Page 1
OWNER’S OPERATION AND INSTALLATION MANUAL
WARNING: Improper installation,
adjustment, alteration, service or maintenance can cause injury or property
damage. Refer to this manual for correct
installation and operational procedures.
For assistance or additional information
consult a qualified installer, service agency,
or gas supplier.
This appliance may be installed in an aftermarket* permanently located, manufactured
(mobile) home, where not prohibited by local
codes.
This appliance is only for use with the type
of gas indicated on the rating plate. This
appliance is not convertible for use with other
gases.
*Aftermarket: Completion of sale, not for purpose of
resale, from the manufacturer.
Do not store, or use gasoline or other flammable
vapors and liquids in the vicinity of this or any
other appliance.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
l Do not try to light any appliance.
l Do not touch any electrical switch; do not
use any phone in your building.
l Immediately call your gas supplier from a
neighbor’s phone. Follow the gas supplier’s
instructions.
l If you cannot reach your gas supplier,
call the fire department.
Installation and service must be performed
by a qualified installer, service agency or
gassupplier.
MN200EBC MN200EHBC
MN300EBC MN300EHBC
BLUE FLAME VENT-FREE
NATURAL GAS
SPACE HEATER
WARNING: If the information in
this manual is not followed exactly,
a fire or explosion may result
causing property damage, personal
injury, or loss of life.
WARNING: This is an unvented gas-
fired heater. It uses air (oxygen) from the
room in which it is installed.Provisions
for adequate combustion and ventilation air
must be provided. Refer to Air For Combustion and Ventilation section on page 5 of
this manual.
WATER VAPOR: A BY-PRODUCT OF UNVENTED
ROOM HEATERS
Water vapor is a by-product of gas combustion.An
unvented room heater products approximately one (1)
ounce (30ml) of water for every 1,000 BTU’s(.3KW’s)
of gas input per hour. Refer to page 4.
Installer: Please leave these instructions with the
consumer.
Consumer: Please retain these instructions for
future use.
Continental Appliance Inc./US Office
5 Musick 4600 Highlands Parkway S.E.
Irvine Suite# D/E
CA 92618 Smyrna GA 30080
TOLL FREE NUMBER: 1-877-886-5989
Nanjing PRO-COM Electric Appliance Co.,Ltd.
#6 Chuangye Road,High New Tech.Zone,
Great Bridge Road North,Nanjing,210061,China.
PR-MCL051-04-0506
Page 2
Table of Contents
Safety Information......................................................................................2
..
Product Features..................................................................................... 3
..
Local Codes..............................................................................................3
..
Unpacking................................................................................................. 4
Air for Combustion and Ventilation......................................................... 5
..
Installation.................................................................................................. 7
..
Connecting to Gas Supply....................................................................... 9
Checking Gas Connections...................................................................10
Operating Your Heater.............................................................................11
Cleaning & Maintenance.........................................................................14
..
Replacement Parts..................................................................................16
Specifications....................................................................................... ...16
Troubleshooting........................................................................................17
Parts List...........................................................................................................20
Make certain you read and understand all warnings. Keep this
manual for reference. It is your
guide to safe and proper operation
of this heater.
SAFETY INFORMATION
IMPORTANT: Read this
owner’s manual carefully and
completely before trying to
assemble, operate, or service
this heater. Improper use of
this heater can cause serious
injury or death from burns,
fire, explosion, electrical
shock, and carbon monoxide
poisoning.
DANGER: Carbon monoxide
poisoning may lead to death!
When used without fresh air, heater
may give off CARBON MONOXIDE, an
odorless, poisonous gas.
WARNING
DO NOT INSTALL HEATER UNTIL ALL
NECESSARY PROVISIONS ARE
MADE FOR COMBUSTION AND VEN-
TILATION AIR . CONSULT THE WRIT-
TEN INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED
WITH THE HEATER FOR INFORMTION
CONCERNING COMBUSTION AND
VENTILATION AIR. IN THE ABSENCE
OF INSTRUCTIONS. REFER TO THE
NATIONAL FUEL GAS CODE.
ANSI Z223. 1. SECTION 5.3 OR
APPLICABLE LOCAL CODES.
This heater is equipped with a PILOT
LIGHT SAFETY SYSTEM designed to
turn off the heater if not enough fresh
air is available
If heater shuts off, do not relight until
you provide fresh air.
If heater keeps shutting off have it ser-
viced . Keep burner and control com-
partment clean.
DO NOT TAMPER WITH PILOT LIGHT
SAFETY SYSTEM!
Early signs of carbon monoxide poi-
soning resemble the flu with
headache, dizziness and/or
nausea. If you have these signs,
heater may not be working properly.
Get fresh air at once! Have heater
serviced.Some people - pregnant
women, persons with heart or lung
disease, anemia, those under the
influnce of alcohol, those at hight
altitude - are more affected by car-
bon monoxide than others.
CARBON MONOXIDE POISON-
ING MAY LEAD TO DEATH!
