
Sample to Insight__
February 2021
QIAGEN® Plasmid
Purification Handbook
QIAGEN Plasmid Mini, Midi, Maxi, Mega, and
Giga Kits
For purification of ultrapure, transfection-grade
plasmid DNA

2
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Contents
Kit Contents ............................................................................................................... 3
Shipping and Storage ................................................................................................. 4
Intended Use .............................................................................................................. 4
Safety Information ....................................................................................................... 5
Quality Control ........................................................................................................... 5
Introduction ................................................................................................................ 6
Principle and procedure .................................................................................... 6
Equipment and Reagents to Be Supplied by User ............................................................ 8
Important Notes .......................................................................................................... 9
Protocol: Plasmid or Cosmid DNA Purification Using QIAGEN Plasmid Mini Kit .............. 17
Protocol: Plasmid or Cosmid DNA Purification Using QIAGEN Plasmid Midi and Maxi Kits
.............................................................................................................................. 23
Protocol: Plasmid or Cosmid DNA Purification Using QIAGEN Plasmid Mega and Giga Kits
.............................................................................................................................. 30
Protocol: Very Low-Copy Plasmid/Cosmid Purification Using QIAGEN-tip 100 or
QIAGEN-tip 500 ...................................................................................................... 39
Troubleshooting Guide .............................................................................................. 47
Appendix A: Agarose Gel Analysis of the Purification Procedure .................................... 52
Appendix B: Composition of Buffers ............................................................................ 56
Ordering Information ................................................................................................ 59
Document Revision History ......................................................................................... 64

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
3
Kit Contents
QIAGEN Plasmid Kit
Catalog no.
QIAGEN-tip 20 25 100 – – – – –
QIAGEN-tip 100 – – 25 100 – – –
QIAGEN-tip 500 – – – – 10 25 4 x 25
Buffer P1 20 ml 2 x 20 ml 110 ml 500 ml 110 ml 2 x 150 ml 8 x 150 ml
Buffer P2 20 ml 2 x 20 ml 110 ml 500 ml 110 ml 2 x 150 ml 8 x 150 ml
Buffer P3 20 ml 2 x 20 ml 110 ml 500 ml 110 ml 2 x 150 ml 8 x 150 ml
Buffer QBT 60 ml 2 x 60 ml 2 x 60 ml 500 ml 2 x 60 ml 2 x 200 ml 8 x 200 ml
Buffer QC 2 x 60 ml 2 x 240 ml 3 x 205 ml 5 x 500 ml 3 x 240 ml 4 x 500 ml 16 x 500 ml
Buffer QF 30 ml 140 ml 200 ml 4 x 140 ml 200 ml 510 ml 4 x 510 ml
RNase A* 2 mg 2 x 2 mg 11 mg 50 mg 11 mg 2 x 15 mg 8 x 15 mg
LyseBlue® 20 µl 2 x 20 µl 110 µl 500 µl 110 µl 2 x 150 µl 8 x 150 µl
Quick-Start Protocol 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
* Provided in a 10 mg/ml or 100 mg/ml solution.
QIAGEN Plasmid Kit
Catalog no.
QIAGEN-tip 2500 5 25 – –
QIAGEN-tip 10000 – – 5 –
Buffer P1 2 x 150 ml 3 x 500 ml 3 x 250 ml 110 ml
Buffer P2 2 x 150 ml 3 x 500 ml 3 x 250 ml 110 ml
Buffer P3 2 x 150 ml 3 x 500 ml 3 x 250 ml 110 ml
Buffer QBT 200 ml 2 x 500 ml 2 x 200 ml 2 x 60 ml
Buffer QC 5 x 240 ml 11 x 500 ml 7 x 500 ml 3 x 240 ml
Buffer QF 200 ml 2 x 510 ml 510 ml 2 x 85 ml
RNase A* 2 x 15 mg 3 x 50 mg 3 x 25 mg 11 mg
LyseBlue 2 x 150 µl 3 x 500 µl 3 x 250 µl 110 µl
Quick-Start Protocol 1 1 1 1
* Provided in a 10 mg/ml or 100 mg/ml solution.
Mini (25)
12123
Mega (5)
12181
Mini (100)
12125
Midi (25)
12143
Mega (25)
12183
Midi (100)
12145
Maxi (10)
12162
Giga (5)
12191
Maxi (25)
12163
Plasmid Buffer Set
19046
Maxi (100)
12165

4
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Shipping and Storage
QIAGEN-tips should be stored dry and at room temperature (15–25°C). Under these
conditions, the components are stable for 2 years without showing any reduction in
performance and quality, unless otherwise indicated on the label.
The QIAGEN Plasmid Kits should be stored at room temperature. After adding RNase A, Buffer
P1 should be stored at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the components are stable for 6 months
without showing any reduction in performance and quality.
Other buffers and RNase A stock solution can be stored for 2 years at room temperature.
Intended Use
The QIAGEN Plasmid Kits are intended for molecular biology applications. These products
are not intended for the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of a disease.
All due care and attention should be exercised in the handling of the products. We recommend
all users of QIAGEN products to adhere to the NIH guidelines that have been developed for
recombinant DNA experiments, or to other applicable guidelines.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
5
Safety Information
When working with chemicals, always wear a suitable lab coat, disposable gloves, and
protective goggles. For more information, please consult the appropriate safety data sheets
(SDSs). These are available online in convenient and compact PDF format at
www.qiagen.com/safety, where you can find, view, and print the SDS for each QIAGEN kit
and kit component.
Quality Control
In accordance with QIAGEN’s ISO-certified Quality Management System, each lot of the
QIAGEN Plasmid Kit is tested against predetermined specifications to ensure consistent
product quality.

6
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
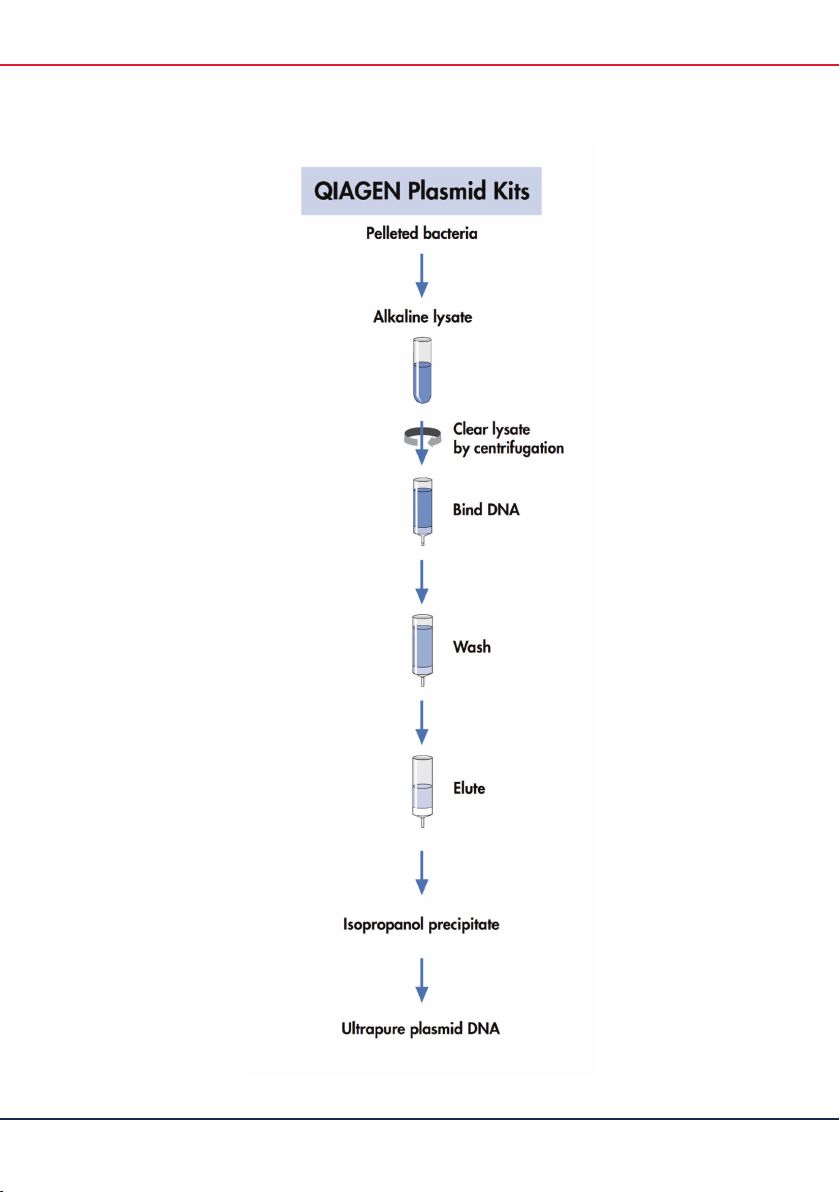
Introduction
The QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Kits are based on the remarkable selectivity of patented
QIAGEN resin, allowing purification of ultrapure supercoiled plasmid DNA with high yields.
Anion-exchange–based QIAGEN-tips yield transfection-grade DNA, which is highly suited for
use in a broad variety of demanding applications such as transfection, in vitro transcription
and translation, and enzymatic modifications. QIAGEN offers the most comprehensive
portfolio of tailored plasmid purification kits for any scale, throughput, or downstream
application. Select the optimum kit for your requirements by visiting our online selection
guide at www.qiagen.com/plasmidselectionguide. For transfection, QIAGEN also offers the
®
advanced PolyFect
combined with the high-quality plasmid DNA obtained from QIAGEN, QIAfilter, HiSpeed
and EndoFree
page 59).
Principle and procedure
, SuperFect®, and Effectene® transfection reagents. These reagents,
®
Plasmid Kits, provide optimal transfection results (see “Ordering Information”,
®
,
QIAGEN plasmid purification protocols are based on a modified alkaline lysis procedure,
followed by binding of plasmid DNA to QIAGEN resin under appropriate low-salt and pH
conditions. RNA, proteins, dyes, and low-molecular–weight impurities are removed by a
medium-salt wash. Plasmid DNA is eluted in a high-salt buffer and then concentrated and
desalted by isopropanol precipitation.
Each disposable QIAGEN-tip packed with QIAGEN resin is designed to operate by gravity
flow, reducing the amount of hands-on time required for the purification procedure.
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
7

8
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Equipment and Reagents to Be Supplied by User
When working with chemicals, always wear a suitable lab coat, disposable gloves, and
protective goggles. For more information, consult the appropriate safety data sheets (SDSs),
available from the product supplier.
For all protocols
Standard microbiological equipment for growing and harvesting bacteria
(e.g., inoculating loop, culture tubes and flasks, 37°C shaking incubator, and centrifuge
with rotor and tubes or bottles for harvesting cells)
QIArack (cat. no. 19015) or equivalent holder (see “Setup of QIAGEN-tips”, page 14)
Ice
Isopropanol
Ethanol, 70%
Plasmid resuspension buffer (e.g., TE buffer, pH 8.0, or Tris·Cl, pH 8.5)
For the QIAGEN Plasmid Mini Kit protocol
Microcentrifuge
1.5 ml or 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes
For QIAGEN Plasmid Midi, Maxi, Mega, and Giga Kit protocols
Centrifugation tubes or vessels with suitable capacity for the volumes specified in the
appropriate protocol
Refrigerated centrifuge capable of ≥20,000 x
centrifuge tubes or bottles
g
with a rotor for the appropriate

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
9
Important Notes
Please take a few moments to read this handbook carefully before beginning the DNA
preparation. If QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Kits are new to you, please visit our plasmid
resource page at www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo. Also be sure to read and follow the
appropriate detailed protocol.
Plasmid size
Plasmids up to approximately 150 kb can be purified using QIAGEN plasmid purification
protocols. Constructs larger than 45–50 kb, however, may exhibit somewhat reduced elution
efficiencies. Prewarming the elution buffer to 65°C may help to increase the yield of large
plasmids. For the isolation of large cosmid and plasmid DNA constructs, the QIAGEN LargeConstruct Kit is available (see “Ordering Information”, page 59).
Plasmid/cosmid copy number
Plasmids and cosmids vary in copy number, depending on the origin of replication they
contain, their size, and the size of insert. The protocols in this handbook are grouped
according to the copy number of the plasmid or cosmid to be purified.
High- and low-copy plasmids and cosmids should be purified using one of these protocols:
“Protocol: Plasmid or Cosmid DNA Purification
Using QIAGEN Plasmid Mini Kit”, page 17
“Protocol: Plasmid or Cosmid DNA Purification
Using QIAGEN Plasmid Midi and Maxi Kits”, page 23
“Protocol: Plasmid or Cosmid DNA Purification
Using QIAGEN Plasmid Mega and Giga Kits”, page 30

