Puricom Rider User Manual

MU
User
Manual
Household
Softener


CONTENT
0. MAIN SPECIFICATIONS
1. PRESENTATION
2. INTRODUCTION
3. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
4. UNPACKAGING AND CONTENTS VERIFICATION
5. WARNINGS
6. SYSTEM INSTALLATION
7. START UP
8. MAINTENANCE/ SANITIZING
9. TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
10. MAINTENANCE MANUAL
11. EQUIPMENT INSTALLATION AND INITIAL
OPERATION REGISTRATION SHEET TECHNICIAN
12. GUARANTEE CERTIFICATE
4
5
5
9
10
11
12
15
17
20
22
24
25

0. MAIN SPECIFICATIONS
1. MAIN SPECIFICATIONS
Español
User Manual
ELECTRONIC TIMER
Allows to control all parameters
REGENERATIONS
Delayed or immediate/ programming
MIXING VALVE
Allows to regulate the residual hardnes
INTEGRATED BY-PASS
Allows to isolate the system from installation
TRANSFORMER
Outside
EASY TANK SALT FILLING
Special for Softener
ESP
FRA
ENG
KEEP THIS MANUAL THAT INCLUDES THE SERVICE BOOK AND THE GUARANTEE SECTION.
IT WILL PROVIDE YOU A BETTER POST-SALE SERVICE.
MULTILINGUAL TIMMER
English / French / Spanish
4

1. PRESENTATION
The water treatment equipment that you have bought is
a soener of last generation with one of the most advanced control heads in the market.
This is a system which combines the properties and advantages of the classic Denver with a more eicient water
and salt consumption, thus contributing both to the protection of our environment and the household economy.
Your soener RIDER will provide you and your family the
following advantages.
BENEFITS AND ADVANTAG
• ENERGY SAVINGS: Avoid the future incrustations in
the pipes and connections.
• Great wellness sensation in the shower.
• So and smooth skin.
• Increases the life time of electronic devices and
heating systems.
• ECONOMIC SAVINGS: Reduces the consumption of
soaps, soeners and chemical products.
• Low cost of maintenance.
• Automatic function, your only concern is to add
salt to the tank storage from time to time.
It is important that you keep and read this manual
carefully before the installation and starting up of
this equipment. If you have any doubt about the installation, use or maintenance of this equipment, please
contact with the technical assistance service (T.A.S.) of
your distributor.
1.1. SOFTENER SAFETY
Your safety and other’s safety are very important. We have
included safety messages in this manual and on your
appliance.
This is the safety alert symbol.
This symbol alerts you to the potential hazards that
can be risky for you and for others.
All safety messages will follow the safety alert symbol or either the word “DANGER” or “WARNING”.
• DANGER: Severe or fatal risk if the following instructions are not immediately followed.
• WARNING: All safety messages provide information
about the possible danger, how to reduce the risk of injury and what might happen if the instructions are not
followed.
1.2. BEFORE STARTING
See ‘Section 5’ before installing the water soener. Carefully follow the instructions for the installation (Warranty
may be considered void, if the installation is faulty).
Please read the entire manual before undertaking installation. Then, collect all necessary materials and tools for
the installation.
Check the plumbing installation.
All installations must be done according to the law in
force in each region or country.
Please be careful when handling the water soener. Do
not knock it over, let go of it or place it onto sharp objects.
Under no circumstances should the soener be installed
outdoors, since it must be protected against sunlight and
rough environmental conditions.
2. INTRODUCTION
The RIDER soeners equipments will avoid you all kind
of problems caused by the hardness of the water and will
reduce a lot the maintance requested by your electronical
devices. They will have a longer life.
These systems come with a residual hardness regulator
as standard, which allows selecting the appropriate hardness for your home.
Its user-friendly electronic programmer will allow you to
put the system into operation in an easy and fast manner.
What is hardness?
