Page 1
19-0305; Rev 2; 9/95
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
_______________General Description
The MAX1649/MAX1651 BiCMOS, step-down, DC-DC
switching controllers provide high efficiency over loads
ranging from 1mA to more than 2.5A. A unique, currentlimited pulse-frequency-modulated (PFM) control scheme
gives these devices the benefits of pulse-width-modulation (PWM) converters (high efficiency at heavy loads),
while using only 100µA of supply current (vs. 2mA to
10mA for PWM converters). Dropout performance down
to 300mV is provided by a high switch duty cycle (96.5%)
and a low current-sense threshold (110mV).
A high switching frequency (up to 300kHz) allows these
devices to use miniature external components.
The MAX1649/MAX1651 have dropout voltages less
than 0.3V at 500mA and accept input voltages up to
16V. Output voltages are preset at 5V (MAX1649), or
3.3V (MAX1651). They can also be adjusted to any
voltage from 1.5V to the input voltage by using two
resistors.
These step-down controllers drive external P-channel
MOSFETs at loads greater than 12.5W. If less power is
required, use the MAX639/MAX640/MAX653 step-down
converters with on-chip FETs, which allow up to a
225mA load current.
________________________Applications
PDAs
High-Efficiency Step-Down Regulation
5V-to-3.3V Green PC Applications
Battery-Powered Applications
____________________________Features
♦ More than 90% Efficiency (10mA to 1.5A Loads)
♦ More than 12.5W Output Power
♦ Less than 0.3V Dropout Voltage at 500mA
♦ 100µA Max Quiescent Supply Current
♦ 5µA Max Shutdown Supply Current
♦ 16V Max Input Voltage
♦ 5V (MAX1649), 3.3V (MAX1651), or Adjustable
Output Voltage
♦ Current-Limited Control Scheme
♦ Up to 300kHz Switching Frequency
♦ Up to 96.5% Duty Cycle
______________Ordering Information
PART TEMP. RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
MAX1649CPA
MAX1649CSA 0°C to +70°C 8 SO
MAX1649C/D 0°C to +70°C Dice*
MAX1649EPA -40°C to +85°C 8 Plastic DIP
MAX1649ESA -40°C to +85°C 8 SO
MAX1651CPA
MAX1651CSA 0°C to +70°C 8 SO
MAX1651C/D 0°C to +70°C Dice*
MAX1651EPA -40°C to +85°C 8 Plastic DIP
MAX1651ESA -40°C to +85°C 8 SO
* Dice are tested at TA= +25°C.
0°C to +70°C 8 Plastic DIP
0°C to +70°C 8 Plastic DIP
MAX1649/MAX1651
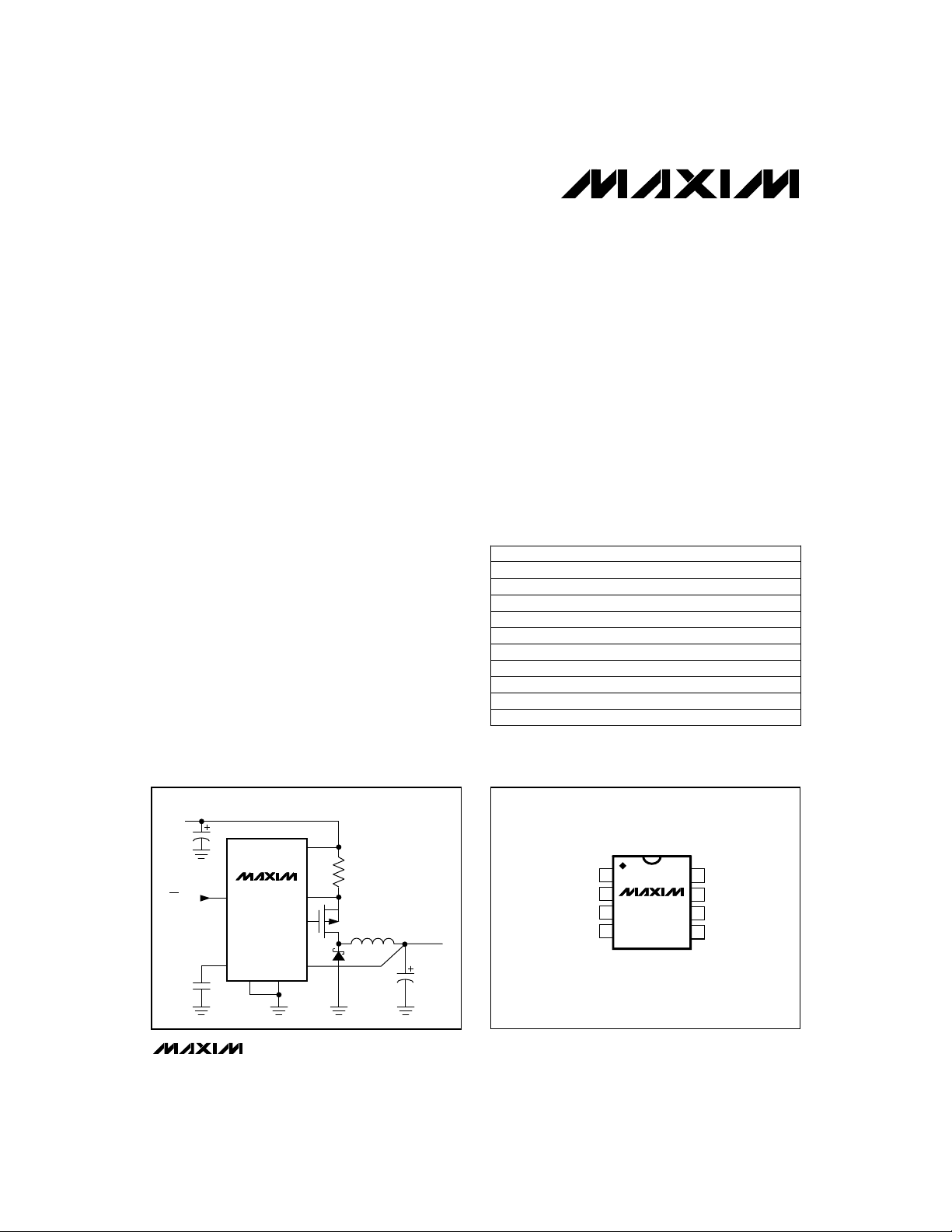
__________Typical Operating Circuit
INPUT
3.6V TO 16V
V+
ON/OFF
REF
MAX1651
FB GND
CSSHDN
EXT
OUT
________________________________________________________________
P
OUTPUT
3.3V
__________________Pin Configuration
TOP VIEW
OUT
1
FB
2
SHDN
REF
MAX1649
3
MAX1651
4
DIP/SO
Maxim Integrated Products
Call toll free 1-800-998-8800 for free samples or literature.
