Page 1

200-Channel VHF/AIR/UHF
with WX Alert
Desktop Scanner
20-423
Owner’s Manual
Please read before using this equipment.
A
Page 2

ˆ
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the RadioShack
200-Channel VHF/AIR/UHF Desktop
Scanner. This scanner gives you direct
access to over 25,000 frequencies, including
those used by police and fire departments,
ambulance services, government agencies,
air, and amateur radio services. You can
select up to 200 channels to scan, and you
can change your selection at any time.
The secret to your scanner's ability to scan
so many frequencies is its built-in
microprocessor. Your scanner also has
these special features:
Four Service Banks
preset frequencies in separate fire/police, air,
ham radio, and marine banks, to make it
easy to locate specific types of calls.
Two-Second Scan Delay
scanning for 2 seconds before moving to
another channel, so you can hear more
replies.
Ten Channel-Storage Banks
store up to 20 channels in each of 10
different banks, to group channels so you
can more easily identify calls.
20 Monitor Memories
save up to 20 frequencies you locate during
a search, so you can move selected
frequencies to channel storage later.
Memory Backup
frequencies stored in memory for about 1
hour during a power loss.
HyperSearch
you set the scanner to search at up to 50
steps per second and to scan at up to 25
channels per second, to help quickly find
interesting transmissions.
2
TM
— let you search
— delays
— let you
— let you temporarily
— keeps the channel
HyperScan
and
RadioShack and RadioShack.com are trademarks used by RadioShack Corporation.
Hyperscan, Hypersearch, and Adaptaplug are trademarks used by RadioShack Corporation.
TM— let
©
2001 RadioShack Corporation.
All Rights Reserved.
Introduction
Duplicate Frequency Check
automatically notifies you if you are about to
store a frequency you have already stored,
to help avoid wasting storage space.
Direct Search
and unlisted frequencies starting from a
specified frequency.
Priority Channel
frequency in the priority channel to be
scanned every 2 seconds so you do not miss
important calls.
Weather Band (WX) Key
preprogrammed weather frequencies to keep
you informed about current weather
conditions.
Weather Alert
alarm tone to advise of hazardous weather
conditions when the scanner detects an alert
signal on the local NOAA weather channel.
Lock-Out Function
scanner to skip over specified channels or
frequencies when scanning or searching.
Liquid Crystal Display
view and change programming information
at any time.
Display Backlight
easy to read in low light situations.
Supplied Telescoping Antenna
scanner receive strong local signals.
External Antenna Terminal
connect an external antenna (not supplied)
to the scanner.
— lets you search for new
— lets you program a
— automatically sounds the
— lets you set your
— makes the scanner
—
— scans seven
— makes it easy to
— lets the
— lets you
Page 3

Dual Conversion
— helps prevent
interference from image frequencies.
To reduce the risk the of fire or
WARNING:
shock hazard, do not expose this produ ct to rain or
moisture.
CAUTION
..
RISK OF ELECTRIC
TO REDUCE THE RISK OF ELEC-
CAUTION:
TRIC SHOCK, DO NOT REMOVE COVER OR
BACK. NO USER-SERVICEABLE PARTS INSIDE.
REFER SERVICING TO QUALIFIED PERSONNEL.
The lightning symbol is intended to alert you
to the presence of uninsulat ed dangerous
voltage within this product’s enclosure that
might be of sufficient magnitude to constitute a risk of electric shock. Do not open the
product’s case.
The exclamation symbol is intende d to inform you that important operating and
maintenance instructions are incl uded in
!
the literature accompanying this p roduct.
SHOCK
DO NOT OPEN
..
!
Your scanner receives these frequencies
(MHz):
• connecting your scanner to an outlet
that is on a different electrical circuit
from the receiver
• contacting your local RadioShack store
for help
If you cannot eliminate the interference, the
FCC requires that you stop using your
scanner.
This device complies with Part 15 of the
Rules
. Operation is subject to the following
FCC
two conditions: (1) this device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device
must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
29–30 10m Amateur Radio
30–50 VHF Lo
50–54 6 m Amateur Radio
108–136.9875 Air
137–144 Government
144–148 2 m Amateur Radio
148–174 VHF Hi
380–420 Government
420–450 70 cm Amateur Radio
450–470 UHF Lo
470–512 UHF “T” Band
FCC NOTICE
Your scanner might cause TV or radio
interference even when it is operating
properly. To determine whether your scanner
is causing the interference, turn off your
scanner. If the interference goes away, your
scanner is causing it. Try to eliminate the
interference by:
• moving your scanner away from the
receiver
SCANNING LEGALLY
Your scanner covers frequencies used by
many different groups including police and
fire departments, ambulance services,
government agencies, private companies,
amateur radio services, military operations,
pager services, and wireline (telephone and
telegraph) service providers. It is legal to
listen to almost every transmission your
scanner can receive. However, there are
some transmissions you should never
intentionally listen to. These include:
• telephone conversations (cellular,
cordless, or other private means of
telephone signal transmission)
• pager transmissions
• any scrambled or encrypted
transmissions
According to the
Privacy Act
and possible imprisonment for intentionally
listening to, using, or divulging the contents
of such a transmission unless you have the
consent of a party to the communication
(unless such activity is otherwise illegal).
Electronic Communications
(ECPA), you are subject to fines
Introduction
3
Page 4

This scanner has been designed to prevent
reception of illegal transmissions. This is
done to comply with the legal requirement
that scanners be manufactured so as to not
be easily modifiable to pick up those
transmissions. Do not open your scanner's
case to make any modifications that could
allow it to pick up transmissions that it is not
ˆ
Contents
Preparation ............................................................................................................................. 6
Power Sources .................................................................................................................. 6
Using AC Power ......................................................................................................... 6
Using Vehicle Battery Power ...................................................................................... 6
Connecting an Antenna .................................................................................................... 7
Connecting the Supplied Antenna ............................................................................. 7
Connecting an Outdoor Antenna ............................................................................... 7
Understanding Your Scanner ................................................................................................ 8
A Look at the Controls ....................................................................................................... 8
A Look at the Display ........................................................................................................ 9
Understanding Service Banks/Banks .............................................................................. 10
Channel Storage Banks ........................................................................................... 10
Service Banks .......................................................................................................... 11
Operation ............................................................................................................................ .. 14
Turning On the Scanner/Setting Volume and Squelch .................................................... 14
Storing Known Frequencies into Channels ..................................................................... 14
Finding and Storing Active Frequencies ......................................................................... 15
Searching the Service Banks ................................................................................... 15
Using Direct Search ................................................................................................. 16
Using the Monitor Memory .................................................. ... .................................... ..... 17
ýýýý
Listening to a Monitor Memory
Moving a Frequency from a Monitor Memory to a Channel ..................................... 17
Scanning the Stored Channels ....................................................................................... 17
Scanning Options .................................................................................................... 18
Turning Channel Storage Banks On and Off ................................................................... 18
Monitoring a Stored Channel .......................................................................................... 18
Clearing a Stored Channel .............................................................................................. 18
Listening to the Marine Bank ........................................................................................... 19
Listening to the Weather Band ........................................................................................ 19
Weather Channel Frequency Chart ........................................................................ 19
Using the Weather Alert ........................................................................................... 19
Special Features ................................................................................................................... 20
Frequency ............................................................... 17
legal to listen to. Doing so could subject you
to legal penalties.
We encourage responsible, legal scanner
use.
Warning:
receive cellular radio telephone service
signals is prohibited under
under federal law.
Modification of this device to
FCC rules
and
4
Contents
Page 5

