Page 1
December 1994
ADC12451 Dynamically-Tested Self-Calibrating
12-Bit Plus Sign A/D Converter with Sample-and-Hold
Y
General Description
The ADC12451 is a CMOS 12-bit plus sign successive approximation analog-to-digital converter whose dynamic
specifications (S/N, THD, etc.) are tested and guaranteed.
On request, the ADC12451 goes through a self-calibration
cycle that adjusts linearity, zero and full-scale errors. The
ADC12451 also has the ability to go through an Auto-Zero
cycle that corrects the zero error during every conversion.
The analog input to the ADC12451 is tracked and held by
the internal circuitry, so an external sample-and-hold is not
required. The ADC12451 has a S
rectly controls the track-and-hold state of the A/D. A unipolar analog input voltage range (0V to
b
range (
5V toa5V) can be accommodated withg5V sup-
/H control input which di-
a
5V) or a bipolar
plies.
The 13-bit data result is available on the eight outputs of the
ADC12451 in two bytes, high-byte first and sign extended.
The digital inputs and outputs are compatible with TTL or
CMOS logic levels.
Applications
Y
Digital Signal Processing
Y
Audio
Telecommunications
Y
High Resolution Process Control
Y
Instrumentation
Features
Y
Self-calibration provides excellent temperature stability
Y
Internal sample-and-hold
Y
8-bit mP/DSP interface
Y
Bipolar input range with a singlea5V reference
Key Specifications
Y
Resolution 12 bits plus sign
Y
Conversion Time 7.7 ms (max)
Y
Sampling Rate 83 kHz (max)
Y
Bipolar Signal/Noise 73.5 dB (min)
Y
Total Harmonic Distortion
Y
Aperture Time 100 ns
Y
Aperture Jitter 100 ps
Y
Zero Error
Y
Positive Full-Scale Error
Y
Power Consumption
@
g
5V 113 mW (max)
b
78.0 dB (max)
g
2 LSB (max)
g
1.5 LSB (max)
ADC12451 Dynamically-Tested Self-Calibrating 12-Bit
Plus Sign A/D Converter with Sample-and-Hold
rms
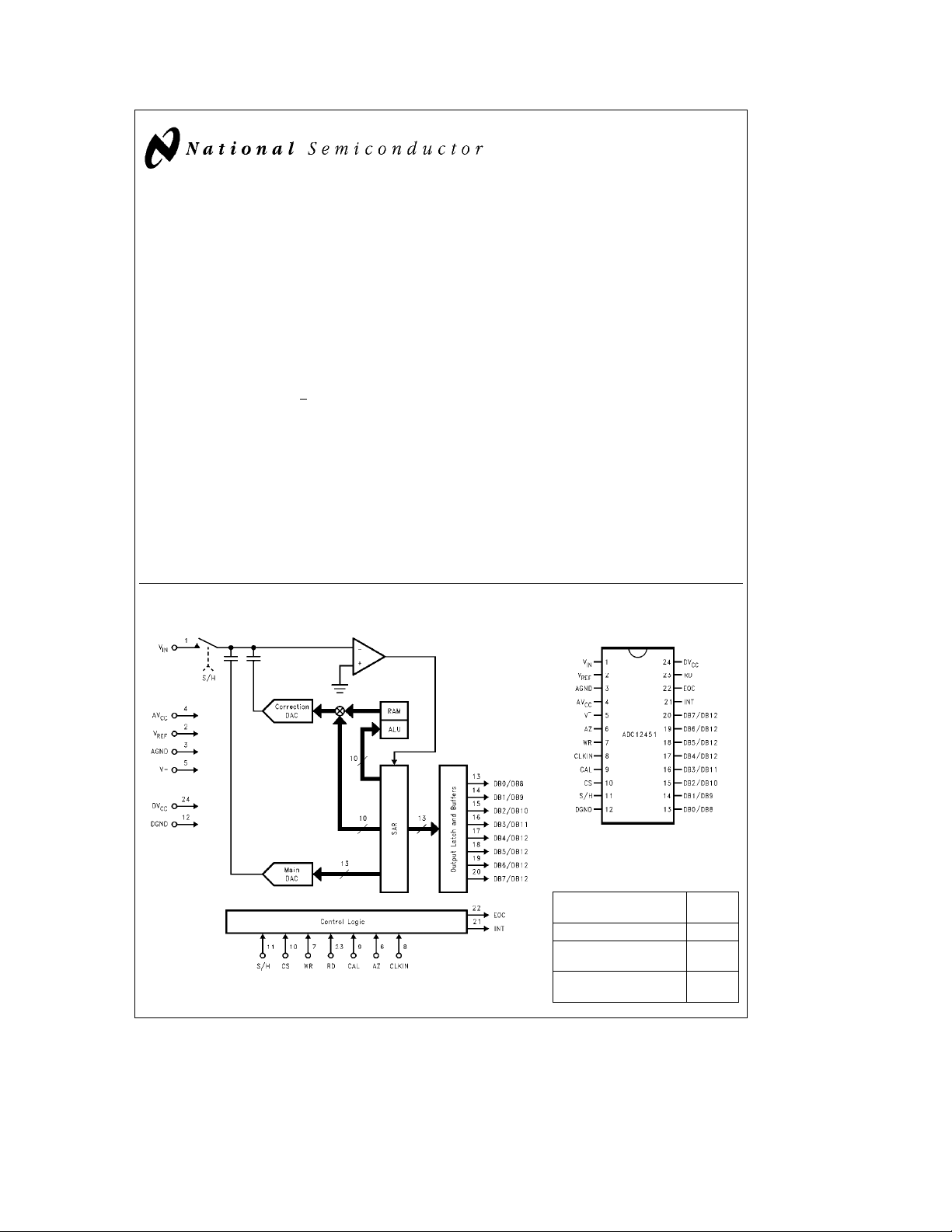
Simplified Block Diagram
Connection Diagram
Dual-In-Line Package
Top View
TL/H/11025– 2
Ordering Information
Industrial
b
(
40§CsT
s
A
ADC12451CIJ J24A
Military
TL/H/11025– 1
b
(
55§CsT
s
A
ADC12451CMJ,
TRI-STATEÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M115/Printed in U. S. A.
