Page 1

DS26504
www.maxim-ic.com
T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The DS26504 is a building-integrated timing-supply
(BITS) clock-recovery element. It also functions as a
basic T1/E1 transceiver. The receiver portion can
recover a clock from T1, E1, 64kHz composite clock
(64KCC), and 6312kHz synchronization timing
interfaces. In T1 and E1 modes, the Synchronization
Status Message (SSM) can also be recovered. The
transmit portion can directly interface to T1, E1, or
64KCC synchronization interfaces as well as source
the SSM in T1 and E1 modes. The DS26504 can
translate between any of the supported inbound
synchronization clock rates to any supported
outbound rate. The DS26504 can also accept an 8kHz
as well as a 19.44MHz reference clock. A separate
output is provided to source a 6312kHz clock. The
device is controlled through a parallel, serial, or
hardware controller port.
APPLICATIONS
BITS Timing
Rate Conversion
FEATURES
§ Accepts 8kHz and 19.44MHz References in
Addition to T1, E1, and 64kHz Composite Clock
§ GR378 Composite Clock Compliant
§ G.703 2048kHz Synchronization Interface
Compliant
§ G.703 64kHz Option A & B Centralized Clock
Synchronization Interface Compliant
§ G.703 64kHz Japanese Composite Clock
Synchronization Interface Compliant
§ G.703 6312kHz Japanese Synchronization
Interface Compliant
§ Interfaces to Standard T1/J1 (1.544MHz) and E1
(2.048MHz)
§ Interface to CMI-Coded T1/J1 and E1
§ T1/E1 Transmit Payload Clock Output
§ Short- and Long-Haul Line Interface
§ Transmit and Receive T1 BOC SSM Messages
with Receive Message Change of State and
Validation Indication
§ Transmit and Receive E1 Sa(n) Bit SSM
Messages with Receive Message Change of State
Indication
§ Crystal-Less Jitter Attenuator with Bypass Mode
for T1 and E1 Operation
§ Fully Independent Transmit and Receive
Functionality
§ Internal Software-Selectable Receive and
Transmit Side Termination for
75Ω/100Ω/110Ω/120Ω/133Ω
§ Monitor Mode for Bridging Applications
§ Accepts 16.384MHz, 12.8MHz, 8.192MHz,
4.096MHz, 2.048MHz, or 1.544MHz Master
Clock
§ 64kHz, 8kHz, and 400Hz Outputs in Composite
Clock Mode
§ 8-Bit Parallel Control Port, Multiplexed or
Nonmultiplexed, Intel or Motorola
§ Serial (SPI) Control Port and Hardware Control
Mode
§ Provides LOS, AIS, and LOF Indications through
Hardware Output Pins
§ Fast Transmitter Output Disable through Device
Pin for Protection Switching
§ IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Boundary Scan
§ 3.3V Supply with 5V Tolerant Inputs and
Outputs
§ Pin and Software Compatible with the DS26502
and DS26503
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART TEMP RANGE PIN-PACKAGE
DS26504L 0°C to +70°C 64 LQFP
DS26504LN -40°C to +85°C 64 LQFP
Note: Some revisions of this device may incorporate deviations from published specifications known as errata. Multiple revisions of any device
may be simultaneously available through various sales channels. For information about device errata, click here: www.maxim-ic.com/errata
1 of 128
REV: 070105
.
Page 2

DS26502 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FEATURES ............................................................................................................................ 7
1.
1.1 GENERAL .................................................................................................................................. 7
1.2 LINE INTERFACE ........................................................................................................................ 7
1.3 JITTER ATTENUATOR (T1/E1 MODES ONLY)................................................................................ 7
1.4 FRAMER/FORMATTER................................................................................................................. 8
1.5 TEST AND DIAGNOSTICS............................................................................................................. 8
1.6 CONTROL PORT......................................................................................................................... 8
2. SPECIFICATIONS COMPLIANCE ............................................................................... 9
3. BLOCK DIAGRAMS......................................................................................................... 11
4. PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION................................................................................... 14
4.1 TRANSMIT PLL ........................................................................................................................ 14
4.2 TRANSMIT SIDE ....................................................................................................................... 14
4.3 RECEIVE SIDE ......................................................................................................................... 15
4.4 CONTROLLER INTERFACE ......................................................................................................... 16
4.5 JTAG...................................................................................................................................... 20
4.6 LINE INTERFACE ...................................................................................................................... 21
4.7 POWER ................................................................................................................................... 21
5. PINOUT ................................................................................................................................. 22
6. HARDWARE CONTROLLER INTERFACE ............................................................ 25
6.1 TRANSMIT CLOCK SOURCE....................................................................................................... 25
6.2 INTERNAL TERMINATION ........................................................................................................... 25
6.3 LINE BUILD-OUT ...................................................................................................................... 26
6.4 RECEIVER OPERATING MODES ................................................................................................. 27
6.5 TRANSMITTER OPERATING MODES ........................................................................................... 27
6.6 MCLK PRE-SCALER ................................................................................................................ 28
6.7 PAYLOAD CLOCK OUTPUT ........................................................................................................ 28
6.8 OTHER HARDWARE CONTROLLER MODE FEATURES .................................................................. 29
7. PROCESSOR INTERFACE........................................................................................... 30
7.1 PARALLEL PORT FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION.............................................................................. 30
7.2 SPI SERIAL PORT INTERFACE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION .......................................................... 30
7.2.1 Clock Phase and Polarity ..................................................................................................................... 30
7.2.2 Bit Order............................................................................................................................................... 30
7.2.3 Control Byte ......................................................................................................................................... 30
7.2.4 Burst Mode........................................................................................................................................... 30
7.2.5 Register Writes..................................................................................................................................... 31
7.2.6 Register Reads .................................................................................................................................... 31
7.3 REGISTER MAP........................................................................................................................ 32
7.3.1 Power-Up Sequence ............................................................................................................................ 34
7.3.2 Test Reset Register ............................................................................................................................. 34
7.3.3 Mode Configuration Register ............................................................................................................... 35
7.4 INTERRUPT HANDLING.............................................................................................................. 37
7.5 STATUS REGISTERS ................................................................................................................. 37
7.6 INFORMATION REGISTERS ........................................................................................................ 38
7.7 INTERRUPT INFORMATION REGISTERS ....................................................................................... 38
2 of 128
Page 3

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
8. T1 FRAMER/FORMATTER CONTROL REGISTERS......................................... 39
8.1 T1 CONTROL REGISTERS......................................................................................................... 39
9. E1 FRAMER/FORMATTER CONTROL REGISTERS ........................................ 45
9.1 E1 CONTROL REGISTERS......................................................................................................... 45
9.2 E1 INFORMATION REGISTERS................................................................................................... 48
10. I/O PIN CONFIGURATION OPTIONS....................................................................... 52
11. T1 SYNCHRONIZATION STATUS MESSAGE ..................................................... 55
11.1 T1 BIT-ORIENTED CODE (BOC) CONTROLLER .......................................................................... 55
11.2 TRANSMIT BOC....................................................................................................................... 55
11.3 RECEIVE BOC......................................................................................................................... 56
12. E1 SYNCHRONIZATION STATUS MESSAGE ..................................................... 64
12.1 SA/SI BIT ACCESS BASED ON CRC4 MULTIFRAME .................................................................... 64
12.1.1 Sa Bit Change of State......................................................................................................................... 65
12.2 ALTERNATE SA/SI BIT ACCESS BASED ON DOUBLE-FRAME ........................................................ 76
13. LINE INTERFACE UNIT (LIU) ...................................................................................... 79
13.1 LIU OPERATION....................................................................................................................... 80
13.2 LIU RECEIVER......................................................................................................................... 80
13.2.1 Receive Level Indicator........................................................................................................................ 80
13.2.2 Receive G.703 Section 10 Synchronization Signal ............................................................................. 81
13.2.3 Monitor Mode ....................................................................................................................................... 81
13.3 LIU TRANSMITTER ................................................................................................................... 81
13.3.1 Transmit Short-Circuit Detector/Limiter................................................................................................ 82
13.3.2 Transmit Open-Circuit Detector ........................................................................................................... 82
13.3.3 Transmit BPV Error Insertion ............................................................................................................... 82
13.3.4 Transmit G.703 Section 10 Synchronization Signal (E1 Mode)........................................................... 82
13.4 MCLK PRE-SCALER ................................................................................................................ 82
13.5 JITTER ATTENUATOR................................................................................................................ 82
13.6 CMI (CODE MARK INVERSION) OPTION..................................................................................... 83
13.7 LIU CONTROL REGISTERS........................................................................................................ 84
13.8 RECOMMENDED CIRCUITS ........................................................................................................ 92
13.9 COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................................. 94
14. LOOPBACK CONFIGURATION.................................................................................. 98
15. 64KHZ SYNCHRONIZATION INTERFACE ............................................................ 99
15.1 RECEIVE 64KHZ SYNCHRONIZATION INTERFACE OPERATION...................................................... 99
15.2 TRANSMIT 64KHZ SYNCHRONIZATION INTERFACE OPERATION.................................................. 100
16. 6312KHZ SYNCHRONIZATION INTERFACE ..................................................... 101
16.1 RECEIVE 6312KHZ SYNCHRONIZATION INTERFACE OPERATION................................................ 101
16.2 TRANSMIT 6312KHZ SYNCHRONIZATION INTERFACE OPERATION.............................................. 101
17. JTAG BOUNDARY SCAN ARCHITECTURE AND TEST ACCESS PORT.............. 102
17.1 INSTRUCTION REGISTER......................................................................................................... 106
17.2 TEST REGISTERS................................................................................................................... 107
17.3 BOUNDARY SCAN REGISTER .................................................................................................. 107
17.4 BYPASS REGISTER................................................................................................................. 107
3 of 128
Page 4

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
17.5 IDENTIFICATION REGISTER ..................................................................................................... 107
18. FUNCTIONAL TIMING DIAGRAMS......................................................................... 110
18.1 PROCESSOR INTERFACE ........................................................................................................ 110
18.1.1 Parallel Port Mode.............................................................................................................................. 110
18.1.2 SPI Serial Port Mode.......................................................................................................................... 110
19. OPERATING PARAMETERS ..................................................................................... 113
20. AC TIMING PARAMETERS AND DIAGRAMS.................................................... 115
20.1 MULTIPLEXED BUS................................................................................................................. 115
20.2 NONMULTIPLEXED BUS .......................................................................................................... 118
20.3 SERIAL BUS........................................................................................................................... 121
20.4 RECEIVE SIDE AC CHARACTERISTICS ..................................................................................... 123
20.5 TRANSMIT SIDE AC CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................... 125
21. REVISION HISTORY...................................................................................................... 127
22. PACKAGE INFORMATION ......................................................................................... 128
4 of 128
Page 5

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 3-1. Block Diagram ......................................................................................................................................... 11
Figure 3-2. Loopback Mux Diagram (T1/E1 Modes Only) ......................................................................................... 12
Figure 3-3. Transmit PLL Clock Mux Diagram .......................................................................................................... 12
Figure 3-4. Master Clock PLL Diagram ..................................................................................................................... 13
Figure 13-1. Basic Network Connection .................................................................................................................... 79
Figure 13-2. Typical Monitor Application ................................................................................................................... 81
Figure 13-3. CMI Coding ........................................................................................................................................... 83
Figure 13-4. Basic Interface....................................................................................................................................... 92
Figure 13-5. Protected Interface Using Internal Receive Termination ...................................................................... 93
Figure 13-6. E1 Transmit Pulse Template ................................................................................................................. 95
Figure 13-7. T1 Transmit Pulse Template ................................................................................................................. 95
Figure 13-8. Jitter Tolerance (T1 Mode) .................................................................................................................... 96
Figure 13-9. Jitter Tolerance (E1 Mode).................................................................................................................... 96
Figure 13-10. Jitter Attenuation (T1 Mode)................................................................................................................ 97
Figure 13-11. Jitter Attenuation (E1 Mode) ............................................................................................................... 97
Figure 15-1. 64kHz Composite Clock Mode Signal Format ...................................................................................... 99
Figure 17-1. JTAG Functional Block Diagram ......................................................................................................... 102
Figure 17-2. TAP Controller State Diagram............................................................................................................. 105
Figure 18-1. SPI Serial Port Access, Read Mode, CPOL = 0, CPHA = 0 ............................................................... 110
Figure 18-2. SPI Serial Port Access, Read Mode, CPOL = 1, CPHA = 0 ............................................................... 110
Figure 18-3. SPI Serial Port Access, Read Mode, CPOL = 0, CPHA = 1 ............................................................... 110
Figure 18-4. SPI Serial Port Access, Read Mode, CPOL = 1, CPHA = 1 ............................................................... 111
Figure 18-5. SPI Serial Port Access, Write Mode, CPOL = 0, CPHA = 0 ............................................................... 111
Figure 18-6. SPI Serial Port Access, Write Mode, CPOL = 1, CPHA = 0 ............................................................... 111
Figure 18-7. SPI Serial Port Access, Write Mode, CPOL = 0, CPHA = 1 ............................................................... 112
Figure 18-8. SPI Serial Port Access, Write Mode, CPOL = 1, CPHA = 1 ............................................................... 112
Figure 20-1. Intel Bus Read Timing (BTS = 0 / BIS[1:0] = 00) ............................................................................... 116
Figure 20-2. Intel Bus Write Timing (BTS = 0 / BIS[1:0] = 00) ................................................................................ 116
Figure 20-3. Motorola Bus Timing (BTS = 1 / BIS[1:0] = 00)................................................................................... 117
Figure 20-4. Intel Bus Read Timing (BTS = 0 / BIS[1:0] = 01) ................................................................................ 119
Figure 20-5. Intel Bus Write Timing (BTS = 0 / BIS[1:0] = 01) ................................................................................ 119
Figure 20-6. Motorola Bus Read Timing (BTS = 1 / BIS[1:0] = 01) ......................................................................... 120
Figure 20-7. Motorola Bus Write Timing (BTS = 1 / BIS[1:0] = 01) ......................................................................... 120
Figure 20-8. SPI Interface Timing Diagram, CPHA = 0, BIS[1:0] = 10 .................................................................... 122
Figure 20-9. SPI Interface Timing Diagram, CPHA = 1, BIS[1:0] = 10 .................................................................... 122
Figure 20-10. Receive Timing—T1, E1, 64KCC Mode............................................................................................ 124
Figure 20-11. Transmit Timing—T1, E1, 64KCC Mode........................................................................................... 126
5 of 128
Page 6

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2-1. T1-Related Telecommunications Specifications ........................................................................................ 9
Table 2-2. E1-Related Telecommunications Specifications ...................................................................................... 10
Table 5-1. LQFP Pinout ............................................................................................................................................. 22
Table 6-1. Transmit Clock Source ............................................................................................................................. 25
Table 6-2. Internal Termination.................................................................................................................................. 25
Table 6-3. E1 Line Build-Out ..................................................................................................................................... 26
Table 6-4. T1 Line Build-Out...................................................................................................................................... 26
Table 6-5. Receive Path Operating Mode ................................................................................................................. 27
Table 6-6.Transmit Path Operating Mode ................................................................................................................. 27
Table 6-7. MCLK Pre-Scaler for T1 Mode ................................................................................................................. 28
Table 6-8. MCLK Pre-Scaler for E1 Mode ................................................................................................................. 28
Table 6-9. Other Operational Modes ......................................................................................................................... 29
Table 7-1. Port Mode Select ...................................................................................................................................... 30
Table 7-2. Register Map Sorted By Address ............................................................................................................. 32
Table 8-1. T1 Alarm Criterion .................................................................................................................................... 44
Table 9-1. E1 Sync/Resync Criterion......................................................................................................................... 46
Table 9-2. E1 Alarm Criterion .................................................................................................................................... 49
Table 10-1. TS_8K_4 Pin Functions.......................................................................................................................... 53
Table 10-2. RLOF_CCE Pin Functions ..................................................................................................................... 53
Table 11-1. T1 SSM Messages ................................................................................................................................. 55
Table 12-1. E1 SSM Messages ................................................................................................................................. 64
Table 13-1. Transformer Specifications..................................................................................................................... 94
Table 15-1. Specification of 64kHz Clock Signal at Input Port .................................................................................. 99
Table 15-2. Specification of 64kHz Clock Signal at Output Port ............................................................................. 100
Table 16-1. Specification of 6312kHz Clock Signal at Input Port ............................................................................ 101
Table 16-2. Specification of 6312kHz Clock Signal................................................................................................. 101
Table 17-1. Instruction Codes for IEEE 1149.1 Architecture................................................................................... 106
Table 17-2. ID Code Structure................................................................................................................................. 107
Table 17-3. Device ID Codes................................................................................................................................... 107
Table 17-4. Boundary Scan Control Bits ................................................................................................................. 108
Table 19-1. Thermal Characteristics........................................................................................................................ 113
Table 19-2. Theta-JA (qJA) vs. Airflow...................................................................................................................... 113
Table 19-3. Recommended DC Operating Conditions ............................................................................................ 113
Table 19-4. Capacitance.......................................................................................................................................... 113
Table 19-5. DC Characteristics................................................................................................................................ 114
Table 20-1. AC Characteristics, Multiplexed Parallel Port....................................................................................... 115
Table 20-2. AC Characteristics, Nonmultiplexed Parallel Port ................................................................................ 118
Table 20-3. AC Characteristics, Serial Bus ............................................................................................................. 121
Table 20-4. Receive Side AC Characteristics ......................................................................................................... 123
Table 20-5. Transmit Side AC Characteristics ........................................................................................................ 125
6 of 128
Page 7

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
1. FEATURES
1.1 General
§ 64-pin, 10mm x 10mm LQFP package
§ 3.3V supply with 5V tolerant inputs and outputs
§ Evaluation kits
§ IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Boundary Scan
§ Driver source code available from the factory
1.2 Line Interface
§ Requires a single master clock (MCLK) for E1, T1, or J1 operation. Master clock can be
2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, 12.8MHz (available in CPU-interface mode only), or
16.384MHz. Option to use 1.544MHz, 3.088MHz, 6.176MHz, or 12.552MHz for T1-only
operation.
§ Fully software configurable
§ Short- and long-haul applications
§ Automatic receive sensitivity adjustments
§ Ranges include 0dB to -43dB or 0dB to -12dB for E1 applications; 0dB to -36dB or 0dB to -15dB
for T1 applications
§ Receive level indication in 2.5dB steps from -42.5dB to -2.5dB
§ Internal receive termination option for 75Ω, 100Ω, 110W, 120Ω, and 133Ω lines
§ Monitor application gain settings of 20dB, 26dB, and 32dB
§ G.703 receive-synchronization signal mode
§ Flexible transmit-waveform generation
§ T1 DSX-1 line build-outs
§ E1 waveforms include G.703 waveshapes for both 75Ω coax and 120Ω twisted cables
§ AIS generation independent of loopbacks
§ Alternating ones and zeros generation
§ Square-wave output
§ Open-drain output option
§ Transmitter power-down
§ Transmitter 50mA short-circuit limiter with exceeded indication of current limit
§ Transmit open-circuit-detected indication
1.3 Jitter Attenuator (T1/E1 Modes Only)
§ 32-bit or 128-bit crystal-less jitter attenuator
§ Requires only a 2.048MHz master clock for both E1 and T1 operation with the option to use
1.544MHz for T1 operation
§ Can be placed in either the receive or transmit path or disabled
§ Limit trip indication
7 of 128
Page 8

1.4 Framer/Formatter
§ Fully independent transmit and receive functionality
§ Full receive and transmit path transparency
§ T1 framing formats include D4 and ESF
§ Detailed alarm and status reporting with optional interrupt support
§ RCL, RLOS, and RAIS alarms interrupt on change of state
§ Japanese J1 support includes:
- Ability to calculate and check CRC6 according to the Japanese standard
- Ability to generate yellow alarm according to the Japanese standard
1.5 Test and Diagnostics
§ Remote and local loopback
1.6 Control Port
§ 8-bit parallel or serial control port
§ Multiplexed or nonmultiplexed buses
§ Intel or Motorola formats
§ Supports polled or interrupt-driven environments
§ Software access to device ID and silicon revision
§ Software-reset supported
§ Automatic clear on power-up
§ Flexible register space resets
§ Hardware reset pin
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
8 of 128
Page 9

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
2. SPECIFICATIONS COMPLIANCE
The DS26504 meets all applicable sections of the latest telecommunications specifications including
those listed in the following tables.
Table 2-1. T1-Related Telecommunications Specifications
ANSI T1.102: Digital Hierarchy Electrical Interface
ANSI T1.231: Digital Hierarchy–Layer 1 In-Service Performance Monitoring
ANSI T1.403: Network and Customer Installation Interface–DS1 Electrical Interface
TR62411
(ANSI) “Digital Hierarchy–Electrical Interfaces”
(ANSI) “Digital Hierarchy–Formats Specification”
(ANSI) “Digital Hierarchy–Layer 1 In-Service Digital Transmission Performance Monitoring”
(ANSI) “Network and Customer Installation Interfaces – DS1 Electrical Interface”
(AT&T) “Requirements for Interfacing Digital Terminal Equipment to Services Employing the Extended
Super frame Format”
(AT&T) “High Capacity Digital Service Channel Interface Specification”
(TTC) “Frame Structures on Primary and Secondary Hierarchical Digital Interfaces”
(TTC) “ISDN Primary Rate User-Network Interface Layer 1 Specification”
9 of 128
Page 10