Natural Gas: Natural gas is
odorless. An odor-making agent
is added to natural gas.The odor
helps you detect a natural gas
leak. However, the odor added
to natural gas can fade. Natural
gas may be present even
though no odor exists.
WARNING
2
Page 3

3
1. This appliance is only for use
with the type of gas indicated
on the rating plate. This
appliance is not convertible for
use with other gases.\
2. If you smell gas
l Shut off gas supply.
l Do not try to light any appliance.
l Do not touch any electrical
switch, do not use any phone in
WARNING: Do not use
any accessory not approved
for use with this heater.
Carefully supervise young
children when they are in the
same room with heater.
Make sure grill guard is in
place before running the heater.
Keep the appliance area clear
and free from combustible
materials, gasoline, and other
flammable vapors and liquids.
Due to high temperatures, heater
should be kept out of traffic and
away from furniture and draperies.
Front surface of heater becomes
very hot when running heater.
Keep children and adults away
from hot surface to avoid burns
or clothing ignition. Heater will
remain hot for a time after shut
down. Allow surface to cool
before touching.
Do not place clothing or other
flammable material on or near
the appliance. Never place any
objects on the heater.
WARNING: Any change to
this heater or its controls can
be dangerous.
your building.
l Immediately call your gas sup-
plier from a neighbor’s phone.
Follow the gas supplier’s
instructions.
l If you cannot reach your gas
supplier, call the fire department.
3. This heater shall not be in stalled
in a bedroom or bathroom.
4. This heater needs fresh, outside
air ventilation to run properly. This
heater has an Oxygen Depletion
Sensor (ODS) safety shutoff
system.The ODS shuts down the
heater if not enough fresh air
is available. See Fresh Air for
Combustion and Ventilation
pages 5 and 6.
5. Keep all air openings in front and
bottom of heater clear and free of
debris. This will insure enough air
for proper combustion.
6. If heater shuts off. Do not relight
until you provide fresh, outside
air. If heater keeps shutting off,
have it serviced.
7. Do not operate
l Where flammable liquids or
vapors are used or stored
l Under dusty conditions
8. Before using furniture polish,
wax, carpet cleaner, or similar
products, turn heater off.If
heated, the vapors from these
products may create a white
powder residue within burner
box or on adjacent walls or
furniture.
9. Do not use heater if any part
has been under water. Immediately call a qualified service technician to inspect the room heater
and to replace any part of the
control system and any gas control which has been under water.
10.Turn off and unplug heater and
let cool before servicing. Only a
qualified service person should
service and repair heater.
11.Operating heater above elevations
of 4,500 feet could cause pilot
outage.
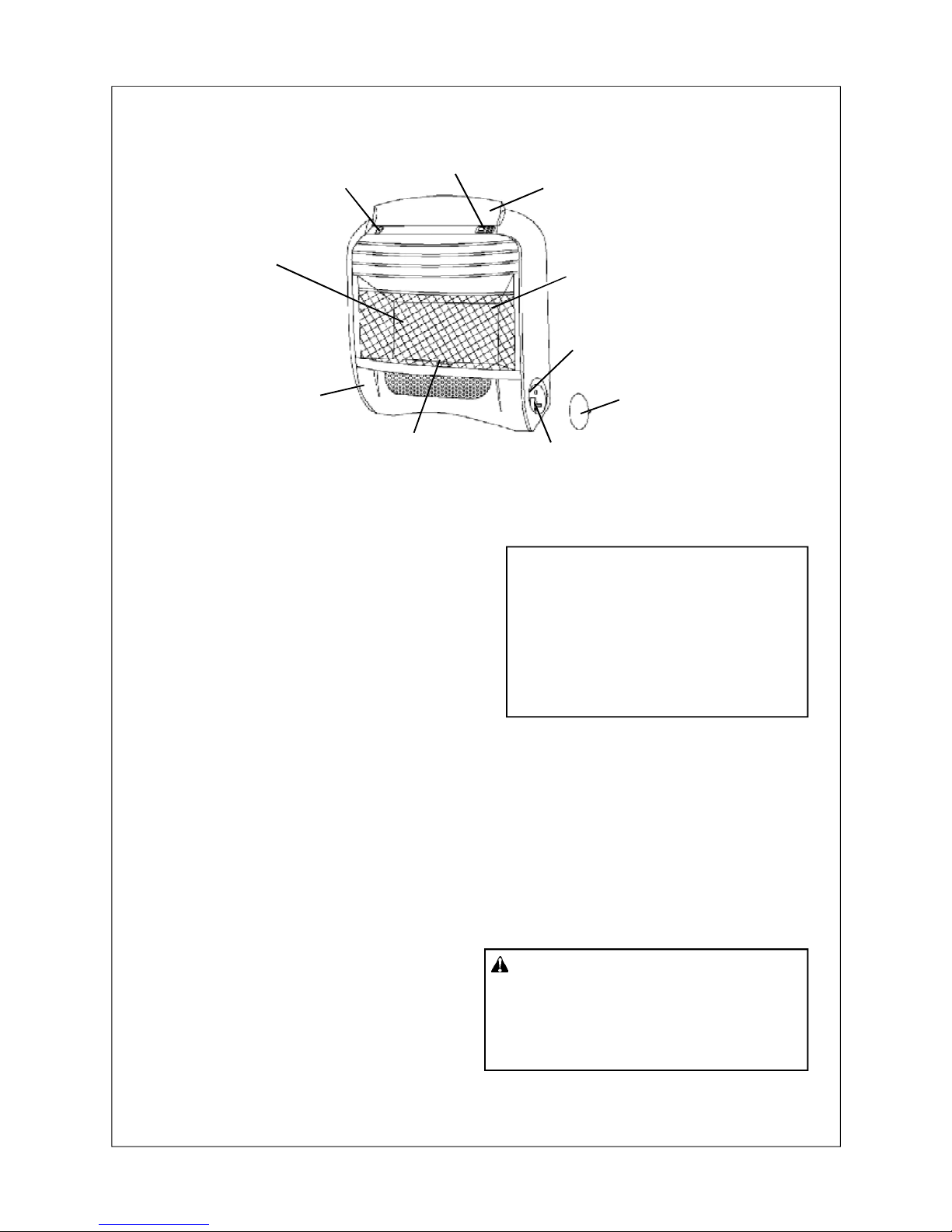
PRODUCT FEATURES
(See Figure 1,page 4)
SAFETY PILOT
This heater has a pilot with an
Oxygen Depletion Sensor(ODS)
safety shutoff system.