TL/H/11025
ADC12451CMJ/883
85§C)
125§C)
Package
Package
J24A
Page 2
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Notes1&2)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales
Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
Negative Supply Voltage (Vb)
Voltage at Logic Control Inputs
Voltage at Analog Inputs
(V
IN,VREF
AVCC-DVCC(Note 7) 0.3V
Input Current at any Pin (Note 3)
Package Input Current (Note 3)
Power Dissipation at 25
Storage Temperature Range
ESD Susceptability (Note 5) 2000V
Soldering Information
J Package (10 Seconds) 300
e
e
DV
CC
)(V
AVCC) 6.5V
CC
b
0.3V to (V
b
b
0.3V) to (V
C (Note 4) 875 mW
§
b
65§Ctoa150§C
CC
CC
b
a
a
g
g
6.5V
0.3V)
0.3V)
5mA
20 mA
§
Operating Ratings (Notes1&2)
Temperature Range T
ADC12451CIJ
ADC12451CMJ,
ADC12451CMJ/883
DVCCand AVCCVoltage
(Notes6&7) 4.5V to 5.5V
Negative Supply Voltage (V
Reference Voltage
(V
, Notes6&7) 3.5V to AV
REF
C
s
s
T
MIN
b
40§CsT
b
55§CsT
b
)
b
T
A
MAX
s
a
85§C
A
s
a
125§C
A
4.5V tob5.5V
a
50 mV
CC
Converter Electrical Characteristics
The following specifications apply for V
conversion control, and f
other limits T
e
T
A
J
e
3.5 MHz unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
CLK
e
25§C. (Notes 6, 7 and 8)
CC
e
e
DV
AV
CC
CC
ea
5.0V, V
b
Symbol Parameter Conditions
STATIC CHARACTERISTICS
Positive Integral Linearity Error After Auto-Cal, (Notes 11 & 12)
Negative Integral Linearity Error After Auto-Cal, (Notes 11 & 12)
Positive or Negative Differential Linearity After Auto-Cal (Notes 11 & 12) 12 Bits
Zero Error (Notes 12 & 13) AZe‘‘0’’, f
CLK
e
After Auto-Cal Only
Positive Full-Scale Error (Note 12) AZe‘‘0’’, f
CLK
e
Auto-Cal Only
Negative Full-Scale Error (Note 12) AZe‘‘0’’, f
CLK
e
Auto-Cal Only
V
Analog Input Voltage V
IN
e
Power Supply Sensitivity Zero Error (Note 14) AV
Full-Scale Error
V
CC
REF
e
4.75V, V
DV
CC
e
5Vg5%,
b
Linearity Error
C
REFVREF
C
IN
Input Capacitance 80 pF
Analog Input Capacitance 65 pF
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
Bipolar Effective Bits (Note 17) f
Unipolar Effective Bits (Note 17) f
S/N Bipolar Signal to Noise Ratio (Note 17) f
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
1 kHz, V
20.67 kHz, V
1 kHz, V
20.67 kHz, V
1 kHz, V
10 kHz, V
20.67 kHz, V
e
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
IN
eb
5.0V, V
REF
ea
5.0V, using S/H input for
e
e
T
A
T
J
MIN
to T
Typical Limit Units
(Note 9) (Note 10, 19) (Limit)
g
(/2 LSB
g
(/2 LSB
1.75 MHz
1.75 MHz
1.75 MHz
eb
5Vg5%
g
4.85V 12.6 Bits
e
g
4.85V 12.6 11.9 Bits(min)
IN
4.85 V
p-p
e
4.85 V
IN
g
4.85V 78 dB
g
4.85V 78 dB
e
g
4.85V 78 73.5 dB(min)
IN
g
1 LSB
g2/g
g
1 LSB
g
1.5/g2.5 LSB(max)
g
1 LSB
g
1.5/g3.0 LSB(max)
b
b
0.05 V(min)
a
V
CC
g
(/8 LSB
g
(/8 LSB
g
(/8 LSB
11.8 Bits
11.8 11.1 Bits(min)
p-p
3.0 LSB(max)
0.05 V(max)
MAX
; all
2
Page 3

Converter Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
The following specifications apply for V
conversion control, and f
other limits T
e
T
A
J
e
3.5 MHz unless otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
CLK
e
25§C. (Notes 6, 7 and 8)
CC
e
e
AV
CC
ea
DV
CC
5.0V, V
b
eb
Symbol Parameter Conditions
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
S/N Unipolar Signal to Noise Ratio (Note 17) f
THD Bipolar Total Harmonic Distortion (Note 17) f
THD Unipolar Total Harmonic Distortion (Note 17) f
Bipolar Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise f
(Note 17)
Unipolar Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise f
(Note 17)
Bipolar Two Tone Intermodulation Distortion V
(Note 17) f
Unipolar Two Tone Intermodulation Distortion V
(Note 17) f
b
3 dB Bipolar Full Power Bandwidth V
b
3 dB Unipolar Full Power Bandwidth V
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
f
IN
e
f
IN
e
IN
e
IN2
e
IN
e
IN2
e
IN
e
IN
1 kHz, V
10 kHz, V
20.67 kHz, V
1 kHz, V
20.67 kHz, V
1 kHz, V
20.67 kHz, V
1 kHz, V
10 kHz, V
20 kHz, V
1 kHz, V
10 kHz, V
20 kHz, V
g
20 kHz
4.85 V
20 kHz
g
4.85 V
e
4.85 V
IN
e
IN
IN
e
g
IN
IN
e
4.85 V
IN
IN
e
g
IN
e
IN
e
IN
e
4.85 V
IN
e
IN
e
IN
4.85V, f
IN1
p-p,fIN1