10
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Very low-copy plasmids and very low-copy cosmids (<10 copies per cell) should be purified
using “Protocol: Very Low-Copy Plasmid/Cosmid Purification Using QIAGEN-tip 100 or
QIAGEN-tip 500”, page 39, which uses extremely large culture volumes to obtain good
yields.
For more details, visit our plasmid resource page at www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
Host strains
The strain used to propagate a plasmid can have a substantial influence on quality of the
®
purified DNA. Host strains such as DH1, DH5
QIAGEN protocols. The slower-growing strain XL1-Blue also yields DNA of very high quality.
Strain HB101 and its derivatives, such as TG1 and the JM100 series, contain large amounts
of carbohydrates that are released during lysis and can inhibit enzyme activities if not
completely removed. In addition, some strains, such as JM101, JM110, and HB101, have
high levels of endonuclease activity and yield DNA of lower quality. If the quality of purified
DNA is not as expected, a change of host strain should be considered. If difficulty is
encountered with strains such as TG1 and Top10F, we recommend either reducing the amount
of culture volume or doubling the volumes of Buffers P1, P2, and P3 to improve the ratio of
biomass to lysis buffers for optimized lysis conditions.
α, and C600 yield high-quality DNA with

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
11
Table 1. Origins of replication and copy numbers of various plasmids and cosmids
DNA construct Origin of replication Copy number Classification
Plasmids
pUC vectors pMB1* 500–700 High copy
pBluescript® vectors ColE1 300–500 High copy
pGEM® vectors pMB1* 300–400 High copy
pTZ vectors pMB1* >1000 High copy
pBR322 and derivatives pMB1* 15–20 Low copy
pACYC and derivatives p15A 10–12 Low copy
pSC101 and derivatives pSC101 ~5 Very low copy
Cosmids
SuperCos pMB1 10–20 Low copy
pWE15 ColE1 10–20 Low copy
* The pMB1 origin of replication is closely related to that of ColE1 and falls in the same incompatibility group. The
high-copy plasmids listed here contain mutated versions of this origin.
Culture media
QIAGEN plasmid purification protocols are optimized for use with cultures grown in standard
9
Luria Bertani (LB) medium to a cell density of approximately 3–4 x 10
corresponds to a pellet wet weight of approximately 3 g/liter medium. Please note that a
number of slightly different LB culture broths, containing different concentrations of NaCl, are
commonly used. We recommend growing cultures in LB medium containing 10 g NaCl per
liter (Table 2) to obtain the highest plasmid yields.
cells/ml, which typically
Rich media are not recommended for plasmid preparation with QIAGEN-tips. If rich media
must be used, growth time must be optimized and culture volumes reduced. For more details,
visit our plasmid resource page at www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
12
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Table 2. Composition of Luria Bertani (LB)* medium
Contents Per liter
Tryptone 10 g
Yeast extract 5 g
NaCl 10 g
* See Appendix B, page 56, for preparation of LB medium.
Culture volume
Do not exceed the maximum recommended culture volumes given at the beginning of each
protocol (and on the card inside the back cover of this handbook). Using larger culture volumes
will lead to an increase in biomass and can affect the efficiency of alkaline lysis, leading to
reduced yield and purity of the preparation.
The protocol for the QIAGEN Plasmid Kits is optimized for use with cultures grown in standard
9
LB medium, grown to a cell density of approximately 3–4 x 10
harvesting cultures after approximately 12–16 hours of growth, which typically is the transition
from logarithmic into stationary growth phase. It is best to assess the cell density of the culture
and, if that is too high, to reduce the culture volumes accordingly or increase the volumes of
Buffers P1, P2, and P3. A high ratio of biomass to lysis buffers will result in poor lysis conditions
and subsequently low DNA yield and purity. For determination of cell density, calibration of
each individual spectrophotometer is required to facilitate accurate conversion of OD
measurements into the number of cells per milliliter. This can be achieved by plating serial
dilutions of a culture onto LB-agar plates in the absence of antibiotics. The counted colonies
are used to calculate the number of cells per milliliter, which is then set in relation to the
measured OD
values.
600
cells per ml. We advise
600

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
13
Capacity of QIAGEN-tips
QIAGEN-tips are available in a variety of sizes for preparation of as little as 20 µg or as much
as 10 mg plasmid DNA (Figure 1). The maximum plasmid-binding capacities of the
QIAGEN-tips 20, 100, 500, 2500, and 10000 are at least 20 µg, 100 µg, 500 µg, 2.5 mg,
and 10 mg, respectively. Actual yields will depend on culture volume, culture medium, plasmid
copy number, size of insert, and host strain. For more details, visit our plasmid resource page
at www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
Figure 1. QIAGEN-tip 20 to QIAGEN-tip 10000.

14
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Setup of QIAGEN-tips
QIAGEN-tips may be held upright in a suitable collection vessel such as a tube or flask, using
the tip holders provided with the kits (Figure 2A). Alternatively, the QIAGEN-tips 20, 100,
500, and 2500 may be placed in the QIArack (cat. no. 19015) (Figure 2B).
A
Figure 2. Setup of QIAGEN-tips (A) with tip holder or (B) with the QIArack.
B
Optional if using the QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridge for lysate clearing:
Figure 3. The vacuum-operated QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridge in use. Note that the bottle is not included in kits.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
15
Analytical gel analysis
The success of the plasmid purification procedure can be monitored on an analytical gel
Figure 4, page 53). We recommend removing and saving aliquots where indicated during
(
the purification procedure (samples 1–4). If the plasmid DNA is of low yield or low quality,
the samples can be analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis to determine the stage of the
purification where the problem occurred (see page 53).
Convenient stopping points in protocols
For all protocols, the purification procedure can be stopped and continued later by freezing
the cell pellets obtained by centrifugation. The frozen cell pellets can be stored at
−30 to −15°C for several weeks. In addition, the DNA eluted from the QIAGEN-tip can be
stored overnight at 2–8°C,* after which the protocol can be continued.
Using LyseBlue reagent
LyseBlue is a color indicator that provides visual identification of optimum buffer mixing. This
prevents common handling errors that lead to inefficient cell lysis and incomplete precipitation
of SDS, genomic DNA, and cell debris. This makes LyseBlue ideal for use by researchers who
have not had much experience with plasmid preparations, as well as experienced scientists
who want to be assured of maximum product yield.
LyseBlue can be added to the resuspension buffer (Buffer P1) bottle before use. Alternatively,
smaller amounts of LyseBlue can be added to aliquots of Buffer P1, enabling single plasmid
preparations incorporating visual lysis control to be performed.
LyseBlue reagent should be added to Buffer P1 at a ratio of 1:1000 to achieve the required
working concentration (e.g., 10 µl LyseBlue into 10 ml Buffer P1). Make sufficient
LyseBlue/Buffer P1 working solution for the number of plasmid preps being performed.
* Longer storage is not recommended.

16
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
LyseBlue precipitates after addition into Buffer P1. This precipitate will completely dissolve after
addition of Buffer P2. Shake Buffer P1 before use to resuspend LyseBlue particles.
The plasmid preparation procedure is performed as usual. After addition of Buffer P2 to
Buffer P1, the color of the suspension changes to blue. Mixing should result in a
homogeneously colored suspension. If the suspension contains localized regions of colorless
solution or if brownish cell clumps are still visible, continue mixing the solution until a
homogeneously colored suspension is achieved.
Upon addition of neutralization buffer (Buffer P3 or Buffer N3), LyseBlue turns colorless. The
presence of a homogeneous solution with no traces of blue indicates that SDS from the lysis
buffer has been effectively precipitated.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
17
Protocol: Plasmid or Cosmid DNA Purification
Using QIAGEN Plasmid Mini Kit
This protocol is designed for preparation of up to 20 µg of high-copy plasmid or cosmid DNA
using the QIAGEN Plasmid Mini Kit. For additional protocols, such as for cosmid, low-copynumber plasmid, BACs, PACs, P1s, and double-stranded M13 replicative form purification,
see the recommendations at www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
Important points before starting
New users are advised to familiarize themselves with the detailed protocol provided in
this handbook. In addition, extensive background information is provided on our plasmid
resource page, www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
Optional: Remove samples at indicated steps to monitor the procedure on an analytical
gel (see Appendix A, “Agarose
Things to do before starting
gel analysis
”, page 53).
Before use, centrifuge RNase A briefly, and then add into Buffer P1 to obtain a final
concentration of 100 μg/ml.
Check Buffer P2 for SDS precipitation due to low storage temperatures. If necessary,
dissolve the SDS by warming to 37°C.
Prechill Buffer P3 at 4°C.
Optional: Add the provided LyseBlue reagent to Buffer P1 and mix before use. Use 1 vial
LyseBlue reagent per bottle Buffer P1 for a final dilution of 1:1000 (e.g., 10 µl LyseBlue
into 10 ml Buffer P1). LyseBlue provides visual identification of optimum buffer mixing,
thereby preventing the common handling errors that lead to inefficient cell lysis and
incomplete precipitation of SDS, genomic DNA, and cell debris. For more details, see
“Using LyseBlue reagent” on page 15.

18
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Procedure
1. Pick a single colony from a freshly streaked selective plate and inoculate a starter culture
of 2–5 ml LB medium containing the appropriate selective antibiotic. Incubate for
approximately 8 h at 37°C with vigorous shaking (approx. 300 rpm).
Use a tube or flask with a volume of at least 4 times the volume of the culture.
2. Dilute the starter culture 1/500 to 1/1000 into 3 ml selective LB medium. Grow at 37°C
for 12–16 h with vigorous shaking (approx. 300 rpm).
Use a flask or vessel with a volume of at least 4 times the volume of the culture. The culture
should reach a cell density of approximately 3–4 x 109 cells per milliliter, which typically
corresponds to a pellet wet weight of approximately 3 g/liter medium.
3. Harvest the bacterial cells by centrifugation at 6000 x g for 15 min at 4°C.
If you wish to stop the protocol and continue later, freeze the cell pellets at −30 to −15°C.
4. Resuspend the bacterial pellet in 0.3 ml of Buffer P1.
Ensure that RNase A has been added to Buffer P1.
If LyseBlue reagent has been added to Buffer P1, vigorously shake the buffer bottle before
use to ensure LyseBlue particles are completely resuspended. The bacteria should be
resuspended completely by vortexing or pipetting up and down until no cell clumps remain.
5. Add 0.3 ml of Buffer P2, mix thoroughly by vigorously inverting the sealed tube
4−6 times, and incubate at room temperature for 5 min.
Do not vortex because this will result in shearing of genomic DNA. The lysate should
appear viscous. Do not allow the lysis reaction to proceed for more than 5 min. After use,
the bottle containing Buffer P2 should be closed immediately to avoid acidification from
in the air.
CO
2

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
19
If LyseBlue has been added to Buffer P1, the cell suspension will turn blue after addition of
Buffer P2. Mixing should result in a homogeneously colored suspension. If the suspension
contains localized colorless regions or if brownish cell clumps are still visible, continue
mixing the solution until a homogeneously colored suspension is achieved.
6. Add 0.3 ml of chilled Buffer P3, mix immediately and thoroughly by vigorously inverting
4–6 times, and incubate on ice for 5 min.
Precipitation is enhanced by using chilled Buffer P3 and incubating on ice. After addition of
Buffer P3, a fluffy white material forms and the lysate becomes less viscous. The
precipitated material contains genomic DNA, proteins, cell debris, and KDS. The lysate
should be mixed thoroughly to ensure even potassium dodecyl sulphate precipitation. If the
mixture still appears viscous, more mixing is required to completely neutralize the solution.
If LyseBlue reagent has been used, the suspension should be mixed until all trace of blue
has gone and the suspension is colorless. A homogeneous colorless suspension indicates
that the SDS has been effectively precipitated.
7. Centrifuge at maximum speed in a microcentrifuge for 10 min. Remove the supernatant
containing plasmid DNA promptly.
Before loading the centrifuge, the sample should be mixed again. Centrifugation should be
performed at maximum speed in 1.5 ml or 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes (e.g., 10,000–
13,000 rpm in a microcentrifuge). Maximum speed corresponds to 14,000–18,000 x
for most microcentrifuges. After centrifugation, the supernatant should be clear. If the
supernatant is not clear, a second, shorter centrifugation should be carried out to avoid
applying any suspended or particulate material to the column. Suspended material (which
causes the sample to appear turbid) will clog the column and reduce or eliminate flow.
Optional: Remove a 50 µl sample from the cleared lysate and save it for an analytical gel
(sample 1).
g