8
GND
EXT
7
CS
6
5
V+
1
Page 2
5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage, V+ to GND.......................................-0.3V, +17V
REF, SHDN, FB, CS, EXT, OUT.......................-0.3V, (V+ + 0.3V)
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
Plastic DIP (derate 9.09mW/°C above +70°C) .............727mW
SO (derate 5.88mW/°C above +70°C)..........................471mW
Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
= +70°C)
A
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(V+ = 5V, TA= T
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS
V+ Input Voltage Range V+ 3.0 16 V
Supply Current
MAX1649/MAX1651
FB Trip Point
FB Input Current I
Output Voltage V
Reference Voltage V
REF Load Regulation mV410
Output Voltage
Line Regulation
Output Voltage
Load Regulation
Efficiency
SHDN Input Current V+ = 16V, SHDN = 0V or V+ 1 µA
SHDN Input Voltage High V
SHDN Input Voltage Low V
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
MAX
CONDITIONS
V
< V+
OUT
V+ = 16V, SHDN ≤ 0.4V (operating, switch off)
V+ = 16V, SHDN ≥ 1.6V (shutdown)
I+
V+ = 10V, SHDN ≥ 1.6V (shutdown)
MAX1649C, MAX1651C
MAX1649E, MAX1651E
MAX1649C, MAX1651C
FB
MAX1649E, MAX1651E
Circuit of
OUT
Figure 1
MAX1649C, MAX1651C, I
REF
MAX1649E, MAX1651E, I
0µA ≤ I
3V ≤ V+ ≤ 16VREF Line Regulation 40 100 µV/V
Circuit of
Figure 1
Circuit of
Figure 1
Circuit of
Figure 1
3V ≤ V+ ≤ 16V 1.6 V
IH
3V ≤ V+ ≤ 16V 0.4 V
IL
≤ 100µA, sourcing only
REF
Operating Temperature Ranges
MAX1649C_A, MAX1651C_A ..............................0°C to +70°C
MAX1649E_A, MAX1651E_A............................-40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range.............................-65°C to +160°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10sec).............................+300°C
78 100
2
15
1.470 1.5 1.530
1.4625 1.5 1.5375
±50
±70
MAX1649, V+ = 5.5V to 16V
MAX1651, V+ = 3.6V to 16V
= 0µA
REF
= 0µA
REF
MAX1649, 5.5V ≤ V+ ≤ 16V,
I
= 1A
LOAD
MAX1651, 3.6V ≤ V+ ≤ 16V,
I
= 1A
LOAD
MAX1649, 0A ≤ I
VIN= 10V
MAX1651, 0A ≤ I
VIN= 5V
MAX1649, V+ = 10V,
I
= 1A
LOAD
MAX1651, V+ = 5V,
I
= 1A
LOAD
LOAD
LOAD
≤ 1.5A,
≤ 1.5A,
4.80 5.0 5.20
3.17 3.3 3.43
1.470 1.5 1.530
1.4625 1.5 1.5375
2.6
1.7
-47
-45
90
90
µA
V
nA
V
V
mV/V
mV/A
%
2 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Page 3
5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
(V+ = 5V, TA= T
PARAMETER
Current-Limit Trip Level
(V+ to CS)
Maximum Duty Cycle 95 96.5 %
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at TA= +25°C.)
