Page 1

Modicon
TSX Momentum
Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
User Guide
890 USE 155 00 Version 1.0
Page 2

Page 3

174 CEV 300 10
Modicon TSX Momentum
Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
User Guide
890 USE 155 00
31001624
04/99
Breite: 185 mm
Höhe: 230 mm
Breite: 178 mm
Höhe: 216 mm
Page 4

Page 5

Preface
Data, Illustrations, Alterations
Data and illustrations are not binding. We reserve the right to alter products in
line with our policy of continuous product development.
Trademarks
All terms used in this publication to denote Schneider Automation products are
trademarks of Schneider Automation Incorporated.
All other terms used in this publication to denote products may be registered
trademarks and/or trademarks of the corresponding corporations.
Microsoft and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation,
Windows is a brand name of Microsoft Corporation in the USA and other
countries.
IBM is a registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
Copyright
All rights are reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including
copying, processing or by online file transfer, without permission in writing by
Schneider Automation Incorporated. You are not authorized to translate this
document into any other language.
1999 Schneider Automation Incorporated. All rights reserved.
v
Page 6

Page 7

Contents
Contents
Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
174 CEV 300 10 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1 Introducing the Modbus to Ethernet Bridge 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1.1 Bridge Applications 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1.2 Overview: Installation and Configuration 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2 Mapping Modbus and IP Addresses 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2.1 Mapping for a Modbus Master 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2.2 Mapping for a Modbus Slave 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3 Front Panel Layout 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4 Specifications 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installing the Bridge Hardware 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1 Mounting the Bridge on the DIN Rail 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.1 Before You Install the Bridge 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.2 Mounting the Bridge 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2 Connecting the Power Wiring 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 Connecting the Serial Cable (RJ45 Port) 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.4 Compatible Modbus Devices and Cables 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.5 Modbus Cable Pinouts 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.6 Connecting the Serial Cable (Wiring Terminals) 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.7 Setting the Serial Port Switch 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.8 Connecting the Ethernet Cable 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
890–USE–155–00
Configuring the Bridge 29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 Before You Start 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1.1 Configuration Overview 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1.2 Safety 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 Connecting by the RS–232 Port 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Connecting by Telnet (IP Address Not Assigned) 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.4 Connecting by Telnet (IP Address Assigned) 33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.5 Using the Configuration Menu 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.5.1 Configuration Menu 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.5.2 Modbus Master Device: Additional Menu Items 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.5.3 Configuration Options: 1 ... 5 35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.5.4 Viewing and Changing Configuration Parameters 35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.5.5 Commands: Default settings, Save, Quit without save 35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
vii
Breite: 178 mm
Page 8

Contents
3.6 Option 1: Network/IP Settings 36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.7 Option 2: Serial and Mode Settings 38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8 Option 3: Modem Control Settings 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.9 Option 4: Advanced Modbus Protocol Settings 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.10 Option 5: Unit ID to IP Address Mapping Table 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.10.1 How the Address Mapping Works 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.10.2 Example: Address Mapping 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.10.3 Entering New Address Mapping 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.10.4 Exiting the Mapping Menu 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Using Panel Software 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1 Using Concept or Modsoft 46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.1 Software Versions 46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.2 Modbus Slave Address 46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2 Using Other Software 47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2.1 Intellution FIX MMI 47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2.2 WinTech Modscan 47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2.3 Worderware MMI 47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Glossary 49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
viii
890–USE–155–00
Page 9

Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
174 CEV 300 10
H Introducing the Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
H Mapping Modbus and IP Addresses
H Front Panel Layout
H Specifications
1
9
Page 10
Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
1.1 Introducing the Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
1.1.1 Bridge Applications
The Modicon Modbus to Ethernet Bridge provides a means for transacting messages
between Ethernet TCP/IP devices and Modbus serial devices. It supports up to eight
concurrent transactions between Modbus Master and Slave devices, handling the
conversion of TCP/IP and Modbus RTU/ASCII protocols transparently to the user
application.
Ethernet nodes using TCP/IP can function as Modbus Masters, originating messages
to the Bridge for delivery to Modbus Slave devices connected to the Bridge’s Modbus
port. The Bridge forwards the messages to the Slave devices using Modbus RTU or
ASCII protocol and returns their responses to the Master.
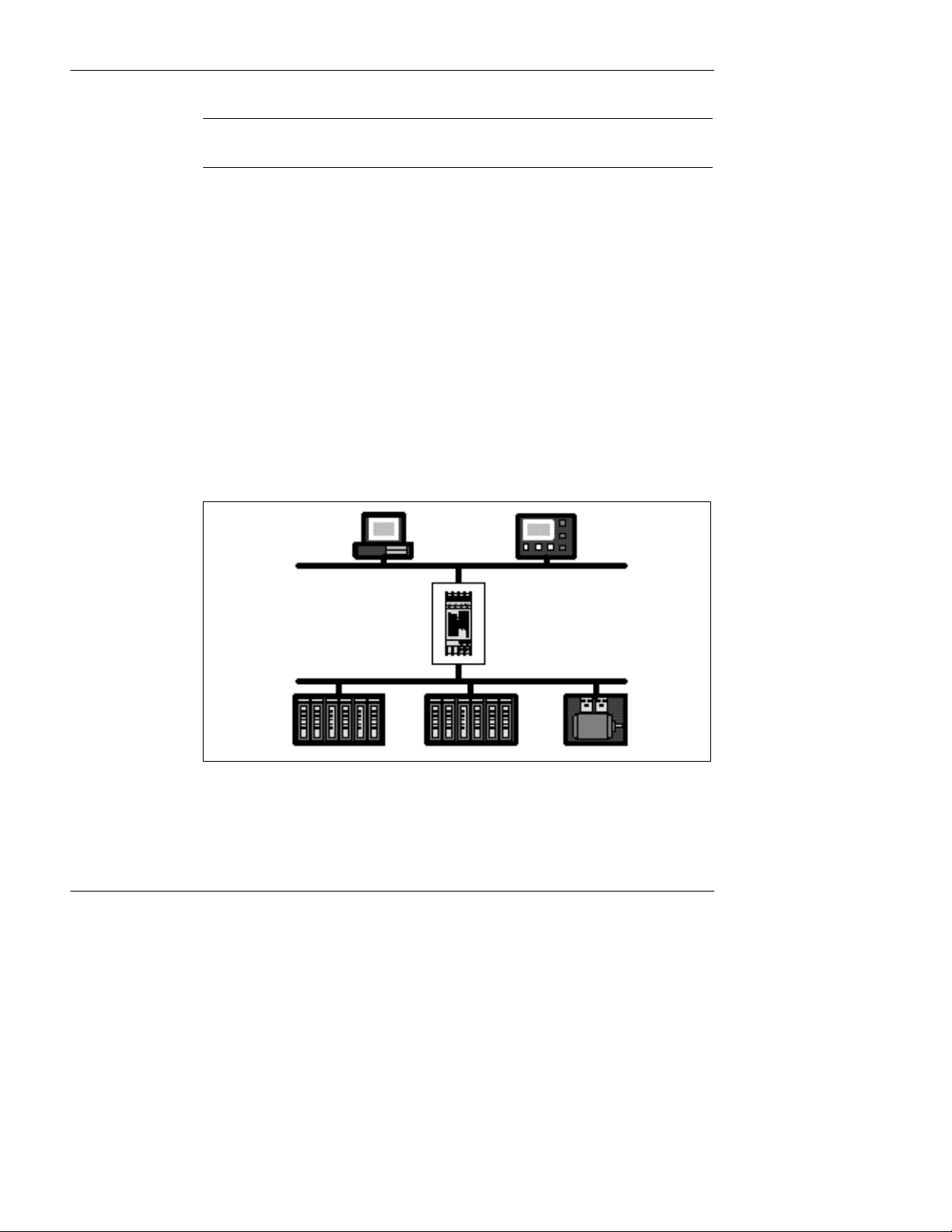
Figure 1 shows a typical application in which a Bridge connects two Modbus Masters
on Ethernet to several Modbus Slave serial devices.
Figure 1 Bridging Between Ethernet and Modbus
10
Ethernet
Bridge
174 CEV 300 10
Modbus
The bridge also allows multiple Modbus networks to be linked together across an
Ethernet connection. Multiple Bridges can furnish an Ethernet link between widely
separated Modbus networks. This extends the message path beyond the cable
lengths allowed for serial connections, and allows a Master on any Modbus network to
access Slave devices on another network.
Page 11
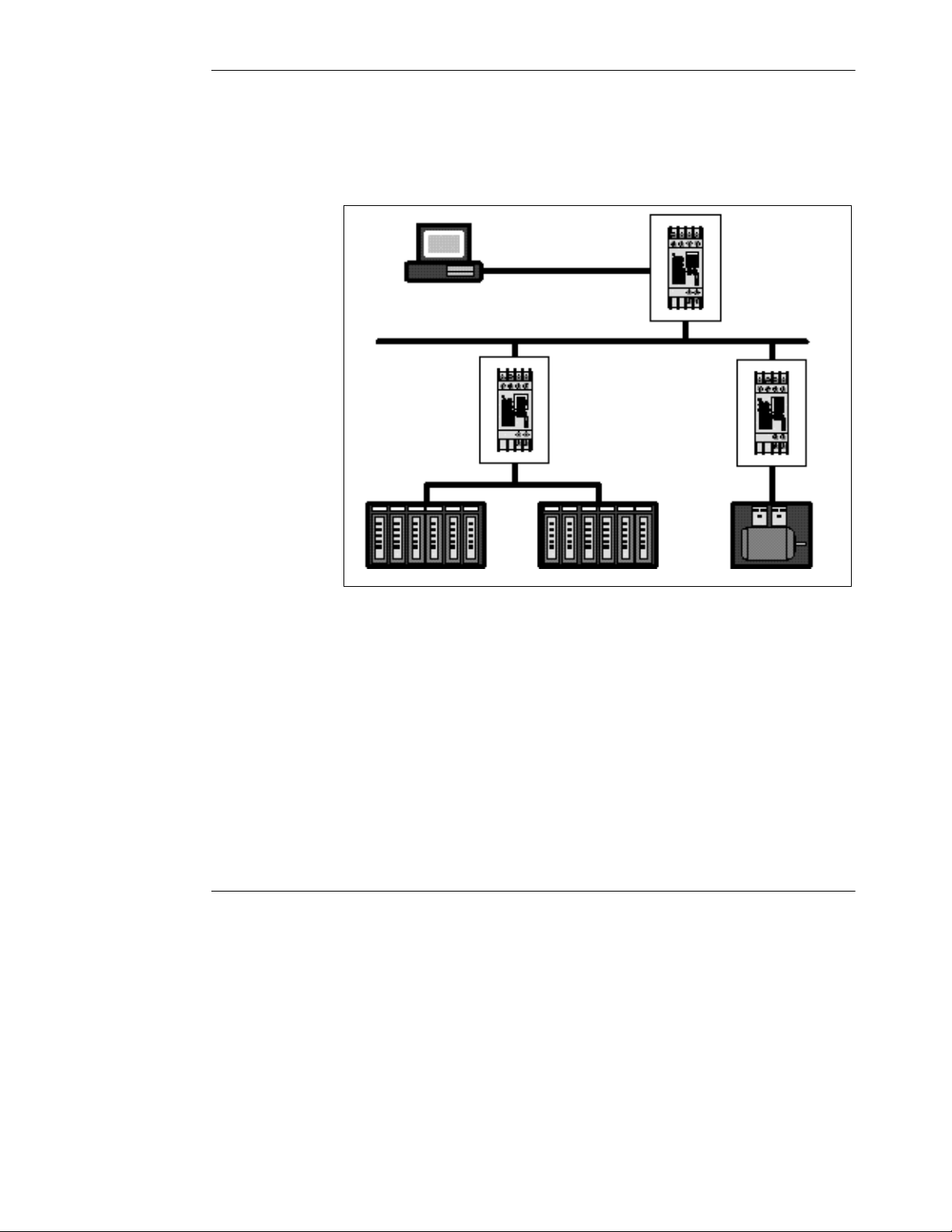
Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
Figure 2 shows a typical application in which three Bridges join Modbus networks
through a common Ethernet link.
Figure 2 Bridging Between Multiple Modbus Networks
Modbus
Ethernet
Bridges (3 units)
174 CEV 300 10
Modbus
1.1.2 Overview: Installation and Configuration
The Bridge is designed for easy ‘snap’ mounting on a standard DIN rail.
Its front panel has connectors for power, ground, Ethernet and Modbus cables. It has
a switch for selecting either an RS–232 or RS–422/485 interface for the Modbus port.
Indicators show the status of communication at the Ethernet and Modbus ports.
The Bridge contains a configuraton utility program stored in its non–volatile memory .
With this utility you can assign the Bridge’s Ethernet and Modbus parameters, using an
ASCII terminal at the serial port or a Telnet connection over Ethernet.
The Bridge contains a factory–assigned MAC address that is derived from the serial
number printed on the Bridge’s label. This allows you to establish an Ethernet
connection to the Bridge to assign its IP address and the other parameters for your
application.
Modbus
11
Page 12

Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
1.2 Mapping Modbus and IP Addresses
The Bridge maps messages between Modbus and IP addresses according to the type
of device you have configured at its Modbus port.
1.2.1
1.2.2
Mapping for a Modbus Master
When you configure a Modbus Master device at the Bridge’s serial port, you can
assign up to eight entries into an internal mapping table that is maintained in the
Bridge’s memory. You enter your intended mapping into the table during your
configuration of the Bridge.
Each table entry maps a single Modbus address, or a range of addresses, to a
destination IP address.
When the Bridge receives a message from the Master, it searches the mapping table
for an entry matching the Modbus address in the message. If one is found, the Bridge
sends the message to the IP address for that entry . If a matching entry is not found,
the Bridge returns an exception response to the Master application.
Note that the original Modbus address is retained in the message transmitted to the IP
destination. If the remote IP node is another Bridge, the message’s Modbus address
can be used to identify a Slave device at that Bridge’s serial port.
Mapping for a Modbus Slave
When you configure a Modbus Slave device or network with multiple Slaves at the
Bridge’s serial port, you have two options for routing messages to a Slave destination.
You assign your choice during your configuration of the Bridge.
Your options are: Message address routing; or, Fixed address routing.
12
You can specify that the Bridge must route each message to the Slave device that is
identified in the Modbus address field of the message. This allows you to address any
Slave device in a network of up to 247 devices at the Bridge’s Modbus port.
You can specify that the Bridge must route all messages to one fixed Slave address
that you define in the Bridge’s configuration. With this option the Modbus address field
is ignored, and each message is routed to that fixed Slave address only . This limits
addressing to a single device at the port.
Page 13

Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
Figure 3 shows an example of message address mapping between a Modbus Master
and a Modbus Slave using two Bridges with an Ethernet link.
Figure 3 Mapping Modbus and IP Addresses
Modbus
Master
Modbus message to
Slave address 10
Bridge
A
Ethernet
192.168.001.024
Bridge
Modbus – IP Address
Mapping Entry:
010 : 192.168.001.024
B
Modbus
Slave(s)
These are the events in the message routing:
H The Modbus Master sends its message containing address 10 decimal to
Bridge A.
H You have set an entry in the mapping table in Bridge A. Your entry specifies that
messages with address 10 are to be mapped to IP address 192.168.001.024.
H Bridge B has that IP address and receives the message.
H Depending on the option you set in Bridge B, the message is routed either to
the Modbus Slave device at address 10 as specified in the message, or to a
fixed Slave address in the range 1 ... 247.
Bridge routes message to Slave
according to user–defined setup:
Message Slave Address (10)
or
Fixed Slave Address (1 ... 247)
13
Page 14

Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
1.3 Front Panel Layout
Figure 4 Front Panel Layout
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9
14
MODBUS
10 11
15
12 13
16 17
18
ETHERNET
19 20
21 22
14
Page 15
Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
Table 1 Front Panel Components (See Figure 4)
Item
5, 6, 7 Wire terminal NC No connection
Component Name Purpose
1 Wire terminal RxD or Rx – Modbus signal:
2 Wire terminal CTS or Rx + Modbus signal:
3 Wire terminal RTS or Tx + Modbus signal:
4 Wire terminal TxD or Tx – Modbus signal:
8 Wire terminal GND Modbus signal ground
9 Reset switch RST Push to reset and initialize Bridge
10 LED (Red) Fault or
Configuration
11 LED (Green) Ready ON: Bridge is ready for communication
12 LED (Yellow) Active Ethernet Flashing: Indicates activity at Bridge’s
13 LED (Green) Link Good ON: Bridge has good connection at
14 Connector (RJ45) Ethernet port RJ45 connector for Ethernet 10BaseT
15 Connector (RJ45) Modbus port RJ45 connector for Modbus RS–232 or
16 LED (Yellow) Modbus Tx Flashing: Indicates transmission or
17 LED (Yellow) Modbus Rx Flashing: Indicates reception at Modbus
18 Switch Modbus interface
selection
19 Wire terminal DC + Operating power, positive
20 Wire terminal Ground Earth ground
21 Wire terminal DC – Operating power , negative
22 Wire terminal Ground Earth ground
RS–232: RxD (Receive Data)
RS–422.485: RxD– (Receive Data –)
RS–232: CTS (Clear to Send)
RS–422/485: RxD+ (Receive Data +)
RS–232: RTS (Request to Send)
RS–422/485: TxD– (Transmit Data +)
RS–232: TxD (Transmit Data)
RS–422/485: TxD– (Transmit Data –)
ON: Fault in Bridge communication
(or) Bridge is in Configuration Menu
on both ports
Ethernet port
Ethernet port
cable
RS–485 cable
upload at Modbus port
port
UP: Modbus port is RS–232
DOWN: Modbus port is RS–422/485
15
Page 16
Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
1.4 Specifications
Table 2 Power
Parameter
Operating Power, Nominal 12 or 24 V dc
Operating Power Range 9 ... 30 V dc
Maximum Power Drain 3 W
Connection Screw terminals
Fuse External, supplied by customer.
Grounding Screw terminals provided for power ground
Table 3 Environmental
Parameter
T emperature, Operating IEC 68–2–14
Humidity, Operating IEC 68–2–3 20 ... 90% RH, non–condensing
Table 4 Ethernet Interface
Parameter
Protocol Ethernet v2 encapsulation
Connector RJ45 connector for 10baseT cable
Specification
Fuse value according to supply voltage
(see Maximum Power Drain)
and safety (Earth) ground
Reference Limits
0...60_ C ambient
Specification
TCP/IP Version 4
16
Table 5 Serial Interface
Parameter
Modbus Protocol RTU or ASCII
Serial Protocol Switch selectable, RS–232 or RS–485
Baud Rate 300 ... 38400 +/– 2%
Connector RJ45 connector, screw terminals
Specification
Supports RS–232 RTS/CTS handshaking
RS–485 setting supports RS–422 devices
Supports 2–wire and 4–wire RS–485
Supports up to 16 RS–485 devices
RJ45 port connects to Modicon M1, Compact, 984 Slot Mount
controllers by direct cable. Cable adapters and adapter kits
are available for other products.
Page 17

Modbus to Ethernet Bridge
Table 6 Packaging
Parameter
Dimensions 35 x 95 x 60 mm (1.4 x 3.7 x 2.4 in)
Enclosure Material High–impact plastic
Weight, Product 0.5 kg (1.0 lb)
Weight, Shipping 0.9 kg (2.0 lb)
Mounting Method DIN rail: DIN EN S0 022 (35 mm)
Table 7 Agency Approval
Parameter
UL, CSA, CE Approved
FM Pending
Description
Specification
17
Page 18

Page 19

Installing the Bridge Hardware
H Mounting the Bridge on the DIN Rail
H Connecting the Power Wiring
H Connecting the Serial Cable (RJ45 Port)
H Compatible Modbus Devices and Cables
H Modbus Cable Pinouts
H Connecting the Serial Cable (Wiring Terminals)
H Setting the Serial Port Switch
H Connecting the Ethernet Cable
2
19
Page 20

Installing the Bridge Hardware
2.1 Mounting the Bridge on the DIN Rail
2.1.1 Before You Install the Bridge
The Bridge has an Ethernet MAC address printed on the label on its side panel. The
address is required for your Ethernet network administrator to configure the Bridge.
Before you install the Bridge on the DIN rail, write down the MAC address and give it
to your network administrator. The label may not be visible after you install the Bridge.
Warning
COMMUNICATION DISRUPTION HAZARD Connecting any device to an active
Ethernet network can disrupt communication on the network. Before you
connect the Bridge to your network, and before you apply power to the Bridge,
heed the steps in Chapter 3 for configuring the Bridge in your application.
Failure to observe this precaution can result in injury or equipment damage.
2.1.2
Mounting the Bridge
The Bridge is designed for mounting on a standard DIN rail. Figure 5 shows how to
mount the Bridge
1. Note the slot on the Bridge’s rear panel. Position the top edge of the slot over the
top edge of the DIN rail.
2. Snap the Bridge into place on the lower edge of the rail.
Figure 5 Mounting the Bridge on the DIN Rail
1
2
Mounting Completed
20
Page 21

2.2 Connecting the Power Wiring
Figure 6 shows the connections for operating power and ground.
Operating power must be fused externally to the Bridge. The Bridge draws 3W
maximum (9 ... 30 V dc). Select a fuse value according to the supply voltage.
Figure 6 Connecting the Power Wiring
Installing the Bridge Hardware
9 ... 30 V DC
Fused
Ground
Frame
Safety
Ground
(Earth)
21
Page 22

