Page 1

MPAP-200
RS-422/485 PCMCIA
SYNCHRONOUS ADAPTER
for PCMCIA Card Standard compatible machines
User's Manual
QUATECH, INC. TEL: (330) 655-9000
5675 Hudson Industrial Parkway FAX: (330) 655-9010
Hudson, Ohio 44236 www.quatech.com
Page 2

Copyright 2001 Quatech, Inc.
NOTICE
The information contained in this document is protected by copyright, and cannot be
reproduced in any form without the written consent of Quatech, Inc. Likewise, any software
programs that might accompany this document are protected by copyright and can be used only
in accordance with any license agreement(s) between the purchaser and Quatech, Inc. Quatech,
Inc. reserves the right to change this documentation or the product to which it refers at any time
and without notice.
The authors have taken due care in the preparation of this document and every attempt
has been made to ensure its accuracy and completeness. In no event will Quatech, Inc. be liable
for damages of any kind, incidental or consequential, in regard to or arising out of the
performance or form of the materials presented in this document or any software programs that
might accompany this document.
Quatech, Inc. encourages feedback about this document. Please send any written
comments to the Technical Support department at the address listed on the cover page of this
document.
WARRANTY INFORMATION
Page 3

Quatech Inc. warrants the MPAP-200 to be free of defects for five (5) years from the
date of purchase. Quatech Inc. will repair or replace any board that fails to perform under normal
operating conditions and in accordance with the procedures outlined in this document during the
warranty period. Any damage that results from improper installation, operation, or general
misuse voids all warranty rights.
Although every attempt has been made to guarantee the accuracy of this manual, Quatech
Inc. assumes no liability for damages resulting from errors in this document. Quatech Inc.
reserves the right to edit or append to this document at any time without notice.
Please complete the following information and retain for your records. Have this
information available when requesting warranty service.
DATE OF PURCHASE:
MODEL NUMBER: MPAP-200
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: Single Channel PCMCIA RS-422/485
Synchronous Communications
Adapter
SERIAL NUMBER:
1 Introduction
.......................................................
1.1 System Requirements
2 Hardware Installation
3 DOS / Windows 3.x Software Installation
...........................................
..............................................
...........................
7
7
8
9
Page 4

3.1 MPAP-200 Client Driver for DOS
3.1.1 Hot Swapping
..............................................
3.1.2 DOS client driver installation
3.1.3 Auto Fallback configuration
3.2 DOS Client Driver examples
3.3 MPAP-200 Enabler for DOS
3.3.1 Hot Swapping is not supported
3.3.2 DOS Enabler Installation
3.3.3 Configuring a card
.........................................
3.3.4 Releasing a card's configuration
3.4 DOS Enabler Examples
4 Windows 95/98 Installation
4.3 Configuration Options
5 OS/2 Software Installation
5.1 System Requirements
........................................
........................................
.........................................
.........................................
..........................................
5.2 OS/2 Client Driver Installation
...................................
...................................
...................................
..............................
...............................
................................
.............................
............................
.................................
5.2.1 Tying a configuration to a particular socket
5.2.2 Auto Fallback configuration
5.2.3 Hot Swapping
..............................................
................................
5.3 OS/2 Client Driver Configuration Examples
5.4 Monitoring The Status Of PCMCIA Cards
5.5 Installing OS/2 PCMCIA Support
6 Using the MPAP-200 with Syncdrive
7 Addressing
8 Interrupts
9 SCC General Information
9.1 Accessing the registers
........................................................
........................................................
.........................................
.........................................
9.2 Baud Rate Generator Programming
9.3 SCC Data Encoding Methods
9.4 Support for SCC Channel B
9.4.1 Receive data and clock signals
..............................
...............................
............................
..................................
..................................
..............................
9.4.2 Extra clock support for channel A
9.4.3 Extra handshaking for channel A
9.4.4 Other signals are not used
9.5 SCC Incompatibility Warnings
9.5.1 Register Pointer Bits
.......................................
9.5.2 Software Interrupt Acknowledge
10 FIFO Operation
.................................................
10.1 Enabling and disabling the FIFOs
..................................
................................
...........................
...........................
.............................
................
....................
.....................
..........................
11
11
11
12
12
14
14
14
14
16
17
18
22
23
23
23
24
24
24
25
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
34
34
35
35
35
35
35
36
36
36
37
37
Page 5

10.2 Accessing the FIFOs
10.2.1 Transmit FIFO
10.2.2 Receive FIFO
10.3 SCC configuration for FIFO operation
..........................................
...........................................
.............................................
........................
10.3.1 Using channel A for both transmit and receive
10.3.2 Using channel B for receive
10.4 FIFO status and control
10.4.1 Interrupt status
...........................................
10.4.2 Resetting the FIFOs
......................................
.......................................
10.4.3 Reading current FIFO status
10.4.4 Controlling the FIFOs
.....................................
................................
..............................
10.5 Accessing the SCC while FIFOs are enabled
10.6 Receive pattern detection
10.7 Receive FIFO timeout
11 Communications Register
12 Configuration Register
...........................................
13 Interrupt Status Register
14 FIFO Status Register
15 FIFO Control Register
.............................................
...........................................
16 Receive Pattern Character Register
17 Receive Pattern Count Register
18 Receive FIFO Timeout Register
19 External Connections
19.1 SYNCA (pin 21)
............................................
..............................................
19.2 MPA-200 and EIA-530 Compatibility
19.3 Null-modem cables
20 DTE Interface Signals
21 Specifications
....................................................
...........................................
............................................
22 Software Troubleshooting
22.1 DOS Client Driver
............................................
22.1.1 Generic "SuperClient" Drivers
22.1.2 Lack of Available Resources
22.1.3 Multiple Configuration Attempts
.....................................
........................................
........................................
.........................................
...............................
...................................
..................................
.........................
........................................
............................
...............................
..........................
22.1.4 Older Versions of Card and Socket Services
22.2 DOS Enabler
22.2.1 With Card and Socket Services
22.2.2 Socket Numbers
22.2.3 Memory range exclusion
22.3 OS/2 Client Driver
.................................................
............................
..........................................
..................................
...........................................
.............
...................
................
37
37
38
38
39
40
41
41
42
42
42
42
43
44
45
47
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
56
57
58
60
61
61
61
61
61
61
62
62
62
62
62
Page 6

22.3.1 Resources Not Available
..................................
22.3.2 Insufficient Number Of Command Line Arguments
22.3.3 Bad Parameters
...........................................
........
62
62
63
Page 7

1 Introduction
The Quatech MPAP-200/300 is a PCMCIA Type II (5 mm) card and is PCMCIA PC Card
Standard Specification 2.1 compliant. It provides a single-channel RS-422/485 synchronous
communication port. The base address and IRQ are configured through the PCMCIA hardware
and software using utility programs provided by Quatech. There are no switches or jumpers to
set.
The MPAP-200/300 uses a Zilog 85230-compatible Serial Communications Controller
(SCC). The SCC can support asynchronous formats, byte-oriented synchronous protocols such
as IBM Bisync, and bit-oriented synchronous protocols such as HDLC and SDLC. The SCC also
offers internal functions such as on-chip baud rate generators, and digital phase-lock loop
(DPLL) for recovering data clocking from received data streams.
Because the PCMCIA 2.1 standard does not include a direct memory access (DMA)
interface, the MPAP-200/300 supports only interrupt-driven communications. To compensate
for the lack of DMA, the MPAP-200/300 is equipped with 1024-byte FIFOs for transmit and
receive data. The FIFOs provide for high data throughput with very low interrupt overhead.
Hereafter, the MPAP-200/300 will be referred to as the MPAP-200.
1.1 System Requirements
16 bytes of contiguous I/O address space
one hardware interrupt (IRQ)
One available PCMCIA Type II socket
7
Page 8

2 Hardware Installation
Hardware installation for the MPAP-200 is a very simple process:
1. Insert the MPAP-200 into a vacant PCMCIA Type II adapter socket.
2. If PCMCIA Card and Socket Services and a Quatech MPAP-200 Client Driver are
installed, the MPAP-200 will be configured for use automatically. Under DOS, it is also
possible to use the Quatech MPAP-200 enabler program. (Software installation and
configuration is covered in other chapters of this manual.)
3. Attach the narrow connector on the supplied cable to the socket on the end of the
MPAP-200. The connector is keyed so that it can only be inserted in one orientation.
The connector should attach firmly and smoothly. Do not force the connector into the
socket!
4. Attach the male DB-25 connector on the supplied cable to the external equipment in use.
8
Page 9