Using the Delay Function ............................................................................................... 20
Locking Out Channels and Frequencies ........................................................................ 20
Locking Out Channels ............................................................................................. 20
Locking Out Frequencies ........................................................................................ 20
Reviewing Locked-Out
Frequencies ........................................................................................................................... 21
Removing All Locked-Out Tags From Frequencies ................................................. 21
Removing All Lockout Tags from Frequencies in All Service Banks ....................... 21
Using Priority .............................................. ... .................................... ...................... 21
Turning the Key Tone On and Off ................................................................................... 21
Using a Computer to Program the Scanner ................................................................... 22
Birdie Frequencies .................................. .................................... .................................... 22
United States Broadcast Band ....................................................................................... 22
Guide to the Action Bands .................................................................................................. 23
Typical Band Usage ................................................................................................ 23
Primary Usage ................................... ... ..................................... .............................. 23
Band Allocation .......................................................................... ... ................................. 24
Avoiding Image Frequencies .......................................................................................... 27
Frequency Conversion ................................................................................................... 27
Troubleshooting ................................................................................................................... 28
Resetting/Initializing the Scanner ................................. ... ... .................................... ... ... .. 28
Resetting the Scanner ............................................................................................. 28
Initializing the Scanner ............................................................................................ 29
Care ................................................................................................................................ 29
Specifications .................................................................................................................... .. 30
Contents
5
Page 6
ˆ
Preparation
POWER SOURCES
Using AC Power
You can power the scanner using the
supplied 12V, 300mA AC adapter.
Cautions:
Y ou must use a Class 2 power
source that supplies 12V DC
!
and delivers at least 300 mA.
Its center tip must be set to positive and
its plug must fit the scanner's
jack. The supplied adapter meets these
specifications. Using an adapter that
does not meet these specifications
could damage the scanner or the
adapter.
• Always connect the AC adapter to the
scanner before you connect it to AC
power. When you finish, disconnect the
adapter from AC power before you
disconnect it from the scanner.
Warning:
use the AC adapter’s polarized plug with an
extension cord, receptacle, or other outlet
unless you can fully insert the blades to
prevent blade exposure.
To prevent electric shock, do not
DC12V
Using Vehicle Battery Power
You can power the scanner from a vehicle’s
12V power source (such as cigarette-lighter
socket) using a 12V, 300-mA DC cord and a
size M Adaptaplug™ connector (neither
supplied). Both are available at your local
RadioShack store.
Cautions:
You must use a power cord
that can carry 12V DC and at
!
least 300 mA. Its center tip
must be set to positive and its plug must
fit the scanner's
cord that does not meet these
specifications could damage the
scanner or the cord.
• Always connect the DC cord to the
scanner before you connect it to the
power source. When you finish,
disconnect the cord from the power
source before you disconnect it from the
scanner.
Follow these steps to power the scanner
from a vehicle’s cigarette-lighter socket.
DC12V
jack. Using an
Follow these steps to power the scanner
from a standard AC outlet.
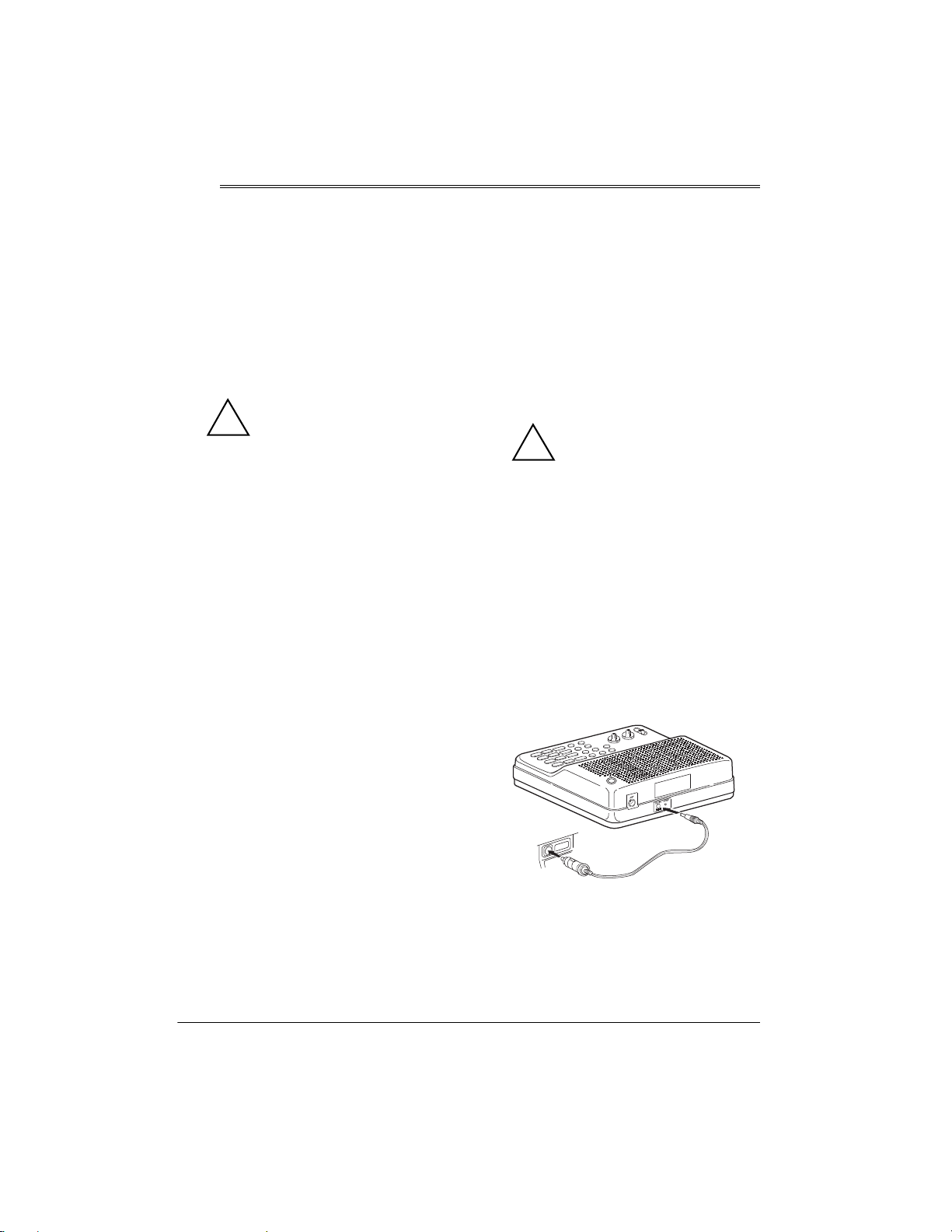
1. Insert the AC adapter’s barrel plug into
DC12V
the
scanner.
2. Plug the adapter into a standard AC
outlet.
6
jack on the back of the
Preparation
1. Connect the adaptaplug connector to
the DC cord so the tip reads positive (+).
2. Insert the DC cord’s barrel plug into the
DC12V
jack on the back of the scanner.
Page 7
3. Plug the cord into the vehicle’s
cigarette-lighter socket.
Notes
:
• If you use a 12V DC cord and your
vehicle's engine is running, you might
hear electrical noise on the scanner
caused by the engine. This is normal.
to hear, adjust the antenna's length
according to the chart below.
Frequency Antenna Length
29–174 MHz Extend fully
380–512 MHz Extend 2 segments
• Mobile use of this scanner is unlawful or
requires a permit in some areas. Check
the laws in your area.
CONNECTING AN ANTENNA
Connecting the Supplied Antenna
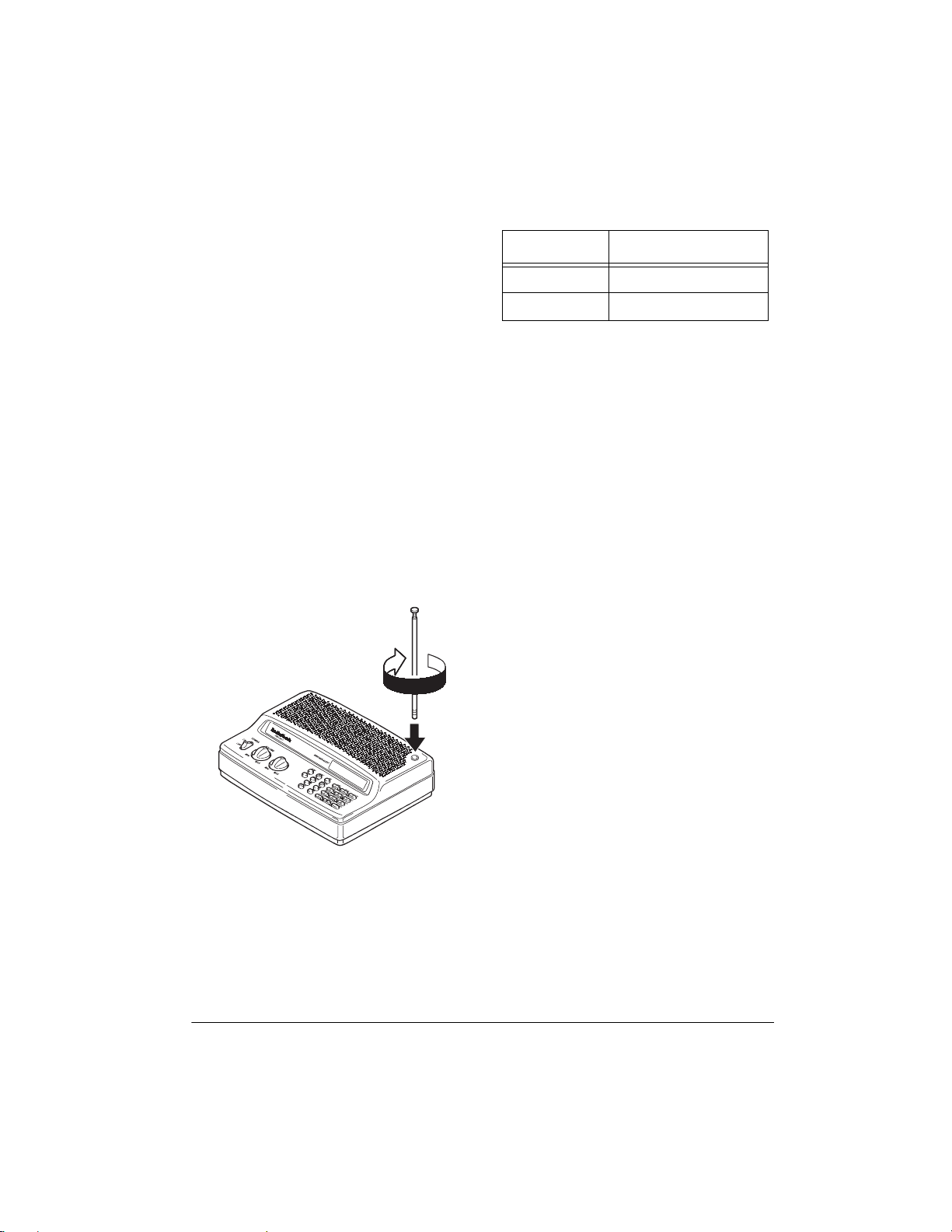
You must install an antenna before you can
operate the scanner.
The supplied telescoping antenna helps your
scanner receive strong local signals. To
install the antenna, thread it clockwise into
the hole on top of the scanner.
The scanner's sensitivity depends on its
location and the antenna's length. For the
best reception of the transmissions you want
Connecting an Outdoor Antenna
Instead of the supplied antenna, you can
connect an outdoor base-station or mobile
antenna (neither supplied) to your scanner.
Your local RadioShack store sells a variety
of antennas. Choose the one that best meets
your needs.
When deciding on an outdoor antenna and
its location, consider these points:
• The antenna should be located as high
as possible.
• The antenna and antenna cable should
be as far as possible from sources of
electrical noise (appliances, other
radios, and so on).
• The antenna should be vertical for the
best performance.
To connect an optional base-station or
mobile antenna, first remove the supplied
antenna from the scanner. Always use 50
Ohm coaxial cable, such as RG-58 or RG-8,
to connect the base-station or mobile
antenna. For lengths over 50 feet, use RG-8
low-loss dielectric coaxial cable. If the
antenna cable's connector does not fit in the
ANT
jack on the back of the scanner, you
might also need a PL-259-to-Motorola
antenna plug adapter. Your local
RadioShack store carries a wide variety of
coaxial antenna cable and connectors.
Once you choose an antenna, follow the
mounting instructions supplied with the
antenna. Then route the antenna's cable to
Preparation
7
Page 8
the scanner and connect the cable to the
ANT
jack.
Warning:
install or remove an outdoor antenna. If the
antenna starts to fall, let it go! It could contact
overhead power lines. If the antenna touches
a power line, contact with the antenna, mast,
ˆ
Use extreme caution when you
Understanding Y our Scanner
cable, or guy wires can cause electrocution
and death. Call the power company to
remove the antenna. Do not attempt to do so
yourself.
Caution:
edges or moving parts that might damage it.
Do not run the cable over sharp
Once you understand a few simple terms
used in this manual and familiarize yourself
with your scanner's features, you can put the
scanner to work for you. You simply
determine the type of communications you
want to receive, then set the scanner to scan
them.
frequency
A
station (expressed in kHz or MHz). To find
active frequencies, you can use the
function.
is the tuning location of a
search
You can also search the
banks
, which are preset groups of
frequencies categorized by type of service.
When you find a frequency, you can store it
into a programmable memory location called
channel
a
channels in a
can then
see if there is activity on the frequencies
stored there. Each time the scanner finds an
active frequency, it stays on that channel
until the transmission ends.
, which is grouped with your other
channel-storage bank
scan
the channel-storage banks to
service-search
. You
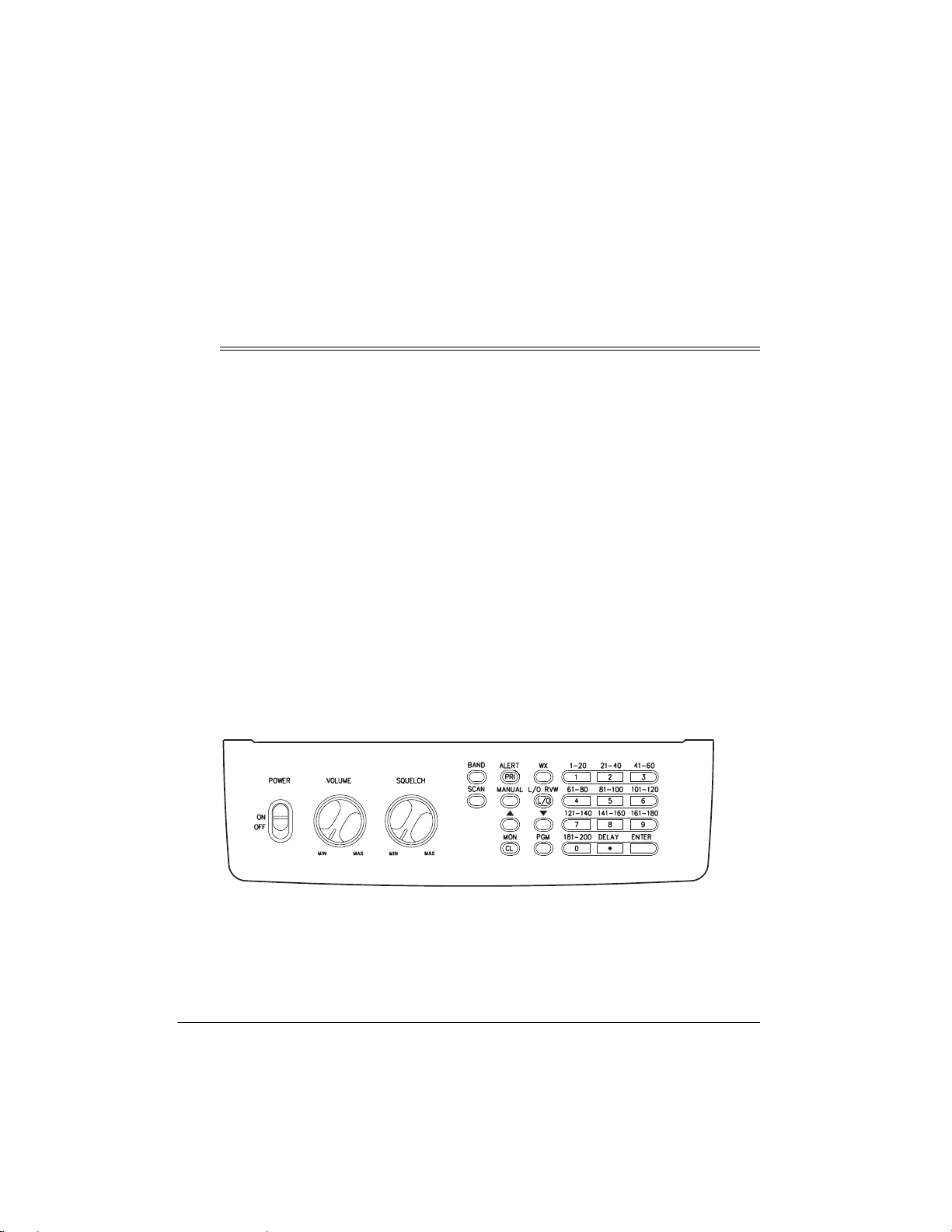
A LOOK AT THE CONTROLS
Some of the scanner’s keys perform more than one function (such as
marked with more than one label. The steps in this Owner’s Manual show only the label on the
key appropriate to the action being performed.
MON/CL
) and are
POWER
— turns the scanner on and off.
VOLUME
SQUELCH
to an incoming signal.
8
— adjusts the volume.
— adjusts the scanner’s sensitivity
BAND
— lets you search service banks.
PRI/ALERT
and off, or sets the scanner to WX alert
mode.
Understanding Your Scanner
— turns the priority function on
Page 9