MAX
SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITSCONDITIONS
3V ≤ V+ ≤ 16V 80 110 140
CS
3V ≤ V+ ≤ 16VCS Input Current ±1 µA
V+ = 12VSwitch Maximum On-Time 24 32 40 µstON(max)
V+ = 12VSwitch Minimum Off-Time 0.8 1.1 1.8 µst
(min)
OFF
C
= 0.001µF, V+ = 12VEXT Rise Time 25 ns
EXT
C
= 0.001µF, V+ = 12VEXT Fall Time 25 ns
EXT
t
ON
OFF
x 100%
tON+ t
mVV
__________________________________________Typical Operating Characteristics
(TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
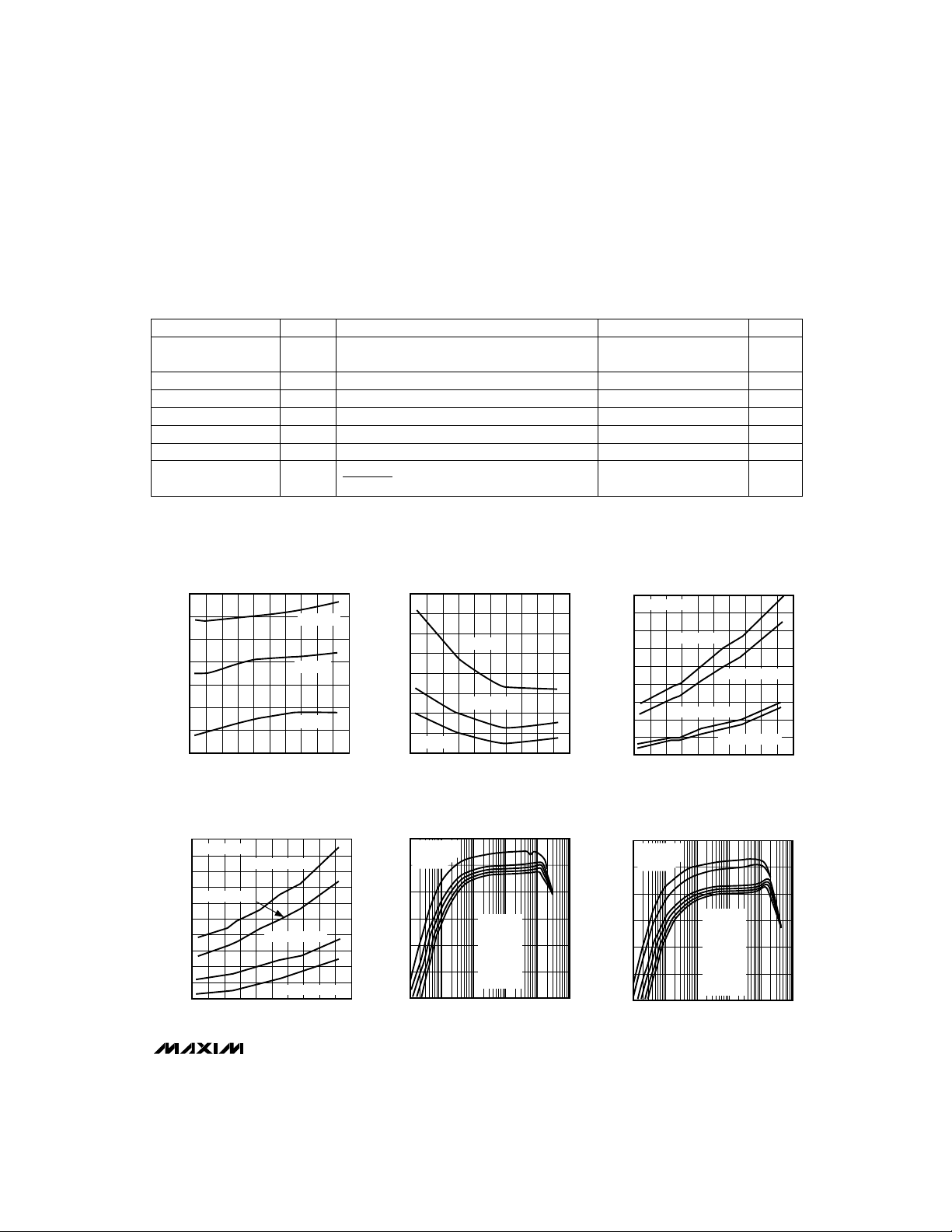
SUPPLY CURRENT vs. TEMPERATURE
80
78
76
74
I+ (µA)
72
70
68
66
-60 -20 60 140
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
V+ = 16V
V+ = 10V
V+ = 4V
MAX1649-TOC06
SHUTDOWN CURRENT
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
I+ (µA)
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
vs. TEMPERATURE
V+ = 16V
V+ = 8V
V+ = 4V
-60 -20 60 140
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAX1649-TOC05
(ns)
FALL
& t
RISE
t
EXT RISE AND FALL TIMES
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
vs. TEMPERATURE (1nF)
C
= 1nF
EXT
V+ = 5V, t
RISE
V+ = 5V, t
FALL
V+ = 15V, t
RISE
V+ = 15V, t
FALL
-60 -20 60 140
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAX1649/MAX1651
MAX1649/51-01
EXT RISE AND FALL TIMES
vs. TEMPERATURE (5nF)
240
C
= 5nF
EXT
220
200
180
V+ = 5V, t
(ns)
160
FALL
140
& t
120
RISE
t
100
80
60
40
-60 -20 60 140
V+ = 5V, t
RISE
FALL
V+ = 15V, t
V+ = 15V, t
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 3
RISE
FALL
MAX1649/51-02
vs. LOAD CURRENT (V
100
V
OUT
CIRCUIT OF
FIGURE 1
90
80
70
EFFICIENCY (%)
60
50
40
0.1
EFFICIENCY
= 5V)
OUT
= 5V
TOP TO
BOTTOM:
= 6V
V
IN
= 8V
V
IN
= 10V
V
IN
= 12V
V
IN
= 15V
V
IN
1 10 10k
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
100 1k
MAX1649/51-A1
vs. LOAD CURRENT (V
100
V
OUT
CIRCUIT OF
FIGURE 1
90
80
70
EFFICIENCY (%)
60
50
40
0.1
EFFICIENCY
= 3.3V)
OUT
= 3.3V
TOP TO
BOTTOM:
= 4.3V
V
IN
= 5V
V
IN
= 8V
V
IN
= 10V
V
IN
= 12V
V
IN
= 15V
V
IN
1 10 10k
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
100 1k
MAX1649/51-A2
Page 4
5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
____________________________Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
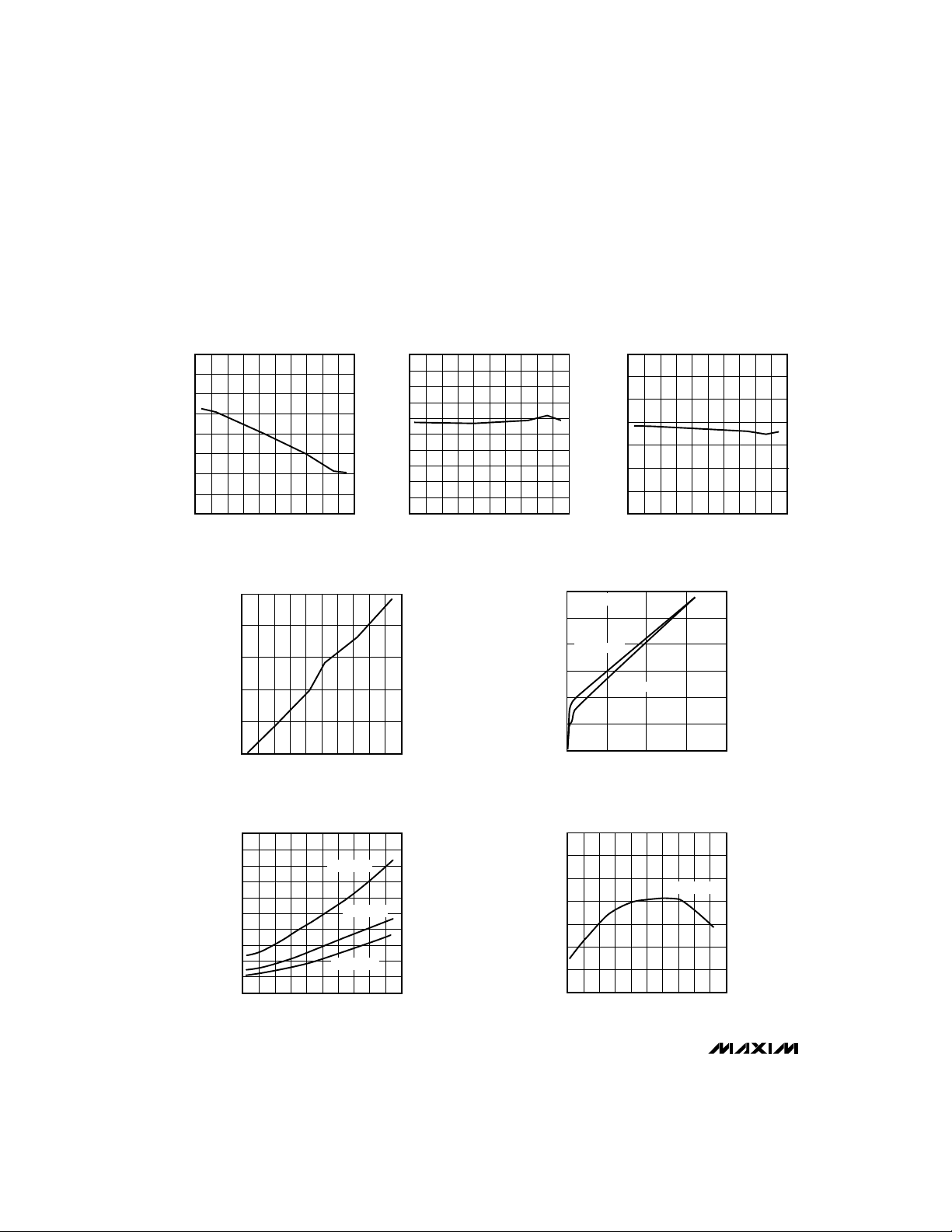
SWITCH ON-TIME
vs. TEMPERATURE
34.0
33.5
33.0
32.5
(µs)
32.0
ON
t
31.5
31.0
30.5
30.0
-60 -20 60 140
