled; all interconnected
MAX6960s on the same 4-wire bus resynchronize
with a 0.9537µs delay between adjacent devices.
0x0D
CF1
IP S
Table 19. Global Panel Configuration—Ripple Sync Control (R Data Bit D4) Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Mux flip is disabled: all interconnected MAX6960s
on the same 3-wire bus resynchronize to the
multiplex timing shown in Figure 11.
0x0D PI C 0 R
IP S
Mux flip is enabled: all interconnected MAX6960s on
the same 3-wire bus resynchronize with MAX6960s
with even driver addresses (0, 2, 4 to 254) operating
to the multiplex timing shown in Figure 11, and
MAX6960s with odd driver addresses (1, 3, 5 to 255)
operating to the flipped multiplex timing shown in
Figure 12.
0x0D PI C 1 R
IP S
Table 20. Global Panel Configuration—Mux Flip Control (F Data Bit D5) Format
CODE (HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
PI
PI
DP1 DP0
DP1 DP0
CODE (HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
DP1 DP0
DP1 DP0
Page 20

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
20 ______________________________________________________________________________________
2/256th
(MIN ON)
3/256th
4/256th
251/256th
252/256th
253/256th
249/256th
250/256th
254/256th
(MAX ON)
ROW 0 ANODE
DRIVER INTENSITY
SETTINGS
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
ROW/CATHODE
(LIT)
CURRENT SOURCE ENABLED
HIGH-Z
ROW/CATHODE
(UNLIT)
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
START OF
NEXT CYCLE
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 0
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 1
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 2
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 3
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 4
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 5
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 6
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 7
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 0
ROW 0's 122µs MULTIPLEX TIMESLOT
MINIMUM 1.91µs INTERDIGIT BLANKING INTERVAL
ONE COMPLETE 0.977ms MULTIPLEX CYCLE AROUND 8 ROWS
Figure 11. Multiplex Timing Diagram (No Flip; OSC = 4.194304MHz)
Page 21

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 21
START OF
NEXT CYCLE
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 0
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 1
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 2
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 3
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 4
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 5
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 6
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 7
122µs TIMESLOT
ROW 0
2/256th
(MIN ON)
3/256th
4/256th
251/256th
252/256th
253/256th
249/256th
250/256th
254/256th
(MAX ON)
ROW 0 ANODE
DRIVER INTENSITY
SETTINGS
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
LOW
ROW/CATHODE
(LIT)
CURRENT SOURCE ENABLED
HIGH-Z
ROW/CATHODE
(UNLIT)
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
HIGH-Z
ROW 0's 122µs MULTIPLEX TIMESLOT
MINIMUM 1.91µs INTERDIGIT BLANKING INTERVAL
ONE COMPLETE 0.977ms MULTIPLEX CYCLE AROUND 8 ROWS
Figure 12. Multiplex Timing Diagram (Flipped; OSC = 4.194304MHz)
Page 22

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
22 ______________________________________________________________________________________
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Display panel is built with monocolor or RGB
digits (permanently set this way for MAX6962 and
MAX6963)
0x0D PI 0 F R
S
Display panel is built with RGY digits
0x0D PI 1 F R
S
Table 21. Global Panel Configuration—Color Control (C Data Bit D6) Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
D0
Four display memory planes (0, 1, 2, 3) available;
pixel level-intensity control is 1 bit per pixel per
color (on/off) (permanently set this way for
MAX6961 and MAX6963)
0x0D 0 C F R
S
Two display memory planes (0, 1) available;
pixel level-intensity control is 2 bits per pixel per
color (4 levels)
0x0D 1 C F R
S
Table 22. Global Panel Configuration—Planes/Intensity Control (PI Data Bit D7) Format
PATTERN OF MULTIPLEX CYCLES
FOR WHICH A PIXEL IS ENABLED
PIXEL
PIXEL
DATA
PIXEL
INTENSITY
SETTING
11
Both 1 1 Full
1
Arithmetic 1 0 2/3
1
Geometric 1 0 1/2
0
Arithmetic 0 1 1/3
0
Geometric 0 1 1/4
0
Both 0 0 Off
0
Table 23. Frame Modulation with Pixel Intensity
PATTERN OF MULTIPLEX CYCLES
FOR WHICH A PIXEL IS ENABLED
PIXEL
PIXEL
DATA
PIXEL
INTENSITY
SETTING
11
Both 1 1 Full
1
Arithmetic 1 0 2/3
1
Geometric 1 0 1/2
0
Arithmetic 0 1 1/3
0
Geometric 0 1 1/4
0
Both 0 0 Off
0
Table 24. Pixel Intensity Scale Register Format
CODE (HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
DP1 DP0 IP
DP1 DP0 IP
CODE (HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
DP1 DP0 IP
DP1 DP0 IP
GRADUATION
012345678910
11111111111
10110110110
10101010101
01001001001
01000100010
00000000000
GRADUATION
012345678910
11111111111
10110110110
10101010101
01001001001
01000100010
00000000000
Page 23