4.85V, (Note 17) 25 20.67 kHz(min)
, (Note 17) 32 20.67 kHz(min)
p-p
Aperture Time 100 ns
Aperture Jitter 100 ps
5.0V, V
p-p
4.85 V
e
4.85 V
4.85V
e
g
4.85V
p-p
e
4.85 V
4.85V
g
4.85V
g
4.85V
p-p
4.85 V
4.85 V
e
19.375 kHz,
e
19.375 kHz,
p-p
p-p
p-p
ea
REF
5.0V, using S/H input for
e
e
T
A
T
J
MIN
Typical Limit Units
(Note 9) (Note 10, 19) (Limit)
73 dB
73 dB
p-p
p-p
73 68.7 dB(min)
b
82 dB
b
b
b
b
b
b
b
b
b
b
b
b
80
78.0 dB(max)
82 dB
b
80
73.1 dB(max)
88 dB
84 dB
80 dB
90 dB
86 dB
82 dB
78
78
to T
MAX
dB(max)
dB(max)
; all
rms
3
Page 4
Digital and DC Electrical Characteristics
The following specifications apply for DV
otherwise specified. Boldface limits apply for T
CC
e
ea
AV
A
CC
5.0V, V
e
e
T
T
J
MIN
Symbol Parameter Condition
V
IN(1)
V
IN(0)
I
IN(1)
I
IN(0)
a
V
T
b
V
T
V
H
V
OUT(1)
V
OUT(0)
I
OUT
I
SOURCE
I
SINK
DI
CC
AI
CC
b
I
Logical ‘‘1’’ Input Voltage for V
All Inputs except CLK IN
Logical ‘‘0’’ Input Voltage for V
All Inputs except CLK IN
Logical ‘‘1’’ Input Current V
Logical ‘‘0’’ Input Current V
CLK IN Positive-Going
Threshold Voltage
CLK IN Negative-Going
Threshold Voltage
CLK IN Hysteresis
[
V
a
(min)bV
T
b
]
(max)
T
Logical ‘‘1’’ Output Voltage V
Logical ‘‘0’’ Output Voltage V
TRI-STATEÉOutput Leakage V
Current
Output Source Current V
Output Sink Current V
DVCCSupply Current CSe‘‘1’’ 1 2.5 mA(max)
AVCCSupply Current CSe‘‘1’’ 2.8 10 mA(max)
VbSupply Current CSe‘‘1’’ 2.8 10 mA(max)
e
5.25V
CC
e
4.75V
CC
e
5V 0.005 1 mA(max)
IN
e
0V
IN
e
4.75V:
CC
eb
I
OUT
eb
I
OUT
e
4.75V,
CC
e
I
1.6 mA
OUT
e
0V
OUT
e
V
5V 0.01 3 mA(max)
OUT
e
0V
OUT
e
5V 20 8.0 mA(min)
OUT
b
to T
eb
MAX
5.0V, V
; all other limits T
REF
ea
5.0V, and f
e
T
A
J
e
3.5 MHz unless
CLK
e
25§C. (Notes 6 and 7)
Typical Limit Units
(Note 9) (Note 10, 19) (Limit)
2.0 V(min)
0.8 V(max)
b
0.005
b
1 mA(max)
2.8 2.7 V(min)
2.1 2.3 V(max)
0.7 0.4 V(min)
360 mA 2.4 V(min)
10 mA 4.5 V(min)
0.4 V(max)
b
0.01
b
20
b
3 mA(max)
b
6.0 mA(min)
AC Electrical Characteristics
The following specifications apply for DV
Boldface limits apply for T
e
T
A
J
e
CC
e
T
MIN
to T
AV
CC
MAX
ea
; all other limits T
Symbol Parameter Conditions
f
CLK
Clock Frequency MHz
Clock Duty Cycle 50 %
t
C
t
C
Conversion Time using WR 27(1/f
to start a Conversion
e
f
3.5 MHz, AZe‘‘1’’ 7.7 7.95 ms(max)
CLK
e
f
1.75 MHz, AZe‘‘0’’ 15.4 15.65 ms(max)
CLK
Conversion Time using S/H AZe‘‘1’’ 34(1/f
to start a Conversion
e
f
3.5 MHz, AZe‘‘1’’ 9.7 9.95 ms(max)
CLK
5.0V, V
4
b
eb
e
A
e
5.0V, t
T
t
r
f
e
25§C. (Notes 6 and 7)
J
e
20 ns unless otherwise specified.
Typical Limit Units
(Note 9) (Note 10, 19) (Limit)
0.5 MHz(min)
6.0 3.5 MHz(max)
40 %(min)
60 %(max)
) 27(1/f
CLK
) 34(1/f
CLK
)a250 ns (max)
CLK
)a250 ns (max)
CLK
Page 5

AC Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
The following specifications apply for DV
Boldface limits apply for T
e
T
A
J
e
CC
e
T
MIN
to T
AV
CC
MAX
ea
; all other limits T
Symbol Parameter Conditions
t
A
t
IA
t
ZA
t
D(EOC)L
t
CAL
t
W(CAL)L
t
W(WR)L
t
ACC
t0H,t
t
PD(INT)
t
RR
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The guaranteed
specifications apply only for the test conditions listed. Some performance characteristics may degrade when the device is not operated under the listed test
conditions.
Note 2: All voltages are measured with respect to AGND and DGND, unless otherwise specified.
Note 3: When the input voltage (V
5 mA. The 20 mA maximum package input current rating allows the voltage at any four pins, with an input current limit of 5 mA, to simultaneously exceed the power
supply voltages.
Note 4: The power dissipation of this device under normal operation should never exceed 191 mW (Quiescent Power Dissipation
output). Caution should be taken not to exceed absolute maximum power rating when the device is operating in a severe fault condition (ex. when any inputs or
outputs exceed the power supply). The maximum power dissipation must be derated at elevated temperatures and is dictated by T
temperature), i
is P
resistance (i
Note 5: Human body model, 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 kX resistor.