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Table 2-2. E1-Related Telecommunications Specifications
ITUT G.703 Physical/Electrical Characteristics of G.703 Hierarchical Digital Interfaces
ITUT G.736 Characteristics of Synchronous Digital Multiplex Equipment operating at 2048kbps
ITUT G.742 Second-Order Digital Multiplex Equipment Operating at 8448kbps
ITUT G.772
ITUT G.775
ITUT G.823 The control of jitter and wander within digital networks, which are based on 2.048kbps
hierarchy
ETSI 300 233
(ITU) “Synchronous Frame Structures used at 1544, 6312k, 2048, 8488, and 44,736kbps Hierarchical
Levels”
(ITU) “Frame Alignment and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) Procedures Relating to Basic Frame
Structures Defined in Recommendation G.704”
(ITU) “Characteristics of primary PCM Multiplex Equipment Operating at 2048kbps”
(ITU) Characteristics of a synchronous digital multiplex equipment operating at 2048kbps”
(ITU) “Loss Of Signal (LOS) and Alarm Indication Signal (AIS) Defect Detection and Clearance
Criterion”
(ITU) “The Control of Jitter and Wander Within Digital Networks Which are Based on the 2048kbps
Hierarchy”
(ITU) “Primary Rate User-Network Interface – Layer 1 Specification”
(ITU) “Error Performance Measuring Equipment Operating at the Primary Rate and Above”
(ITU) “In-service code violation monitors for digital systems”
(ETSI) “Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Primary rate User-Network Interface (UNI); Part
1/ Layer 1 specification”
(ETSI) “Transmission and multiplexing; Physical/electrical characteristics of hierarchical digital
interfaces for equipment using the 2048kbps-based plesiochronous or synchronous digital hierarchies”
(ETSI) “Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Access digital section for ISDN primary rate”
(ETSI) “Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN); Attachment requirements for terminal equipment
to connect to an ISDN using ISDN primary rate access”
(ETSI) “Business Telecommunications (BT); Open Network Provision (ONP) technical requirements;
2048lkbps digital unstructured leased lines (D2048U) attachment requirements for terminal equipment
interface”
(ETSI) “Business Telecommunications (BTC); 2048kbps digital structured leased lines (D2048S);
Attachment requirements for terminal equipment interface”
(ITU) “Synchronous Frame Structures used at 1544, 6312, 2048, 8488, and 44,736kbps Hierarchical
Levels”
(ITU) “Frame Alignment and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) Procedures Relating to Basic Frame
Structures Defined in Recommendation G.704”
10 of 128
Page 11
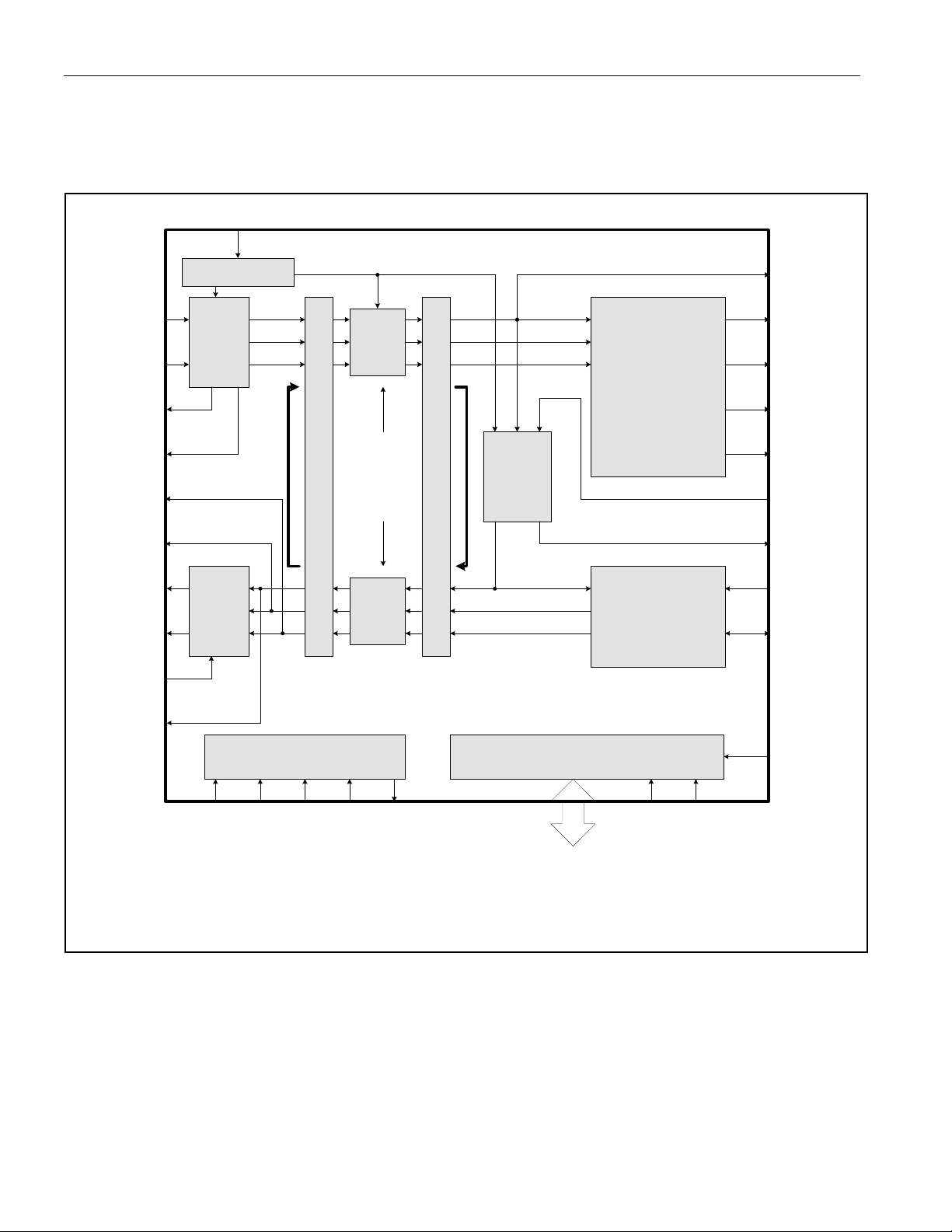
3. BLOCK DIAGRAMS
Figure 3-1. Block Diagram
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
MCLK
DS26504
RTIP
RRING
RLOS
RAIS
TNEGO
TPOSO
TTIP
TRING
THZE
MASTER CLOCK
CLOCK
RX
LIU
LIU
RX
+ DATA
- DATA
TX
LIU
L
O
C
A
L
L
O
O
P
TRANSMIT PATH
B
A
C
K
M
U
X
JA CLOCK
JA
JA
ENABLED
ENABLED
AND IN RX
AND IN RX
PATH
PATH
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
CAN BE
ASSIGNED TO
RECEIVE OR
OR DISABLED
JA
ENABLED
AND I N TX
PATH
R
E
M
O
T
E
L
O
O
P
B
A
C
K
M
U
X
PLL
CLOCK
MUX
TX CLOCK
+ DATA
- DATA
T1/E1 SSM
FRAMER
64KCC
DECODER
T1/E1 SSM
FORMATTER
64KCC
CODER
RCLK
LOF_CCE
RSER
RS_8K
400HZ
TCLK
PLL_OUT
TSER
TS_8K_4
TCLKO
JTAG PORT
JTAG PORTJTAG PORTJTAG PORT
PARALLEL/SERIAL CPU I/F
HARDWARE CONTROLLER
JTDOJTDIJTCLKJTMS JTRST BIS1 BIS0
PARALLEL,
SERIAL, OR
HARDWARE
CONTROLLER
11 of 128
TSTRST
Page 12
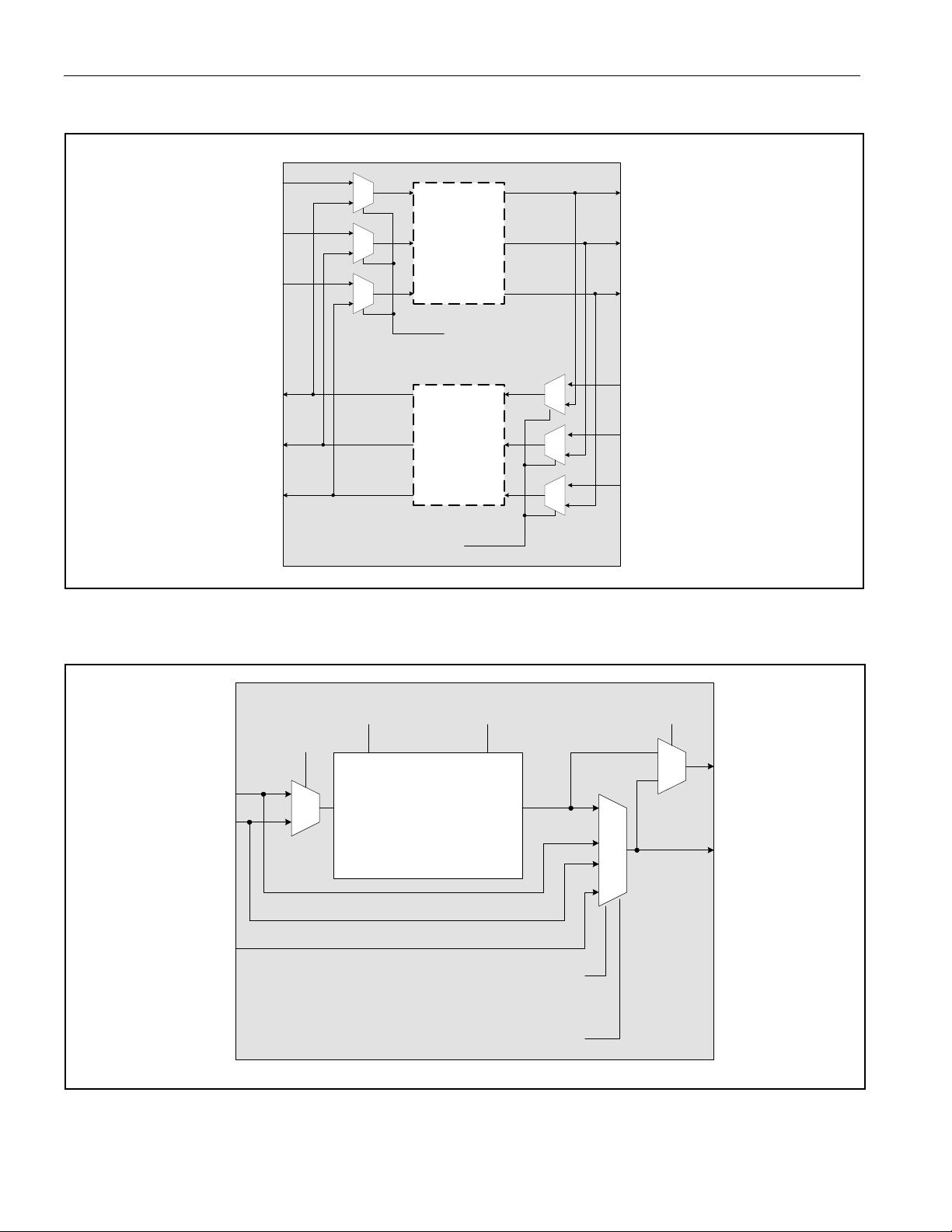
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Figure 3-2. Loopback Mux Diagram (T1/E1 Modes Only)
CLOCK
FROM RX
LIU
+ DATA
- DATA
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
ENABLED AND
IN RX PATH
LOCAL
LOOPBACK
(LBCR.3)
TO TX
LIU
CLOCK
+ DATA
- DATA
JITTER
ATTENUATOR
ENABLED AND
IN TX PATH
REMOTE
LOOPBACK
(LBCR.4)
+ DATA
- DATA
Figure 3-3. Transmit PLL Clock Mux Diagram
TPCR.3
TPCR.4
TPCR.6
TPCR.7
RCLK
+ DATA
- DATA
TX CLOCK
TPCR.5
TO RX
FRAMER
FROM TX
FORMATTER
RECOVERED CLOCK
TCLK PIN
JA CLOCK
TPCR.2
IN
SEL
TX PLL
OUTPUT = 8kHz -
19.44MHz
(HARDWARE MODE PIN NAME)
12 of 128
OUT
SEL
PLL_OUT PIN
TX CLOCK
TPCR.0
(TCSS0)
TPCR.1
(TCSS1)
Page 13
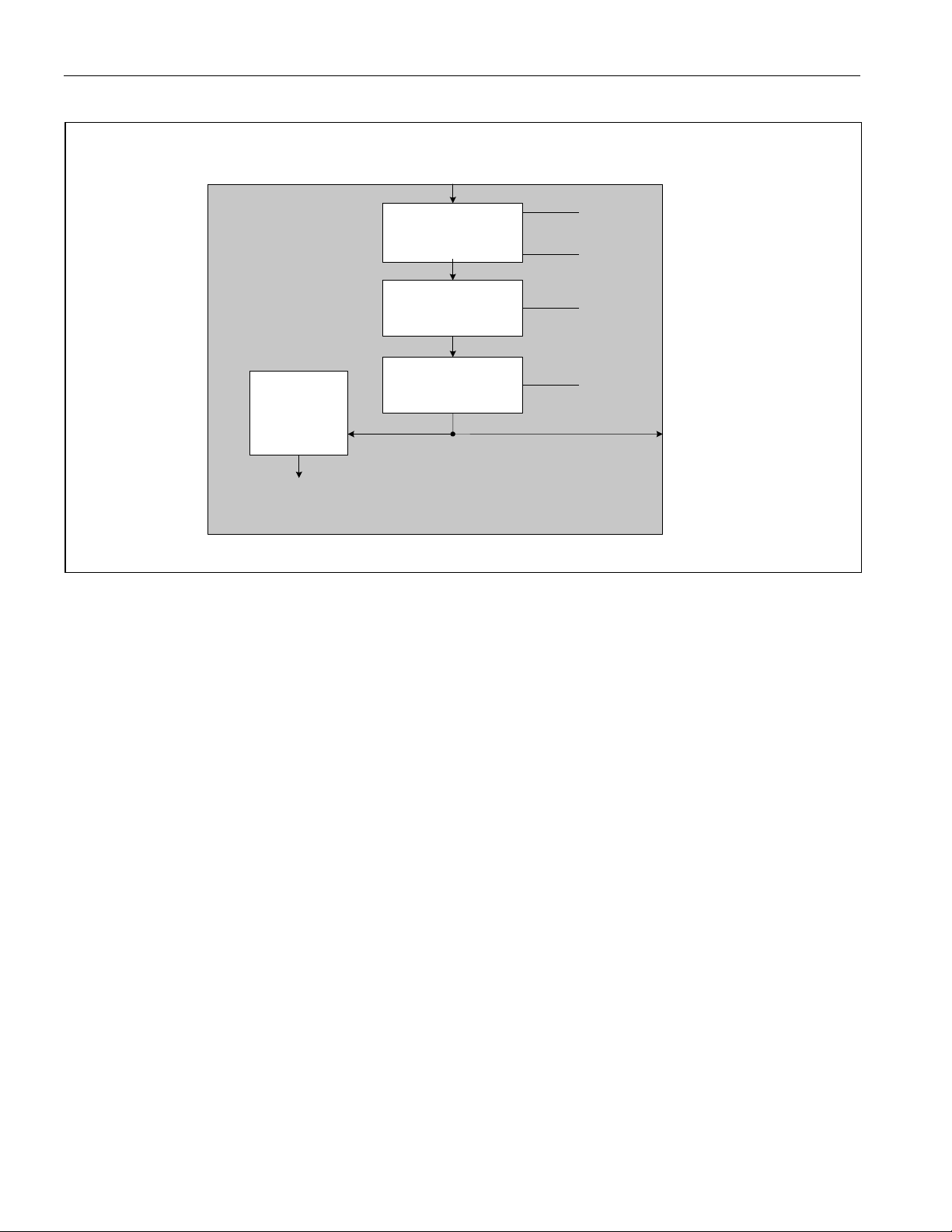
Figure 3-4. Master Clock PLL Diagram
MCLK PIN
PRE-SCALER
DIVIDE BY 1, 2, 4,
OR 8
12.8MHz to
2.048MHz PLL
w/ bypass
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
LIC4.6
(MPS0)
LIC4.7
(MPS1)
LIC2.7
(JACKS1)
X12,X16
MULTIPLER
PLL
TO CLOCK AND DATA
RECOVERY ENGINE IN
RECEIVE LIU
2.048MHz to
1.544MHz PLL
w/ bypass
(HARDWARE MODE)
LIC2.3
(JACKS0)
JA CLOCK
13 of 128
Page 14
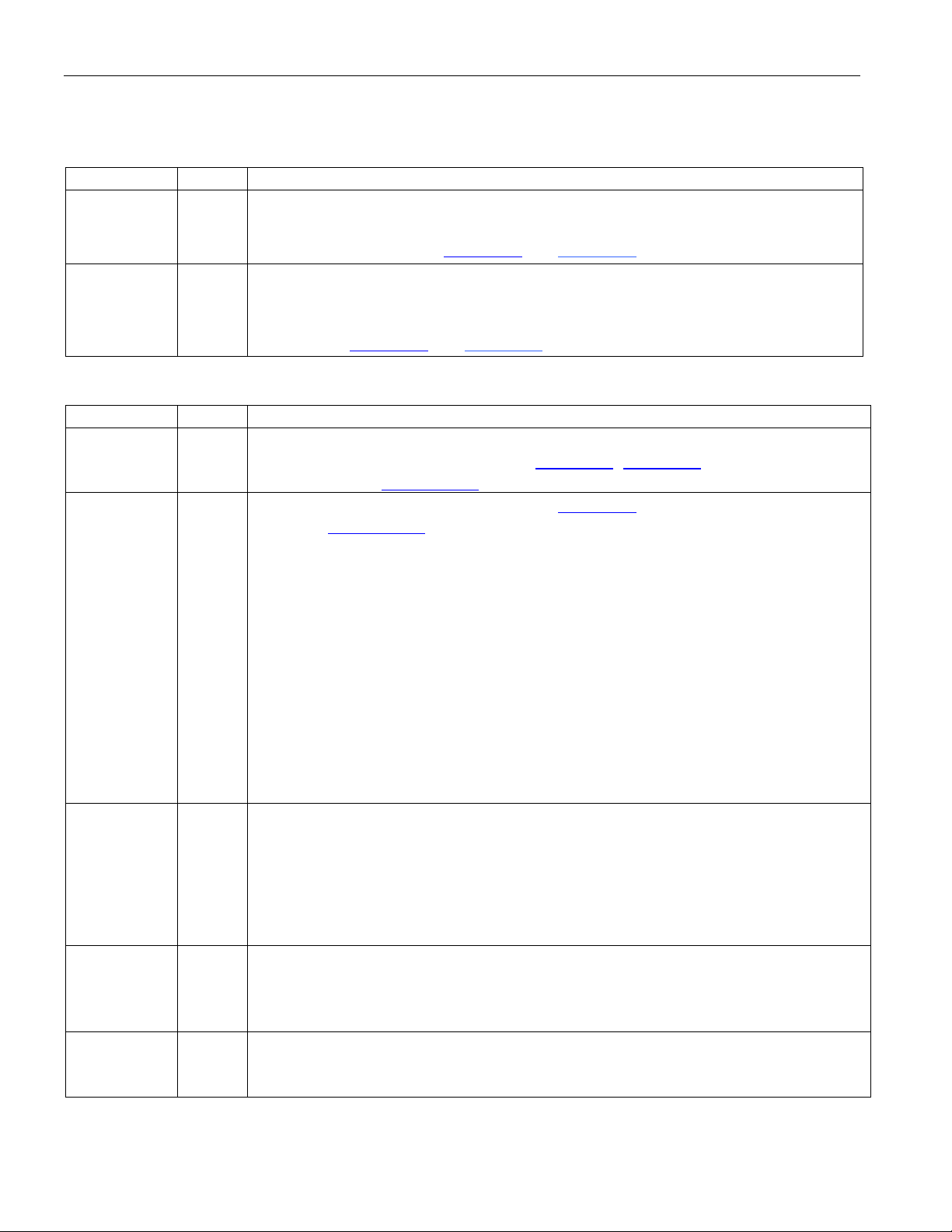
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
4. PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
4.1 Transmit PLL
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Transmit PLL Output. This pin can be selected to output the 1544kHz,
PLL_OUT O
2048kHz, 64kHz, or 6312kHz output from the internal TX PLL or the internal
signal, TX CLOCK. See Figure 3-3 and Figure 3-4.
Transmit Clock Input. A 64kHz, 1.544MHz, 2.048MHz, or 6312kHz primary
TCLK I
clock. May be selected by the TX PLL mux to either directly drive the transmit
section or be converted to one of the other rates prior to driving the transmit
section. See Figure 3-3 and Figure 3-4.
4.2 Transmit Side
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Transmit Serial Data. Source of transmit data sampled on the falling edge of
TSER I
TX CLOCK (an internal signal). See Figure 3-1, Figure 3-3, and the transmit
timing diagram (Figure 20-11).
TSYNC, 8kHz Sync, 400Hz Sync. See Figure 3-1 and the transmit timing
diagram (Figure 20-11).
TS_8K_4 I/O
TCLKO O
TPOSO O
TNEGO O
T1/E1 Mode: In input mode, this pin is sampled on the falling edge of TX
CLOCK (an internal signal) and a pulse at this pin will establish either frame or
multiframe boundaries for the transmit side.
In output mode, this pin is updated on the rising edge of TX CLOCK (an internal
signal) and can be programmed to output a frame or multiframe sync pulse
useful for aligning data.
64KCC Mode: In input mode, this pin is sampled on the falling edge of TX
CLOCK (an internal signal) and will establish the boundary for the 8kHz portion
of the Composite Clock or the 400Hz boundary based on the setting of IOCR1.3.
In output mode, this pin is updated on the rising edge of TX CLOCK (an internal
signal) and will indicate the 8kHz or 400Hz composite clock alignment.
Transmit Clock Output. Buffered clock that is used to clock data through the
transmit-side formatter (i.e., either TCLK or RCLK).
Payload Mode: When payload mode is enabled, this pin outputs a gapped clock
based on the signal selected for transmit clock. In T1 operation, the clock is
gapped during the F-bit position. In E1 mode, the clock is gapped during time
slots 0 and 16.
Transmit Positive-Data Output. In T1 or E1 mode, updated on the rising edge
of TCLKO with the bipolar data out of the transmit-side formatter. Can be
programmed to source NRZ data via the output-data format (IOCR1.0) control
bit. In 64KCC or 6312kHz mode this pin will be low.
Transmit Negative-Data Output. In T1 or E1 mode, updated on the rising edge
of TCLKO with the bipolar data out of the transmit-side formatter. In 64KCC or
6312kHz mode this pin is low.
14 of 128
Page 15
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
4.3 Receive Side
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Receive Clock. Recovered 1.544MHz (T1), 2.048MHz (E1), 6312 kHz (G.703
Synchronization Interface), or 64kHz (Composite Clock) clock.
RCLK O
RS_8K O
400HZ O
RSER O
RLOF_CCE O
RLOS O
Payload Mode: When payload mode is enabled, this pin outputs a gapped clock
based on the internal RCLK. In T1 operation, the clock is gapped during the Fbit position. In E1 mode, the clock is gapped during time slots 0 and 16.
Receive Sync/8kHz Clock
T1/E1 Mode: An extracted pulse, one RCLK wide, is output at this pin that
identifies either frame (IOCR1.5 = 0) or multiframe (IOCR1.5 = 1) boundaries.
If set to output frame boundaries, then through IOCR1.6, RS_8K can also be set
to output double-wide pulses on signaling frames in T1 mode.
64KCC Mode: This pin outputs the extracted 8kHz portion of the composite
clock signal.
6312kHz Mode: This pin is in a high-impedance state.
400Hz Clock Output
T1/E1 Mode: This pin is in a high-impedance state.
64KCC Mode: This pin outputs the 400Hz clock if enabled.
6312kHz Mode: This pin is in a high-impedance state.
Receive Serial Data
T1/E1 Mode: This is the received NRZ serial data updated on the rising edges of
RCLK.
64KCC Mode: This pin is in a high-impedance state.
6312kHz Mode: This pin is in a high-impedance state.
Receive Loss of Frame or Composite Clock Error. This output can be
configured to be a Loss-of-Transmit Clock indicator via IOCR.4 when operating
in T1 or E1 mode.
T1/E1 Mode: Set when the receive synchronizer is searching for frame
alignment (RLOF mode), or set when the signal at the TCLK pin has not
transitioned for approximately 15 periods of the scaled MCLK (LOTC mode).
64KCC Mode: Active high when errors are detected in the 8kHz clock or 400Hz
clock.
6312kHz Mode: This pin is in a high-impedance state.
Receive Loss of Signal
T1 Mode: High when 192 consecutive zeros detected.
E1 Mode: High when 255 consecutive zeros detected.
64KCC Mode: High when consecutive zeros detected for a minimum of 120ms
or the input signal falls below 0.3vp.
6312kHz Mode: High when consecutive zeros detected for a minimum of 60ms.
15 of 128
Page 16
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Receive Alarm Indication Signal
T1 Mode: Toggles high when the receive Blue Alarm is detected.
RAIS O
E1 Mode: Toggles high when the receive AIS is detected.
64KCC Mode: This pin is in a high-impedance state.
6312kHz Mode: This pin is in a high-impedance state.
4.4 Controller Interface
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Active-Low Interrupt/Jitter Attenuator Clock Source Select 1
INT
: Flags host controller during events, alarms, and conditions defined in the
INT/
I/O
JACKS
TMODE1 I
TMODE2 I
TSTRST I
status registers. Active-low open-drain output.
JACKS: Hardware Mode: JA Clock Select. Set this pin high for T1 mode
operation when either a 2.048MHz, 4.096MHz, 8.192MHz, or 16.382MHz
signal is applied at MCLK.
Transmit Mode Select 1. In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this bit is used to
configure the transmit operating mode.
Transmit Mode Select 2. In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this bit is used to
configure the transmit operating mode.
Tri-State Control and Device Reset. A dual-function pin. A zero-to-one
transition issues a hardware reset to the DS26504 register set. Configuration
register contents are set to the default state. Leaving TSTRST high tri-states all
output and I/O pins (including the parallel control port). Set low for normal
operation. Useful for in-board level testing.
Bus Interface Mode Select 1, 0. These bits select the processor interface mode
of operation.
BIS[1:0] I
BIS[1:0] : 00 = Parallel Port Mode (Multiplexed)
01 = Parallel Port Mode (Nonmultiplexed)
10 = Serial Port Mode
11 = Hardware Mode
Data Bus D[7] or Address/Data Bus AD[7]/Receive Internal Termination
Disable
A[7]: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), it serves as the data bus
AD[7]/
RITD
I/O
D[7].
AD[7]: In multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), it serves as the
multiplexed address/data bus AD[7].
RITD: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), it disables the internal receive
termination.
16 of 128
Page 17
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Data Bus D[6] or Address/Data Bus AD[6]/Transmit Internal Termination
Disable
A[6]: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), it serves as the data bus
AD[6]/
TITD
I/O
D[6].
AD[6]: In multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), it serves as the
multiplexed address/data bus AD[6].
TITD: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), it disables the internal transmit
termination.
Data Bus D[5] or Address/Data Bus AD[5]/Receive Framing Mode Select
Bit 1
A[5]: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), it serves as the data bus
AD[5]/
RMODE1
I/O
D[5].
AD[5]: In multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), it serves as the
multiplexed address/data bus AD[5].
RMODE1: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), it selects the receive side
operating mode.
Data Bus D[4] or Address/Data Bus AD[4]/Receive Framing Mode Select
Bit 0
A[4]: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), it serves as the data bus
AD[4]/
RMODE0
I/O
D[4].
AD[4]: In multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), it serves as the
multiplexed address/data bus AD[4].
AD[3]/
TSM
AD[2]/
RSM/SCLK
I/O
I/O
RMODE0: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), it selects the receive side
operating mode.
Data Bus D[3] or Address/Data Bus AD[3]/TS_8K_4 Mode Select
A[3]: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), it serves as the data bus
D[3].
AD[3]: In multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), it serves as the
multiplexed address/data bus AD[3].
TSM: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin selects the function of
TS_8K_4. See the register descriptions for more detailed information.
Data Bus D[2] or Address/Data Bus AD[2]/RS_8K Mode Select/Serial
Clock
A[2]: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), it serves as the data bus
D[2].
AD[2]: In multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), it serves as the
multiplexed address/data bus AD[2].
RSM: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin selects the function of
RS_8K. See the register descriptions for more detailed information.
SCLK: In Serial Port Mode, this pin is the serial clock input.
17 of 128
Page 18
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Data Bus D[1] or Address/Data Bus AD[1]/Receive Mode Select 3/Master
Out-Slave In
A[1]: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), it serves as the data bus
D[1].
AD[1]/
RMODE3/
MOSI
AD[0]/
TCSS0/
MISO
TCSS1
A6/
MPS0
I/O
I/O
I
I
AD[1]: In multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), it serves as the
multiplexed address/data bus AD[1].
RMODE3: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin selects the receive side
operating mode.
MOSI: Serial data input called Master Out-Slave In for clarity of data transfer
direction.
Data Bus D[0] or Address/Data Bus AD[0]/Transmit Clock Source
Select 0/Master In-Slave Out
A[0]: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), it serves as the data bus
D[0].
AD[0]: In multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), it serves as the
multiplexed address/data bus AD[0].
TCSS0: Transmit Clock Source Select 0.
MISO (output): In serial bus mode (BIS[1:0] = 10), this pin serves as the serial
data output Master In-Slave Out.
Transmit Clock Source Select 1
Address Bus Bit A[6]/MCLK Prescale Select 0
A6: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), this pin serves as A[6]. In
multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), these pins are not used and should
be tied low.
A5/CPOL/
TMODE0
MPS0: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), MCLK prescale select is used to set
the prescale value for the PLL.
Address Bus Bit A[5]/Serial Port Clock Polarity Select/Transmit Mode
Select 0
A5: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), this pin serves as A[5]. In
multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), these pins are not used and should
be tied low.
I
CPOL: In Serial Port Mode (BIS[1:0] = 10), this pin selects the serial port clock
polarity. See the functional timing diagrams for the Serial Port Interface.
TMODE0: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin is used to configure the
transmit operating mode.
18 of 128
Page 19
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Address Bus Bit A[4]/Serial Port Clock Phase Select/Line Build-Out
Select 2
A4: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), this pin serves as A[4]. In
A4/CPHA/
L2
multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), these pins are not used and should
be tied low.
I
CPHA: In Serial Port Mode (BIS[1:0] = 10), this pin selects the serial port
clock phase. See the functional timing diagrams for the Serial Port Interface.
L2: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin selects the line build-out value.
Address Bus Bit A[3]/Line Build-Out Select 1
A3: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), this pin serves as A[3]. In
A3/
L1
multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), these pins are not used and should
I
be tied low.
L1: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin selects the line build-out value.
Address Bus Bit A[2]/Line Build-Out Select 0
A2: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), this pin serves as A[2]. In
A2/
L0
multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), these pins are not used and should
I
be tied low.
A1/
TAIS
A0/
E1TS
BTS/
HBE
L0: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin selects the line build-out value.
Address Bus Bit A[1]/Transmit AIS
A1: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), this pin serves as A[1]. In
multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), these pins are not used and should
be tied low.
I
TAIS: When set to 1 and in T1/E1 operating modes, the transmitter transmits an
AIS pattern.
TAIS (64KCC): When set = 0 and in any 64KCC mode, the device transmits an
all-ones signal without BPVs. When set = 1, normal 64KCC transmission is
enabled.
Address Bus Bit A[0]/E1 Termination Select
A0: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), this pin serves as A[0]. In
multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), these pins are not used and should
I
be tied low.
E1TS: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin selects the E1 internal
termination value (0 = 120W, 1 = 75W).
Bus Type Select/Transmit and Receive B8ZS/HDB3 Enable
BTS: Strap high to select Motorola bus timing; strap low to select Intel bus
timing. This pin controls the function of the RD (DS), ALE (AS), and WR
(R/W) pins. If BTS = 1, then these pins assume the function listed in
I
parentheses ().
HBE: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin enables transmit and receive
B8ZS/HDB3 when in T1/E1 operating modes.
19 of 128
Page 20
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Active-Low Read Input-Data Strobe/Receive Mode Select Bit 2
RD(DS)/
RMODE2
RD (DS
I
RMODE2: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), this pin selects the receive side
): DS is active high when BIS[1:0] = 01. See the bus timing diagrams.
operating mode.
Active-Low Chip Select/Remote Loopback Enable
CS
: This active-low signal must be low to read or write to the device. This
CS/
RLB
signal is used for both the parallel port and the serial port modes.
I
RLB: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), when high, remote loopback is
enabled. This function is only valid when the transmit side and receive side are
in the same operating mode.
Address Latch Enable (Address Strobe)/Address Bus Bit 7/MCLK
Prescale Select 1
ALE (AS): In multiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 00), this pin serves to
ALE (AS)/
A7/MPS1
demultiplex the bus on a positive-going edge.
I
A7: In nonmultiplexed bus operation (BIS[1:0] = 01), this pin serves as A[7].
MPS1: In Hardware Mode (BIS[1:0] = 11), MCLK prescale select is used to set
the prescale value for the PLL.
Active-Low Write Input (Read/Write)/Transmit Mode Select 3
WR
WR (R/W)/
TMODE3
I
: In Processor Mode, this pin is the active-low write signal.
TMODE3: In Hardware Mode, this pin selects the transmit-side operating
mode.
4.5 JTAG
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
JTCLK I
JTMS I
JTDI I
JTDO O
JTRST I
JTAG Clock. This clock input is typically a low frequency (less than 10MHz)
50% duty cycle clock signal.
JTAG Mode Select (with pullup). This input signal is used to control the
JTAG controller state machine and is sampled on the rising edge of JTCLK.
JTAG Data Input (with pullup). This input signal is used to input data into
the register that is enabled by the JTAG controller state machine and is sampled
on the rising edge of JTCLK.
JTAG Data Output. This output signal is the output of an internal scan shift
register enabled by the JTAG controller state machine and is updated on the
falling edge of JTCLK. The pin is in the high-impedance mode when a register
is not selected or when the JTRST signal is high. The pin goes into and exits the
high-impedance mode after the falling edge of JTCLK.
Active-Low JTAG Reset. This input forces the JTAG controller logic into the
reset state and forces the JTDO pin into high impedance when low. This pin
should be low while power is applied and set high after the power is stable.
The pin can be driven high or low for normal operation, but must be high for
JTAG operation.
20 of 128
Page 21
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
4.6 Line Interface
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
Master Clock Input. A (50ppm) clock source. This clock is used internally for
both clock/data recovery and the jitter attenuator for both T1 and E1 modes. A
MCLK I
RTIP I
RRING I
TTIP O
TRING O
THZE I
quartz crystal can be applied across MCLK and XTALD rather than the clock
source. The clock rate can be 16.384MHz, 8.192MHz, 4.096MHz, or
2.048MHz. When using the DS26504 in T1-only operation, a 1.544MHz
(50ppm) clock source can be used.
Receive Tip. Analog input for clock recovery circuitry. This pin connects via a
1:1 transformer to the network. See the Line Interface Unit section for details.
Receive Ring. Analog input for clock recovery circuitry. This pin connects via
a 1:1 transformer to the network. See the Line Interface Unit section for details.
Transmit Tip. Analog line-driver output. This pin connects via a 1:2 step-up
transformer to the network. See the Line Interface Unit section for details.
Transmit Ring. Analog line-driver output. This pin connects via a 1:2 step-up
transformer to the network. See the Line Interface Unit section for details.
Transmit High-Impedance Enable. When high, TTIP and TRING will be
placed into a high-impedance state.
4.7 Power
NAME TYPE FUNCTION
DVDD —
RVDD —
TVDD —
DVSS — Digital Signal Ground. 0.0V. Should be tied to the RVSS and TVSS pins.
RVSS —
TVSS —
Digital Positive Supply. 3.3V ±5%. Should be tied to the RVDD and TVDD
pins.
Receive Analog Positive Supply. 3.3V ±5%. Should be tied to the DVDD and
TVDD pins.
Transmit Analog Positive Supply. 3.3V ±5%. Should be tied to the DVDD
and RVDD pins.
Receive Analog Signal Ground. 0.0V. Should be tied to the DVSS and TVSS
pins.
Transmit Analog Signal Ground. 0.0V. Should be tied to the DVSS and
RVSS pins.
21 of 128
Page 22
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
5. PINOUT
Table 5-1. LQFP Pinout
MODE
PIN TYPE
1 I/O AD2 SCLK RSM
2 I/O AD3 — TSM
3 I/O AD4 — RMODE0
4 I/O AD5 — RMODE1
5 I/O AD6 — TITD
6 I/O AD7 — RITD
7, 24,
58
8, 22,
56
9 I A0 — E1TS
10 I A1 — TAIS
11 I A2 — L0
12 I A3 — L1
13 I A4 CPHA L2
14 I A5 CPOL TMODE0
15 I A6 — MPS0
16 I ALE (AS)/A7 — MPS1
17 I TCLK TCLK TCLK External Transmit Clock Input
I DVDD DVDD DVDD Digital Positive Supply
I DVSS DVSS DVSS Digital Signal Ground
PARALLEL
PORT
SERIAL
PORT
HARDWARE
Parallel Port Mode: Address/Data Bus Bit 2
Serial Port Mode: Serial Clock
Hardware Mode: RS_8K Mode Select
Parallel Port Mode: Address/Data Bus Bit 3
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to VSS.
Hardware Mode: TS_8K_4 Mode Select
Parallel Port Mode: Address/Data Bus Bit 4
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to VSS.
Hardware Mode: Receive Mode Select 0
Parallel Port Mode: Address/Data Bus Bit 5
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to VSS.
Hardware Mode: Receive Mode Select 1
Parallel Port Mode: Address/Data Bus Bit 6
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to VSS.
Hardware Mode: Transmit Internal Termination Disable
Parallel Port Mode: Address/Data Bus Bit 7
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to V
Hardware Mode: Receive Internal Termination Disable
Parallel Port Mode: Address Bus Bit 0
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to VSS.
Hardware Mode: E1 Internal Termination Select
Parallel Port Mode: Address Bus Bit 1
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to VSS.
Hardware Mode: Transmit AIS
Parallel Port Mode: Address Bus Bit 2
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to VSS.
Hardware Mode: Line Build-Out Select 0
Parallel Port Mode: Address Bus Bit 3
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to VSS.
Hardware Mode: Line Build-Out Select 1
Parallel Port Mode: Address Bus Bit 4
Serial Port Mode: Serial Port Clock Phase Select
Hardware Mode: Line Build-Out Select 2
Parallel Port Mode: Address Bus Bit 5
Serial Port Mode: Serial Port Clock Polarity Select
Hardware Mode: Transmit Mode Select 0
Parallel Port Mode: Address Bus Bit 6
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to VSS.
Hardware Mode: MCLK Prescaler Select 0
Parallel Port Mode: Address Latch Enable/Address Bus
Bit 7
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to V
Hardware Mode: MCLK Prescaler Select 1
FUNCTION
.
SS
.
SS
22 of 128
Page 23
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
MODE
PIN TYPE
PARALLEL
PORT
SERIAL
PORT
HARDWARE
FUNCTION
18 O TCLKO TCLKO TCLKO Transmit Clock Output
19 O TNEGO TNEGO TNEGO Transmit Negative-Data Output
20 O TPOSO TPOSO TPOSO Transmit Positive-Data Output
21 I TSER TSER TSER Transmit Serial Data
23 I/O TS_8K_4 TS_8K_4 TS_8K_4
T1/E1 Mode: Transmit Frame/Multiframe Sync
64KCC Mode: Transmit 8kHz or 400Hz Sync
25 O RCLK RCLK RCLK Receive Clock
26 O RS_8K RS_8K RS_8K
T1/E1 Mode: Receive Frame/Multiframe Boundary
64KCC Mode: Receive 8kHz Output
27 O 400HZ 400HZ 400HZ 400Hz Output in Composite Clock Mode
28 O RSER RSER RSER Receive Serial Data
29 O RAIS RAIS RAIS Receive Alarm Indication Signal
30 O RLOF_CCE RLOF_CCE RLOF_CCE Receive Loss of Frame_Composite Clock Error
Parallel Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to
.
V
31 I — — TCSS1
SS
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to V
Hardware Mode: Transmit Clock Source Select 1
32 O RLOS RLOS RLOS Receive Loss of Signal
33 I JTMS JTMS JTMS IEEE 1149.1 Test Mode Select
34 I JTCLK JTCLK JTCLK IEEE 1149.1 Test Clock Signal
35 I JTRST JTRST JTRST IEEE 1149.1 Test Reset
36 I JTDI JTDI JTDI IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Input
37 O JTDO JTDO JTDO IEEE 1149.1 Test Data Output
38 I RVDD RVDD RVDD Receive Analog Positive Supply
39 I TSTRST TSTRST TSTRST Test/Reset
40,
43, 45
I RVSS RVSS RVSS Receive Analog Signal Ground
41 I RTIP RTIP RTIP Receive Analog Tip Input
42 I RRING RRING RRING Receive Analog Ring Input
44 I MCLK MCLK MCLK Master Clock Input
Parallel Port Mode: Interrupt
46 I/O INT INT JACKS
Serial Port Mode: Interrupt
Hardware Mode: Jitter Attenuator Clock Select
47 O PLL_OUT PLL_OUT PLL_OUT Transmit PLL (TX PLL) Clock Output
Parallel Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to
.
V
48 I — — TMODE2
SS
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to V
Hardware Mode: Transmit Mode Select 2
Parallel Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to
.
V
49 I — — TMODE1
SS
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to V
Hardware Mode: Transmit Mode Select 1
50 I THZE THZE THZE Transmit High-Impedance Enable
51 O TTIP TTIP TTIP Transmit Analog Tip Output
52 I TVSS TVSS TVSS Transmit Analog Signal Ground
53 I TVDD TVDD TVDD Transmit Analog Positive Supply
54 O TRING TRING TRING Transmit Analog Ring Output
Parallel Port Mode: Bus Type Select (Motorola/Intel)
55 I BTS — HBE
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to V
Hardware Mode: Receive and Transmit HDB3/B8ZS
Enable
57 I BIS0 BIS0 BIS0 Bus Interface Select Mode 0
23 of 128
.
SS
.
SS
.
SS
.
SS
Page 24
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
MODE
PIN TYPE
PARALLEL
PORT
SERIAL
PORT
HARDWARE
FUNCTION
59 I BIS1 BIS1 BIS1 Bus Interface Select Mode 1
Parallel Port Mode: Chip Select (Active Low)
60 I CS CS RLB
Serial Port Mode: Chip Select (Active Low)
Hardware Mode: Remote Loopback Enable
Parallel Port Mode: Read Input (Data Strobe), Active
61 I RD (DS) — RMODE2
Low
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to V
Hardware Mode: Receive Mode Select 2
Parallel Port Mode: Write Input (Read/Write), Active
62 I WR (R/W) — TMODE3
Low
Serial Port Mode: Unused, should be connected to V
Hardware Mode: Transmit Mode Select 3
Parallel Port Mode: Address/Data Bus Bit 0
63 I/O AD0 MISO TCSS0
Serial Port Mode: Serial Data Out (Master In-Slave
Out)
Hardware Mode: Transmit Clock Source Select 0
Parallel Port Mode: Address/Data Bus Bit 1
64 I/O AD1 MOSI RMODE3
Serial Port Mode: Serial Data In (Master Out-Slave In)
Hardware Mode: Receive Mode Select 3
.
SS
.
SS
24 of 128
Page 25
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
6. HARDWARE CONTROLLER INTERFACE
In Hardware Controller mode, the parallel and serial port pins are reconfigured to provide direct access to
certain functions in the port. Only a subset of the device’s functionality is available in hardware mode.
Each register description throughout the data sheet indicates the functions that may be controlled in
hardware mode and several alarm indicators that are available in both hardware and processor mode.
Also indicated are the fixed states of the functions not controllable in hardware mode.
6.1 Transmit Clock Source
Refer to Figure 3-3. In Hardware Controller mode, the input to the TX PLL is always TCLK PIN. TX
CLOCK is selected by the TCSS0 and TCSS1 pins, as shown in Table 6-1
the same signal as select for TX CLOCK. If the user wants to slave the transmitter to the recovered
clock, then the RCLK pin must be tied to the TCLK pin externally.
. The PLL_OUT pin is always
Table 6-1. Transmit Clock Source
TCSS1
PIN 31
0 0 The TCLK pin is the source of transmit clock.
TCSS0
PIN 63
TRANSMIT CLOCK SOURCE
0 1 The PLL_CLK is the source of transmit clock.
1 0
1 1 The signal present at RCLK is the transmit clock.
The scaled signal present at MCLK as the transmit
clock.
6.2 Internal Termination
In Hardware Controller mode, the internal termination is automatically set according to the receive or
transmit mode selected. It can be disabled via the TITD and RITD pins. If internal termination is enabled
in E1 mode, the E1TS pin is use to select 75W or 120W termination. The E1TS pin applies to both
transmit and receive.
Table 6-2. Internal Termination
PIN FUNCTION
Transmit Internal Termination Disable. Disables the internal transmit termination.
TITD
PIN 5
RITD
PIN 6
E1TS
PIN 9
The internal transmit termination value is dependent on the state of the TMODEx pins.
0 = internal transmit termination enabled
1 = internal transmit termination disabled
Receive Internal Termination Disable. Disables the internal receive termination. The
internal receive termination value is dependent on the state of the RMODEx pins.
0 = internal receive termination enabled
1 = internal receive termination disabled
E1 Termination Select. Selects 120W or 75W internal termination when one of the E1
modes is selected and internal termination is enabled. If E1 is selected for both transmit
and receive, then both terminations will be the same.
0 = 75W
1 = 120W
25 of 128
Page 26
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
6.3 Line Build-Out
Table 6-3. E1 Line Build-Out
L2
PIN 13
0 0 0 75Ω normal 1:2 N.M. 0
0 0 1 120Ω normal 1:2 N.M. 0
1 0 0 75Ω with high return loss (Note 2) 1:2 21dB 6.2Ω
1 0 1 120Ω with high return loss (Note 2) 1:2 21dB 11.6Ω
1 1 0
1 1 1
L1
PIN 12
L0
PIN 11
APPLICATION
75W normal + enable transmit and receive
gapped clock
120W normal + enable transmit and receive
gapped clock
N
(Note 1)
RETURN
LOSS
Rt
(Note 1)
1:2 N.M 0
1:2 N.M 0
Table 6-4. T1 Line Build-Out
L2
PIN 13
0 0 0 DSX-1 (0 to 133 feet)/0dB CSU 1:2 N.M. 0
0 0 1 DSX-1 (133 to 266 feet) 1:2 N.M. 0
0 1 0 DSX-1 (266 to 399 feet) 1:2 N.M. 0
0 1 1 DSX-1 (399 to 533 feet) 1:2 N.M. 0
1 0 0 DSX-1 (533 to 655 feet) 1:2 N.M. 0
1 0 1 Reserved — — —
1 1 0 Reserved — — —
1 1 1
N.M. = not meaningful
Note 1: Transformer turns ratio.
Note 2: TTD pin must be connected high in this mode.
L1
PIN 12
L0
PIN 11
APPLICATION
DSX-1 (0 to 133ft)/0dB CSU + enable
transmit and receive gapped clock
N
(Note 1)
RETURN
LOSS
Rt
(Note 1)
1:2 N.M. 0
26 of 128
Page 27
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
6.4 Receiver Operating Modes
Table 6-5. Receive Path Operating Mode
RMODE3
PIN 64
0 0 0 0 T1 D4 Framing Mode
0 0 0 1 T1 ESF Framing Mode
0 0 1 0 J1 D4 Framing Mode
0 0 1 1 J1 ESF Framing Mode
0 1 0 0 E1 FAS Framing Mode
0 1 0 1 E1 CAS Framing Mode
0 1 1 0 E1 CRC4 Framing Mode
0 1 1 1 E1 CAS and CRC4 Framing Mode
1 0 0 0 E1 G.703 2048kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 0 1 64kHz + 8kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 1 0
1 0 1 1 6312kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 1 0 0 GR378 64kHz Composite Clock
1 1 0 1 G.703 Level B 64kHz + 8kHz Synchronization Interface
1 1 1 0 Reserved
1 1 1 1 Reserved
RMODE2
PIN 61
RMODE1
PIN 4
RMODE0
PIN 3
RECEIVE PATH OPERATING MODE
64kHz + 8kHz + 400Hz Synchronization Interface
Mode
6.5 Transmitter Operating Modes
Table 6-6.Transmit Path Operating Mode
TMODE3
PIN 62
0 0 0 0 T1 D4 Framing Mode
0 0 0 1 T1 ESF Framing Mode
0 0 1 0 J1 D4 Framing Mode
0 0 1 1 J1 ESF Framing Mode
0 1 0 0 E1 FAS Framing Mode
0 1 0 1 E1 CAS Framing Mode
0 1 1 0 E1 CRC4 Framing Mode
0 1 1 1 E1 CAS and CRC4
1 0 0 0 E1 G.703 2048 kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 0 1 64kHz + 8kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 1 0
1 0 1 1 6312kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 1 0 0 GR378 64kHz Composite Clock
1 1 0 1
1 1 1 0 Reserved
1 1 1 1 Reserved
TMODE2
PIN 48
TMODE1
PIN 49
TMODE0
PIN 14
64kHz + 8kHz + 400Hz Synchronization Interface
Mode
G.703 Level B 64kHz + 8kHz Synchronization
Interface
TRANSMIT PATH OPERATING MODE
27 of 128
Page 28
6.6 MCLK Pre-Scaler
Table 6-7. MCLK Pre-Scaler for T1 Mode
MPS1
PIN 16
0 0 0 1.544
0 1 0 3.088
1 0 0 6.176
1 1 0 12.352
0 0 1 2.048
0 1 1 4.096
1 0 1 8.192
1 1 1 16.384
MPS0
PIN 15
JACKS
PIN 46
MCLK
(MHz)
Table 6-8. MCLK Pre-Scaler for E1 Mode
MPS1
PIN 16
0 0 0 2.048
0 1 0 4.096
1 0 0 8.192
1 1 0 16.384
MPS0
PIN 15
JACKS
PIN 46
MCLK
(MHz)
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
6.7 Payload Clock Output
The TCLKO and RCLK pins can output a clock with the F-Bit (T1) or the TS0 and TS16 (E1) bit
position gapped out. This function is only available in T1 or E1 mode. This is useful in basic transceiver
applications where a payload or “demand” clock is needed. In Hardware Mode, the payload clock output
is selected by the L0, L1, and L2 line build-out pins. In Hardware Mode, this function is only available in
certain build-out modes. See the line build-out tables in Section 6.3 for selecting the payload clock mode.
28 of 128
Page 29