Installing the Bridge Hardware
2.3 Connecting the Serial Cable (RJ45 Port)
Figure 7 shows serial cable connections for several Modicon CPUs for operation as
Modbus Master or Slave devices. The figure also shows a typical connection to a
standard PC 9–pin serial port for setting up the Bridge configuration.
Table 8 lists other compatible devices and cables.
Figure 7 Connecting the Serial Cable (RJ45 Port)
Modbus Port (RJ45)
RJ45 to RJ45 Cables
110 XCA 282 01 (3 ft / 1 m)
110 XCA 282 02 (10 ft / 3 m)
110 XCA 282 03 (20 ft / 6 m)
RJ45 to DB9 Adapters
1
110 XCA 203 01
(Kit)
2
110 XCA 203 00
(Pre–wired)
E984–26x/27x/28x
110 CPU 3x/4x/5x/6x 984–38x, 48x, 68x, 78x
TSX Momentum M1
NULL
Modem
2
MF
A984,
E984–24x/25x
1
1
PC
with
Serial Port
22
Page 23

Installing the Bridge Hardware
2.4 Compatible Modbus Devices and Cables
The Bridge connects directly by RJ45 cable to various products shown in Figure 7.
Table 8 below lists other Modbus devices and their cable connections to the Bridge.
Connections are RS–232 unless indicated otherwise.
Cable pinout references are to the diagrams in Figure 8 on page 24.
Table 8 Compatible Modbus Devices and Cables
Device
Part Number
MM–PM10–2xx PanelMate Plus 1000 (RS232) A
MM–PM10–2xx PanelMate Plus 1000 (RS422) B
AS–J478–000 Modbus Modem, Fixed Modem Control C
AS–J478–000 Modbus Modem, Variable Modem Control D
AS–J347–001 184/384 Controller Modbus Interface E
AS–J375–000 Micro 84 Controller Modbus Interface E
AS–P190–xxx P190 Programming Panel E
AS–884A–xxx 884 Controller E
AS–984x–xxx 984A, B, X Controller E
– – PC Serial Port, 9–Pin F
AS–P892–000 ASCII/RIO Interface G
140 CPU 424 xx Quantum Controller, 486 G
140 CPU 534 xx Quantum Controller, 586 G
PC–0984–xxx 984 Controller, 38x/48x/68x/78x Slot Mount G
PC–A984–xxx 984 Controller , Compact G
PC–E984–24x/25x 984 Controller, Compact G
PC–E984–455 984 Controller, 484 Replacement G
PC–M984–xxx Micro–984 Controller G
NW–BM85xxxx BM85 Bridge Multiplexer G
– – Generic Modbus Serial Device, 9–Pin G
110 VPU 192 00 Programmer, Handheld H
AS–A584–xxx 584A, L, M Controller See 584 Note
TSX SCx TSX Controllers, Modbus Interface See TSX Note
Device
Description
Cable Pinout
(Figure 8)
584 Note
Use cable AS–W192–XXX with Adapter 1 10 XCA 204 02, pinouts in Figure 8 cable E.
TSX Note
TSX Controller products offer multiple options for cable connection to the Bridge.
Refer to your product guidebook for more information.
23
Page 24

Installing the Bridge Hardware
2.5 Modbus Cable Pinouts
References in this figure are to the devices listed in Table 8 on page 23.
Figure 8 Modbus Cable Pinouts
A
Adapter Kit: 110 XCA 203 01
DB9M Wire RJ45
2 Red 4
3 Black 3
5 Green 5
Shield White 8
Adapter Kit: 110 XCA 203 01
B
DB9M Wire RJ45
1 Black 3
4 Red 4
5 Green 5
6 Yellow 6
9 Brown 7
Shield White 8
Adapter Kit: 110 XCA 204 01
C
DB25M Wire RJ45
1 White 8
2 Red 4
3 Black 3
7 Green 5
4
6
20
Adapter Kit: 110 XCA 204
D
DB25M Wire RJ45
2 Red 4
3 Black 3
6 Blue 1
7 Green 5
20 Orange 2
5 Yellow 6
4 Brown 7
1 White 8
01
Adapter Kit: 110 XCA 204 01
E
DB25M Wire RJ45
3 Red 4
2 Black 3
20 Blue 1
7 Green 5
6 Orange 2
4 Yellow 6
5 Brown 7
1 White 8
Adapter Kit: 110 XCA 203 02
F
DB9F Wire RJ45
2 Red 4
3 Black 3
4
6 Orange 2
5 Green 5
76
87
Shield White 8
Adapter Kit: 110 XCA 203 01
G
DB9M Wire RJ45
2 Red 4
3 Black 3
5 Green 5
6 Orange 2
7 Yellow 6
8 Brown 7
Shield White 8
H
Adapter: None
RJ45 (Prog) RJ45 (Bridge)
12
21
34
43
55
66
77
88
24
Page 25

Installing the Bridge Hardware
Figure 9 shows the layout of DB9–RJ45 and DB25–RJ45 Adapter Kits available from
Schneider Automation. Each kit contains three jumper wires and a pin insertion tool.
Follow the pinout diagrams in Figure 8 for assembling the adapter for your product.
Figure 9 DB to RJ45 Adapter Kits
DB9M (110 XCA 203 01)
Pin 1
Pin 1
DB9F (110 XCA 203 02)
DB25M (110 XCA 204 01)
Pin 1
Pin 1
DB25F (110 XCA 204 02)
Pin 1
Pin 1
25
Page 26

Installing the Bridge Hardware
2.6 Connecting the Serial Cable (Wiring Terminals)
Figure 10 shows the connection for serial cables at the Bridge’s wiring terminals.
Figure 10 Connecting the Serial Cable (Wiring Terminals)
RxD CTS RTS TxD
Signal
Ground
26
Terminating
Resistor
1/8 W
120 Ω
R
Signal
Ground
RRR
RS–485
2–Wire
RS–232
RxD– RxD+ TxD+TxD–Data–Data+
RS–485 / RS–422
4–Wire
Signal
Ground
Page 27

2.7 Setting the Serial Port Switch
Figure 1 1 shows the front panel switch for setting the Bridge’s serial port interface.
Before you place the Bridge into service, set the switch for the type of interface used in
your application:
H UP: RS–232 interface.
H DOWN: RS–422 or RS–485 interface.
Figure 11 Setting the Serial Port Switch
Installing the Bridge Hardware
Serial Port Switch
UP: RS–232
DOWN: RS–422 or RS–485
Warning
COMMUNICATION DISRUPTION HAZARD The serial port switch is a hardware
function. It is not sensed by the Bridge’s firmware. Changing the switch
setting while the Bridge is operating can disrupt communication on the
network. Do not change the switch setting unless you have first verified that it
will be safe for your application. Failure to observe this precaution can result
in injury or equipment damage.
27
Page 28

Installing the Bridge Hardware
2.8 Connecting the Ethernet Cable
Figure 12 shows the RJ45 port connection for the 10baseT Ethernet cable.
Figure 12 Connecting the Ethernet Cable
Ethernet Port (RJ45)
Warning
COMMUNICATION DISRUPTION HAZARD Connecting any device to an active
Ethernet network can disrupt communication on the network. Before you
connect the Bridge to your network, and before you apply power to the Bridge,
heed the steps in Chapter 3 for configuring the Bridge in your application.
Failure to observe this precaution can result in injury or equipment damage.
28
Page 29

Configuring the Bridge
H Before You Start
H Connecting by the RS–232 Port
H Connecting by Telnet (IP Address Not Assigned)
H Connecting by Telnet (IP Address Assigned)
H Using the Configuration Menu
H Option 1: Network/IP Settings
H Option 2: Serial and Mode Settings
H Option 3: Modem Control Settings
H Option 4: Advanced Modbus Protocol Settings
H Option 5: Unit_ID to IP Address Mapping Table
3
29
Page 30