Note 6: Two on-chip diodes are tied to the analog input as shown below. Errors in the A/D conversion can occur if these diodes are forward biased more than
50 mV. This means that if AV
Acquisition Time R
(Note 15)
SOURCE
Internal Acquisition Time
(when using WR
Auto Zero Time
Acquisition Time
Control Only)
a
f
CLK
e
Delay from Hold Command Using WR Control 200 350 ns(max)
to Falling Edge of EOC
Using S/H Control 100 150 ns(max)
Calibration Time 1399 (1/f
e
f
CLK
Calibration Pulse Width (Note 16) 60 200 ns(min)
minimum WR Pulse Width 60 200 ns(min)
maximum Access Time C
(Delay from Falling Edge of 50 95 ns(max)
RD
to Output Data Valid)
TRI-STATE Control (Delay R
1H
from Rising Edge of RD C
to Hi-Z State)
e
100 pF
L
e
1kX,
L
e
100 pF 30 70 ns(max)
L
maximum Delay from Falling Edge
of RD
or WR to Reset of INT
Delay between Successive RD Pulses 30 60 ns(min)
) at any pin exceeds the power supply rails (V
IN
(package junction to ambient thermal resistance), and TA(ambient temperature). The maximum allowable power dissipation at any temperature
JA
e
b
(T
DMax
TA)/iJAor the number given in the Absolute Maximum Ratings, whichever is lower. For this device, T
JMax
) of the ADC12451 with CMJ, and CIJ suffixes when board mounted is 51§C/W.
JA
and DVCCare minimum (4.75 VDC) and Vbis maximum (b4.75 VDC), the analog input full-scale voltage must be
CC
b
5.0V, V
eb
e
A
e
5.0V, t
T
t
r
f
e
25§C. (Notes 6 and 7)
J
e
20 ns unless otherwise specified.
Typical Limit Units
(Note 9) (Note 10, 19) (Limit)
e
50X
3.5 3.5 ms(min)
7(1/f
) 7(1/f
33(1/f
CLK
) 33(1/f
CLK
CLK)
)a250 ns (max)
CLK
(max)
1.75 MHz 18.8 19.05 ms(max)
) 1399 (1/f
CLK
) (max)
CLK
3.5 MHz 399 400 ms(max)
100 175 ns(max)
k
IN
Vbor V
l
(AVCCor DVCC), the current at that pin should be limited to
IN
a
1 TTL Load on each digital
(maximum junction
JMax
e
150§C, and the typical thermal
JMax
s
g
4.8 VDC.
TL/H/11025– 4
5
Page 6
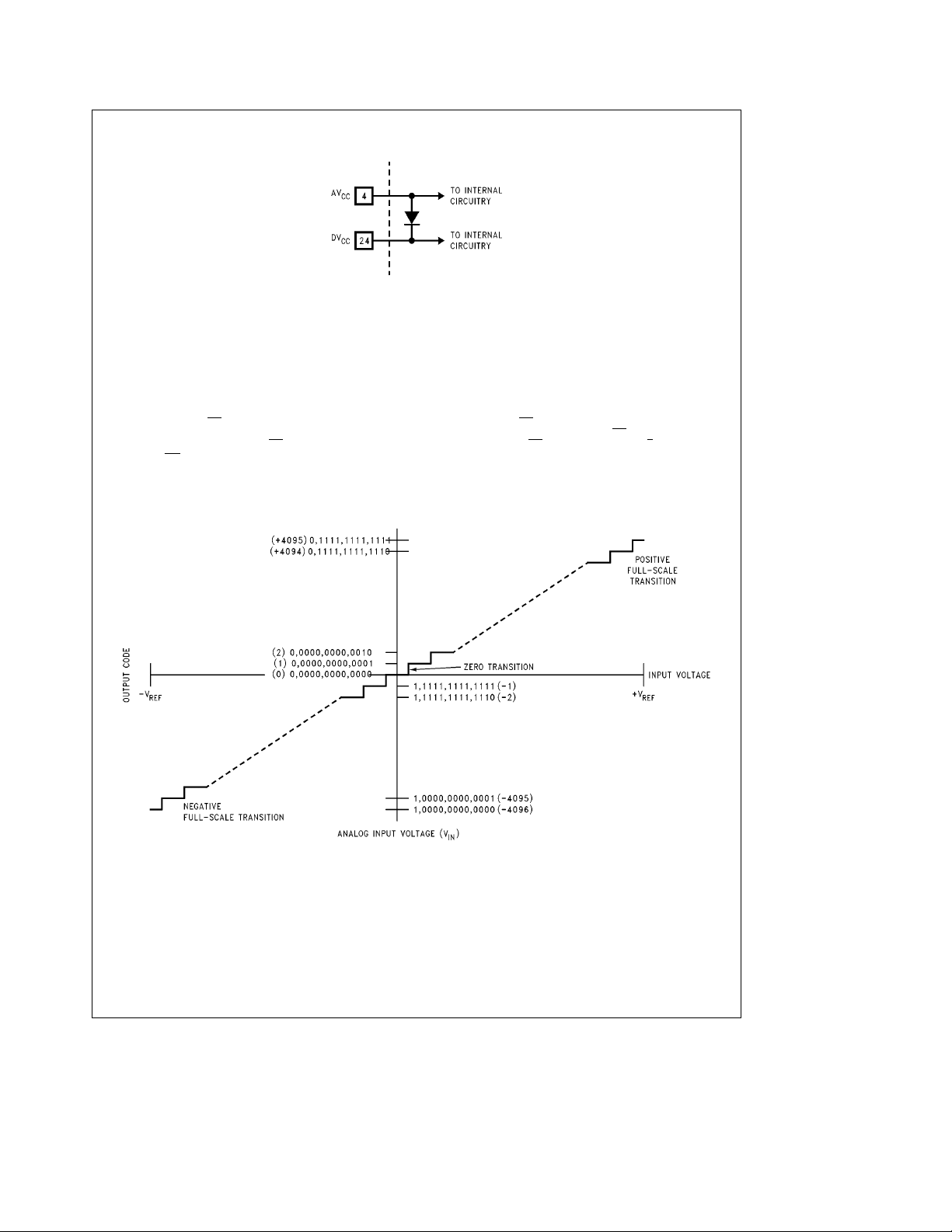
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Note 7: A diode exists between AVCCand DVCCas shown below.