MAX1649/MAX1651
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAX1649/51-03
(µs)
OFF
t
CS TRIP LEVEL
vs. TEMPERATURE
120
115
110
105
CS TRIP LEVEL (mV)
100
95
-60 -20 60 140
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
1.5
1.4
1.3
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
-60 -20 60 140
MAX1649/51-06
SWITCH OFF-TIME
vs. TEMPERATURE
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAXIMUM DUTY CYCLE
100
99
MAX1649/51-04
98
97
96
DUTY CYCLE (%)
95
94
93
-60 -20 60 140
DROPOUT VOLTAGE
vs. LOAD CURRENT
600
CIRCUIT OF
FIGURE 1
500
400
V
= 4.80V
OUT
300
200
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (mV)
100
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0
V
= 3.17V
OUT
LOAD CURRENT (A)
vs. TEMPERATURE
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
MAX1649/51-05
MAX1649/51-A3
REFERENCE OUTPUT RESISTANCE
250
200
150
100
50
REFERENCE OUTPUT RESISTANCE (Ω)
0
vs. TEMPERATURE
I
REF
I
REF
-60 -20 60 140
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
= 10µA
I
REF
= 100µA
MAX1649-TOC07
= 50µA
REFERENCE OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
REFERENCE OUTPUT VOLTAGE
1.506
1.504
1.502
1.500
1.498
1.496
1.494
1.492
vs. TEMPERATURE
I
REF
-60 -20 60 140
20 100-40 0 8040 120
TEMPERATURE (°C)
= 10µA
4 _______________________________________________________________________________________
MAX1649-TOC01
Page 5

5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
____________________________Typical Operating Characteristics (continued)
(TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
LINE-TRANSIENT RESPONSE
CIRCUIT OF FIGURE 1, I
A: V
= 5V, 100mV/div, AC-COUPLED
OUT
B: V+ = 6V TO 16V, 5V/div
MAX1649
5ms/div
= 1A
LOAD
A
16V
B
6V
SHDN RESPONSE TIME
MAX1649
CIRCUIT OF FIGURE 1, V+ = 10V
A: V
= 5V, 100mV/div, AC-COUPLED
OUT
B: I
= 30mA TO 1.6A, 1A/div
LOAD
5V
OUTPUT
0V
4V
SHDN
INPUT
0V
MAX1649
LOAD-TRANSIENT RESPONSE
1.6A
0A
200µs/div
MAX1649/MAX1651
A
B
CIRCUIT OF FIGURE 1, V+ = 10V, I
1ms/div
LOAD
= 1A
_______________________________________________________________________________________
5
Page 6

5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
______________________________________________________________Pin Description
NAME FUNCTION
PIN
Sense Input for fixed 5V or 3.3V output operation. OUT is internally connected to the on-chip voltage divider.