20
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
8. Equilibrate a QIAGEN-tip 20 by applying 1 ml Buffer QBT, and allow the column to
empty by gravity flow.
Place QIAGEN-tips into a QIArack over the waste tray or use the tip holders provided with
each kit (see “Setup of QIAGEN-tips”, page 14). Flow of buffer will begin automatically by
reduction in surface tension due to the presence of detergent in the equilibration buffer.
Allow the QIAGEN-tip to drain completely. QIAGEN-tips can be left unattended because
the flow of buffer will stop when the meniscus reaches the upper frit in the column.
9. Apply the supernatant from step 7 to the QIAGEN-tip 20 and allow it to enter the resin
by gravity flow.
The supernatant should be loaded onto the QIAGEN-tip promptly. If it is left too long and
becomes cloudy due to further precipitation of protein, it must be centrifuged again before
loading to prevent clogging of the QIAGEN-tip.
Optional: Remove a 50 µl sample of the flow-through and save for an analytical gel
(sample 2).
10. Wash the QIAGEN-tip 20 with 2 x 2 ml Buffer QC.
Allow Buffer QC to move through the QIAGEN-tip by gravity flow.
Optional: Remove a 220 µl sample of the combined wash fractions and save for an
analytical gel (sample 3).
11. Elute DNA with 0.8 ml Buffer QF.
Collect the eluate in a 1.5 or 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes (not supplied).
Note: For constructs larger than 45–50 kb, prewarming the elution buffer to 65°C may help
to increase yield.
Optional: Remove a 45 µl sample of the eluate and save for an analytical gel (sample 4).

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
21
12. Precipitate DNA by adding 0.7 volumes (0.56 ml per 0.8 ml of elution volume) of
room-temperature isopropanol to the eluted DNA. Mix and centrifuge immediately at
≥15,000 x
g
rpm for 30 min in a microcentrifuge. Carefully decant the supernatant.
All solutions should be at room temperature to minimize salt precipitation. Isopropanol
pellets have a glassy appearance and may be more difficult to see than the fluffy,
salt-containing pellets that result from ethanol precipitation. Marking the outside of the tube
before centrifugation allows the pellet to be easily located. Isopropanol pellets are more
loosely attached to the side of the tube; take care when removing the supernatant.
g
13. Wash DNA pellet with 1 ml of 70% ethanol and centrifuge at 15,000 x
for 10 min.
Carefully decant the supernatant without disturbing the pellet.
The 70% ethanol removes precipitated salt and replaces isopropanol with the more volatile
ethanol, making the DNA easier to redissolve.
14. Air-dry the pellet for 5–10 min, and redissolve the DNA in a suitable volume of buffer
(e.g., TE buffer, pH 8.0, or 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 8.5).
Redissolve the DNA pellet by rinsing the walls to recover the DNA. Pipetting the DNA up
and down to promote resuspension may cause shearing and should be avoided.
Overdrying the pellet will make the DNA difficult to redissolve. DNA dissolves best under
slightly alkaline conditions; it does not easily dissolve in acidic buffers.

22
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Determination of yield
To determine the yield, DNA concentration should be determined by both UV
spectrophotometry at 260 nm and quantitative analysis on an agarose gel. For reliable
spectrophotometric DNA quantification,
A
readings should lie between 0.1 and 1.0.
260
Agarose gel analysis
We recommend removing and saving aliquots during the purification procedure (samples 1–
4). If the plasmid DNA is of low yield or quality, the samples can be analyzed by agarose gel
electrophoresis to determine the stage of the purification procedure where the problem
occurred (see page 53).

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
23
Protocol: Plasmid or Cosmid DNA Purification
Using QIAGEN Plasmid Midi and Maxi Kits
This protocol is designed for preparation of up to 100 µg high- or low-copy plasmid or cosmid
DNA using the QIAGEN Plasmid Midi Kit, or up to 500 µg using the QIAGEN Plasmid Maxi
Kit. For additional protocols, such as for purification of very low-copy plasmids or cosmids of
less than 10 copies per cell, see page 39 or visit www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
Low-copy plasmids that have been amplified in the presence of chloramphenicol should be
treated as high-copy plasmids when choosing the appropriate culture volume.
Table 3. Maximum recommended culture volumes*
QIAGEN-tip 100 QIAGEN-tip 500
High-copy plasmids 25 ml 100 ml
Low-copy plasmids 100 ml 500 ml
* For the QIAGEN-tip 100, the expected yields are 75–100 µg for high-copy plasmids and 20–100 µg for low-copy
plasmids. For the QIAGEN-tip 500, the expected yields are 300–500 µg for high-copy plasmids and 100–500 µg
for low-copy plasmids.
Important points before starting
New users are advised to familiarize themselves with the detailed protocol provided in
this handbook. In addition, extensive background information is provided on our plasmid
resource page, www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
If working with low-copy vectors, it may be beneficial to increase the lysis buffer volumes
to increase the efficiency of alkaline lysis and, thereby, the DNA yield. In case additional
Buffers P1, P2, and P3 are needed, their compositions are provided in Appendix B
on page 56. Alternatively, the buffers may be purchased separately (see “Ordering
Information”, page 59).

24
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Optional: Remove samples at the indicated steps to monitor the procedure on an
analytical gel (see page 53).
The symbol denotes values for QIAGEN-tip 100, using the QIAGEN Plasmid Midi Kit;
denotes values for QIAGEN-tip 500, using the QIAGEN Plasmid Maxi Kit.
Things to do before starting
Before use, centrifuge RNase A briefly, and then add into Buffer P1 to obtain a final
concentration of 100 μg/ml.
Check Buffer P2 for SDS precipitation due to low storage temperatures. If necessary,
dissolve the SDS by warming to 37°C.
Prechill Buffer P3 at 4°C.
Optional: Add the provided LyseBlue reagent to Buffer P1 and mix before use. Use 1 vial
LyseBlue reagent per bottle Buffer P1 for a final dilution of 1:1000 (e.g., 10 µl LyseBlue
into 10 ml Buffer P1). LyseBlue provides visual identification of optimum buffer mixing
thereby preventing the common handling errors that lead to inefficient cell lysis and
incomplete precipitation of SDS, genomic DNA, and cell debris. For more details, see
“Using LyseBlue reagent” on page 15.
Procedure
1. Pick a single colony from a freshly streaked selective plate and inoculate a starter culture
of 2–5 ml LB medium containing the appropriate selective antibiotic. Incubate for
approximately 8 h at 37°C with vigorous shaking (approx. 300 rpm).
Use a tube or flask with a volume of at least 4 times the volume of the culture.
2. Dilute the starter culture 1/500 to 1/1000 into selective LB medium.
For high-copy plasmids, inoculate 25 ml or 100 ml medium with 25–50 µl or
100–200 µl of starter culture.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
25
For low-copy plasmids, inoculate 100 ml or 500 ml medium with 100–200 µl or
250–500 µl of starter culture.
Grow at 37°C for 12–16 h with vigorous shaking (approx. 300 rpm).
Use a flask or vessel with a volume of at least 4 times the volume of the culture. The culture
should reach a cell density of approximately 3–4 x 109 cells per milliliter, which typically
corresponds to a pellet wet weight of approximately 3 g/liter medium.
g
3. Harvest the bacterial cells by centrifugation at 6000 x
for 15 min at 4°C.
If you wish to stop the protocol and continue later, freeze the cell pellets at −30 to −15°C.
4. Resuspend the bacterial pellet in 4 ml or 10 ml Buffer P1.
For efficient lysis, it is important to use a vessel that is large enough to allow complete
mixing of the lysis buffers. Ensure that RNase A has been added to Buffer P1.
If LyseBlue reagent has been added to Buffer P1, vigorously shake the buffer bottle before
use to ensure LyseBlue particles are completely resuspended. The bacteria should be
resuspended completely by vortexing or pipetting up and down until no cell clumps remain.
5. Add 4 ml or 10 ml Buffer P2, mix thoroughly by vigorously inverting the sealed tube
4–6 times, and incubate at room temperature for 5 min.
Do not vortex, because this will result in shearing of genomic DNA. The lysate should
appear viscous. Do not allow the lysis reaction to proceed for more than 5 min. After use,
the bottle containing Buffer P2 should be closed immediately to avoid acidification from
in the air.
CO
2
If LyseBlue has been added to Buffer P1, the cell suspension will turn blue after addition of
Buffer P2. Mixing should result in a homogeneously colored suspension. If the suspension
contains localized colorless regions or if brownish cell clumps are still visible, continue
mixing the solution until a homogeneously colored suspension is achieved.

26
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
6. Add 4 ml or 10 ml of chilled Buffer P3, mix immediately and thoroughly by
vigorously inverting 4–6 times, and incubate on ice for 15 min or 20 min.
Precipitation is enhanced by using chilled Buffer P3 and incubating on ice. After addition of
Buffer P3, a fluffy white material forms and the lysate becomes less viscous. The
precipitated material contains genomic DNA, proteins, cell debris, and KDS. The lysate
should be mixed thoroughly to ensure even potassium dodecyl sulfate precipitation. If the
mixture still appears viscous, more mixing is required to completely neutralize the solution.
If LyseBlue reagent has been used, the suspension should be mixed until all trace of blue
has gone and the suspension is colorless. A homogeneous colorless suspension indicates
that the SDS has been effectively precipitated.
g
7. Centrifuge at ≥20,000 x
for 30 min at 4°C. Remove supernatant containing plasmid
DNA promptly.
Before loading the centrifuge, the sample should be mixed again. Centrifugation should be
performed in non-glass tubes (e.g., polypropylene). After centrifugation the supernatant
should be clear.
Note: Instead of centrifugation steps 7 and 8, the lysate can be efficiently cleared by
filtration using QIAfilter Kits or Cartridges (see www.qiagen.com/products/discovery-and-
translational-research/dna-rna-purification/dna-purification/plasmid-dna/qiafilterplasmid-kits).
g
8. Centrifuge the supernatant again at ≥20,000 x
for 15 min at 4°C. Remove
supernatant containing plasmid DNA promptly.
This second centrifugation step should be carried out to avoid applying suspended or
particulate material to the QIAGEN-tip. Suspended material (causing the sample to appear
turbid) can clog the QIAGEN-tip and reduce or eliminate gravity flow.
Optional: Remove a 240 µl or 120 µl sample from the cleared lysate supernatant and
save for an analytical gel (sample 1) to determine whether growth and lysis conditions
were optimal.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
27
9. Equilibrate a QIAGEN-tip 100 or QIAGEN-tip 500 by applying 4 ml or
10 ml Buffer QBT, and allow the column to empty by gravity flow.
Flow of buffer will begin automatically by reduction in surface tension due to the presence
of detergent in the equilibration buffer. Allow the QIAGEN-tip to drain completely.
QIAGEN-tips can be left unattended because the flow of buffer will stop when the meniscus
reaches the upper frit in the column.
10. Apply the supernatant from step 8 to the QIAGEN-tip and allow it to enter the resin by
gravity flow.
The supernatant should be loaded onto the QIAGEN-tip promptly. If it is left too long and
becomes cloudy due to further precipitation of protein, it must be centrifuged again or
filtered before loading to prevent clogging of the QIAGEN-tip.
Optional: Remove a 240 µl or 120 µl sample from the flow-through and save for an
analytical gel (sample 2) to determine the efficiency of DNA binding to the QIAGEN resin.
11. Wash the QIAGEN-tip with 2 x 10 ml or 2 x 30 ml Buffer QC.
Allow Buffer QC to move through the QIAGEN-tip by gravity flow. The first wash is
sufficient to remove contaminants in the majority of plasmid DNA preparations. The second
wash is especially necessary when large culture volumes or bacterial strains producing
large amounts of carbohydrates are used.
Optional: Remove a 400 µl or 240 µl sample from the combined wash fractions and
save for an analytical gel (sample 3).
12. Elute DNA with 5 ml or 15 ml Buffer QF.
Collect the eluate in a 15 ml or 50 ml tube (not supplied). Use of polycarbonate
centrifuge tubes is not recommended as polycarbonate is not resistant to the alcohol used in
subsequent steps.