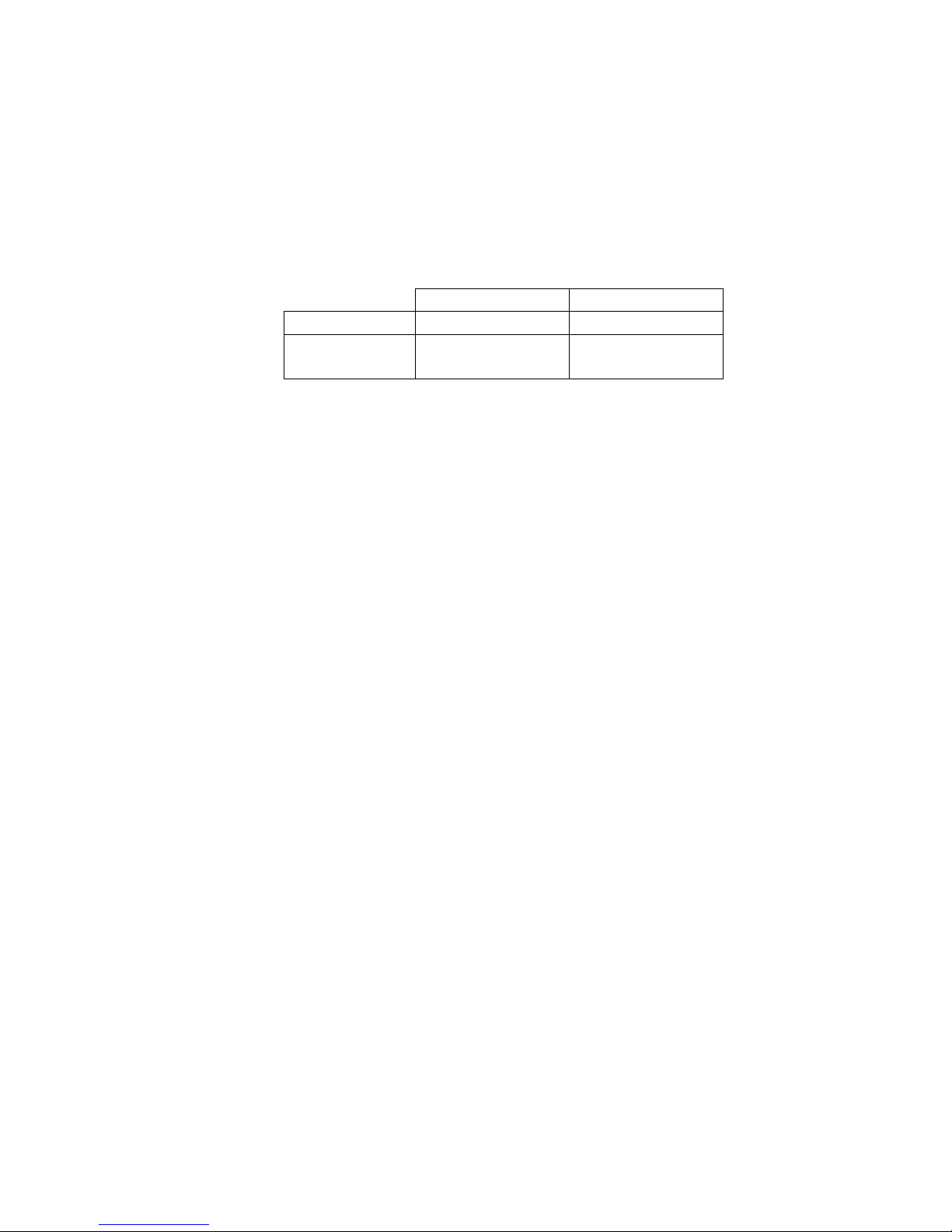
3 DOS / Windows 3.x Software Installation
Two DOS configuration software programs are provided with the MPAP-200: a client
driver and a card enabler. These programs are executed from DOS (before entering Windows)
and allow operation of the MPAP-200 in both the DOS and Windows 3.x environments. Table 1
highlights the differences between these programs.
EnablerClient Driver
File name
File type
Interfaces to
Automatic configuration of
MPAP-200 upon insertion
(Hot Swapping)
PCMCIA Card and Socket
Services software required
Recommendation
PCMCIA card and
Socket Services
(socket-independent)
Best for most users.
MPAP2EN.EXEMPAP2CL.SYS
DOS executableDOS device driver
socket controller (Intel
82365 or compatible
only)
noyes
noyes
Use if Card and
Socket Services
software is not
available and the
system has an Intel
82365 or compatible
socket controller.
Table 1 --- Client driver versus enabler for DOS/Windows 3.x.
Do not use both the client driver and the enabler!
If you are unsure whether Card and Socket Services software is currently installed on
your system, install the client driver. When loaded, the client driver will display an error
message if Card and Socket Services software is not detected. If you receive such an error
message, remove the client driver software and install the enabler instead.
IMPORTANT
9
Page 10

3.1 MPAP-200 Client Driver for DOS
In order to use the MPAP-200 client driver, the system must be configured with Card and
Socket Services software. Card and Socket Services software is not provided with the
MPAP-200 but is available from Quatech.
3.1.1 Hot Swapping
The client driver supports "hot swapping." After installation, it is not necessary for the
MPAP-200 to be inserted in the PCMCIA socket at boot time. When the card is inserted, it will
be configured according to the command line options. When the card is removed, the resources
it used will be made available for other devices.
If the MPAP-200 is in a socket at boot time, the client driver will display a message
indicating whether the card can be successfully configured and what resources will be used. This
is helpful if the user allows Card Services to select resources instead of specifying them on the
command line.
3.1.2 DOS client driver installation
The MPAP-200 client driver accepts between zero and eight sets of desired
configurations from the user on the command line. When an MPAP-200 is inserted, desired
configurations are tried in the order they appear on the command line from left to right. If the
user does not provide any desired configurations, the client driver will ask Card Services to
automatically determine a configuration for the card.
Each desired configuration must be enclosed in parentheses and must be separated from
other desired configurations by a space on the command line. Within each desired configuration,
parameters are separated using commas (no spaces). In the descriptions below, replace the '#'
symbols with the appropriate numeric values.
1. Copy the file MPAP2CL.SYS from the MPAP-200 distribution diskette onto the system's
hard drive.
2. Using an ASCII text editor, open the system's CONFIG.SYS file located in the root
directory of the boot drive.
3. Locate the line(s) in the CONFIG.SYS file where the Card and Socket Services software
is installed.
4. BELOW the line(s) installing the Card and Socket Services software, add the following
line to the CONFIG.SYS file:
10
Page 11

DEVICE=drive:\path\MPAP2CL.SYS (S#,B#,I#) ... (S#,B#,I#)
where drive:\path specifies the drive letter and directory to which you copied the client
driver file, and (S#,B#,I#) ... (S#,B#,I#) stand for a variable number of desired configurations.
The configuration parameters are described below.
S# The PCMCIA socket into which the MPAP-200 must be inserted for this
configuration to be used. This value is a decimal number ranging from 0 to 15. If
this parameter is not used, the configuration can apply to any socket.
B# The base I/O address of the MPAP-200. This number must be a three-digit
hexadecimal value ending in 0. If this parameter is omitted, a base address will be
assigned by Card Services.
I# The interrupt level (IRQ) of the MPAP-200. This decimal number must be one of
the following values: 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15, or 0 if no IRQ is desired. If
this parameter is omitted, an interrupt level will be assigned by Card Services.
5. Save the CONFIG.SYS file and exit the text editor.
6. Insert an MPAP-200 card in a PCMCIA socket, and reboot the computer. (If a card is
present in a socket at boot time, the card's configuration is reported on the screen as the
client driver loads. This feature can be used to verify the changes just made to the
CONFIG.SYS file.)
7. If the Client Driver reports the desired configuration, the installation process is complete
and the MPAP-200 may be removed from the system if desired.
8. If configuration of the card fails, the client driver will display an error message. If
"Invalid command line option" is displayed, correct the entry in the CONFIG.SYS file
and reboot the computer again. If "Card and Socket Services not found" is displayed,
install Card and Socket Services on the system or use the enabler program instead of the
client driver.
3.1.3 Auto Fallback configuration
The client driver can be instructed to try desired configurations first but fallback to
allowing Card Services to determine a configuration if none of the desired configurations are
available. This is done by adding a null configuration "()" to the end of the command line.
3.2 DOS Client Driver examples
Example: Attempt to configure an MPAP-200 inserted into any socket with a base address and
IRQ automatically assigned by Card Services.
DEVICE=C:\MPAP-200\MPAP2CL.SYS
11
Page 12

Example: Attempt to configure an MPAP-200 inserted into any socket with a base address of
300 hex and an IRQ assigned by Card Services. If address 300 hex is unavailable, the card will
not be configured.
DEVICE=C:\MPAP-200\MPAP2CL.SYS (b300)
Example: Attempt to configure an MPAP-200 inserted into socket 0 with a base address of 300
hex and IRQ 5. If address 300 hex or IRQ 5 is unavailable, the card will not be configured. In
addition, if an MPAP-200 is inserted into any other socket, it will not be configured.
DEVICE=C:\MPAP-200\MPAP2CL.SYS (s0,b300,i5)
Example: Attempt to configure an MPAP-200 inserted into any socket with a base address of
300 hex and IRQ 5. If address 300 hex or IRQ 5 is unavailable, attempt to configure the card
with a base address assigned by Card Services and IRQ 10. If IRQ 10 is also unavailable,
attempt to configure the card with a base address and an IRQ assigned by Card and Socket
Services.
DEVICE=C:\MPAP-200\MPAP2CL.SYS (b300,i5) (i10) ()
Example: Attempt to configure an MPAP-200 inserted into socket 0 with a base address of 300
hex and IRQ 5. Attempt to configure an MPAP-200 inserted into socket 1 with a base address of
340 hex and IRQ 10. This type of configuration may be desirable in systems where more than
one MPAP-200 is to be installed. It allows the user to force the MPAP-200 address and IRQ
settings to be socket-specific which may simplify cable connections and software development.
DEVICE=C:\MPAP-200\MPAP2CL.SYS (s0,b300,i5) (s1,b340,i10)
12
Page 13

3.3 MPAP-200 Enabler for DOS
For systems that are not using PCMCIA Card and Socket Services software, the
MPAP-200 DOS enabler may be used to enable and configure the card. The enabler will operate
on any DOS system using an Intel 82365SL (PCIC) or PCIC-compatible PCMCIA socket adapter
including the Cirrus Logic CL-PD6710/6720, the VLSI VL82C146, and the Vadem VG-365
among others.
IMPORTANT
The enabler can be used ONLY if Card and Socket
Services is NOT installed on the system!
3.3.1 Hot Swapping is not supported
The MPAP-200 enabler does not support automatic configuration of adapters upon
insertion, commonly referred to as "Hot Swapping". The enabler must be executed after
insertion of an MPAP-200 card. If more than one MPAP-200 is installed in a system, the enabler
must be executed separately for each card. A card that is removed and reinserted must be
reconfigured by executing the enabler again.
3.3.2 DOS Enabler Installation
To install the DOS enabler program, copy the file MPAP2EN.EXE from the MPAP-200
distribution diskette onto the system's hard drive. No setup steps are required.
IMPORTANT
The enabler requires a region of high DOS memory when configuring
an MPAP-200. This region is 1000H bytes (4KB) long and by default
begins at address D0000H (the default address may be changed using
the "W" option). If a memory manager such as EMM386, QEMM, or
386Max is installed on the system, this region of DOS memory must
be excluded from the memory manager's control. Consult the
documentation provided with the memory manager software for
instructions on how to exclude this memory region.
3.3.3 Configuring a card
13
Page 14

The enabler requires a single desired configuration to be provided on the command line.
The card will not be configured if the desired configuration is not provided. The desired
configuration must be enclosed in parentheses and it contains parameters separated using
commas (no spaces). In the descriptions below, replace the '#' symbols with the appropriate
numeric values.
MPAP1EN (S#,B#,I#,W#)
S# The PCMCIA socket into which the MPAP-200 will be inserted. This value is a
decimal number ranging from 0 to 15. This parameter is always required when
configuring a card.
B# The base I/O address of the MPAP-200. This number must be a three-digit
hexadecimal value ending in 0. This parameter is always required when
configuring a card.
I# The interrupt level (IRQ) of the MPAP-200. This decimal number must be one of
the following values: 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15, or 0 if no IRQ is desired.
This parameter is always required when configuring a card.
W# (optional) The base address of the memory window used by the enabler. This
two-digit hexadecimal number can be one of the following values: C8, CC, D0
(default), D4, D8, or DC. Use D4 for a memory window at segment D400, D8 for
a memory window at segment D800, etc. If this parameter is omitted, the default
setting of D000 will be used.
14
Page 15

