Page 1
Motor driver ICs
Reversible motor driver
BA6287F
The BA6287F is a reversible-motor driver with a maximum output current of 1.0A. Two logic inputs allow four output
modes: forward, reverse, stop (idling), and brake. A built-in power saving circuit suppresses current consumption when
the motor is in stop mode.
Applications
VCRs and audio equipment in general
Features
1) Built-in power saving circuit suppresses the stop
mode current dissipation.
2) Output voltage can be set arbitrarily with the V
REF pin.
3) Interfaces with TTL devices.
4) Built-in thermal shutdown circuit.
Absolute maximum ratings (Ta = 25C)
Recommended operating conditions (Ta = 25C)
439
Page 2
Motor driver ICs BA6287F
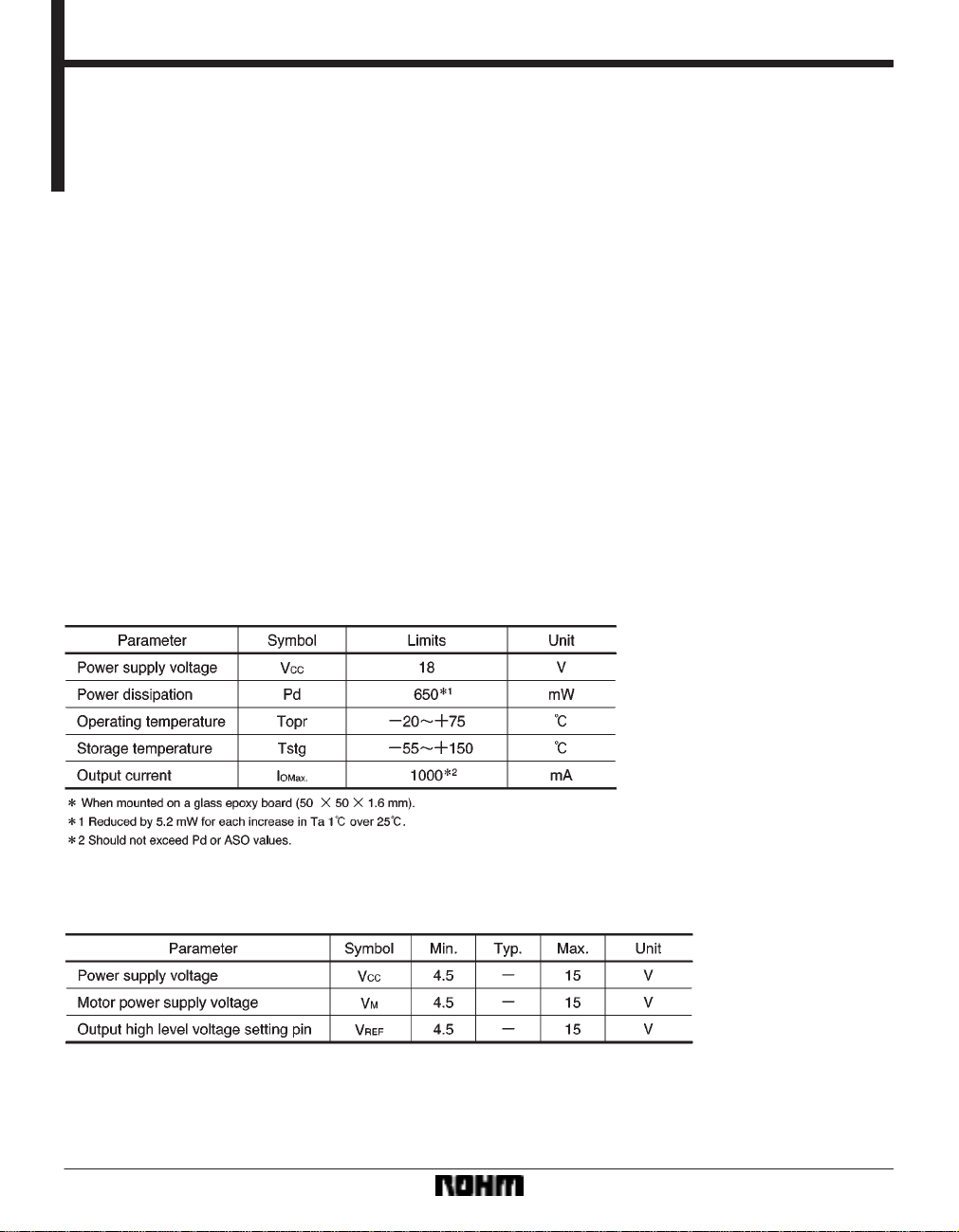
Block diagram
Pin descriptions
Input / output circuits
440
Page 3

Motor driver ICs BA6287F
Electrical characteristics (unless otherwise noted, Ta = 25C, VCC = 9V, VM=9V, VREF = 9V)
Circuit operation
(1) Input section
The four output modes are controlled by two logic inputs.
