Page 1

General Description
The MAX19999 dual-channel downconverter provides
8.3dB of conversion gain, +24dBm input IP3, +11.4dBm
1dB input compression point, and a noise figure of
10.5dB for 3000MHz to 4000MHz WiMAX™ and LTE
diversity receiver applications. With an optimized LO frequency range of 2650MHz to 3700MHz, this mixer is
ideal for low-side LO injection architectures.
In addition to offering excellent linearity and noise performance, the MAX19999 also yields a high level of
component integration. This device includes two double-balanced passive mixer cores, two LO buffers, and
a pair of differential IF output amplifiers. Integrated onchip baluns allow for single-ended RF and LO inputs.
The MAX19999 requires a nominal LO drive of 0dBm
and a typical supply current of 388mA at VCC= +5.0V
or 279mA at VCC= +3.3V.
The MAX19999 is pin compatible with the MAX19997A
1800MHz to 2900MHz mixer and pin similar with the
MAX19985/MAX19985A and MAX19995/MAX19995A
series of 700MHz to 2200MHz mixers, making this
entire family of downconverters ideal for applications
where a common PCB layout is used across multiple
frequency bands.
The MAX19999 is available in a compact 6mm x 6mm,
36-pin thin QFN package with an exposed pad.
Electrical performance is guaranteed over the extended
temperature range, from TC= -40°C to +85°C.
Applications
3.5GHz WiMAX and LTE Base Stations
Fixed Broadband Wireless Access
Microwave Links
Wireless Local Loop
Private Mobile Radios
Military Systems
Features
o 3000MHz to 4000MHz RF Frequency Range
o 2650MHz to 3700MHz LO Frequency Range
o 50MHz to 500MHz IF Frequency Range
o 8.3dB Conversion Gain
o +24dBm Input IP3
o 10.5dB Noise Figure
o +11.4dBm Input 1dB Compression Point
o 74dBc Typical 2 x 2 Spurious Rejection at
P
RF
= -10dBm
o Dual Channels Ideal for Diversity Receiver
Applications
o Integrated LO Buffer
o Integrated LO and RF Baluns for Single-Ended
Inputs
o Low -3dBm to +3dBm LO Drive
o Pin Compatible with the MAX19997A 1800MHz to
2900MHz Mixer
o Pin Similar to the MAX9995/MAX9995A and
MAX19995/MAX19995A 1700MHz to 2200MHz
Mixers and the MAX9985/MAX9985A and
MAX19985/MAX19985A 700MHz to 1000MHz
Mixers
o 39dB Channel-to-Channel Isolation
o Single +5.0V or +3.3V Supply
o External Current-Setting Resistors Provide Option
for Operating Device in Reduced-Power/ReducedPerformance Mode
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
________________________________________________________________
Maxim Integrated Products
1
Ordering Information
19-4293; Rev 0; 10/08
For pricing, delivery, and ordering information, please contact Maxim Direct at 1-888-629-4642,
or visit Maxim’s website at www.maxim-ic.com.
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX19999ETX+ -40°C to +85°C 36 Thin QFN-EP*
MAX19999ETX+T -40°C to +85°C 36 Thin QFN-EP*
WiMAX is a trademark of WiMAX Forum.
+
Denotes a lead-free/RoHS-compliant package.
*
EP = Exposed pad.
T = Tape and reel.
Pin Configuration/Functional Diagram and Typical
Application Circuit appear at end of data sheet.
Page 2
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
+5.0V SUPPLY DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(
Typical Application Circuit
, no input RF or LO signals applied, VCC= +4.75V to +5.25V, TC= -40°C to +85°C. Typical values are at
V
CC
= +5.0V, TC= +25°C, unless otherwise noted. R1 = R4 = 750Ω, R2 = R5 = 698Ω.)
+3.3V SUPPLY DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(
Typical Application Circuit
, no input RF or LO signals applied, TC= -40°C to +85°C. Typical values are at
V
CC
= +3.3V, TC= +25°C, unless otherwise noted. R1, R4 = 1.1kΩ; R2, R5 = 845Ω.) (Note 5)
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
VCCto GND...........................................................-0.3V to +5.5V
RF_, LO to GND.....................................................-0.3V to +0.3V
IFM_, IFD_, IFM_SET, IFD_SET, LO_ADJ_M,
LO_ADJ_D to GND.................................-0.3V to (V
CC
+ 0.3V)
RF_, LO Input Power ......................................................+15dBm
RF_, LO Current (RF and LO are DC shorted to GND
through balun).................................................................50mA
Continuous Power Dissipation (Note 1) ..............................8.7W
θ
JA
(Notes 2, 3)..............................................................+38°C/W
θ
JC
(Note 3).....................................................................7.4°C/W
Operating Case Temperature Range
(Note 4) ...................................................T
C
= -40°C to +85°C
Junction Temperature......................................................+150°C
Storage Temperature Range .............................-65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C
Note 1: Based on junction temperature TJ= TC+ (θJCx VCCx ICC). This formula can be used when the temperature of the exposed
pad is known while the device is soldered down to a PCB. See the
Applications Information
section for details. The junction
temperature must not exceed +150°C.
Note 2: Junction temperature T
J
= TA+ (θJAx VCCx ICC). This formula can be used when the ambient temperature of the PCB is
known. The junction temperature must not exceed +150°C.
Note 3: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a four-
layer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maxim-ic.com/thermal-tutorial
.
Note 4: T
C
is the temperature on the exposed pad of the package. TAis the ambient temperature of the device and PCB.
