Page 1
Features
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
NC
I/O0
A8
A9
A11
NC
OE
A10
CE
I/O7
I/O6
432
1
323130
14151617181920
I/O1
I/O2
GND
DC
I/O3
I/O4
I/O5
A7
A12
A14DCVCCWEA13
• Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply
• Fast Read Access Time – 200 ns
• Automatic Page Write Operation
– Internal Address and Data Latches for 64 Bytes
– Internal Control Timer
• Fast Write Cycle Times
– Page Write Cycle Time: 10 ms Maximum
– 1- to 64-byte Page Write Operation
• Low Power Dissipation
– 15 mA Active Current
– 20 µA CMOS Standby Current
• Hardware and Software Data Protection
• DATA Polling for End of Write Detection
• High Reliability CMOS Technology
– Endurance: 10,000 Cycles
– Data Retention: 10 Years
• JEDEC Approved Byte-wide Pinout
• Commercial and Industrial Temperature Ranges
256K (32K x 8)
Battery-Voltage
Parallel
EEPROMs
™
Description
The AT28BV256 is a high-performance Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read
Only Memory. Its 256K of memory is organized as 32,768 words by 8 bits. Manufactured with Atmel’s advanced nonvolatile CMOS technology, the device offers access
times to 200 ns with power dissipation of just 54 mW. When the device is deselected,
OE
A11
A13
WE
VCC
A14
A12
µA.
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
(continued)
PDIP, SOIC
Top V ie w
1
A14
2
A12
3
A7
4
A6
5
A5
6
A4
7
A3
8
A2
9
A1
10
A0
11
I/O0
12
I/O1
13
I/O2
14
GND
TSOP
Top V ie w
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
VCC
27
WE
26
A13
25
