Page 1
PCMM05
PYLE
'?"
MAX
HOLD
a~B
®
~
•••
CO
B.Bp~
~IGLDltil
Cfi~
CARBON
MONOXIDE
METER
(E
"-
WWW.PYLEAUDIO .COM
~
Page 2

Carbon Monoxide Meter
Instruction Sheet
Introduction
The Carbon Monoxide Meter detects the presence
(CO) and measures concentrations between 1-1000 parts per million (PPM) .
The Meter indicates the presence
•
Bya
reading on the LCD
•
Bya
beeper tone.
in
of
carbon monoxide
PPM.
Safety Information-Read First
• Do not use the Meter as a personal safety monitor.
• Learn and recognize the effects
0-1
PPM
9PPM
50 PPM OSHA enclosed space 8-hour average level.*
100 PPM OSHA exposure limit.*
200 PPM
800 PPM Dizziness, nausea and convulsions.
*U.S. Department
(OSHA) Regulation 1917.24: The CO content
maintained at not more than 50 PPM (0.005%). Remove employees from
enclosed space if the
Normal background levels .
ASHRAE Standard 62-1989 for living areas.
Mild headache, fatigue , nausea and dizziness.
Death within 2 to 3 hours.
of
Labor, Occupational Safety & Health Administration
CO
of
CO poisoning.
concentration exceeds 100 PPM(0.01
What the Meter Does
The Meter indicates the presence
The beeper functions much like clicking
• Above 200 PPM, the beeper sounds continuously with the concentration
• From 35 PPM to 200 PPM, the beeper sounds discontinuously with the
concentration
of
CO.
of
CO by a reading on the LCD and a beeper tone .
of
a Geiger counter:
of
carbon monoxide
in
two ways:
in
any enclosed space shall be
o/~)
.
of
CO.
jpeCI
S T f
Temperature
Operating:
Storage:
Operating
Measurement
Measurement
Accuracy
Warm
Battery
Auto
Sensor
Typical
Ica Ions
humidity
up
period
power
type
sensor
range
Resolution
off
life
O°C to + 50°C
-30 °C to + 60°C
0-99% Relative humidity (non-condensing)
o to 1000PPM
1PPM
± 5%
or
± 10 PPM
<2 seconds
9V,
N EDA 1604A
Meter automatically shuts down after 15 minutes
of
inactivity
Stabilized electrochemical Gas-specific (CO)
3 years
or
I EC 6LR61,
or
equivalent.
Page 3

Instrument Familiarization:
(
.-
1.
CO sensor
2.
LCD Display
3. MAX Hold button
4.
Data Hold button
5. Back-light button
6. Power button
7.
Battery door
16
1
1~
,
~ . ------.~
I'
\l~"~
i " u!
.
c'-=-
!
'!
I \
I
!!
\\-=:;'
I
!!
!!
I!
I
I i J
Ij
I -I
I
lJ
~
DATA HOLD
The Data Hold function allows the meter to "freeze" a measurement for later reference.
1.
Press the DATA HOLD button to "freeze" the reading on the indicator.
The indicator
2.
Press the DATA HOLD button to return to normal operation.
MAX
Hold
To
hold the highest reading on the LCD, press the MAX hold button. The MAX hold button is
located on the left side of the meter (bottom button). The meter reading will not change as
readings change, rather it
button was pressed. Press the MAX hold button again to return to normal operation.
"HOLD" will be appear
will only display the highest reading encountered since the MAX hold
_
in
::::\
11
(J<!{FFllil
i,!
- I J
ii
[ '
=:0,/
MET
E"
J
the display.
;:il
I
;'
'
0 1
.
I
1
1
i
j
BACKLIGHT
1.
Press the "BACKLIGHT"
2.
Press it again, the "light" close.
POWER
1. Press the power button, power is on and the meter can measure.
2.
Pull it again , Power is off.
BATTERY
1.
As battery power is not sufficient, LCD will
type 9V is required.
2.
Open battery cover, then take out the battery from instrument and replace with a new
9-Volt battery and place the battery cover back.
BUTTON
BUTTON
REPLACEME
key,
the "light" will be appear in the display.
display"
2
0 " replacement with one battery
Page 4
Common Sources of CO
Common sources of potentially dangerous levels
• Poorly maintained furnaces, gas heaters,
• Dirty
or
plugged chimneys, or flue exhausts.
• Poorly maintained gas, oil,
• Internal combustion engines (e.g
or
kerosene appliances.
.,
automobiles, lawnmowers, blowers).
of
or
fireplaces.