Figures 1b
TL/H/11025– 5
and1c).
To guarantee accuracy, it is required that the AVCCand DVCCbe connected together to a power supply with separate bypass filters at each VCCpin.
Note 8: Accuracy is guaranteed at f
Note 9: Typicals are at T
Note 10: Limits are guaranteed to National’s AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
Note 11: Positive linearity error is defined as the deviation of the analog value, expressed in LSBs, from the straight line that passes through positive full scale and
zero. For negative linearity error the straight line passes through negative full scale and zero. (See
Note 12: The ADC12451’s self-calibration technique ensures linearity, full scale, and offset errors as specified, but noise inherent in the self-calibration process will
result in a repeatability uncertainty of
Note 13: If T
Note 14: After an Auto-Zero or Auto-Cal cycle at the specified power supply extremes.
Note 15: When using the WR
end of the interval of t
clock is synchronous to the rising edge of WR
Note 16: The CAL
Note 17: The specifications for these parameters are valid after an Auto-Cal cycle has been completed.
Note 18: The ADC12451 reference ladder is composed solely of capacitors.
Note 19: A military RETS electrical test specification is available on request. At time of printing, the ADC12451CMJ/883 RETS specification complies fully with the
boldface limits in this column.
A
J
changes then an Auto-Zero or Auto-Cal cycle will have to be re-started, see the typical performance characteristic curves.
, therefore making tAend a minimum 6 clock periods or a maximum 7 clock periods after the rising edge of WR. If the falling edge of the
A
line must be high before a conversion is started.
e
3.5 MHz. At higher or lower clock frequencies accuracy may degrade, see the typical performance characteristic curves.
CLK
e
25§C and represent most likely parametric norm.
g
0.20 LSB.
control to start a conversion if the clock is asynchronous to the rising edge of WR an uncertainty of one clock period will exist in the
then tAwill end exactly 6.5 clock periods after the rising edge of WR. This does not occur when S/H control is used.
FIGURE 1a. Transfer Characteristic
6
TL/H/11025– 6
Page 7

Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
FIGURE 1b. Simplified Error Curve vs Output Code without Auto-Cal or Auto-Zero Cycles
FIGURE 1c. Simplified Error Curve vs Output Code after Auto-Cal Cycle
Typical Performance Characteristics
Zero Error Change vs
Ambient Temperature
Zero Error vs V
REF
TL/H/11025– 7
TL/H/11025– 8
Linearity Error vs V
REF
TL/H/11025– 9
7
Page 8

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Linearity Error vs
Clock Frequency
Full Scale Error Change vs
Ambient Temperature
Bipolar Signal-to-
a
Distortion Ratio vs
Noise
Input Source Impedance
Bipolar Signal-to-
a
Distortion Ratio vs
Noise
Input Frequency
Bipolar Signal-to-
a
Distortion Ratio vs
Noise
Input Signal Level
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 20 kHz Sine Wave Input
Unipolar Signal-to-
a
Distortion Ratio vs
Noise
Input Frequency
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 1 kHz Sine Wave Input
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 40 kHz Sine Wave Input
Unipolar Signal-to-
a
Distortion Ratio vs
Noise
Input Signal Level
Bipolar Spectral Response
with 10 kHz Sine Wave Input
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 1 kHz Sine Wave Input
TL/H/11025– 10
8
Page 9

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 10 kHz Sine Wave Input
Test Circuits
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 20 kHz Sine Wave Input
TL/H/11025– 12
Unipolar Spectral Response
with 40 kHz Sine Wave Input
TL/H/11025– 11
TL/H/11025– 13
FIGURE 2. TRI-STATE Test Circuits and Waveforms
TL/H/11025– 14
9
TL/H/11025– 15
Page 10

Timing Diagrams
Using WR Control to Start a Conversion with Auto-Zero (CALe1, AZe0)
Auto-Cal Cycle
TL/H/11025– 16
TL/H/11025– 17
10
Page 11

Timing Diagrams (Continued)
Using WR
Control to Start a Conversion without Auto-Zero (CAL 1, AZe1)
Using S/H Control to Start a Conversion without Auto-Zero (AZe1, CALe1)
TL/H/11025– 18
TL/H/11025– 19
11
Page 12

1.0 Pin Descriptions
DVCC(24),
AV
CC
b
(5) The analog negative supply voltage pin. V
V
DGND (12), The digital and analog ground pins. AGND
AGND (3) and DGND must be connected together ex-
V
REF
VIN(1) The analog input voltage pin. To guarantee
CS (10) The Chip Select control input. This input is
RD
(23) The Read control input. With both CS and RD
WR (7) The Write control input. The conversion is
S
/H (11) The sample and hold control input. This con-
CLKIN (8) The external clock input pin. The typical clock
CAL
AZ
(6) The Auto-Zero control input. With the AZ pin
The digital and analog positive power supply
(4)
pins. The digital and analog power supply
voltage range of the ADC12451 isa4.5V to
a
5.5V. To guarantee accuracy, it is required
that the AV
gether to the same power supply with sepa-
and DVCCbe connected to-
CC
rate bypass capacitors (10 mF tantalum in
parallel with a 0.1 mF ceramic) at each V
pin.
CC
has a range ofb4.5V tob5.5V and needs
bypass capacitors of 10 mF tantalum in parallel with a 0.1 mF ceramic.
ternally to guarantee accuracy.
(2) The reference input voltage pin. To maintain
accuracy the voltage at this pin should not
exceed the AV
50 mV or go below
or DVCCby more than
CC
a
3.5 VDC.
accuracy the voltage at this pin should not
exceed V
b
V
active low and enables the WR
by more than 50 mV or go below
CC
by more than 50 mV.
,RDand S/H
functions.
low the TRI-STATE output buffers are enabled and the INT
started on the rising edge of the WR
when CS
output is reset high.
pulse
is low. When this control line is
used the end of the analog input voltage acquisition window is internally controlled by the
ADC12451.
trol input can also be used to start a conversion. With CS
low the falling edge of S/H
starts the analog input acquisition window.