The ODS/pilot shuts off the heater
if there is not enough fresh air.
AUTOMATIC IGNITION
SYSTEM
This heater is equipped with an
automatic control system.
This system requires no matches,
or batteries to light heater.
TOUCH PAD
THERMOSTATIC HEAT
CONTROL
This heater has a control module with
a thermostat sensing bulb. set
temperrature with touch pad. This results in the greatest heater comfort
and may result in lower gas bills.
SAFETY INFORMATION
MANUL OVERRIDE
CONTROL SYSTEM
(MN200EHBC, MN300EHBC)
There are two control systems,
electric and manual overide.If no
electric power is available,you can
operate heater by manual overide.
LOCAL CODES
This heater is designed for vent-free
operation. Some state and local
codes prohibit the use of vent-free
heater.
Modeles MN200EBC MN200EHBC
MN300EBC MN300EHBC are
equipped for Natural Gas. Field
conversion is not permitted.
WARNING
Page 4
4
PRODUCT FEATURES
LOCAL CODES continued
Install and use heater with care. Follow all local
codes. In the absence of local codes, use the
latest edition of National Fuel Gas code ANSI
Z223.1, also known as NFPA 54*.
*Available from:
American National Standards Institute, Inc.
1430 Broadway
New York, NY 10018
National Fire Protection Association, Inc.
Batterymarch Park
Quincy, MA 02269
Figure1-Vent-Free Heater
UNPACKING
1. Remove heater from carton.
2. Remove all protective packaging applied to
State of Massachusetts : The installation must be
made by a licensed plumber or gas fitter in the
Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Sellers of unvented propane or natural gas-fired
supplemental room heaters shall provide to each
purchaser a copy of 527 CMR30 upon sale of the
unit.
In the State of Massachusetts, unvented propane
and natural gas-fired space heaters shall be prohibited in bedrooms and bathrooms.
Water vapor is a by-product of gas combustion. An ventfree room heater products approximately one (1) ounce
(30ml) of water for every 1,000 BTU’s (.3KW’s) of gas
input per hour.
Vent-free room heaters are recommended as
supplemental heat (a room) rather than a primary heat
source (an entire house) . In most supplemental heat
application, the water vapor does not create a problem.
In most applications, the water vapor enhances the
low humidity atmosphere experience during cold
weather.
The following steps will help insure that water vapor
does not become a problem.
1. Be sure the heater is sized properly for the application,
including ample combustion and ventilation air.
WATER VAPOR: A BY-PRODUCT OF VENT-FREE ROOM HEATERS
IMPORTANT: Vent-free heaters add moisture to
the air. Although this is beneficial, installing heater
in rooms without enough ventilation air may cause
mildew to form from too much moisture. See Fresh
Air for Combustion and Ventilation, pages 5 and 6.
heater for shipment.
3. Check heater for any shipping damage. If
heater is damaged, promptly inform dealer
where you bought heater.
Touch Pad
ON/OFF Switch
Burners
Lower Front Panel
Satety Pilot
Control Knob for Manual Overide
Control System
Door
Ignitor for Manual Overide Control
System
Grill Guard
Cabinet Top
2. If high humidity is experienced, a dehumidifier may
be used to help lower the water vapor content of the air.
3. Do not use vent-free room heater as the primary
heat source.
Page 5
5
PROVIDING ADEQUATE
VENTILATION
The following are excerpts from
National Fuel Gas Code. NFPA 54/
ANSI Z223.1, Section 5.3. Air for
Combustion and Ventilation. All
spaces in homes fall into one of
the three following ventilation
classifications:
1. Unusually Tight Construction
2. Unconfined Space
3. Confined Space
The information on pages 5 through
6 will help you classify your space
and provide adequate ventilation.
