Page 1
Chapter 5
Diagnostics and
Troubleshooting
This chapter describes the WinLink 1000 diagnostic functions, which
include:
• Get Link Information
• Monitoring Performance
• Error detection and alarms including Link Compatibility
• Diagnostic tests (local and remote loopbacks on E1 or T1 link)
• Troubleshooting
• Frequently asked questions.
5.1 Automatic Link Data Collection (Get Link
Information)
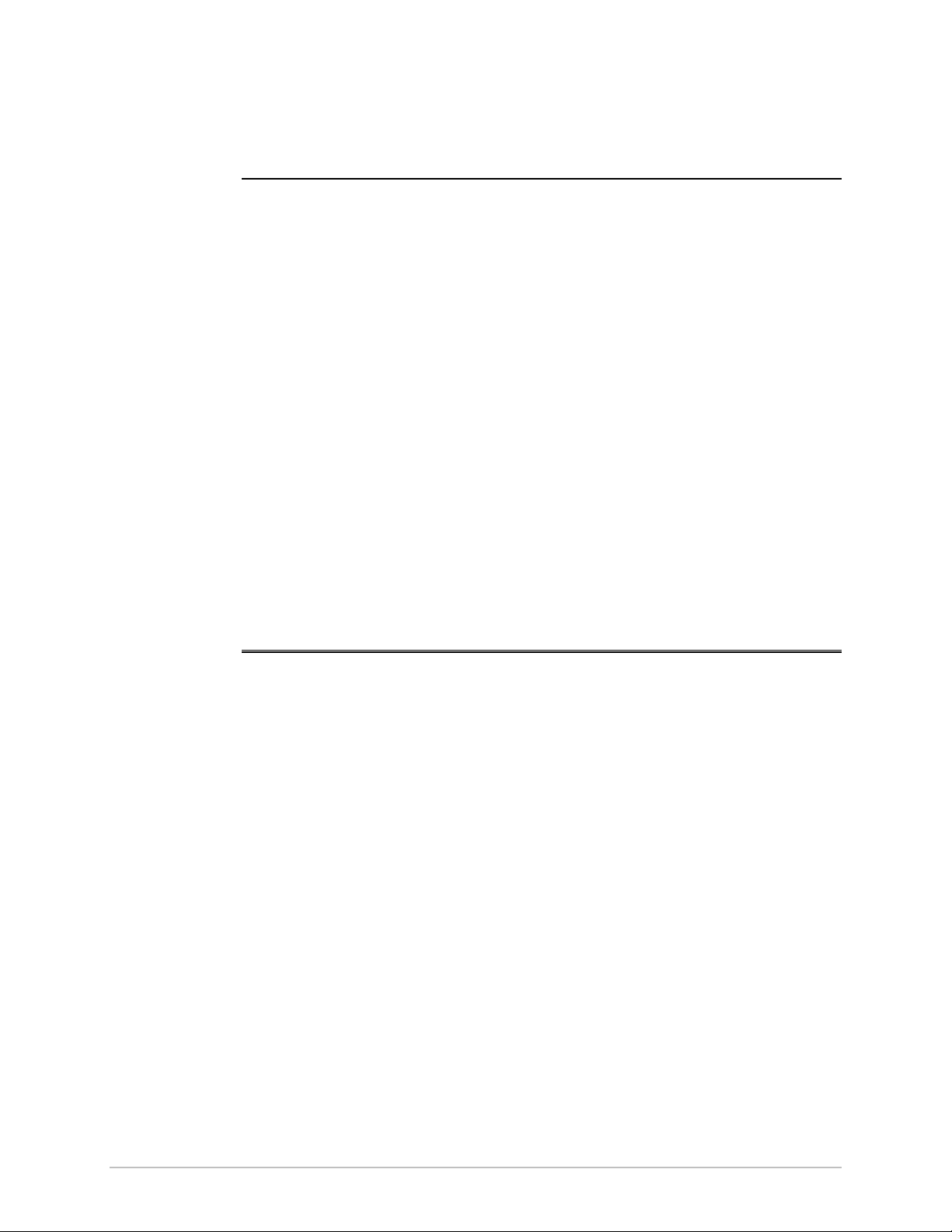
The Get Link Information feature collects all the link and Manager
information which can be used for diagnostics.
In the event of needing to contact technical support please send this
file so as to speed up the assistance.
Æ
To get link information
1. Click Help on the menu bar, select Link Information.
The Get Link Information dialog box appears. See
2. Select or deselect the data options. If the file is to be sent to
Technical Support leave all options checked.
3. Click File Path to get to the directory to save the file in.
4. Click Start to save the information.
The file is saved as Link Information.txt
Figure 5-1
.
Automatic Link Data Collection (Get Link Information) 5-1
Page 2
Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
Figure 5-1. Get Link Information
5.2 Monitoring Performance
WinLink 1000 constantly monitors traffic over the radio link and
collects the following statistics data:
• Site 1/Site 2 received traffic rate (in Mbps)
• Site 1/Site 2 received frames rate (in Mbps)
• Radio signal strength (in dBm)
• Error (Blocks).
The statistics (monitor) log and event log can be saved as TXT files.
New alarms are automatically added to the text file, as they enter the
event log.
Saving the Monitor Log
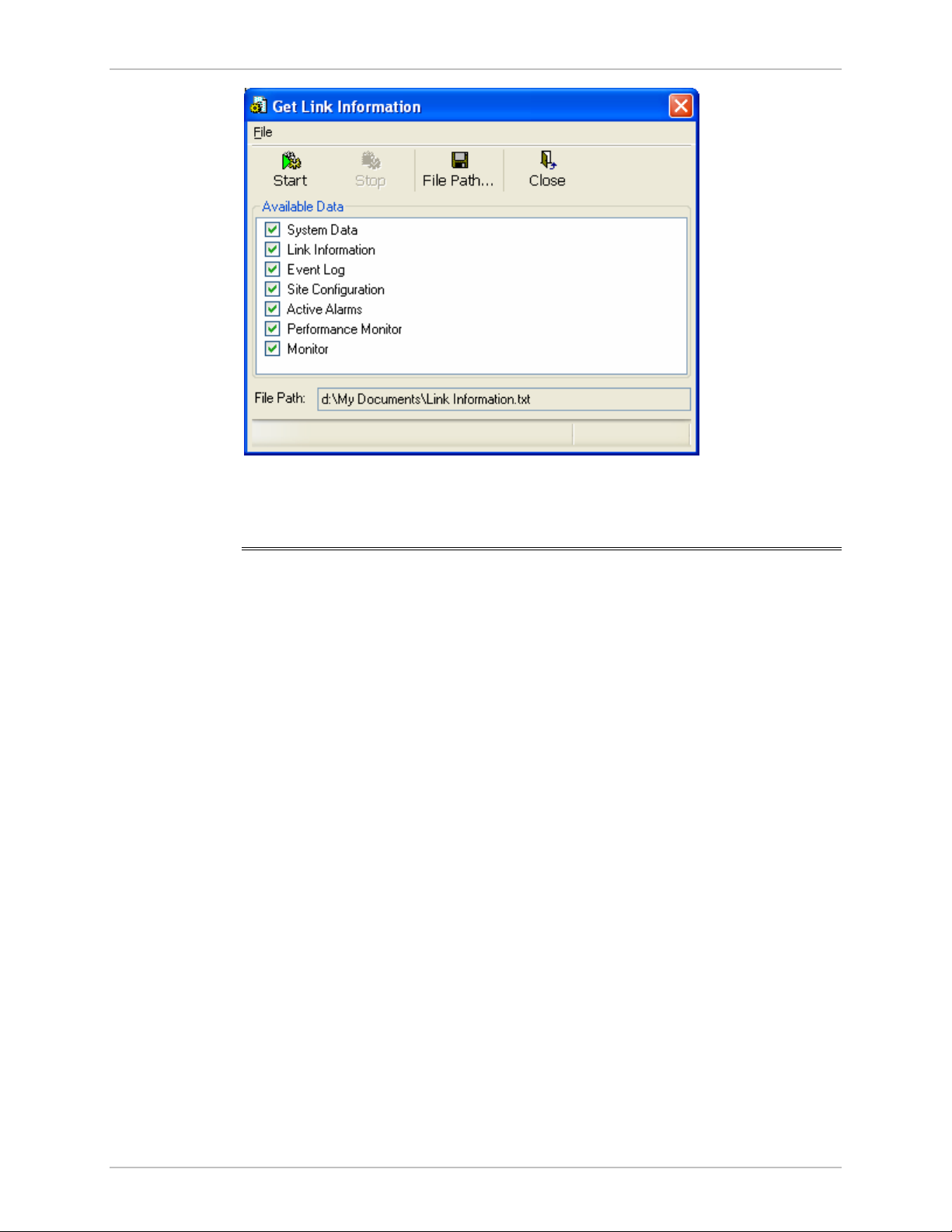
Æ
To save the monitor log:
1. From the Tools menu, choose Preferences.
The Preferences dialog box appears (see
2. Click the Monitor Tab.
3. Select the file to save.
5-2 Monitoring Performance
Figure 5-2
).
Page 3
WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
4. Click the check box to open the file for saving.
5. Click the
button and in the Select File dialog box indicate in
which folder and under what name the alarm log file is to be saved.
6. Set the time interval for adding data to the file.
7. Click OK to save the file
Figure 5-2. Preferences Dialog Box, Monitor Tab
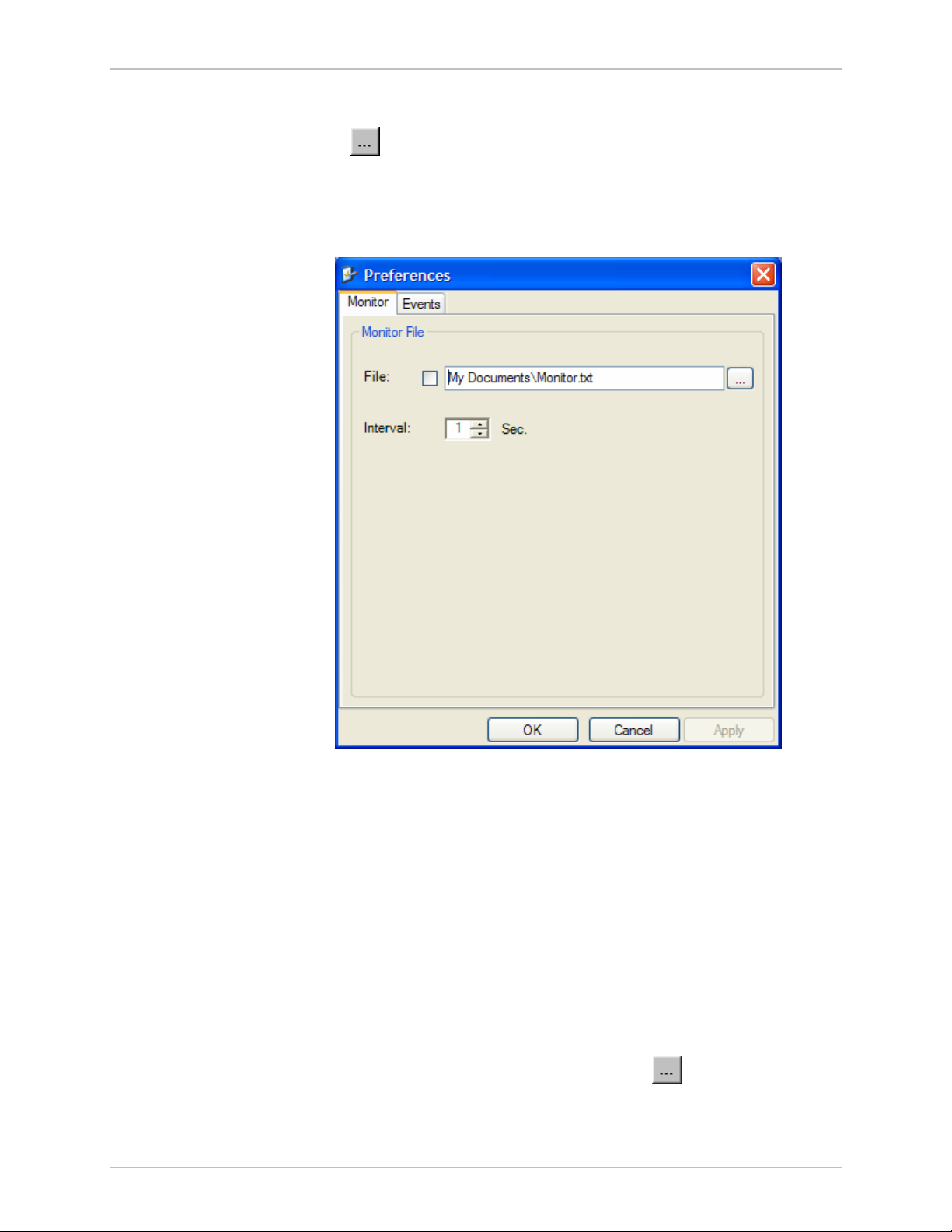
Setting the Events Preferences
You can define a color that the traps are displayed in the monitor pane,
according to severity of the event. The severity is predefined.
Æ
To set the trap color:
1. From the Tools menu, choose Preferences.
The Preferences dialog box appears).
2. Click the Events Tab (see
3. Select the Event priority type and click on the
A color chart opens.
Monitoring Performance 5-3
Figure 5-3
).
button.
Page 4

Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
4. Select the desired color.
5. Repeat for all the trap types.
Æ
To set the trap background color:
• Click Background Color to change the text background.
Æ
To reset the trap colors:
• Click Reset Settings to return to the default color settings.
Saving the Events Log
Æ
To save the event log:
1. From the Tools menu, choose Preferences.
The Preferences dialog box appears (see
Figure 5-3
).
2. Click the Events Tab.
3. Select the file to save.
4. Click the check box to open the file for saving.
5. Click the
button and in the Select File dialog box indicate in
which folder and under what name the alarm log file is to be saved,
and click OK.
5-4 Monitoring Performance
Page 5
WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Figure 5-3. Preferences Dialog Box, Event Log Tab
Monitoring Performance 5-5
Page 6

Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
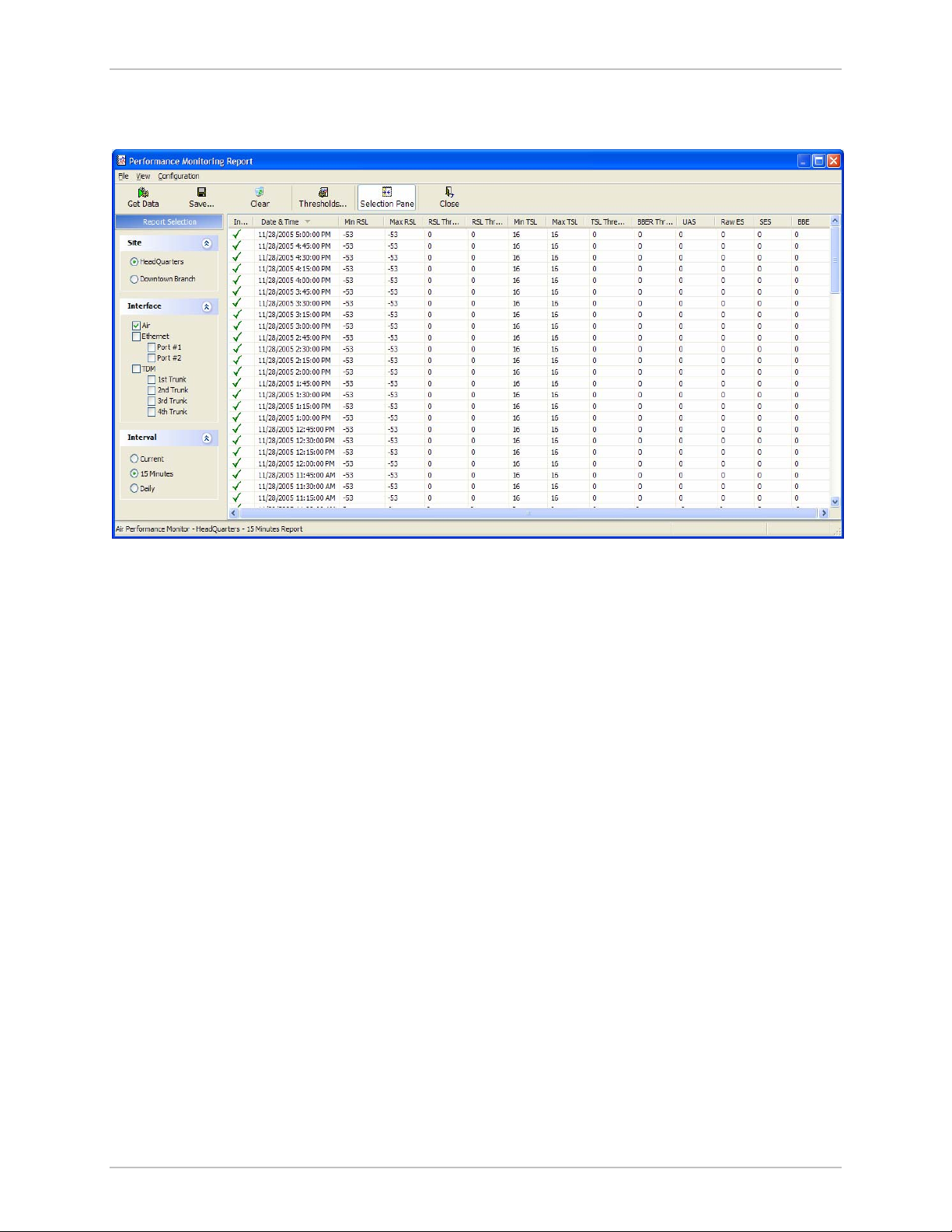
5.3 Viewing Performance Reports
The Performance Monitor Report displays performance views of each of
the interfaces
for each of the interfaces (ES, SES, and UAS), as well as Specific data per
Interface type (e.g., TX and RX bytes for Ethernet). For the Air Interface,
user defined thresholds data are collected. Refer to
Table
5-2
Data is collected and selectively displayed based on three time intervals
as selected by the Interval radio buttons:
• Current (t=0)
• 15 minutes Intervals
• Daily.
1
(see
Figure 5-4
). Several performance data are collected
Table 5-1
and
.
UAS – This parameter counts the time the air link was not providing
any service. There are several potential reasons for this situation; one
of the sites has a power failure, high interference, maintenance
operation etc.
Radio BBER Threshold – This parameter counts the seconds in which
the radio performance is below a user specified threshold. The
threshold is measured in percent. The threshold can be set from 0.1%
up to 50%.
For links with E1/T1 service the recommended value is 1% (system
default). Excellent TDM service is expected below the 1% threshold,
meaning that for 1% threshold, the expected BBER value should be 0 if
there are no problems during the 15 min interval. If the BBER threshold
increases some degraded service might be noticed.
For links with Ethernet only service, 8% threshold is recommended and
not 1% meaning that for 8% threshold, the recommended BBER value
should be 0 if there are no problems during the 15 min interval. Since
WinLink 1000 provides a loss less Ethernet service, there is throughput
degradation in case of interference. The degradation is proportional to
the BBER.
Radio RSS Threshold can also be used to indicate problems in the radio
channel. After verifying the RSS according to the link budget calculator
1
Ethernet performance is not collected in PoE systems.
5-6 Viewing Performance Reports
Page 7
WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
during the installation. A value of -5dB from the current RSS is
recommended as a threshold.
Figure 5-4. Performance Monitoring Report window
Viewing Performance Reports 5-7
Page 8

Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
Table 5-1. Explanation of performance data
Data type Reported value Explanation
Generic PM Data
UAS – Unavailable
Seconds
Seconds in which the
interface was out of
service.
ES – Error Second The number of
seconds in which there
was at least an error
block. Note that
notation of an error
block is different per
interface.
SES – Severe Error
Second
The number of
seconds in which the
service quality is low
(the actual BBER ratio
varies per interface).
BBE – Background
Block Error
The number of error
block in an interval.
Integrity A flag indicating that
the data is valid. Note
that the PM data is not
valid if not all the
values were stored
2
.
Air Interface PM Data
Max RSL The maximum of the
receive signal level
(measured in dBm).
Min RSL The minimum of the
receive signal level
(measured in dBm).
Max TSL The maximum of the
transmit signal level
(measured in dBm)
2
Possible reasons are: Clock changes within the interval and Power up reset
3
The transmit power is fixed. The value can be changed only by user
configuration
5-8 Viewing Performance Reports
3
.
Page 9

WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Data type Reported value Explanation
Min TSL The minimum of the
transmit signal level
(measured in dBm).
RSL Threshold 1 This parameter counts
the number of seconds
in which the RSL is
below the specified
threshold.
RSL Threshold 2 This parameter counts
the number of seconds
in which the RSL is
below the specified
threshold.
TSL Threshold 1 This parameter counts
the number of seconds
in which the RSL is
above the specified
threshold.
Ethernet Interface PM
Data
BBER Threshold The BBER Threshold
value counts the
number of seconds in
which the Background
Block Error Ratio
(BBER) exceeds the
specified threshold.
Note, that the system
is design for excellent
quality of service with
BBER of less then 1%.
(at 1% BBER expected
TDM BER is less than
1E-6.
Received Bytes The number of Mega
bytes received in the
specified port within
the interval
Viewing Performance Reports 5-9
Page 10
Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
Data type Reported value Explanation
Transmitted Bytes The number of Mega
bytes received in the
specified port within
the interval.
Table 5-2. Action of the tool bar button commands
Button Action
Get Data Uploads the selected report from the ODU.
Save Saves the data in a CSV or Text format for additional analysis.
Clear Removes the current data from the window.
Selection pane Selects the site, interface, and interval to be displayed.
Threshold
Close Closes the Performance Monitor Report window.
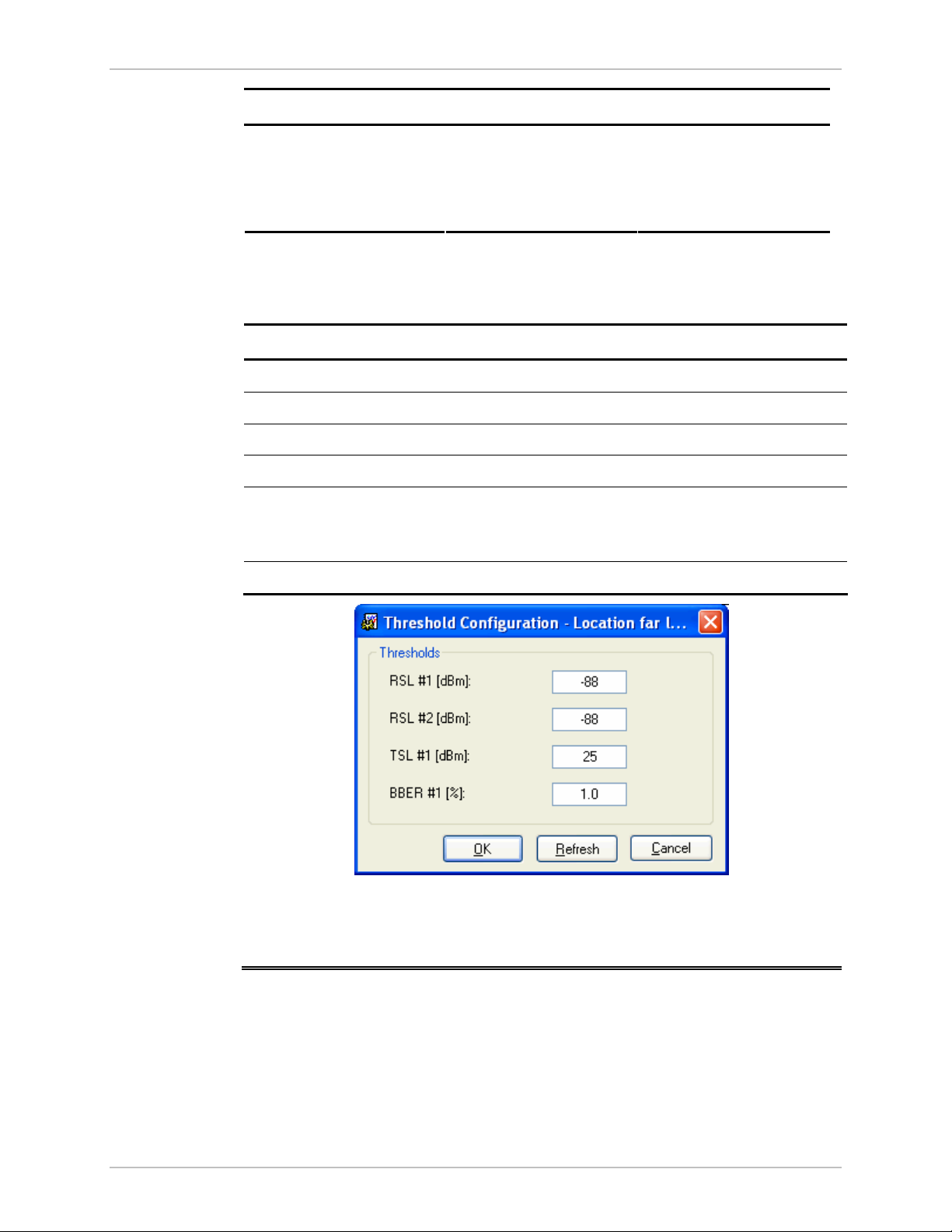
Opens the threshold configuration dialog box (Figure
set the Air Interface thresholds. Note that threshold change is
effected immediately, but it does not change any historical data.
Figure 5-5. Threshold configuration dialog box
5-5) to
5.4 Error Detection and Alarms
WinLink 1000 detects compatibility problems, fault conditions of the
radio or user links, and initiates alarms to alert the user.
5-10 Error Detection and Alarms
Page 11
WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
To store the Event Log, first define the IP address, subnet mask,
default gateway and trap address of the management PC, see
for details.
4
Chapter
Alarms (traps) are displayed in the Event Log in the lower panel of the
Main Menu screen. The event log may be saved as a TXT file.
The event log includes the following fields:
• Sequential number (ID)
• Date and time stamp
• Message
• Trap source
• IP address of the ODU that initiated alarm.
Error Detection and Alarms 5-11
Page 12

Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
Table 5-3. WinLink 1000 Alarms and Information Messages
Message Description
Radio Link – Sync Radio link is synchronized
Radio Link – Out Of Sync Radio link lost synchronization
Link Has Been Reset ODU was reset due to internal problem
TDM Interface – Normal TDM interface is operating properly
TDM Interface – LOS Loss of Synchronization is reported by TDM interface
TDM Interface – LOS
TDM Interface – AIS
TDM Interface – Loopback
Link Resetting Wireless link reset from the management station. This
Local ODU Resetting The local ODU reset from the management station.
Monitor was stopped since no
connection to the link
TDM Service – Normal
TDM Service – Alarm Error has been detected on a TDM line
Configuration problem detected The link needs to be reinstalled
Channel Scanning in progress The ODU is scanning the channels for the remote ODU
Transmitting on <frequency>
GHz
Radar activity was detected in
<site>, on channel <frequency>
GHz
Loss of Signal is reported by TDM interface
Alarm Indication Signal is reported by TDM interface
A loopback is active on TDM interface
alarm is caused by automatic reset after link
configuration.
No ODU-to-IDU traffic was detected during the last 20
minutes.
TDM service is operating properly
The ODU is transmitting on the frequency channel listed
For DFS versions only. Radar is detected; the channel is
prohibited for 30 minutes.
Monitoring fo Radar activity on
channel <frequency> GHz
Bit Failed indication Indicates ODU hardware problem. Send error code to
Link Status Indicates incorrect connection or incompatibility between
Site Status Indicates incorrect connection or operation at the site.
For DFS versions only. ODU is looking for Radar activity.
Technical Support.
versions. Available in 1.620 versions and above.
Available in 1.620 versions and above.
5-12 Error Detection and Alarms
Page 13
WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Æ
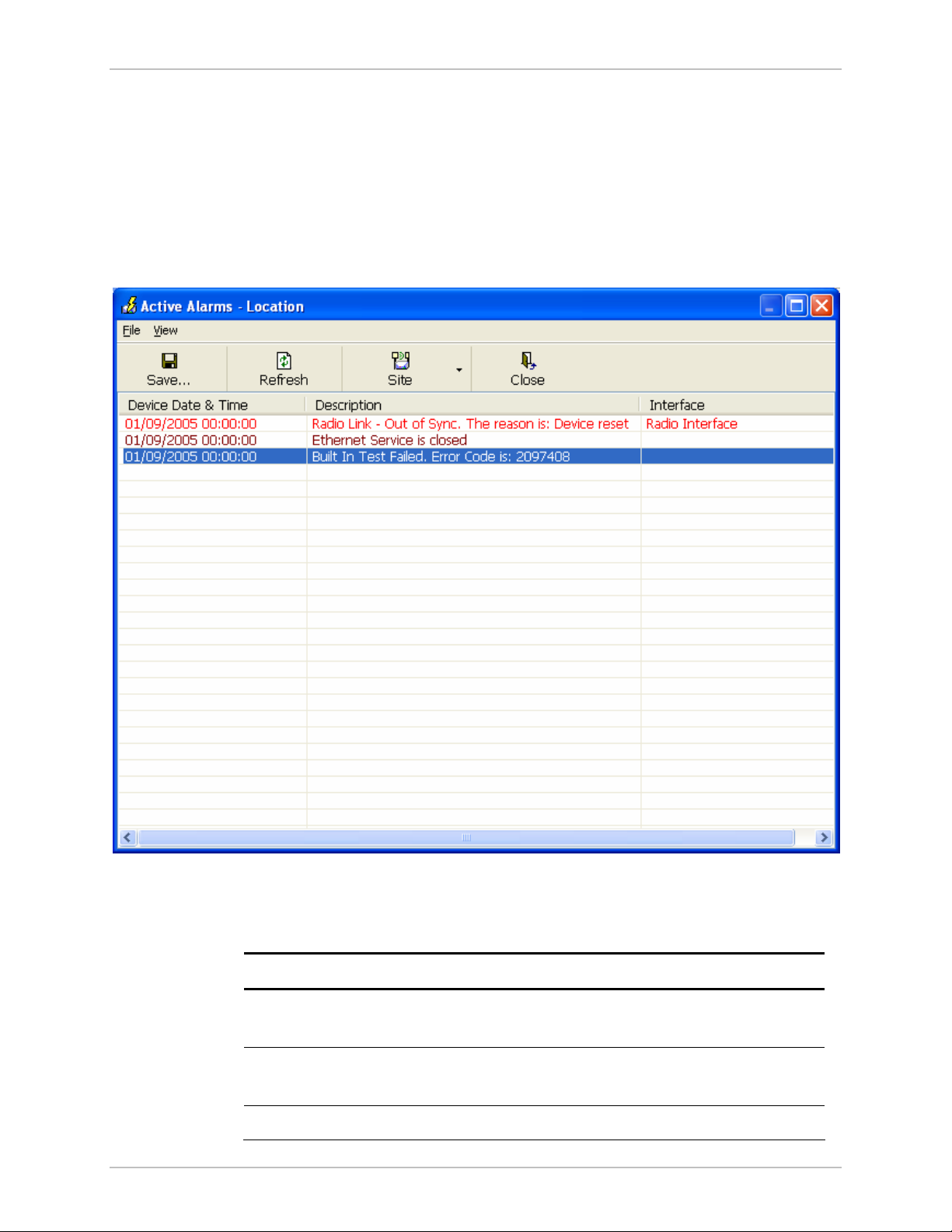
To view summary of saved alarms
• From the Tools menu, choose Active Alarm Summary.
The Active Alarms Summary window opens. See
Table 5-4
; for
an explanation of the command buttons.
Figure 5-6. Active Alarms Summary
Table
Command Action
Save Saves the alarms in CSV or text format for further
Refresh Reads the alarms from the ODU, and displays the
Site Selects site for the active alarms.
Error Detection and Alarms 5-13
5-4. Active Alarms command buttons
analysis.
alarms.
Page 14
Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
Close Closes the active alarm window.
5.5 Remote Power Fail Indication
Remote power fail indication indicates to one side that the other side
has had a power failure. The failed site sends a final trap indication
about the power loss just before powering off.
A Dying-Gasp circuit identifies the power failure at a minimum interval
of 20 milliseconds before the IDU crash, during that interval a message
notifying the power failure is sent to the remote end.
Alarm output number 4 indicates link loss due to power failure at the
remote end.
5.6 Link Compatibility
WinLink 1000 indicates the version compatibility via software traps. As
new hardware is added to existing networks compatibility issues may
arise. An incompatibility issue is indicated to the user via a change of
color of the Link Status box on the Main Menu screen. Trap messages
in the Event Log indicate the problems or limitations and suggest
upgrades when appropriate.
The following Link Status messages are given:
fullCompatibility - different software versions that are fully compatible.
Message indicates that upgrade is available.
restrictedCompatibility - different software versions that operate
correctly. However, new features are not supported
softwareUpgradeRequired - different software versions with limited
operation. The link will operate as Ethernet only; a full service will not
be available. The message is software upgrade required.
versionsIncompatibility - different software versions that are not
compatible. User needs to perform local upgrades.
Table 5-5. Link Compatibility Trap Messages
Link State Link Link Status Site Description Site Link Status
5-14 Link Compatibility
Page 15
WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
State
Text
fullCompatibility Active Green SW
restrictedCompatibility Active -
SW
Version
mismatch
softwareUpgradeRequired Active –
SW
Upgrade
Required
versionsIncompatibility Not
Active SW
Upgrade
Required
Color Desc.
Upgrade Available
Magenta
(Same as
authentication
error)
Brown (Major) SW Upgrade
Red Local SW Upgrade
SW Upgrade
Recommended
Required
Required
Color
Color
Yellow Green
Yellow Magenta
(Same as
authentication
error)
Yellow Brown (Major)
Yellow Red
5.7 Testing WinLink 1000
WinLink 1000 supports activation of the internal and external
loopbacks on the local and remote units.
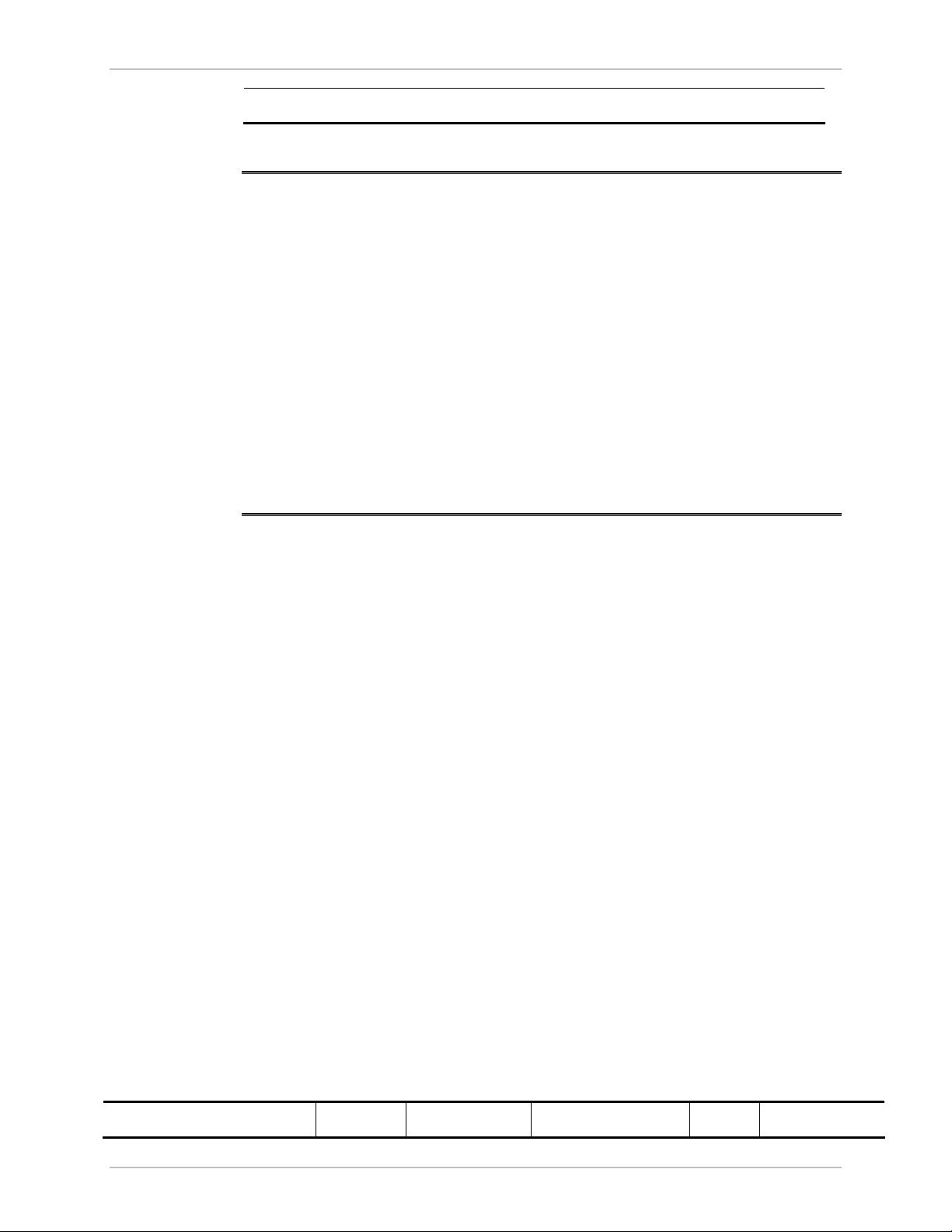
Æ
To activate a loopback:
1. From the Maintenance menu, choose Set Loopbacks.
The Loopbacks dialog box appears (see
2. From the Local or Remote drop-down box, select a loopback that
you intend to run, and click OK.
A confirmation message appears.
3. Click OK to activate a loopback.
WinLink 1000 activates selected loopback. A loopback status
arrow in the Main menu turns green to indicate an active
loopback.
Æ
To deactivate a loopback:
Figure 5-7
).
• From the From the Local or Remote drop-down box of the
Loopbacks dialog box, select None and click OK.
Testing WinLink 1000 5-15
Page 16
Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
A loopback is deactivated and the corresponding status arrow in
the Main menu becomes dimmed.
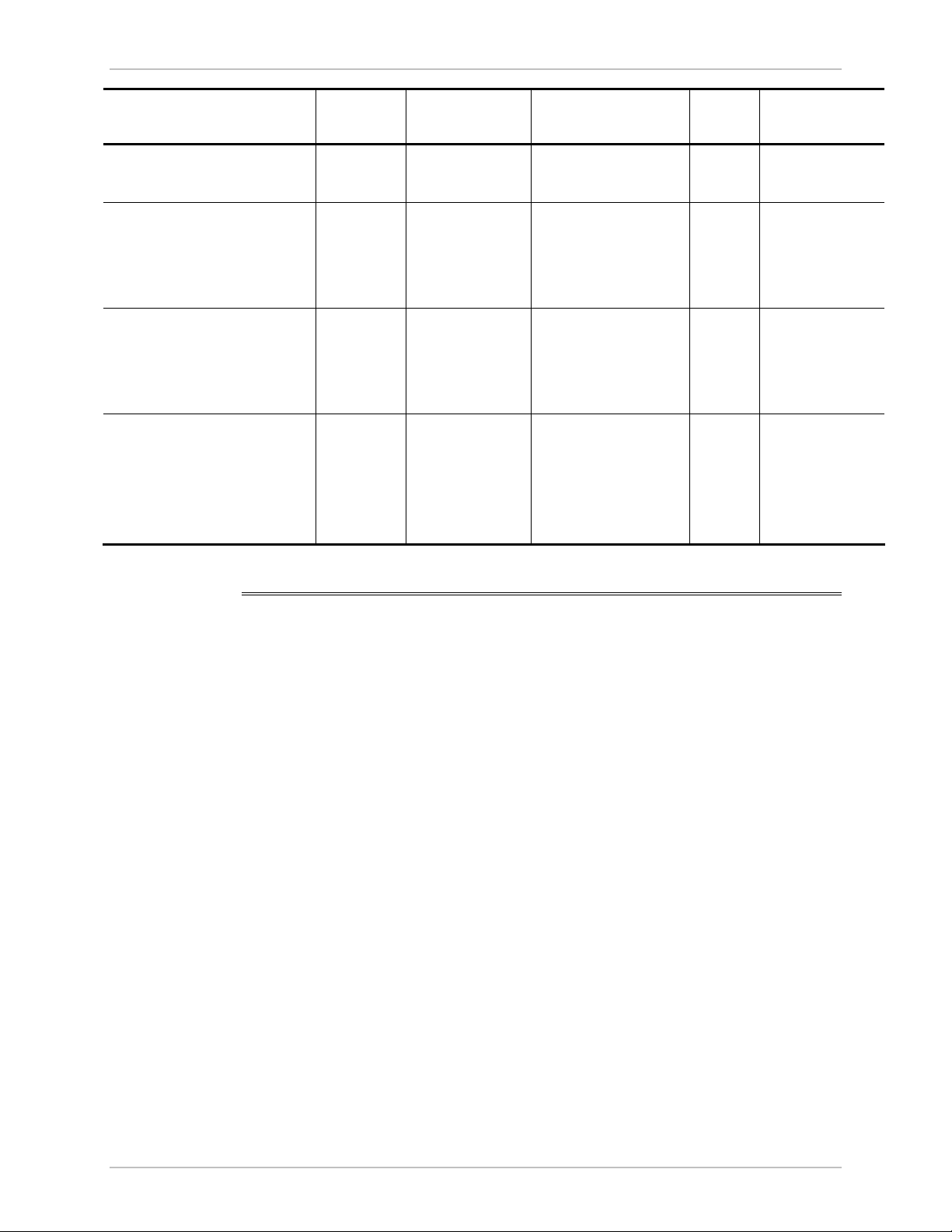
Local External Loopback
Local WinLink 1000 can be set to an external loopback to test the local
E1/T1 port and its connection to the local side user equipment. In this
mode, data coming from the local user equipment is looped back to it
Figure 5-8
(see
connected to the local unit.
Figure 5-7. Loopbacks Dialog Box
). This loopback is initiated from a management station
E1
/T1
Interface
Testing
Equipment
Local ODU
Management
Station
Figure 5-8. Local External Loopback
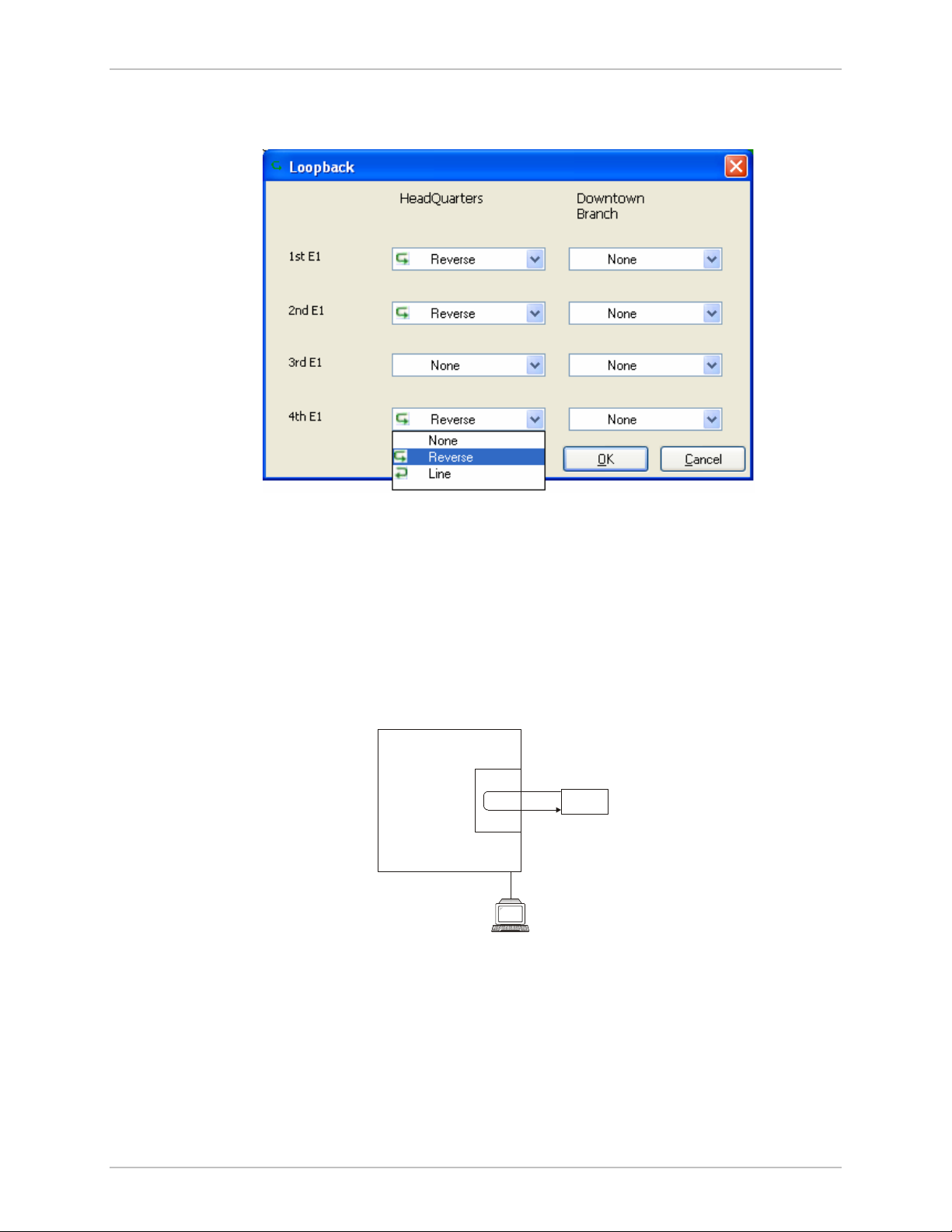
Remote Internal Loopback
Remote WinLink 1000 can be set to an internal loopback to test
connection between the local and remote units, the local E1/T1 port
and its connection to the local side user equipment. In this mode, data
5-16 Testing WinLink 1000
Page 17
WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
coming from the local WinLink 1000 is looped back to it (see
). This loopback is initiated from a management station connected to
9
the local unit.
E1/T1
Interface
Figure 5-9. Remote Internal Loopback
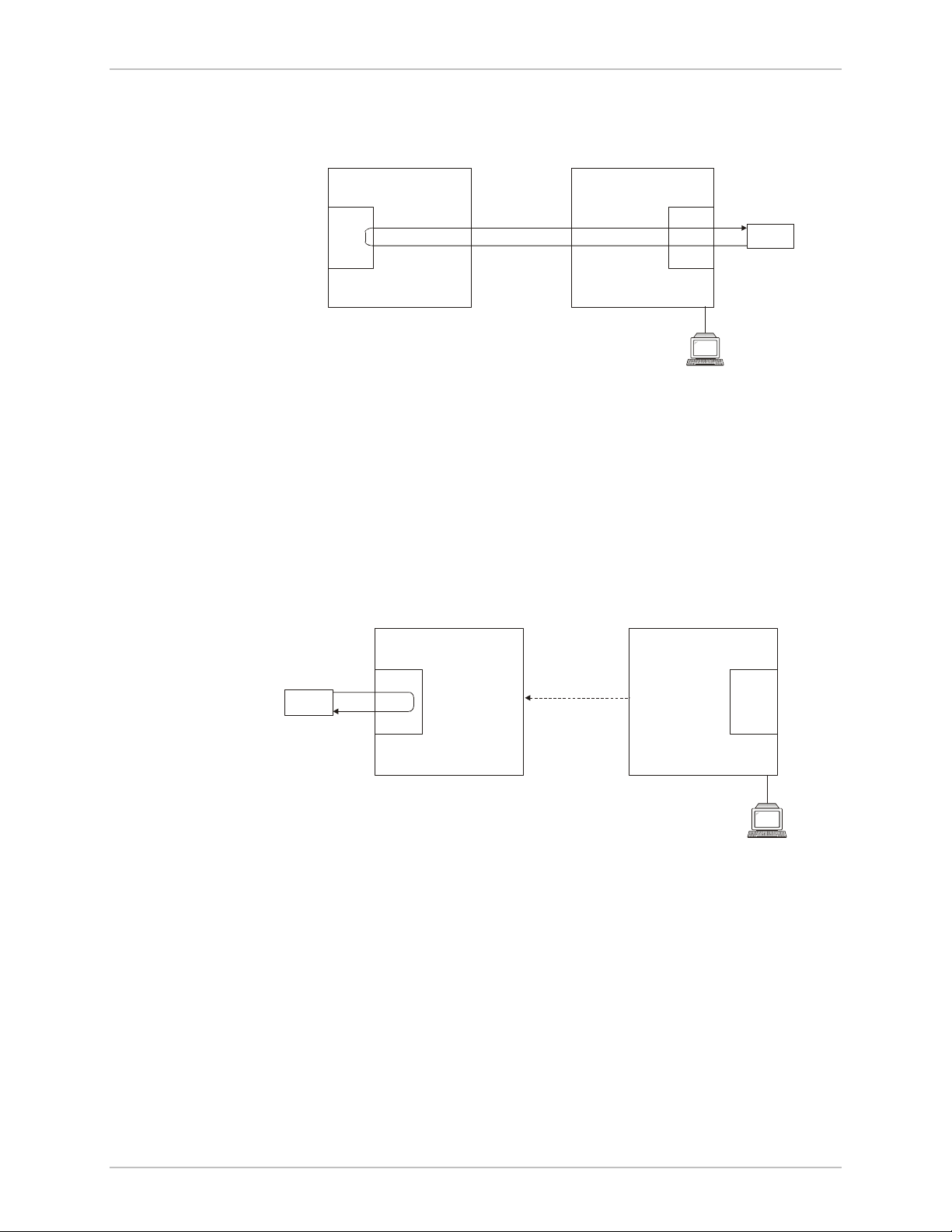
Remote External Loopback
Remote WinLink 1000 can be set to an external loopback to test the
remote E1/T1 port and its connection to the remote side user
equipment. In this mode, data coming from the remote user equipment
is looped back to it (see
inband command sent from a management station connected to the
local unit.
Remote ODU Local ODU
Figure 5-10
). This loopback is initiated by an
E1
/T1
Interface
Management
Station
Figure 5-
Testing
Equipment
Testing
Equipment
Local Internal Loopback
Local WinLink 1000 can be set to close an internal loopback to test
connection between the local and remote units, remote E1/T1 port and
its connection to the remote side user equipment. In this mode, data
coming from the remote user equipment is looped back to it (see
Figure 5-11
from a management station connected to the local unit.
E1
/T1 E1
Interface
Inband Loopback
Activation Command
Remote ODU
Local ODU
/T1
Interface
Management
Station
Figure 5-10. Remote External Loopback
). This loopback is initiated by an inband command sent
Testing WinLink 1000 5-17
Page 18
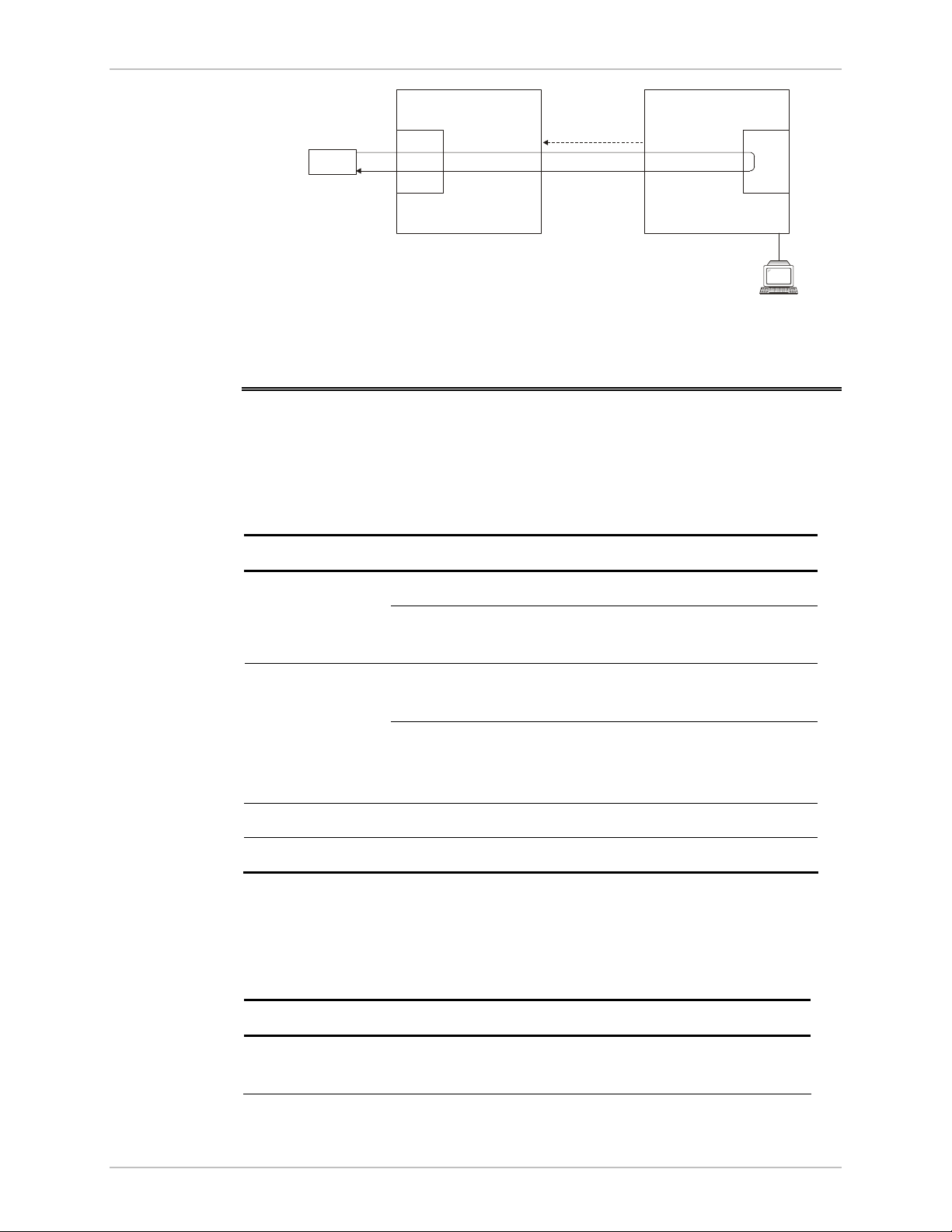
Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
E1/T1
Interface
Testing
Equipment
Remote ODU
Figure 5-11. Local Internal Loopback
5.8 Troubleshooting
Use
Table 5-7
Symptom Remedy
and
Table 5-7
to diagnose any faults in the system.
Table 5-6. Troubleshooting
Inband Loopback
Activation Command
Local ODU
E1
/T1
Interface
Management
Station
Verify that AC power is connected to the IDU. No power
Verify that the ODU cable is properly wired and
connected.
No signal
Complete the installation procedure from the
management software.
Verify the ODU alignment. Check that the radio
configuration of both site A and site B units are the
same (channel and SSID).
Weak signal Verify the ODU alignment, reconfigure the link.
Verify the beeper sounds the Best Signal sequence.
The WinLink 1000 LEDs show faults in the system or the link.
Table 5-7. Troubleshooting with WinLink 1000 LEDs
LED Status Remedy
PWR Off Check that AC adapter is connected to the
IDU-E and the AC power outlet.
5-18 Troubleshooting
Page 19

WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
IDU Orange Check that the IDU/ODU cable is properly
wired and connected.
ODU Red Check that the IDU/ODU cable is properly
wired and connected.
AIR I/F
SERVICE
Orange Complete the installation procedure from
the management software.
Red Check the ODU Antenna alignment. Check
that the radio configuration of both site A
and site B units are the same (channel and
SSID).
Off Check the TDM service configuration in the
NMS.
Orange Check that the system is not in loopback
mode.
Check the site B IDU ports and cables and
site B external equipment.
Red Check the site A IDU ports, cables and
external equipment.
5.9 Replacing an ODU
Prior to any action verify that both ODUs have the same software
version (Configuration > Configure site >Inventory). If one ODU has an
old software version, perform a software upgrade. It is important to
configure the new ODU exactly the same as the old ODU to avoid
configuration mismatches, which will disrupt the link.
An ODU may be replaced with a new ODU in one several ways.
• Use the backup
If a backup of the configuration is available, restore that
configuration using Configuration > Configure site > Restore.
• Manual Configuration
The new ODU can be configured manually according to the link
configuration, remember to use the same settings for SSID,
channels, link password, IP addresses, and names.
• Restore Factory Setup
From version 1.6xx the feature of Restore Factory Setup is
Replacing an ODU 5-19
Page 20

Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
available. Using this feature we recommend putting the remaining
ODU back to factory setup Configuration>Configure site>Advance
option, and then activate the second ODU reconfiguring the link
from scratch.
Option number 3 is our recommended option preventing configuration
mismatches.
5.10 Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What performance issues will arise due to environmental conditions?
A: WinLink 1000 is not sensitive to environmental conditions. However
if heavy rain or snowfall is expected ensure the performance by
allowing a higher fade margin in the link budget planning calculations.
Q: When using the WinLink 1000, what is the potential for interference
between our system and other cellular or wireless Networks devices?
A: The WinLink 1000 is a robust system. However since it operates in
unlicensed band there maybe some interference. Nevertheless, the fact
that we can manually set the frequency gives us the flexibility to find a
clear channel. In addition each WinLink 1000 link uses unique user
configurable SSID code.
Q: What protocol does the WinLink 1000 use, i.e. 802.11?
A: WinLink 1000 uses a proprietary protocol; this protocol contains
improved options that more efficiently support the clock
reconstruction from the TDM services.
Q: What type of security is offered on WinLink 1000?
A: WinLink 1000 has three levels of security:
1. AES hardware mechanism
2. Each unit uses a unique SSID link-specific code (up to 24
alphanumeric characters)
3. Proprietary protocol protects from eavesdropping from other
systems.
5-20 Frequently Asked Questions
Page 21

WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Q: Can we use horizontal and vertical polarization on the same
frequency to double the number of wireless links?
A: Installing two WinLink 1000 systems in the same band with cross
polarization provides 20–25 dB separations. Nevertheless, since there
are reflections, the cross polarization separation is decreased and
spatial separation is recommended.
Q: Could you add the frequency of 5.735 to the manual selection in
order to increase the number of 20 MHz channels to six?
A: Currently the system provides fixed channels, with one manual
frequency setting. The manual setting provides flexibility of spectrum
selection, including 5.735 MHz.
Q: Can we mange WinLink 1000 using SNMPc other than the supplied
management software that comes with the units?
A: Yes. The WinLink 1000 is SNMP-based. WinLink 1000 can be
managed when using other SNMP software after implementing RADWIN
MIB’s.
Q: Can WinLink 1000 be managed and configured via Telnet?
A: No. Use only the WinLink 1000 software manager.
Q: Can I use WinLink 1000 with any vendor’s external antenna?
A: RADWIN supplies the WinLink 1000 external ODU with an N-type
typical connector. Any vendor’s external antenna that is of the same
type and of equal or less directional gain as an antenna that RADWIN
authorized with its specific external ODU product can be used. That is
given that it can be cascaded to our external unit. Please note that dB
losses in the cascading cable between the external ODU and antenna
should be taken into consideration. (In the supplied cascading cable of
one meter we have 1 dB loss)
Q: Do we need to add external arrestors on WinLink 1000 cables?
A: The WinLink 1000 ODU includes arrestors and lightning protection.
Therefore there is no need to add additional arrestors.
Q: What is the actual Ethernet data rate and maximum throughput?
A: The maximum net throughput of WinLink 1000 is full duplex 18
Mbps.
Frequently Asked Questions 5-21
Page 22

Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
WinLink 1000 is a symmetrical system
Q: What is the sensitivity for each rate of the WinLink 1000?
A: The rate sensitivities are:
Rate
[Mbps]
12 -84
18 -81
36 -74
48 -68
Sensitivity
[dB]
Q: Does WinLink 1000 withhold any MAC Addresses?
A: The WinLink 1000 is a layer 2 Bridge (VLAN transparent). The builtin switch contains a MAC Address table up to 2047.
Q: Can I use any category 5e cable in order to connect the IDU and
ODU?
A: The cable should be suitable for outdoor use, and shielded Category
5e.
Q: What are the BER values expected in the WinLink 1000 link?
A: 10-11 (according to BER sensitivity threshold)
Q: Does WinLink 1000 use DSSS technique?
A: No, WinLink 1000 uses the advanced OFDM technique.
Q: What are the main advantages of the WinLink 1000 solution (e.g.,
wireline, wireless, etc.) over other possible alternatives?
A:
• Easy and intuitive installation using audio indication.
• Easy configuration using the management software of overall link
site-to-site, there is no need to travel between the two sites in
order to change the configuration.
• Easy migration between transition channels site-to-site.
• Full backup option – backup and restore using ini files.
• Very light ODU (1.5 kg).
5-22 Frequently Asked Questions
Page 23

WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Chapter 5 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
• No RF loses between IDU and ODU.
• Robust Air Interface Layer 2 ARQ insures “error-free” Ethernet
service even in harsh conditions. Retransmit mechanism for TDM
ensures low BER.
• Integrated up to 4 E1/T1 and Ethernet radio over one single
product.
• Supports a variety of applications Voice and Data over single radio –
no need for external mediation device.
• Smooth migration to VoIP applications.
• Carrier class compliant with ITU standards for E1 and T1.
• Low and constant TDM latency (8 msec).
• Extremely accurate recovered clock low cost replacement to PDH
radios.
5.11 Technical Support
Technical support for this product can be obtained from the local
distributor from whom it was purchased.
For further information, please contact the RADWIN distributor nearest
you or one of RADWIN's offices worldwide. This information can be
found at
www.radwin.com.
Technical Support 5-23
Page 24

Appendix A
Wiring Specifications
A.1 ODU-IDU and ODU-(O-PoE) Cables
The ODU-IDU and ODU-(O-PoE) cables are standard CAT-5, 4 twistedpair 24 AWG FTP, terminated with RJ-45 connectors on both ends.
They are covered by a cable gland on the ODU and O-PoE side for
hermetic sealing.
Table A-1
shows the connector pinout.
Table A-1. ODU-IDU and ODU-(O-POE) Cable Connector Pinout
IDU RJ-45 Wire Color Function ODU RJ-45
1
twisted
2 pair Green Ethernet (RxT) 2
3
twisted
6 pair Orange Ethernet (TxN) 6
4
twisted
5 pair White/Blue Power (+) 5
7
twisted
White/Green
White/Orange
Blue
White/Brown
Ethernet (RxN)
Ethernet (TxT)
Power (+)
Power (−)
1
3
4
7
8 pair Brown
ODU-IDU and ODU-(O-PoE) Cables A-1
Power (−)
8
Page 25

Appendix A Wiring Specifications WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
Figure A-1. RJ-45 wiring for IDU-ODU and (O-PoE)-ODU cable
A.2 User Port Connectors
Trunk Port
The IDU includes ports for connecting E1/T1 and 10/100BaseT
Ethernet user devices.
The Trunk (E1/T1) interface terminates in an 8-pin RJ-45 balanced
connector, wired in accordance to
Table A-2
.
Table A-2. E1/T1 Connector Pinout
Pin Function
4,5 Receive (input)
1,2 Transmit
(output)
A-2 User Port Connectors
Page 26

WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix A Wiring Specifications
LAN Port
The LAN 10/100BaseT interface terminates in an 8-pin RJ-45
connector, wired in accordance to
Table A-3. Fast Ethernet Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Function
1 TD (+) Transmit Data
(positive)
2 TD (–) Transmit Data
(negative)
3 RD (+) Receive Data
(positive)
6 RD (–) Receive Data
(negative)
Table A-3
.
A.3 IDU-C Connectors
IDU-C DC Power Terminal
Table A-4. Terminal Block 3-pin -48VDC
Pin Connection
Right +
Center Chassis
Left –
IDU-C Connectors A-3
Page 27

Appendix A Wiring Specifications WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
IDU-C Alarm Connector
Table Table A-5 lists the alarm connector pinout.
Table A-5. Alarm Connector (Dry-Contact)
Pin Description
1 Input 1 Positive
6 Input 1 Negative
2 Input 2 Positive
7 Input 2 Negative
3 Output 1 Normally
Closed
8 Output 1 Common
4 Output 1 Normally Open
Alarm Connector
Input 1
+ve
Input 2
N/C
Output 1
Output 2
N/O
N/O
9 Output 2 Common
5 Output 2 Normally Open
12+ve
6-ve
7- ve
3
Ext. current limit resistor
4
8COM
Ext. current limit resistor
7
9COM
10 to 50 VDC alarm voltage
-10 to -50 VDC alarm voltage
Alarm LED
Alarm Buzzer
Ext. DC Power
Ext. DC Power
Figure A-2. Example for connecting the alarm connector
A-4 IDU-C Connectors
Page 28

WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix A Wiring Specifications
A.4 O-PoE to PC LAN Cable
When connecting the O-PoE ETH port cable directly to PC, a crossed
LAN CAT-5, 4 twisted-pair 24 AWG FTP, terminated with RJ-45
connectors on both ends must be used.
Table A-16
shows the connector pinout.
Table
A-6. O-POE to PC Cable Connector Pinout
O-PoE (ETH)
RJ-45
1
twisted
2 pair Green Ethernet (RxT) 6
3
twisted
6 pair Orange Ethernet (TxN) 2
4
twisted
Wire Color Function PC
White/Green
White/Orange
Blue
Ethernet (RxN)
Ethernet (TxT)
NA
3
1
4
5 pair White/Blue NA 5
7
twisted
8 pair Brown NA 8
White/Brown
NA
7
O-PoE to PC LAN Cable A-5
Page 29

Appendix B
Mast and Wall Installation
B.1 Mounting the ODU or O-PoE
The ODU or O-PoE can be mounted on a mast or a wall.
ODU or O-PoE Mounting Kit Contents
The ODU or O-PoE mounting kit includes the following items:
• One Large Clamp (see figure B-1)
• One Small Clamp (see figure B-2)
• One Arm (see figure B-3)
• Four Screw hex head M8x40
• Two Screw hex head M8x70
• Four Washer flat M8
• Three Washer spring M8
• Two M8 Nuts.
Figure B-1. Large
Clamp
Figure B-2. Small
Clamp
Figure B-3. Arm
Mounting the ODU or O-PoE B-1
Page 30

Appendix B Mast and Wall Installation WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
Mounting WinLink 1000 on a Mast
B-2 Mounting the ODU or O-PoE
Page 31

WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix B Mast and Wall Installation
Mounting WinLink 1000 on a Wall
Mounting the ODU or O-PoE B-3
Page 32

Appendix B Mast and Wall Installation WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
B.2 Mounting an External Antenna
The optional external antenna can be mounted on a mast.
External Antenna Mounting Kit Contents
The external antenna mounting kit includes the following items:
• Twelve flat washers
• Eight spring washers
• Eight hex nuts
• Four bolts
• One U-bracket
• One pivoting bracket
• Two metal strap clamps.
Æ
To install external antenna on the mast:
1. Attach the U-bracket to the back of the antenna using four flat
washers, four spring washers and four hex nuts.
2. Attach the pivoting bracket to the U-bracket using eight flat
washers, four spring washers, four hex nuts and four bolts.
3. Pass both strap clamps through the vertical slots in the pivoting
bracket.
4. Attach the antenna to the mast using the two strap clamps.
5. Adjust the required tilt using the angular scale and tighten all bolts
and nuts at the required position.
B-4 Mounting an External Antenna
Page 33

Appendix C
Link Budget Calculator
C.1 Overview
The Link Budget Calculator is a utility for calculating the expected
performance of the WinLink 1000 wireless link and the possible
configurations for a specific link range.
The utility allows you to calculate the expected RSS of the link, and find
the type of services and their effective throughput as a function of the
link range and deployment conditions.
The Link Budget Calculator is supplied on the WinLink 1000 Manager
CD. After installation, it may also be accessed from the menu bar of
the WinLink Manager (see
Figure C-1
).
WinLink 1000 Overview C-1
Page 34

Appendix C Link Budget Calculator Installation and Operation Manual
Figure C-1. Accessing the Link Budget Manager Calculator
C.2 Description of Parameters
The parameters described in this section are indicated in
A Fade Margin (FM) the margin taken in consideration as part of the
parameters needed as spare for high availability. Min level accepted by the
LBC is 6dB.
B EIRP Tx Power + Antenna Gain (*) – in some products they are limited to a
max value due to local regulation and type approval.
Example 1:
10 x Log (Value in mW) = (Value in dBm)
1W is the maximum EIRP (Tx Power + Antenna Gain (*)) that is
allowed in
5.4 GHz ETSI products by ETSI regulation, (*) considering cable loss.
Figure C-2
.
Note: 3 dB = 2 x Power
C-2 Description of Parameters WinLink 1000
Page 35

Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C Link Budget Calculator
1W = 1000 mW Æ 10 x Log (1000) = 30 dBm
2W = 2000 mW Æ 10 x Log (2000) =33 dBm
C Max/ Min range (distance) WinLink 1000 sensitivity threshold in -60dB
range
(-30 dBm < RSS (sensitivity) <-90 dBm, in addition Propagation Delay is
also considered 3.3uS / 1 km (refer to Throughput vs Distance guideline
Example 2:
RSS = Tx(power) + Ant(Tx) + Ant(Rx) – loss
loss = 32.5 + 20 Log (D) + 20 Log (f);
D – Distance in km, f – Center Frequency
D Climate/Terrain Factor see
E Expected FM and RSS, refer to A and B
F Required Antenna Height, this is the required antenna height considering
the Fresnel Zone, see
guideline.
Figure C-3
Figure C-5
and
Figure C-4
. Refer to WinLink 1000 site-survey
based on antenna beam
Considering LOS (clear
G Channel Bandwidth required with the available Radio Frame Pattern (RFP)
for collocated HSS systems.
Line of Site
)
WinLink 1000 Description of Parameters C-3
Page 36

Appendix C Link Budget Calculator Installation and Operation Manual
Figure C-2. Link Budget Screen
C-4 Description of Parameters WinLink 1000
Page 37

Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C Link Budget Calculator
Figure C-3. Climate and Terrain Factor
Figure C-4. Geographical Conditions
WinLink 1000 Description of Parameters C-5
Page 38

Appendix C Link Budget Calculator Installation and Operation Manual
Figure C-5. Fresnel Zone
Note
C.3 Using the Link Budget Calculator
The Link Budget Calculator comprises of one table where all the link
parameters are defined.
Æ
To calculate the link budget
1. Select your system product from the dropdown list of products.
2. Select the rate from the dropdown list. The rate defines the air-
interface rate in Mbps. The system operates in TDD mode and has
overhead of the air-interface protocol and therefore the accurate
actual throughput is provided in the ‘Service’ Row and the effective
Ethernet throughput is provided in the ‘Ethernet Rate’.
•
Throughput can be decreased as a function of range due to
propagation delay.
The remaining fields are completed automatically depending on the
product selected in the product field. Standard WinLink 1000
system parameters are entered as default. Fields in blue boxes may
be edited if non-standard antennas and cables are used.
The Fade margin is the minimum margin that is required for LOS
conditions. For degraded link conditions, a larger fade margin
should be taken into account.
The Tx power EIRP for the system is given in dBm and Watts.
C-6 Using the Link Budget Calculator WinLink 1000
Page 39

Installation and Operation Manual Appendix C Link Budget Calculator
3. Type the required link distance and select units of distance,
kilometers or miles.
4. Select the general conditions
5. Select the services required
6. Click Calculate
The Expected Performance parameters are calculated and
displayed in the lower part of the table.
Expected RSS – this is the number that the WinLink 1000
Manager software shows when the WinLink 1000 ODUs are best
aligned.
Ethernet Rate – Maximum throughput available with the chosen
system.
If the expected performance is not suitable for your application, select
a different data rate and re-calculate.
WinLink 1000 Using the Link Budget Calculator C-7
Page 40

Appendix D
AIND Antenna Alignment
Procedure
Use this procedure when using the all indoor system WinLink 1000ANID or manually aligning two WinLink 1000 units.
To achieve the best benefit and link budget from the WinLink
installation, the link antennas must be aligned; the two antennas
should exactly face each other.
In order to achieve the best performance, the line of sight must be as
clear as possible with no obstructions between the two sites.
Prior to attempting WinLink alignment, install the hardware and
software in accordance with the WinLink 1000 Installation and
Operation Manual.
people are needed to perform the alignment procedures.
Figure D-1
shows the link setup. At least two
Once the alignment is complete, you are able to evaluate the quality of
the link.
Site A
AirMux
IDUx
Figure D-1. WinLink 1000 Link Setup
IDUx
Site B
Expected Signal Level D-1
Page 41