arithmetic (off, 1/3, 2/3, full) or geometric (off, 1/4, 1/2,
full). The setting is made on a digit-by-digit basis, so
each color on an RGY or RGB panel can use the most
appropriate graduation type.
Digit Intensity Control
The digit intensity registers (Tables 25 and 26) set the
fractions of the panel intensity PWM value that are
applied to the two display digits. The PWM for each
digit is calculated as n/256th of the panel intensity
value, where n is the value in the digit’s digit intensity
register. The digit intensity registers enable configuring
relative adjustments in digit intensity, while the display
panel is still controlled as a whole by the panel intensity.
These adjustments are typically used to calibrate out
luminosity differences between LEDs from different
batches. They can also be used to color balance RGY
displays so that, for example, full panel intensity of a
red-green panel is a consistent orange hue.
Panel Intensity Control
Digital control of panel display brightness is provided
by an internal pulse-width modulator, which is controlled by the panel intensity register (Table 27). The
modulator scales the average segment current in 253
steps from a maximum of 255/256 down to 2/256 of the
peak current. The maximum effective PWM duty cycle
for a digit is therefore 254/256, given by the maximum
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 23
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
CODE (HEX)
D4
D0
0/256 0x03 0 0 0 0000 0
1/256 0x03 0 0 0 0000 1
2/256 0x03 0 0 0 0001 0
3/256 0x03 0 0 0 0001 1
4/256 0x03 0 0 0 0010 0
— 0x03 ————————
251/256 0x03 1 1 1 1101 1
252/256 0x03 1 1 1 1110 0
253/256 0x03 1 1 1 1110 1
254/256 0x03 1 1 1 1111 0
255/256 (max on) 0x03 1 1 1 1111 1
Table 25. Digit 0 Intensity Register Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS CODE
(HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0/256 0x04 0 0 000000
1/256 0x04 0 0 000001
2/256 0x04 0 0 000010
3/256 0x04 0 0 000011
4/256 0x04 0 0 000100
— 0x04 ————————
251/256 0x04 1 1 111011
252/256 0x04 1 1 111100
253/256 0x04 1 1 111101
254/256 0x04 1 1 111110
255/256 (max on) 0x04 1 1 111111
Table 26. Digit 1 Intensity Register Format
D7 D6 D5
D3 D2 D1
Page 24