A8
24
A9
23
A11
22
OE
21
A10
20
CE
19
I/O7
18
I/O6
17
I/O5
16
I/O4
15
I/O3
28
A10
27
CE
26
I/O7
25
I/O6
24
I/O5
23
I/O4
22
I/O3
21
GND
20
I/O2
19
I/O1
18
I/O0
17
A0
16
A1
15
A2
the CMOS standby current is less than 200
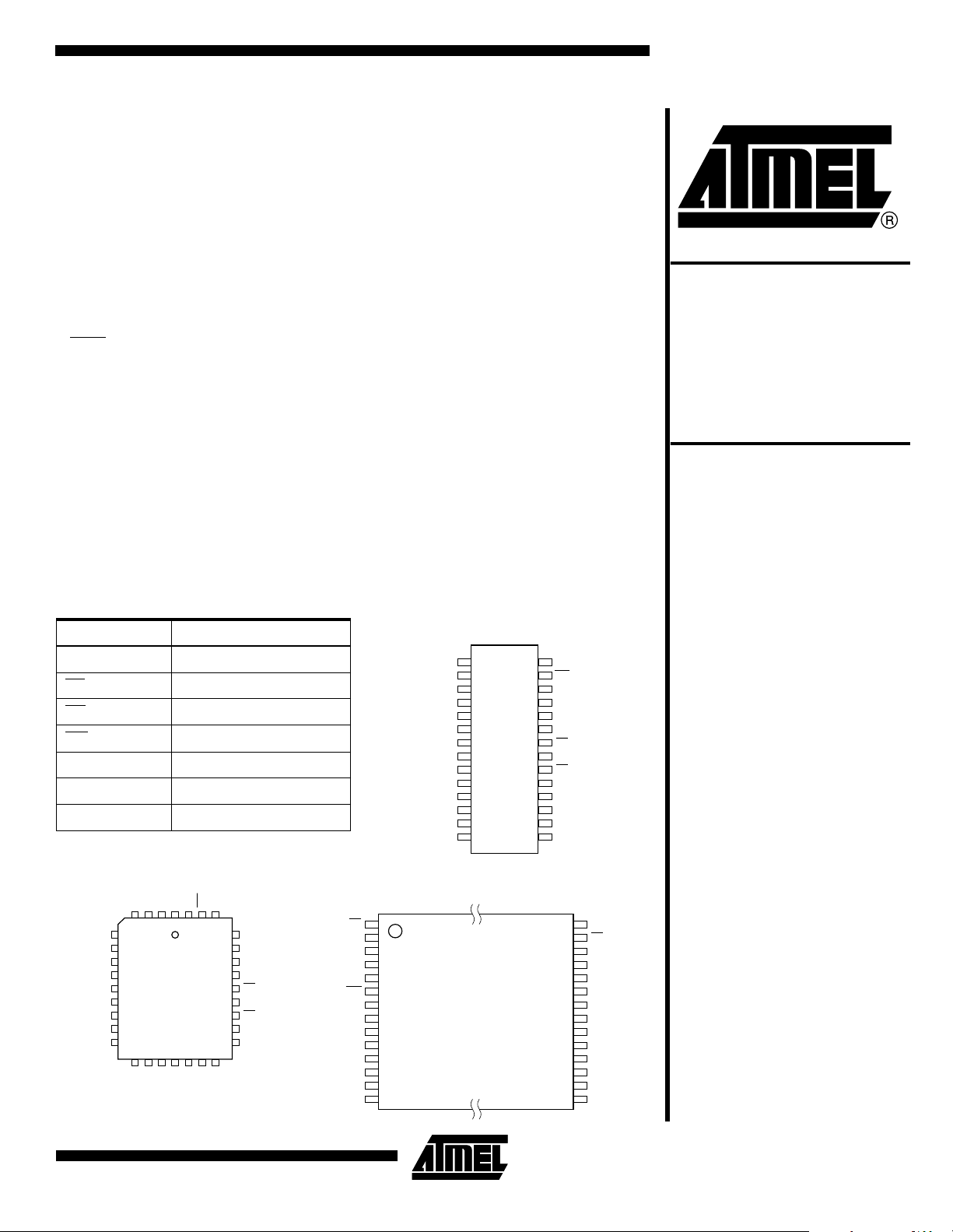
Pin Configurations
Pin Name Function
A0 - A14 Addresses
CE
OE Output Enable
WE
I/O0 - I/O7 Data Inputs/Outputs
NC No Connect
DC Don’t Connect
Note: PLCC package pins 1 and 17
are DON’T CONNECT.
Chip Enable
Write Enable
PLCC
Top View
AT28BV256
Rev. 0273G–11/99
1
Page 2
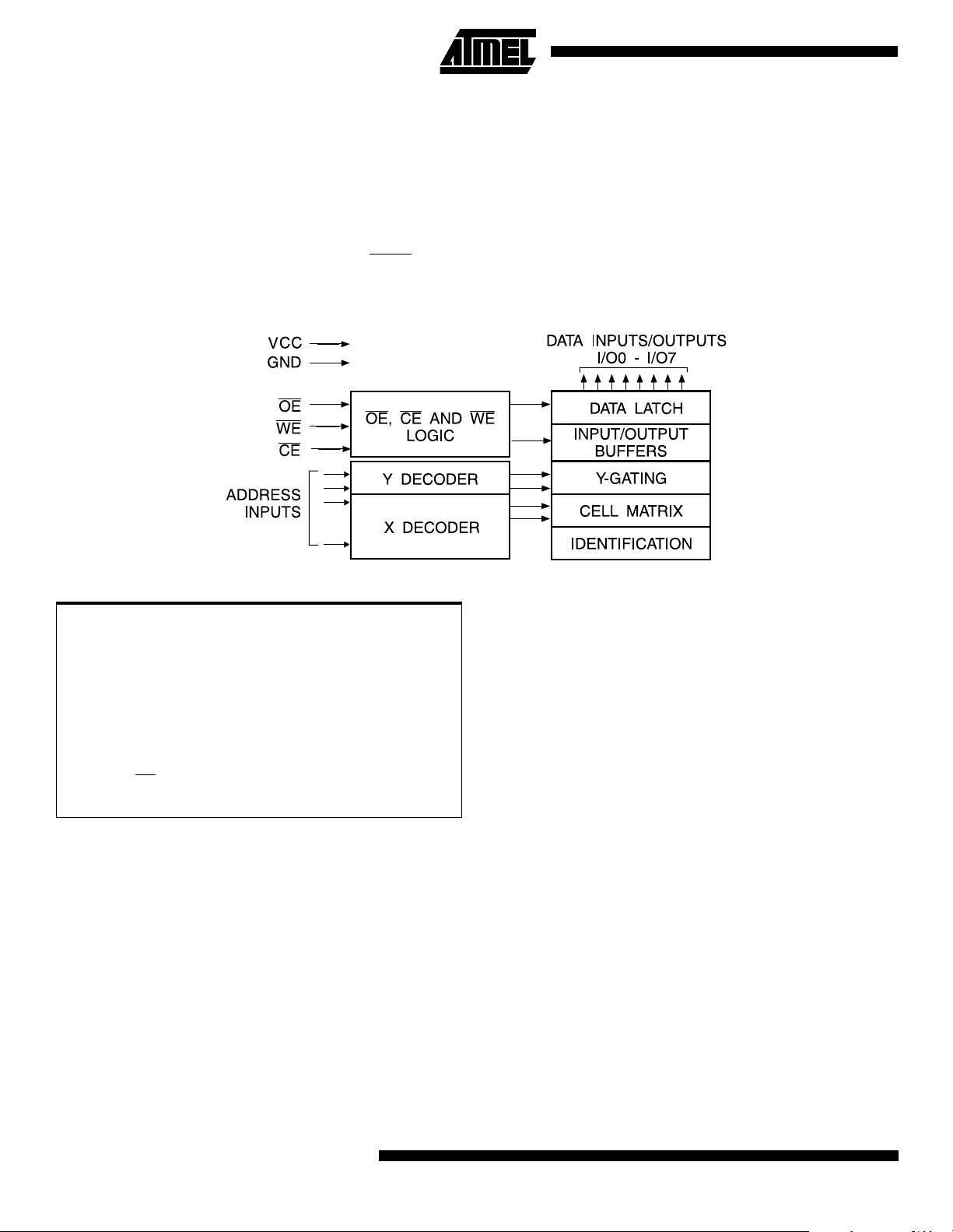
The AT28BV256 is accessed like a Static RAM for the read
or write cycle without the need for external components.
The device contains a 64-byte page register to allow writing
of up to 64 bytes simultaneously. During a write cycle, the
addresses and 1 to 64 bytes of data are internally latched,
freeing the address and data bus for other operations. Following the initiation of a write cycle, the device will automatically write the latched data using an internal control timer.
The end of a write cycle can be detected by DATA
polling
Block Diagram
of I/O7. Once the end of a write cycle has been detected a
new access for a read or write can begin.
Atmel’s 28BV256 has additional features to ensure high
quality and manufacturability. The device utilizes internal
error correction for extended endurance and improved data
retention characteristics. An optional software data protection mechanism is available to guard against inadvertent
writes. The device also includes an extra 64 bytes of
EEPROM for device identification or tracking.
Absolute Maximum Ratings*
Temperature under Bias ................................ -55°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature ..................................... -65°C to +150°C
All Input Voltages (including NC Pins)
with Respect to Ground...................................-0.6V to +6.25V
All Output Voltages
with Respect to Ground.............................-0.6V to V
Voltage on OE
with Respect to Ground...................................-0.6V to +13.5V
and A9
+ 0.6V
CC
*NOTICE: Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute
Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and
functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions beyond those indicated in the
operational sections of this specification is not
implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability
2
AT28BV256
Page 3

Device Operation
READ: The AT28BV256 is accessed like a Static RAM.
When CE
at the memory location determined by the address pins is
asserted on the outputs. The outputs are put in the high
impedance state when either CE
line control gives designers flexibility in preventing bus contention in their system.
BYTE WRITE: A low pulse on the WE
CE
cycle. The address is latched on the falling edge of CE
WE
rising edge of CE
started it will automatically time itself to completion. Once a
programming operation has been initiated and for the duration of t
operation.