WX
— scans through the seven
preprogrammed weather channels.
PGM
(Program) — programs frequencies into
channels.
SCAN
— scans through the programmed
channels.
MANUAL
directly enter a channel number.
L/O RVW, L/O
lets you review locked-out frequencies, or
lets you lock out selected channels/
frequencies so they will not be scanned or
searched.
8888#
scanner will search or scan.
MON/CL
monitor memories or clears an incorrect
entry.
— stops scanning and lets you
(Lock Out Review/Lock Out) —
9999
— enters the direction the
and
(Monitor/Clear) — accesses the 20
Number Keys
label and a range of numbers. Use the digits
on the keys to enter the numbers for a
channel or a frequency. Use the range of
numbers above the key (21–40, for example)
to select the channel in a channel-storage
bank.
DELAY/.
the selected channel, or enters a decimal
point (necessary when programming
frequencies).
ENTER
A LOOK AT THE DISPLAY
The display shows the scanner’s current operating mode.
— each key has a single-digit
—- programs a 2-second delay for
—- enters frequencies into channels.
FD/PD
— appears when you search the fire/
police service bank.
BANK
— appears with numbers (1–10).
Bank numbers with a bar under them show
which ones are turned on for scanning.
AIR
— appears when you search the air
service bank.
HAM
— appears when you search the ham
radio service bank.
MARINE
marine service bank.
— appears when you search the
Understanding Your Scanner
8888
9999
or
— indicates the search or scan
direction.
M
— flashes with a number (1–20) to show
which monitor memory you are listening to.
CH
—- the digits that precede this indicator
(1–200 and P) show which channel the
scanner is tuned to.
L/O
— appears when you manually select a
channel you locked out while scanning or
when you review a locked out frequency.
WX
— appears when you scan the weather
channels.
9
Page 10

