Quadrox WebCCTV Installation Manual

WebCCTV
Installation Manual
Let’s make things safer!

© Qua
drox 1997
–
2005
© Quadrox 1997
–
2005
WebCCTV Installation Manual
2
Contents
CONTENTS.......................................................................................................................................................................................................2
1 INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................................................................................. 4
2 GETTING STARTED...........................................................................................................................................................................6
2.1 E
QUIPMENT CHECKLIST
2.1.1
2.1.2
2.1.3
2.2 S
2.2.1
2.2.2
2.2.3
2.2.4
2.2.5
2.2.6
2.2.7
2.3 WEBCCTV
2.3.1
2.3.2
2.3.3
2.3.4
2.3.5
2.3.6
2.4 T
2.4.1
2.4.2
2.4.3
2.5 O
2.5.1
2.5.2
2.5.3
3 UPGRADING AND RESTORING WEBCCTV................................................................................................................................34
3.1 U
3.2 S
3.3 R
4 ADVANCED TOPICS.........................................................................................................................................................................36
4.1 E
4.1.1
4.1.2
Hardware..................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Software……………………………………………………………....................................................................................................... 6
Documentation............................................................................................................................................................................. 6
TARTING UP FOR THE FIRST TIME
Turning power on/off.................................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.2.1.1 Turning power on.................................................................................................................................................................7
2.2.1.2 Turning power off or restarting ............................................................................................................................................8
Logging on to the XPe system...................................................................................................................................................... 8
Desktop icons overview................................................................................................................................................................ 9
Changing password.................................................................................................................................................................... 10
Setting time................................................................................................................................................................................. 12
2.2.5.1 Through WebCCTV Web Application...............................................................................................................................12
2.2.5.2 Through XPe OS................................................................................................................................................................13
2.2.5.2.1 Changing time zone........................................................................................................................................................ 13
2.2.5.2.2 Time synchronization..................................................................................................................................................... 13
Changing keyboard settings....................................................................................................................................................... 14
Adjusting screen resolution........................................................................................................................................................ 16
IN THE NETWORK
Network overview....................................................................................................................................................................... 17
Connecting WebCCTV to the local network............................................................................................................................... 18
Assigning IP address.................................................................................................................................................................. 19
Firewall configuration............................................................................................................................................................... 19
Connecting a client .................................................................................................................................................................... 22
2.3.5.1 Minimum client requirements............................................................................................................................................. 22
2.3.5.2 Client configuration............................................................................................................................................................ 22
Connecting WebCCTV to the Internet........................................................................................................................................ 25
2.3.6.1 Creating a network connection........................................................................................................................................... 25
2.3.6.2 Router and firewall............................................................................................................................................................. 26
2.3.6.2.1 Configuring router.......................................................................................................................................................... 26
2.3.6.2.2 Configuring firewall....................................................................................................................................................... 28
ESTING WEB
PERATOR MODE
PGRADING WEB
AVING & RESTORING CONFIGURATION
ESTORING PREINSTALLED SOFTWARE
XTENDING STORAGE SPACE
4.1.2.1 Multiple Logical Disks....................................................................................................................................................... 39
4.1.2.2 Single Disk Extension........................................................................................................................................................41
CCTV .......................................................................................................................................................................... 30
Local client test.......................................................................................................................................................................... 30
Connection test........................................................................................................................................................................... 30
Remote client test....................................................................................................................................................................... 31
Locking WebCCTV..................................................................................................................................................................... 32
Switching to Operator mode....................................................................................................................................................... 32
Automatic logon as Operator..................................................................................................................................................... 33
Adding hard disk........................................................................................................................................................................ 36
Configuring added hard disk......................................................................................................................................................37
Version 4.4 Series
........................................................................................................................................................................ 6
........................................................................................................................................................7
.............................................................................................................................................................17
............................................................................................................................................................................... 32
CCTV
SOFTWARE
...................................................................................................................................................34
............................................................................................................................................. 34
............................................................................................................................................... 34
..............................................................................................................................................................36

WebCCTV Installation Manual
4.2
V
IDEO CLIENT COMPONENT (ACTIVE
4.3 C
HANGING NETWORK PORTS
4.3.1
4.3.2
4.3.3
4.4 WEBCCTV
4.5 C
5 STORAGE / BANDWIDTH CONSIDERATIONS........................................................................................................................... 51
5.1 T
5.2 F
5.2.1
5.2.2
5.2.3
5.2.4
5.2.5
6 SECURITY POLICY .......................................................................................................................................................................... 57
6.1 P
6.2 S
6.2.1
6.2.2
6.2.3
6.2.4
6.2.5
6.2.6
6.3 E
7 TROUBLESHOOTING ...................................................................................................................................................................... 66
7.1 P
7.1.1
7.1.2
7.2 S
7.2.1
7.2.2
7.2.3
7.2.4
7.2.5
7.2.6
7.3 I
7.3.1
7.3.2
7.3.3
7.3.4
8 APPENDICES......................................................................................................................................................................................76
Changing WebCCTV video ports...............................................................................................................................................48
Changing TCP port....................................................................................................................................................................48
Changing remote desktop port...................................................................................................................................................49
POWER ON AFTER POWER FAILURE
ONFIGURING AUDIO OVER THE INTERNET
ERMINOLOGY AND BASIC VIDEO TECHNOLOGY
ACTORS THAT INFLUENCE BIT RATE AND VIDEO QUALITY
Compression technique (codec).................................................................................................................................................. 53
Resolution ..................................................................................................................................................................................54
Frame rate .................................................................................................................................................................................55
“Differential” live streaming..................................................................................................................................................... 56
Activity detection for storage...................................................................................................................................................... 56
ROPER USE OF WEB
ECURITY POLICY
Password policy......................................................................................................................................................................... 59
Operator mode........................................................................................................................................................................... 61
Windows security updates..........................................................................................................................................................61
Network security ........................................................................................................................................................................ 61
6.2.4.1 Dedicated network versus integration with the corporate network ..................................................................................... 62
6.2.4.2 Internet Connection............................................................................................................................................................62
6.2.4.3 Limiting the number of protocols....................................................................................................................................... 62
6.2.4.4 Firewall .............................................................................................................................................................................. 63
6.2.4.5 Allowing only known clients..............................................................................................................................................63
6.2.4.6 Securing the applications....................................................................................................................................................63
6.2.4.7 VPN.................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
Other types of access.................................................................................................................................................................. 64
3rd party security tools................................................................................................................................................................ 64
RROR RECOVERY MECHANISMS
ROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS
Preliminary checklist..................................................................................................................................................................66
Analyzing the problem................................................................................................................................................................ 67
OLUTIONS FOR COMMON PROBLEMS
Start up problems....................................................................................................................................................................... 68
Monitor problems....................................................................................................................................................................... 70
Windows logon problems........................................................................................................................................................... 70
Remote connection problems...................................................................................................................................................... 71
Camera problems.......................................................................................................................................................................72
WebCCTV software problems....................................................................................................................................................72
F YOU NEED FURTHER ASSISTANCE
Before you call........................................................................................................................................................................... 74
Collecting the necessary information......................................................................................................................................... 74
How to contact Quadrox............................................................................................................................................................ 75
How to allow remotely access to your WebCCTV by Quadrox support...................................................................................... 75
CCTV................................................................................................................................................................58
............................................................................................................................................................................... 59
X)............................................................................................................................................. 46
..............................................................................................................................................................48
.................................................................................................................................. 49
......................................................................................................................................... 49
................................................................................................................................ 51
................................................................................................................53
........................................................................................................................................................65
..............................................................................................................................................................66
................................................................................................................................................. 68
....................................................................................................................................................74
3
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
4
1 Introduction
WebCCTV is a unique digital video surveillance solution, which combines three major
functions in one Network Video Recorder (NVR) or Digital Video Recorder (DVR): local
digital recording, multiplexing and simultaneous transmission of the video via existing
networks (TCP/IP). To a standard WebCCTV, up to 20 cameras can be permanently recorded
while multiple operators at different locations on the network are accessing the WebCCTV
device.
Being a networked device, WebCCTV utilizes two basic principles of the
Internet/Intranet technology:
WebCCTV works over the TCP/IP network protocol, which provides maximum
connectivity. This means that the existing computer network infrastructure can be
used eliminating extra installation expenses.
WebCCTV uses a web-based user interface to view live images, recordings, etc.
More specific it uses Microsoft Internet Explorer.
Remote and Local Monitoring
To remotely monitor the connected cameras, the
WebCCTV uses Web Browser technology. To
locally monitor video, the WebCCTV also
provides a local interface via a PC monitor
directly connected to the WebCCTV. This local
interface allows an operator to see live video
from the connected cameras without the need for
additional client computers on a network.
