Page 1
DS1258Y/AB
PRODUCT PREVIEW
DS1258Y/AB
128K x 16 Nonvolatile SRAM
FEATURES
• 10 year minimum data retention in the absence of
external power
• Data is automatically protected during a power loss
• Separate upper byte and lower byte chip select inputs
• Unlimited write cycles
• Low–power CMOS
• Read and write access times as fast as 70 ns
• Lithium energy source is electrically disconnected to
retain freshness until power is applied for the first time
• Full ±10% operating range (DS1258Y)
• Optional ±5% operating range (DS1258AB)
• Optional industrial temperature range of –40°C to
85°C, designated IND
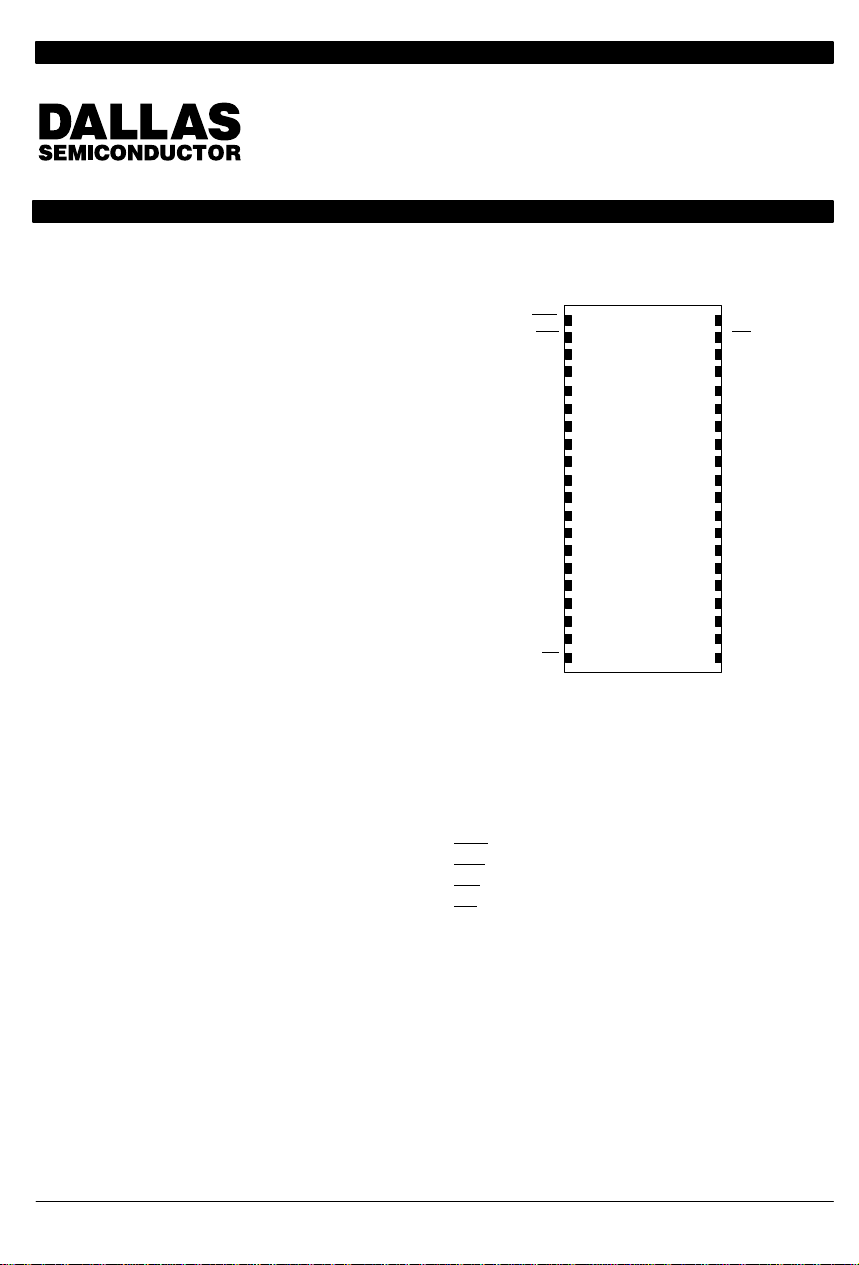
PIN ASSIGNMENT
CEU
1
CEL WE
2
3
DQ14
4
DQ13
5
DQ12
6
DQ11
7
DQ10
8
DQ9
9
DQ8
10
GND
11
DQ7
12
DQ6
13
DQ5
14
DQ4
15
DQ3
16
DQ2
17
DQ1
18
DQ0
19
20
OE
40–PIN ENCAPSULATED PACKAGE
740 MIL EXTENDED
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
PIN DESCRIPTION
A0–A16 – Address Inputs
DQ0–DQ15 – Data In/Data Out
CEU
CEL
WE
OE – Output Enable
V
CC
GND – Ground
– Chip Enable Upper Byte
– Chip Enable Lower Byte
– Write Enable
– Power Supply (+5V)
V
CC
A16DQ15
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
GND
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
DESCRIPTION
The DS1258 128K x 16 Nonvolatile SRAMs are
2,097,152 bit fully static, nonvolatile SRAMs, organized
as 131,072 words by 16 bits. Each NV SRAM has a self
contained lithium energy source and control circuitry
which constantly monitors V
condition. When such a condition occurs, the lithium
energy source is automatically switched on and write
Copyright 1995 by Dallas Semiconductor Corporation.
All Rights Reserved. For important information regarding
patents and other intellectual property rights, please refer to
Dallas Semiconductor data books.
for an out–of–tolerance
CC
protection is unconditionally enabled to prevent data
corruption. DIP–package DS1258 devices can be used
in place of solutions which build nonvolatile 128K x 16
memory by utilizing a variety of discrete components.
There is no limit to the number of write cycles which the
DS12658Y/AB can accept, and no additional support
circuitry is required for microprocessor interfacing.
100395 1/9
Page 2
DS1258Y/AB
READ MODE
The DS1258 devices execute a read cycle whenever
WE (Write Enable) is inactive (high) and either/both of
CEU or CEL (Chip Enables) are active (low) and OE