Confined and Unconfined
Space
The National Fuel Gas Code ANSI
Z223.1 defines a confined space as
a space whose volume is less than
50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btu per hour
(4.8 m3 per kw) of the aggregate in-
put rating of all appliances in-
stalled in that space and an uncon-
fined space as a space whose
volume is not less than 50 cubic
feet per 1,000 Btu per hour (4.8 m
3
per kw) of the aggregate input rat-
ing of all appliances installed in
that space. Rooms communicating
directly with the space in which the
appliances are installed*, through
openings not furnished with doors,
are considered a part of the uncon-
fined space.
This heater shall not be installed
in a confined space or unusually
tight construction unless provisions
are provided for adequate combus-
tion and ventilation ai r.
*
Adjoining rooms are communicat-
ing only if there are doorless pas-
sageways or ventilation grills be-
tween them.
Unusually Tight Construction
The air that leaks around doors and
windows may provide enough fresh
air for combustion and ventilation.
However, in buildings of unusually
tight construction, you must provide
additional fresh air.
Unusually tight construction is
defined as construction where:
a. Walls and ceilings exposed to
the outside atmosphere have a
continuous water vapor retarder
with a rating of one perm (6×10
-11
kg
per pa-sec-m2) or less with openings
gasketed or sealed and
b. Weather stripping has been
added on openable windows and
doors and
c. Caulking or sealants are applied
to areas such as joints around
window and door frames, between
sole plates and floors, between
wall-ceiling joints, between wall
panels, at penetrations for plumbing,
electrical, and gas lines, and at
other openings. If your home meets
all of the three criteria above, you
must provide additional fresh air.
See Ventilation Air From Outdoors,
page 6.
If your home does not meet all of
the three criteria above, see Deter-
mining Fresh-Air Flow for Heater
Location, page 5.
DETERMINING FRESH-AIR FLOW FOR HEATER LOCATION
Determining if you have a Confined or Unconfined Space*
Use this worksheet to determine if you have a confined or unconfined space.
Space: Includes the room in which you will install heater plus any adjoining rooms with doorless passageways
or ventilation grills between the rooms.
1. Determine the volume of the space (length×width×height).
Length×Width×Height= cu.ft. (volume of space)
Example: Space size20ft. (length)×16ft.( width)×8ft. (ceiling height)=2560cu. ft. (volume of space)
If additional ventilation to adjoining room is supplied with grills or openings, add the volume of these rooms
to the total volume of the space.
2. Divide the space volume by 50 cubic feet to determine the maximum Btu/Hr the space can support.
(volume of space)÷ 50 cu. ft.=(Maximum Btu/Hr the space can support)
Example: 2560 cu. ft. (volume of space)÷50 cu.ft.=51.2 or 51.200(maximum Btu/Hr the space can support)
AIR FOR COMBUSTION
AND VENTILATION
WARNING: This heater shall
not be installed in a confined
space or unusually tight con-
struction unless provisions are
provided for adequate combus-
tion and ventilation air. Read the
following instructions to insure
proper fresh air for this and
other fuel-burning appliances in
your home.
Page 6

6
Rework worksheet, adding the space of the adjoining unconfined space. The combined spaces must have enough fresh
air to supply all appliances in both spaces.
Ventilation Air From Inside Building
This fresh air would come from an adjoining
unconfined space. When ventilating to an adjoining unconfined space, you must provide two permanent openings: one within 12" of the ceiling and
one within 12" of the floor on the wall connecting
the two spaces (see options 1 and 2, Figure 2). You
can also remove door into adjoining room (see
option 3, Figure 2). Follow the National Fuel Gas
Code NFPA 54/ANSI Z223.1. Section 5.3, Air for Combustion and Ventilation for required size of ventila-
tion grills or ducts.
If the actual Btu/Hr used is less than the maximum Btu/Hr the space can support, the space is an
unconfined space. You will need no additional fresh air ventilation.
Example:
Gas water heater 40,000 Btu/Hr
Vent free heater + 18,000 Btu/Hr
Total = 58,000 Btu/Hr
3. Add the Btu/Hr of all fuel burning appliances in the space.
Vent-free heater Btu/Hr
Gas water heater* Btu/Hr
Gas furnace Btu/Hr
Vented gas heater Btu/Hr
Gas Fireplace logs Btu/Hr
Other gas appliances* + Btu/Hr
Total = Btu/Hr
*Do not include direct-vent gas appliances. Direct-vent draws combustion air from the outdoors and
vents to the outdoors.
4. Compare the maximum Btu/Hr the space can support with the actual amount of Btu/Hr used.
Btu/Hr (maximum the space can support)
Btu/Hr (actual amount of Btu/Hr used)
Example : 51,200 Btu/Hr(maximum the space can support)
58,000 Btu/Hr(actual amount of Btu/Hr used)
The space in the above example is a confined space because the actual Btu/Hr used is more than the
maximum Btu/Hr the space can support.
