Page 1

Prism FC420 Bridge Option
User’s Guide
Introduction 3
Fibre Channel Overview ..........................................................................................4
Library Operation after Prism FC420 Bridge Installation ...................................4
Cabling the Library for Fibre Channel 4
One- and Two-Drive Library Cabling ....................................................................5
Cabling an ATL M2500 with Three or More Drives.............................................6
Setting SCSI IDs 10
Configuring FC420 Firmware 11
Setting up an Ethernet Connection .......................................................................11
Verifying Current FC420 Firmware......................................................................13
Scanning the SCSI Busses on the Library.............................................................14
Creating a Map File for the FC420 ........................................................................14
Making Other Configuration Changes.................................................................14
Restoring the PC to Its Original Configuration...................................................15
Prism FC420 Services Software Commands 15
Prism FC420 Service Software Operation ............................................................15
Command Syntax ....................................................................................................15
List of Abbreviations...............................................................................................16
Command Listing....................................................................................................16
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0, September 2003 1
Page 2

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Prism FC420 Blink Codes 27
2 6207947-04fN 15
Page 3
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Introduction 0
This document explains how to configure and operate the FC420 Fibre
Channel bridge option installed in the Quantum ATL M-Series library.
For FC420 installation steps, refer to the FC420 Fibre Channel Bridge Quick
Reference Guide (PN 6473033).
For a description of ATL M-Series library operating procedures, see the
Quantum ATL M-Series Library User’s Guide (PN 6423002).
Note: If you do not have an MC300 Prism Management Card (PMC),
refer to Configuring FC420 Firmware
troubleshoot your FC420 bridge (or bridges).
to configure and
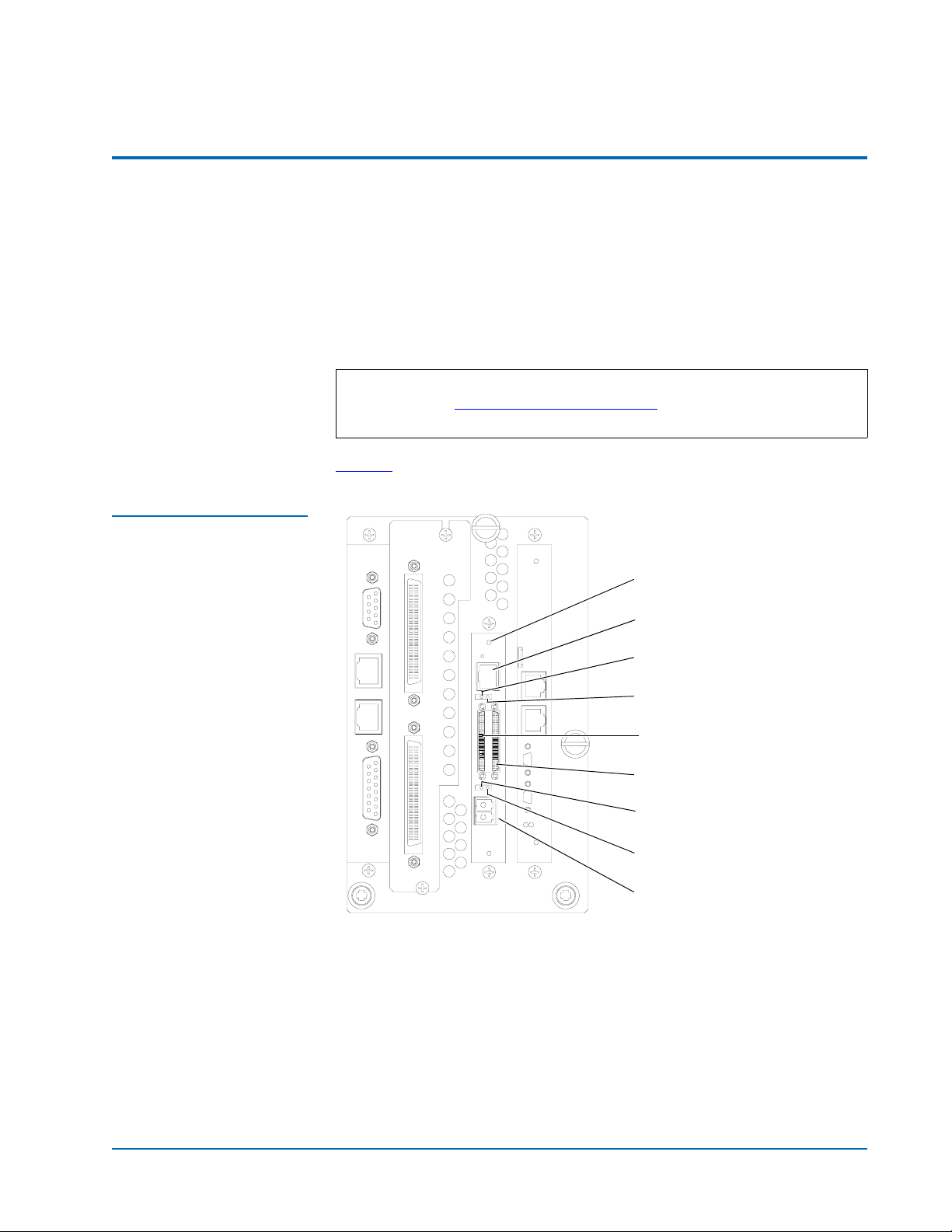
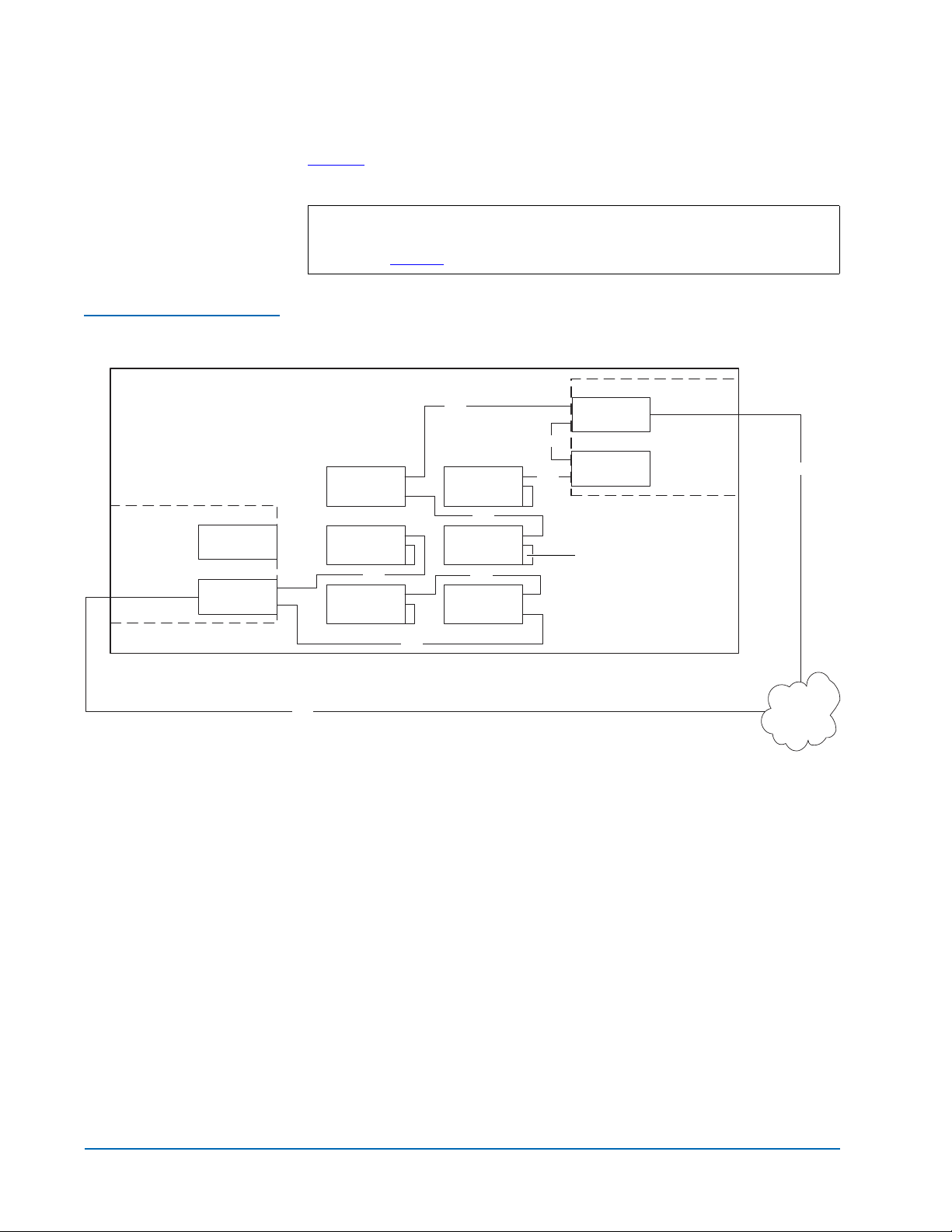
Figure 1 FC420 Bridge
Components
Figure 1
identifies the components of the FC420 bridge.
Ready/Fault LED
Ethernet port
Activity LED for SCSI port 0
Activity LED for SCSI port 1
SCSI port 0
SCSI port 1
Fibre Channel speed LED
Fibre Channel activity LED
SFP Fibre Channel connector
Introduction 3
Page 4