MAX6960–MAX6963
255/256 digit intensity multiplied by the maximum
255/256 panel intensity. The minimum interdigit blanking time is therefore 4/256 of a cycle, or 4/256 x 122µs
digit period = 1.91µs.
Peak-Segment Current Selection
The LED drive current can be selected between either
a 40mA peak per segment and a lower 20mA peak current on a digit-by-digit basis using the R
ISET0
and
R
ISET1
pins. R
ISET0
should be open circuit to select
20mA, or connected to GND to select 40mA segment
current for digit 0. R
ISET1
selects segment current for
digit 1 in the same manner. The MAX6960 is guaranteed to drive 40mA peak segment current into a 2.4V
LED with a minimum supply voltage of 3.15V, and
20mA peak segment current into a 2.2V LED with a
minimum supply voltage of 2.7V.
Global Driver Indirect Address Register
The global driver indirect address register is used to
store the driver address identifying which of 256
MAX6960s is accessed for 16-bit transmission when a
local register is read (Table 28).
Global Display Indirect Address Register
The global display indirect address registers are used
to store the 14-bit display memory address identifying
which byte of display memory across all the interconnected MAX6960s is written by an 8-bit transmission
(Table 29). The 14-bit address stored in these two registers increments after every 8-bit transmission, and
overflows from address 0x3FFF to address 0x0000.
Global Plane Counter
The global plane counter (Table 30) allows any display
plane to be selected as the current display plane, or
configures the MAX6960 for automatic plane sequencing. The display plane is switched to the newly selected
plane on the rising edge of CS at the end of the 16-bit
transmission. When automatic plane sequencing is
selected, the current display plane is initialized to plane
P0. The current display plane is incremented through
all four planes P0–P3 (planes/intensity = 0) or both
planes P0–P1 (planes/intensity = 1) at the frame rate
selected, and then restarts at plane P0 again. The
plane sequencing continues until the global plane
counter is reconfigured. If the global plane counter is
used for the automatic sequencing of animations, the
user should ensure that the plane ahead of the current
display plane is updated before the automatic plane
switchover to achieve artifact-free animation.
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
24 ______________________________________________________________________________________
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS CODE
(HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Global driver indirect address 0x08
8-bit driver indirect address 0x00 to 0xFF
LSB
Table 28. Global Driver Indirect Address Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS CODE
(HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0x02 0000000 0
0x02 0000000 1
2/256 (min on)
0x02 0000001 0
3/256 0x02 0 0 00001 1
4/256 0x02 0 0 00010 0
5/256 0x02 0 0 00010 1
— 0x02 ——————— —
251/256 0x02 1 1 11101 1
252/256 0x02 1 1 11110 0
253/256 0x02 1 1 11110 1
254/256 0x02 1 1 11111 0
255/256 (max on) 0x02 1 1 11111 1
Table 27. Panel Intensity Register Format
MSB
Page 25

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 25
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS CODE
(HEX)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
D0
Global display indirect address LSB 0x09 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
D0
Global display indirect address MSB 0x0A X X
D9
D8
Table 29. Global Display Indirect Address Format
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
PLANES/INTENSITY BIT
(SEE TABLE 22):
0 FOR 1 BIT/PIXEL;
4 PLANES
1 FOR 1 BIT/PIXEL;
4 PLANES
ADDRESS
CODE
(HEX)
D6
D0
PLANE COUNTER — 0x0B
Fast
Auto
Counter setting
Manual selection to plane 0—counter
disabled
X 0x0B X 0
0
Manual selection to plane 1—counter
disabled
X 0x0B X 0
1
Manual selection to plane 2—counter
disabled
0 0x0B X 0
0
Manual selection to plane 0—counter
disabled
1 0x0B X 0
1
Manual selection to plane 3—counter
disabled
0 0x0B X 0
0
Manual selection to plane 1—counter
disabled
1 0x0B X 0
1
SLOW PLANE COUNTER 01
X
Auto slow plane counter—1 frame
every second
— 0x0B 0 1
1
Auto slow plane counter—1 frame
every 2s
— 0x0B 0 1
0
— 01——
—
Auto slow plane counter—1 frame
every 62s
— 0x0B 0 1
0
Auto slow plane counter—1 frame
every 63s
— 0x0B 0 1
1
FAST PLANE COUNTER 11
X
Auto fast plane counter—1 frame per
second
— 0x0B 1 1
1
Table 30. Global Plane Counter Register Format
D13 D12 D11 D10
D7
slow
manual
D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
XXXX0
XXXX0
XXXX1
XXXX1
XXXX1
XXXX1
XXXXX
00000
00001
———
11111
11111
XXXXX
00000
Page 26

