Page 1

General Description
The MAX2038 8-channel variable-gain amplifier (VGA)
and programmable octal mixer array is designed for
high linearity, high dynamic range, and low noise performance targeting ultrasound imaging and Doppler
applications. Each amplifier features differential inputs
and outputs and a total gain range of 42dB (typ). In
addition, the VGAs offer very low output-referred noise
performance suitable for interfacing with 12-bit ADCs.
The MAX2038 VGA is optimized for less than ±0.25dB
absolute gain error to ensure minimal channel-to-channel ultrasound beamforming focus error. The device’s
differential outputs are designed to directly drive ultrasound ADCs through an external passive anti-aliasing
filter. A switchable clamp is also provided at each
amplifier’s output to limit the output signals, thereby
preventing ADC overdrive or saturation.
Dynamic performance of the device is optimized to
reduce distortion to support second-harmonic imaging.
The device achieves a second-harmonic distortion
specification of -70dBc at V
OUT
= 1.5V
P-P
and f
IN
=
5MHz and an ultrasound-specific*, two-tone, third-order
intermodulation distortion specification of -52dBc at
V
OUT
= 1.5V
P-P
and f
IN
= 5MHz.
The MAX2038 also integrates an octal quadrature mixer
array and programmable LO phase generators for a
complete CW beamforming solution. The LO phase
selection for each channel can be programmed using a
digital serial interface and a single high-frequency clock
or the LOs for each complex mixer pair can be directly
driven using separate 4 x LO clocks. The serial interface
is designed to allow multiple devices to be easily daisy
chained to minimize program interface wiring. The LO
phase dividers can be programmed to allow 4, 8, or 16
quadrature phases. The input path of each CW mixer
consists of a selectable lowpass filter for optimal CWD
noise performance. The outputs of the mixers are
summed into I and Q differential current outputs. The
mixers and LO generators are designed to have exceptionally low noise performance of -155dBc/Hz at 1kHz
offset from a 1.25MHz carrier.
The MAX2038 operates from a +5.0V power supply,
consuming only 120mW/channel in VGA mode and
269mW/channel in normal power CW mode. A lowpower CW mode is also available and consumes only
226mW/channel. The device is available in a lead-free
100-pin TQFP package (14mm x 14mm x 1mm) with an
exposed pad. Electrical performance is guaranteed
over a 0°C to +70°C temperature range.
Applications
Ultrasound Imaging Sonar
Features
o 8-Channel Configuration
o High Integration for Ultrasound Imaging
Applications
o Pin Compatible with the MAX2037 Ultrasound VGA
VGA Features
o Maximum Gain, Gain Range, and Output-Referred
Noise Optimized for Interfacing with 12-Bit ADCs
Maximum Gain of 29.5dB
Total Gain Range of 42dB
22nV/√√Hz Ultra-Low Output-Referred Noise at
5MHz
o ±0.25dB Absolute Gain Error
o 120mW Consumption per Channel
o Switchable Output VGA Clamp Eliminating ADC
Overdrive
o Fully Differential VGA Outputs for Direct ADC
Drive
o Variable Gain Range Achieves 42dB Dynamic
Range
o -70dBc HD2 at V
OUT
= 1.5V
P-P
and fIN= 5MHz
o Two-Tone Ultrasound-Specific* IMD3 of
-52dBc at V
OUT
= 1.5V
P-P
and fIN= 5MHz
CW Doppler Mixer Features
o Low Mixer Noise of -155dBc/Hz at 1kHz Offset
from 1.25MHz Carrier
o Serial-Programmable LO Phase Generator for 4, 8,
16 LO Quadrature Phase Resolution
o Optional Individual Channel 4 x fLOLO Input
Drive Capability
o 269mW Power Consumption per Channel (Normal
Power Mode) and 226mW Power Consumption
per Channel (Low-Power Mode)
o CWD Implementation Is Fully Compliant with All
Patents Related to Ultrasound Imaging
Techniques
MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
________________________________________________________________
Maxim Integrated Products
1
Ordering Information
19-4375; Rev 0; 1/09
EVALUATION KIT
AVAILABLE
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
+
Denotes a lead(Pb)-free/RoHS-compliant package.
D = Dry packing.
T = Tape and reel.
*
EP = Exposed pad.
Pin Configuration appears at end of data sheet.
*
See the Ultrasound-Specific IMD3 Specification in the
Applications Information section.
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX2038CCQ+D 0°C to +70°C 100 TQFP-EP*
MAX2038CCQ+TD 0°C to +70°C 100 TQFP-EP*
Page 2
MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
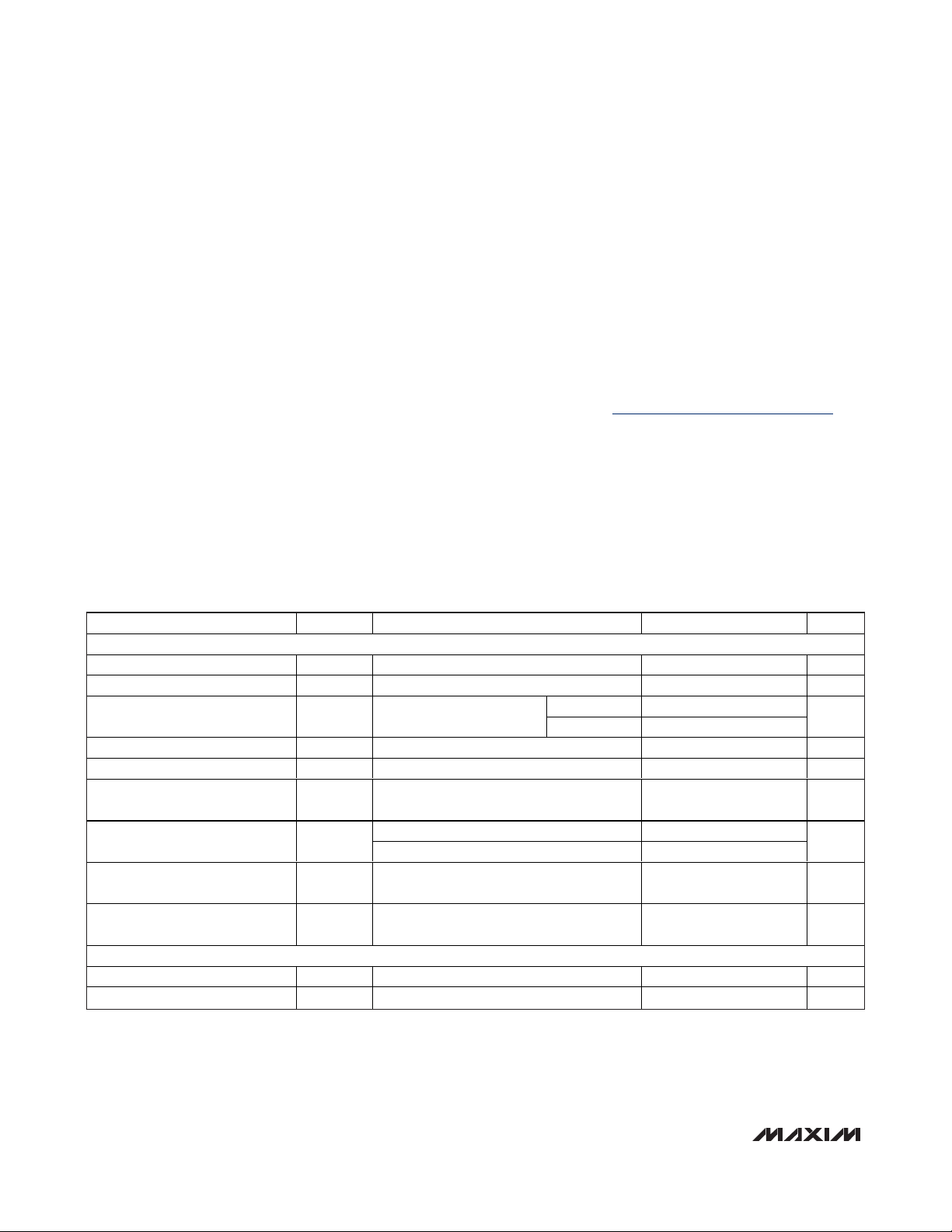
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS—VGA MODE
(
Typical Application Circuit
, Figure 7. V
CC
= V
REF =
4.75V to 5.25V, V
CM
= (3/5)V
REF
, T
A =
0°C to +70°C, V
GND
= 0, LOW_PWR = 0,
M4_EN = 0, CW_FILTER = 0 or 1, TMODE = 0, PD = 0, CW_VG = 1, CW_M1 = 0, CW_M2 = 0, no RF signals applied, capacitance to
GND at each of the VGA differential outputs is 60pF, differential capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF,
R
L =
1kΩ, CW mixer outputs pulled up to +11V through four separate ±0.1% 115Ω resistors, all CW channels programmed off.
Typical values are at V
CC
= V
REF
= 5V, T
A =
+25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 2)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
VCC, V
REF
to GND .................................................-0.3V to +5.5V
Any Other Pins to GND...............................-0.3V to (V
CC
+ 0.3V)
CW Mixer Output Voltage to GND (CW_IOUT+, CW_IOUT-,
CW_QOUT+, CW_QOUT-) ................................................13V
VGA Differential Input Voltage (VGIN_+, VGIN_-)............8.0V
P-P
Analog Gain Control Differential Input Voltage
(VG_CTL+, VG_CTL-) ..................................................8.0V
P-P
CW Mixer Differential Input Voltage
(CWIN_+, CWIN_-).......................................................8.0V
P-P
CW Mixer LVDS LO Differential Input Voltage..................8.0V
P-P
Continuous Power Dissipation (TA= +70°C)
100-Pin TQFP (derated 45.5mW/°C above +70°C)...3636.4mW
Operating Temperature Range...............................0°C to +70°C
Junction Temperature......................................................+150°C
θ
JC
(Note 1) .....................................................................+2°C/W
θ
JA
(Note 1) ...................................................................+22°C/W
Storage Temperature Range .............................-40°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
Note 1: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a four-
layer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maxim-ic.com/thermal-tutorial
.
VGA MODE
Supply Voltage Range V
VCC External Reference
Total Power-Supply Current
VCC Supply Current I
V
REF
Current Consumption per
Amplifier Channel
Differential Analog Control
Voltage Range
Differential Analog Control
Common-Mode Voltage
Analog Control Input
Source/Sink Current
LOGIC INPUTS
CMOS Input High Voltage V
CMOS Input Low Voltage V
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDTIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Current I
CC
V
REF
VCC
REF
V
CM
IH
IL
(Note 3) 4.75 5 5.25 V
Refers to VCC supply
current plus V
Refers to VCC supply current 24 27 mA
Minimum gain +2
Maximum gain -2
REF
current
PD = 0 204 231
PD =1 27 33
4.75 5 5.25 V
2.85 3 3.15 V
2.3 V
mA
192 216 mA
12 15 mA
V
4.5 5 mA
0.8 V
P-P
Page 3
MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
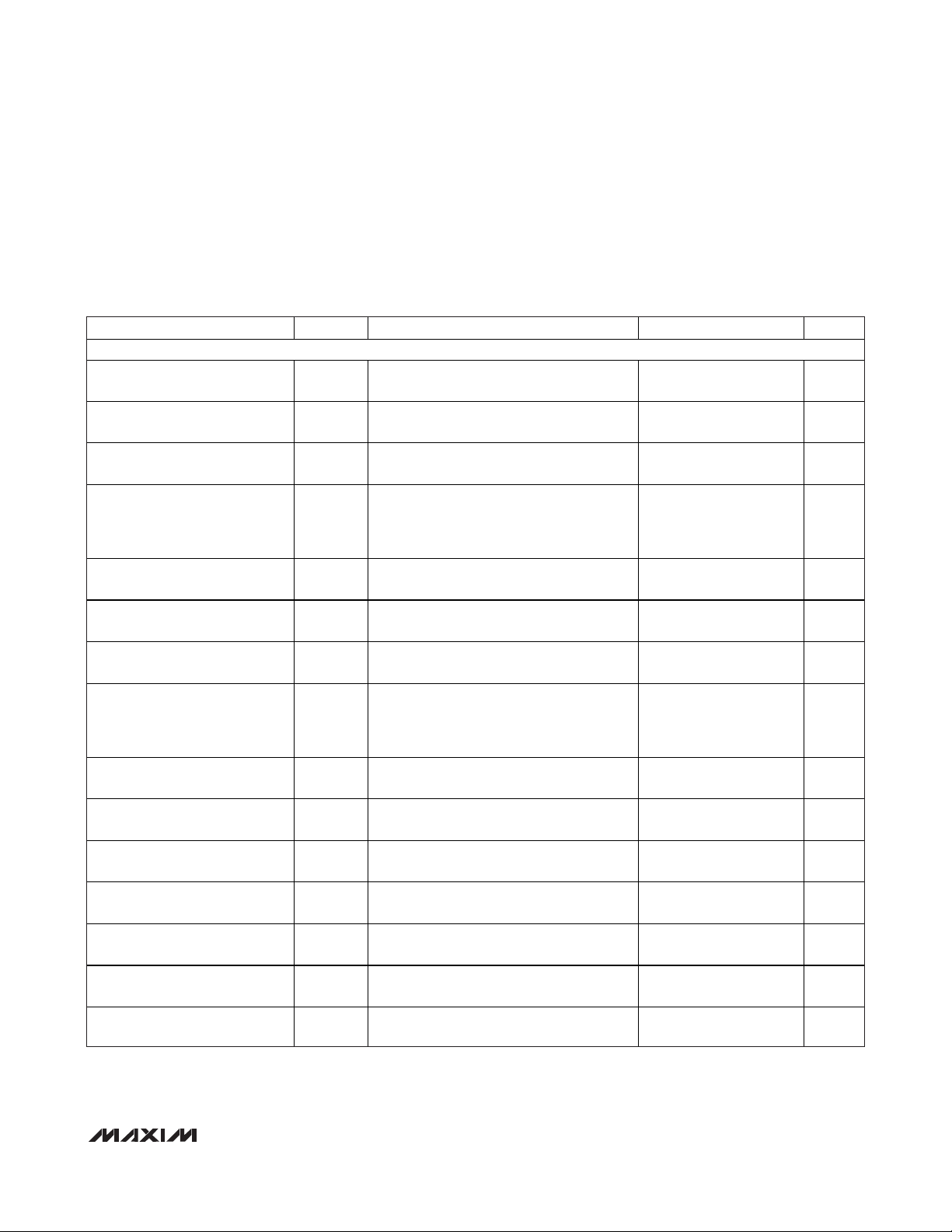
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS—CW MIXER MODE
(
Typical Application Circuit
, Figure 7. V
CC
= V
REF =
4.75V to 5.25V, T
A =
0°C to +70°C, V
GND
= 0, LOW_PWR = 0,
M4_EN = 0, CW_FILTER = 0 or 1, TMODE = 0, PD = 0, CW_VG = 0, CW_M1 = 0, CW_M2 = 0, no RF signals applied,
capacitance to GND at each of the VGA differential outputs is 60pF, differential capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF,
R
L =
1kΩ, CW mixer outputs pulled up to +11V through four separate ±0.1% 115Ω resistors. Typical values are at VCC= V
REF
= 5V,
T
A =
+25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 2)
CW MIXER MODE
Current in Full-Power Mode
5V V
Current in Full-Power Mode
11V V
Current in Full-Power Mode
5V V
Power Dissipation in Full-Power
Mode
Current in Low-Power Mode
5V V
Current in Low-Power Mode
11V V
Current in Low-Power Mode
5V V
Power Dissipation in Low-Power
Mode
Mixer LVDS LO Input CommonMode Voltage
LVDS LO Differential Input
Voltage
LVDS LO Input
Common-Mode Current
LVDS LO Differential
Input Resistance
Mixer IF Common-Mode Output
Current
DATA Output High Voltage
DATA Output Low Voltage
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDTIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Supply
CC
Supply
MIX
Supply
REF
Supply
CC
Supply
MIX
Supply
REF
I
CC_FP
I
MIX_FP
I
REF_FP
P
DISS_FP
I
CC_LP
I
MIX_LP
I
REF_LP
P
DISS_LP
Refer s to V
Refer s to V
Refer s to V
Total power dissipation (all 8 channels
including both 5V (V
mixer pullup supply power dissipation in the
device) (Note 4)
LOW _P WR = 1; r efer s to V
( al l 8 channel s)
LOW _P WR = 1; r efer s to V
( al l 8 channel s)
LOW _P WR = 1; r efer s to V
( al l 8 channel s)
LOW_PWR = 1; total power dissipation
(all 8 channels including both 5V (V
V
REF
dissipation in the device) (Note 4)
Modes 1 and 2 (Note 5)
Modes 1 and 2 200 700 mV
Per pin 150 200 µA
Modes 1 and 2 (Note 6) 30 kΩ
Common-mode current in each of the
differential mixer outputs (Note 7)
DOUT voltage when terminated in DIN
(daisy chain) (Note 8)
DOUT voltage when terminated in DIN
(daisy chain) (Note 8)
sup p l y cur r ent ( al l 8 channel s) 245 265 mA
C C
sup p l y c ur r ent ( al l 8 channel s) 106 120 mA
M IX
sup p l y c ur r ent ( al l 8 channel s) 17 21 mA
RE F
and V
CC
C C
M IX
R E F
) and 11V mixer pullup supply power
) and 11V
REF
sup p l y cur r ent
sup p l y cur r ent
sup p l y cur r ent
CC
and
2.15 2.41 W
245 265 mA
53 60 mA
17 21 mA
1.81 2.06 W
1.25
±0.2
3.25 3.75 mA
4.5 V
0.5 V
V
P-P
Page 4
MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
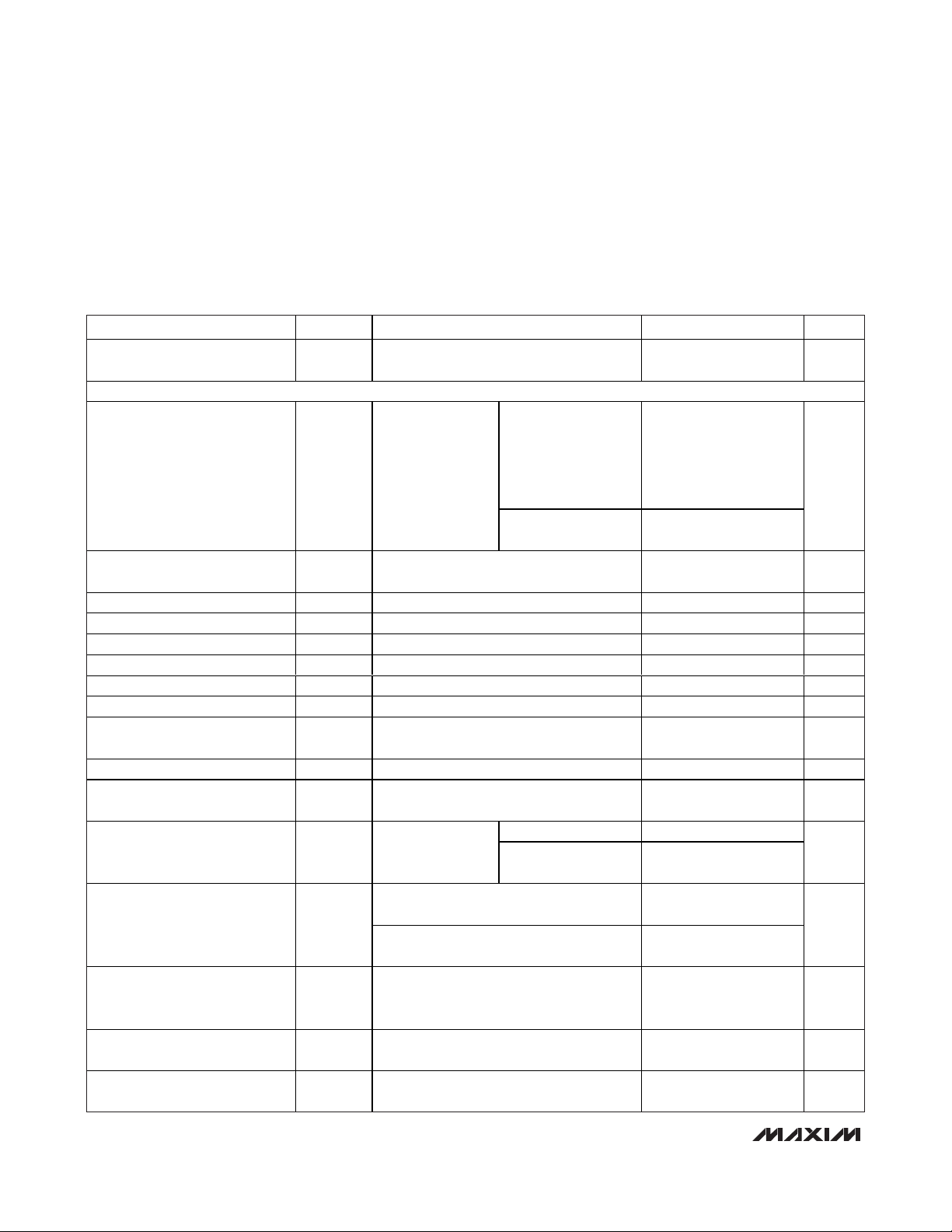
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS—VGA MODE
(
Typical Application Circuit
, Figure 7. VCC= V
REF
= 4.75V to 5.25V, V
CM
= (3/5)V
REF
, TA= 0°C to +70°C, V
GND
= 0, LOW_PWR = 0,
M4_EN = 0, CW_FILTER = 1, TMODE = 0, PD = 0, CW_VG = 1, CW_M1 = 0, CW_M2 = 0, VG_CLAMP_MODE = 1, f
RF
= fLO/16 =
5MHz, capacitance to GND at each of the VGA differential outputs is 60pF, differential capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF,
R
L
= 1kΩ, CW mixer outputs pulled up to +11V through four separate ±0.1% 115Ω resistors, differential mixer inputs are driven from
a low impedance source. Typical values are at V
CC
= V
REF
= 5V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 2)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Mode Select Response Time
VGA MODE
Full-Scale Bandwidth f
Small-Signal Bandwidth f
Differential Input Resistance R
Input Effective Capacitance C
Differential Output Resistance R
Maximum Gain +29.5 dB
Minimum Gain -12.5 dB
Gain Range 42 dB
Absolute Gain Error
VGA Gain Response Time 40dB gain change to within 1dB final value 1 µs
Input-Referred Noise
Output-Referred Noise
Second Harmonic HD2
Third-Order Intermodulation
Distortion
Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk
Maximum Output Voltage at
ClampON
-1.3dB
-1.3dB
IN
IN
OUT
IMD3
CW_VG set from logic 1 to 0 or from 0 to 1
(Note 9)
2µs
Differential output
capacitance is 10pF,
V
OUT
= 1.5V
P-P
,
1.3dB bandwidth,
gain = 10dB
V
= 1.5mV
OUT
P-P
gain = 10dB
capacitance to GND
at each single-ended
output is 60pF,
= 1kΩ
R
L
No capacitive load
= 1kΩ
R
L
, 3dB bandwidth,
18
29
30 MHz
170 200 230 Ω
fRF = 10MHz, each input to ground 15 pF
100 Ω
T
= +25°C, full gain range 0% to 100%,
A
V
= 5V
REF
VG_CTL set for maximum gain,
no input signal
±0.25 ±1.5 dB
2 nV/√Hz
No input signal 22
VG_CTL set for
+10dB of gain
V G_C LAM P _M OD E = 1, V G_C TL set for
+ 10d B of g ai n, f
V G_C LAM P _M OD E = 1, V G _C TL set for
+ 10d B of g ai n, f
V G_C LT set for + 10d B of g ai n, f
= 5.01MHz, V
f
R F2
V
= 5V (Note 3)
REF
V
OUT
= 1V
differential, f
P-P
VG_CTL set for +10dB of gain
VG_CLAMP_MODE = 0, VG_CTL set for
+20dB of gain, 350mV
V
offset
= 5M H z, V
R F
= 10M H z, V
R F
= 1.5V
OUT
P-P
= 1.5V
OUT
= 1.5V
OU T
OU T
RF1
,
P-P
= 10MHz,
R F
P-P
= 1.5V
= 5M H z,
differential input
, 1kHz
P - P
P - P
55
-70
-55 -65
-40 -52 dBc
-80 dB
2.4
MHz
nV/√Hz
dBc
V
P-P
d i ffer enti al
Page 5
MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
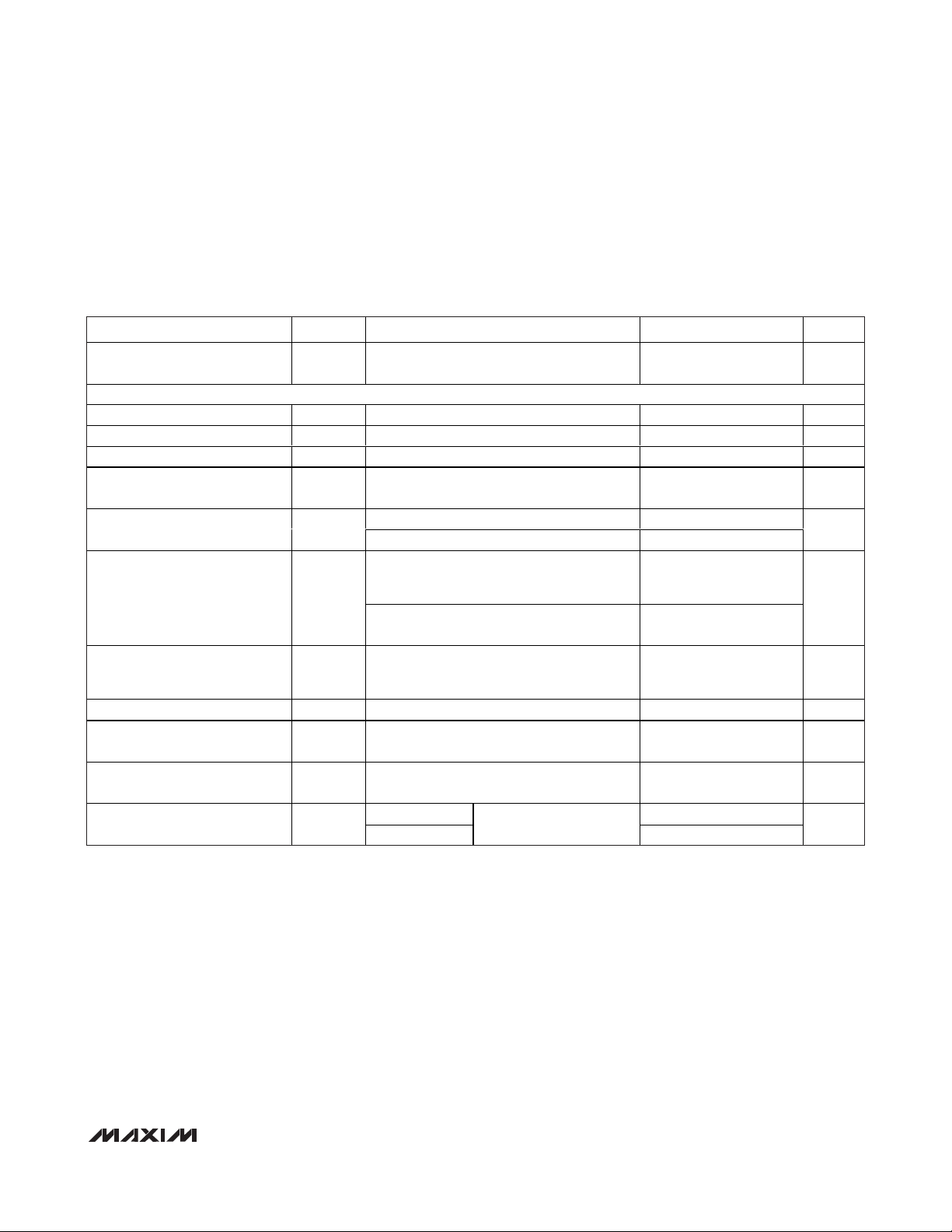
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS—CW MIXER MODE
(
Typical Application Circuit
, Figure 7. VCC= V
REF
= 4.75V to 5.25V, TA= 0°C to +70°C, V
GND
= 0, LOW_PWR = 0, M4_EN = 0,
CW_FILTER = 1, TMODE = 0, PD = 0, CW_VG = 0, CW_M1 = 0, CW_M2 = 0, VG_CLAMP_MODE = 1, f
RF
= fLO/16 = 5MHz, capaci-
tance to GND at each of the VGA differential outputs is 60pF, differential capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF, R
L
= 1kΩ, CW
mixer outputs pulled up to +11V through four separate ±0.1% 115Ω resistors, differential mixer inputs are driven from a low impedance source. Typical values are at V
CC
= V
REF
= 5V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 2)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Maximum Output Voltage at
ClampOFF
CW MIXER MODE
Mixer RF Frequency Range 0.9 7.6 MHz
Mixer LO Frequency Range 1 7.5 MHz
Mixer IF Frequency Range 100 kHz
Maximum Input Voltage Range 1.8
Differential Input Resistance
Input-Referred Noise Voltage
Third-Order Intermodulation
Distortion
M i xe r O utp ut V ol tag e C om p l i ance (Note 11) 4.75 12 V
Channel-to-Channel Phase
Matching
Channel-to-Channel Gain
Matching
Transconductance (Note 13)
IMD3
VG_CLAMP_MODE = 1, VG_CTL set for
+20dB of gain, 350mV
CW_FILTER = 0 633
CW_FILTER = 1 1440
M od e 3, fRF = fLO/4 = 1.25M H z, m easur ed at a
1kH z offset fr eq uency; cl utter tone at 0.9V
d i ffer enti al m easur ed at the m i xer i np ut
M od e 3, RF ter m i nated i nto 50Ω; f
1.25M H z, m easur ed at 1kH z offset
M od e 1, f
i np ut, D op p l er tone f
fr om cl utter tone, f
Measured under zero beat conditions,
f
= 5MHz, f
RF
Measured under zero beat conditions,
f
= 5MHz, fLO/16 = 5MHz (Note 12)
RF
CW_FILTER = 1 2.8
CW FILTER = 0
= 5M H z at 0.9V
RF 1
LO
/16 = 5MHz (Note 12)
LO
differential input
P-P
P - P
/4 =
L O
d i ffer enti al
P - P
= 5.01M H z at 25d Bc
RF 2
/16 = 5M H z ( N ote 10)
f
= 1.1MHz, 1V
RF
d i ffer enti al , fLO/16 = 1MHz
P - P
2.8
6
4.6
-50 dBc
±3.0 Degrees
±2 dB
2.8
V
d i ffer enti al
V
d i ffer enti al
nV/√Hz
mS
P-P
P-P
Ω
Page 6