Continuous Activity-Based Recording
By default, a WebCCTV continuously records all images from all the connected cameras
based on activity detection. In this case, only movement is recorded. If there is no movement,
no recording takes place. If necessary, the WebCCTV can be set to record continuously.
Intelligent Storage Option
WebCCTV uses a first-in/first-out (FIFO) overwrite principle. Once the disk is full, the oldest
images are overwritten.
Semi-Continuous recording (recording based on activity detection) allows a WebCCTV to
store pre- and post-alarm video. Pre- and Post-alarm images are often more important than the
images at the time of the alarm event itself. Up to 5 minutes of pre- and post-alarm video can
be stored per event.
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
5
WebCCTV makes a distinction between common activity recordings and pre/post alarm
recordings. In the way that, alarm recordings have a higher storage priority and will not be
overwritten by non-alarm recordings.
The WebCCTV is operational even when no live monitoring occurs. While the
WebCCTV continuously records images from all the cameras, video is transmitted
from the server to the client only when an Internet browser is connected to
WebCCTV and someone is live-viewing images from one or more cameras.
Version 4.4 Series
WebCCTV Installation Manual
6
2 Getting started
This chapter provides basic information to get you started installing and using your
WebCCTV.
2.1 Equipment checklist
Carefully unpack your WebCCTV and check for the presence of all items listed below.
2.1.1 Hardware
Check to make sure you have all following items:
1 x WebCCTV
1 x Power cord
1 x WebCCTV Recovery DVD
1 x empty DVD for “Save Settings”
1 x USB or PS/2 mouse
1 x Keyboard
If you want more specific information about your server hardware, please contact
your installer/distributor.
It is possible to add extra hard disks to the unit if requested to extend the storage
space. Contact your installer/distributor.
2.1.2 Software
The following software is preinstalled:
Microsoft Windows XP Embedded Operating system
WebCCTV4 Video security software suite
Adobe Acrobat Reader 8.0 or higher
2.1.3 Documentation
WebCCTV Installation manual in PDF format
WebCCTV User manual in PDF format
Alarm Component Installation manual in PDF format
Quadrox POS Printer manual in PDF format
Remote POS Monitor manual in PDF format
WebCCTV NVS400 Guide
WebCCTV NVS1000/2000/4000 Guide
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
2.2 Starting up for the first time
This chapter provides information on the following procedures:
Turning the power on and off
Logging on to the XPe system
Desktop icons overview
Changing the password
Setting the time
Changing keyboard language
Adjust screen resolution
Connect monitor, keyboard and mouse before turning on the power and configuring
WebCCTV.
2.2.1 Turning power on/off
7
2.2.1.1 Turning power on
To turn the power on, follow the steps below:
1. On the front side of your WebCCTV, you’ll find an On/Off button. This is a one-touch
button. When pressing it briefly, WebCCTV will begin its start-up procedure. You can
verify the correct start-up sequence by checking the following:
The fans are turning and make a humming noise.
The power indicator is illuminated.
The hard disk indicator is flashing.
2. When you have a monitor connected, you can see that:
First it lists all the hardware components.
Second it starts loading the Windows XPe operating system
3. After about 1.5 to 2 minutes, the WebCCTV should be fully started.
The first time you turn on the power of your WebCCTV, its initial screen will be the Windows
XPe logon screen.
WebCCTV does not logon automatically by default.
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
8
2.2.1.2 Turning power off or restarting
Before shutting down or restarting a WebCCTV, there are some important precautions to make
note of. Because a WebCCTV is constantly recording (24h) activity video on the disk, the hard
disk is used very frequently. If a user shuts down the WebCCTV while it is writing to the hard
disk, there is always a danger of damaging the hard disk. This may result in having an
unbootable WebCCTV afterwards. There are two options:
Restart or shutdown WebCCTV through the normal Windows interface:
1. On the taskbar at the bottom of your screen, click the Start button in the lower left
corner.
2. On the start menu, in the lower right corner, click Shut Down.
3. On the Shut Down Windows dialog box, select the Restart or Shut Down tab.
4. Click OK to shutdown or restart.
5. Wait until the WebCCTV completely has shut down before unplugging the power
cord.
Restart or shutdown WebCCTV by using the shutdown button on the unit itself:
1. On the front of the unit there is a button to shut down the WebCCTV.
2. Because our WebCCTV is ACPI enabled, clicking this button once for a brief
moment will initiate a graceful shutdown. This is handled by the MS Windows XP
embedded Operating System, because it detects the click on the shutdown button
and will shutdown automatically.
3. Please be patient because it can take nearly a minute before the WebCCTV actually
shuts down completely. The WebCCTV has stopped when the green power
indicator has gone out.
4. Wait until the WebCCTV completely has shut down before unplugging the power
cord.
2.2.2 Logging on to the XPe system
For access to the WebCCTV’s operating system, you have to specify a Username and
Password.
The first time you turn on the power of a WebCCTV, after its boot sequence (see above) has
completed, its initial screen will be the Windows XPe logon prompt:
The default Administrative username is: Administrator
The default Administrative password is: webcctvnvr
It is highly recommended to change the Administrative password as soon as possible.
If you use an ‘AZERTY’ keyboard, this becomes zebcctvnvr. See Chapter 2.3.6 how
to change this to Azerty settings.
Version 4.4 Series
WebCCTV Installation Manual
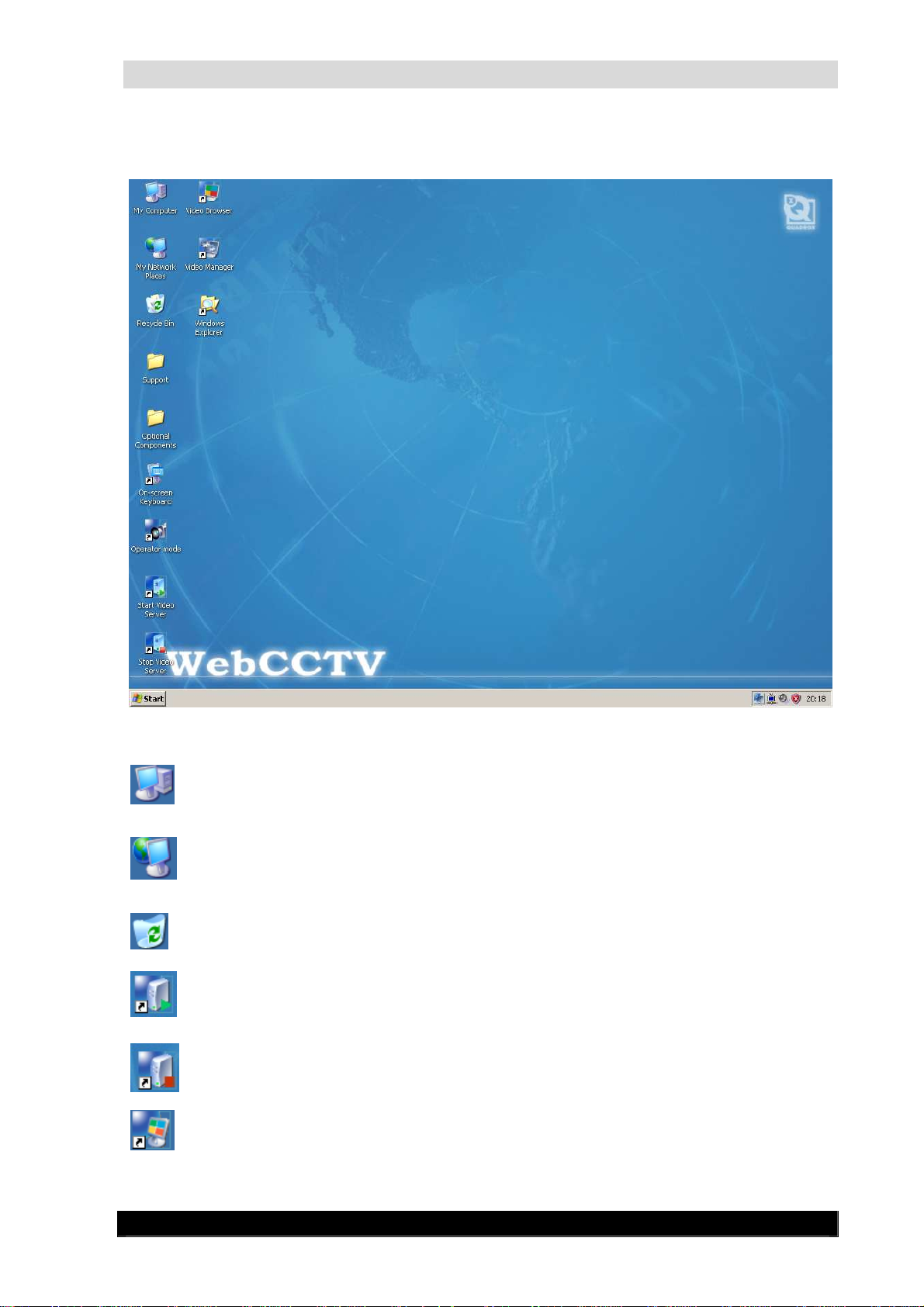
2.2.3 Desktop icons overview
9
WebCCTV’s Desktop Screen
My Computer. By double-clicking this icon, the user can see an overview of all
configured disk drives/partitions on the WebCCTV.