Current flows from OUT1 to OUT2 when F
IN is LOW, and from OUT2 to OUT1 when RIN is HIGH
R
and F
IN is LOW (refer to the truth table). The input circuit
IN is HIGH and
can be operated by a logic circuit with a current capacity
of 120 170µA.
Input / output truth table
(3) Power saving circuit
All circuits are turned OFF when the F
IN and RIN input pins
are both put to LOW level. This circuit saves power during standby mode by leaving the outputs OPEN.
(4) Thermal shutdown circuit
When the thermal shutdown circuit is activated at the
chip temperature of about 175C (typical), the outputs
are left OPEN. The temperature difference between the
activation and deactivation settings is about 15C. When
the thermal shutdown circuit is deactivated, the outputs
revert to the status determined by input mode.
(2) Output section
Current flows from OUT1 to OUT2 during forward rotation, and from OUT2 to OUT1 during reverse rotation.
The output voltages V
OH [V]=VREFVCE (sat) (PNP)VBE (NPN)
V
OL [V]=VCE (sat) (NPN)
V
CE and VBE are functions of the output current (see elec-
V
OH and VOL are given by :
trical characteristic curves). The output current can be
set with the V
REF pin.
Application example
441
Page 4

Motor driver ICs BA6287F
Operation notes
(1) The quality of these products have been carefully
checked; however, use of the products with applied voltages, operating temperatures, or other parameters that
exceed the absolute maximum rating given may result in
the damage of the IC and the product it is used in. If the
IC is damaged, the short mode and open modes cannot
be specified, so if the IC is to be used in applications
where parameters may exceed the absolute maximum
ratings, then be sure to incorporate fuses, or other physical safety measures.
(2) GND potential
The potential for pin 1 must be kept lower than the potentials of the other pins regardless of the circumstances.
(3) Input pins
Voltage should never be applied to the input pins when
the V
CC voltage is not applied to the IC. Similarly, when
CC is applied, the voltage on each input pin should be
V
less than V
CC and within the guaranteed range for the
electrical characteristics.
(4) Back-rush voltage
Depending on the ambient conditions, environment, or
motor characteristics, the back-rush voltage may fluctuate. Be sure to confirm that the back-rush voltage will not
adversely affect the operation of the IC.
(5) Large current line
Large currents are carried by the motor power supply and
motor ground for these ICs.
Therefore, the layout of the pattern of the PC board and
the constants of certain parameters for external components, such as the capacitor between the power supply
and ground, may cause this large output current to flow
back to the input pins, resulting in output oscillation or
other malfunctions. To prevent this, make sure that the
PC board layout and external circuit constants cause no
problems with the characteristics of these ICs.
(6) Power dissipation
The power dissipation will fluctuate depending on the
mounting conditions of the IC and the ambient environment. Make sure to carefully check the thermal design of
the application where these ICs will be used.
(7) Power consumption
The power consumption by the IC varies widely with the
power supply voltage and the output current. Give full
consideration to the power dissipation rating and the
thermal resistance data and transient thermal resistance
data, to provide a thermal design so that none of the ratings for the IC are exceeded.
(8) ASO
Make sure that the output current and supply voltage do
not exceed the ASO values.
(9) Precautions for input mode switching
To ensure reliability, it is recommended that the mode
switching for the motor pass once through the open
mode.
(10) In-rush current
There are no circuits built into these ICs that prevent inrush currents. Therefore, it is recommended to place a
current limiting resistor or other physical countermeasure.
(11) Factors regarding the thermal, power supply, and
motor conditions
If the potential of the output pin sways greatly and goes
below the potential of ground, the operation of the IC may
malfunction or be adversely affected. In such a case,
place a diode between the output and ground, or other
measure, to prevent this.
(12) HIGH level output voltage setting pin
Ensure that the voltage applied to V
the voltage on the motor power supply pin or the V
REF does not exceed
CC pin.