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS—CW MIXER MODE (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit
, Figure 7. VCC= V
REF
= 4.75V to 5.25V, TA= 0°C to +70°C, V
GND
= 0, LOW_PWR = 0, M4_EN = 0,
CW_FILTER = 1, TMODE = 0, PD = 0, CW_VG = 0, CW_M1 = 0, CW_M2 = 0, VG_CLAMP_MODE = 1, f
RF
= fLO/16 = 5MHz, capaci-
tance to GND at each of the VGA differential outputs is 60pF, differential capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF, R
L
= 1kΩ, CW
mixer outputs pulled up to +11V through four separate ±0.1% 115Ω resistors, differential mixer inputs are driven from a low impedance source. Typical values are at V
CC
= V
REF
= 5V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 2)
Note 2: Specifications at TA= +25°C and TA = +70°C are guaranteed by production test. Specifications at TA= 0°C are guaran-
teed by design and characterization.
Note 3: Noise performance of the device is dependent on the noise contribution from the supply to V
REF
. Use a low-noise supply for
V
REF
. V
CC
and V
REF
can be connected together to share the same supply voltage if the supply for V
CC
exhibits low noise.
Note 4: Total on-chip power dissipation is calculated as P
DISS
= V
CC
x ICC+ V
REF
x I
REF
+ [11V - (I
MIX
/4) x 115] x I
MIX
.
Note 5: Note that the LVDS CWD LO clocks are DC-coupled. This is to ensure immediate synchronization when the clock is first
turned on. An AC-coupled LO is problematic in that the RC time constant associated with the coupling capacitors and the
input impedance of the pin causes there to be a period of time (related to the RC time constant) when the DC level on the
chip side of the capacitor is outside the acceptable common-mode range and the LO swing does not exceed both the
logic thresholds required for proper operation. This problem associated with AC-coupling would cause an inability to
ensure synchronization among beam-forming channels. The LVDS signal is terminated differentially with an external 100Ω
resistor on the board.
Note 6: External 100Ω resistor terminates the LVDS differential signal path.
Note 7: The mixer common-mode current (3.25mA/channel) is specified as the common-mode current in each of the differential
mixer outputs (CW_QOUT+, CW_QOUT-, CW_IOUT+, CW_IOUT-).
Note 8: Specification guaranteed only for DOUT driving DIN of the next device in a daisy-chain fashion.
Note 9: This response time does not include the CW output highpass filter. When switching to VGA mode, the CW outputs stop
drawing current and the output voltage goes to the rail. If a highpass filter is used, the recovery time can be excessive and
a switching network is recommended as shown in the
Applications Information
section.
Note 10: See the
Ultrasound-Specific IMD3 Specification
in the
Applications Information
section.
Note 11: Mixer output-voltage compliance is the range of acceptable voltages allowed on the CW mixer outputs.
Note 12: Channel-to-channel gain-and-phase matching measured on 30 pieces during engineering characterization at room tem-
perature. Each mixer is used as a phase detector and produces a DC voltage in the IQ plane. The phase is given by the
angle of the vector drawn on that plane. Multiple channels from multiple parts are compared to each other to produce the
phase variation.
Note 13: Transconductance is defined as the quadrature summing of the CW differential output current at baseband divided by the
mixer’s input voltage.
SERIAL SHIFT REGISTER
Serial Shift Register
Programming Rate
Minimum Data Set-Up Time t
Minimum Data Hold Time t
Minimum Data Clock Time t
Minimum Data Clock Pulse Width
High
Minimum Data Clock Pulse Width
Low
Minimum Load Line t
Minimum Load Line High to
Mixer Clock On
Minimum Data Clock to Load
Line High
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
DSU
HLD
DCLK
t
DCLKPWH
t
DCLKPWL
LD
t
MIXCLK
t
CLH
30 ns
2ns
100 ns
30 ns
30 ns
30 ns
30 ns
30 ns
10 MHz
Page 7
MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
Typical Operating Characteristics
(Figure 7, VCC= V
REF
= 4.75V to 5.25V, V
GND
= 0, PD = 0, VG_CLAMP_MODE = 1, fRF= 5MHz, capacitance to GND at each of the
VGA differential outputs is 60pF, differential capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF, R
L
= 1kΩ, TA= 0°C to +70°C. Typical
values are at V
CC
= V
REF
= 5V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
0
1.0
0.5
2.0
1.5
3.0
2.5
3.5
4.5
4.0
5.0
0 5.0 7.52.5 10.0 12.5 15.0 17.5 20.0
OVERDRIVE PHASE DELAY
vs. FREQUENCY
MAX2038 toc01
FREQUENCY (MHz)
OVERDRIVE PHASE DELAY (ns)
V
IN1
= 35mV
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
V
IN2
= 87.5mV
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
GAIN = 20dB
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
0755025 100 125 150 175 200
POWER-SUPPLY MODULATION RATIO
MAX2038 toc02
FREQUENCY (kHz)
PSMR (dBc)
V
OUT
= 1.5V
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
V
MOD
= 50mV
P-P
, f
CARRIER
= 5MHz,
GAIN = 10dB
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
-15 -5 5 15 25 35
TWO-TONE ULTRASOUND-SPECIFIC
IMD3 vs. GAIN
MAX2038 toc03
GAIN (dB)
IMD3 (dBc)
V
OUT
= 1V
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
f = 10MHz
f = 2MHz
f = 5MHz
-100
-80
-90
-60
-70
-40
-50
-30
-10
-20
0
-15 5-5 15 25 35
SECOND HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. GAIN
MAX2038 toc04
GAIN (dB)
HD2 (dBc)
V
OUT
= 1V
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
f = 12MHz
f = 2MHz
f = 5MHz
-100
-80
-90
-60
-70
-40
-50
-30
-10
-20
0
-15 5-5 15 25 35
THIRD HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. GAIN
MAX2038 toc05
GAIN (dB)
HD3 (dBc)
V
OUT
= 1V
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
f = 12MHz
f = 2MHz
f = 5MHz
OVERLOAD RECOVERY TIME
MAX2038 toc06
DIFFERENTIAL
OUTPUT
1.0V/div
DIFFERENTIAL
INPUT
1.0V/div
400ns/div
f = 5MHz
OUTPUT 1V
P-P
TO OVERLOAD AND BACK TO 1V
P-P
OVERLOAD RECOVERY TIME
OUTPUT 100mV
AND BACK TO 100mV
P-P
TO OVERLOAD
P-P
400ns/div
MAX2038 toc07
f = 5MHz
DIFFERENTIAL
OUTPUT
2.0V/div
DIFFERENTIAL
INPUT
2.0V/div
Page 8