My Network Places. By double-clicking this icon, the user can see an overview of
all Network places visited. By right clicking and then choosing ‘Properties’, the user
can see an overview of all network connections possible and can adjust the TCP/IP
settings of the WebCCTV.
Recycle Bin. Temporarily stores all deleted files and folders prior to permanent
deletion.
Start Video Server. By double-clicking this icon, the user can start the
WebCCTV’s video server. If the video server is already started, double-clicking
doesn’t change anything.
Stop Video Server. By double-clicking this icon, the user can stop the WebCCTV’s
video server. If the video server is already stopped, double-clicking doesn’t change
anything.
Video Browser. By double-clicking this icon, the user starts the WebCCTV webapplication on the local WebCCTV.
Version 4.4 Series
WebCCTV Installation Manual
Video Manager. By double-clicking this icon, the user starts WebCCTV webapplication on the local WebCCTV. The system can be managed and configured
here
Optional Components. This folder contains links to the setup files for the Alarm
Component, Remote POS monitor, etc.
Support. A folder that contains a few support tools to administer the WebCCTV
server application such as the Event Viewer, Registry editor, etc.
Operator mode toggle. This switch enables the user to switch back and forth
between Operator mode (a restricted operational mode where only the local
interface is present) and Administrator mode (a non-restricted mode where all
system manipulations are allowed).
On screen keyboard. This on screen keyboard can be used as a virtual keyboard
when no physical keyboard is present and connected to the WebCCTV.
Windows Explorer. The user can use this application to browse through the
contents of the local hard disks.
10
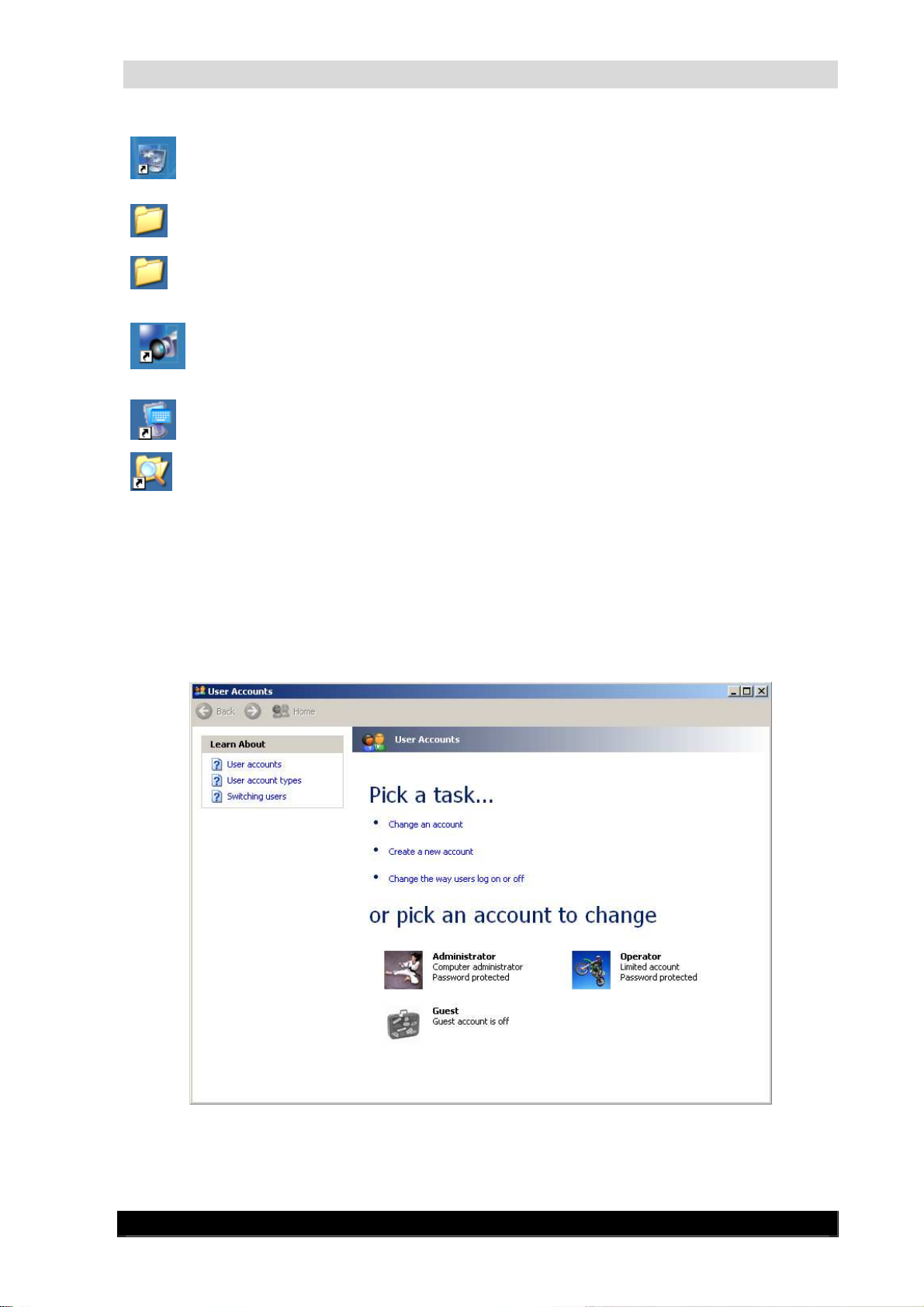
2.2.4 Changing password
To change the Administrative password, follow the steps below:
Go to Start->Control Panel.
When in Control Panel, select User Accounts from the right-hand list.
User Accounts Screen
In the User Accounts screen, select the Administrator user.
Version 4.4 Series
WebCCTV Installation Manual
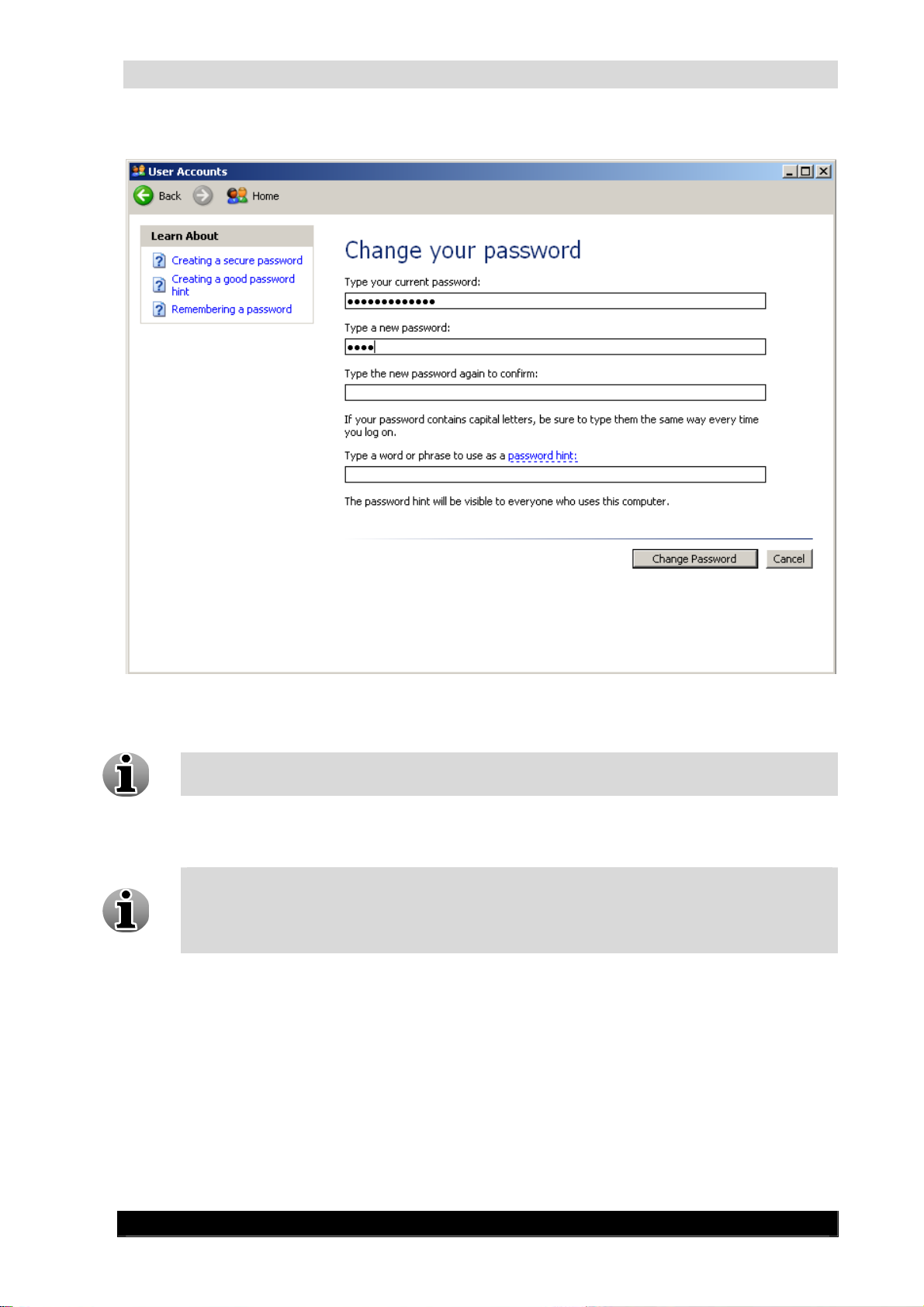
Click Change my password link.
