Page 1

RADWIN 5000 HPMP
Point to Multipoint Broadband Wireless
USER MANUAL
RELEASE 3.2.00
UM 5000-3200/08.11
Page 2

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 i
RADWIN 5000 HPMP
User Manual
Notice
This manual contains information that is proprietary to RADWIN Ltd. (RADWIN hereafter). No
part of this publication may be reproduced in any form whatsoever without prior written
approval by RADWIN.
Right, title and interest, all information, copyrights, patents, know-how, trade secrets and
other intellectual property or other proprietary rights relating to this manual and to the
RADWIN products and any software components contained therein are proprietary products
of RADWIN protected under international copyright law and shall be and remain solely with
RADWIN.
The RADWIN name is a registered trademark o f RA DWIN Ltd. No right, license, or interest to
such trademark is granted hereunder, and you agree that no such right, license, or interest
shall be asserted by you with respect to such trademark.
You shall not copy, reverse compile or reverse assemble all or any portion of the User Manual
or any other RADWIN documentation or products. You are prohibited from, and shall not,
directly or indirectly, develop, market, distribute, license, or sell any product that supports
substantially similar functionality based or derived in any way from RADWIN products. Your
undertaking in this paragraph shall survive the termination of this Agreement.
This Agreement is effective upon your opening of a RADWIN product package and shall
continue until terminated. RADWIN may terminate this Agreement upon the breach by you of
any term thereof. Upon such termination by RADWIN, you agree to return to RADWIN any
RADWIN products and documentation and all copies and portions thereof.
For further information contact RADWIN at one of the addresses under Worldwide
Contacts below or contact your local distributor.
Disclaimer
The parameters quoted in this document must be specifically confirmed in writing before they
become applicable to any particular order or contract. RADWIN reserves the right to mak e
alterations or amendments to the detail specification at its discretion. The publication of
information in this document does not imply freedom from patent or other rights of RADWIN,
or others.
Trademarks
WinLink 1000 and RADWIN 2000 are trademarks of RADWIN Ltd.
Windows 2000, XP Pro, Vista, Windows 7 and Internet Explorer are trademarks
of Microsoft Inc.
Mozilla and Firefox are trademarks of the Mozilla Foundation.
Other product names are trademarks of their respective manufacturers.
Page 3

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 ii
RADWIN Worldwide Offices
Corporate and EMEA Regional Headquarters
Corporate and EMEA Headquarters
27 Habarzel Street
Tel Aviv, 69710
Israel
Tel: +972.3.766.2900
Fax: +972.3.766.2902
Email:
sales@radwin.com
North America Regional
Headquarters
900 Corporate Drive
Mahwah, NJ, 07430
USA
Tel: +1-877-RADWIN US
(+1-877 723-9468)
Tel: +1-201-252-4224
Fax: +1-201-621-8911
Email:
salesna@radwin.com
Customer Support - North America:
Hours: 9 am - 6 pm EST (Mon - Fri)
Email:
supportusa@radwin.com
APAC Regional Headquarters
53A, Grange Road #15-02
Spring Grove ,249566
Singapore
Tel: +65.6638.7864
Email:
salessg@radwin.com
RADWIN Regional Offices
RADWIN Brazil
Av. Chucri Zaidan, 920 – 9º
São Paulo, 04583-904
Brazil
Tel: +55.11.3048-4110
Email:
salesbr@radwin.com
RADWIN Mexico
Quinto #20 Col El Centinela
Mexico, DF, O4450
Mexico
Tel: +52 (55) 5689 8970
Email:
salesmx@radwin.com
RADWIN Peru
Av. Antares 213
Lima, 33
Peru
Tel: +511.6285105
Fax: +511-990304095
Email:
salespe@radwin.com
RADWIN India
E-13,B-1 Extn., Mohan Co-operative Industrial Estate
New Delhi, 110 044
India
Tel: +91-11-40539178
Email:
salesin@radwin.com
RADWIN Philippines
5 Bur Bank St.
Laguna, Belair, Santa Rosa
Laguna Philippines
Tel: +63 928 7668230
Email:
salesph@radwin.com
RADWIN South Africa
P.O. Box 3554, Rivonia
Johannesburg ,2128
South Africa
Tel: +27 (0)82 551 5600
Email:
sales@radwin.com
RADWIN Italy and Spain
Piazza Arenella 7/H
Napoli ,80128
Italy
Tel:+390815564116
Fax: +39335433620
Email:
salesit@radwin.com
RADWIN Central America
Calle La Cañada # 108-E
Jardines de la Hacienda
Ciudad Merliot El Salvador
Tel: +503 2278-5628
Email:
sales@radwin.com
RADWIN South East Asia
All Season Mansion
87/38 Wireless Road Lumpinee
Bangkok ,10330
Thailand
Tel: +66811707503
Email:
sales@radwin.com
Page 4

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 iii
Regulatory Compliance
General Note
This system has achieved Type Approval in various countries around the world. This means
that the system has been tested against various local technical regulations and found to
comply. The frequency bands in which the system operates may be “unlicensed” and in these
bands, the system can be used provided it does not cause interference.
FCC - Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment
does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Changes or modifications to this equipment not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Warning
It is the responsibility of the installer to ensure that when using the outdoor
antenna kits in the United States (or where FCC rules apply), only those
antennas certified with the product are used. The use of any antenna other
than those certified with the product is expressly forbidden by FCC rules 47
CFR part 15.204.
Warning
It is the responsibility of the installer to ensure that when configuring the
radio in the United States (or where FCC rules apply), the Tx power is set
according to the values for which the product is certified. The use of Tx
power values other than those, for which the product is certified, is
expressly forbidden by FCC rules 47 CFR part 15.204.
Caution
Outdoor units and antennas should be installed ONLY by experienced
installation professionals who are familiar with local building and safety
codes and, wherever applicable, are licensed by the appropriate
government regulatory authorities. Failure to do so may void the product
warranty and may expose the end user or the service provider to legal and
financial liabilities. Resellers or distributors of this equipment are not liable
for injury, damage or violation of regulations associated with the installation
of outdoor units or antennas. The installer should configure the output
power level of antennas according to country regulations and antenna type.
Page 5

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 iv
Indoor Units comply with part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
(1) These devices may not cause harmful interference.
(2) These devices must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
Canadian Emission Requirements for Indoor Units
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numẻrique de la classe B est conforme ả la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
China MII
Operation of the equipment is only allowed under China MII 5.8GHz band regulation
configuration with EIRP limited to 33 dBm (2 Watt).
India WPC
Operation of the equipment is only allowed under India WPC GSR-38 for 5.8GHz band
regulation configuration.
Unregulated
In countries where the radio is not regulated the equipment can be oper ated in any regulation
configuration, best results will be obtained using Universal regulation configuration.
Safety Practices
Applicable requirements of National Electrical Code (NEC), NFPA 70; and the National
Electrical Safety Code, ANSI/IEEE C2, must be considered during installation.
NOTES:
1. A Primary Protector is not required to protect the exposed wiring as long as the exposed
wiring length is limited to less than or equal to 140 feet, and instructions are provided to
avoid exposure of wiring to accidental contact with lightning and power conductors in
accordance with NEC Sections 725-54 (c) and 800-30.
In all other cases, an appropriate Listed Primary Protector must be provided. Refer to Articles
800 and 810 of the NEC for details.
2. For protection of ODU against direct lightning strikes, appropriate requirements of NFPA
780 should be considered in addition to NEC.
3. For Canada, appropriate requirements of the CEC 22.1 including Section 60 and additional
requirements of CAN/CSA-B72 must be considered as applicable.
Warning
• Where Outdoor units are configurable by software to Tx power values
other than those for which the product is certified, it is the responsibility of the Professional Installer to restrict the Tx power to the certified limits.
• This product was tested with special accessories - indoor unit (IDU or
PoE), FTP CAT-5e shielded cable with sealing gasket, 12 AWG
grounding cable - which must be used with the unit to insure compliance.
Page 6

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 v
Brief
Table of Contents
Part 1: Basic Installation
Chapter 1 Introduction
Chapter 2 Site Preparation
Chapter 3 Hardware Installation
Part 2: Sector Installation
Chapter 4 Getting Started with the RADWIN Manager
Chapter 5 Installing the Sector
Part 3: Sector Management
Chapter 6 Managing the Sector
Chapter 7 Direct HSU Configuration
Chapter 8 Monitoring and Diagnostics
Part 4: Site Synchronization
Chapter 9 Hub Site Synchronization
Chapter 10 Using the RADWIN GSU
Part 5: Advanced Installation Topics
Chapter 11 Software Upgrade
Chapter 12 VLAN Functionality with RADWIN 5000 HPMP
Chapter 13 False Radar Mitigation Facilities
Chapter 14 FCC/IC DFS Considerations
Chapter 15 Quality of Service
Part 6: Field Installation Topics
Chapter 16 Pole and Wall Installation
Chapter 17 Lightning Protection and Grounding Guidelines
Chapter 18 Link Budget Calculator
Chapter 19 Spectrum View
Chapter 20 Using the Web Interface
Part 7: Product Reference
Appendix A Technical Specifications
Appendix B Wiring Specifications
Appendix C MIB Reference
Appendix D RF Exposure
Appendix E Setting Antenna Parameters
Appendix F Regional Notice: French Canadian
Index
Page 7

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 vi
Full
Table of Contents
Part 1: Basic Installation
Chapter 1 Introduction
Welcome to RADWIN 5000 HPMP!...............................................................1-1
RADWIN 5000 HPMP Highlights................. .. .... .. .. ... .. ................................. .. .1-1
What’s New in Release 3.2.00 ......................................................................1-1
Some Terminology ........................................... .. ... .. .. .. .. ..............................1-2
Key features of RADWIN 5000 HPMP
............................................................1-2
RADWIN 5000 HPMP Components
...............................................................1-3
The RADWIN Manager...................... .. .. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. ... .. .....1-4
Conventions Used in this Manual ..................................................................1-4
Notifications
............................................................................................1-4
Typographical conventions
.........................................................................1-4
Viewing and Printing
.................................................................................1-5
Chapter 2 Site Preparation
Planning the Sector Site.................... .. .. .. .. .. .. ................................. .. .. ... .. .. .. .2-1
Overview
................................................................................................2-1
The Site Survey.............................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. ... .. .. ...2-1
Introduction
............................................................................................2-1
Recommended Equipment
..........................................................................2-1
Stage 1: Preliminary Survey .........................................................................2-2
Stage 2: Physical Survey..............................................................................2-3
Additional Outdoor Site Requirements
...........................................................2-3
Additional Indoor Site Requirements
.............................................................2-4
Stage 3: RF Survey......................................................................................2-4
RF Planning for Dense Installations and Collocated Sites................................2-4
Chapter 3 Hardware Installation
Safety Practices...........................................................................................3-1
Preventing overexposure to RF energy
..........................................................3-1
Grounding
...............................................................................................3-1
Protection against Lightning
.......................................................................3-2
General
..................................................................................................3-2
Package Contents........................................................................................3-2
HBS and HSU ODU Package Contents
...........................................................3-2
External Antenna Package Contents
.............................................................3-4
Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Devices
..............................................................3-5
Hub Site Synchronization (HSS) Unit
............................................................3-6
GSU
.......................................................................................................3-6
Additional Tools and Materials Required........................................................3-7
Tools and Materials
...................................................................................3-7
Cables and connectors
...............................................................................3-7
Hardware Installation Sequence ...................................................................3-8
Outdoor installation.....................................................................................3-9
Preparing the ODU before Deployment
.........................................................3-9
Mounting the ODU
....................................................................................3-9
Mounting external antennas
.....................................................................3-10
Mounting the Lightning Protection Devices
..................................................3-10
Outdoor Connections
...............................................................................3-10
Installing a Sector using PoE Devices
.......................................................... 3-11
Connecting User Equipment
......................................................................3-11
Aligning HSUs to an HBS............................................................................3-11
Part 2: Sector Installation
Page 8

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 vii
Chapter 4 Getting Started with the RADWIN Manager
What we will do here...................................................................................4-1
Installing the RADWIN Manager Application ..................................................4-1
Minimum System Requirements
...................................................................4-1
Installing the Software
..............................................................................4-2
Getting Started with the RADWIN Manager ...................................................4-3
The RADWIN Manager log-on Concept.............................. .. .. .. .. ....................4-4
Log-on Errors and Cautions..........................................................................4-7
Unsupported Device
..................................................................................4-7
Incorrect IP Address
.................................................................................4-7
Incorrect Password
...................................................................................4-8
Invalid Read/Write Community String
...........................................................4-8
Exploring the RADWIN Manager Main Window - HBS .....................................4-8
HBS Main Button Menu
..............................................................................4-9
Sector Status Panel
...................................................................................4-9
Base Station Panel
....................................................................................4-9
HBS Events Log
.....................................................................................4-11
HBS Main Window - HSUs Panel
................................................................4-12
Exploring the RADWIN Manager Main Window - HSU...................................4-15
Logging on to an HSU.......... .. ... .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ................4-15
HSU Main Button Menu
............................................................................4-17
HSU Link Status
.....................................................................................4-17
HSU Events Log
.....................................................................................4-18
HSU Link Performance
.............................................................................4-18
Setting RADWIN Manager Preferences........................................................4-18
Monitor
................................................................................................4-19
Events
..................................................................................................4-20
Advanced
..............................................................................................4-21
What Comes Next?.......... .. .. .. ... ................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ....................4-21
Chapter 5 Installing the Sector
Scope of this Chapter ..................................................................................5-1
Concepts ....................................................................................................5-1
Workflow....................................................................................................5-2
Default RADWIN 5000 HPMP Settings...........................................................5-2
Configuring the Sector out of the Box - IP Addresses .....................................5-4
Activating the HBS.......................................................................................5-9
Pre-configuring the HSUs for Service .......................... .. .. .. .. .. .. ....................5-18
Pre-configuration from the HBS
.................................................................5-18
Pre-configuring from a Direct Link
..............................................................5-22
The Final Outcome
.................................................................................5-25
Registering the HSUs for Service ............... .. .. .. ................................. .. ... .. .. . 5-26
Choosing Diversity Antenna Mode During Registration..................................5-30
Deactivating the HBS.................................................................................5-31
Deregistering an HSU ................................................................................5-31
Where has my HSU gone?..........................................................................5-31
Part 3: Sector Management
Chapter 6 Managing the Sector
Scope of this Chapter ..................................................................................6-1
Configuring an HBS .............................. .. .. .. .. ................................. .. .. ... .. .. .. .6-1
Configuration Menu Buttons
.......................................................................6-1
System
...................................................................................................6-2
Air Interface
............................................................................................6-3
Tx and Antenna
.......................................................................................6-4
Hub Site Sync [HSS]
.................................................................................6-5
Management
...........................................................................................6-6
Page 9