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(Figure 7, VCC= V
REF
= 4.75V to 5.25V, V
GND
= 0, PD = 0, VG_CLAMP_MODE = 1, fRF= 5MHz, capacitance to GND at each of the
VGA differential outputs is 60pF, differential capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF, R
L
= 1kΩ, TA= 0°C to +70°C. Typical
values are at V
CC
= V
REF
= 5V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
CHANNEL-TO-CHANNEL CROSSTALK
-60
V
= 1.5V
OUT
f = 10MHz, ADJACENT CHANNELS
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
CROSSTALK (dB)
-90
-95
-100
-15 5-5 15 25 35
GAIN vs. DIFFERENTIAL ANALOG
CONTROL VOLTAGE (VG_CTL)
35
25
15
5
GAIN (dB)
-5
-15
-25
-2.5 -0.5-1.5 0.5 1.5 2.5
vs. GAIN
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
GAIN (dB)
VG_CTL (V
DIFFERENTIAL)
P-P
f = 5MHz
CHANNEL-TO-CHANNEL CROSSTALK
vs. FREQUENCY
-30
V
= 1V
DIFFERENTIAL
OUT
P-P
GAIN = 10dB, ADJACENT CHANNELS
-40
MAX2038 toc08
-50
-60
-70
-80
CROSSTALK (dB)
-90
-100
-110
1 10 100
FREQUENCY (MHz)
LARGE-SIGNAL BANDWIDTH
vs. FREQUENCY
40
V
= 1.5V
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
FREQUENCY (MHz)
MAX2038 toc11
OUT
VG_CTL = -2V
35
30
25
20
GAIN (dB)
15
10
5
0
0.1 10 1001 1000
OUTPUT-REFERRED NOISE VOLTAGE
50
f = 5MHz
Hz)
√
MAX2038 toc09
40
30
20
10
OUTPUT-REFERRED NOISE VOLTAGE (nV/
0
-15 5-5 15 25 35
LARGE-SIGNAL BANDWIDTH
vs. FREQUENCY
30
V
= 1.5V
OUT
P-P
VG_CTL = -1V
25
MAX2038 toc12
20
15
10
GAIN (dB)
5
0
-5
-10
0.1 10 1001 1000
FREQUENCY (MHz)
vs. GAIN
GAIN (dB)
DIFFERENTIAL
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
MAX2038 toc10
MAX2038 toc13
LARGE-SIGNAL BANDWIDTH
vs. FREQUENCY
20
V
= 1.5V
OUT
VG_CTL = +0.6V
15
10
5
0
GAIN (dB)
-5
-10
-15
-20
0.1 10 1001 1000
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
FREQUENCY (MHz)
MAX2038 toc14
-10
GAIN (dB)
-15
-20
-25
-30
LARGE-SIGNAL BANDWIDTH
vs. FREQUENCY
10
V
= 1.5V
OUT
VG_CTL = +1.5V
5
0
-5
0.1 10 1001 1000
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
P-P
FREQUENCY (MHz)
MAX2038 toc15
LARGE-SIGNAL BANDWIDTH
vs. FREQUENCY
5
V
= 1V
DIFFERENTIAL
OUT
P-P
VG_CTL = +1.7V
0
-5
-10
-15
GAIN (dB)
-20
-25
-30
-35
0.1 10 1001 1000
FREQUENCY (MHz)
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
MAX2038 toc16
Page 9