MAX6960–MAX6963
Global Clear Planes Command
Writing the global clear planes counter (Table 31) allows
any or all display memory planes to be cleared with one
command. The selected plane(s) are cleared on the rising edge of CS at the end of the 16-bit transmission.
Fault Detection
LED Fault Detection
The MAX6960 detects open-circuit and short-circuit
LEDs. It can only detect an LED fault when attempting
to light that LED, so a good strategy to check a panel is
to program the panel with all LEDs on power-up to
check the displays.
The fault and device ID register (Table 32) uses 3 bits
to flag and distinguish open-circuit (open flag), shortcircuit (short flag), and overtemperature (OT flag)
faults, and a fourth flag (fault flag), which is an OR of
the open flag, short flag, and OT flag.
The fault and device ID register is cleared on powerup, and can also be cleared by writing to it. The fault
flags are NOT cleared by a read. When writing the fault
register, the data written is ignored; all fault flags are
cleared, including the OT flag. It is possible to clear all
MAX6960s on a bus by performing a global write to the
fault and device ID register.
Overtemperature Fault Detection
The MAX6960 contains an overtemperature (OT) detection circuit, which trips at a die temperature of typically
+150°C. The OT event is latched, and is readable in the
fault and device ID register (Table 32). When the OT
trips, the MAX6960 shutdown bit in the configuration
register (Table 31) is cleared, and the driver goes into
shutdown. Data is not lost; the effect is the same as the
user setting the shutdown bit. The user can attempt to
set the shutdown bit at any time. However, if the driver
is still over temperature, then the attempt to set the
shutdown bit is ignored. The OT fault flag is NOT automatically cleared when the device cools, or when the
device is taken out of shutdown.
The fault and device ID register is cleared on powerup, and can also be cleared by writing to it. The fault
flags are NOT cleared by a read. When writing the fault
register, the data written is ignored; all fault flags are
cleared, including the LED flags. It is possible to clear
all MAX6960s on a bus by performing a global write to
the fault and device ID register.
Applications Information
Setting LED Drive Current
The MAX6960 can be configured for pretrimmed 20mA
or 40mA LED current, or a 20mA to 40mA adjustable
current, on a digit-by-digit basis by the RISET0 and
RISET1 pin connections (Figures 13 and 14). The digit
intensity registers can be used to digitally adjust the
segment current, again on a digit-by-digit basis, by
controlling the PWM. Some applications best use one
or the other technique; some applications may require
the flexibility of both.
Power Supplies
The MAX6960 operates from a single 2.7V to 3.6V
power supply. Accuracy of the LED drive current of
20mA is guaranteed over this supply range. Accuracy
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
26 ______________________________________________________________________________________
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
PLANES/INTENSITY BIT
(SEE TABLE 22):
0 FOR 1 BIT/PIXEL;
4 PLANES
1 FOR 1 BIT/PIXEL;
4 PLANES
ADDRESS
CODE
(HEX)
D6
D0
PLANE COUNTER 0x0B
Fast
Auto
Counter setting
Auto fast plane counter—2 frames per
second
0x0B 1 1
0
— 11
—
Auto fast plane counter— 62 frames
per second
0x0B 1 1
0
Auto fast plane counter— 63 frames
per second
0x0B 1 1
1
Table 30. Global Plane Counter Register Format (continued)
D7
slow
D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
manual
00001
—————
11111
11111
Page 27