6.8 Other Hardware Controller Mode Features
Table 6-9. Other Operational Modes
PIN DESCRIPTION
RSM
PIN 1
TSM
PIN 2
RLB
PIN 60
TAIS
PIN 10
HBE
PIN 55
RS_8K Mode Select: Selects frame or multiframe pulse at RS_8K pin.
0 = frame mode
1 = multiframe mode
TS_8K_4 Mode Select: In T1 or E1 operation, selects frame or multiframe mode for the
TS_8K_4 pin.
0 = frame mode
1 = multiframe mode
Remote Loopback Enable: In this loopback, data input to the framer portion of the
DS26504 will be transmitted back to the transmit portion of the LIU. Data will continue
to pass through the receive side framer of the DS26504 as it would normally and the data
from the transmit side formatter will be ignored.
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
Transmit AIS. In T1, E1, and J1 modes, this pin transmits an unframed all-ones pattern.
0 = normal transmission
1 = transmit AIS alarm
In any 64KCC mode, this pin transmits all ones without any sub-rate encoding (no
BPVs).
0 = transmit all-ones pattern without BPVs (sub-rates)
1 = normal transmission
Receive and Transmit HDB3/B8ZS Enable
0 = HDB3/B8ZS disabled
1 = HDB3/B8ZS enabled
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
29 of 128
Page 30
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
7. PROCESSOR INTERFACE
The DS26504 is controlled via a nonmultiplexed (BIS[1:0] = 01) or a multiplexed (BIS[1:0] = 00)
parallel bus. There is also a serial bus mode option, as well as a hardware mode of operation. The bus
interface type is selected by BIS1 and BIS0 as shown in Table 7-1.
Table 7-1. Port Mode Select
BIS1 BIS0 PORT MODE
0 0 Parallel Port Mode (Multiplexed)
0 1 Parallel Port Mode (Nonmultiplexed)
1 0 Serial Port Mode (SPI)
1 1 Hardware Mode
7.1 Parallel Port Functional Description
In parallel mode, the DS26504 can operate with either Intel or Motorola bus timing configurations. If the
BTS pin is tied low, Intel timing will be selected; if tied high, Motorola timing will be selected. All
Motorola bus signals are listed in parentheses (). See the timing diagrams in the AC Electrical
Characteristics section for more details.
7.2 SPI Serial Port Interface Functional Description
A serial SPI bus interface is selected when the bus select is 10 (BIS[1:0] = 10). In this mode, a
master/slave relationship is enabled on the serial port with three signal lines (SCK, MOSI, and MISO)
and a chip select (CS), with the DS26504 acting as the slave. Port read/write timing is not related to the
system read/write timing, thus allowing asynchronous, half-duplex operation. See the AC Electrical
Characteristics section for the AC timing characteristics of the serial port.
7.2.1 Clock Phase and Polarity
Clock Phase and Polarity are selected by the CPHA and CPOL pins. The slave device should always be
configured to match the bus master. See the SPI Serial Port Mode section for detailed functional timing
diagrams.
7.2.2 Bit Order
The most significant bit (MSB) of each byte is transmitted first.
7.2.3 Control Byte
The bus master will transmit two control bytes following a chip select to a slave device. The MSB will be
a R/W bit (1 = read, 0 = write). The next 6 bits will be padded with zeros. The LSB of the first byte will
be A[7]. The second control byte will be the address bits (A[6:0]) of the target register, followed by a
Burst bit in the LSB position (1 = Burst, 0 = Nonburst).
7.2.4 Burst Mode
The last bit of the second control byte (LSB) is the Burst Mode bit. When the Burst bit is enabled (set to
1) and a read operation is performed, the register address is automatically incremented after the LSB of
the previous byte read to the next register address. Data will be available on the next clock edge following
the LSB of the previous byte read. When the Burst bit is enabled (set to 1) and a write operation is
performed, the register address will be automatically incremented to the next byte boundary following the
LSB of the previous register write, and 8 more data bits will be expected on the serial bus. Burst accesses
30 of 128
Page 31

