Page 1
DS2154
PRELIMINARY
DS2154
Enhanced E1 Single Chip Transceiver
FEATURES
• Complete E1(CEPT) PCM–30/ISDN–PRI transceiver
functionality
• Onboard long and short haul line interface for clock/
data recovery and waveshaping
• 32–bit or 128–bit crystal–less jitter attenuator
• Generates line build outs for both 120Ω and 75Ω lines
• Frames to FAS, CAS, and CRC4 formats
• Dual onboard two–frame elastic store slip buffers that
can connect to asynchronous backplanes up to
8.192 MHz
• 8–bit parallel control port that can be used directly on
either multiplexed or non–multiplexed buses
• Extracts and inserts CAS signaling
• Detects and generates Remote and AIS alarms
• Programmable output clocks for Fractional E1, H0,
and H12 applications
• Fully independent transmit and receive functionality
• Full access to both Si and Sa bits aligned with CRC
multiframe
• Four separate loopbacks for testing functions
PACKAGE OUTLINE
100
1
ORDERING INFORMATION
DS2154L (0°C to 70°C)
DS2154LN (–40°C to +85°C)
• Large counters for bipolar and code violations, CRC4
codeword errors, FAS errors, and E bits
• Pin compatible with DS2152 T1 Enhanced Single–
Chip Transceiver
• 5V supply; low power CMOS
• 100–pin 14mm
DESCRIPTION
The DS2154 Enhanced Single–Chip Transceiver
(ESCT) contains all of the necessary functions for connection to E1 lines. The device is an upward compatible
version of the DS2153 Single–Chip Transceiver. The
onboard clock/data recovery circuitry coverts the AMI/
Copyright 1997 by Dallas Semiconductor Corporation.
All Rights Reserved. For important information regarding
patents and other intellectual property rights, please refer to
Dallas Semiconductor data books.
2
body LQFP package
HDB3 E1 waveforms to a NRZ serial stream. The
DS2154 automatically adjusts to E1 22AWG (0.6 mm)
twisted–pair cables from 0 to over 2km in length. The
device can generate the necessary G.703 waveshapes
for both 75 ohm coax and 120 ohm twisted cables. The
031197 1/69
Page 2
DS2154
onboard jitter attenuator (selectable to either 32 bits or
128 bits) can be placed in either the transmit or receive
G.704, G.706, G.823, G.932, and I.431 as well as ETS
300 011, 300 233, and 300 166.
data paths. The framer locates the frame and multiframe boundaries and monitors the data stream for
alarms. It is also used for extracting and inserting
signaling data, Si, and Sa bit information. The device
contains a set of internal registers which the user can
access and control the operation of the unit. Quick
access via the parallel control port allows a single controller to handle many E1 lines. The device fully meets
1.0 INTRODUCTION
The DS2154 is a super–set version of the popular
DS2153 E1 Single–Chip Transceiver offering the new
features listed below. All of the original features of the
DS2153 have been retained and software created for
the original devices is transferrable into the DS2154.
all of the latest E1 specifications including ITU G.703,
NEW FEATURE
SECTION
Option for non–multiplexed bus operation 1 and 2
Crystal–less jitter attenuation 12
Additional hardware signaling capability including:
Receive signaling reinsertion to a backplane multiframe sync
Availability of signaling in a separate PCM data stream
Signaling freezing
Interrupt generated on change of signaling data
Improved receive sensitivity: 0 dB to –43 dB 12
Per–channel code insertion in both transmit and receive paths 8
Expanded access to Sa and Si bits 11
RCL, RLOS, RRA, and RAIS alarms now interrupt on change of state 4
8.192 MHz clock synthesizer 1
Per–channel loopback 8
Addition of hardware pins to indicate carrier loss and signaling freeze 1
Line interface function can be completely decoupled from the framer/formatter to
allow:
Interface to optical, HDSL, and other NRZ interfaces
“tap” the transmit and receive bipolar data streams for monitoring purposes
Be able corrupt data and insert framing errors, CRC errors, etc.
Transmit and receive elastic stores now have independent backplane clocks 1
Ability to monitor one DS0 channel in both the transmit and receive paths 6
Access to the data streams in between the framer/formatter and the elastic stores 1
AIS generation in the line interface that is independent of loopbacks 1 and 3
Transmit current limiter to meet the 50 mA short circuit requirement 12
Option to extend carrier loss criteria to a 1 ms period as per ETS 300 233 3
Automatic RAI generation to ETS 300 011 specifications 3
7
1
031197 2/69
Page 3
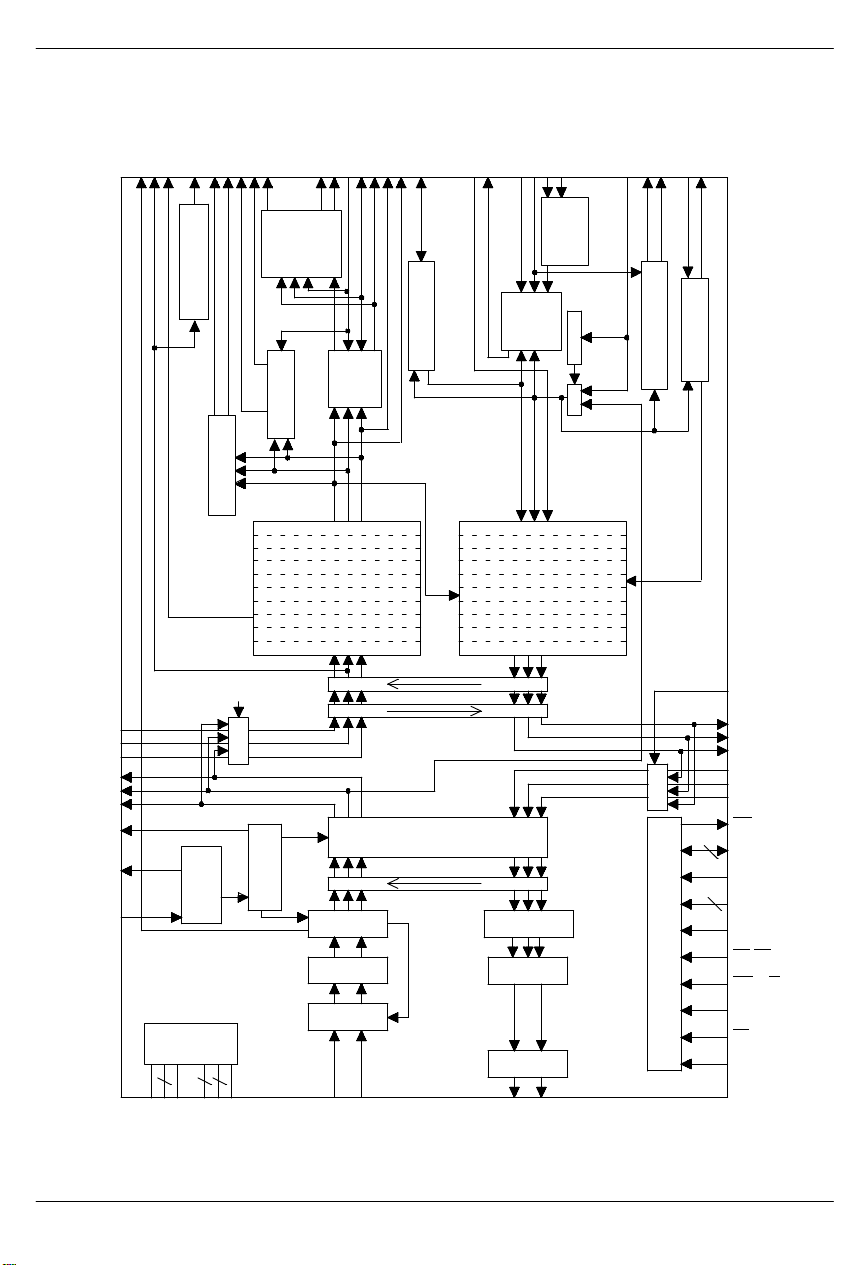
DS2154 ENHANCED E1 SINGLE–CHIP TRANSCEIVER Figure 1–1
LOTC
RCL
RCLK
RLOS
8MCLK
RLINK
RLCLK
RCHBLK
RCHCLK
RSIGF
RSIG
RSER
RSYSCLK
RSYNC
RMSYNC
RFSYNC
RDATA
TSYNC
TDATA
TESO
TSSYNC
TSYSCLK
TSER
TSIG
SIGNALING
HARDWARE
STORE
ELASTIC
CLOCK
DATA
SYNC
SA INSERTION
HDB3 ENCODE
LIU AIS
WAVE–
SHAPING
LINE
DRIVERS
RPOSI
RCLKI
RNEGI
RNEGO
RCLKO
RPOSO
8XCLK
XTALD
MCLK
SYNTHESIZER
8.182 MHz CLOCK
16.384 MHz
CLOCK/
CRYSTAL
INTERFACE
POWER
CONNECTIONS
4
3
4
BUFFER
SIGNALING
TIMING
CONTROL
Sa EXTRACTION
PER–CHANNEL CODE INSERT
FRAMER
RECEIVE SIDE
LIUCMUX
MHz
2.048
VCO / PLL
SYNC
SA AND SI EXTRACTION
SIGNALING EXTRACTION
E–BIT COUNTER
FAS ERROR COUNTER
CRC ERROR COUNTER
ALARM DETECTION
SYNCHRONIZER
BPV COUNTER
HDB3 DECODER
32.768 MHz
CLOCK/DATA
RECOVERY
PEAK
DETECT
EQUALIZER
SYNC CONTROL
STORE
ELASTIC
CLOCK
DATA
PER–CHANNEL CODE INSERT
SIDE
TRANSMIT
FORMATTER
PER–CHANNEL LOOPBACK
FRAMER LOOPBACK
REMOTE LOOPBACK
JITTER ATTENUA TION
(CAN BE PLACED IN EITHER
TRANSMIT OR RECEIVE PATH)
LOCAL LOOPBACK
FAS WORD INSERTION
SI BIT INSERTION
E–BIT INSERTION
SIGNALING INSERTION
CRC4 GENERAITON
AIS GENERAITON
GENERATION
INSERTION
LOTCMUX
TCLK
TCHBLK
TCHCLK
TLINK
STIMING CONTROL
MUX
(ROUTED TO ALL BLOCKS)
PARALLEL AND TEST CONTROL PORT
TLCLK
Sa INSERTION
7
LIUC
TPOSO
TCLKO
TNEGO
TNEGI
TCLKI
TPOSI
INT
D0 to D7/
AD0 to AD7
8
MUX
A0 to A6
ALE(AS)/A7
RD
WR(R/W)
BTS
CS
TEST
DS2154
(DS)
RVDD
TVDD
DVDD
RVSS
TVSS
DVSS
RRING
RTIP
TRING
TTIP
031197 3/69
Page 4
DS2154
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The analog AMI/HDB3 waveform off of the E1 line is
transformer coupled into the RRING and RTIP pins of
the DS2154. The device recovers clock and data from
the analog signal and passes it through the jitter attenuation mux to the receive side framer where the digital
serial stream is analyzed to locate the framing/multiframe pattern. The DS2154 contains an active filter that
reconstructs the analog received signal for the non–linear losses that occur in transmission. The device has a
usable receive sensitivity of 0 dB to –43 dB which allows
the device to operate on cables over 2km in length. The
receive side framer locates the FAS frame and CRC and
CAS multiframe boundaries as well as detects incoming
alarms including, carrier loss, loss of synchronization,
AIS, and Remote Alarm. If needed, the receive side
elastic store can be enabled in order to absorb the
phase and frequency differences between the recovered E1 data stream and an asynchronous backplane
clock which is provided at the RSYSCLK input. The
clock applied at the RSYSCLK input can be either a
2.048 MHz clock or a 1.544 MHz clock. The RSYSCLK
can also be a bursty clock with speeds up to 8.192 MHz.
The transmit side of the DS2154 is totally independent
from the receive side in both the clock requirements and
characteristics. Data off of a backplane can be passed
through a transmit side elastic store if necessary. The
transmit formatter will provide the necessary frame/multiframe data overhead for E1 transmission. Once the
data stream has been prepared for transmission, it is
sent via the jitter attenuation mux to the waveshaping
and line driver functions. The DS2154 will drive the E1
line from the TTIP and TRING pins via a coupling transformer. The line driver can handle both 75Ω and
120Ω lines and it has options for high return loss
applications. The line driver contains a current limiter
that will restrict the maximum current into a 1Ω load to
less than 50 mA (rms).
READER’S NOTE
This data sheet assumes a particular nomenclature of
the E1 operating environment. There are 32 eight–bit
timeslots in an E1 systems which are number 0 to 31.
Timeslot 0 is transmitted first and received first. These
32 timeslots are also referred to as channels with a numbering scheme of 1 to 32. Timeslot 0 is identical to channel 1, timeslot 1 is identical to Channel 2, and so on.
Each timeslot (or channel) is made up of eight bits which
are numbered 1 to 8. Bit number 1 is the MSB and is
transmitted first. Bit number 8 is the LSB and is transmitted last. Throughout this data sheet, the following
abbreviations will be used:
FAS Frame Alignment Sig-
CRC4 Cyclical Redundancy
nal
CAS Channel Associated
CCS Common Channel
Signaling
MF Multiframe Sa Additional bits
Si International bits E–bit CRC4 Error bits
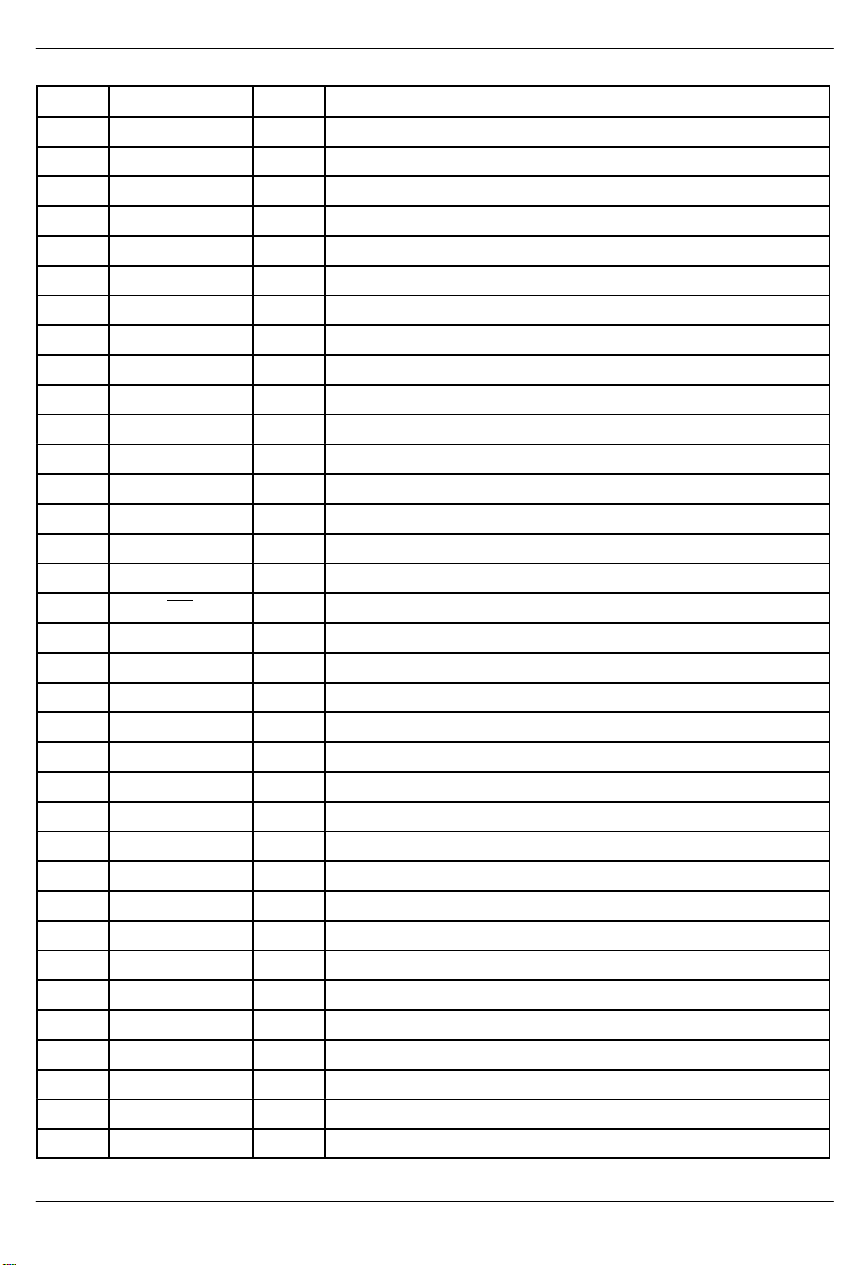
PIN LIST Table 1–1
PIN SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
1 RCHBLK O Receive Channel Block.
2 NC – No Connect.
3 8MCLK O 8.192 MHz Clock.
4 NC – No Connect.
5 NC – No Connect.
6 RCL O Receive Carrier Loss.
7 NC – No Connect.
8 NC – No Connect.
031197 4/69
Check
Signaling
Page 5
PIN DESCRIPTIONTYPESYMBOL
9 NC – No Connect.
10 NC – No Connect.
11 BTS I Bus Type Select.
12 LIUC I Line Interface Connect.
13 8XCLK O Eight Times Clock.
14 TEST I Test.
15 NC – No Connect.
16 RTIP I Receive Analog T ip Input.
17 RRING I Receive Analog Ring Input.
18 RVDD – Receive Analog Positive Supply.
19 RVSS – Receive Analog Signal Ground.
20 RVSS – Receive Analog Signal Ground.
21 MCLK I Master Clock Input.
22 XT ALD O Quartz Crystal Driver.
23 NC – No Connect.
24 RVSS – Receive Analog Signal Ground.
25 INT O Interrupt.
26 NC – No Connect.
27 NC – No Connect.
28 NC – No Connect.
29 TTIP O Transmit Analog T ip Output.
30 TVSS – Transmit Analog Signal Ground.
31 TVDD – Transmit Analog Positive Supply.
32 TRING O T ransmit Analog Ring Output.
33 TCHBLK O Transmit Channel Block.
34 TLCLK O Transmit Link Clock.
35 TLINK I Transmit Link Data.
36 NC – No Connect.
37 TSYNC I/O Transmit Sync.
38 TPOSI I Transmit Positive Data Input.
39 TNEGI I Transmit Negative Data Input.
40 TCLKI I Transmit Clock Input.
41 TCLKO O Transmit Clock Output.
42 TNEGO O Transmit Negative Data Output.
43 TPOSO O Transmit Positive Data Output.
DS2154
031197 5/69
Page 6
DS2154
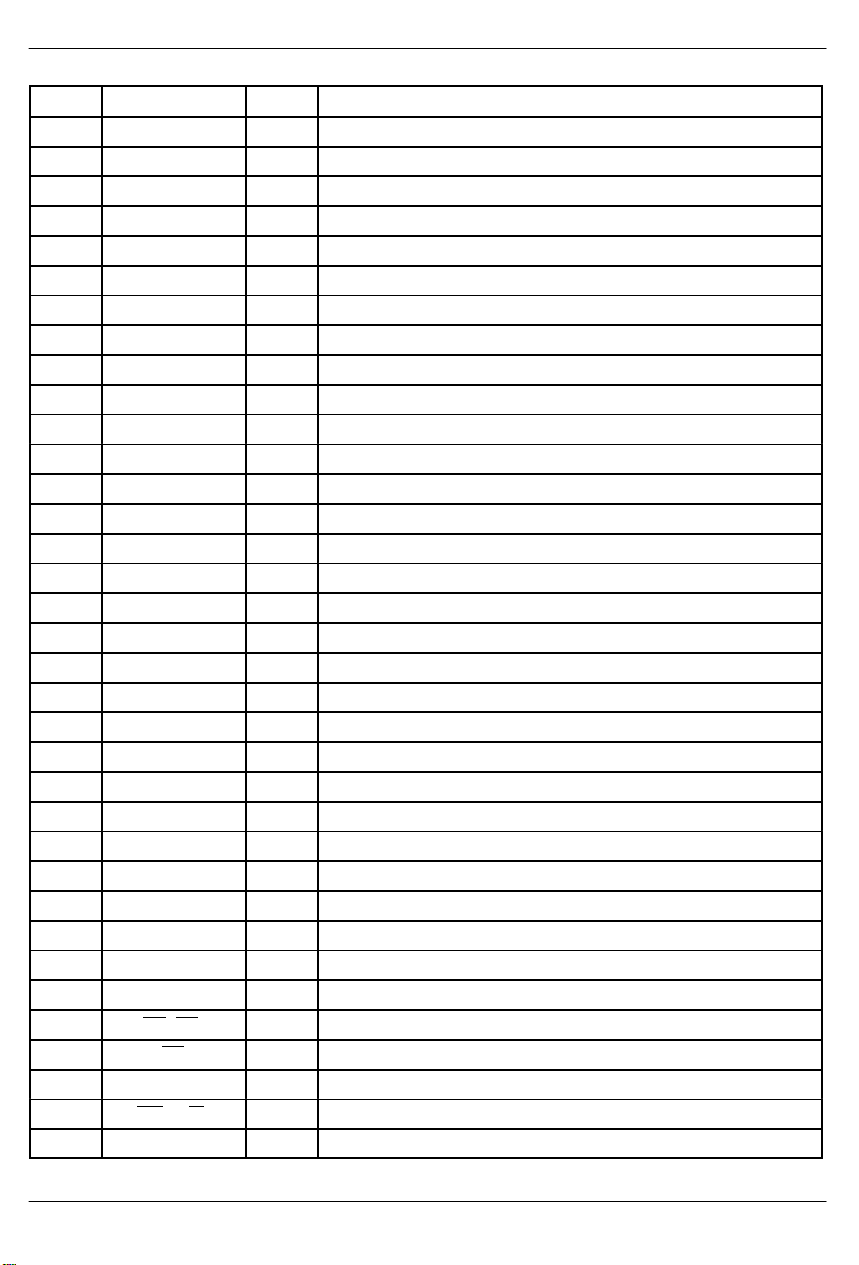
PIN DESCRIPTIONTYPESYMBOL
44 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply.
45 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground.
46 TCLK I Transmit Clock.
47 TSER I Transmit Serial Data.
48 TSIG I Transmit Signaling Input.
49 TESO O Transmit Elastic Store Output.
50 TDATA I Transmit Data.
51 TSYSCLK I Transmit System Clock.
52 TSSYNC I Transmit System Sync.
53 TCHCLK O Transmit Channel Clock.
54 NC – No Connect.
55 MUX I Bus Operation.
56 D0/AD0 I/O Data Bus Bit 0 / Address/Data Bus Bit 0.
57 D1/AD1 I/O Data Bus Bit 1 / Address/Data Bus Bit 1.
58 D2/AD2 I/O Data Bus Bit 2 / Address/Data Bus Bit 2.
59 D3/AD3 I/O Data Bus Bit 3 / Address/Data Bus Bit 3.
60 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground.
61 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply.
62 D4/AD4 I/O Data Bus Bit 4 / Address/Data Bus Bit 4.
63 D5/AD5 I/O Data Bus Bit 5 / Address/Data Bus Bit 5.
64 D6/AD6 I/O Data Bus Bit 6 / Address/Data Bus Bit 6.
65 D7/AD7 I/O Data Bus Bit 7 / Address/Data Bus Bit 7.
66 A0 I Address Bus Bit 0.
67 A1 I Address Bus Bit 1.
68 A2 I Address Bus Bit 2.
69 A3 I Address Bus Bit 3.
70 A4 I Address Bus Bit 4.
71 A5 I Address Bus Bit 5.
72 A6 I Address Bus Bit 6.
73 A7/ALE I Address Bus Bit 7 / Address Latch Enable.
74 RD (DS) I Read Input (Data Strobe).
75 CS I Chip Select.
76 NC – No Connect.
77 WR (R/W) I Write Input (Read/Write).
78 RLINK O Receive Link Data.
031197 6/69
Page 7
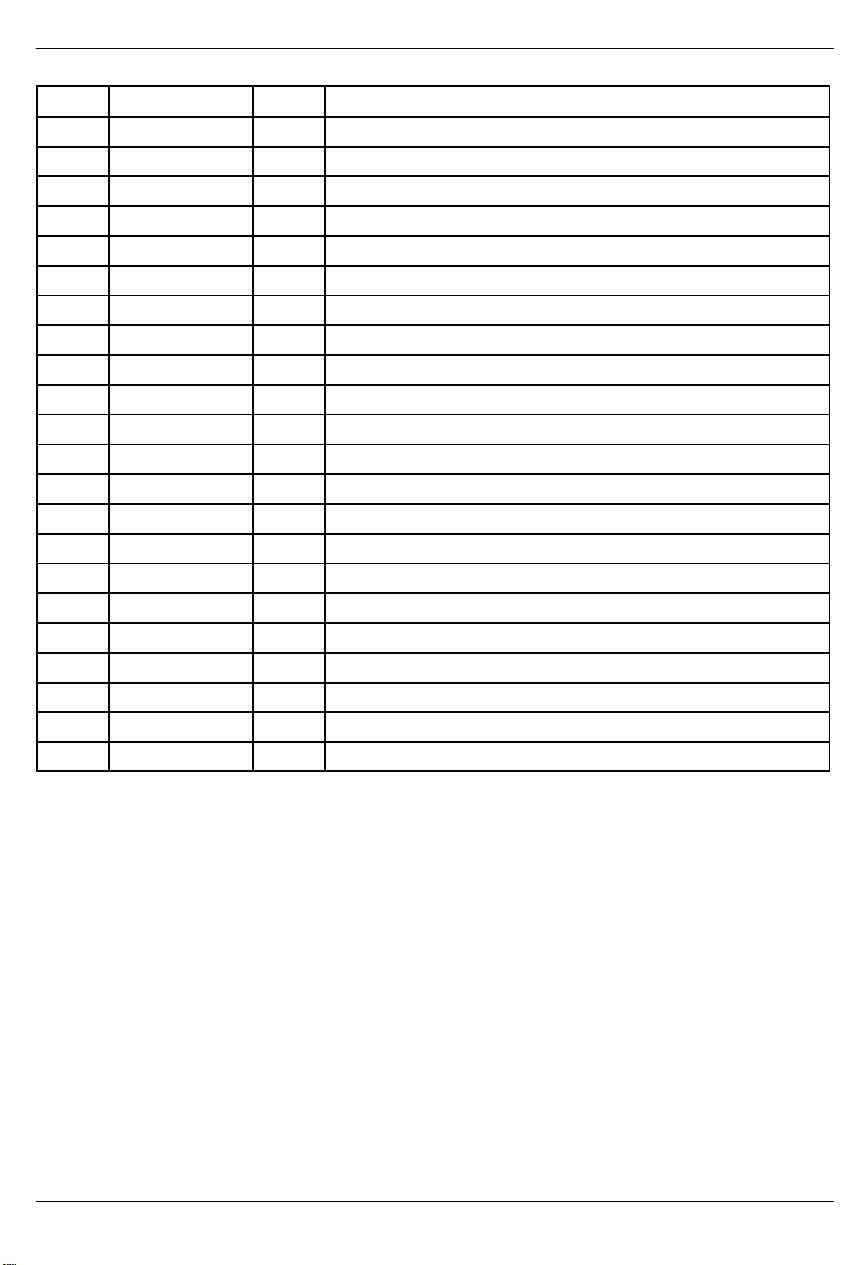
PIN DESCRIPTIONTYPESYMBOL
79 RLCLK O Receive Link Clock.
80 DVSS – Digital SIgnal Ground.
81 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply.
82 RCLK O Receive Clock.
83 DVDD – Digital Positive Supply.
84 DVSS – Digital Signal Ground.
85 RDATA O Receive Data.
86 RPOSI I Receive Positive Data Input.
87 RNEGI I Receive Negative Data Input.
88 RCLKI I Receive Clock Input.
89 RCLKO O Receive Clock Output.
90 RNEGO O Receive Negative Data Output.
91 RPOSO O Receive Positive Data Output.
92 RCHCLK O Receive Channel Clock.
93 RSIGF O Receive Signaling Freeze Output.
94 RSIG O Receive Signaling Output.
95 RSER O Receive Serial Data.
96 RMSYNC O Receive Multiframe Sync.
97 RFSYNC O Receive Frame Sync.
98 RSYNC I/O Receive Sync.
99 RLOS/LOTC O Receive Loss Of Sync / Loss Of Transmit Clock.
100 RSYSCLK I Receive System Clock.
DS2154
NOTE:
Leave all no connect (NC) pins open circuited.
DS2154 PIN DESCRIPTION Table 1–2
TRANSMIT SIDE DIGITAL PINS
Transmit Clock [TCLK]. A 2.048 MHz primary clock.
Used to clock data through the transmit side formatter.
Must be present for the parallel control port to operate
properly. If not present, the Loss Of Transmit Clock
(LOTC) function can provide a clock.
Transmit Serial Data [TSER]. Transmit NRZ serial
data. Sampled on the falling edge of TCLK when the
transmit side elastic store is disabled. Sampled on the
falling edge of TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic
store is enabled.
Transmit Channel Clock [TCHCLK]. A 256 KHz clock
which pulses high during the LSB of each channel. Synchronous with TCLK when the transmit side elastic
store is disabled. Synchronous with TSYSCLK when
the transmit side elastic store is enabled. Useful for parallel to serial conversion of channel data.
Transmit Channel Block [TCHBLK]. A user programmable output that can be forced high or low during any of
the 32 E1 channels. Synchronous with TCLK when the
transmit side elastic store is disabled. Synchronous
with TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic store is
031197 7/69
Page 8