OUT
1
2 FB
3 SHDN
4 REF 1.5V Reference Output that can source 100µA. Bypass with 0.1µF.
5 V+ Positive Power-Supply Input
6 CS
7 EXT Gate Drive for External P-Channel MOSFET. EXT swings between V+ and GND.
8 GND Ground
Although it is connected to the output of the circuit, the OUT pin does not supply current. Leave OUT unconnected
for adjustable-output operation.
Feedback Input. Connect to GND for fixed-output operation. Connect a resistor divider between OUT, FB, and
GND for adjustable-output operation. See
Active-High Shutdown Input. Part is placed in shutdown when SHDN is driven high. In shutdown mode, the reference, output, and external MOSFET are turned off. Connect to GND for normal operation.
Current-Sense Input. Connect current-sense resistor between V+ and CS. When the voltage across the resistor
equals the current-limit trip level, the external MOSFET is turned off.
Setting the Output Voltage
section.
MAX1649/MAX1651
V
IN
C4
C1
0.1µF
*
47µH
L1
**
330µF
100µF
OUTPUT
@ 1.5A
C2
MAX1649
MAX1651
3
SHDN
4
REF
FB GND
28
C3
0.1µF
Figure 1. Test Circuit
5
V+
R1
0.05Ω
6
CS
EXT
OUT
NSQ03A02L
*SILICONIX SURFACE-MOUNT MOSFET
**SUMIDA CDRH125-470
P1
7
Si9430
1
D1
_______________Detailed Description
The MAX1649/MAX1651 are BiCMOS, step-down,
switch-mode power-supply controllers that provide
adjustable and fixed outputs of 5V and 3.3V, respectively. Their unique control scheme combines the
advantages of pulse-frequency-modulation (low supply
current) and pulse-width-modulation (high efficiency at
high loads). An external P-channel power MOSFET
allows peak currents in excess of 3A, increasing the
output current capability over previous PFM devices.
Figure 2 is the block diagram.
The MAX1649/MAX1651 offer four main improvements
over prior solutions:
1) The converters operate with miniature surface-mount
inductors, due to their 300kHz switching frequency.
2) The current-limited PFM control scheme allows
greater than 90% efficiencies over a wide range of
load currents (10mA to 1.5A).
3) Dropout voltage has been reduced to less than
300mV for many applications.
4) The quiescent supply current is only 100µA.
PFM Control Scheme
The MAX1649/MAX1651 use a proprietary, current-limited PFM control scheme. As with traditional PFM converters, the external power MOSFET is turned on when
the voltage comparator senses that the output is out of
regulation. However, unlike traditional PFM converters,
switching is accomplished through the combination of a
peak current limit and a pair of one-shots that set the
maximum switch on-time (32µs) and minimum switch
off-time (1.1µs). Once off, the off-time one-shot holds
the switch off for 1.1µs. After this minimum time, the
switch either 1) stays off if the output is in regulation, or
2) turns on again if the output is out of regulation.
The MAX1649/MAX1651 also limit the peak inductor current, which allows them to run in continuous-conduction
mode and maintain high efficiency with heavy loads
(Figure 3). This current-limiting feature is a key component of the control circuitry. Once turned on, the switch
stays on until either 1) the maximum on-time one-shot
turns it off (32µs later), or 2) the current limit is reached.
EXT swings from V+ to GND and provides the drive output for an external P-channel power MOSFET.
6 _______________________________________________________________________________________
Page 7

5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
FBV+
DUAL-MODE™
COMPARATOR
MAX1649/MAX1651
MAX1649
SHDN
REF
™ Dual-Mode is a trademark of Maxim Integrated Products
MAX1651
MINIMUM
Q
OFF-TIME
ONE-SHOT
TRIG
TRIG
MAXIMUM
ON-TIME
ONE-SHOT
Q
ERROR
COMPARATOR
1.5V
REFERENCE
COMPARATOR
CURRENT
GND
50mV
N
FROM V+
QS
F/F
R
110mV
FROM V+
OUT
EXT
CS
Figure 2. Block Diagram
Shutdown Mode
When SHDN is high, the MAX1649/MAX1651 enter shutdown mode. In this mode, the internal biasing circuitry is
turned off (including the reference) and the supply current drops to less than 5µA. EXT goes high, turning off the
external MOSFET. SHDN is a logic-level input. Connect
SHDN to GND for normal operation.
