Page 1
Features
• Write Protect Pin for Hardware Data Protection
– Utilizes Different Array Protection Compared to the AT24C02/04/08/16
• Low-voltage and Standard-voltage Operation
– 2.7 (V
– 1.8 (V
• Internally Organized 256 x 8 (2K), 512 x 8 (4K), 1024 x 8 (8K) or 2048 x 8 (16K)
• 2-wire Serial Interface
• Schmitt Trigger, Filtered Inputs for Noise Suppression
• Bi-directional Data Transfer Protocol
• 100 kHz (1.8V, 2.5V, 2.7V) and 400 kHz (5V) Clock Rate for AT24C02A, 04A and 08A
• 100 kHz (1.8V) and 400 kHz (2.5V, 2.7V and 5V) Clock Rate for AT24C16A
• 8-byte Page (2K), 16-byte Page (4K, 8K, 16K) Write Modes
• Partial Page Writes are Allowed
• Self-timed Write Cycle (10 ms max)
• High Reliability
– Endurance: One Million Write Cycles
– Data Retention: 100 Years
• Automotive Grade and Extended Temperature Devices Available
• 8-lead JEDEC SOIC, 8-pin PDIP, and 8-lead TSSOP Packages
= 2.7V to 5.5V)
CC
= 1.8V to 5.5V)
CC
2-wire Serial
EEPROM
2K (256 x 8)
4K (512 x 8)
8K (1024 x 8)
Description
The AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A provides 2048/4096/8192/16384 bits of serial electrically erasable and programmable read only memory (EEPROM) organized as
256/512/1024/2048 words of 8 bits each. The device is optimized for use in many
industrial and commercial applications where low power and low voltage operation are
essential. The AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A is available in space saving 8-pin PDIP, 8-lead
JEDEC SOIC, and 8-lead TSSOP (AT24C02A/04A) packages and is accessed via a
2-wire serial interface. In addition, the entire family is available in 2.7V (2.7V to 5.5V)
and 1.8V (1.8V to 5.5V) versions.
Pin Configurations
A0
A1
A2
GND
A0
A1
A2
GND
8-pin PDIP
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
8-lead SOIC
1
2
3
4
VCC
WP
SCL
SDA
VCC
8
WP
7
SCL
6
SDA
5
Pin Name Function
A0 - A2 Address Inputs
SDA Serial Data
SCL Serial Clock Input
WP Write Protect
NC No-connect
16K (2048 x 8)
AT24C02A
AT24C04A
AT24C08A
AT24C16A
8-lead TSSOP
1
A0
2
A1
3
A2
4
GND
8
VCC
7
WP
6
SCL
5
SDA
Rev. 0976D–12/01
1
Page 2
Absolute Maximum Ratings*
Operating Temperature.................................. -55°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature ..................................... -65°C to +150°C
Voltage on Any Pin
with Respect to Ground.....................................-1.0V to +7.0V
Maximum Operating Voltage .......................................... 6.25V
DC Output Current........................................................ 5.0 mA
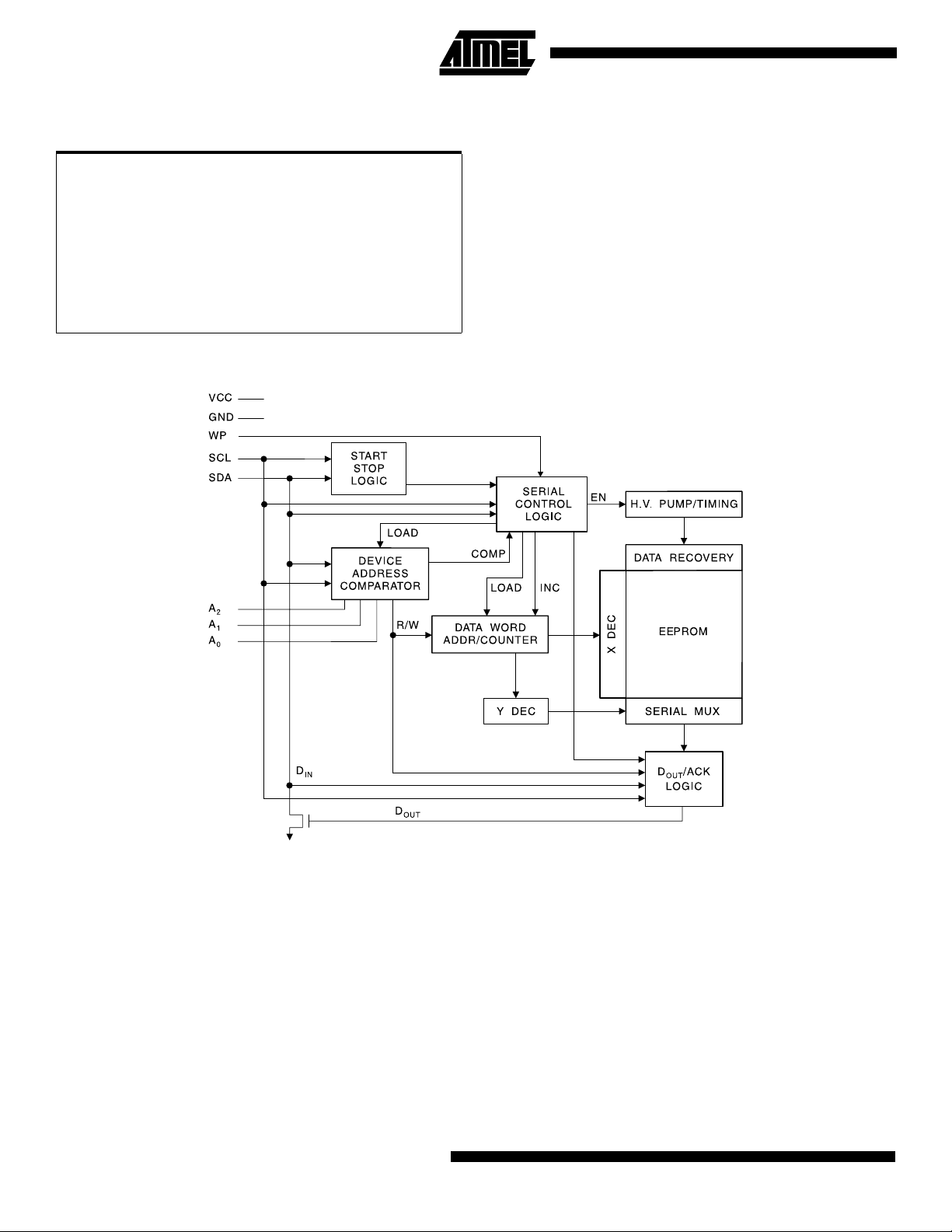
Block Diagram
*NOTICE: Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute
Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and
functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions beyond those indicated in the