28
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Note: For constructs larger than 45–50 kb, prewarming the elution buffer to 65°C may help
to increase yield.
Optional: Remove a 100 µl or 60 µl sample of the eluate and save for an analytical
gel (sample 4).
If you wish to stop the protocol and continue later, store the eluate at 4°C. Storage periods
longer than overnight are not recommended.
13. Precipitate DNA by adding 3.5 ml or 10.5 ml (0.7 volumes) room-temperature
g
isopropanol to the eluted DNA. Mix and centrifuge immediately at ≥15,000 x
for
30 min at 4°C. Carefully decant the supernatant.
All solutions should be at room temperature to minimize salt precipitation, although
centrifugation is carried out at 4°C to prevent overheating of the sample. Alternatively,
disposable conical-bottom centrifuge tubes can be used for centrifugation at 5000 x
g
60 min at 4°C. Isopropanol pellets have a glassy appearance and may be more difficult to
see than the fluffy, salt-containing pellets that result from ethanol precipitation. Marking the
outside of the tube before centrifugation allows the pellet to be more easily located.
Isopropanol pellets are also more loosely attached to the side of the tube, and care should
be taken when removing the supernatant.
for
14. Wash DNA pellet with 2 ml or 5 ml of room-temperature 70% ethanol, and
g
centrifuge at ≥15,000 x
for 10 min. Carefully decant the supernatant without
disturbing the pellet.
Alternatively, disposable conical-bottom centrifuge tubes can be used for centrifugation at
g
5000 x
for 60 min at 4°C. The 70% ethanol removes precipitated salt and replaces
isopropanol with the more volatile ethanol, making the DNA easier to redissolve.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
29
15. Air-dry the pellet for 5–10 min, and redissolve the DNA in a suitable volume of buffer
(e.g., TE buffer, pH 8.0, or 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 8.5).
Redissolve the DNA pellet by rinsing the walls to recover the DNA, especially if glass tubes
have been used. Pipetting the DNA up and down to promote resuspension may cause
shearing and should be avoided. Overdrying the pellet will make the DNA difficult to
redissolve. DNA dissolves best under slightly alkaline conditions; it does not easily dissolve
in acidic buffers.
Determination of yield
To determine the yield, DNA concentration should be determined by both UV
spectrophotometry at 260 nm and quantitative analysis on an agarose gel. For reliable
A
spectrophotometric DNA quantification,
readings should lie between 0.1 and 1.0.
260
Agarose gel analysis
We recommend removing and saving aliquots during the purification procedure
(samples 1−4). If the plasmid DNA is of low yield or quality, the samples can be analyzed by
agarose gel electrophoresis to determine the stage of the purification procedure where the
problem occurred (see page 53).

30
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Protocol: Plasmid or Cosmid DNA Purification
Using QIAGEN Plasmid Mega and Giga Kits
This protocol is designed for preparation of up to 2.5 mg of high- or low-copy plasmid or
cosmid DNA using the QIAGEN Plasmid Mega Kit, or up to 10 mg using the QIAGEN Plasmid
Giga Kit. For additional protocols, such as for purification of very low-copy plasmids or
cosmids <10 copies per cell, see page 39 or visit www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
Low-copy plasmids that have been amplified in the presence of chloramphenicol should be
treated as high-copy plasmids when choosing the appropriate culture volume.
Table 4. Maximum recommended culture volumes*
QIAGEN-tip 2500 QIAGEN-tip 10000
High-copy plasmids 500 ml (1.5 g pellet wet weight)† 2.5 liters (7.5 g pellet wet weight)†
Low-copy plasmids 2.5 liters (7.5 g pellet wet weight)† 5 liters†‡ (15 g pellet wet weight)†‡
* For the QIAGEN-tip 2500, the expected yields are 1.5–2.5 mg for high-copy plasmids and 0.5–2.5 mg for low-
copy plasmids. For the QIAGEN-tip 10000, the expected yields are 7.5–10 mg for high-copy plasmids and 1–5 mg
for low-copy plasmids.
†
On average, a healthy 1 liter shaker culture yields a pellet with a wet weight of approximately 3 g. When working
with fermentation cultures, however, the pellet wet weight may be significantly higher. Therefore, when using
fermented cultures, please refer to the pellet wet weight instead of the recommended culture volumes.
‡
Requires doubled amounts of alkaline lysis buffers.
Important points before starting
New users are advised to familiarize themselves with the detailed protocol provided in
this handbook. In addition, extensive background information is provided on our plasmid
resource page, www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
31
If working with low-copy vectors, it may be beneficial to increase the lysis buffer volumes
to increase the efficiency of alkaline lysis, and thereby the DNA yield. In case additional
Buffers P1, P2, and P3 are needed, their compositions are provided in Appendix B,
page 56. Alternatively, the buffers may be purchased separately (see “Ordering
Information, page 59).
Optional: Remove samples at the indicated steps to monitor the procedure on an
analytical gel (see page 53).
The symbol denotes values for QIAGEN-tip 2500, using the QIAGEN Plasmid Mega
Kit; denotes values for QIAGEN-tip 10000, using the QIAGEN Plasmid Giga Kit.
Things to do before starting
Before use, centrifuge RNase A briefly, and then add into Buffer P1 to obtain a final
concentration of 100 μg/ml.
Check Buffer P2 for SDS precipitation due to low storage temperatures. If necessary,
dissolve the SDS by warming to 37°C.
Prechill Buffer P3 at 4°C.
Optional: Add the provided LyseBlue reagent to Buffer P1 and mix before use. Use 1 vial
LyseBlue reagent per bottle Buffer P1 for a final dilution of 1:1000 (e.g., 10 µl LyseBlue
into 10 ml Buffer P1). LyseBlue provides visual identification of optimum buffer mixing
thereby preventing the common handling errors that lead to inefficient cell lysis and
incomplete precipitation of SDS, genomic DNA, and cell debris. For more details, see
“Using LyseBlue reagent” on page 15.
Optional: If using a QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridges (cat. no. 19781) for lysate clearing,
screw the QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridge onto a 45 mm-neck glass bottle and connect it
to a vacuum source. Do not overtighten the QIAfilter Cartridge on the bottle neck,
because the QIAfilter Cartridge plastic may crack.

32
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Procedure
1. Pick a single colony from a freshly streaked selective plate, and inoculate a starter culture
of 5–10 ml LB medium containing the appropriate selective antibiotic. Incubate for
approximately 8 h at 37°C with vigorous shaking (approx. 300 rpm).
Use a tube or flask with a volume at least 4 times the volume of the culture.
2. Dilute the starter culture 1/500 to 1/1000 into selective LB medium.
For high-copy plasmids, inoculate 500 ml or 2.5 liters medium with
500–1000 µl or 2.5–5 ml of starter culture.
For low-copy plasmids, inoculate 2.5 liters or 5 liters medium with
2.5–5 ml or 5–10 ml of starter culture.
Grow at 37°C for 12–16 h with vigorous shaking (approx. 300 rpm).
Use a flask or vessel with a volume at least 4 times the volume of the culture. The culture
should reach a cell density of approximately 3–4 x 109 cells per milliliter, which typically
corresponds to a pellet wet weight of approximately 3 g/liter medium.
g
3. Harvest the bacterial cells by centrifugation at 6000 x
for 15 min at 4°C.
Note: For Giga preparations of low-copy plasmids using 5 liters of culture, volumes of
Buffers P1, P2, and P3 in steps 4–6 should be doubled, due to the very large number of
cells harvested. For routine Giga preparation of low-copy plasmids, additional Buffers P1,
P2, and P3 may need to be purchased (see “Ordering Information”, page 59) or prepared
(see “Preparation of buffers”, page 57).
If you wish to stop the protocol and continue later, freeze the cell pellets at −30 to −15°C .

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
33
4. Resuspend the bacterial pellet in 50 ml or 125 ml of Buffer P1.
For efficient lysis, it is important to use a vessel that is large enough to allow complete
mixing of the lysis buffers. We recommend a 500 ml bottle for Mega preparations and a
1000 ml bottle for Giga preparations. Ensure that RNase A has been added to Buffer P1.
If LyseBlue reagent has been added to Buffer P1, vigorously shake the buffer bottle before
use to ensure LyseBlue particles are completely resuspended. The bacteria should be
resuspended completely by vortexing or pipetting up and down until no cell clumps remain.
5. Add 50 ml or 125 ml of Buffer P2, mix thoroughly by vigorously inverting
4−6 times, and incubate at room temperature for 5 min.
Do not vortex, because this will result in shearing of genomic DNA. The lysate should
appear viscous. Do not allow the lysis reaction to proceed for more than 5 min. After use,
the bottle containing Buffer P2 should be closed immediately to avoid acidification of
Buffer P2 from CO
in the air.
2
If LyseBlue has been added to Buffer P1, the cell suspension will turn blue after addition of
Buffer P2. Mixing should result in a homogeneously colored suspension. If the suspension
contains localized colorless regions or if brownish cell clumps are still visible, continue
mixing the solution until a homogeneously colored suspension is achieved.
6. Add 50 ml or 125 ml of chilled Buffer P3, mix immediately and thoroughly by
vigorously inverting 4–6 times, and incubate on ice for 30 min.
Precipitation is enhanced by using chilled Buffer P3 and incubating on ice. After addition of
Buffer P3, a fluffy white material forms and the lysate becomes less viscous. The
precipitated material contains genomic DNA, proteins, cell debris, and KDS. The lysate
should be mixed thoroughly to avoid localized potassium dodecyl sulfate precipitation.
If LyseBlue reagent has been used, the suspension should be mixed until all trace of blue
has gone and the suspension is colorless. A homogeneous colorless suspension indicates
that the SDS has been effectively precipitated.

34
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Optional: If using a QIAfilter for lysate clearing instead of centrifugation go to step 9.
7. Centrifuge at ≥20,000 x g for 30 min at 4°C. Remove supernatant containing plasmid
DNA promptly.
Before loading the centrifuge, the sample should be mixed again. Centrifugation should be
performed in 250 or 500 ml non-glass tubes (e.g., polypropylene; not supplied).
Note: Instead of centrifugation steps 7 and 8, the lysate can be efficiently cleared by
filtration using a QIAfilter Kits or Cartridges (see www.qiagen.com/products/discovery-
and-translational-research/dna-rna-purification/dna-purification/plasmid-dna/qiafilterplasmid-kits).
8. Centrifuge the supernatant again at ≥20,000 x g for 15 min at 4°C. Remove
supernatant containing plasmid DNA promptly.
This step should be carried out to avoid applying suspended or particulate material to the
QIAGEN-tip. Suspended material (causing the sample to appear turbid) can clog the
QIAGEN-tip and reduce or eliminate gravity flow.
Optional: Remove a 120 µl or 75 µl sample from the cleared lysate supernatant and
save for an analytical gel (sample 1) to determine whether growth and lysis conditions
were optimal.
Note: After this step, proceed to step 12. Steps 9–11 should be skipped if not using the
QIAfilter for clearing of the lysate.
9. Pour the lysate into the QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridge and incubate at room temperature
for 10 min.
Important: This 10 min incubation at room temperature is essential for optimal performance
of the QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridge. Do not agitate the QIAfilter Cartridge during this
time. A precipitate containing proteins, genomic DNA, and detergent will float and form a
layer on top of the solution. This ensures convenient filtration without clogging.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
35
10. Switch on the vacuum source. After all liquid has been pulled through, switch off the
vacuum source. Leave the QIAfilter Cartridge attached.
11. Add 50 ml (both ▲ Mega and ● Giga) Buffer FWB2 to the QIAfilter Cartridge and
gently stir the precipitate using a sterile spatula. Switch on the vacuum source until the
liquid has been pulled through completely. Gentle stirring of the precipitate enhances the
flow of liquid through the filter unit. Take care not to disperse the precipitate, as this may
result in carryover of cell debris and KDS, which will affect flow and binding
characteristics of the QIAGEN column. The filtered lysate in the bottle contains the
plasmid DNA.
Optional: Remove a ▲ 120 µl or ● 75 µl sample from the cleared lysate and save for an
analytical gel (sample 1) to determine whether growth and lysis conditions were optimal.
12. Equilibrate a QIAGEN-tip 2500 or QIAGEN-tip 10000 by applying 35 ml or
75 ml Buffer QBT, and allow the column to empty by gravity flow.
Flow of buffer will begin automatically by reduction in surface tension due to the presence
of detergent in the equilibration buffer. Allow the QIAGEN-tip to drain completely.
QIAGEN-tips can be left unattended because the flow of buffer will stop when the meniscus
reaches the upper frit in the column.
13. Apply the supernatant from step 8 to the QIAGEN-tip and allow it to enter the resin by
gravity flow.
The supernatant should be loaded onto the QIAGEN-tip promptly. If it is left too long and
becomes cloudy due to further precipitation of protein, it must be centrifuged again or
filtered before loading to prevent clogging of the QIAGEN-tip.
Optional: Remove a 120 µl or 75 µl sample from the flow-through and save for an
analytical gel (sample 2) to determine efficiency of DNA binding to the QIAGEN resin.