11
Changing Password Screen
Enter your current password.
The default Administrator password is webcctvnvr.
Enter a new password and confirm it.
Click Change Password button to save new Administrator account password.
When you change the Administrator password in Windows, the Administrator
password of the WebCCTV application is automatically changed to this password.
This means also that when you change your password in the WebCCTV application,
that your Windows password will be changed automatically!
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
12
2.2.5 Setting time
For the WebCCTV to function properly, it is very important to use the applicable Time Zone
setting. This can be done in two ways, or by the WebCCTV application configuration (See
WebCCTV User Manual Chapter 3.3.10 Time Synchronisation), or by the Windows XPe
OS configuration.
We strongly advise you to use the WebCCTV application way as this is the easiest
way to configure your time settings.
2.2.5.1 Through WebCCTV Web Application
Time synchronization allows you to synchronize time on all devices connected to your unit
(e.g. cameras) and synchronize your server with a specific time server. This can be done by
going to the Settings menu in the Video Manager Web Application and selecting the Time
Synchronisation link in the top bar
Time Synchronization Screen
There are three options:
Use video server as a (proxy) time server – The unit will synchronize with an
external time server if configured in the bottom part of the screen. If empty, the unit
will act as a time server for itself and the connected devices (e.g. cameras).
Synchronize all devices with an external time server – The unit and all the
connected devices (e.g. cameras) will be synchronized with an external time server.
Configure the IP address or DNS name of the external time server in the bottom part of
the screen.
Manually configure time synchronization on each device separately (not
recommended) – No synchronization at all is performed, neither for the unit nor for
the connected devices (e.g. cameras)
If your unit is part of a domain, this menu will not be available. The unit and
connected devices (e.g. cameras) will be synchronized automatically with the Active
Directory of the domain.
Click Apply to save the settings.
Version 4.4 Series
WebCCTV Installation Manual
2.2.5.2 Through XPe OS
2.2.5.2.1 Changing time zone
To change the time zone, follow the steps below:
In Control Panel, in the left upper corner click the link ‘Switch to Classic view’.
When in classic view, select Date & Time from the right-hand list.
On the Date and Time properties dialog, select the tab ‘Time Zone’
When on the ‘Time Zone’ tab, select the correct time zone.
Click OK to save the ‘Date and Time’ changes.
To adjust the Date and time manually follow the steps below:
In the Control Panel, in the left upper corner click the ‘Switch to Classic view’ link.
When in classic view, select Date & Time from the right-hand list.
On the Date and Time properties dialog, select the ‘Date & Time’ tab.
When on the ‘Date & Time’ tab, set the correct date and time.
Click OK to save the ‘Date and Time’ changes.
2.2.5.2.2 Time synchronization
13
Synchronize your computer time with the atomic clock on the Internet for the best time
accuracy.
Optionally the installer/user can configure a WebCCTV to synchronize its time and date
automatically on a regular basis using a so-called ‘Time Server’. These special servers exist
often on bigger corporate networks or on the Internet. To set this up, follow the steps below:
Click Settings -> Control panel.
In Control Panel, in the left upper corner click the ‘Switch to Classic view’ link.
When in classic view, select Date & Time from the right-hand list. On the Date and
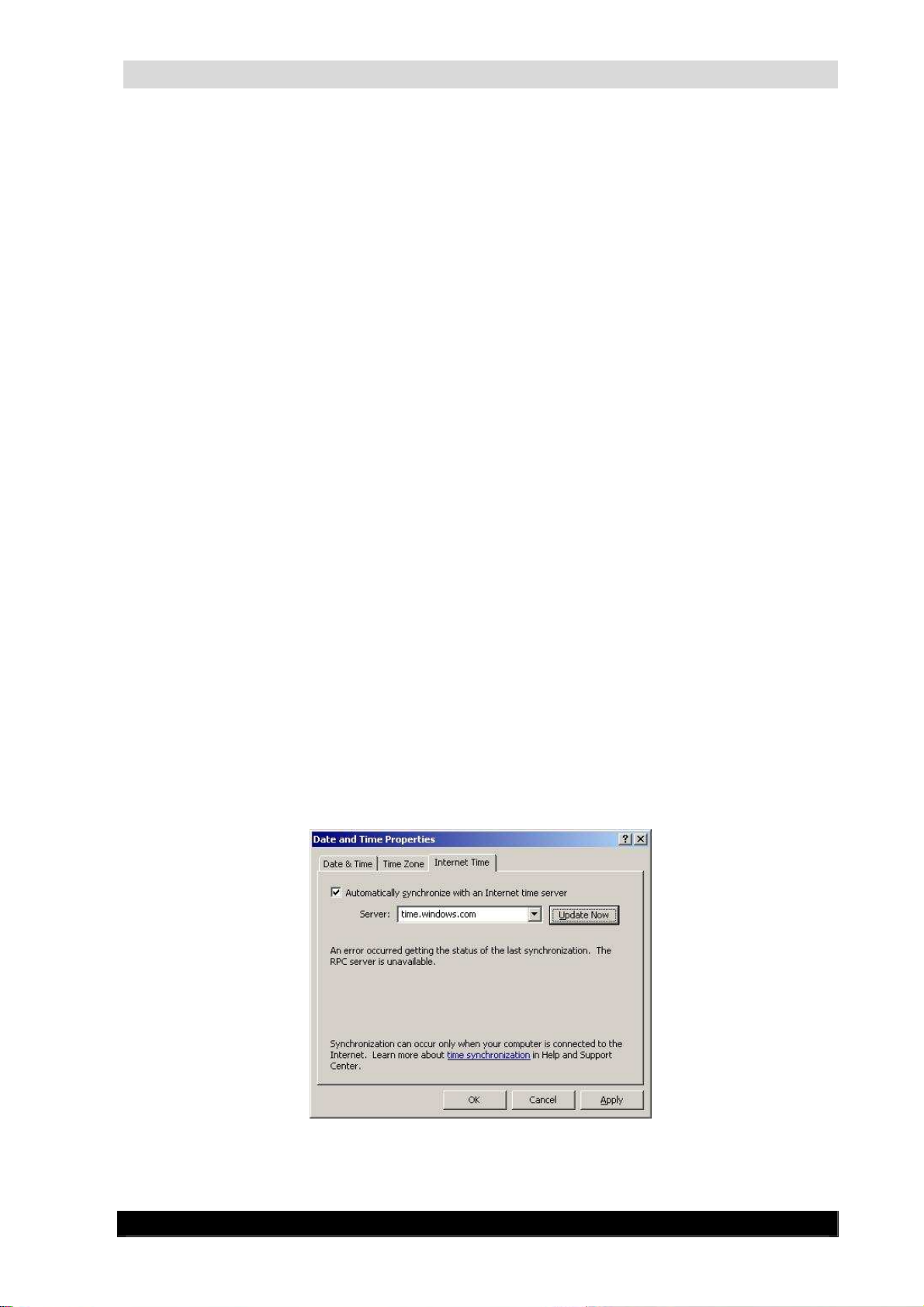
Time properties dialog, select the tab ‘Internet Time’. You’ll see the following
screen:
Version 4.4 Series
Internet Time Screen
WebCCTV Installation Manual
Check the box ‘Automatically synchronize with an Internet time server’.
