Page 1
Series 441 Installation and Operating Instructions
(8 to 30) V dc
(4 to 20) mA
1
2
+
+
RTD
3
5
6
3
5
6
RTD
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
RTD
1 SAFETY NOTES
Safe and secure operation of the head transmitter can only be guaranteed if the operating instructions and all safety notes contained
are understood and followed.
1.1 Correct Use
The unit is a universal, presettable temperature transmitter for resistance thermometer (RTD), thermocouple (TC) as well as resistance
and voltage sensors. The unit is constructed for mounting in a connection head (form B) and a field housing. The manufacturer
cannot be held responsible for damage caused by misuse of the unit.
1.2 Installation, commissioning and operation
The unit is constructed using the most up-to-date production equipment and complies with the safety requirements of the EU guidelines.
If it is installed incorrectly or misused certain application dangers can occur. Trained personnel must do installation, wiring and
maintenance of the unit. These personnel must have read and understood these instructions and must follow them to the letter.
2 FUNCTION AND SYSTEM CONSTRUCTION
2.1 Function
Provides electronic monitoring and transformation of various input signals into an analog output signal in industrial temperature
measurement. The head transmitter is mounted in a connection head form B or separated from the sensor in a field housing.
Setting up of the head transmitter is done using PC and configuration software. The configuration kit is required for setting up the
head transmitter.
2.2 Measurement system
Transforming the following input signals:
• Resistance thermometers (RTD) and resistance sensors (in 2, 3 or 4 wire connection systems)
• Thermocouples (TC)
• Voltage sensors into a scalable analog output signal (4...20 or 20...4) mA
Fault monitoring of:
• Measurement range override or undercut
• Sensor breakage and short circuit - not for thermocouples (TC)
3 INSTALLATION
3.1 Installation conditions
Ambient temperature: (-40 to 85) °C [-40 to 185] °F
Installation area: Field housing; connection head Form B according to DIN 43 729
Installation angle: No limit
Safety notes: The unit must only be powered by a power supply that operates using an IEC 61010-1 compliant energy limited
circuit.
3.2 Installation
• Feed the sensor leadwires through the central hole in the head transmitter
• Position the head transmitter in the connection head in such way so that the current output terminals (terminals 1 and 2) are
towards the cable entry gland.
• Feed the installation screws through the holes in the head transmitter.
• Screw the head transmitter into the field housing using a screwdriver while not over tightening.
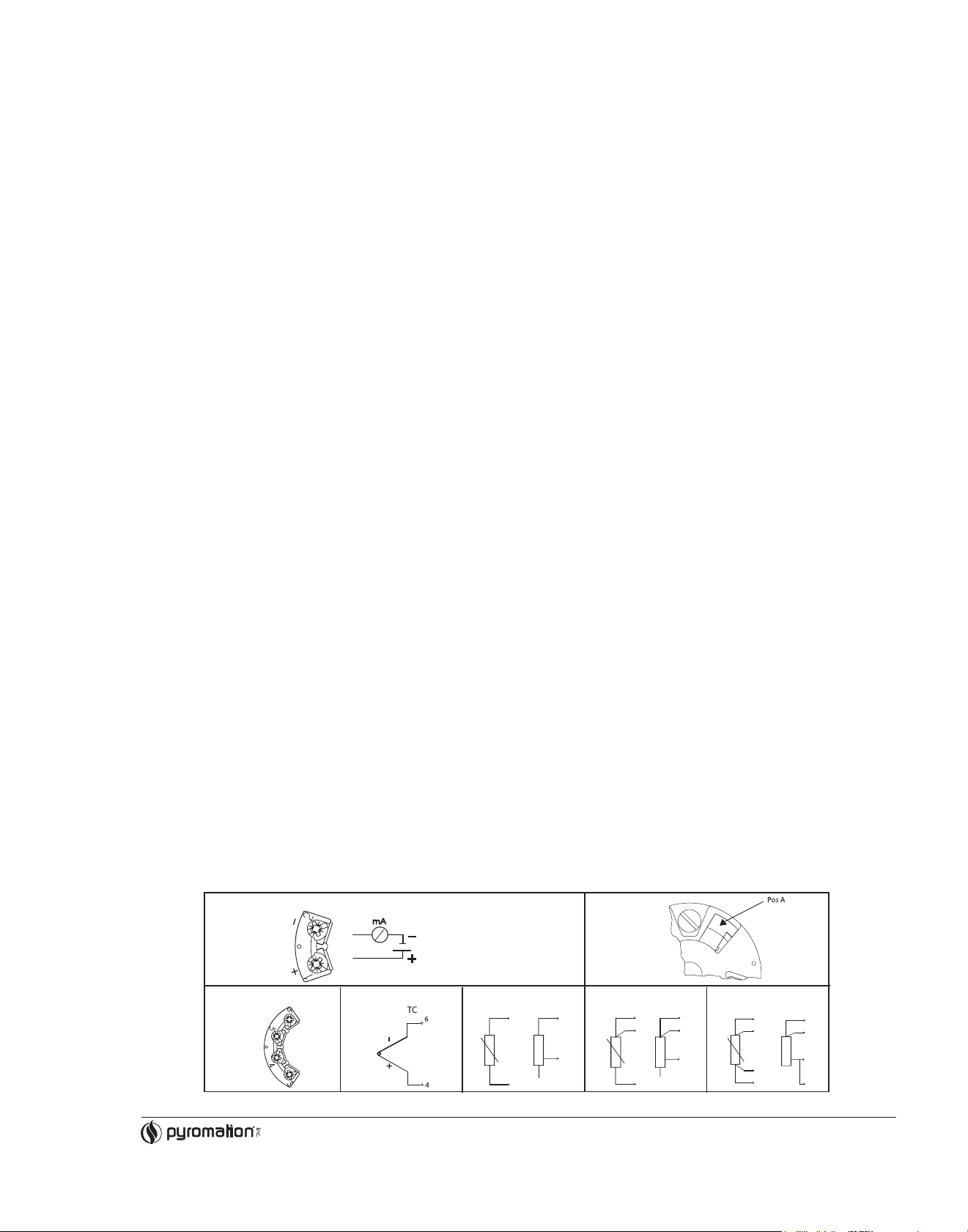
4 WIRING
4.1 Overview
Power supply and current output
Sensor Connection 2-Wire 3-Wire 4-Wire
Phone (260) 484-2580 • FAX (260) 482-6805 or (800) 837-6805 • www.pyromation.com
Terminal layout
6
3
SETUP socket
6
3
© Copyright 2006 Pyromation, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
441-D1 of 4
Page 2
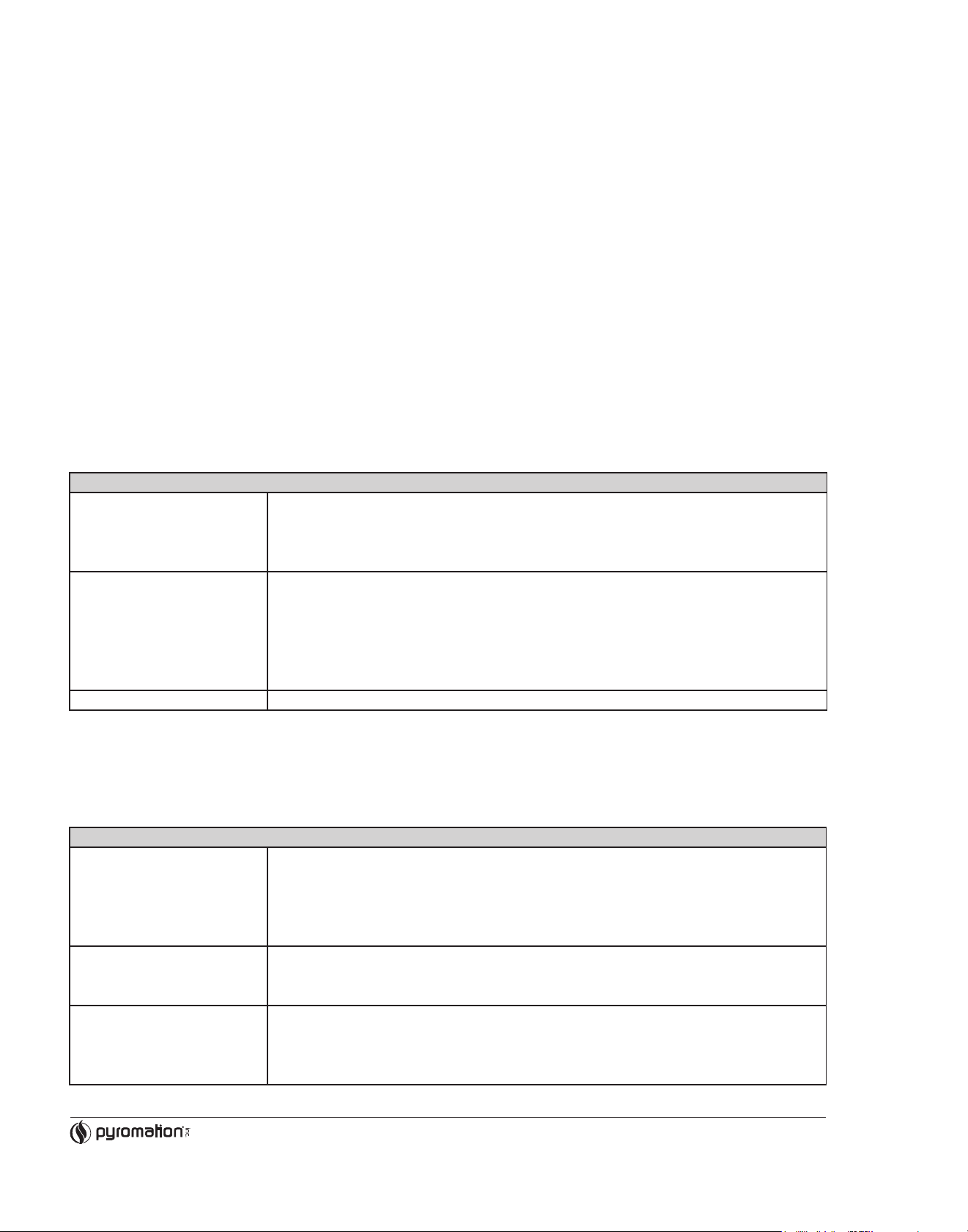
4.2 Measurement unit connection
Attention: Switch off power supply before opening the housing cover. Do not install or connect the unit to power. If this is not followed
parts of the electronic circuit will be damaged.