The rising edge of S
/H ends the acquisition
window and starts a conversion.
frequency range is 500 kHz to 6.0 MHz.
(9) The Auto-Calibration control input. When
CAL
is low the ADC12451 is reset and a calibration cycle is initiated. During the calibration cycle the values of the comparator offset
voltage and the mismatch errors in the capacitor reference ladder are determined and
stored in RAM. These values are used to correct the errors during a normal cycle of A/D
conversion.
held low during a conversion, the ADC12451
goes into an auto-zero cycle before the actual A/D conversion is started. This Auto-Zero
cycle corrects for the comparator offset voltage. The total conversion time (t
creased by 26 clock periods when Auto-Zero
)isin-
C
is used.
EOC (22) The End-of-Conversion control output. This
output is low during a conversion or a calibration cycle.
INT
(21) The Interrupt control output. This output goes
low when a conversion has been completed
and indicates that the conversion result is
available in the output latches. Reading the result or starting a conversion or calibration cycle will reset this output high.
b
DB0/DB8 - The TRI-STATE output pins. Twelve bit plus
DB7/DB12
(13–20)
sign output data access is accomplished using
two successive RD
s of one byte each, high
byte first (DB8 –DB12). The data format used
is two’s complement sign bit extended with
DB12 the sign bit, DB11 the MSB and DB0 the
LSB.
2.0 Functional Description
The ADC12451 is a 12-bit plus sign A/D converter with the
capability of doing Auto-Zero or Auto-Calibration routines to
minimize zero, full-scale and linearity errors. It is a successive-approximation A/D converter consisting of a DAC,
comparator and a successive-approximation register (SAR).
Auto-Zero is an internal calibration sequence that corrects
for the A/D’s zero error caused by the comparator’s offset
voltage. Auto-Cal is a calibration cycle that not only corrects
zero error but also corrects for full-scale and linearity errors
caused by DAC inaccuracies. Auto-Cal minimizes the errors
of the ADC12451 without the need of trimming during its
fabrication. An Auto-Cal cycle can restore the accuracy of
the ADC12451 at any time, which ensures accuracy over
temperature and time.
2.1 DIGITAL INTERFACE
On power up, a calibration sequence should be initiated by
pulsing CAL
CAL
remains low during the calibration cycle of 1399 clock periods. During the calibration sequence, first the comparator’s
offset is determined, then the capacitive DAC’s mismatch
error is found. Correction factors for these errors are then
stored in internal RAM.
A conversion is initiated by taking CS
low an Auto-Zero cycle, which takes approximately 26 clock
periods, is inserted before the analog input is sampled and
the actual conversion is started. AZ
the complete conversion sequence. After Auto-Zero the acquisition opens and the analog input is sampled for appproximately 7 clock periods. If AZ
not inserted after the rising edge of WR
acquisition window opens when the ADC12451 completes a
conversion, signaled by the rising edge of EOC. At the end
of the acquisition window EOC goes low, signaling that the
analog input is no longer being sampled and that the A/D
successive approximation conversion has started.
low with CS and S/H high. To acknowledge the
signal, EOC goes low after the falling edge of CAL, and
must remain low during
is high, the Auto-Zero cycle is
and WR low. If AZ is
. In this case the
12
Page 13

2.0 Functional Description (Continued)
A conversion sequence can also be controlled by the S
and CS
inputs. Taking CS and S/H low starts the acquisition
window for the analog input voltage. The rising edge of S
immediately puts the A/D in the hold mode and starts the
conversion. Using S
the acquisition window to other signals, which may be necessary in a DSP environment.
During a conversion, the sampled input voltage is successively compared to the output of the DAC. First, the acquired input voltage is compared to analog ground to determine its polarity. The sign bit is set low for positive input
voltages and high for negative. Next the MSB of the DAC is
set high with the rest of the bits low. If the input voltage is
greater than the output of the DAC, then the MSB is left
high; otherwise it is set low. The next bit is set high, making
the output of the DAC three quarters or one quarter of full
scale. A comparison is done and if the input is greater than
the new DAC value this bit remains high; if the input is less
than the new DAC value the bit is set low. This process
continues until each bit has been tested. The result is then
stored in the output latch of the ADC12451. Next INT
low, and EOC goes high to signal the end of the conversion.
The result can now be read by taking CS
enable the DB0/DB8 –DB7/DB12 output buffers. The high
byte of data is relayed first on the data bus outputs as
shown below:
DB0/ DB1/ DB2/ DB3/ DB4/ DB5/ DB6/ DB7/
DB8 DB9 DB10 DB11 DB12 DB12 DB12 DB12
Bit 8 Bit 9 Bit 10 MSB Sign Bit Sign Bit Sign Bit Sign Bit
Taking CS and RD low a second time will relay the low byte
of data on the data bus outputs as shown below:
DB0/ DB1/ DB2/ DB3/ DB4/ DB5/ DB6/ DB7/
DB8 DB9 DB10 DB11 DB12 DB12 DB12 DB12
LSB Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7
The table in
control inputs on the function of the ADC12451. The Test
Mode, where RD
low, is used during manufacture to thoroughly check out
/H will simplify synchronizing the end of
and RD low to
Figure 3
summarizes the effect of the digital
and S/H are high and CS and CAL are
/H
/H
goes
the operation of the ADC12451. Care should be taken not to
inadvertently be in this mode, since DB2, DB3, DB5, and
DB6 become active outputs, which may cause data bus
contention.
2.2 RESETTING THE A/D
The ADC12451 is reset whenever a new conversion is started by taking CS
analog input is being sampled or when EOC is low, the
Auto-Cal correction factors may be corrupted, therefore requiring an Auto-Cal cycle before the next conversion. When
using WR
conversion, a new conversion can be restarted only after
EOC has gone high signaling the end of the current conversion. When using WR
version can be restarted during the first 26 clock periods
after the rising edge of WR
high without corrupting the Auto-Cal correction factors.