DS2154
enabled. Useful for blocking clocks to a serial UART or
LAPD controller in applications where not all E1 channels are used such as Fractional E1, 384K bps (H0),
768K bps, 1920K bps (H12) or ISDN–PRI. Also useful
for locating individual channels in drop–and–insert
applications, for external per–channel loopback, and for
per–channel conditioning. See Section 9 for details.
Transmit System Clock [TSYSCLK]. 1.544 MHz or
2.048 MHz clock. Only used when the transmit side
elastic store function is enabled. Should be tied low in
applications that do not use the transmit side elastic
store. Can be burst at rates up to 8.192 MHz.
Transmit Link Clock [TLCLK]. 4 KHz to 20 KHz
demand clock (Sa bits) for the TLINK input. See Section
11 for details.
Transmit Link Data [TLINK]. If enabled, this pin will be
sampled on the falling edge of TCLK for data insertion
into any combination of the Sa bit positions (Sa4 to
Sa8). See Section 11 for details.
Transmit Sync [TSYNC]. A pulse at this pin will establish either frame or multiframe boundaries for the transmit side. This pin can also be programmed to output
either a frame or multiframe pulse. Always synchronous
with TCLK.
Transmit Frame Sync [TSSYNC]. Only used when the
transmit side elastic store is enabled. A pulse at this pin
will establish either frame or multiframe boundaries for
the transmit side. Should be tied low in applications that
do not use the transmit side elastic store. Always synchronous with TSYSCLK.
Transmit Data [TDATA]. Sampled on the falling edge
of TCLK with data to be clocked through the transmit
side formatter. This pin is normally tied to TESO.
Transmit Positive Data Output [TPOSO]. Updated on
the rising edge of TCLKO with the bipolar data out of the
transmit side formatter. Can be programmed to source
NRZ data via the Output Data Format (TCR1.7) control
bit. This pin is normally tied to TPOSI.
Transmit Negative Data Output [TNEGO]. Updated
on the rising edge of TCLKO with the bipolar data out of
the transmit side formatter . This pin is normally tied to
TNEGI.
Transmit Clock Output [TCLKO]. Buf fered clock that
is used to clock data through the transmit side formatter
(i.e. either TCLK or RCLKO if Loss Of Transmit Clock is
enabled and in effect or RCLKI if remote loopback is
enabled). This pin is normally tied to TCLKI.
Transmit Positive Data Input [TPOSI]. Sampled on
the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be transmitted out
onto the E1 line. Can be internally connected to TPOSO
by tying the LIUC pin high.
Transmit Negative Data Input [TNEGI]. Sampled on
the falling edge of TCLKI for data to be transmitted out
onto the E1 line. Can be internally connected to TNEGO
by tying the LIUC pin high.
Transmit Clock Input [TCLKI]. Line interface transmit
clock. Can be internally connected to TCLKO by tying
the LIUC pin high.
Transmit Signaling Input [TSIG]. When enabled, this
input will be sample signaling bits for reinsertion into
outgoing PCM E1 data stream. Sampled on the falling
edge of TCLK when the transmit side elastic store is disabled. Sampled on the falling edge of TSYSCLK when
the transmit side elastic store is enabled. See Section
13 for timing examples.
Transmit Elastic Store Data Output [TESO].
Updated on the rising edge of TCLK with data out of the
the transmit side elastic store whether the elastic store
is enabled or not. This pin is normally tied to TDATA.
031197 8/69
RECEIVE SIDE DIGITAL PINS
Receive Link Data [RLINK]. Updated with the full
recovered E1 data stream on the rising edge of RCLK.
Receive Link Clock [RLCLK]. 4 KHz to 20 KHz clock
(Sa bits) for the RLINK output. See Section 11 for
details.
Receive Clock [RCLK]. 2.048 MHz clock that is used
to clock data through the receive side framer.
Page 9

DS2154
Receive Channel Clock [RCHCLK]. 256 KHz clock
which pulses high during the LSB of each channel.
Synchronous with RCLK when the receive side elastic
store is disabled. Synchronous with RSYSCLK when
the receive side elastic store is enabled. Useful for parallel to serial conversion of channel data.
Receive Channel Block [RCHBLK]. A user programmable output that can be forced high or low during any of
the 32 E1 channels. Synchronous with RCLK when the
receive side elastic store is disabled. Synchronous with
RSYSCLK when the receive side elastic store is
enabled. Useful for blocking clocks to a serial UART or
LAPD controller in applications where not all E1 channels are used such as Fractional E1, 384K bps service,
768K bps, or ISDN–PRI. Also useful for locating individual channels in drop–and–insert applications, for external per–channel loopback, and for per–channel conditioning. See Section 9 for details.
Receive Serial Data [RSER]. Received NRZ serial
data. Updated on rising edges of RCLK when the
receive side elastic store is disabled. Updated on the
rising edges of RSYSCLK when the receive side elastic
store is enabled.
Receive Sync [RSYNC]. An extracted pulse, one
RCLK wide, is output at this pin which identifies either
frame or CAS/CRC multiframe boundaries. If the
receive side elastic store is enabled, then this pin can be
enabled to be an input at which a frame or multiframe
boundary pulse synchronous with RSYSCLK is applied.
Receive Frame Sync [RFSYNC]. An extracted 8 KHz
pulse, one RCLK wide, is output at this pin which identifies frame boundaries.
Receive Multiframe Sync [RMSYNC]. Only used
when the receive side elastic store is enabled. An
extracted pulse, one RSYSCLK wide, is output at this
pin which identifies multiframe boundaries. If the
receive side elastic store is disabled, then this output will
output multiframe boundaries associated with RCLK.
Receive Data [RDA T A]. Updated on the rising edge of
RCLK with the data out of the receive side framer.
Receive System Clock [RSYSCLK]. 1.544 MHz or
2.048 MHz clock. Only used when the elastic store
function is enabled. Should be tied low in applications
that do not use the elastic store. Can be burst at rates up
to 8.192 MHz.
Receive Signaling Output [RSIG]. Outputs signaling
bits in a PCM format. Updated on rising edges of RCLK
when the receive side elastic store is disabled. Updated
on the rising edges of RSYSCLK when the receive side
elastic store is enabled. See Section 13 for timing
examples.
Receive Loss of Sync / Loss of Transmit Clock
[RLOS/LOTC]. A dual function output that is controlled
by the TCR2.0 control bit. This pin can be programmed
to either toggle high when the synchronizer is searching
for the frame and multiframe or to toggle high if the TCLK
pin has not been toggled for 5 µs.
Receive Carrier Loss [RCL]. Set high when the line
interface detects a loss of carrier. [Note: a test mode
exists to allow the DS2154 to detect carrier loss at
RPOSI and RNEGI in place of detection at RTIP and
RRING].
Receive Signaling Freeze [RSIGF]. Set high when the
signaling data is frozen via either automatic or manual
intervention. Used to alert downstream equipment of
the condition.
8 MHz Clock [8MCLK]. 8.192 MHz output clock that is
referenced to the clock that is output at the RCLK pin.
Receive Positive Data Output [RPOSO]. Updated on
the rising edge of RCLKO with the bipolar data out of the
line interface. This pin is normally tied to RPOSI.
Receive Negative Data Output [RNEGO]. Updated
on the rising edge of RCLKO with the bipolar data out of
the line interface. This pin is normally tied to RNEGI.
Receive Clock Output [RCLKO]. Buffered recovered
clock from the E1 line. This pin is normally tied to
RCLKI.
Receive Positive Data Input [RPOSI]. Sampled on
the falling edge of RCLKI for data to be clocked through
the receive side framer. RPOSI and RNEGI can be tied
together for a NRZ interface. Can be internally connected to RPOSO by tying the LIUC pin high.
031197 9/69
Page 10