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
are terminated when CS is removed. If CS is removed before all 8 bits of the data are read, the remaining
data will be lost. If CS is removed before all 8 bits of data are written to the part, no write access will
occur and the target register will not be updated.
Note: During a Burst-Read access, data must be fetched internally to the part as the LSB of the previous
byte is transmitted out. If this pre-fetch read access occurs to a Clear-On-Read register or a FIFO register
address, and the Burst access is terminated without reading this byte out of the port, the data will be lost
and/or the register cleared. Users should not terminate their Burst Read accesses at the address byte
proceeding a Clear-On-Read register or a FIFO register. Data loss could occur due to the internal prefetch operation performed by the interface.
7.2.5 Register Writes
The register write sequence is shown in the functional timing diagrams in Section 18. After a CS, the bus
master transmits a write control byte containing the R/W bit, the target register address, and the Burst bit.
These two control bytes will be followed by the data byte to be written. After the first data byte, if the
Burst bit is set, the DS26504 auto-increments its address counter and writes each byte received to the next
higher address location. After writing address FFh, the address counter rolls over to 00h and continues to
auto-increment.
7.2.6 Register Reads
The register read sequence is shown in Section 18. After a CS, the bus master transmits a read control
byte containing the R/W bit, the target register address, and the Burst bit. After these two control bytes,
the DS26504 responds with the requested data byte. After the first data byte, if the Burst bit is set, the
DS26504 auto-increments its address counter and transmits the byte stored in the next higher address
location. Note the warning mentioned above, as data loss could potentially occur due to the data pre-fetch
that is required to support this mode. After reading address FFh, the address counter rolls over to 00h and
continues to auto-increment.
31 of 128
Page 32

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
7.3 Register Map
Table 7-2. Register Map Sorted By Address
ADDRESS TYPE REGISTER NAME
00 R/W Test Reset Register TSTRREG
01 R/W I/O Configuration Register 1 IOCR1
02 R/W I/O Configuration Register 2 IOCR2
03 R/W T1 Receive Control Register 1 T1RCR1
04 R/W T1 Receive Control Register 2 T1RCR2
05 R/W T1 Transmit Control Register 1 T1TCR1
06 R/W T1 Transmit Control Register 2 T1TCR2
07 R/W T1 Common Control Register T1CCR
08 R/W Mode Configuration Register MCREG
09 R/W Transmit PLL Control Register 1 TPCR1
0A R/W Transmit PLL Control Register 2 —
0B — Reserved (Note 1)
0C — Reserved (Note 1)
0D — Reserved (Note 1)
0E — Reserved (Note 1)
0F — Reserved (Note 1)
10 R Device Identification Register IDR
11 R Information Register 1 INFO1
12 R Information Register 2 INFO2
13 R Interrupt Information Register IIR
14 R Status Register 1 SR1
15 R/W Interrupt Mask Register 1 IMR1
16 R Status Register 2 SR2
17 R/W Interrupt Mask Register 2 IMR2
18 R Status Register 3 SR3
19 R/W Interrupt Mask Register 3 IMR3
1A R Status Register 4 SR4
1B R/W Interrupt Mask Register 4 IMR4
1C R Information Register 3 INFO3
1D R/W E1 Receive Control Register E1RCR
1E R/W E1 Transmit Control Register E1TCR
1F R/W BOC Control Register BOCC
20 R/W Loopback Control Register LBCR
21 R Status Register 5 —
22 R/W Internal Mask Register 5 —
23-2F — Reserved (Note 1)
30 R/W Line Interface Control 1 LIC1
31 R/W Line Interface Control 2 LIC2
32 R/W Line Interface Control 3 LIC3
33 R/W Line Interface Control 4 LIC4
34 R/W Transmit Line Build-Out Control TLBC
35-3F — Reserved (Note 1)
40 R/W Transmit Align Frame Register TAF
41 R/W Transmit Non-Align Frame Register TNAF
REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
32 of 128
Page 33

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
ADDRESS TYPE REGISTER NAME
REGISTER
ABBREVIATION
42 R/W Transmit Si Align Frame TSiAF
43 R/W Transmit Si Non-Align Frame TSiNAF
44 R/W Transmit Remote Alarm Bits TRA
45 R/W Transmit Sa4 Bits TSa4
46 R/W Transmit Sa5 Bits TSa5
47 R/W Transmit Sa6 Bits TSa6
48 R/W Transmit Sa7 Bits TSa7
49 R/W Transmit Sa8 Bits TSa8
4A R/W Transmit Sa Bit Control Register TSACR
4B-4F — Reserved (Note 1)
50 R Receive FDL Register RFDL
51 R/W Transmit FDL Register TFDL
52 R/W Receive Facility Data Link Match Register 1 RFDLM1
53 R/W Receive Facility Data Link Match Register 2 RFDLM2
54-55 — Reserved (Note 1)
56 R Receive Align Frame Register RAF
57 R Receive Non-Align Frame Register RNAF
58 R Receive Si Align Frame RSiAF
59 R Receive Si Non-Align Frame RSiNAF
5A R Receive Remote Alarm Bits RRA
5B R Receive Sa4 Bits RSa4
5C R Receive Sa5 Bits RSa5
5D R Receive Sa6 Bits RSa6
5E R Receive Sa7 Bits RSa7
5F R Receive Sa8 Bits RSa8
60-EF — Reserved (Note 1)
F0 R/W Test Register 1 TEST1 (Note 2)
F1 R/W Test Register 2 TEST2 (Note 2)
F2 R/W Test Register 3 TEST3 (Note 2)
F3 R/W Test Register 4 TEST4 (Note 2)
F4 R/W Test Register 5 TEST5 (Note 2)
F5 R/W Test Register 6 TEST6 (Note 2)
F6 R/W Test Register 7 TEST7 (Note 2)
F7 R/W Test Register 8 TEST8 (Note 2)
F8 R/W Test Register 9 TEST9 (Note 2)
F9 R/W Test Register 10 TEST10 (Note 2)
FA R/W Test Register 11 TEST11 (Note 2)
FB R/W Test Register 12 TEST12 (Note 2)
FC R/W Test Register 13 TEST13 (Note 2)
FD R/W Test Register 14 TEST14 (Note 2)
FE R/W Test Register 15 TEST15 (Note 2)
FF R/W Test Register 16 TEST16 (Note 2)
Note 1: Register reserved for future use and must remain = 0.
Note 2: TEST1 to TEST16 registers are used only by the factory and must remain = 0.
33 of 128
Page 34

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
7.3.1 Power-Up Sequence
The DS26504 contains an on-chip power-up reset function that automatically clears the writeable register
space immediately after power is supplied to the device. The user can issue a chip reset at any time.
Issuing a reset will disrupt signals flowing through the DS26504 until the device is reprogrammed. The
reset can be issued through hardware using the TSTRST pin or through software using the SFTRST
function in the master mode register. The LIRST (LIC2.6) should be toggled from zero to one to reset the
line interface circuitry. (It will take the DS26504 about 40ms to recover from the LIRST bit being
toggled.)
7.3.2 Test Reset Register
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — TEST1 TEST0 — — — SFTRST
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Software-Issued Reset (SFTRST). A zero-to-one transition causes the register space in the DS26504 to be cleared. A
reset clears all configuration and status registers. The bit automatically clears itself when the reset has completed.
Bits 1, 2, 3, 6, 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bits 4 and 5: Test Mode Bits (TEST0 and TEST1). Test modes are used to force the output pins of the DS26504 into known
states. This can facilitate the checkout of assemblies during the manufacturing process and also be used to isolate devices from
shared buses.
TEST1 TEST0 EFFECT ON OUTPUT PINS
0 0 Operate normally
0 1 Force all output pins into tri-state (including all I/O pins and parallel port pins)
1 0 Force all output pins low (including all I/O pins except parallel port pins)
1 1 Force all output pins high (including all I/O pins except parallel port pins)
X X X X X X X X
TSTRREG
Test Reset Register
00h
34 of 128
Page 35

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
7.3.3 Mode Configuration Register
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TMODE3 TMODE2 TMODE1 TMODE0 RMODE3 RMODE2 RMODE1 RMODE0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bits 0 to 3: Receive Mode Configuration (RMODE[0:3]). Used to select the operating mode of the receive path for the
DS26504.
Bits 4 to 7: Transmit Mode Configuration (TMODE[4:7]). Used to select the operating mode of the transmit path for the
DS26504.
TMODE3
PIN 62
RMODE3 RMODE2 RMODE1 RMODE0 RECEIVE PATH OPERATING MODE
0 0 0 0 T1 D4 Framing Mode
0 0 0 1 T1 ESF Framing Mode
0 0 1 0 J1 D4 Framing Mode
0 0 1 1 J1 ESF Framing Mode
0 1 0 0 E1 FAS Framing Mode
0 1 0 1 E1 CAS Framing Mode
0 1 1 0 E1 CRC4 Framing Mode
0 1 1 1 E1 CAS and CRC4 Framing Mode
1 0 0 0 E1 G.703 2048 kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 0 1 64kHz + 8kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 1 0 64kHz + 8kHz + 400Hz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 1 1 6312kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 1 0 0 GR378 64kHz Composite Clock
1 1 0 1 G.703 Level B 64kHz + 8kHz Synchronization Interface
1 1 1 0 Reserved
1 1 1 1 Reserved
TMODE3 TMODE2 TMODE1 TMODE0 TRANSMIT PATH OPERATING MODE
0 0 0 0 T1 D4 Framing Mode
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 J1 D4 Framing Mode
0 0 1 1 J1 ESF Framing Mode
0 1 0 0 E1 FAS Framing Mode
0 1 0 1 E1 CAS Framing Mode
0 1 1 0 E1 CRC4 Framing Mode
0 1 1 1 E1 CAS and CRC4
1 0 0 0 E1 G.703 2048 kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 0 1 64kHz + 8kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 1 0 64kHz + 8kHz + 400Hz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 0 1 1 6312kHz Synchronization Interface Mode
1 1 0 0 GR378 64kHz Composite Clock
1 1 0 1 G.703 Level B 64kHz + 8kHz Synchronization Interface
1 1 1 0 Reserved
1 1 1 1 Reserved
MCREG
Mode Configuration Register
08h
TMODE2
PIN 48
TMODE1
PIN 49
TMODE0
PIN 14
RMODE3
PIN 64
T1 ESF Framing Mode (Note: In this mode, the TFSE
(T1TCR2.6) bit should be set = 0.)
RMODE2
PIN 61
RMODE1
PIN 4
RMODE0
PIN 3
35 of 128
Page 36

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TPLLOFS1 TPLLOFS0 PLLOS TPLLIFS1 TPLLIFS0 TPLLSS TCSS1 TCSS0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
For more information on all the bits in the Transmit PLL control register, refer to Figure 3-3
Bits 0 and 1: Transmit Clock (TX CLOCK) Source Select (TCSS[0:1]). These bits control the output of the TX PLL
Clock Mux function. See Figure 3-3
TCSS1 TCSS0
0 0 The TCLK pin is the source of transmit clock.
0 1 The PLL_CLK is the source of transmit clock.
1 0 The scaled signal present at MCLK as the transmit clock.
1 1 The signal present at RCLK is the transmit clock.
Bit 2: Transmit PLL_CLK Source Select (TPLLSS). Selects the reference signal for the TX PLL.
0 = Use the recovered network clock. This is the same clock available at the RCLK pin (output).
1 = Use the externally provided clock present at the TCLK pin.
Bit 3 and 4: Transmit PLL Input Frequency Select (TPLLIFS[0:1]). These bits, along with TPLLIFS2 (TPCR2.0), are
used to indicate the reference frequency being input to the TX PLL.
TPLLIFS2
(TPCR2.0)
0 0 0 1.544MHz
0 0 1 2.048MHz
0 1 0 64kHz
0 1 1 6312kHz
1 0 0 8kHz
1 0 1 19.44MHz
Bit 5: PLL_OUT Select (PLLOS). This bit selects the source for the PLL_OUT pin. See Figure 3-3
0 = PLL_OUT is sourced directly from the TX PLL.
1 = PLL_OUT is the output of the TX PLL mux.
Bits 6 and 7: Transmit PLL Output Frequency Select (TPLLOFS[0:1]). These bits, along with TPLLOFS1 (TPCR2.1),
are used to select the TX PLL output frequency.
TPLLOFS2
(TPCR2.1)
0 0 0 1.544MHz
0 0 1 2.048MHz
0 1 0 64kHz
0 1 1 6312kHz
1 0 0 8kHz
1 0 1 19.44MHz
0 0 0 0 0 0
TPLLIFS1 TPLLIFS0
TPLLOFS1 TPLLOFS0
TPCR1
Transmit PLL Control Register 1
09h
.
TRANSMIT CLOCK (TX CLOCK) SOURCE
(See Figure 3-3
TX PLL INPUT
FREQUENCY
TX PLL OUTPUT
FREQUENCY
TCSS1
PIN 31
.
)
TCSS0
PIN 63
.
36 of 128
Page 37