You must provide additional fresh air. Your options are as follows:
A. Rework worksheet, adding the space of an adjoining room. If the extra space provides an unconfined
space, remove door to adjoining room or add ventilation grills between rooms. See Ventilation Air From
inside Building.
B. Vent room directly to the outdoors. See Ventilation Air From Outdoors .
C. Install a lower Btu/Hr heater, if lower Btu/Hr size makes room unconfined.
Figure 2 -Ventilation Air from Inside Building
NOTE: If the area in which the heater may be operated is smaller than that defined as an unconfined space
or if the building is of unusually tight construction, provide adequate combustion and ventilation air by one
of the methods described in the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1, Section 5.3 or applicable local
Figure 3 -Ventilation Air from Outdoors
Ventilation Air From Outdoors
Provide extra fresh air by using ventilation grills or
ducts: You must provide two permanent openings:
one within 12" of the ceiling and one within
12" of the floor.
Connect these items directly to the outdoors or
spaces open to the outdoors.
These spaces include attics and crawl spaces. Follow the National Fuel Gas Code NFPA 54/ANSI
Z223.1, Section 5.3. Air for Combustion and Ventilation for required size of ventilation grills or ducts.
IMPORTANT: Do not provide openings for inlet or
outlet air into attic if attic has a thermostat-controlled power vent.
Heated air entering the attic will activate the power vent.
Page 7
7
NOTICE: This heater is intended for use as supplemental
heat. Use this heater along with
your primary heating system. Do
not install this heater as your
primary heat source. If you have a
central heating system, you may
run system’s circulating blower
while using heater. This will help
circulate the heat throughout the
house. In the event of a power
outage, you can use this heater
as your primary heat source.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: A qualified service
person must install heater. Follow all local codes.
WARNING: Electrical
Grounding Instructions
This appliance is equipped with a
three-prong (grounding) plug for
your protection aginst shock hazard
and should be plugged directly into
a properly grounded three-prong re-
ceptacle
WARNING: Never install the
heater
l in a bedroom or bathroom.
l in a recreational vehicle.
l where curtains, furniture,
clothing, or other flammable
objects are less than 36 inches
from the front, top, or sides
of the heater.
l as a fireplace insert.
l in high traffic areas.
l in windy or drafty areas.
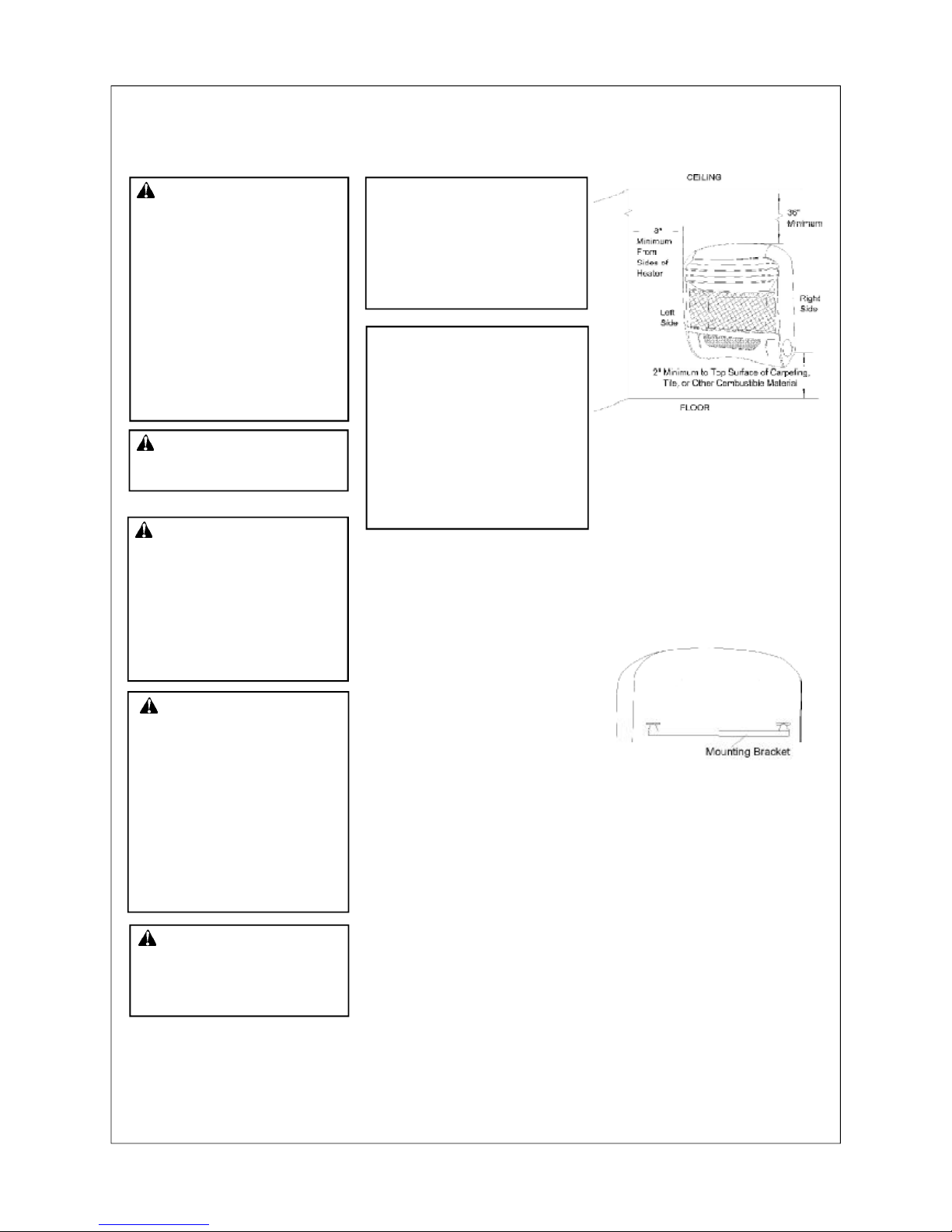
WARNING: Maintain the minimum clearances shown in Figure 4. If you can, provide greater
clearances from floor, ceiling,
and joining wall.