DS2154
Receive Negative Data Input [RNEGI]. Sampled on
the falling edge of RCLKI for data to be clocked through
the receive side framer. RPOSI and RNEGI can be tied
together for a NRZ interface. Can be internally connected to RNEGO by tying the LIUC pin high.
Receive Clock Input [RCLKI]. Clock used to clock
data through the receive side framer. This pin is normally tied to RCLKO. Can be internally connected to
RCLKO by tying the LIUC pin high. RCLKI must be
present for the parallel control port to operate properly.
PARALLEL CONTROL PORT PINS
Interrupt [INT]. Flags host controller during conditions
and change of conditions defined in the Status Registers 1 and 2. Active low, open drain output.
3–State Control [Test]. Set high to 3–state all output
and I/O pins (including the parallel control port). Set low
for normal operation. Useful in board level testing.
Bus Operation [MUX]. Set low to select non–multiplexed bus operation. Set high to select multiplexed bus
operation.
Data Bus [D0 to D7] or Address/Data Bus [AD0 to
AD7]. In non–multiplexed bus operation (MUX=0),
serves as the data bus. In multiplexed bus operation
(MUX=1), serves as a 8–bit multiplexed address / data
bus.
Address Bus [A0 to A6]. In non–multiplexed bus
operation (MUX=0), serves as the address bus. In multiplexed bus operation (MUX=1), these pins are not
used and should be tied low.
serves as the upper address bit. In multiplexed bus
operation (MUX=1), serves to demultiplex the bus on a
positive–going edge.
Write Input [WR] (Read/Write [R/W]). WR is an active
low signal.
LINE INTERFACE PINS
Master Clock Input [MCLK]. 2.048 MHz (± 50 ppm)
clock source with TTL levels is applied at this pin. This
clock is used internally for both clock/data recovery and
for jitter attenuation. A quartz crystal of 2.048 MHz may
be applied across MCLK and XTALD instead of the TTL
level clock source.
Quartz Crystal Driver [XTALD]. A quartz crystal of
2.048 MHz may be applied across MCLK and XTALD
instead of a TTL level clock source at MCLK. Leave
open circuited if a TTL clock source is applied at MCLK.
Eight Times Clock [8XCLK]. 16.384 MHz clock that is
frequency locked to the 2.048 MHz clock provided from
the clock/data recovery block (if the jitter attenuator is
enabled on the receive side) or from the TCLKI pin (if the
jitter attenuator is enabled on the transmit side). Can be
internally disabled via the TEST2 register if not needed.
Line Interface Connect [LIUC]. Tie low to separate the
line interface circuitry from the framer/formatter circuitry
and activate the TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/
RCLKI pins. Tie high to connect the the line interface circuitry to the framer/formatter circuitry and deactivate
the TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins.
When LIUC is tied high, the TPOSI/TNEGI/TCLKI/
RPOSI/RNEGI/RCLKI pins should be tied low.
Bus Type Select [BTS]. Strap high to select Motorola
bus timing; strap low to select Intel bus timing. This pin
controls the function of the RD\(DS), ALE(AS), and
WR\(R/W\) pins. If BTS=1, then these pins assume the
function listed in parenthesis ().
Read Input [RD] (Data Strobe [DS]). RD and DS are
active low signals.
Chip Select [CS]. Must be low to read or write to the
device. CS is an active low signal.
A7 or Address Latch Enable [ALE] (Address Strobe
[AS]). In non–multiplexed bus operation (MUX=0),
031197 10/69
Receive Tip and Ring [RTIP and RRING]. Analog
inputs for clock recovery circuitry. These pins connect
via a 1:1 transformer to either the E1 line. See Section
12 for an example.
Transmit T ip and Ring [TTIP and TRING]. Analog line
driver outputs. These pins connect via a 1:1.15 or
1:1.36 step–up transformer to the E1 line. See Section
12 for an example.
SUPPLY PINS
Digital Positive Supply [DVDD]. 5.0 volts ± 5%.
Should be tied to the RVDD and TVDD pins.
Page 11
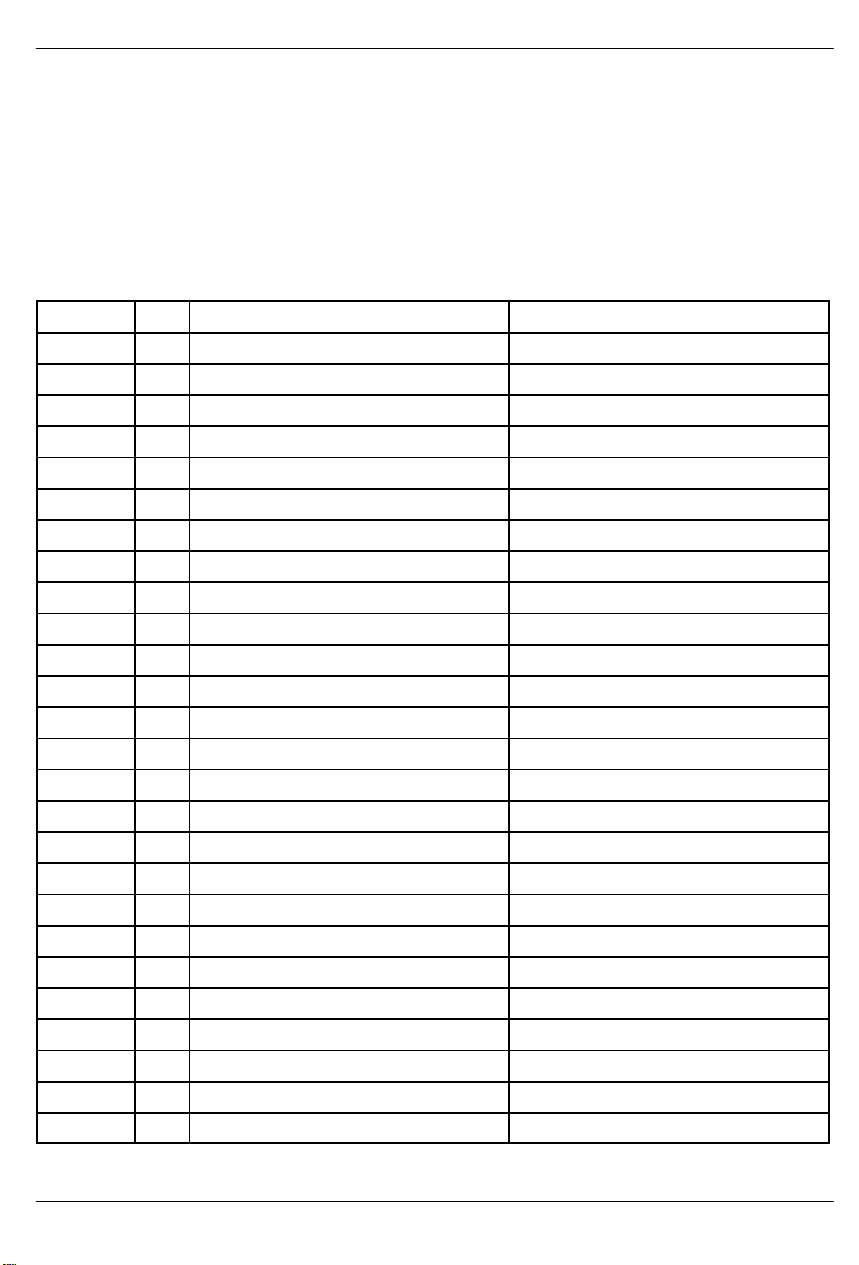
DS2154
Receive Analog Positive Supply [RVDD]. 5.0 volts
± 5%. Should be tied to the DVDD and TVDD pins.
Transmit Analog Positive Supply [TVDD]. 5.0 volts
± 5%. Should be tied to the RVDD and DVDD pins.
Receive Analog Signal Ground [RVSS]. 0.0 volts.
Should be tied to the DVSS and TVSS pins.
Transmit Analog Ground [TVSS]. 0.0 volts. Should
be tied to the RVSS and DVSS pins.
Digital Signal Ground [DVSS]. 0.0 volts. Should be
tied to the RVSS and TVSS pins.
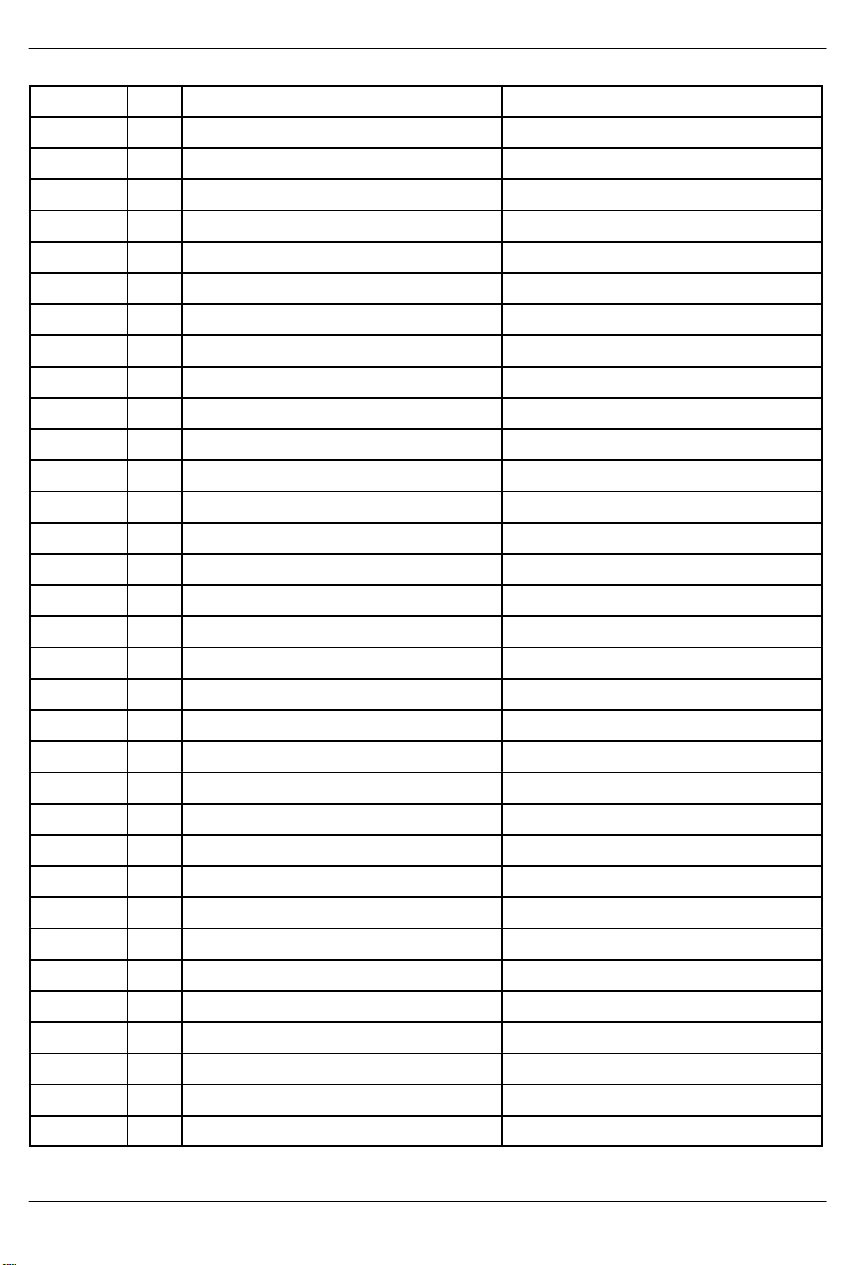
DS2154 REGISTER MAP Table 1–3
ADDRESS R/W REGISTER NAME REGISTER ABBREVIATION
00 R BPV or Code Violation Count 1. VCR1
01 R BPV or Code Violation Count 2. VCR2
02 R CRC4 Error Count 1 / FAS Error Count 1. CRCCR1
03 R CRC4 Error Count 2. CRCCR2
04 R E–Bit Count 1 / FAS Error Count 2. EBCR1
05 R E–Bit Count 2. EBCR2
06 R/W Status 1. SR1
07 R/W Status 2. SR2
08 R/W Receive Information. RIR
09 – not present. –
0A – not present. –
0B – not present. –
0C – not present. –
0D – not present. –
0E – not present. –
0F R Device ID Register . IDR
10 R/W Receive Control 1. RCR1
11 R/W Receive Control 2. RCR2
12 R/W Transmit Control 1. TCR1
13 R/W Transmit Control 2. TCR2
14 R/W Common Control 1. CCR1
15 R/W Test 1. TEST1 (set to 00h)
16 R/W Interrupt Mask 1. IMR1
17 R/W Interrupt Mask 2. IMR2
18 R/W Line Interface Control. LICR
19 R/W Test 2. TEST2 (set to 00h)
031197 11/69
Page 12
DS2154
ADDRESS REGISTER ABBREVIATIONREGISTER NAMER/W
1A R/W Common Control 2. CCR2
1B R/W Common Control 3. CCR3
1C R/W Transmit Sa Bit Control. TSaCR
1D R/W Not present. –
1E R Synchronizer Status. SSR
1F R Receive Non–Align Frame. RNAF
20 R/W T ransmit Align Frame. TAF
21 R/W T ransmit Non–Align Frame. TNAF
22 R/W T ransmit Channel Blocking 1. TCBR1
23 R/W T ransmit Channel Blocking 2. TCBR2
24 R/W T ransmit Channel Blocking 3. TCBR3
25 R/W T ransmit Channel Blocking 4. TCBR4
26 R/W Transmit Idle 1. TIR1
27 R/W Transmit Idle 2. TIR2
28 R/W Transmit Idle 3. TIR3
29 R/W Transmit Idle 4. TIR4
2A R/W Transmit Idle Definition. TIDR
2B R/W Receive Channel Blocking 1. RCBR1
2C R/W Receive Channel Blocking 2. RCBR2
2D R/W Receive Channel Blocking 3. RCBR3
2E R/W Receive Channel Blocking 4. RCBR4
2F R Receive Align Frame. RAF
30 R Receive Signaling 1. RS1
31 R Receive Signaling 2. RS2
32 R Receive Signaling 3. RS3
33 R Receive Signaling 4. RS4
34 R Receive Signaling 5. RS5
35 R Receive Signaling 6. RS6
36 R Receive Signaling 7. RS7
37 R Receive Signaling 8. RS8
38 R Receive Signaling 9. RS9
39 R Receive Signaling 10. RS10
3A R Receive Signaling 11. RS11
031197 12/69
Page 13
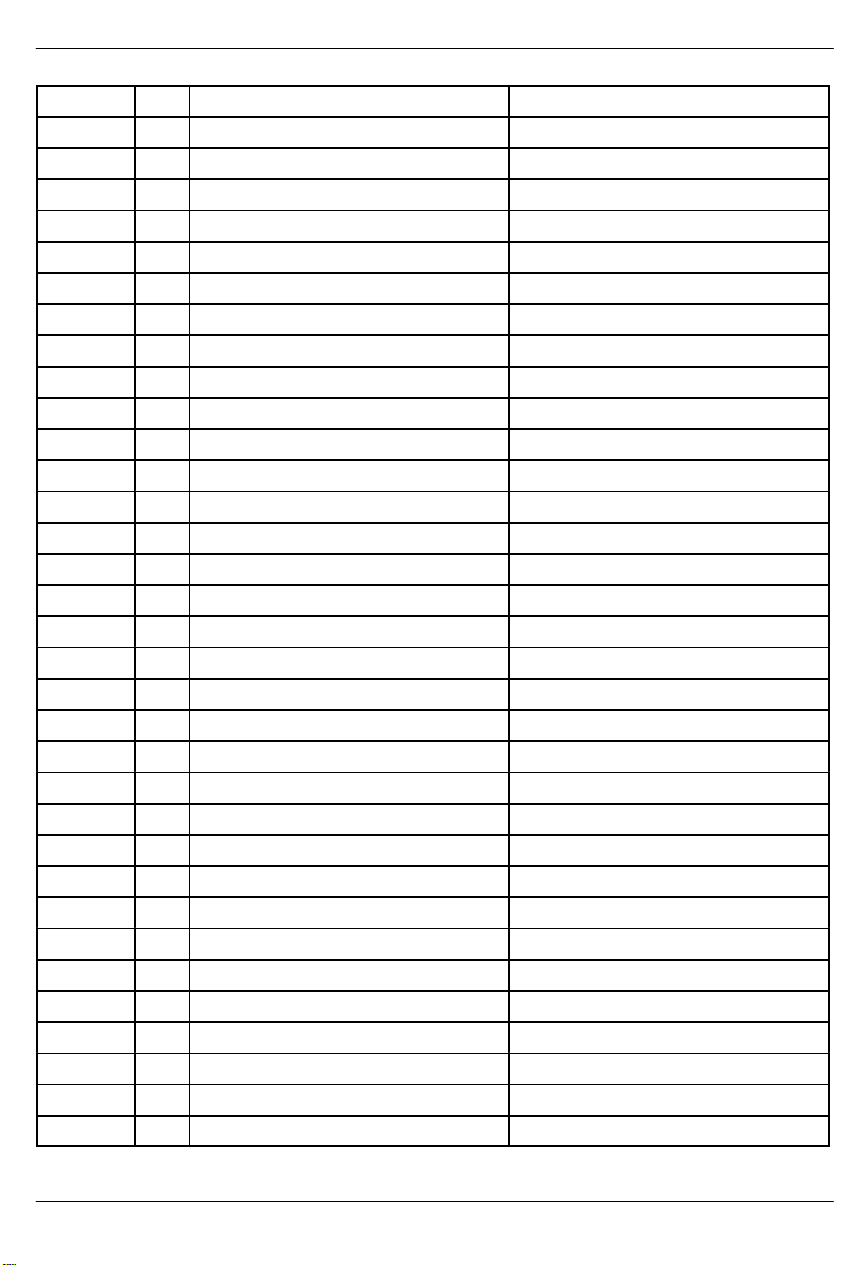
ADDRESS REGISTER ABBREVIATIONREGISTER NAMER/W
3B R Receive Signaling 12. RS12
3C R Receive Signaling 13. RS13
3D R Receive Signaling 14. RS14
3E R Receive Signaling 15. RS15
3F R Receive Signaling 16. RS16
40 R/W T ransmit Signaling 1. TS1
41 R/W T ransmit Signaling 2. TS2
42 R/W T ransmit Signaling 3. TS3
43 R/W T ransmit Signaling 4. TS4
44 R/W T ransmit Signaling 5. TS5
45 R/W T ransmit Signaling 6. TS6
46 R/W T ransmit Signaling 7. TS7
47 R/W T ransmit Signaling 8. TS8
48 R/W T ransmit Signaling 9. TS9
48 R/W T ransmit Signaling 10. TS10
4A R/W Transmit Signaling 11. TS11
4B R/W Transmit Signaling 12. TS12
4C R/W Transmit Signaling 13. TS13
4D R/W Transmit Signaling 14. TS14
4E R/W Transmit Signaling 15. TS15
4F R/W Transmit Signaling 16. TS16
50 R/W Transmit Si Bits Align Frame. TSiAF
51 R/W Transmit Si Bits Non–Align Frame. TSiNAF
52 R/W Transmit Remote Alarm Bits. TRA
53 R/W Transmit Sa4 Bits. TSa4
54 R/W Transmit Sa5 Bits. TSa5
55 R/W Transmit Sa6 Bits. TSa6
56 R/W Transmit Sa7 Bits. TSa7
57 R/W Transmit Sa8 Bits. TSa8
58 R Receive Si Bits Align Frame. RSiAF
59 R Receive Si Bits Non–Align Frame. RSiNAF
5A R Receive Remote Alarm Bits. RRA
5B R Receive Sa4 Bits. RSa4
DS2154
031197 13/69
Page 14
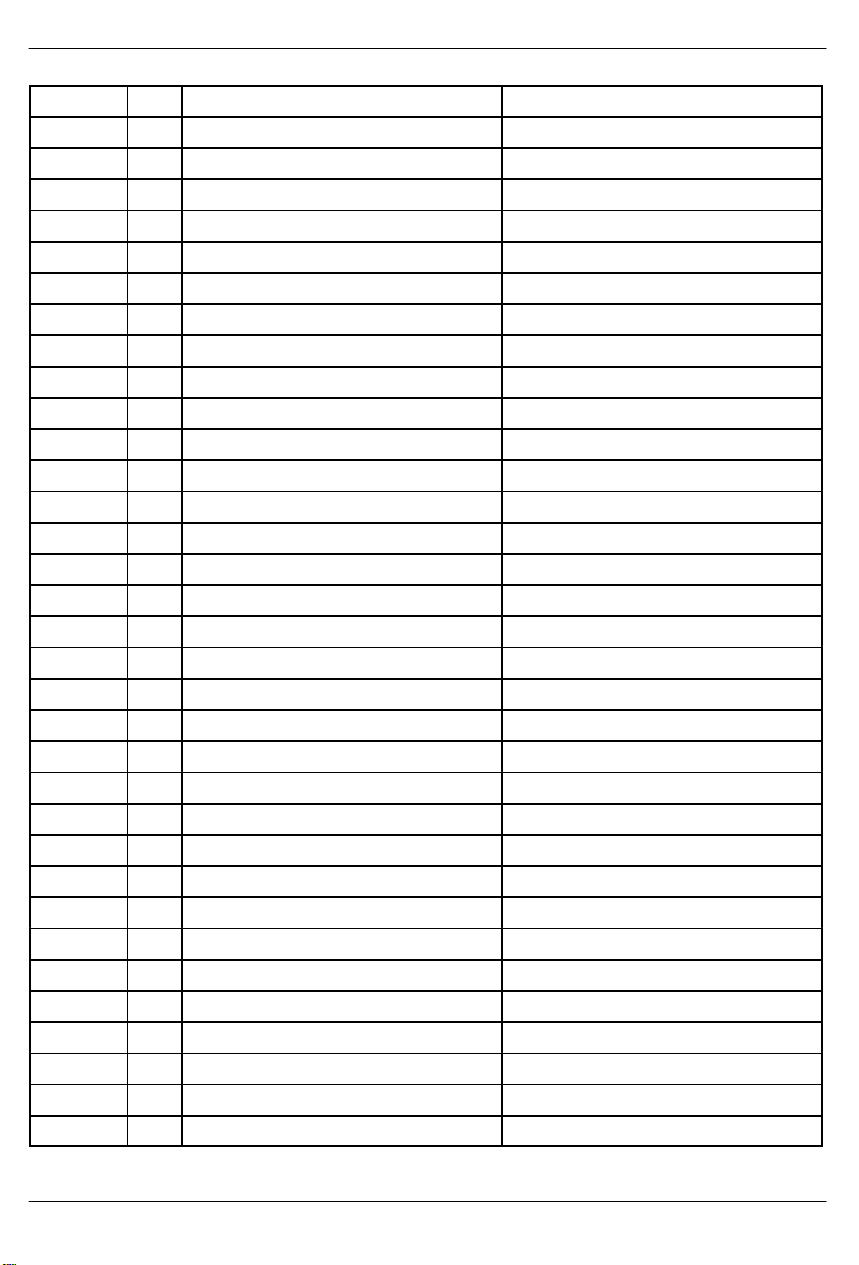
DS2154
ADDRESS REGISTER ABBREVIATIONREGISTER NAMER/W
5C R Receive Sa5 Bits. RSa5
5D R Receive Sa6 Bits. RSa6
5E R Receive Sa7 Bits. RSa7
5F R Receive Sa8 Bits. RSa8
60 R/W T ransmit Channel 1. TC1
61 R/W T ransmit Channel 2. TC2
62 R/W T ransmit Channel 3. TC3
63 R/W T ransmit Channel 4. TC4
64 R/W T ransmit Channel 5. TC5
65 R/W T ransmit Channel 6. TC6
66 R/W T ransmit Channel 7. TC7
67 R/W T ransmit Channel 8. TC8
68 R/W T ransmit Channel 9. TC9
69 R/W T ransmit Channel 10. TC10
6A R/W Transmit Channel 11. TC11
6B R/W Transmit Channel 12. TC12
6C R/W Transmit Channel 13. TC13
6D R/W Transmit Channel 14. TC14
6E R/W Transmit Channel 15. TC15
6F R/W Transmit Channel 16. TC16
70 R/W T ransmit Channel 17. TC17
71 R/W T ransmit Channel 18. TC18
72 R/W T ransmit Channel 19. TC19
73 R/W T ransmit Channel 20. TC20
74 R/W T ransmit Channel 21. TC21
75 R/W T ransmit Channel 22. TC22
76 R/W T ransmit Channel 23. TC23
77 R/W T ransmit Channel 24. TC24
78 R/W T ransmit Channel 25. TC25
79 R/W T ransmit Channel 26. TC26
7A R/W Transmit Channel 27. TC27
7B R/W Transmit Channel 28. TC28
7C R/W Transmit Channel 29. TC29
031197 14/69
Page 15
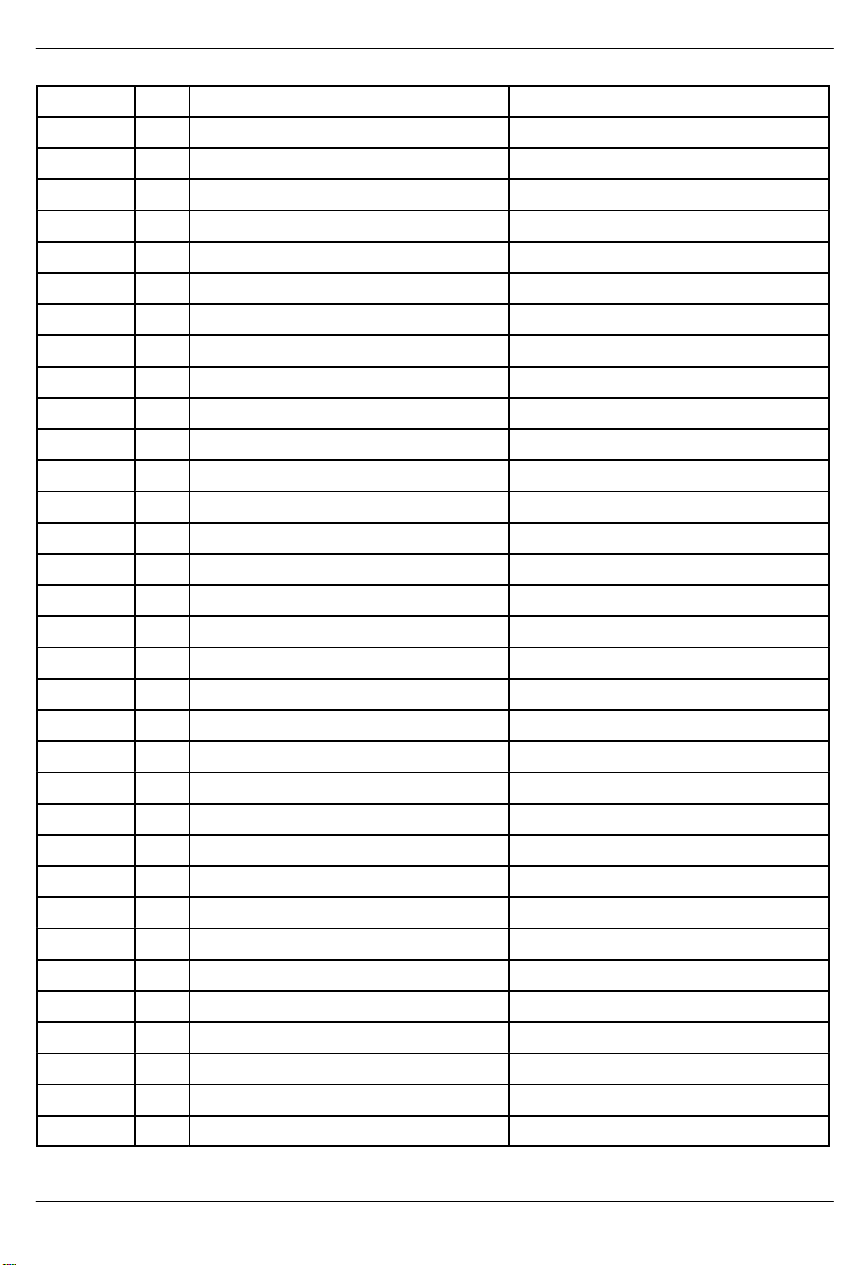
ADDRESS REGISTER ABBREVIATIONREGISTER NAMER/W
7D R/W Transmit Channel 30. TC30
7E R/W Transmit Channel 31. TC31
7F R/W Transmit Channel 32. TC32
80 R/W Receive Channel 1. RC1
81 R/W Receive Channel 2. RC2
82 R/W Receive Channel 3. RC3
83 R/W Receive Channel 4. RC4
84 R/W Receive Channel 5. RC5
85 R/W Receive Channel 6. RC6
86 R/W Receive Channel 7. RC7
87 R/W Receive Channel 8. RC8
88 R/W Receive Channel 9. RC9
89 R/W Receive Channel 10. RC10
8A R/W Receive Channel 11. RC11
8B R/W Receive Channel 12. RC12
8C R/W Receive Channel 13. RC13
8D R/W Receive Channel 14. RC14
8E R/W Receive Channel 15. RC15
8F R/W Receive Channel 16. RC16
90 R/W Receive Channel 17. RC17
91 R/W Receive Channel 18. RC18
92 R/W Receive Channel 19. RC19
93 R/W Receive Channel 20. RC20
94 R/W Receive Channel 21. RC21
95 R/W Receive Channel 22. RC22
96 R/W Receive Channel 23. RC23
97 R/W Receive Channel 24. RC24
98 R/W Receive Channel 25. RC25
99 R/W Receive Channel 26. RC26
9A R/W Receive Channel 27. RC27
9B R/W Receive Channel 28. RC28
9C R/W Receive Channel 29. RC29
9D R/W Receive Channel 30. RC30
DS2154
031197 15/69
Page 16
DS2154
ADDRESS REGISTER ABBREVIATIONREGISTER NAMER/W
9E R/W Receive Channel 31. RC31
9F R/W Receive Channel 32. RC32
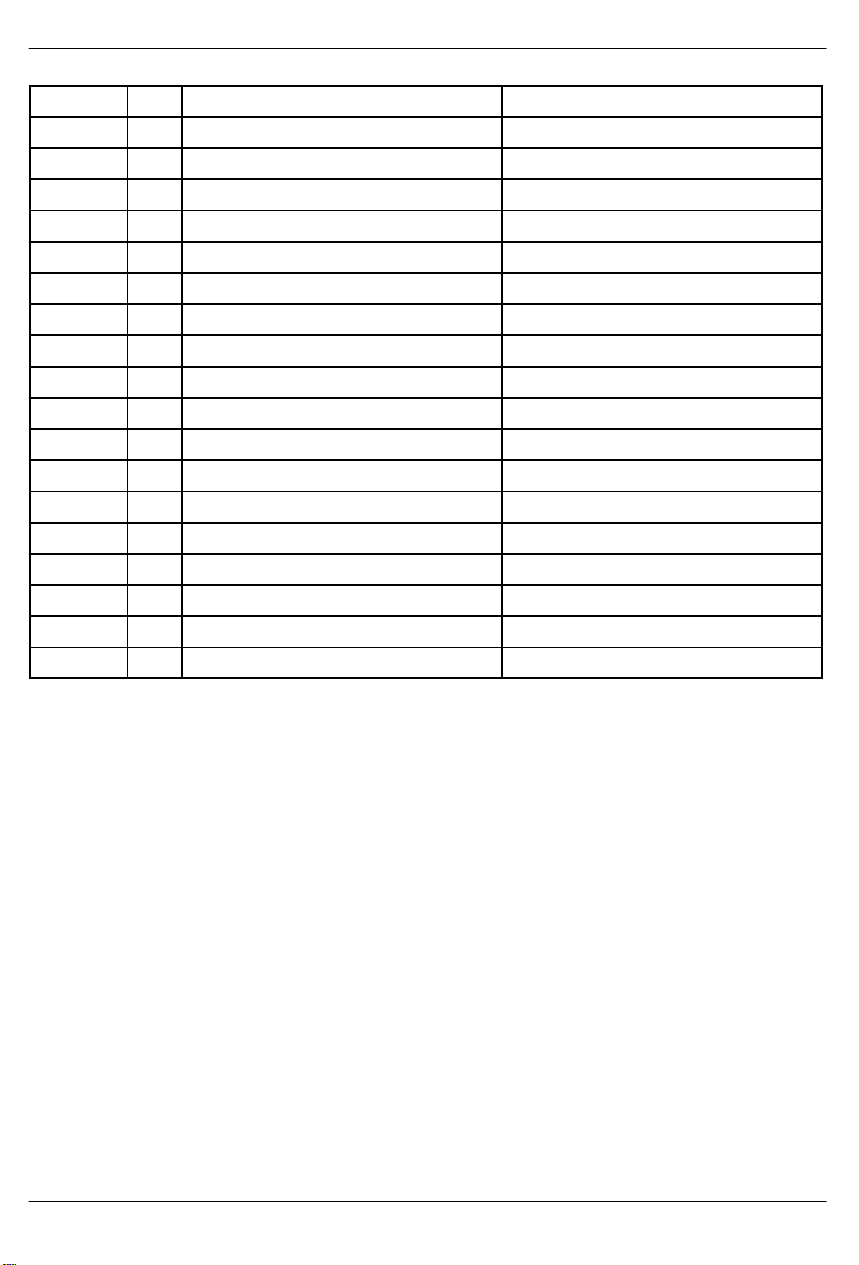
A0 R/W Transmit Channel Control 1. TCC1
A1 R/W Transmit Channel Control 2. TCC2
A2 R/W Transmit Channel Control 3. TCC3
A3 R/W Transmit Channel Control 4. TCC4
A4 R/W Receive Channel Control 1. RCC1
A5 R/W Receive Channel Control 2. RCC2
A6 R/W Receive Channel Control 3. RCC3
A7 R/W Receive Channel Control 4. RCC4
A8 R/W Common Control 4. CCR4
A9 R T ransmit DS0 Monitor. TDS0M
AA R/W Common Control 5. CCR5
AB R Receive DS0 Monitor. RDS0M
AC R/W Test 3. TEST3 (set to 00h)
AD R/W Not Used. (set to 00h)
AE R/W Not Used. (set to 00h)
AF R/W Not Used. (set to 00h)
NOTES:
1. T est Registers 1, 2, and 3 are used only by the factory; these registers must be cleared (set to all zeros) on power–up initialization to insure proper operation.
2. Register banks Bxh, Cxh, Dxh, Exh, and Fxh are not accessible.
2.0 PARALLEL PORT
The DS2154 is controlled via either a non–multiplexed
(MUX=0) or a multiplexed (MUX=1) bus by an external
microcontroller or microprocessor. The DS2154 can
operate with either Intel or Motorola bus timing configurations. If the BTS pin is tied low, Intel timing will be
selected; if tied high, Motorola timing will be selected.
All Motorola bus signals are listed in parenthesis (). See
the timing diagrams in the A.C. Electrical Characteristics in Section 14 for more details.
3.0 CONTROL, ID AND TEST REGISTERS
The operation of the DS2154 is configured via a set of
nine control registers. Typically, the control registers
are only accessed when the system is first powered up.
Once the DS2154 has been initialized, the control registers will only need to be accessed when there is a
change in the system configuration. There are two
Receive Control Register (RCR1 and RCR2), two
Transmit Control Registers (TCR1 and TCR2), and five
Common Control Registers (CCR1 to CCR5). Each of
the nine registers are described in this section.
There is a device IDentification Register (IDR) at
address 0FH. The MSB of this read–only register is
fixed to a one indicating that the DS2154 is present. The
pin–for–pin compatible T1 version of the DS2154 also
has an ID register at address 0FH and the user can read
the MSB to determine which chip is present since in the
DS2154 the MSB will be set to a one and in the DS2152
it will be set to a zero. The lower four bits of the IDR are
used to display the die revision of the chip.
The T est Registers at addresses 15, 19, and AC hex are
used by the factory in testing the DS2154. On power–
up, the T est Registers should be set to 00 hex in order for
the DS2154 to operate properly.
031197 16/69
Page 17
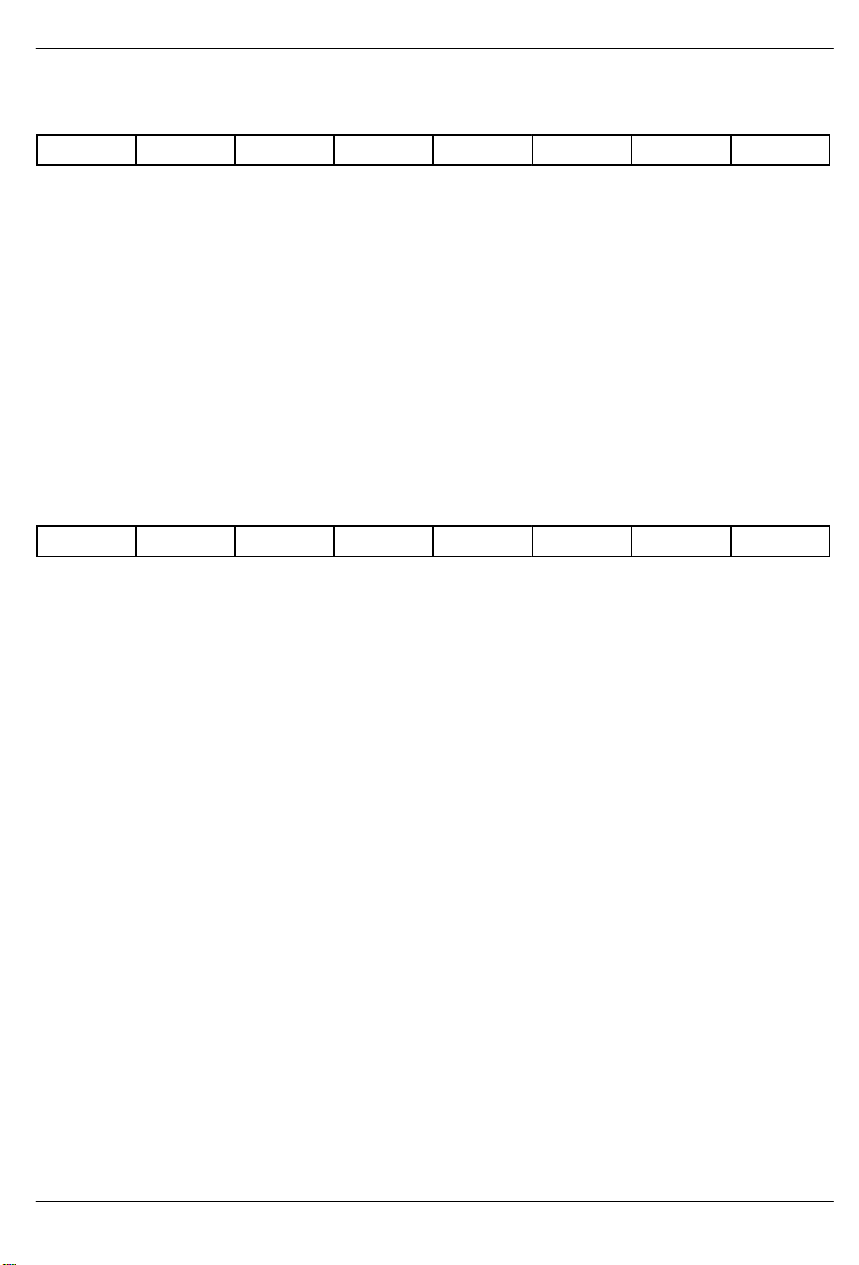
IDR: DEVICE IDENTIFICATION REGISTER (Address= 0F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
T1E1 0 0 0 ID3 ID2 ID1 ID0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
T1E1 IDR.7 T1 or E1 Chip Determination Bit.
0=T1 chip
1=E1 chip
ID3 IDR.3 Chip Revision Bit 3. MSB of a decimal code that represents the chip revi-
sion.
ID2 IDR.1 Chip Revision Bit 2.
ID1 IDR.2 Chip Revision Bit 1.
ID0 IDR.0 Chip Revision Bit 0. LSB of a decimal code that represents the chip revi-
sion.
RCR1: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=10 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RSMF
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RSMF RCR1.7 RSYNC Multiframe Function. Only used if the RSYNC pin is pro-
RSM RCR1.6 RSYNC Mode Select.
RSIO RCR1.5 RSYNC I/O Select. (note: this bit must be set to zero when RCR2.1=0).
– RCR1.4 Not Assigned. Should be set to zero when written.
– RCR1.3 Not Assigned. Should be set to zero when written.
FRC RCR1.2 Frame Resync Criteria.
SYNCE RCR1.1 Sync Enable.
RESYNC RCR1.0 Resync. When toggled from low to high, a resync is initiated. Must be
RSM RSIO – – FRC SYNCE RESYNC
grammed in the multiframe mode (RCR1.6=1).
0=RSYNC outputs CAS multiframe boundaries
1=RSYNC outputs CRC4 multiframe boundaries
0=frame mode (see the timing in Section 13)
1=multiframe mode (see the timing in Section 13)
0=RSYNC is an output (depends on RCR1.6)
1=RSYNC is an input (only valid if elastic store enabled)
0=resync if FAS received in error 3 consecutive times
1=resync if FAS or bit 2 of non–F AS is received in error 3 consecutive times
0=auto resync enabled
1=auto resync disabled
cleared and set again for a subsequent resync.
DS2154
031197 17/69
Page 18
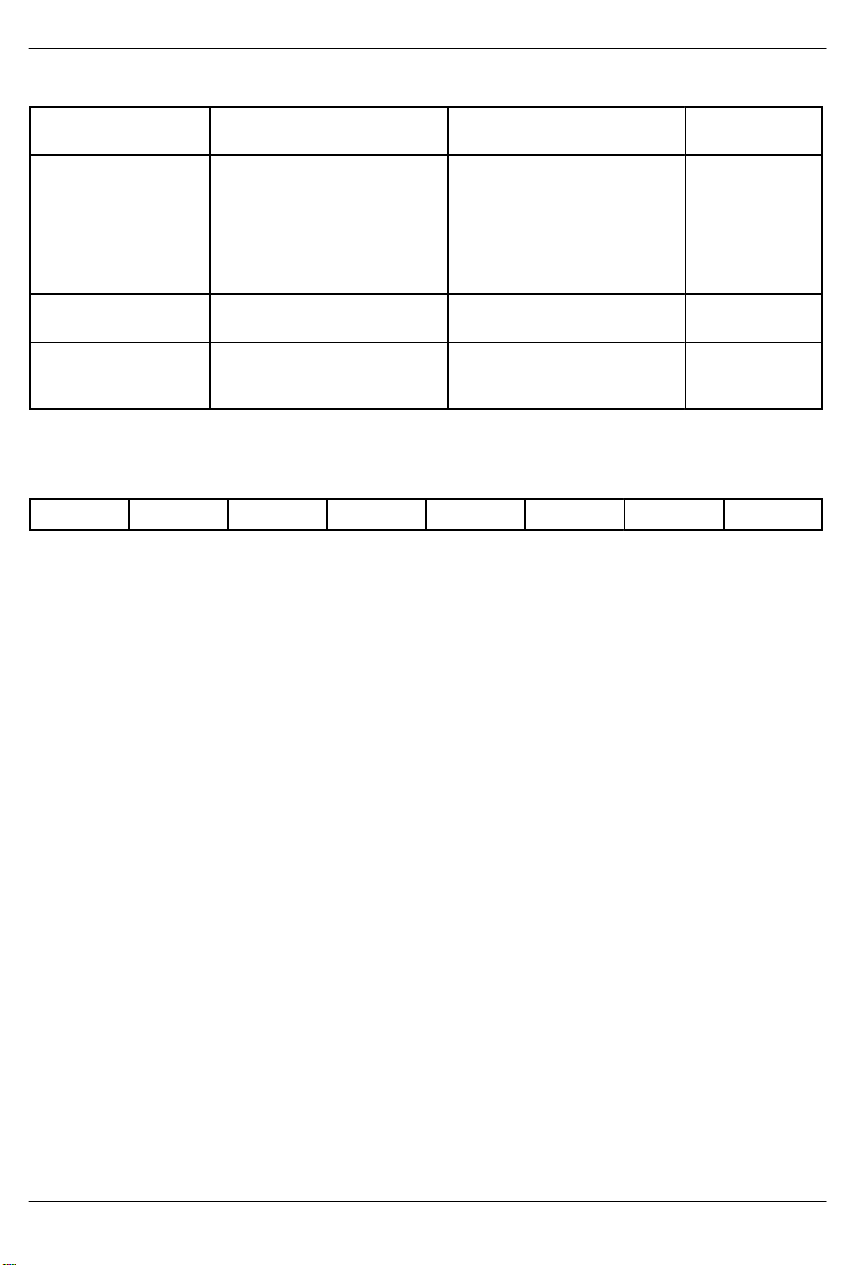
DS2154
SYNC/RESYNC CRITERIA Table 3–1
FRAME OR MULTI-
FRAME LEVEL
FAS FAS present in frame N and
CRC4 Two valid MF alignment words
CAS Valid MF alignment word found
SYNC CRITERIA RESYNC CRITERIA ITU SPEC.
Three consecutive incorrect
N + 2, and FAS not present in
FAS received
frame N + 1
Alternate (RCR1.2=1) the
above criteria is met or three
consecutive incorrect bit 2 of
non–FAS received
915 or more CRC4 code words
found within 8 ms
out of 1000 received in error
Two consecutive MF alignment
and previous timeslot 16 con-
words received in error
tains code other than all zeros
4.2 and 4.3.2
RCR2: RECEIVE CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=11 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Sa8S Sa7S Sa6S Sa5S Sa4S RBCS RESE –
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Sa8S RCR2.7 Sa8 Bit Select. Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa8 bit position; set
Sa7S RCR2.6 Sa7 Bit Select. Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa7 bit position; set
Sa6S RCR2.5 Sa6 Bit Select. Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa6 bit position; set
Sa5S RCR2.4 Sa5 Bit Select. Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa5 bit position; set
Sa4S RCR2.3 Sa4 Bit Select. Set to one to have RLCLK pulse at the Sa4 bit position; set
RBCS RCR2.2 Receive Side Backplane Clock Select.
RESE RCR2.1 Receive Side Elastic Store Enable.
– RCR2.0 Not Assigned. Should be set to zero when written.
to zero to force RLCLK low during Sa8 bit position. See Section 13 for timing details.
to zero to force RLCLK low during Sa7 bit position. See Section 13 for timing details.
to zero to force RLCLK low during Sa6 bit position. See Section 13 for timing details.
to zero to force RLCLK low during Sa5 bit position. See Section 13 for timing details.
to zero to force RLCLK low during Sa4 bit position. See Section 13 for timing details.
0=if RSYSCLK is 1.544 MHz
1=if RSYSCLK is 2.048 MHz
0=elastic store is bypassed
1=elastic store is enabled
G.706
4.1.1
4.1.2
G.706
G.732
5.2
031197 18/69
Page 19