of the LED drive current of 40mA is guaranteed over a
supply range of 3.15V to 3.6V.
Bypass each of the 5 V+ power-supply pins to GND
with a 0.1µF capacitor as close to the device as possible. Add a 10µF to 100µF bulk decoupling capacitor to
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 27
REGISTER DATA
REGISTER
ADDRESS
CODE
(HEX)
D6
D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Fault (read) 0x05
Fault
Part ID X X
Short
flag
Open
flag
Fault (write) clears fault register status 0x05 0 Part ID X X 0 0 0
Device is MAX6960 0x05 X 0 0 X X X X X
Device is MAX6961 0x05 X 0 1 X X X X X
Device is MAX6962 0x05 X 1 0 X X X X X
Device is MAX6963 0x05 X 1 1 X X X X X
No LED or OT faults 0x05 0 Part ID X X 0 0 0
At least one open-circuit LED fault 0x05 1 Part ID X X X X 1
At least one short-circuit LED fault 0x05 1 Part ID X X X 1 X
Overtemperature fault 0x05 1 Part ID X X 1 X X
Table 32. Fault and Device ID Register Format
REGISTER DATA
ACTION
ADDRESS
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
GLOBAL CLEAR PLANES
0x0C
GREENP3GREENP2GREENP1GREEN
P0
RED P0
Clear all red plane P0
display memory
0x0C X XXXXXX1
Clear all red plane P1
display memory
0x0C X XXXXX1X
Clear all red plane P2
display memory*
0x0C X XXXX1XX
Clear all red plane P3
display memory*
0x0C X X X X 1 X X X
Clear all green plane P0
display memory
†
0x0C X X X 1 X X X X
Clear all green plane P1
display memory
†
0x0C X X 1 XXXXX
Clear all green plane P2
display memory
†*
0x0C X 1 XXXXXX
Clear all green plane P3
display memory
†*
0x0C 1 XXXXXXX
Table 31. Global Clear Planes Register Format
*These bit settings are ignored when the global panel configuration register bit PI is clear (i.e., ignored in 2-bits-per-pixel mode).
†These bit settings are ignored when the global panel configuration register bit C is clear (i.e., ignored in monocolor mode).
CODE (HEX)
RED P3 RED P2 RED P1
D7
flag
D5
OT flag
Page 28

MAX6960–MAX6963
the supply bus at least every several MAX6960s. Each
MAX6960 draws a peak current of either 40mA x 16
segments = 640mA (current setting = high) or 20mA x
16 segments = 320mA (current setting = low), regardless of the PWM plane and pixel intensity settings. If
ripple sync and/or mux flip are enabled, then the timing
of these peak currents is desynchronized between drivers, providing an easier load to the power supply. For
all but the smallest display panels, it is necessary to
use 2oz copper boards to minimize the voltage drops
across the supply planes with the high currents that are
required. Set the supply voltage to 3.6V at the panel
supply input to allow the most margin for on-board supply voltage drops. For the TQFN package, connect the
exposed pad to GND.
RST
Input
After power-up, each MAX6960 uses the 3-wire interface to determine its driver address within the other
interconnected MAX6960s. This process cannot take
place until all MAX6960s have powered up. In many
systems, the MAX6960s are operated from different
regulated supplies with different power-up delays. Hold
RST of every interconnected MAX6960 low until 50ms
after the last MAX6960 has powered up. RST must be
driven by a CMOS logic output supplied by V+. A
supervisor such as the MAX6821x526, which has an
adjustable power-up reset delay is a good choice.
Package Dissipation
Typical full-power (all segments on) device power dissipation is 671mW (V+ = 3.3V, V
LED
= 2.3V, I
LED
=
40mA, 254/256 full intensity). Consider the effect of one
or more shorted display LEDs in planning dissipation
handling. The MAX6960 remains under the 1023mW
MQFP package dissipation limit at +70°C with V+ =
3.6V and V
LED
= 2.1V. The TQFN package is preferred
for 40mA segment current applications because the
2.16W package dissipation limit easily handles worstcase applications including multiple shorted LEDs.
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
28 ______________________________________________________________________________________
V
REF
TO RED
LED DRIVERS
R
INT
R
INT
RISET0
42
V
REF
TO GREEN
LED DRIVERS
R
INT
R
INT
RISET1
43
MAX6960
MAX6961
MAX6962
MAX6963
Figure 13. RISET0 and RISET1 Internal Architecture
MAX6960–
MAX6963
MAX6960–
MAX6963
MAX6960–
MAX6963
42
43
RISET0
RISET1
42
43
RISET0
RISET1
42
43
RISET0
RISET1
NO CONNECTION
NO CONNECTION
R0
R1
SETTING LED CURRENT
TO 40mA
ADJUSTABLE LED CURRENT
20mA
SETTING LED CURRENT
TO 20mA
Figure 14. RISET0 and RISET1 Pin Connections
Page 29