If configuration is successful, the enabler will display a message showing the
configuration on the screen. If the MPAP-200 is not successfully configured, then the
information in this section along with the Troubleshooting chapter of this manual should be
consulted to determine the cause of the problem.
3.3.4 Releasing a card's configuration
Before removing a MPAP-200 from its PCMCIA socket, the enabler should be executed
again to free the system resources allocated when the card was installed. Use the 'R' parameter to
do this.
MPAP1EN (S#,R,W#)
S# The PCMCIA socket into which the MPAP-200 will be inserted. This value is a
decimal number ranging from 0 to 15. This parameter is always required when
releasing a card's configuration.
R Release the resources previously allocated to the MPAP-200. This parameter is
always required when releasing a card's configuration. This option must not be
used when configuring an MPAP-200.
W# (optional) The base address of the memory window used by the enabler. This
two-digit hexadecimal number can be one of the following values: C8, CC, D0
(default), D4, D8, or DC. Use D4 for a memory window at segment D400, D8 for
a memory window at segment D800, etc. If this parameter is omitted, the default
setting of D000 will be used.
15
Page 16

3.4 DOS Enabler Examples
Example: Configure the MPAP-200 in socket 0 with a base address of 300H and IRQ 5.
MPAP2EN.EXE (s0,b300,i5)
Example: Configure the MPAP-200 in socket 1 with a base address of 300H and IRQ 3 using a
configuration memory window at segment D800.
MPAP2EN.EXE (s1,b300,i3,wd8)
Example: Release the configuration used by the MPAP-200 in socket 0.
MPAP2EN.EXE (s0,r)
Example: Release the configuration used by the MPAP-200 in socket 1 using a configuration
memory window at segment CC00.
MPAP2EN.EXE (s1,r,wcc)
16
Page 17

4 Windows 95/98 Installation
Windows 95/98 maintains a registry of all known hardware installed in your computer.
Inside this hardware registry Windows keeps track of all of your system resources, such as I/O
locations, IRQ levels, and DMA channels. The "Add New Hardware Wizard" utility was
designed to add new hardware and update this registry.
An "INF" configuration file is included with the MPAP-200 to allow easy configuration
in the Windows 95/98 environment. Windows uses the "INF" file to determine the system
resources required by the MPAP-200, searches for available resources to fill the boards
requirements, and then updates the hardware registry with an entry that allocates these resources.
The Syncdrive DLL and VxD can then be used to access the card.
4.1 Using the "Add New Hardware" Wizard
The following instructions provide step-by-step instructions on installing the MPAP-200
in Windows 98 using the "Add New Hardware" wizard. Windows 95 uses a similar process to
load the INF file from a floppy disk with slightly different dialog boxes.
1. After inserting an MPAP-200 for the first time, the "Add New Hardware" wizard will
start. Click the "Next" button.
17
Page 18
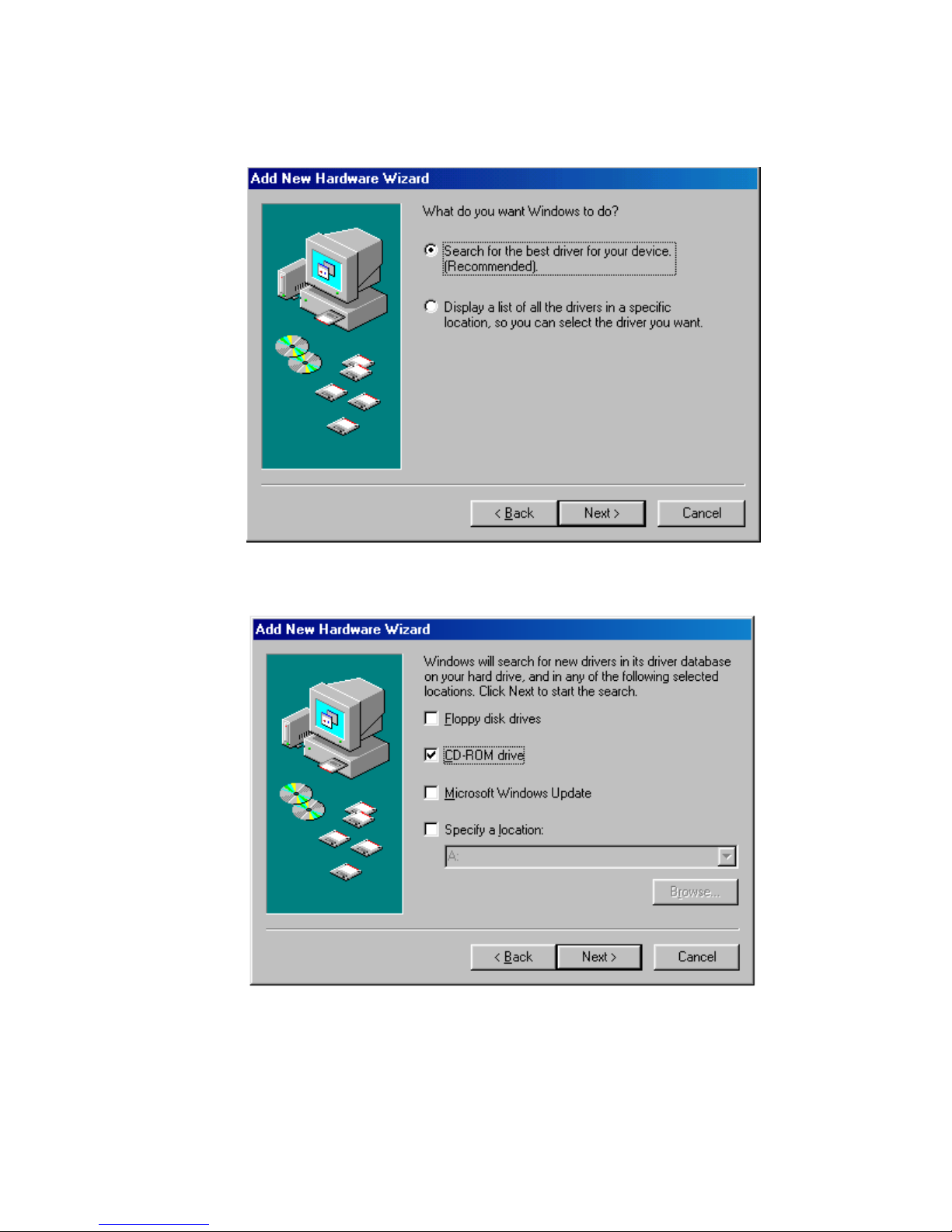
2. Click the "Next" button. Select the radio button for "Search for the best driver for your
device." Click the "Next" button to continue.
3. On the next dialog, select the "CD-ROM drive" checkbox. Insert the Quatech COM CD
(shipped with the card) into the CD drive. Click the "Next" button.
4. Windows should locate the INF file on the CD and display a dialog that looks like this.
Click the "Next" button.
18
Page 19
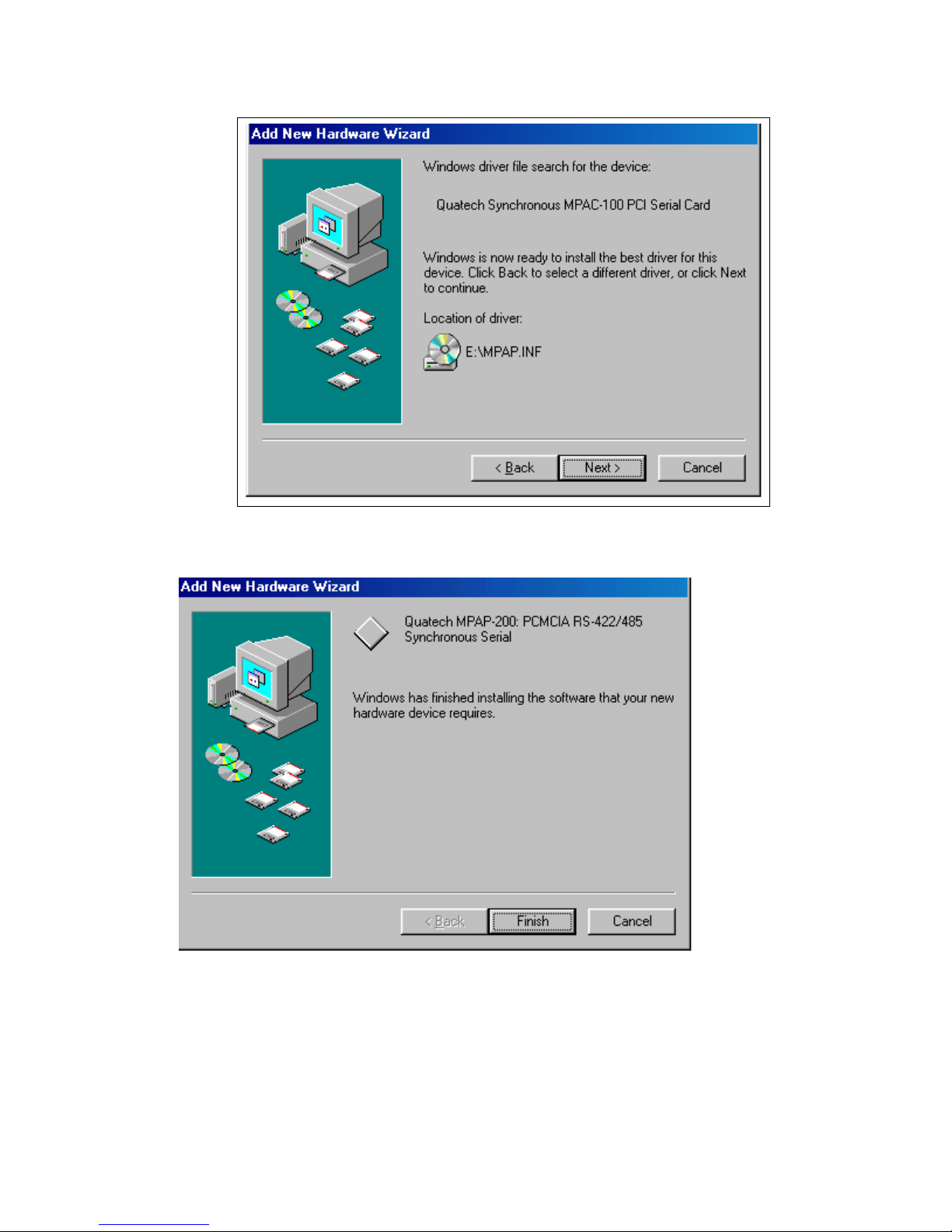
5. Windows will copy the INF file from the CD and display a final dialog indicating that the
process is complete. Click the "Finish" button.
19
Page 20

4.2 Viewing Resources with Device Manager
The following instructions provide step-by-step instructions on viewing resources used by
the MPAP-200 in Windows 95/98 using the "Device Manager" utility.
1. Double click the "System" icon inside the Control Panel folder. This opens up the
System Properties box.
2. Click the "Device Manager" tab located along the top of the System Properties box. This
lists all hardware devices registered inside the Windows registry. Additional information
is available on any of these devices by click on the device name and then selecting the
"Properties" button.
3. Double click the device group "Synchronous_Communication". The MPAP-200 model
name should appear in the list of adapters.
4. Double click the MPAP-200 model name and a properties box should open for the
hardware adapter.
5. Click the "Resources" tab located along the top of the properties box to view the
resources Windows has allocated for the MPAP-200 match the hardware configuration.
20
Page 21