36
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
14. Wash the QIAGEN-tip with a total of 200 ml or a total of 600 ml Buffer QC.
Allow Buffer QC to move through the QIAGEN-tip by gravity flow. The first half of the
volume of wash buffer is sufficient to remove contaminants in the majority of plasmid DNA
preparations. The second half is particularly necessary when large culture volumes or
bacterial strains producing large amounts of carbohydrates are used.
Optional: Remove a 160 µl or 120 µl sample from the combined wash fractions and
save for an analytical gel (sample 3).
15. Elute DNA with 35 ml or 100 ml Buffer QF.
Use of polycarbonate centrifuge tubes for collection is not recommended because
polycarbonate is not resistant to the alcohol used in subsequent steps.
Optional: Remove a 22 µl or 20 µl sample of the eluate and save for an analytical
gel (sample 4).
Note: For constructs larger than 45–50 kb, prewarming the elution buffer to 65°C may help
to increase yield.
If you wish to stop the protocol and continue later, store the eluate at 4°C. Storage periods
longer than overnight are not recommended.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
37
16. Precipitate DNA by adding 24.5 ml or 70 ml (0.7 volumes) room-temperature
g
isopropanol to the eluted DNA. Mix and centrifuge immediately at ≥15,000 x
for
30 min at 4°C. Carefully decant the supernatant.
All solutions should be at room temperature to minimize salt precipitation, although
centrifugation is carried out at 4°C to prevent overheating of the sample. Alternatively,
disposable conical-bottom centrifuge tubes can be used for centrifugation at 5000 x
60 min at 4°C. Isopropanol pellets have a glassy appearance and may be more difficult to
see than the fluffy, salt-containing pellets that result from ethanol precipitation. Marking the
outside of the tube before centrifugation allows the pellet to be more easily located.
Isopropanol pellets are also more loosely attached to the side of the tube, and care should
be taken when removing the supernatant.
17. Wash DNA pellet with 7 ml or 10 ml of room-temperature 70% ethanol, and
g
centrifuge at ≥15,000 x
for 10 min. Carefully decant the supernatant without
disturbing the pellet.
Alternatively, disposable conical-bottom centrifuge tubes (not supplied) can be used for
g
centrifugation at 5000 x
for 60 min at 4°C. The 70% ethanol removes precipitated
salt and replaces isopropanol with the more volatile ethanol, making the DNA easier
to redissolve.
g
for
18. Air-dry the pellet for 10–20 min, and redissolve the DNA in a suitable volume of buffer
(e.g., TE buffer, pH 8.0, or 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 8.5).
Redissolve the DNA pellet by rinsing the walls to recover the DNA, especially if glass tubes
have been used. Pipetting the DNA up and down to promote resuspension may cause
shearing and should be avoided. Overdrying the pellet will make the DNA difficult to
redissolve. DNA dissolves best under slightly alkaline conditions; it does not easily dissolve
in acidic buffers.

38
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Determination of yield
To determine the yield, DNA concentration should be determined by both UV
spectrophotometry at 260 nm and quantitative analysis on an agarose gel. For reliable
A
spectrophotometric DNA quantification,
readings should lie between 0.1 and 1.0.
260
Agarose gel analysis
We recommend removing and saving aliquots during the purification procedure (samples 1–4).
If the plasmid DNA is of low yield or quality, the samples can be analyzed by agarose gel
electrophoresis to determine the stage of the purification procedure where the problem occurred
(see page 53).

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
39
Protocol: Very Low-Copy Plasmid/Cosmid
Purification Using QIAGEN-tip 100 or
QIAGEN-tip 500
Very low-copy plasmids and cosmids of less than 10 copies per cell often require large culture
volumes to yield significant amounts of DNA (for additional information, see
www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo). This protocol is suitable for QIAGEN-tip 100 or
QIAGEN-tip 500. After alkaline lysis, there is an additional isopropanol precipitation step to
decrease the amount of lysate before DNA is bound to the QIAGEN-tip. Culture volumes and
tip sizes are selected to match the quantity of DNA expected to the capacity of the
QIAGEN-tip. For purification of P1 and BAC DNA using QIAGEN-tips, please contact
QIAGEN Technical Services at support.qiagen.com. For purification of large cosmid and
plasmid DNA constructs, for example, BAC, PAC, or P1 DNA, the QIAGEN Large-Construct
Kit is available (see “Ordering Information”, page 59).
Details of yields, culture volumes, QIAGEN-tip sizes, and buffer volumes to be used for
purification of very low-copy plasmids and cosmids are given in Table 5.

40
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Table 5. Parameters for purification of very low-copy plasmids and cosmids of less than 10 copies per cell
Required DNA yield* Up to 100 µg Up to 500 µg
Culture volume 500 ml 2.5 liters
Buffer P1† 20 ml 125 ml
Buffer P2† 20 ml 125 ml
Buffer P3† 20 ml 125 ml
QIAGEN-tip QIAGEN-tip 100 QIAGEN-tip 500
Buffer QBT (for equilibration) 4 ml 10 ml
Buffer QC (for washing) 2 x 10 ml 2 x 30 ml
Buffer QF (for elution) 5 ml 15 ml
* For very-low-copy plasmids, expected yields are 20–100 µg for the QIAGEN-tip 100 and 100–500 µg for the
QIAGEN-tip 500.
†
Volumes of lysis Buffers P1, P2, and P3 are higher than in the standard protocols on pages 23–30 to efficiently lyse
the large number of cells required for purification of very low-copy plasmids and cosmids.
Important points before starting
New users are advised to familiarize themselves with the detailed protocol provided in
this handbook. In addition, extensive background information is provided on our plasmid
resource page, www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
If working with low-copy vectors, it may be beneficial to increase the lysis buffer volumes
to increase the efficiency of alkaline lysis, and thereby the DNA yield. In case additional
Buffers P1, P2, and P3 are needed, their compositions are provided in Appendix B, page
53. Alternatively, the buffers may be purchased separately (see “Ordering Information”,
page 59).
Optional: Remove samples at the indicated steps to monitor the procedure on an
analytical gel (see page 53).
The symbol denotes values for QIAGEN-tip 100, using the QIAGEN Plasmid Midi Kit;
denotes values for QIAGEN-tip 500, using the QIAGEN Plasmid Maxi Kit.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
41
Things to do before starting
Before use, centrifuge RNase A briefly, and then add into Buffer P1 to obtain a final
concentration of 100 μg/ml.
Check Buffer P2 for SDS precipitation due to low storage temperatures. If necessary,
dissolve the SDS by warming to 37°C.
Prechill Buffer P3 at 4°C.
Optional: Add the provided LyseBlue reagent to Buffer P1 and mix before use. Use 1 vial
LyseBlue reagent per bottle Buffer P1 for a final dilution of 1:1000 (e.g., 10 µl LyseBlue
into 10 ml Buffer P1). LyseBlue provides visual identification of optimum buffer mixing
thereby preventing the common handling errors that lead to inefficient cell lysis and
incomplete precipitation of SDS, genomic DNA, and cell debris. For more details, see
“Using LyseBlue reagent” on page 15.
Procedure
1. Pick a single colony from a freshly streaked selective plate, and inoculate a starter culture
of 2–10 ml LB medium containing the appropriate selective antibiotic. Incubate for
approximately 8 h at 37°C with vigorous shaking (approx. 300 rpm).
Use a tube or flask with a volume of at least 4 times the volume of the culture.
2. Dilute the starter culture 1/500 to 1/1000 into 500 ml or 2.5 liters of selective
LB medium using 500–1000 µl or 2.5–5 ml of starter culture. Grow at 37°C for
12–16 h with vigorous shaking (approx. 300 rpm).
Use a flask or vessel with a volume of at least 4 times the volume of the culture. The culture
should reach a cell density of approximately 3–4 x 10
corresponds to a pellet wet weight of approximately 3 g/liter medium.
3. Harvest the bacterial cells by centrifugation at 6000 x
If you wish to stop the protocol and continue later, freeze the cell pellets at −30 to −15°C.
9
cells per ml, which typically
g
for 15 min at 4°C.

42
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
4. Resuspend the bacterial pellet in 20 ml or 125 ml Buffer P1.
For efficient lysis, it is important to use a vessel that is large enough to allow complete
mixing of the lysis buffers. Ensure that RNase A has been added to Buffer P1.
If LyseBlue reagent has been added to Buffer P1, vigorously shake the buffer bottle before
use to ensure LyseBlue particles are completely resuspended. The bacteria should be
resuspended completely by vortexing or pipetting up and down until no cell clumps remain.
5. Add 20 ml or 125 ml Buffer P2, mix thoroughly by vigorously inverting the sealed
tube 4–6 times, and incubate at room temperature for 5 min.
Do not vortex, because this will result in shearing of genomic DNA. The lysate should
appear viscous. Do not allow the lysis reaction to proceed for more than 5 min. After use,
the bottle containing Buffer P2 should be closed immediately to avoid acidification of
Buffer P2 from CO
in the air.
2
If LyseBlue has been added to Buffer P1, the cell suspension will turn blue after addition of
Buffer P2. Mixing should result in a homogeneously colored suspension. If the suspension
contains localized colorless regions or if brownish cell clumps are still visible, continue
mixing the solution until a homogeneously colored suspension is achieved.
6. Add 20 ml or 125 ml chilled Buffer P3, mix immediately and thoroughly by
vigorously inverting 4–6 times, and incubate on ice for 30 min.
Precipitation is enhanced by using chilled Buffer P3 and incubating on ice. After addition of
Buffer P3, a fluffy white material forms and the lysate becomes less viscous. The
precipitated material contains genomic DNA, proteins, cell debris, and KDS. The lysate
should be mixed thoroughly to avoid localized potassium dodecyl sulfate precipitation.
If LyseBlue reagent has been used, the suspension should be mixed until all trace of blue
has gone and the suspension is colorless. A homogeneous colorless suspension indicates
that the SDS has been effectively precipitated.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
43
7. Centrifuge at ≥20,000 x g for 30 min at 4°C. Remove supernatant containing plasmid
DNA promptly.
Before loading the centrifuge, the sample should be mixed again. Centrifugation should be
performed in non-glass tubes (e.g., polypropylene; not supplied). After centrifugation, the
supernatant should be clear.
g
8. Centrifuge the supernatant again at ≥20,000 x
for 15 min at 4°C. Remove
supernatant containing plasmid DNA promptly. Alternatively, the sample can be filtered
over a prewetted, folded filter.
This second centrifugation step completely clears the lysate of precipitated material.
Optional: Remove a 600 µl or 750 µl sample from the cleared lysate supernatant and
save for an analytical gel (sample 1) to determine whether growth and lysis conditions
were optimal.
9. Precipitate the DNA by adding 42 ml or 262.5 ml (0.7 volumes) of room-
g
temperature isopropanol to the lysate. Centrifuge at ≥15,000 x
for 30 min at 4°C, and
carefully decant the supernatant.
This isopropanol precipitation reduces the sample volume to facilitate loading of the
column. It also serves to remove unwanted metabolites such as proteins and
lipopolysaccharides.
10. Redissolve the DNA pellet in 500 µl TE buffer, pH 8.0, and add Buffer QBT to obtain a
final volume of 5 ml or 12 ml for selected QIAGEN-tip 100 or
QIAGEN-tip 500, respectively.
TE buffer is used to facilitate redissolving of the DNA. Buffer QBT provides optimal DNA
binding conditions.