RECOMMENDED AC OPERATING CONDITIONS
Supply Voltage VCC 4.75 5 5.25 V
Supply Current ICC Total supply current 388 420 mA
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Supply Voltage V
Supply Current I
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
CC
CC
(Note 6) 3 3.3 3.6 V
Total supply current 279 mA
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RF Frequency f
LO Frequency f
IF Frequency f
LO Drive Level P
RF
LO
IF
LO
(Notes 5, 7) 3000 4000 MHz
(Notes 5, 7) 2650 3700 MHz
Using Mini-Circuits TC4-1W-17 4:1
transformer as defined in the Typical
Application Circuit, IF matching
components affect the IF frequency range
(Notes 5, 7)
Using alternative Mini-Circuits TC4-1W-7A
4:1 transformer, IF matching components
affect the IF frequency range (Notes 5, 7)
(Note 7) -3 +3 dBm
100 500
50 250
MHz
Page 3
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
+5.0V SUPPLY AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(
Typical Application Circuit
, VCC= +4.75V to +5.25V, RF and LO ports are driven from 50Ω sources, PLO= -3dBm to +3dBm,
P
RF
= -5dBm, fRF= 3200MHz to 3900MHz, fLO= 2800MHz to 3600MHz, fIF= 350MHz, fRF> fLO, TC= -40°C to +85°C. Typical val-
ues are at V
CC
= +5.0V, PRF= -5dBm, PLO= 0dBm, fRF= 3550MHz, fLO= 3200MHz, fIF= 350MHz, TC= +25°C, unless otherwise
noted.) (Note 8)
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Conversion Gain G
Conversion Gain Flatness
Gain Variation Over Temperature TC
Input Compression Point IP
Third-Order Input Intercept Point IIP3
Third-Order Input Intercept Point
Variation Over Temperature
Noise Figure NF
Noise Figure Temperature
Coefficient
Noise Figure Under Blocking
Conditions
2RF-2LO Spurious Rejection 2 x 2
3RF-3LO Spurious Rejection 3 x 3
RF Input Return Loss
LO Input Return Loss
IF Output Impedance Z
TC = +25°C (Notes 6, 9) 7.3 8.3 9.3 dB
C
f
= 3200MHz to 3900MHz, over any
TC
NF
CG
1dB
SSB
NF
IF
RF
100MHz band
fRF = 3200MHz to 3900MHz, TC = -40°C to
+85°C
(Notes 6, 9, 10) 9.8 11.4 dBm
f
- f
RF1
(Notes 6, 9)
f
RF
P
RF
(Notes 6, 9)
f
RF1
Single sideband, no blockers present
(Notes 5, 6)
Single sideband, no blockers present,
f
RF
Single sideband, no blockers present,
T
C
f
BLOC KE R
f
RF
B
V
C C
f
RF
3150MHz, f
175MHz, T
f
RF
3150MHz, f
116.67MHz, T
LO on and IF terminated into a matched
impedance
RF and IF terminated into a matched
impedance
Nominal differential impedance at the IC’s
IF outputs
= 1MHz, PRF = -5dBm per tone
RF2
= 3550MHz, f
= -5dBm per tone, TC = +25°C
- f
= 1MHz, TC = -40°C to +85°C ±0.3 dBm
RF2
= 3500MHz, TC = +25°C (Notes 5, 6)
= -40°C to +85°C
= 3700M H z, P
= 3450M H z, fLO = 3100M H z, P LO = 0d Bm,
= 5.0V, TC = + 25°C ( Notes 5, 6, 11)
= 3500MHz, fLO =
SPUR
= +25°C
C
= 3500MHz, fLO =
SPUR
RF1
= fLO +
= fLO +
= +25°C
C
- f
= 1MHz,
RF2
BLOC KE R
PRF = -10dBm,
(Notes 5, 6)
P
(Notes 6, 9)
PRF = -10dBm,
(Notes 5, 6)
P
(Notes 6, 9)
= 8d Bm,
= -5dBm,
RF
= -5dBm,
RF
21.6 24.3
22 24.3
68 74
63 69
77 86
67 76
0.15 dB
-0.01 dB/°C
10.5 13
10.5 11.5
0.018 dB/°C
21 25 dB
15.4 dB
14 dB
200 Ω
dBm
dB
dBc
dBc
Page 4
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
+3.3V SUPPLY AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(
Typical Application Circuit,
typical values are at VCC= +3.3V, PRF= -5dBm, PLO= 0dBm, fRF= 3550MHz, fLO= 3200MHz,
f
IF
= 350MHz, TC= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 8)
+5.0V SUPPLY AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit
, VCC= +4.75V to +5.25V, RF and LO ports are driven from 50Ω sources, PLO= -3dBm to +3dBm,
P
RF
= -5dBm, fRF= 3200MHz to 3900MHz, fLO= 2800MHz to 3600MHz, fIF= 350MHz, fRF> fLO, TC= -40°C to +85°C. Typical val-
ues are at V
CC
= +5.0V, PRF= -5dBm, PLO= 0dBm, fRF= 3550MHz, fLO= 3200MHz, fIF= 350MHz, TC= +25°C, unless otherwise
noted.) (Note 8)
IF Output Return Loss
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RF-to-IF Isolation 28 dB
LO Leakage at RF Port (Notes 6, 9) -31 -24 dBm
2LO Leakage at RF Port -30 dBm
LO Leakage at IF Port -23 dBm
Channel Isolation
Conversion Gain G
Conversion Gain Flatness
Gain Variation Over Temperature TC
Input Compression Point IP
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RF terminated into 50Ω, LO driven by a 50Ω
source, IF transformed to 50Ω using
external components shown in the Typical
Application Circuit
RFMAIN (RFDIV ) converted power
measured at IFDIV (IFMAIN), relative to
IFMAIN (IFDIV), all unused ports terminated
to 50Ω (Notes 6, 9)
C
f
= 3200MHz to 3900MHz, over any
RF
100MHz band
fRF = 3200MHz to 3900MHz, TC = -40°C to
CG
+85°C
1dB
36 39 dB
18 dB
8.0 dB
0.15 dB
-0.01 dB/°C
8.4 dBm
Third-Order Input Intercept Point IIP3 f
Third-Order Input Intercept
Variation Over Temperature
Noise Figure NF
Noise Figure Temperature
Coefficient
2RF-2LO Spurious Rejection 2 x 2 f
3RF-3LO Spurious Rejection 3 x 3 f
RF Input Return Loss
LO Input Return Loss
TC
SSB
NF
- f
RF1
f
RF1
Single sideband, no blockers present 10.5 dB
Single sideband, no blockers present,
T
C
SPUR
SPUR
LO on and IF terminated into a matched
impedance
RF and IF terminated into a matched
impedance
= 1MHz, PRF = -5dBm per tone 20.3 dBm
RF2
- f
= 1MHz, TC = -40°C to +85°C ±0.3 dBm
RF2
= -40°C to +85°C
= fLO + 175MHz
= fLO + 116.67MHz
PRF = -10dBm 74
= -5dBm 69
P
RF
PRF = -10dBm 75
= -5dBm 65
P
RF
0.018 dB/°C
16 dB
15.5 dB
dBc
dBc
Page 5
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 5
+3.3V SUPPLY AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit,
typical values are at VCC= +3.3V, PRF= -5dBm, PLO= 0dBm, fRF= 3550MHz, fLO= 3200MHz,
f
IF
= 350MHz, TC= +25°C, unless otherwise noted.) (Note 8)
Note 5: Not production tested.