Hardness is the quantity of scaling salts present in water,
which are mainly composed of low solubility salts of calcium and magnesium. The main salts causing hardness
are listed below:
Calcium bicarbonate:
Calcium chloride:
Calcium sulphate:
Magnesium bicarbonate:
Magnesium chloride:
Magnesium sulphate:
These salts, due to their chemical properties, have a tendency to precipitate, producing scale on pipes and obstructing them as they accumulate.
In the same way, hardness has a high tendency to scale
on the electrical resistors from heaters and to precipitate
in heaters when temperature increases.
The combination of hard minerals and soap produces a
soap curdling, wich reducest he cleansing properties of
soap.
The precipitation of hard minerals build a layer on cook-
Ca(COH)²
CaCl
CaSO
Mg(COH)²
MgCl
MgSO
5
Español
User Manual
ing utensils, connections and plumbing fixtures. It may
even alter the taste of food.
Español
Main problems:
User Manual
· Precipitation on pipes, fixtures and appliances.
· Incrase of the energy consumption due to the generated
isolation.
· Higher soap consumption
· Reduction of the electical appliances’ service life and
increase of the maintenance needed.
All these problems are greatly reduced when using a water soening system.
For the most part of Europe, hardness is indicater in
French hydrometic degrees, but there are also other
measuring units, according to each region.
Below are the most usual equivalences.
UNITS
1 ppm of Calcium
1 ppm ofMagnesium
1 ppm de CaCO3
1º French (ºHF)
1º German (ºd)
1º Englisch (ºe)
1 mmol/L
1 mval/L=eq/L
ppm of CaCO
2,5
4,13
1
10
17,8
14,3
100
50
3
º French
0,25
0,413
0,1
1
1,78
1,43
10
5
How does your system work?
Water soening is carried out by means of an ion exchange process. On this purpose, the system uses resins
with the chemical capacity of capturing Calcium (Ca) and
Magnesium (Mg) ions and removing them from water.
When Calcium and Magnesium ions are captured by the
resin, two Sodium (Na) ions are released which, due to its
chemical properties, produce salts with a higher solubility , thus avoiding all hardness-related problems.
Therefore, when water gets soened, its sodium level
increases.
Further information on this procedure can be found in
‘Section 2.8’.
Ion exchange resins:
They are synthetic compounds, usually with a spherical
shape, able to capture certain chemical substances present in water, which then exchange for other substances.
Water soening uses strong cation resins, which are composed of styrene copolymers and divinylbenzene with a
sulphur base.
The exchange resin charge is located inside the vessel of
the soener, attending an important part of volume of
the same (between 60 and 75% depending on the model).
It is compulsory that one part of the vessel remains free to
allow a correct regeneration of the resin bed.
During the treatment process the water gets through the
multiway valve by the entrance connection, flows to the
upper part of the soener through the distributor producing this way an ionic exchange inside the resin bed.
The treated water is collected by the distributor and driven through the inner tube through the vessel till the multiway valve. It is sent with the out connection till the main
water pipe for consumption. In this point the system has
a counter for treated water to be contabilized.
2.3 Regeneration of the system
The quantity of calcium and magnesium ions that the
resin may retain is limited; therefore, the water volume
a water soener can treat is limited as well. The system
must periodically carry out a process known as regeneration, which allows the resin to recharge with sodium ions,
so it can continue soening water.
In RIDER systems the regeneration process starts automatically when the systems detects that the exchange capacity is going to finish, the timer incorporated in the system allows to configurate in a dierent way the starting
of the regeneration, please see section 6.3 in order to get
more information about how the programme works.