• Sensors: Connect the sensor lead to the respective head transmitter terminals (Terminals 3 to 6) by following the wiring diagram
(see figure 4.1).
• Output signal and power supply: Open the PG cable gland on the head transmitter or field housing. Feed the cable through the
opening in the PG cable gland and then connect the cable cores to terminals 1 and 2 according to the wiring diagram (see figure
4.1).
• PC configuration (SETUP socket): Open the flap on the SETUP socket (Figure 4.1, Pos. A) and connect the SETUP connection
cable.
Note: The screws on the terminals must be screwed tightly. Head transmitter configuration during measurement operation is possible.
There is no need to disconnect leads.
POTENTIAL LEVELING
Please take note when installing the head transmitter remotely in a field housing. The screen on the (4 to 20) mA signal output must
have the same potential as the screen at the sensor connections. When using earthed thermocouples, screening of the output
(4 to 20) mA cable is recommended. In plants with strong electromagnetic fields, screening of all cables with a low ohm connection
to the transmitter housing is recommended.
5 OPERATION
5.1 Short form instructions (SETUP)
PRESETTABLE PARAMETERS
• Sensor type
Standard settings
• Connection mode (2, 3 or 4 wire connection)
• Units (°C or °F)
• Measurement range start (depends on sensor)
• Measurement range end (depends on sensor)
• Cold junction compensation (internal/external on TC connection)
• Compensation resistance (0 to 20) Ω on 2 wire connection
Expanded settings
Service functions • Simulation (on/off)
For detailed TransComm operating instructions, please read the online documentation contained in the software.
• Fault condition reaction (≤ 3.6 mA or ≥ 21.0 mA)
• Output (analog standard/inverse)
• Damping (0 to 8) s
• Offset (-9.9 to +9.9) ˚C [-17.8 to +17.8] ˚F
• Measurement point identification/TAG Service functions
5.2 Communication
The head transmitter must be set up using a PC and configuration kit. The following points must be taken into account if trouble
free setting up is to be achieved:
• Configuration software installation
• Connect the head transmitter to the PC using the connection cable from the configuration kit.
CONFIGURATION SOFTWARE INSTALLATION
• IBM PC or compatible computer (minimum Pentium 166 MHz)
• Windows 95/98/ME/NT4.0/2000
System conditions
Recommended minimum configuration
• 64 MB RAM
• Minimum30 MB free memory on hard drive
• CD-ROM drive
• Screen resolution 800 x 600 Pixel
• Free serial interface
• Pentium 400 MHz
• 128 MB main RAM
• 120 MB free hard drive memory
• Screen resolution 1024 x 768 Pixel
Installation start
Start Windows
1. Place installations-CD in the respective drive
2. Start “Install.exe” and follow the installation instructions
3. If required the help/operating manual can be printed out once the software has been successfully installed.
© Copyright 2004 Pyromation, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Phone (260) 484-2580 • FAX (260) 482-6805 or (800) 837-6805 • www.pyromation.com
2 of 4441-D
Page 3

Connecting the head transmitter to the PC using the configuration kit connection cable
1. Connect the SETUP connector of the interface cable to the SETUP socket in the head transmitter (see figure 4.1, Pos. A).