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(Figure 7, VCC= V
REF
= 4.75V to 5.25V, V
GND
= 0, PD = 0, VG_CLAMP_MODE = 1, fRF= 5MHz, capacitance to GND at each of the
VGA differential outputs is 60pF, differential capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF, R
L
= 1kΩ, TA= 0°C to +70°C. Typical
values are at V
CC
= V
REF
= 5V, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
-100
-90
-95
-80
-85
-70
-75
-65
-45
-50
-55
-60
-40
56525 45 85 105
HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT LOAD CAPACITANCE
MAX2038 toc20
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT LOAD (pF)
HARMONIC DISTORTION (dBc)
THIRD HARMONIC
SECOND HARMONIC
V
OUT
= 1V
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
f = 5MHz, GAIN = 10dB
-100
-80
-90
-60
-70
-40
-50
-30
-10
-20
0
02010 30 40 50
HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. FREQUENCY
MAX2038 toc21
FREQUENCY (MHz)
HARMONIC DISTORTION (dBc)
V
OUT
= 1V
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
GAIN = 10dB
THIRD HARMONIC
SECOND HARMONIC
-70
-60
-50
-40
-10
-20
-30
0
015510 2025
TWO-TONE ULTRASOUND-SPECIFIC IMD3
vs. FREQUENCY
MAX2038 toc22
FREQUENCY (MHz)
IMD3 (dBc)
V
OUT
= 1V
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
GAIN = 10dB
0
20
15
50
10
5
25
30
35
40
45
0.40
-0.40
-0.35
-0.30
-0.25
-0.20
-0.15
-0.10
-0.05
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
GAIN ERROR HISTOGRAM
MAX2038 toc23
GAIN ERROR (dB)
% OF UNITS
SAMPLE SIZE = 202 UNITS,
f
IN_
= 5MHz, GAIN = 10dB
-20
-10
-15
0
-5
10
5
15
20
-15 5-5 15 25 35
OUTPUT COMMON-MODE OFFSET VOLTAGE
vs. GAIN
MAX2038 toc24
GAIN (dB)
OFFSET VOLTAGE (mV)
0.1 10 100
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT IMPEDANCE
MAGNITUDE vs. FREQUENCY
MAX2038 toc25
FREQUENCY (MHz)
|
Z
OUT|
1
200
60
80
100
120
140
180
160
LARGE-SIGNAL BANDWIDTH
0
V
= 0.5V
OUT
VG_CTL = +2V
-5
-10
-15
-20
GAIN (dB)
-25
-30
-35
-40
0.1 10 1001 1000
vs. FREQUENCY
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
DIFFERENTIAL
P-P
FREQUENCY (MHz)
HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE
0
V
= 1V
DIFFERENTIAL
OUT
-10
MAX2038 toc17
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
HARMONIC DISTORTION (dBc)
-80
-90
-100
01.50.5 1.0 2.0 2.5 3.0
P-P
f = 5MHz, GAIN = 10dB
THIRD HARMONIC
SECOND HARMONIC
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V
MAX2038 toc18
HARMONIC DISTORTION (dBc)
)
P-P
HARMONIC DISTORTION
vs. DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT LOAD RESISTANCE
-40
V
= 1V
DIFFERENTIAL
OUT
-45
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
-85
-90
-95
-100
200 1100500 800 1400 1700 2000
P-P
f = 5MHz, GAIN = 10dB
DIFFERENTIAL OUTPUT LOAD (Ω)
THIRD HARMONIC
SECOND HARMONIC
MAX2038 toc19
Page 10

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(Figure 7, VCC= V
REF
= 4.75V to 5.25V, V
GND
= 0, LOW_PWR = 0, M4_EN = 0, CW_FILTER = 1, TMODE = 0, PD = 0, CW_VG = 0,
CW_M1 = 0, CW_M2 = 0, CW mixer outputs pulled up to 11V through four separate ±0.1% 115Ω resistors, differential mixer inputs
are driven from a low-impedance source.
CW FILTER RESPONSE
(CW_FILTER = 1)
MAX2038 toc26
FREQUENCY (MHz)
LOSS (dB)
14128 104 62
-12
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
-14
016
CW FILTER RESPONSE
(CW_FILTER = 0)
MAX2038 toc27
FREQUENCY (MHz)
LOSS (dB)
14128 104 62
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
5
-30
016
CW IMD3 vs. FREQUENCY
(MODE 1, V
RF
= 900mV
P-P DIFF
, VCC = V
REF
)
MAX2038 toc28
FREQUENCY (MHz)
CW IMD3 (dBc)
642
-53
-52
-51
-50
-49
-48
-47
-46
-54
0
8
4.75
5.00
5.25
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
INPUT-REFERRED NOISE vs. CLUTTER VOLTAGE
(MODE 4, F_CLUTTER = 1.25MHz AT 1kHz OFFSET)
14
12
10
8
MAX2038 toc29
6
4
INPUT-REFERRED NOISE (nV/√Hz)
2
0
0
CLUTTER VOLTAGE (V
P-P DIFF
1.51.00.5
2.0
)
Page 11

MAX2038
Pin Description
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1 CWIN2- CW Mixer Channel 2 Inverting Differential Input
2 CWIN2+ CW Mixer Channel 2 Noninverting Differential Input
3 VGIN3- VGA Channel 3 Inverting Differential Input
4 VGIN3+ VGA Channel 3 Noninverting Differential Input
5, 10, 19,
24, 29, 34,
58, 79,
81, 96
6 CWIN3- CW Mixer Channel 3 Inverting Differential Input
7 CWIN3+ CW Mixer Channel 3 Noninverting Differential Input
8 VGIN4- VGA Channel 4 Inverting Differential Input
9 VGIN4+ VGA Channel 4 Noninverting Differential Input
11 CWIN4- CW Mixer Channel 4 Inverting Differential Input
12 CWIN4+ CW Mixer Channel 4 Noninverting Differential Input
13 EXT_C1
14 EXT_C2
15 EXT_C3
16, 42, 46,
54, 72,
82, 87
17 VGIN5- VGA Channel 5 Inverting Differential Input
18 VGIN5+ VGA Channel 5 Noninverting Differential Input
20 CWIN5- CW Mixer Channel 5 Inverting Differential Input
21 CWIN5+ CW Mixer Channel 5 Noninverting Differential Input
22 VGIN6- VGA Channel 6 Inverting Differential Input
23 VGIN6+ VGA Channel 6 Noninverting Differential Input
25 CWIN6- CW Mixer Channel 6 Inverting Differential Input
26 CWIN6+ CW Mixer Channel 6 Noninverting Differential Input
27 VGIN7- VGA Channel 7 Inverting Differential Input
28 VGIN7+ VGA Channel 7 Noninverting Differential Input
30 CWIN7- CW Mixer Channel 7 Inverting Differential Input
31 CWIN7+ CW Mixer Channel 7 Noninverting Differential Input
32 VGIN8- VGA Channel 8 Inverting Differential Input
33 VGIN8+ VGA Channel 8 Noninverting Differential Input
35 CWIN8- CW Mixer Channel 8 Inverting Differential Input
36 CWIN8+ CW Mixer Channel 8 Noninverting Differential Input
GND Ground
External Compensation. Connect a 4.7μF capacitor to ground as c lose as possible to the pin to
bypass the internal biasing circuitry.
External Compensation. Connect a 4.7μF capacitor to ground as c lose as possible to the pin to
bypass the internal biasing circuitry.
External Compensation. Connect a 4.7μF capacitor to ground as c lose as possible to the pin to
bypass the internal biasing circuitry.
V
CC
5V Power Supply. Connect to an external +5V power supply. Bypass each VCC supply to ground
with 0.1μF capacitors as close as possible to the pins.
Page 12

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Pin Description (continued)
PIN NAME FUNCTION
+5V Reference Supply. Connect to a low-noise power supply. Bypass to GND with a 0.1µF capacitor
37, 93 V
REF
as close as possible to the pins. Note that noise performance of the device is dependent on the noise
contribution from the supply to V
connected together to share the same supply voltage if the supply for V
. Use a low-noise supply for V
REF
. V
REF
and V
CC
exhibits low noise.
CC
REF
can be
38 EXT_RES
39 CW_VG
40 PD
41 CW_FILTER
43 M4_EN
44 LOW_PWR Low-Power Enable. Set high to enable low-power CW mixer mode for the device.
45 DOUT
47 N.C. No Connect. Leave this pin unconnected.
48 LO8 CW LO Input for Channel 8. LO clock input for modes 3 and 4.
49 VGOUT8+ VGA Channel 8 Noninverting Differential Output
50 VGOUT8- VGA Channel 8 Inverting Differential Output
51 LO7 CW LO Input for Channel 7. LO clock input for modes 3 and 4.
52 VGOUT7+ VGA Channel 7 Noninverting Differential Output
53 VGOUT7- VGA Channel 7 Inverting Differential Output
55 LO6 CW LO Input for Channel 6. LO clock input for modes 3 and 4.
56 VGOUT6+ VGA Channel 6 Noninverting Differential Output
57 VGOUT6- VGA Channel 6 Inverting Differential Output
59 LO5 CW LO Input for Channel 5. LO clock input for modes 3 and 4.
60 VGOUT5+ VGA Channel 5 Noninverting Differential Output
61 VGOUT5- VGA Channel 5 Inverting Differential Output
62 VG_CTL-
63 VG_CTL+
64 LO_LVDS- CW LVDS LO Inverting Differential Input. LO clock inverting input for modes 1 and 2.
65 LO_LVDS+ CW LVDS LO Noninverting Differential Input. LO clock noninverting input for modes 1 and 2.
66 LO4 CW LO Input for Channel 4. LO clock input for modes 3 and 4.
67 VGOUT4+ VGA Channel 4 Noninverting Differential Output
68 VGOUT4- VGA Channel 4 Inverting Differential Output
69 LO3 CW LO Input for Channel 3. LO clock input for modes 3 and 4.
70 VGOUT3+ VGA Channel 3 Noninverting Differential Output
External Resistor. Connect a 0.1% 7.5kΩ resistor to ground as close as possible to the pin to set the
bias for the internal biasing circuitry.
CW Mixer VGA Enable. Selects for VGA or CW mixer operation. Set CW_VG to a logic-high to enable
the VGAs while the CW mixers are powered down. Set CW_VG to a logic-low to enable the CW mixers
while the VGAs are powered down.
Power-Down Switch. Drive PD high to set the device in power-down mode. Drive PD low for normal
operation.
CW Filter Mode Corner Frequency Select. Selects in corner frequency of the internal lowpass filter for
the CW path. Set CW_FILTER to a logic-high for a corner frequency of 9.5MHz. Set CW_FILTER to a
logic-low for a corner frequency of 4.5MHz.
Mode 4 Enable. Set M4_EN to a logic-high to override the serial port and activate all 8 channels of the
CW path.
Serial Port Data Output. Data output for ease of daisy-chaining CW channels for analog beamforming
programming.
VGA Analog Gain Control Differential Input. Set the differential voltage to -2V for maximum gain
(+29.5dB), and to +2V for minimum gain (-12.5dB).
Page 13