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — —
Default 0 0
Bit 0: Transmit Clock Source Select (TPLLOFS2). This bit, along with TPLLOFS0 (TPCR1.7) and TPLLOFS1
(TPCR1.6), is used to indicate the reference frequency being input to the TX PLL. See the table in TPCR1 register description.
Bit 1: Transmit Clock Source Select (TPLLIFS2). This bit, along with TPLLIFS0 (TPCR1.4) and TPLLIFS1 (TPCR1.3), is
used to the frequency being output from the TX PLL. See the table in TPCR1 register description.
Bits 2 to 7: Unused
TPCR2
Transmit PLL Control Register 2
0Ah
— — — — TPLLOFS2 TPLLIFS2
7.4 Interrupt Handling
Various alarms, conditions, and events in the DS26504 can cause interrupts. For simplicity, these are all
referred to as events in this explanation. All STATUS registers can be programmed to produce interrupts.
Each status register has an associated interrupt mask register. For example, SR1 (Status Register 1) has an
interrupt control register called IMR1 (Interrupt Mask Register 1). Status registers are the only sources of
interrupts in the DS26504. On power-up, all writeable registers are automatically cleared. Because bits in
the IMRx registers must be set = 1 to allow a particular event to cause an interrupt, no interrupts can
occur until the host selects which events are to product interrupts. As there are potentially many sources
of interrupts on the DS26504, several features are available to help sort out and identify which event is
causing an interrupt. When an interrupt occurs, the host should first read the IIR register (interrupt
information register) to identify which status register(s) is producing the interrupt. Once that is
determined, the individual status register or registers can be examined to determine the exact source.
Once an interrupt has occurred, the interrupt handler routine should clear the IMRx registers to stop
further activity on the interrupt pin. After all interrupts have been determined and processed, the interrupt
hander routine should restore the state of the IMRx registers.
7.5 Status Registers
When a particular event or condition has occurred (or is still occurring in the case of conditions), the
appropriate bit in a status register will be set to a one. All the status registers operate in a latched fashion,
which means that if an event or condition occurs, a bit is set to a one. It remains set until the user reads
that bit. An event bit is cleared when it is read and it is not set again until the event has occurred again.
Condition bits such as RLOS remain set if the alarm is still present.
The user always precedes a read of any of the status registers with a write. The byte written to the register
informs the DS26504 which bits the user wishes to read and have cleared. The user writes a byte to one of
these registers, with a one in the bit positions he or she wishes to read, and a zero in the bit positions he or
she does not wish to obtain the latest information on. When a one is written to a bit location, the read
register is updated with the latest information. When a zero is written to a bit position, the read register is
not updated and the previous value is held. A write to the status registers is immediately followed by a
read of the same register. This write-read scheme allows an external microcontroller or microprocessor to
37 of 128
Page 38

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
individually poll certain bits without disturbing the other bits in the register. This operation is key in
controlling the DS26504 with higher-order languages.
Status register bits are divided into two groups: condition bits and event bits. Condition bits are typically
network conditions such as loss of frame or all-ones detect. Event bits are typically markers such as the
one-second timer. Each status register bit is labeled as a condition or event bit. Some of the status
registers have bits for both the detection of a condition and the clearance of the condition. For example,
SR2 has a bit that is set when the device goes into a loss-of-frame state (SR2.0, a condition bit) and a bit
that is set (SR2.4, an event bit) when the loss-of-frame condition clears (goes in sync). Some of the status
register bits (condition bits) do not have a separate bit for the “condition clear” event but rather the status
bit can produce interrupts on both edges, setting, and clearing. These bits are marked as “double interrupt
bits.” An interrupt is produced when the condition occurs and when it clears.
7.6 Information Registers
Information registers operate the same as status registers except they cannot cause interrupts. INFO3
register is a read-only register and it reports the status of the E1 synchronizer in real time. INFO3
information bits are not latched, and it is not necessary to precede a read of these bits with a write.
7.7 Interrupt Information Registers
The Interrupt Information Registers (IIRs) provide an indication of which Status Registers (SR1 to SR4)
are generating an interrupt. When an interrupt occurs, the host can read IIR to quickly identify which of
the four status registers are causing the interrupt.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — — SR4 SR3 SR2 SR1
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Status Register 1 (SR1)
Bit 1: Status Register 2 (SR2)
Bit 2: Status Register 3 (SR3)
Bit 3: Status Register 4 (SR4)
Bits 4 to 7: Unused
X X X X X X X X
0 = Status Register 1 interrupt not active.
1 = Status Register 1 interrupt active.
0 = Status Register 2 interrupt not active.
1 = Status Register 2 interrupt active.
0 = Status Register 3 interrupt not active.
1 = Status Register 3 interrupt active.
0 = Status Register 4 interrupt not active.
1 = Status Register 4 interrupt active.
IIR
Interrupt Information Register
13h
38 of 128
Page 39

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
8. T1 FRAMER/FORMATTER CONTROL REGISTERS
The T1 framer portion of the DS26504 is configured via a set of five control registers. Typically, the
control registers are only accessed when the system is first powered up. Once the DS26504 has been
initialized, the control registers only need to be accessed when there is a change in the system
configuration. There are two receive control registers (T1RCR1 and T1RCR2), two transmit control
registers (T1TCR1 and T1TCR2), and a common control register (T1CCR). Each of these registers is
described in this section.
8.1 T1 Control Registers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — ARC OOF1 OOF2 SYNCC SYNCT SYNCE RESYNC
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Resynchronize (RESYNC). When toggled from low to high, a resynchronization of the receive side framer is initiated.
Must be cleared and set again for a subsequent resync.
Bit 1: Sync Enable (SYNCE)
0 = auto resync enabled
1 = auto resync disabled
Bit 2: Sync Time (SYNCT)
0 = qualify 10 bits
1 = qualify 24 bits
Bit 3: Sync Criterion (SYNCC)
In D4 Framing Mode:
0 = search for Ft pattern, then search for Fs pattern
1 = cross-couple Ft and Fs pattern
In ESF Framing Mode:
0 = search for FPS pattern only
1 = search for FPS and verify with CRC6
Bits 4 and 5: Out-of-Frame Select Bits (OOF2, OOF1)
OOF2 OOF1
0 0 2/4 frame bits in error
0 1 2/5 frame bits in error
1 0 2/6 frame bits in error
1 1 2/6 frame bits in error
Bit 6: Auto Resync Criterion (ARC)
0 = resync on OOF or RLOS event
1 = resync on OOF only
Bit 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
T1RCR1
T1 Receive Control Register 1
03h
OUT-OF-FRAME
CRITERION
39 of 128
Page 40

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — RB8ZS — — — RJC RD4YM
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Receive Side D4 Yellow Alarm Select (RD4YM)
Bit 1: Receive Japanese CRC6 Enable (RJC)
Bits 2, 3, 4, 6, 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 5: Receive B8ZS Enable (RB8ZS)
0 0
0 = zeros in bit 2 of all channels
1 = a one in the S-bit position of frame 12 (J1 Yellow Alarm Mode)
0 = use ANSI/AT&T/ITU CRC6 calculation (normal operation)
1 = use Japanese standard JT–G704 CRC6 calculation
0 = B8ZS disabled
1 = B8ZS enabled
T1RCR2
T1 Receive Control Register 2
04h
HBE
PIN 55
0 0 0 0 0
40 of 128
Page 41

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TJC TFPT TCPT — — — — TYEL
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0:Transmit Yellow Alarm (TYEL)
Bits 1 to 4: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 5: Transmit CRC Pass-Through (TCPT)
Bit 6: Transmit F-Bit Pass-Through (TFPT)
Bit 7: Transmit Japanese CRC6 Enable (TJC)
RMODEx
PINS
0 = do not transmit yellow alarm
1 = transmit yellow alarm
0 = source CRC6 bits internally
1 = CRC6 bits sampled at TSER during F-bit time
0 = F bits sourced internally
1 = F bits sampled at TSER
0 = use ANSI/AT&T/ITU CRC6 calculation (normal operation)
1 = use Japanese standard JT–G704 CRC6 calculation
T1TCR1
T1 Transmit Control Register 1
05h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
41 of 128
Page 42

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TB8ZS TFSE — FBCT2 FBCT1 TD4YM — TB7ZS
Default 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Transmit-Side Bit 7 Zero-Suppression Enable (TB7ZS)
Bits 1 and 5: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 2: Transmit-Side D4 Yellow Alarm Select (TD4YM)
Bit 3: F-Bit Corruption Type 1 (FBCT1). A low-to-high transition of this bit causes the next three consecutive Ft (D4
framing mode) or FPS (ESF framing mode) bits to be corrupted causing the remote end to experience a loss of frame (loss of
synchronization).
Bit 4: F-Bit Corruption Type 2 (FBCT2). Setting this bit high enables the corruption of one Ft (D4 framing mode) or FPS
(ESF framing mode) bit in every 128 Ft or FPS bits as long as the bit remains set.
Bit 6: Transmit Fs-Bit Insertion Enable (TFSE). Only set this bit to a 1 in D4 framing applications. Must be set to 1 to
source the Fs pattern from the TFDL register. In all other modes this bit must be set = 0.
Bit 7: Transmit B8ZS Enable (TB8ZS)
HBE
PIN 55
0 = no stuffing occurs
1 = bit 7 forced to a 1 in channels with all 0s
0 = 0s in bit 2 of all channels
1 = a 1 in the S-bit position of frame 12
0 = Fs-bit insertion disabled
1 = Fs-bit insertion enabled
0 = B8ZS disabled
1 = B8ZS enabled
T1TCR2
T1 Transmit Control Register 2
06h
1 0 0 0 0 0 0
42 of 128
Page 43

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — TRAI-CI TAIS-CI — PDE —
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bits 0, 2, 5, 6, 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 1: Pulse-Density Enforcer Enable (PDE). The framer always examines the transmit and receive data streams for
violations of these, which are required by ANSI T1.403. No more than 15 consecutive zeros and at least N ones in each and
every time window of 8 x (N + 1) bits, where N = 1 through 23. When this bit is set to one, the DS26504 forces the transmitted
stream to meet this requirement no matter the content of the transmitted stream. When running B8ZS, this bit should be set to
zero, as B8ZS encoded data streams cannot violate the pulse-density requirements.
Bit 3: Transmit AIS-CI Enable (TAIS-CI). Setting this bit causes the AIS-CI code to be transmitted from the framer to the
LIU, as defined in ANSI T1.403.
Bit 4: Transmit RAI-CI Enable (TRAI-CI). Setting this bit causes the ESF RAI-CI code to be transmitted in the FDL bit
position.
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 = disable transmit pulse-density enforcer
1 = enable transmit pulse-density enforcer
0 = do not transmit the AIS-CI code
1 = transmit the AIS-CI code
0 = do not transmit the ESF RAI-CI code
1 = transmit the ESF RAI-CI code
T1CCR
T1 Common Control Register
07h
43 of 128
Page 44

Table 8-1. T1 Alarm Criterion
ALARM SET CRITERION CLEAR CRITERION
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Blue Alarm (AIS)
(Note 1)
D4 Yellow Alarm (RAI)
(T1RCR2.0 = 0)
Japanese Yellow Alarm
(T1RCR2.0 = 1)
ESF Yellow Alarm (RAI)
Red Alarm (RLOS)
(Also known as Loss of Signal)
Over a 3ms window, five or
fewer zeros are received
Bit 2 of 256 consecutive
channels is set to zero for at
least 254 occurrences
12th framing bit is set to one
for two consecutive
occurrences
16 consecutive patterns of
00FF appear in the FDL
192 consecutive zeros are
received
Over a 3ms window, six or more zeros
are received
Bit 2 of 256 consecutive channels is
set to zero for less than 254
occurrences
12th framing bit is set to zero for two
consecutive occurrences
14 or fewer patterns of 00FF hex out of
16 possible appear in the FDL
14 or more ones out of 112 possible bit
positions are received, starting with the
first one received
Note 1: The definition of Blue Alarm (or Alarm Indication Signal) is an unframed, all-ones signal. Blue Alarm detectors should be able to
operate properly in the presence of a 10E-3 error rate, and they should not falsely trigger on a framed, all-ones signal. The Blue Alarm
criterion in the DS26504 has been set to achieve this performance.
44 of 128
Page 45

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
9. E1 FRAMER/FORMATTER CONTROL REGISTERS
The E1 framer portion of the DS26504 is configured via a set of two control registers. Typically, the
control registers are only accessed when the system is first powered up. Once the DS26504 has been
initialized, the control registers only need to be accessed when there is a change in the system
configuration. There is one receive control register (E1RCR) and one transmit control register (E1TCR).
There are also two information registers and a status register, as well as an interrupt mask register. Each
of these registers is described in this section.
9.1 E1 Control Registers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — RLOSA RHDB3 — — FRC SYNCE RESYNC
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Resync (RESYNC). When toggled from low to high, a resync is initiated. Must be cleared and set again for a
subsequent resync.
Bit 1: Sync Enable (SYNCE)
Bit 2: Frame Resync Criterion (FRC)
Bits 3, 4, 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 5: Receive HDB3 Enable (RHDB3)
Bit 6: Receive Loss-of-Signal Alternate Criterion (RLOSA). Defines the criterion for a Receive Loss-of-Signal condition.
0 0
0 = auto resync enabled
1 = auto resync disabled
0 = resync if FAS received in error three consecutive times
1 = resync if FAS or bit 2 of non-FAS is received in error three consecutive times
0 = HDB3 disabled
1 = HDB3 enabled
0 = RLOS declared upon 255 consecutive zeros (125µs)
1 = RLOS declared upon 2048 consecutive zeros (1ms)
E1RCR
E1 Receive Control Register
1Dh
HBE
PIN 55
0 0 0 0 0
45 of 128
Page 46

Table 9-1. E1 Sync/Resync Criterion
FRAME OR
MULTIFRAME
LEVEL
FAS FAS present in frame N and
CRC4 Two valid MF alignment
CAS Valid MF alignment word
SYNC CRITERION RESYNC CRITERION ITU SPEC.
N + 2, and FAS not present in
frame N + 1
words found within 8ms
found and previous time slot
16 contains code other than
all zeros
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Three consecutive incorrect FAS
received
Alternate: (E1RCR.2 = 1) The above
criterion is met or three consecutive
incorrect bit 2 of non-FAS received
915 or more CRC4 code words out of
1000 received in error
Two consecutive MF alignment
words received in error
G.706
4.1.1
4.1.2
G.706
4.2 and 4.3.2
G.732 5.2
46 of 128
Page 47

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TFPT — ARA TSiS AEBE TUA1 THDB3 AAIS
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Automatic AIS Generation (AAIS)
Bit 1: Transmit HDB3 Enable (THDB3)
Bit 2: Transmit Unframed All Ones (TUA1)
0 = transmit data normally
1 = transmit an unframed all-ones code to LIU
Bit 3: Automatic E-Bit Enable (AEBE)
0 = E bits not automatically set in the transmit direction
1 = E bits automatically set in the transmit direction
Bit 4: Transmit International Bit Select (TSiS)
Bit 5: Automatic Remote Alarm Generation (ARA)
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Bit 6:Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 7: Transmit Time Slot 0 Pass-Through (TFPT)
0 0 0 0 0 0
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
0 = HDB3 disabled
1 = HDB3 enabled
0 = sample Si bits at TSER pin
1 = source Si bits from TAF and TNAF registers (in this mode, E1TCR1.7 must be set to 0)
0 = FAS bits/Sa bits/remote alarm sourced internally from the TAF and TNAF registers
1 = FAS bits/Sa bits/remote alarm sourced from TSER
E1TCR
E1 Transmit Control Register
1Eh
HBE
PIN 55
0
47 of 128
Page 48

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
9.2 E1 Information Registers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — — — CRCRC FASRC CASRC
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: CAS Resync Criterion Met Event (CASRC). Set when two consecutive CAS MF alignment words are received in
error.
Bit 1: FAS Resync Criterion Met Event (FASRC). Set when three consecutive FAS words are received in error.
Bit 2: CRC Resync Criterion Met Event (CRCRC). Set when 915/1000 codewords are received in error.
Bits 3 to 7: Unused
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CSC5 CSC4 CSC3 CSC2 CSC0 FASSA CASSA CRC4SA
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: CRC4 MF Sync Active (CRC4SA). Set while the synchronizer is searching for the CRC4 MF alignment word.
Bit 1: CAS MF Sync Active (CASSA). Set while the synchronizer is searching for the CAS MF alignment word.
Bit 2: FAS Sync Active (FASSA). Set while the synchronizer is searching for alignment at the FAS level.
Bits 3 to 7: CRC4 Sync Counter Bits (CSC0, CSC2 to CSC5). The CRC4 sync counter increments each time the 8ms-CRC4
multiframe search times out. The counter is cleared when the framer has successfully obtained synchronization at the CRC4
level. The counter can also be cleared by disabling the CRC4 mode (E1RCR.3 = 0). This counter is useful for determining the
amount of time the framer has been searching for synchronization at the CRC4 level. ITU G.706 suggests that if
synchronization at the CRC4 level cannot be obtained within 400ms, then the search should be abandoned and proper action
taken. The CRC4 sync counter will roll over. CSC0 is the LSB of the 6-bit counter. (Note: The second LSB, CSC1, is not
accessible. CSC1 is omitted to allow resolution to >400ms using 5 bits.)
X X X X X X X X
X X X X X X X X
INFO2
Information Register 2
12h
INFO3
Information Register 3 (Real Time)
1Ch
48 of 128
Page 49

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Table 9-2. E1 Alarm Criterion
ALARM SET CRITERION CLEAR CRITERION
RLOF
An RLOF condition exists on power-up
— —
prior to initial synchronization, when a
resync criterion has been met, or when a
manual resync has been initiated via
E1RCR.0
RLOS
RRA
255 or 2048 consecutive zeros received as
determined by E1RCR.0
Bit 3 of non-align frame set to one for
three consecutive occasions
In 255-bit times, at least 32
ones are received
Bit 3 of non-align frame set to
zero for three consecutive
occasions
RUA1
RDMA
Fewer than three zeros in two frames (512
bits)
Bit 6 of time slot 16 in frame 0 has been
More than two zeros in two
frames (512 bits)
—
set for two consecutive multiframes
V52LNK
Two out of three Sa7 bits are zero — G.965
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name ID7 ID6 ID5 ID4 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
Default 0 0 0 0 N N N N
HW
Mode
Bits 0 to 3: Chip Revision Bits (ID0 to ID3). The lower four bits of the IDR are used to display the die revision of the chip.
ID0 is the LSB of a decimal code that represents the chip revision.
Bits 4 to 7: Device ID (ID4 to ID7). The upper four bits of the IDR are used to display the DS26504 ID. The DS26504 ID is
0010.
DS26502 = 0000
DS26503 = 0001
DS26504 = 0010
X X X X X X X X
IDR
Device Identification Register
10h
ITU
SPEC.
G.775/G.962
O.162
2.1.4
O.162
1.6.1.2
49 of 128
Page 50

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RYELC RAISC RLOSC RLOFC RYEL RAIS RLOS RLOF
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Receive Loss-of-Frame Condition (RLOF). Set when the DS26504 is not synchronized to the received data stream.
Bit 1: Receive Loss-of-Signal Condition (RLOS). Set when 255 (or 2048 if E1RCR.6 = 1) E1 mode or 192 T1 mode
consecutive zeros have been detected. In 6312kHz Synchronization Interface Mode, this bit will be set when the signal
received is out of range as defined by the G.703 Appendix II specification.
Bit 2: Receive Alarm Indication Signal (T1= Blue Alarm, E1= AIS) Condition (RAIS). Set when an unframed all-ones
code is received.
Bit 3: Receive Yellow Alarm Condition (RYEL) (T1 only). Set when a yellow alarm is received.
Bit 4: Receive Loss-of-Frame Clear Event (RLOFC). Set when the framer achieves synchronization; will remain set until
read.
Bit 5: Receive Loss-of-Signal Clear Event (RLOSC). Set when loss-of-signal condition is no longer detected.
Bit 6: Receive Alarm Indication Signal Clear Event (RAISC). Set when the unframed all-ones condition is no longer
detected.
Bit 7: Receive Yellow Alarm Clear Event (RYELC) (T1 only). Set when the yellow alarm condition is no longer detected
X X X X X
SR2
Status Register 2
16h
RAIS
PIN 29
RLOS
PIN 32
LOF
PIN 30
.
50 of 128
Page 51

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RYELC RAISC RLOSC RLOFC RYEL RAIS RLOS RLOF
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Receive Loss-of-Frame Condition (RLOF)
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising edge only
Bit 1: Receive Loss-of-Signal Condition (RLOS)
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising edge only
Bit 2: Receive Alarm Indication Signal Condition (RAIS)
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising edge only
Bit 3: Receive Yellow Alarm Condition (RYEL)
1 = interrupt enabled–interrupts on rising edge only
Bit 4: Receive Loss-of-Frame Clear Event (RLOFC)
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 5: Receive Loss-of-Signal Condition Clear (RLOSC)
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 6: Receive Alarm Indication Signal Clear Event (RAISC)
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 7: Receive Yellow Alarm Clear Event (RYELC)
1 = interrupt enabled
X X X X X X X X
0 = interrupt masked
0 = interrupt masked
0 = interrupt masked
0 = interrupt masked
0 = interrupt masked
0 = interrupt masked
0 = interrupt masked
IMR2
Interrupt Mask Register 2
17h
51 of 128
Page 52

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
10. I/O PIN CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name G703TE RSMS2 RSMS1 RLOFF
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Output Data Format (ODF)
0 = bipolar data at TPOS and TNEG
1 = NRZ data at TPOS; TNEG = 0
Bit 1: TS_8K_4 I/O Select (TSIO). This bit determines whether the TS_8K_4 pin is an input or and output. See Table 10-1
0 = TS_8K_4 is an input
1 = TS_8K_4 is an output
Bit 2: TS_8K_4 Mode Select (TSM). In T1 or E1 operation, selects frame or multiframe mode for the TS_8K_4 pin. In
6312kHz or 64KCC mode, this bit should be set = 0. See Table 10-1
0 = frame mode
1 = multiframe mode
Bit 3: Composite Clock Sync Mode_Transmit Signaling Double-Wide Sync (CSM_TSDW). In 64kHz Composite Clock
mode, this bit determines whether the TS_8K_4 pin is an 8kHz or a 400Hz reference input (TS_8K_4 pin in input mode,
IOCR1 = 0), or an 8kHz or 400Hz reference output (TS_8K_4 pin in output mode, IOCR1 = 1). In T1 mode, setting this bit =
1 and setting TSIO = 1 will cause the sync pulse output on TS_8K_4 to be two clocks wide during signaling frames. In E1 or
6312kHz mode, this bit should be set = 0. See Table 10-1
0 = (CC64K) 8kHz reference, (T1) normal sync pulses
1 = (CC64K) 400Hz reference, (T1) double-wide sync pulses during signaling frames
Bit 4: RLOF_CCE Output Function (RLOFF). In T1 or E1 receive mode, this bit determines the function of the
RLOF_CCE pin. In 64KCC or 6312kHz receive mode, this bit should be set = 0.
0 = receive loss of frame (RLOF)
1 = loss-of-transmit clock (LOTC)
Bit 5: RS_8K Mode Select 1(RSMS1). In T1 or E1 receive mode, this bit selects a frame or multiframe output pulse at
RS_8K pin. IOCR.6 may be used to select other functions for the RS_8K pin.
0 = frame mode
1 = multiframe mode
Bit 6: RS_8K Mode Select 2 (RSMS2). In T1 and E1 receive mode, this bit along with IOCR.5 selects the function of the
RS_8K pin.
T1 Mode: (when IOCR.5 set = 0)
E1 Mode: (when IOCR.5 set = 1)
Bit 7: G.703 Timing Enable (G703TE). Setting this bit causes the 8kHz and 400Hz outputs to have timing relationships to
the 64kHz composite clock signal as specified in G.703. This bit allows backward compatibility with earlier devices in the
DS2650x family. Note: This applies to 64KCC modes only.
0 = legacy timing mode
1 = G.703 timing mode
0 0
0 = do not pulse double-wide in signaling frames
1 = do pulse double-wide in signaling frames
0 = RS_8K outputs CAS multiframe boundaries
1 = RS_8K outputs CRC4 multiframe boundaries
IOCR1
I/O Configuration Register 1
01h
RSM
PIN 1
.
CSM_TSDW
0 0
.
TSM TSIO ODF
TSM
PIN 2
0 0
.
52 of 128
Page 53