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Fibre Channel Overview
The Quantum ATL M-Series libraries are controlled by a host computer via an
0
LVD SCSI differential bus using the SCSI-2 medium changer command set.
The library’s Prism Architecture™ allows for easy conversion from the SCSI
host interface to a Fibre Channel host interface by installing the FC420 bridge
option.
Fibre Channel is a serial data transfer architecture for use with computers and
mass storage devices. Fibre Channel is rapidly emerging to challenge SCSI as
the interface of choice for host-to-storage applications.
Fibre Channel advantages include:
• Connection distances of up to 10 Kilometers
• Up to 2 Gb/sec data transfer rates with Auto-negotiate
• Support for up to 126 devices on a loop
• Support for 24-bit addressing for over 16 million devices in point-to-point
mode or fabric, when using a Fibre Channel switch or multiple Fibre
Channel switches
• Operating system independence
• Interconnect flexibility
• Fibre Channel fabric switches provide full direct connectivity between all
ports on a storage area network (SAN), which can increase the total
throughput of all devices on the SAN
Library Operation after Prism FC420 Bridge Installation
0
Once the Prism FC420 bridge SCSI to Fibre Channel option is installed and
tested, the library operates exactly as a library with a SCSI host interface. User
operation of the library via the graphical user interface (GUI) panel is
unchanged.
Cabling the Library for Fibre Channel 0
The cabling configuration used for the ATL M-Series library with the FC420
bridge option depends on the following factors:
• Number of tape drives installed
• Tape drive type (DLT8000, SDLT 220, SDLT 320, SDLT 600, HP LTO Gen
1, or HP LTO Gen 2)
• Number of FC420 bridges installed
• Data transfer rate of the storage area network (SAN)
4 Cabling the Library for Fibre Channel
Page 5
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
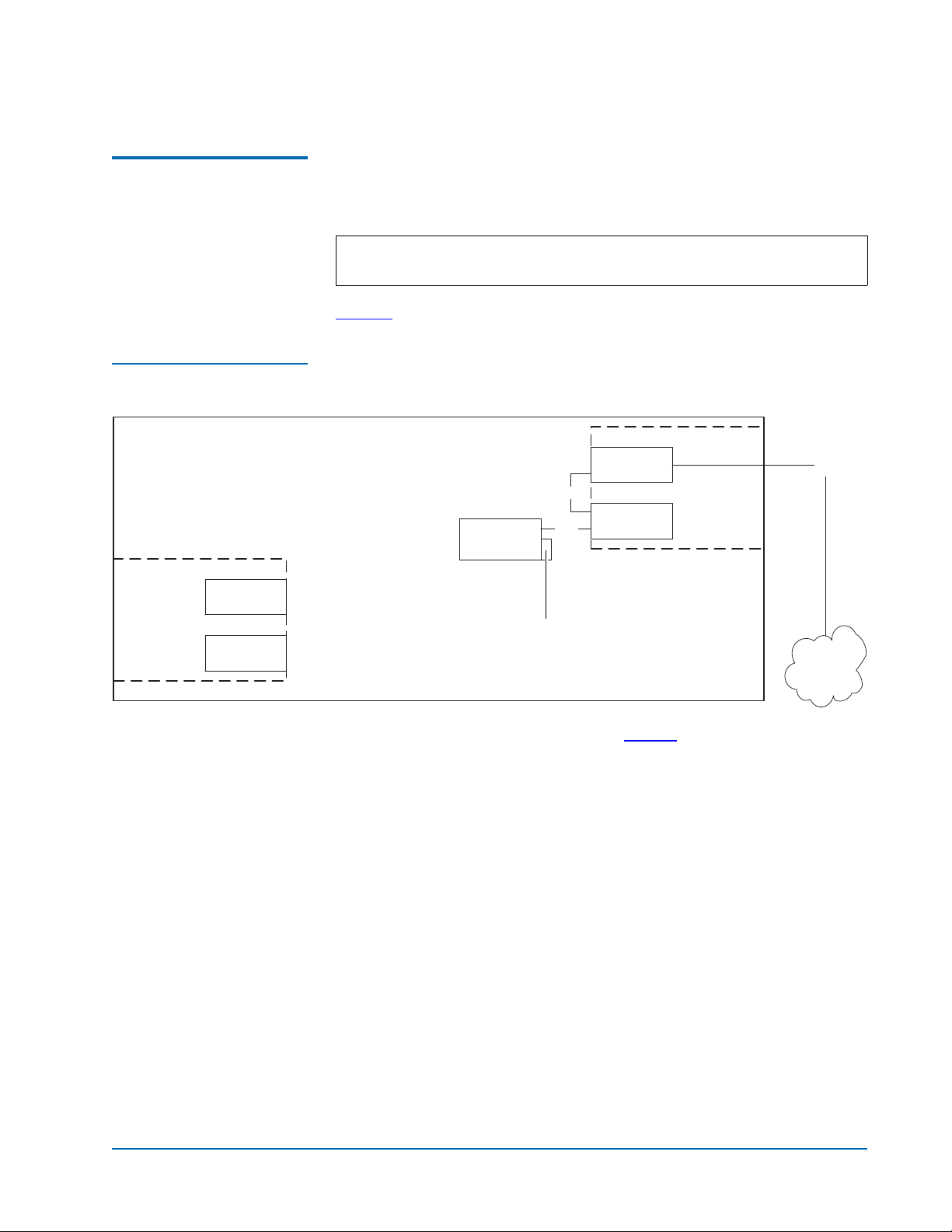
One- and Two-Drive Library Cabling
Figure 2 One-Drive Library
Cabling
M1500 or M2500
Auxiliary
electronics
module
(M2500 only)
Slot for FC420
If you are cabling an ATL M1500 library, or an ATL M2500 library with only
0
one or two tape drives, the cabling is the same regardless of drive type or
SAN. One- or two-drive libraries require only one FC420 bridge.
Note: HP LTO Gen 2 and SDLT 600 require 2 GB SAN connections. All
other drive types may have either a 1 GB or 2 GB SAN connection.
Figure 2
shows the cabling for a one-drive library.
FC420
SCSI
SCSI controller
Drive 1
SCSI
Primary
electronics
module
Fibre
Slot for FC420
Terminator
SAN
In a one-drive configuration (as shown in figure 2), a SCSI daisy chain is
established from one of the SCSI ports on the FC420 bridge to the SCSI
controller and then to drive 1, where the daisy chain is terminated. The SCSI
controller is included in the chain to pass SCSI commands to the robot.
The SCSI controller and drive 1 must be on the same SCSI bus because the
SCSI controller has termination disabled.
Cabling the Library for Fibre Channel 5
Page 6
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
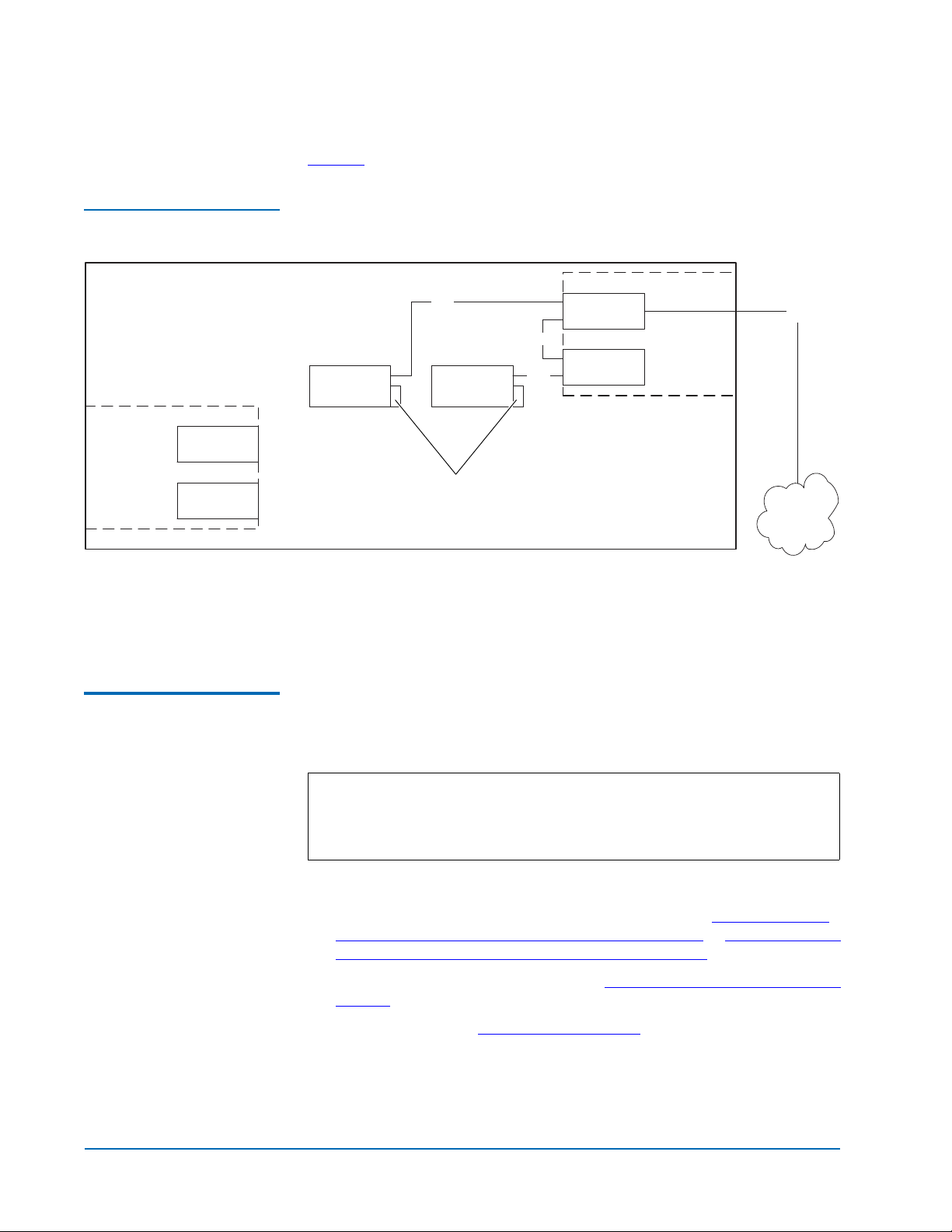
Figure 3 shows typical cabling for a two-drive library.
Figure 3 Two-Drive Library
Cabling
M1500 or M2500
Auxiliary
electronics
module
(M2500 only)
Slot for FC420
SCSI
Drive 2 Drive 1
SCSI
SCSI
FC420
SCSI controller
Primary
electronics
module
Fibre
Slot for FC420
Cabling an ATL M2500 with Three or More Drives
Terminator
SAN
In a two-drive library, the second drive (drive 2) should be connected to the