Note 6: Guaranteed by design and characterization.
Note 7: Operation outside this range is possible, but with degraded performance of some parameters. See the
Typical Operating
Characteristics
section.
Note 8: All limits reflect losses of external components, including a 0.9dB loss at f
IF
= 350MHz due to the 4:1 impedance trans-
former. Output measurements were taken at IF outputs of the
Typical Application Circuit
.
Note 9: 100% production tested for functional performance.
Note 10: Maximum reliable continuous input power applied to the RF or IF port of this device is +12dBm from a 50Ω source.
Note 11: Measured with external LO source noise filtered so the noise floor is -174dBm/Hz. This specification reflects the effects of
all SNR degradations in the mixer, including the LO noise as defined in Application Note 2021:
Specifications and
Measurement of Local Oscillator Noise in Integrated Circuit Base Station Mixers
.
IF Output Impedance Z
IF Output Return Loss
RF-to-IF Isolation 28 dB
LO Leakage at RF Port -36 dBm
2LO Leakage at RF Port -34 dBm
LO Leakage at IF Port -27 dBm
Channel Isolation
PARAMETER SYMBOL CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
Nominal differential impedance at the IC’s
IF
IF outputs
RF terminated into 50Ω, LO driven by a 50Ω
source, IF transformed to 50Ω using
external components shown in the Typical
Application Circuit
RFM AIN ( RFD IV ) conver ted p ow er
m easur ed at IFD IV ( IFM AIN ) , r el ati ve to
IFM AIN ( IFD IV ) , al l unused p or ts ter m i nated
to 50Ω
200 Ω
19 dB
38.5 dB
Page 6
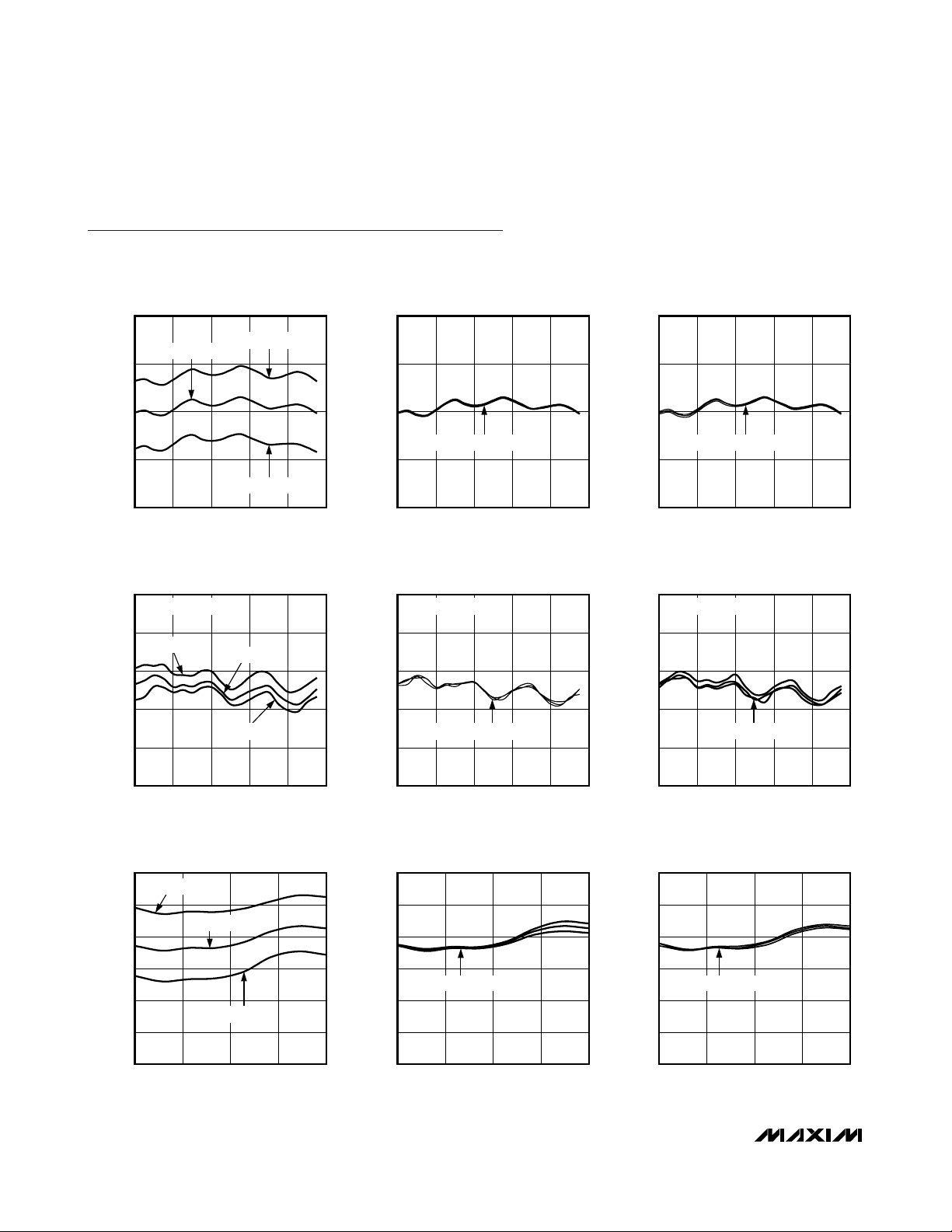
Typical Operating Characteristics
(
Typical Application Circuit
, VCC= +5.0V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
CONVERSION GAIN vs. RF FREQUENCY
10
9
TC = +25°C
8
CONVERSION GAIN (dB)
7
6
3000 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
INPUT IP3 vs. RF FREQUENCY
27
PRF = -5dBm/TONE
26
25
24
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
23
TC = +85°C
TC = +25°C
TC = -30°C
TC = +85°C
TC = -30°C
CONVERSION GAIN vs. RF FREQUENCY
10
MAX19999 toc01
3800360034003200
9
8
CONVERSION GAIN (dB)
7
6
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
3000 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
3800360034003200
MAX19999 toc02
INPUT IP3 vs. RF FREQUENCY
27
PRF = -5dBm/TONE
MAX19999 toc04
26
25
24
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
23
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
MAX19999 toc05
CONVERSION GAIN vs. RF FREQUENCY
10
9
8
CONVERSION GAIN (dB)
7
6
3000 4000
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
INPUT IP3 vs. RF FREQUENCY
27
PRF = -5dBm/TONE
26
25
24
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
23
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
MAX19999 toc03
3800360034003200
MAX19999 toc06
MAX19999 toc08
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
22
3000 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
NOISE FIGURE vs. RF FREQUENCY
13
12
11
10
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
9
8
7
3200 3375 3550 3725 3900
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
22
3000 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
NOISE FIGURE vs. RF FREQUENCY
13
TC = +85°C
12
11
10
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
9
8
7
3200 3900
TC = +25°C
TC = -30°C
372535503375
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
22
3800360034003200
3000 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
3800360034003200
NOISE FIGURE vs. RF FREQUENCY
13
12
MAX19999 toc07
11
10
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
9
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
8
7
3200 3375 3550 3725 3900
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
3800360034003200
MAX19999 toc09
Page 7

Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit
, VCC= +5.0V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
_______________________________________________________________________________________
7
2RF-2LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
90
PRF = -5dBm
80
TC = +85°C
70
2RF-2LO RESPONSE (dBc)
60
50
3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000
TC = +25°C
TC = -30°C
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
3RF-3LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
95
PRF = -5dBm
85
90
MAX19999 toc10
80
70
2RF-2LO RESPONSE (dBc)
60
50
300032003400360038004000
95
MAX19999 toc13
85
2RF-2LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
PRF = -5dBm
PLO = 0dBm
PLO = +3dBm
PLO = -3dBm
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
3RF-3LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
PRF = -5dBm
MAX19999 toc11
MAX19999 toc14
2RF-2LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