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
______________________________________________________________________________________ 13
Pin Description (continued)
PIN NAME FUNCTION
71 VGOUT3- VGA Channel 3 Inverting Differential Output
73 LO2 CW LO Input for Channel 2. LO clock input for modes 3 and 4.
74 VGOUT2+ VGA Channel 2 Noninverting Differential Output
75 VGOUT2- VGA Channel 2 Inverting Differential Output
76 LO1 CW LO Input for Channel 1. LO clock input for modes 3 and 4.
77 VGOUT1+ VGA Channel 1 Noninverting Differential Output
78 VGOUT1- VGA Channel 1 Inverting Differential Output
80 DIN Serial Port Data Input. Data input to program the serial shift registers.
83 CLK Serial Port Data Clock. Clock input for programming the serial shift registers.
84 CW_M1
85 CW_M2
86
88 LOAD
89 CW_QOUT+
90 CW_QOUT-
91 CW_IOUT- C W M i xer Inver ti ng D i ffer enti al In- P hase Outp ut. C W m i xer outp ut for ei g ht i n- p hase m i xer s com b i ned .
92 CW_IOUT+
94 VGIN1- VGA Channel 1 Inverting Differential Input
95 VGIN1+ VGA Channel 1 Noninverting Differential Input
97 CWIN1- CW Mixer Channel 1 Inverting Differential Input
98 CWIN1+ CW Mixer Channel 1 Noninverting Differential Input
99 VGIN2- VGA Channel 2 Inverting Differential Input
100 VGIN2+ VGA Channel 2 Noninverting Differential Input
—EP
VG_CLAMP_
MODE
CW Mode Select Input 1. Input for programming beamforming mode 1, 2, 3, or 4. See Table 1 for
mode programming details.
CW Mode Select Input 2. Input for programming beamforming mode 1, 2, 3, or 4. See Table 1 for
mode programming details.
VGA Clamp Mode Enable. Drive VG_CLAMP_MODE high to enable high VGA clamp mode. VGA
output is clamped at typically 2.4V
clamp mode. VGA output is clamped at typically 2.8V
Serial Port Load. Loads the data from the serial shift registers into the I/Q phase dividers. Pull LOAD
bus from high to low and from low to high for programming the I/Q phase dividers.
CW Mixer Noninverting Differential Quadrature Output. CW Mixer output for eight quadrature mixers
combined.
CW Mixer Inverting Differential Quadrature Output. CW mixer output for eight quadrature mixers
combined.
CW Mixer Noninverting Differential In-Phase Output. CW Mixer output for eight in-phase mixers
combined.
Exposed Pad. Internally connected to GND. Connect EP to a large PCB ground plane to maximize
thermal performance.
differential. Drive VG_CLAMP_MODE low to enable low VGA
P-P
differential.
P-P
Page 14

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
14 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Detailed Description
The MAX2038 is an 8-channel VGA integrated with a
programmable octal quadrature mixer array designed
for ultrasound imaging and Doppler applications. The
device is optimized for efficient power consumption,
high dynamic range, and for exceptionally low noise
performance. The VGA path features differential inputs,
analog variable gain control, differential outputs for
direct ADC drive, and a selectable output voltage
clamp to avoid ADC overdrive. The integrated octal
quadrature mixer array includes serial programmable
LO phase generators for CWD beamforming applications. The LO phase dividers can be programmed for 4,
8, or 16 quadrature phases. Lowpass filters are integrated at the input paths of each CW mixer. The outputs for the mixers are summed into single I/Q
differential current outputs.
The MAX2038 also integrates an octal quadrature mixer
array and programmable LO phase generators for a
complete continuous wave (CW) Doppler beamforming
solution. The LO phase selection for each channel is
programmed using a digital serial interface and a single high-frequency clock, or the LOs for each complex
mixer pair can be directly driven using separate 4 x LO
clocks. The serial interface is designed to allow multiple
devices to be easily daisy chained in order to minimize
program interface wiring. The LO phase dividers can
be programmed to allow 4, 8, or 16 quadrature phases.
The input path of each CW mixer consists of a selectable lowpass filter for optimal CWD noise performance.
The outputs of the mixers are summed into single I and
Q differential current outputs. The mixers and LO generators are designed to have exceptionally low noise
performance of -155dBc/Hz at 1kHz offset from a
1.25MHz carrier, measured with 900mV
P-P
differential
clutter signal.
Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA)
The MAX2038’s VGAs are optimized for high linearity,
high dynamic range, and low output-noise performance,
making this component ideal for ultrasound imaging
applications. The VGA paths also exhibit a channel-tochannel crosstalk of -80dB at 10MHz and an absolute
gain error of less than ±0.25dB for minimal channel-tochannel focusing error in an ultrasound system. Each
VGA path includes circuitry for adjusting analog gain, an
output buffer with differential output ports (VGOUT_+,
VGOUT_-) for driving ADCs, and differential input ports
(VGIN_+, VGIN_-), which are ideal for directly interfacing to the MAX2034 quad LNA. See the
High-Level
Wave Mixer and Programmable Beamformer Functional
Diagram
for details.
The VGA has an adjustable gain range from -12.5dB to
+29.5dB, achieving a total dynamic range of 42dB
(typ). The VGA gain can be adjusted through the differential gain control inputs VG_CTL+ and VG_CTL-. Set
the differential gain-control input voltage at +2V for minimum gain and -2V for maximum gain. The differential
analog control common-mode voltage is 3V (typ).
High-Level Wave Mixer and
Programmable Beamformer
_
Functional Diagram
+5V
V
CC
VG_CTL+
VG_CTL-
VGIN1+
VGIN1-
•
•
•
•
•
•
VGIN8+
VGIN8-
LOW_PWR
CWIN1+
CWIN1-
CWIN8+
CWIN8-
•
•
•
PD
•
•
•
+5V (LOW NOISE)
V
REF
MAX2038
50Ω
VGA
I&Q
•
•
•
I&Q
50Ω
50Ω
50Ω
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
VGA
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
VG_CLAMP_MODE
VGOUT1+
VGOUT1-
•
•
•
VGOUT8+
VGOUT8-
CW_IOUT+
CW_IOUT-
CW_QOUT+
CW_QOUT-
CW_VG
CW_FILTER
GND
Page 15

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
______________________________________________________________________________________ 15
VGA Clamp
A clamp is provided to limit the VGA output signals to
avoid overdriving the ADC or to prevent ADC saturation. Set VG_CLAMP_MODE low to clamp the VGA differential outputs at 2.4V
P-P
. Set the VG_CLAMP_MODE
high to disable the clamp.
Power-Down
The device can also be powered down with PD. Set PD
to logic-high for power-down mode. In power-down
mode, the device draws a total supply current of 27mA.
Set PD to a logic-low for normal operation.
Overload Recovery
The device is also optimized for quick overload recovery
for operation under the large input-signal conditions that
are typically found in ultrasound input buffer imaging
applications. See the
Typical Operating Characteristics
for an illustration of the rapid recovery time from a transmit-related overload.
Octal Continuous Wave (CW) Mixer
The MAX2038 CW mixers are designed using an active
double-balanced topology. The mixers achieve high
dynamic range and high linearity performance, with
exceptionally low noise, which is ideal for ultrasound
CWD signal reception. The octal quadrature mixer
array provides noise performance of -155dBc/Hz at
1kHz from a 1.25MHz carrier, and a two-tone thirdorder ultrasound specific intermodulation product of
typically -50dBc. See the
Ultrasound-Specific IMD3
Specification
in the
Applications Information
section
.
The octal array exhibits quadrature and in-phase differential current outputs (CW_QOUT+, CW_QOUT-,
CW_IOUT+, CW_IOUT-) to produce the total CWD
beamformed signal. The maximum differential current
output is typically 3mA
P-P
and the mixer output-compli-
ance voltage ranges from 4.75V to 12V.
High-Level CW Mixer and Programmable
Beamformer Functional Diagram
CWIN8
•
•
•
CWIN2
CWIN1
V
CC
V
REF
•
•
•
CW_IOUT2+
CW_QOUT2-
CW_FILTER M4_EN
MAX2038
CW_IOUT+
CW_IOUT-
•••
•••
•••
•••
CW_QOUT-
CW_QOUT+
I Q
LO_LVDS+
LO_LVDS-
LOAD
DIN
CLK
CHANNEL 1
I/Q
DIVIDER
PHASE
SELECTOR
5
5-BIT
SR
CW_M1
IQ I Q
CHANNEL 2
I/Q
DIVIDER
PHASE
SELECTOR
5
5-BIT
SR
•••
•••
•••
GNDCW_M2
•••
•••
•••
LOW_PWR PD
CHANNEL 8
I/Q
DIVIDER
PHASE
SELECTOR
5
5-BIT
SR
LO1
LO2
•
•
•
LO8
DOUT
Page 16