PAGE WRITE: The page write operation of the
AT28BV256 allows 1 to 64 bytes of data to be written into
the device during a single internal programming period. A
page write operation is initiated in the same manner as a
byte write; the first byte written can then be followed by 1 to
63 additional bytes. Each successive byte must be written
within 150
exceeded the AT28BV256 will cease accepting data and
commence the internal programming operation. All bytes
during a page write operation must reside on the same
page as defined by the state of the A6 - A14 inputs. For
each WE
tion, A6 - A14 must be the same.
The A0 to A5 inputs are used to specify which bytes within
the page are to be written. The bytes may be loaded in any
order and may be altered within the same load period. Only
bytes which are specified for writing will be written; unnecessary cycling of other bytes within the page does not
occur.
DATA
to indicate the end of a write cycle. During a byte or page
write cycle an attempted read of the last byte written will
result in the complement of the written data to be presented
on I/O7. Once the write cycle has been completed, true
data is valid on all outputs, and the next write cycle may
begin. DATA
cycle.
TOGGLE BIT: In addition to DATA
provides another method for determining the end of a write
cycle. During the write operation, successive attempts to
and OE are low and WE is high, the data stored
or OE is high. This dual-
or CE input with
or WE low (respectively) and OE high initiates a write
or
, whichever occurs last. The data is latched by the first
or WE. Once a byte write has been
, a read operation will effectively be a polling
WC
µs (t
) of the previous byte. If the t
BLC
BLC
limit is
high to low transition during the page write opera-
POLLING: The AT28BV256 features DATA Polling
Polling may begin at anytime during the write
Polling the AT28BV256
AT28BV256
read data from the device will result in I/O6 toggling
between one and zero. Once the write has completed, I/O6
will stop toggling and valid data will be read. Reading the
toggle bit may begin at any time during the write cycle.
DATA PROTECTION: If precautions are not taken, inadvertent writes may occur during transitions of the host system power supply. Atmel has incorporated both hardware
and software features that will protect the memory against
inadvertent writes.
HARDWARE PROTECTION: Hardware features protect
against inadvertent writes to the AT28BV256 in the following ways: (a) V
1.8V (typical) the device will automatically time out 10 ms
(typical) before allowing a write; (b) write inhibit—holding
any one of OE
cycles; and (c) noise filter—pulses of less than 15 ns (typical) on the WE
SOFTWARE DATA PROTECTION: A software-controlled
data protection feature has been implemented on the
AT28BV256. Software data protection (SDP) helps prevent
inadvertent writes from corrupting the data in the device.
SDP can prevent inadvertent writes during power-up and
power-down as well as any other potential periods of system instability.
The AT28BV256 can only be written using the software
data protection feature. A series of three write commands
to specific addresses with specific data must be presented
to the device before writing in the byte or page mode. The
same three write commands must begin each write operation. All software write commands must obey the page
mode write timing specifications. The data in the 3-byte
command sequence is not written to the device; the
address in the command sequence can be utilized just like
any other location in the device.
Any attempt to write to the device without the 3-byte
sequence will start the internal write timers. No data will be
written to the device; however, for the duration of t
operations will effectively be polling operations.
DEVICE IDENTIFICATION: An extra 64 bytes of EEPROM
memory are available to the user for device identification.
By raising A9 to 12V
7FC0H to 7FFFH the additional bytes may be written to or
read from in the same manner as the regular memory
array.
power-on delay—once VCC has reached
CC
low, CE high or WE high inhibits write
or CE inputs will not initiate a write cycle.