operational sections of this specification is not
implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device
reliability.
Pin Description
2
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
SERIAL CLOCK (SCL): The SCL input is used to positive edge clock data into each
EEPROM device and negative edge clock data out of each device.
SERIAL DATA (SDA): The SDA pin is bidirectional for serial data transfer. This pin is
open-drain driven and may be wire-ORed with any number of other open-drain or open
collector devices.
DEVICE/PAGE ADDRESSES (A2, A1, A0): The A2, A1 and A0 pins are device
address inputs that must be hard wired for the AT24C02A. As many as eight 2K devices
may be addressed on a single bus system (device addressing is discussed in detail
under the Device Addressing section).
The AT24C04A uses the A2 and A1 inputs for hard wire addressing and a total of four
4K devices may be addressed on a single bus system. The A0 pin is a no-connect.
0976D–12/01
Page 3
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
The AT24C08A only uses the A2 input for hardwire addressing and a total of two 8K
devices may be addressed on a single bus system. The A0 and A1 pins are noconnects.
The AT24C16A does not use the device address pins, which limits the number of
devices on a single bus to one. The A0, A1 and A2 pins are no-connects.
WRITE PROTECT (WP): The AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A have a Write Protect pin that
provides hardware data protection. The Write Protect pin allows normal read/write operations when connected to ground (GND). When the Write Protect pin is connected to
, the write protection feature is enabled and operates as shown in the following
V
CC
table.
WP Pin
Status
At V
CC
At GND Normal Read/Write Operations
24C02A 24C04A 24C08A 24C16A
Upper Half
(1K) Array
Part of the Array Protected
Upper Half
(2K) Array
Full (8K)
Array
Full (16K)
Array
Memory Organization AT24C02A, 2K SERIAL EEPROM: Internally organized with 32 pages of 8 bytes each,
the 2K requires an 8-bit data word address for random word addressing.
AT24C04A, 4K SERIAL EEPROM: The 4K is internally organized with 32 pages of 16
bytes each. Random word addressing requires a 9-bit data word address.
AT24C08A, 8K SERIAL EEPROM: The 8K is internally organized with 64 pages of 16
bytes each. Random word addressing requires a 10-bit data word address.
AT24C16A, 16K SERIAL EEPROM: The 16K is internally organized with 128 pages of
16 bytes each. Random word addressing requires an 11-bit data word address.
Pin Capacitance
Applicable over recommended operating range from TA = 25°C, f = 1.0 MHz, VCC = +1.8V.
Symbol Test Condition Max Units Conditions
C
I/O
C
IN
Note: 1. This parameter is characterized and is not 100% tested.