SRCH
— appears during service bank and
direct frequency searches.
P
— appears when the scanner is tuned to
the priority channel.
SCAN
— appears when you scan channels.
MAN
— appears when you manually select a
channel.
PGM
— appears while you program
frequencies into the scanner's channels.
PRI
— appears when you turn on the priority
feature.
DLY
— appears when you program a 2-
second delay.
Error
— appears when you make an entry
error.
-dUPL-
try to store a frequency that is already stored
in another channel.
-d-
search.
-b-
frequency search.
Ch-FULL
a frequency during a search when all
channels are full.
(Duplicate) — appears when you
— appears during a direct frequency
— appears during a service bank
— appears when you try to enter
ALErt
— appears when the scanner is
watching the WX alert tone.
WIrEd
— appears when you turn on the
wired programming mode.
StArt
— appears when the scanner starts
wired programming.
C-Err
— appears when the scanner
receives a check sum error during wired
programming.
D-Err
— appears when the scanner finds a
data error while using wired programming.
End
— appears when the scanner finishes
wired programming.
oFF tonE
tone off.
on tonE
tone on.
— appears when you set the key
— appears when you set the key
UNDERSTANDING SERVICE
BANKS/BANKS
Channel Storage Banks
F L-out
search from a locked-out frequency.
FLo -FULL
lockout a frequency during a search when 50
frequencies are already locked out.
L-r
frequencies.
dEFAULt
the locked-out frequencies from the service
bank.
FLo ALL-CL
all the locked out frequencies during a
service bank/direct search.
10
— appears when you start direct
— appears when you try to
— appears when you review the lockout
— appears when you unlock all
— appears when you remove
Understanding Your Scanner
To make it easier to identify and select the
channels you want to listen to, channels are
divided into 10 banks of 20 channels each.
Use each channel-storage bank to group
frequencies, such as those used by the
police department, fire department,
ambulance services, or aircraft (see “Guide
to the Action Bands” on Page 23). For
example, the police department might use
four frequencies, one for each side of town.
You could program the police frequencies
starting with Channel 1 (the first channel in
bank 1) and program the fire department
frequencies starting with Channel 21 (the
first channel in bank 2).
Page 11

Service Banks
The scanner is preprogrammed with the
frequencies allocated by fire/police, aircraft,
ham radio, and marine services. In these
service banks, you can search through the
frequencies and store them in channels for
fire/police, aircraft, ham radio, and marine
banks. This is handy for quickly finding active
frequencies instead of searching through an
entire band.
Note:
The frequencies in the scanner's
service bank are preset. You cannot change
them.
Air
Group
— 108.000–136.9875 12.5
Frequency Range
(MHz)
Amateur Radio
Group
1 29.000–29.700 5
2 50.000–54.000 5
3 144.000–148.000 5
4 420.000–450.000 12.5
Frequency Range
(MHz)
Step
(kHz)
Step
(kHz)
Understanding Your Scanner
11
Page 12

Marine
Channel Frequency (MHz) Channel Frequency (MHz)
06 156.3000 64 156.2250
07 156.3500 65 156.2750
08 156.4000 66 156.3250
09 156.4500 67 156.3750
10 156.5000 68 156.4250
11 156.5500 69 156.4750
12 156.6000 70 156.5250
13 156.6500 71 156.5750
14 156.7000 72 156.6250
15 156.7500 73 156.6750
16 156.8000 74 156.7250
17 156.8500 77 156.8750
18 156.9000 78 156.9250
19 156.9500 79 156.9750
12
20 157.0000/161.6000 80 157.0250
21 157.0500 81 157.0750
22 157.1000 82 157.1250
23 157.1500 83 157.1750
24 157.2000/161.8000 84 157.2250/161.8250
25 157.2500/161.8500 85 157.2750/161.8750
26 157.3000/161.9000 86 157.3250/161.9250
27 157.3500/161.9500 87 157.3750/161.9750
28 157.4000/162.0000 88 157.4250
Understanding Your Scanner
Page 13

Fire/Police
Group
1 33.420–33.980 20
2 153.770–154.130 60
Frequency Range
(MHz)
37.020–37.420 20
39.020–39.980 20
42.020–42.940 20
44.620–45.860 40
45.880 —
45.900 —
45.940–46.060 40
46.080–46.500 20
154.145–154.445 15
154.650–154.950 15
155.010–155.370 60
155.415–155.700 15
155.730–156.210 60
Step
(kHz)
158.730–159.210 60
166.250 —
170.150 —
3 453.0375–453.9625 12.5
458.0375–458.9625 12.5
460.0125–460.6375 12.5
465.0125–465.6375 12.5
Understanding Your Scanner
13
Page 14

ˆ
Operation
TURNING ON THE
SCANNER/SETTING
VOLUME AND SQUELCH
1. Turn
2. Slide
3. Turn
4. Turn
5. To turn off the scanner when yo u finish,
SQUELCH
until the indicator points to
POWER
scanner.
VOLUME
hissing sound.
SQUELCH
hissing sound stops.
Notes:
• To listen to a weak or distant station,
SQUELCH
turn
reception is poor, turn
clockwise to cut out weak
transmissions.
SQUELCH
•If
hear a hissing sound, the scanner
does not scan or search properly.
POWER
slide
fully counterclockwise
MIN
.
ON
to
to turn on the
clockwise until you hear a
clockwise, just until the
counterclockwise. If
SQUELCH
is adjusted so you always
OFF
to
.
STORING KNOWN
FREQUENCIES INTO
CHANNELS
Good references for active frequencies are
the RadioShack
Frequency Directory
Frequency Directory
directories every year, so be sure to get a
current copy.
Police Call, Aeronautical
Maritime
, and
. We update these
Follow these steps to store frequencies into
channels.
PGM
1. Press
(1–200) where you want to store a
frequency, then press
channel number appears.
2. Use the number keys and • to enter the
frequency (including the decimal point)
you want to store.
3. Press
the channel.
Notes
• If you made a mistake in Step 2,
Error
beeps when you press
Simply start again from Step 2.
• Your scanner automatically rounds
the entered frequency down to the
closest valid frequency. For example,
if you enter a frequency for 151.473,
your scanner accepts it as 151.470.
• If you entered a frequency that is
already stored in another channel,
the scanner beeps three times and
displays the lowest channel number
where the frequency is already
stored, and
frequency flashes. If you want to
store the frequency anyway, press
ENTER
the frequency.
• Press
to pause 2 seconds on this channel
after a transmission ends before it
proceeds to the next channel (see
“Using the Delay Function” on
Page 20). The scanner also stores
this setting in the channel.
, enter the channel number
PGM
again. The
ENTER
to store the frequency into
:
appears and the scanner
ENTER
-dUPL-
again. Press
DELAY
if you want the scanner
then the
MON/CL
.
to clear
14
Operation
Page 15

4. To program the next channel in
sequence, press
2 and 3.
PGM
and repeat Steps
FINDING AND STORING
ACTIVE FREQUENCIES
Searching the Service Banks
• T o reverse the search direction at any
8888
9999
or
time, hold down
scanner reverses the search
direction.
• To search the band up or down in
small increments repeatedly press
8888
and release
Banks” on Page 11).
or
until the
9999
(see “Service
Your scanner contains groups of preset
frequencies called service banks. Each
service bank is associated with a specific
activity (see “Understanding Service Banks/
Banks” on Page 10). You can search for fire/
police, air, ham, and marine transmissions
even if you do not know the specific
frequencies that are used in your area. Then
you can store the frequencies you found into
the scanner's channels or monitor memories.
Note:
You can use the scanner's delay
feature while searching the service banks
(see “Using the Delay Function” on
Page 20).
The following steps describe the operation of
the HAM, FD/PD, and AIR service banks. To
listen to the marine bank, see “Listening to
the Marine Bank” on Page 19.
BAND
1. Press
name (such as
frequency and the group number (if any)
appear.
2. To select a different band, repeatedly
press
appears on the display. After about 2
seconds, the scanner begins searching
rapidly up or down in that band for an
active frequency.
Notes
• To search through the frequencies,
hold down
seconds. The scanner tunes through
the frequencies until it finds an active
frequency .
. The last selected band
HAM
SRCH, -b-
),
BAND
until the desired band name
:
8888
9999
or
for a few
, the
• T o pause the search while receiving a
8888
signal, press and release
T o continue the search, hold down
9999
for about 2 seconds.
or
• To move quickly up or down through
the frequencies, press and hold down
8888
9999
or
. The scanner tunes through
the frequencies until you release
9999
or
.
• Use the number keys to select search
groups.
3. When the scanner finds an active
frequency, it stops searching and
displays the frequency's number. To
store the displayed frequency in the
lowest available channel, press
then press
frequency flash twice, and the scanner
stores the displayed frequency. The
scanner then continues to search for
frequencies.
Notes:
• If there is no empty channel,
FULL
To store more frequencies, you must
clear some channels. See “Clearing a
Stored Channel” on Page 18. To
continue searching after
appears, press and hold down
9999
• If you entered a frequency that is
already stored in another channel,
dUPL-
channel containing the duplicate
ENTER
. The channel and
appears when you press
.
and the lowest-numbered
or
PGM
Ch-
Ch-FULL
9999
PGM
8888
8888
8888
or
-
.
.
Operation
15
Page 16