Connecting Multiple MAX6960s to
the 4-Wire Bus
Up to 256 MAX6960s can be interconnected to share
the same 4-wire bus in parallel, sharing a common CS.
The maximum of 256 devices is set by the automatic
address allocation limit. Care is needed to achieve the
successful parallel interconnection of more than 16
MAX6960s due to the high-capacitive loading this presents onto the 4-wire bus. It is generally necessary to
either buffer and drive the CLK, DIN, and CS lines to
small groups of drivers, or to reduce the 4-wire data
rate from the 20Mb/s limit, if more than approximately
16 MAX6960s are used. The exact limit depends on the
application’s 4-wire data rate requirement, the capaci-
tive drive capability of the host’s CLK, DIN, and CS dri-
vers, and the effective capacitance of the CLK, DIN,
and CS routing on the circuit board. The circuit in
Figure 15 shows one way of fanning out the CLK, DIN,
and CS lines to 128 MAX6960s, and fanning in the
DOUT lines back into one DOUT line. The CLK, DIN,
and CS lines are buffered with standard CMOS bus
buffers, with each buffer output driving 16 CLK, DIN, or
CS inputs. The tri-state DOUT outputs are also connected together in groups of 16, and fed into octal analog
multiplexers. The analog multiplexers are used here as
data selectors, with the very low (10Ω) switch resistance providing an effective logic power driver. Note,
however, that while the MAX6960’s DOUT output is tristate, the selected DOUT from this power driver is not.
Using the MAX6960 as Controller for
Higher Voltage or Higher Current
The MAX6960 can be used as a graphic controller with
external drive transistors for applications requiring
higher peak segment currents and/or a higher drive
voltage (multiple LEDs in series for each pixel). The
panel and pixel-level intensity control is still available
because PWM techniques are used, but the peak segment current is set by external current-limiting resistors
in series with the LEDs, instead of the MAX6960’s internal precision constant-current sources. Figure 16
shows example output drivers that interface the
MAX6960 to control anode-row displays at a higher
segment current and drive voltage. Sixteen instances of
the low-current cathode column driver, and eight
instances of the high-current anode row driver are
required per MAX6960.
To use these drivers, choose R1 to set the desired
peak segment current I
PEAK
according to the driver
supply voltage V
DRIVER
and the LED forward voltage
drop V
LED
:
I
PEAK
= (V
DRIVER
- V
LED
- V
CE(SAT)Q1
) /
(R1 + R
DS(ON)Q2
) A
Choose R2 to pass 5mA in order to drop 5V across R3
to provide 5V gate drive to logic-level pFET Q2:
R2 = (V
DRIVER
- V
CE(SAT)Q3
- 5) x 200Ω
Rate Q1 at segment current I
PEAK
, and rate Q2 at row
current, which is 16 times I
PEAK
.
Using the MAX6960 as Driver/Controller
for RGB Displays
A MAX6960 can drive an 8 x 16 LED matrix, and so one
MAX6960 can drive two 8 x 8 monocolor digits or one 8
x 8 RGY digit. A MAX6960 cannot directly drive an 8 x
8 RGB display digit, but MAX6960s can nevertheless
be used to build RGB panels.
The MAX6960 drivers provide 3 x 2 = 6 bits of color
control to an RGB panel, or 64 colors.
The best way to drive RGB LEDs with the MAX6960 is to
use three 3-wire buses, one for each color (Figure 17). A
single 4-wire interface must be used, with three CSs,
again one for each color. The red and green LEDs are
driven directly by their MAX6960s, and are connected
cathode row as normal. The blue LEDs cannot be driven
directly by their MAX6960s because the blue LED forward voltage is too high, so external drive transistors
must be used as discussed previously. The blue LEDs
are therefore connected anode row. The MAX6960 is
suitable to drive discrete RGB matrix displays using
either separate LEDs for the red, green, and blue or sixterminal surface-mount or through-hole RGB LEDs. The
six-terminal LEDs must be used to give individual access
to the anodes and cathodes. The MAX6960 is not suitable to drive prewired RGB 8 x 8 matrix displays
because the row/column wiring is incorrect.
Synchronization is achieved by writing the global panel
configuration registers for every driver at the same
time. The user must therefore provide a method for driving all three CSs together when writing the global
panel configuration register. This complexity aside, the
three-bus method automatically organizes the display
memory into three color planes. Also, ripple sync and
mux flip can be enabled or disabled in any manner
desired. The digit limit for one set of three 3-wire buses
is 768 RGB digits using 256 MAX6960s. The structure
can be repeated to build a very large panel.
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 29
Page 30