Configuring the Bridge
3.1 Before You Start
3.1.1 Configuration Overview
Your Bridge must be configured to match your system application. Before you start to
configure the Bridge, get the Bridge’s Ethernet and serial port parameters from your
network administrator.
Here is your check list for obtaining the configuration information:
H Ethernet IP address.
H Ethernet Gateway address, if applicable to your Bridge’s network.
H Serial port interface: RS–232, RS–422, RS–485.
H Serial port communication: Baud rate, Data bits, Parity mode, Stop bits.
H Serial port modem controls: RTS/CTS timing values.
H Serial port device: Modbus Master or Modbus Slave.
H Modbus Protocol: RTU or ASCII.
H Modbus Timeout values: Character timeout, Message timeout.
H Modbus Slave only: Address source from Unit_ID header, or Fixed address.
H Modbus Slave only: Allowing broadcasts to serial port: Enable or Disable.
H Modbus Master only: Mapping of Modbus Slave addresses to IP addresses.
30
3.1.2
Safety
Warning
COMMUNICATION DISRUPTION HAZARD When you view or change the
configuration of a running Bridge, you will be restarting it on the network.
This will disrupt communication with the Bridge. Ensure that this action will
not cause any undesirable effect on your application. Failure to observe this
precaution can result in injury or equipment damage.
Warning
DUPLICATE ADDRESS HAZARD Having two or more devices with the same IP
address can cause unpredictable operation of your network. Ensure that you
will be assigning a unique IP address to the Bridge. Failure to observe this
precaution can result in injury or equipment damage.
Page 31

3.2 Connecting by the RS–232 Port
To configure the Bridge at its local RS–232 port, use a serial terminal emulation
program and a modem cable. See Figure 7 for a connection example.
Regardless of any serial parameters currently set into the Bridge for a user application,
it will always use the following parameters for setup: 9600 baud, 8 data bits, No parity ,
1 Stop bit (9600,8,N,1). Set your emulator to these parameters.
Figure 13 Example: RS–232 Serial Terminal Emulator Properties
Configuring the Bridge
Force the Bridge into its Configuration mode as follows:
H Ensure the emulator is connected to the Bridge’s serial port and ready.
H Hold down the ‘X’ key on your emulator keyboard. While holding the key down,
initialize the Bridge by cycling its power or by pressing its Reset button.
The Bridge will enter its configuration mode, and you will see this opening screen:
Schneider Automation, Inc. – Modbus Bridge (174 CEV 300 10)
Serial Number 101–161 Software Version V01.00 (990402)
Press Enter to go into Setup Mode, wait to close
At this screen, press <Enter> to go to the Configuration Menu (see Section 3.5).
31
Page 32

Configuring the Bridge
3.3 Connecting by Telnet (IP Address Not Assigned)
If the Bridge does not yet have an IP address stored in its memory , you can establish
an initial connection using its MAC address. This will allow you to access the Bridge’s
Configuration Menu, assign an IP address, and make it persistent in the Bridge.
If you are not sure about whether your Bridge has a stored IP address, you must
connect at its serial port and access its Configuration Menu. Section 3.2 describes
how to connect to the serial port.
T elnet Host Requirement
In order to use Telnet to set an initial IP address for the Bridge, your Telnet host must
be on the same Ethernet subnetwork as the Bridge, both physically and in its IP range.
Otherwise the configuration will not work.
Step 1 Get the Bridge’s MAC Address. The Bridge’s MAC address is printed on the label
on the Bridge’s side panel.
Example: MAC address: 00 20 4A 01 65 A1.
Step 2 Issue an “arp” Command to the Bridge. Open a Console or DOS window. Issue
an arp command to the Bridge with this syntax:
32
Syntax: arp –s <IP_address> <MAC_address>
Example (UNIX): arp –s 192.168.1.23 00:20:4A:01:65:A1
Example (DOS): arp –s 192.168.1.23 00–20–4A–01–65–A1
Step 3 Connect by Telnet to Port 1. Open a Telnet connection to the IP address you
assigned in Step 2, using port 1. This connection will fail, but the Bridge will change
its IP address to the one in this Telnet connection. This will allow you to make your
final connection for configuring the Bridge.
Step 4 Connect by Telnet to Port 9999. Open a new a Telnet connection to the IP address
using port 9999. This connection will succeed. You should now see the Bridge’s
opening screen:
Schneider Automation, Inc. – Modbus Bridge (174 CEV 300 10)
Serial Number 101–161 Software Version V01.00 (990402)
Press Enter to go into Setup Mode, wait to close
At this screen, press <Enter> to go to the Configuration Menu (see Section 3.5).
Page 33

Configuring the Bridge
3.4 Connecting by Telnet (IP Address Assigned)
If the Bridge already has an IP address stored in its memory , and you know that
address, you can establish a Telnet connection to the Bridge using port 9999.
If you do not know the IP address currently stored in the Bridge, you can find that
address by connecting to the Bridge’s serial port and accessing its Configuration
Menu. Section 3.2 describes how to connect to the serial port.
If you want to verify the existence of an Ethernet device at a known IP address, you
can use the PING utility. Refer to your Ethernet documents for a description of PING.
T elnet Host Requirement
In order to use Telnet to set an initial IP address for the Bridge, your Telnet host must
be on the same Ethernet subnetwork as the Bridge, both physically and in its IP range.
Otherwise the configuration will not work.
Figure 14 Example: Telnet Connection
When the connection is established, you should see the Bridge’s opening screen:
Schneider Automation, Inc. – Modbus Bridge (174 CEV 300 10)
Serial Number 101–161 Software Version V01.00 (990402)
Press Enter to go into Setup Mode, wait to close
At this screen, press <Enter> to go to the Configuration Menu (see Section 3.5).
33
Page 34

Configuring the Bridge
3.5 Using the Configuration Menu
When the Bridge enters its configuration mode it displays its opening screen:
Schneider Automation, Inc. – Modbus Bridge (174 CEV 300 10)
Serial Number 101–161 Software Version V01.00 (990402)
Press Enter to go into Setup Mode, wait to close
At this screen, press <Enter> to see the Configuration Menu.
3.5.1
Configuration Menu
The Configuration Menu shows the Bridge’s current settings. Here is an example:
Modbus Bridge Firmware Setup, Schneider Automation, Inc.
1) Network/IP Settings:
IP Address ................... 192.168.1.23
Default Gateway .............. 192.168.1.30
Netmask ...................... 255.255.255.000
2) Serial & Mode Settings:
Protocol ..................... Modbus/RTU, Slave(s) attached
Serial Interface ............. 19200,8,E,1,RS232
3) Modem Control Settings:
RTS Output ................... Fixed High/Active
4) Advanced Modbus Protocol Settings:
Slave Addr/Unit ID Source .... Modbus/TCP header
Modbus Serial Broadcasts ..... Disabled
Character, Message Timeout ... 00050 ms, 05000 ms
Commands: D)efault settings, S)ave, Q)uit without save
Select Command or Parameter (1...4) to change: __
3.5.2 Modbus Master Device: Additional Menu Items
If the serial port has already been configured for a Modbus Master device, menu item
4 will omit references to a Slave device, showing only the following:
4) Advanced Modbus Protocol Settings:
Character, Message Timeout ... 00100 ms, 05000 ms
34
Menu item 5 will show current mapping between Modbus addresses and IP addresses.
5) Unit ID –> IP Address Table: (followed by the current mapping table).
Page 35