The Calibration Cycle cannot be reset once started. On
power-up the ADC12451 automatically goes through a Calibration Cycle that takes typically 1399 clock cycles. For reasons that will be discussed in Section 3.8, a new calibration
cycle needs to be started after the completion of the automatic one.
and WR or S/H low. If this is done when the
or S/H without Auto-Zero (AZe1) to start a
with Auto-Zero (AZe0) a new con-
(tZ) or after EOC has returned
3.0 Analog Considerations
3.1 REFERENCE VOLTAGE
The voltage applied to the reference input of the converter
defines the voltage span of the analog input (the difference
between V
codes and 4096 negative output codes exist. The A-to-D
can be used in either ratiometric or absolute reference applications. The voltage source driving V
very low output impedance and very low noise. The circuit in
Figure 4a
appropriate for use with the ADC12451. The simple reference circuit of
does not require a low full-scale error.
and AGND), over which 4095 positive output
IN
must have a
REF
is an example of a very stable reference that is
Figure 4b
may be used when the application
Digital Control Inputs
CS WR S/H RD CAL AZ
ßß 1 1 1 1 Start Conversion without Auto-Zero
ß 1 ß 1 1 1 Start Conversion synchronous with rising edge of S
ß 11ß1 1 Read Conversion Result without Auto-Zero
ßß 1 1 1 0 Start Conversion with Auto-Zero
ß 11ß1 0 Read Conversion Result with Auto-Zero
1X1XßX Start Calibration Cycle
0 X X 1 0 X Test Mode (DB2, DB3, DB5, and DB6 become active)
FIGURE 3. Function of the A/D Control Inputs
13
A/D Function
/H without Auto-Zero
Page 14

3.0 Analog Considerations (Continued)
FIGURE 4a. Low Drift Extremely Stable Reference Circuit
In a ratiometric system, the analog input voltage is proportional to the voltage used for the A/D reference. When this
voltage is the system power supply, the V
tied to V
of the system reference as the analog input and A/D refer-
. This technique relaxes the stability requirement
CC
ence move together maintaining the same output code for a
given input condition.
For absolute accuracy, where the analog input varies between very specific voltage limits, the reference pin can be
biased with a time and temperature stable voltage source.
In general, the magnitude of the reference voltage will require an initial adjustment to null out full-scale errors.
3.2 ACQUISITION WINDOW
As shown in the timing diagrams there are three different
methods of starting a conversion, each of which affects the
acquisition window and timing.
With Auto-Zero high a conversion can be started with the
WR
or S/H controls. In either method of starting a conversion the rising edge of EOC signals the actual beginning of
the acquisition window. At this time a voltage spike may be
noticed on the analog input of the ADC12451 whose amplitude is dependent on the input voltage and the source resistance. The timing diagrams for these two methods of
starting a conversion do not show the acquisition window
starting at this time because the acquisition time (t
start after the conversion result high and low bytes have
been read. This is necessary since activating and deactivating the digital outputs (DB0/DB7 –DB8/DB12) causes current fluctuations in the ADC12451’s internal DV
This generates digital noise which couples into the capacitive ladder that stores the analog input voltage. Therefore,
the time interval between the rising edge of EOC and the
second read is inappropriate for analog input voltage acquisition.
When WR
is used to start a conversion with AZ low the
Auto-Zero cycle is inserted before the acquisition window. In
REF
pin can be
) must
A
lines.
CC
Errors without any trims:
25
C
§
g
0.075%
g
0.024%
g
(/2 LSB
TL/H/11025– 20
Full Scale
Zero
Linearity
FIGURE 4b. Simple Reference Circuit
this method the acquisition window is internally controlled
by the ADC12451 and lasts for approximately 7 clock periods. Since the acquisition window needs to be at least
3.5 ms at all times, when using Auto-Zero the maximum
clock frequency is limited to 2 MHz. The zero error with the
Auto-Zero cycle is production tested at a clock frequency of
1.75 MHz. This accommodates easy switching between a
conversion with the Auto-Zero cycle (f
without (f
e
3.5 MHz) as shown in
CLK
CLK
Figure 5
FIGURE 5. Switching between a Conversion with and
without Auto-Zero when Using WR
3.3 INPUT CURRENT
Because the input network of the ADC12451 is made up of
a switch and a network of capacitors a charging current will
flow into or out of (depending on the input voltage polarity)
of the analog input pin (V
sampling period. The peak value of this current will depend
) on the start of the analog input
IN
on the actual input voltage applied and the source resistance.
3.4 NOISE
The leads to the analog input pin should be kept as short as
possible to minimize input noise coupling. Both noise and
undesired digital clock coupling to this input can cause errors. Input filtering can be used to reduce the effects of
these noise sources.
TL/H/11025– 21
b
40§Ctoa85§C
g
0.2%
g
0.024%
g
(/2 LSB
e
1.75 MHz) and
.
TL/H/11025– 22
Control
14
Page 15

3.0 Analog Considerations (Continued)
3.5 INPUT BYPASS CAPACITORS
An external capacitor can be used to filter out any noise due
to inductive pickup by a long input lead and will not degrade
the accuracy of the conversion result.
3.6 INPUT SOURCE RESISTANCE
The analog input can be modeled as shown in
External R
voltage on C
input voltage. With t
analog input voltage to settle properly.
will lengthen the time period necessary for the
S
to settle to within (/2 LSB of the analog
REF
A
e
3.5 ms, R
s
1kXwill allow a 5V
S
3.7 POWER SUPPLIES
Noise spikes on the V
conversion errors as the comparator will respond to this
and Vbsupply lines can cause
CC
noise. The A/D is especially sensitive during the Auto-Zero
or -Cal procedures to any power supply spikes. Low inductance tantalum capacitors of 10 mF or greater paralleled
with 0.1 mF ceramic capacitors are recommended for supply
bypassing. Separate bypass capacitors should be placed
close to the DV
voltage source is available in the system, a separate
,AVCCand Vbpins. If an unregulated
CC
LM340LAZ-5.0 voltage regulator for the A-to-D’s V
other analog circuitry) will greatly reduce digital noise on the
supply line.