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
30 ______________________________________________________________________________________
0–15
16–31
32–47
48–63
64–79
80–95
96–111
112–127
DIN
DIN DRIVERS
1
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
G1
G2
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
IC1A
74VHC541
0–15
16–31
32–47
48–63
64–79
80–95
96–111
112–127
CS DRIVERS
1
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
G1
G2
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
IC2A
74VHC541
0–15
0–15
16–31
32–47
48–63
64–79
80–95
96–111
112–127
15–31
32–47
48–63
64–79
80–95
96–111
112–127
CLK
CLK DRIVERS
1
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
G1
G2
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A
Y
B
W
C
D
E
F
G
H
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
IC3A
74VHC541
IC8
74AC4078
CS
48–63
64–79
80–95
13
14
12
1
5
2
4
6
11
X0
X1
X3
X4
X5
X6
X7
INH
A
3
X
10
9
15
X2
B
C
MAX4617
IC6A
0V
0V0V0V
DOUT DRIVERS
1kΩ1kΩ1k
Ω
96–111
112–127
13
14
12
1
5
2
4
6
11
74LV27
1
13
10
9
8
11
X0
X1
X3
X4
X5
X6
X7
INH
A
3
X
10
9
15
X2
B
C
V+
MAX4617
0V
0V0V
DOUT DRIVERS
1kΩ1k
Ω
0–15
16–31
32–47
13
14
12
1
5
2
4
6
11
X0
X1
X3
X4
X5
X6
X7
INH
A
3
X
10
9
15
X2
B
C
MAX4617
IC5A
0V
0V0V0V
DOUT DRIVERS
1kΩ1kΩ1k
Ω
DOUT
5
74LV27
4
3
6
13
74LV27
IC7A
IC7B
IC7C
2
1
12
V+
V+
Figure 15. MAX6960–MAX6963 High-Speed 4-Wire Interface Expansion
Page 31

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 31
V
DRIVER
V
DRIVER
Q2
Q3
Q1
V+
OV 0V
0V
G
S
D
R4
47kΩ
R1
R6
820Ω
R5
820Ω
R3
1kΩ
R2
ROW1–ROW8
COL1–COL16
ANODE ROW DRIVE
(1 OF 8)
CATHODE COLUMN DRIVE
(1 OF 16)
Figure 16. Current and Voltage Boosting MAX6960–MAX6963
with External Transistors
Chip Information
TRANSISTOR COUNT: 120,579
PROCESS: BiCMOS
MAX6960-MAX6963
CONNECT EXPOSED PAD (TQFN ONLY) TO GND.
TOP VIEW
TQFN
7mm x 7mm
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
GND
OSC
CS
DIN
DOUT
CLK
RST
COL1
COL2
COL3
V+
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
1
2
345678910
11
GND
RISET1
RISET0
ADDCLK
ADDIN
ADDOUT
V+
COL16
COL15
COL14
V+
GND
ROW8
ROW7
ROW6
ROW5
GND
ROW4
ROW3
ROW2
ROW1
GND
33
32
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
23
COL4
COL5
COL6
COL7
COL8
V+
COL9
COL10
COL11
COL12
COL13
Pin Configuration (continued)
Page 32