Appendix D AIND Antenna Alignment Procedure WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
D.1 Expected Signal Level
Based on the link budget parameters of the actual WinLink sites, you
need to calculate the expected signal level that will be received by the
receiving site.
Use the Link Budget Calculator utility supplied on the WinLink 1000
Manager Software CD-ROM to calculate the expected performance of
the WinLink 1000 wireless link. The utility allows you to determine the
RSS of the link, and find the number of E1/T1 services available at
various data rates, with the minimum and maximum distance.
D.2 Performing WinLink 1000-AIND Alignment
The supervisor of the antenna alignment is situated at the receive site
with the Spectrum Analyzer.
Equipment Setup
Æ
To set up the antenna alignment equipment:
1. Coarsely align the two antennas. Use the compass readings taken
during the Site Survey to point the antennas in the correct direction.
2. Connect the equipment as shown in
spectrum analyzer in place of the remote WinLink 1000-AIND.
3. Turn on the CW transmit signal from site A (from the WinLink 1000
NMS).
4. 4. At site B, tune the SA to the frequency transmitted.
5. 5. Increase the SA sensitivity according to the expected receive
signal.
Align the antennas:
Note
•
When one antenna is moved, the opposite ite is passive s
•
Move the antennas very slowly
Figure D-1
but connect a
1. Slowly move the site B antenna azimuth axis (the elevation axis
should be locked) until you see the best signal on the SA Lock the
azimuth axis.
D-2 Performing WinLink 1000-AIND Alignment
Page 42

WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix D AIND Antenna Alignment Procedure
2. Slowly move the site A antenna azimuth axis (the elevation axis
should be locked) until you see the best signal on the SA.
Lock the azimuth axis.
3. Slowly move the site B antenna elevation axis (the azimuth axis
should be locked) until you see the best signal on the SA.
Lock the elevation axis.
4. Slowly move the site A antenna elevation axis (the azimuth axis
should be locked) until you see the best signal on the SA.
Lock the elevation axis.
5. Repeat steps 1 to 4 until the reading on the SA is equal or as close
as possible to the calculated receive signal (for Rx Power Level see
Expected Signal Level
).
When the SA reads the expected receive signal, the antennas are
aligned and there is an indication of a good link between the sites.
6. Tighten the antenna azimuth axis and elevation axis.
7. Stop the CW function. The NMS will restart the system.
8. Connect WinLink 1000-AIND unit to external antenna. See WinLink
1000 Installation and Operation Manual for details. The operational
link is shown in
Figure 2-3
.
9. Configure WinLink 1000 NMS at both sites to operate at the pure
channel frequency found in the RF survey. WinLink 1000 is now
ready for operation.
D.3 Configuring the Link
1. Run the Installation Wizard in the WinLink 1000 Manager Software
to set the configuration of the link. Configure the link in accordance
with the parameters calculated in the Link Budget Calculator.
2. WinLink 1000 has a unique identification number, the SSID. Each
side of the link looks for its partner with the same SSID. Therefore
both sides of the link must be configured with the same SSID.
3. The WinLink 1000 link is now ready for operation.
Configuring the Link D-3
Page 43

Appendix D AIND Antenna Alignment Procedure WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
D.4 Evaluating the Link
With the link operating at a pure channel as determined by the
RF survey procedure, the recommended performance threshold of an
WinLink 1000 link is the following:
RSS: –84 dBm minimum
There are cases when there is no line of sight, but still the link is of an
acceptable quality.
If the link is not within the acceptable limit, see
Troubleshooting
.
D-4 Evaluating the Link
Page 44

WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual Appendix D AIND Antenna Alignment Procedure
D.5 Troubleshooting
If the link is not within the acceptable limit as defined in
Link
, check the following:
• Verify that both antennas have the same polarization
(horizontal/vertical).
• Check all the WinLink 1000-AIND cable connectors for faulty
connections.
• Verify that there are no obstacles in the Fresnel zone of the antenna
path such as large buildings, trees, etc.
• Use a spectrum analyzer with suitable sensitivity to measure the
signal at the distance between the sites.
If nothing improves the receive power level, check the overall link.
• Reduce the distance of the link–move the equipment from one site
closer to the other site–where it is possible to actually see the
antennas with the naked eye.
• If you now get the expected receive signal level, you can assume
that the equipment is operational, and the problem arises from
interference between the sites.
Evaluating the
Troubleshooting D-5
Page 45

Appendix E
Antenna Characteristics
An antenna is the radiating and receiving element from which the radio
signal, in the form of RF power, is radiated to its surroundings and vice
versa. The transmission range is a function of the antenna gain and
transmitting power. These factors are limited by country regulations.
WinLink 1000 may be operated with an integrated antenna attached to
the ODU unit, or with an external antenna wired to the ODU via an Ntype connector. All cables and connections must be connected
correctly to reduce losses. The required antenna impedance is 50Ω.
Table E-1. Antenna Characteristics
Type Gain
5.8, 5.4, 5.3 GHz
Integrat
ed
External Flat
5.8 GHz only
External Dish 32.5 80 50 4.5 Dia 900 Dia 35.4 10 22 N-type No
4.9 GHz
External Flat
External Dish 27 80 50 5 Dia 600 Dia 23.6 5.0 11.0 N-type Yes
2.4 GHz
Integrat
ed
External Grid 24 80 50 7.5
Flat
panel
panel
panel
Flat
panel
Max Range
[
dBi]
[km][miles]
22 40 25 9.0
28 80 50 4.5
21 24 15 9.0
17 40 25 20
Beam
[degrees
]
305×305×58 12×12×2.3
600×600×51 23.6×23.6×2
305×305×58 12×12×2.3
305×305×58 12×12×2.3
600×997×380 23.5×39.2×1
Dimensions
[mm] [in]
5
Weight
[kg]
[Ib]
0.5 1.1 NR Yes
5.0 11.0 N-type No
0.5 1.1 N-type Yes
0.5 1.1 NR Yes
2.0 4.6 N-type No
Connector Lightning
Protection
Antenna Characteristics E-1
Page 46

Appendix E Antenna Characteristics WinLink 1000 Installation and Operation Manual
The Parabolic dish antenna is a high-gain, reflector
antenna used for radio, television, and data
communications. The relatively short wavelength of
electromagnetic (radio) energy at these frequencies allows
reasonably sized reflectors to exhibit the very desirable
highly directional response for both receiving and
transmitting.
Parabolic Dish
Antenna
Used for 2.4 GHz applications. Due to the large size, the
grid design minimizes weight and windloading.
Grid Antenna
E-2 Antenna Characteristics
Page 47

Appendix F
Hub Site Synchronization
F.1 Introduction
HSS is an ordering option, WinLink 1000 ODU units are supplied with
special hardware for the collocation of several units, using a method
called Hub Site Synchronization (HSS). HSS uses an external cable
connected to all collocated WinLink 1000 radios. This cable carries
pulses sent to each radio, which synchronize their transmission with
each other.
This pulse synchronization ensures that the transmission of packets
occurs at the same time for all collocated units. This synchronized
transmission also results in all of the hub units receiving data at the
same time, eliminating the possibility of interference that could result
if some units transmit while other units at the same location receive.
HSS supports installation of up to eight collocated units.
Figure F-1
units.
shows interference caused by non-synchronized collocated
WinLink 1000 Introduction F-1
Page 48

Appendix F Hub Site Synchronization Installation and Operation Manual
Figure F-1. Interference caused by collocated units
Figure F-2. Collocated units using Hub Site Synchronization
F.2 Hardware Installation
HSS supports installation of up to eight collocated units. In addition to
each unit being connected to its IDU or PoE device, the collocated unit
has an additional cable that is connected to the HSS Unit. The HSS Unit
is a compact, weatherproof (IP67) connector box that is installed on
the same mast as the ODUs. All collocated units connect to this box via
CAT 5e cable. Prepared lengths are available for purchase.
F-2 Hardware Installation WinLink 1000
Page 49

Installation and Operation Manual Appendix F Hub Site Synchronization
The HSS is supplied with ten protective covers; any port not in use
must be closed with a protective cover.
Figure F-3. HSS Interconnection Unit
Note
Ensure that the collocated units are connected in sequence from SYNC
1. If an ODU is removed form the hub site, then all remaining ODUs
must be reconnected to maintain the connectivity.
Æ
To connect an ODU to the HSS
1. Unscrew the protective cover from the port marked SYNC 1.
2. Connect the RJ-45 connector from one end of the prepared CAT 5e
cable to SYNC 1.
3. Connect the other end of the CAT 5e cable to the ODU connector
labeled SYNC.
4. Tighten the protective seal that is on the prepared cable over the
RJ-45 connector.
5. Repeat for all ODUs that are to be collocated at the hub site. The
next ODU to be connected is inserted to SYNC 2, followed by SYNC
3 and so on.
F.3 Architecture
One of the collocated ODUs at the hub site acts as the Hub Sync Master
(HSM); all the other collocated units are Hub Sync Clients. The Hub
WinLink 1000 Architecture F-3
Page 50

Appendix F Hub Site Synchronization Installation and Operation Manual
Sync Master generates the pulses that synchronize the timing of the
Hub Sync Clients.
A Hub Sync Client can be configured to be two different types:
Hub Sync Client–Continue Transmission (HSC-CT): In the event that the
unit loses synchronization with the Hub Sync Master, the link remains
active. However, without synchronization pulses, it is possible that this
unit will cause interference.
Hub Sync Client–Disable Transmission (HSC-DT): In the event that the
unit loses synchronization with the Hub Sync Master, the link is
dropped until the synchronization pulses resume. This setting prevents
the unit from causing interference.
The remote ODUs that are not located at the hub site, are called
Independent Units and do not require HSS hardware.
Figure F-4. HSS Typical Application
F.4 Radio Frame Pattern Table
The synchronization pulse is termed Radio Frame Pattern (RFP). Four
RFP pulses are available. The RFP is selected depending on the type of
services that the
complete system is to provide see
the RFP that gives you the Best Fit for the system services and select
the Channel Bandwidth accordingly.
Note
F-4 Radio Frame Pattern Table WinLink 1000
The RFP must be the same for each link within the collocated system.
Table F-1
. Select
Page 51

Installation and Operation Manual Appendix F Hub Site Synchronization
Table F-1. Radio Frame Pattern Table
Channel Bandwidth
20 MHz 10 MHz 5 MHz
RFP TDM & EDO TDM EDO TDM EDO
A Best fit Non Optimal Not Available
B Not Available Best fit Non Optimal Best fit Non Optimal
C Not Available Not
Available
D Not Available Not Available Not
Best fit Not
Available
Available
Non Optimal
Best fit
WinLink 1000 Radio Frame Pattern Table F-5
Page 52

Appendix F Hub Site Synchronization Installation and Operation Manual
F.5 HSS Link Configuration
For HSS-enabled units, the Hub Site Synchronization Settings dialog
box appears in the Link Configuration Wizard.
Figure F-5. Hub Site Synchronization Settings dialog box
The Synchronization Status dialog box displays the current status of
each side of the link.
• Operation: Type of unit
Hub Sync Master (HSM)
Hub Sync Client – Disable Transmission (HSC-DT)
Hub Sync Client – Continue Transmission (HSC-CT)
Independent Unit
• Synchronization:
F-6 HSS Link Configuration WinLink 1000
Page 53

Installation and Operation Manual Appendix F Hub Site Synchronization
N/A- for Master or Independent Units
Synchronized – for Hub Site Clients
Not Synchronized – for Hub Site Clients
• External Pulses: The status of the pulses running through the HSS
cable. The Master generates such pulses. The severity of each of
these states is indicated by green, yellow or red text color. Possible
states are described in
Table F-2
.
Table F-2. External Pulse Status
Status Description Text Color
Not Detected Sync pulses not
detected
Generating Unit is HSM and is
generating RFP pulses
Generating and
Detected
Generating and
Improper Detected
Detected HSC detecting pulses Green
Unit is HSM and
generating RFP pulses
and is also receiving
pulses from another
unit. Incorrect
configuration.
Unit is HSM and
generating RFP pulses
and is also receiving
incorrect pulses from
another unit. Incorrect
configuration.
Green
Green
Red
Red
Improper Detected Incorrect RFP and BW
configuration
Multiple Sources
Detected
More than one HSM
generating pulses.
Incorrect configuration.
Red
Red
Æ
To configure the Operational States of the hub site unit
1. Click the Enabled check box
2. Click the Configure button
WinLink 1000 HSS Link Configuration F-7
Page 54