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Table 10-1. TS_8K_4 Pin Functions
TRANSMIT
MODE
T1/E1 0 0 0 Frame sync input
T1/E1 0 0 1 Frame sync output
T1/E1 0 1 0 Multiframe sync input
T1/E1 0 1 1 Multiframe sync output
64KCC 0 0 0 8kHz input reference
64KCC 0 0 1 8kHz output reference
64KCC 1 0 0 400Hz input reference
64KCC 1 0 1 400Hz output reference
IOCR1.3 IOCR1.2 IOCR1.1 TS_8K_4 FUNCTION
Table 10-2. RLOF_CCE Pin Functions
RECEIVE
MODE
T1/E1 0 Indicate Loss of Frame
T1/E1 1 Indicates Loss-of-Transmit Clock
64KCC 0 Indicates Composite Clock Error
IOCR1.4 RLOF_CCE PIN FUNCTION
53 of 128
Page 54

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
IOCR2
I/O Configuration Register 2
02h
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name
RCLKINV TCLKINV RS_8KINV
TS_8K_4INV — — TPCOE RPCOE
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0: Receive Payload Clock Output Enable (RPCOE). Setting this bit enables a gapped receive clock at the RCLK pin. In
E1 mode, the clock is gapped during TS0 and TS16. In T1 mode, the clock is gapped during the F-Bit. Note: This function is
only available in T1 or E1 mode.
Bit 1: Transmit Payload Clock Output Enable (TPCOE). Setting this bit enables a gapped transmit clock at the TCLKO
pin. In E1 mode, the clock is gapped during TS0 and TS16. In T1 mode, the clock is gapped during the F-Bit. Note: This
function is only available in T1 or E1 mode.
Bits 2 and 3: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 4: TS_8K_4 Invert (TS_8K_4INV)
0 = no inversion
1 = invert
Bit 5: RS_8K Invert (RS_8KINV)
0 = no inversion
1 = invert
Bit 6: TCLK Invert (TCLKINV)
0 = no inversion
1 = invert
Bit 7: RCLK Invert (RCLKINV)
0 = no inversion
1 = invert
54 of 128
Page 55

DS26502 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
11. T1 SYNCHRONIZATION STATUS MESSAGE
The DS26504 has a BOC controller to handle SSM services in T1 mode.
Table 11-1. T1 SSM Messages
QUALITY
LEVEL
1 Stratum 1 Traceable 0000010011111111
2 Synchronized Traceablity Unknown 0000100011111111
3 Stratum 2 Traceable 0000110011111111
4 Stratum 3 Traceable 0001000011111111
5 SONET Minimum Clock Traceable 0010001011111111
6 Stratum 4 Traceable 0010100011111111
7 Do Not Use for Synchronization 0011000011111111
User Assignable Reserved for Network Synchronization Use 0100000011111111
DESCRIPTION BOC CODE
11.1 T1 Bit-Oriented Code (BOC) Controller
The DS26504 contains a BOC generator on the transmit side and a BOC detector on the receive side. The
BOC function is available only in T1 mode. In typical BITS applications, the BOC controller would be
used to transmit and receive Synchronization Status Messages in T1 mode over the data link.
11.2 Transmit BOC
Bits 0 through 5 in the TFDL register contain the BOC or synchronization status message to be
transmitted. Setting BOCC.0 = 1 causes the transmit BOC controller to immediately begin inserting the
BOC sequence into the FDL bit position. The transmit BOC controller automatically provides the abort
sequence. BOC messages will be transmitted as long as BOCC.0 is set. TFSE (T1TCR2.6) must be set =
0 when using the transmit BOC function.
To transmit a BOC, use the following:
1) Write 6-bit code into the TFDL register.
2) Set SBOC bit in BOCC register = 1.
55 of 128
Page 56

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
11.3 Receive BOC
The receive BOC function is enabled by setting BOCC.4 = 1. The RFDL register will now operate as the
receive BOC message and information register. The lower six bits of the RFDL register (BOC message
bits) are preset to all ones. When the BOC bits change state, the BOC change of state indicator, SR3.0,
alerts the host. The host then reads the RFDL register to get the BOC message. A change of state occurs
when either a new BOC code has been present for time determined by the receive BOC filter bits, RBF0
and RBF1, in the BOCC register.
To receive a BOC, use the following:
1) Set integration time via BOCC.1 and BOCC.2.
2) Enable the receive BOC function (BOCC.4 = 1).
3) Enable interrupt (IMR3.0 = 1).
4) Wait for interrupt to occur.
5) Read the RFDL register.
6) The lower six bits of the RFDL register is the message.
56 of 128
Page 57

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
BOCC
BOC Control Register
1Fh
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — RBOCE RBR RBF1 RBF0 SBOC
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0: Send BOC (SBOC). Set = 1 to transmit the BOC code placed in bits 0 to 5 of the TFDL register.
Bits 1 and 2: Receive BOC Filter Bits (RBF0, RBF1). The BOC filter sets the number of consecutive patterns that must be
received without error prior to an indication of a valid message.
RBF1 RBF0
CONSECUTIVE BOC CODES FOR
VALID SEQUENCE IDENTIFICATION
0 0 None
0 1 3
1 0 5
1 1 7
Bit 3: Receive BOC Reset (RBR). A zero-to-one transition resets the BOC circuitry. Must be cleared and set again for a
subsequent reset.
Bit 4: Receive BOC Enable (RBOCE). Enables the receive BOC function. The RFDL register reports the received BOC
code.
0 = receive BOC function disabled
1 = receive BOC function enabled. The RFDL register reports BOC messages.
Bits 5, 6, 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
57 of 128
Page 58

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name: RFDL (RFDL register bit usage when BOCC.4 = 1)
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — RBOC5 RBOC4 RBOC3 RBOC2 RBOC1 RBOC0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: BOC Bit 0 (RBOC0)
Bit 1: BOC Bit 1 (RBOC1)
Bit 2: BOC Bit 2 (RBOC2)
Bit 3: BOC Bit 3 (RBOC3)
Bit 4: BOC Bit 4 (RBOC4)
Bit 5: BOC Bit 5 (RBOC5)
Bits 6 and 7: This bit position is unused when BOCC.4 = 1.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Receive FDL Register
50h
RFDLM1, RFDLM2
Receive FDL Match Register 1, Receive FDL Match Register 2
52h, 53h
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RFDLM7 RFDLM6 RFDLM5 RFDLM4 RFDLM3 RFDLM2 RFDLM1 RFDLM0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Receive FDL Match Bit 0 (RFDLM0). LSB of the FDL Match Code.
Bit 1: Receive FDL Match Bit 1 (RFDLM1)
Bit 2: Receive FDL Match Bit 2 (RFDLM2)
Bit 3: Receive FDL Match Bit 3 (RFDLM3)
Bit 4: Receive FDL Match Bit 4 (RFDLM4)
Bit 5: Receive FDL Match Bit 5 (RFDLM5)
Bit 6: Receive FDL Match Bit 6 (RFDLM6)
Bit 7: Receive FDL Match Bit 7 (RFDLM7). MSB of the FDL Match Code.
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
58 of 128
Page 59

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — LOTC BOCC RFDLAD RFDLF TFDLE RMTCH RBOC
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Receive BOC Detector Change-of-State Event (RBOC). Set whenever the BOC detector sees a change of state to a
valid BOC. The setting of this bit prompts the user to read the RFDL register.
Bit 1: Receive FDL Match Event (RMTCH). Set whenever the contents of the RFDL register matches RFDLM1 or
RFDLM2.
Bit 2: TFDL Register Empty Event (TFDLE). Set when the transmit FDL buffer (TFDL) empties.
Bit 3: RFDL Register Full Event (RFDLF). Set when the receive FDL buffer (RFDL) fills to capacity.
Bit 4: RFDL Abort Detect Event (RFDLAD). Set when eight consecutive ones are received on the FDL.
Bit 5: BOC Clear Event (BOCC). Set when 30 FDL bits occur without an abort sequence.
Bit 6: Loss-of-Transmit Clock Event (LOTC). Set when the signal at the TCLK pin has not transitioned for approximately
15 periods of the scaled MCLK.
Bit 7: Unused
X X X X X X X X
SR3
Status Register 3
18h
59 of 128
Page 60

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
IMR3
Interrupt Mask Register 3
19h
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — LOTC BOCC RFDLAD RFDLF TFDLE RMTCH RBOC
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
X X X X X X X X
Bit 0: Receive BOC Detector Change-of-State Event (RBOC)
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 1: Receive FDL Match Event (RMTCH)
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 2: TFDL Register Empty Event (TFDLE)
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 3: RFDL Register Full Event (RFDLF)
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 4: RFDL Abort Detect Event (RFDLAD)
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 5: BOC Clear Event (BOCC)
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 6: Loss-of-Transmit Clock Event (LOTC)
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
Bit 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
60 of 128
Page 61

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — RSA1 RSA0 TMF TAF RMF RCMF RAF
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Receive Align Frame Event (RAF). (E1 only) Set every 250µs at the beginning of align frames. Used to alert the host
that Si and Sa bits are available in the RAF and RNAF registers.
Bit 1: Receive CRC4 Multiframe Event (RCMF). (E1 only) Set on CRC4 multiframe boundaries; will continue to be set
every 2ms on an arbitrary boundary if CRC4 is disabled.
Bit 2: Receive Multiframe Event (RMF)
Bit 3: Transmit Align Frame Event (TAF). (E1 only) Set every 250µs at the beginning of align frames. Used to alert the host
that the TAF and TNAF registers need to be updated.
Bit 4: Transmit Multiframe Event (TMF)
Bit 5: Receive Signaling All Zeros Event (RSA0). (E1 only) Set when over a full MF, time slot 16 contains all zeros.
Bit 6: Receive Signaling All Ones Event (RSA1). (E1 only) Set when the contents of time slot 16 contains fewer than three
zeros over 16 consecutive frames. This alarm is not disabled in the CCS signaling mode.
Bit 7: Unused
X X X X X X X X
E1 Mode: Set every 2ms (regardless if CAS signaling is enabled or not) on receive multiframe boundaries. Used to
alert the host that signaling data is available.
T1 Mode: Set every 1.5ms on D4 MF boundaries or every 3ms on ESF MF boundaries.
E1 Mode: Set every 2ms (regardless if CRC4 is enabled) on transmit multiframe boundaries. Used to alert the host
that signaling data needs to be updated.
T1 Mode: Set every 1.5ms on D4 MF boundaries or every 3ms on ESF MF boundaries.
SR4
Status Register 4
1Ah
61 of 128
Page 62

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — RSA1 RSA0 TMF TAF RMF RCMF RAF
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Receive Align Frame Event (RAF)
Bit 1: Receive CRC4 Multiframe Event (RCMF)
Bit 2: Receive Multiframe Event (RMF)
Bit 3: Transmit Align Frame Event (TAF)
Bit 4: Transmit Multiframe Event (TMF)
Bit 5: Receive Signaling All-Zeros Event (RSA0)
Bit 6: Receive Signaling All-Ones Event (RSA1)
Bit 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
X X X X X X X X
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
IMR4
Interrupt Mask Register 4
1Bh
62 of 128
Page 63

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TFDL7 TFDL6 TFDL5 TFDL4 TFDL3 TFDL2 TFDL1 TFDL0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Note: Also used to insert Fs framing pattern in D4 framing mode.
The transmit FDL register (TFDL) contains the FDL information that is to be inserted on a byte-basis into the outgoing T1 data
stream. The LSB is transmitted first.
Bit 0: Transmit FDL Bit 0 (TFDL0). LSB of the transmit FDL code.
Bit 1: Transmit FDL Bit 1 (TFDL1)
Bit 2: Transmit FDL Bit 2 (TFDL2)
Bit 3: Transmit FDL Bit 3 (TFDL3)
Bit 4: Transmit FDL Bit 4 (TFDL4)
Bit 5: Transmit FDL Bit 5 (TFDL5)
Bit 6: Transmit FDL Bit 6 (TFDL6)
Bit 7: Transmit FDL Bit 7 (TFDL7). MSB of the transmit FDL code.
0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
TFDL
Transmit FDL Register
51h
63 of 128
Page 64

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
12. E1 SYNCHRONIZATION STATUS MESSAGE
The DS26504 provides access to both the transmit and receive Sa/Si bits. In E1, the Sa bits are used to
transmit and receive the SSM. The primary method to access the Sa (and Si) bits is based on CRC4
multiframe access. An alternate method is based on double-frame access. The DS26504 provides an
interrupt on a change of state for the Sa-bit-based messages.
Table 12-1. E1 SSM Messages
QUALITY
LEVEL
0 Quality unknown (existing sync network) 0000
1 Reserved 0001
2 Rec. G.811 (Traceable to PRS) 0010
3 Reserved 0011
4 SSU-A (Traceable to SSU type A, see G.812) 0100
5 Reserved 0101
6 Reserved 0110
7 Reserved 0111
8 SSU-B (Traceable to SSU type B, see G.812) 1000
9 Reserved 1001
10 Reserved 1010
11 Synchronous Equipment Timing Source 1011
12 Reserved 1100
13 Reserved 1101
14 Reserved 1110
15 Do not use for synchronization 1111
DESCRIPTION
In E1 operation, SSMs are transmitted using one of the Sa bits—Sa4, Sa5, Sa6, Sa7, or Sa8. The SSM is
transmitted MSB first in the first frame of the multiframe. Each multiframe will contain two SSMs, one in
each sub-multiframe. An SSM is declared valid when the message in three sub-multiframes are alike.
Sa BIT
MESSAGE
12.1 Sa/Si Bit Access Based on CRC4 Multiframe
On the receive side, there is a set of eight registers (RSiAF, RSiNAF, RRA, RSa4 to RSa8) that report the
Si and Sa bits as they are received. These registers are updated on CRC4 multiframes. A bit in Status
Register 4 (SR4.1) indicates the multiframe boundary. The host can use the SR4.1 bit to know when to
read these registers. The user has 2ms to retrieve the data before it is lost. The MSB of each register is the
first received. See the following register descriptions for more details.
On the transmit side, there is also a set of eight registers (TSiAF, TSiNAF, TRA, TSa4 to TSa8) that, via
the transmit Sa bit control register (TSaCR), can be programmed to insert both Si and Sa data. Data is
sampled from these registers with the setting of the transmit multiframe bit in status register 2 (SR4.4).
The host can use the SR4.4 bit to know when to update these registers. It has 2ms to update the data or
else the old data will be retransmitted. The MSB of each register is the first bit transmitted. See the
following register descriptions for details.
64 of 128
Page 65

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
12.1.1 Sa Bit Change of State
The DS26504 can provide an interrupt whenever one of the multiframe based Sa bit patterns changes.
Using the SR5 and IMR5 registers, the user can enable interrupts on a change of state for Sa4, Sa5, Sa6,
Sa7 and Sa8 multiframe bit patterns. This function is useful for monitoring the Sa6-based SSM message.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — Sa8COS Sa7COS Sa6COS Sa5COS Sa4COS
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa4 Change of State (Sa4COS). Set when any Sa4 bit in the 16-frame multiframe has changed state.
Bit 1: Sa5 Change of State (Sa5COS). Set when any Sa5 bit in the 16-frame multiframe has changed state.
Bit 2: Sa6 Change of State (Sa6COS). Set when any Sa6 bit in the 16-frame multiframe has changed state.
Bit 3: Sa7 Change of State (Sa7COS). Set when any Sa7 bit in the 16-frame multiframe has changed state.
Bit 4: Sa8 Change of State (Sa8COS). Set when any Sa8 bit in the 16-frame multiframe has changed state.
Bits 5, 6, 7: Unused
X X X X X X X X
SR5
Status Register 5
21h
65 of 128
Page 66

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — Sa8COS Sa7COS Sa6COS Sa5COS Sa4COS
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa4 Change of State (Sa4COS)
Bit 1: Sa5 Change of State (Sa5COS)
Bit 2: Sa6 Change of State (Sa6COS)
Bit 3: Sa7 Change of State (Sa7COS)
Bit 4: Sa8 Change of State (Sa8COS)
Bits 5, 6, 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
X X X X X X X X
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
IMR5
Interrupt Mask Register 5
22h
66 of 128
Page 67

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name SiF0 SiF2 SiF4 SiF6 SiF8 SiF10 SiF12 SiF14
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Si Bit of Frame 14(SiF14)
Bit 1: Si Bit of Frame 12(SiF12)
Bit 2: Si Bit of Frame 10(SiF10)
Bit 3: Si Bit of Frame 8(SiF8)
Bit 4: Si Bit of Frame 6(SiF6)
Bit 5: Si Bit of Frame 4(SiF4)
Bit 6: Si Bit of Frame 2(SiF2)
Bit 7: Si Bit of Frame 0(SiF0)
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name SiF1 SiF3 SiF5 SiF7 SiF9 SiF11 SiF13 SiF15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Si Bit of Frame 15(SiF15)
Bit 1: Si Bit of Frame 13(SiF13)
Bit 2: Si Bit of Frame 11(SiF11)
Bit 3: Si Bit of Frame 9(SiF9)
Bit 4: Si Bit of Frame 7(SiF7)
Bit 5: Si Bit of Frame 5(SiF5)
Bit 6: Si Bit of Frame 3(SiF3)
Bit 7: Si Bit of Frame 1(SiF1)
X X X X X X X X
X X X X X X X X
RSiAF
Receive Si Bits of the Align Frame
58h
RSiNAF
Receive Si Bits of the Non-Align Frame
59h
67 of 128
Page 68

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RRAF1 RRAF3 RRAF5 RRAF7 RRAF9 RRAF11 RRAF13 RRAF15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 15(RRAF15)
Bit 1: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 13(RRAF13)
Bit 2: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 11(RRAF11)
Bit 3: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 9(RRAF9)
Bit 4: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 7(RRAF7)
Bit 5: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 5(RRAF5)
Bit 6: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 3(RRAF3)
Bit 7: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 1(RRAF1)
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RSa4F1 RSa4F3 RSa4F5 RSa4F7 RSa4F9 RSa4F11 RSa4F13 RSa4F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa4 Bit of Frame 15(RSa4F15)
Bit 1: Sa4 Bit of Frame 13(RSa4F13)
Bit 2: Sa4 Bit of Frame 11(RSa4F11)
Bit 3: Sa4 Bit of Frame 9(RSa4F9)
Bit 4: Sa4 Bit of Frame 7(RSa4F7)
Bit 5: Sa4 Bit of Frame 5(RSa4F5)
Bit 6: Sa4 Bit of Frame 3(RSa4F3)
Bit 7: Sa4 Bit of Frame 1(RSa4F1)
X X X X X X X X
X X X X X X X X
RRA
Receive Remote Alarm
5Ah
RSa4
Receive Sa4 Bits
5Bh
68 of 128
Page 69

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RSa5F1 RSa5F3 RSa5F5 RSa5F7 RSa5F9 RSa5F11 RSa5F13 RSa5F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa5 Bit of Frame 15(RSa5F15)
Bit 1: Sa5 Bit of Frame 13(RSa5F13)
Bit 2: Sa5 Bit of Frame 11(RSa5F11)
Bit 3: Sa5 Bit of Frame 9(RSa5F9)
Bit 4: Sa5 Bit of Frame 7(RSa5F7)
Bit 5: Sa5 Bit of Frame 5(RSa5F5)
Bit 6: Sa5 Bit of Frame 3(RSa5F3)
Bit 7: Sa5 Bit of Frame 1(RSa5F1)
X X X X X X X X
RSa5
Receive Sa5 Bits
5Ch
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RSa6F1 RSa6F3 RSa6F5 RSa6F7 RSa6F9 RSa6F11 RSa6F13 RSa6F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa6 Bit of Frame 15(RSa6F15)
Bit 1: Sa6 Bit of Frame 13(RSa6F13)
Bit 2: Sa6 Bit of Frame 11(RSa6F11)
Bit 3: Sa6 Bit of Frame 9(RSa6F9)
Bit 4: Sa6 Bit of Frame 7(RSa6F7)
Bit 5: Sa6 Bit of Frame 5(RSa6F5)
Bit 6: Sa6 Bit of Frame 3(RSa6F3)
Bit 7: Sa6 Bit of Frame 1(RSa6F1)
X X X X X X X X
RSa6
Receive Sa6 Bits
5Dh
69 of 128
Page 70

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RSa7F1 RSa7F3 RSa7F5 RSa7F7 RSa7F9 RSa7F11 RSa7F13 RSa7F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa7 Bit of Frame 15(RSa7F15)
Bit 1: Sa7 Bit of Frame 13(RSa7F13)
Bit 2: Sa7 Bit of Frame 11(RSa7F11)
Bit 3: Sa7 Bit of Frame 9(RSa7F9)
Bit 4: Sa7 Bit of Frame 7(RSa7F7)
Bit 5: Sa7 Bit of Frame 5(RSa7F5)
Bit 6: Sa7 Bit of Frame 3(RSa7F3)
Bit 7: Sa7 Bit of Frame 1(RSa4F1)
X X X X X X X X
RSa7
Receive Sa7 Bits
5Eh
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name RSa8F1 RSa8F3 RSa8F5 RSa8F7 RSa8F9 RSa8F11 RSa8F13 RSa8F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa8 Bit of Frame 15(RSa8F15)
Bit 1: Sa8 Bit of Frame 13(RSa8F13)
Bit 2: Sa8 Bit of Frame 11(RSa8F11)
Bit 3: Sa8 Bit of Frame 9(RSa8F9)
Bit 4: Sa8 Bit of Frame 7(RSa8F7)
Bit 5: Sa8 Bit of Frame 5(RSa8F5)
Bit 6: Sa8 Bit of Frame 3(RSa8F3)
Bit 7: Sa8 Bit of Frame 1(RSa8F1)
X X X X X X X X
RSa8
Receive Sa8 Bits
5Fh
70 of 128
Page 71