90
PRF = -5dBm
80
70
2RF-2LO RESPONSE (dBc)
60
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
50
3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
3RF-3LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
95
PRF = -5dBm
85
MAX19999 toc12
MAX19999 toc15
75
3RF-3LO RESPONSE (dBc)
65
55
13
12
(dBm)
1dB
11
INPUT P
10
9
TC = -30°C, +25°C, +85°C
3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
INPUT P
TC = -30°C
3200 3375 3550 3725 3900
vs. RF FREQUENCY
1dB
TC = +85°C
TC = +25°C
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
75
3RF-3LO RESPONSE (dBc)
65
55
300032003400360038004000
13
MAX19999 toc16
12
(dBm)
1dB
11
INPUT P
10
9
3200 3375 3550 3725 3900
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
INPUT P
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
vs. RF FREQUENCY
1dB
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
75
3RF-3LO RESPONSE (dBc)
65
55
3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000
13
MAX19999 toc17
12
(dBm)
1dB
11
INPUT P
10
9
3200 3375 3550 3725 3900
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
INPUT P
1dB
VCC = 5.25V
VCC = 5.0V
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
vs. RF FREQUENCY
MAX19999 toc18
VCC = 4.75V
Page 8

Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit
, VCC= +5.0V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
CHANNEL ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
50
45
40
CHANNEL ISOLATION (dB)
35
30
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT (dBm)
-50
TC = -30°C, +25°C, +85°C
3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
TC = +25°C, +85°C
TC = -30°C
CHANNEL ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
50
MAX19999 toc19
45
40
CHANNEL ISOLATION (dB)
35
30
300032003400360038004000
0
-10
MAX19999 toc22
-20
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT (dBm)
-50
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
CHANNEL ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
50
MAX19999 toc20
45
40
CHANNEL ISOLATION (dB)
35
30
3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000
0
-10
MAX19999 toc23
-20
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT (dBm)
-50
MAX19999 toc21
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
MAX19999 toc24
-60
2600 2800 3000 3200 3400 3600
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
40
TC = +85°C
30
20
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION (dB)
10
3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000
TC = +25°C
TC = -30°C
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
-60
40
MAX19999 toc25
30
20
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION (dB)
10
260028003000320034003600
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
300032003400360038004000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
-60
2600 2800 3000 3200 3400 3600
40
MAX19999 toc26
30
20
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION (dB)
10
3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
MAX19999 toc27
Page 9

Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit
, VCC= +5.0V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
_______________________________________________________________________________________
9
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
-10
-20
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3100 3500 3900
TC = -30°C, +25°C, +85°C
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
-10
-20
TC = -30°C, +25°C, +85°C
-10
MAX19999 toc28
-20
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3100 3500 3900
-10
MAX19999 toc31
-20
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
-10
MAX19999 toc29
-20
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
-10
MAX19999 toc32
-20
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
2700 3100 3500 3900
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
MAX19999 toc30
MAX19999 toc33
-30
-40
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3100 3500 3900
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
RF PORT RETURN LOSS
vs. RF FREQUENCY
0
5
10
15
20
RF PORT RETURN LOSS (dB)
25
30
3000 3200 3400 3600 3800 4000
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
-30
-40
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3100 3500 3900
fIF = 350MHz
MAX19999 toc34
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
-30
-40
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3100 3500 3900
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
IF PORT RETURN LOSS vs. IF FREQUENCY
0
fLO = 3200MHz
5
10
15
20
IF PORT RETURN LOSS (dB)
25
30
50 140 230 320 410 500
VCC = 4.75V, 5.0V, 5.25V
IF FREQUENCY (MHz)
MAX19999 toc35
Page 10

Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit
, VCC= +5.0V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit,
VCC= +3.3V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
LO PORT RETURN LOSS vs. LO FREQUENCY
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
LO PORT RETURN LOSS (dB)
MAX19999 toc36
2650 2900 3150 3400 3650
25
20
15
10
5
0
PLO = -3dBm
PLO = 0dBm
PLO = +3dBm
CONVERSION GAIN vs. RF FREQUENCY
MAX19999 toc38
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
CONVERSION GAIN (dB)
3800360034003200
7
8
9
10
6
3000 4000
TC = +25°C
TC = -30°C
VCC = 3.3V
TC = +85°C
CONVERSION GAIN vs. RF FREQUENCY
MAX19999 toc39
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
CONVERSION GAIN (dB)
3800360034003200
7
8
9
10
6
3000 4000
VCC = 3.3V
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
CONVERSION GAIN vs. RF FREQUENCY
MAX19999 toc40
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
CONVERSION GAIN (dB)
3800360034003200
7
8
9
10
6
3000 4000
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. TEMPERATURE (TC)
400
VCC = 5.25V
390
MAX19999 toc37
380
370
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
360
350
VCC = 4.75V
-35 -15 5 25 45 65 85
TEMPERATURE (°C)
VCC = 5.0V
Page 11

Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit,
VCC= +3.3V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
______________________________________________________________________________________
11
INPUT IP3 vs. RF FREQUENCY
23
TC = +85°C
22
TC = +25°C
21
20
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
19
18
3000 4000
TC = -30°C
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
NOISE FIGURE vs. RF FREQUENCY
13
TC = +85°C
12
11
PRF = -5dBm/TONE
VCC = 3.3V
3800360034003200
VCC = 3.3V
MAX19999 toc41
MAX19999 toc44
INPUT IP3 vs. RF FREQUENCY
23
22
21
20
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
19
18
3000 4000
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
PRF = -5dBm/TONE
VCC = 3.3V
NOISE FIGURE vs. RF FREQUENCY
13
12
11
VCC = 3.3V
MAX19999 toc42
INPUT IP3 (dBm)
3800360034003200
MAX19999 toc45
INPUT IP3 vs. RF FREQUENCY
23
22
21
20
19
18
3000 4000
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
PRF = -5dBm/TONE
3800360034003200
NOISE FIGURE vs. RF FREQUENCY
13
12
11
MAX19999 toc43
MAX19999 toc46
10
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
9
TC = -30°C
8
7
3200 3900
TC = +25°C
372535503375
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
2RF-2LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
90
80
70
2RF-2LO RESPONSE (dBc)
60
50
TC = +85°C
TC = -30°C
3000 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
PRF = -5dBm
VCC = 3.3V
TC = +25°C
3600 380034003200
10
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
9
8
7
3200 3900
90
MAX19999 toc47
80
70
2RF-2LO RESPONSE (dBc)
60
50
3000 4000
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBmPLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBmPLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
372535503375
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
2RF-2LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
PRF = -5dBm
PLO = 0dBm
PLO = +3dBm
34003200 38003600
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
VCC = 3.3V
PLO = -3dBm
10
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
9
8
7
3200 3900
90
MAX19999 toc48
80
70
2RF-2LO RESPONSE (dBc)
60
50
3000 4000
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
372535503375
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
2RF-2LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
PRF = -5dBm
MAX19999 toc49
VCC = 3.6V
VCC = 3.3V
VCC = 3.0V
34003200 38003600
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
Page 12
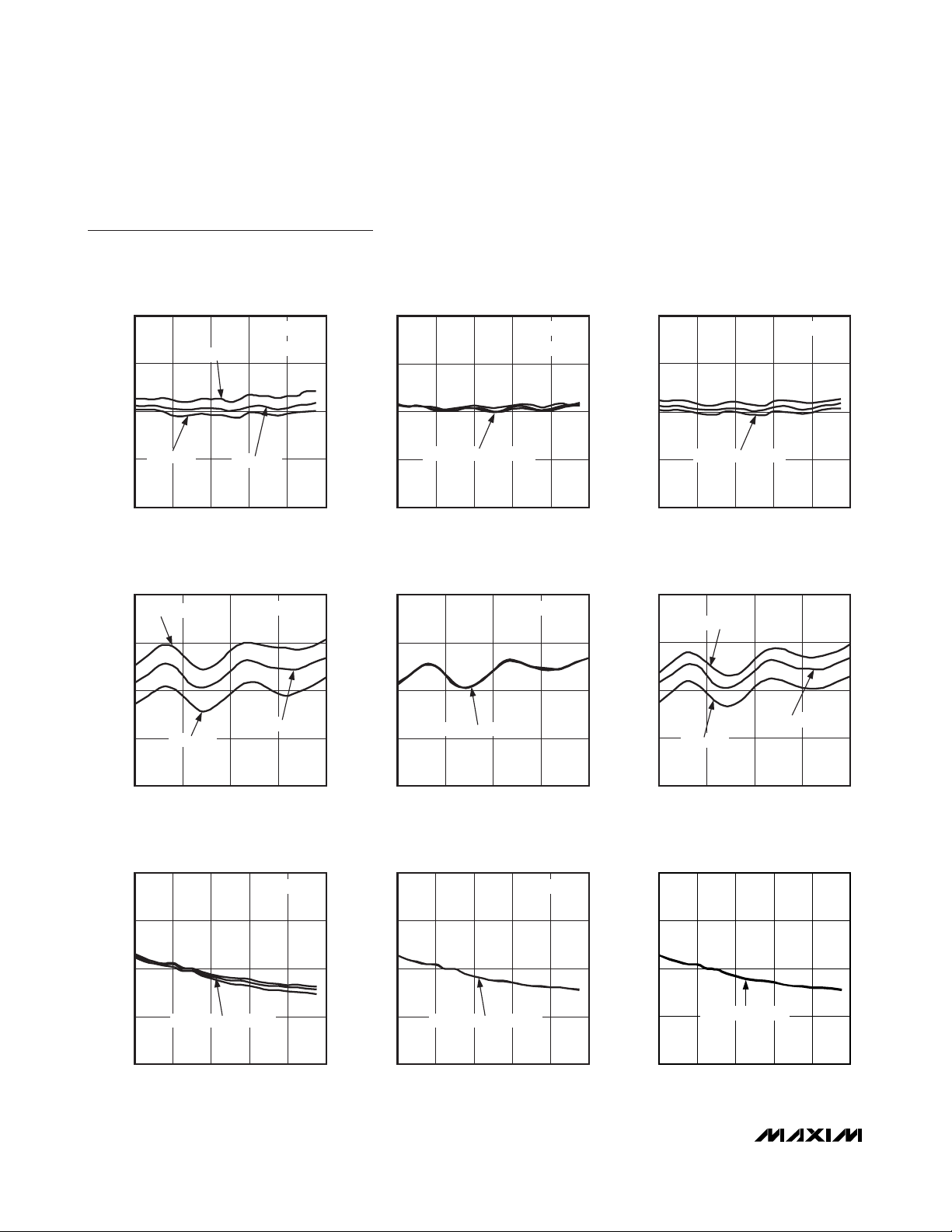
Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit,
VCC= +3.3V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
3RF-3LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
85
75
TC = +85°C
65
3RF-3LO RESPONSE (dBc)
(dBm)
INPUT P
TC = -30°C
55
45
3000 4000
INPUT P
10
TC = +85°C
9
1dB
8
7
34003200 38003600
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
vs. RF FREQUENCY
1dB
TC = -30°C
TC = +25°C
TC = +25°C
PRF = -5dBm
VCC = 3.3V
VCC = 3.3V
85
MAX19999 toc50
75
65
3RF-3LO RESPONSE (dBc)
55
45
3000 4000
10
MAX19999 toc53
9
(dBm)
1dB
8
INPUT P
7
3RF-3LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
PRF = -5dBm
VCC = 3.3V
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
34003200 38003600
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
INPUT P
vs. RF FREQUENCY
1dB
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
VCC = 3.3V
85
MAX19999 toc51
75
65
3RF-3LO RESPONSE (dBc)
55
45
3000 4000
10
MAX19999 toc54
9
(dBm)
1dB
8
INPUT P
7
3RF-3LO RESPONSE vs. RF FREQUENCY
PRF = -5dBm