TCR1: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=12 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
ODF TFPT T16S TUA1 TSiS TSA1 TSM TSIO
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
ODF TCR1.7 Output Data Format.
0=bipolar data at TPOSO and TNEGO
1=NRZ data at TPOSO; TNEGO=0
TFPT TCR1.6 Transmit Timeslot 0 Pass Through.
0=FAS bits/Sa bits/Remote Alarm sourced internally from the TAF and
TNAF registers
1=FAS bits/Sa bits/Remote Alarm sourced from TSER
T16S TCR1.5 T ransmit T imeslot 16 Data Select.
0=sample timeslot 16 at TSER pin
1=source timeslot 16 from TS0 to TS15 registers
TUA1 TCR1.4 Transmit Unframed All Ones.
0=transmit data normally
1=transmit an unframed all one’s code at TPOSO and TNEGO
TSiS TCR1.3 Transmit International Bit Select.
0=sample Si bits at TSER pin
1=source Si bits from TAF and TNAF registers (in this mode, TCR1.6 must
be set to 0)
TSA1 TCR1.2 Transmit Signaling All Ones.
0=normal operation
1=force timeslot 16 in every frame to all ones
TSM TCR1.1 TSYNC Mode Select.
0=frame mode (see the timing in Section 13)
1=CAS and CRC4 multiframe mode (see the timing in Section 13)
TSIO TCR1.0 TSYNC I/O Select.
0=TSYNC is an input
1=TSYNC is an output
DS2154
NOTE:
See Figure 13–1 1 for more details about how the Transmit Control Registers affect the operation of the DS2154.
031197 19/69
Page 20
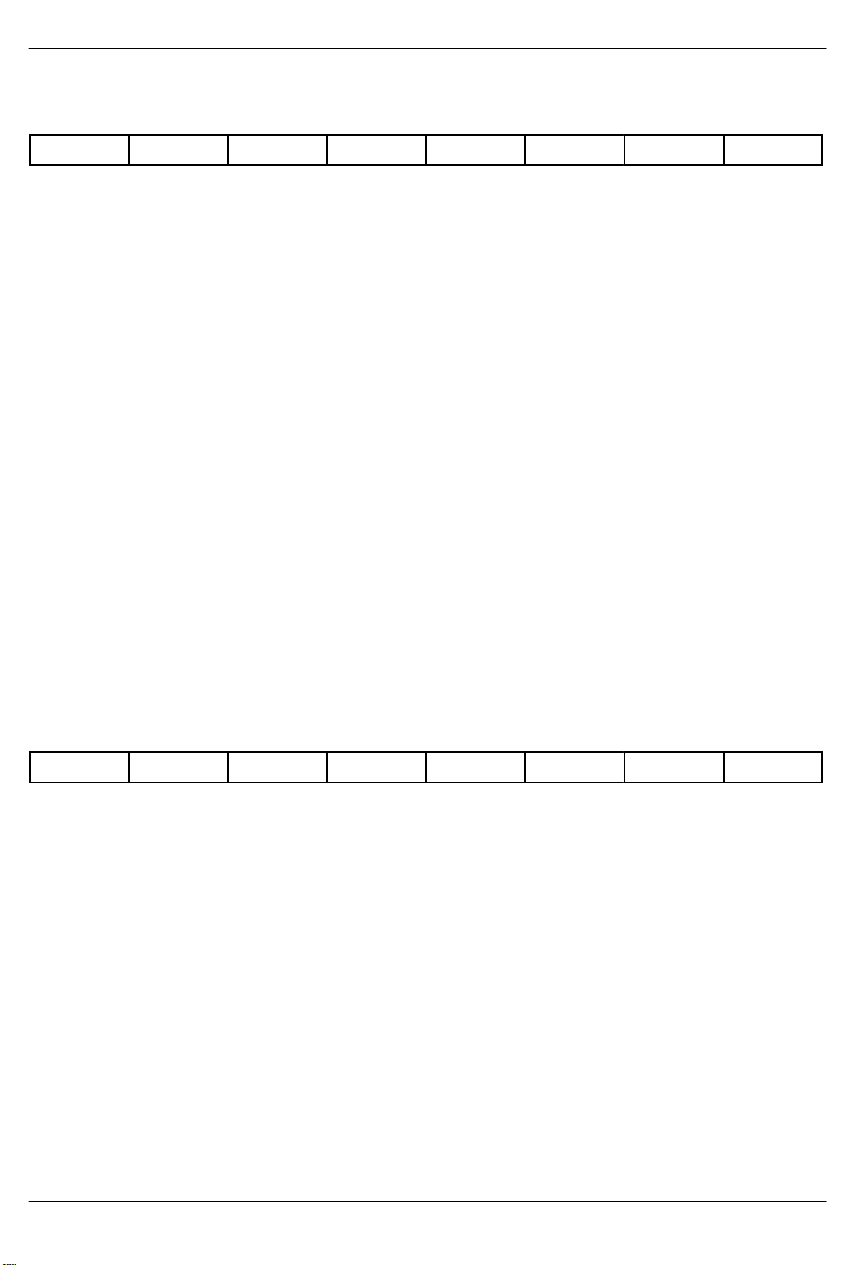
DS2154
TCR2: TRANSMIT CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=13 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Sa8S Sa7S Sa6S Sa5S Sa4S ODM AEBE PF
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Sa8S TCR2.7 Sa8 Bit Select. Set to one to source the Sa8 bit from the TLINK pin; set to
Sa7S TCR2.6 Sa7 Bit Select. Set to one to source the Sa7 bit from the TLINK pin; set to
Sa6S TCR2.5 Sa6 Bit Select. Set to one to source the Sa6 bit from the TLINK pin; set to
Sa5S TCR2.4 Sa5 Bit Select. Set to one to source the Sa5 bit from the TLINK pin; set to
Sa4S TCR2.3 Sa4 Bit Select. Set to one to source the Sa4 bit from the TLINK pin; set to
ODM TCR2.2 Output Data Mode.
AEBE TCR2.1 Automatic E–Bit Enable.
PF TCR2.0 Function of RLOS/LOTC Pin.
zero to not source the Sa8 bit. See Section 13 for timing details.
zero to not source the Sa7 bit. See Section 13 for timing details.
zero to not source the Sa6 bit. See Section 13 for timing details.
zero to not source the Sa5 bit. See Section 13 for timing details.
zero to not source the Sa4 bit. See Section 13 for timing details.
0=pulses at TPOSO and TNEGO are one full TCLKO period wide
1=pulses at TPOSO and TNEGO are 1/2 TCLKO period wide
0=E–bits not automatically set in the transmit direction
1=E–bits automatically set in the transmit direction
0=Receive Loss of Sync (RLOS)
1=Loss of Transmit Clock (LOTC)
CCR1: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 1 (Address=14 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
FLB
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
FLB CCR1.7 Framer Loopback.
THDB3 CCR1.6 Transmit HDB3 Enable.
TG802 CCR1.5 Transmit G.802 Enable. See Section 13 for details.
TCRC4 CCR1.4 Transmit CRC4 Enable.
RSM CCR1.3 Receive Signaling Mode Select.
031197 20/69
THDB3 TG802 TCRC4 RSM RHDB3 RG802 RCRC4
0=loopback disabled
1=loopback enabled
0=HDB3 disabled
1=HDB3 enabled
0=do not force TCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26
1=force TCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26
0=CRC4 disabled
1=CRC4 enabled
0=CAS signaling mode
1=CCS signaling mode
Page 21
DS2154
RHDB3 CCR1.2 Receive HDB3 Enable.
0=HDB3 disabled
1=HDB3 enabled
RG802 CCR1.1 Receive G.802 Enable. See Section 13 for details.
0=do not force RCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26
1=force RCHBLK high during bit 1 of timeslot 26
RCRC4 CCR1.0 Receive CRC4 Enable.
0=CRC4 disabled
1=CRC4 enabled
FRAMER LOOPBACK
When CCR1.7 is set to a one, the DS2154 will enter a
Framer LoopBack (FLB) mode. See Figure 1–1 for
more details. This loopback is useful in testing and
debugging applications. In FLB, the DS2154 will loop
data from the transmit side back to the receive side.
1. Data will be transmitted as normal at TPOSO and
TNEGO.
2. Data input via RPOSI and RNEGI will be ignored.
3. The RCLK output will be replaced with the TCLK
input.
When FLB is enabled, the following will occur:
CCR2: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 2 (Address=1A Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
ECUS VCRFS AAIS ARA RSERC LOTCMC RFF RFE
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
ECUS CCR2.7 Error Counter Update Select. See Section 5 for details.
VCRFS CCR2.6 VCR Function Select. See Section 5 for details.
AAIS CCR2.5 Automatic AIS Generation.
ARA CCR2.4 Automatic Remote Alarm Generation.
RSERC CCR2.3 RSER Control.
LOTCMC CCR2.2 Loss of Transmit Clock Mux Control. Determines whether the transmit
RFF CCR2.1 Receive Force Freeze. Freezes receive side signaling at RSIG (and
0=update error counters once a second
1=update error counters every 62.5 ms (500 frames)
0=count BiPolar Violations (BPVs)
1=count Code Violations (CVs)
0=disabled
1=enabled
0=disabled
1=enabled
0=allow RSER to output data as received under all conditions
1=force RSER to one under loss of frame alignment conditions
side formatter should switch to the ever present RCLKO if the TCLK should
fail to transition (see Figure 1–1).
0=do not switch to RCLKO if TCLK stops
1=switch to RCLKO if TCLK stops
RSER if CCR3.3=1); will override Receive Freeze Enable (RFE). See Section 7–2 for details.
0=do not force a freeze event
1=force a freeze event
031197 21/69
Page 22