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 viii
Inventory
................................................................................................6-9
Security
................................................................................................6-10
Date and Time
.......................................................................................6-14
Ethernet Service Configuration
..................................................................6-16
Operations
............................................................................................ 6-18
Advanced: False Radar Mitigation for HBS
...................................................6-19
HSU Connection Table....... ................................. ... .. .. .. .. .. ..........................6-19
Configuring an HSU from the HBS Main Window..........................................6-20
Configuration Menu Buttons
.....................................................................6-20
System
.................................................................................................6-21
Tx & Antenna
........................................................................................ 6-22
Management
......................................................................................... 6-23
Inventory
..............................................................................................6-24
Security
................................................................................................6-25
Date & Time
.......................................................................................... 6-26
Ethernet
...............................................................................................6-27
Operations
............................................................................................ 6-28
Advanced: False Radar Mitigation
..............................................................6-28
Replacing an HSU...................................................................................... 6-29
Updating HSU Services .............................................................................. 6-32
Suspending an HSU...................................................................................6-33
Changing the Sector Band..........................................................................6-33
Configuration with Telnet...........................................................................6-37
Telnet Access to the HBS
.........................................................................6-37
Telnet Access to the HSU
.........................................................................6-39
Chapter 7 Direct HSU Configuration
Scope of this Chapter ..................................................................................7-1
Configuring an HSU.......................... .. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. ... .......7-1
Configuration Menu Buttons
.......................................................................7-3
System
...................................................................................................7-4
Air Interface
............................................................................................7-5
Tx & Antenna
..........................................................................................7-7
Management
...........................................................................................7-8
Inventory
................................................................................................7-9
Security
................................................................................................7-10
Date & Time
.......................................................................................... 7-11
Ethernet
...............................................................................................7-12
Operations
............................................................................................ 7-13
Advanced
..............................................................................................7-14
Advanced: False Radar Mitigation
..............................................................7-14
Chapter 8 Monitoring and Diagnostics
Retrieving Link Information (Get Diagnostics)................................................8-1
Throughput Checking ......................................... ... .. .. .. .. .. ............................8-4
Recent Events.............................................................................................8-5
Performance Monitoring...................... .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..........8-7
HBS
.......................................................................................................8-8
HSU
.....................................................................................................8-10
More on the Thresholds
...........................................................................8-12
RADWIN Manager Traps............................................................................8-13
Active Alarms............................................................................................8-14
Other Diagnostic Aids ................................................................................8-14
Link Budget Calculator
.............................................................................8-14
Online Help
........................................................................................... 8-15
Customer Support
..................................................................................8-15
Part 4: Site Synchronization
Chapter 9 Hub Site Synchronization
Page 10

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 ix
Scope of this Chapter ..................................................................................9-1
What is Hub Site Synchronization?...............................................................9-1
Hardware Installation ..................................................................................9-3
Connecting an HSS Unit
.............................................................................9-3
Using a Single HSS Unit
.............................................................................9-4
Using More than One HSS Unit
....................................................................9-4
ODU/HSS Unit Connection Pinout .................................................................9-6
Radio Frame Pattern (RFP)............................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..................9-6
Without HSS
............................................................................................9-7
RFP and HSS
...........................................................................................9-7
RFP: General Radio Frame Pattern
...............................................................9-8
Sector Configuration and HSS ................. .. .. .. .. .. .. .................................. .. .. .. .9-8
Chapter 10 Using the RADWIN GSU
What is it for . ................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. ... .. ...10-1
GSU Functionality......................................................................................10-1
Typical GSU Scenarios ...............................................................................10-1
Independent Distributed Sites
...................................................................10-1
Multiple Distributed Sites with Communication
..............................................10-2
Cascaded Sites using Shifted Phase Transmission
.........................................10-3
GSU Redundancy ...................................................................................... 10-3
GSU Kit Contents.......................................................................................10-4
GSU Installation ........................................................................................ 10-4
Overview
..............................................................................................10-4
Preparing the GSU for Use
........................................................................10-5
Mounting the GSU
..................................................................................10-5
Configuring the GSU
...............................................................................10-5
GSU Preferences
.................................................................................. 10-15
GSU Monitoring and Diagnostics...............................................................10-15
GSU Telnet Support................................................................................. 10-15
Software Update for GSUs................... .. .. .. .. .. .. ................................. .. ... .. . 10-16
Part 5: Advanced Installation Topics
Chapter 11 Software Upgrade
What is the Software Upgrade Utility?.........................................................11-1
Upgrading an Installed Sector ....................................................................11-2
Chapter 12 VLAN Functionality with RADWIN 5000 HPMP
VLAN Tagging - Overview ....................... .. .. .. .. .. .. .................................. .. .. . 12-1
VLAN Terminology
..................................................................................12-1
VLAN Background Information on the WEB
..................................................12-1
Scope of this Chapter ................................................................................12-1
Requirements............................................................................................12-1
VLAN Tagging....................... ... .. .. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ............12-1
QinQ (Double Tagging) for Service Providers
...............................................12-2
VLAN Untagging
.....................................................................................12-3
Port Functionality
...................................................................................12-3
VLAN Configuration Using the RADWIN Manager .........................................12-5
Management Traffic and Ethernet Service Separation
....................................12-5
Managing the HBS over the Air from an HSU
................................................12-5
Configuration of VLAN Tagging for Ethernet Service
......................................12-6
Chapter 13 False Radar Mitigation Facilities
Who needs it ............................................................................................13-1
DFS and False Radar Mitigation............. .. .. .. .. .. .... ... ................................. .. . 13-1
About DFS
............................................................................................ 13-1
What is False Radar Mitigation
..................................................................13-1
Configuring False Radar Mitigation..............................................................13-2
FCC/IC Considerations...............................................................................13-3
Page 11

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 x
Chapter 14 FCC/IC DFS Considerations
FCC 5.4GHz Device Registration .................................................................14-1
Registering the Device. .. .. .. ................................. ... .. .. .. .. ............................14-1
TDWR Table .............................................................................................14-5
Chapter 15 Quality of Service
Prerequisites............................................................................................. 15-1
QoS - Overview.........................................................................................15-1
Setting up QoS.......................................................................................... 15-1
Setting up the HBS for QoS
......................................................................15-2
Setting up an HSU for QoS
.......................................................................15-3
Part 6: Field Installation Topics
Chapter 16 Pole and Wall Installation
ODU Mounting Kit Contents........................................................................ 16-1
Mounting an ODU on a Pole .......................................................................16-2
Mounting an ODU on a Wall.......................................................................16-3
Mounting an External Antenna .......................... .. ... .. .. .. .............................. 16-4
Mounting a Connectorized ODU Horizontally................................................16-4
Chapter 17 Lightning Protection and Grounding Guidelines
Grounding for Antenna Cable ............................ .. ... .. ................................. . 17-1
Grounding for Indoor/Outdoor Units ...........................................................17-2
ODU Grounding
......................................................................................17-2
IDU Grounding
.......................................................................................17-3
The RADWIN Lightning Protection Kit ...... .. .... .. .. .. ... .. .. ................................ 17-3
Using Lightning Protectors and Grounding...................................................17-3
Mounting RADWIN Lighting Protection unit ....................... .. .. .. .. .. .. ..............17-6
Internal ESD Protection circuits ..................................................................17-7
Chapter 18 Link Budget Calculator
Overview..................................................................................................18-1
User Input
............................................................................................ 18-1
Link Budget Calculator Internal Data
.......................................................... 18-1
Calculations ..............................................................................................18-2
EIRP
....................................................................................................18-2
Expected RSS and Fade Margin
.................................................................18-2
Min and Max Range
................................................................................18-2
Service
.................................................................................................18-2
Availability
............................................................................................ 18-2
Antenna Height
......................................................................................18-3
About the Fresnel Zone..............................................................................18-3
Running the Link Budget Calculator........................................................... 18-5
Chapter 19 Spectrum View
What is Spectrum View? ..................... .. .. .. .. .. .. ................................. .. ... .. .. . 19-1
Who needs it ............................................................................................19-1
Scope of this Chapter ................................................................................19-1
Two Ways to Run Spectrum View...............................................................19-1
Where is the Spectrum View Data stored ....................................................19-2
Spectrum View Main Window: HBS.............................................................19-2
Spectrum View Display Function Buttons.....................................................19-5
Running Spectrum View from the HBS ........................................................ 19-6
Running Spectrum View from an HSU.........................................................19-8
Chapter 20 Using the Web Interface
What is it For........................ ... .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ................20-1
Who Needs it............................................................................................20-1
How it Works............................................................................................20-2
What it Provides.................... ... .. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..............20-2
Page 12

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 xi
Prerequisites............................................................................................. 20-3
Hardware
..............................................................................................20-3
Software
...............................................................................................20-3
Technical Background
.............................................................................20-3
Special Considerations Working with the WI................................................20-3
Advanced Configurations
..........................................................................20-3
Operational Effects
.................................................................................20-3
Some Working Tips
.................................................................................20-3
Scope of this Chapter ................................................................................20-4
Logging on ..... .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. ................................. .. ... .. .. . 20-4
HBS Management.. .. .. .. .. .. .. ................................. ... .. .. .. .. .. .. ........................20-5
The Main Window
...................................................................................20-5
Configure
..............................................................................................20-6
Events
................................................................................................ 20-11
Reset
................................................................................................. 20-11
HSU Management .......................... .. .. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. ... ...20-11
The Main Window
................................................................................. 20-11
Part 7: Product Reference
Appendix A Technical Specifications
Scope of these Specifications .......................................................................A-1
ODU - HBS and HSU............ .. ... .. .. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..............A -1
GbE PoE Device - Indoor, AC for HBS only ....................................................A-3
PoE Device - Indoor, AC.................... .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ............A-4
PoE Device - Outdoor, DC................. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. ............A-5
GSU ...........................................................................................................A-6
Antenna Characteristics ...............................................................................A-6
Appendix B Wiring Specifications
ODU-PoE Cable (HBS and HSU)............. .. .... .. .. .. .. ... .. .. ................................. .B-1
HBS/HSS Unit Connection Pinout..................................................................B-1
User Port Connectors..................................................................................B-2
LAN Port
.................................................................................................B-2
DC Power Terminals....................................................................................B-2
DC PoE
...................................................................................................B-2
Appendix C MIB Reference
Introduction................................................................................................C-1
About the MIB
.........................................................................................C-1
Terminology
............................................................................................C-1
Interface API ..............................................................................................C-1
Control Method
........................................................................................C-1
Community String
.....................................................................................C-2
Private MIB Structure .. .. .. .. .. .................................. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..........................C-2
MIB Parameters ..........................................................................................C-3
Supported Variables from the RFC 1213 MIB
..................................................C-3
Private MIB Parameters
.............................................................................C-5
MIB Traps
.............................................................................................C-29
General
................................................................................................C-29
Trap Parameters
....................................................................................C-30
RADWIN Manager Traps............................................................................C-34
Appendix D RF Exposure
Appendix E Setting Antenna Parameters
Antenna Issues ...........................................................................................E-1
About Single and Dual Antennas...................................................................E-1
Dual Antennas at the HBS and an HSU
.........................................................E-1
Single Antennas at Both Sites
.....................................................................E-2
Single at One Site, Dual Antennas at the Other
..............................................E-2
Page 13

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 xii
Considerations for Changing Antenna Parameters..........................................E-3
Appendix F Regional Notice: French Canadian
Procédures de sécurité ................................................................................F-1
Généralités
..............................................................................................F-1
Mise à la terre
.........................................................................................F-1
Protection contre la foudre
.........................................................................F-1
Précautions de sécurité pendant le montage de ODU
.......................................F-2
Connecter la terre à IDU-C
.........................................................................F-2
Installation sur pylône et mur.......................................................................F-2
Contenu du kit de montage ODU
.................................................................F-3
Montage sur un pylône
..............................................................................F-3
Montage sur un mur
.................................................................................F-5
Montage d'une antenne externe
..................................................................F-6
Contenu du kit de montage d'une antenne externe
.........................................F-6
Index
Page 14