available FC420 port, creating a second SCSI bus. This utilizes the FC420
bridge fully and maximizes the communication bandwidth available to each
tape drive.
When cabling an ATL M2500 with three or more tape drives, you need to
know the type of tape drive installed in the library and the data transfer rate
0
of the SAN to determine the correct SCSI configuration.
Note: As with the one- and two-drive configurations, all Fibre-to-SCSI
cabling configurations must include the SCSI controller so that
SCSI commands intended for the robot are communicated
successfully.
To cable a library with:
• SDLT 220, SDLT 320, or HP LTO Gen 1 drives, refer to SDLT 220, SDLT
320, or HP LTO Gen 1 Drive Cabling with a 1 Gb SAN or SDLT 220, SDLT
320, or HP LTO Gen 1 Drive Cabling with a 2 Gb SAN
• SDLT 600 or HP LTO Gen 2 drives, see SDLT 600 or HP LTO Gen 2 Drive
Cabling
• DLT8000 drives, see DLT8000 Drive Cabling
6 Cabling the Library for Fibre Channel
Page 7
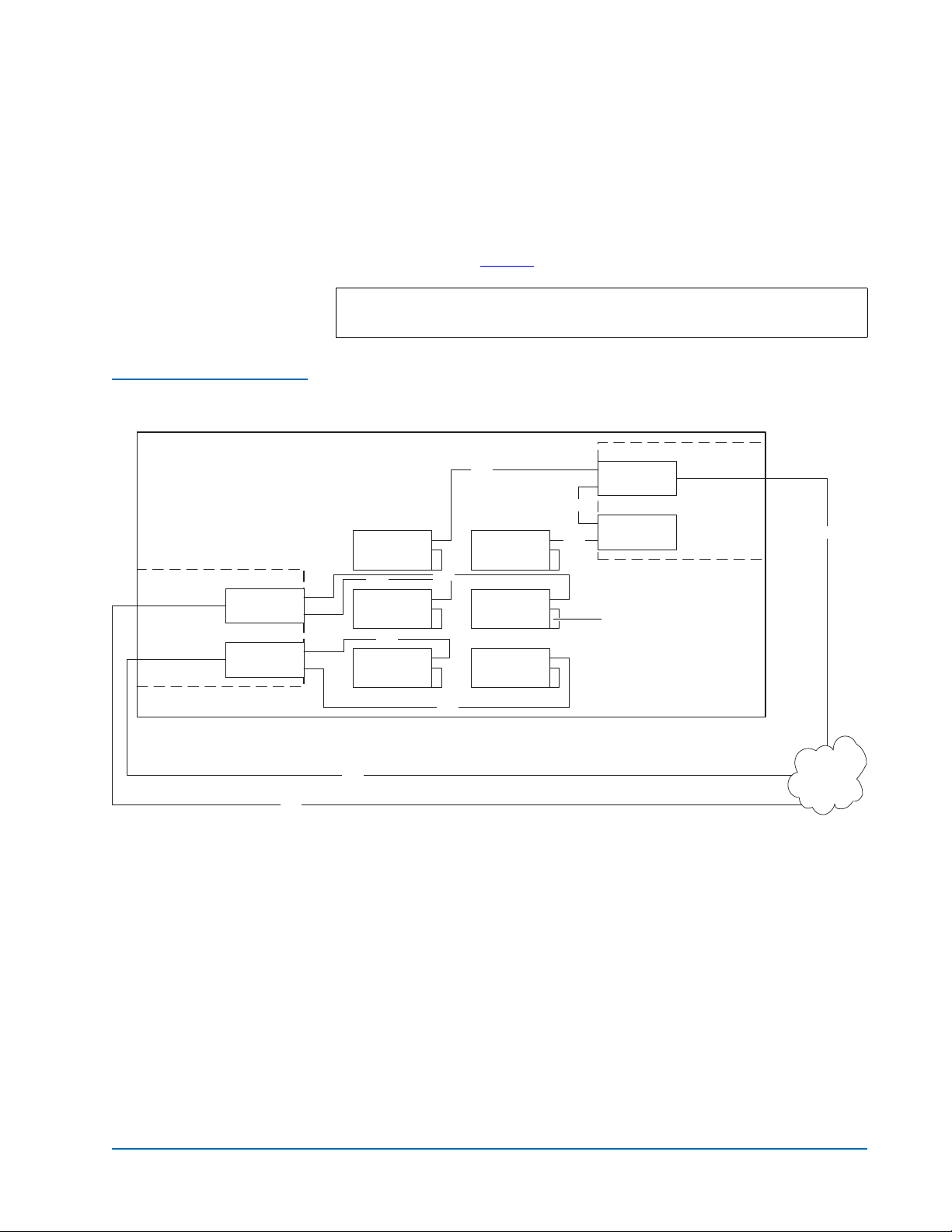
Figure 4 One-Drive-PerFC420-Port Cabling
M2500
Auxiliary
electronics
module
FC420
FC420
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
SDLT 220, SDLT 320, or HP LT O Gen 1 Drive Cabling with a 1 Gb SAN 0
If an ATL M2500 containing SDLT 220, SDLT 320, or HP LTO Gen 1 drives is
connected to a 1 Gb SAN, a ratio of one tape drive per FC420 SCSI port is
recommended. This means that three- and four-drive libraries require a
second FC420 bridge, and five- and six-drive libraries require three FC420
bridges, as shown in figure 4
.
Note: SDLT and LTO tape drives are sometimes referred to as
Superdrives.
SCSI
Drive 2 Drive 1
SCSI
Drive 4 Drive 3
SCSI
Drive 6 Drive 5
SCSI
SCSI
SCSI
FC420
SCSI controller
Terminator
Primary
electronics
module
Fibre
Fibre
SCSI
Fibre
1 Gb SAN
SDLT 220, SDLT 320, or HP LT O Gen 1 Drive Cabling with a 2 Gb SAN 0
If an ATL M2500 containing SDLT 220, SDLT 320, or HP LTO Gen 1 drives is
connected to a 2 Gb SAN, a maximum ratio of two tape drives per FC420 SCSI
port is recommended. This means that one FC420 bridge could manage up to
four tape drives, but a second FC420 bridge is required for libraries with five
or six tape drives.
Cabling the Library for Fibre Channel 7
Page 8
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Figure 5 shows a six-drive library utilizing a two-drive per SCSI port cabling
scheme.
Note: To increase the bandwidth available to each tape drive, install
Figure 5 Two-Drive-perFC420-Port Cabling
M2500
additional FC420 bridges and use the cabling configuration shown
in figure 4
Drive 2 Drive 1
.
SCSI
SCSI
SCSI
FC420
SCSI controller
Primary
electronics
module
Fibre
Auxiliary
electronics
module
Slot for FC420
FC420
Fibre
SCSI
Drive 4 Drive 3
SCSI
Drive 6 Drive 5
SCSI
SCSI
Terminator
2 Gb SAN
8 Cabling the Library for Fibre Channel
Page 9
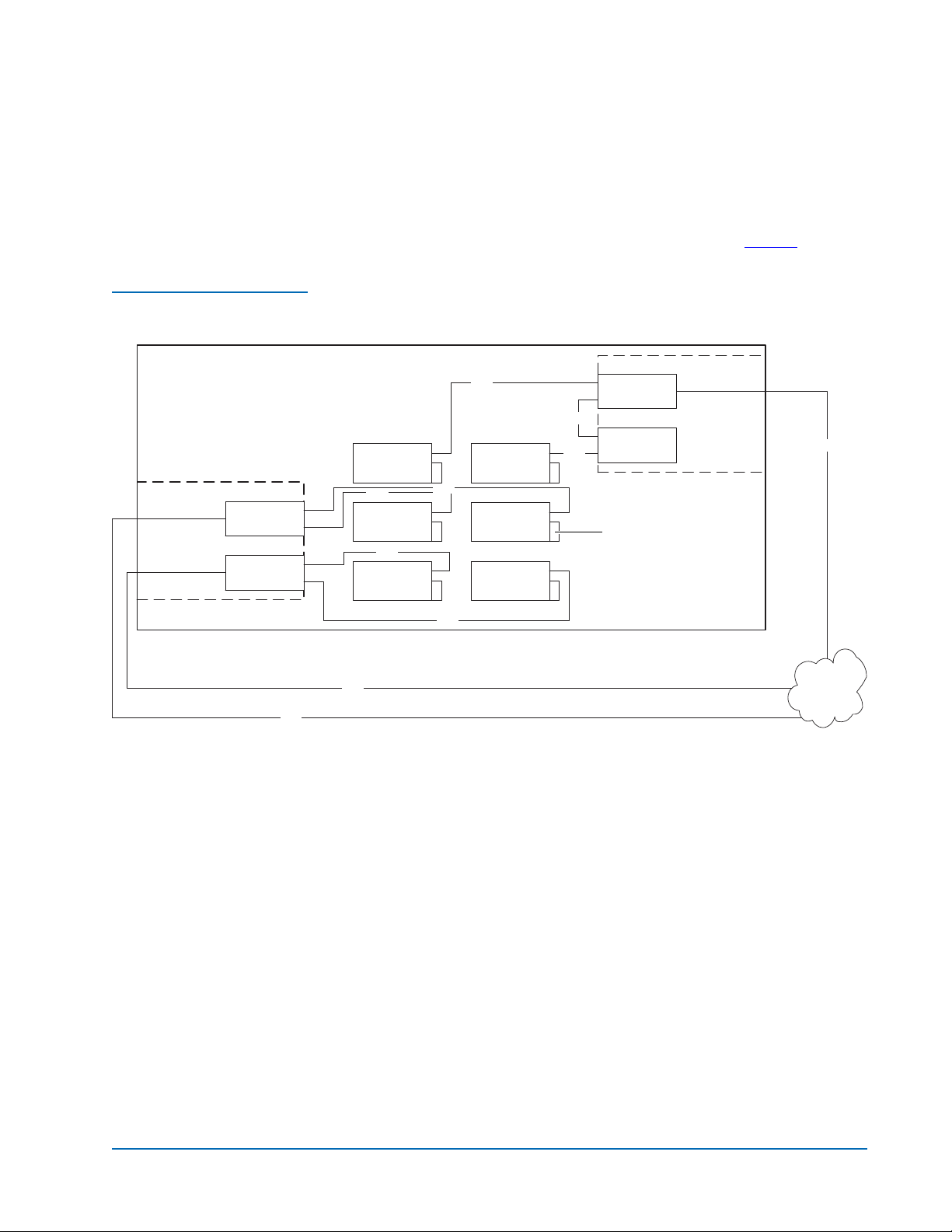
Figure 6 SDLT 600 or HP
LTO Gen 2 Drive Cabling
M2500
Auxiliary
electronics
module
FC420
FC420
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
SDLT 600 or HP LTO Gen 2 Drive Cabling 0
SDLT 600 and HP LTO Gen 2 drives can only be used with a 2 Gb SAN. A
ratio of one tape drive per FC420 SCSI port is recommended. This means that
three- and four-drive libraries require a second FC420 bridge, and five- and
six-drive libraries require three FC420 bridges, as shown in figure 6
SCSI
Drive 2 Drive 1
SCSI
Drive 4 Drive 3
SCSI
Drive 6 Drive 5
SCSI
SCSI
SCSI
FC420
SCSI controller
Terminator
Primary
electronics
module
.
Fibre
Fibre
Fibre
SCSI
2 Gb SAN
Cabling the Library for Fibre Channel 9
Page 10