Appendix F Hub Site Synchronization Installation and Operation Manual
The Hub Site Configuration dialog box with the current status of
the ODUs is displayed.
3. Select the type of unit configuration from the drop-down list.
Because only the relevant options are displayed according to the
hardware configuration of each unit, usually the remote site will
have only the Independent Unit option available.
4. Select the appropriate RFP radio button. Some RFP options may be
disabled depending on the BW previously selected.
Note
Take care to avoid incorrect configuration of bandwidth, RFP or to set
multiple Hub Sync Masters, as system interference can occur. WinLink
1000 gives error messages and tool tips if the system is configured
with mismatches.
Figure F-6. Hub Site Configuration dialog box
F-8 HSS Link Configuration WinLink 1000
Page 55

Installation and Operation Manual Appendix F Hub Site Synchronization
F.6 Site Configuration
For units that support HSS, the Hub Site Sync option appears in the Air
Interface section and displays the current HSS of the unit. Configure
the unit from the Link Configuration Wizard according to the procedure
described above.
Figure F-7. Site Configuration – Hub Site Sync dialog box
Figure F-8 is displayed when the hardware does not support HSS.
These units may be used as independent remote units.
WinLink 1000 Site Configuration F-9
Page 56

Appendix F Hub Site Synchronization Installation and Operation Manual
Figure F-8. HSS Not Supported
F-10 Site Configuration WinLink 1000
Page 57

Appendix G
BRS Installation Procedure
G.1 BRS Link Activation
In accordance with 2.5 GHz standard, WinLink 1000-BRS systems links
must be activated before use. This is done at both ODUs independently
before installation on site. Both ODUs must be configured the same.
Æ
To Activate a BRS Link
1. Install WinLink 1000 Manager software as usual.
2. When the Manager Main Screen is displayed it appears with the Link
Status label red and showing Inactive. The Link Configuration and
Link installation buttons are disabled.
WinLink 1000 BRS Link Activation G-1
Page 58

Appendix G BRS Installation Procedure Installation and Operation Manual
Figure G-1. Inactive Manager Screen
3. Click Configuration>Configure Location
The Air Interface dialog box opens,
Figure G-2
.
G-2 BRS Link Activation WinLink 1000
Page 59

Installation and Operation Manual Appendix G BRS Installation Procedure
Figure G-2. BRS Air Interface dialog box
4. Set the appropriate Frequency Band Plan and Bandwidth.
5. Select the required frequency band, and click Apply.
6. Click Installation Mode
7. Repeat for the remote ODU.
WinLink 1000 BRS Link Activation G-3
Page 60

Appendix G BRS Installation Procedure Installation and Operation Manual
Note
Figure G-3. BRS Channel Settings Pre-Transition
8. Perform the remainder of the Installation procedure as defined in
the Installation section.
G.2 BRS Link Configuration
The BRS link is reconfigured during the Link Installation or the Link
Configuration wizards, or from the Air Interface screen.
Both sites in a BRS Link must be configured identically.
Any changes to the frequency settings cause the link to resynchronize. A short loss of servi e will occur during resynchronization.
c
G-4 BRS Link Configuration WinLink 1000
Page 61

Installation and Operation Manual Appendix G BRS Installation Procedure
Æ
To Configure BRS Channel Settings
1. Set the Band Plan.
2. Select the Bandwidth required,
Single Band
Double Band
3. Select the Frequency from the pull-down menu.
4. Click Next. The system is re-synchronized to the changes.
Figure G-4. BRS Channel Settings Post-Transition
WinLink 1000 BRS Link Configuration G-5
Page 62

Appendix H
RF Exposure
The antennas used for the following transmitters must be installed to
provide a separation distance as specified. They must not be colocated or operated in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
Product FCC ID Antenna gain [dBi] Min. Safety Distance [cm]
F58A/HE/FCC/INT Q3KAMWL1580 22 109
F58A/HE/FCC/EXT Q3KAMWL1580 28 217
F58A/HE/FCC/EXT
Q3KAMWL1580 32.5 364
F58A/FCC/AIND/EXT
F24A/FCC/INT Q3KAMWL1240 16 16
F24A/FCC/EXT Q3KAMWL1240 24 40
F24A/HE/FCC/EXT Q3KAMWL1240H 24 71
F24A/HE/FCC/INT Q3KAMWL1240H 15.2 37
F25/HE/BRS/EXT Q3KAMWL1250 24 56
F25/HE/BRS/INT Q3KAMWL1250 17.5 27
WinLink 1000 H-1
Page 63

Index
—A—
AC power
connecting, 2-7
Active Alarm Summary, 5-10
Adaptive modulation, 1-4
Adaptive Modulation, 4-8
Advanced configuration, 4-14
Advanced Encryption System, 1-3
Advanced Tab, 4-21
AIND All Indoor Radio Unit, 2-5
Air Interface, 1-8
configuration, 4-14
rate, 4-7
Alarm connector, 1-4, 1-9, A-3
Alarms, 5-9
list of, 5-10
Antenna, 1-4
Antenna characteristics, E-1
Application, 1-1
—B—
Backup, 4-29
button, 4-14
Band Plan, G-3
Beeper
muting, 4-28
restore, 4-28
sequence, 2-9
Bridge configuration, 4-14, 4-20
BRS, G-1
BRS Link Activation, G-1
BRS Link Configuration, G-4
Buzzer. See Beeper
—C—
Change password, 4-26
Channel select, 2-16
Clear Counters, 3-5
Community String, 4-24
change dialog box, 4-24
forgotten string, 4-26
Read-Only, 4-24
Read-Write, 4-24
Trap, 4-24
types, 4-24
Community values, 4-14
Configuration
advanced, 4-13
air interface, 4-13
bridge, 4-13
community values, 4-13
contact details, 4-13
editing, 4-13
external alarms, 4-13
inventory, 4-13
LAN connection, 4-13
location details, 4-13
management, 4-13
restoring, 4-30
saving, 4-29
security, 4-14
system, 4-13
transmit power, 4-13, 4-15
wizard, 4-1
Configure
system parameters, 4-1
Connecting
AC power, 2-7
DC power, 2-7
user equipment, 2-24
Connectivity icon, 3-6
I-1
Page 64

Index Installation and Operation Manual
Connectors
Alarm, A-3
IDU-E, A-2
Contact person, 4-14
Contents, of package, 2-1
—D—
Date & Time synchronizing, 4-18
Date and Time, 4-14, 4-18
DC power
connecting, 2-7
Default Gateway, 4-14, 4-17
Default password
link password, 4-27
management, 2-10
Default settings, 3-4
Description, 1-5
DFS, 1-3, 2-17, 4-5
Diagnostics, 1-3, 5-1
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS), 1-3, 2-
17, 4-5
—E—
E1/T1 Connector Pinout, A-2
Editing
configuration, 4-13
contact person, 4-14
location details, 4-14
Encryption icon, 3-6
Environment, 1-9
Equipment required, 2-2
Estimated Time Between Errors, 3-6
ETBE. See Estimated Time Between Errors
Event colors, 5-3
Event log, 3-6, 5-9
save, 5-4
External antenna, 1-4
mounting, B-4
—F—
Factory default, 4-31
FAQ, 5-17
Fast Ethernet Pinout, A-2
Features, 1-2
—G—
Get Link Information, 5-1
Grid Antenna, E-1
—H—
HSS. See Hub Site Synchronization
Hub Site Synchronization, 1-5, F-1
Hub Sync Clients, F-3
Hub Sync Master, F-3
—I—
Icon
Connectivity, 3-6
Encryption, 3-6
IDU Aging time, 4-21
Ethernet Bridge, 4-22
Fast aging mode, 4-22
Hub Mode, 4-22
IDU-2E1-AL
rear panel, 2-5
IDU-C, 1-6, 1-7
front panel, 2-5
IDU-E, 1-6, 1-7
rear panel, 2-5
Indicators, 1-9
Indoor Unit. See IDU
Information messages, 5-10
Information Rate, 4-23
Install mode, 4-14
button, 4-14
Installation, 2-1
management software, 2-6
sequence, 2-3
software, 2-6
wizard, 2-12
Inventory, 4-14
IP address, 4-14, 4-17
—L—
LAN connection, 4-14
LAN interface, 1-2, 1-8
LAN Port, A-2
LEDs
front panel, 3-2
rear panel, 3-2
Line code, 2-21, 4-12
I-2 WinLink 1000
Page 65

Installation and Operation Manual Index
Link Budget Calculator
overview, C-1
using, C-5
Link Compatibility, 1-4, 5-12
Link configuration, 4-1
Link details, 3-6
Link Information, 5-1
Link installation, 2-12
Link password, 4-14
Link Status, 3-6
Location details, 4-14
Loopback
activate, 5-13
deactivate, 5-13
external, 5-13
internal, 5-14
—M—
Main menu, 3-5
Management
addresses, 4-17
configuration, 4-14
Default Gateway, 4-14
definitions, 4-14
IP address, 4-14
options, 1-3
program, 2-6
Subnet Mask, 4-14
Trap Destination, 4-14
Monitor log
save, 5-2
Monitor pane, 3-6
Monitoring, 1-3
Monitoring Performance, 5-2
Mounting
mast, B-2
wall, B-3
Mute
button, 4-14
Muting the beeper, 4-14, 4-28
—O—
ODU, 1-6, 1-7
aligning, 2-8
beeper, 2-8
connecting, 2-5
mounting, 2-4
ODU Bridge Mode, 4-21
ODU-IDU cable
pinout, A-1
Operating temperature, 2-1
O-PoE, 1-5, 1-6, 1-7
Outdoor PoE (O-PoE)
mounting, B-1
Outdoor Unit. See ODU
Outdoor Unit (ODU)
mounting, B-1
—P—
Package contents, 2-1
Panel
AIND unit, 2-5
IDU-2E1-AL, 2-5
IDU-C, 2-5
IDU-E, 2-5
Parabolic dish antenna, E-1
Password
changing, 4-26
default, 2-10
PC requirements, 2-6
Performance Monitor Report, 5-5
commands, 5-8
data, 5-7
time intervals, 5-5
Performance monitoring, 1-3
Physical description, 1-5
Physical dimensions, 1-9
Pinout
alarm connector, A-3
DC power connector, A-2
E1/T1 Connector, A-2
Fast Ethernet connector, A-2
Pinout ODU-IDU cable, A-1
Power
IDU, 2-7
IDU-C, 2-7
IDU-E, 2-7
O-PoE, 2-7
Power specifications, 1-9
Power supply, 2-7
AC, 2-7
Preferences, 5-2, 5-3, 5-4
WinLink 1000 I-3
Page 66

Index Installation and Operation Manual
event colors, 5-3
reset event colors, 5-3
Prerequisites, 2-1
—Q—
Quality bar, 2-17, 4-6
—R—
Radio signal strength, 3-6
Re-installing the Link, 4-30
Reselect Channel, 2-17, 4-4, 4-6
Reset, 4-30
factory defaults, 4-31
Restore
button, 4-14
Restoring configuration, 4-30
—S—
Saving, 4-29
Saving the Monitor Log, 5-2
Security configuration, 4-14
Service parameters, 4-7
Setup, 2-1
Site requirements, 2-1
SSID, 2-15
Statistics, 3-6, 5-2
Status Bar, 3-6
Subnet Mask, 4-14, 4-17
System Configuration, 4-14
—T—
TDM
interface, 1-3, 1-8
Traffic LEDs, 3-3
TDM clock
automatic mode, 4-9
TDM status, 3-6
Technical Specifications, 1-8
Telnet, 4-32
Toolbar, 3-5
TPC, 1-4
Traffic rate, 3-6
Transmission Rate, 4-7
Transmit power, 4-15
limits, 4-17
Transmit Power Control, 1-4
Trap colors
background, 5-3
reset, 5-3
set, 5-3
Trap Destination, 4-14, 4-17
Troubleshooting, 5-1, 5-15
Trunk Port, A-2
Turning off, 3-7
Turning on, 3-1
Typical application, 1-1
Typical installation, 2-3
—U—
User equipment, 2-24
—W—
Wireless link, 1-2
I-4 WinLink 1000
 Loading...
Loading...