3.8 THE CALIBRATION CYCLE
On power up the ADC12451 goes through an Auto-Cal cycle which cannot be interrupted. Since the power supply,
reference, and clock will not be stable at power up, this first
calibration cycle will not result in an accurate calibration of
the A/D. A new calibration cycle needs to be started after
the power supplies, reference, and clock have been given
enough time to stabilize. During the calibration cycle, correction values are determined for the offset voltage of the
sampled data comparator and any linearity and gain errors.
These values are stored in internal RAM and used during an
analog-to-digital conversion to bring the overall full-scale,
offset, and linearity errors down to the specified limits. Fullscale error typically changes
g
0.2 LSB over temperature
and linearity error changes even less; therefore it should be
necessary to go through the calibration cycle only once after power up if Auto-Zero is used to correct the zero error
Figure 6
(and
CC
change. Since Auto-Zero cannot be activated with S
version method it may be necessary to do a calibration cycle more than once.
3.9 THE AUTO-ZERO CYCLE
To correct for any change in the zero (offset) error of the
A/D, the auto-zero cycle can be used. It may be necessary
.
to do an auto-zero cycle whenever the ambient temperature
changes significantly. (See the curve titled ‘‘Zero Error
Change vs Ambient Temperature’’ in the Typical Performance Characteristics.) A change in the ambient temperature
will cause the V
change, which may cause the zero error of the A/D to be
greater than
tain the zero error to
of the sampled data comparator to
OS
g
1 LSB. An auto-zero cycle will typically main-
g
1 LSB or less.
4.0 Dynamic Performance
Many applications require the A/D converter to digitize ac
signals, but the standard dc integral and differential nonlinearity specifications will not accurately predict the A/D converter’s performance with ac input signals. The important
specifications for ac applications reflect the converter’s ability to digitize ac signals without significant spectral errors
and without adding noise to the digitized signal. Dynamic
characteristics such as signal-to-noise (S/N), signal-to-
a
noise
distortion ratio (S/(NaD)), effective bits, full power
bandwidth, aperture time and aperture jitter are quantitative
measures of the A/D converter’s capability.
An A/D converter’s ac performance can be measured using
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) methods. A sinusoidal waveform is applied to the A/D converter’s input, and the transform is then performed on the digitized waveform. S/(N
and S/N are calculated from the resulting FFT data, and a
spectral plot may also be obtained. Typical values for S/N
are shown in the table of Electrical Characteristics, and
spectral plots of S/(N
formance curves.
The A/D converter’s noise and distortion levels will change
with the frequency of the input signal, with more distortion
and noise occurring at higher signal frequencies. This can
be seen in the S/(N
curves will also give an indication of the full power bandwidth (the frequency at which the S/(N
3 dB).
a
D) are included in the typical per-
a
D) versus frequency curves. These
/H con-
a
D) or S/N drops
a
D)
FIGURE 6. Analog Input Equivalent Circuit
15
TL/H/11025– 23
Page 16

4.0 Dynamic Performance (Continued)
Effective number of bits can also be useful in describing the
A/D’s noise performance. An ideal A/D converter will have
some amount of quantization noise, determined by its resolution, which will yield an optimum S/N ratio given by the
following equation:
where n is the A/D’s resolution in bits.
The effective bits of a real A/D converter, therefore, can be
found by:
As an example, an ADC12451 with ag5V, 10 kHz sine
wave input signal will typically have a S/N of 78 dB, which is
equivalent to 12.6 effective bits.
e
S/N
(6.02cna1.8) dB
n(effective)
S/N(dB)b1.8
e
6.02
5.0 Typical Applications
Power Supply Bypassing
Two sample/hold specifications, aperture time and aperture
jitter, are included in the Dynamic Characteristics table
since the ADC12451 has the ability to track and hold the
analog input voltage. Aperture time is the delay for the A/D
to respond to the hold command. In the case of the
ADC12451, the hold command is internally generated.
When the Auto-Zero function is not being used, the hold
command occurs at the end of the acquisition window, or
seven clock periods after the rising edge of the WR
delay between the internally generated hold command and
the time that the ADC12451 actually holds the input signal is
the aperture time. For the ADC12451, this time is typically
100 ns. Aperture jitter is the change in the aperture time
from sample to sample. Aperture jitter is useful in determining the maximum slew rate of the input signal for a given
accuracy. For example, an ADC12451 with 100 ps of aperture jitter operating with a 5V reference can have an effective gain variation of about 1 LSB with an input signal whose
slew rate is 12 V/ms.
. The
Protecting the Analog Inputs
TL/H/11025– 25
Note: External protection diodes should be able to withstand the op amp current limit.
16
TL/H/11025– 24
Page 17

17
Page 18

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters)
Order Number ADC12451CMJ, ADC12451CMJ/883 or ADC12451CIJ
NS Package Number J24A
Plus Sign A/D Converter with Sample-and-Hold
ADC12451 Dynamically-Tested Self-Calibrating 12-Bit
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF NATIONAL
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or 2. A critical component is any component of a life
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant support device or system whose failure to perform can
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and whose be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life
failure to perform, when properly used in accordance support device or system, or to affect its safety or
with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can effectiveness.
be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury
to the user.
National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor National Semiconductor
Corporation Europe Hong Kong Ltd. Japan Ltd.
1111 West Bardin Road Fax: (
Arlington, TX 76017 Email: cnjwge@tevm2.nsc.com Ocean Centre, 5 Canton Rd. Fax: 81-043-299-2408
Tel: 1(800) 272-9959 Deutsch Tel: (
Fax: 1(800) 737-7018 English Tel: (
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
Fran3ais Tel: (
Italiano Tel: (
a
49) 0-180-530 85 86 13th Floor, Straight Block, Tel: 81-043-299-2309
a
49) 0-180-530 85 85 Tsimshatsui, Kowloon
a
49) 0-180-532 78 32 Hong Kong
a
49) 0-180-532 93 58 Tel: (852) 2737-1600
a
49) 0-180-534 16 80 Fax: (852) 2736-9960
 Loading...
Loading...