(Output Enable) is active (low). The unique address
specified by the 17 address inputs (A0–A16) defines
which of the 131,072 words of data is accessed. The
status of CEU and CEL determines whether all or part of
the addressed word is accessed. If CEU is active with
CEL inactive, then only the upper byte of the addressed
word is accessed. If CEU
then only the lower byte of the addressed word is
accessed. If both the CEU and CEL inputs are active
(low), then the entire 16 bit word is accessed. Valid data
will be available to the 16 data output drivers within t
(Access Time) after the last address input signal is
stable, providing that CEU, CEL and OE access times
are also satisfied. If OE, CEU, and CEL access times
are not satisfied, then data access must be measured
from the later occuring signal, and the limiting parameter is either t
for CEU, CEL, or tOE for OE rather than
CO
address access.
is inactive with CEL active,
ACC
WRITE MODE
The DS1258 devices execute a write cycle whenever
WE and either/both of CEU or CEL are active (low) after
address inputs are stable. The unique address specified by the 17 address inputs (A0–A16) defines which of
the 131,072 words of data is accessed. The status of
and CEL determines whether all or part of the
CEU
addressed word is accessed. If CEU is active with CEL
inactive, then only the upper byte of the addressed word
is accessed. If CEU is inactive with CEL active, then
only the lower byte of the addressed word is accessed.
If both the CEU
entire 16–bit word is accessed. The write cycle is terminated by the earlier rising edge of CEU
WE
. All address inputs must be kept valid throughout
the write cycle. WE
minimum recovery time (tWR) before another cycle can
be initiated. The OE control signal should be kept inactive (high) during write cycles to avoid bus contention.
However, if the output drivers are enabled (CEU and/or
, and OE active) then WE will disable the outputs in
CEL
t
from its falling edge.
ODW
and CEL inputs are active (low), then the
READ/WRITE FUNCTION Table 1
V
OE WE CEL CEU
H H X X I
L H L L
L H L H
L H H L High–Z Output
X L L L
X L L H
X L H L High–Z Input
X X H H I
CC
CURRENT
CCO
I
CCO
I
CCO
CCS
DQ0–DQ7 DQ8–DQ15
High–Z High–Z Output Disabled
Output Output
Output High–Z
Input Input
Input High–Z
High–Z High–Z Output Disabled
and/or CEL, or
must return to the high state for a
CYCLE
PERFORMED
Read Cycle
Write Cycle
100395 2/9
Page 3