, read
WC
± 0.5V and using address locations
3
Page 4
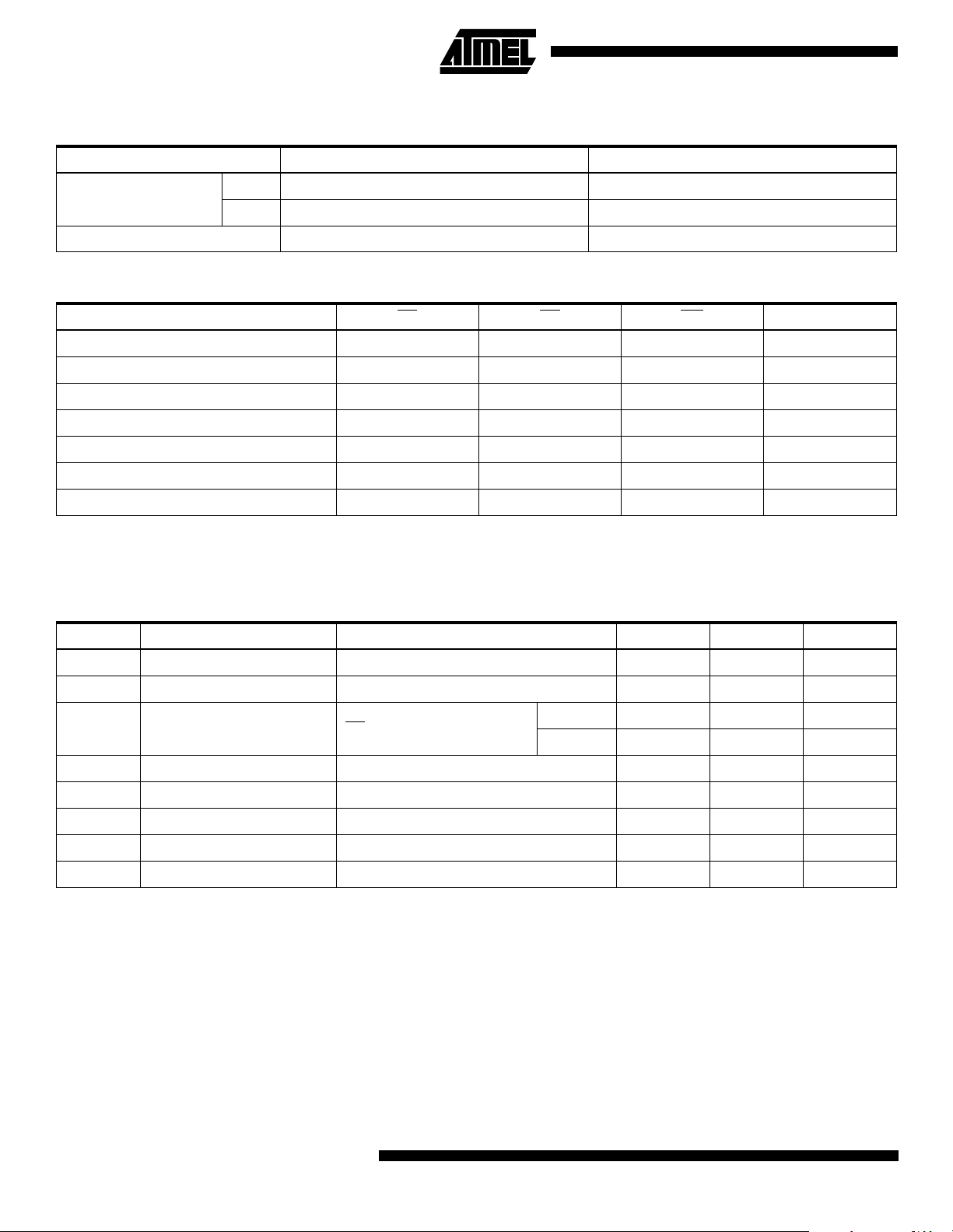
DC and AC Operating Range
AT28BV256-20 AT28BV256-25
Operating
Temperature (Case)
V
Power Supply 2.7V - 3.6V 2.7V - 3.6V
CC
Com. 0°C - 70°C0°C - 70°C
Ind. -40°C - 85°C-40°C - 85°C
Operating Modes
Mode CE OE WE I/O
Read V
(2)
Write
Standby/Write Inhibit V
IL
V
IL
IH
Write Inhibit X X V
Write Inhibit X V
Output Disable X V
Chip Erase V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
(1)
X
IL
IH
(3)
V
H
V
IH
V
IL
D
OUT
D
IN
XHigh Z
IH
X
XHigh Z
V
IL
High Z
Notes: 1. X can be VIL or VIH.