Input/Output Capacitance (SDA) 8 pF V
Input Capacitance (A0, A1, A2, SCL) 6 pF VIN = 0V
I/O
= 0V
0976D–12/01
3
Page 4
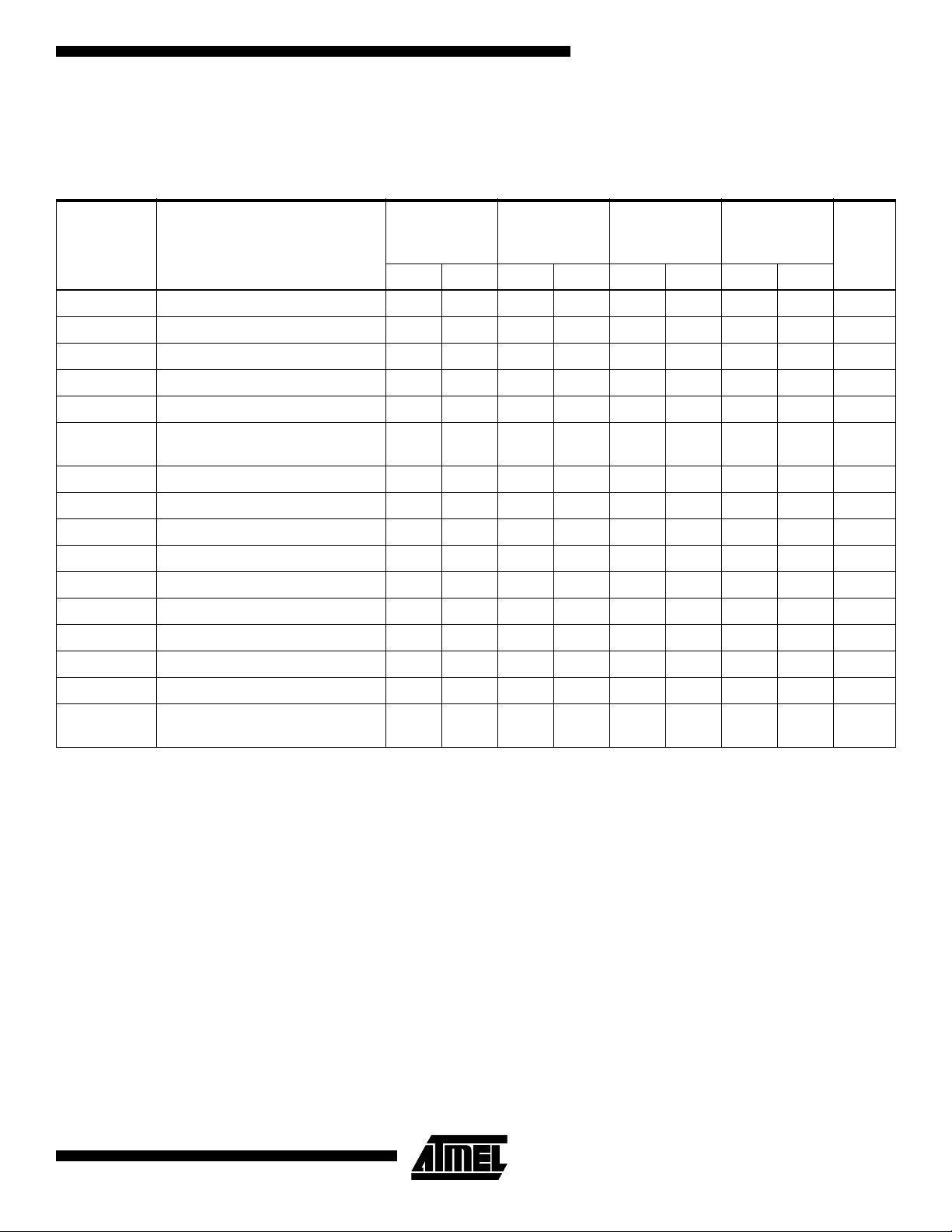
DC Characteristics
Applicable over recommended operating range from: TAI = -40°C to +85°C, VCC = +1.8V to +5.5V, TAC = 0°C to +70°C,
= +1.8V to +5.5V (unless otherwise noted).
V
CC
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min Typ Max Units
V
V
V
V
I
I
I
CC1
CC2
CC3
CC4
CC
CC
SB1
Supply Voltage 1.8 5.5 V
Supply Voltage 2.5 5.5 V
Supply Voltage 2.7 5.5 V
Supply Voltage 4.5 5.5 V
Supply Current VCC = 5.0V READ at 100 kHz 0.4 1.0 mA
Supply Current VCC = 5.0V WRITE at 100 kHz 2.0 3.0 mA
Standby Current VCC =
1.8V
= VCC or V
V
IN
SS
0.6 3.0 µA
I
I
I
I
I
V
V
V
V
SB2
SB3
SB4
LI
LO
OL2
OL1
Standby Current VCC =
2.5V
Standby Current VCC =
2.7V
Standby Current VCC =
5.0V
Input Leakage Current VIN = VCC or V
Output Leakage Current V
IL
IH
Input Low Level
Input High Level
(1)
(1)
Output Low Level VCC =
3.0V
Output Low Level VCC =
1.8V
V
= VCC or V
IN
= VCC or V
V
IN
= VCC or V
V
IN
= V
OUT
= 2.1 mA 0.4 V
I
OL
I
= 0.15 mA 0.2 V
OL
CC
or V
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
Note: 1. VIL min and VIH max are reference only and are not tested.
1.4 4.0 µA
1.6 4.0 µA
8.0 18.0 µA
0.10 3.0 µA
0.05 3.0 µA
-0.6 VCC x 0.3 V
VCC x 0.7 VCC + 0.5 V
4
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
0976D–12/01
Page 5
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
AC Characteristics
Applicable over recommended operating range from TA = -40°C to +85°C, VCC = +1.8V to +5.5V, CL = 1 TTL Gate and
100 pF (unless otherwise noted).
Symbol Parameter
f
SCL
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
I
t
AA
t
BUF
t
HD.STA
t
SU.STA
t
HD.DAT
t
SU.DAT
t
R
t
F
t
SU.STO
t
DH
t
WR
Endurance
Clock Frequency, SCL 100 100 400 400 kHz
Clock Pulse Width Low 4.7 4.7 1.3 1.2 µs
Clock Pulse Width High 4.0 4.0 0.6 0.6 µs
Noise Suppression Time
Clock Low to Data Out Valid 0.1 4.5 0.1 4.5 0.2 0.9 0.1 0.9 µs
Time the bus must be free before
a new transmission can start
Start Hold Time 4.0 4.0 0.6 0.6 µs
Start Set-up Time 4.7 4.7 0.6 0.6 µs
Data In Hold Time 0 0 0 0 µs
Data In Set-up Time 200 200 100 100 ns
Inputs Rise Time
Inputs Fall Time
Stop Set-up Time 4.7 4.7 0.6 0.6 µs
Data Out Hold Time 100 100 100 50 ns
Write Cycle Time 10 10 10 10 ms
(2)
5.0V, 25°C, Page Mode 1M 1M 1M 1M
AT24C02A/
04A/08A/16A
1.8V
AT2402A/04A/
08A
2.5V, 2.7V
AT24C16A
2.5V
AT24C02A/
04A/08A/16A
5.0V
UnitsMin Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
(1)
(2)
(2)
(2)
4.74.71.31.2 µs
100 100 100 50 ns
1.0 1.0 0.3 0.3 µs
300 300 300 300 ns
Write
Cycles
Notes: 1. This parameter is characterized and is not 100% tested (TA = 25°C).
2. This parameter is characterized and is not 100% tested.
0976D–12/01
5
Page 6