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 xiii
List of Figures
FIGURE 1-1 SINGLE SECTOR BASE STATION..............................................................1-3
F
IGURE 1-2 SMALL FORM FACTOR ANTENNA IN CONNECTORIZED ODU.............................1-3
F
IGURE 1-3 HIGH GAIN INTEGRATED ANTENNA...........................................................1-3
F
IGURE 1-4 CONNECTORIZED ODU.......... .. .. .. .. ................................. .. .. .. .. .. ............1-3
F
IGURE 3-1 ODU MOUNTING KIT...........................................................................3-3
F
IGURE 3-2 ODU FORM FACTORS ..........................................................................3-3
F
IGURE 3-3 EXTERNAL ANTENNAS FOR USE WITH RADWIN 5000 HBS - LEFT: 60° OR 90° FLAT EX-
TERNAL; RIGHT: 120° INTEGRATED.............................................................................3-4
F
IGURE 3-4 EXTERNAL ANTENNAS FOR USE WITH RADWIN 55XX HSU - LEFT: STANDARD INTEGRATED;
CENTER AND RIGHT, PARABOLIC, DIFFERENT SIZES AND GAINS............................................3-4
F
IGURE 3-5 GBE POE DEVICE - SHOWING EXTRA ETHERNET PORT..................................3-5
F
IGURE 3-6 BASIC POE DEVICE - SHOWING THE RADIO ETHERNET PORT ..........................3-5
F
IGURE 3-7 RUGGEDIZED DC-POE DEVICE: INPUT IS -20 TO -60 VDC (SINGLE INPUT) .....3-6
F
IGURE 3-8 HSS INTERCONNECTION UNIT ...............................................................3-6
F
IGURE 3-9 GENERAL GSU CONFIGURATION .............................................................3-7
F
IGURE 3-10 TYPICAL HSU INSTALLATION WITH EXTERNAL ANTENNA..............................3-9
F
IGURE 3-11 BEEP SEQUENCE FOR ANTENNA ALIGNMENT............................................3-12
F
IGURE 4-1 PINGING THE BASE STATION..................................................................4-4
F
IGURE 4-3 EXTENDED LOG-ON WINDOW .................................................................4-5
F
IGURE 4-4 LOG ON WINDOW EXPOSING THE USER TYPES. ...........................................4-5
F
IGURE 4-5 OPENING RADWIN MANAGER WINDOW - HBS................ .. .. ......................4-7
F
IGURE 4-6 UNSUPPORTED DEVICE MESSAGE.............................................................4-7
F
IGURE 4-7 UNREACHABLE DEVICE MESSAGE .............................................................4-8
F
IGURE 4-8 INVALID USER TYPE OR PASSWORD..........................................................4-8
F
IGURE 4-9 HBS MAIN BUTTON MENU .....................................................................4-9
F
IGURE 4-10 SECTOR STATUS PANEL.......................................................................4-9
F
IGURE 4-11 BASE STATION DETAIL PANEL ............................................................4-10
F
IGURE 4-12 EVENTS LOG PANEL .........................................................................4-11
F
IGURE 4-13 HBS MAIN WINDOW (REDUCED) - UP TO 16 HSUS ...............................4-12
F
IGURE 4-14 HBS MAIN WINDOW (REDUCED) - INDICATING A PROBLEM.......................4-12
F
IGURE 4-15 HSU DISPLAY - DETAIL.....................................................................4-13
F
IGURE 4-16 HSU DISPLAY - CONTEXT MENU (RIGHT CLICK).......................................4-14
F
IGURE 4-17 HSU ON HBS DISPLAY - EXTRACT. SCROLL RIGHT FOR MORE HSU FIELDS...4-14
F
IGURE 4-18 LOGGING ON TO AN HSU..................................................................4-15
F
IGURE 4-19 OPENING RADWIN MANAGER WINDOW - HSU......................................4-16
F
IGURE 4-20 HSU MAIN BUTTON MENU .................................................................4-17
F
IGURE 5-1 LOGGING ON WITH FACTORY DEFAULT IP ADDRESS .....................................5-4
F
IGURE 5-2 LOGGING ON WITH LOCAL CONNECTION ..................................................5-5
F
IGURE 5-3 MAIN WINDOW FOR UN-CONFIGURED HBS ODU............................... .........5-6
F
IGURE 5-6 HBS READY FOR CONFIGURATION AND ACTIVATION.....................................5-9
F
IGURE 5-7 THE SECTOR SHOWING HSUS CONFIGURED BUT UNREGISTERED ...................5-17
F
IGURE 5-10 FULLY FUNCTIONAL SECTOR ...............................................................5-30
F
IGURE 6-1 VLAN FOR MANAGEMENT .....................................................................6-7
F
IGURE 6-2 SECTOR SECURITY SETTINGS ...............................................................6-10
F
IGURE 6-5 CHANGING THE COMMUNITY STRING .....................................................6-13
F
IGURE 6-6 ALTERNATIVE COMMUNITY DIALOG BOX .................................................6-14
F
IGURE 6-7 DATE AND TIME CONFIGURATION .........................................................6-15
F
IGURE 6-8 CHANGE DATE AND TIME....................................................................6-15
F
IGURE 6-9 SETTING ETHERNET SERVICES..............................................................6-16
F
IGURE 6-10 RESTORE FACTORY SETTINGS AND LICENSE ACTIVATION ..........................6-18
F
IGURE 6-11 HSU INTERCOMMUNICATION..............................................................6-20
F
IGURE 6-12 HSU CONFIGURATION WINDOW (HBS).............. .. .. .. ............................6-21
Page 15

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 xiv
F
IGURE 6-13 HSU CONFIGURATION - SETTING ANTENNA TYPE AND PARAMETERS.............6-22
F
IGURE 6-14 HSU CONFIGURATION - IP ADDRESSES ................................................6-23
F
IGURE 6-15 UNIT 10.101 IS DOWN AND UNIT 10.102 IS AVAILABLE AND NOT REGISTERED6-29
F
IGURE 6-18 TELNET SESSION LOG ON TO THE HBS........ .. ... .. ................................. . 6-37
F
IGURE 6-19 TELNET MANAGEMENT WINDOW - HSU.................... .. ..........................6-39
F
IGURE 7-1 DIRECT OR OVER THE AIR CONNECTION TO A REGISTERED HSU.....................7-2
F
IGURE 7-2 DIRECT CONNECTION TO A STAND-ALONE HSU..........................................7-3
F
IGURE 7-3 HSU CONFIGURATION WINDOW (DIRECT)................................................7-4
F
IGURE 7-4 HSU CONFIGURATION - AIR INTERFACE FOR REGISTERED HSU.....................7-5
F
IGURE 7-5 HSU CONFIGURATION - AIR INTERFACE FOR STAND-ALONE HSU ...................7-5
F
IGURE 7-6 HSU CONFIGURATION - AIR INTERFACE UNREGISTERED HSU .......................7-6
F
IGURE 8-3 RECENT EVENTS: LEFT- HBS, CENTER HSU FROM HBS, RIGHT HSU DIRECT...8-6
F
IGURE 8-4 PERFORMANCE MONITORING: LEFT- HBS, CENTER HSU FROM HBS, RIGHT HSU DIRECT
8-7
F
IGURE 8-5 SETTING THE UPPER TRAFFIC THRESHOLD .................................................8-8
F
IGURE 8-6 HBS - PERFORMANCE MONITORING REPORT - VALID DATA ...........................8-9
F
IGURE 8-7 HBS - PERFORMANCE MONITORING REPORT - SHOWING INVALID DATA ......... 8-10
F
IGURE 8-8 HSU - PERFORMANCE MONITORING REPORT - BOTH VALID AND INVALID DATA (1 OF 3)8-
11
F
IGURE 8-9 HSU - PERFORMANCE MONITORING REPORT - BOTH VALID AND INVALID DATA (2 OF 3)8-
11
F
IGURE 8-10 HSU - PERFORMANCE MONITORING REPORT - BOTH VALID AND INVALID DATA (3 OF 3)
8-11
F
IGURE 9-1 INTERFERENCE CAUSED BY COLLOCATED UNITS...........................................9-2
F
IGURE 9-2 COLLOCATED UNITS USING HUB SITE SYNCHRONIZATION (1) ........................9-2
F
IGURE 9-3 COLLOCATED UNITS USING HUB SITE SYNCHRONIZATION (2) ........................9-2
F
IGURE 9-4 HSS INTERCONNECTION UNIT ...............................................................9-3
F
IGURE 9-5 HSS WIRING SCHEMATIC......................................................................9-4
F
IGURE 9-6 HSS SYNC SIGNAL PATH WITH ODU 1 AS HSS MASTER ..............................9-4
F
IGURE 9-7 CASCADING TWO HSS UNITS.................................................................9-5
F
IGURE 9-8 CASCADING THREE HSS UNITS...............................................................9-5
F
IGURE 9-9 RADIO FRAME PATTERN .......................................................................9-7
F
IGURE 9-10 HSS SETTINGS WINDOW ....................................................................9-9
F
IGURE 9-11 SETTING HBS AS HSM OR HSC.........................................................9-10
F
IGURE 9-12 HBS AS HSM................................................................................ 9-10
F
IGURE 10-1 GSU SCENARIO - INDEPENDENT DISTRIBUTED SITES................................10-2
F
IGURE 10-2 GSU SCENARIO - COMMUNICATING DISTRIBUTED SITES ...........................10-2
F
IGURE 10-3 PHASE SHIFTED TRANSMISSION - PHASE SHIFT IS 1/2 THE RFD .................10-3
F
IGURE 10-4 MAKE THE GSUS THE FIRST TWO COLLOCATED UNITS..............................10-4
F
IGURE 10-5 GENERAL GSU CONFIGURATION..........................................................10-5
F
IGURE 10-6 GSU MAIN WIDOW AT STARTUP .........................................................10-6
F
IGURE 10-7 SITE CONFIGURATION: SYSTEM ..........................................................10-7
F
IGURE 10-8 SITE CONFIGURATION: GPS SYNC UNIT...............................................10-8
F
IGURE 10-9 SITE CONFIGURATION: MANAGEMENT ................................................ 10-10
F
IGURE 10-10 SITE CONFIGURATION: INVENTORY.................................................. 10-11
F
IGURE 10-11 SITE CONFIGURATION: SECURITY.................................................... 10-12
F
IGURE 10-12 SETTING THE DATE AND TIME FOR TRAP REPORTING ............................ 10-13
F
IGURE 10-13 SITE CONFIGURATION: OPERATIONS................................................ 10-14
F
IGURE 10-14 SITE CONFIGURATION: OPERATIONS................................................ 10-15
F
IGURE 11-1 SOFTWARE UPGRADE UTILITY - MAIN WINDOW......................................11-2
F
IGURE 11-5 SOFTWARE UPGRADE IN PROGRESS - NOTE THE STOP BUTTON ...................11-4
F
IGURE 11-6 SOFTWARE UPGRADE COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY.....................................11-4
F
IGURE 12-1 VLAN SCENARIOS HANDLE BY RADWIN 5000 HBS ...............................12-2
F
IGURE 12-2 SEPARATING CLIENT DATA STREAMS USING DOUBLE TAGGING.....................12-2
Page 16

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 xv
F
IGURE 16-1 LARGE CLAMP ................................................................................16-1
F
IGURE 16-2 SMALL CLAMP ................................................................................16-1
F
IGURE 16-3 ARM ............................................................................................16-1
F
IGURE 16-4 MOUNTING ON A POLE .....................................................................16-2
F
IGURE 16-5 MOUNTING ON A WALL ....................................................................16-3
F
IGURE 16-6 MOUNTED ODUS WITH CORRECT “WATER NOSE”....................................16-4
F
IGURE 16-7 INCORRECTLY MOUNTED ODU (NO “WATER NOSE”)................................16-4
F
IGURE 17-1 GROUNDING ANTENNA CABLES............................................................17-2
F
IGURE 17-2 RADWIN LIGHTNING PROTECTION KIT................................................17-3
F
IGURE 17-3 GROUNDING A TYPICAL POLE INSTALLATION ...........................................17-4
F
IGURE 17-4 GROUNDING A TYPICAL WALL INSTALLATION ..........................................17-5
F
IGURE 17-5 ODU LIGHTNING PROTECTOR AND GROUNDING......................................17-6
F
IGURE 17-6 LIGHTNING PROTECTOR AND GROUNDING AT BUILDING ENTRY POINT ........... 17-7
F
IGURE 18-1 FRESNEL ZONE ............................................................................... 18-4
F
IGURE 18-3 LINK BUDGET WINDOW - STARTUP ......................................................18-5
F
IGURE 18-4 RADWIN 5000 HPMP LBC MAIN WINDOW ........................................ 18-6
F
IGURE 18-5 BAND SELECTOR .............................................................................18-7
F
IGURE 18-6 CALCULATION OF DISTANCE FROM SITE COORDINATES.............................18-8
F
IGURE 18-7 CLIMACTIC C FACTORS.....................................................................18-9
F
IGURE 18-8 CLIMACTIC C FACTOR DESCRIPTION................................................... 18-10
F
IGURE 18-9 WORLD MAP SHOWING C FACTOR CONTOURS....................................... 18-10
F
IGURE 18-10 LBC - RESULTS SECTION .............................................................. 18-11
F
IGURE 19-1 SPECTRUM VIEW DATA PANEL FOR THE HBS, READY FOR DATA ..................19-4
F
IGURE 19-2 SPECTRUM VIEW ANALYSIS COLOR CODES.............................................19-7
F
IGURE 19-3 HSU SPECTRUM ANALYSIS IN COMPLETE ISOLATION FROM THE SECTOR......... 19-9
F
IGURE 19-4 HSU SPECTRUM ANALYSIS WITHIN THE SECTOR......................................19-9
F
IGURE 20-1 WEB INTERFACE - LOG ON ................................................................20-4
F
IGURE 20-2 WEB INTERFACE - MAIN WINDOW, HBS...............................................20-5
F
IGURE 20-3 SECTOR STATUS PANEL.....................................................................20-5
F
IGURE 20-4 HSU HAYDN DEREGISTERED..............................................................20-6
F
IGURE C-1 TOP LEVEL SECTIONS OF THE PRIVATE MIB..............................................C-2
F
IGURE C-2 PRODUCT MIB........................................................... .. .. .. .. .. .. ............C-3
F
IGURE F-1 GRANDE CLAME...................................................................................F-3
F
IGURE F-2 PETITE CLAME ....................................................................................F-3
F
IGURE F-3 BRAS ...............................................................................................F-3
F
IGURE F-4 MONTAGE SUR UN PYLÔNE ....................................................................F-4
F
IGURE F-5 MONTAGE SUR UN MUR ........................................................................F-5
Page 17