2. Refer to AC programming waveforms.
= 12.0V ± 0.5V.
3. V
H
DC Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Max Units
I
LI
I
LO
I
SB
I
CC
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
Input Load Current VIN = 0V to VCC + 1V 10 µA
Output Leakage Current V
= 0V to V
I/O
CC
10 µA
Com. 20 µA
VCC Standby Current CMOS CE = V
V
Active Current f = 5 MHz; I
CC
- 0.3V to VCC + 1V
CC
= 0 mA 15 mA
OUT
Ind. 50 µA
Input Low Voltage 0.6 V
Input High Voltage 2.0 V
Output Low Voltage IOL = 1.6 mA 0.3 V
Output High Voltage IOH = -100 µA2.0V
4
AT28BV256
Page 5

AC Read Characteristics
tR, tF < 20 ns
Symbol Parameter
AT28BV256
AT28BV256-20 AT28BV256-25
UnitsMin Max Min Max
t
t
t
t
t
ACC
CE
OE
DF
OH
(1)
(2)
(3)(4)
Address to Output Delay 200 250 ns
CE to Output Delay 200 250 ns
OE to Output Delay 0 80 0 100 ns
CE or OE to Output Float 0 55 0 60 ns
Output Hold from OE, CE or Address, whichever
occurred first
AC Read Waveforms
(1)(2)(3)(4)
t
ACC
t
CE
t
00ns
OE
t
DF
t
OH
Notes: 1. CE may be delayed up to t
2. OE may be delayed up to tCE - tOE after the falling edge of CE without impact on tCE or by t
without impact on t
is specified from OE or CE whichever occurs first (CL = 5 pF).
3. t
DF
ACC
.
- tCE after the address transition without impact on t
ACC
ACC
.
- tOE after an address change
ACC
4. This parameter is characterized and is not 100% tested.
Input Test Waveforms and
Output Test Load
Measurement Level
Pin Capacitance
f = 1 MHz, T = 25°C
Symbol Typ Max Units Conditions
C
IN
C
OUT
Note: 1. This parameter is characterized and is not 100% tested.
(1)
46pFV
812pFV
IN
OUT
= 0V
= 0V
5
Page 6

AC Write Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units
t
, t
AS
t
AH
t
CS
t
CH
t
WP
t
DS
tDH, t
t
DV
OES
OEH
Address, OE Set-up Time 0 ns
Address Hold Time 50 ns
Chip Select Set-up Time 0 ns
Chip Select Hold Time 0 ns
Write Pulse Width (WE or CE) 200 ns
Data Set-up Time 50 ns
Data, OE Hold Time 0 ns
Time to Data Valid NR
(1)
Note: 1. NR = No Restriction.
AC Write Waveforms
WE Controlled
t
OES
t
AS
t
AH
t
OEH
t
CH
CE Controlled
t
t
OES
t
t
CS
AS
CS
t
WPH
t
WP
t
DV
t
AH
t
DV
t
WP
t
DS
t
DS
t
OEH
t
CH
t
DH
t
WPH
t
DH
6
AT28BV256
Page 7

AT28BV256
Page Mode Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units
t
WC
t
AS
t
AH
t
DS
t
DH
t
WP
t
BLC
t
WPH
Programming Algorithm
Write Cycle Time 10 ms
Address Set-up Time 0 ns
Address Hold Time 50 ns
Data Set-up Time 50 ns
Data Hold Time 0 ns
Write Pulse Width 200 ns
Byte Load Cycle Time 150 µs
Write Pulse Width High 100 ns
LOAD DATA AA
TO
ADDRESS 5555
Notes for software program code:
1. Data Format: I/O7 - I/O0 (Hex);
Address Format: A14 - A0 (Hex).
LOAD DATA 55
TO
ADDRESS 2AAA
2. Data protect state will be re-activated at the end of
program cycle.
3. 1 to 64 bytes of data are loaded.