3.5.3 Configuration Options: 1 ... 5
These are your configuration options. Each option is described in detail in the
following sections of this book:
1) Network/IP Settings: See Section 3.6.
H
2) Serial & Mode Settings: See Section 3.7.
H
3) Modem Control Settings: See Section 3.8.
H
H
4) Advanced Modbus Protocol Settings: See Section 3.9.
5) Unit ID –> IP Address Table: See Section 3.10.
H
Configuring the Bridge
3.5.4
3.5.5
Viewing and Changing Configuration Parameters
When you view the Bridge’s configuration parameters, you can retain their current
values or change them.
Retaining the Current Value
In all cases, if you press <Enter> when the current value is displayed, you will retain
the current value. For example, if the Bridge’s current values are as shown below ,
pressing <Enter> at each field will retain that current value:
IP Address : (192) .(168) .(001) .(023)
Changing a Value
To change a value, type the new value into the field at the point shown on your screen.
For example, to change the Bridge’s IP address to: 192.168.1.24:
IP Address : (192) .(168) .(001) .(023) 24
In this example, you would type the 24 immediately following the (023). Then press
<Enter> for the Bridge to accept your entry .
Commands: Default settings, Save, Quit without save
These are your commands:
E D)efault settings: Restores the Bridge’s factory–installed default
H
settings for all parameters except the Ethernet IP settings.
H
S S)ave: Stores the current settings into the Bridge’s memory, and exits the
configuration. The Bridge will restart immediately using the current settings.
Q Q)uit without save: Exits the configuration. The Bridge will restart
H
immediately using the settings it had prior to the last Save.
35
Page 36

Configuring the Bridge
3.6 Option 1: Network/IP Settings
When you select option 1 on the Configuration Menu, the Bridge displays its current
Ethernet settings. Here is an example:
IP Address : (192) .(168) .(001) .(023)
Set Gateway IP Address (Y):
Gateway IP Address : (192) .(168) .(001) .(030)
Set Netmask (N for default) (Y): (255) .(255) .(255) .(000)
IP Address
The four entry fields for the IP address are shown as parenthesis ( ).
To retain the Bridge’s current IP address, just press <Enter> at each field. To assign
a new IP address, enter it into each field.
IP 0.0.0.0: Note that setting the IP address to all zero (0.0.0.0) causes the Bridge to
be in an “Address Not Assigned” status. It reports its address as: 0.0.0.0/DHCP.
Disregard the reference to DHCP.
36
Set Gateway IP Address
The Gateway IP Address is used only if your Ethernet network is larger than one
continuous network (it contains subnetworks).
Each node within the subnetwork can directly reach all the other nodes within the
same subnetwork. If the Bridge’s subnetwork has a gateway to another subnetwork,
the Gateway IP Address parameter identifies the gateway’s address.
Set Netmask
If the Bridge’s subnetwork has a gateway node, the Bridge needs to know how to
recognize which IP addresses it can communicate with directly on its own subnetwork
and which addresses it must refer to the gateway node.
The Netmask (subnetwork mask) specifies which portion of the an IP address defines
devices on the local subnetwork, and which portion defines the entire subnetwork the
devices are on. By comparing IP addresses with the subnetwork mask, the Bridge can
determine which addresses are on its subnetwork and which are not.
Users can define different subnetwork masks to support their requirements. For
example, common “Class C” IP addresses assume a default subnetwork mask of
Page 37

Configuring the Bridge
0xFFFFFF00 or 255.255.255.0, using the lower 8 bits for the host part of the IP
address. This allows up to 255 devices on the local subnetwork.
This default mask is the example shown in the menu above.
If the user desires to have multiple subnetworks with up to 32 devices on each the
subnetwork mask could define 5 “host” bits or 255.255.255.224. With this setting, the
decimal value 224 configures the lower 8 bits of the address, with the upper 3 of these
bits addressing up to 8 subnetworks, and the lowest 5 bits forming the part of the
address for the 32 local devices.
If you wish to specify a subnetwork mask, enter
your values for the mask.
Enter
N to use the default subnetwork mask of 255.255.255.0.
Y at the menu prompt and then enter
37
Page 38

Configuring the Bridge
3.7 Option 2: Serial and Mode Settings
When you select option 2 on the Configuration Menu, the Bridge displays its current
serial port settings. Here is an example:
Attached Device (1=Slave, 2=Master) (001):
Serial Protocol (1=Modbus/RTU, 2=Modbus/ASCII) (001):
Interface Type (1=RS232, 2=RS422, 3=RS485) (001):
Enter Serial Parameters (9600,8,E,1):
Attached Device
Identify the type of Modbus device (Slave or Master) attached to the Bridge’s serial
port. The default is Slave.
Serial Protocol
Identify the type of Modbus protocol (RTU or ASCII) to be used at the serial port.
The default is RTU.
Interface T ype
Identify the type of communication interface (RS232, RS422 or RS485) used at the
serial port. The default is RS232.
38
Enter Serial Parameters
Enter the serial communication parameters used at the port, delimited by commas:
<baudrate>,<databits>,<parity>,<stopbits>
The defaults are: 9600,8,E,1.
The allowed values are:
H Baud rate: 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400
H Data bits: 7, 8
H Parity: E, O, N
H Stop bits: 1, 2.
Page 39

3.8 Option 3: Modem Control Settings
When you select option 3 on the Configuration Menu, the Bridge displays:
RTS/CTS Mode (1=Fixed, 2=Variable) (001):
RTS/CTS Mode
RTS (Request to Send) and CTS (Clear to Send) are serial port signals that coordinate
the starting and stopping of data requests between the Bridge and its port device. You
can customize the RTS/CTS mode.
The options are: Fixed or V ariable. The default is Fixed. This causes the Bridge to
apply RTS/CTS with no time delays.
if you enter
2 to select the Variable option, you can specify timing values to allow a
slower device to respond in the RTS/CTS dialog. When you choose this option the
Bridge displays:
Delay after output RTS (0–1275 msec, 5 ms resolution) (00000):
Wait for CTS to go active (N):
Delay after CTS going active (0–1275 msec, 5 ms res) (00000):
Delay dropping RTS after TX (0–1275 msec, 5 ms res) (00000):
Configuring the Bridge
Example
If you select the RTS/CTS Variable mode and enter the following values:
RTS/CTS Mode (1=Fixed, 2=Variable) (001): 2
Delay after output RTS (0–1275 msec, 5 ms resolution) (00000): 200
Wait for CTS to go active (N): Y
Delay after CTS going active (0–1275 msec, 5 ms res) (00000): 250
Delay dropping RTS after TX (0–1275 msec, 5 ms res) (00000): 300
... you are specifying that after the Bridge asserts RTS it should wait up to 200 ms for
the serial port device to respond with CTS. It will then wait 250 ms before sending
data to the device. It will wait 300 ms before dropping RTS at the end of transmission.
Your new values will be now be shown in the Bridge’s Configuration Menu:
3) Modem Control Settings:
RTS Output ................... Variable, Delay 0200 ms, Hold 0250 ms
CTS Input to TX Delay ........ 0300 ms
39
Page 40