Click "Cancel" to exit without making changes.
6. If changes to the automatic configuration are necessary for compatibility with existing
programs, uncheck the "Use Automatic Settings" box and double-click on the Resource
Type that needs to be changed. Caution should be used to avoid creating device conflicts
with other hardware in the system.
4.3 Configuration Options
If the "Use Automatic Settings" box is unchecked, various options can be enabled by
selecting a different basic configuration in the "Setting based on" drop down box. (Revision B5
hardware and later only.)
0000 Factory default. Suggested for nearly all customers.
0001 Reserved. DO NOT USE!
0002 Memory-mapped mode with no IRQ. Not suggested for use.
21
Page 22

5 OS/2 Software Installation
An OS/2 client driver is provided with the MPAP-200. This client driver works with
OS/2's Card and Socket Services to allow operation of the MPAP-200 under OS/2.
5.1 System Requirements
OS/2 2.1 or later.
OS/2 PCMCIA Card and Socket Services support must be installed. See
"Installing OS/2 PCMCIA support" below if you do not already have this support
installed.
5.2 OS/2 Client Driver Installation
The MPAP-200 OS/2 client driver requires desired configurations from the user on the
command line. If no desired configurations are provided by the user, the client driver will NOT
ask Card Services to attempt to determine a hardware configuration for the card.
The client driver will attempt to configure an MPAP-200 with the first available
configuration listed from left to right on the command line. Each desired configuration must be
enclosed in parentheses and must be separated from other desired configurations by a space on
the command line. Within each desired configuration, the parameters are separated using
commas (no spaces).
1. Copy the MPAP200.SYS client driver file from the distribution disk to any convenient
directory on the hard disk.
2. Open the CONFIG.SYS file using any ASCII text editor.
3. Add the following line to the CONFIG.SYS file:
DEVICE=drive:\path\MPAP200.SYS (addr,irq) ... (addr,irq)
where drive:\path specifies the drive letter and directory to which you copied the client
driver file, and (addr,irq) ... (addr,irq) stand for a variable number of desired configurations.
The configuration parameters are described below.
22
Page 23

addr (required) The base I/O address of the MPAP-200. This number must be a
three-digit hexadecimal value ending in 0.
irq (required) The interrupt level (IRQ) of the MPAP-200. This decimal number
must be one of the following values: 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15, or 0 if no IRQ
is desired.
4. Save the CONFIG.SYS file, exit the text editor, shutdown the system, and reboot to
activate the changes.
5.2.1 Tying a configuration to a particular socket
A configuration can be made specific to a socket by appending "=Sx" after the closing
parenthesis, where "X" is the desired socket number.
5.2.2 Auto Fallback configuration
OS/2 Card Services is capable of automatically determining a configuration for a
PCMCIA device, but due to limitations in Quatech's "Syncdrive" driver software, the client
driver does not support this feature. This support is planned for a future release of both the client
driver and Syncdrive.
5.2.3 Hot Swapping
The client driver supports "hot swapping." After installation, it is not necessary for the
MPAP-200 to be inserted in the PCMCIA socket at boot time. When the card is inserted, it will
be configured according to the command line options. When the card is removed, the resources
it used will be made available for other devices.
23
Page 24

5.3 OS/2 Client Driver Configuration Examples
Example: Configure the MPAP-200 at base address 300 hex and IRQ 5. Configuration
will fail if any of these resources are already in use. Only one MPAP-200 can be used.
DEVICE=C:\MPAP-200\MPAP200.SYS (300,5)
Example: Configure the MPAP-200 at base address 300 hex and IRQ 5. Configuration
will fail if any of these resources are already in use. Only one MPAP-200 can be used.
DEVICE=C:\MPAP-200\MPAP200.SYS (300,5)
Example: Configure the MPAP-200 at base address 300 hex and IRQ 5. If any of these
resources are not available, the second choice is to configure the MPAP-200 at base address
110 hex and IRQ 15. Up to two MPAP-200s can be used.
DEVICE=C:\MPAP-200\MPAP200.SYS (300,5) (110,15)
Example: If an MPAP-200 is inserted into socket 1, configure it at base address 300 hex
and IRQ 5. If any of these resources are not available, the card will not be configured. If an
MPAP-200 is inserted into socket 2, configure it at base address 110 hex and IRQ 15. If any of
these resources are not available, the card will not be configured. Up to two MPAP-200s can be
used.
DEVICE=C:\MPAP-200\MPAP200.SYS (300,5)=S1 (110,15)=S2
5.4 Monitoring The Status Of PCMCIA Cards
OS/2 Warp provides a utility called "Plug and Play for PCMCIA" that can be used to
monitor the status of each PCMCIA socket. In OS/2 2.1, this utility is called "Configuration
Manager". Under OS/2 Warp 4.0, when an MPAP-200 is inserted, the Card Type for the
appropriate socket will display "I/O." Clicking on the "Card" icon brings up a dialog where the
name displayed for the card can be changed to "Quatech MPAP-200" or any other desired name.
Under releases of OS/2 older than Warp 4.0, the default Card Type displayed may not
read "I/O," but the card should be configured properly by the client driver.
If the card is successfully configured, the Card Status will display "Ready". If the card
cannot be configured, the Card Status will be "Not Ready". You can view the resources claimed
by a configured card by double-clicking on that card's line or status icon.
5.5 Installing OS/2 PCMCIA Support
24
Page 25

If PCMCIA support was not selected when OS/2 was installed, add it by using the
Selective Install facility in the System Setup folder. Full PCMCIA support is built into OS/2
Warp 3.0 and later. On OS/2 2.1 and 2.11, PCMCIA Card Services is built in, but you must add
Socket Services separately. The necessary files can be found on Compuserve in the
OS2SUPPORT forum library 23 in the file OS2PCM.ZIP, and may be available elsewhere.
Quatech does not distribute these files.
25
Page 26

6 Using the MPAP-200 with Syncdrive
Syncdrive is a synchronous communications software driver package designed to aid
users of Quatech synchronous communication hardware in the development of their application
software. Syncdrive is included free of charge with all Quatech MPA-series synchronous
communication products. The MPAP-200 is backward-compatible with software written for
Quatech ISA-bus synchronous adapters and it operates with Syncdrive.
Syncdrive, however, is not aware of the plug-and-play nature of PCMCIA cards. A
Syncdrive application will expect to see the MPAP-200 at a specific base address and a specific
IRQ. When using Syncdrive with PCMCIA cards, it is necessary to obtain the base address and
IRQ assigned to the card by the PCMCIA Card Services and provide those values in the channel
configuration array.
For DOS, Windows 3.1, or OS/2, the client driver or enabler supplied with the card must
be used to configure the MPAP-200 with the settings expected by the Syncdrive application
before the application tries to use the card.
Under Windows 95/98, the card is automatically configured. To find the settings, click
the right mouse button on the My Computer icon and select Properties. Select the Device
Manager tab and double-click the card's entry under the "Synchronous Communication" section.
Select the Resources tab to see the card's base address and IRQ. Use these settings with the
Syncdrive application. Windows 95/98 may
Settings" box is unchecked.
Syncdrive does not receive notifications of card insertion or card
removal events. Therefore it cannot support hot swapping without the user taking some kind of
action to force the Syncdrive application to initialize a newly-inserted card.
A future release of Syncdrive may permit automatic configuration by retrieving hardware
settings from the MPAP-200 client driver. For now, the user should consider the client driver to
be a replacement for jumper settings; it sets the card in a predetermined configuration before the
Syncdrive application is started.
allow changes to the settings if the "Use Automatic
26
Page 27

7 Addressing
The MPAP-200 occupies a continuous 16-byte block of I/O addresses. For example, if
the base address is set to 300 hex, then the MPAP-200 will occupy address locations 300 hex to
30F hex. If the computer in which the MPAP-200 is installed is running PCMCIA Card and
Socket Services, the base address is set by the client driver. If PCMCIA Card and Socket
Services are not being used, the base address is set by the MPAP-200 enabler program.
The first four bytes of address space on the MPAP-200 contain the internal registers of
the SCC. Other Quatech architecture-specific registers occupy eight more bytes. The remainder
of the address space is reserved for future use. The MPAP-200 address map is shown in Table 2.
Register DescriptionAddress
SCC Data Port, Channel ABase + 0
SCC Control Port, Channel ABase + 1
SCC Data Port, Channel BBase + 2
SCC Control Port, Channel BBase + 3
Communications RegisterBase + 4
Configuration RegisterBase + 5
ReservedBase + 6
ReservedBase + 7
Interrupt Status RegisterBase + 8
FIFO Status RegisterBase + 9
FIFO Control RegisterBase + A
Receive Pattern Character RegisterBase + B
Receive Pattern Count RegisterBase + C
Receive FIFO Timeout RegisterBase + D
ReservedBase + E
ReservedBase + F
Table 2 --- MPAP-200 Address Assignments
Information on the internal registers of the SCC can be found in Table 3 and Table 4 and
in the technical reference manuals available from Zilog. The other onboard registers are fully
described in subsequent chapters of this manual.
27
Page 28

8 Interrupts
The MPAP-200 will operate using the interrupt level (IRQ) assigned by the PCMCIA
system. Interrupts can come from the SCC or the external FIFOs.
When using interrupts with the MPAP-200, the application must have an interrupt service
routine (ISR). There are several things that an ISR must do to allow proper system operation:
1. If the external FIFOs are enabled, read the Interrupt Status Register (see page 38) to
determine whether the interrupt was caused by a FIFO event or by the SCC.
2. If the TX_FIFO bit is set, at least 512 bytes can be written to the Tx FIFO. If the
RX_FIFO bit is set, at least 512 bytes can be read from the Rx FIFO. I/O block move
instructions may be useful. Check the FIFO Status Register (see page 40) after servicing
the FIFO(s) to see if further FIFO service is required.
3. If the SCC bit is set, do an SCC software interrupt acknowledge by reading Read Register
2 in channel B of the SCC. The value read can also be used to vector to the appropriate
part of the ISR.
4. Service the SCC interrupt by reading the receiver buffer, writing to the transmit buffer,
issuing commands to the SCC, etc.
5. Write a Reset Highest Interrupt Under Service (IUS) command to the SCC by writing
0x38 to Write Register 0.
6. Check for other interrupts pending in the SCC by reading Read Register 3. Perform
further interrupt servicing if necessary.
7. For applications running under DOS, a nonspecific End of Interrupt must be submitted to
the interrupt controller. For Interrupts 2-7 this is done by writing a 0x20 to port 0x20.
For Interrupts 10-12, 14 and 15 this is done by writing a 0x20 to port 0x60, then a 0x20 to
port 0x20 (due to the interrupt controllers being cascaded). Device drivers running under
other operating systems may have varying requirements concerning the End of Interrupt
command.
For further information on these subjects or any others involving the SCC contact Zilog
for a complete technical manual.
28
Page 29