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
16 ______________________________________________________________________________________
CW Mixer Output Summation
The outputs from the octal mixer array are summed
internally to produce the total CWD summed beamformed signal. The octal array produces eight differential quadrature (Q) outputs and eight differential
in-phase (I) outputs. All quadrature and in-phase outputs are summed into single I and Q differential current
outputs (CW_QOUT+, CW_QOUT-, CW_IOUT+,
CW_IOUT-).
LO Phase Select
The LO phase dividers can be programmed through the
shift registers to allow for 4, 8, or 16 quadrature phases
for a complete CW beamforming solution.
CWD Beamforming Modes
There are four separate modes of operating the CWD
beamformer. See Table 1 for a summary of the different
modes of operation. The mode of operation can be
selected by the CW_M1 and CW_M2 logic inputs.
Phase generation is controlled through the serial interface. See the
Serial Interface
section in the
Applications
Information
section for details on how to program for dif-
ferent quadrature phases.
Mode 1
For mode 1 operation, the LO_LVDS input frequency is
typically 16 x fLO. As the CWD LO frequency range is
1MHz to 7.5MHz, the input frequency ranges from
16MHz to 120MHz. This high LO clock frequency
requires a differential LVDS input. The 16 x fLOinput is
then divided by 16 to produce 16 phases. These 16
phases are generated for each of the 8 channels and
programmed for the selected phase by a serial shift
register. Each channel has a corresponding 5-bit shift
register, which is used to program the output phase of
the divide-by-16 circuit. The first 4 bits of the shift register are for programming the 16 phases, the fifth bit
turns each channel on/off individually. For mode 1, set
both CW_M1 and CW_M2 to a logic-low.
Table 1. Summary of CWD Beamforming Methods
Table 2. Mode 1 Logic Table (B4 = 0:
Channel On/B4 = 1: Channel Off)
N/A = Not applicable.
MODE 1
CW_M1 = 0
CW_M2 = 0
PHASE
(DEG)
0 0 0 0 0 0/1
22.5 0 0 0 1 0/1
45 0 0 1 0 0/1
67.5 0 0 1 1 0/1
90 0 1 0 0 0/1
112.5 0 1 0 1 0/1
135 0 1 1 0 0/1
157.5 0 1 1 1 0/1
180 1 0 0 0 0/1
202.5 1 0 0 1 0/1
225 1 0 1 0 0/1
247.5 1 0 1 1 0/1
270 1 1 0 0 0/1
292.5 1 1 0 1 0/1
315 1 1 1 0 0/1
337.5 1 1 1 1 0/1
MSB LSB SHUTDOWN
DCBA SD
(B0) (B1) (B2) (B3) (B4)
NO. OF
CW_M1 CW_M2 MODE
0 0 1 16 x LVDS 16 phases 1 Yes 4 0
0 1 2 8 x LVDS 8 phases 1 Yes 3 1 MSB
1 0 3 4 x 3V CMOS 4 phases 8 Yes 2 2 MSBs
1 1 4 4 x 3V CMOS
LO INPUT
FREQUENCY
CLOCK
INTERFACE
PHASE
RESOLUTION
Quadrature
provided
CLOCK
INPUTS
PER CHIP
8 No N/A N/A
PROGRAM
BY SERIAL
SHIFT
REGISTER
(SSR)
NO. OF
USEFUL
BITS IN
SSR
NO. OF
DON’T-
CARE BITS
IN SSR
Page 17

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
______________________________________________________________________________________ 17
Mode 2
The LO_LVDS input frequency is 8 x fLO(typ) for mode
2 operation. The CWD LO frequency range is 1MHz to
7.5MHz, and the input frequency ranges from 8MHz to
60MHz. This high LO clock frequency requires a differential LVDS input. The 8 x f
LO
input is then divided by 8
to produce 8 phases. These 8 phases are generated
for each of the 8 channels and programmed for the
selected phase by the serial shift register. Note that the
serial shift register is common to modes 1, 2, 3, and
where each channel has a corresponding 5-bit shift
register, which is used to program the output phase.
However, since mode 2 generates 8 phases only, 3 of
the 4 phase-programming bits are used; 5 bits are still
loaded per channel using the serial shift register, but
the phase-programming MSB is a don’t-care bit. The
fifth bit in the shift register always turns each channel
on/off individually. For mode 2, set CW_M1 to a logiclow and set CW_M2 to a logic-high. See Table 3.
Mode 3
The LO_LVDS input is not used in this mode. Separate
4 x fLOclock inputs are provided using LO1–LO8 for
each channel. The CWD LO frequency range is 1MHz
to 7.5MHz, and the input frequency provides ranges
from 4MHz to 30MHz. Note that the LO clock frequency
can utilize 3V CMOS inputs. The 4 x fLOLO1–LO8
inputs are divided by 4 to produce 4 phases. These
4 phases are generated for each of the 8 channels and
programmed for the selected phase by the serial shift
register. For mode 3, 4 phases are generated, and only
2 of the 4 phase-programming bits are required where
the 2-phase programming MSBs are “don’t-care” bits.
For mode 3, set CW_M1 to a logic-high and set CW_M2
to a logic-low. See Table 4.
Mode 4
The LO_LVDS input is not used in this mode. The
appropriate phases are externally provided using separate 4 x fLOLO1–LO8 inputs for each channel. A 4 x f
LO
input is required so the device can internally generate
accurate duty-cycle independent quadrature LO drives.
Note that the serial shift register is not used in this
mode. The CWD LO frequency range is 1MHz to
7.5MHz and the input frequency ranges from 4MHz to
30MHz. The appropriate inputs are provided at LO1 to
LO8. A reset line is provided to the customer so that
they can synchronize all the CWD channels. The reset
line is implemented through the RESET. For mode 4, set
both CW_M1 and CW_M2 to logic-high. See Table 5.
Table 3. Mode 2 Logic Table (DC = Don’t
Care, B4 = 0: Channel On/B4 = 1: Channel
Off)
Table 4. Mode 3 Logic Table (DC = Don’t
Care, B4 = 0: Channel On/B4 = 1: Channel
Off)
Table 5. Mode 4 Logic Table
N/A = Not applicable.
MODE 2
CW_M1 = 0
CW_M2 = 1
PHASE
(DEG)
0 DC000 0/1
45 DC 0 0 1 0/1
90 DC 0 1 0 0/1
135 DC 0 1 1 0/1
180 DC 1 0 0 0/1
225 DC 1 0 1 0/1
270 DC 1 1 0 0/1
315 DC 1 1 1 0/1
DCBA SD
(B0) (B1) (B2) (B3) (B4)
SHUTDOWN
MODE 3
CW_M1 = 1
CW_M2 = 0
PHASE
(DEG)
0 DC DC 0 0 0/1
90 DC DC 0 1 0/1
180 DC DC 1 0 0/1
270 DC DC 1 1 0/1
DCBA SD
(B0) (B1) (B2) (B3) (B4)
SHUTDOWN
MODE 4
CW_M1 = 1
CW_M2 = 1
PHASE
(DEG)
Serial bus
not used in
mode 4
DCBA SD
(B0) (B1) (B2) (B3) (B4)
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
SHUTDOWN
Page 18

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
18 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Synchronization
Figure 1 illustrates the serial programming of the 8 individual channels through the serial data port. Note that
the serial data can be daisy chained from one part to
another, allowing a single data line to be used to program multiple chips in the system.
CW Lowpass Filter
The MAX2038 also includes selectable lowpass filters
between each CW differential input pair and corresponding mixer input. Shunt capacitors and resistors
are integrated on chip for high band and low band. The
parallel capacitor/resistor networks, which appear differentially across each of the CW differential inputs, are
selectable through the CW_FILTER. Drive CW_FILTER
high to set the corner frequency of the filter to be fC=
9.5MHz. Drive CW_FILTER low to set the corner frequency equal to fC= 4.5MHz. The CW_VG allows the filter inputs to be disconnected from input nodes (internal
to chip) to prevent overloading the LNA output and to
not change the PW input common-mode voltage.
VGA and CW Mixer Operation
During normal operation, the MAX2038 is configured
such that either the VGA path is enabled while the mixer
array is powered down (VGA mode), or the quadrature
mixer array is enabled while the VGA path is powered
down (CW mode). During VGA mode, besides powering
down the CW mixer array, the differential inputs to the
lowpass filters and CW mixers also are internally disconnected from the input nodes, making the CW differential
inputs (CWIN_+, CWIN_-) high impedance. The CW
mode disconnects the VGA inputs internally from the
input ports of the device. For VGA mode, set CW_VG to a
logic-high, while for CW mode, set CW_VG to a logic-low.
Power-Down and Low-Power Modes
During device power-down, both the VGA and CW
mixer are disabled regardless of the logic set at
CW_VG. Both the VGA and CW mixer inputs are high
impedance since the internal switches to the inputs are
all disconnected. The total supply current of the device
reduces to 27mA. Set PD to a logic-high for device
power-down.
A low-power mode is available to lower the required
power for CWD operation. When selected, the complex
mixers operate at lower quiescent currents and the total
per-channel current is lowered to 53mA. Note that
operation in this mode slightly reduces the dynamic
performance of the device. Table 6 shows the logic
function of standard operating modes.
Figure 1. Data Flow of Serial Shift Register
Table 6. Logic Function of Standard Operating Modes
N/A = Not applicable.
CHANNEL 1
DATA_IN
CLOCK
ABCDSD
B3 B2 B1 B0 B4
CHANNEL 5
ABCDSD
B3 B2 B1 B0 B4
ABCDSD
B3 B2 B1 B0 B4
ABCDSD
B3 B2 B1 B0 B4
CHANNEL 2
CHANNEL 6
CHANNEL 3
ABCDSD
B3 B2 B1 B0 B4
CHANNEL 7
ABCDSD
B3 B2 B1 B0 B4
CHANNEL 4
ABCDSD
B3 B2 B1 B0 B4
CHANNEL 8
ABCDSD
B3 B2 B1 B0 B4
DATA_OUT
PD
CW_VG
INPUT
INPUT
1 1 N/A Off Off Off Off 27 0
1 0 N/A Off Off Off Off 27 0
0 0 0 Off On Off On 245 106
0 0 1 Off On Off On 245 53
0 1 N/A On Off On Off 204 0
LOW_PWR VGA
CW
MIXER
INTERNAL
SWITCH
TO VGA
INTERNAL
SWITCH TO LPF
AND CW MIXER
CURRENT
5V V
CC
CONSUMPTION
(mA)
11V V
CURRENT
MIX
CONSUMPTION
(mA)
Page 19