Configuring the Bridge
3.9 Option 4: Advanced Modbus Protocol Settings
When you select option 4 on the Configuration Menu, the Bridge displays parameters
for the type of Modbus device (Slave or Master) at its serial port.
Slave Device: Slave device parameters are:
Slave Address (0 for auto, or 1...255 fixed) (000):
Allow Modbus Broadcasts (1–Yes, 2=No) (002):
Character Timeout (10–1275 msec, 5 ms res) (00050):
Message Timeout (500–60000 msec, 250 ms res) (05000):
Master Device: Master device parameters are:
Character Timeout (10–1275 msec, 5 ms res) (00050):
Message Timeout (500–60000 msec, 250 ms res) (05000):
Slave Address
The Bridge’s Slave Address parameter specifies how the Bridge will direct messages
received from Ethernet to a Slave device at the serial port.
40
Each message originated from a Modbus Master contains a Unit_ID field that
addresses a Modbus Slave destination device. The Bridge can be configured to use
that Unit_ID address as received, or to substitute a fixed address instead.
Setting the Slave Address parameter to 0 (zero) configures the Bridge to use the
Unit_ID field as received in the message. It will pass the message out its Modbus port
to the Slave device addressed in the Unit_ID field.
Setting the Slave Address parameter to any non–zero value causes the Bridge to
always use that fixed value as the Slave address for all messages sent out its Modbus
port, regardless of the Unit_ID contained in the message. This routes all messages to
a single device.
The allowable non–zero range for entering this value is 1 ... 255 decimal. Note that
Modbus Slave addresses are valid in the range 1 ... 247 only .
The default is 0 (zero), specifying the Bridge to use the received Unit_ID field.
Page 41

Configuring the Bridge
Allow Modbus Broadcasts
This parameter specifies whether the Bridge may allow a Modbus Broadcast message
to be sent to Slave devices at its serial port, or not allow those messages. Broadcast
messages are those received by the Bridge containing a Unit_ID of 0 (zero).
If Modbus Broadcasts are allowed, broadcast messages are passed to the serial port
as received with the Unit_ID contents of 0 (zero).
If Modbus Broadcasts are not allowed, the Unit_ID in the message is disregarded and
the message is sent to Slave address 1 at the serial port.
The default is to not allow Broadcast messages to the serial port.
Character Timeout
This parameter sets the timeout value between successive characters in messages.
If this timeout is exceeded, the Bridge returns an error response to the originating
Master. Typically RTU protocol already contains a 3.5 character timeout, but some
serial devices might have internal interrupts or other delays which can cause pauses of
5 to 10 characters during transmission. This parameter can be set to accommodate
those devices.
The allowable range is 10 ... 1275 msec in 5 msec increments.
The default is 50 msec.
Message Timeout
This parameter sets the timeout value for the expected response from a Slave device.
If a response is not received within this time, the Bridge continues with other tasks if
any are pending from other Master devices. The Master application must provide its
own method of handling the message timeout.
The allowable range is 500 ... 60000 msec (0.5 ... 60 sec) in 250 msec increments.
The default is 5000 msec (5 sec).
41
Page 42

Configuring the Bridge
3.10 Option 5: Unit ID to IP Address Mapping Table
If you have specified the Bridge’s serial port Attached Device parameter as a Modbus
Master (see Section 3.7), you will need to map the Slave addresses received in
messages from that Master to their intended IP address destinations. The Bridge
maps the one–byte Modbus Slave address to an IP address for delivery on Ethernet.
3.10.1
3.10.2
How the Address Mapping Works
The Bridge contains an address mapping table with eight entries. Each entry maps a
Modbus Slave address (range 1 ... 247 decimal) to a standard IP address
(XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX).
When the Bridge receives a message from the Master at its serial port, the Bridge
searches the table for a match between the message’s Slave address and a Slave
address entry in the mapping table. If a match is found, the Bridge forwards the
message to the IP address specified in that location in the table. If a match is not
found, a message timeout will occur. If a match is found, but there is not an active
TCP connection at the IP address, a message timeout will occur. The Master
application must provide its own method of handling the message timeout.
The Bridge begins its search at table location 1, and continues in the sequence
1, 2 ... 8. It stops at the first location which matches the Slave address, and sends the
message to the corresponding IP address. Thus any duplicate entry , if one exists in
the table, will be ignored.
If you have configured the serial port for a Modbus Master, you must use the mapping
table to associate the ranges of Slave addresses in your Master application to the IP
destination addresses for those Slaves.
Example: Address Mapping
If you have configured the serial port for a Modbus Master, and have entered your
mapping, it will appear on the Bridge’s initial Configuration Menu. Here is an example.
5) Unit ID –> IP Address Table:
001–001: 192.168.001.020 002–002: 192.168.001.021
003–003: 192.168.001.022 010–010: 192.168.001.024
011–247: 192.168.001.025
42
In this example, the Bridge maps Modbus Slave address 1 to IP address 192.168.1.20.
It maps Slave addresses 2, 3, 10 as shown in the table. It maps any Slave address in
the range 1 1 ... 247 to IP address 192.168.1.25.
Page 43

3.10.3 Entering New Address Mapping
When you select option 5 on the Configuration Menu, the Bridge displays it current
mapping. Then it prompts:
A)dd, D)elete, E)xit –– select function:
Adding a New Map Entry
Press
A to add a new entry into the mapping table. The Bridge will prompt you to
enter the new mapping values. The values will go into the first available (empty) table
location. Here is an example:
Modbus addr from (000): 1
Modbus addr to (000): 1
Slave IP address (192) .(168) . (001) .(020)
Deleting a Map Entry
D to delete an entry from the mapping table. The Bridge will prompt you to
Press
enter the number of the table location you want to delete. Here is an example:
Delete entry number: 1
Configuring the Bridge
3.10.4
Changing an Existing Map Entry
If you want to change an existing entry in the mapping table, you must first delete that
entry and then add your changes as a new entry .
H Press
H Press
D to delete the current entry from the table.
A to add a new entry into the table, supplying the values for the new
entry.
Exiting the Mapping Menu
Press E to exit the Mapping Table menu and return to the initial Configuration Menu.
The Configuration Menu will display the new mapping (see Section 3.10.2).
Note that when you return to the Configuration Menu, you must select Save on that
menu to save the address mapping in the Bridge’s memory. Selecting Save will also
restart the Bridge. See Section 3.5 for a description of your Configuration Menu.
43
Page 44

Page 45

Using Panel Software
H Using Concept or Modsoft
H Using Other Software
4
45
Page 46

Using Panel Software
4.1 Using Concept or Modsoft
4.1.1 Software Versions
To support Modbus/TCP to the Bridge, you need Concept version 2.1 or later, or
Modsoft version 2.6 or later. Set the communications parameters as follows:
H Protocol: TCP/IP
H Dest_Port: 502
H Dest_Index: Modbus Slave address
Note that the Bridge contains an internal Slave Address configuration option
which might affect the delivery of messages to a Slave device at its serial port.
With this option, the Bridge may be configured internally to use the Dest_Index
address exactly as received in the message, or it may be configured to steer all
messages to a fixed Slave address, ignoring the Dest_Index address.
H TCP/IP Address: as required.
46
4.1.2
Modbus Slave Address
This is an additional explanation of how the Bridge uses the Modbus Slave address.
In a Modbus TCP message sent to the Bridge, the Slave address (defined in panel
software as the Dest_Index address) is stored in the Unit_ID field of the message.
This field is used to address a unique Slave device on a Modbus network which may
contain multiple Slave devices.
The Bridge’s internal configuration contains a Slave Address parameter which can be
set to override the Unit_ID address received in the message. Section 3.9 of this book
describes how to set up the Slave Address parameter.
If the parameter is set to 0 (zero), the message will be delivered to the Slave device
whose address is defined in the Unit_ID field. If the parameter is set to a non–zero
value (range 1 ... 255), the message will be delivered to the Slave device at that
numerical address, regardless of the contents of the Unit_ID field.
For example: If you are accessing the device at Modbus Slave address 34, you must:
H Set the Dest_Index field to 34, and
H Ensure the Bridge’s internal Slave Address parameter is configured to 0 (zero).
Page 47