frequency flash for about 3 seconds.
If you want to store the frequency
anyway, press
delete the frequency later.
4. To store the displayed frequency in the
selected channel, press
channel number you want to enter the
channel and press
ENTER
press
frequency flash twice, and the scanner
stores the displayed frequency. The
scanner continues to search for
frequencies.
5. To store the displayed frequency in the
monitor memory, press
monitor memory number, M, and the
frequency flash twice.
6. To search for another active frequen cy
in the selected band, hold down
9999
until the radio begins searching.
7. To select a different band and search for
another active frequency, begin again
from Step 2.
ENTER
again. Y ou can
PGM
, press the
PGM
again, then
. The channel and
MON/CL
. The
8888
or
8888
9999
or
2. Hold down
to search up or down.
8888
9999
or
appear on the display.
Notes:
• T o reverse the search direction at any
time, hold down
seconds.
• To search up or down in th e selected
band in small increments (in steps of
5 or 12.5 kHz), press and release
9999
.
or
• To pause the search, press and
release
again, hold down
• To quickly move up or down through
the frequencies, press and hold down
8888
the frequencies until you release
or
8888
9999
or
. The scanner tunes through
9999
.
for a few seconds
-d-, SRCH
8888
9999
or
9999
or
. T o begin searching
8888
or
for a few
9999
.
, and
8888
8888
Using Direct Search
During a direct search, the scanner searches
up or down, starting from a frequency you
specify. Follow these steps to use direct
search.
Note
: You can use the scanner's delay
feature while using direct search.
1. Press
16
MANUAL
frequency (including the decimal point)
you want to use as a starting point for
the search.
Note:
To start from a frequency already
stored in one of your scanner's
channels, press
the desired channel number, then press
MANUAL
or
PGM
PGM
or
MANUAL
again.
, then enter the
PGM
or
, enter
Operation
3. When the scanner finds an active
frequency, it stops searching and
displays the frequency. To store the
displayed frequency in the lowest
PGM
8888
or
then press
Ch-
appears,
9999
available channel, press
ENTER
. The channel and frequency
flash twice, and the scanner stores the
frequency. The scanner continues to
search for frequencies.
Notes:
• If there is no empty channel,
FULL
appears. To store more
frequencies, you must clear some
channels. “Clearing a Stored
Channel” on Page 18. To continue
searching after
press and hold down
Ch-FULL
.
Page 17

• If you entered a frequency that is
already stored in another channel,
dUPL-
and the lowest-numbered
channel containing the duplicate
frequency flash for about 3 seconds.
If you want to store the frequency
ENTER
anyway, press
• To store the displayed frequency in
the selected channel, press
press the channel number you want
to use and press
ENTER
press
frequency flash twice, and the
scanner stores the frequency. Then
the scanner continues to search for
frequencies.
. The channel and
again.
PGM
again, then
PGM
,
-
the current monitor memory frequency
appears. To select other monitor memories,
enter the desired monitor memory's number
(1–20), then press
MON/CL
again.
Moving a Frequency from a
Monitor Memory to a Channel
1. Press
PGM
, enter the channel number
where you want to store the frequency,
then press
selected channel number appear.
PGM
again.
PGM
and the
4. To store the frequency in the monitor
8888
MON/CL
or
memory, press
memory number, and the frequency
flash twice.
5. To search for another active frequency,
hold down
. M, the monitor
9999
.
USING THE MONITOR
MEMORY
The scanner has 20 monitor memories that
you can use to temporarily store frequencies
while you decide whether to save them into
channels. This is handy for quickly storing an
active frequency when you are searching
through an entire band. You can store a
frequency into a monitor memory during a
service bank or direct search.
You can select monitor memories manually,
but you cannot scan them. See "Listening to
a Monitor Memory Frequency."
Listening to a Monitor Memory
Frequency
2. Press
3. Enter the desired monitor memory's
4. Press
5. To move another monitor memory
MON/CL
number, and CH flash, and the monitor
memory frequency appear.
number (1–20), then press
again. The selected monitor memory's
frequency appears.
ENTER
frequency in the selected channel.
frequency to the next channel, press
PGM
and repeat Steps 2–4.
. M, a monitor memory
MON/CL
. The scanner stores the
SCANNING THE STORED
CHANNELS
To set the scanner to continuously scan
through all channels with stored frequencies,
SCAN
SCAN
.
press
scanner begins to rapidly scan until it finds
an active frequency.
and 8 appear, and the
To recall a frequency stored in the monitor
memory, press
monitor memory number, and CH flash and
MANUAL
then
MON/CL
. M, the
If the scanner finds an active frequency, it
stops and displays that channel and
Operation
17
Page 18

frequency number, then it automatically
begins scanning again when the
transmission ends on that frequency.
Scanning Options
While scanning you can select from several
options to enhance your scanning enjoyment.
• To reverse the scanning direction at any
8888
time, press
• To set the scanner to remain on the
current channel for 2 seconds after the
transmission ends, see “Using the Delay
Function” on Page 20.
• To set the scanner to remain on the
current channel even after the
transmission stops, press
any time during the transmission so
appears and
“Monitoring a Stored Channel.”
• To lock out channels so the scanner
does not stop for a transmission on
those channels, see “Locking Out
Channels and Frequencies” on Page 20.
9999
or
.
SCAN
disappears. See
MANUAL
at
MAN
TURNING CHANNEL
STORAGE BANKS ON AND
OFF
To turn off banks while scanning, press the
bank’s number key until the bar under the
bank’s number disappears. The scanner
does not scan any of the channels within the
banks you have turned off.
To turn on banks while scanning, press the
bank’s number key until a bar appears under
the bank’s number.
Notes:
• You cannot turn off all banks. There
must be at least one active bank.
• You can manually select any channel in
a bank, even if the bank is turned off.
• When you turn on the bank while
scanning, the scanner moves to the
selected bank's first channel and
continues scanning.
MONITORING A STORED
CHANNEL
You can continuously monitor a specific
channel without scanning. This is useful if
you hear an emergency broadcast on a
channel and do not want to miss any details
— even though there might be periods of
silence — or if you simply want to monitor
that channel.
Follow these steps to manually select a
channel.
1. Press
2. Enter the channel number (1–200).
3. Press
MANUAL
MANUAL
.
again.
CLEARING A STORED
CHANNEL
If you no longer want a frequency stored in a
channel (and you do not want to replace that
frequency with a different one), follow these
steps to clear the stored frequency.
1. Press
2. Use the number keys to select the
3. Press
4. Press 0, then press
MANUAL
or to stop scanning.
desired channel number, then press
MANUAL
PGM
frequency number changes to
000.0000
cleared.
to exit the service banks
.
PGM
.
appears.
ENTER
. The
to indicate the channel is
18
Operation
Page 19

5. To clear another channel, use the
number keys to enter that channel
number, then press
repeatedly press
channel number appears. Then repeat
Step 4.
PGM
again. Or,
PGM
until the desired
Weather Channel Frequency
Chart
Weather
Channel
Frequency (MHz)
LISTENING TO THE MARINE
BANK
1. To listen to the marine bank, repeatedly
BAND
press
2. To change the channel, press either
9999
or
, or enter the two-digit channel.
3. To scan through the marine bank, rotate
SQUELCH
disappears, then hold down either
9999
for about 2 seconds.
disappears and
4. To exit scanning and to ch ange the
channel manually, hold down
for about 2 seconds.
MARINE
until
clockwise until the hiss just
appears.
8888
MAN
SCAN
appears.
8888
9999
or
8888
or
LISTENING TO THE
WEATHER BAND
The FCC (Federal Communications
Commission) has allocated seven
frequencies for use by the National Oceanic
and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
NOAA broadcasts your local forecast and
regional weather information on one or more
of these frequencies. We have programmed
your scanner with these seven frequencies.
1 162.400
2 162.425
3 162.450
4 162.475
Using the
This scanner can receive NOAA weather
alert tone broadcasts in case of an
emergency. The weather alert tone sound
warns you of serious weather conditions.
To listen for an alert tone, press
while you are tuned to the weather channel.
ALErt
weather alert, it sounds a tone. Press any
key to mute the tone. To cancel the alert
monitoring and return to the weather channel
standard broadcast, press
5 162.500
6 162.525
7 162.550
Weather Alert
appears. If the scanner detects a
PRI/ALERT
PRI/ALERT
again.
To hear your local forecast and regional
WX
weather information, press
begins to scan the weather band.
You will probably receive one frequency
better than the others for your area. The
scanner should stop within a few seconds on
that frequency. If the broadcast is weak,
WX
press
again to resume scanning.
. The scanner
Operation
19
Page 20