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 xvi
List of Tables
TABLE 4-1 PC REQUIREMENTS FOR THE RADWIN MANAGER APPLICATION ......................4-1
T
ABLE 4-2 PRECONFIGURED SETUP .........................................................................4-3
T
ABLE 4-3 USER TYPES, DEFAULT PASSWORDS AND FUNCTION.......................................4-6
T
ABLE 4-4 HBS MAIN BUTTON BAR FUNCTIONS..........................................................4-9
T
ABLE 4-5 HBS DETAIL PANEL BUTTON BAR FUNCTIONS............................................4-10
T
ABLE 4-6 HSU STATUS BALL COLOR CODES........................................................... 4-13
T
ABLE 4-7 HSU MAIN WINDOW DETAIL DISPLAY CONTEXT MENU AND BUTTON BAR FUNCTIONS4-14
T
ABLE 4-8 HSU MAIN BUTTON BAR FUNCTIONS........................................................4-17
T
ABLE 5-1 DEFAULT SETTINGS...............................................................................5-2
T
ABLE 5-2 PARAMETER VALUES USED IN THE DEMONSTRATION SECTOR............................5-3
T
ABLE 6-1 HBS TELNET - DISPLAY COMMANDS .......................................................6-38
T
ABLE 6-2 HBS TELNET - SET IMMEDIATE COMMANDS..............................................6-38
T
ABLE 6-3 HBS TELNET - SET COMMANDS REQUIRING RESET.....................................6-38
T
ABLE 6-4 HSU TELNET - DISPLAY COMMANDS.......................................................6-39
T
ABLE 6-5 HSU TELNET - SET IMMEDIATE COMMANDS .............................................6-39
T
ABLE 6-6 HSU TELNET - SET COMMANDS REQUIRING RESET.....................................6-40
T
ABLE 8-1 GET DIAGNOSTICS DATA AND DESCRIPTION ...............................................8-1
T
ABLE 8-2 HBS PERFORMANCE MONITORING FIELDS ..................................................8-9
T
ABLE 8-3 HSU PERFORMANCE MONITORING FIELDS................................................8-12
T
ABLE 8-4 RADWIN MANAGER TRAP MESSAGES .....................................................8-13
T
ABLE 9-1 ODU/HSS UNIT CONNECTION PINOUT .....................................................9-6
T
ABLE 9-2 RADIO FRAME PATTERN TABLE - RADWIN 5000 HBS.................................9-7
T
ABLE 9-3 RADIO FRAME PATTERN TABLE - RADWIN 2000........................................9-7
T
ABLE 9-4 RADIO FRAME PATTERN TABLE - WINLINK 1000.........................................9-7
T
ABLE 9-5 LEGEND FOR RADIO FRAME PATTERN TABLES..............................................9-8
T
ABLE 9-6 EXTERNAL PULSE STATUS.....................................................................9-11
T
ABLE 11-1 SWU FILES BY PRODUCT....................................................................11-3
T
ABLE 12-1 PORT SETTINGS - INGRESS DIRECTION...................................................12-4
T
ABLE 12-2 PORT SETTINGS - EGRESS DIRECTION....................................................12-5
T
ABLE 12-3 VLAN CONFIGURATION OPTIONS - TAG MODE........................................ 12-8
T
ABLE 14-1 LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE LOCATIONS OF TDWRS...................................14-5
T
ABLE 15-1 DEFAULT PRIORITIES AN D ALLOCATION BY VLAN ID AND DIFFSERV............. 15-1
T
ABLE 16-1 BILL OF MATERIALS: ODU MOUNTING KIT..............................................16-1
T
ABLE 19-1 SPECTRUM VIEW ANALYSIS DISPLAY BUTTONS FUNCTIONALITY....................19-5
T
ABLE 20-1 PRECONFIGURED SETUP......................................................................20-2
T
ABLE B-1 ODU-POE RJ-45 CONNECTOR PINOUT.....................................................B-1
T
ABLE B-2 HBS/HSS UNIT CONNECTION PINOUT......................................................B-1
T
ABLE B-3 FAST ETHERNET CONNECTOR PINOUT .......................................................B-2
T
ABLE B-4 TERMINAL BLOCK 2-PIN -48VDC.............................................................B-2
T
ABLE C-1 SUPPORTED RFC 1213 VARIABLES ..........................................................C-3
T
ABLE C-2 PRIVATE MIB PARAMETERS ....................................................................C-5
T
ABLE C-3 MIB TRAPS ......................................................................................C-30
T
ABLE D-1 SAFETY DISTANCES FOR RADWIN 5000 HPMP FCC AND IC PRODUCTS ........ D-1
T
ABLE D-2 SAFETY DISTANCES FOR RADWIN 5000 HPMP ETSI PRODUCTS.................. D-1
T
ABLE E-1 MIMO - DIVERSITY SETTINGS.................................................................E-3
T
ABLE E-2 RADWIN 5000 HPMP AIR RATES ..........................................................E-3
Page 18

RADWIN 5000 HPMP
Point to Multipoint Broadband Wireless
USER MANUAL
RELEASE 3.2.00
Part 1: Basic Installation
UM 5000-3200/08.11
Page 19

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 1-1
Chapter 1
Introduction
Welcome to RADWIN 5000 HPMP!
RADWIN 5000 HPMP delivers up to 200Mbps and is the ideal choice for last mile enterprise
connectivity and high-end applications that demand assured performance with guaranteed
bandwidth per subscriber.
RADWIN 5000 HPMP sector base station delivers up to 200Mbps, providing the highest end
user capacity in the market to best support data and high resolution video applications, today
and tomorrow. By delivering high capacity over a single radio unit, RADWIN solution saves
valuable tower space, eases maintenance efforts and reduces the total cost of ownership per
megabit. Offering a variety of powerful SUs, RAD WIN 5000 HPMP enables service capacit y of
up to 50Mbps for enterprise customers.
RADWIN 5000 HPMP Highlights
• High capacity Sector Base Station
• 200 Mbps aggregate throughput
• Ethernet connectivity
• High capacity end user equipment - 10, 20, 50Mbps
• Up to 16 Subscriber Units per sector
• Guaranteed SLA and capacity per Subscriber Unit
• Small and constant latency - 4 to 10msec typical under full sector load
• Wide range of frequency bands - 4.9 to 6GHz
What’s New in Release 3.2.00
• Extensions to traffic VLAN support
•HSU replacement
• 5/10/20/40 MHz channel bandwidth support
• Telnet Interface support
• Web Interface support
• Improved False Radar Mitigation
• Manager On-Line Help
Page 20

Some Terminology Chapter 1
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 1-2
• QoS support
•Spectrum View
• Support for 3.3, 3.8 and 2.5 GHz bands
Some Terminology
A Point to Multipoint network is typically abbreviated to PtMP. The PtMP networks
described in this Manual are of course, radio links.
A PtMP link consists of at least one high Base Station radio linked to several Subscriber
Unit radios. The SUs are sometimes called Customer Premises Equipment (CPEs). The
terminology comes from the field of telephony.
The RADWIN 5000 HPMP product suite supports considerably higher capacity than other current technologies (such as Wi-Max). We distinguish between generic BSs and SUs and RADWIN units, relabeling the latter, HBSs and HSUs (H = high capacity).
The radio links are effected by using a sector antenna with the HBS. The HSUs use directional antennas aligned to the HBS.
A Sector consists of an HBS and a group of HSUs within the angular sector covered by the
HBS antenna. A Sector is typically 60° or 120° depending of course on the choice of antenna.
HBSs may be collocated to provide sectorial coverage up to 360°.
The RF characteristics of a Sector will be common to each radio: Frequency (regulation),
band and channel bandwidth. Adjacent Sectors in a PtMP network will typically use different
frequencies and non-overlapping bands to mitigate HBS self interference.
Key features of RADWIN 5000 HPMP
»
200 Mbps aggregate throughput
» Configurable Maximum Information Rate (MIR) per HSU
» Advanced OFDM & MIMO 2x2 for nLOS performance
» Enhanced interference mitigation capability
» Inter & intra site sync to reduce self interference
» Long range – up to 40 km/25 miles
» Dedicated traffic bandwidth allocation ensuring SLA & latency
» Low latency – min < 3ms, typical 4 to 10ms
» Channel bandwidth – 5/10/20/40 MHz
» Regulation - FCC/ETSI/WPC/MII/Universal
» Multi band HBSs and HSUs
» Simple to deploy
» Web Interface for sector management
» Fully integrated with RADWIN Legacy solutions:
• Coexists with RADWIN 2000 and WinLink 1000 products
• Common RADWIN Manager
Page 21

RADWIN 5000 HPMP Components Chapter 1
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 1-3
• Common RNMS
RADWIN 5000 HPMP Components
RADWIN 5000 HBS High Capacity Base Station
The HBS consists of RADWIN 5000 HBS HBS ODU, a sector dualpole antenna and a PoE device, which provides a L AN interf ace to
user equipment.
A single HBS supports up to 16 HSUs.
Figure 1-1: Single Sector Base Station
RADWIN 55xx HSU High Capacity Subscriber Units
An HSU consists of a RADWIN 55xx HSU ODU. It may be a small form factor (SFF) model with
a built in antenna, or a regular integrated or connectorized unit. The latter should use a dual
pole antenna for best performance.
Figure 1-2: Small form factor
antenna in connectorized ODU
Figure 1-3: High gain integrated
antenna
Figure 1-4: Connectorized ODU
Page 22

The RADWIN Manager Chapter 1
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 1-4
The RADWIN Manager
The RADWIN Manager is an SNMP-based management application which manages a complete sector over a single IP address. It can also manage HSUs separately.
The intuitive, easy-to-use RADWIN Manager has a graphical Microsoft Windows interface.
Conventions Used in this Manual
Notifications
Notifications consist of Notes, Cautions and Warnings.
Typographical conventions
General
Where a term is defined or introduced for the first time, it is shown in Boldface. You will
have noticed this usage in the Terminology section above.
Software
The RADWIN Manager is a Microsoft Windows application following the user interface conventions of familiar Microsoft Windows programs.
Note
The purpose of a Note is to
• Draw your attention to something that may not be obvious or counter-intuitive
• Emphasize a special feature or peculiarity of the RADWIN 5000 HPMP
• Offer an external reference for additional information
• Add a caveat that would not qualify as a full Caution or Warning (see
below)
• Provide additional background to what follows
• Offer a recommendation
• Highlight an indication of something to watch out for
• Advise you if an action has “side effects” i.e. it may disturb something
else that would be best left undisturbed
• Remind you of something that should be kept in mind
Caution
A Caution is a notification of risk of damage to equipment or of service
degradation
Warning
A Warning is a notification of risk of danger to persons operating near the
equipment
Page 23

Viewing and Printing Chapter 1
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 1-5
Viewing and Printing
This manual is optimized for viewing online as a PDF file. To this end it uses an 11 point
Tahoma typeface for main text. Tables for most part, use 7 or 8 point fonts. Here are a few
pointers for hard-copy printing:
• The text and table typefaces used are large enough to print the manual at two pages
per sheet
• For good legibility, use a commercial grade laser printer. A color printer is of course
best, however a monochrome printer set to use gray-scale gives acceptable results
• Better quality ink jet printers also give good output
Page 24

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 2-1
Chapter 2
Site Preparation
Planning the Sector Site
Overview
Sector site planning consists of a set of surveys, which must be carried out before any equipment is deployed. If for some reason, the outcome of any of these surveys is negative, HBS
or HSU re-location will need to be considered.
A Site Survey consists of three stages:
1. Preliminary survey - The pr oposed sector is analyzed in the office using a topogr aphic
map. You should use additional tools such as the Link Budget Calculator or the Radio Planner.
2. Physical survey - The locations of the indoor and outdoor equipment are determined
on-site.
3. Radio Frequency (RF) survey - It is recommended that the installation area be scanned
with a spectrum analyzer, to identify RF interference so as to determine a clear channel for
radio installation (on-site).
The Site Survey
Introduction
RADWIN wireless links must be planned before installation. The designated installation sites
must be appraised to determine that the wireless system is able to operate efficiently and
provide connectivity without signal degradation.
RADWIN 5000 HPMP offers a wide operating frequency range. A free frequency channel must
be determined within the operating range, for optimum performance.
Recommended Equipment
Stage 1: Preliminary Survey
• Topo logic al map of the area
• Urban map of the area
•Compass
Page 25

Stage 1: Preliminary Survey Chapter 2
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 2-2
• Link Budget Calculator and/or Radio Planner
Stage 2: Physical Survey
• 100 meter tape measure
• Ohmmeter, to check ground connection
•Binoculars
•Map
• Digital camera
• Paper, pencil, and a clipboard
• GPS device (optional)
• Compass (optional)
Stage 3: RF Survey
• Spectrum Analyzer with Max Hold function and screen capture facility that can store
multiple images, for documentation purposes
• RF accessories (connectors and cables)
• Communication devices (for example, cellular phones, or a set of walkie-talkies)
Stage 1: Preliminary Survey
A preliminary survey is necessary before visiting potential installation sites. As much detail as
possible should be obtained about the designated ODU installation sites and the area
between them.
To perform a preliminary survey:
1. Mark the designated installation sites on a topographic map of the area.
2. Measure the distance between the sites; check that it is within the specified range of
the equipment.
3. On the urban map, check for developed areas situated between the installation sites.
Pay attention to these areas when performing the physical site survey; there may be
tall buildings, RF towers, or transmitters, which could cause interference to a sector.
4. Check the area between the two sites for obstructions such as:
• High ground - hills or mountains
• Lakes or large bodies of water. Water has a reflection effect on RF signals like a
building. This type of reflection causes the received amplitude to be reduced. As
a rule of thumb, the presence of a large body of water between sector sites may
double the required antenna height.
5. Determine and record the compass bearings between HBS and HSU ODUs, relative to
north.
6. If there are obstructions between the two sites, calculate the Fresnel Zone (see
Chapter 18 for details).
7. If the sites chosen do not meet requirements, consider alternative sites.
8. Use the Link Budget Calculator (on the CD supplied with the equipment or using the
RADWIN Manager) to determine the expected performance.
Page 26
Stage 2: Physical Survey Chapter 2
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 2-3
Stage 2: Physical Survey
The physical site survey reviews the environment of the proposed installation location, to
ensure that the sector sites are suitable for the wireless network. The results of the physical
site survey should be recorded.
To perform a physical survey:
1. From the compass readings taken in the preliminary survey, find the azimuth (horizontal position) that each HSU ODU should face towards the HBS ODU.
2. Using binoculars, locate any obstructions such as tall trees, high buildings, hills or
mountains. Look for other RF towers between the two sites. Mark the locations of
the obstructions on the map.
3. Determine the location for the ODU (having regard for existing rooftop installations
and tower space). It should be above any obstructions, considering the Fresnel zone
(see Chapter 18).
4. If you need to install an ODU on a tower, make sure that the tower is far enough
from overhead electric power lines.
5. Determine a location for the indoor equipment; it should be as close as possible to
the ODU. At an existing site, there is probably an equipment room with cable-routing
channels.
6. Measure and record the path length of the cable from each ODU position to the
indoor equipment room.
7. Determine the ground and lightning connection points of the installation. The ODU
and PoE must both be grounded.
8. Using the Ohmmeter, measure and record the resistance of the require d installation
to the grounding point. The resistance must be less than 1O ohm.
9. Review the results of the physical site survey. Decide if the site is suitable for the
wireless network installation.
• If the site is suitable, continue with stage 3, the RF survey
• If the site is not suitable, survey another site
Additional Outdoor Site Requirements
The ambient outdoor operating temperature should be -35 to 60 C (-31 to 140F).
Note
It is advisable to go on a clear day, so y ou can more easily see any
obstructions between the two sites.
Note
Outdoor CAT-5e; Maximum cable length: 100m for 10/100BaseT and 75m
for 1000BaseT (GbE PoEs)
Page 27