LOAD DATA A0
TO
ADDRESS 5555
WRITES ENABLED
(2)
LOAD DATA XX
TO
ANY ADDRESS
LOAD LAST BYTE
LAST ADDRESS
Software Protected Program Cycle Waveforms
(3)
TO
(3)
ENTER DATA
PROTECT STATE
(1)(2)(3)
t
WP
t
AS
t
AH
t
DS
t
WPH
t
DH
t
BLC
t
Notes: 1. A0 - A14 must conform to the addressing sequence for the first three bytes as shown above.
2. A6 through A14 must specify the same page address during each high to low transition of WE (or CE) after the software
code has been entered.
3. OE
must be high only when WE and CE are both low.
WC
7
Page 8

DATA Polling Characteristics
(1)
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
t
DH
t
OEH
t
OE
t
WR
Data Hold Time 0 ns
OE Hold Time 0 ns
OE to Output Delay
(2)
Write Recovery Time 0 ns
Notes: 1. These parameters are characterized and not 100% tested.
2. See “AC Read Characteristics” on page 5.
DATA Polling Waveforms
t
OEH
t
DH
t
OE
t
WR
ns
Toggle Bit Characteristics
(1)
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
t
DH
t
OEH
t
OE
t
OEHP
t
WR
Data Hold Time 10 ns
OE Hold Time 10 ns
OE to Output Delay
(2)
OE High Pulse 150 ns
Write Recovery Time 0 ns
Notes: 1. These parameters are characterized and not 100% tested.
2. See “AC Read Characteristics” on page 5.
Toggle Bit Waveforms
t
OEH
t
t
DH
OE
t
WR
ns
Notes: 1. Toggling either OE or CE or both OE and CE will operate toggle bit.
2. Beginning and ending state of I/O6 will vary.
3. Any address location may be used but the address should not vary.
8
AT28BV256
Page 9

AT28BV256
9
Page 10

Ordering Information
I
t
ACC
(ns)
200 15 0.02 AT28BV256-20JC
250 15 0.02 AT28BV256-25JC
Note: 1. See Valid Part Numbers table below.
(mA)
CC
15 0.02 AT28BV256-20JI
15 0.02 AT28BV256-25JI
(1)
Ordering Code Package Operation RangeActive Standby
AT28BV256-20PC
AT28BV256-20SC
AT28BV256-20TC
AT28BV256-20PI
AT28BV256-20SI
AT28BV256-20TI
AT28BV256-25PC
AT28BV256-20SC
AT28BV256-25TC
AT28BV256-25PI
AT28BV256-20SI
AT28BV256-25TI
32J
28P6
28S
28T
32J
28P6
28S
28T
32J
28P6
28S
28T
32J
28P6
28S
28T
Commercial
(0° to 70°C)
Industrial
(-40° to 85°C)
Commercial
(0° to 70°C)
Industrial
(-40° to 85°C)
Valid Part Numbers
The following table lists standard Atmel products that can be ordered.
Device Numbers Speed Package and Temperature Combinations
AT28BV256 20 JC, JI, PC, PI, SC, SI, TC, TI
AT28BV256 25 JC, JI, PC, PI, SC, SI, TC, TI
Die Products
Reference Section: Parallel EEPROM Die Products
Package Type
32J 32-lead, Plastic J-leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC)
28P6 28-lead, 0.600" Wide, Plastic Dual Inline Package (PDIP)
28S 28-lead, 0.300" Wide, Plastic Gull Wing Small Outline (SOIC)
28T 28-lead, Plastic Thin Small Outline Package (TSOP)
10
AT28BV256
Page 11

Packaging Information
AT28BV256
32J, 32-lead, Plastic J-leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC)
Dimensions in Inches and (Millimeters)
JEDEC STANDARD MS-016 AE
.045(1.14) X 45˚
.032(.813)
.026(.660)
.050(1.27) TYP
PIN NO. 1
IDENTIFY
.553(14.0)
.547(13.9)
.300(7.62) REF
.430(10.9)
.390(9.90)
.453(11.5)
.447(11.4)
.495(12.6)
.485(12.3)