2. Connect the RS232C connector to a free serial interface socket on the PC. In order to achieve optimum connection tighten the
RS232C connector screws to the PC.
Note: Configuration of the head transmitter must be done with power applied.
6 COMMISSIONING
6.1 Installation check
Monitor all connections making sure they are tight. In order to guarantee fault free operation the terminal screws must be tight
onto the connection cables. The unit is now ready for operation.
6.2 Commissioning
Once the power supply has been connected the head transmitter is operational.
Set up using the PC configuration software
The head transmitter left the factory with a default parameter configuration. If no customer specific configuration was mentioned
on the order the default parameter configuration is constructed as follows:
Sensor Pt100 (RTD)
Connection mode 3-wire
Measurement range
and units
(0 to 100) °C
Hint: If a change has been made to the measurement point then the head transmitter can be re-configured. In order to reconfigure the parameters follow these instructions:
• Install the configuration software and make connection to the PC (see Chapter 5, Operation).
• For detailed operating instructions for the PC configuration software, please read the online documentation contained in the
software.
Interactive setting up of the temperature transmitter
Customer specific linearization and sensor matching is done using the TransComm configuration software. The program
calculates the linearization coefficients X0 to X4, that need to be entered into the PC configuration software.
6.3 Function check
Measuring the analog (4 to 20) mA output signal or following failure signals:
Underranging
Overranging Linear increase from 20.0 to 20.5 mA
Linear drop from 4.0 to 3.8 mA
Failure, e.g. sensor
breakage; sensor short
circuit
≤ 3.6 mA (“low”) or ≥ 21 mA (“high”), can be selected
The “high” alarm setting can be set between 21.6 mA and 23 mA, thus providing the flexibility needed to meet the
requirements of various control systems.
7 MAINTENANCE
The head transmitter is maintenance free.
8 TROUBLESHOOTING
Always start troubleshooting with the checklists below if faults occur after start up or during operation. This takes you directly (via
various queries) to the cause of the problem and the appropriate remedial measures. Note: Due to its design, the device cannot
be repaired. However, it is possible to send the device in for examination.
General errors
Problem Possible cause Remedy
Device not reacting
Output current < 3.6 mA
Supply voltage does not match that
specified on the nameplate.
No contact between connecting cables
and terminals.
Signal cable is wired incorrectly. Check wiring.
Electronics are defective. Replace the device.
Phone (260) 484-2580 • FAX (260) 482-6805 or (800) 837-6805 • www.pyromation.com
Apply the correct voltage.
Check the contacting of the cables and correct if necessary.
© Copyright 2004 Pyromation, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
441-D3 of 4
Page 4

Application errors for RTD sensor connection
Problem Possible Cause Remedy
Incorrect sensor orientation. Install the sensor correctly.
Heat conducted by sensor. Observe the face-to-face length of the sensor.
Measured value is incorrect/
inaccurate
Failure current (≤ 3.6 mA or
≥ 21 mA)
Device programming is incorrect
(number of wires).
Device programming is incorrect
(scaling).
Incorrect RTD configured
Sensor connection.
The cable resistance of the sensor
(2-wire) was not compensated.
Offset incorrectly set. Check offset.
Faulty sensor. Check the sensor.
RTD connected incorrectly Connect the connecting cables correctly (terminal diagram).
Incorrect device programming (e.g.
number of wires).
Incorrect programming
Change the Connection type device.
Change scaling.
Change the Sensor type device function.
Check that the sensor is connected correctly.
Compensate the cable resistance.
Change the Connection type device function.
Incorrect sensor type set in the Sensor type device function. Set the correct
sensor type.
Application errors for TC sensor connection
Problem Possible Cause Remedy
Incorrect sensor orientation. Install the sensor correctly.
Measured value is incorrect/
inaccurate
Failure current (≤ 3.6 mA or
≥ 21 mA)
Heat conducted by sensor. Observe the face-to-face length of the sensor.
Device programming is incorrect
(scaling).
Incorrect thermocouple type (TC)
configured
Incorrect comparison measuring point
set.
Interference via the thermocouple wire
welded in the thermowell (interference
voltage coupling).
Offset incorrectly set. Check offset.
Faulty sensor. Check the sensor.
Sensor is connected incorrectly. Connect the connecting cables correctly (terminal diagram).
Incorrect programming
Change scaling.
Change the Sensor type device function.
Set the correct reference junction.
Use a sensor where the thermocouple wire is not welded.
Incorrect sensor type set in the Sensor type device function. Set the correct
sensor type.
© Copyright 2004 Pyromation, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Phone (260) 484-2580 • FAX (260) 482-6805 or (800) 837-6805 • www.pyromation.com
4 of 4441-D
 Loading...
Loading...