Additional Indoor Site Requirements Chapter 2
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 2-4
Additional Indoor Site Requirements
The ambient operating temperature should be 0 to 50°C (32 to 122 °F) at a humidity of up to
90%, non condensing
Stage 3: RF Survey
The RF survey examines the wireless environment of the installation site, to determine
whether there are available channels within the radio operating frequency band. An RF survey
is performed using a spectrum analyzer.
It is advisable to familiarize yourself with the spectrum analyzer before going out on site, specifically the Max Hold and Marker functions.
You should perform the RF survey at each of the proposed sector sites.
The survey should be carried out during a busy time of day, to best judge the worst-case
radio interference. Allow 2-4 hours duration for a good RF survey.
RF Planning for Dense Installations and Collocated Sites
Interference may arise from
• Self-interference from collocated RADWIN radios
• Other collocated radio devices installed on the same site.
To avoid or minimize interference, follow these recommendations:
• For collocated RADWIN units, use an HSS unit to synchronize between them. Select a
different operating channels for each collocated RADWIN unit.
• If one or more collocated units are not RADWIN units, ensure that there is a physical
separation of at least three meters between a RADWIN unit and any other collocated
radio on the site.
• Use the largest possible frequency gap between these units
• Choose the best frequency channel (as clear as possible from interference). Y ou may
be able to change the band used for the sector - depending on HBS model and regulations.
• Decreasing the Tx Power of a sect or will reduce collocation interference
Note
Use the Link Budget Calculator to determine the minimum Tx Power
required to maintain sector stability.
Page 28

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-1
Chapter 3
Hardware Installation
This chapter sets out the requirements and procedures for the hardware installation and
alignment of a RADWIN 5000 HPMP sector in accordance with the prior planning as set out in
Chapter 2. It is intended to guide qualified field technicians.
Safety Practices
Preventing overexposure to RF energy
To protect against overexposure to RF energy, install the ODUs so as to provide and maintain
minimal separation distances from all persons.
When the system is operational, avoid standing directly in front of the antenna. Strong RF
fields are present when the transmitter is on. The ODU must not be deployed in a location
where it is possible for people to stand or walk inadvertently in front of the antenna.
Grounding
All RADWIN products should be grounded during operation. In addition:
•The ODU should be earthed by a wire with diameter of at least 12AWG.
RADWIN 5000 HPMP ODUs must be properly grounded to protect against lightning. It
is the user's responsibility to install the equipment in accordance with Section 810 of
the National Electric Code, ANSI/NFPA No.70-1984 or Section 54 of the Canadian
Electrical Code. These codes describe correct installation procedures for grounding
Warning
Outdoor units and antennas should be installed ONLY by experienced
installation professionals who are familiar with local building and safety
codes and, wherever applicable, are licensed by the appropriate
government regulatory authorities. Failure to do so may expose the end
user or the service provider to legal and financial liabilities. RADWIN and its
resellers or distributors are not liable for injury, damage or violation of
regulations associated with the installation of outdoor units or antennas.
Note
The material in this chapter is generic to all RADWIN radio products unless
stated otherwise.
Page 29

Protection against Lightning Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-2
outdoor units, masts, lead-in wiring and discharge units. It also lays down the size of
grounding conductors and connection requirements for grounding electrodes.
RADWIN 5000 HPMP ODUs must be grounded to a Protective Earth as described in
Chapter 17 and in accordance with the Local Electrical Regulations.
Further, you should -
• Always make the ground connection first and disconnect it last
• Never connect telecommunication cables to ungrounded equipment
• Ensure that all other cables are disconnected before disconnecting the ground
More detailed guidelines are supplied in Chapter 17.
Protection against Lightning
The use of lightning protection is dependent on regulatory and end user requirements. All of
RADWIN outdoor units are designed with surge limiting circuits to minimize the risk of damage due to lightning strikes. RADWIN recommends the use of additional surge arrestor
devices to protect the equipment from nearby lightning strikes.
See Chapter 17 for detailed installation instructions of lightning protection devices.
General
• It is recommended that installation of the outdoor unit be contracted to a professional
installer.
• Before working on equipment connected to power lines or telecommunication lines,
you should remove jewelry or any other metallic object that may come into contact
with energized parts.
• Use extreme care when installing antennas near power lines.
• Use extreme care when working at heights.
• When using an AC power source for RADWIN 5000 HPMP PoEs always use the AC
power adapter supplied by RADWIN.
• Use the right tools. In addition to standard tools required for any kind of ODU or
antenna installation, RADWIN 5000 HPMP ODUs require additional specific tools
detailed on page 3-7 below.
Package Contents
The RADWIN 5000 HPMP packages include the following items:
HBS and HSU ODU Package Contents
The ODU package contains:
• One HBS or HSU ODU - see Figure 3-2 below for front and rear view
• An ODU mounting kit - see Figure 3-1 below
• A CD containing -
• the RADWIN Manager
•Quick Start Guide
• User Manual - the document you are reading
Page 30

HBS and HSU ODU Package Contents Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-3
• Link Budget Calculator
• Label showing the MAC address and the alternative Community string. The label is
self-adhesive. You should keep this label safe
• Cable glands (to be used with the ODU-PoE cable)
Figure 3-1: ODU Mounting kit
The ODU comes in two basic form factors as shown in Figure 3-2 below:
Figure 3-2: ODU Form Factors
• Integrated Antenna ODU
This ODU has an integrated 370mm (1.2ft) flat panel antenna. The ODU contains both
the radio and the antenna as a single unit housed in a weatherproof case.
Front Rear
ConnectorizedIntegrated Antenna
Page 31

External Antenna Package Contents Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-4
• Connectorized ODU
This ODU has 2xN-type connectors for connecting an external antenna
• HSU only - SFF (Connectorized) ODU
The SFF ODU is slightly “fatter” and heavier than a regular connectorized ODU since it
requires extra space for the built-in antenna.
External Antenna Package Contents
The HBS requires a dual pole sector antenna. HSUs may use any suitable dual pole directional
antenna.
External antennas are available for the RADWIN 5000 HPMP radios, varying in operating frequencies, form factor, size and gain.
Figure 3-3: External Antennas for use with RADWIN 5000 HBS
- Left: 60° or 90° flat external;
Right: 120° integrated
Figure 3-4: External Antennas for use with RADWIN 55xx HS U - Left: Standard integrated;
center and right, parabolic, different sizes and gains.
See the RADWIN products catalog for a mor detailed offering of external antennas. External
antennas are also available from third party antenna vendors.
Antenna kits contain -
•An antenna
• Two RF cable 1m (3’) long
Page 32

Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Devices Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-5
• Mounting kit
Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Devices
GbE PoE
RADWIN’s Gigabit Power over
Ethernet (GbE PoE) device provides
data and power to RADWIN 5000
5000 outdoor units. The PoE device
is available with a variety of AC
cables with different plug types.
This the recommended unit for use
with an HBS.
It differs externally from the regular
PoE in Figure 3-6 below, having
an extra LAN port for management.
Figure 3-5: GbE PoE device - showing extra Ethernet port
Basic PoE Device
The basic PoE device provides Ethernet service only,
with power for the ODU. The PoE device is extremely
compact, having one Ethernet port, one ODU port and
a standard 3 pin male AC power socket. The unit is
supplied with a standard three pin power cable.
It may be used for both the HBS and the HSUs. It will
not support Gigabit performance on the HBS.
Figure 3-6: Basic PoE device - showing the radio Ethernet port
Page 33

Hub Site Synchronization (HSS) Unit Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-6
Outdoor (Ruggedized) DC PoE Device
This unit may be used or both the HBS and the HSUs. It will not
support Gigabit performance on the HBS.
Figure 3-7: Ruggedized DC-PoE Device: Input is -20 to -60 VDC (single input)
Hub Site Synchronization (HSS) Unit
The HSS unit synchronizes collocated ODUs to prevent self interference. It is particularly useful at a multi-sector base station employing several HBSs.
A single HSS unit supports up to ten collocated ODUs. In addition to each unit being connected to its PoE device, the collocated unit has an additional cable that is connected to the
HSS Unit. The HSS Unit is a compact, weatherproof (IP67) connector box that is installed on
the same mast as the ODUs. All collocated units connect to this box using CAT-5e cable.
Cables in prepared lengths are available for purchase.
The HSS unit is supplied with ten protective cove rs; any port not in use must be closed with a
protective cover.
Figure 3-8: HSS Interconnection Unit
See Chapter 9 for further details about the use of HSS.
GSU
The GPS-based synchronization unit (GSU) is designed to handle inter-site interferences
under large-scale deployment scenarios.
The GSU is an outdoor unit consisting of a standard WinLink 1000 enclosure, a GPS antenna
and a PoE device.
Page 34

Additional Tools and Materials Required Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-7
The GSU is connected to the HSS Unit using a standard HSS cable. It synchronizes the transmission timing of multiple Hub-Sites to the same clock source thus eliminating self interference (see Chapter 10).
Figure 3-9: General GSU configuration
See Chapter 10 for further details about the use of GSU.
Additional Tools and Materials Required
The following is a list of the equipment and materials required to install RADWIN 5000 HPMP
hardware.
Tools and Materials
• Crimping tool for RJ-45 (if the ODU-PoE cable is without connectors)
• Spanner/wrench 13 mm (½”)
• Drill (for wall mounting only)
•Cable ties
• Sealing material
Cables and connectors
• ODU grounding cable 12AWG
Page 35

Hardware Installation Sequence Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-8
• ODU-PoE cable (outdoor class, CAT-5e, 4 twisted pairs, 24AWG), up to 100 m. for
100BaseT connection. For a 1000BaseT connection (HBS only) use an ODU-PoE cable
no longer than 75m.
• A crossed Ethernet LAN cable is required if you set up ODUs using the “Local Connection” method.
Hardware Installation Sequence
The following steps are required to install a RADWIN 5000 HPMP system:
1. Mounting the ODUs, page 3-9.
2. Mounting the external antennas (if used), page 3-10.
3. Mounting the Lightning Protection devices (if used), page 3-10.
4. Outdoor connections, page 3-10.
5. Connecting the PoEs, page 3-11.
6. Other Indoor connections, page 3-11.
7. Aligning the HSUs to the HBS, page 3-11.
See Figure 3-10 below, which illustrates a typical installation of a RADWIN 55xx HSU with
an external antenna.
Note
For 1000BaseT, you should use RADWIN supplied ODU-PoE cables, which
guarantee 1Gb performance. RADWIN cannot guarantee 1Gb performance
if you use third party cables.
Page 36

Outdoor installation Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-9
Figure 3-10: Typical HSU installation with external antenna
The HBS installation differs only in the antenna type: It uses a sector antenna.
The installation steps are detailed in the following sections.
Outdoor installation
Preparing the ODU before Deployment
Each ODU should be pre-loaded with an IP address. This may be done prior to deployment in
the field, or on-site using a Laptop computer. The process is quite straight-forward and
described in Chapter 4.
Mounting the ODU
The ODU can be mounted on a pole or a wa ll. In both installations, the supplied mounting kit
is used to secure the ODU.
To mount the ODU on a pole or a wall:
1. Ensure that the ODU is properly grounded.
2. Mount the ODU onto the pole or wall. Ensure that the unit is oriented so that the
cable connectors are at the bottom. (If they are on top, water may penetrate
Note
A mast-sited ODU typically uses a pole attached to the mast.
Page 37
Mounting external antennas Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-10
into the unit causing damage.) It is possible to mount an ODU horizontally. See
Chapter 16 for details.
3. Refer also to Chapter 16 for detailed ODU mounting kit contents and schematics.
Mounting external antennas
If you are using ODU with an integrated antenna, skip to Mounting the Lightning Protec-
tion Devices below.
The supplied mounting kit is used to mount the antenna onto a pole. The antennas must be
aligned for maximum throughput.
To mount an external antenna:
1. To mount an external antenna, ensure that the antenna is properly grounded and
then mount the antenna onto the pole. Refer to Chapter 16 for detailed antenna
mounting instructions.
2. Follow the mounting instructions supplied with the antenna.
Mounting the Lightning Protection Devices
The use of lightning protection is dependent on regulatory and end user requirements. The
RADWIN 5000 HPMP ODU is designed with surge limiting circuits to minimize the risk of damage due to lightning strikes. RADWIN recommends the use of additional surge arrestor
devices to protect the equipment from nearby lightning strikes.
Refer to Chapter 17 for detailed installation instructions of lightning protection devices.
Outdoor Connections
To complete the outdoor connections:
1. Connect the ground cable to the ODU chassis as marked on the ODU.
Warning
Prior to connecting cables to the ODU, the protective earth terminal (screw)
of the ODU must be connected to an external protective ground conductor
or to a grounded pole.
• Only a qualified person using the proper safety equipment should
climb the antenna mast
• Only qualified professional personnel should install or dismantle
ODUs and masts
Note
• Do not tighten the ODU to its mounting brackets until the alignment
process of the antenna is complete.
• Ensure that there are no direct obstructions in front of the ODU or
interference from man-made obstacles.
Warning
Never stand in front of a live antenna!
Page 38