CAUTION: If you install the
heater in a home garage
l heater pilot and burner must
be at least 18 inches above
floor.
l locate heater where moving
vehicle will not hit it.
CHECK GAS TYPE
Use only Natural gas. If your gas
supply is not Natural, do not install
heater. Call dealer where you
bought heater for proper type heater.
LOCATING HEATER
This heater is designed for mounting on a wall, set on floor, away
from a wall.
Purchase optional floor mounting
stand from your dealer.
See Accessories, page 16.
For convenience and efficiency,
install heater
l where there is easy access for
operation, inspection, and service
l in coldest part of room
Figure 4 -Mounting Clearances
As Viewed From Front Of Heater
FASTENING HEATER TO WALL
Mounting Bracket
The mounting bracket is located
on back panel of heater (see
Figure 5). It has been taped there
for shipping. Remove mounting
bracket from back panel.
Figure 5 -Mounting Bracket
Location
CAUTION: This heater creates
warm air currents. These currents
move heat to wall surfaces next
to heater. Installing heater
next to vinyl or cloth wall coverings or operating heater where
impurities (such as tobacco
smoke, aromatic candles, cleaning fluids, oil or kerosene lamps,
etc.) in the air exist may discolor
walls.
Page 8

8
INSTALLATION
continued
Methods For Attaching Mounting
Bracket To Wall
Only use last hole on each end
of mounting bracket to attach
bracket to wall. These two holes
are 16 inches apart from their
centers. Attach mounting bracket to
wall only in one of two ways:
1. Attaching to wall stud
2. Attaching to wall anchor
Note: Wall anchors, mounting screws
are in hardware package. The hardware package is provided with
heater.
Attaching to Wall Stud: This method
provides the strongest hold. Insert
mounting screws through mounting
bracket and into wall studs.
Attaching to Wall Anchor: This
method allows you to attach
mounting bracket to hollow walls
(wall areas between studs) or to
solid walls (concrete or masonry).
Decide which method better
suits your needs. Either method
will provide a secure hold for the
mounting bracket.
2. Mark screw locations on
wall. (see Figure 6)
Note: Only mark last hole on
each end of mounting bracket.
Insert mounting screws through
these holes only.
3. Remove tape and mounting
bracket from wall.
Marking Screw Locations
1. Tape mounting bracket to wall
where heater will be located.
Make sure mounting bracket is
level.
Attaching to Wall Stud Method
For attaching mounting bracket to
wall studs
1. Drill holes at marked locations
using 9/64" drill bit.
2. Place mounting bracket onto
wall. Line up last hole on each
end of bracket with holes drilled
in wall.
3. Insert mounting screws through
bracket and into wall studs.
4. Tighten screws until mounting
bracket is firmly fastened to
wall studs.
Attaching to Wall Anchor
Method
For attaching mounting bracket to
hollow walls (wall areas between
studs) or solid walls (concrete or
masonry)
1. Drill holes at marked locations
using 5/16" drill bit. For solid
walls (concrete or masonry), drill
at least 1" deep.
2. Fold wall anchor as shown in
Figure 7 below.
Figure 7- Folding Anchor
3. Insert wall anchor (wings first)
into hole. Tap anchor flush to
wall.
4. For thin walls (1/2" or less),
insert red key into wall anchor.
Push red key to "pop" open an-
chor wings (see Figure 8).
Model MN200EBC MN200EHBC
WARNING: Maintain the
minimum clearances shown in
Figure 6. If you can, provide greater
clearances from floor, ceiling, and
joining wall.
Figure 6 - Mounting Bracket
Clearances
Model MN300EBC MN300EHBC
IMPORTANT: Do not ham-
mer key! For thick walls (over 1/
2" thick) or solid walls,
do not pop open wings.
5. Place mounting bracket onto
wall. Line up last hole on
each end of bracket with wall
anchors.