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 7
In normal operation, the device's typical quiescent cur-
Quiescent Current
rent is 78µA. In an actual application, even with no load,
additional current is drawn to supply external feedback
resistors (if used) and the diode and capacitor leakage
currents. In the circuit of Figure 1, with V+ at 5V and
V
at 3.3V, typical no-load supply current for the
OUT
entire circuit is 90µA.
Page 8

5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
V
V+ = 10V, I
LOAD
MAX1649/MAX1651
Figure 3. MAX1649 Continuous-Conduction Mode, Heavy
Load-Current Waveform (500mA/div)
CIRCUIT OF FIGURE 1, R1 = 75mΩ
2µs/div
= 1.3A
1.5A
1A
0A
IN
5
V+
EXT
OUT
R1
0.05Ω
6
CS
7
1
2
FB
D1
1N5820
MAX1649
MAX1651
3
SHDN
4
REF
GND
C3
0.1µF
R2 = R3
= 1.5V
V
REF
Figure 4. Adjustable-Output Operation
8
V
OUT
– 1
(
)
V
REF
P1
Si9430
C4
0.1µF
47µH
L1
R2
330µF
R3
150k
C1
100µF
OUTPUT
@ 1.5A
C2
When delivering high output currents, the MAX1649/
Modes of Operation
MAX1651 operate in continuous-conduction mode. In
this mode, current always flows in the inductor, and
the control circuit adjusts the switch duty cycle to maintain regulation without exceeding the switch current
capability (Figure 3). This provides excellent load-transient response and high efficiency.
In discontinuous-conduction mode, current through the
inductor starts at zero, rises to a peak value, then
ramps down to zero. Although efficiency is still excellent, the output ripple increases slightly, and the switch
waveform exhibits ringing (at the inductor's self-resonant frequency). This ringing is to be expected and
poses no operational problems.
Dropout
The MAX1649/MAX1651 are in dropout when the input
voltage (V+) is low enough that the output drops below
the minimum output voltage specification (see
Electrical Characteristics
). The dropout voltage is the
difference between the input and output voltage when
dropout occurs. See the
Characteristics
for the Dropout Voltage vs. Load
Typical Operating
Current and Dropout Voltage vs. Temperature graphs.
8 _______________________________________________________________________________________
__________________Design Procedure
The MAX1649/MAX1651 are preset for 5V and 3.3V output voltages, respectively; tie FB to GND for fixed-output
operation. They may also be adjusted from 1.5V (the
reference voltage) to the input voltage, using external
resistors R2 and R3 configured as shown in Figure 4. For
adjustable-output operation, 150kΩ is recommended for
resistor R3—high enough to avoid wasting energy, yet
low enough to avoid RC delays caused by parasitic
capacitance at FB. R2 is given by:
where V
REF
= 1.5V.
When using external resistors, it does no harm to connect OUT and the output together, or to leave OUT
unconnected.
The current-sense resistor limits the peak switch current to 110mV/R
the current-sense resistor, and 110mV is the currentlimit trip level (see
Setting the Output Voltage
V
OUT
R2 = R3 x
——— -1
(
V
REF
Current-Sense Resistor Selection
, where R
SENSE
SENSE
Electrical Characteristics
)
is the value of
).
Page 9

5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
To maximize efficiency and reduce the size and cost
of external components, minimize the peak current.
However, since the available output current is a function of the peak current, the peak current must not be
too low.
To choose the proper current-sense resistor for a particular output voltage, determine the minimum input
voltage and the maximum load current. Next, referring to Figures 5a or 5b, using the minimum input voltage, find the curve with the largest sense resistor that
provides sufficient output current. It is not necessary
to perform worst-case calculations. These curves take
into account the sense-resistor (±5%) and inductor
(47µH ±10%) values, the diode drop (0.4), and the
IC’s current-sense trip level (85mV); an external MOSFET on-resistance of 0.07Ω is assumed for VGS= -5V.
Standard wire-wound and metal-film resistors have an
inductance high enough to degrade performance.
Surface-mount (chip) resistors have very little inductance
and are well suited for use as current-sense resistors.
A U-shaped wire resistor made by IRC works well in
through-hole applications. Because this resistor is a
band of metal shaped as a “U”, its inductance is less
than 10nH (an order of magnitude less than metal film
resistors). Resistance values between 5mΩ and 0.1Ω
are available (see Table 1).
Inductor Selection
The MAX1649/MAX1651 operate with a wide range of
inductor values, although for most applications coils
between 10µH and 68µH take best advantage of the con-
trollers’ high switching frequency. With a high inductor
value, the MAX1649/MAX1651 will begin continuous-current operation (see
Detailed Description
) at a lower fraction of full-load current. In general, smaller values produce higher ripple (see below) while larger values require
larger size for a given current rating.
In both the continuous and discontinuous modes, the
lower limit of the inductor is important. With a too-small
inductor value, the current rises faster and overshoots the
desired peak current limit because the current-limit comparator has a finite response time (300ns). This reduces
efficiency and, more importantly, could cause the current
rating of the external components to be exceeded.