DS2154
RFE CCR2.0 Receive Freeze Enable. See Section 7–2 for details.
0=no freezing of receive signaling data will occur
1=allow freezing of receive signaling data at RSIG (and RSER if
CCR3.3=1).
AUTOMATIC ALARM GENERATION
When either CCR2.4 or CCR2.5 is set to one, the
DS2154 monitors the receive side to determine if any of
the following conditions are present: loss of receive
frame synchronization, AIS alarm (all one’s) reception,
or loss of receive carrier (or signal). If any one (or more)
of the above conditions is present, then the DS2154 will
either force an AIS alarm (if CCR2.5=1) or a Remote
Alarm (CCR2.4=1) to be transmitted via the TPOSO
and TNEGO pins. It is an illegal state to have both
CCR2.4 and CCR2.5 set to one at the same time. If
CCR2.4=1, then RAI will be transmitted according to
ETS 300 011 specifications and a constant Remote
Alarm will be transmitted if the DS2154 cannot find
CRC4 multiframe synchronization within 400 ms as per
G.706.
CCR3: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 3 (Address=1B Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TESE
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TESE CCR3.7 Transmit Side Elastic Store Enable.
TCBFS CCR3.6 Transmit Channel Blocking Registers (TCBR) Function Select.
TIRFS CCR3.5 Transmit Idle Registers (TIR) Function Select. See Section 8 for details.
ESR CCR3.4 Elastic Stores Reset. Setting this bit from a one to a zero will force the
RSRE CCR3.3 Receive Side Signaling Re–Insertion Enable. See Section 7–2 for
TSRE CCR3.2 Transmit Side Signaling Re–Insertion Enable. See Section 7–2 for
TBCS CCR3.1 Transmit Side Backplane Clock Select.
TCBFS TIRFS ESR RSRE TSRE TBCS RCLA
0=elastic store is bypassed
1=elastic store is enabled
0=TCBRs define the operation of the TCHBLK output pin
1=TCBRs define which signaling bits are to be inserted
0=TIRs define in which channels to insert idle code
1=TIRs define in which channels to insert data from RSER (i.e., Per=Channel Loopback function)
elastic stores to a known depth. Should be toggled after RSYSCLK and
TSYSCLK have been applied and are stable. Must be set and cleared
again for a subsequent reset. Do not leave this bit set high.
details.
0=do not re–insert signaling bits into the data stream presented at the
RSER pin
1=re–insert the signaling bits into data stream presented at the RSER pin
details.
0=do not re–insert signaling bits into the data stream presented at the
TSER pin
1=re–insert the signaling bits into data stream presented at the TSER pin
0=if TSYSCLK is 1.544 MHz
1=if TSYSCLK is 2.048 MHz
031197 22/69
Page 23

DS2154
RCLA CCR3.0 Receive Carrier Loss (RCL) Alternate Criteria.
POWER–UP SEQUENCE
On power–up, after the supplies are stable, the DS2154
should be configured for operation by writing to all of the
internal registers (this includes the T est Registers) since
the contents of the internal registers cannot be predicted on power–up. Next, the LIRST (CCR5.7) bit
should be toggled from zero to one to reset the line interface circuitry (it will take the DS2154 about 40 ms to
0=RCL declared upon 255 consecutive zeros (125 us)
1=RCL declared upon 2048 consecutive zeros (1 ms)
recover from the LIRST bit being toggled). Finally, after
the RSYSCLK and TSYSCLK inputs are stable, the
ESR bit should be toggled from a zero to a one and then
back to zero (this step can be skipped if the elastic
stores are not being used). Both TCLK and RCLKI must
be present for the parallel control port to operate properly.
CCR4: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 4 (Address=A8 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RLB LLB LIAIS TCM4 TCM3 TCM2 TCM1 TCM0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RLB CCR4.7 Remote Loopback.
LLB CCR4.6 Local Loopback.
LIAIS CCR4.5 Line Interface AIS Generation Enable. See Figure 1–1 for details.
TCM4 CCR4.4 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 4. MSB of a channel decode that deter-
TCM3 CCR4.3 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 3.
TCM2 CCR4.2 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 2.
TCM1 CCR4.1 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 1.
TCM0 CCR4.0 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 0. LSB of the channel decode.
0=loopback disabled
1= loopback enabled
0=loopback disabled
1=loopback enabled
0=allow normal data from TPOSI/TNEGI to be transmitted at TTIP and
TRING
1=force unframed all ones to be transmitted at TTIP and TRING
mines which transmit channel data will appear in the TDS0M register. See
Section 6 for details.
REMOTE LOOPBACK
When CCR4.7 is set to a one, the DS2154 will be forced
into Remote LoopBack (RLB). In this loopback, data
input via the RPOSI and RNEGI pins will be transmitted
back to the TPOSO and TNEGO pins. Data will continue to pass through the receive side framer of the
DS2154 as it would normally and the data from the
transmit side formatter will be ignored. Please see
Figure 1–1 for more details.
LOCAL LOOPBACK
When CCR4.6 is set to a one, the DS2154 will be forced
into Local LoopBack (LLB). In this loopback, data will
continue to be transmitted as normal through the transmit side of the DS2154. Data being received at RTIP
and RRING will be replaced with the data being transmitted. Data in this loopback will pass through the jitter
attenuator. Please see Figure 1–1 for more details.
031197 23/69
Page 24

DS2154
CCR5: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 5 (Address=AA Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
LIRST – – RCM4 RCM3 RCM2 RCM1 RCM0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
LIRST CCR5.7 Line Interface Reset. Setting this bit from a zero to a one will initiate an
– CCR5.6 Not Assigned. Should be set to zero when written
– CCR5.5 Not Assigned. Should be set to zero when written.
RCM4 CCR5.4 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 4. MSB of a channel decode that deter-
RCM3 CCR5.3 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 3.
RCM2 CCR5.2 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 2.
RCM1 CCR5.1 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 1.
RCM0 CCR5.0 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 0. LSB of the channel decode.
4.0 STATUS AND INFORMATION
REGISTERS
There is a set of four registers that contain information
on the current real time status of the DS2154, Status
Register 1 (SR1), Status Register 2 (SR2), Receive
Information Register (RIR), and Synchronizer Status
Register (SSR). When a particular event has occurred
(or is occuring), the appropriate bit in one of these four
registers will be set to a one. All of the bits in these registers operate in a latched fashion (except for the SSR).
This means that if an event or an alarm occurs and a bit
is set to a one in any of the registers, it will remain set
until the user reads that bit. The bit will be cleared when
it is read and it will not be set again until the event has
occurred again (or in the case of the RUA1, RRA, RCL,
and RLOS alarms, the bit will remain set if the alarm is
still present).
The user will always precede a read of the SR1, SR2,
and RIR registers with a write. The byte written to the
register will inform the DS2154 which bits the user
wishes to read and have cleared. The user will write a
byte to one of these three registers, with a one in the bit
positions he or she wishes to read and a zero in the bit
positions he or she does not wish to obtain the latest
information on. When a one is written to a bit location,
the read register will be updated with the latest information. When a zero is written to a bit position, the read
register will not be updated and the previous value will
internal reset that affects the clock recovery state machine and jitter attenuator. Normally this bit is only toggled on power–up. Must be cleared and set
again for a subsequent reset.
mines which receive channel data will appear in the RDS0M register. See
Section 6 for details.
be held. A write to the status and information registers
will be immediately followed by a read of the same register. The read result should be logically AND’ed with the
mask byte that was just written and this value should be
written back into the same register to insure that bit does
indeed clear. This second write step is necessary
because the alarms and events in the status registers
occur asynchronously in respect to their access via the
parallel port. This write–read–write scheme allows an
external microcontroller or microprocessor to individually poll certain bits without disturbing the other bits in
the register. This operation is key in controlling the
DS2154 with higher–order software languages.
The SSR register operates differently than the other
three. It is a read only register and it reports the status of
the synchronizer in real time. This register is not latched
and it is not necessary to precede a read of this register
with a write.
The SR1 and SR2 registers have the unique ability to
initiate a hardware interrupt via the INT
output pin. Each
of the alarms and events in the SR1 and SR2 can be
either masked or unmasked from the interrupt pins via
the Interrupt Mask Register 1 (IMR1) and Interrupt Mask
Register 2 (IMR2) respectively.
The interrupts caused by alarms in SR1 (namely RUA1,
RRA, RCL, and RLOS) act differently than the interrupts
031197 24/69
Page 25

DS2154
caused by events in SR1 and SR2 (namely RSA1,
RDMA, RSA0, RSLIP, RMF, RAF, TMF, SEC, TAF,
when the user reads the alarm bit that caused the inter-
rupt to occur even if the alarm is still present.
LOTC, RCMF , and TSLIP). The alarm caused interrupts
will force the INT
pin low whenever the alarm changes
state (i.e. the alarm goes active or inactive according to
the set/clear criteria in Table 4–1). The INT pin will be
allowed to return high (if no other interrupts are present)
The event caused interrupts will force the INT
when the event occurs. The INT
pin will be allowed to
return high (if no other interrupts are present) when the
user reads the event bit that caused the interrupt to
occur.
RIR: RECEIVE INFORMATION REGISTER (Address=08 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TESF TESE JALT RESF RESE CRCRC FASRC CASRC
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TESF RIR.7 Transmit Side Elastic Store Full. Set when the transmit side elastic store
TESE RIR.6 Transmit Side Elastic Store Empty. Set when the transmit side elastic
JALT RIR.5 Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip. Set when the jitter attenuator FIFO reaches to
RESF RIR.4 Receive Side Elastic Store Full. Set when the receive side elastic store
RESE RIR.3 Receive Side Elastic Store Empty. Set when the receive side elastic
CRCRC RIR.2 CRC Resync Criteria Met. Set when 915/1000 code words are received in
FASRC RIR.1 FAS Resync Criteria Met. Set when 3 consecutive FAS words are
CASRC RIR.0 CAS Resync Criteria Met. Set when 2 consecutive CAS MF alignment
buffer fills and a frame is deleted.
store buffer empties and a frame is repeated.
within 4–bits of its limit; useful for debugging jitter attenuation operation.
buffer fills and a frame is deleted.
store buffer empties and a frame is repeated.
error.
received in error.
words are received in error.
pin low
SSR: SYNCHRONIZER STATUS REGISTER (Address=1E Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CSC5 CSC4 CSC3 CSC2 CSC0 FASSA CASSA CRC4SA
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CSC5 SSR.7 CRC4 Sync Counter Bit 5. MSB of the 6–bit counter.
CSC4 SSR.6 CRC4 Sync Counter Bit 4.
CSC3 SSR.5 CRC4 Sync Counter Bit 3.
CSC2 SSR.4 CRC4 Sync Counter Bit 2.
CSC0 SSR.3 CRC4 Sync Counter Bit 0. LSB of the 6–bit counter. The next to LSB is
not accessible.
031197 25/69
Page 26

DS2154
FASSA SSR.2 FAS Sync Active. Set while the synchronizer is searching for alignment at
the FAS level.
CASSA SSR.1 CAS MF Sync Active. Set while the synchronizer is searching for the CAS
MF alignment word.
CRC4SA SSR.0 CRC4 MF Sync Active. Set while the synchronizer is searching for the
CRC4 MF alignment word.
CRC4 SYNC COUNTER
The CRC4 Sync Counter increments each time the 8 ms
CRC4 multiframe search times out. The counter is
cleared when the DS2154 has successfully obtained
synchronization at the CRC4 level. The counter can
also be cleared by disabling the CRC4 mode
amount of time the DS2154 has been searching for synchronization at the CRC4 level. ITU G.706 suggests
that if synchronization at the CRC4 level cannot be
obtained within 400 ms, then the search should be
abandoned and proper action taken. The CRC4 Sync
Counter will rollover.
(CCR1.0=0). This counter is useful for determining the
SR1: STATUS REGISTER 1 (Address=06 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RSA1 RDMA RSA0 RSLIP RUA1 RRA RCL RLOS
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RSA1 SR1.7 Receive Signaling All Ones / Signaling Change. Set when the contents
RDMA SR1.6 Receive Distant MF Alarm. Set when bit–6 of timeslot 16 in frame 0 has
RSA0 SR1.5 Receive Signaling All Zeros / Signaling Change. Set when over a full
RSLIP SR1.4 Receive Side Elastic Store Slip. Set when the elastic store has either re-
RUA1 SR1.3 Receive Unframed All Ones. Set when an unframed all ones code is re-
RRA SR1.2 Receive Remote Alarm. Set when a remote alarm is received at RPOSI
RCL SR1.1 Receive Carrier Loss. Set when 255 (or 2048 if CCR3.0=1) consecutive
RLOS SR1.0 Receive Loss of Sync. Set when the device is not synchronized to the
of timeslot 16 contains less than three zeros over 16 consecutive frames.
This alarm is not disabled in the CCS signaling mode. Both RSA1 and
RSA0 will be set if a change in signaling is detected.
been set for two consecutive multiframes. This alarm is not disabled in the
CCS signaling mode.
MF, timeslot 16 contains all zeros. Both RSA1 and RSA0 will be set if a
change in signaling is detected.
peated or deleted a frame of data.
ceived at RPOSI and RNEGI.
and RNEGI.
zeros have been detected at RTIP and RRING. [Note: a test mode exists to
allow the DS2154 to detect carrier loss at RPOSI and RNEGI in place of
detection at RTIP and RRING].
receive E1 stream.
031197 26/69
Page 27

ALARM CRITERIA Table 4–1
ALARM SET CRITERIA CLEAR CRITERIA
RSA1
(receive signaling
all ones)
RSA0
(receive signaling
all zeros)
RDMA
(receive distant
over 16 consecutive frames (one full
MF) timeslot 16 contains less than
three zeros
over 16 consecutive frames (one full
MF) timeslot 16 contains all zeros
bit 6 in timeslot 16 of frame 0 set to
one for two consecutive MF
over 16 consecutive frames (one full
MF) timeslot 16 contains three or
more zeros
over 16 consecutive frames (one full
MF) timeslot 16 contains at least a
single one
bit 6 in timeslot 16 of frame 0 set to
zero for a two consecutive MF
multiframe alarm)
RUA1
(receive unframed
less than three zeros in two frames
(512–bits)
more than two zeros in two frames
(512–bits)
all ones)
RRA
(receive remote
bit 3 of non–align frame set to one for
three consecutive occasions
bit 3 of non–align frame set to zero for
three consecutive occasions
alarm)
RCL
(receive carrier
255 (or 2048) consecutive zeros
received
in 255–bit times, at least 32 ones are
received
loss)
SR2: STATUS REGISTER 2 (Address=07 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RMF
RAF TMF SEC TAF LOTC RCMF TSLIP
DS2154
ITU
SPEC.
G.732
4.2
G.732
5.2
O.162
2.1.5
O.162
1.6.1.2
O.162
2.1.4
G.775 /
G.962
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RMF SR2.7 Receive CAS Multiframe. Set every 2 ms (regardless if CAS signaling is
enabled or not) on receive multiframe boundaries. Used to alert the host
that signaling data is available.
RAF SR2.6 Receive Align Frame. Set every 250 µs at the beginning of align frames.
Used to alert the host that Si and Sa bits are available in the RAF and RNAF
registers.
TMF SR2.5 Transmit Multiframe. Set every 2 ms (regardless if CRC4 is enabled) on
transmit multiframe boundaries. Used to alert the host that signaling data
needs to be updated.
SEC SR2.4 One Second Timer. Set on increments of one second based on RCLK. If
CCR2.7=1, then this bit will be set every 62.5 ms instead of once a second.
TAF SR2.3 T ransmit Align Frame. Set every 250 µs at the beginning of align frames.
Used to alert the host that the TAF and TNAF registers need to be updated.
LOTC SR2.2 Loss of Transmit Clock. Set when the TCLK pin has not transitioned for
one channel time (or 3.9 µs). Will force the LOTC pin high if enabled via
TCR2.0.
RCMF SR2.1 Receive CRC4 Multiframe. Set on CRC4 multiframe boundaries; will con-
tinue to be set every 2 ms on an arbitrary boundary if CRC4 is disabled.
TSLIP SR2.0 Transmit Elastic Store Slip. Set when the elastic store has either re-
peated or deleted a frame of data.
031197 27/69
Page 28

DS2154
IMR1: INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 1 (Address=16 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RSA1 RDMA RSA0 RSLIP RUA1 RRA RCL RLOS
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RSA1 IMR1.7 Receive Signaling All Ones / Signaling Change.
RDMA IMR1.6 Receive Distant MF Alarm.
RSA0 IMR1.5 Receive Signaling All Zeros / Signaling Change.
RSLIP IMR1.4 Receive Elastic Store Slip Occurrence.
RUA1 IMR1.3 Receive Unframed All Ones.
RRA IMR1.2 Receive Remote Alarm.
RCL IMR1.1 Receive Carrier Loss.
RLOS IMR1.0 Receive Loss of Sync.
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
IMR2: INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER 2 (Address=17 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
RMF RAF TMF SEC TAF LOTC RCMF TSLIP
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RMF IMR2.7 Receive CAS Multiframe.
RAF IMR2.6 Receive Align Frame.
TMF IMR2.5 Transmit Multiframe.
031197 28/69
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
Page 29

DS2154
SEC IMR2.4 One Second Timer.
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
TAF IMR2.3 Transmit Align Frame.
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
LOTC IMR2.2 Loss Of Transmit Clock.
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
RCMF IMR2.1 Receive CRC4 Multiframe.
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
TSLIP IMR2.0 Transmit Side Elastic Store Slip Occurrence.
0=interrupt masked
1=interrupt enabled
5.0 ERROR COUNT REGISTERS
There are a set of four counters in the DS2154 that
record bipolar or code violations, errors in the CRC4
SMF code words, E bits as reported by the far end, and
word errors in the FAS. Each of these four counters are
automatically updated on either one second boundaries
(CCR2.7=0) or every 62.5 ms (CCR2.7=1) as determined by the timer in Status Register 2 (SR2.4). Hence,
these registers contain performance data from either
the previous second or the previous 62.5 ms. The user
can use the interrupt from the timer to determine when to
read these registers. The user has a full second (or
62.5 ms) to read the counters before the data is lost.
16–bit counter that records either BiPolar Violations
(BPVs) or Code Violations (CVs). If CCR2.6=0, then the
VCR counts bipolar violations. Bipolar violations are
defined as consecutive marks of the same polarity. In
this mode, if the HDB3 mode is set for the receive side
via CCR1.2, then HDB3 code words are not counted as
BPVs. If CCR2.6=1, then the VCR counts code violations as defined in ITU O.161. Code violations are
defined as consecutive bipolar violations of the same
polarity. In most applications, the DS2154 should be
programmed to count BPVs when receiving AMI code
and to count CVs when receiving HDB3 code. This
counter increments at all times and is not disabled by
loss of sync conditions. The counter saturates at 65,535
5.1 BPV or Code Violation Counter
Violation Count Register 1 (VCR1) is the most significant word and VCR2 is the least significant word of a
and will not rollover. The bit error rate on a E1 line would
have to be greater than 10**
saturate.
–2
before the VCR would
VCR1: UPPER BIPOLAR VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER 1 (Address=00 Hex)
VCR2: LOWER BIPOLAR VIOLATION COUNT REGISTER 2 (Address=01 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
V15
V7 V6 V5 V4 V3 V2 V1 V0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
V14 V13 V12 V11 V10 V9 V8
V15 VCR1.7 MSB of the 16–bit bipolar or code violation count .
V0 VCR2.0 LSB of the 16–bit bipolar or code violation count.
VCR1
VCR2
031197 29/69
Page 30

DS2154
5.2 CRC4 Error Counter
CRC4 Count Register 1 (CRCCR1) is the most significant word and CRCCR2 is the least significant word of a
10–bit counter that records word errors in the Cyclic
Redundancy Check 4 (CRC4). Since the maximum
CRC4 count in a one second period is 1000, this counter
cannot saturate. The counter is disabled during loss of
sync at either the FAS or CRC4 level; it will continue to
count if loss of multiframe sync occurs at the CAS level.
CRCCR1: CRC4 COUNT REGISTER 1 (Address=02 Hex)
CRCCR2: CRC4 COUNT REGISTER 2 (Address=03 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
(note 1) (note 1) (note 1) (note 1) (note 1) (note 1) CRC9 CRC8
CRC7 CRC6 CRC5 CRC4 CRC3 CRC2 CRC1 CRC0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CRC9 CRCCR1.1 MSB of the 10–bit CRC4 error count.
CRC0 CRCCR2.0 LSB of the 10–bit CRC4 error count.
CRCCR1
CRCCR2
NOTE:
1. The upper six bits of CRCCR1 at address 02 are the most significant bits of the 12–bit FAS error counter.
5.3 E–Bit Counter
E–bit Count Register 1 (EBCR1) is the most significant
word and EBCR2 is the least significant word of a 10–bit
counter that records Far End Block Errors (FEBE) as
reported in the first bit of frames 13 and 15 on E1 lines
running with CRC4 multiframe. These count registers
will increment once each time the received E–bit is set to
zero. Since the maximum E–bit count in a one second
period is 1000, this counter cannot saturate. The
counter is disabled during loss of sync at either the FAS
or CRC4 level; it will continue to count if loss of multiframe sync occurs at the CAS level.
EBCR1: E–BIT COUNT REGISTER 1 (Address=04 Hex)
EBCR2: E–BIT COUNT REGISTER 2 (Address=05 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
(note 1) (note 1) (note 1) (note 1) (note 1) (note 1) EB9 EB8
EB7 EB6 EB5 EB4 EB3 EB2 EB1 EB0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
EB9 EBCR1.1 MSB of the 10–bit E–Bit count.
EB0 EBCR2.0 LSB of the 10–bit E–Bit count.
NOTE:
The upper six bits of EBCR1 at address 04 are the least significant bits of the 12–bit FAS error counter.
031197 30/69
EBCR1
EBCR2
Page 31

DS2154
5.4 FAS Error Counter
FAS Count Register 1 (F ASCR1) is the most significant
word and FASCR2 is the least significant word of a
12–bit counter that records word errors in the Frame
Alignment Signal in timeslot 0. This counter is disabled
during loss of frame synchronization conditions, it is not
disabled during loss of synchronization at either the
CAS or CRC4 multiframe level. Since the maximum
FAS word error count in a one second period is 4000,
this counter cannot saturate.
FASCR1: FAS BIT COUNT REGISTER 1 (Address=02 Hex)
FASCR2: FAS BIT COUNT REGISTER 2 (Address=04 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
FAS11
FAS5 FAS4 F AS3 FAS2 FAS1 FAS0 (note 1) (note 1)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
FAS10 FAS9 FAS8 FAS7 FAS6 (note 2) (note 2)
FAS11 FASCR1.7 MSB of the 12–bit FAS error count.
FAS0 FASCR2.2 LSB of the 12–bit FAS error count.
FASCR1
FASCR2
NOTES:
1. The lower two bits of FASCR1 at address 02 are the most significant bits of the 10–bit CRC4 error counter.
2. The lower two bits of FASCR2 at address 04 are the most significant bits of the 10–bit E–Bit counter.
6.0 DS0 MONITORING FUNCTION
The DS2154 has the ability to monitor one DS0 64K bps
channel in the transmit direction and one DS0 channel
in the receive direction at the same time. In the transmit
direction the user will determine which channel is to be
monitored by properly setting the TCM0 to TCM4 bits in
the CCR4 register. In the receive direction, the RCM0 to
RCM4 bits in the CCR5 register need to be properly set.
The DS0 channel pointed to by the TCM0 to TCM4 bits
will appear in the Transmit DS0 Monitor (TDS0M) register and the DS0 channel pointed to by the RCM0 to
RCM4 bits will appear in the Receive (RDS0M) register.
The TCM4 to TCM0 and RCM4 to RCM0 bits should be
programmed with the decimal decode of the appropriate
E1 channel. For example, if DS0 Channel 6 (timeslot 5)
in the transmit direction and DS0 Channel 15 (timeslot
14) in the receive direction needed to be monitored,
then the following values would be programmed into
CCR4 and CCR5:
TCM4=0 RCM4=0
TCM3=0 RCM3=1
TCM2=1 RCM2=1
TCM1=0 RCM1=1
TCM0=1 RCM0=0
CCR4: DS0 MONITORING FUNCTION (Address=A8 Hex)
[repeated here from section 3 for convenience]
(MSB) (LSB)
RLB LLB LIAIS TCM4 TCM3 TCM2 TCM1 TCM0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
RLB CCR4.7 Remote Loopback. See Section 3 for details.
LLB CCR4.6 Local Loopback. See Section 3 for details.
LIAIS CCR4.5 Line Interface AIS Generation Enable. See Section 3 for details.
TCM4 CCR4.4 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 4. MSB of a channel decode that deter-
mines which transmit DS0 channel data will appear in the TDS0M register.
031197 31/69
Page 32