9 SCC General Information
The Serial Communications Controller (SCC) is a dual channel, multi-protocol data
communications peripheral. The MPAP-200 provides a single channel for communications,
however, portions of the second channel can be utilized to support some special circumstances.
The SCC can be configured to satisfy a wide variety of serial communications applications.
Some of its protocol capabilities include:
SDLC/HDLC (Bit Synchronous) Communications
Abort sequence generation and checking
Automatic zero insertion and deletion
Automatic flag insertion between messages
Address field recognition
I-field residue handling
CRC generation and detection
SDLC loop mode with EOP recognition/loop entry and exit
Byte-oriented Synchronous Communications
Internal/external character synchronization
1 or 2 sync characters in separate registers
Automatic Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) generation/detection
Asynchronous Communications
5, 6, 7, or 8 bits per character
1, 1-1/2, or 2 stop bits
Odd, even, or no parity
Times 1, 16, 32, or 64 x clock modes
Break generation and detection
Parity, overrun and framing error detection
NRZ, NRZI, or FM encoding/decoding
29
Page 30

9.1 Accessing the registers
The mode of communication desired is established and monitored through the bit values
of the internal read and write registers. The register set of the SCC includes 16 write registers
and 9 read registers. These registers only occupy four address locations, which start at the
MPAP-200's physical base address that is configured via the on board switches. This and all
other addresses are referenced from this base address in the form Base+Offset. An example of
this is Base+1 for the SCC Control Port, Channel A.
There are two register locations per SCC channel, a data port and a control port.
Accessing the internal SCC registers is a two step process that requires loading a register pointer
to perform the addressing to the correct data register. The first step is to write to the control port
the operation and address for the appropriate channel. The second step is to either read data from
or write data to the control port. The only exception to this rule is when accessing the transmit
and receive data buffers. These registers can be accessed with the two step process described or
with a single read or write to the data port. The following examples illustrate how to access the
internal registers of the SCC. Table 3 on page 20 describes the read registers and Table 4 on
page 21 describes the write registers for each channel.
The MPAP-200 has been designed to assure that all back to back access timing
requirements of the SCC are met without the need for any software timing control. The standard
of adding jmp $+2 between I/O port accesses is not required when accessing the MPAP-200.
Example 1: Enabling the transmitter on channel A.
mov dx, base ; load base address
add dx, ContA ; add control reg A offset (1)
mov al, 05H ; write the register number
out dx, al
mov al, 08H ; write the data to the register
out dx, al
Example 2: Monitoring the status of the transmit and receive buffers in RR0 of Channel A.
Register 0 is addressed by default if no register number is written to WR0 first.
mov dx, base ; load base address
add dx, ContA ; add control reg A offset (1)
in ax, dx ; read the status
30
Page 31

Example 3: Write data into the transmit buffer of channel A.
mov dx, base ; load base address
out dx, al ; write data in ax to buffer
Example 4: Read data from the receive buffer of channel A.
mov dx, base ; load base address
in al, dx ; write data in ax to buffer
Transmit, Receive buffer statuses and external status RR0
RR1
Special Receive Condition status, residue codes, error
conditions
RR2
Modified Channel B interrupt vector and Unmodified
Channel A interrupt vector
Interrupt Pending bits RR3
LSB of frame byte count register RR6
MSB of frame byte count and FIFO status registerRR7
Receive buffer RR8
Miscellaneous status parameters RR10
Lower byte of baud rate time constantRR12
Upper byte of baud rate time constantRR13
External/Status interrupt information RR15
Table 3 --- SCC read register description
The SCC can perform three basic forms of I/O operations: polling, interrupts, and block
transfer. Polling transfers data, without interrupts, by reading the status of RR0 and then reading
or writing data to the SCC buffers via CPU port accesses. Interrupts on the SCC can be sourced
from the receiver, the transmitter, or External/Status conditions. At the event of an interrupt,
Status can be determined, then data can be written to or read from the SCC via CPU port
accesses. Further information on this subject is found on page 17. For block transfer mode,
DMA transfers are used, so this type of operation is not supported
on the MPAP-200.
The SCC incorporates additional circuitry supporting serial communications. This
circuitry includes clocking options, baud rate generator (BRG), data encoding, and internal
loopback. The SCC may be programmed to select one of several sources to provide the transmit
and receive clocks. These clocks can be programmed in WR11 to come from the RTXC pin, the
TRXC pin, the output of the BRG, or the transmit output of the DPLL. The MPAP-200 uses the
TRXC pin for its clock-on-transmit and the RTXC pin for its clock-on-receive. Programming of
the clocks should be done before enabling the receiver, transmitter, BRG, or DPLL.
31
Page 32

WR0
Command Register, Register Pointer, CRC initialization, and
resets for various modes
Interrupt control, Wait/DMA request controlWR1
Interrupt vectorWR2
Receiver initialization and control WR3
WR4
Transmit/Receive miscellaneous parameters and codes, clock rate,
stop bits, parity
Transmitter initialization and control WR5
Sync character (1st byte) or SDLC address field WR6
Sync character (2nd byte) or SDLC FlagWR7
Special HDLC Enhancement Register WR7'
Transmit bufferWR8
Master interrupt control and reset WR9
WR10
Miscellaneous transmitter/receiver control bits, NRZI, NRZ, FM
coding, CRC reset
Clock mode and source controlWR11
Lower byte of baud rate time constant WR12
Lower byte of baud rate time constant WR13
WR14
Miscellaneous control bits: baud rate generator, DPLL control, auto
echo
External/Status interrupt control WR15
Table 4 --- SCC write register description
For complete information regarding the SCC registers please refer to Zilog's Z85230
technical manual.
32
Page 33
9.2 Baud Rate Generator Programming
The baud rate generator (hereafter referred to as the BRG) of the SCC consists of a 16-bit
down counter, two 8-bit time constant registers, and an output divide-by-two. The time constant
for the BRG is programmed into WR12 (least significant byte) and WR13 (most significant
byte). The equation relating the baud rate to the time constant is given below while Table 5
shows the time constants associated with a number of popular baud rates when using the standard
MPAP-200 9.8304 MHz clock.
Time_Const =
2 % baud_Rate % Clock_Mode
Where: Clock_Frequency = 9.8304 x 10
Clock_Mode = 1, 16, 32, or 64
Baud_Rate = desired baud rate
Time ConstantBaud Rate
(for Clock_Frequency = 9.8304 MHz )
Clock_Frequency
- 2
6
007E (hex)12638400
00FE (hex) 25419200
01FE (hex) 5109600
03FE (hex) 10224800
07FE (hex) 20462400
0FFE (hex) 40941200
1FFE (hex) 8190600
3FFE (hex) 16382300
Table 5 --- time constants for common baud rates
9.3 SCC Data Encoding Methods
The SCC provides four different data encoding methods, selected by bits 6 and 5 in
WR10. These four include NRZ, NRZI, FM1 and FM0. The SCC also features a digital
phase-locked loop (DPLL) that can be programmed to operate in NRZI or FM modes. Also, the
SCC contains two features for diagnostic purposes, controlled by bits in WR14. They are local
loopback and auto echo.
For further information on these subjects or any others involving the SCC contact Zilog
for a complete technical manual.
33
Page 34

9.4 Support for SCC Channel B
The MPAP-200 is a single-channel device. Portions of SCC channel B are used to
augment channel A. Channel B cannot be used for transmit, but may be used for receive, subject
to certain limitations.
9.4.1 Receive data and clock signals
The receive data signals RXDA and RXDB are tied together. The receive clock input
signals RTXCA and RTXCB are also tied together. This can be useful in unusual applications.
It would be possible to run the receiver and transmitter at different baud rates, using channel B's
baud rate generator and receiver for the received data. Of course, the channel A transmitter and
receiver can be run at different speeds simply by having external data clocks supplied to TRXCA
and RTXCA from the cable.
The W/REQB signal is used to generate DMA requests between the SCC and the external
FIFOs if channel B is used for receive.
9.4.2 Extra clock support for channel A
The TRXCB clock output can be routed back to RTXCA as another way to use the
channel B baud rate generator to derive an independent clock for the channel A receiver. This is
controlled by the RCKEN bit in the Communications Register (see page 34).
9.4.3 Extra handshaking for channel A
The SCC does not provide a DSR input for either channel. The MPAP-200 routes the
DSR signal from the connector to the DCDB input of the SCC. Software can therefore use
DCDB as a surrogate for DSR on channel A.
9.4.4 Other signals are not used
All channel B signals not listed above are not available at the connector. The CTSB and
SYNCB inputs are tied to their inactive states. The TXDB, DTR/REQB, and RTSB outputs are
left open.
34
Page 35

9.5 SCC Incompatibility Warnings
Due to the SCC implementation used by the MPAP-200, there are two minor
incompatibilities that the software programmer must avoid.
9.5.1 Register Pointer Bits
In a Zilog 85230, the control port register pointer bits can be set in either channel. With
the implementation on the MPAP-200, however, both parts of an SCC control port access must
use the same I/O address.
IMPORTANT
The programmer must be certain not to mix channel usage during
the two-part access of SCC control ports. It would be highly
irregular for code to be written in such fashion, so this restriction is
not expected to be burdensome.
The following sequences will work:
Write Control Port A (set pointer bits for desired register)
Read or Write Control Port A (read or write desired channel A register)
Write Control Port B (set pointer bits for desired register)
Read or Write Control Port B (read or write desired channel B register)
The following sequences will NOT work:
Write Control Port A (set pointer bits for desired register)
Read or Write Control Port B (read or write desired channel B register)
Write Control Port B (set pointer bits for desired register)
Read or Write Control Port A (read or write desired channel A register)
9.5.2 Software Interrupt Acknowledge
The 85230's software interrupt acknowledge mechanism is not supported. Bit 5 of Write
Register 9 (Software INTACK Enable) is forced to 0. Software must employ the "Interrupt
Without Acknowledge" interrupt method using Read Registers 2 and 3 to process interrupts.
35
Page 36