Calculate the minimum inductor value as follows:
L(min) = ——————————––——
(V+(max) - V
∆I x I
OUT
LIM
) x 0.3µs
where ∆I is the inductor-current overshoot factor,
I
LIM
= VCS/R
, and 0.3µs is the time it takes the com-
SENSE
parator to switch. Set ∆I = 0.1 for an overshoot of 10%.
For highest efficiency, use a coil with low DC resis-
tance; a value smaller than 0.1V/I
works best. To
LIM
minimize radiated noise, use a toroid, pot core, or
shielded-bobbin inductor. Inductors with a ferrite core
or equivalent are recommended. Make sure the inductor’s saturation-current rating is greater than I
LIM
(max).
However, it is generally acceptable to bias the inductor
into saturation by about 20% (the point where the
inductance is 20% below its nominal value).
MAX1649/MAX1651
3.0
V
= 5V
OUT
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
MAXIMUM OUTPUT CURRENT (A)
0
5.0 5.4 5.8 6.2 6.6 16.0
Figure 5a. MAX1649 Current-Sense Resistor Graph
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
rs = 0.030
rs = 0.040
rs = 0.050
rs = 0.060
rs = 0.080
rs = 0.100
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
1649 Fig05a
3.0
V
= 3.3V
OUT
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
MAXIMUM OUTPUT CURRENT (A)
0
3.0 3.4 3.8 4.2 4.6 16.0
Figure 5b. MAX1651 Current-Sense Resistor Graph
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
rs = 0.030
rs = 0.040
rs = 0.050
rs = 0.060
rs = 0.080
rs = 0.100
1651 Fig05b
Page 10

5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
Table 1. Component Selection Guide
PRODUCTION
METHOD
Surface Mount
Miniature
Through-Hole
Low-Cost
MAX1649/MAX1651
Through-Hole
INDUCTORS CAPACITORS DIODES
Sumida
CDRH125-470 (1.8A)
CDRH125-220 (2.2A)
CoilCraft
DO3316-473 (1.6A)
DO3340-473 (3.8A)
Sumida
RCH875-470M (1.3A)
CoilCraft
PCH-45-473 (3.4A)
AVX
TPS series
Sprague
595D series
Sanyo
OS-CON series
low-ESR organic
semiconductor
Nichicon
PL series
low-ESR electrolytics
United Chemi-Con
LXF series
Motorola
MBRS340T3
Nihon
NSQ series
Motorola
1N5817 to
1N5823
CURRENT-SENSE
RESISTORS
Dale
WSL Series
IRC
LRC series
IRC
OAR series
Siliconix
Little Foot series
Motorola
medium-power
surface-mount products
Motorola
Motorola
TMOS power MOSFETs
MOSFETS
The peak current of Figure 1 is 2.35A for a 1.5A output.
The inductor used in this circuit is specified to drop by
10% at 2.2A (worst case); a curve provided by the
manufacturer shows that the inductance typically drops
by 20% at 2.7A. Using a slightly underrated inductor
can sometimes reduce size and cost, with only a minor
impact on efficiency.
Table 1 lists inductor types and suppliers for various
applications. The efficiencies of the listed surfacemount inductors are nearly equivalent to those of the
larger size through-hole versions.
Diode Selection
The MAX1649/MAX1651’s high switching frequency
demands a high-speed rectifier. Schottky diodes, such
as the 1N5817 through 1N5823 (and their surfacemount equivalents), are recommended. Choose a
diode with an average current rating equal to or greater
than I
(max) and a voltage rating higher than
LIM
V+(max).
External Switching Transistor
The MAX1649/MAX1651 drive P-channel enhancementmode MOSFET transistors only. The choice of power
transistor is primarily dictated by the input voltage and
the peak current. The transistor’s on-resistance, gatesource threshold, and gate charge must also be appropriately chosen. The drain-to-source and gate-tosource breakdown voltage ratings must be greater than
V+. The total gate-charge specification is normally not
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________
critical, but values should be less than 100nC for best
efficiency. The MOSFET should be capable of handling
the peak current and, for maximum efficiency, have a
very low on-resistance at that current. Also, the onresistance must be low for the minimum available VGS,
which equals V+(min). Select a transistor with an onresistance between 50% and 100% of the currentsense resistor. The Si9430 transistor chosen for the
Typical Operating Circuit
has a drain-to-source rating
of -20V and a typical on-resistance of 0.070Ω at 2A with
VGS= -4.5V. Tables 1 and 2 list suppliers of switching
transistors suitable for use with these devices.
Capacitor Selection
Output Filter Capacitor
The primary criterion for selecting the output filter
capacitor is low equivalent series resistance (ESR),
rather than high capacitance. An electrolytic capacitor
with low enough ESR will automatically have high
enough capacitance. The product of the inductor-current variation and the output filter capacitor’s ESR
determines the amplitude of the high-frequency ripple
seen on the output voltage. When a 330µF, 10V
Sprague surface-mount capacitor (595D series) with
ESR = 0.15Ω is used, 40mV of output ripple is typically
observed when stepping down from 10V to 5V at 1A.
The output filter capacitor's ESR also affects efficiency.
Again, low-ESR capacitors perform best. Table 1 lists
some suppliers of low-ESR capacitors.