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TsiF0 TsiF2 TsiF4 TsiF6 TsiF8 TsiF10 TsiF12 TsiF14
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Si Bit of Frame 14(TsiF14)
Bit 1: Si Bit of Frame 12(TsiF12)
Bit 2: Si Bit of Frame 10(TsiF10)
Bit 3: Si Bit of Frame 8(TsiF8)
Bit 4: Si Bit of Frame 6(TsiF6)
Bit 5: Si Bit of Frame 4(TsiF4)
Bit 6: Si Bit of Frame 2(TsiF2)
Bit 7: Si Bit of Frame 0(TsiF0)
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TsiF1 TsiF3 TsiF5 TsiF7 TsiF9 TsiF11 TsiF13 TSiF15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Si Bit of Frame 15(TSiF15)
Bit 1: Si Bit of Frame 13(TsiF13)
Bit 2: Si Bit of Frame 11(TsiF11)
Bit 3: Si Bit of Frame 9(TsiF9)
Bit 4: Si Bit of Frame 7(TsiF7)
Bit 5: Si Bit of Frame 5(TsiF5)
Bit 6: Si Bit of Frame 3(TsiF3)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
TSiAF
Transmit Si Bits of the Align Frame
42h
TSiNAF
Transmit Si Bits of the Non-Align Frame
43h
Bit 7: Si Bit of Frame 1(TsiF1)
71 of 128
Page 72

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TRAF1 TRAF3 TRAF5 TRAF7 TRAF9 TRAF11 TRAF13 TRAF15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 15(TRAF15)
Bit 1: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 13(TRAF13)
Bit 2: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 11(TRAF11)
Bit 3: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 9(TRAF9)
Bit 4: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 7(TRAF7)
Bit 5: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 5(TRAF5)
Bit 6: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 3(TRAF3)
Bit 7: Remote Alarm Bit of Frame 1(TRAF1)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
TRA
Transmit Remote Alarm
44h
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TSa4F1 TSa4F3 TSa4F5 TSa4F7 TSa4F9 TSa4F11 TSa4F13 TSa4F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa4 Bit of Frame 15(TSa4F15)
Bit 1: Sa4 Bit of Frame 13(TSa4F13)
Bit 2: Sa4 Bit of Frame 11(TSa4F11)
Bit 3: Sa4 Bit of Frame 9(TSa4F9)
Bit 4: Sa4 Bit of Frame 7(TSa4F7)
Bit 5: Sa4 Bit of Frame 5(TSa4F5)
Bit 6: Sa4 Bit of Frame 3(TSa4F3)
Bit 7: Sa4 Bit of Frame 1(TSa4F1)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
TSa4
Transmit Sa4 Bits
45h
72 of 128
Page 73

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TSa5F1 TSa5F3 TSa5F5 TSa5F7 TSa5F9 TSa5F11 TSa5F13 TSa5F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa5 Bit of Frame 15(TSa5F15)
Bit 1: Sa5 Bit of Frame 13(TSa5F13)
Bit 2: Sa5 Bit of Frame 11(TSa5F11)
Bit 3: Sa5 Bit of Frame 9(TSa5F9)
Bit 4: Sa5 Bit of Frame 7(TSa5F7)
Bit 5: Sa5 Bit of Frame 5(TSa5F5)
Bit 6: Sa5 Bit of Frame 3(TSa5F3)
Bit 7: Sa5 Bit of Frame 1(TSa5F1)
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TSa6F1 TSa6F3 TSa6F5 TSa6F7 TSa6F9 TSa6F11 TSa6F13 TSa6F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa6 Bit of Frame 15(TSa6F15)
Bit 1: Sa6 Bit of Frame 13(TSa6F13)
Bit 2: Sa6 Bit of Frame 11(TSa6F11)
Bit 3: Sa6 Bit of Frame 9(TSa6F9)
Bit 4: Sa6 Bit of Frame 7(TSa6F7)
Bit 5: Sa6 Bit of Frame 5(TSa6F5)
Bit 6: Sa6 Bit of Frame 3(TSa6F3)
Bit 7: Sa6 Bit of Frame 1(TSa6F1)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
TSa5
Transmit Sa5 Bits
46h
TSa6
Transmit Sa6 Bits
47h
73 of 128
Page 74

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TSa7F1 TSa7F3 TSa7F5 TSa7F7 TSa7F9 TSa7F11 TSa7F13 TSa7F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa7 Bit of Frame 15(TSa7F15)
Bit 1: Sa7 Bit of Frame 13(TSa7F13)
Bit 2: Sa7 Bit of Frame 11(TSa7F11)
Bit 3: Sa7 Bit of Frame 9(TSa7F9)
Bit 4: Sa7 Bit of Frame 7(TSa7F7)
Bit 5: Sa7 Bit of Frame 5(TSa7F5)
Bit 6: Sa7 Bit of Frame 3(TSa7F3)
Bit 7: Sa7 Bit of Frame 1(TSa4F1)
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name TSa8F1 TSa8F3 TSa8F5 TSa8F7 TSa8F9 TSa8F11 TSa8F13 TSa8F15
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Sa8 Bit of Frame 15(TSa8F15)
Bit 1: Sa8 Bit of Frame 13(TSa8F13)
Bit 2: Sa8 Bit of Frame 11(TSa8F11)
Bit 3: Sa8 Bit of Frame 9(TSa8F9)
Bit 4: Sa8 Bit of Frame 7(TSa8F7)
Bit 5: Sa8 Bit of Frame 5(TSa8F5)
Bit 6: Sa8 Bit of Frame 3(TSa8F3)
Bit 7: Sa8 Bit of Frame 1(TSa8F1)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
TSa7
Transmit Sa7 Bits
48h
TSa8
Transmit Sa8 Bits
49h
74 of 128
Page 75

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name SiAF SiNAF RA Sa4 Sa5 Sa6 Sa7 Sa8
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Additional Bit 8 Insertion Control Bit (Sa8)
Bit 1: Additional Bit 7 Insertion Control Bit (Sa7)
Bit 2: Additional Bit 6 Insertion Control Bit (Sa6)
Bit 3: Additional Bit 5 Insertion Control Bit (Sa5)
Bit 4: Additional Bit 4 Insertion Control Bit (Sa4)
Bit 5: Remote Alarm Insertion Control Bit (RA)
Bit 6: International Bit in Non-Align Frame Insertion Control Bit (SiNAF)
Bit 7: International Bit in Align Frame Insertion Control Bit (SiAF)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 = do not insert data from the TSa8 register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TSa8 register into the transmit data stream
0 = do not insert data from the TSa7 register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TSa7 register into the transmit data stream
0 = do not insert data from the TSa6 register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TSa6 register into the transmit data stream
0 = do not insert data from the TSa5 register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TSa5 register into the transmit data stream
0 = do not insert data from the TSa4 register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TSa4 register into the transmit data stream
0 = do not insert data from the TRA register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TRA register into the transmit data stream
0 = do not insert data from the TSiNAF register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TSiNAF register into the transmit data stream
0 = do not insert data from the TSiAF register into the transmit data stream
1 = insert data from the TSiAF register into the transmit data stream
TSACR
Transmit Sa Bit Control Register
4Ah
75 of 128
Page 76

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
12.2 Alternate Sa/Si Bit Access Based on Double-Frame
On the receive side, the RAF and RNAF registers will always report the data as it received in the Sa and
Si bit locations. The RAF and RNAF registers are updated on align frame boundaries. The setting of the
receive align frame bit in status register 4 (SR4.0) will indicate that the contents of the RAF and RNAF
have been updated. The host can use the SR4.0 bit to know when to read the RAF and RNAF registers.
The host has 250ms to retrieve the data before it is lost.
On the transmit side, data is sampled from the TAF and TNAF registers with the setting of the transmit
align frame bit in status register 4 (SR4.3). The host can use the SR4.3 bit to know when to update the
TAF and TNAF registers. It has 250ms to update the data or else the old data will be retransmitted. If the
TAF and TNAF registers are only being used to source the align frame and non-align frame-sync
patterns, then the host need only write once to these registers. Data for the Si bit can come from the Si
bits of the RAF and TNAF registers, the TSiAF and TSiNAF registers, or passed through from the TSER
pin.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Si FAS6 FAS5 FAS4 FAS3 FAS2 FAS1 FAS0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Frame Alignment Signal Bit 0 (FAS0). In normal operation this bit will be = 1.
Bit 1: Frame Alignment Signal Bit 1 (FAS1). In normal operation this bit will be = 1.
Bit 2: Frame Alignment Signal Bit 2 (FAS2). In normal operation this bit will be = 0.
Bit 3: Frame Alignment Signal Bit 3 (FAS3). In normal operation this bit will be = 1.
Bit 4: Frame Alignment Signal Bit 4 (FAS4). In normal operation this bit will be = 1.
Bit 5: Frame Alignment Signal Bit 5 (FAS5). In normal operation this bit will be = 0.
Bit 6: Frame Alignment Signal Bit 6 (FAS6). In normal operation this bit will be = 0.
Bit 7: International Bit (Si)
X X X X X X X X
RAF
Receive Align Frame Register
56h
76 of 128
Page 77

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Si 1 A Sa4 Sa5 Sa6 Sa7 Sa8
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Additional Bit 8 (Sa8)
Bit 1: Additional Bit 7 (Sa7)
Bit 2: Additional Bit 6 (Sa6)
Bit 3: Additional Bit 5 (Sa5)
Bit 4: Additional Bit 4 (Sa4)
Bit 5: Remote Alarm (A)
Bit 6: Frame Nonalignment Signal Bit (1). In normal operation this bit will be = 1.
Bit 7: International Bit (Si)
X X X X X X X X
RNAF
Receive Non-Align Frame Register
57h
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Si 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
Default 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Frame Alignment Signal Bit (1)
Bit 1: Frame Alignment Signal Bit (1)
Bit 2: Frame Alignment Signal Bit (0)
Bit 3: Frame Alignment Signal Bit (1)
Bit 4: Frame Alignment Signal Bit (1)
Bit 5: Frame Alignment Signal Bit (0)
Bit 6: Frame Alignment Signal Bit (0)
Bit 7: International Bit (Si)
0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
TAF
Transmit Align Frame Register
40h
77 of 128
Page 78

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Si 1 A Sa4 Sa5 Sa6 Sa7 Sa8
Default 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 0: Additional Bit 8 (Sa8)
Bit 1: Additional Bit 7 (Sa7)
Bit 2: Additional Bit 6 (Sa6)
Bit 3: Additional Bit 5 (Sa5)
Bit 4: Additional Bit 4 (Sa4)
Bit 5: Remote Alarm (used to transmit the alarm A)
Bit 6: Frame Nonalignment Signal Bit (1)
Bit 7: International Bit (Si)
TNAF
Transmit Non-Align Frame Register
41h
78 of 128
Page 79

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
13. LINE INTERFACE UNIT (LIU)
The LIU in the DS26504 contains three sections: the receiver, which handles clock and data recovery; the
transmitter, which generates waveshapes and drives the network line; and the jitter attenuator. These three
sections are controlled by the line interface control registers (LIC1–LIC4), which are described below.
The DS26504 can switch among T1, E1, and 64KCC networks without changing any external
components on either the transmit or receive side. Figure 13-1 shows a network connection using
minimal components. In this configuration the DS26504, using a fixed 120Ω external termination, can
connect to T1, J1, E1, 64KCC, or 6312kHz without any component change. The receiver can adjust the
120Ω termination to 100Ω, 110Ω, or 75Ω. The transmitter can adjust its output impedance to provide
high return loss characteristics for 75Ω, 100Ω, 110Ω, and 120Ω lines. Other components may be added to
this configuration to meet safety and network protection requirements. This is covered in the
Recommended Circuits section (Section 13.8).
Figure 13-1. Basic Network Connection
TTIP
TRANSMIT
LINE
2:1
1mF
TRING
DS26504
BACKPLANE
CONNECTIONS
RECEIVE
LINE
RTIP
RRING
1:1
60 60
0.01mF
79 of 128
Page 80

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
13.1 LIU Operation
The LIU interfaces the T1, E1, 64KCC, and 6312kHz signals to the various types of network media
through coupling transformers. The LIU transmit and receive functions are independent. For example, the
receiver can be in T1 mode while the transmitter is in E1 mode. The 6312kHz transmission is an
exception to the other modes. For transmission, 6312kHz is only available as a 0 to 3.3V signal on the
TCLKO pin. It is not output to the TTIP and TRING pins for coupling to twisted pair. Because the G.703
specifications of the transmit pulse shape for Japanese 6312kHz are unclear, the user can externally filter
this signal to generate a sine-wave type of signal. However, on the receive side, 6312kHz can be input
through the receive transformer to the RTIP and RRING pins.
13.2 LIU Receiver
The analog AMI/HDB3 E1 waveform, AMI/B8ZS T1 waveform, or AMI 64KCC waveform is
transformer-coupled into the RTIP and RRING pins of the DS26504. The user has the option to use
internal termination, software-selectable for 75/100/110/120W applications, or external termination. The
LIU recovers clock and data from the analog signal and passes it through the jitter attenuation mux.
(Note: The jitter attenuator is only available in T1 or E1 mode.) The DS26504 contains an active filter
that reconstructs the analog-received signal for the nonlinear losses that occur in long-haul T1 and E1
transmission. The receiver is configurable for various T1 and E1 monitor applications. The device has a
usable receive sensitivity of 0dB to –43dB for E1 and 0dB to –36dB for T1, which allows the device to
operate on 0.63mm (22AWG) cables up to 2.5km (E1) and 6000ft (T1) in length.
The DS26504’s LIU is designed to be fully software selectable for E1 and T1 without the need to change
any external resistors for the receive-side. The receiver will allow the user to configure the DS26504 for
75Ω, 100Ω, 110Ω, 120Ω, or 133W receive termination by setting the RT0(LIC4.0), RT1(LIC4.1), and
RT2(LIC4.2). When using the internal termination feature, the resistors labeled R in Figure 13-4 should
be 60Ω each. If external termination is used, RT0, RT1, and RT2 should be set to zero and the resistors
labeled R in Figure 13-4 need to be 37.5Ω, 50Ω, 55Ω, 60Ω, or 66.5W each, depending on the required
termination.
There are two ranges of receive sensitivity for T1 and E1, which is selectable by the user. The EGL bit of
LIC1 (LIC1.4) selects the full or limited sensitivity.
Normally, the clock that is output at the RCLK pin is the recovered clock from the waveform presented at
the RTIP and RRING inputs. If the jitter attenuator is placed in the receive path (as is the case in most
applications), the jitter attenuator restores the RCLK to an approximate 50% duty cycle. If the jitter
attenuator is either placed in the transmit path or is disabled, the RCLK output can exhibit slightly shorter
high cycles of the clock. This is due to the highly over-sampled digital clock-recovery circuitry. See the
Receive AC Timing Characteristics section for more details. When no signal is present at RTIP and
RRING, a receive loss-of-signal (RLOS) condition will occur and the signal at RCLK will be derived
from the scaled signal present on the MCLK pin.
13.2.1 Receive Level Indicator
The DS26504 reports the signal strength at RTIP and RRING in 2.5dB increments via RL3–RL0 located
in the Information Register 1 (INFO1). This feature is helpful when trouble-shooting line performance
problems.
80 of 128
Page 81

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
X
13.2.2 Receive G.703 Section 10 Synchronization Signal
The DS26504 can receive a 2.048MHz square-wave synchronization clock as specified in Section 10 of
ITU G.703. To use the DS26504 in this mode, set the mode configuration bits in the Mode Configuration
Register (MCREG).
13.2.3 Monitor Mode
Monitor applications in both E1 and T1 require various flat-gain settings for the receive-side circuitry.
The DS26504 can be programmed to support these applications via the monitor mode control bits MM1
and MM0 in the LIC3 register.
Figure 13-2. Typical Monitor Application
T1/E1 LINE
PRIMARY
T1/E1 TERMINATING
DEVICE
Rm Rm
MONITOR
PORT JACK
F
M
R
SECONDARY T1/E1
TERMINATING
DEVICE
Rt
DS26504
13.3 LIU Transmitter
The DS26504 uses a phase-lock loop along with a precision digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to create
the waveforms that are transmitted onto the E1 or T1 line. The waveforms created by the DS26504 meet
the latest ETSI, ITU, ANSI, and AT&T specifications. The waveform that is to be generated is set by the
transmit mode bits (TMODE[3:0]) in the MCREG register, as well as the L2/L1/L0 bits in register LIC1
if applicable.
ITU specification G.703 requires an accuracy of ±50ppm for both T1 and E1. TR62411 and ANSI specs
require an accuracy of ±32ppm for T1 interfaces. The transmit clock can be sourced from the recovered
clock (RCLK), the pre-scaled MCLK, the TCLK pin, or the TX PLL. See the TX PLL clock mux
diagram in Figure 3-3
(less than 0.005UI
transmit clock source. Also, the waveforms created are independent of the duty cycle of TCLK. The
transmitter in the DS26504 couples to the transmit twisted pair (or coaxial cable in some applications) via
a 1:2 step-up transformer. For the device to create the proper waveforms, the transformer used must meet
the specifications listed in Table 13-1. The DS26504 has the option of using software-selectable transmit
termination.
. Due to the nature of the design of the transmitter in the DS26504, very little jitter
broadband from 10Hz to 100kHz) is added to the jitter present on the selected
P-P
81 of 128
Page 82

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
The transmit line drive has two modes of operation: fixed gain or automatic gain. In the fixed gain mode,
the transmitter outputs a fixed current into the network load to achieve a nominal pulse amplitude. In the
automatic gain mode, the transmitter adjusts its output level to compensate for slight variances in the
network load. See the Transmit Line Build-Out Control (TLBC) register for details.
13.3.1 Transmit Short-Circuit Detector/Limiter
The DS26504 has an automatic short-circuit limiter that limits the source current to 50mA (RMS) into a
1W load. This feature can be disabled by setting the SCLD bit (LIC2.1) = 1. TCLE (SR1.2) provides a
real-time indication of when the current limiter is activated. If the current limiter is disabled, TCLE will
indicate that a short-circuit condition exists. Status Register SR1.2 provides a latched version of the
information, which can be used to activate an interrupt when enable via the IMR1 register. When set low,
the TPD bit (LIC1.0) will power-down the transmit line driver and tri-state the TTIP and TRING pins.
13.3.2 Transmit Open-Circuit Detector
The DS26504 can also detect when the TTIP or TRING outputs are open circuited. TOCD (SR1.1) will
provide a real-time indication of when an open circuit is detected. SR1 provides a latched version of the
information (SR1.1), which can be used to activate an interrupt when enabled via the IMR1 register.
13.3.3 Transmit BPV Error Insertion
When IBPV (LIC2.5) is transitioned from a zero to a one, the device waits for the next occurrence of
three consecutive ones to insert a BPV. IBPV must be cleared and set again for another BPV error
insertion.
13.3.4 Transmit G.703 Section 10 Synchronization Signal (E1 Mode)
The DS26504 can transmit the 2.048MHz square-wave synchronization clock. To transmit the 2.048MHz
clock, when in E1 mode, set the mode configuration bits in the Mode Configuration Register (MCREG).
13.4 MCLK Pre-Scaler
A 2.048MHz x N (where N = 1 to 4), 1.544MHz x N (where N = 1 to 4), or 12.8MHz (available in CPU
interface mode only) clock must be applied to MCLK. A pre-scaler (divide by 2, 4, or 8) and PLLs are
selected to product an internal 2.048MHz or 1.544MHz clock. ITU specification G.703 requires an
accuracy of ±50ppm for both T1 and E1. TR62411 and ANSI specs require an accuracy of ±32ppm for
T1 interfaces. A pre-scaler divides the 16.384MHz, 12.8MHz, 8.192MHz, or 4.096MHz clock down to
2.048MHz. An on-board PLL for the jitter attenuator converts the 2.048MHz clock to a 1.544MHz rate
for T1 applications. Setting JACKS (LIC2.3) to a logic 0 bypasses this PLL.
13.5 Jitter Attenuator
The DS26504’s jitter attenuator can be set to a depth of either 32 bits or 128 bits via the JABDS bit
(LIC1.2). The 128-bit mode is used in applications where large excursions of wander are expected. The
32-bit mode is used in delay-sensitive applications. The characteristics of the attenuation are shown in
Figure 13-10
transmit path by appropriately setting or clearing the JAS bit (LIC1.3). The jitter attenuator can also be
disabled (in effect, removed) by setting the DJA bit (LIC1.1). Either the recovered clock from the
clock/data recovery block or the clock applied at the TCLK pin is adjusted to create a smooth jitter-free
clock that is used to clock data out of the jitter attenuator FIFO. It is acceptable to provide a
gapped/bursty clock at the TCLK pin if the jitter attenuator is placed on the transmit side. If the incoming
jitter exceeds either 120UI
and Figure 13-11. The jitter attenuator can be placed in either the receive path or the
(buffer depth is 128 bits) or 28UI
P-P
(buffer depth is 32 bits), then the
P-P
82 of 128
Page 83

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
DS26504 will divide the internal nominal 32.768MHz (E1) or 24.704MHz (T1) clock by either 15 or 17
instead of the normal 16 to keep the buffer from overflowing. When the device divides by either 15 or 17,
it also sets the Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip (JALT) bit in Status Register 1 (SR1.4).
13.6 CMI (Code Mark Inversion) Option
The DS26504 provides a CMI interface for connection to optical transports. This interface is a unipolar
1T2B type of signal. Ones are encoded as either a logical one or zero level for the full duration of the
clock period. Zeros are encoded as a zero-to-one transition at the middle of the clock period.
Figure 13-3. CMI Coding
Transmit and receive CMI is enabled via LIC4.7. When this register bit is set, the TTIP pin outputs CMIcoded data at normal levels. This signal can be used to directly drive an optical interface. When CMI is
enabled, the user can also use HDB3/B8ZS coding. When this register bit is set, the RTIP pin becomes a
unipolar CMI input. The CMI signal is processed to extract and align the clock with data.
CLOCK
DATA
CMI
01 11001
83 of 128
Page 84