44
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
11. Equilibrate a QIAGEN-tip 100 or QIAGEN-tip 500 by applying 4 ml or
10 ml Buffer QBT, and allow the column to empty by gravity flow.
Flow of buffer will begin automatically by reduction in surface tension due to the presence
of detergent in the equilibration buffer. Allow the QIAGEN-tip to drain completely.
QIAGEN-tips can be left unattended because the flow of buffer will stop when the meniscus
reaches the upper frit in the column.
12. Apply the DNA solution from step 10 to the QIAGEN-tip and allow it to enter the resin
by gravity flow.
Optional: Remove a 50 µl or 24 µl sample from the flow-through and save for an
analytical gel (sample 2) to determine the efficiency of DNA binding to the QIAGEN resin.
13. Wash the QIAGEN-tip with 2 x 10 ml or 2 x 30 ml Buffer QC.
Allow Buffer QC to move through the QIAGEN-tip by gravity flow. The first wash is
sufficient to remove contaminants in the majority of plasmid DNA preparations. The second
wash is particularly necessary when large culture volumes or bacterial strains producing
large amounts of carbohydrates are used.
Optional: Remove a 200 µl or 120 µl sample from the combined wash fractions and
save for an analytical gel (sample 3).
14. Elute DNA with 5 ml or 15 ml Buffer QF.
Use of polycarbonate tubes (not supplied) to collect the eluate is not recommended as
polycarbonate is not resistant the alcohol used in subsequent steps.
Note: For constructs larger than 45–50 kb, prewarming the elution buffer to 65°C may help
to increase yield.
Optional: Remove a 50 µl or 30 µl sample of the eluate and save for an analytical
gel (sample 4).

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
45
If you wish to stop the protocol and continue later, store the eluate at 4°C. Storage periods
longer than overnight are not recommended.
15. Precipitate DNA by adding 3.5 ml or 10.5 ml (0.7 volumes) of room-temperature
g
isopropanol to the eluted DNA. Mix and centrifuge immediately at ≥15,000 x
for
30 min at 4°C. Carefully decant the supernatant.
All solutions should be at room temperature to minimize salt precipitation, although
centrifugation is carried out at 4°C to prevent overheating of the sample. Alternatively,
disposable conical-bottom centrifuge tubes (not supplied) can be used for centrifugation at
g
5000 x
for 60 min at 4°C. Isopropanol pellets have a glassy appearance and may be
more difficult to see than the fluffy, salt-containing pellets that result from ethanol
precipitation. Marking the outside of the tube before centrifugation allows the pellet to be
more easily located. Isopropanol pellets are also more loosely attached to the side of the
tube, and care should be taken when removing the supernatant.
16. Wash DNA pellet with 2 ml or 5 ml room-temperature 70% ethanol, and
g
centrifuge at ≥15,000 x
for 10 min. Carefully decant the supernatant without
disturbing the pellet.
Alternatively, disposable conical-bottom centrifuge tubes (not supplied) can be used for
g
centrifugation at 5000 x
for 60 min at 4°C. The 70% ethanol removes precipitated salt
and replaces isopropanol with the more volatile ethanol, making the DNA easier to
redissolve.
17. Air-dry the pellet for 5–10 min, and redissolve the DNA in a suitable volume of buffer
(e.g., TE buffer, pH 8.0, or 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 8.5).
Redissolve DNA pellet by rinsing the walls to recover the DNA, especially if glass tubes
have been used. Pipetting the DNA up and down to promote resuspension may cause
shearing and should be avoided. Overdrying the pellet will make the DNA difficult to
redissolve. DNA dissolves best under alkaline conditions; it does not easily dissolve
in acidic buffers.

46
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Determination of yield
To determine the yield, DNA concentration should be determined by both UV
spectrophotometry and quantitative analysis on an agarose gel.
Agarose gel analysis
We recommend removing and saving aliquots during the purification procedure
(samples 1−4). If the plasmid DNA is of low yield or quality, the samples can be analyzed
by agarose gel electrophoresis to determine the stage of the purification procedure where
the problem occurred (see page 53).

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
47
Comments and suggestions
Low or no DNA yield
No DNA in lysate (sample 1)
a) Plasmid did not propagate
Please read ”Growth of Bacterial Cultures” on our web page
b) Alkaline lysis was inefficient
If cells have grown to very high densities or a larger amount of cultured medium than
c) Insufficient lysis for low-copy
For low copy-plasmid preparations, doubling the volumes of lysis Buffers P1, P2, and
d) Lysate incorrectly prepared
Check Buffer P2 for SDS precipitation resulting from low storage temperatures and
DNA in flow-through fraction (sample 2)
a) Column was overloaded
Check the culture volume and yield against the capacity of the QIAGEN-tip, as
Troubleshooting Guide
This troubleshooting guide may be helpful in solving any problems that may arise. For more
information, see also the Frequently Asked Questions page our Technical Support Center:
www.qiagen.com/FAQ/FAQList.aspx. The scientists in QIAGEN Technical Services are
always happy to answer any questions you may have about either the information or protocols
in this handbook (for contact information, visit support.qiagen.com).
www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo, and check that the conditions for optimal
growth were met.
recommended was used, the ratio of biomass to lysis reagent is shifted. This may
result in poor lysis conditions, because the volumes of Buffers P1, P2, and P3 are not
sufficient for setting the plasmid DNA free efficiently. Reduce culture volume or
increase volumes of Buffers P1, P2, and P3.
Also, insufficient mixing of lysis reagents will result in reduced yield. Mix thoroughly
after addition of Buffers P1, P2, and P3 to achieve homogeneous suspensions. Use
LyseBlue to visualize efficiency of mixing.
plasmids
P3 may help to increase plasmid yield and quality (see page 39 and background
on our web page www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo).
dissolve the SDS by warming. The bottle containing Buffer P2 should always be
closed immediately after use. Lysis buffers prepared in the laboratory should be
prepared according to the instructions on page
If necessary, prepare fresh Buffers P1, P2, and P3.
detailed at the beginning of each protocol. Reduce the culture volume accordingly,
or select a larger QIAGEN-tip if a higher yield is desired. For very low-copy number
plasmid and cosmid preps requiring very large culture volumes, please see page
57.
39.

48
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Comments and suggestions
b) SDS (or other ionic
Chill Buffer P3 before use. If the lysate is cleared by centrifugation, load onto
c) Inappropriate salt or pH
Ensure that any buffers prepared in the laboratory were prepared according to the
d) Column flow was uneven
Store QIAGEN-tips at room temperature. If stored under cold, damp conditions for
DNA in Buffer QC wash fraction (sample 3)
a) Column was overloaded
Check the culture volume and yield against the capacity of the QIAGEN-tip, as
detailed at the beginning of each protocol. Reduce the culture volume
b) Buffer QC was incorrect
Check pH and salt concentration of Buffer QC. Recover DNA by
No DNA in eluate (sample 4)
a) No DNA in the lysate
See section “No DNA in lysate (sample 1)”, page 47.
b) Elution Buffer QF or QN
Check pH and salt concentration of Buffer QF or QN. Recover DNA by eluting
c) DNA passed through in the
See previous two sections.
Little or no DNA after precipitation
a) DNA failed to precipitate
Ensure that the precipitate is centrifuged at ≥15,000 x g for 30 min.
b) DNA pellet was lost
Isopropanol pellets are glassy and may be difficult to see. Mark the outside of
c) DNA was poorly redissolved
Check that DNA is completely redissolved. Be sure to wash any DNA off the
detergent) was in lysate
conditions in buffers
was incorrect
flow-through or wash fraction
QIAGEN-tip promptly after centrifugation. If lysate is too viscous for effective mixing
of Buffer P3, reduce culture volume or increase volumes of Buffers P1, P2, and P3.
Use LyseBlue to visualize efficiency of mixing.
instructions provided on page 57.
prolonged periods of time, the resin may clump. This problem can be overcome by
shaking the column before use.
accordingly, or select a larger QIAGEN-tip if a higher yield is desired. For very
low-copy-number plasmid and cosmid preps requiring very large culture
volumes, please see page
precipitation, and purify on a new QIAGEN-tip. For details, please refer to
www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
with fresh buffer.
39.
Recover DNA by centrifuging for longer and at higher speeds. Try another
isopropanol batch.
the tube before centrifugation. Isopropanol pellets may also be loosely attached
to the side of the tube, so pour supernatant off gently.
walls, particularly if glass tubes and a fixed-angle rotor are used. Up to half of
the total DNA may be smeared on the walls. Alternatively, a swinging bucket
rotor can be used to ensure that the pellet is located at the bottom of the tube.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
49
Comments and suggestions
Plasmid DNA difficult to redissolve
a) Pellet was overdried
Air-dry pellet instead of using a vacuum, especially if the DNA is of high
b) Residual isopropanol
Ensure that pellets are washed with 70% ethanol to remove traces of
c) Too much salt in pellet
Ensure that isopropanol is at room temperature for precipitation, and wash the
d) Buffer pH was too low
Ensure that the pH of the buffer used for redissolving is ≥8.0 because DNA
e) Resuspension volume
Increase resuspension volume if the solution above the pellet is highly viscous.
Contaminated DNA/poor-quality DNA
a) Genomic DNA in the eluate
Mixing of bacterial lysate was too vigorous. The lysate must be handled gently
b) RNA in the eluate
RNase A digestion was insufficient. Check culture volume against
as detailed in
c) Nuclease contamination
Check buffers for nuclease contamination and replace if necessary. Use new
d) Lysis time was too long
Ensure that lysis step (Buffer P2) does not exceed 5 min.
e) Overloaded alkaline lysis
Check the culture volume and yield against the capacity of the QIAGEN-tip.
f) Plasmid DNA is
DNA was poorly buffered. Redissolve DNA in TE buffer, pH 8.0, to inhibit
g) Endonuclease-containing
Refer to background information on www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo and
molecular weight. Redissolve DNA by warming the solution slightly and
allowing more time for redissolving.
in pellet
too low
isopropanol. Redissolve DNA by warming the solution slightly and allowing
more time for redissolving. Increase volume of buffer used for redissolving
if necessary.
pellet twice with room temperature 70% ethanol. Recover DNA by increasing
the volume of buffer used for redissolving.
does not dissolve well in acidic solutions.
after addition of Buffers P2 and P3 to prevent shearing of chromosomal DNA.
Reduce culture volume if lysate is too viscous for gentle mixing.
recommended volumes, and reduce if necessary. Check that the RNase A
provided with the kit has been used. If Buffer P1 is more than 6 months old,
add more RNase A. Recover DNA by precipitating the eluate, digesting with
RNase A, and purifying on a new QIAGEN-tip
www.qiagen.com/goto/plasmidinfo.
glass- and plasticware, and wear gloves.
Reduce the culture volume accordingly or alternatively increase the volumes of
Buffers P1, P2, and P3.
nicked/sheared/degraded
host
nuclease activity and maintain stable pH during storage.
consider changing
Escherichia coli
host strain.