ˆ
Special Features
USING THE DELAY
FUNCTION
Many agencies use a two-way radio system
that has a period of several seconds
between a query and a reply. To avoid
missing a reply, you can program a 2–
second delay into any channel or frequency.
When your scanner stops on any channel or
DLY
frequency with a programmed delay,
appears and the scanner continues to
monitor that frequency for an additional 2
seconds after the transmission stops before
resuming scanning or searching.
You can program a 2 second delay in any of
these ways:
• If the scanner is scanning and stops on
an active channel, quickly press
before it continues scanning.
• If the desired channel is not selected,
manually select the channel, then press
DELAY
.
• If the scanner is searching, press
DELAY
automatically adds a 2-second delay to
every transmission it stops on in that
band.
To turn off the delay, press
scanner is monitoring the channel or
frequency.
DLY
.
appears and the scanner
DELAY
DLY
disappears.
while the
DELAY
LOCKING OUT CHANNELS
AND FREQUENCIES
You can increase the scanning or search
speed by locking out individual channels or
frequencies that have a continuous
transmission, such as a weather channel
(see the “Weather Channel Frequency
Chart” on Page 19) or birdie frequency (see
“Birdie Frequencies” on Page 22).
Locking Out Channels
To lock out a channel while scanning, press
until
:
L/O (L/O RVW)
L/O
appears.
when the scanner
L/O (L/O RVW)
and release
stops on the channel.
To lock out a channel manually, select the
channel then press and release
RVW)
To unlock a channel, manually select that
channel again, then press
O
disappears from the display.
Notes
• The scanner automatically locks out
empty channels.
• Y ou can still manually tune to locked-out
channels.
Locking Out Frequencies
To lock out a frequency during a service
bank, or a direct search, press
when the scanner stops on the frequency.
The scanner locks out the frequency then
continues searching. You can lock out
frequencies in both direct search and service
bank searches.
Note
: You can lock out as many as 50
frequencies during a search. If you try to lock
out more,
“Reviewing Locked-Out Frequencies” on
Page 21and “Removing All Locked-Out Tags
From Frequencies” on Page 21).
FLo -FULL
appears (see
L/O (L/O RVW)
L/O (L/O
L/
.
20
Special Features
Page 21

Reviewing Locked-Out
Frequencies
tags, press
reviewing the lockout frequencies.
MON/CL
to continue
To review the frequencies you locked out,
hold down
during a search.
8888
or
in sequence. When you reach the highest
frequency, the scanner beeps twice then
returns to the lowest locked-out frequency.
L/O (L/O RVW)
L-r
9999
, all locked-out frequencies appear
at least 2 seconds
appears. As you press
Removing All Locked-Out Tags
From Frequencies
1. Start a service bank or direct search.
See “Using Direct Search” on Page 16.
2. To review the fre quencies you locked
out, hold down
seconds during the search.
appears.
3. Hold down
RVW)
FLo ALL-CL
.
4. Press
ENTER
The frequency clears and
appears. To exit without clearing all
locked out frequencies, press
L/O (L/O RVW)
MON/CL
then press
appears.
to clear all lockout tags.
for about 2
L-r
L/O (L/O
000.0000
MON/CL
Removing All Lockout Tags from
Frequencies in All Service Banks
1. Start a service bank or direct search.
See “Using Direct Search” on Page 16.
2. To review the fre quencies you locked
out, hold down
seconds during the search.
appears.
3. Hold down
dEFAULt
4. Press
ENTER
frequencies in all the service banks
(except the weather and marine banks).
If you do not want to clear the lockout
L/O (L/O RVW)
MON/CL
appears.
then press
to clear the lockout
for about 2
L-r
BAND
.
Using Priority
You can scan the programmed channels
using the priority feature, and still not miss an
important or interesting call.
Follow these steps to program the priority
channel.
PGM
1. Press
2. Enter the desired frequency using the
number keys.
3. Press
4. To turn on the priority feature, press
(ALERT)
The scanner checks the priority channel
every 2 seconds and stays on the
channel if there is activity.
when the scanner is set to the priority
channel.
5. To turn off the priority feature, press
PRI
.
If you designate a weather frequency as the
priority channel, the scanner detects the
weather alert tone while the priority feature is
on. When the scanner detects a weather
alert tone,
alert tone, press any key. The scanner
continues to monitor the weather channel.
, then press
ENTER
.
while scanning.
disappears.
ALErt
flashes. To cancel the
PRI/ALERT
TURNING THE KEY TONE
ON AND OFF
The scanner is preset to sound a tone each
time you press one of its keys. You can turn
the key tone on or off.
1. If the scanner is on, slide
to turn it off.
PRI
appears.
PCH
POWER
.
PRI
appears
PRI
OFF
to
.
Special Features
21
Page 22

2. While you hold down 2 and
on the scanner. The display shows
tonE
keys.
or on
tonE
. Then release the
ENTER
, turn
oFF
The known birdie frequencies to watch for
are:
29.800 122.9375 388.3875
USING A COMPUTER TO
PROGRAM THE SCANNER
You can connect your scanner to a personal
computer and program frequencies into the
scanner from the computer using an optional
cable and software.
Note:
The necessary cable and software,
and additional information about using your
personal computer to program your scanner,
are available at your local RadioShack store.
BIRDIE FREQUENCIES
Every scanner has birdie frequencies.
Birdies are signals created inside the
scanner’s receiver. These operating
frequencies might interfere with
transmissions on the same frequencies. If
you program one of these frequencies, you
hear only noise on that frequency. If the
interference is not severe, you might be able
SQUELCH
to turn
birdie.
To find the birdies in your scanner, follow
these steps.
clockwise to cut out the
30.375 128.000 398.5625
32.075 128.375 414.6125
38.400 136.5875 426.7875
40.000 149.400 431.1625
40.980 152.655 441.3875
51.200 160.470 457.4375
112.4875 162.200 462.7875
115.200 168.495 478.8375
120.5125 384.550
UNITED STATES
BROADCAST BAND
In the United States, there are several
broadcast bands. The standard AM and FM
bands are probably the most well known.
There are also four television audio
broadcast bands — the lower three transmit
on the VHF band and the fourth transmits on
the UHF band. You can use your scanner to
monitor the 470–512 MHz portion of the UHF
band.
1. Disconnect the antenna and move it
away from the receiver. Make sure that
no other operating radio or TV sets are
nearby.
2. Search in each frequency band from the
lowest frequency to the highest. If the
search stops on a frequency, but you
hear no sound, chances are you have
located a birdie. Note all birdie
frequencies for reference.
22
Special Features
Page 23

ˆ
Guide to the Action Bands
Typical Band Usage
HF Band (3.00–30.00 MHz)
10 m Amateur
High Range
VHF Band (30.00–300.0 MHz)
Low Range
6 m Amateur
U.S. Government
2 m Amateur
High Range
UHF Band (300.00 MHz–3.0 GHz)
U.S. Government
70 cm Amateur
Low Range
FM-TV Audio Broadcast, Wide Band
29.00–29.70 MHz
29.70–29.90 MHz
30.00–50.00 MHz
50.00–54.00 MHz
137.00–144.00 MHz
144.00–148.00 MHz
148.00–174.00 MHz
380.00–420.00 MHz
420.00–450.00 MHz
450.00–470.00 MHz
470.00–512.00 MHz
Primary Usage
As a general rule, most of the radio activity is concentrated on the following frequencies:
VHF Band
Government, Police, and Fire 153.785–155.980 MHz
Emergency Services 158.730–159.460 MHz
Railroad 160.000–161.900 MHz
UHF Band
Land-Mobile Paired Frequencies 450.000–470.000 MHz
Base Stations 451.025–454.950 MHz
Mobile Units 456.025–459.950 MHz
Repeater Units 460.025–464.975 MHz
Control Stations 465.025–469.975 MHz
Note:
Remote control stations and mobile units operate at 5 MHz higher than their associated
base stations and relay repeater units.
Guide to the Action Bands
23
Page 24