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
32 ______________________________________________________________________________________
MAX6960
ADDIN ADDOUT
MAX6960
ADDIN ADDOUT
MAX6960
ADDIN ADDOUT
3.3V
ANODE
ROWS
(DIGITS 0, 1)
CATHODE COLUMNS
DIGIT 0
RED
DIGIT 1
RED
ANODE
ROWS
(DIGITS 2, 3)
CATHODE COLUMNS
DIGIT 2
RED
DIGIT 3
RED
ANODE
ROWS
(DIGITS 4, 5)
CATHODE COLUMNS
DIGIT 4
RED
DIGIT 5
RED
TO NEXT MAX6960
MAX6960
ADDIN ADDOUT
MAX6960
ADDIN ADDOUT
MAX6960
ADDIN ADDOUT
3.3V
CATHODE COLUMNS
DIGIT 0
GREEN
DIGIT 1
GREEN
CATHODE COLUMNS
DIGIT 2
GREEN
DIGIT 3
GREEN
CATHODE COLUMNS
DIGIT 4
GREEN
DIGIT 5
GREEN
TO NEXT MAX6960
MAX6960
ADDIN ADDOUT
MAX6960
ADDIN ADDOUT
MAX6960
ADDIN ADDOUT
3.3V
CATHODE COLUMNS
DIGIT 0
BLUE
DIGIT 1
BLUE
CATHODE COLUMNS
DIGIT 2
BLUE
DIGIT 3
BLUE
CATHODE COLUMNS
DIGIT 4
BLUE
DIGIT 5
BLUE
TO NEXT MAX6960
ROW0–ROW8 COL0–COL8 COL9–COL16 ROW0–ROW8 COL0–COL8 COL9–COL16 ROW0–ROW8 COL0–COL8 COL9–COL16
ROW0–ROW8 COL0–COL8 COL9–COL16 ROW0–ROW8 COL0–COL8 COL9–COL16 ROW0–ROW8 COL0–COL8 COL9–COL16
ROW0–ROW8 COL0–COL8 COL9–COL16 ROW0–ROW8 COL0–COL8 COL9–COL16 ROW0–ROW8 COL0–COL8 COL9–COL16
Figure 17. Connecting MAX6960–MAX6963s to RGB Displays
Page 33

MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
______________________________________________________________________________________ 33
Package Information
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.)
MQFP44.EPS
D
1
1
21-0826
PACKAGE OUTLINE
44L MQFP, 1.60 LEAD FORM
Page 34

32, 44, 48L QFN.EPS
e
L
e
L
A1AA2
E/2
E
D/2
D
DETAIL A
D2/2
D2
b
L
k
E2/2
E2
(NE-1) X e
(ND-1) X e
e
C
L
C
L
C
L
C
L
k
DETAIL B
e
L
L1
PROPRIETARY INFORMATION
DOCUMENT CONTROL NO.APPROVAL
TITLE:
REV.
2
2
21-0144
DALLAS
SEMICONDUCTOR
PACKAGE OUTLINE
32, 44, 48, 56L THIN QFN, 7x7x0.8mm
D
PROPRIETARY INFORMATION
DOCUMENT CONTROL NO.APPROVAL
TITLE:
REV.
2
1
21-0144
DALLAS
SEMICONDUCTOR
PACKAGE OUTLINE
32, 44, 48, 56L THIN QFN, 7x7x0.8mm
D
Package Information (continued)
(The package drawing(s) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information
go to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.)
MAX6960–MAX6963
4-Wire Serially Interfaced
8 x 8 Matrix Graphic LED Drivers
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
34 ____________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600
© 2005 Maxim Integrated Products Printed USA is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...