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
13.7 LIU Control Registers
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name L2 L1 L0 EGL JAS JABDS DJA TPD
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Transmit Power-Down (TPD)
Bit 1: Disable Jitter Attenuator (DJA)
Bit 2/Jitter Attenuator Buffer Depth Select (JABDS)
Bit 3: Jitter Attenuator Select (JAS)
Bit 4: Receive Equalizer Gain Limit (EGL). This bit controls the sensitivity of the receive equalizer.
Bits 5, 6, 7: Line Build-Out Select (L0 to L2). When using the internal termination, the user needs only to select 000 for 75Ω
operation or 001 for 120Ω operation. This selects the proper voltage levels for 75Ω or 120Ω operation. Using TT0 and TT1 of
the LICR4 register, users can then select the proper internal source termination. Line build-outs 100 and 101 are for backwards
compatibility with older products only.
E1 Mode
L2 L1 L0 APPLICATION N (Note 1) RETURN LOSS Rt (Note 1)
0 0 0 75Ω normal 1:2 N.M. 0
0 0 1 120Ω normal 1:2 N.M. 0
1 0 0 75Ω with high return loss (Note 2) 1:2 21dB 6.2Ω
1 0 1 120Ω with high return loss (Note 2) 1:2 21dB 11.6Ω
N.M. = Not meaningful
Note 1: Transformer turns ratio.
Note 2: TT0 and TT1 of the LIC4 register must be set to zero in this configuration.
L2
PIN 13
0 = powers down the transmitter and tri-states the TTIP and TRING pins
1 = normal transmitter operation
0 = jitter attenuator enabled
1 = jitter attenuator disabled
0 = 128 bits
1 = 32 bits (use for delay-sensitive applications)
0 = place the jitter attenuator on the receive side
1 = place the jitter attenuator on the transmit side
T1 Mode: 0 = -36dB (long haul)
1 = -15dB (limited long haul)
E1 Mode: 0 = -43dB (long haul)
1 = -12dB (short haul)
LIC1
Line Interface Control 1
30h
L1
PIN 12
L0
PIN 11
0 0 0 0 1
84 of 128
Page 85

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
T1 Mode
L2 L1 L0 APPLICATION N (Note 1) RETURN LOSS Rt (Note 1)
0 0 0 DSX-1 (0 to 133 feet)/0dB CSU 1:2 N.M. 0
0 0 1 DSX-1 (133 to 266 feet) 1:2 N.M. 0
0 1 0 DSX-1 (266 to 399 feet) 1:2 N.M. 0
0 1 1 DSX-1 (399 to 533 feet) 1:2 N.M. 0
1 0 0 DSX-1 (533 to 655 feet) 1:2 N.M. 0
1 0 1 Reserved — — —
1 1 0 Reserved — — —
1 1 1 Reserved — — —
N.M. = Not meaningful
Note 1: Transformer turns ratio.
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
TLBC
Transmit Line Build-Out Control
34h
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — AGCE GC5 GC4 GC3 GC2 GC1 GC0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bits 0 to 5: Gain Control Bits 0 to 5 (GC0 toGC5). The GC0 through GC5 bits control the gain setting for the nonautomatic
gain mode. Use the tables below for setting the recommended values. The LBO (line build-out) column refers to the value in
the L0–L2 bits in LIC1 (Line Interface Control 1) register.
NETWORK MODE LBO GC5 GC4 GC3 GC2 GC1 GC0
0 1 0 0 1 1 0
1 0 1 1 0 1 1
2 0 1 1 0 1 0
T1, Impedance Match Off
3 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 1 0 0 1 1 1
5 1 0 0 1 1 1
6 0 1 0 0 1 1
7 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 1 1 1 1 0
1 0 1 0 1 0 1
2 0 1 0 1 0 1
T1, Impedance Match On
3 0 1 1 0 1 0
4 1 0 0 0 1 0
5 1 0 0 0 0 0
6 0 0 1 1 0 0
7 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 1
E1, Impedance Match Off
1 1 0 0 0 0 1
4 1 0 1 0 1 0
5 1 0 1 0 0 0
E1, Impedance Match On
0 0 1 1 0 1 0
1 0 1 1 0 1 0
Bit 6: Automatic Gain Control Enable (AGCE)
0 = use Transmit AGC, TLBC bits 0–5 are “don’t care”
1 = do not use Transmit AGC, TLBC bits 0–5 set nominal level
Bit 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
85 of 128
Page 86

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name JACKS1 LIRST IBPV TAIS JACKS0 RCCFE SCLD CLDS
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Custom Line-Driver Select (CLDS). Setting this bit to a one redefines the operation of the transmit line driver. When
this bit is set to a one and LIC1.5 = LIC1.6 = LIC1.7 = 0, the device generates a square wave at the TTIP and TRING outputs
instead of a normal waveform. When this bit is set to a one and LIC1.5 = LIC1.6 = LIC1.7 ¹ 0, the device forces TTIP and
TRING outputs to become open-drain drivers instead of their normal push-pull operation. This bit should be set to zero for
normal operation of the device.
Bit 1: Short Circuit Limit Disable (in E1 mode) (SCLD). Controls the 50mA (RMS) current limiter.
Bit 2: Receive Composite Clock Filter Enable (RCCFE) (64KCC mode only). Setting this bit enables the PLL filter on the
received 64kHz composite clock. Note: The 8kHz and 400Hz output are not filtered.
0 = Receive Composite Clock Filter disabled
1 = Receive Composite Clock Filter enabled
Bit 3: Jitter Attenuator Mux (JACKS0). This bit, along with JACKS1 (LIC2.3), MPS0 (LIC4.6), and MPS1 (LIC4.7),
controls the source for JA CLOCK from the MCLK pin. Note: This bit must be configured even if the jitter attenuator is
disabled. The clock and data recovery engine also uses the JA CLOCK. Setting this bit enables the 12.8MHz to 2.048MHz
conversion PLL. See the table in the LIC4 register description for more details on setting up the JA CLOCK source.
Bit 4: Transmit Alarm Indication Signal (TAIS). In T1, E1, or J1 modes, this bit causes an all-ones pattern to be
transmitted.
In all 64KCC modes, this bit disables the BPV-encoded sub-rates.
Bit 5: Insert BPV (IBPV). A zero-to-one transition on this bit causes a single BPV to be inserted into the transmit data
stream. Once this bit has been toggled from a zero to a one, the device waits for the next occurrence of three consecutive ones
to insert the BPV. This bit must be cleared and set again for a subsequent error to be inserted.
Bit 6: Line Interface Reset (LIRST). Setting this bit from a zero to a one initiates an internal reset that resets the clock
recovery state machine and recenters the jitter attenuator. Normally this bit is only toggled on power-up. Must be cleared and
set again for a subsequent reset.
Bit 7: Jitter Attenuator Clock Select 1 (JACKS1). This bit, along with JACKS0 (LIC2.3), MPS0 (LIC4.6), and MPS1
(LIC4.7), controls the source for JA CLOCK from the MCLK pin. Note: This bit must be configured even if the jitter
attenuator is disabled. The clock and data recovery engine also uses the JA CLOCK. Setting this bit enables the 12.8MHz to
2.048MHz conversion PLL. See the table in the LIC4 register description for more details on setting up the JA CLOCK source.
0 0 0
0 = enable 50mA current limiter
1 = disable 50mA current limiter
0 = transmit an unframed all-ones code
1 = transmit data normally
0 = transmit all ones without BPVs
1 = transmit normal 64KCC
0 = 12.8MHz to 2.048MHz PLL bypassed
1 = 12.8MHz to 2.048MHz PLL enabled
LIC2
Line Interface Control 2
31h
TAIS
PIN 10
JACKS0
PIN 46
0 0 0
86 of 128
Page 87

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name CMIE CMII EX133 MM1 MM0 — — TAOZ
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bit 0: Transmit Alternate Ones and Zeros (TAOZ). Transmit a …101010… pattern at TTIP and TRING.
0 = disabled
1 = enabled
Bits 1 and 2: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bits 3 and 4: Monitor Mode (MM0 and MM1). Note: This function is only available in T1 or E1 mode.
MM1 MM0 INTERNAL LINEAR GAIN BOOST (dB)
0 0 Normal operation (no boost)
0 1 20
1 0 26
1 1 32
Bit 5: Eternal 133W Resistor Select (EX133). This bit is used to indicate to the device’s internal receive termination control
circuitry that either a 120W or 133W external resistor is used. Used in conjunction with the RT0, RT1, and RT2 bits in the
LIC4 register. Note: A fixed 133W external resistor allows the internal termination to create all other termination values.
A fixed 120W external resistor allows the internal termination to create all other termination values except 133W.
0 = indicates a 120W external resistor is connected
1 = indicates a 133W external resistor is connected
Bit 6: CMI Invert (CMII)
0 = CMI normal at TTIP and RTIP
1 = invert CMI signal at TTIP and RTIP
Bit 7: CMI Enable (CMIE)
0 = disable CMI mode
1 = enable CMI mode
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
LIC3
Line Interface Control 3
32h
87 of 128
Page 88

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
LIC4
Line Interface Control 4
33h
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name MPS1 MPS0 TT2 TT1 TT0 RT2 RT1 RT0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
MPS1
PIN 16
MPS0
PIN 15
— — — — — —
Bits 0 to 2: Receive Termination Select (RT0 to RT2)
RT2 RT1 RT0
EX133
(LIC3.5)
EXTERNAL
RESISTOR VALUE
RECEIVE TERMINATION
0 0 0 X — External Resistor Value
0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1
0 1 0 0
0 1 0 1
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1
1 0 1 1
120W 75W
133W 75W
120W 100W
133W 100W
120W 120W (External Resistor Value)
133W 120W
120W 110W
133W 110W
133W 133W (External Resistor Value)
1 1 0 X — External Resistor Value
1 1 1 X — External Resistor Value
Note: A fixed 133W external resistor allows the internal termination to create all other termination values. A fixed
120W external resistor allows the internal termination to create all other termination values except 133W.
Bits 3, 4, 5: Transmit Termination Select (TT0 to TT2)
TT2 TT1 TT0
INTERNAL TRANSMIT
TERMINATION CONFIGURATION
0 0 0 Termination Disabled
0 0 1 75Ω Enabled
0 1 0 100Ω Enabled
0 1 1 120Ω Enabled
1 0 0 110Ω Enabled
1
0 1
133W Enabled
1 1 0 Disabled
1 1 1 Disabled
Bits 6 and 7: MCLK Prescaler (MPS0 and MPS1) (T1 Mode)
MCLK
(MHz)
MPS1 MPS0
JACKS0
(LIC2.3)
JACKS1
(LIC2.7)
1.544 0 0 0 0
3.088 0 1 0 0
6.176 1 0 0 0
12.352 1 1 0 0
12.80 0 0 1 1
2.048 0 0 1 0
4.096 0 1 1 0
8.192 1 0 1 0
16.384 1 1 1 0
88 of 128
Page 89

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Bits 6 and 7: MCLK Prescaler (MPS0 and MPS1) (E1 Mode)
MCLK
(MHz)
2.048 0 0 0 0
4.096 0 1 0 0
8.192 1 0 0 0
12.8 0 0 0 1
16.384 1 1 0 0
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — — RL3 RL2 RL1 RL0
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bits 0 to 3: Receive Level Bits (RL0 to RL3). Real-time bits.
RL3 RL2 RL1 RL0 RECEIVE LEVEL (dB)
0 0 0 0 Greater than -2.5
0 0 0 1 -2.5 to -5.0
0 0 1 0 -5.0 to -7.5
0 0 1 1 -7.5 to -10.0
0 1 0 0 -10.0 to -12.5
0 1 0 1 -12.5 to -15.0
0 1 1 0 -15.0 to -17.5
0 1 1 1 -17.5 to -20.0
1 0 0 0 -20.0 to -22.5
1 0 0 1 -22.5 to -25.0
1 0 1 0 -25.0 to -27.5
1 0 1 1 -27.5 to -30.0
1 1 0 0 -30.0 to –32.5
1 1 0 1 -32.5 to -35.0
1 1 1 0 -35.0 to -37.5
1 1 1 1 Less than -37.5
Bits 4 to 7: Unused
MPS1 MPS0
INFO1
Information Register 1
11h
X X X X X X X X
JACKS0
(LIC2.3)
JACKS1
(LIC2.7)
89 of 128
Page 90

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — JALT — TCLE TOCD —
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bits 0, 3, 5, 6, 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 1: Transmit Open-Circuit-Detect Condition (TOCD). Set when the device detects that the TTIP and TRING outputs are
open-circuited.
Bit 2: Transmit Current-Limit-Exceeded Condition (TCLE). Set when the 50mA (RMS) current limiter is activated
whether the current limiter is enabled or not.
Bit 4: Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip Event (JALT). Set when the jitter attenuator FIFO reaches to within 4 bits of its useful
limit. This bit is cleared when read. Useful for debugging jitter-attenuation operation.
X X X X X X X X
SR1
Status Register 1
14h
90 of 128
Page 91

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — JALT — TCLE TOCD —
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bits 0, 3, 5, 6, 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 1: Transmit Open-Circuit-Detect Condition (TOCD)
Bit 2: Transmit Current-Limit-Exceeded Condition (TCLE)
Bit 4: Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip Event (JALT)
X X X X X X X X
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled–generates interrupts on rising and falling edges
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled–generates interrupts on rising and falling edges
0 = interrupt masked
1 = interrupt enabled
IMR1
Interrupt Mask Register 1
15h
91 of 128
Page 92

13.8 Recommended Circuits
Figure 13-4. Basic Interface
TRANSMIT
LINE
RECEIVE
LINE
2:1
1:1
R R
0.1mF
C
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
VDD
DS26504
TTIP
TRING
DV
DV
TV
TV
RV
DD
SS
DD
SS
DD
0.1mF
0.1mF
0.1mF
0.01mF
10mF
+
10mF
+
RTIP
RV
SS
RRING
NOTES:
1) ALL RESISTOR VALUES ARE ±1%.
2) RESISTORS R SHOULD BE SET TO 60W EACH IF THE INTERNAL RECEIVE-SIDE
TERMINATION FEATURE IS ENABLED. WHEN THIS FEATURE IS DISABLED, R =
37.5W FOR 75W COAXIAL E1 LINES, 60W FOR 120W TWISTED PAIR E1 LINES, OR
50W FOR 100W TWISTED PAIR T1 LINES.
3) C = 10µF CERAMIC.
92 of 128
Page 93

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
Figure 13-5. Protected Interface Using Internal Receive Termination
V
DD
TRANSMIT
LINE
F1
F2
2:1
X2
S1
C1
0.1mF
D1 D2
D4
D3
V
DD
D5 D6
DS26504
TTIP
TRING
DV
DV
TV
TV
RV
RV
DD
SS
DD
SS
DD
SS
0.1mF
0.1mF
0.1mF
1:1
RTIP
RRING
RECEIVE
LINE
F3
F4
X1
S2
0.1mF
D8
D7
60 60
0.01mF
10mF
+
10mF
+
V
DD
68mF
+
0.1mF
NOTES:
1) ALL RESISTOR VALUES ARE ±1%.
2) X1 AND X2 ARE VERY LOW DCR TRANSFORMERS
3) C1 = 10µF CERAMIC.
4) S1 AND S2 ARE 6V TRANSIENT SUPPRESSERS.
5) D1 TO D8 ARE SCHOTTKY DIODES.
6) THE FUSES, F1–F4, ARE OPTIONAL TO PREVENT AC POWER-LINE CROSSES
FROM COMPROMISING THE TRANSFORMERS.
7) THE 68mF IS USED TO KEEP THE LOCAL POWER-PLANE POTENTIAL WITHIN
TOLERANCE DURING A SURGE.
93 of 128
Page 94

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
13.9 Component Specifications
Table 13-1. Transformer Specifications
SPECIFICATION RECOMMENDED VALUE
Turns Ratio 3.3V Applications 1:1 (receive) and 1:2 (transmit) ±2%
Primary Inductance
Leakage Inductance
Intertwining Capacitance 40pF maximum
Transmit Transformer DC Resistance
Primary (Device Side)
Secondary
Receive Transformer DC Resistance
Primary (Device Side)
Secondary
600mH minimum
1.0mH maximum
1.0Ω maximum
2.0Ω maximum
1.2Ω maximum
1.2Ω maximum
94 of 128
Page 95

Figure 13-6. E1 Transmit Pulse Template
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
SCALED AMPLITUDE
0.2
0.1
0
(in 75 ohm systems, 1.0 on the scale = 2.37Vpeak
in 120 ohm systems, 1.0 on the scale = 3.00Vpeak)
-0.1
-0.2
194ns
219ns
TIME (ns)
Figure 13-7. T1 Transmit Pulse Template
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
269ns
G.703
Template
0
50 100 150 20 0 250-50-100-150-200-250
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
NORMALIZED AMPLITUDE
-0.1
-0.2
-0.3
-0.4
-0.5
-500 -300 -100 0 300 500 700
T1.102/87, T1.4 03,
CB 119 (Oct. 7 9), &
I.431 Template
-400 -200 200 400 600100
TIME (ns)
MAXIMUM CURVE
UI Time Amp.
-0.77
-500
-0.39
-255
-0.27
-175
-0.27
-175
-0.12
-75
0.00
0
0.27
175
0.35
225
0.93
600
1.16
750
0.05
0.05
0.80
1.15
1.15
1.05
1.05
-0.07
0.05
0.05
MINIMUM CURVE
UI Time Am p.
-0.77
-0.23
-0.23
-0.15
0.00
0.15
0.23
0.23
0.46
0.66
0.93
1.16
-500
-150
-150
-100
0
100
150
150
300
430
600
750
-0.05
-0.05
0.50
0.95
0.95
0.90
0.50
-0.45
-0.45
-0.20
-0.05
-0.05
95 of 128
Page 96

Figure 13-8. Jitter Tolerance (T1 Mode)
1K
DS26502
Tolerance
100
TR 62411 (Dec. 90)
10
1
UNIT INTERVALS (UIpp)
ITU-T G.823
0.1
1
10 100 1K 10K 100K
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 13-9. Jitter Tolerance (E1 Mode)
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
DS26504
TOLERANCE
UNIT INTERVALS (UIpp)
1k
100
10
1
0.1
DS26504
DS26502
TOLERANCE
Tolerance
40
1.5
Minimum Tolerance
Level as per
ITU G.823
1
20
10 100 1k 10k 100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
96 of 128
2.4k
18k
0.2
Page 97

Figure 13-10. Jitter Attenuation (T1 Mode)
-20dB
-40dB
JITTER ATTENUATION (dB)
-60dB
0dB
Curve A
C
u
r
1 10 100 1K 10K
DS26502
v
e
DS26504
B
T1 MODE
T1 MODE
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 13-11. Jitter Attenuation (E1 Mode)
0dB
DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
TR 62411 (Dec. 90)
Prohibited Area
100K
JITTER ATTENUATION (dB)
-20dB
-40dB
-60dB
TBR12
Prohibited
Area
DS26502
DS26504
E1 MODE
E1 MODE
1 10 100 1K 10K
FREQUENCY (Hz)
97 of 128
ITU G.7XX
Prohibited Area
100K
Page 98

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
14. LOOPBACK CONFIGURATION
Register Name:
Register Description:
Register Address:
Bit # 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name — — — — LLB RLB — —
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
HW
Mode
Bits 0, 1, 4 to 7: Unused, must be set = 0 for proper operation.
Bit 2: Remote Loopback (RLB). In this loopback, data received at RTIP and RRING will be looped back to the transmit LIU.
Received data will continue to pass through the receive side framer of the DS26504 as it would normally and the data from the
transmit side formatter will be ignored.
1 = loopback enabled
Bit 3: Local Loopback (LLB). In this loopback, data will continue to be transmitted as normal through the transmit side of the
DS26504. Data being received at RTIP and RRING will be replaced with the data being transmitted. Data in this loopback will
pass through the jitter attenuator if enabled.
0 0 0 0 0
0 = loopback disabled
0 = loopback disabled
1 = loopback enabled
LBCR
Loopback Control Register
20h
RLB
PIN 60
0 0
98 of 128
Page 99

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
15. 64kHz SYNCHRONIZATION INTERFACE
The 64kHz synchronization interface conforms to Appendix II of G.703. It consists of a composite clock,
where a 64kHz clock signal is generated or decoded, along with embedded frequencies of 8kHz and
400Hz. Those signals consist of AMI code with an 8kHz bipolar violation removed at every 400Hz.
There are two separate modes referred to in the specification, one with both the 64kHz clock and the
8kHz clock, and the second with the 64kHz clock, the 8kHz clock, and the 400Hz clock.
Figure 15-1. 64kHz Composite Clock Mode Signal Format
Violation
8 kHz
400 Hz
125 us
No
Violation
125 us
Violation
Violation
125 us
Violation
125 us
No
Violation
15.1 Receive 64kHz Synchronization Interface Operation
In the receive path, the three clock frequencies are decoded from the AMI waveform with bipolar
violations that is received at the LIU interface. The 8kHz frequency and the 400Hz frequency are decoded
from the presence or absence of bipolar violations as described in G.703.
Table 15-1. Specification of 64kHz Clock Signal at Input Port
Frequency
Signal format
Alarm condition
a) 64kHz + 8kHz, or
b) 64kHz + 8kHz + 400Hz
a) AMI with 8kHz bipolar violation,
b) AMI with 8kHz bipolar violation removed at every 400Hz
Alarm should not be occurred against the amplitude ranged
0.63-1.1 V
0-P
99 of 128
Page 100

DS26504 T1/E1/J1/64KCC BITS Element
15.2 Transmit 64kHz Synchronization Interface Operation
In the transmit path, the framer generateS the appropriate AMI waveform with the correct bipolar
violations as described by G.703 and GR.378. If an 8kHz signal is present on the TS_8K_4 pin, the
bipolar violations are generated synchronously with this signal. If it is absent, the part arbitrarily
generates the bipolar violation at an 8kHz frequency.
Table 15-2. Specification of 64kHz Clock Signal at Output Port
BPV SUBRATES LOAD PULSE WIDTH AMPLITUDE
G.703 Level A
G.703 Level B
G.703 Japanese
GR.378
8kHz
8kHz
8kHz + 400Hz
8kHz
110W £ 7.8 ± 0.78ms £1V
± 0.1V
0-P
110W 9.8 to 10.9ms 3.0V ± 0.5V
110W £ 7.8 ± 0.78ms £1 V
133W
5/8 period
(9.7ms)
± 0.1V
0-P
2.7V – 5.5V
100 of 128
 Loading...
Loading...