The regeneration of a soener system is made of dierent
parts, each with a concrete finality
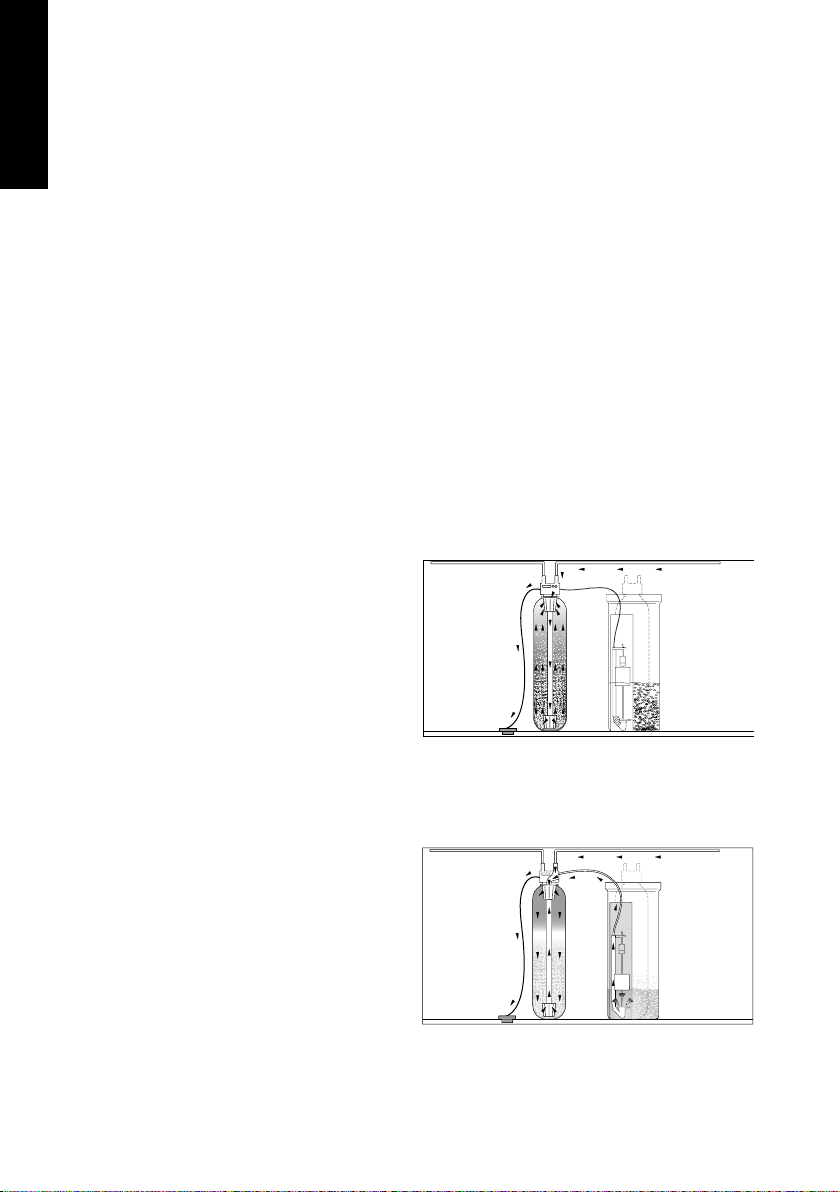
Backwashing:
The water gets into the vessel through an inferior collector, making a washing and a floing of the resin bed and
allowing, this way, the following regeneration process.
Conditioned water Water inlet
To the drain
Brine aspiration:
Through an aspiration process for venturi eect the system suctions the brine liquid solution previously prepared for the regenerating tank. This salt solution is introduced into the soening vessel getting in contact with the
ionic exchange resin and starting the regeneration.
Conditioned water
To the drain
Slow rinse:
It refers to the movement in the resin bed of the salt solution previosly aspirated, this way the contact of the salt
with the resin is higher and the regeneration of the same
is optimized.