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
DLT8000 Drive Cabling 0
A single FC420 bridge installed in an ATL M2500 library with DLT8000 tape
drives can manage up to four drives per SCSI port. Figure 7
cabling configuration, with the SCSI controller and three drives on one SCSI
bus, and three drives on the other SCSI bus.
Note: To increase the bandwidth available to each drive, install
Figure 7 DLT8000 Drive
Cabling
M2500
shows a typical
additional FC420 bridges and use the cabling configuration shown
in figure 4
Drive 2 Drive 1
or in figure 5.
SCSI
SCSI
SCSI
FC420
SCSI controller
Primary
electronics
module
Fibre
Auxiliary
electronics
module
Slot for FC420
Slot for FC420
SCSI
Drive 4 Drive 3
SCSI
Drive 6 Drive 5
SCSI
SCSI
Terminator
SAN
Setting SCSI IDs 0
Use the information in table 1 to set the SCSI device addressing (SCSI IDs) for
the library.
Table 1 SCSI ID Settings
Device SCSI ID Device SCSI ID
SCSI Controller 0 Drive 4 4
Drive 1 1 Drive 5 15
Drive 2 2 Drive 6 14
Drive 3 3
10 Setting SCSI IDs
Page 11

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Configuring FC420 Firmware 0
Each FC420 bridge installed must be configured using the FC420 Bridge
Services software. To configure the FC420 bridge successfully, it is important
to:
• Know exactly how the SCSI cabling in the library is configured,
including:
• How many FC420 bridges are present in the library
• How many SCSI buses are present in the library
• How many SCSI devices are connected to each bus (this was
established in the previous section of this document)
• Use the FC420 Bridge Services software to create a Map file identifying
which SCSI devices are connected to which Fibre Channel ports on the
FC420 board
The major steps for manually configuring FC420 bridge firmware are:
Setting up an Ethernet Connection
Note: If you have an MC300 PMC, refer to the MC300 Prism Management
Card User’s Guide, PN 6473040, to configure your FC420 bridge (or
bridges), instead of the following steps.
• Setting up an Ethernet Connection
• Verifying Current FC420 Firmware
• Scanning the SCSI Busses on the Library
• Creating a Map File for the FC420
Note: These major steps must be repeated for each FC420 bridge in the
library.
To set up an Ethernet connection between the FC420 bridge and a service PC
0
or other stand-alone computer equipped with Windows or Windows NT:
Note: The FC420 bridge has DHCP enabled, which searches for a server
to get an address. The DHCP server for this application is the
MC300 PMC, which is the default. If you have an MC300 PMC, do
not perform this procedure, refer to the MC300 Prism Management
Card User’s Guide, PN 6311631, for FC420 bridge administration.
1 Connect a Field Service Notebook to the FC420.
a Turn on the Field Service Notebook.
b Disconnect the Ethernet cable to the FC420 bridge.
Configuring FC420 Firmware 11
Page 12

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
2 After the ten minute wait period, attach one end of a CAT-5 crossover
3 Attach the other end of the CAT-5 crossover cable to the NIC port on the
4 Right-click the network icon on the computer’s desktop.
c Power-cycle the library.
d Wait ten minutes.
cable to the RJ-45 connector at the top of the FC420 bridge.
computer.
This establishes a physical connection between the FC420 bridge and the
computer.
In some versions of Windows, this icon may be labeled
Neighborhood
Network Places
. In other versions of Windows, this icon may be labeled My
or something similar.
Network
Windows displays a pop-up menu.
5 On the pop-up menu, select
Properties.
Windows displays a Network dialog box.
6 Click
7 Double-click the
Protocols (Windows NT) or right-click the connection and select
Properties (Windows 2000 or later).
TCP/IP Protocol menu item.
Windows displays the
TCP/IP Properties dialog box.
Note: Make a note of the current network settings before changing
them. You will need this information if you wish to return the
computer to its previous configuration after configuring the
FC420 bridge.
8 Select the option that allows you to specify an IP address.
In some version of Windows this option is shown as
Address
Following IP Address
. In other versions of Windows, this option is shown as Use the
.
Specify an IP
The IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway fields become active.
9 In the
IP Address field, type 10.0.0.x (where x is a number between 2 and
253).
10 In the
Subnet Mask field, type 255.255.255.0.
Note: Do not type anything in the Gateway field.
11 Click OK until all the dialog boxes close.
12 Configuring FC420 Firmware
Page 13