DS2154
TCM3 CCR4.3 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 3.
TCM2 CCR4.2 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 2.
TCM1 CCR4.1 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 1.
TCM0 CCR4.0 Transmit Channel Monitor Bit 0. LSB of the channel decode that deter-
mines which transmit DS0 channel data will appear in the TDS0M register.
TDS0M: TRANSMIT DS0 MONITOR REGISTER (Address=A9 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
B1 TDS0M.7 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 8. MSB of the DS0 channel (first bit to be trans-
B2 TDS0M.6 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 7.
B3 TDS0M.5 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 6.
B4 TDS0M.4 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 5.
B5 TDS0M.3 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 4.
B6 TDS0M.2 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 3.
B7 TDS0M.1 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 2.
B8 TDS0M.0 Transmit DS0 Channel Bit 1. LSB of the DS0 channel (last bit to be trans-
mitted).
mitted).
CCR5: COMMON CONTROL REGISTER 5 (Address=AA Hex)
[repeated here from section 3 for convenience]
(MSB) (LSB)
LIRST – – RCM4 RCM3 RCM2 RCM1 RCM0
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
LIRST CCR5.7 Line Interface Reset. See Section 3 for details.
– CCR5.6 Not Assigned. Should be set to zero when written.
– CCR5.5 Not Assigned. Should be set to zero when written.
RCM4 CCR5.4 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 4. MSB of a channel decode that deter-
RCM3 CCR5.3 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 3.
RCM2 CCR5.2 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 2.
RCM1 CCR5.1 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 1.
RCM0 CCR5.0 Receive Channel Monitor Bit 0. LSB of the channel decode that deter-
031197 32/69
mines which receive DS0 channel data will appear in the RDS0M register.
mines which receive DS0 channel data will appear in the RDS0M register.
Page 33

RDS0M: RECEIVE DS0 MONITOR REGISTER (Address=AB Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
B1 RDS0M.7 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 8. MSB of the DS0 channel (first bit to be
received).
B2 RDS0M.6 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 7.
B3 RDS0M.5 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 6.
B4 RDS0M.4 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 5.
B5 RDS0M.3 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 4.
B6 RDS0M.2 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 3.
B7 RDS0M.1 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 2.
B8 RDS0M.0 Receive DS0 Channel Bit 1. LSB of the DS0 channel (last bit to be
received).
7.0 SIGNALING OPERATION
The DS2154 contains provisions for both processor
based (i.e., software based) signaling bit access and for
hardware based access. Both the processor based
access and the hardware based access can be used
simultaneously if necessary. The processor based
signaling is covered in Section 7.1 and the hardware
based signaling is covered in Section 7.2.
7.1 PROCESSOR BASED SIGNALING
The Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) bits
embedded in the E1 stream can be extracted from the
receive stream and inserted into the transmit stream by
the DS2154. Each of the 30 voice channels has four
signaling bits (A/B/C/D) associated with it. The numbers in parenthesis () are the voice channel associated
with a particular signaling bit. The voice channel numbers have been assigned as described in the ITU documents. Please note that this is different than the channel
numbering scheme (1 to 32) that is used in the rest of the
data sheet. For example, voice channel 1 is associated
with timeslot 1 (Channel 2) and voice Channel 30 is
associated with timeslot 31 (Channel 32). There is a set
of 16 registers for the receive side (RS1 to RS16) and 16
registers on the transmit side (TS1 to TS16). The
signaling registers are detailed below.
DS2154
031197 33/69
Page 34

DS2154
RS1 TO RS16: RECEIVE SIGNALING REGISTERS (Address=30 to 3F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
0
A(1) B(1) C(1) D(1) A(16) B(16) C(16) D(16)
A(2) B(2) C(2) D(2) A(17) B(17) C(17) D(17)
A(3) B(3) C(3) D(3) A(18) B(18) C(18) D(18)
A(4) B(4) C(4) D(4) A(19) B(19) C(19) D(19)
A(5) B(5) C(5) D(5) A(20) B(20) C(20) D(20)
A(6) B(6) C(6) D(6) A(21) B(21) C(21) D(21)
A(7) B(7) C(7) D(7) A(22) B(22) C(22) D(22)
A(8) B(8) C(8) D(8) A(23) B(23) C(23) D(23)
A(9) B(9) C(9) D(9) A(24) B(24) C(24) D(24)
A(10) B(10) C(10) D(10) A(25) B(25) C(25) D(25)
A(11) B(11) C(11) D(11) A(26) B(26) C(26) D(26)
A(12) B(12) C(12) D(12) A(27) B(27) C(27) D(27)
A(13) B(13) C(13) D(13) A(28) B(28) C(28) D(28)
A(14) B(14) C(14) D(14) A(29) B(29) C(29) D(29)
A(15) B(15) C(15) D(15) A(30) B(30) C(30) D(30)
0 0 0 X Y X X
RS1 (30)
RS2 (31)
RS3 (32)
RS4 (33)
RS5 (34)
RS6 (35)
RS7 (36)
RS8 (37)
RS9 (38)
RS10 (39)
RS11 (3A)
RS12 (3B)
RS13 (3C)
RS14 (3D)
RS15 (3E)
RS16 (3F)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
X RS1.0/1/3 Spare Bits.
Y RS1.2 Remote Alarm Bit (integrated and reported in SR1.6).
A(1) RS2.7 Signaling Bit A for Channel 1.
D(30) RS16.0 Signaling Bit D for Channel 30.
Each Receive Signaling Register (RS1 to RS16) reports
the incoming signaling from two timeslots. The bits in
the Receive Signaling Registers are updated on multiframe boundaries so the user can utilize the Receive
Multiframe Interrupt in the Receive Status Register 2
(SR2.7) to know when to retrieve the signaling bits. The
user has a full 2 ms to retrieve the signaling bits before
the data is lost. The RS registers are updated under all
conditions. Their validity should be qualified by checking for synchronization at the CAS level. In CCS signaling mode, RS1 to RS16 can also be used to extract
signaling information. Via the SR2.7 bit, the user will be
informed when the signaling registers have been loaded
031197 34/69
with data. The user has 2 ms to retrieve the data before
it is lost. The signaling data reported in RS1 to RS16 is
also available at the RSIG and RSER pins.
A change in the signaling bits from one multiframe to the
next will cause the RSA1 (SR1.7) and RSA0 (SR1.5)
status bits to be set at the same time. The user can
enable the INT
pin to toggle low upon detection of a
change in signaling by setting either the IMR1.7 or
IMR1.5 bit. Once a signaling change has been
detected, the user has at least 1.75 ms to read the data
out of the RS1 to RS16 registers before the data will be
lost.
Page 35

TS1 TO TS16: TRANSMIT SIGNALING REGISTERS (Address=40 to 4F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
0
A(1) B(1) C(1) D(1) A(16) B(16) C(16) D(16)
A(2) B(2) C(2) D(2) A(17) B(17) C(17) D(17)
A(3) B(3) C(3) D(3) A(18) B(18) C(18) D(18)
A(4) B(4) C(4) D(4) A(19) B(19) C(19) D(19)
A(5) B(5) C(5) D(5) A(20) B(20) C(20) D(20)
A(6) B(6) C(6) D(6) A(21) B(21) C(21) D(21)
A(7) B(7) C(7) D(7) A(22) B(22) C(22) D(22)
A(8) B(8) C(8) D(8) A(23) B(23) C(23) D(23)
A(9) B(9) C(9) D(9) A(24) B(24) C(24) D(24)
A(10) B(10) C(10) D(10) A(25) B(25) C(25) D(25)
A(11) B(11) C(11) D(11) A(26) B(26) C(26) D(26)
A(12) B(12) C(12) D(12) A(27) B(27) C(27) D(27)
A(13) B(13) C(13) D(13) A(28) B(28) C(28) D(28)
A(14) B(14) C(14) D(14) A(29) B(29) C(29) D(29)
A(15) B(15) C(15) D(15) A(30) B(30) C(30) D(30)
0 0 0 X Y X X
DS2154
TS1 (40)
TS2 (41)
TS3 (42)
TS4 (43)
TS5 (44)
TS6 (45)
TS7 (46)
TS8 (47)
TS9 (48)
TS10 (49)
TS11 (4A)
TS12 (4B)
TS13 (4C)
TS14 (4D)
TS15 (4E)
TS16 (4F)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
X TS1.0/1/3 Spare Bits.
Y TS1.2 Remote Alarm Bit.
A(1) TS2.7 Signaling Bit A for Channel 1.
D(30) TS16.0 Signaling Bit D for Channel 30.
Each Transmit Signaling Register (TS1 to TS16) contains the CAS bits for two timeslots that will be inserted
into the outgoing stream if enabled to do so via TCR1.5.
On multiframe boundaries, the DS2154 will load the values present in the Transmit Signaling Register into an
outgoing signaling shift register that is internal to the
device. The user can utilize the Transmit Multiframe bit
in Status Register 2 (SR2.5) to know when to update the
signaling bits. The bit will be set every 2 ms and the user
has 2 ms to update the TSR’s before the old data will be
retransmitted. ITU specifications recommend that the
ABCD signaling not be set to all zeros because they will
emulate a CAS multiframe alignment word.
The TS1 register is special because it contains the CAS
multiframe alignment word in its upper nibble. The
upper nibble must always be set to 0000 or else the terminal at the far end will lose multiframe synchronization.
If the user wishes to transmit a multiframe alarm to the
far end, then the TS1.2 bit should be set to a one. If no
alarm is to be transmitted, then the TS1.2 bit should be
cleared. The three remaining bits in TS1 are the spare
bits. If they are not used, they should be set to one. In
CCS signaling mode, TS1 to TS16 can also be used to
insert signaling information. Via the SR2.5 bit, the user
will be informed when the signaling registers need to be
loaded with data. The user has 2 ms to load the data
before the old data will be retransmitted.
Via the CCR3.6 bit, the user has the option to use the
Transmit Channel Blocking Registers (TCBRs) to determine on a channel by channel basis, which signaling
bits are to be inserted via the TSRs (the corresponding
bit in the TCBRs=1) and which are to be sourced from
the TSER or TSIG pin (the corresponding bit in the
031197 35/69
Page 36

DS2154
TCBRs=0). See the Transmit Data Flow diagram in
Section 13 for more details.
7.2 HARDWARE BASED SIGNALING
7.2.1 Receive Side
In the receive side of the hardware based signaling,
there are two operating modes for the signaling buffer;
signaling extraction and signaling re–insertion. Signaling extraction involves pulling the the signaling bits from
the receive data stream and buffering them over a 2 multiframe buffer and outputing them in a serial PCM fashion on a channel–by–channel basis at the RSIG output
pin. This mode is always enabled. In this mode, the
receive elastic store may be enabled or disabled. If the
receive elastic store is enabled, then the backplane
clock (RSYSCLK) must be 2.048 MHz. The ABCD
signaling bits are output on RSIG in the lower nibble of
each channel. See the timing diagrams in Section 13 for
an example. The RSIG data is updated once a multiframe (2 ms) unless a freeze is in effect.
The other hardware based signaling operating mode
called signaling re–insertion can be invoked by setting
the RSRE control bit high (CCR3.3=1). In this mode, the
user will provide a multiframe sync at the RSYNC pin
and the signaling data will be re–aligned in the PCM
data stream provided at the RSER output pin according
to this applied multiframe boundary. In this mode, the
elastic store must be enabled and the backplane clock
(RSYSCLK) must be 2.048 MHz.
The signaling data in the two multiframe buffer will be
frozen in a known good state upon either a loss of synchronization (OOF event), carrier loss, or frame slip. T o
allow this freeze action to occur, the RFE control bit
(CCR2.0) should be set high. The user can force a
freeze by setting the RFF control bit (CCR2.1) high.
Setting the RFF bit high causes the same freezing
action as if a loss of synchronization, carrier loss, or slip
has occurred. The RSIGF output pin provides a hard-
ware indication that a freeze is in effect. The RSIGF pin
will go high immediately upon detection of any of the
events that can cause a freeze to occur. The RSIGF pin
will return low 3 ms to 5 ms after the event subsides. The
RSIGF pin action cannot be disabled.
The 2 multiframe buffer provides an approximate 1 multiframe delay in the signaling bits provided at the RSIG
pin (and at the RSER pin if RSRE=1 via CCR3.3). When
freezing is enabled (RFE=1), the signaling data will be
held in the last known good state until the corrupting
error condition subsides. When the error condition subsides, the signaling data will be held in the old state for
an additional 3 ms to 5 ms before being allowed to be
updated with new signaling data.
7.2.2 Transmit Side
Via the TSRE control bit (CCR3.2), the DS2154 can be
set up to take the signaling data presented at the TSIG
pin and re–insert the signaling data into the PCM data
stream that is being input at the TSER pin. The signaling
re–insertion capabilities of the DS2154 are available
whether the transmit side elastic store is enabled or disabled. If the transmit side elastic store is enabled, the
backplane clock (TSYSCLK) must be 2.048 MHz.
When signaling re–insertion is enabled on the DS2154
(TSRE=1), then the user must enable the Transmit
Channel Blocking Register Function Select (TCBFS)
control bit (CCR3.6=1). This is needed so that the CAS
multiframe alignment word, multiframe remote alarm,
and spare bits can be added to timeslot 16 in frame 0 of
the multiframe. The TS1 register should be programmed with the proper information. If CCR3.6=1,
then a zero in the TCBRs implies that signaling data is to
be sourced from TSER (or TSIG if CCR3.2=1) and a one
implies that signaling data for that channel is to be
sourced from the Transmit Signaling (TS) registers.
See definition below.
031197 36/69
Page 37

DS2154
TCBR1/TCBR2/TCBR3/TCBR4: DEFINITION WHEN CCR3.6=1
(MSB) (LSB)
CH20
CH24 CH8 CH23 CH7 CH22 CH6 CH21 CH5
CH28 CH12 CH27 CH11 CH26 CH10 CH25 CH9
CH32 CH16 CH31 CH15 CH30 CH14 CH29 CH13
*=CH1 and CH17 should be set to one to allow the internal TS1 register to create the CAS Multiframe Alignment Word
and Spare/Remote Alarm bits.
CH4 CH19 CH3 CH18 CH2 CH17* CH1*
TCBR1(22)
TCBR2(23)
TCBR3(24)
TCBR4(25)
The user can also take advantage of this functionality to
intermix signaling data from the TSIG pin and from the
internal Transmit Signaling Registers (TS1 to TS16). As
an example, assume that the user wishes to source all
the signaling data except for voice channels 5 and 10
from the TSIG pin. In this application, the following bits
and registers would be programmed as follows:
CONTROL BITS REGISTER VALUES
TSRE=1 (CCR3.2) TS1=0Bh (MF alignment word, remote alarm etc.)
TCBFS=1 (CCR3.6) TCBR1=03h (source timeslot 16, frame 1 data)
T16S=1 (TCR1.5) TCBR2=01h (source voice Channel 5 signaling data from TS6)
8.0 PER–CHANNEL CODE GENERATION
The DS2154 can replace data on a channel–by–channel basis in both the transmit and receive directions.
The transmit direction is from the backplane to the E1
line and is covered in Section 8.1. The receive direction
is from the E1 line to the backplane and is covered in
Section 8.2.
8.1 TRANSMIT SIDE CODE GENERATION
In the transmit direction there are two methods by which
channel data from the backplane can be overwritten
with data generated by the DS2154. The first method
which is covered in Section 8.1.1 was a feature contained in the original DS2153 while the second method
which is covered in Section 8.1.2 is a new feature of the
DS2154.
TCBR3=04h (source voice Channel 10 signaling data from TS11)
TCBR4=00h
nels should be overwritten with the code placed in the
Transmit Idle Definition Register (TIDR). This method
allows the same 8–bit code to be placed into any of the
32 E1 channels. If this method is used, then the CCR3.5
control bit must be set to zero.
The Transmit Idle Registers (TIRs) have an alternate
function that allow them to define a Per–Channel LoopBack (PCLB). If the CCR3.5 control bit is set to one,
then the TIRs will determine which channels (if any)
from the backplane should be replaced with the data
from the receive side or in other words, off of the E1 line.
See Figure 1–1. If this mode is enabled, then transmit
and receive clocks and frame syncs must be synchronized. One method to accomplish this would be to tie
RCLK to TCLK and RFSYNC to TSYNC. There are no
restrictions on which channels can be loopback or on
how many channels can be looped back.
8.1.1 Simple Idle Code Insertion and
Per–Channel Loopback
The first method involves using the Transmit Idle Registers (TIR1/2/3/4) to determine which of the 32 E1 chan-
031197 37/69
Page 38
DS2154
TIR1/TIR2/TIR3/TIR4: TRANSMIT IDLE REGISTERS (Address=26 to 29 Hex)
[Also used for Per–Channel Loopback]
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
CH32 CH31 CH30 CH29 CH28 CH27 CH26 CH25
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH32 TIR4.7 Transmit Idle Registers.
CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
0=do not insert the Idle Code in the TIDR into this channel
CH1 TIR1.0 1=insert the Idle Code in the TIDR into this channel
TIR1 (26)
TIR2 (27)
TIR3 (28)
TIR4 (29)
NOTE:
If CCR3.5=1, then a zero in the TIRs implies that channel data is to be sourced from TSER and a one implies that
channel data is to be sourced from the output of the receive side framer (i.e., Per–Channel Loopback; see Figure 1–1).
TIDR: TRANSMIT IDLE DEFINITION REGISTER (Address=2A Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
TIDR7
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
TIDR7 TIDR.7 MSB of the Idle Code (this bit is transmitted first)
TIDR0 TIDR.0 LSB of the Idle Code (this bit is transmitted last)
TIDR6 TIDR5 TIDR4 TIDR3 TIDR2 TIDR1 TIDR0
8.1.2 Per–Channel Code Insertion
The second method involves using the Transmit Channel Control Registers (TCC1/2/3/4) to determine which
of the 32 E1 channels should be overwritten with the
code placed in the Transmit Channel Registers (TC1 to
TC32). This method is more flexible than the first in that
it allows a different 8–bit code to be placed into each of
the 32 E1 channels.
TC1 TO TC32: TRANSMIT CHANNEL REGISTERS (Address=60 to 7F Hex)
(for brevity , only channel one is shown; see Table 1–3 for other register address)
(MSB) (LSB)
C7
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
C7 TC1.7 MSB of the Code (this bit is transmitted first)
C0 TC1.0 LSB of the Code (this bit is transmitted last)
031197 38/69
C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C0
TC1 (60)
Page 39
DS2154
TCC1/TCC2/TCC3/TCC4: TRANSMIT CHANNEL CONTROL REGISTER (Address=A0 to A3 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
CH32 CH31 CH30 CH29 CH28 CH27 CH26 CH25
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH32 TCC4.7 Transmit Channel 32 Code Insertion Control Bit
8.2 RECEIVE SIDE CODE GENERATION
On the receive side, the Receive Channel Control Registers (RCC1/2/3/4) are used to determine which of the
CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
CH1 TCC1.0 Transmit Channel 1 Code Insertion Control Bit
0=do not insert data from the TC1 register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TC1 register into the transmit data stream
0=do not insert data from the TC32 register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TC32 register into the transmit data stream
32 E1 channels off of the E1 line and going to the backplane should be overwritten with the code placed in the
Receive Channel Registers (RC1 to RC32).
TCC1 (A0)
TCC2 (A1)
TCC3 (A2)
TCC4 (A3)
RC1 TO RC32: RECEIVE CHANNEL REGISTERS (Address=80 to 9F Hex)
(for brevity , only channel one is shown; see Table 1–3 for other register address)
(MSB) (LSB)
C7
C6 C5 C4 C3 C2 C0
RC1 (80)
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
C7 RC1.7 MSB of the Code (this bit is sent first to the backplane)
C0 RC1.0 LSB of the Code (this bit is sent last to the backplane)
RCC1/RCC2/RCC3/RCC4: RECEIVE CHANNEL CONTROL REGISTER (Address=A4 to A7 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
CH32 CH31 CH30 CH29 CH28 CH27 CH26 CH25
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH1 RCC1.0 Receive Channel 1 Code Insertion Control Bit
0=do not insert data from the RC1 register into the receive data stream
1=insert data from the RC1 register into the receive data stream
CH32 RCC4.7 Receive Channel 32 Code Insertion Control Bit
0=do not insert data from the RC32 register into the receive data stream
1=insert data from the RC32 register into the receive data stream
RCC1 (A4)
RCC2 (A5)
RCC3 (A6)
RCC4 (A7)
031197 39/69
Page 40

DS2154
9.0 CLOCK BLOCKING REGISTERS
The Receive Channel blocking Registers (RCBR1 /
RCBR2 / RCBR3 / RCBR4) and the Transmit Channel
Blocking Registers (TCBR1 / TCBR2 / TCBR3 / TCBR4)
control RCHBLK and TCHBLK pins respectively. (The
RCHBLK and TCHBLK pins are user programmable
outputs that can be forced either high or low during individual channels). These outputs can be used to block
clocks to a USART or LAPD controller in ISDN–PRI
applications. When the appropriate bits are set to a one,
the RCHBLK and TCHBLK pin will be held high during
the entire corresponding channel time. See the timing in
Section 13 for an example. The TCBRs have alternate
mode of use. Via the CCR3.6 bit, the user has the option
to use the TCBRs to determine on a channel by channel
basis, which signaling bits are to be inserted via the
TSRs (the corresponding bit in the TCBRs=1) and
which are to be sourced from the TSER or TSIG pins
(the corresponding bit in the TCBR=0). See Section 7
for more details about this mode of operation.
RCBR1/RCBR2/RCBR3/RCBR4: RECEIVE CHANNEL BLOCKING REGISTERS
(Address=2B to 2E Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
CH32 CH31 CH30 CH29 CH28 CH27 CH26 CH25
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH32 RCBR4.7 Receive Channel Blocking Registers.
CH1 RCBR1.0 1=force the RCHBLK pin high during this channel time
0=force the RCHBLK pin to remain low during this channel time
RCBR1 (2B)
RCBR2 (2C)
RCBR3 (2D)
RCBR4 (2E)
TCBR1/TCBR2/TCBR3/TCBR4: TRANSMIT CHANNEL BLOCKING REGISTERS
(Address=22 to 25 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
CH8 CH7 CH6 CH5 CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
CH16 CH15 CH14 CH13 CH12 CH11 CH10 CH9
CH24 CH23 CH22 CH21 CH20 CH19 CH18 CH17
CH32 CH31 CH30 CH29 CH28 CH27 CH26 CH25
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
CH32 TCBR4.7 Transmit Channel Blocking Registers.
0=force the TCHBLK pin to remain low during this channel time
CH1 TCBR1.0 1=force the TCHBLK pin high during this channel time
TCBR1 (22)
TCBR2 (23)
TCBR3 (24)
TCBR4 (25)
NOTE:
If CCR3.6=1, then a zero in the TCBRs implies that signaling data is to be sourced from TSER (or TSIG if CCR3.2=1)
and a one implies that signaling data for that channel is to be sourced from the Transmit Signaling (TS) registers. See
definition below.
031197 40/69
Page 41