BAND ALLOCATION
To help decide which frequency ranges to scan, use the following listing of the typical services
that use the frequencies your scanner receives. These frequencies are subject to change, and
might vary from area to area. For a more complete listing, refer to the
available at your local RadioShack store.
Abbreviations Services
AIR ................................................................................................................................... Aircraft
BIFC .................................................................................... Boise (ID) Interagency Fire Cache
BUS ............................................................................................................................. Business
CAP ..................................................................................................................... Civil Air Patrol
CCA .......................................................... ....................................................... Common Carrier
CSB ........................................................................................................ Conventional Systems
CTSB ........................................................................................ Conventional/Trunked Systems
FIRE ................................................................................................................. Fire Department
HAM ........................................................................................................ Amateur (Ham) Radio
GOVT ........................................................................................................ Federal Government
GMR ........................................................................................................ General Mobile Radio
GTR ................................................................................................................. General Trunked
IND .................................. .................................... ..................................... .... Industrial Services
(Manufacturing, Construction, Farming, Forest Products)
MAR ...................................................................................................... Military Amateur Radio
MARI ..................................................................................................... Maritime Limited Coast
(Coast Guard, Marine Telephone, Shipboard Radio, Private Stations)
MARS ......................................................................................... Military Affiliate Radio System
MED ............................................................................................ Emergency/Medical Services
MIL ......................................................................................................................... U.S. Military
MOV ................................ ... .................................... ... .................. Motion Picture/Video Industry
NEW ........................................................................................................... New Mobile Narrow
NEWS ............................................................................... Relay Press (Newspaper Reporters)
OIL .......................................... ... ..................................... .. ..................... Oil/Petroleum Industry
POL .............................................................................................................. Police Department
PUB ................................................................................................................... Public Services
(Public Safety, Local Government, Forestry Conservation)
PSB ....................................................................................................................... Public Safety
PTR .............................. ... ... ...................................................................... ........ Private Trunked
ROAD ........................................................................................ Road & Highway Maintenance
RTV .............................. ... ... .................................... ... ... .... Radio/TV Remote Broadcast Pickup
TAXI ....................................................................................................................... Taxi Services
TELB .............................................................................................................. Mobile Telephone
(Aircraft, Radio Common Carrier, Landline Companies)
TELM .................................................................................................... Telephone Maintenance
TOW ........................................... .................................. ... .. .................................. ... .. Tow Trucks
TRAN .................................................................................................... Transportation Services
(Trucks, Tow Trucks, Buses, Railroad, Other)
TSB ................................................................................................................ Trunked Systems
TVn ...................................................................................................... FM-TV Audio Broadcast
USXX ..................................................................................................... Government Classified
UTIL ....................................................................................................... Power & Water Utilities
WTHR ........................................................................................................................... Weather
Beyond Police Call
,
HIGH FREQUENCY (HF)—(3 MHz–30MHz)
10 m Amateur Band (28.0–29.7 MHz)
29.000–29.700 ................................................................................................................... HAM
24
Guide to the Action Bands
Page 25

VERY HIGH FREQUENCY (VHF)—(30 MHz–300 MHz)
VHF Low Band (29.7–50 MHz—in 5 kHz steps)
29.700–29.790 ..................................................................................................................... IND
29.900–30.550 .......................................................................................................... GOVT, MIL
30.580–31.980 ............................................................................................................ IND, PUB
32.000–32.990 .......................................................................................................... GOVT, MIL
33.020–33.980 .................................................................................................. BUS, IND, PUB
34.010–34.990 .......................................................................................................... GOVT, MIL
35.020–35.980 ....................................................................................... BUS, PUB, IND, TELM
36.000–36.230 .......................................................................................................... GOVT, MIL
36.230–36.990 ............................................................................. Oil Spill Cleanup, GOVT, MIL
37.020–37.980 ............................................................................................................ PUB, IND
38.000–39.000 .......................................................................................................... GOVT, MIL
39.020–39.980 .................................................................................................................... PUB
40.000–42.000 ............................................................................................... GOVT, MIL, MARI
42.020–42.940 .................................................................................................................... POL
42.960–43.180 ..................................................................................................................... IND
43.220–43.680 ................................................................................................ TEL M, IND, PUB
43.700–44.600 .................................................................................................................. TRAN
44.620–46.580 ........................................................................................................... POL, PUB
46.600–46.990 ................................................................................................................. GOVT
47.020–47.400 .................................................................................................................... PUB
47.420 ....................................................................................................... American Red Cross
47.440–49.580 ............................................................................................................ IND, PUB
49.610–49.990 ..................................................................................................................... MIL
6 m Amateur Band (50–54 MHz)
50.00–54.00 ....................................................................................................................... HAM
U.S. Government Band (138–144 MHz)
137.000–144.000 ...................................................................................................... GOVT, MIL
2 m Amateur Band (144–148 MHz)
144.000–148.000 ............................................................................................................... HAM
VHF High Band (148–174 MHz)
148.050–150.345 .............................................................................................. CAP, MAR, MIL
150.775–150.790 ................................................................................................................MED
150.815–150.980 ....................................................................................TOW, Oil Spill Cleanup
150.995–151.475 .................................................................................................... ROAD, POL
151.490–151.955 ........................................................................................................ IND, BUS
151.985 ............................................................................................................................. TELM
152.0075 ............................................................................................................................ MED
152.030–152.240 .............................................................................................................. TELB
152.270–152.480 .............................................................................................. IND, TAXI, BUS
152.510–152.840 .............................................................................................................. TELB
152.870–153.020 ....................................................................................................... IND, MOV
153.035–153.725 ................................................................................................ IND, OIL, UTIL
153.740–154.445 ...................................................................................................... PUB, FIRE
154.490–154.570 ........................................................................................................ IND, BUS
154.585 ............................................................................................................ Oil Spill Cleanup
154.600–154.625 ................................................................................................................ BUS
154.655–156.240 ................................................................................ MED, ROAD, POL, PUB
156.255–157.425 ....................................................................................................... OIL, MARI
157.450 .............................................................................................................................. MED
Guide to the Action Bands
25
Page 26

157.470–157.515 .............................................................................................................. TOW
157.530–157.725 ....................................................................................................... IND, TAXI
157.740 .............................................................................................................................. BUS
157.770–158.100 .............................................................................................................. TELB
158.130–158.460 .......................................................................... BUS, IND, OIL, TELM, UTIL
158.490–158.700 .............................................................................................................. TELB
158.730–159.465 .......................................................................................... POL, PUB, ROAD
159.480 ................................................................................................................................ OIL
159.495–161.565 ............................................................................................................. TRAN
161.580–162.000 ............................................................................................. OIL, MARI, RTV
162.0125–162.35 ......................................................................................... GOVT, MIL, USXX
162.400–162.550 ............................................................................................................ WTHR
162.5625–162.6375 ..................................................................................... GOVT, MIL, USXX
162.6625 ............................................................................................................................ MED
162.6875–163.225 ....................................................................................... GOVT, MIL, USXX
163.250 .............................................................................................................................. MED
163.275–166.225 ......................................................................................... GOVT, MIL, USXX
166.250 ......................................................................................................... GOVT, RTV, FIRE
166.275–169.400 ................................................................................................... GOVT, BIFC
169.445–169.505 .................................................................................. Wireless Mikes, GOVT
169.55–169.9875 ......................................................................................... GOVT, MIL, USXX
170.000–170.150 ................................................................................ BIFC, GOVT, RT V, FIRE
170.175–170.225 ............................................................................................................. GOVT
170.245–170.305 ............................................................................................... Wireless Mikes
170.350–170.400 ..................................................................................................... GOVT, MIL
170.425–170.450 ............................................................................................................... BIFC
170.475 .............................................................................................................................. PUB
170.4875–173.175 ....................................................................... GOVT, PUB, Wireless Mikes
173.225–173.5375 .............................................................................. MOV, NEWS, UTIL, MIL
173.5625–173.5875 .......................................................................... MIL Medical/Crash Crews
173.60–173.9875 ............................................................................................................. GOVT
ULTRA HIGH FREQUENCY (UHF)—(300 MHz–3 GHz)
U. S. Government Band (380–406 MHz)
381.800–383.900 ............................................................................................................. GOVT
U. S. Government Band (406–450 MHz)
406.125–419.975 ................................................................................................. GOVT, USXX
70 cm Amateur Band (420–450 MHz)
420.000–450.000 ............................................................................................................... HAM
Low Band (450–470 MHz)
450.050–450.925 ................................................................................................................ RTV
451.025–452.025 ................................................................................... IND, OIL, TELM, UTIL
452.0375–453.00 ..................................................................... IND, TAXI, TRAN TOW, NEWS
453.0125–454.000 ...................................................................................................... PUB, OIL
454.025–454.975 .............................................................................................................. TELB
455.050–455.925 ................................................................................................................ RTV
457.525–457.600 ............................................................................................................... BUS
458.025–458.175 ............................................................................................................... MED
460.0125–460.6375 ........................................................................................ FIRE, POL, PUB
460.650–462.175 ............................................................................................................... BUS
462.1875–462.450 ..................................................................................................... BUS, IND
462.4625–462.525 ................................................................................. IND, OIL, TELM, UTIL
462.550–462.925 ..................................................................................................... GMR, BUS
26
Guide to the Action Bands
Page 27

462.9375–463.1875 ........................................................................................................... MED
463.200–467.925 ................................................................................................................ BUS
FM-TV Audio Broadcast, UHF Wide Band (470–512 MHz)
(Channels 14 through 20 in 6 MHz steps)
475.750 .................................................................................................................... Channel 14
481.750 .................................................................................................................... Channel 15
487.750 .................................................................................................................... Channel 16
493.750 .................................................................................................................... Channel 17
499.750 .................................................................................................................... Channel 18
505.750 .................................................................................................................... Channel 19
511.750 .................................................................................................................... Channel 20
Note:
Some cities use the 470–512 MHz band for land/mobile service.
AVOIDING IMAGE FREQUENCIES
You might discover one of your regular stations on another frequency that is not listed. It might
be what is known as an image frequency. For example, you might find a service that regularly
uses a frequency of 453.275 also on 474.675.
To see if it is an image, do a little math.
Note the new frequency. 474.675
Double the intermediate frequency of 10.7 MHz (21.400)
and subtract it from the new frequency. –21.400
If the answer is the regular frequency, 453.275
then you have tuned to an image.
Occasionally, you might get interference on a weak or distant channel from a strong broadcast
21.4 MHz above or below the tuned frequency. This is rare, and the image signal is usually
cleared whenever there is a broadcast on the actual frequency.
FREQUENCY CONVERSION
The tuning location of a station can be expressed in frequency (kHz or MHz) or in wavelength
(meters). The following information can help you make the necessary conversions.
1 MHz (million) = 1,000 kHz (thousand)
To convert MHz to kHz, multiply the number of MHz by 1,000:
30.62 MHz × 1000 = 30,620 kHz
To convert from kHz to MHz, divide the number of kHz by 1,000.
127,800 kHz ÷ 1000 = 127.8 MHz
To convert MHz to meters, divide 300 by the number of MHz.
300 ÷ 50 MHz = 6 meters
Guide to the Action Bands
27
Page 28