Installing a Sector using PoE Devices Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-11
2. Connect the lightning protection device to the ODU (see Chapter 17).
3. Attach the ODU-PoE cable to the ODU RJ-45 connector (see Appendix B for the
connector pinout)
4. Screw in the cable glands to ensure hermetic sealing of the ODU.
5. Secure the cables to the pole, mast or brackets using UV-rated cable ties.
Installing a Sector using PoE Devices
A typical PoE device is a very simple unit having a power input connector and two Ethernet
ports. It is AC powered, and has a power LED .
To prepare a sector using PoE devices:
1. To connect the ODU to the PoE device, route the cable from the ODU to the PoE
device, secure the cable along its pat h and co nnec t t he c able to th e LAN-OUT RJ-45
connector on the PoE device.
2. Connect it to AC power.
3. Repeat steps 1 to 2 for all ODUs in the sector.
Connecting User Equipment
To connect user equipment to a PoE device:
• Connect a user switch, router or any other compatible device to the PoE device RJ-45
port designated LAN-IN. Refer to Appendix B for connector pinouts.
Aligning HSUs to an HBS
You perform HSU antenna alignment to an HBS using the HSU ODU’s audible tone.
To align an HSU to its HBS:
1. Ensure that the sector antenna of the HBS is aligned precisely to the sector it is
intended to cover. Use a compass and topographical maps to do this.
2. For both the HBS and HSUs: Using a coax cable with N- Type connectors, connect the
vertical polarization connector of the antenna to the ANT 1 connector of the ODU.
Then, using a second coax cable with N-Type connectors, connect the horizontal
polarization connector of the antenna to the ANT 2 connector of the ODU.
3. Ensure that power is connected to the site PoEs across the sector.
4. Provided that an HSU detects the signal from the HBS, the ODU starts beeping 20
seconds after power up, and continues beeping until the HSU is aligned to the HBS,
and the alignment is complete.
Note
There is no particular reason to use ANT 1 and ANT 2 in that order: They
just have to be the same for each ODU in the sector. Further, adopting a
convention like “ANT 1 is always vertical” avoids mistakes across a large
sector.
Page 39

Aligning HSUs to an HBS Chapter 3
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 3-12
The details are described in the next two steps. “Antenna” refers both to an external
antenna and an integrated antenna. The two steps should be carried out for each
HSU in the sector.
5. Make a horizontal sweep of 180 degrees with the HSU antenna so that the strongest
signal from the HBS can be detected.
6. Slowly turn the HSU antenna back towards the position of the HBS, listening to the
tone until the best signal is reached. See the following figure for audible signal variations.
Figure 3-11: Beep Sequence for antenna alignment
7. Secure the HSU antenna to the pole/wall.
Warning
Never stand in front of a live antenna!
Note
• Three beeps and a pause is 'best signal so far'
• Two beeps and a pause is 'signal quality increased'
• One beep and pause is 'no change in signal'
• Long beep and short pause is 'signal quality decreased'
• One beep and a long pause is 'no air link'
• Any other signal does not relate to antenna alignment
Page 40

RADWIN 5000 HPMP
Point to Multipoint Broadband Wireless
USER MANUAL
RELEASE 3.2.00
Part 2: Sector Installation
UM 5000-3200/08.11
Page 41

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-1
Chapter 4
Getting Started with the
RADWIN Manager
What we will do here
This chapter is a quick “hands-on” tour of a running sector. We show you how to install the
RADWIN Manager software on your managing PC, connect it to an operating base station and
then log on. We then explain the use of the various objects on the RADWIN Manager main
window.
The background acquired here will enable you to understand the direction and purpose of the
detailed procedures (described in later chapters), required to build a RADWIN 5000 HPMP
sector from the ground up.
Installing the RADWIN Manager Application
Minimum System Requirements
The RADWIN Manager application is distributed on a CD. Operating system specific PC
resources required by the application are set out in Table 4-1 below:
Requirements common to all systems are:
• Hard disk: 1 GB free space
• Network: 10/100BaseT NIC
• Graphics: 1024x768 screen resolution with 16 bit color
Table 4-1: PC Requirements for the RADWIN Manager Application
Windows Version
XP Pro
Vista/7t
32 bit 64 bit
Memory 512 Mb 1 Gb 2 Gb
Processor P IV P IV Dual Core
Page 42

Installing the Software Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-2
• Any modern Web browser to view additional material, use the Web Interface or get
help from the RADWIN Web site.
Installing the Software
Any PC running the RADWIN Manager application can be used to configure a RADWIN 5000
HPMP sector.
To install the RADWIN Manager application:
1. Insert the CD into the CD/DVD drive of your computer.
2. The CD opening window appears:
3. Choose Install RADWIN Manager and follow the on-screen instructions of the installation wizard to complete the setup of the RADWIN Manager application.
If the installation program fails to start, browse to your CD/DVD drive, chose the
setup.exe program and run it.
Page 43
Getting Started with the RADWIN Manager Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-3
Getting Started with the RADWIN Manager
We will look at a preconfigured sector, setup as follows:
To start the RADWIN Manager:
1. Connect the managing computer to the HBS PoE LAN port.
2. Check that you have connectivity to the HBS ODU. You can do this by opening up a
command line session (Start|Run and then type, cmd). At the command prompt,
type
ping 192.168.10.200
Table 4-2: Preconfigured setup
Unit Location Attribute Value Remark
HBS HBS_10.200
IP Address 192.168.10.200
All communicating HSUs and HBS in
the same subnet
Net Mask
255.255.255.0
Default Gateway
0.0.0.0
Sector ID EBG_20560334 Inherited by all communicating HSUs
Contact Bach Optional
Name Bach’s Office Location of Contact - optional
Band 5.730 - 5.845 GHz FCC/IC Inherited by all communicating HSUs
Channel Bandwidth 20MHz Inherited by all communicating HSUs
HSU
HSU_10.101
IP Address 192.168.10.101
All communicating HSUs and HBS in
the same subnet
Net Mask
255.255.255.0
Default Gateway
0.0.0.0
Contact Haydn Optional
Name Haydn’s Offic e Location of Contact - optional
HSU_10.102
IP Address 192.168.10.102
All communicating HSUs and HBS in
the same subnet
Net Mask
255.255.255.0
Default Gateway
0.0.0.0
Contact Mozart Optional
Name Mozart’s Office Lo cation of Contact - optional
Tip
Choose your unit names carefully. For example, for three collocated HBSs
each with 16 HSUs covering 360°, matters get out of hand very quickly if
units are poorly named. They can always be identified by their IP
addresses, but that is a poor substitute for effective naming. A URL -like
naming pattern based on HBS_n.HSU_y is clear and familiar to all Internet
users.
In a scenario like our example (one HBS, two HSUs) that would have been
be unduly complicated and detracting.
Page 44
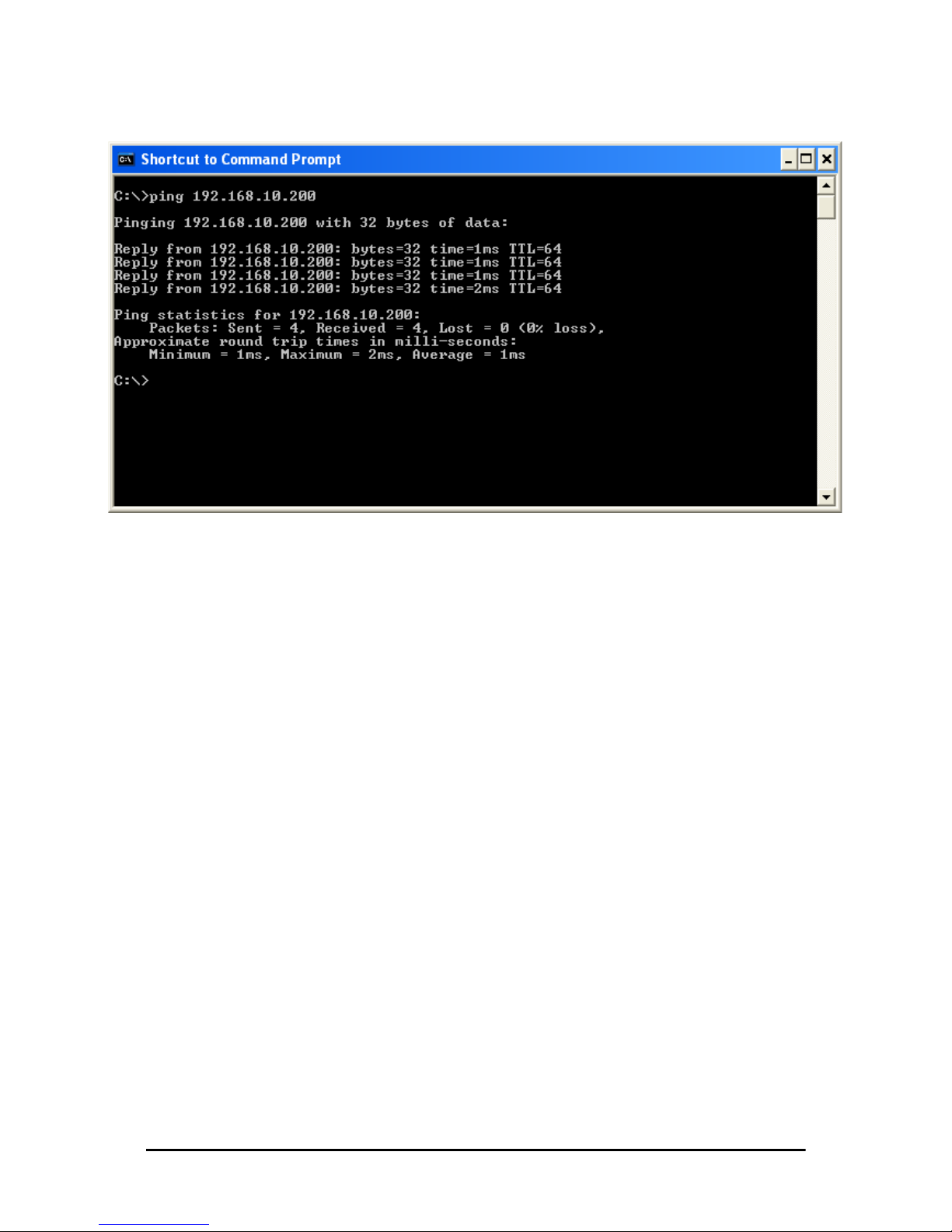
The RADWIN Manager log-on Concept Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-4
You should see somethi ng like this:
Figure 4-1: Pinging the base station.
Any other response from ping means that the HBS ODU is not responding. Check
your Ethernet connection and that both the PoE and ODU are switched on and then
try again. If you do not succeed, seek assistance from RADWIN Customer Support.
Pinging the HSUs should yield similar responses.
3. Dismiss the command line session.
4. Open the RADWIN Manager from the desktop icon, or click Start|Programs|RAD-
WIN Manager|RADWIN Manager.
The Log-on dialog box appears.
Figure 4-2: Log-on window
The RADWIN Manager log-on Concept
The RADWIN Manager provides three levels of access in one of two entry modes. To see
them, click Options at any time in the Log on window (Figure 4-2 above). You are offered
an
extended
log-on window:
Page 45

The RADWIN Manager log-on Concept Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-5
Figure 4-3: Extended log-on window
At the User Type field, click the list button:
Figure 4-4: Log on window exposing the user types.
There are three user types:
•An
Observer
has read-only access to the sector. An Observer can monitor the sector,
generate reports, but may not change any sector parameters.
•An
Operator
can install and configure the sector.
•An
Installer
can, in addition to functioning as an Operator, also change the operating
frequency band (or regulation). The latter function has legal ramifications, requiring
familiarity with local regulations.
If you are connecting through the RNMS server check the RMNS connect button and enter
your server IP address.
Page 46

The RADWIN Manager log-on Concept Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-6
The following table summarizes these options:
The Network Manager should change the default passwords as soon as poss ible.
Continuing the log-on procedure:
5. If your User Type is not Operator, then choose it now.
6. Enter the password.
7 . If y ou are a user with R ead- Write permission, click Options to enter the Community
options if required.
The RADWIN Manager main window is displayed:
Table 4-3: User types, default passwords and function
User Type
Default
Password
Function Community
Community
String
Observer
admin
Monitoring Read-Only
public
Operator
admin
Installation,
configuration
Read-Write
netman
Installer
wireless
Operator plus
set band
Read-Write
netman
Note
• Leave the default Community passwords,
netman
for read-write,
and
public
for read-only.
• If you are a user with read-only permission, then you may only log
on as Observer.
Page 47

Log-on Errors and Cautions Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-7
Figure 4-5: Opening RADWIN Manager window - HBS
Log-on Errors and Cautions
Unsupported Device
Attempting to connect to an unsupported device on an otherwise valid IP address (for example, a LAN printer) will result in the following error message:
Figure 4-6: Unsupported device message
Incorrect IP Address
If the IP address chosen is invalid or the sector is unreachable, the following error message
will be displayed:
Page 48