DS2154
TCBR1/TCBR2/TCBR3/TCBR4: DEFINITION WHEN CCR3.6=1
(MSB) (LSB)
CH20
CH24 CH8 CH23 CH7 CH22 CH6 CH21 CH5
CH28 CH12 CH27 CH11 CH26 CH10 CH25 CH9
CH32 CH16 CH31 CH15 CH30 CH14 CH29 CH13
*=CH1 and CH17 should be set to one to allow the internal TS1 register to create the CAS Multiframe Alignment Word
and Spare/Remote Alarm bits.
CH4 CH19 CH3 CH18 CH2 CH17* CH1*
TCBR1(22)
TCBR2(23)
TCBR3(24)
TCBR4(25)
10.0 ELASTIC STORES OPERATION
The DS2154 contains dual two–frame (512 bits) elastic
stores, one for the receive direction, and one for the
transmit direction. These elastic stores have two main
purposes. First, they can be used to rate convert the E1
data stream to 1.544 Mbps (or a multiple of 1.544 Mbps)
which is the T1 rate. Secondly, they can be used to
absorb the differences in frequency and phase between
the E1 data stream and an asynchronous (i.e., not frequency locked) backplane clock which can be
1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz. The backplane clock can
burst at rates up to 8.192 MHz. Both elastic stores contain full controlled slip capability which is necessary for
this second purpose. The elastic stores can be forced to
a known depth via the Elastic Store Reset bit (CCR3.4).
T oggling the CCR3.4 bit forces the read and write pointers into opposite frames. Both elastic stores within the
DS2154 are fully independent and no restrictions apply
to the sourcing of the various clocks that are applied to
them. The transmit side elastic store can be enabled
whether the receive elastic store is enabled or disabled
and vice versa. Also, each elastic store can interface to
either a 1.544 MHz or 2.048 MHz backplane without
regard to the backplane rate the other elastic store is interfacing.
10.1 RECEIVE SIDE
If the receive side elastic store is enabled (RCR2.1=1),
then the user must provide either a 1.544 MHz (RCR2.2
=0) or 2.048 MHz (RCR2.2=1) clock at the RSYSCLK
pin. The the user has the option of either providing a
frame/multiframe sync at the RSYNC pin (RCR1.5=1)
or having the RSYNC pin provide a pulse on frame/multiframe boundaries (RCR1.5=0). If the user wishes to
obtain pulses at the frame boundary , then RCR1.6 must
be set to zero and if the user wishes to have pulses
occur at the multiframe boundary, then RCR1.6 must be
set to one. The DS2154 will always indicate frame
boundaries via the RFSYNC output whether the elastic
store is enabled or not. If the elastic store is enabled,
then either CAS (RCR1.7=0) or CRC4 (RCR1.7=1) multiframe boundaries will be indicated via the RMSYNC
output. If the user selects to apply a 1.544 MHz clock to
the RSYSCLK pin, then every fourth channel of the
received E1 data will be deleted and a F–bit position
(which will be forced to one) will be inserted. Hence
Channels 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25, and 29 (timeslots 0, 4, 8,
12, 16, 20, 24, and 28) will be deleted from the received
E1 data stream. Also, in 1.544 MHz applications, the
RCHBLK output will not be active in Channels 25
through 32 (or in other words, RCBR4 is not active).
See Section 13 for timing details. If the 512–bit elastic
buffer either fills or empties, a controlled slip will occur . If
the buffer empties, then a full frame of data (256–bits)
will be repeated at RSER and the SR1.4 and RIR.3 bits
will be set to a one. If the buffer fills, then a full frame of
data will be deleted and the SR1.4 and RIR.4 bits will be
set to a one.
10.2 TRANSMIT SIDE
The operation of the transmit elastic store is very similar
to the receive side. The transmit side elastic store is
enabled via CCR3.7. A 1.544 MHz (CCR3.1=0) or
2.048 MHz (CCR3.1=1) clock can be applied to the
TSYSCLK input. The TSYSCLK can be a bursty clock
with rates up to 8.192 MHz. If the user selects to apply a
1.544 MHz clock to the TSYSCLK pin, then the data
sampled at TSER will be ignored every fourth channel.
Hence Channels 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25, and 29 (timeslots
0, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, and 28) will be ignored. The user
must supply a 8 KHz frame sync pulse to the TSSYNC
input. See Section 13 for timing details. Controlled slips
in the transmit elastic store are reported in the SR2.0 bit
and the direction of the slip is reported in the RIR.6 and
RIR.7 bits.
031197 41/69
Page 42

DS2154
11.0 ADDITIONAL (Sa) AND
INTERNATIONAL (Si) BIT OPERATION
The DS2154 provides for access to both the Sa and the
Si bits via three different methods. The first is via a hardware scheme using the RLINK/RLCLK and TLINK/
TLCLK pins. The first method is discussed in
Section 11.1. The second involves using the internal
RAF/RNAF and TAF/TNAF registers and is discussed
in Section 11.2 The third method which is covered in
Section 11.3 involves an expanded version of the
second method and is one of the features added to the
DS2154 from the original DS2153 definition.
11.1 HARDWARE SCHEME
On the receive side, all of the received data is reported
at the RLINK pin. Via RCR2, the user can control the
RLCLK pin to pulse during any combination of Sa bits.
This allows the user to create a clock that can be used to
capture the needed Sa bits. If RSYNC is programmed
to output a frame boundary, it will identify the Si bits. See
Section 13 for detailed timing.
On the transmit side, the individual Sa bits can be either
sourced from the internal TNAF register (see
Section 11.2 for details) or from the external TLINK pin.
Via TCR2, the DS2154 can be programmed to source
any combination of the additional bits from the TLINK
pin. If the user wishes to pass the Sa bits through the
DS2154 without them being altered, then the device
should be set up to source all five Sa bits via the TLINK
pin and the TLINK pin should be tied to the TSER pin. Si
bits can be inserted through the TSER pin via the clearing of the TCR1.3 bit. Please see the timing diagrams
and the transmit data flow diagram in Section 13 for
examples.
11.2 INTERNAL REGISTER SCHEME
BASED ON DOUBLE–FRAME
On the receive side, the RAF and RNAF registers will
always report the data as it received in the Additional
and International bit locations. The RAF and RNAF registers are updated with the setting of the Receive Align
Frame bit in Status Register 2 (SR2.6). The host can
use the SR2.6 bit to know when to read the RAF and
RNAF registers. It has 250 us to retrieve the data before
it is lost.
On the transmit side, data is sampled from the TAF and
TNAF registers with the setting of the Transmit Align
Frame bit in Status Register 2 (SR2.3). The host can
use the SR2.3 bit to know when to update the T AF and
TNAF registers. It has 250 us to update the data or else
the old data will be retransmitted. Data in the Si bit position will be overwritten if either the DS2154 is programmed: (1) to source the Si bits from the TSER pin,
(2) in the CRC4 mode, or (3) have automatic E–bit insertion enabled. Data in the Sa bit position will be overwritten if any of the TCR2.3 to TCR2.7 bits are set to one
(please see Section 11.1 for details). Please see the
register descriptions for TCR1 and TCR2 and the Transmit Data Flow diagram in Section 13 for more details.
RAF: RECEIVE ALIGN FRAME REGISTER (Address=2F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Si
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Si RAF.7 International Bit.
0 RAF.6 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
0 RAF.5 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
1 RAF.4 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
1 RAF.3 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
0 RAF.2 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
1 RAF.1 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
1 RAF.0 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
031197 42/69
0 0 1 1 0 1 1
Page 43

RNAF: RECEIVE NON–ALIGN FRAME REGISTER (Address=1F Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Si 1 A Sa4 Sa5 Sa6 Sa7 Sa8
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Si RNAF.7 International Bit.
1 RNAF.6 Frame Non–Alignment Signal Bit.
A RNAF.5 Remote Alarm.
Sa4 RNAF .4 Additional Bit 4.
Sa5 RNAF .3 Additional Bit 5.
Sa6 RNAF .2 Additional Bit 6.
Sa7 RNAF .1 Additional Bit 7.
Sa8 RNAF .0 Additional Bit 8.
TAF: TRANSMIT ALIGN FRAME REGISTER (Address=20 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Si 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
[Must be programmed with the seven bit FAS word; the DS2154 does not automatically set these bits]
DS2154
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Si TAF.7 International Bit.
0 TAF.6 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
0 TAF.5 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
1 TAF.4 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
1 TAF.3 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
0 TAF.2 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
1 TAF.1 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
1 TAF.0 Frame Alignment Signal Bit.
TNAF: TRANSMIT NON–ALIGN FRAME REGISTER (Address=21 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
Si 1 A Sa4 Sa5 Sa6 Sa7 Sa8
[Bit 2 must be programmed to one; the DS2154 does not automatically set this bit]
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
Si TNAF.7 International Bit.
1 TNAF.6 Frame Non–Alignment Signal Bit.
031197 43/69
Page 44

DS2154
A TNAF.5 Remote Alarm (used to transmit the alarm).
Sa4 TNAF.4 Additional Bit 4.
Sa5 TNAF.3 Additional Bit 5.
Sa6 TNAF.2 Additional Bit 6.
Sa7 TNAF.1 Additional Bit 7.
Sa8 TNAF.0 Additional Bit 8.
11.3 INTERNAL REGISTER SCHEME
BASED ON CRC4 MULTIFRAME
On the receive side, there is a set of eight registers
(RSiAF , RSiNAF , RRA, RSa4 to RSa8) that report the Si
and Sa bits as they are received. These registers are
updated with the setting of the Receive CRC4 Multiframe bit in Status Register 2 (SR2.1). The host can use
the SR2.1 bit to know when to read these registers. The
user has 2 ms to retrieve the data before it is lost. The
MSB of each register is the first received. Please see
the register descriptions below and the Transmit Data
Flow diagram in Section 13 for more details.
On the transmit side, there is also a set of eight registers
(TSiAF , TSiNAF , TRA, TSa4 to TSa8) that via the Transmit Sa Bit Control Register (TSaCR), can be programmed to insert both Si and Sa data. Data is sampled
from these registers with the setting of the Transmit Multiframe bit in Status Register 2 (SR2.5). The host can
use the SR2.5 bit to know when to update these registers. It has 2 ms to update the data or else the old data
will be retransmitted. The MSB of each register is the
first bit transmitted. Please see the register descriptions
below and the Transmit Data Flow diagram in Section
13 for more details.
031197 44/69
Page 45

DS2154
REGISTER
NAME
ADDRESS
(HEX)
FUNCTION
RSiAF 58 The eight Si bits in the align frame
RSiNAF 59 The eight Si bits in the non–align frame
RRA 5A The eight reportings of the receive remote alarm (RA)
RSa4 5B The eight Sa4 reported in each CRC4 multiframe
RSa5 5C The eight Sa5 reported in each CRC4 multiframe
RSa6 5D The eight Sa6 reported in each CRC4 multiframe
RSa7 5E The eight Sa7 reported in each CRC4 multiframe
RSa8 5F The eight Sa8 reported in each CRC4 multiframe
TSiAF 50 The eight Si bits to be inserted into the align fram
TSiNAF 51 The eight Si bits to be inserted into the non–align frame
TRA 52 The eight settings of remote alarm (RA)
TSa4 53 The eight Sa4 settings in each CRC4 multiframe
TSa5 54 The eight Sa5 settings in each CRC4 multiframe
TSa6 55 The eight Sa6 settings in each CRC4 multiframe
TSa7 56 The eight Sa7 settings in each CRC4 multiframe
TSa8 57 The eight Sa8 settings in each CRC4 multiframe
TSaCR: TRANSMIT Sa BIT CONTROL REGISTER (Address=1C Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
SiAF
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
SiAF TSaCR.7 International Bit in Align Frame Insertion Control Bit.
SiNAF TSaCR.6 International Bit in Non–Align Frame Insertion Control Bit.
RA TSaCR.5 Remote Alarm Insertion Control Bit.
Sa4 TSaCR.4 Additional Bit 4 Insertion Control Bit.
Sa5 TSaCR.3 Additional Bit 5 Insertion Control Bit.
SiNAF RA Sa4 Sa5 Sa6 Sa7 Sa8
0=do not insert data from the TSiAF register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TSiAF register into the transmit data stream
0=do not insert data from the TSiNAF register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TSiNAF register into the transmit data stream
0=do not insert data from the TRA register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TRA register into the transmit data stream
0=do not insert data from the TSa4 register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TSa4 register into the transmit data stream
0=do not insert data from the TSa5 register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TSa5 register into the transmit data stream
031197 45/69
Page 46

DS2154
Sa6 TSaCR.2 Additional Bit 6 Insertion Control Bit.
Sa7 TSaCR.1 Additional Bit 7 Insertion Control Bit.
Sa8 TSaCR.0 Additional Bit 8 Insertion Control Bit.
0=do not insert data from the TSa6 register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TSa6 register into the transmit data stream
0=do not insert data from the TSa7 register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TSa7 register into the transmit data stream
0=do not insert data from the TSa8 register into the transmit data stream
1=insert data from the TSa8 register into the transmit data stream
12.0 LINE INTERFACE FUNCTIONS
The line interface function in the DS2154 contains three
sections; (1) the receiver which handles clock and data
recovery, (2) the transmitter which waveshapes and
drives the E1 line, and (3) the jitter attenuator. Each of
the these three sections is controlled by the Line Interface Control Register (LICR) which is described below.
LICR: LINE INTERFACE CONTROL REGISTER (Address=18 Hex)
(MSB) (LSB)
L2 L1 L0 EGL JAS JABDS DJA TPD
SYMBOL POSITION NAME AND DESCRIPTION
L2 LICR.7 Line Build Out Bit 2. Transmit waveshape setting; see Table 12–2.
L1 LICR.6 Line Build Out Bit 1. Transmit waveshape setting; see Table 12–2.
L0 LICR.5 Line Build Out Bit 0. Transmit waveshape setting; see Table 12–2.
EGL LICR.4 Receive Equalizer Gain Limit.
JAS LICR.3 Jitter Attenuator Select.
JABDS LICR.2 Jitter Attenuator Buffer Depth Select
DJA LICR.1 Disable Jitter Attenuator.
TPD LICR.0 Transmit Power Down.
12.1 RECEIVE CLOCK AND DATA
RECOVERY
The DS2154 contains a digital clock recovery system.
See the DS2154 Block Diagram in Section 1 and
Figure 12–1 for more details. The DS2154 couples to
the receive E1 shielded twisted pair or COAX via a 1:1
transformer. See Table 12–3 for transformer details.
The 2.048 MHz clock attached at the MCLK pin is internally multiplied by 16 via an internal PLL and fed to the
0=–12 dB
1=–43 dB
0=place the jitter attenuator on the receive side
1=place the jitter attenuator on the transmit side
0=128–bits
1=32–bits (use for delay sensitive applications)
0=jitter attenuator enabled
1=jitter attenuator disabled
0=normal transmitter operation
1=powers down the transmitter and 3–states the TTIP and TRING pins
clock recovery system. The clock recovery system
uses the clock from the PLL circuit to form a 16 times
oversampler which is used to recover the clock and
data. This oversampling technique offers outstanding
jitter tolerance (see Figure 12–2).
Normally, the clock that is output at the RCLKO pin is the
recovered clock from the E1 AMI/HDB3 waveform presented at the RTIP and RRING inputs. When no AMI sig-
LICR
031197 46/69
Page 47

DS2154
nal is present at RTIP and RRING, a Receive Carrier
Loss (RCL) condition will occur and the RCLKO will be
sourced from the clock applied at the MCLK pin. If the
jitter attenuator is either placed in the transmit path or is
disabled, the RCLKO output can exhibit slightly shorter
high cycles of the clock. This is due to the highly oversampled digital clock recovery circuitry. If the jitter
attenuator is placed in the receive path (as is the case in
most applications), the jitter attenuator restores the
RCLK to being close to 50% duty cycle. Please see the
Receive AC Timing Characteristics in Section 14 for
more details.
12.2 TRANSMIT WAVESHAPING AND LINE
DRIVING
The DS2154 uses a set of laser–trimmed delay lines
along with a precision Digital–to–Analog Converter
(DAC) to create the waveforms that are transmitted onto
the E1 line. The waveforms created by the DS2154
meet the ITU G.703 specifications. See Figure 12–3.
The user will select which waveform is to be generated
by properly programming the L2/L1/L0 bits in the Line
Interface Control Register (LICR). The DS2154 can set
set up in a number of various configurations depending
on the application. See Table 12–2 and Figure 12–1.
LINE BUILD OUT SELECT IN LICR Table 12–2
LLL
210
000 75 ohm normal (See Note 1) 1:1.15 step–up NM 0 ohms
001 120 ohm normal 1:1.15 step–up NM 0 ohms
010 75 ohm w/ protection resistors 1:1.15 step–up NM 8.2 ohms
011 120 ohm w/ protection resistors 1:1.15 step–up NM 8.2 ohms
100 75 ohm w/ high return loss 1:1.15 step–up 21dB 27 ohms
110 75 ohm w/ high return loss 1:1.36 step–up 21dB 18 ohms
100 120 ohm w/ high return loss 1:1.36 step–up 21dB 27 ohms
APPLICATION TRANSFORMER
RETURN
LOSS
RT (SEE
FIGURE 12–1)
NOTE:
1. This LBO is not recommended for use in the A2 revision of the DS2154.
Due to the nature of the design of the transmitter in the
DS2154, very little jitter (less then 0.005 UIpp broadband from 10 Hz to 100 KHz) is added to the jitter present on TCLK. Also, the waveforms that they create are
independent of the duty cycle of TCLK. The transmitter
in the DS2154 couples to the E1 transmit shielded
twisted pair or COAX via a 1:1.15 or 1:1.36 step up
transformer as shown in Figure 12–1. In order for the
devices to create the proper waveforms, this transformer used must meet the specifications listed in
T able 12–3 The line driver in the DS2154 contains a current limiter that will prevent more than 50 mA (rms) from
being sourced in a 1 ohm load.
TRANSFORMER SPECIFICATIONS Table 12–3
SPECIFICATION RECOMMENDED VALUE
Turns Ratio 1:1 (receive) and 1:1.15 or 1:1.36 (transmit) ± 5%
Primary Inductance 600 uH minimum
Leakage Inductance 1.0 uH maximum
Intertwining Capacitance 40 pF maximum
DC Resistance 1.2 ohms maximum
031197 47/69
Page 48

DS2154
12.3 JITTER ATTENUATOR
The DS2154 contains an onboard jitter attenuator that
can be set to a depth of either 32 or 128 bits via the
JABDS bit in the Line Interface Control Register (LICR).
The 128–bit mode is used in applications where large
excursions of wander are expected. The 32–bit mode is
used in delay sensitive applications. The characteristics of the attenuation are shown in Figure 12–4. The jitter attenuator can be placed in either the receive path or
the transmit path by appropriately setting or clearing the
JAS bit in the LICR. Also, the jitter attenuator can be disabled (in effect, removed) by setting the DJA bit in the
LICR. In order for the jitter attenuator to operate properly, a 2.048 MHz clock (±50 ppm) must be applied at the
MCLK pin or a crystal with similar characteristics must
be applied across the MCLK and XTALD pins. If a crystal is applied across the MCLK and XTALD pins, then
the maximum effective series resistance should be 40
ohms and capacitors should be placed from each leg of
the crystal to ground as shown in Figure 12–1. Onboard
circuitry adjusts either the recovered clock from the
clock/data recovery block or the clock applied at the
TCLKI pin to create a smooth jitter free clock which is
used to clock data out of the jitter attenuator FIFO. It is
acceptable to provide a gapped/bursty clock at the
TCLKI pin if the jitter attenuator is placed on the transmit
side. If the incoming jitter exceeds either
120 UIpp (buffer depth is 128 bits) or 28 UIpp (buffer
depth is 32 bits), then the DS2154 will divide the internal
nominal 32.768 MHz clock by either 15 or 17 instead of
the normal 16 to keep the buffer from overflowing.
When the device divides by either 15 or 17, it also sets
the Jitter Attenuator Limit Trip (JAL T) bit in the Receive
Information Register (RIR.5).
DS2154 EXTERNAL ANALOG CONNECTIONS Figure 12–1
0.47 uF
(non–
polarized)
E1 TRANSMIT
LINE
1.15:1 or 1.36:1
(larger winding toward
the network)
Rt
Rt
TTIP
TRING
DS2154
DVDD
DVSS
RVDD
RVSS
TVDD
TVSS
61
60
0. 01u F
18
19
31
30
0. 1uF
0. 1uF
0. 1uF
+5V
E1 RECEIVE
LINE
1:1
RTIP
RRING
Rr Rr
0.1 uF
XTALD
MCLK
XTALD
MCLK
2. 048MHz
C1/C2
–or–
2.048 MHz
NOTES:
1. All resistor values are ±1%.
2. The Rt resistors are used to increase the transmitter return loss or to protect the device from over–voltage.
3. The Rr resistors are used to terminate the receive E1 line.
4. For 75 ohm termination, Rr=37.5 ohms/for 120 ohm termination Rr=60 ohm.
5. See the separate Application Note for details on how to construct a protected interface.
6. Either a crystal can be applied across the MCLK and XTALD pins or a TTL level clock can be applied to just MCLK.
7. C1 and C2 should be 5 pF lower than two times the nominal loading capacitance of the crystal to adjust for the
input capacitance of the DS2154.
031197 48/69
Page 49

DS2154 JITTER TOLERANCE Figure 12–2
1K
DS2154
1.5
DS2154
TOLERANCE
UNIT INTERVALS (UIpp)
100
10
1
0.1
40
MINIMUM TOLERANCE
LEVEL AS PER
ITU G.823
20
1
10 100 1K 10K 100K
FREQUENCY (Hz)
DS2154 TRANSMIT WAVEFORM TEMPLATE Figure 12–3
1. 2
1. 1
1. 0
0. 9
0. 8
0. 7
0. 6
0. 5
0. 4
0. 3
0. 2
SCALED AMPLITUDE
0. 1
0
(in 75 ohm systems, 1.0 on the scale = 2.37Vpeak
–0. 1
in 120 ohm systems, 1.0 on the scale = 3.00Vpeak)
–0. 2
194 ns
219 ns
2.4K
0.2
18K
269 ns
G.703
Template
0
TIME (ns)
50 100 150 200 250–50–100–150–200–250
031197 49/69
Page 50

DS2154
DS2154 JITTER ATTENUATION Figure 12–4
0 dB
–20 dB
DS2154 JITTER
ATTENUATION
–40 dB
JITTER ATTEN UATION (dB)
–60 dB
1 10 100 1K 10K
CURVE
40
FREQUENCY (Hz)
ITU G.7XX
PROHIBITED AREA
ETS 300 011 AND TBR12
PROHIBITED AREA
100K
031197 50/69
Page 51