50
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Comments and suggestions
h) Shearing during redissolving
Redissolve DNA gently, without vortexing or vigorous pipetting. Avoid using
i) Particles in redissolved DNA
Centrifuge the DNA solution and transfer supernatant to a new tube. The
Poor DNA performance
a) Too much salt in pellet
Ensure that isopropanol is at room temperature for precipitation, and wash the
b) Residual protein
Check culture volume against the recommended volumes and reduce if
Extra DNA bands on analytical gel
a) Dimer form of plasmid
Dimers or multimers of supercoiled plasmid DNA are formed during replication
b) Plasmid has formed
This species runs faster than closed circular DNA on a gel and is resistant to
c) Possible deletion mutants
Some sequences are poorly maintained in plasmids. Check for deletions by
Blocked QIAGEN-tip
Lysate was turbid
Ensure that the lysate is clear before it is loaded onto the column. Ensure that
force and centrifugation time.
QIAfilter Cartridge clogs during filtration
a) Too large culture volume
Use no more than the culture volume recommended in the protocol.
b) Inefficient mixing after
Mix well until a fluffy white material has formed and the lysate is no longer
small pipette tips.
particles have no effect on DNA quality. Alternatively, use HiSpeed kits
containing QIAprecipitator, which filters the eluate.
pellet twice with room temperature 70% ethanol. Precipitate the DNA again to
remove the salt.
denatured supercoils
used
necessary. Ensure that the bacterial lysate is cleared properly by centrifugation
at ≥20,000 x
of plasmid DNA. Typically, when purified plasmid DNA is electrophoresed,
both the supercoiled monomer and dimer form of the plasmid are detected
upon ethidium bromide staining of the gel (see
of these forms is often host dependent.
restriction digestion (see Figure 4, page 53). Do not incubate cells for longer
than 5 min in Buffer P2. Mix immediately after addition of Buffer P3.
restriction analysis. Cosmid clones, in particular, should always be prepared
from freshly streaked, well-isolated colonies because cosmids are not stable in
E. coli
Buffer P3 is chilled before use. Check gAlternatively, clear the lysate using a QIAfilter Cartridge. To clear a blocked
QIAGEN-tip, positive pressure may be applied (e.g., by using a syringe fitted
into a rubber stopper with a hole).
g
for 45 min, or using a QIAfilter Cartridge.
for long periods of time.
Figure 4, page 53). The ratio
addition of Buffer P3
viscous.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
51
Comments and suggestions
c) Mixing too vigorous after
After addition of Buffer P3 the lysate should be mixed immediately but gently.
d) QIAfilter Cartridge was
After addition of Buffer P3 the lysate should be loaded immediately after being
e) QIAfilter Cartridge was
Pour the lysate into the QIAfilter Cartridge immediately after addition of
f) Incubation after addition
Ensure incubation is performed at room temperature in the QIAfilter Cartridge.
g) Incubation time after
Incubate with Buffer P3 as indicated in the protocol. If the precipitate has not
h) Vacuum was weak or
Ensure that the vacuum generates a vacuum pressure of −200 to −600 millibars
QIAfilter Cartridge clogs after addition of Buffer FWB2
Precipitate was not stirred after
After addition of Buffer FWB2 to the QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridge, gently stir
Lysate not clear after filtration
Precipitate was forced through
Filter until all of the lysate has passed through the QIAfilter Midi or Maxi
addition of Buffer P3
not loaded immediately
after addition of Buffer P3
not agitated during
incubation
of Buffer P3 on ice instead
of at RT
addition of Buffer P3 too
short
negligible (QIAfilter
Mega-Giga Cartridges
only)
(QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridges only)
addition of Buffer FWB2
Vigorous mixing disrupts the precipitate into tiny particles which may clog the
QIAfilter Cartridge.
poured into the QIAfilter Cartridge. Decanting after incubation may disrupt the
precipitate into tiny particles which may clog the QIAfilter Cartridge.
Buffer P3 and do not agitate during the 10 minute incubation. Agitation causes
the precipitate to be disrupted into tiny particles, instead of forming a layer.
Precipitate flotation is more efficient at room temperature than on ice.
risen to the top after the 10 minute incubation, carefully run a sterile pipet tip
or sterile spatula around the cartridge wall to dislodge the precipitate before
continuing with the filtration.
(−150 to −450 mg Hg).
the precipitate using a sterile spatula.
(QIAfilter Midi and Maxi Cartridges only)
the QIAfilter Cartridge
Cartridge, but do not apply extreme force. Approximately 10 ml (QIAfilter
Midi) or 25 ml (QIAfilter Maxi) of lysate are typically recovered.

52
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Appendix A: Agarose Gel Analysis of the
Purification Procedure
DNA yields and quality can be readily analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Poor yields
and quality can be caused by a number of different factors. To determine the stage of the
procedure where the problem occurred, save fractions from different steps of the purification
procedure (see below and Table 6) and analyze by agarose gel electrophoresis.
Preparation of samples
Remove aliquots from the cleared lysate (sample 1), flow-through (sample 2), combined Buffer
QC wash fractions (sample 3), and Buffer QF/QN eluate (sample 4), as indicated in each
protocol and in Table 6. Precipitate the nucleic acids with 1 volume of isopropanol, rinse the
pellets with 70% ethanol, drain well, and resuspend in 10 µl TE buffer, pH 8.0.
Table 6. Sample volumes required for agarose gel analysis
Very low-copy
Sample Protocol step Mini Midi Maxi Mega Giga 100 500
1 Cleared lysate 50 µl 240 µl 120 µl 120 µl 75 µl 600 µl 750 µl
2 Flow-through 50 µl 240 µl 120 µl 120 µl 75 µl 50 µl 24 µl
3 Combined
wash fractions
4 Eluate 45 µl 100 µl 60 µl 22 µl 20 µl 50 µl 30 µl
% of prep represented
by each sample volume
220 µl 400 µl 240 µl 160 µl 120 µl 200 µl 120 µl
5.50% 2.00% 0.40% 0.08% 0.02% 1.00% 0.20%
plasmids/cosmids
QIAGEN-tip

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
53
Figure 4. Agarose gel analysis of the plasmid purification procedure.
Agarose
gel analysis
Run 2 µl of each sample on a 1% agarose gel* for analysis of the fractions at each stage of the
plasmid purification procedure. Figure 4 shows an analytical gel of the different fractions,
together with examples of problems that can arise at each step. If you find that you have a
problem with a particular step of the protocol, turn to the hints in the relevant section of the
“Troubleshooting Guide”, page 47. If the problem remains unresolved, or if you have any
further questions, please contact QIAGEN Technical Services via support.qiagen.com.
L: Cleared lysate containing supercoiled and open circular plasmid DNA and degraded
RNA (sample 1).
* When working with chemicals, always wear a suitable lab coat, disposable gloves, and protective goggles. For
more information, consult the appropriate safety data sheets (SDSs), available from the product supplier.

54
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
F: Flow-through fraction containing only degraded RNA is depleted of plasmid DNA which
is bound to the QIAGEN resin (sample 2).
W1: First wash fraction, in which the remaining traces of RNA are removed without affecting
the binding of the DNA (sample 3).
W2: Second wash fraction, which ensures that the resin is completely cleared of RNA and
other contaminants, leaving only pure plasmid DNA on the column (sample 3).
E: The eluate containing pure plasmid DNA with no other contaminating nucleic acids
(sample 4).
M: Lambda DNA digested with
Hin
dIII.*
Lanes 1–5 illustrate some atypical results that may be observed in some preparations,
depending on plasmid type and host strain.
Lane 1: Supercoiled (lower band) and open circular form (upper band) of the high-copy
plasmid pUC18 with an additional band of denatured supercoiled DNA migrating
just below the supercoiled form. This form may result from prolonged alkaline lysis
with Buffer P2 and is resistant to restriction digestion.
Lane 2: Multimeric forms of supercoiled plasmid DNA (pTZ19) which may be observed with
some host strains and should not be mistaken for genomic DNA. Multimeric plasmid
DNA can easily be distinguished from genomic DNA by a simple restriction
digestion–linearization of a plasmid sample displaying multimeric bands will yield a
single defined band with the size of the linearized plasmid monomer (see lane 3).
* When working with chemicals, always wear a suitable lab coat, disposable gloves, and protective goggles. For
more information, consult the appropriate SDSs, available from the product supplier.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
55
Lane 3: Linearized form of plasmid pTZ19 after restriction digestion with
Eco
RI.
Lane 4: Sample contaminated with bacterial chromosomal DNA, which may be observed if
the lysate is treated too vigorously (e.g., vortexing during incubation steps with Buffer
P2 or P3). Genomic DNA contamination can easily be identified by digestion of the
Eco
sample with
RI. A smear is observed, in contrast to the linear band seen after
digestion of multimeric plasmid forms.
Lane 5:
Eco
RI digestion of a sample contaminated with bacterial genomic DNA which gives
a smear above the plasmid DNA.

56
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Appendix B: Composition of Buffers
Buffer Composition Storage
Buffer P1 (resuspension buffer) 50 mM Tris·Cl, pH 8.0;
10 mM EDTA;
100 µg/ml RNase A
Buffer P2 (lysis buffer) 200 mM NaOH, 1% SDS (w/v) 15–25°C
Buffer P3 (neutralization buffer) 3.0 M potassium acetate, pH 5.5 15–25°C or 2–8°C
Buffer FWB2 (QIAfilter wash buffer) 1 M potassium acetate pH 5.0 15–25°C
Buffer QBT (equilibration buffer) 750 mM NaCl;
50 mM MOPS, pH 7.0;
15% isopropanol (v/v);
0.15% Triton
Buffer QC (wash buffer) 1.0 M NaCl;
50 mM MOPS, pH 7.0;
15% isopropanol (v/v)
Buffer QF (elution buffer) 1.25 M NaCl;
50 mM Tris·Cl, pH 8.5;
15% isopropanol (v/v)
Buffer QN (elution buffer) 1.6 M NaCl;
50 mM MOPS, pH 7.0;
15% isopropanol (v/v)
TE 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 8.0;
1 mM EDTA
STE 100 mM NaCl;
10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 8.0;
1 mM EDTA
®
X-100 (v/v)
2–8°C, after addition
of RNase A
15–25°C
15–25°C
15–25°C
15–25°C
15–25°C
15–25°C

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
57
Preparation of buffers
Buffer compositions are given per liter of solution. Do not autoclave MOPS- or isopropanolcontaining buffers; sterilize by filtration instead.
Buffer calculations are based on Tris base adjusted to pH with HCl (Tris·Cl). If using Tris·HCl
reagent, the quantities used should be recalculated.
P1: Dissolve 6.06 g Tris base, 3.72 g Na2EDTA·2H2O in 800 ml distilled water. Adjust
the pH to 8.0 with HCl. Adjust the volume to 1 liter with distilled water. Add 100 mg
RNase A per liter of P1.
P2: Dissolve 8.0 g NaOH pellets in 950 ml distilled water, 50 ml 20% SDS (w/v) solution.
The final volume should be 1 liter.
P3: Dissolve 294.5 g potassium acetate in 500 ml distilled water. Adjust the pH to 5.5
with glacial acetic acid (~110 ml). Adjust the volume to 1 liter with distilled water.
FWB2: Dissolve 98.2 g potassium acetate in 500 ml distilled water. Adjust the pH to 5.0 with
glacial acetic acid (~36 ml). Adjust the volume to 1 liter with distilled water.
QBT: Dissolve 43.83 g NaCl, 10.46 g MOPS (free acid), in 800 ml distilled water. Adjust
the pH to 7.0 with NaOH. Add 150 ml pure isopropanol and 15 ml 10% Triton X-100
solution (v/v). Adjust the volume to 1 liter with distilled water.
QC: Dissolve 58.44 g NaCl and 10.46 g MOPS (free acid) in 800 ml distilled water.
Adjust the pH to 7.0 with NaOH. Add 150 ml pure isopropanol. Adjust the volume
to 1 liter with distilled water.