Enter the name or IP-address of a known time server into the 'Server' edit box. Note
that when using a name in the IP-address settings of the WebCCTV server, a correct
DNS IP-address should be supplied. Otherwise this name will never be resolved/found.
If you use an IP-address there is no need to provide a DNS server.
Click OK to save the ‘Internet Time’ changes.
The default Internet Time Server is time.windows.com; however you can use other
time servers for synchronization, such as those provided below:
time.nist.gov (IP-address: 192.43.244.18)
utcnist.colorado.edu (IP-address: 128.138.140.44)
Make sure that there is no computer in the network with the same IP address.
2.2.6 Changing keyboard settings
14
Open the Support folder on the desktop. Double click on the desired keyboard icon and follow
the instructions. Once completed, your keyboard settings are changed. The following keyboard
layout icons can be found in the support folder:
Dutch (Belgium) German
Dutch Italian
English Russian
French (Belgium) Spanish
French Ukrainian
If you don’t find an icon for your desired keyboard layout (Language), follow the steps below:
In Control Panel, in the left upper corner click the link ‘Switch to Classic view’.
When in classic view, select Regional and Language Options from the right-hand list.
In the Regional and Language Options dialog, select the ‘Languages’ tab.
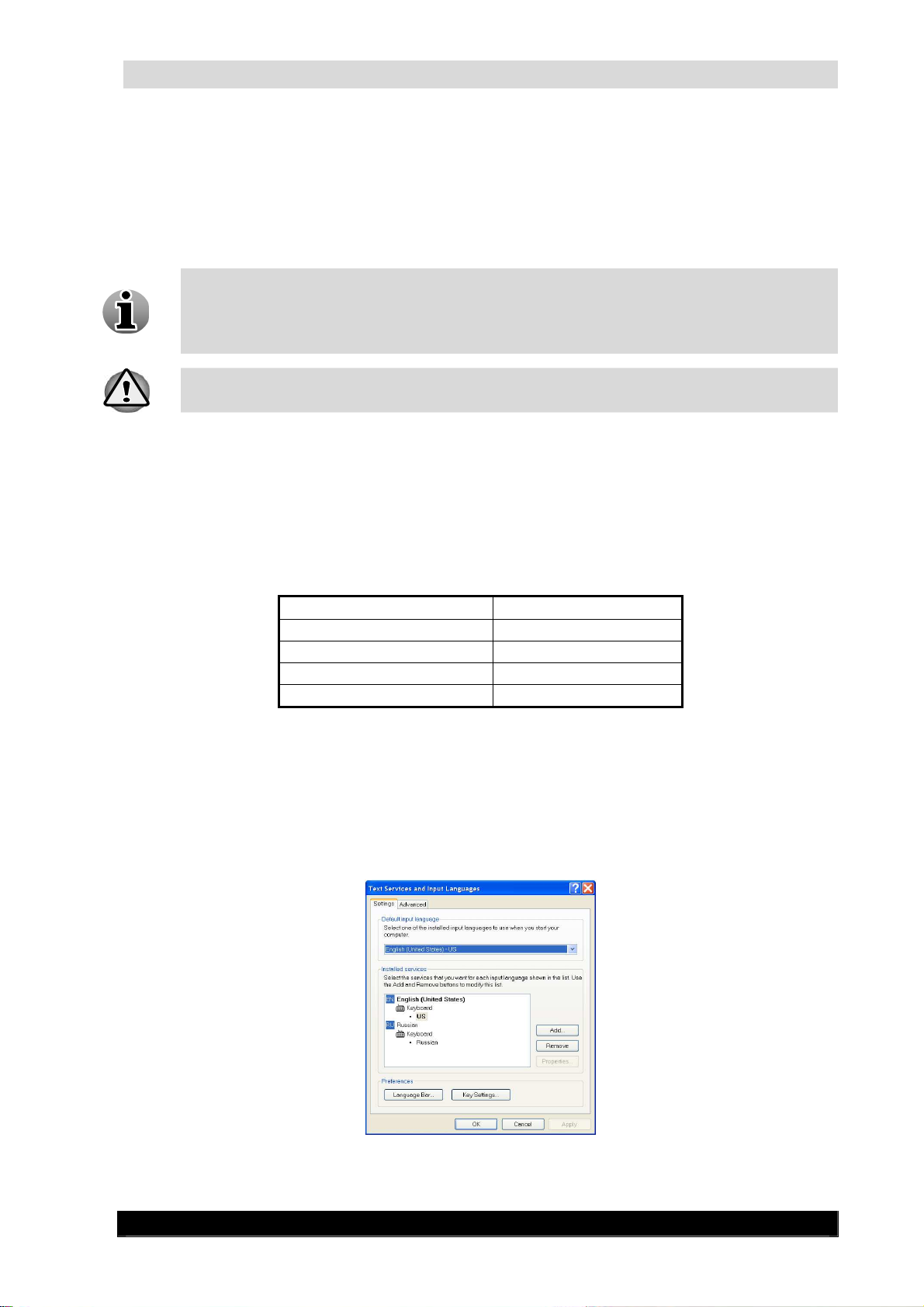
When on the ‘Languages’ tab, click the ‘Details’ button. The following window
appears:
Version 4.4 Series
Keyboard Settings Screen
WebCCTV Installation Manual
In the Text services and Input languages dialog, add the desired keyboard layout.
After adding the new keyboard layout, delete the other keyboard layouts.
Use the ‘Default Input Language’ combo box to select the keyboard layout you added.
Click OK to change the keyboard layout.
In the Regional and Language Options dialog, select the ‘Advanced’ tab.
Select your language in the upper list box and enable the check box for Default user
account settings. Click OK or Yes for all pop ups.
It’s possible that your computer will restart if this is necessary to apply the
changes
15
Click OK to save the ‘Regional and Language Options’ changes.
Version 4.4 Series
WebCCTV Installation Manual
2.2.7 Adjusting screen resolution
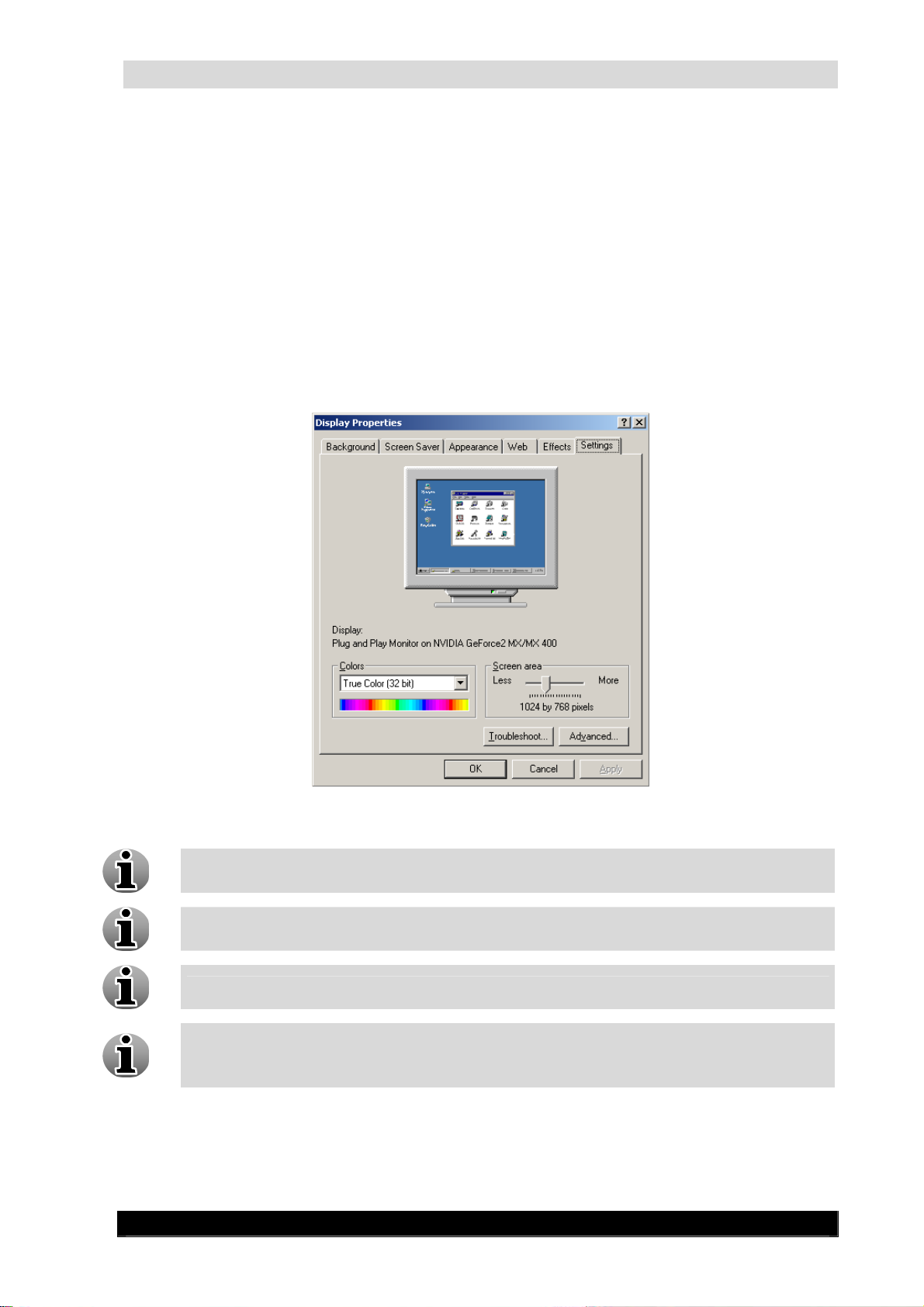
To adjust the screen resolution, follow the steps below:
Click Start-> Settings-> Control panel-> Display.