13.0 TIMING DIAGRAMS/SYNC FLOWCHART/TRANSMIT DATA FLOW DIAGRAM
RECEIVE SIDE TIMING Figure 13–1
15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15FRAME# 1612345614
RSYNC1/
RFSYNC
2
RSYNC
3
RLCLK
4
RLINK
NOTES:
1. RSYNC in the frame mode (RCR1.6=0).
2. RSYNC in the multiframe mode (RCR1.6=1).
3. RLCLK is programmed to pulse high during the Sa4 bit position.
4. RLINK will always output all five Sa bits as well as the rest of the receive data stream.
5. This diagram assumes the CAS MF begins with the FAS word.
RECEIVE SIDE BOUNDARY TIMING (WITH ELASTIC STORE DISABLED) Figure 13–2
DS2154
RCLK
RSER/
RDATA
RSYNC/
RFSYNC
RSIG
RCHCLK
RCHBLK
RLINK
RLCLK
CHANNEL 32
MSB
CHANNEL 32 CHANNEL 2
1
2
BCD
A
LSB
Si
1
CHANNEL 1
A MSBSa4 Sa5 Sa6 Sa7 Sa8
CHANNEL 1
NOTE 4
NOTES:
1. RCHBLK is programmed to block Channel 2.
2. RLCLK is programmed to pulse high during the Sa4 bits position.
3. Shown is a non–align frame boundary.
4. RSIG normally contains the CAS multiframe alignment nibble (0000) in Channel 1.
CHANNEL 2
MSBSa4 Sa5 Sa6 Sa7 Sa8
031197 51/69
Page 52

DS2154
RECEIVE SIDE 1.544 MHz BOUNDARY TIMING (WITH ELASTIC STORE ENABLED) Figure 13–3
RSYSCLK
1
RSER
RSYNC2/
RMSYNC
RSYNC
RCHCLK
RCHBLK
LSB MSB LSB MSBF
3
4
CHANNEL 24/32 CHANNEL 1/2CHANNEL 23/31
NOTES:
1. Data from the E1 Channels 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25, and 29 is dropped (Channel 2 from the E1 link is mapped
to Channel 1 of the T1 link, etc.) and the F–bit position is added (forced to one).
2. RSYNC is in the output mode (RCR1.5=0).
3. RSYNC is in the input mode (RCR1.5=1).
4. RCHBLK is programmed to block Channel 24.
RECEIVE SIDE 2.048 MHz BOUNDARY TIMING (WITH ELASTIC STORE ENABLED) Figure 13–4
RSYSCLK
CHANNEL 32 CHANNEL 1CHANNEL 31
RSER
RSYNC
RMSYNC
RSYNC
RSIG
RCHCLK
RCHBLK
1
/
2
CHANNEL 31 CHANNEL 1
A BCD
3
LSB MSB LSB MSB
CHANNEL 32
ABCD
NOTE 4
NOTES:
1. RSYNC is in the output mode (RCR1.5=0).
2. RSYNC is in the input mode (RCR1.5=1).
3. RCHBLK is programmed to block Channel 1.
4. RSIG normally contains the CAS multiframe alignment nibble (0000) in Channel 1.
031197 52/69
Page 53

TRANSMIT SIDE TIMING Figure 13–5
DS2154
FRAME#
TSYNC1/
TFSYNC
TSYNC
TLCLK
TLINK
2
3
3
15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
16 1 2 3 4 5 614
NOTES:
1. TSYNC in the frame mode (TCR1.1=0).
2. TSYNC in the multiframe mode (TCR1.1=1).
3. TLINK is programmed to source only the Sa4 bit.
4. This diagram assumes both the CAS MF and the CRC4 begin with the align frame.
TRANSMIT SIDE BOUNDARY TIMING Figure 13–6
TCLK
TSER
TSYNC
TFSYNC
TSYNC
TSIG
1
/
2
CHANNEL 32
B
LSB Si 1 A Sa4 Sa5 Sa6 Sa7 Sa8 MSB MSBLSB
CHANNEL 1
CD ABCD
CHANNEL 2CHANNEL 1
CHANNEL 2
TCHCLK
3
TCHBLK
4
TLCLK
TLINK
4
Don’t Care
Don’t Care
NOTES:
1. TSYNC is in the input mode (TCR1.0=0).
2. TSYNC is in the output mode (TCR1.0=1).
3. TCHBLK is programmed to block Channel 2.
4. TLINK is programmed to source the Sa4 bits.
5. The signaling data at TSIG during Channel 1 is normally overwritten in the transmit formatter with the CAS
multiframe alignment nibble (0000).
6. Shown is a non–align frame boundary.
031197 53/69
Page 54

DS2154
TRANSMIT SIDE 1.544 MHz BOUNDARY TIMING
(WITH ELASTIC STORE ENABLED) Figure 13–7
TSYSCLK
TSER
TSSYNC
TCHCLK
TCHBLK
LSB MSB MSBLSB
1
CHANNEL 24
F–BIT
NOTES:
1. TCHBLK is programmed to block Channel 23.
2. The F–bit position is ignored by the DS2154.
TRANSMIT SIDE 2.048 MHz (WITH ELASTIC STORE ENABLED) Figure 13–8
CHANNEL 1CHANNEL 23
TSYSCLK
TSER
TSSYNC
TSIG
TCHCLK
TCHBLK
CHANNEL 31
A
BCD
1
LSB MSB LSB
NOTE:
1. TCHBLK is programmed to block Channel 31.
CHANNEL 32
CHANNEL 32
ABCD
CHANNEL 1CHANNEL 31
MSB
CHANNEL 1
031197 54/69
Page 55

DS2154
G.802 TIMING Figure 13–9
TIMESLOT# 30 31 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 0 1 2 3 4
RSYNC/
TSYNC
RCHCLK/
TCHCLK
RCHBLK/
1
TCHBLK
DETAIL
RCLK/RSYSCLK
TCLK/TSYSCLK
TIMESLOT 25 TIMESLOT 26
RSER/TSER
RCHCLK/TCHCLK
RCHBLK/TCHCLK
LSB MSB
NOTE:
1. RCHBLK or TCHBLK is programmed to pulse high during timeslots 1 to 15, 17 to 25, and during bit 1 of timeslot 26.
031197 55/69
Page 56

DS2154
DS2154 SYNCHRONIZATION FLOWCHART Figure 13–10
POWER UP
RLOS=1
FAS SEARCH
FASSA=1
RLOS=1
RESYNC IF
RCR1.1=0
INCREMENT CRC4
SYNC COUNTER;
CRC4SA=0
SET FASRC
(RIR.1)
CRC4 RESYNC
CRITERIA MET
(RIR.2)
8 MS
TIME
OUT
FAS RESYNC
CRITERIA MET
CHECK FOR >=915
OUT OF 1000 CRC
CRC WORD ERROS
CRC4 MULTIFRAME
SEARCH (IF ENABLED
VIA CCR 1.0)
CRC4SA=1
CRC4 SYNC CRITERIA
MET; CRC4SA=0;
RESET CRC4 SYNC
COUNTER
CHECK FOR FAS
FRAMING ERROR
(DEPENDS ON
RCR1.2)
IF CRC4 IS ON
(CCR1.0=1)
FAS SYNC
CRITERIA MET
FASSA=0
SYNC DECLARED
RLOS=0
CAS MULTIFRAME
SEARCH (IF ENABLED
VIA CCR1.3)
CASSA=1
CAS SYNC
CRITERIA MET
CASSA=0
031197 56/69
IF CAS IS ON
(CCR1.3=0)
CAS RESYNC
CRITERIA MET;
SET CASRC
(RIR.0)
CHECK FOR CAS
MF WORD ERROR
Page 57

DS2154 TRANSMIT DATA FLOW Figure 13–1 1
TSER
&
TDATA
TC1 TO TC32
TLINK
RSER
(note 1)
DS2154
TAF
TNAF
0
TIMESLOT 0
PASS–THROUGH
(TCR1.6)
TCBR1/2/3/4
CCR3.6
1
1
Si BIT INSERTION
CONTROL
(TCR1.3)
CRC4 MULTIFRAME
ALIGNMENT WORD
GENERATION(CCR1.4)
E–BIT GENERATION
TCR1.5
KEY
= REGISTER
= DEVICE PIN
= SELECTOR
PER–CHANNEL CODE
GENERATION
(TCC1/2/3/4)
0
RECEIVE SIDE
CRC4 ERROR
DETECTOR
0
(TCR2.1)
1
0
Sa BIT INSERTION
CONTROL (TCR2.3
THRU TCR2.7)
AUTO REMOTE
ALARM GENERATION
(CCR2.4)
Sa BIT INSERTION
CONTROL REGISTER
TSa4 to TSa8
1
0
1
(TSaCR)
0
IDLE CODE/CHANNEL
INSERTION CONTROL
VIA TIR1/2/3/4
0
SIGNALING BIT
INSERTION CONTROL
CRC4 ENABLE
DS0 MONITOR
TSiAF
TSiNAF
TRA
TS1 TO TS16
1
0
(CCR.4)
TRANSMIT UNFRAMED
ALL ONES (TCR1.4) OR
AUTO AIS (CCR2.5)
0
TRANSMIT SIGNALLING
1
0
TPOS,
TNEG
CODE WORD
GENERATION
1
TIDR
01
TIR FUNCTION SELECT
(CCR3.5)
AIS
GENERATION
1
ALL ONES
(TCR1.2)
AIS
GENERATION
1
NOTES:
1. TCLK should be tied to RCLK and TSYNC should be tied to RFSYNC for data to be properly sourced from RSER.
2. Auto Remote Alarm if enabled will only overwrite bit 3 of timeslot 0 in the Non Align Frames if the alarm needs
to be sent.
031197 57/69
Page 58

DS2154
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Voltage on Any Pin Relative to Ground –1.0V to +7.0V
Operating Temperature for DS2154L 0°C to 70°C
Operating Temperature for DS2154LN –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature –55°C to +125°C
Soldering Temperature 260°C for 10 seconds
* This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operation sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods of time may affect reliability.
RECOMMENDED DC OPERATING CONDITIONS (0°C to 70°C for DS2154L;
–40°C to +
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Logic 1 V
Logic 0 V
Supply V
IH
IL
DD
2.0 VDD + 0.3 V
–0.3 +0.8 V
4.75 5.25 V 1
85°C for DS2154LN)
CAPACITANCE (tA=25°C)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Input Capacitance C
Output Capacitance C
IN
OUT
5 pF
7 pF
DC CHARACTERISTICS (0°C to 70°C; VDD=5V ± 5% for DS2154L;
–40°C to +
85°C; V
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Supply Current @ 5V I
Input Leakage I
Output Leakage I
Output Current (2.4V) I
Output Current (0.4V) I
DD
LO
OH
OL
IL
–1.0 +1.0 µA 3
–1.0 mA
+4.0 mA
75 mA 2
=5V ± 5% for DS2154LN)
DD
1.0 µA 4
NOTES:
1. Applies to RVDD, TVDD, and DVDD.
2. TCLK=RCLK=TSYSCLK=RSYSCLK=2.048 MHz; outputs open circuited.
3. 0.0V < V
4. Applied to INT
031197 58/69
< VDD.
IN
when 3–stated.
Page 59

AC CHARACTERISTICS – MULTIPLEXED PARALLEL
PORT (MUX=1) (0°C to 70°C; V
–40°C to +
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Cycle Time t
Pulse Width, DS low or RD high PW
Pulse Width, DS high or RD low PW
Input Rise/Fall times tR, t
R/W Hold Time t
R/W Set Up time before DS high t
CS Set Up time before DS, WR or
active
RD
CS Hold time t
Read Data Hold time t
Write Data Hold time t
Muxed Address valid to AS or
ALE fall
Muxed Address Hold time t
Delay time DS, WR or RD to AS
or ALE rise
Pulse Width AS or ALE high PW
Delay time, AS or ALE to DS, WR
or RD
Output Data Delay time from DS
or RD
Data Set Up time t
See Figures 14–1 to 14–3 for details.
CYC
RWH
RWS
t
CS
CH
DHR
DHW
t
ASL
AHL
t
ASD
t
ASED
t
DDR
DSW
EL
EH
F
ASH
200 ns
100 ns
100 ns
10 ns
50 ns
20 ns
0 ns
10 50 ns
0 ns
15 ns
10 ns
20 ns
30 ns
10 ns
20 80 ns
50 ns
85°C; V
=5V ± 5% for DS2154L;
DD
=5V ± 5% for DS2154LN)
DD
20 ns
DS2154
031197 59/69
Page 60

DS2154
AC CHARACTERISTICS – RECEIVE SIDE (0°C to 70°C; VDD=5V ± 5% for DS2154L;
–40°C to +
85°C; V
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
RCLKO Period t
RCLKO Pulse Width t
RCLKO Pulse Width t
RCLKI Period t
RCLKI Pulse Width t
RSYSCLK Period t
RSYSCLK Pulse Width t
RSYNC Set Up to RSYSCLK
Falling
RSYNC Pulse Width t
RPOSI/RNEGI Set Up to RCLKI
Falling
RPOSI/RNEGI Hold From RCLKI
Falling
RSYSCLK/RCLKI Rise and Fall
Times
Delay RCLKO to RPOSO,
RNEGO Valid
Delay RCLK to RSER, RDATA,
RSIG, RLINK Valid
Delay RCLK to RCHCLK,
RSYNC, RCHBLK, RFSYNC,
t
t
CP
CH
t
t
SH
t
t
SU
PW
t
SU
t
HD
tR, t
t
DD
t
t
LP
LH
LL
LH
CL
CL
SP
SP
SL
D1
D2
200
200
150
150
75
75
122
122
50
50
20 tSH–5 ns
50 ns
20 ns
20 ns
F
488 ns
244
244
244
244
488 ns
648
488
RLCLK
Delay RSYSCLK to RSER,
RSIG Valid
Delay RSYSCLK to RCHCLK,
RCHBLK, RMSYNC, RSYNC
t
D3
t
D4
See Figures 14–4 to 14–6 for details.
=5V ± 5% for DS2154LN)
DD
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
25 ns
50 ns
50 ns
50 ns
50 ns
50 ns
1
1
2
2
3
4
NOTES:
1. Jitter attenuator enabled in the receive path.
2. Jitter attenuator disabled or enabled in the transmit path.
3. RSYSCLK=1.544 MHz.
4. RSYSCLK=2.048 MHz.
031197 60/69
Page 61

14.0 A. C. AND D. C. CHARACTERISTICS
INTEL BUS READ AC TIMING (BTS=0/MUX=1) Figure 14–1
t
CYC
PW
ALE
t
ASD
ASH
WR
t
RD
PW
ASD
EL
t
t
CS
ASED
CS
t
ASL
AD0-AD7
t
AHL
INTEL BUS WRITE AC TIMING (BTS=0/MUX=1) Figure 14–2
t
CYC
PW
ALE
t
ASD
ASH
t
DDR
PW
DS2154
EH
t
CH
t
DHR
RD
WR
CS
AD0-AD7
t
ASD
t
ASED
PW
PW
EL
t
CS
t
ASL
t
AHL
EH
t
CH
t
DHW
t
DSW
031197 61/69
Page 62

DS2154
MOTOROLA BUS AC TIMING (BTS=1/MUX=1) Figure 14–3
PW
ASH
AS
DS
t
ASD
PW
EL
R/W
t
AD0-AD7
(READ)
ASL
t
AHL
CS
t
AD0-AD7
(WRITE)
ASL
t
AHL
RECEIVE SIDE AC TIMING Figure 14–4
RCLK
t
D1
RSER/RDAT A/RSIG
t
D2
RCHCLK
RCHBLK
t
D2
RFSYNC/RMSYNC
t
D2
1
RSYNC
t
D2
2
RLCLK
t
D1
RLINK
Sa4 TO Sa8
BIT POSITION
t
ASED
t
RWS
t
CS
CHANNEL 1
t
D2
MSB OF
t
CYC
t
DDR
PW
t
EH
DSW
t
RWH
t
DHR
t
CH
t
DHW
NOTES:
1. RSYNC is in the output mode (RCR1.5=0).
2. RLCLK will only pulse high during Sa bit locations as defined in RCR2; no relationship between RLCLK and
RSYNC or RFSYNC is implied.
031197 62/69
Page 63

DS2154
AC CHARACTERISTICS – TRANSMIT SIDE (0°C to 70°C; VDD=5V ± 5% for DS2154L;
–40°C to +
85°C; V
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
TCLK Period t
TCLK Pulse Width t
TCLKI Period t
TCLKI Pulse Width t
TSYSCLK Period t
TSYSCLK Pulse Width t
TSYNC or TSSYNC Set Up to
TCLK or TSYSCLK falling
TSYNC or TSSYNC Pulse Width t
TSER, TSIG, TDATA, TLINK,
TPOSI, TNEGI Set Up to
CP
CH
t
CL
LH
t
SP
t
SP
SH
t
t
SU
PW
t
SU
LP
LL
SL
75
75
75
75
122
122
50
50
20 tCH–5 or
50 ns
20 ns
488 ns
488 ns
648
448
TCLK, TSYSCLK, TCLKI Falling
TSER, TSIG, TDATA, TLINK,
TPOSI, TNEGI Hold from
t
HD
20 ns
TCLK, TSYSCLK, TCLKI Falling
TCLK, TCLKI, or TSYSCLK Rise
and Fall Times
Delay TCLKO to TPOSO,
TNEGO Valid
Delay TCLK to TESO Valid t
Delay TCLK to TCHBLK,
TCHBLK, TSYNC, TLCLK
Delay TSYSCLK to TCHCLK,
TCHBLK
tR, t
t
DD
D1
t
D2
t
D3
F
See Figures 14–7 to 14–9 for details.
=5V ± 5% for DS2154LN)
DD
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
–5
t
SH
25 ns
50 ns
50 ns
50 ns
75 ns
1
2
NOTES:
1. TSYSCLK=1.544 MHz.
2. TSYSCLK=2.048 MHz.
031197 63/69
Page 64

DS2154
RECEIVE SYSTEM SIDE AC TIMING Figure 14–5
RSYSCLK
RSER/RSIG
RCHCLK
RCHBLK
RMSYNC
1
RSYNC
2
RSYNC
t
t
R
t
F
t
D3
MSB
OF CHANNEL 1
t
D4
t
D4
t
D4
t
D4
t
t
SU
PW
SL
t
SH
t
SP
NOTES:
1. RSYNC is in the output mode (RCR1.5=0).
2. RSYNC is in the input mode (RCR1.5=1).
RECEIVE LINE INTERFACE AC TIMING Figure 14–6
RCLKO
t
DD
RPOSO, RNEGO
t
F
t
SU
RPOSI, RNEGI
031197 64/69
RCLKI
t
R
t
LL
t
CL
t
HD
t
LH
t
LP
t
CH
t
CP
Page 65

TRANSMIT SIDE AC TIMING Figure 14–7
TCLK
TESO
TSER/TSIG/
TDATA
TCHCLK
TCHBLK
TSYNC
TSYNC
TLCLK
TLINK
t
R
t
D1
1
2
5
t
F
t
D2
t
D2
t
t
D2
t
SU
DS2154
t
CP
t
CL
t
SU
t
HD
t
D2
t
SU
PW
t
HD
t
CH
NOTES:
1. TSYNC is in the output mode (TCR1.0=1).
2. TSYNC is in the input mode (TCR1.0=0).
3. TSER is sampled on the falling edge of TCLK when the transmit side elastic store is disabled.
4. TCHCLK and TCHBLK are synchronous with TCLK when the transmit side elastic store is disabled.
5. TLINK is only sampled during Sa–bit locations as defined in TCR2; no relationship between TLCLK/TLINK
and TSYNC is implied.
031197 65/69
Page 66

DS2154
TRANSMIT SYSTEM SIDE AC TIMING Figure 14–8
t
SP
t
t
R
t
F
SL
t
SH
TSYSCLK
t
SU
TSER
t
t
D3
HD
TCHCLK
t
D3
TCHBLK
t
t
SU
PW
TSSYNC
NOTES:
1. TSER is only sampled on the falling edge of TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic store is enabled.
2. TCHCLK and TCHBLK are synchronous with TSYSCLK when the transmit side elastic store is enabled.
TRANSMIT LINE INTERFACE SIDE AC TIMING Figure 14–9
TCLKO
TPOSO, TNEGO
t
DD
TCLKI
TPOSI, TNEGI
031197 66/69
t
R
t
F
t
SU
t
HD
t
LP
t
LL
t
LH
Page 67

AC CHARACTERISTICS – NON–MULTIPLEXED PARALLEL
PORT (MUX=0 ) (0°C to 70°C; V
–40°C to +
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Set Up Time for A0 to A7 Valid to
Active
CS
Set Up Time for CS Active to
either RD
, WR, or DS Active
Delay Time from either RD or DS
Active to Data Valid
Hold Time from either RD, WR, or
Inactive to CS Inactive
DS
Hold Time from CS Inactive to
Data Bus 3–state
Wait Time from either WR or DS
Active to Latch Data
Data Set Up Time to either WR or
Inactive
DS
Data Hold Time from either WR or
Inactive
DS
Address Hold from either
or DS inactive
WR
See Figures 14–10 to 14–13 for details.
t1 0 ns
t2 0 ns
t3 75 ns
t4 0 ns
t5 5 20 ns
t6 75 ns
t7 10 ns
t8 10 ns
t
9
10 ns
85°C; V
=5V ± 5% for DS2154T;
DD
=5V ± 5% for DS2154TN)
DD
INTEL BUS READ AC TIMING (BTS=0/MUX=0) Figure 14–10
DS2154
A0 TO A7
D0 TO D7
WR
CS
RD
t
1
0 ns min.
ADDRESS VALID
0 ns min.
t
2
t
3
75 ns max.
DATA VALID
5 ns min. / 20 ns max.
t
5
t
4
0 ns min.
031197 67/69
Page 68

DS2154
INTEL BUS WRITE AC TIMING (BTS=0/MUX=0) Figure 14–1 1
t9 10 ns min.
A0 TO A7
ADDRESS VALID
D0 TO D7
RD
t
1
0 ns min.
CS
WR
t
0 ns min. 0 ns min.
2
t
6
75 ns min.
MOTOROLA BUS READ AC TIMING (BTS=1/MUX=0) Figure 14–12
A0 TO A7
D0 TO D7
R/W
CS
DS
ADDRESS VALID
DATA VALID
5 ns min. /20 ns max.
t
1
0 ns min.
t
0 ns min. 0 ns min.
2
t
3
75 ns max.
10 ns
min.
t
t
8
7
10 ns
min.
t
4
t
5
t
4
MOTOROLA BUS WRITE AC TIMING (BTS=1/MUX=0) Figure 14–13
A0 TO A7
D0 TO D7
R/W
CS
DS
031197 68/69
ADDRESS VALID
t
1
0 ns min.
t
0 ns min. 0 ns min.
2
t
6
75 ns min.
t7t
10 ns
min.
8
10 ns
min.
t
9
t
4
10 ns min.
Page 69

DS2154 100–PIN LQFP
DS2154
PKG 100–PIN
DIM MIN MAX
A – 1.60
A1 0.05 –
A2 1.35 1.45
B 0.17 0.27
C 0.09 0.20
D 15.80 16.20
D1 14.00 BSC
E 15.80 16.20
E1 14.00 BSC
e 0.50 BSC
L 0.45 0.75
031197 69/69
 Loading...
Loading...