Device Operation CLOCK and DATA TRANSITIONS: The SDA pin is normally pulled high with an exter-
nal device. Data on the SDA pin may change only during SCL low time periods (refer to
Data Validity timing diagram). Data changes during SCL high periods will indicate a start
or stop condition as defined below.
START CONDITION: A high-to-low transition of SDA with SCL high is a start condition
which must precede any other command (refer to Start and Stop Definition timing
diagram).
STOP CONDITION: A low-to-high transition of SDA with SCL high is a stop condition.
After a read sequence, the stop command will place the EEPROM in a standby power
mode (refer to Start and Stop Definition timing diagram).
ACKNOWLEDGE: All addresses and data words are serially transmitted to and from
the EEPROM in 8 bit words
received each word. This happens during the ninth clock cycle.
STANDBY MODE: The AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A features a low power standby mode
which is enabled: (a) upon power-up and (b) after the receipt of the STOP bit and the
completion of any internal operations.
MEMORY RESET: After an interruption in protocol, power loss or system reset, any 2wire part can be reset by following these steps: (a) Clock up to 9 cycles, (b) look for SDA
high in each cycle while SCL is high and then (c) create a start condition as SDA is high.
.
The EEPROM sends a zero to acknowledge that it has
6
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
0976D–12/01
Page 7

AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
Bus Timing (SCL: Serial Clock, SDA: Serial Data I/O)
Write Cycle Timing (SCL: Serial Clock, SDA: Serial Data I/O)
SCL
SDA 8th BIT
WORD n
Note: 1. The write cycle time tWR is the time from a valid stop condition of a write sequence to the end of the interval
clear/write cycle.
ACK
STOP
CONDITION
(1)
t
WR
START
CONDITION
0976D–12/01
7
Page 8

Data Validity
Start and Stop Definition
Output Acknowledge
8
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
0976D–12/01
Page 9

AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
Device Addressing The 2K, 4K and 8K EEPROM devices all require an 8 bit device address word following
a start condition to enable the chip for a read or write operation (refer to Figure 1).
The device address word consists of a mandatory one, zero sequence for the first four
most significant bits as shown. This is common to all the EEPROM devices.
The next 3 bits are the A2, A1 and A0 device address bits for the 2K EEPROM. These 3
bits must compare to their corresponding hard-wired input pins.
The 4K EEPROM only uses the A2 and A1 device address bits with the third bit being a
memory page address bit. The two device address bits must compare to their corresponding hard-wired input pins. The A0 pin is no-connect.
The 8K EEPROM only uses the A2 device address bit with the next 2 bits being for
memory page addressing. The A2 bit must compare to its corresponding hard-wired
input pin. The A1 and A0 pins are no-connect.
The 16K EEPROM does not use the device address pins, which limits the number of
devices on a single bus to one. The A0, A1 and A2 pins are no-connects.
The eighth bit of the device address is the read/write operation select bit. A read operation is initiated if this bit is high and a write operation is initiated if this bit is low.
Upon a compare of the device address, the EEPROM will output a zero. If a compare is
not made, the chip will return to a standby state.
Write Operations BYTE WRITE: A write operation requires an 8 bit data word address following the
device address word and acknowledgement. Upon receipt of this address, the EEPROM
will again respond with a zero and then clock in the first 8 bit data word. Following
receipt of the 8 bit data word, the EEPROM will output a zero and the addressing
device, such as a microcontroller, must terminate the write sequence with a stop condition. At this time the
nonvolatile memory. All inputs are disabled during this write cycle and the EEPROM will
not respond until the write is complete (refer to Figure 2).
PAGE WRITE: The 2K EEPROM is capable of an 8-byte page write, and the 4K, 8K and
16K devices are capable of 16-byte page writes.
A page write is initiated the same as a byte write, but the microcontroller does not send
a stop condition after the first data word is clocked in. Instead, after the EEPROM
acknowledges receipt of the first data word, the microcontroller can transmit up to seven
(2K) or fifteen (4K, 8K, 16K) more data words. The EEPROM will respond with a zero
after each data word received. The microcontroller must terminate the page write
sequence with a stop condition (refer to Figure 3).
The data word address lower three (2K) or four (4K, 8K, 16K) bits are internally incremented following the receipt of each data word. The higher data word address bits are
not incremented, retaining the memory page row location. When the word address,
internally generated, reaches the page boundary, the following byte is placed at the
beginning of the same page. If more than eight (2K) or sixteen (4K, 8K, 16K) data words
are transmitted to the EEPROM, the data word address will “roll over” and previous data
will be overwritten.
EEPROM enters an internally-timed write cycle, tWR, to the
0976D–12/01
ACKNOWLEDGE POLLING: Once the internally-timed write cycle has started and the
EEPROM inputs are disabled, acknowledge polling can be initiated. This involves sending a start condition followed by the device address word. The read/write bit is
representative of the operation desired. Only if the internal write cycle has completed
will the EEPROM respond with a zero allowing the read or write sequence to continue.
9
Page 10