ˆ
Troubleshooting
If your scanner stops operating properly, these suggestions might help you eliminate the
problem. If the scanner still does not operate properly, take it to your local RadioShack store for
assistance.
PROBLEM SUGGESTION
Scanner is on, but will not scan. Be sure
Scanner receives stations poorly or
not at all.
The scanner’s keys do not work, or
the display shows random segments.
Scanner does not work at all. Check that the power supply (AC adapter/AC outlet) is working.
Scanner locks on frequencies that
have an unclear transmission.
SQUELCH
Scanner/Setting Volume and Squelch” on Page 14.
MAN
Be sure
Check the antenna (indoor or outdoor).
Signals may be blocked from being received by the scanner due
to metal frames or material in the building. Change
the scanner’s location and try again.
The scanner might be locked. Reset the scanner. If that does
not work, reinitialize the scanner. See “Resetting/Initializing the
Scanner.”
The scanner might be locked. Reset the scanner. If that does
not work, reinitialize the scanner. See “Resetting/Initializing the
Scanner.”
SQUELCH
Be sure
Be sure birdie frequencies are not programmed, or listen to
birdie frequencies manually. See “Birdie Frequencies” on
Page 22.
is adjusted properly. See “Turning On the
is not displayed. If it is, press
is adjusted properly.
SCAN
.
RESETTING/INITIALIZING
THE SCANNER
If the scanner's display locks up or does not
work properly after you connect a power
source, you might need to reset or initialize
the scanner.
Important
reset the scanner. If that does not work, you
can initialize the scanner; however, this
clears all information stored in your
scanner's memory.
Resetting the Scanner
1. Turn off the scanner, then turn it on
28
: If you have problems, first try to
again.
Troubleshooting
2. Insert a pointed object, such as a
straightened paper clip, into the reset
opening on the back of the scanner (as
shown) and gently press then release
the reset button inside the opening. If
the scanner still does not work properly,
you might need to initialize the scanner.
Page 29

Initializing the Scanner
Important
: This procedure clears all information you stored in the scanner's memory.
Initialize the scanner only when you are sure
the scanner is not working properly.
1. Turn off the scanner, then turn it on
again.
2. Hold down
MON/CL
3. While you hold down
.
MON/CL
, insert a
pointed object, such as a straightened
RESET
paper clip, into the
opening on
the back of the scanner and gently press
then release the reset button inside the
opening. The display should clear.
4. When the display reappears, release
MON/CL
Note:
before you release
.
You must release the reset button
MON/CL
, otherwise the
memory might not clear.
CARE
Keep the scanner dry; if it gets wet, wipe it
dry immediately. Use and store the scanner
only in normal temperature environments.
Handle the scanner carefully; do not drop it.
Keep the scanner away from dust and dirt,
and wipe it with a damp cloth occasionally to
keep it looking new.
Modifying or tampering with the scanner’s
internal components can cause a
malfunction and might invalidate its warranty
and void your FCC authorization to operate
it. If your scanner is not performing as it
should, take it to your local RadioShack store
for assistance.
Troubleshooting
29
Page 30

ˆ
Specifications
Frequency Coverage:
Ham ................................................................................................ 29–30 MHz (5.0 kHz Steps)
VHF Lo ........................................................................................... 30–50 MHz (5.0 kHz Steps)
Ham ................................................................................................ 50–54 MHz (5.0 kHz Steps)
Air .................................................................................... 108–136.9875 MHz (12.5 kHz Steps)
Government ................................................................................... 137–144 MHz (5 kHz Steps)
Ham ............................................................................................... 144–148 MHz (5 kHz Steps)
VHF Hi ........................................................................................... 148–174 MHz (5 kHz Steps)
Ham/Government ..................................................................... 380–450 MHz (12.5 kHz Steps)
UHF Lo ..................................................................................... 450–470 MHz (12.5 kHz Steps)
UHF Hi (T) ................................................................................ 470–512 MHz (12.5 kHz Steps)
Channels of Operation ................................................200 Channels and 20 Monitor Memories
Sensitivity (20 dB S/N):
29–54 MHz ............................................................................................................... 0.5 µV
108–136.9875 MHz .................................................................................................. 1.0 µV
137–174 MHz ........................................................................................................... 0.5 µV
380–512 MHz ........................................................................................................... 0.7 µV
Selectivity:
±10 kHz ..................................................................................................................... –6 dB
±18 kHz ..................................................................................................... ... ... ........ –50 dB
Spurious Rejection ............................................................................... 50 dB (FM at 154 MHz)
Scanning Rate ................................................................................. Up to 25 Channels/Second
Search Rate .......................................................................................... Up to 50 Steps/Second
Delay Time .............................. .................................................................................. 2 Seconds
Intermediate Frequencies (IF):
1st ........................................................................................................................ 10.7 MHz
2nd ......................................................................................................................... 455 kHz
IF Interference Ratio (10.7 MHz) ................................................................... 70 dB at 154 MHz
Squelch Sensitivity:
Threshold ................................................................................................. Less than 0.5 µV
Tight (FM) .................................................................................................... (S+N)/N 25 dB
Tight (AM) ................................................................................................... (S+N)/N 20 dB
Antenna impedance .................................................................................................... 50 Ohms
30
Specifications
Page 31

Audio Output Power (10% THD) ......................................................................... 0.8 W Nominal
Built-in Speaker ............................................................ 3 inch (77 mm), 8-Ohm, Dynamic Type
Power Requirements ............................................................................... 120 V AC, 60 Hz, 8W
Current Drain ................................................................................................................. 300 mA
Operating Temperature ........................................................................................ 32°F to 110°F
(0°C to 43°C)
1
Dimensions (HWD) ............................................................................... 2
/16 × 81/4 × 67/8 inches
(52 × 210 × 175 mm)
Weight (without antenna and batteries) ............................................................................. 24 oz
(680 g)
Supplied Accessories .............................................................................. Telescoping Antenna,
AC Adapter
Specifications are typical; individual units might vary. Specifications are subject to change and
improvement without notice.
Specifications
31
Page 32

Limited One-Year Warranty
This product is warranted by RadioShack against manufacturing defects in material and workmanship under normal use for one (1) year from the date of purchase from Radi oSha ck company- owned
stores and authorized RadioShack franchisees and dealers. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED HEREIN, RadioShack MAKES NO EXPRESS WARRANTIES AND ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING
THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, ARE LIMITED
IN DURATION TO THE DURATION OF THE WRITTEN LIMITED WARRANTIES CONTAINED
HEREIN. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED HEREIN, RadioShack SHALL HAVE NO LIABILITY OR RESPONSIBILITY TO CUSTOMER OR ANY OTHER PERSON OR ENTITY WITH RESPECT T O ANY
LIABILITY, LOSS OR DAMAGE CAUSED DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY BY USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT OR ARISING OUT OF ANY BREACH OF THIS WARRANTY, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, ANY DAMAGES RESULTING FROM INCONVENIENCE, LOSS
OF TIME, DATA, PROPERTY, REVENUE, OR PROFIT OR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, EVEN IF RadioShack HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts or the exclusion or limit ation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitations or exclusions may not apply to
you.
In the event of a product defect during the warranty period, take the product and the RadioShack
sales receipt as proof of purchase date to any RadioShack store. RadioShack will, at its option, unless otherwise provided by law: (a) correct the defect by product repair without charge for parts and
labor; (b) replace the product with one of the same or similar design; or (c) refund the purchase
price. All replaced parts and products, and products on which a refund is made, become the property of RadioShack. New or reconditioned parts and products may be used in the performance of
warranty service. Repaired or replaced parts and products are warranted for the remainder of the
original warranty period. You will be charged for repair or replacement of the product made after the
expiration of the warranty period.
This warranty does not cover: (a) damage or failure caused by or attributable to acts of God, abuse,
accident, misuse, improper or abnormal usage, failure to follow instructions, improper installation or
maintenance, alteration, lightning or other incidence of excess voltage or current; (b) any repairs
other than those provided by a RadioShack Authorized Service Facility; (c) consumables such as
fuses or batteries; (d) cosmetic damage; (e) transportation, shipping or insurance costs; or (f) costs
of product removal, installation, set-up service adjustment or reinstallat i on.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights which vary from
state to state.
RadioShack Customer Relations, 200 Taylor Street, 6th Floor, Fort Worth, TX 76102
12/99
RadioShack Corporation
Fort Worth, Texas 76102
A
20-423
GE-01D-5370
11A01
Printed in China
 Loading...
Loading...