58
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
QF: Dissolve 73.05 g NaCl and 6.06 g Tris base in 800 ml distilled water and adjust the
pH to 8.5 with HCl. Add 150 ml pure isopropanol. Adjust the volume to 1 liter with
distilled water.
QN: Dissolve 93.50 g NaCl and 10.46 g MOPS (free acid) in 800 ml distilled water and
adjust the pH to 7.0 with NaOH. Add 150 ml pure isopropanol. Adjust the volume to
1 liter with distilled water.
STE: Dissolve 5.84 g NaCl, 1.21 g Tris base, and 0.37 g Na
EDTA·2H2O in 800 ml
2
distilled water. Adjust the pH to 8.0 with HCl. Adjust the volume to 1 liter with
distilled water.
Note: Always recheck pH of buffers after preparation.
Preparation of LB medium
Dissolve 10 g tryptone, 5 g yeast extract, and 10 g NaCl in 800 ml distilled water. Adjust
the pH to 7.0 with 1 N NaOH. Adjust the volume to 1 liter with distilled water. Sterilize
by autoclaving.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
59
Product
Ordering Information
Contents Cat. no.
QIAGEN Plasmid Mini
Kit (25)
QIAGEN Plasmid Mini
Kit (100)
QIAGEN Plasmid Midi
Kit (25)
QIAGEN Plasmid Midi
Kit (100)
QIAGEN Plasmid Maxi
Kit (10)
QIAGEN Plasmid Maxi
Kit (25)
QIAGEN Plasmid Maxi
Kit (100)
Plasmid Buffer Set Buffers P1, P2, P3, QBT, QC, QF, RNase A; for
QIAGEN-tip 20 (25) 25 columns 10023
QIAGEN-tip 100 (25) 25 columns 10043
25 QIAGEN-tip 20, reagents, buffers 12123
100 QIAGEN-tip 20, reagents, buffers 12125
25 QIAGEN-tip 100, reagents, buffers 12143
100 QIAGEN-tip 100, reagents, buffers 12145
10 QIAGEN-tip 500, reagents, buffers 12162
25 QIAGEN-tip 500, reagents, buffers 12163
100 QIAGEN-tip 500, reagents, buffers 12165
19046
100 plasmid mini-, 25 midi-, or 10 maxipreps
QIAGEN-tip 500 (25) 25 columns 10063
QIAGEN-tip 2500 (25) 25 columns 10083
QIAGEN-tip 10000 (5) 5 columns 10091

60
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Product
QIAGEN Plasmid
of transfection
QIAGEN Plasmid
Plus
25 QIAGEN Plasmid
Plus
Maxi Columns,
Maxi Cartridges
QIAGEN Plasmid
Plus
25 QIAGEN Plasmid
Plus
Midi Columns,
Midi Cartridges
QIAGEN Plasmid
Plus
5 QIAGEN Plasmid
Plus
Mega Columns,
Mega-Giga Cartridges
QIAGEN Plasmid
Plus
Mega Kit (5)
5 QIAGEN Plasmid
Plus
Mega Columns,
extender tubes, reagents, buffers, 5 QIAfilter
QIAGEN Plasmid
Plus
For 4 x 96 plasmid minipreps: TurboFilter 96
Universal System
QIAfilter Plasmid Kits
cosmid DNA
Contents Cat. no.
Plus
Kits — for the fastest and most convenient purification
-grade plasmid DNA suitable for all applications
Maxi Kit (25)
Midi Kit (25)
Giga Kit (5)
96 BioRobot Kit (4)
— for fast purification of transfection-grade plasmid or
QIAfilter Plasmid Midi
Kit (25)
extender tubes, reagents, buffers, 25 QIAfilter
extender tubes, reagents, buffers, 25 QIAfilter
extender tubes, reagents, buffers, 5 QIAfilter
Plates and Plasmid
Plus
96 Plates, buffers,
reagents, flat-bottom blocks, S-Blocks, and
elution microtubes; for use with the BioRobot
25 QIAGEN-tip 100, reagents, buffers,
25 QIAfilter Midi Cartridges
12963
12943
12991
12981
960241
12243
QIAfilter Plasmid Maxi
Kit (10)
QIAfilter Plasmid Mega
Kit (5)
10 QIAGEN-tip 500, reagents, buffers,
10 QIAfilter Maxi Cartridges
5 QIAGEN-tip 2500, reagents, buffers,
5 QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridges
12262
12281

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
61
Product
HiSpeed Plasmid Kits
plasmid or cosmid DNA
plus syringes, reagents, buffers
plus syringes, reagents, buffers
plus syringes, reagents, buffers
EndoFree Plasmid Kits
transfection
Contents Cat. no.
QIAfilter Plasmid Giga
Kit (5)*
QIAfilter Midi
Cartridges (25)
QIAfilter Maxi
Cartridges (25)
QIAfilter Mega-Giga
Cartridges (5)
— for ultrafast purification of transfection-grade
HiSpeed Plasmid Midi
Kit (25)
HiSpeed Plasmid Maxi
Kit (10)
HiSpeed Plasmid Maxi
Kit (25)
— for purification of endotoxin-free advanced
-grade plasmid or cosmid DNA
5 QIAGEN-tip 10000, reagents, buffers,
12291
5 QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridges
25 QIAfilter Midi Cartridges 19743
25 QIAfilter Maxi Cartridges 19763
5 QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridges,
19781
Buffer FWB2
25 HiSpeed Midi Tips, 25 QIAfilter Midi
12643
Cartridges, 25 QIAprecipitator Midi Modules
10 HiSpeed Maxi Tips, 10 QIAfilter Maxi
12662
Cartridges, 10 QIAprecipitator Maxi Modules
25 HiSpeed Maxi Tips, 25 QIAfilter Maxi
12663
Cartridges, 25 QIAprecipitator Maxi Modules
EndoFree Plasmid Maxi
Kit (10)
EndoFree Plasmid Mega
Kit (5)
10 QIAGEN-tip 500, reagents, 10 QIAfilter
Maxi Cartridges, endotoxin-free buffers
5 QIAGEN-tip 2500, reagents, 5 QIAfilter
Mega-Giga Cartridges, endotoxin-free buffers
* For purification of low-copy plasmids and cosmids, QIAfilter Plasmid Mega Kits are a better choice than QIAfilter
Plasmid Giga Kits, due to the large culture volumes required and the limited capacity of the QIAfilter Mega-Giga
Cartridge.
12362
12381

62
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Product
QIAprep
plasmid
CompactPrep
grade plasmid DNA
QIAGEN Large
up to 200 µg cosmid DNA, free of genomic DNA
Transfection products
or 50–100 transfections in 6-well plates
Contents Cat. no.
EndoFree Plasmid Giga
Kit (5)*
®
Spin Kit — for purification of molecular biology grade
DNA
QIAprep Spin Miniprep
Kit (50)
®
Plasmid Kits* — for fast purification of molecular biology
CompactPrep Plasmid
Midi Kit (25)
CompactPrep Plasmid
Maxi Kit (25)
-Construct Kit — for purification of BAC, PAC, and P1 DNA or
QIAGEN LargeConstruct Kit (10)
PolyFect Transfection
Reagent (1 ml)
5 QIAGEN-tip 10000, reagents, 5 QIAfilter
12391
Mega-Giga Cartridges, endotoxin-free buffers
50 QIAprep Spin Columns, 27104
27104
reagents, buffers, collection tubes (2 ml)
25 CompactPrep Midi Columns, extender
12843
tubes, reagents, buffers, LyseBlue
25 CompactPrep Maxi Columns, extender
12863
tubes, reagents, buffers, LyseBlue
10 QIAGEN-tip 500, reagents, buffers, ATP-
†
dependent exonuclease
12462
For 25–65 transfections in 60 mm dishes
301105
Effectene Transfection
Reagent (1 ml)
SuperFect Transfection
Reagent (1.2 ml)
For 40 transfections in 60 mm dishes or 160
transfections in 12-well plates
For 40 transfections in 60 mm dishes or 160
transfections in 12-well plates
* CompactPrep Kits require use of a vacuum device for operation (e.g., QIAvac 24 Plus, cat. no. 19413).
†
ATP solution for exonuclease digestion is not provided.
301425
301305

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
63
Product
Accessories
Contents Cat. no.
QIAvac 24 Plus Vacuum manifold for processing
19413
1–24 spin columns: QIAvac 24 Plus Vacuum
manifold, luer plugs, quick couplings
QIArack
1 rack for 12 x QIAGEN-tip 20,
19015
8 x QIAGEN-tip 100, 6 x QIAGEN-tip 500 or
HiSpeed Midi Tips, 4 x QIAGEN-tip 2500 or
HiSpeed Maxi Tips, and 10 QIAfilter Midi or
Maxi Cartridges
RNase A (17,500 U) 2.5 ml (100 mg/ml; 7000 units/ml solution) 19101
Plasmid Buffer Set Buffers P1, P2, P3, QBT, QC, QF, RNase A;
19046
for 100 plasmid minipreps, 25 midipreps, or
10 maxipreps
EndoFree Plasmid Buffer
Set
Buffers P1, P2, P3, QBT, QC, QN, ER, TE,
endotoxin-free water, RNase A; for 10 plasmid
19048
megapreps or 5 gigapreps (endotoxin-free)
Buffer P1 500 ml Resuspension Buffer (RNase A not
19051
included
Buffer P2 500 ml Lysis Buffer 19052
Buffer P3 500 ml Neutralization Buffer 19053
For up-to-date licensing information and product-specific disclaimers, see the respective
QIAGEN kit handbook or user manual. QIAGEN kit handbooks and user manuals are
available at www.qiagen.com or can be requested from QIAGEN Technical Services or your
local distributor.

64
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Document Revision History
Date Changes
03/2020 Revised page references to point to the correct pages in the handbook. Reworded
06/2020 Fixed error in the “Kit Contents” section (the QIAGEN Plasmid Giga Kit [cat. no. 12191]
02/2021 Added a figure for QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridge, the QIAfilter protocol, troubleshooting
instructions for adding RNase A into Buffer P1 (to obtain a final concentration of 100
μg/ml), for clarity. Replaced/removed nonworking URL/link references. Erroneous reference
to Table 3 corrected to Table 5 (in “Protocol: Very Low-Copy Plasmid/Cosmid Purification
Using QIAGEN tip 100 or QIAGEN tip 500”). Erroneous reference to Table 4 corrected to
Table 6 (in “Appendix A: Agarose Gel Analysis of the Purification Procedure”).
should contain 5 QIAGEN-tip 10000, not QIAGEN-tip 2500). Replaced the nonworking
URL/link for the online selection guide in the “Introduction” section. Inserted catalog number
for QIArack in page 8. Changed all instances of precise storage temperature (from
“−20°C” to “−30 to −15°C”).
guide regarding QIAfilter, and “QIAfilter Midi Cartridges”, “QIAfilter Maxi Cartridges”,
and “QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridges” to the Ordering Information section. Removed
“QIAGEN Plasmid Mega Kits” and “QIAGEN Plasmid Giga Kit” from the Ordering
Information section.

QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
65
Limited License Agreement for the QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Kit
Use of this product signifies the agreement of any purchaser or user of the product to the following terms:
1. The product may be used solely in accordance with the protocols provided with the product and this handbook and for use with components contained in the kit
only. QIAGEN grants no license under any of its intellectual property to use or incorporate the enclosed components of this kit with any components not included
within this kit except as described in the protocols provided with the product, this handbook, and additional protocols available at www.qiagen.com. Some of
these additional protocols have been provided by QIAGEN users for QIAGE N users. These protocols have not been thoroughly tested or optimized by
QIAGEN. QIAGEN neither guarantees them nor warrants that they do not infringe the rights of third-parties.
2. Other than expressly stated licenses, QIAGEN makes no warranty that this kit and/or its use(s) do not infringe the rights of third-parties.
3. This kit and its components are licensed for one-time use and may not be reused, refurbished, or resold.
4. QIAGEN specifically disclaims any other licenses, expressed or implied other than those expressly stated.
5. The purchaser and user of the kit agree not to take or permit anyone else to take any steps that could lead to or facilitate any acts prohibited above. QIAGEN
may enforce the prohibitions of this Limited License Agreement in any Court, and shall recover all its investigative and Court costs, including attorney fees, in any
action to enforce this Limited License Agreement or any of its intellectual property rights relating to the kit and/or its components.
For updated license terms, see www.qiagen.com.
Trademarks: QIAGEN
(Thermo Fisher Scientific or its subsidiaries); pBluescript
names, trademarks, etc. used in this document, even when not specific ally marked as such, are not to be considered unprotected by law.
02/2021 HB-1193-005 © 2021 QIAGEN, all rights reserved.
®
, Sample to Insight®, QIAprep®, CompactPrep®, Effectene®, EndoFree®, HiSpeed®, LyseBlue®, PolyFect®, SuperFect® (QIAGEN Group); DH5®
®
(Agilent Technologies, Inc.); pGEM® (Promega Corporation), Triton® (Union Carbide Corporation). Registered

66
QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook 02/2021
Ordering
HB-1193-005 02/2021
www.qiagen.com/shop | Technical Support support.qiagen.com | Website www.qiagen.com
 Loading...
Loading...