On the Settings tab, under Screen resolution, drag the slider, and then click Apply.
When prompted to apply the settings, click OK. Your screen will turn black for a
moment.
Once your screen resolution changes, you have 15 seconds to confirm the change.
Click Yes to confirm the change; click No or do nothing to revert to your previous
setting.
16
A higher screen resolution reduces the size of the items on your screen and increases
the relative space on your desktop.
Your monitor and video adapter determine how high you can change your screen
resolution. You may not be able to increase the resolution beyond a certain point.
Changes to screen resolution affect all users that log on to the computer.
Only the recommended screen resolutions are listed. For additional settings, click the
Advanced button on the Settings tab, click the Adapter tab, and then click List all
Modes. Select the resolution, colour level, and refresh rate you want.
Version 4.4 Series
Display Properties Screen
WebCCTV Installation Manual
17
2.3 WebCCTV in the network
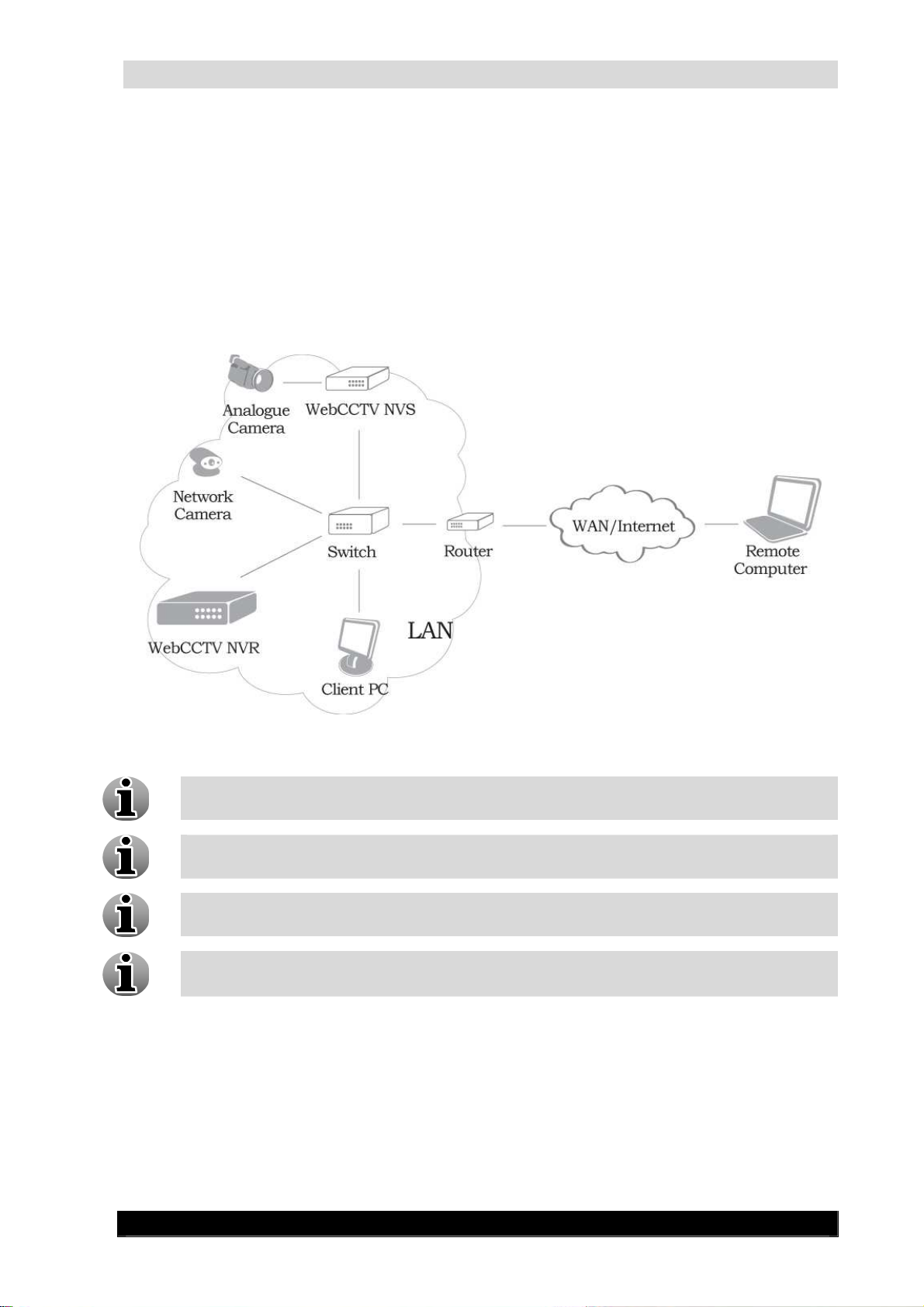
2.3.1 Network overview
This chapter gives the schematic representation of the network camera and WebCCTV NVS
connections.
To connect your network camera and NVS properly look at the following figure:
Connecting Network Camera and WebCCTV NVS Scheme Screen
To configure your network camera, please refer to the manufacturer’s manual
supplied with the network camera.
To add a network camera to WebCCTV, refer to the Camera Wizard chapter in the
WebCCTV User manual.
Please note that a list of all supported cameras may be found in Appendix C.
Analogue cameras can also be connected directly to the WebCCTV when a digitizer
card is present on the WebCCTV.
Version 4.4 Series
WebCCTV Installation Manual
18
2.3.2 Connecting WebCCTV to the local network
When you start your WebCCTV, Windows XPe detects your network adapter and
automatically starts the local area connection. Unlike other types of connections, the local area
connection is created automatically, and you do not have to click the local area connection in
order to start.
A local area connection is the only type of connection that is automatically created
and activated.