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
12 If you are using Windows NT, open a DOS window and type:
Verifying Current FC420 Firmware
ipconfig/release <
ipconfig/renew <
Enter>
Enter>
Note: This step is not required for other versions of Windows.
13 Turn on the library.
14 Establish a Telnet connection to the FC420 bridge. To do this:
a Start a Telnet session from the computer desktop by selecting
Run.
Start >
b In the Run dialog box, type telnet 10.0.0.1 and then click OK.
The Telnet window opens, indicating a connection with the FC420
bridge. When you see a
Ready prompt, command line mode is
available.
To determine the current version of FC420 firmware, type info at the Ready
0
prompt and then press <
Enter>. This command returns the firmware version
and gives the firmware revision date. Use this information to determine the if
the FC420 bridge has current firmware.
If the FC420 firmware requires updating, follow these steps:
1 Contact your support representative and obtain the latest copy of the
firmware.
2 If you have not done so already, establish an Ethernet connection
between the computer with the new FC420 driver and the FC420 bridge
to be updated (see Setting up an Ethernet Connection
).
3 On the computer, open a command prompt window.
4 In the command prompt window, type
FC420_IP_address is the IP address for the FC420 bridge) and then press
<
Enter>.
ftp FC420_IP_address (where
Note: Before entering the FTP command, close all prior connections
to the FC420.
5 When prompted for a username, type sysadmin (or the current system
administrator ID) and then press <
Enter>.
6 When prompted for a password, type sysadmin (or the current system
administrator ID) and then press
<Enter>.
7 At the command line, type bin and then press <Enter>.
8 At the command line, type put firmware_filename (where firmware_filename
is the name of the firmware file) and then press <Enter>.
Several messages appear on the screen. Finally, a success message
appears.
Configuring FC420 Firmware 13
Page 14

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
9 Type bye or quit and then press <Enter>.
10 Power cycle the library.
Scanning the SCSI Busses on the Library
0
Creating a Map File for the FC420
To confirm that the SCSI busses are cabled properly:
1 At the
Ready prompt, type scsitargets 0, and then press <Enter>.
This command scans and displays all SCSI devices found on SCSI bus 0.
2 If the second SCSI port on the FC420 bridge is being utilized, wait for the
Ready prompt to reappear, then type scsitargets 1 and press <Enter>.
Each FC420 bridge in the library requires a map file to identify the SCSI
0
devices in the library electronically connected to each Fibre Channel port on
the board.
To create the FC420 Map, perform the following steps:
1 At the
Ready prompt, type scsiportlist and then press <Enter>.
This command returns a list of available SCSI ports and their current
status.
2 If there are no SCSI bus failures, type
automap and press <Enter>.
The automap command executes.
3 When the
<Enter>.
4 When the
Ready prompt reappears, type saveconfiguration and press
Ready prompt reappears, type firmwarerestart and press <Enter>.
Making Other Configuration Changes
0
The preceding firmware configuration steps are mandatory to ensure
successful library operation. After completing these procedures, you may
want to make other configuration changes by issuing additional service
commands.
Service Command List
For your convenience, all service commands for the FC420 bridge are listed in
Prism FC420 Service Software Operation
Using the Help Command
You can also obtain a list of service commands by typing help and then
pressing
<Enter>.
To get more information about a particular command, type help
command_name and then press <Enter>, where command_name is the exact
name of the command about which you want information.
14 Configuring FC420 Firmware
0
.
0
Page 15

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Restoring the PC to Its Original Configuration
0
Once you have finished configuring the FC420 bridge, return the PC to its
original configuration by opening the
the network settings to their original values.
TCP/IP Properties dialog box and return
Prism FC420 Services Software Commands 0
The Prism FC420 Services Software is resident on each FC420 bridge, and is
used to configure the bridge for use in the library. The software uses a
Command Line Interface (CLI).
Prism FC420 Service Software Operation
0
The Command Line Interface provides access to the FC420 services through a
set of ASCII-based command lines. Commands have four types of operation:
• Immediate— cause an immediate action; not preceded by a get or set
operation.
• Get—returns the current value of a parameter or setting. This command
may be abbreviated to “g.”
• Set—changes the value of a parameter or setting. This command may be
abbreviated “s,” and does not take effect until a
is sent.
SaveConfiguration command
• Usage—if the form of an operation cannot be determined, it is assumed to
be the “Usage” form and a brief help message is displayed.
The commands are not case sensitive.
Decimal numbers may be entered as raw numerical input, such as 123.
Octal numbers must be preceded by the number 0, for example 0713.
Hexadecimal numbers must be preceded by the C-style of 0x prefix, such as
9x1FA4.
Quoted strings are treated as a single parameter for any command which
expects character input, regardless of space in the string.
Several non-immediate commands require a
modified parameters take effect. When such a command is executed an
asterisk appears next to the command line prompt.
Command Syntax 0 The following is a list of syntax used to describe command lines:
• [ ] indicates required entry
• < > indicates optional entry
• | indicates choose one entry
SaveConfiguration before their
Prism FC420 Services Software Commands 15
Page 16