Incorrect Password Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-8
Figure 4-7: Unreachable device message
Incorrect Password
If you type an incorrect password in the Login window, the follwing message will be displayed:
Figure 4-8: Invalid user type or password
Invalid Read/Write Community String
This will result in the same message as shown in Figure 4-7.
To deal with lost or forgotten Community Strings:
1. Send an email request for to RADWIN Customer Support for an alternative key. Your
email must include the ODU serial number shown on the adhesive sticker on rear of
one of your ODUs.
2. The reply will contain an alternative key, which functions as a temporary master
Community String. Copy/paste the supplied alternative key to both the Read-Only
and Read-Write fields in the log-on window (Figure 4-3). This gets you to the RAD-
WIN Manager main window.
3. Use the procedure on page 6-10 to enter new Community Strings.
Exploring the RADWIN Manager Main Window - HBS
The following sections describe the panels of main window shown in Figure 4-5.
Page 49

HBS Main Button Menu Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-9
HBS Main Button Menu
Figure 4-9: HBS main button menu
Sector Status Panel
The sector level information is shown here. There is nothing that can be changed for an
active sector. The parameters are set before the base station is activated and are duplicated
for each HSU in the sector.
Figure 4-10: Sector Status panel
The last two items are of special interest: The Status (shown as Active) indicates whether
the HBS has been activated or not. The Time Slots bar indicates how many out of 16 time
slots, have been allocated to HSUs. Allocation of time slots between HSU provides a basic
form of prioritization between them. Normally you would not leave unallocated time slots
unless you intended to add more HSUs. Every HSU requires at least one time slot.
Base Station Panel
The displayed items in the Base Station panel are straight forward.
Table 4-4: HBS main button bar functions
Menu Item Purpose Reference
Preferences
Monitor - File location, interval and throughput units page 4-19
Events - Color coding for events log and events log file location page 4-20
Advanced - Enable/disable check for updates, monitoring interval and time-out page 4-21
Software Upgrade Perform software upgrade for a sector Chapter 11
Get Diagnostics Run and store diagnostics for all or some members of a sector Chapter 8
Log Off Return to log-on window
Help side arrow
Link Budget Calculator Chapter 18
Check Updates
About
Help Button View this User Manual
Page 50

Base Station Panel Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-10
Figure 4-11: Base Station detail Panel
The Tx Ratio shows the allocation of throughput between downlink and uplink traffic at the
HBS. Here it is set to 70% downlink and 30% uplink. The Tx Ratio is not only sector-wide: If
you use HSS (Chapter 9) to collocated several HBSs (to cover adjacent sectors), they must
all use the same Tx Ratio.
The Rx Rate and Tx Rate are the traffic receive and transmit rates through the HBS ODU
under load.
The button bar provides the necessary functionality to configure and manage the HBS.
The foregoing description relates to an activated HBS. The Detail Panel title bar for an inactive
HBS looks like this:
Table 4-5: HBS Detail Panel button bar functions
Menu
Icon
Purpose Reference
HBS Configuration Chapter 6
Recent Events Log page 8-5
Performance Monitor page 8-7
Active Alarms page 8-14
Spectrum View Chapter 19
Estimated Throughput page 8-4
Change Band (as Installer only) page 6-33
HSU Connection Table page 6-19
Reset the HBS
Deactivate the HBS page 5-31
Page 51

HBS Events Log Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-11
Clicking the Activate button initiates an activation Wizard. The Activate button in the title bar
is hidden, leaving it looking like this:
The Activation process is covered in detail in Chapter 5.
At any time, the current status of the HBS is shown in the Sector Status Panel, Figure 4-10.
HBS Events Log
The Events Log records system failures, loss of synchronization, loss of signal, compatibility
problems and other fault conditions and events.
Alarms (traps) are displayed in the Events Log in the lower panel of the main window. The
Events Log may be saved as a text file.
The Events Log includes the following fields:
» Sequential number (ID)
» Date and time stamp
» Message
» Trap source
» IP address of the ODU that initiated alarm.
For complete information about internal traps and alarms see Chapter 8.
The events are displayed in the Events Log in the lower right-hand panel of the RADWIN
Manager main window:
Figure 4-12: Events Log panel
The events log provides a color coded event list. Green items (like the one in Figure 4-12)
are informational. You can set the color coding for critical, cautionary and informational messages from the Preferences button
Note
The foregoing event types include events from all links for which this
managing computer has been defined as the traps address. Only events
from RADWIN equipment will be shown.
Page 52

HBS Main Window - HSUs Panel Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-12
HBS Main Window - HSUs Panel
Figure 4-13: HBS Main Window (Reduced) - up to 16 HSUs
If you have a large number of HSUs in the sector, it may be helpful to filter the display. You
have the following choices:
The following case has colored fields indicating a problem requiring your attention:
Figure 4-14: HBS Main Window (Reduced) - indicating a problem
Page 53

HBS Main Window - HSUs Panel Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-13
If you mouse-over the colored RSS area, you will receive a tool tip telling you that RSS for
Radio 1 is higher than for Radio 2, or something similar.
Figure 4-15: HSU display - detail
The little ball on the top left of the HSU is color coded as follows:
Right click an HSU to get its context menu:
Table 4-6: HSU Status ball color codes
Color Description
Green Registered, in sync
Red Registered, no sync
Grey Deregistered
Purple Authentication error
Blue Belongs to another sector
Page 54

HBS Main Window - HSUs Panel Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-14
Figure 4-16: HSU display - context menu (right click)
To switch to a list display, click the top right list button:
Figure 4-17: HSU On HBS display - extract. Scroll right for more HSU fields
The button bar in Figure 4-17 follows the same pattern as the context menu in Figure 4-
16.
Table 4-7: HSU main window detail display context menu and button bar functions
Menu Item
Menu
Icon
Purpose Reference
Register Register an HSU to a sector page 5-26
Configure Site configuration for the HSU page 6-20
Recent Events Recent events log per HSU page 8-5
Performance
Monitoring
Performance Monitoring per HSU page 8-7
Active Alarms Display Active Alarms page 8-14
Page 55

Exploring the RADWIN Manager Main Window - HSU Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-15
Exploring the RADWIN Manager Main Window - HSU
You may log on to an HSU over the air from an HBS or by directly connecting a Managing
Computer to the HSU whether through a switch or directly to its PoE. You can log on over the
air to any registered HSU. The HSU main window is different from the HBS main window,
however it uses the same GUI and the same names for common fields.
Logging on to an HSU
You can log on to an HSU of an established sector. The log on procedur e is the same as for an
HBS. Suppose we log on to HSU with IP address 10.103.7.6: We initially receive the following
caution:
Figure 4-18: Logging on to an HSU
Upon clicking OK to dismiss the caution, we get a variation of the previous main window:
Estimate
Throughput
Estimate throughput per HSU page 8-4
Update Service
Service evaluation and Time Slot allocation
per HSU; also MIMO/Diversity selection
page 6-32
Suspend ... Suspend Service page 6-33
Replace Replace an HSU page 6-29
Reset Reset the HSU
Deregister Deregister the HSU page 5-31
Table 4-7: HSU main window detail display context menu and button bar functions (Contin-
Menu Item
Menu
Icon
Purpose Reference
Page 56

Logging on to an HSU Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-16
Figure 4-19: Opening RADWIN Manager window - HSU
Page 57

HSU Main Button Menu Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-17
HSU Main Button Menu
The HSU main button menu is similar to the HBS main button menu. The only new item is in
the Configure button.
Figure 4-20: HSU main button menu
HSU Link Status
Table 4-8: HSU main button bar functions
Menu Item Purpose
Configure
The Configure button opens HSU site configuration. The additional functions in
the detail menu work in the same way as the corresponding functions for the
HBS.
Preferences
Monitor - File location, interval and throughput units
Events - Color coding for events log and events log file location
Advanced - Enable/disable check for updates, monitoring interval and time-out
Get Diagnostics Run and store diagnostics for all or some members of a sector
Log Off Return to log-on window
Help
Link Budget Calculator
Check for updates
About
Help Button View this User Manual
Page 58

HSU Events Log Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-18
HSU Events Log
The HSU events display is functionally identical to that of the HBS.
HSU Link Performance
For convenience
The HSU Link Performance panel shows the same fields as in Figure 4-15. For convenience
we also display the corresponding parameters for the HBS.
Setting RADWIN Manager Preferences
The Preferences tabs appearing on both the HBS and HSU relate entirely to the way the Manager displays certain items for the connected unit. They are completely local to the managing
computer. They are also functionally identical for both the HBS and HSUs.
Note
Each technician servicing a sector will need to set up his managing
computer (typically a laptop) with his own preferences.
Page 59

Monitor Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-19
Monitor
The Monitor file contains a vast amount of information and can become inordinately large
very quickly . You should therefore choose a longer sampling interval if you intend to store this
information for a lengthy duration.
For the HBS, it will show details for the HBS itself and all registered HSUs.
For an HSU, it will record the information just for that HSU. You should use distinctive file
names for HBS and HSU Monitor files.
The content of the Monitor file will be discussed in more detail in Chapter 8.
Page 60

Events Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-20
Events
Here you may choose your own color coding for the Recent Event display (see Chapter 8).
You may also choose a location and file name for the events log for storage. These settings
are again, per HBS or HSU. To avoid over-writing, you should use file names reflecting their
source ODU.
Page 61

Advanced Chapter 4
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 4-21
Advanced
Many alert messages in the RADWIN Manager have an option of the form “Do not show this
message again”. These alert messages can be reverted to their default state (shown) by clicking the Restore Alerts button. You will be asked to confirm:
If you are not connected to the Internet, disable the Check for updates check box. If you
have a slow connection to the internet, you may wish to increase the monitoring and timeout
intervals.
What Comes Next?
The purpose of this chapter was to offer an overview of a running RADWIN 5000 HPMP a sector. The next three chapters will cover respectively, detailed sector setup considerations, sector management and monitoring and diagnostics. The foregoing background should provide
sufficient “signposts” to ensure that you do not become lost in the plethora of details required
to commission and manage a fully operational sector.
Page 62

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-1
Chapter 5
Installing the Sector
Scope of this Chapter
Chapter 4, offered an overview of a running Sector as motivation for the technical installa-
tion details set out below.
Assuming that the Sector equipment is in place as described in earlier chapters, sector instal-
lation has two phases:
• Configuring and activating the HBS
• Bringing up the HSUs - configuration and registration
The same RADWIN Manager program is used for both the HBS and the HSUs. Much of the
process is common to both types of ODU. We will cover the HBS in detail; for the HSUs we
will concentrate on those items which are different. In any event, where setup procedures are
common we will point them out.
Concepts
A HBS out of the box, must be configured with
• Basic RF parameters such as frequency band, channel bandwidths and Sector ID
• Networking parameters such as IP address, Subnet mask and default gateway
At this point, the HBS ODU is in an inactive state, powered up, configurable but not transmitting anything.
Upon activation, the HBS will commence transmitting and receiving packets related to sector management only - that is no service. Activation and Deactivation are effected quite simply by clicking a toggle button.
Assuming that the Sector HSUs are mounted aligned and powered up, the HSUs will dis-
cover the HBS establishing links for management only. At this point the HSUs may be managed over the air.
As soon as the HSUs are configured to your satisfaction, you must register them on the HBS.
Registration of an HSU enables service traffic between the HSU and the HBS.
During the registration process, you assign time slots to each HSU. A total of 16 time slots
are available to each HBS to be distributed among the HSUs in the sector. The relative number of time slots determines the relative amount of service each HSU will receive. Each HSU
Page 63
Workflow Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-2
receives at least one time slot. To disable an HSU you must deregister it. (A suspend mechanism is also available, to suspend service on an HSU for a limited period.)
For each registered HSU, you can set separately, the uplink and downlink Maximum Infor-
mation Rate (MIR) in Mbps or leave it at Best Effort.
You may also manage an HSU Connection table to enable and disable connectivity
between HSUs in a sector.
Workflow
In this chapter, we assume that you are familiar with the material of Chapter 4. W e will concentrate on setup workflow assuming that you are familiar with GUI.
Prior to commencing, you should have written sector plan along the lines of Table 5-2.
Default RADWIN 5000 HPMP Settings
The default settings of the RADWIN 5000 HPMP configuration parameters are listed in
Table 5-1 below.
Table 5-1: Default settings
Unit Parameter Default Value
HBS
IP Address 10.0.0.120
Net Mask
255.0.0.0
Default Gateway
0.0.0.0
Location Location
Contact Person
Name Contact
Factory default band Product dependent
Channel Bandwidth 20MHz
RADWIN Manager log-on
passwords
Observer admin
Operator admin
Installer wireless
Link Password wireless-p2mp
Page 64

Default RADWIN 5000 HPMP Settings Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-3
For convenience, we repeat the table of parameters used in our demonstration sector. Parameters not listed are left at their default values.
HSU
IP Address 10.0.0.120
Net Mask
255.0.0.0
Default Gateway
0.0.0.0
Location Location
Contact Person
Name Name
RADWIN Manager log-on
passwords
Observer admin
Operator admin
Installer wireless
Link Password wireless-p2mp
Table 5-2: Parameter values used in the demonstration sector
Unit Location Attribute Value Remark
HBS HBS_10.200
IP Address 192.168.10.200
All communicating HSUs and HBS in
the same subnet
Net Mask
255.255.255.0
Default Gateway
0.0.0.0
Sector ID EBG_20560334 Inherited by all communicating HSUs
Contact Bach Optional
Name Bach’s Office Location of Contact - optional
Band 5.730 - 5.845 GHz FCC/IC Inherited by all communicating HSUs
Channel Bandwidth 20MHz Inherited by all communicating HSUs
HSU
HSU_10.101
IP Address 192.168.10.101
All communicating HSUs and HBS in
the same subnet
Net Mask
255.255.255.0
Default Gateway
0.0.0.0
Contact Haydn
Name Haydn’s Office
HSU_10.102
IP Address 192.168.10.102
All communicating HSUs and HBS in
the same subnet
Net Mask
255.255.255.0
Default Gateway
0.0.0.0
Contact Mozart
Name Mozart’s Office
Table 5-1: Default settings (Continued)
Unit Parameter Default Value
Page 65