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
34003200 38003600
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
INPUT P
VCC = 3.0V
vs. RF FREQUENCY
1dB
VCC = 3.6V
VCC = 3.3V
MAX19999 toc52
MAX19999 toc55
6
3200 3900
3550 37253375
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
CHANNEL ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
50
45
40
CHANNEL ISOLATION (dB)
35
30
3000 4000
TC = -30°C, +25°C, +85°C
3400 38003200 3600
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
VCC = 3.3V
MAX19999 toc56
6
3200 3900
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
372535503375
CHANNEL ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
50
45
40
CHANNEL ISOLATION (dB)
35
30
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
3000 4000
3400 38003200 3600
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
VCC = 3.3V
6
3200 3900
CHANNEL ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
50
MAX19999 toc57
45
40
CHANNEL ISOLATION (dB)
35
30
3000 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
372535503375
MAX19999 toc58
3800360034003200
Page 13

Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit,
VCC= +3.3V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
______________________________________________________________________________________
13
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT (dBm)
-50
-60
2600 3600
TC = +85°C
TC = +25°C
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
40
VCC = 3.3V
TC = +85°C
30
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
2600 3600
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
3400320030002800
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
VCC = 3.3V
TC = -30°C
3400320030002800
0
-10
MAX19999 toc59
-20
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT (dBm)
-50
-60
2600 3600
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION vs. RF FREQUENCY
40
VCC = 3.3V
MAX19999 toc62
30
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
VCC = 3.3V
3400320030002800
0
-10
MAX19999 toc60
-20
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT IF PORT (dBm)
-50
-60
40
MAX19999 toc63
30
MAX19999 toc61
MAX19999 toc64
20
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION (dB)
TC = -30°C
10
3000 4000
TC = +25°C
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
-10
-20
TC = -30°C, +25°C, +85°C
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3900
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
VCC = 3.3V
35003100
20
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION (dB)
10
3800360034003200
3000 4000
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
3800360034003200
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
-10
MAX19999 toc65
-20
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3900
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
VCC = 3.3V
35003100
20
RF-TO-IF ISOLATION (dB)
10
3000 4000
-10
MAX19999 toc66
-20
-30
-40
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3900
3800360034003200
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
MAX19999 toc67
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
35003100
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
Page 14

Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(
Typical Application Circuit,
VCC= +3.3V, LO is low-side injected for a 350MHz IF, PLO= 0dBm, PRF= -5dBm, TC=+25°C, unless
otherwise noted.)
MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
14 ______________________________________________________________________________________
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT
vs. LO FREQUENCY
-10
VCC = 3.3V
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT vs.
LO FREQUENCY
-10
VCC = 3.3V
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT vs.
LO FREQUENCY
-10
-20
TC = -30°C, +25°C, +85°C
-30
-40
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3900
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
0
5
10
15
20
RF PORT RETURN LOSS (dB)
25
30
3000 4000
MAX19999 toc68
-20
-30
-40
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
35003100
-50
2700 3100 3500 3900
RF PORT RETURN LOSS vs.
RF FREQUENCY
VCC = 3.3V fIF = 350MHz
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
34003200 3600 3800
RF FREQUENCY (MHz)
PLO = -3dBm, 0dBm, +3dBm
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
MAX19999 toc71
MAX19999 toc69
-20
-30
-40
2LO LEAKAGE AT RF PORT (dBm)
-50
2700 3100 3500 3900
IF PORT RETURN LOSS vs.
IF FREQUENCY
0
5
10
15
20
IF PORT RETURN LOSS (dB)
25
30
50 500
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
230140 320 410
IF FREQUENCY (MHz)
fLO = 3200MHz
MAX19999 toc70
VCC = 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
MAX19999 toc72
LO PORT RETURN LOSS vs.