DS1258Y/AB
DATA RETENTION MODE
The DS1258AB provides full functional capability for
VCC greater than 4.75 volts, and write protects by 4.5
volts. The DS1258Y provides full functional capability
greater than 4.5 volts and write protects by 4.25
for V
CC
volts. Data is maintained in the absence of VCC without
any additional support circuitry. The nonvolatile static
RAMs constantly monitor VCC. Should the supply voltage decay, the NV SRAMs automatically write protect
themselves, all inputs become “don’t care,” and all outputs become high impedance. As V
proximately 3.0 volts, a power switching circuit connects the lithium energy source to RAM to retain data.
falls below ap-
CC
During power-up, when V
rises above approximately
CC
3.0 volts, the power switching circuit connects external
VCC to RAM and disconnects the lithium energy source.
Normal RAM operation can resume after V
exceeds
CC
4.75 volts for the DS1258AB and 4.5 volts for the
DS1258Y.
FRESHNESS SEAL
The DS1258 devices are shipped from Dallas Semiconductor with the lithium energy sources disconnected,
guaranteeing full energy capacity. When V
applied at a level greater than V
, the lithium energy
TP
source is enabled for battery backup operation.
CC
is first
100395 3/9
Page 4

DS1258Y/AB
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Voltage on Any Pin Relative to Ground –0.3V to +7.0V
Operating Temperature 0°C to +70°C, –40°C to +85°C for IND parts
Storage Temperature –40°C to +70°C, –40°C to +85°C for IND parts
Soldering Temperature 260°C for 10 seconds
* This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operation sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods of time may affect reliability.
RECOMMENDED DC OPERATING CONDITIONS (tA: See Note 10)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
DS1258Y Power Supply Voltage V
DS1258AB Power Supply Voltage V
Logic 1 V
Logic 0 V
CC
CC
IH
IL
4.5 5.0 5.5 V
4.75 5.0 5.25 V
2.2 V
CC
0.0 +0.8 V
V
(VCC=5V ± 5% for DS1258AB)
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (t
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Input Leakage Current I
I/O Leakage Current
> VIH < V
CE
CC
Output Current @ 2.4V I
Output Current @ 0.4V I
Standby Current
, CEL=2.2V
CEU
Standby Current
, CEL=VCC - 0.5V
CEU
Operating Current I
Write Protection Voltage
(DS1258Y)
Write Protection Voltage
(DS1258AB)
IL
I
IO
OH
OL
I
CCS1
I
CCS2
CCO1
V
TP
V
TP
-2.0 +2.0
-1.0 +1.0
-1.0 mA
4.25 4.37 4.5 V
4.50 4.62 4.75 V
: See Note 10) (VCC=5V ± 10% for DS1258Y)
A
A
A
2.0 mA
10 20 mA
6 10 mA
170 mA
CAPACITANCE (tA = 25°C)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Input Capacitance C
Input/Output Capacitance C
100395 4/9
IN
I/O
20 25 pF
5 10 pF
Page 5

AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (t
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
UNITS
NOTES
DS1258Y–70
PARAMETER SYMBOL
Read Cycle Time t
Access Time t
OE to Output Valid t
CE to Output Valid t
OE or CE to Output Valid t
Output High Z from Deselection t
Output Hold from Address
Change
Write Cycle Time t
Write Pulse Width t
Address Setup Time t
Write Recovery Time t
Output High Z from WE t
Output Active from WE t
Data Setup Time t
Data Hold Time t
RC
ACC
OE
CO
COE
OD
t
OH
WC
WP
AW
WR1
t
WR2
ODW
OEW
DS
DH1
t
DH2
DS1258AB–70
MIN MAX MIN MAX
70 100 ns
5 5 ns 5
5 5 ns
70 100 ns
55 75 ns 3
0 0 ns
5
15
5 5 ns 5
30 40 ns 4
0
10
DS1258Y/AB
(VCC=5V ± 5% for DS1258AB)
: See Note 10) (VCC=5V ± 10% for DS1258Y)
A
DS1258Y–100
DS1258AB–100
70 100 ns
35 50 ns
70 100 ns
25 35 ns 5
5
15
25 35 ns 5
0
10
UNITS NOTES
ns
ns
ns
ns
12
13
12
13
READ CYCLE
SEE NOTE 1
V
ADDRESSES
CEU, CEL t
OE
D
OUT
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
t
V
COE
t
RC
V
IH
V
IL
t
ACC
CO
IL
IH
t
OE
V
IL
t
COE
V
V
OH
V
OL
V
IH
IH
OUTPUT
DATA VALID
V
IH
V
IL
t
OH
t
OD
t
OD
V
OH
V
OL
100395 5/9
Page 6

DS1258Y/AB
WRITE CYCLE 1
ADDRESSES
CEU, CEL
t
WC
V
IH
V
IL
t
AW
V
V
IL
IL
V
V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
IL
WE
D
OUT
D
IN
SEE NOTES 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 AND 12
WRITE CYCLE 2
ADDRESSES
CEU, CEL
WE
t
WP
V
IH
t
ODW
V
IL
HIGH
IMPEDANCE
V
IH
V
IL
t
DS
t
OEW
t
WR1
V
IH
t
DH1
V
IH
DATA IN STABLE
V
IL
t
WC
V
IH
V
IL
t
AW
V
IH
V
IL
t
WP
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
V
t
WR2
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
IL
IH
V
IL
D
OUT
D
IN
SEE NOTES 2, 3, 4, 6, 7 AND 13
100395 6/9
t
COE
t
ODW
V
IH
V
IL
t
DS
t
DATA IN STABLE
DH2
V
IH
V
IL
Page 7