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
List of Abbreviations 0 The following is a list of abbreviations used to describe command lines:
• fp Fibre Channel port number (0)
• fl Fibre Channel LUN (0 - 31)
•sb SCSI bus number (0 - 1)
• st SCSI target ID (1 - 15)
•sl SCSI LUN (0 - 7)
Command Listing 0 Table 2 lists the currently available Prism FC420 Services Software
commands.
Table 2 Prism FC420
Services Commands
Command Description Default Syntax
AutoMap
(Immediate)
BootFibreDelay
BootScan
BootScanPorts
ClearEvent
(Immediate)
Automatically maps all currently
operational SCSI devices attached to the
FC420 bridge.
Issue an
command before issuing an
command because
FCPortList and a SCSIPortList
AutoMap
AutoMap ignores
devices attached to a non-operational
SCSI bus and assigns devices to a nonoperational Fibre Channel port.
Selects/displays the boot fibre delay (in
seconds).
Enables/disables the boot scan feature.
This feature provides dynamic mapping
of SCSI devices to fibre port/LUN
combinations via a SCSI port at boot
time.
Selects/displays the ports to be used for
a boot scan.
Clears the contents of the event log.
automap
automap [fp]
0 set bootfibredelay [0 | 15 | 30]
get bootfibredelay
enabled set bootscan [enabled |
disabled]
get bootscan
all set bootscanports [fp | all | auto]
get bootscanports
clearevent
DhcpFixedDelay
Selects/displays the delay interval (in
seconds) between DHCP client requests.
16 Prism FC420 Services Software Commands
5 set dhcpfixeddelay [0 | 15 | 30]
get dhcpfixeddelay
Page 17
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
Command Description Default Syntax
September 2003
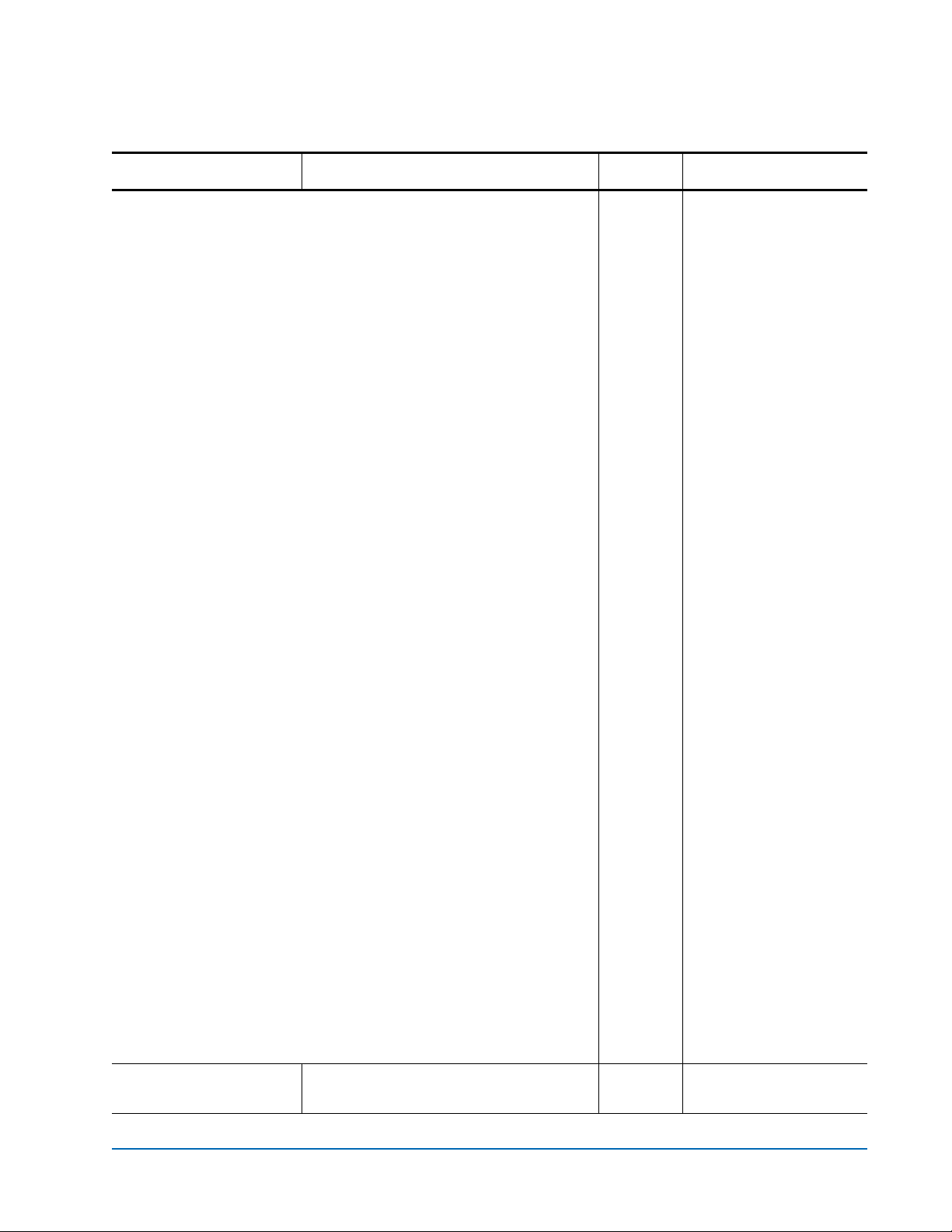
DispEvent
Sets the switches that control the
filtering performed when displaying
events.
Switches have the following settings:
[subsystem] switch: mask that controls which subsystem events are
displayed. The mask is a byte value with the following bit patterns
corresponding to the currently supported subsystems:
0x01 FCP Processor/i960 Interaction
0x02 SCSI Processor/i960 Interaction
0x04 Ethernet (Future)
0x08 Extended copy
0x20 NVRAM & Flash
0x40 ECC & Parity
0x80 Performance
To display events from several different subsystems, use a mask
value equal to the logical OR of the corresponding subsystem
values. To display events from all subsystems enter the value
0x7F
for the mask.
[event_level] switch: mask that controls what reporting level events are
displayed. The mask is a byte value with the following bit patterns
corresponding to the currently supported reporting levels:
set dispevent [subsystem]
[event_level] [status]
get dispevent
0x00
0x00
0x01 Info; general information
0x02 Warning; unexpected situation/condition
0x04 Critical; operation limited/curtailed
0x08 Failure; hard failure
0x10 Other; otherwise not categorized
0x20 Debug; tracking events
To display events from several different reporting levels, use a mask
value equal to the logical OR of the corresponding reporting levels.
To display events for all reporting levels enter the value
0x7F for the
mask.
switch: This switch has the following two values which
[status]
correspond to the status of the events to be displayed:
all All events, regardless of their status values are displayed.
ngood Only events with a status other than good are displayed.
DispFcPortDB
(Immediate)
Displays the contents of the specified
Fibre port’s internal database.
Prism FC420 Services Software Commands 17
ngood
dispfcportdb <f p>
Page 18
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Command Description Default Syntax
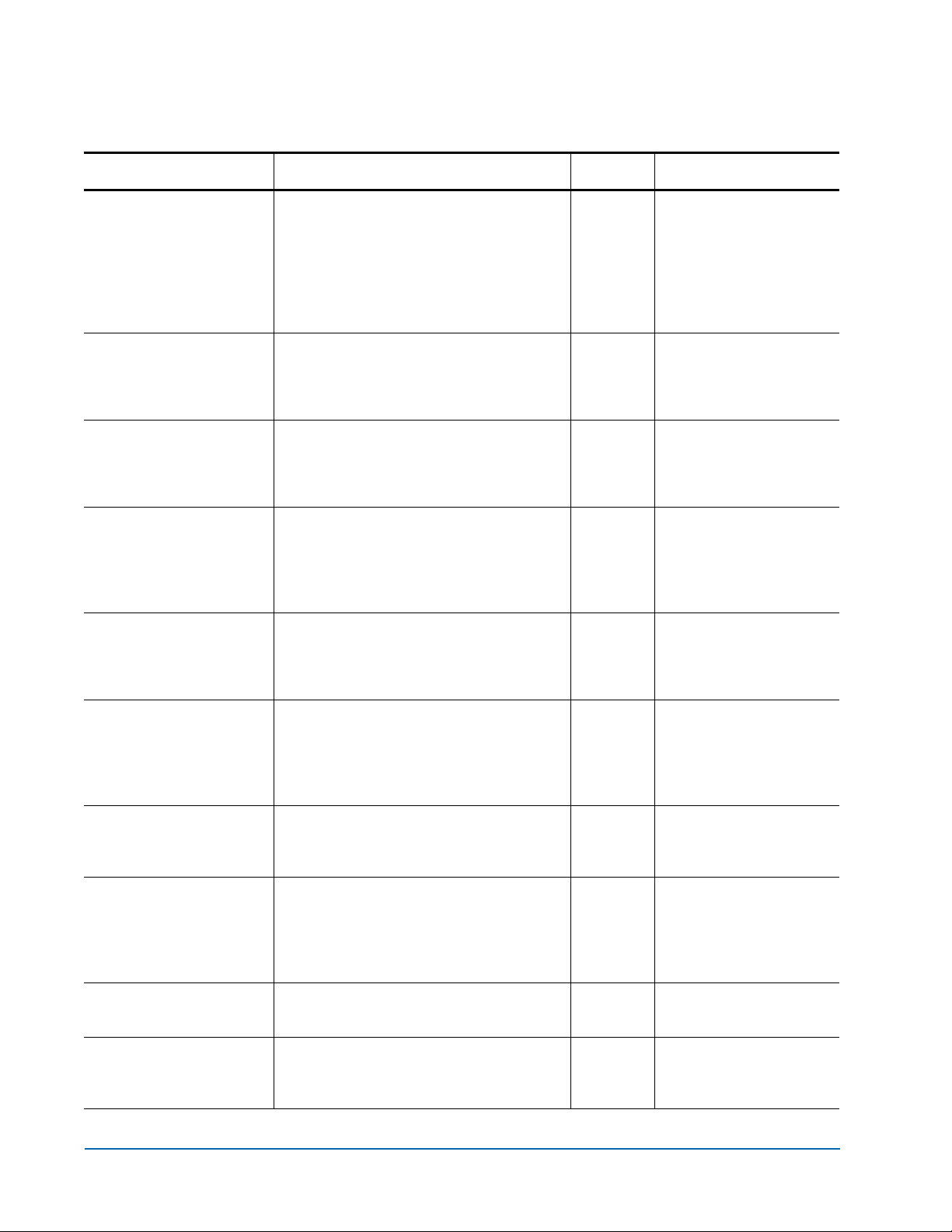
DisplayEvent
(Immediate)
EccLog
ErrorLog
EthernetSpeed
Exit
(Immediate)
Displays the current contents of the
event log. The log is filtered by the
current switch settings as described in
the
DispEvent section. If the optional all is
selected, the display filtering is
temporarily suspended and all logged
events are displayed.
Resets/displays the ECC error statistics
for the FC420 bridge. The
displays the statistics; the
get command
set command
resets the statistic counters to zero.
Resets/displays the error logs for the
FC420 bridge. The
displays the logs; the
get command
set command
resets the logs to zero.
Sets/displays the Ethernet speed of the
Fibre connection. If
auto is selected, the
current speed of the connection is
indicated in parentheses in the response
to the
get ethernetspeed command.
Exits the current Telnet command line
interface (CLI) session). This command
has no effect during a serial or in-band
CLI session.
displayevent <all>
set ecclog clear
get ecclog
set errorlog clear
get errorlog
auto set ethernetspeed [10 | 100 |
auto]
get ethernetspeed
exit
FcAck0
FcClass2
FcConnMode
FcDataRate
FcFairArb
Specifies whether ACK0 or ACK1 will
be returned in response to a Class 2
Fibre Channel data frame or sequence.
When enabled, this option sends ACK0;
when disabled, this option sends ACK1.
Specifies whether the FC420 bridge will
support Fibre Channel Class 2
(Multiplexed) or Class 3 service.
Sets/displays the Fibre Channel
connection mode for the FC420 to
arbitrated loop or point-to-point.
Loop-ptp and ptp-loop will auto-negotiate
starting with the first topology type.
Sets/displays the data rate (in Gb/s) at
which the FC420 bridge will operate.
Turns on or off the FC-AL arbitration
fairness. Applies to all three Fibre
Channel ports on each board.
disabled set fcack0 [enabled | disabled]
get fcack0
disabled set fcclass2 [enabled |
disabled]
get fcclass2
ptp-loop
auto set fcdatarate [1gb | 2gb | auto]
enabled set fcfairarb [enabled |
set fcconnmode [loop | ptp |
loop-ptp | ptp-loop]
get fcconnmode
get fcdatarate
disabled]
get fcfairarb
18 Prism FC420 Services Software Commands
Page 19