Read Operations Read operations are initiated the same way as write operations with the exception that
the read/write select bit in the device address word is set to one. There are three read
operations: current address read, random address read and sequential read.
CURRENT ADDRESS READ: The internal data word address counter maintains the
last address accessed during the last read or write operation, incremented by one. This
address stays valid between operations as long as the chip power is maintained. The
address “roll over” during read is from the last byte of the last memory page to the first
byte of the first page. The address “roll over” during write is from the last byte of the current page to the first byte of the same page.
Once the device address with the read/write select bit set to one is clocked in and
acknowledged by the EEPROM, the current address data word is serially clocked out.
The microcontroller does not respond with an input zero but does generate a following
stop condition (refer to Figure 4).
RANDOM READ: A random read requires a “dummy” byte write sequence to load in the
data word address. Once the device address word and data word address are clocked
in and acknowledged by the EEPROM, the microcontroller must generate another start
condition. The microcontroller now initiates a current address read by sending a device
address with the read/write select bit high. The EEPROM acknowledges the device
address and serially clocks out the data word. The microcontroller does not respond
with a zero but does generate a following stop condition (refer to Figure 5).
SEQUENTIAL READ: Sequential reads are initiated by either a current address read or
a random address read. After the microcontroller receives a data word, it responds with
an acknowledge. As long as the EEPROM receives an acknowledge, it will continue to
increment the data word address and serially clock out sequential data words. When the
memory address limit is reached, the data word address will “roll over” and the sequential read will continue. The sequential read operation is terminated when the
microcontroller does not respond with a zero but does generate a following stop condition (refer to Figure 6).
Figure 1. Device Address
2K
4K
16K
A
A
A
0
1
MSB
0
1
0
001
1P2P0
0
1
1
18K 1
2
A
A
0
2
A
0
P
2
P1
R/W
0
1
LSB
R/W
P0
1
R/W
1
P0
R/W
10
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
0976D–12/01
Page 11

Figure 2. Byte Write
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
SDA LINE
Figure 3. Page Write
S
T
A
R
DEVICE
T
ADDRESS
SDA LINE
M
S
B
L
S
B
Figure 4. Current Address Read
S
T
A
R
DEVICE
T
ADDRESS
M
S
B
W
R
I
T
E
WORD ADDRESS (n) DATA (n) DATA (n + 1) DATA (n + x)
A
R
/
C
K
W
S
T
A
R
T
W
R
I
T
E
L
A
R
/
S
C
W
B
K
A
C
K
DEVICE
ADDRESS
WORD ADDRESS
M
S
B
R
E
A
D
L
S
B
S
T
O
DATA
A
C
K
A
C
K
S
T
O
P
P
A
C
K
A
C
K
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
SDA LINE
M
S
B
R
L
A
/
S
C
B
K
W
DATA
N
O
A
C
K
0976D–12/01
11
Page 12

Figure 5. Random Read
S
T
A
R
T
SDA LINE
Figure 6. Sequential Read
DEVICE
ADDRESS
M
S
B
W
R
I
T
E
R
L
A
M
/
S
C
B
W
DUMMY WRITE
S
K
B
WORD
ADDRESS n
S
T
DEVICE
A
R
ADDRESS
T
L
A
M
S
C
B
S
K
B
R
E
A
D
A
L
C
S
K
B
DATA n
S
T
O
P
N
O
A
C
K
12
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
0976D–12/01
Page 13

AT24C02A Ordering Information
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
tWR (max)
(ms)
10 1500 4 100 AT24C02A-10PI-2.7
10 800 3 100 AT24C02A-10PI-1.8
ICC (max)
(µA)
ISB (max)
(µA)
f
MAX
(kHz) Ordering Code Package Operation Range
AT24C02AN-10SI-2.7
AT24C02A-10TI-2.7
AT24C02AN-10SI-1.8
AT24C02A-10TI-1.8
8P3
8S1
8T
8P3
8S1
8T
Industrial
(-40°C to 85°C)
Industrial
(-40°C to 85°C)
Package Type
8P3 8-pin, 0.300" Wide, Plastic Dual Inline Package (PDIP)
8S1 8-lead, 0.150" Wide, Plastic Gull Wing Small Outline (JEDEC SOIC)
8T 8-lead, 0.170" Wide, Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP)
Options
-2.7 Low Voltage (2.7V to 5.5V)
-1.8 Low Voltage (1.8V to 5.5V)
0976D–12/01
13
Page 14