CO are:
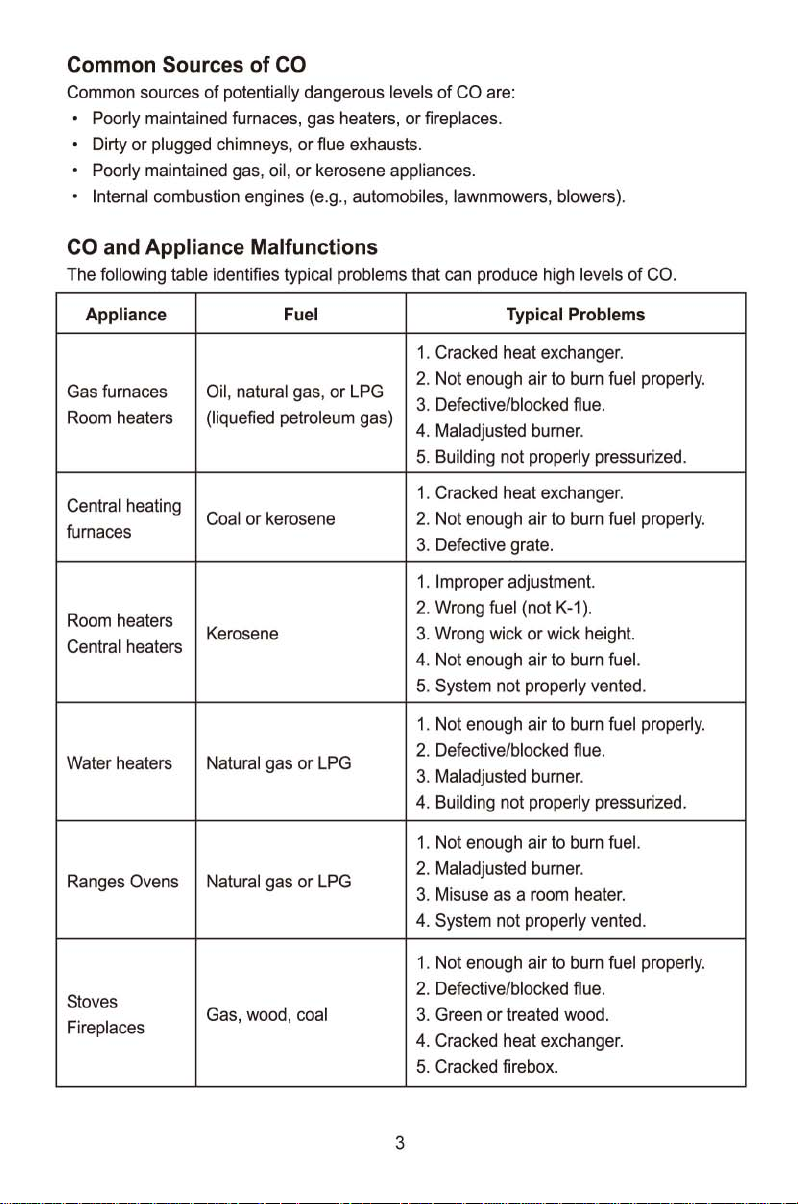
CO and Appliance Malfunctions
The following table identifies typical problems that can produce high levels of CO.
Appliance
Gas furnaces Oil, natural gas,
Room heaters (liquefied petroleum gas)
Central heating
furnaces
Room heaters
Central heaters
Water heaters
Ranges Ovens Natural gas
Coal
Kerosene
Natural gas
or
kerosene
Fuel
or
or
or
LPG
LPG
LPG
Typical
1.
Cracked heat exchanger.
2.
Not enough air to burn fuel properly.
3. Defective/blocked flue .
4. Maladjusted burner.
5.
Building not properly pressurized.
1.
Cracked heat exchanger.
2.
Not enough air to burn fuel properly.
3.
Defective grate.
1.
Improper adjustment.
2.
Wrong fuel (not K-1).
3.
Wrong wick
4. Not enough air to burn
5. System not properly vented.
1.
Not enough air to burn fuel properly.
2. Defective/blocked
3.
Maladjusted burner.
4.
Building not properly pressurized.
1. Not enough air to burn
2. Maladjusted burner.
3.
Misuse as a room heater.
4. System not
Problems
or
wick height.
fuel.
flue .
fuel.
properly vented.
Stoves
Fireplaces
Gas, wood, coal
1. Not enough air to burn
2. Defective/blocked
3.
Green
or
treated wood.
4. Cracked heat exchanger.
5.
Cracked firebox.
3
fuel properly.
flue .
 Loading...
Loading...