6. Insert mounting screws through
bracket and into wall anchors.
7. Tighten screws until mounting
bracket is firmly fastened to wall.
Placing Heater on Mounting
Bracket
1. Locate two horizontal slots on
back panel of heater (see
Figure 9).
2. Place heater onto mounting
bracket. Slide horizontal slots
onto stand-out tabson
mounting bracket.
Figure 9 - Mounting Heater Onto
Mounting Bracket
Figure 8 - Popping Open Anchor
Wing For Thin Walls
Only Insert Mounting
Screws Through Last
Hole On Each End
Adjoining Wall
Floor
Only Insert Mounting
Screws Through Last
Hole On Each End
Adjoining Wall
Floor
Page 9

9
INSTALLATION
continued
Installing Bottom Bracket (See
Figure10)
1. Install bottom bracket to heater
bottom with two screws. It may
be more convenient to remove
heater from wall mounting .
bracket to attach bottom bracket
2. Place heater on mounting
bracket.
3. Locate two bottom mounting
holes on wall. These holes are
near bottom on heater (see
Figure 10).
4. Mark screw locations on wall.
5. Remove heater from mounting
bracket.
6. If installing bottom mounting
screws into hollow or solid wall,
install wall anchors. Follow steps
1 through 4 under Attaching To
Wall Anchor Method. If install-
ing bottom mounting Screw into
wall stud, drill holes at
markedlocations using 9/64" drill
bit.
7. Replace heater onto mounting
bracket.
8. Tighten both screws until heater
is firmly secured to wall. Do not
over tighten.
Figure 10 - Installing Bottom Bracket
CONNECTING TO GAS
SUPPLY
IMPORTANT : Check your gas
line pressure before connecting
heater to gas line.Gas line pressure must be no greater than 14
inches of water.If gas line pressure is higher,heater regulator
damage could occur.
Figure 11- Gas Meter
WARNING:Do not over tighten
gas connections.
WARNING: A qualified
service person must connect
heater to gas supply. Follow all
local codes.
WARNING: This appliance
requires a 3/8" NPT (National
Pipe Thread) inlet connection
to the pressure regulator.
WARNING: Never connect
heater to private ( non-utility )
gas well.This gas is commonly
known as well-head gas.
CAUTION: Use only new, black
iron or steel pipe. Internally-tinned
copper tubing may be used in
certain areas. Check your local
codes. Use pipe of large enough
diameter to allow proper gas volume
to heater. If pipe is too small,
undue loss of pressure will occur.
CAUTION: Use pipe joint
sealant that is resistant to liquid
natural gas.
CAUTION: Aviod damage
to regulator. Hold gas regulator
with wrench when connecting to
gas piping and/or fittings.
INSTALLATION NEEDS
Before installing heater, make sure
you have the items listed below.
l piping (check local codes)
l sealant (resistant to Natural
gas)
l equipment shutoff valve*
l ground joint union
l test gauge connection*
l sediment trap
l tee joint
l pipe wrench
*A CSA/AGA design-certified equipment shutoff valve with 1/8" NPT
tap is an acceptable alternative to
test gauge connection. Purchase
the optional CSA/AGA design certified equipment shutoff valve from
your dealer. See Accessories, page
16.
Page 10

10
INSTALLATION
*A CSA/AGA design-certified equipment shutoff valve with 1/8" NPT tap is
an acceptable alternative to test gauge connection. Purchase the optional
CSA/AGA design-certified equipment shutoff valve from your dealer.
IMPORTANT: Install an equipment
shutoff valve in an accessible
location. The equipment shutoff
valve is for turning on or shutting
off the gas to the appliance.
Install sediment trap in supply line
as shown in Figure 12. Locate
sediment trap where it is within
reach for cleaning. Locate sediment trap where trapped matter
Figure 12 -Gas Connection
Apply pipe joint sealant lightly to
male threads. This will prevent
excess sealant from going into
pipe. Excess sealant in pipe could
result in clogged heater valves.
CHECKING GAS
CONNECTIONS
Pressure Testing Gas Supply
Piping System
Test Pressures In Excess Of
1/2 PSIG (3.5 K Pa)
1. Disconnect appliance with its
appliance main gas valve (control
valve) and equipment shutoff
valve from gas supply piping
system. Pressures in excess of
1/2 psig will damage heater
regulator.
2. Cap off open end of gas pipe
where equipment shutoff valve
was connected.
3. Pressurize supply piping system
by either using compressed air
or opening main gas valve lo-
cated on or near gas meter.
4. Check all joints of gas supply
piping system. Apply mixture of
liquid soap and water to gas
joints. Bubbles forming show a
leak.
5. Correct all leaks at once.
6. Reconnect heater and equipment
shutoff valve to gas supply. Check
reconnected fittings for leaks.
Test Pressures Equal To or
Less Than 1/2 PSIG (3.5 K Pa)
1. Close equipment shutoff valve
(see Figure 13).
2. Pressurize supply piping system
by either using compressed air
or opening main gas valve lo-
cated on or near gas meter.