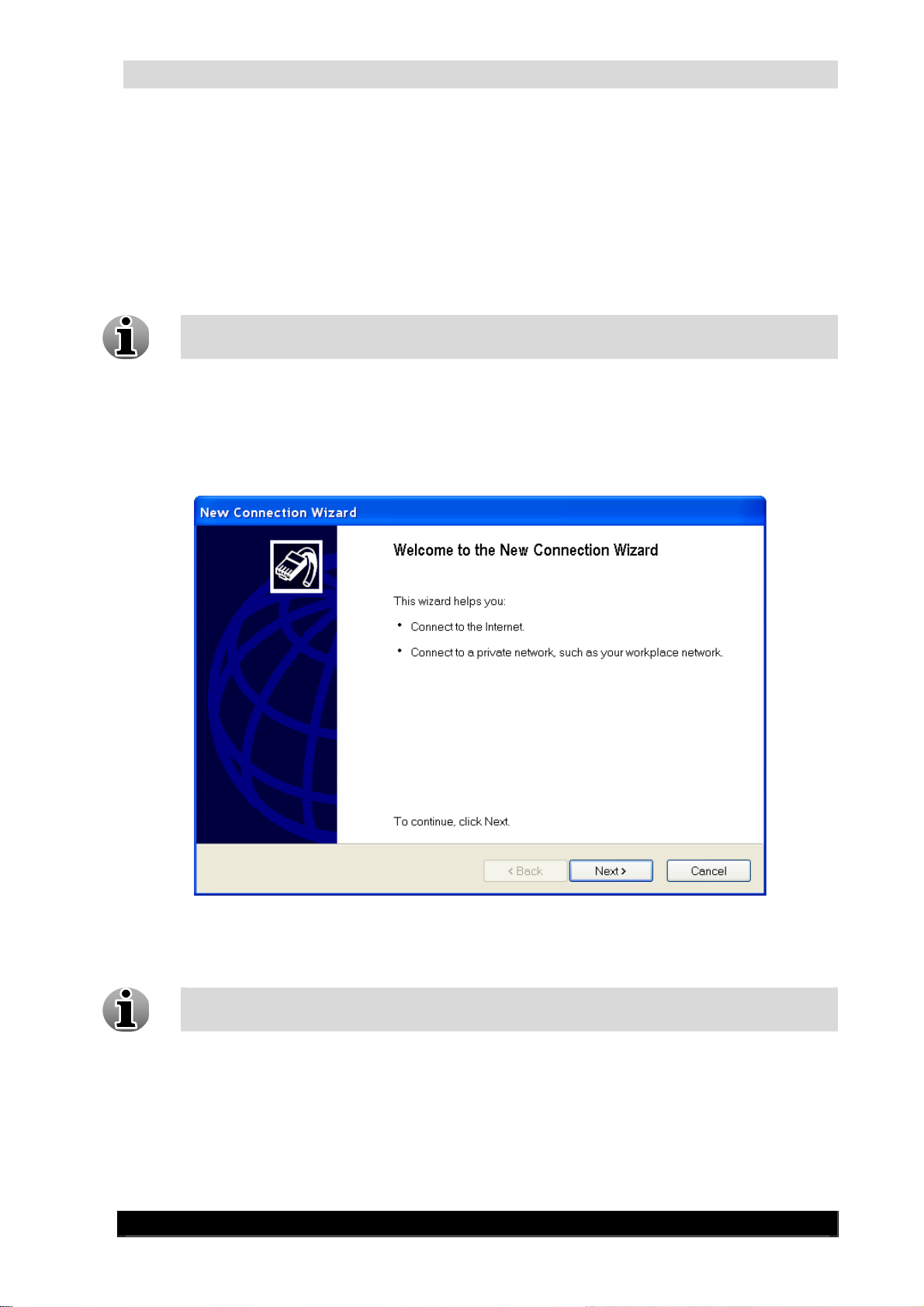
To establish connections of another type follow the steps below:
1. Click Start -> Settings -> Control panel -> Network connections
2. In the Network connections window click File-> New connection. You’ll see the
following window:
Network Connection Wizard Screen
Follow the prompts the network connection wizard provides to define your unit in the network.
For obtaining more detailed information about your network settings, please contact
your system administrator.
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
19
2.3.3 Assigning IP address
If you cannot use DHCP or APIPA for IP address and subnet assignment, the IP address for
the Windows XPe–based client must be manually configured. The required values include the
following:
An IP address for each network adapter installed on the computer.
The Subnet mask corresponding to each network adapter's local network.
In order to facilitate remote connections to WebCCTV, it is recommended you use a
static IP-address.
To manually configure an IP address, follow the steps below:
Click Start->Settings->Control Panel.
In Control Panel, select Network and Internet Connections.
On the Network and Internet Connections sheet, select Network Connections.
In Network Connections, right-click the local area connection that you want to
modify.
Select Properties.
On the General tab of the Properties sheet, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP).
Click Properties.
On the General tab of the TCP/IP Properties sheet, select the Use the following IP
address option.
Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for the selected adapter in
their respective text boxes. The network administrator must provide these values for
individual users, based on the IP addressing scheme for your site. The value in the IP
Address text box identifies the IP address for this network adapter. The value in the
Subnet Mask text box is used to identify the network ID for the selected network
adapter. If needed, the DNS server address can be entered also.
Click OK to save the IP addressing information.
Click OK to save the connection properties.
2.3.4 Firewall configuration
The following ports need to be opened for connections going towards the WebCCTV:
1. TCP Port 80: Web application
2. TCP Port 1518: Control connection
3. UDP Ports 4096 till 4223: Video streaming
4. TCP Port 3389: Remote Desktop connection (Optional). Frequently asked by
support when you have an issue)
5. TCP Port 5666: Q-Monitor Service.
RTP uses two UDP ports per stream (versus one in the old streaming format in
versions prior to V4.0.0.0), one for RTP (the video stream itself) and one for RTCP
(QoS signal stream), limiting the software to a maximum of 64 concurrent streams.
This number can be limited (e.g. for security purposes) or extended using the Settings
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
20
> Network settings page. In that case, Quadrox recommends you to open a number of
spare ports to avoid switching issues, e.g. 4 ports extra. The first port in the range
should be even.
Like all applications which communicate over networks, WebCCTV uses communication
channels to pass data (commands, video, web-pages, etc …) back and forth. The network
language that the WebCCTV uses is called TCP/IP. This is not a unique language but a
family of related network languages, called network protocols. These TCP/IP protocols are the
network protocols used on the Internet and on most networks throughout the world today.
WebCCTV uses two protocols specifically: TCP and UDP.
A communication channel on a TCP/IP network can be represented as a tunnel with two
endpoints. The two programs communicating with one another are each said to be at each
endpoint. These endpoints are called ports.
When the two programs communicating with one another are not located on the same
corporate network (like most communication between a program on a client PC and a program
running on another computer on the Internet), often there is some kind of guardian device in
between them. These guardian devices are called Firewalls. Their job is to guard all network
communication between the corporate network and the Internet and block certain unwanted
communications while allowing the desired communication to pass.
There are several levels on which a firewall can guard network communication. The most
common way is to allow or disallow certain ports to be used, depending on which applications
are allowed to communicate.
A firewall guards a port in a certain direction. Communication that is initiated from the
Internet towards the corporate network is called incoming traffic, while communication from
the corporate network towards the Internet is called outgoing traffic. Note that the initiation of
the communication is important: once a connection is made, data can be transferred in both
directions.
Let’s apply this principle to WebCCTV network communication. The WebCCTV client (the
ActiveX component embedded in Internet Explorer at the client machine) will try to create
network connections to the WebCCTV server. The eventual result of these connections will be
video data streaming from the WebCCTV server to the WebCCTV client, but since the
WebCCTV client initiates them, they are referred to as connections towards the WebCCTV.
From the client perspective, it is outgoing traffic, while for the server it is incoming traffic.
In order for the WebCCTV to function correctly, the appropriate ports need to be
opened for communication towards the WebCCTV.
There are three port configurations to perform:
1. TCP Port 80: to allow external users to see the web interface (HTTP traffic). This port
is usually opened by default.
Some ISPs block port 80. Please inform yourself.
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
21
2. TCP Port 1518: to allow external users to receive alarms, control PTZ cameras, send
commands, etc. This is called the WebCCTV control signal.
3. UDP Ports 4096 thru 4223: By default the WebCCTV uses a range of UDP ports to
transport video streams. These UDP ports are not listening all the time. The WebCCTV
software enables them at random to enhance security.
Typically when the UDP ports are not opened correctly, the user only sees the webinterface but no live images.
To allow Quadrox support personnel to get remote access to the WebCCTV, TCP Port
3389 needs to be opened for Remote Desktop Connection.
If the Video Server is monitored by the Quadrox Monitoring Department, TCP Port
5666 needs to be opened.
A firewall can be placed on several positions in the network. The most common place is at the
edge of the corporate network, or in other words between the corporate network and the
Internet. Recently it also became popular to place a firewall to protect the network traffic from
a single computer. A firewall that is placed between the computer and the network is referred
to as a ‘Personal Firewall’ application.
In practice, a corporate network firewall is often integrated with the router connecting the LAN
and the internet. For more information on routers, see the section on connecting the
WebCCTV to the internet. A personal firewall is software running on the computer that it
protects. Personal firewall applications can be installed separately but are also included in the
Windows XP operating system (Service Pack 2) and in many virus protection software
packages.
There are several scenarios where firewall configuration is necessary:
1. A user on a corporate network or at home behind a broadband router wants to access a
WebCCTV on the Internet
2. A user on the Internet wants to access a WebCCTV on a corporate network.
These situations are explained in more detail in the section on how to connect your WebCCTV
to the internet. If a user on a corporate network wants to connect to a WebCCTV on another
network, a logical combination of these two situations can be applied.
1. A user with a personal firewall application on his computer wants to access a
WebCCTV on the corporate network or on the Internet.
2. There is a personal firewall application installed on the WebCCTV.
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
2.3.5 Connecting a client
2.3.5.1 Minimum client requirements
Operating system
Windows XP SP3
Windows Vista
Windows 7
64-bit Operating Systems are supported.
Hardware
Intel Dual Core or higher
1024 MB RAM
128 MB RAM on the video card
22
Software
Internet Explorer 7 or higher
DirectX 9.0c
VC++ 8.0 runtime library
Media players and codecs
Windows Media Player 11
Windows Media Formats 11
Some useful downloads are available in the System Downloads menu. See the User
Manual for more information.