(13) The input pins have temperature-dependent characteristics. Take the temperature effect into consideration when using the IC.
(14) To eliminate motor noise, connect a capacitor between OUT1 and GND and between OUT2 and GND. Alternatively, connect a capacitor between OUT1 and
OUT2, and also a diode between OUT1 and GND and
between OUT2 and GND (see Fig. 2).
442
Page 5

Motor driver ICs BA6287F
Electrical characteristic curves
443
Page 6
Motor driver ICs BA6287F
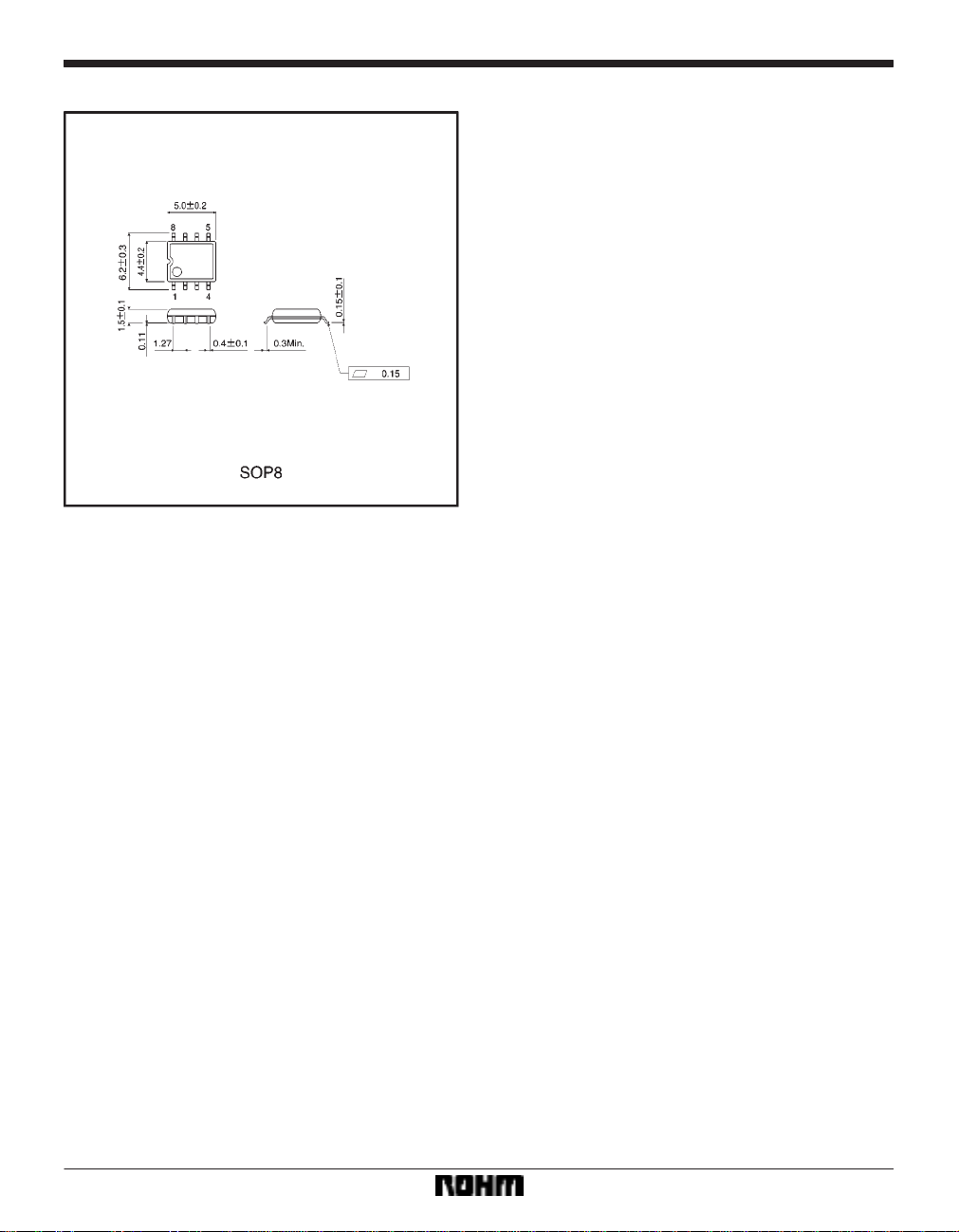
External dimensions (Units: mm)
444
 Loading...
Loading...