4.2 Using Other Software
4.2.1 Intellution FIX MMI
The Bridge allows Windows workstations with Intellution FIX software to access
Modbus devices by TCP/IP over Ethernet.
The current version of this software does not support the Modbus/TCP Unit_ID field.
Therefore if you have configured the Bridge for a Slave device at its serial port, you
must configure the Bridge’s internal Slave Address parameter for that device. This
restricts the Bridge to a single Slave device at its port.
Refer to your software product’s documentation for further information.
Using Panel Software
4.2.2
4.2.3
WinTech Modscan
WinTech supplies ModScan32 software, which can select and poll coils and registers
from various Modbus RTU/ASCII and Modbus TCP devices.
This software supports the Modbus/TCP Unit_ID field, so RS–485 multiple–drop
configurations are supported through the Bridge.
Refer to your software product’s documentation for further information.
Worderware MMI
The Bridge allows Windows workstations with Wonderware software to access
Modbus devices by TCP/IP over Ethernet. You will need the Wonderware Modicon
Ethernet I/O Server software, at version 7.0.0.15 or higher.
The current version of this software does not support the Modbus/TCP Unit_ID field.
Therefore if you have configured the Bridge for a Slave device at its serial port, you
must configure the Bridge’s internal Slave Address parameter for that device. This
restricts the Bridge to a single Slave device at its port.
Refer to your software product’s documentation for further information.
47
Page 48

Page 49

Glossary
5
address
On a network, the identification of a station. In a frame, a grouping of bits that identifies
the frame’s source or destination.
API
Application Program Interface. The specification of functions and data used by one
program module to access another; the programming interface that corresponds to the
boundary between protocol layers.
ARP
Address Resolution Protocol. A network layer protocol used to determine the physical
address which corresponds to the IP address for a host on the network. ARP is a
sub–protocol which operates under TCP/IP.
BOOTP
Bootstrap Protocol. A TCP/IP–based protocol that allows a host to configure itself
dynamically. Provides a means to assign a host its IP address, typically without user
intervention.
bps
Bits per second.
bridge
A device that connects two or more physical networks which use the same protocol.
Bridges read frames and decide whether to transmit or block them based on their
destination address.
client
A computer process requesting service from other computer processes.
dest_idx
The destination field in a Modbus message. Corresponds to the Modbus device
addressed in the message.
49
Page 50

Glossary
default gateway
The IP address of the network or host to which all packets addressed to an unknown
network or host are sent. The default gateway is typically a router or other device.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A network protocol used to configure IP
addresses dynamically. DHCP is an extension of BOOTP.
DNS
Domain Name System. A protocol within TCP/IP used to find IP addresses based on
host names.
field
A logical grouping of contiguous bits that convey one kind of information, such as the
start or end of a message, an address, data or an error check.
frame
A group of bits which form a discrete block of information. Frames contain network
control information or data. The size and composition of a frame is determined by the
network technology being used.
framing types
Two common framing types are Ethernet II and IEEE 802.3.
50
FTP
File Transfer Protocol. A networking protocol used to exchange files between stations
on a network or over the Internet.
gateway
A device which connects networks with dissimilar network architectures and which
operates at the Application Layer. This term may refer to a router.
host
A node on a network.
hostname
A domain name given to a specific computer on a network and used to address that
computer.
HTTP
HyperText Transport Protocol. A protocol used to deliver hypertext documents.
hub
A device which connects a series of flexible and centralized modules to create a
network.
Page 51

Glossary
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol. A protocol within TCP/IP used to report errors in
datagram transmission.
Internet
The global interconnection of TCP/IP based computer communication networks.
IP
Internet Protocol. A common network layer protocol. IP is most often used with TCP.
IP Address
Internet Protocol Address. A 32–bit address assigned to hosts using TCP/IP.
layer
In the OSI model, a portion of the structure of a device which provides defined services
for the transfer of information.
MAC Address
Media Access Control address. The hardware address of a device. A MAC address is
assigned to an Ethernet TCP/IP module in the factory .
network
Interconnected devices sharing a common data path and protocol for communication.
node
An addressable device on a communications network.
OSI model
Open System Interconnection model. A reference standard describing the required
performance of devices for data communication. Produced by the International
Standards Organization.
packet
The unit of data sent across a network.
PING
Packet Internet Groper. A program used to test whether a destination on a network can
be reached.
port
An access point for data entry or exit within a host using TCP services.
protocol
Describes message formats and a set of rules used by two or more devices to
communicate using those formats.
51
Page 52

Glossary
repeater
A device that connects two sections of a network and conveys signals between them
without making routing decisions or filtering packets.
router
A device that connects two or more sections of a network and allows information to
flow between them. A router examines every packet it receives and decides whether to
block the packet from the rest of the network or transmit it. The router will attempt to
send the packet through the network by the most efficient path.
server
Provides services to clients. This term may also refer to the computer on which the
service is based.
socket
The association of a port with an IP address, serving as an identification of sender or
recipient.
stack
The software code which implements the protocol being used. In the case of the NOE
modules it is TCP/IP.
STP
Shielded Twisted Pair. A type of cabling consisting of several strands of wire
surrounded by foil shielding, twisted together.
52
subnet
A physical or logical network within an IP network, which shares a network address
with other portions of the network.
subnet mask
Used to indicate which bits in an IP address identify a subnet.
switch
A network device which connects two or more separate network segments and allows
traffic to be passed between them. A switch determines whether a frame should be
blocked or transmitted based on its destination address.
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol.
TCP/IP
A protocol suite consisting of the Transmission Control Protocol and the Internet
Protocol; the suite of communications protocols on which the Internet is based.
Page 53

Glossary
UDP
User Datagram Protocol. A protocol which transmits data over IP.
URL
Uniform Resource Locator. The network address of a file.
UTP
Unshielded Twisted Pair. A type of cabling consisting of insulated cable strands which
are twisted together in pairs.
Winsock
The Microsoft implementation of the Windows Sockets networking API based on the
Berkeley UNIX Sockets interface for supporting TCP/IP.
WWW
World Wide Web. A hypertext–based, distributed information system in which clients
and servers are freely available.
53
Page 54

Page 55

Modicon, Square D and Telemacanique are PLC brand names from Schneider. These products are sold in
the US by Square D; in Canada, Latin America, Europe, Asia, Asia/Pacific and Middle East by Schneider;
in Germany by AEG Schneider Automation; in China and Persian Gulf by Schneider Automation; in South
Africa by ASA Systems Automation; in Austria by Online.
United States:
Schneider Automation, Inc.
One High Street
North Andover, MA 01845
Tel: (1) 978–794–0800
Fax: (1) 978–975–9400
France:
Schneider Automation S.A.
245, Route des Lucioles - BP147
F–06903 Sophia - Antipolis Cedex
Tel: (33) 92 96 20 00
Fax: (33) 93 65 37 15
Germany:
Schneider Automation GmbH
Steinheimer Strasse 117
D–63500 Seligenstadt
Tel: (49) 6182 81–2584
Fax: (49) 6182 81–2860
 Loading...
Loading...