10 FIFO Operation
The MPAP-200 is equipped with 1024-byte external FIFOs in the transmit and receive
data paths. These FIFOs are implemented as extensions of the SCC's small internal FIFOs. They
have been designed to be as transparent as possible to the software operating the MPAP-200. By
using these FIFOs, it is possible to achieve high data rates despite the MPAP-200 not supporting
DMA.
The
FIFOs are disabled by default after card insertion, power-up, or a socket reset.
10.1 Enabling and disabling the FIFOs
The FIFOs must be enabled or disabled as a pair. It is not possible to operate only the
transmit FIFO or only the receive FIFO. The FIFOs are enabled by setting bit 2 of the
Configuration Register to a logic 1. The FIFOs are disabled by clearing the same bit.
10.2 Accessing the FIFOs
When the FIFOs are enabled, they are accessed through either the channel A or channel B
SCC Data Port address. Writing to Base+0 or Base+2 will cause a byte to be written into the
transmit FIFO. Reading from Base+0 or Base+2 will cause a byte to be read from the receive
FIFO.
The FIFOs cannot be accessed if they are disabled. If the FIFOs are disabled, reads or
writes of the SCC Data Ports access the receive or transmit register of the appropriate SCC
channel. Any control port writes of SCC write register 8 (transmit buffer) or control port reads
of SCC read register 8 (receive buffer) directly access the SCC, whether the FIFOs are enabled or
not.
10.2.1 Transmit FIFO
The transmit FIFO always services the transmitter of channel A of the SCC. If the FIFOs
are enabled, an I/O write to either SCC Data Port (channel A or channel B) will write a byte to
the transmit FIFO. If the FIFOs are not enabled, an I/O write to the SCC Data Port will instead
write directly to the internal transmit buffer of the specified channel of the SCC.
36
Page 37

10.2.2 Receive FIFO
The receive FIFO can service the receiver of either channel A or channel B of the SCC.
If RXSRC (bit 1) of the Configuration Register (see page 36) is logic 1, the receive FIFO will
service SCC channel B. If RXSRC is logic 0, the receive FIFO will service SCC channel A.
If the FIFOs are enabled, an I/O read from either SCC Data Port (channel A or channel B)
will read a byte from the receive FIFO. If the FIFOs are not enabled, an I/O read from the SCC
Data Port will instead read directly from the internal receive buffer of the specified channel of the
SCC.
10.3 SCC configuration for FIFO operation
The interface between the SCC and the external FIFOs uses the SCC's DMA request
functions. The SCC must therefore be configured for DMA operation in order to use the external
FIFOs. In order to properly configure the SCC, certain bits in various SCC registers need to be
set in a specific manner, as shown on the following pages.
Because the data transfer between the FIFOs and the SCC is controlled entirely by
hardware, per-character transmit and receive interrupts should be disabled. Interrupts on transmit
underruns and/or special receive conditions should usually be enabled so that end-of-frame
conditions can be detected.
IMPORTANT
The DMA operation described in this section is
between the SCC and the external FIFOs, and is
handled entirely by the MPAP-200 hardware.
DMA is not supported between the MPAP-200 and
the host computer due to the lack of DMA facilities
on the PCMCIA bus.
The MPAP-200 is a single-channel device. Accordingly, most applications will use SCC
channel A for both transmit and receive operations. It is possible, however, to use a limited
portion of SCC channel B for receive operations (see page 23). The channel used for receive will
determine how the SCC must be configured.
Do not enable the FIFOs until the SCC has been properly configured for DMA
operation!
37
Page 38

10.3.1 Using channel A for both transmit and receive
This is the mode in which most applications will run. Set RXSRC (bit 1) in the
Configuration Register to logic 0. This will configure the MPAP-200 to use W/REQA for
receive DMA and DTR/REQA for transmit DMA. In addition to any other desired SCC
configuration, ensure that the following bits are set according to Table 6:
FunctionValueBit(s)Register
Enable DMA request on W/REQA. This bit
should be set after the other bits in WR1 are set as
17
desired.
WR1A
4-3
11 or
00
Set W/REQA for DMA Request mode.16
Use W/REQA for receive. 15
Enable receive interrupts on special conditions
only (recommended), or disable them completely.
Disable transmit interrupts.01
Enable DMA request-on-transmit on
12WR14A
DTR/REQA.
Enable WR7A'.10WR15A
Assert transmit DMA request when entry location
05
WR7A'
of internal FIFO is empty.
Set DTR/REQA for W/REQA timing.14
Table 6 --- Configuring the SCC for FIFO use with channel A only
38
Page 39

10.3.2 Using channel B for receive
The MPAP-200 supplies only limited support for SCC channel B. This mode, therefore,
is not recommended for most applications. Set RXSRC (bit 1) in the Configuration Register to
logic 1. This will configure the MPAP-200 to use W/REQA for transmit DMA and W/REQB for
receive DMA. In addition to any other desired SCC configuration, ensure that the following bits
are set according to Table 7:
FunctionValueBit(s)Register
Enable DMA request on W/REQA. This bit
should be set after the other bits in WR1 are set as
17
WR1A
desired.
Set W/REQA for DMA Request mode.16
Use W/REQA for transmit. 05
Disable transmit interrupts.01
Disable DMA request-on-transmit on
02WR14A
DTR/REQA.
Enable WR7A'.10WR15A
WR1B
Assert transmit DMA request when entry location
05WR7A'
of internal FIFO is empty.
Enable DMA request on W/REQB. This bit
should be set after the other bits in WR1 are set as
17
desired.
Set W/REQB for DMA Request mode.16
Use W/REQB for receive.15
4-3
11 or
00
Enable receive interrupts on special conditions
only (recommended), or disable them completely.
Table 7 --- Configuring the SCC for Rx DMA on channel B
39
Page 40

10.4 FIFO status and control
Several registers are used to control the FIFOs and monitor their status. These registers
are detailed in other chapters of this manual.
10.4.1 Interrupt status
Three interrupt statuses, listed in Table 8, can be generated by four events related to FIFO
activity. In each case, a latched bit in the Interrupt Status Register is set to a logic 1 (see page
38). These bits are write-clear, meaning that software must write a 1 to a bit in order to clear it.
IMPORTANT
FIFO-related interrupts will occur only when the
MPAP-200 interrupt source is set to INTSCC. See Table
10 on page 36 for details.
Event
Transmit FIFO drained
past the half-full mark
Receive FIFO filled past
the half-full mark
Receive data timeout with
non-empty FIFO
Special receive pattern
detected
Table 8 --- FIFO-related interrupt statuses
Interrupt Status
Register Bit
TX_FIFO
(bit 1)
RX_FIFO
(bit 2)
RX_PAT
(bit 3)
IMPORTANT
Comment
Software can write at least
512 bytes to the transmit
FIFO.
Software can read at least
512 bytes from the receive
FIFO.
Software can read bytes
from the receive FIFO until
the FIFO is empty.
Software can read data
from the receive FIFO as
desired.
Software can differentiate between the two types of
RX_FIFO interrupts by examining the RXH bit in the
FIFO Status Register. If RXH is clear (logic 0), the
interrupt occurred because of a timeout.
40
Page 41

10.4.2 Resetting the FIFOs
The FIFOs are automatically disabled and reset at powerup or when the MPAP-200 is
inserted into a PCMCIA socket. The transmit and receive FIFOs can also be independently reset
by setting and clearing the appropriate bits in the FIFO Control Register. Resetting a FIFO sets
the appropriate FIFO empty status bit and resets the FIFO's internal read and write pointers. The
SCC's internal FIFOs are not affected when the external FIFOs are reset.
The external FIFOs cannot be reset while they are enabled! FIFO reset commands
will be ignored if the external FIFOs are enabled.
10.4.3 Reading current FIFO status
The FIFO Status Register is a read-only register which always indicates the current status
of both the transmit and receive external FIFOs. Each FIFO can be checked for empty, full, and
half-full (or more) status at any time. For details, see Table 12 on page 39.
10.4.4 Controlling the FIFOs
The FIFO Control Register is a read-write register which can be used to reset either or
both the receive and transmit external FIFOs. Receive pattern detection and receive FIFO
timeout modes are also controlled with this register. For details, see Table 13 on page 40.
10.5 Accessing the SCC while FIFOs are enabled
The SCC channel A and channel B control port registers are always accessible regardless
of whether the external FIFOs are enabled or disabled. While the FIFOs are enabled, SCC data
port accesses are redirected to the FIFOs. Access to the SCC's transmit or receive registers while
the FIFOs are enabled is possible indirectly by using the control port and register 8. Any writes
of SCC Write Register 8 (transmit buffer) or reads of SCC Read Register 8 (receive buffer) will
bypass the external FIFOs.
10.6 Receive pattern detection
The external FIFOs are most useful in bit-synchronous operational modes because the
SCC can generate a Special Condition interrupt when the closing flag of a bit-synchronous frame
is received. This allows the SCC to run with per-character receive interrupts disabled while
DMA transfers occur between the SCC and external FIFOs.
Byte-synchronous modes such as Bisync, however, do not benefit from such a hardware
assist for detecting the end-of-frame condition. On the contrary, with byte-oriented protocols it is
usually necessary to check each byte received against a table of special function codes (e.g.
SYNC, PAD, SDI, STX, EDI, ETX, etc.) to determine where data and frames begin and end.
Unless the frames are of a fixed length, it is therefore difficult to use DMA with
41
Page 42
byte-synchronous modes. This would seem to preclude the use of the MPAP-200's external
FIFOs with byte-oriented protocols.
To make the external FIFOs more useful in byte-synchronous modes, the MPAP-200 can
watch for a given character to be transferred consecutively a specific number of times from the
SCC into the receive FIFO. When this occurs, the RX_PAT bit in the Interrupt Status Register
(see page 38) is set. For instance, the MPAP-200 can watch for the end-of-text character to be
received, or for three consecutive pad characters to be received.
For byte-synchronous operation with simple unique markers in the data stream, this
feature may be quite useful. Even if it is not, however, the MPAP-200 can certainly be operated
with per-character interrupts enabled and the external FIFOs disabled. The tradeoff will be a
heavier interrupt burden and possibly somewhat lower throughput.
NOTE
While most useful in byte-synchronous modes, the
receive pattern detection feature can be used in any
operational mode.
42
Page 43

10.7 Receive FIFO timeout
With asynchronous operational modes, the same problem exists. Namely, how is one to
determine when a reception is complete? While the receive pattern detection may be useful here,
the MPAP-200 also offers a timeout feature on the external receive FIFO.
If the external FIFO is not empty and a time interval equal to a specified number of
character-times has elapsed without any further data being received, a receive FIFO interrupt is
generated and RX_FIFO bit in the Interrupt Status Register (see page 38) is set. A character-time
is approximated by counting eight ticks of the bit clock.
To use this feature, the receive clock must be output on TRXCA. It can come from either
an external source or from the channel A baud rate generator. While the RTXCA signal is
typically used for a receive clock, it is not capable of being an output, so the TRXCA signal must
be used instead. Depending on the application, this may force the transmit and receive clocks to
be the same. For most asynchronous applications, this should not pose a problem.
43
Page 44