Page 11

5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
Table 2. Component Suppliers
COMPANY PHONE FAX
AVX USA or (207) 283-1941
Coiltronics USA (407) 241-7876 (407) 241-9339
CoilCraft USA (708) 639-6400 (708) 639-1469
Dale USA (402) 564-3131 (402) 563-1841
International
Rectifier
IRC USA (512) 992-7900 (512) 992-3377
Motorola USA or (602) 244-4015
Nichicon
Nihon
Sanyo
Siliconix USA or (408) 970-3950
Sprague USA (603) 224-1961 (603) 224-1430
Sumida
United
Chemi-Con
USA (310) 322-3331 (310) 322-3332
USA (708) 843-7500 (708) 843-2798
Japan 81-7-5231-8461 81-7-5256-4158
USA (805) 867-2555 (805) 867-2556
Japan 81-3-3494-7411 81-3-3494-7414
USA (619) 661-6835 (619) 661-1055
Japan 81-7-2070-6306 81-7-2070-1174
USA (708) 956-0666 (708) 956-0702
Japan 81-3-3607-5111 81-3-3607-5144
USA (714) 255-9500 (714) 255-9400
The input bypass capacitor reduces peak currents
drawn from the voltage source, and also reduces the
amount of noise at the voltage source caused by the
switching action of the MAX1649/MAX1651. The input
voltage source impedance determines the size of the
capacitor required at the V+ input. As with the output filter capacitor, a low-ESR capacitor is recommended.
Bypass the IC separately with a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor placed close to the V+ and GND pins.
Bypass REF with a 0.1µF or larger capacitor.
(207) 282-5111
(800) 282-4975
(602) 244-3576
(602) 244-5303
(408) 988-8000
(800) 554-5565
Input Bypass Capacitor
Reference Capacitor
Proper PC board layout is essential because of high
Layout Considerations
current levels and fast switching waveforms that radiate noise. Minimize ground noise by connecting the
anode of the rectifier, the input bypass capacitor
ground lead, and the output filter capacitor ground
lead to a single point (“star” ground configuration). A
ground plane is recommended. Also minimize lead
lengths to reduce stray capacitance, trace resistance,
and radiated noise. In particular, the traces connected
to FB (if an external resistor divider is used) and EXT
must be short. Place the 0.1µF ceramic bypass capacitor as close as possible to the V+ and GND pins.
MAX1649/MAX1651 vs. MAX649/MAX651
The MAX1649 and MAX1651 are pin compatible with
the MAX649 and MAX651, but have been optimized for
improved dropout performance and efficiency—particularly with low input voltages. The MAX1649/MAX1651
feature increased maximum switch duty cycle (96.5%)
and reduced current-limit sense voltage (110mV).
Their predecessors, the MAX649/MAX651, use a higher two-step (210mV/110mV) current-limit sense voltage
to provide tighter current-sense accuracy and reduced
inductor peak current at light loads.
___________________Chip Topography
OUT
FB
SHDN
GND
EXT
0.106"
(2.692mm)
CS
MAX1649/MAX1651
REF
0.081"
(2.057mm)
V+
TRANSISTOR COUNT: 428
SUBSTRATE CONNECTED TO V+
______________________________________________________________________________________ 11
Page 12

5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
________________________________________________________Package Information
INCHES MILLIMETERS
DIM
A2
A
A1
L
D
e
B
D1
MAX1649/MAX1651
D
A
0.101mm
e
A1
B
0.004in.
B1
A3
DUAL-IN-LINE
C
E
E1
0°-15°
eA
eB
Plastic DIP
PLASTIC
PACKAGE
(0.600 in.)
L
0°-8°
C
PKG.
P
P
P
A1
A2
A3
B1
D1
E1
eA
eB
DIM
DIM
A
B
C
E
e
L
PINS
D
D
D
A
A1
B
C
E
e
H
L
MAX
MIN
–
0.015
0.125
0.055
0.016
0.045
0.008
0.050
0.600
0.525
0.100
0.600
–
0.120
INCHES MILLIMETERS
MIN
24
1.230
28
1.430
40
2.025
INCHES MILLIMETERS
MIN
0.053
0.004
0.014
0.007
0.150
0.228
0.016
0.200
–
0.175
0.080
0.020
0.065
0.012
0.090
0.625
0.575
–
–
0.700
0.150
MAX
0.069
0.010
0.019
0.010
0.157
0.244
0.050
MAX
1.270
1.470
2.075
MIN
–
0.38
3.18
1.40
0.41
1.14
0.20
1.27
15.24
13.34
2.54
15.24
–
3.05
MIN
31.24
36.32
51.44
MIN
1.35
0.10
0.35
0.19
3.80
5.80
0.40
1.270.050
MAX
5.08
–
4.45
2.03
0.51
1.65
0.30
2.29
15.88
14.61
–
–
17.78
3.81
MAX
32.26
37.34
52.71
21-0044A
MAX
1.75
0.25
0.49
0.25
4.00
6.20
1.27
Narrow SO
HE
SMALL-OUTLINE
PACKAGE
(0.150 in.)
Maxim cannot assume responsibility for use of any circuitry other than circuitry entirely embodied in a Maxim product. No circuit patent licenses are
implied. Maxim reserves the right to change the circuitry and specifications without notice at any time.
12
__________________Maxim Integrated Products, 120 San Gabriel Drive, Sunnyvale, CA 94086 (408) 737-7600
DIM
D
D
D
MIN
MAX
MIN
8
0.189
0.337
0.386
0.197
0.344
0.394
14
16
4.80
8.55
9.80
MAX
5.00
8.75
10.00
21-0041A
INCHES MILLIMETERS
PINS
© 1995 Maxim Integrated Products Printed USA is a registered trademark of Maxim Integrated Products.
 Loading...
Loading...