Configuring the Sector out of the Box - IP Addresses Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-4
Configuring the Sector out of the Box - IP Addresses
The default log-on IP address for all ODUs in the sector is the same: 10.0.0.120, Subnet Mask
255.0.0.0 and default gateway 0.0.0.0. To get the process started, set up the IP address on
the network card on the managing computer to something like 10.0.0.100, Subnet Mask
255.255.255.0 and Default Gateway 0.0.0.0.
Ensure that you have a direct LAN connection to the ODU, run the RADWIN Manager and log-
on to it.
Figure 5-1: Logging on with factory default IP address
Alternatively, you can log on using Local Connection without need to change your Network
Interface Card address:
Tip
Choose your unit names carefully. For example, for three collocated HBSs
each with 16 HSUs covering 360°, matters get out of hand very quickly if
units are poorly named. They can always be identified by their IP
addresses, but that is a poor substitute for effective naming. A URL -like
naming pattern based on HBS_n.HSU_y is clear and familiar to all Internet
users.
In a scenario like our example (one HBS, two HSUs) that would have been
be unduly complicated and detracting.
Page 66

Configuring the Sector out of the Box - IP Addresses Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-5
Figure 5-2: Logging on with Local Connection
Here is the main display:
Warning
•The Local Connection method uses broadcast packets to “discov er”
the attached ODU
• If you log on using Local Connection, but your physical connection
is not local (i.e. anything other than a direct connection between the
managing computer and the IDU), then any configuration you carry
out may affect other links in the network. Do not do this!
•Do not carry out this procedure using a multi homed managing com-
puter also connected to a network. It will flood the network with
broadcast packets. Further, it will throw any other links on the network into Installation or Inactive mode.
• Network log on (IP address to the ODU) is recommended.
Page 67

Configuring the Sector out of the Box - IP Addresses Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-6
Figure 5-3: Main window for un-configured HBS ODU
Notice the red icon on the top left corner of the window. It will change to green as soon as
the HBS is configured and activated.
To pre-configure the HBS and HSUs prior to deployment in the field:
1. Click the configuration button . The Base Station site configuration widow opens:
Page 68

Configuring the Sector out of the Box - IP Addresses Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-7
Figure 5-4: Site Configuration prior to definition
2. Click the Management tab.
Page 69

Configuring the Sector out of the Box - IP Addresses Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-8
Figure 5-5: Definition of IP address done here
3. Enter the IP address, Subnet Mask and default Gateway and then click OK. You are
offered a warning:
4. Click Yes. The dialog is dismissed and you are returned to the main window. The
Sector Status panel indicated (as expected), Device unreachable.
5. Disconnect the HBS ODU and repeat steps 1 to 3 for each HSU in the sector. The
opening windows will look different, but the HSU site configuration dialogs will be
the same.
At this point you should field-install the units according to the guidelines in Chapter 3. You
should now revert your network card to the Sector Subnet.
Page 70

Activating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-9
Activating the HBS
With all the units in place, log on to the HBS using the new IP address. The main window
looks like this:
Figure 5-6: HBS ready for configuration and activation
Activating the HBS enables it to be discovered by the HSUs. An Activation Wizard will guide
you through the process.
To activate an HBS:
1. Click the Activate button. The Activation Wizard opens.
Page 71

Activating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-10
2. Click Next:
Enter the Sector ID, Name and Location. All fields are mandatory. Here are entries in
accordance with Table 5-2:
Page 72

Activating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-11
Choose your Sector ID it carefully particularly if you are using collocated HBSs for
extra coverage. The Sector Name and Location are convenience items but should be
chosen to ensure that the sector is documented and easily identifiable in your RF
planning. The Link Password may also be changed by clicking Change:
Full details for changing the Link Password may be found on page 6-10.
It is best left as is if there is no pressing need to change it.
3. From the previous Activation Wizard window, click Next.
Note
If you skipped an entry, it will be framed in red like this:
Page 73

Activating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-12
Here you may enter the IP details if didn’t do it earlier. Click Next.
4. The next window is used to set the frequency and channels.
The default frequency for the installed band is shown. Click the right hand selector
wheel to see other available frequencies:
Page 74

Activating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-13
Choosing Other enables you to move up and down by increments of 5 MHz:
5. Choose the required Channel Bandwidth:
Page 75

Activating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-14
6. To use ACS, check the Automatic Channel Selection box:
You can perform a customized channel selection or click Select All to check all the
channel boxes as shown:”
Note
If your hardware supports 200 Mbps net aggregate capacity, you should
chose 40 MHz Channel Bandwidth to enable it.
Page 76

Activating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-15
7. Click Next. The Antenna type and Tx Power window is presented:
The choice of Tx Power, antenna gain and cable loss (between the radio and the
antenna) determines the EIRP and is affected by such considerations as radio limitations and regulatory restrictions.
Before completing antenna installation, you might like to consider the background
information about setting antenna parameters, in Appendix E:
Choose your Antenna Type, Required Tx Power, Antenna Gain and Cable Loss. We
will set Required Tx Power to 6 dBm for our example. Click Next.
Page 77

Activating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-16
8. The Summary window of the Wizard is displayed.
Check that all information showed is correct and click Activate. After a few
moments the sector HSUs will be displayed in the Manager HSU panel.
Warning
When setting Required Tx P ower, it is your responsibility to chose a v alue in
compliance with your local regulations.
Page 78

Activating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-17
Figure 5-7: The sector showing HSUs configured but unregistered
At this point, the HSUs can communicate for management but not for service.
You may see that an HSUs has its RSS entry shaded yellow. Shading of this type indicates a
problem. To see what it is, mouse-over the shaded area. A tool tip appears displaying a message:
You should correct the problem before proceeding.
Further, you may have observed that operating frequency 5.805 GHz shown, is not what we
chose (5.820 GHz). The HBS tries to optimize the frequency to minimize the kind of problem
displayed above.
Page 79

Pre-configuring the HSUs for Service Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-18
Pre-configuring the HSUs for Service
The HSU activities described in this section, may be carried out any time - regardless of
whether or not the HSU is registered for service or not. These activities include among other
things, setting the Location, Contact and Name. We have chosen to do them here since they
reflect the workflow required to set up an operational sector. There are two methods of preconfiguration.
Pre-configuration from the HBS
To pre-configure an HSU for service from the HBS:
1. Right click an HSU to get its context menu:
Figure 5-8: HSU Context menu
2. Click Configure. The Configuration dialog is displayed. Enter a Name Contact and
Location:
p
Page 80

Pre-configuration from the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-19
Location is a site name - typically a building or tower name. Contact is the contact
person at that Location and Name is the Contact location. It might be just a telephone number. Here are our entries:
Page 81

Pre-configuration from the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-20
3. An additional parameter, which might be adjusted here, is the HSU Tx Power (possibly required by regulations). Click Tx & Antenna. The following dialog is displayed:
Set the Antenna T ype, R equired Tx P ower, Antenna Gain and Cable Loss as required.
For our example, we set Tx Power to 5 dBm.
4. Open the Management tab.
Page 82

Pre-configuration from the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-21
Set the HSU IP address, Subnet mask and Default Gateway. You may defer the trap
destinations, VLAN and Protocol settings for now.Here are our settings for this HSU:
5. Click OK. Y ou will be offered a cautionary message:
Page 83

Pre-configuring from a Direct Link Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-22
Click Yes.
6. Return to the HSU context menu (Figure 5-8). Click Reset. The newly entered
parameters for the HSU are now displayed:
7. Repeat the last six steps for each HSU in the sector.
Pre-configuring from a Direct Link
This method is used to pre-configure an HSU in the field during physical installation. Our
example below were captured using a laptop running Windows 7, so the window styles may
look a little different from those in the previous section.
To pre-configure an HSU for service by direct link:
1. Connect your managing computer to the HSU and log on using Local Connection.
Page 84

Pre-configuring from a Direct Link Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-23
2. Click the (top left hand) Configure button.
Page 85

Pre-configuring from a Direct Link Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-24
3. The display and those which follow are almost identical to the corresponding HBS
Configuration panels. Enter the Name, Contact and Location fields as before.
4. Leave Air Interface and Tx & Antenna for now. Open the Management tab and
enter the HSU IP address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway.
5. Click OK to accept your entries. You will be of fered the f ollowing disconnection warning:
6. Click Yes. You will see your configuration changes on the main window:
Page 86

The Final Outcome Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-25
The Final Outcome
Here is the outcome for our example, whichever method used:
You may now carry out an y other adjustments to HS_10.101 either from the HBS or by direct
connection. Notice that as we did for HSU_10.102, we adjusted the Tx Power to keep the RSS
at a reasonable level.
Page 87

Registering the HSUs for Service Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-26
As a partial alternative method, you may enter the Name and Location fields during Registration.
Registering the HSUs for Service
We continue our illustration using HSU at HSU_10.102.
To register an HSU for service:
1. Right click an HSU to get its context menu:
2. Click Register... The Registration window opens:
Note
If you do not see the changes as shown, a hard reset of the HSUs will cause
them to appear.
Page 88

Registering the HSUs for Service Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-27
3. You may edit or add the site Name and Location.
4. If you are using Dual Antennas, you may check the MIMO or Diversity antenna mode.
The choice is HSU specific. For further details about MIMO/Diversity antenna mode,
see Appendix E.
5. Click the Evaluate button. Service evaluation takes a fe w seconds during which the
window is darkened and inactive. Upon completion you may assign time slots to the
HSU:
Page 89

Registering the HSUs for Service Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-28
Figure 5-9: HSU Registration dialog
6. Click the number of time slots to be allocated to the HSU.
The Register button is now enabled.
7. Use the sliders to set uplink and downlink MIR. You may defer this and carry it out
using the HSU Configure option. The MIR acts a s a “throttle”.
8. Click Register it to complete the process. Here is the result for our example:
Page 90

Registering the HSUs for Service Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-29
Observe that the registered HSU LED is now green and that the Time Slots bar on
the left reflects the proportion of time slots allocated.
9. Repeat steps 1 to 8 for other HSUs. Here is the result for our example:
Page 91

Choosing Diversity Antenna Mode During Registration Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-30
Figure 5-10: Fully functional sector
Choosing Diversity Antenna Mode During Registration
Suppose that in Figure 5-9 for HSU_10.102 we had chosen Diversity mode, the outcome
would look like this:
The throughput on this HSU has dropped to about half of its previous value. The other HSU is
left unchanged.
This underlines the flexibility of the RADWIN 5000 HPMP system which enables HSUs to be
independently configured depending on their particular location.
Page 92

Deactivating the HBS Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-31
Deactivating the HBS
From the HBS button bar, click the right hand button followed by Deactivate.
You ware offered a cautionary message:
If you proceed, the HBS display will change to reflect the deactivated state:
Deregistering an HSU
A HSU may be deregistered by using the Deregister entry in an HSU context menu or using
the button from an HSU button bar.
Where has my HSU gone?
Suppose that you installed two collocated HBSs with contiguous sectors. It is possible that an
HSU located close to the common sector boundary may “discover” the wrong HBS. A HSU can
Page 93

Where has my HSU gone? Chapter 5
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 5-32
be “forced” across to another HBS by changing its Sector ID to that of the required HBS. The
method for doing this is covered in Chapter 7.
Page 94

RADWIN 5000 HPMP
Point to Multipoint Broadband Wireless
USER MANUAL
RELEASE 3.2.00
Part 3: Sector Management
UM 5000-3200/08.11
Page 95

RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 6-1
Chapter 6
Managing the Sector
Scope of this Chapter
This chapter deals with managing the sector from the HBS. It covers HBS Configuration and
HSU Configuration from the HBS. HSU direct or over-the-air configuration is a little different
and is covered in Chapter 7.
A Configuration window is available for both th e HBS and the HSUs to change setting without
necessarily dropping service. Nevertheless care must be exercised when changing them. By
way of example, changing an IP address will possibly make a unit unreachable. It is necessary however to have this function in the Configuration window since it is required to initially
set up the unit.
The HBS itself may be configured over-the-air: A scenario for this is where the sector is backhauled by on of the HSUs. There are no significant differences between the two methods,
however some care is required. If for example, you deactivate the HBS over-the-air, you will
lock yourself out of the sector.
Running Spectrum View from the HBS manager over-the-air, will lock you out for the duration
of the Spectrum View timeout period.
Configuring an HBS
Configuration Menu Buttons
Open the Configuration window.
The Backup and Restore buttons provide for backup and restore of the HBS software.
The Refresh button restores the current window to its previous state abandoning any
changes you made, provided that you did not click Apply or OK.
We will work through each of the Configuration tabs in turn:
Page 96

System Chapter 6
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 6-2
System
These items are convenience fields. Name and Location are typically entered during HBS
activation.
Page 97

Air Interface Chapter 6
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 6-3
Air Interface
This panel has the same functionality as the corresponding window in the Activation Wizard
(see Chapter 5). Changing the Sector ID will “percolate” to all registered HSUs. It will of
course, be “picked up” by newly installed and registered HSUs.
Channel Bandwidth and Channel Selection changes will all be sector-wide.
Page 98

Tx and Antenna Chapter 6
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 6-4
Tx and Antenna
This tab is available for both the HBS and HSUs. It has the same meaning in both cases.
For the HBS, changes made here may affect link quality and in the case of antenna type,
cause a sector re-sync.
Changing the antenna type for an HSU will cause a re-sync to that site only.
Page 99

Hub Site Sync [HSS] Chapter 6
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 6-5
Hub Site Sync [HSS]
The External Pulses detected in this example, come from a collocated RADWIN 2000 ODU
configured as Hub Sync Master. (A WinLink 1000 would have done just as well.) To enable
HSS, check the Enabled check box.
Ensure that the correct Operational state is selected - in our example, Hub Site Client -
Continue Tx. Click Apply or OK to ena ble HSS.
.See Chapter 9 for further detail about HSS.
Page 100

Management Chapter 6
RADWIN 5000 HPMP User Manual Release 3.2.00 6-6
Management
If you set the IP and related addresses correctly, there should be little to change here.
The three sub-windows, Trap Destinations, VLAN Management and Protocol dialogs are
generic to the HBS nad the HSUs (direct or over-the-air) and are discussed below.
 Loading...
Loading...