11 Communications Register
The Communications Register is used to set options pertaining to the clocks. The source
and type of clock to be transmitted or received can be specified. External synchronization can
also be controlled with this register. The address of the Communications Register is Base+4.
Table 9 details its bit definitions.
Bit 0Bit 1Bit 2Bit 3Bit 4Bit 5Bit 6Bit 7
TXDENRXDENTCKENRCKENSW_SYNC0EXTSYNC0
Table 9 --- Communications Register - Read/Write
Bit 7: Reserved, always 0.
Bit 6: EXTSYNC --- External Sync Enable:
If this bit is set (logic 1), software-controlled sync is disabled and the SCC's
SYNCA input is driven by the signal coming on pin 21 of the DB-25 connector.
If this bit is clear (logic 0), the SW_SYNC bit can be used to drive SYNCA.
Bit 5: Reserved, always 0.
Bit 4: SW_SYNC --- Software Sync On: This bit is
used to drive the active-low SYNC input of the channel A receiver. The SYNC
signal is asserted when this bit is set (logic 1), and is deasserted when this bit is
clear (logic 0). This is useful in situations where it is necessary to receive
unformatted serial data, as it allows the SCC receiver to be manually placed into
sync under program control. This bit is ignored if bit 6 is set (logic 1).
44
Page 45

Bit 3: RCKEN --- Receive Clock Source: When
set (logic 1), this bit allows the receive clock (RCLK) signal to be generated by
the TRxC pin on channel B of the SCC. When cleared (logic 0), RCLK is
received on pins 17 and 9 of the DB-25 connector.
Bit 2: TCKEN --- Transmit Clock Source:
When set (logic 1), this bit allows the transmit clock (TCLK) to be generated by
the TRxC pin on channel A of the SCC and to be transmitted on pins 24 and 11 of
the DB-25 connector. When cleared (logic 0), the DTE receives TCLK on pins 15
and 12 of the DB-25 connector.
Bit 1: RXDEN --- Enable Receivers:
When set (logic 1), this bit enables the RS-422/485 receivers for data and
handshake signals. When cleared (logic 0), the receivers are disabled.
Bit 0: TXDEN --- Enable Transmitters: When
set (logic 1), this bit enables the RS-422/485 drivers for data and handshake
signals. When cleared (logic 0), the drivers are disabled.
45
Page 46

12 Configuration Register
The Configuration Register is used to set the interrupt source and enable the interface
between the SCC and the external FIFOs. The address of this register is Base+5. Table 10
details the bit definitions of the register.
Bit 0Bit 1Bit 2Bit 3Bit 4Bit 5Bit 6Bit 7
0RXSRCFIFOEN0INTS0INTS101
Table 10 --- Configuration Register - Read/Write
Bit 7: External Data FIFOs Present --- Reserved, always 1. This
bit can be used as an indicator that external data FIFOs are present. Other
MPA-series products that are not equipped with external data FIFOs will return 0
in this bit location.
Bit 6: Reserved, always 0.
Bits 5-4: INTS1, INTS0 --- Interrupt Source and Enable Bits: These
two bits determine the source of interrupts. The only valid source is interrupt
from the SCC (INTSCC). Below is the mapping for these bits. Note that
FIFO-related interrupts will occur only when INTSCC is chosen.
Interrupt SourceINTS0INTS1
Interrupts disabled00
reserved00
INTSCC01
reserved11
Bit 3: Reserved, always 0.
Bit 2: FIFOEN --- External data FIFO enable: If this
bit is set (logic 1), the external data FIFOs are enabled. If this bit is clear (logic
0), the external data FIFOs are disabled. (See page 25 for full details on FIFO
use.)
46
Page 47
Bit 1: RXSRC --- Receive FIFO DMA Source: This
bit determines which SCC pins are used to control transmit and receive DMA
transactions between the SCC and the external FIFOs (when enabled). The
transmit data FIFO is always used with SCC channel A. The receive data FIFO
may be used with SCC channel A by setting RXSRC to logic 0, or with SCC
channel B by setting RXSRC to logic 1. (See page 23 for information on using
channel B.)
RXSRC = 1RXSRC = 0
W/REQBW/REQAReceive DMA
Transmit
DMA
W/REQADTR/REQA
Bit 0: Reserved, always 0.
47
Page 48

13 Interrupt Status Register
The Interrupt Status Register is used to determine the cause of an interrupt generated by
the MPAP-200. The address of this register is Base+8. Table 11 details the bit definitions of the
register. The interrupt source in the Configuration Register (see page 36) must be set to
INTSCC for any of the statuses indicated by this register to occur. This register can be
ignored if the external FIFOs are not being used.
Bit 0Bit 1Bit 2Bit 3Bit 4Bit 5Bit 6Bit 7
SCCTX_FIFORX_FIFORX_PAT0000
Table 11 --- Interrupt Status Register - Read Only/Write Clear
Bits 7-4: Reserved, always 0.
Bit 3: RX_PAT --- Receive Pattern Interrupt: The
receive pattern interrupt occurs when the character set in the Receive Pattern
Character Register is detected 'n' consecutive times in the received data stream,
where 'n' is the value set in the Receive Pattern Count Register. This bit is set
(logic 1) to indicate the interrupt. It remains set until cleared by writing a '1' to
this bit.
Bit 2: RX_FIFO --- Receive FIFO Interrupt:
The receive FIFO interrupt occurs when the number of bytes held in the external
receive FIFO rises above the half-full mark, or when a receive FIFO timeout
occurs. This bit is set (logic 1) to indicate the interrupt. It remains set until
cleared by writing a '1' to this bit.
Bit 1: TX_FIFO --- Transmit FIFO Interrupt: The
transmit FIFO interrupt occurs when the number of bytes held in the external
transmit FIFO falls below the half-full mark. This bit is set (logic 1) to indicate
the interrupt. It remains set until cleared by writing a '1' to this bit.
Bit 0: SCC --- SCC Interrupt:
If this bit is set (logic 1), the SCC has generated an interrupt. Software should
clear the interrupt condition by performing appropriate service on the SCC. This
bit is not latched.
48
Page 49

14 FIFO Status Register
The FIFO Status Register is used to return current status information about the external
FIFOs. The address of this read-only register is Base+9. Table 12 details the bit definitions of
the register. This register can be ignored if the external FIFOs are not being used.
Bit 0Bit 1Bit 2Bit 3Bit 4Bit 5Bit 6Bit 7
TXETXHTXF0RXERXHRXF0
Table 12 --- FIFO Status Register - Read Only
Bit 7: Reserved, always 0.
Bit 6: RXF --- Receive FIFO Full: This
bit is set (logic 1) when the external receive FIFO is completely full. The FIFO
will accept no more data from the SCC.
Bit 5: RXH --- Receive FIFO Half Full: This
bit is set (logic 1) while the external receive FIFO is at least half-full.
Bit 4: RXE --- Receive FIFO Empty:
This bit is set (logic 1) when the external receive FIFO is completely empty.
Bit 3: Reserved, always 0.
Bit 2: TXF --- Transmit FIFO Full:
This bit is set (logic 1) when the external transmit FIFO is completely full.
Further writes to the external transmit FIFO will be ignored.
Bit 1: TXH --- Transmit FIFO Half Full: This
bit is set (logic 1) while the external transmit FIFO is at least half-full.
Bit 0: TXE --- Transmit FIFO Empty:
This bit is set (logic 1) when the external transmit FIFO is completely empty.
49
Page 50

15 FIFO Control Register
The FIFO Control Register is used to control the external data FIFOs. The address of this
register is Base+A (hex). Table 13 details the bit definitions of the register. This register can be
ignored if the external FIFOs are not being used.
Bit 0Bit 1Bit 2Bit 3Bit 4Bit 5Bit 6Bit 7
TX_RESET000RX_RESETEN_TOEN_PAT0
Table 13 --- FIFO Control Register - Read/Write
Bit 7: Reserved, always 0.
Bit 6: EN_PAT --- Enable Receive Pattern Detection: Set this
bit (logic 1), to enable the receive pattern detection circuitry. Clear this bit (logic
0), to disable pattern detection. See page 32 for details on the receive pattern
detection feature.
Bit 5: EN_TO --- Enable Receive Timeout:
Set this bit (logic 1), to enable the external receive FIFO timeout. Clear this bit
(logic 0), to disable the receive FIFO timeout. See page 33 for details on the
receive FIFO timeout feature.
Bit 4: RX_RESET --- Reset Receive FIFO:
Set (logic 1), then clear (logic 0) this bit to reset the external receive FIFO. The
FIFO can be reset only when it is disabled.
Bits 3-1: Reserved, always 0.
Bit 0: TX_RESET --- Reset Transmit FIFO:
Set (logic 1), then clear (logic 0) this bit to reset the external transmit FIFO. The
FIFO can be reset only when it is disabled.
50
Page 51

16 Receive Pattern Character Register
The Receive Pattern Character Register is used to set the character value to be used in
receive pattern detection. The address of this register is Base+B (hex). This register can be
ignored if the external FIFOs are not being used.
Bit 0Bit 1Bit 2Bit 3Bit 4Bit 5Bit 6Bit 7
character value (0-255)
Table 14 --- Receive Pattern Character Register - Read/Write
Bits 7-0: Receive Pattern Character: This is
the numeric value of the character to be detected. See page 32 for details on the
receive character pattern detection feature.
51
Page 52

17 Receive Pattern Count Register
The Receive Pattern Count Register is used to set the counter value to be used in receive
pattern detection. The address of this register is Base+C (hex). This register can be ignored if
the external FIFOs are not being used.
Bit 0Bit 1Bit 2Bit 3Bit 4Bit 5Bit 6Bit 7
counter value (0-255)
Table 15 --- Receive Pattern Count Register - Read/Write
Bits 7-0: Receive Pattern Count:
This value is the number of times that the character stored in the Receive Pattern
Character Register (see page 41) must be consecutively detected for the receive
character pattern detect interrupt to be generated. See page 32 for details on the
receive character pattern detection feature.
52
Page 53

18 Receive FIFO Timeout Register
The Receive FIFO Timeout Register is used to control the operation of the external
receive FIFO timeout feature. The address of this register is Base+D (hex). This register can be
ignored if the external FIFOs are not being used. See page 33 for details on the receive FIFO
timeout feature.
Bit 0Bit 1Bit 2Bit 3Bit 4Bit 5Bit 6Bit 7
timeout interval (0-63)0X16_MODE
Table 16 --- Receive FIFO Timeout Register - Read/Write
Bit 7: X16_MODE --- Clock Mode:
If this bit is set (logic 1), the data clock is divided by 16 (prescaled) before it is fed
to the timeout circuitry. This is useful for asynchronous operation. If this bit is
clear (logic 0), the data clock is not prescaled.
Bit 6: Reserved, always 0.
Bits 5-0: Timeout Interval:
This is the number of character-times that must elapse before a non-empty
external receive FIFO will trigger a timeout condition. This interval assumes
eight bits per character, so it will be an approximation for modes running at
settings other than eight bits per character.
53
Page 54