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
______________________________________________________________________________________ 19
Applications Information
Mode Select Response Time
The mode select response time is the time that the
device takes to switch between CW and VGA modes.
One possible approach to interfacing the CW outputs to
an instrumentation amplifier used to drive an ADC is
shown in Figure 2. In this implementation, there are four
large-value (in the range of 470nF to 1µF) capacitors
between each of the CW_IOUT+, CW_IOUT-,
CW_QOUT+, CW_QOUT- outputs and the circuitry they
are driving. The output of the CW mixer usually drives
the input of an instrumentation amplifier made up of op
amps whose input impedance is set by common-mode
setting resistors.
There are clearly both a highpass corner and a lowpass
corner present in this output network. The lowpass corner is set primarily by the 115Ω mixer pullup resistors,
the series 50Ω resistors, and the shunt 0.022µF capacitor. This lowpass corner is used to filter a combination
of LO leakage and upper sideband. The highpass corner, however, is of a larger concern due to the fact that
it is dominated by the combination of a 1µF DC-blocking capacitor and the pair of shunt 31.6kΩ resistors.
If drawn, the simplified dominant highpass network
would look like Figure 3.
The highpass pole in this case is at f
P
= 1/(2 x pi x RC)
~ 5Hz. Note that this low highpass corner frequency is
required in order to filter the downconverted clutter tone,
which appears at DC, but not interfere with CWD imaging
at frequencies as low as 400Hz. For example, if one wanted to use CWD down to 400Hz, then a good choice for
the highpass pole would be at least a decade below this
(< 40Hz) as not to incur rolloff due to pole. Remember, if
the highpass pole is put at 400Hz, the response is 3dB
down at that corner frequency. The placement of the
highpass pole at 5Hz in the above example is between
the DC and 40Hz limitations just discussed.
The bottom line is that any reasonably sized DC block
between the output of the mixer and the instrumentation
amplifier will pose a significant time constant that slows
the mode select switching speed.
An alternative solution to the approach in Figure 2,
which enables faster mode select response time, is
shown in Figure 4.
In Figure 4, the outputs of the CWD mixers are DCcoupled into the inputs of the instrumentation amplifiers. Therefore, the op amps must be able to accommodate the full compliance range of the mixer outputs,
which is a maximum of 11V when the mixers are disabled, down to the 5V supply of the MAX2038 when the
mixers are enabled. The op amps can be powered
from 11V for the high rail and 5V for the low rail, requiring a 6V op amp.
Figure 2. Typical Example of a CW Mixer’s Output Circuit
Figure 3. Simplified Circuit of Highpass Pole
Figure 4. Improved Mode Select Response Time Achieved with
DC-Coupled Input to Instrumentation Amplifier
CW_IOUT-
CW_IOUT+
115Ω115Ω
50Ω
1μF
31.6kΩ
0.022μF
31.6kΩ
1μF
+11V
1μF
31.6kΩ
+5V
Page 20

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
20 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Serial Interface
The serial interface of the MAX2038 programs the LO for
16, 8, or 4 quadrature phases using a serial shift register implementation. Data is shifted into the device on
DIN. The serial shift register clock is applied to the CLK
input. The serial shift register has 5 bits per channel.
The first 4 bits are for phase programming, and the fifth
bit enables or disables each channel of the mixer array.
Each mixer can be programmed to 1 of 16 phases;
therefore, 4 bits are required for each channel for programming. The master high-frequency mixer clock is
applied to differential inputs LO_LVDS+ and LO_LVDS(for modes 1 and 2) and LO_ (for modes 3 and 4). The
LOAD input is provided to allow the user to load the
phase counters with the programming values to generate the correct LO phases. The input signals for mixing
are applied to the eight differential inputs, CWIN_+ and
CWIN_-. The summed I/Q baseband differential outputs
are provided on CW_IOUT+/- and CW_QOUT+/-.
CW_M1 and CW_M2 are used to select one of the four
possible modes of operation. See Table 1.
The serial interface is designed to allow multiple
devices to be easily daisy chained in order to minimize
program interface wiring. DOUT is available for this
daisy-chain function.
Programming the Beamformer
During normal CWD operation, the mixer clock at LO_ or
LO_LVDS+/- is on and the programming signals on DIN,
CLK, and LOAD are off. (LOAD = high, CLK = low, and
DIN = don’t care, but fixed to a high or low). To start the
programming sequence, turn off the mixer clock. Data is
shifted into the shift register at a recommended 10MHz
programming rate or 100ns minimum data clock
period/time. See Figure 5 for timing details.
After the shift registers are programmed, pull the LOAD
bus to logic-low and then back to logic-high to load the
internal counters into I/Q phase divider/selectors with
the proper values. LOAD must remain low for a minimum time of t
CLH
. The user turns on the mixer clock to
start beamforming. The clock must turn on such that it
starts at the beginning of a mixer clock cycle.
Figure 5. Shift Register Timing Diagram
t
DSUtHLD
t
CLH
DIN
CLK
LOAD
MIXER
CLOCK ON
MIXER
CLOCK ON
t
DCLKPWH
t
DCLK
MIXER
CLOCK OFF
t
DCLKPWL
MIXER
CLOCK OFF
MIXER
CLOCK OFF
t
LD
MIXER
CLOCK ON
t
LDMIXCLK
MIXER
CLOCK ON
Page 21

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
______________________________________________________________________________________ 21
CW Mixer Output Summation
The maximum differential current output is typically
3mA
P-P
and the mixer output compliance voltage
ranges from 4.75V to 12V per mixer channel. The mixer
common-mode current in each of the differential mixer
outputs is typically 3.25mA. The total summed current
would equal N x 3.25mA in each of the 115Ω load
resistors (where N = number of channels). In this case,
the quiescent output voltage at +V
SUM
and -V
SUM
out-
puts would be 11V - (N x 3.25mA x 115) = 11V - (8 x
3.25mA x 115) = 8.05V. The voltage swing at each output, with one channel driven at max output current (differential 3mA
P-P
) while the other channels are not
driven, would be 1.5mA
P-P
x 115Ω or 174mV
P-P
and
the differential voltage would be 348mV
P-P
. The voltage
compliance range is defined as the valid range for
+V
SUM
and -V
SUM
in this example.
External Compensation
External compensation is required for bypassing internal biasing circuitry. Connect as close as possible a
4.7µF capacitor from EXT_C1, EXT_C2, and EXT_C3
(pins 13, 14, 15) to ground.
External Bias Resistor
An external resistor at EXT_RES is required to set the
bias for the internal biasing circuitry. Connect, as close
as possible, a 7.5kΩ (0.1%) resistor from EXT_RES (pin
38) to ground.
Analog Input and Output Coupling
In typical applications, the MAX2038 is being driven from
a low-noise amplifier (such as the MAX2034) and the
VGA is typically driving a discrete differential anti-alias filter into an ADC (such as the MAX1436 octal ADC). The
differential input impedance of the MAX2038 is typically
240Ω. The differential outputs of the VGA are capable of
driving a differential load capacitance to GND at each of
the VGA differential outputs of 60pF, and differential
capacitance across the VGA outputs is 10pF, RL=
1kΩ. The differential outputs have a common-mode
bias of approximately 3.75V. AC-couple these differential outputs if the next stage has a different commonmode input range.
Ultrasound-Specific IMD3 Specification
Unlike typical communications specifications, the two
input tones are not equal in magnitude for the ultrasound-specific IMD3 two-tone specification. In this
measurement, f
1
represents reflections from tissue and
f2 represents reflections from blood. The latter reflections are typically 25dB lower in magnitude, and hence
the measurement is defined with one input tone 25dB
lower than the other. The IMD3 product of interest (f
1
-
(f
2
- f1)) presents itself as an undesired Doppler error
signal in ultrasound applications. See Figure 6.
Board Layout
The pin configuration of the MAX2038 is optimized to
facilitate a very compact physical layout of the device
and its associated discrete components. A typical
application for this device might incorporate several
devices in close proximity to handle multiple channels
of signal processing.
The exposed pad (EP) of the MAX2038’s TQFP-EP
package provides a low thermal-resistance path to the
die. It is important that the PCB on which the MAX2038
is mounted be designed to conduct heat from the EP.
In addition, provide the EP with a low-inductance path
to electrical ground. The EP MUST be soldered to a
ground plane on the PCB, either directly or through an
array of plated via holes.
Figure 6. Ultrasound IMD3 Measurement Technique
-25dB
ULTRASOUND
IMD3
f1 - (f2 - f1)f
1
f
+ (f2 - f1)f
2
2
Page 22

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
22 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Figure 7. Typical Per-Channel Ultrasound Imaging Application
CWD
I CHANNELS
TO 12-BIT
IMAGING
ADC
CWD
TO I CHANNEL
MIX
+V
115Ω
ADC
IN
CWD
Q CHANNELS
IN
TO Q CHANNEL
CWD
ADC
MIX
+V
THIRD-ORDER BUTTERWORTH
ANTI-ALIAS FILTER
REF
V
VG_CTL+ VG_CTL-
CC
V
0.1μF
VGOUT_+
50Ω
VGIN_+
0.1μF
50Ω
VGIN_-
VGOUT_-
115Ω
12μH
CWIN_+
100nF
CW_IOUT+
CW_IOUT-
12μH
CWIN_-
100nF
CW_QOUT-
CW_QOUT+
CW_VG
CW_FILTER
115Ω 115Ω
CWD I/Q LO
LO DIVIDER
MAX2038
ONE CHANNEL
GND
MAX2034
D2, D1, D0
ZIN IN CONTROL
100nF
100nF
+V
IN
+V
ONE CHANNEL
100nF
-V
Page 23

MAX2038
Ultrasound VGA Integrated
with CW Octal Mixer
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600 ____________________
23
© 2009 Maxim Integrated Products is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Pin Configuration
Package Information
For the latest package outline information and land patterns, go
to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.
PACKAGE TYPE PACKAGE CODE DOCUMENT NO.
100 TQFP-EP C100E+3
21-0116
Chip Information
PROCESS: Silicon Complementary Bipolar
LO1
VGOUT1+
VGOUT1-
GND
DIN
GND
V
CLK
CW_M1
CW_M2
VG_CLAMP_MODE
V
LOAD
CW_QOUT+
CW_QOUT-
CW_IOUT-
CW_IOUT+
V
VGIN1-
VGIN1+
GND
CWIN1-
CWIN1+
VGIN2-
VGIN2+
CC
CC
REF
TOP VIEW
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
VGOUT2+
LO2
CC
V
VGOUT2-
75747372717069686766656463626160595857565554535251
VGOUT3+
VGOUT3-
LO3
VGOUT4+
VGOUT4-
LO4
LO_LVDS-
LO_LVDS+
VG_CTL-
VG_CTL+
VGOUT5-
VGOUT5+
LO5
GND
VGOUT6-
MAX2038
LO6
VGOUT6+
CC
V
VGOUT7+
VGOUT7-
*EP
LO7
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
VGOUT8-
VGOUT8+
LO8
N.C.
V
CC
DOUT
LOW_PWR
M4_EN
V
CC
CW_FILTER
PD
CW_VG
EXT_RES
V
REF
CWIN8+
CWIN8-
GND
VGIN8+
VGIN8CWIN7+
CWIN7GND
VGIN7+
VGIN7CWIN6+
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10111213141516171819202122232425
CC
VGIN3-
CWIN2+
VGIN3+
CWIN2-
*EP = EXPOSED PAD
GND
CWIN3-
CWIN3+
VGIN4-
VGIN4+
GND
CWIN4-
EXT_C1
CWIN4+
TQFP
EXT_C3
EXT_C2
V
VGIN5-
GND
VGIN5+
CWIN5+
VGIN6+
CWIN6-
CWIN5-
GND
VGIN6-
 Loading...
Loading...