In case you are using WebCCTV Network Video Servers (NVS) or have IP cameras that
stream in MPEG or H.264, a codec also needs to be installed. We advice you to install the
Quadrox Codec Pack which can be found in the System Downloads menu (See User Manual
for more information) or on the support pages of www.webcctv.com.
2.3.5.2 Client configuration
Hardware video acceleration
In order to enjoy all the features of WebCCTV, the hardware acceleration of your video card
needs to be enabled.
1. Right click on the desktop and choose properties.
2. Select the Settings tab and click the Advanced button.
Version 4.4 Series
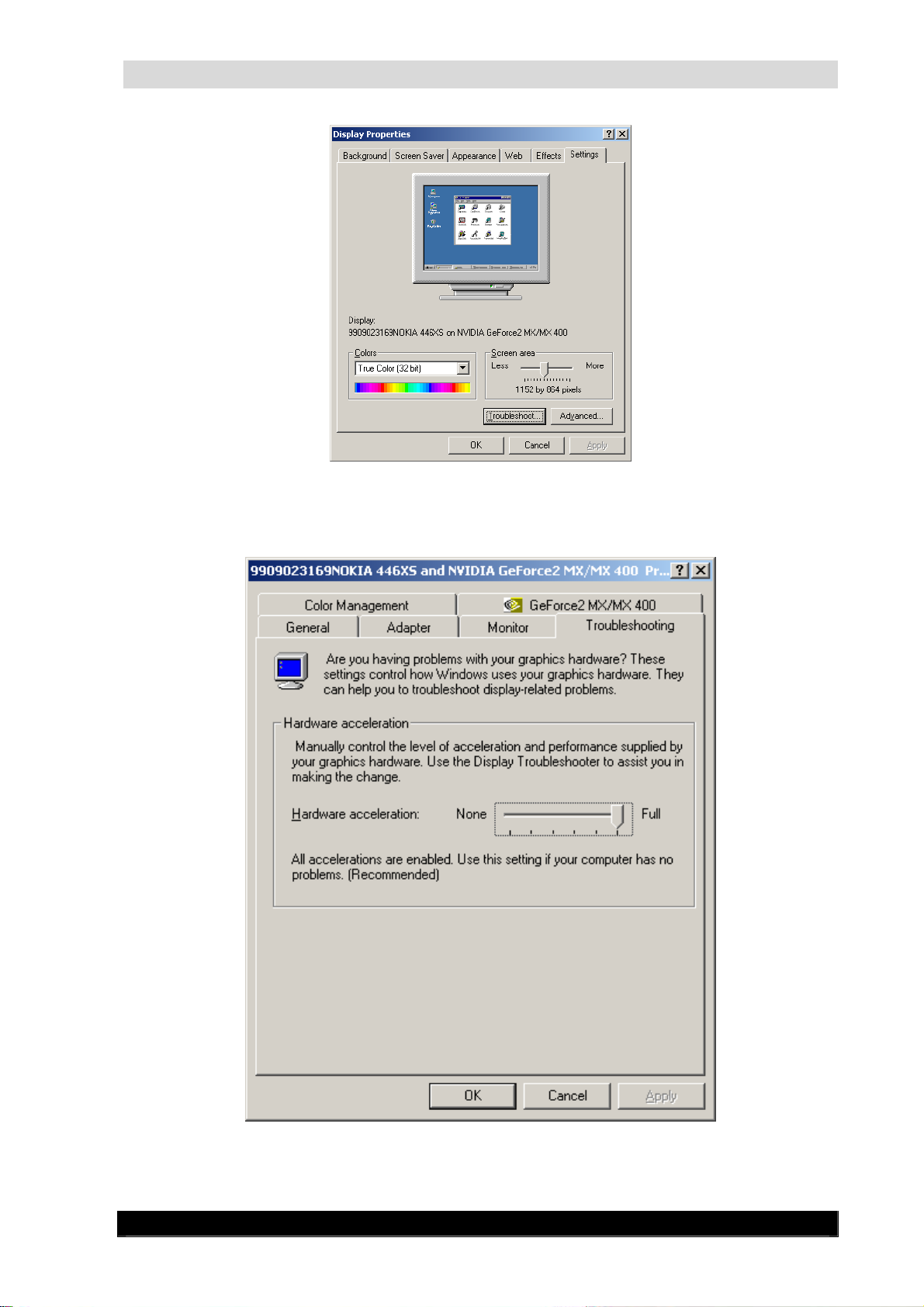
WebCCTV Installation Manual
Display Properties Screen
23
3. Choose the Troubleshooting tab and put the hardware acceleration to Full.
Version 4.4 Series
Troubleshooting Tab Screen

WebCCTV Installation Manual
24
Sometimes the support department will ask you to put this setting to None in order to
customize your system for particular use scenarios.
Firewall
If you have a personal firewall, configure it according to section 2.4.4. The ports for outgoing
connections should be opened.
A personal firewall is included in Windows XP Service Pack 2 and also in some virus
scanners. Separate firewall software exists as well.
The personal firewall in Windows XP Service Pack 2 has all outgoing and necessary
incoming connections open by default. No extra configuration is necessary in this
case.
Internet Explorer settings
Make sure that Internet Explorer allows the installation and execution of signed ActiveX
components.
1. Make sure you are logged on to Windows as an Administrator.
2. Go to the Tools Menu. Choose Internet Options.
3. Go to the Security Tab.
4. Click the Sites button, deselect the https checkbox and add your WebCCTV to the
trusted sites list. Click OK.
5. Click the Custom level button at the bottom.
6. Set the following options to ‘enable’ or ‘prompt’:
7. Download signed ActiveX controls (prompt)
8. Run ActiveX controls and plug-ins (enable)
9. Script ActiveX controls marked as safe (enable)
Adding your WebCCTV to the trusted sites is required to guarantee that all necessary
communication can be established with the WebCCTV server!
Anti-virus and anti-spyware/malware software
Make sure that your anti-virus and anti-spyware/malware software is set to...
1. Allow the WebCCTV ActiveX component to install and execute. (See also Internet
explorer settings)
2. Allow scripts to be executed.
The web application of the WebCCTV relies heavily on both issues.
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
25
2.3.6 Connecting WebCCTV to the Internet
2.3.6.1 Creating a network connection
When you start your WebCCTV, Windows XPe detects your network adapter and
automatically starts the local area connection. Unlike other types of connections, the local area
connection is created automatically, and you do not have to click the local area connection in
order to start.
A local area connection is the only type of connection that is automatically created
and activated.
To establish connections of another type follow the steps below:
Click Settings -> Control panel -> Network and Internet connections
In the Network and Internet connections window click File-> New connection. You’ll
see the following window:
Network Connection Wizard Screen
Follow the prompts the Network connection wizard provides to define your unit in the
network.
For obtaining more detailed information about your network settings please contact
your system administrator.
Version 4.4 Series

WebCCTV Installation Manual
26
2.3.6.2 Router and firewall
To fully understand this section it is important to know what the difference between a router
and a firewall is.
A firewall is the piece of software that takes care of guarding the network communications.
Sometimes the term ‘firewall’ refers to the machine performing firewall tasks. This is
confusing and in fact incorrect: normally a firewall is not a piece of hardware, but a program
running on that hardware.
A router is a piece of hardware that embodies the physical connection between two different
networks (e.g. your local network and the Internet). It redirects (“routes”) data so that it arrives
at the correct place. A router is a hardware device, but its functionality is controlled by
software that runs on the router.
Sometimes the routing functionality is provided by a proxy server, bridge or gateway. While
these are not the same as routers, they can be considered as such for the discussion in this
document.
Router software can have firewall capabilities. In other words, the router software
can have, apart from its normal capability to connect two networks and redirect data,
the capabilities of inspecting, allowing, and denying certain network communication.
As an example, most broadband routers (ADSL, SDSL, cable modems, etc)
nowadays have firewall capabilities and are also being used as such.
In the following schemes the firewall and the router are depicted as two different
entities (nodes on the network), but know that they could be one and the same node
in practical cases.
2.3.6.2.1 Configuring router
The router that forms the connection between the corporate network and the Internet needs to
know which internal machine it has to send network traffic to.
For example, a client machine on the internet requests a connection on port 1518 (the port for
WebCCTV video commands), using the public IP address of the router. The router then needs
to know to which device on the corporate network it needs to send this connection request, in
this case the WebCCTV. So the router needs to know the local IP address on the corporate
network of the WebCCTV. Configurations for different brands and models of routers in the
field can be found in:
Web Resource for Router Configuration and Setup:
http://www.portforward.com/routers.htm
Networking Tips:
http://www.portforward.com/network.htm
If you don’t already have a router you will need to purchase one and configure it as part of you
network.
Useful commands
Version 4.4 Series
 Loading...
Loading...