.025(.635) X 30˚ - 45˚
.595(15.1)
.585(14.9)
AT CONTACT
POINTS
.022(.559) X 45˚ MAX (3X)
.012(.305)
.008(.203)
.530(13.5)
.490(12.4)
.021(.533)
.013(.330)
.030(.762)
.015(.381)
.095(2.41)
.060(1.52)
.140(3.56)
.120(3.05)
28P6, 28-lead, 0.600" Wide, Plastic Dual Inline
Package (PDIP)
Dimensions in Inches and (Millimeters)
JEDEC STANDARD MS-011 AB
1.47(37.3)
.220(5.59)
SEATING
PLANE
MAX
.161(4.09)
.125(3.18)
.110(2.79)
.090(2.29)
.012(.305)
.008(.203)
1.44(36.6)
1.300(33.02) REF
.065(1.65)
.041(1.04)
.630(16.0)
.590(15.0)
.690(17.5)
.610(15.5)
PIN
1
.566(14.4)
.530(13.5)
.090(2.29)
.005(.127)
.065(1.65)
.015(.381)
.022(.559)
.014(.356)
0
REF
15
MAX
MIN
28S, 28-lead, 0.300" Wide, Plastic Gull Wing Small
Outline (SOIC)
Dimensions in Inches and (Millimeters)
28T, 28-lead, Plastic Thin Small Outline Package
(TSOP)
Dimensions in Millimeters and (Inches)*
INDEX
MARK
AREA
0.55 (0.022)
BSC
0
REF
5
7.15 (0.281)
REF
8.10 (0.319)
7.90 (0.311)
0.20 (0.008)
0.10 (0.004)
0.70 (0.028)
0.30 (0.012)
11.9 (0.469)
11.7 (0.461)
0.27 (0.011)
0.18 (0.007)
13.7 (0.539)
13.1 (0.516)
1.25 (0.049)
1.05 (0.041)
0.20 (0.008)
0.15 (0.006)
11
Page 12

Atmel Headquarters Atmel Operations
Corporate Headquarters
2325 Orchard Parkway
San Jose, CA 95131
TEL (408) 441-0311
FAX (408) 487-2600
Europe
Atmel U.K., Ltd.
Coliseum Business Centre
Riverside Way
Camberley, Surrey GU15 3YL
England
TEL (44) 1276-686-677
FAX (44) 1276-686-697
Asia
Atmel Asia, Ltd.
Room 1219
Chinachem Golden Plaza
77 Mody Road Tsimhatsui
East Kowloon
Hong Kong
TEL (852) 2721-9778
FAX (852) 2722-1369
Japan
Atmel Japan K.K.
9F, Tonetsu Shinkawa Bldg.
1-24-8 Shinkawa
Chuo-ku, Tokyo 104-0033
Japan
TEL (81) 3-3523-3551
FAX (81) 3-3523-7581
Atmel Colorado Springs
1150 E. Cheyenne Mtn. Blvd.
Colorado Springs, CO 80906
TEL (719) 576-3300
FAX (719) 540-1759
Atmel Rousset
Zone Industrielle
13106 Rousset Cedex
France
TEL (33) 4-4253-6000
FAX (33) 4-4253-6001
Fax-on-Demand
North America:
1-(800) 292-8635
International:
1-(408) 441-0732
e-mail
literature@atmel.com
Web Site
http://www.atmel.com
BBS
1-(408) 436-4309
© Atmel Corporation 1999.
Atmel Corporation makes no warranty for the use of its products, other than those expressly contained in the Company’s standard warranty which is detailed in Atmel’s Terms and Conditions located on the Company’s web site. The Company assumes no responsibility for
any errors which may appear in this document, reserves the right to change devices or specifications detailed herein at any time without
notice, and does not make any commitment to update the information contained herein. No licenses to patents or other intellectual property of Atmel are granted by the Company in connection with the sale of Atmel products, expressly or by implication. Atmel’s products are
not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems.
®
Marks bearing
Terms and product names in this document may be trademarks of others.
and/or ™ are registered trademarks and trademarks of Atmel Corporation.
Printed on recycled paper.
0273G–11/99/xM
 Loading...
Loading...