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
Command Description Default Syntax
September 2003
FcFullDuplex
FcHard
FcHardAddress
FcInitiator
FcPortList
(Immediate)
Fcp2
Fcp2Conf
Enables/disables full duplex
communication between the FC420
bridge and other Fibre Channel devices.
Enables/disables Fibre Channel hard
address assignment. Under soft
addressing the FC420 loop address is
assigned during loop initialization.
Sets/displays the value used as the FCAL hard address.
Enables/disables the initiator function
of the FC420 bridge on the Fibre channel
network.
Lists the available Fibre Channel ports
and their current status.
Enables/disables the FC420 bridge’s
compliance with the FCP-2 Fibre
Channel specification.
Enables/disables the FC420 bridge’s
capability to request FCP_CONF IUs.
This option is valid only when the
fcp2
command is also enabled.
enabled set fcfullduplex [enabled |
disabled]
get fcfullduplex
disabled set fchard [enabled | disabled]
get fchard
FC port 0
0x03
disabled set fcinitiator [enabled |
enabled set fcp2 [enabled | disabled]
enabled set fcpconf [enabled | disabled]
set fchardaddress [fp
[address]]
get fchardaddress [fp]
disabled]
get fcinitiator
fcportlist
get fcp2
get fcp2conf
Fcp2CRN
FcSCSIBusyStatus
FcT argets
(Immediate)
Enables/disables the FC420 bridge’s
capability to accept CRNs for precise
delivery of SCSI commands. This option
is only valid when the
fcp2 command is
also enabled.
Specify the SCSI status value returned
when the FC420 is unable to accept a
SCSI command due to a temporary lack
of internal resources.
Provides the node name, Fibre LUN,
and inquiry data for every Fibre
Channel target device visible to an
FC420 bridge operating in initiator
mode.
disabled set fcpcrn [enabled | disabled]
get fcp2crn
BUSY set fcscsibusystatus [busy |
qfull]
getfcscsibusystatus
fctargets <fp>
Prism FC420 Services Software Commands 19
Page 20
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Command Description Default Syntax
FcWWName
FibreBridgeModel
FibreBridgeName
Sets/displays the current World Wide
Name (WWN) of the Fibre Channel
interface referenced. Each Fibre port has
a unique WWN. The least significant 6
bits of the WWN are used as the
Ethernet MAC address.
The
set variant of the command allows
the user to change the last three bytes of
each WWN. Please note, however, that
the most significant bit of the three bytes
must be 1 in order to provide WWN
verification. Also note that the last bit of
each WWN may only be assigned one of
the following values: 0, 4, 8, or C for port
0; 1, 5, 9, or D for port 1; and 2, 6, A, or E
for port 2.
Fabric and loop operation is
unpredictable if duplicate WWNs are
used.
Reports the specific FC420 model
information.
Specify the 8-character name assigned to
the FC420 bridge.
10 00 0x,
where
is the
Fibre
port
number.
set fcwwname [portnumber
[0xnn 0xnn 0xnn]]
x
get fcwwname [portnumber]
get fibrebridgemodel
set fibrebridgename [value]
get fibrebridgename
FibreBridgeT argetLUN
FirmwareRestart
(Immediate)
Help
(Immediate)
IdentifyFibreBridge
Info
(Immediate)
IPAddress
Specify the soft target LUN used by the
FC420 when addressed by the host. This
LUN is taken from NVRAM.
Reboots the FC420 firmware.
Displays a list of available commands.
When the optional command name is
present, detailed command-specific
information is displayed.
Causes the Ready LED on the FC420
board to blink continuously until
disabled.
Displays version numbers and other
product information for key
components within the FC420.
Sets/displays the current IP address of
the FC420 bridge. If the
ipdhcp command
is enabled, the get command reports the
current IP address assigned by the
nameserver.
disabled
disabled set identifyfibrebridge [enabled
10.0.0.1 set ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
set FibreBridgeT argetLUN [fp]
[fl] | [disabled] ]
firmwarerestart
help [command name]
| disabled]
get identifyfibrebridge
info
get ipaddress
20 Prism FC420 Services Software Commands
Page 21

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
Command Description Default Syntax
September 2003
IPDHCP
IPGateway
IPSubnetMask
IsReserved
(Immediate)
Enables/disables the capability of the
FC420 bridge to request an IP address
from a DHCP server on the network.
Sets/displays the current default
gateway. If the
enabled, the
ipdhcp command is
get command reports the
current IP gateway assigned by the
nameserver.
Sets/displays the current subnet mask.
If the
ipdhcp command is enabled, the get
command reports the current IP subnet
mask assigned by the nameserver.
Displays the reservation status of the
current FC420 bridge services session/
interface. When a reserve flag is set, the
configuration image is undergoing
modification by another FC420 bridge
services session.
unavailable while in this state.
Set commands are
Get
commands are available, however.
Executing a
restoreconfiguration, or firmwarerestart
saveconfiguration,
command releases the reserved state so
that other users may issue set
commands.
enabled set ipdhcp [enabled | disabled]
get ipdhcp
0.0.0.0 set ipgateway xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
get ipgateway
255.255.
255.0
set ipsubnetmask
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
get ipsubnetmask
isreserved
LogEvent
Sets the switches which control the
filtering performed when logging
events.
The switches have the following meanings and settings:
[enabled | disabled] switch: controls whether or not events logging is
enabled or disabled.
[subsystem]
switch: same as switch for DispEvent (see DispEvent on
page 17)
[event_level]
switch: same as switch for DispEvent (see DispEvent on
page 17)
[status]
switch: same as switch for DispEvent (see DispEvent on page 17)
MaxEnclT empAlrm
Sets/displays the maximum enclosure
temperature alarm of the unit in degrees
C (0-70 degrees C).
Menu
Enables/disables the menu interface.
Entering the command alone without
parameters toggles the current state.
Prism FC420 Services Software Commands 21
set logevent [enabled |
disabled] | [[subsystem]
[event_level] [status]]
get logevent
disabled
3Fh
3Fh
all
70°C set maxencltempalrm [0-70]
get maxencltempalrm
menu <[enabled | disabled]>
Page 22

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Command Description Default Syntax
MinEnclT empAlrm
OEMConfigFile
ParityLog
Performance
Reserve
(Immediate)
Sets/displays the minimum enclosure
temperature alarm of the unit in degrees
C (0-70 degrees C).
Reports the name (i.e., the contents of
the first record) of the OEM
configuration file stored in persistent
memory. This file is used to override the
factory default configuration of the
FC420 bridge.
Resets/displays the parity error
statistics for the FC420 bridge. The
command displays the statistics; the
get
set
command resets the statistic counters to
zero.
Returns the performance data for a userspecified Fibre port.
Reservation of the FC420 is implicit;
once the configuration image is changed
by any user of services (Serial/
Ethernet/Etc.,) the FC420 becomes
RESERVED. Performing a
SaveConfiguration, RestoreConfiguration or
FcRestart RELEASES the FC420 so that
other devices may access it.
0°C set minencltempalrm [0-70]
get minencltempalrm
get oemconfigfile
set paritylog clear
get paritylog
get performance <fp>
reserve
RestoreConfiguration
(Immediate)
When the FC420 services interface is
reserved,
but
set commands are unavailable,
get commands are available. Note
that at least one service interface always
has access to the FC420 at all times. This
interface always reports a RELEASED
status, since it may issue
set commands.
Restore to factory default configuration
or the last saved configuration. The new
configuration must be saved to take
effect.
restoreconfiguration [default |
saved]
22 Prism FC420 Services Software Commands
Page 23

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
Command Description Default Syntax
September 2003
RouteChange
(Immediate)
RouteDisplay
RouteOffline
RouteOnline
SaveConfiguration
(Immediate)
Map a Fibre Channel port (
(
fl) to a SCSI bus (sb), target (st), and LUN
(
sl). Valid route change entries are:
fp (0)
fl (0-31)
sb (0-1)
st (0-15)
sl (0-7)
fp) and LUN
List the currently mapped Fibre
Channel-to-SCSI routes.
Set the status of a route to offline.
Set the status of a route to online.
Save the new configuration. If a
firmware restart is required to make the
change, the user is prompted to confirm
the restart. The user can override the
confirmation request by indicating the
override value on the command line.
routechange [fp] [fl] [sb] [st] [sl]
routedisplay
routedisplay [fp]
routedisplay [online | offline]
routedisplay [fp [fl]]
routedisplay [fp [online | of fline]]
set routeoffline [fp] [fl]
get routeoffline [fp] [fl]
set routeonline [fp] [fl]
get routeonline [fp] [fl]
saveconfiguration < restart |
nonrestart >
ScsiInitID
ScsiPortBusSpeed
ScsiPortList
(Immediate)
ScsiPortReset
(Immediate)
ScsiPortResetOnStartup
Specify the SCSI initiator ID to be used
on the specified SCSI port.
Specifies the transfer rate at which the
FC420 bridge will attempt to negotiate
with SCSI devices. The choices are Fast
SCSI, Ultra SCSI, Ultra 2 SCSI, and Ultra
3 SCSI.
List the available SCSI ports and their
0x07 set scsiinitid [sb [0-15]]
get scsiinitid [sb]
ultra3 set scsiportbusspeed
[portnumber [fast | ultra | ultra 2
| ultra3]]
get scsiportbusspeed
[portnumber]
scsiportlist
status.
Resets the specified SCSI bus.
Specify whether the SCSI port should be
enabled set scsiportresetonstartup [sb
reset on power-up.
Prism FC420 Services Software Commands 23
scsiportreset [sb]
[enabled | disabled]]
get scsiportresetonstartup [sb]
Page 24