AT24C04A Ordering Information
tWR (max)
(ms)
10 1500 4 100 AT24C04A-10PI-2.7
10 800 3 100 AT24C04A-10PI-1.8
ICC (max)
(µA)
ISB (max)
(µA)
f
MAX
(kHz) Ordering Code Package Operation Range
AT24C04AN-10SI-2.7
AT24C04A-10TI-2.7
AT24C04AN-10SI-1.8
AT24C04A-10TI-1.8
8P3
8S1
8T
8P3
8S1
8T
Industrial
(-40°C to 85°C)
Industrial
(-40°C to 85°C)
Package Type
8P3 8-pin, 0.300" Wide, Plastic Dual Inline Package (PDIP)
8S1 8-lead, 0.150" Wide, Plastic Gull Wing Small Outline (JEDEC SOIC)
8T 8-lead, 0.170" Wide, Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP)
Options
-2.7 Low Voltage (2.7V to 5.5V)
-1.8 Low Voltage (1.8V to 5.5V)
14
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
0976D–12/01
Page 15

AT24C08A Ordering Information
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
tWR (max)
(ms)
10 1500 4 100 AT24C08A-10PI-2.7
10 800 3 100 AT24C08A-10PI-1.8
ICC (max)
(µA)
ISB (max)
(µA)
f
MAX
(kHz) Ordering Code Package Operation Range
AT24C08AN-10SI-2.7
AT24C08AN-10SI-1.8
8P3
8S1
8P3
8S1
Industrial
(-40°C to 85°C)
Industrial
(-40°C to 85°C)
Package Type
8P3 8-pin, 0.300" Wide, Plastic Dual Inline Package (PDIP)
8S1 8-lead, 0.150" Wide, Plastic Gull Wing Small Outline (JEDEC SOIC)
Options
-2.7 Low Voltage (2.7V to 5.5V)
-1.8 Low Voltage (1.8V to 5.5V)
0976D–12/01
15
Page 16

AT24C16A Ordering Information
tWR (max)
(ms)
10 1500 4 400 AT24C16A-10PI-2.7
10 800 3 100 AT24C16A-10PI-1.8
ICC (max)
(µA)
ISB (max)
(µA)
f
MAX
(kHz) Ordering Code Package Operation Range
AT24C16AN-10SI-2.7
AT24C16AN-10SI-1.8
8P3
8S1
8P3
8S1
Industrial
(-40°C to 85°C)
Industrial
(-40°C to 85°C)
Package Type
8P3 8-pin, 0.300" Wide, Plastic Dual Inline Package (PDIP)
8S1 8-lead, 0.150" Wide, Plastic Gull Wing Small Outline (JEDEC SOIC)
Options
-2.7 Low Voltage (2.7V to 5.5V)
-1.8 Low Voltage (1.8V to 5.5V)
16
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
0976D–12/01
Page 17

Packaging Information
PIN
1
E1
A1
B
E
B1
C
L
SEATING PLANE
A
8P3 – PDIP
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
D
e
B2
(4 PLACES)
eC
eB
Notes: 1. This package conforms to JEDEC reference MS-001 BA.
2. Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold Flash or Protrusion.
Mold Flash or Protrusion shall not exceed 0.25 mm (0.010").
2325 Orchard Parkway
R
San Jose, CA 95131
TITLE
8P3, 8-lead (0.300"/7.62 mm Wide) Plastic Dual
Inline Package (PDIP)
COMMON DIMENSIONS
(Unit of Measure = mm)
SYMBOL
A – – 4.318
A1 0.381 – –
D 9.144 – 9.652 Note 2
E 7.620 – 8.255
E1 6.096 – 6.604 Note 2
B 0.406 – 0.508
B1 1.397 – 1.651
B2 0.762 – 1.143
L 3.175 – 3.429
C 0.203 – 0.356
eB – – 10.922
eC 0.000 – 1.524
e 2.540 TYP
MIN
NOM
MAX
DRAWING NO.
8P3
NOTE
09/28/01
REV.
B
0976D–12/01
17
Page 18

8S1 – JEDEC SOIC
Top View
1
2
3
H
N
A2
L
e
D
Side View
E
End View
B
A
COMMON DIMENSIONS
(Unit of Measure = mm)
SYMBOL
A ––1.75
B ––0.51
C
C ––0.25
D ––5.00
E ––4.00
e 1.27 BSC
H ––6.20
L ––1.27
MIN
NOM
MAX
NOTE
18
Note:
These drawings are for general information only. Refer to JEDEC Drawing MS-012 for proper dimensions, tolerances, datums, etc.
TITLE
1150 E. Cheyenne Mtn. Blvd.
R
Colorado Springs, CO 80906
8S1, 8-lead (0.150" Wide Body), Plastic Gull Wing
Small Outline (JEDEC SOIC)
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
DRAWING NO.
8S1 A
10/10/01
REV.
0976D–12/01
Page 19