19 External Connections
The MPAP-200 is configured as a Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) device using a
DB-25 male connector. There is no DCE version available.
The control signals the DTE can generate are Request To Send (RTS) and Data Terminal
Ready (DTR). It can receive the signals Carrier Detect (DCD), Clear to Send (CTS), and Data
Set Ready (DSR). All the control signals are controlled through channel A of the SCC, with the
exception of the DSR signal, which is received on the DCDB pin on channel B. (The SCC has
no actual DSR inputs.)
The transmit clock (TCLK, SCC TRxCA pin) can be transmitted on TTCLK or received
on RTCLK, depending on TCKEN. The receive clock (RCLK, SCC RTxC pins) can be received
on RRCLK or can be generated using the TRxCB pin , depending on RCKEN. The receive clock
cannot be transmitted. TCLK and RCLK can also be internally sourced from the channel A baud
rate generator.
Figure 1 shows the DTE clock configuration. On the left are the SCC clock pins and the
clock enable bits from the Communications Register. On the right are the signals at the DB-25
connector.
RTxCA
(RCLK)
RTxCB
TRxCB
RCKEN
TCKEN
TRxCA
(TCLK)
RRCLK
RTCLK
TTCLK
Figure 1 --- MPAP-200 Clock Configuration
54
Page 55

Figure 2 --- MPAP-200 Output Connector Pinout
19.1 SYNCA (pin 21)
-CTS
-RTCLK
-TTCLK
-CD
-RRCLK
+CD
DGND
+DSR
+CTS
+RTS
+RXD
+TXD
CGND
13
12
11
10
CGND
25
24
+TTCLK
-DTR
23
22
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
-DSR
SYNCA
+DTR
-RTS
CGND
+RRCLK
-RXD
+RTCLK
-TXD
If EXTSYNC (bit 6) in the Communications Register is set to a logic 1, the SYNCA
signal from the connector is used to drive the active-low SYNC input of SCC channel A. This is
a single-ended input, inverted by the receiver, so a +5 volt signal on pin 21 will assert SYNCA
(a -5 volt signal will deassert SYNCA). The SCC must be specifically programmed to recognize
external synchronization.
19.2 MPA-200 and EIA-530 Compatibility
The MPAP-200 is designed to be functionally-compatible with Quatech's MPA-200 DTE
adapter for the ISA bus. The MPAP-200 connector pinout varies slightly from that of the
MPA-200, with the local and remote loopback output signals (LL and RL) and the test mode
input signal (TM) replaced with a SYNCA input and two ground conductors.
If the MPAP-200 is to be connected to an EIA-530 device, it may be necessary to swap
the +/- conductors on the TXD and RXD signals.
55
Page 56

Table 17 shows the pin configuration of the MPAP-200 DTE connector. The definitions
of the interchange circuits can be found starting on page 47.
Pin
To
DTE
From
DTE
SCC Pin or Register BitCircuitSignal
CGND1
TxDA pinBA+TXDX2
RxDA pinBB+RXDX3
RTSA pinCA+RTSX4
CTSA pinCB+CTSX5
DCDB pinCC+DSRX6
ABDGND7
DCDA pinCF+CDX8
RTxC pinsDD-RRCLKX9
DCDA pinCF-CDX10
TRxCA pinDA-TTCLKX11
TRxCA pinDB-RTCLKX12
CTSA pinCB-CTSX13
TxDA pinBA-TXDX14
TRxCA pinDB+RTCLKX15
RxDA pinBB-RXDX16
RTxC pinsDD+RRCLKX17
CGND18
RTSA pinCA-RTSX19
DTR/REQA pinCD+DTRX20
SYNCA pinSYNCAX21
DCDB pinCC-DSRX22
DTR/REQA pinCD-DTRX23
TRxCA pinDA+TTCLKX24
CGND25
19.3 Null-modem cables
The MPAP-200 does not use a standard asynchronous PC serial port connector pinout.
Typical off-the-shelf null-modem cables cannot be used with this card!
Table 17 --- Connector Pin Definitions
56
Page 57

20 DTE Interface Signals
CIRCUIT AB - SIGNAL GROUND
CONNECTOR NOTATION: DGND
DIRECTION: Not applicable
This conductor directly connects the DTE circuit ground to the DCE circuit ground.
CIRCUIT BA - TRANSMITTED DATA
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +TXD, -TXD
DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal transfers the data generated by the DTE through the communication channel
to one or more remote DCE data stations.
CIRCUIT BB - RECEIVED DATA
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +RXD, -RXD
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal transfers the data generated by the DCE, in response to data channel line
signals received from a remote DTE data station, to the DTE.
CIRCUIT CA - REQUEST TO SEND
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +RTS, -RTS
DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal controls the data channel transmit function of the local DCE and, on a
half-duplex channel, the direction of the data transmission of the local DCE.
CIRCUIT CB - CLEAR TO SEND
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +CTS, -CTS
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal indicates to the DTE whether the DCE is conditioned to transmit data on the
communication channel.
CIRCUIT CC - DCE Ready (Data Set READY)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +DSR, -DSR
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal indicates the status of the local DCE by reporting to the DTE device that a
communication channel has been established.
CIRCUIT CD - DTE READY (Data Terminal Ready)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +DTR, -DTR
57
Page 58

DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal controls the switching of the DCE to the communication channel. The DTE
will generate this signal to prepare the DCE to be connected to or removed from the
communication channel.
CIRCUIT CF - Received Line Signal Detect (CARRIER DETECT)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +CD, -CD
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal indicates to the DTE whether the DCE is conditioned to receive data from the
communication channel, but does not indicate the relative quality of the data signals
being received.
CIRCUIT DA - TRANSMIT Signal ELEMENT TIMING (DTE Source)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +TTCLK, -TTCLK
DIRECTION: To DCE
This signal, generated by the DTE, provides the DCE with element timing information
pertaining to the data transmitted by the DTE. The DCE can use this information for its
received data.
CIRCUIT DB - TRANSMIT Signal ELEMENT TIMING (DCE Source)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +RTCLK, -RTCLK
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal, generated by the DCE, provides the DTE with element timing information
pertaining to the data transmitted to the DCE. The DCE can use this information for its
received data.
CIRCUIT DD - RECEIVER Signal ELEMENT TIMING (DCE Source)
CONNECTOR NOTATION: +RRCLK, -RRCLK
DIRECTION: From DCE
This signal, generated by the DCE, provides the DTE with element timing information
pertaining to the data transmitted by the DCE. The DTE can use this information for its
received data.
58
Page 59

21 Specifications
Bus interface: PCMCIA PC Card Standard 2.1
Physical Dimensions: Type II (5 mm) PCMCIA card
Controller: 85230-compatible 16-MHz Serial
Communications Controller (SCC)
DTE Interface: Male D-25 connector
Transmit drivers: RS-422/485 compatible,
5 Mbps typical maximum data rate
Receive buffers: RS-422/485 compatible,
5 Mbps typical maximum data rate
I/O Address range: Sixteen-byte contiguous range required,
determined by PCMCIA system
Interrupt levels: One IRQ required, determined by
PCMCIA system
DMA channels: Not supported by PCMCIA 2.1 bus
Power requirements: 100 mA at +5 volts, typical
59
Page 60

22 Software Troubleshooting
This appendix discusses how to resolve some common problems sometimes encountered
when using the MPAP-200 configuration software.
22.1 DOS Client Driver
22.1.1 Generic "SuperClient" Drivers
Many Card and Socket Services packages include a generic client driver (or SuperClient)
which configures standard I/O devices such as serial ports or modems. If one of these generic
client drivers is installed, it may try to configure the MPAP-200 causing the MPAP-200 client
driver to fail installation. In these cases, the user should do one of the following:
1. Place the MPAP-200 client driver above the generic client driver in the CONFIG.SYS.
2. Configure the generic client driver to disable configuration of nonstandard I/O cards.
Consult the Card and Socket Services documentation for availability and details of this
feature.
22.1.2 Lack of Available Resources
One function of the Card and Socket Services software is to track which system resources
(memory addresses, I/O addresses, IRQs, etc.) are available for assignment to inserted PCMCIA
cards. Occasionally, Card Services may incorrectly determine that a particular resource is free
when it is actually in use or vice-versa. Most DOS-based Card and Socket Services generate a
resource table in a file (typically in the form of an .INI file) which the user can modify to adjust
the available system resources.
22.1.3 Multiple Configuration Attempts
Some Card and Socket Services have a setting which aborts the configuration process
after a single configuration failure (such as a request for an unavailable resource). The user
should change this setting to allow for multiple configuration attempts.
22.1.4 Older Versions of Card and Socket Services
Often, older versions of Card and Socket Services (with copyright date of 1993 and
before) don't work correctly with I/O cards such as the MPAP-200. An up-to-date version of
Card and Socket Services should be obtained by contacting Quatech, Inc.
22.2 DOS Enabler
60
Page 61

22.2.1 With Card and Socket Services
The enabler should NOT be used if any Card and Socket Services are present on the
system. If Card and Socket Services is installed, the enabler may interfere with its operation and
with the device(s) it controls. The client driver should be used to configure the MPAP-200 if
Card and Socket Services are installed.
22.2.2 Socket Numbers
The enabler requires the socket number to be specified on the command line. Some
vendors number their sockets beginning with 1 while other vendors number their sockets
beginning with 0. The enabler considers the first socket in the system to be socket 0.
22.2.3 Memory range exclusion
The enabler requires a region of high DOS memory. This region is 1000h bytes (4 KB)
long and by default begins at address D0000H (the address may be changed using the "W"
parameter). If a memory manager such as EMM386, QEMM, or 386Max is installed on the
system, this region of DOS memory must be excluded from the memory manager's control.
Consult the documentation provided with the memory manager software for instructions on how
to exclude this memory region.
Some systems use the high memory area for BIOS shadowing to improve overall system
performance. In order for the enabler to operate, BIOS shadowing must be disabled in the
address range specified for the configuration window. BIOS shadowing can usually be disabled
through the system's CMOS setup utility.
22.3 OS/2 Client Driver
22.3.1 Resources Not Available
It is the user's responsibility to ensure the I/O address and IRQ resources are available.
For OS/2 Warp users, the RMVIEW utility may be useful in finding resource conflicts. Type
"rmview /?" at an OS/2 command prompt for details. On OS/2 Warp 4.0, the Hardware
Manager object in the System Setup folder provides a graphical view of the same information.
22.3.2 Insufficient Number Of Command Line Arguments
The MPAP-200 command line must contain at least one command line argument for each
MPAP-200 to be installed.
22.3.3 Bad Parameters
61
Page 62

The base address or IRQ value may be out of range. Make sure that the base address is a
hexadecimal number between 100 hex and 3F0 hex ending in 0. Make sure that the IRQ is a
decimal number between 2 and 15.
62
Page 63

56
Page 64

MPAP-200 User's Manual
Revision 2.32
March 2004
P/N 940-0129-232
57
 Loading...
Loading...