POWER-DOWN/POWER-UP CONDITION
V
CC
DS1230Y 4.50V
DS1230AB 4.75V
3.2V
DS1258Y/AB
t
REC
t
R
WE
SEE NOTE 11
, CEU, CEL
t
F
t
PD
LEAKAGE CURRENT
IL SUPPLIED FROM
LITHIUM CELL
DATA RETENTION
TIME
t
DR
POWER-DOWN/POWER-UP TIMING (tA: See Note 10)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
CEU, CEL, WE at VIH before
Power-Down
V
Slew from V
CC
V
Slew from 0V to V
CC
to 0V t
TP
TP
CEU, CEL or at VIH after
Power-Up
t
t
REC
PD
t
0
F
R
300
300
2 125 ms
s
s
s
11
(tA = 25°C)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN TYP MAX UNITS NOTES
Expected Data Retention Time t
DR
10 years 9
WARNING:
Under no circumstance are negative undershoots, of any amplitude, allowed when device is in battery backup mode.
NOTES:
1. WE is high for a read cycle.
= VIH or VIL. If OE = VIH during write cycle, the output buffers remain in a high impedance state.
2. OE
is specified as the logical AND of CEU or CEL and WE. tWP is measured from the latter of CEU, CEL or
3. t
WP
going low to the earlier of CEU, CEL or WE going high.
WE
100395 7/9
Page 8

DS1258Y/AB
4. tDS is measured from the earlier of CEU or CEL or WE going high.
5. These parameters are sampled with a 5 pF load and are not 100% tested.
6. If the CEU
or CEL low transition occurs simultaneously with or later than the WE low transition in the output
buffers remain in a high impedance state during this period.
7. If the CEU
or CEL high transition occurs prior to or simultaneously with the WE high transition, the output
buffers remain in high impedance state during this period.
8. If WE
is low or the WE low transition occurs prior to or simultaneously with the CEU or CEL low transition, the
output buffers remain in a high impedance state during this period.
9. Each DS1258 has a built-in switch that disconnects the lithium source until V
is first applied by the user.
CC
The expected tDR is defined as accumulative time in the absence of VCC starting from the time power is first
applied by the user.
10.All AC and DC electrical characteristics are valid over the full operating temperature range. For standard
products, this range is 0°C to 70°C. For industrial products (IND), this range is –40°C to +85°C.
11.In a power down condition the voltage on any pin may not exceed the voltage on V
, t
12.t
13.t
WR1
WR2
are measured from WE going high.
DH1
, t
are measured from CEU OR CEL going high.
DH2
CC
.
DC TEST CONDITIONS
Outputs Open
Cycle = 200 ns
All voltages are referenced to ground
ORDERING INFORMATION
DS1250 TTP–
SSS –
III
Operating Temperature Range
blank: 0° to 70°
IND: –40° to +85°C
Access
Speed
70:
70 ns
100:
100 ns
Package Type
blank: 40–pin 600 mil DIP
VCC Tolerance
AB: ± 5%
Y: ±10%
AC TEST CONDITIONS
Output Load: 100 pF + 1TTL Gate
Input Pulse Levels:
0.0 to 3.0 volts
Timing Measurement Reference Levels
Input: 1.5V
Output: 1.5V
Input Pulse Rise and Fall Times: 5 ns
100395 8/9
Page 9

DS1258Y/AB NONVOLATILE SRAM 40–PIN 740 MIL EXTENDED MODULE
DIM MIN MAX
A IN.
MM
B IN.
1
A
C
F
GKD
MM
C IN.
MM
D IN.
MM
E IN.
MM
F IN.
MM
G IN.
MM
H IN.
MM
J IN.
MM
K IN.
MM
2.080
52.83
0.715
18.16
0.345
8.76
0.085
2.16
0.015
0.38
0.120
3.05
0.090
2.29
0.590
14.99
0.008
0.20
0.015
0.43
DS1258Y/AB
40-PINPKG
2.100
53.34
0.740
18.80
0.365
9.27
0.115
2.92
0.030
0.76
0.160
4.06
0.110
2.79
0.630
16.00
0.012
0.30
0.025
0.58
J
E
H
B
100395 9/9
 Loading...
Loading...