8T– TSSOP
AT24C02A/04A/08A/16A
Top View
123
E1
N
E
Side View
b
e
D
End View
L
L1
A2
COMMON DIMENSIONS
(Unit of Measure = mm)
SYMBOL
A
D 2.90 3.00 3.10 2, 5
E 6.40 BSC
E1 4.30 4.40 4.50 3, 5
A ––1.20
A2 0.80 1.00 1.05
b 0.19 – 0.30 4
e 0.65 BSC
L 0.45 0.60 0.75
L1 1.00 REF
MIN
NOM
MAX
NOTE
Notes:
1. These drawings are for general information only. Refer to JEDEC Drawing MO-153, Variation AA, for proper dimensions, tolerances, datums, etc.
2. Dimension "D" does not include mold Flash, protrusions or gate burrs. Mold Flash, protrusions and gate burrs shall not exceed 0.15 mm (0.006 in) per side.
3. Dimension "E1" does not include inter-lead Flash or protrusions. Inter-lead Flash and protrusions shall not exceed 0.25 mm (0.010 in) per side.
4. Dimension "b" does not include Dambar protrusion. Allowable Dambar protrusion shall be 0.08 mm total in excess of the "b" dimension at maximum
5. Dimension "D" and "E1" to be determined at Datum Plane H.
0976D–12/01
material condition. Dambar cannot be located on the lower radius of the foot. Minimum space between protrusion and adjacent lead is 0.07 mm.
1150 E. Cheyenne Mtn. Blvd.
R
Colorado Springs, CO 80906
TITLE
8T, 8-lead, 4.4 mm Body, Plastic
Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP)
DRAWING NO.
8T
10/26/01
REV.
A
19
Page 20

Atmel Headquarters Atmel Product Operations
Corporate Headquarters
2325 Orchard Parkway
San Jose, CA 95131
TEL (408) 441-0311
FAX (408) 487-2600
Europe
Atmel SarL
Route des Arsenaux 41
Casa Postale 80
CH-1705 Fribourg
Switzerland
TEL (41) 26-426-5555
FAX (41) 26-426-5500
Asia
Atmel Asia, Ltd.
Room 1219
Chinachem Golden Plaza
77 Mody Road Tsimhatsui
East Kowloon
Hong Kong
TEL (852) 2721-9778
FAX (852) 2722-1369
Japan
Atmel Japan K.K.
9F, Tonetsu Shinkawa Bldg.
1-24-8 Shinkawa
Chuo-ku, Tokyo 104-0033
Japan
TEL (81) 3-3523-3551
FAX (81) 3-3523-7581
Atmel Colorado Springs
1150 E. Cheyenne Mtn. Blvd.
Colorado Springs, CO 80906
TEL (719) 576-3300
FAX (719) 540-1759
Atmel Grenoble
Avenue de Rochepleine
BP 123
38521 Saint-Egreve Cedex, France
TEL (33) 4-7658-3000
FAX (33) 4-7658-3480
Atmel Heilbronn
Theresienstrasse 2
POB 3535
D-74025 Heilbronn, Germany
TEL (49) 71 31 67 25 94
FAX (49) 71 31 67 24 23
Atmel Nantes
La Chantrerie
BP 70602
44306 Nantes Cedex 3, France
TEL (33) 0 2 40 18 18 18
FAX (33) 0 2 40 18 19 60
Atmel Rousset
Zone Industrielle
13106 Rousset Cedex, France
TEL (33) 4-4253-6000
FAX (33) 4-4253-6001
Atmel Smart Card ICs
Scottish Enterprise Technology Park
East Kilbride, Scotland G75 0QR
TEL (44) 1355-357-000
FAX (44) 1355-242-743
e-mail
literature@atmel.com
Web Site
http://www.atmel.com
© Atmel Corporation 2001.
Atmel Corporation makes no warranty for the use of its products, other than those expressly contained in the Company’s standard warranty
which is detailed in Atmel’s Terms and Conditions located on the Company’s web site. The Company assumes no responsibility for any errors
which may appear in this document, reserves the right to change devices or specifications detailed herein at any time without notice, and does
not make any commitment to update the information contained herein. No licenses to patents or other intellectual property of Atmel are granted
by the Company in connection with the sale of Atmel products, expressly or by implication. Atmel’s products are not authorized for use as critical
components in life support devices or systems.
AT ME L® is the registered trademark of Atmel.
Other terms and product names may be the trademarks of others.
Printed on recycled paper.
0976D–12/01/0M
 Loading...
Loading...