Water inlet
Brine aspiration,
Venturi effect
6
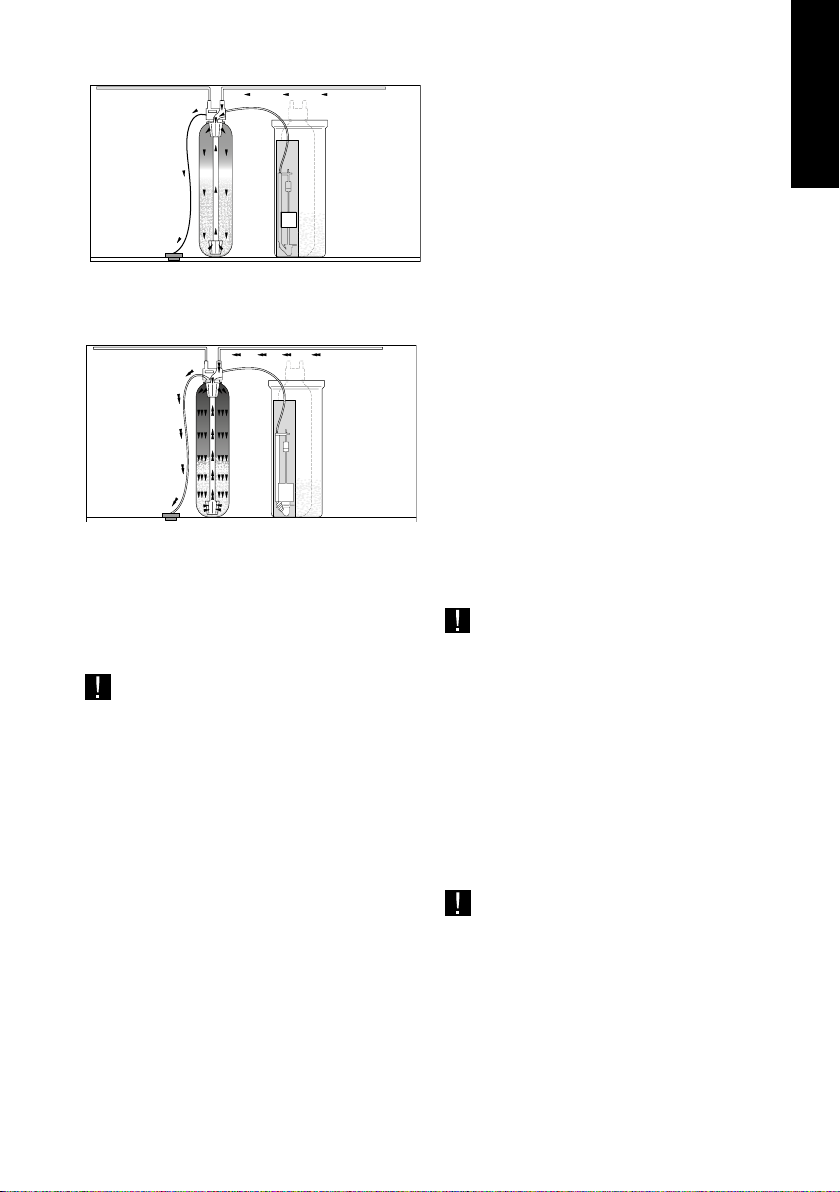
Conditioned water
To the drain
FAST RINSE:
The water flows through the resin bed making a final
wash of the same and ensuring the total removing of the
salt that can be inside the vessel.
Conditioned water
To the drain
Water inlet
Brine aspiration,
Venturi effect
Water inlet
REFILLING THE BRINE TANK:
The volume of water goes automatically to the brine tank
in order to prepare the necessary brine to be consumed
in the next regeneration.This process is automatic, so normally it is not necessary to put more water in the brine
tank (except during the starting up as shown in section 7.
NOTE: During the regeneration process the systems
allows the passage of the non treated water in order
to ensure the disponibilty of the water to be consu-
med.
2.4 Regeneration rate and capacity.
TThe exchange capacity is the quantity of hardness that a
certain resin volume can retain before getting exhausted.
This value is usually expressed as ºHFxm3.
The higher the resin volume of the system is, the higher
will be the quantity of hardness that can be retained before the resin gets exhausted.
Depending on the quantity of sodium chloride used to
regenerate each liter of resin the capacity of exchange
can dier.
2.5 Work Volume
Water soeners using ion exchange must respect certain
contact periods between water to be treated and resin, in
order to ensure that the soening process is carried out
properly.
For the RIDER equipment, please respect the minimum
and maximum flow rates indicated in the Technical Characteristics section.