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Command Description Default Syntax
ScsiPortSelTimeout
ScsiPortSyncTransfer
ScsiPortT aggedQueuing
ScsiPortWideTransfer
ScsiT argets
ScsiT ermination
SerialNumber
SerialPortBaudRate
Show the time (msec) that the bridge
waits for a response from a SCSI device
on the selected port after a selection
request.
Specify whether synchronous SCSI
transfers should be negotiated with
devices on the specified SCSI port.
Specify whether tagged command
queuing is allowed on the SCSI port.
Specify whether wide SCSI transfers
should be negotiated.
List the SCSI devices that are on the
referenced SCSI bus.
Set the internal termination of the
referenced SCSI port.
Reports the FC420 bridge serial number.
Sets the baud rate for the FC420 serial
port (2400, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, or
115200).
256 msec set scsiportseltimeout [sb [256
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1]]
get scsiportseltimeout [sb]
enabled set scsiportsynctransfer [[sb]
[enabled | disabled]]
get scsiportsynctransfer [sb]
disabled set scsiporttaggedqueuing [sb
[enabled | disabled]]
get scsiporttaggedqueuing [sb]
enabled set scsiportwidetransfer [sb
[enabled | disabled]]
get scsitargets [sb]
enabled set scsitermination [sb
[enabled | disabled]]
get scsitermination [sb]
get serialnumber
9600 set serialportbaudrate [rate]
get serialportbaudrate
SerialPortEcho
SerialPortHandshake
SerialPortStopBits
Turn on or off echoing of keyboard
input.
Set the data handshaking method used
for controlling the flow between the
transmitter and receiver (hardware,
software, or none).
Set the number of stop bits for the FC420
serial port (1 or 2).
disabled set serialportecho [enabled |
disabled]
none set serialporthandshake [hard |
xon | none]
get serialporthandshake
1 set serialportstopbits [1 | 2]
get serialportstopbits
24 Prism FC420 Services Software Commands
Page 25

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
Command Description Default Syntax
September 2003
ServicesLUN
SpeedWrite
Identifies the LUNs (one per Fibre port)
to be used during an in-band command
line interface (CLI) session with a given
host. This information is taken from
NVRAM.
Any map coinciding with a userspecified ServicesLUN must first be set
to offline before attempting to change
the ServicesLUN. This map will be
destroyed upon power-cycling the
FC420 bridge. Disabling a ServicesLUN
for a particular Fibre port will destroy
the map to the FC420 bridge for that
port.
Enables/disables SpeedWrite
functionality to any SCSI device
currently mapped to the FC420 bridge.
To enable/disable SpeedWrite for a
particular device, specify the SCSI bus
(sb), the target (st), and the LUN (sl).
Specify “all” to enable/disable this
option for all currently mapped SCSI
devices.
8 set serviceslun [fp] [[fl] |
disabled]
get serviceslun <[fp]>
set speedwrite [sb st sl | all]
[enabled | disabled]
get speedwrite [sb st sl | all]
SpeedWriteDefault
T emperature
VerboseMode
VirtualDriveResponse
Enables/disables SpeedWrite
functionality as a default condition
when SCSI devices are mapped to the
FC420 bridge.
Reports the unit temperature in
degrees C.
Sets the Command Line Interface to
display extended information about a
parameter when the
help command is
given. When verbose mode is enabled,
parameter values are generally
preceded by labels in responses to the
get commands. Only the parameter
value is output when verbose mode is
disabled.
Enables/disables the virtual drive
response feature, which allows the
FC420 bridge to provide proxy
responses to SCSI INQUIRY and TEST
UNIT READY commands in the event of
a SCSI device selection time-out or busy
event.
disabled set speedwritedefault [enabled
| disabled]
get speedwritedefault
get temperature
enabled set verbose [enabled |
disabled]
get verbose
disabled set virtualdriveresponse
[enabled | disabled]
get virtualdriveresponse
Prism FC420 Services Software Commands 25
Page 26
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Command Description Default Syntax
XCDevices
XCError
XCStatus
Displays information about the devices
used in a specified Extended Copy
command. The
obtained using the
cmdnumber variable is
xcstatus command.
This command returns the following
information: device type, vendor ID,
product ID, serial number, and data
direction.
Retrieves any SCSI sense data returned
by an Extended Copy command as the
result of an error.The
is obtained using the
cmdnumber variable
xcstatus command.
This command returns the following
information: SCSI status, sense key,
ASC, and ASCQ. If a device involved in
the command’s data transfer also
returned sense data, the device ID (serial
number) along with sense data for the
device will be displayed.
Allows the user to poll for the status of
Extended Copy commands issued to the
FC420 bridge. Each Extended Copy
command is identified with a unique
number. This number (called
is used when invoking the
xcerror commands.
cmdnumber)
xcdevices and
get xcdevices [cmdnumber]
get xcerror [cmdnumber]
get xcstatus
Zmodem
(Immediate)
Transfers a firmware image or NVRAM
parameter file to or from the bridge
using ZMODEM file transfer protocol.
26 Prism FC420 Services Software Commands
zmodem [send [filename] |
receive]
Page 27

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Prism FC420 Blink Codes 0
During normal library operation, the Ready/Fault LED on the FC420 bridge
is lit, indicating that the bridge is ready to be used.
Figure 8 Primary
Electronics Module with
FC420 Bridge Installed
Ready/Fault LED
If there is an error, the Ready/Fault LED blinks in the following pattern:
• Long pause
• One or more blinks (Count these blinks; this is the first blink digit.)
• Short pause
• One or more blinks (Count these blinks; this is the second blink digit.)
Table 3
provides meanings for these blink codes, listed by first and second
blink digit.
Prism FC420 Blink Codes 27
Page 28

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
Table 3 Blink Code
Summary
First
Blink
Digit
11Fatal SCSI FW POST
Second
Blink
Digit
Error
Code
Classification Failure
failure
Recommended
Action Comments
Reboot board and
record error log
1 2 Fatal CPU POST failure Reboot board and
record error log
1 3 Fatal RAM POST failure Reboot board and
record error log
2 1 Fatal SCSI chip POST
failure
Reboot board and
record error log
2 2 Fatal SRAM POST failure Reboot board and
record error log
23Fatal Extended SRAM
failure
33Fatal DRAM POST
failure
34Fatal Extended DRAM
failure
4 1 Fatal Fibre Channel
controller
Reboot board and
record error log
Reboot board and
record error log
Reboot board and
record error log
Reboot board and
record error log
4 2 Fatal/Non-
fatal/Critical
Fibre Channel
controller chip
failure
4 3 Fatal Fibre Channel
controller chip
initialization failure
5 2 Fatal SCSI controller chip
1 failure
Reboot board and
record error log
Reboot board and
record error log
Reboot board and
record error log
Non-fatal in the
case of port failover
- if applicable (error
code BC)
Critical internal
software incident,
not a hardware
defect (error code
B3)
Fatal internal
software incident,
not a hardware
defect (error code
B4)
28 Prism FC420 Blink Codes
Page 29
Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
First
Blink
Digit
6 2 Fatal SCSI controller chip
6 6 Critical Temperature out of
Second
Blink
Digit
Error
Code
Classification Failure
2 failure
range
Recommended
Action Comments
Reboot board and
record error log
Reboot board Board out of
temperature range
Correct operating
temperature
(cooling, etc.) prior
to reboot.
7 1 Fatal EOS panic code Reboot board Internal software
incident, not a
hardware defect
7 2 Fatal Fibre Channel
Reboot board
transceiver failure
8 1 Fatal Out of memory
error
Reboot board Internal software
incident, not a
hardware defect
8 3 Fatal NVRAM checksum
failure
Reboot board and
check error log
Internal software
incident, not a
hardware defect
(error code A4)
8 4 Fatal MB system error Reboot board and
check error log
Internal software
incident, not a
hardware defect
(error code 93)
Internal software
incident, not a
hardware defect,
reflash board (error
codes 97, 99, and
9A)
Internal software
incidents, not
hardware defects
(error codes 9B, 9C,
9E, 9F, A0, and A1)
Prism FC420 Blink Codes 29
Page 30

Prism FC420 Bridge Option User’s Guide
Document 6473031-04, Ver. 4, Rel. 0
September 2003
First
Blink
Digit
Second
Blink
Digit
Error
Code
Classification Failure
Recommended
Action Comments
8 5 Fatal Ethernet failure Reboot board and
check error log
8 6 Fatal Parity failure Reboot board and
check error log
8 7 Fatal ECC failure Reboot board and
check error log
8 9 Critical Reboot, perform
wzinfo
command at
reboot and return
information to
Quantum
9 3 Non-fatal SES identification
failure
Reboot board and
check error log
Internal software
incident, not a
hardware defect
(error code 98)
Internal software
incident, not a
hardware defect
(error code B5)
Internal SW
hd
incident, not a
hardware defect
9 4 Fatal SES fault requested Reboot board and
check error log
Fault requested via
SES
30 Prism FC420 Blink Codes
 Loading...
Loading...