LO FREQUENCY
0
VCC = 3.3V
5
10
15
LO PORT RETURN LOSS (dB)
20
25
2650 31502900 3400 3650
PLO = -3dBm
PLO = +3dBm
LO FREQUENCY (MHz)
PLO = 0dBm
MAX19999 toc73
300
290
280
270
260
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
250
240
-35 5 25-15 45 65 85
SUPPLY CURRENT vs.
TEMPERATURE (T
VCC = 3.6V
VCC = 3.0V
TEMPERATURE (°C)
C
VCC = 3.3V
)
MAX19999 toc74
Page 15

MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
______________________________________________________________________________________ 15
Detailed Description
The MAX19999 provides high linearity and low noise figure for a multitude of 3000MHz to 4000MHz WiMAX and
LTE base-station applications. This device operates over
an LO range of 2650MHz to 3700MHz and an IF range of
50MHz to 500MHz. Integrated baluns and matching circuitry allow 50Ω single-ended interfaces to the RF and
LO ports. The integrated LO buffer provides a high drive
level to the mixer core, reducing the LO drive required at
the MAX19999’s input to a range of -3dBm to +3dBm.
The IF port incorporates a differential output, which is
ideal for providing enhanced 2RF-2LO performance.
RF Input and Balun
The MAX19999’s two RF inputs (RFMAIN and RFDIV)
provide a 50Ω match when combined with a series DCblocking capacitor. This DC-blocking capacitor is
required because the input is internally DC shorted to
ground through each channel’s on-chip balun. When
using a 1.5pF DC-blocking capacitor, the RF port input
return loss is typically 15dB over the RF frequency
range of 3200MHz to 3900MHz.
LO Input, Buffer, and Balun
A two-stage internal LO buffer allows a wide input
power range for the LO drive. All guaranteed specifications are for an LO signal power from -3dBm to +3dBm.
The on-chip low-loss balun, along with an LO buffer,
drives the double-balanced mixer. All interfacing and
matching components from the LO input to the IF outputs are integrated on chip.
High-Linearity Mixer
The core of the MAX19999 is a pair of double-balanced, high-performance passive mixers. Exceptional
Pin Description
PIN NAME FUNCTION
1 RFMAIN Main Channel RF Input. Internally matched to 50Ω. Requires an input DC-blocking capacitor.
2, 5, 6, 8, 12, 15,
18, 23, 28, 31, 34
3, 7, 20, 22, 24,
25, 26, 27
4, 10, 16, 21,
30, 36
9 RFDIV
11 IFD_SET
13, 14 IFD+, IFD-
17 LO_ADJ_D
19 LO
29 LO_ADJ_M
32, 33 IFM-, IFM+
35 IFM_SET
—EP
GND Ground. Not internally connected. Ground these pins or leave unconnected.
GND
V
CC
Ground. Internally connected to the exposed pad (EP). Connect all ground pins and the exposed
pad together.
Power Supply. Connect bypass capacitors as close as possible to the pin (see the Typical
Application Circuit).
Diversity Channel RF Input. This input is internally matched to 50Ω. Requires a DC-blocking
capacitor.
IF Diversity Amplifier Bias Control. Connect a resistor from this pin to ground to set the bias
current for the diversity IF amplifier.
Diversity Mixer Differential IF Output. Connect pullup inductors from each of these pins to V
(see the Typical Application Circuit).
LO Diversity Amplifier Bias Control. Connect a resistor from this pin to ground to set the bias
current for the diversity LO amplifier.
Local Oscillator Input. This input is internally matched to 50Ω. Requires an input DC-blocking
capacitor.
LO Main Amplifier Bias Control. Connect a resistor from this pin to ground to set the bias current
for the main LO amplifier.
Main Mixer Differential IF Output. Connect pullup inductors from each of these pins to V
(see the Typical Application Circuit).
IF Main Amplifier Bias Control. Connect a resistor from this pin to ground to set the bias current for
the main IF amplifier.
Exposed Pad. Internally connected to GND. Solder this exposed pad to a PCB pad that uses
multiple ground vias to provide heat transfer out of the device into the PCB ground planes. These
multiple via grounds are also required to achieve the noted RF performance
CC
CC
Page 16

MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
16 ______________________________________________________________________________________
linearity is provided by the large LO swing from the onchip LO buffer. When combined with the integrated IF
amplifiers, the cascaded IIP3, 2RF-2LO rejection, and
NF performance is typically +24dBm, 74dBc, and
10.5dB, respectively, for low-side LO injection architectures covering the 3000MHz to 4000MHz RF band.
Differential IF Output Amplifier
The MAX19999 mixers have an IF frequency range of
50MHz to 500MHz. The differential, open-collector IF
output ports require external pullup inductors to VCC.
These pullup inductors are also used to resonate out
the parasitic shunt capacitance of the IC, PCB components, and PCB to provide an optimized IF match at the
frequency of interest. Note that differential IF outputs
are ideal for providing enhanced 2RF-2LO rejection
performance. Single-ended IF applications require a
4:1 balun to transform the 200Ω differential output
impedance to a 50Ω single-ended output. After the
balun, the IF return loss is typically 18dB.
Applications Information
Input and Output Matching
The RF and LO inputs are internally matched to 50Ω. No
matching components are required for RF frequencies
ranging from 3000MHz to 4000MHz. RF and LO inputs
require only DC-blocking capacitors for interfacing.
The IF output impedance is 200Ω (differential). For
evaluation, an external low-loss 4:1 (impedance ratio)
balun transforms this impedance down to a 50Ω singleended output (see the
Typical Application Circuit
).
Reduced-Power Mode
Each channel of the MAX19999 has two pins (LO_ADJ,
IF_SET) that allow external resistors to set the internal
bias currents. Nominal values for these resistors are
given in Table 1. Larger valued resistors can be used to
reduce power dissipation at the expense of some performance loss. If ±1% resistors are not readily available, ±5% resistors can be substituted.