If the working ranges are outside the recommended ranges, the proper operation of the system will be aected
(excessive loss of charge, hardness leakage, etc.)
2.6 Hardness leak
The ion exchange process on which water soening is
based may be aected by dierent factors, which can reduce its eiciency and cause a certain level of hardness
leakage.
High sodium concentration on water to be treated.
It may interfere in the exchange process.
Excessive flow rates
Since there is not enough contact time, some of the hardness may not be retained by the resin.
2.7 Residual hardness
Depending on the final use of treated water, it may be
necessary to obtain fully soened water or, on the contrary, it may be desirable to leave some residual hardness.
These systems have been designed to supply fully softened water, but the by-pass integrates a residual hardness mixer, which allows the regulation of the desired
hardness degree in treated water (see ‘Section 7’).
NOTE: For human consumption water, it is recom-
mended to have a residual hardness between
5 and 8 ºHF if pipes are made of copper, and be-
tween 8 and 10 ºHF if they are made of iron (for
the latter, it is also recommended to install a silicopolyphosphates filter aerwards).
2.8 Sodium increase
Most of the sodium we consume on a daily basis comes
from food, specially processed food, since salt is an excellent preservative and is used as an additive in prepared
products.
Sodium consumption through the water we drink is rather low when compared with that obtained from food.
WARNING: As mentioned above, water soeners re-
duce the Calcium and Magnesium concentration
in water by replacing it for Sodium. Thus, they
increase the sodium level in water.
The maximum recommended sodium level in water for
human consumption is of 200 ppm. Depending on the
sodium concentration and the hardness of water to be
treated, it is possible that soened water contains a higher concentration of sodium than that recommended.
Should this be the case, or if water is to be consumed by
persons who must follow a low-sodium diet, it is recommended to install a household reverse osmosis system to
drink the water.
Español
User Manual
7

The table below can be used as a guideline to know the
increase on sodium concentration in treated water depending on feed water hardness:
Español
User Manual
Initial hardness
in water (ºHF)
10
15
25
30
35
40
45
50
60
Sodium added
by the water
soener (mgNa/litre)
43
65
108
130
152
173
195
217
260
8
3. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Model
Code
Resin volume
Vessel
Working flow
Maximum flow
Maximum hardness
High eiciency configuration
Salt/regeneration
Exchange capacity
Medium capacity configuration
Salt/regeneration
Exchange capacity
High capacity configuration
Salt/regeneration
Exchange capacity
Caudal mínimo
Rango de temperaturas
Rango de presiones
RIDER
795238
25 litres
9x35
3
/h
1,0m
3
1,5m
/h
120ºHF
1,5 Kg Sal
96ºHFxm
3,0 Kg Sal
141ºHFxm
6,25 Kg Sal
175ºHFxm
3
0,1 m
/h
4-35ºC
2,5-8 bar
3.1. Volume of treated water according to inlet hardness
System RIDER
3
HIGH eiciency:
Feed hardness
15 6,40
25 3,84
30 3,20
35 2,74
45 2,13
55 1,75
MEDIUM capacity:
Feed hardness
3
3
3
15 9,40
25 5,64
30 4,70
35 4,03
45 3,13
55 2,56
HIGH capacity:
Feed hardness
15 11,67
25 7,00
30 5,83
35 5,00
45 3,89
55 3,18
141ºHFxm
96ºHFxm
175ºHFxm
3
3
Español
User Manual
Pressure rating
Electrical connection
Rated electrical power
Protection class
Dimensions
Height A
Width B
Depth C
220V/50Hz-24VAC
TIPO III
1100 mm
360 mm
530 mm
C
B
8 bar
4W
DISTRIBUITED BY:
IONFILTER, WATERFILTER, PURICOM
Pol. Ind. L’Ametlla Park - c/Aiguafreda, 8
L’Ametlla del Vallès, Barcelona (España)
T. 902 305 310 - F. +34 936 934 329
A
TECHNICAL SERVICE:
+34 936 934 309
sat@ionfilter.com
9
 Loading...
Loading...