Significant reductions in power consumption can also
be realized by operating the mixer with an optional supply voltage of 3.3V. Doing so reduces the overall power
consumption by up to 53%. See the
+3.3V Supply AC
Electrical Characteristics
table and the relevant +3.3V
curves in the
Typical Operating Characteristics
section
to evaluate the power vs. performance trade-offs.
Layout Considerations
A properly designed PCB is an essential part of any
RF/microwave circuit. Keep RF signal lines as short as
possible to reduce losses, radiation, and inductance.
For the best performance, route the ground pin traces
directly to the exposed pad under the package.
The PCB exposed pad MUST be connected to the
ground plane of the PCB. It is suggested that multiple
vias be used to connect this pad to the lower level
ground planes. This method provides a good RF/thermal-conduction path for the device. Solder the exposed
pad on the bottom of the device package to the PCB.
The MAX19999 evaluation kit can be used as a reference for board layout. Gerber files are available upon
request at www.maxim-ic.com.
Power-Supply Bypassing
Proper voltage-supply bypassing is essential for highfrequency circuit stability. Bypass each VCCpin with
the capacitors shown in the
Typical Application Circuit
.
Exposed Pad RF/Thermal Considerations
The exposed pad (EP) of the MAX19999’s 36-pin thin
QFN-EP package provides a low thermal-resistance
path to the die. It is important that the PCB on which the
MAX19999 is mounted be designed to conduct heat
from the exposed pad. In addition, provide the exposed
pad with a low-inductance path to electrical ground.
The exposed pad MUST be soldered to a ground plane
on the PCB, either directly or through an array of plated
via holes.
Page 17

MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
______________________________________________________________________________________ 17
Table 1. Application Circuit Component Values
*
Use 390nH (0805) inductors for an IF frequency of 200MHz. Contact the factory for details.
DESIGNATION QTY DESCRIPTION SUPPLI ER
C1, C8, C14 3 1.5pF microwave capacitors (0402) Murata Electronics North America, Inc.
C4, C9, C13,
C15, C17, C18
C10, C11, C12,
C19, C20, C21
L1–L4 4 120nH wire-wound high-Q inductors* (0805) Coilcraft, Inc.
R1, R4 2
R2, R5 2
6 0.01µF microwa ve capacitors (0402) Murata Electronics North America, Inc.
6 82pF microwa ve capacitors (0603) Murata Electronics North America, Inc.
750 ±1% resistor (0402). Use for VCC = +5.0V applications.
Larger values can be used to reduce power at the expense
of some performance loss. See the T ypical Operating
Characteristics.
1.1k ±1% resistor (0402). Use for V
Larger values can be used to reduce power at the expense
of some performance loss. See the T ypical Operating
Characteristics.
698 ±1% resistor (0402). Use for VCC = +5.0V applications.
Larger values can be used to reduce power at the expense
of some performance loss. See the T ypical Operating
Characteristics.
845 ±1% resistor (0402). Use for V
Larger values can be used to reduce power at the expense
of some performance loss. See the T ypical Operating
Characteristics.
= +3.3V applications.
CC
= +3.3V applications.
CC
Digi-Key Corp.
Digi-Key Corp.
Digi-Key Corp.
Digi-Key Corp.
0 resistors (1206). The se resi stors can be increased in
R3, R6 2
T1, T2 2 4:1 IF balun TC4-1W-17+ Min i-Circu it s
U1 1 MAX19999 IC (36 TQFN-EP) Max im Integrated Products, Inc.
value to reduce power dissipation in the device but will
reduce the compression point. Full P
achieved using 0.
performance
1dB
Digi-Key Corp.
Page 18

MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to
4000MHz Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
18 ______________________________________________________________________________________
Typical Application Circuit
C19
RF MAIN INPUT
C4
RF DIV INPUT
V
CC
R1
V
CC
C18
CC
V
GND
GND
V
GND
GND
GND
GND
RFDIV
V
CC
+
1
2
3
CC
4
5
6
7
8
9
CC
V
R4
C1
RFMAIN
V
CC
C8
C9
36
10
IFM_SET
35
11
IFD_SET
GND
GND
IFM-
IFM+
34
GND
32
33
MAX19999
EXPOSED
14
13
12
IFD-
IFD+
GND
L1*
CC
V
CC
V
30
16
C21
L2*
C20
LO_ADJ_M
29
17
LO_ADJ_D
R2
GND
28
18
GND
R5
R3
31
PAD
15
T1
4:1
V
CC
GND
27
GND
26
GND
25
GND
24
GND
23
GND
22
V
CC
21
GND
20
LO
19
V
CC
C17
IF MAIN OUTPUT
V
CC
C14
C15
LO
C13
C11
T2
IF DIV OUTPUT
4:1
*USE 390nH (0805) INDUCTORS FOR AN IF FREQUENCY
OF 200MHz. CONTACT THE FACTORY FOR DETAILS.
V
CC
L4*
R6
C12
L3*
C10
Page 19

MAX19999
Dual, SiGe High-Linearity, 3000MHz to 4000MHz
Downconversion Mixer with LO Buffer
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 408-737-7600 ____________________
19
© 2008 Maxim Integrated Products is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Pin Configuration/Functional Diagram
Chip Information
PROCESS: SiGe BiCMOS
Package Information
For the latest package outline information and land patterns, go
to www.maxim-ic.com/packages
.
PACKAGE TYPE PACKAGE CODE DOCUMENT NO.
36 Thin QFN-EP T3666+2
21-0141
TOP VIEW
CC
IFM_SET
RFMAIN
GND
GND
V
GND
GND
GND
GND
RFDIV
V
36
+
1
2
3
4
CC
5
6
7
8
9
10
CC
V
35
11
IFD_SET
GND
34
12
GND
IFM+
33
13
IFD+
THIN QFN-EP
(6mm x 6mm)
EXPOSED PAD ON THE BOTTOM OF THE PACKAGE.
GND
31
MAX19999
EXPOSED
PAD
15
GND
V
CC
V
30
16
CC
LO_ADJ_M
GND
29
28
17
18
GND
LO_ADJ_D
27
GND
26
GND
25
GND
24
GND
23
GND
22
GND
21
V
CC
20
GND
19
LO
IFM-
32
14
IFD-
 Loading...
Loading...