3. Check all joints from gas meter
to equipment shutoff valve (see
Figure 14). Apply mixture of liquid
soap and water to gas joints.
Bubbles forming show a leak.
4. Correct all leaks at once.
State of Massachusetts : The installation must be made by a licensed
plumber or gas fitter in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Sellers of unvented propane or natural gas-fired supplemental room
heaters shall provide to each purchaser a copy of 527 CMR30 upon
sale of the unit.
In the State of Massachusetts,
unvented propane and natural gasfired space heaters shall be prohibited in bedooms and bathrooms.
is not likely to freeze. A sediment
trap traps moisture and
contaminants. This keeps them
from going into heater controls. If
sediment trap is not installed or is
installed wrong, heater may not run
properly.
WARNING: Test all gas
piping and connections for leaks
after installing or servicing. Correct
all leaks at once.
WARNING: Never use an
open flame to check for a leak. Apply
a mixture of liquid soap and water to
all joints. Bubbles forming show a
leak. Correct all leaks at once.
CAUTION: Make sure exter-
nal regulator has been installed between gas supply and heater. See
guidelines under Connecting to Gas
Supply.
Page 11

11
Figure 13 -Equipment Shutoff Valve
CHECKING GAS
CONNECTIONS
Continued
Pressure Testing Heater Gas
Connections
1. Open equipment shutoff valve
(see Figure 13).
2. Open main gas valve located on or
near gas meter.
3. Make sure no power to heater.
4. Check all joints from equipment
shutoff valve to control valve
(see Figure 14 ). Apply mixture of
liquid soap and water to gas
joints. Bubbles forming show
a leak.
5. Correct all leaks at once.
6. Light heater (see Operating
Heater, pages 11 and 12). Check
the rest of the internal joints for
leaks.
7. Turn off gas (see page 12 ).
FOR YOUR SAFETY
READ BEFORE LIGHTING
A. This appliance is equipped with an
ignition device which auto matically
lights the pilot. Do not try to light
the pilot by hand.
B. BEFORE LIGHTING smell all
around the appliance area for
gas. Be sure to smell next to
the floor because some gas is
heavier than air and will settle
on the floor .
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
l Do not try to light any appliance.
l Do not touch any electric switch;
do not use any phone in your
building.
l Immediately call your gas
supplier from a neighbor’s
phone. Follow the gas
supplier’s instructions.
l If you cannot reach your
gas supplier, call the fire
department.
C. Use only your hand to push
on button. Never use tools. If
the does notoperate. don’t try to
repair it, call a qualified service
technician or gas supplier.
Force or attempted repair may
result in a fire or explosion.
D. Do not use this appliance if any
part has been under water.
Immediately call a qualified
service technician to inspect
the appliance and to replace
any part of the control system
and any gas control which has
been under water.
Figure 14 -Checking Gas
Connections
OPERATING YOUR HEATER
For MN200EHBC, MN 300EHBC
models with manual overrside make
sure the Control Knob in the
ELECTRIC postion.(See Figure 15).
WARNING: If you do not
follow these instructions exactly,
a fire or explosion may result in
causing property damage,personal
injury or loss of life.
OPERATING
INSTRUCTION
1. STOP! Read the safety informa-
tion obove before lighting.
2. Disconnect or turn off all electric
power to heater.
3. This appliance is equipped with
an ignition device which automati-
cally lights the pilot. Do not try to light
the pilot by hand.
4. Wait five (5) minutes to clear out
any gas. Then smell for gas, includ-
ing near the floor. If you smell gas,
STOP! Follow “B” in the safety in-
formation above. If you don’t smell
gas, go to next step.
5. Plug into a properly grounded three-
prong receptacle, set ON/OFF
switch on, you will hear a high pitch
sound that indicates the burner is
ready to be operated.
6. Make sure Control Knob is in ELEC-
TRIC position.
7. Press IGN/OFF button an electric
spark will ignite the pilot.
8. Press BURNER button for desired
burner operation.
AUTO: Burner will automatically turn
on or off to desired temperature
setting, press or for desired
temperature setting.
MAN: Burner operates continuously.
OFF:The main burner will shut off.
9. If the appliance will not operate,
follow the instructions “To Turn Off
Gas To Appliance” and call your
service technician or gas supplier.
Note: The thermostat sensing bulb
measures the temperature of air near
the heater cabinet. This may not al-
ways agree with room temperature
(depending on housing construction,
installation location, room size, air
temperatures, etc.) Frequent use of
your heater will let you determine your
own comfort levels.
Clock setting: Press CLOCK button
to select item (hour, minute). The se-
lected item will flash. Press or
to change to correct time (hour,
minute). Press CLOCK button again,
to set clock.
SETTING CLOCK
Page 12

12
OPERATING YOUR HEATER
continued
AUTO ON: With burner off, press
TIMER button. Then press or to
change to the scheduled time, then
press the TIMER button again, the
TIMER starts timing and the TIMER
will flash. Burner will automatically
come on at the set time.
SETTING TIMER
AUTO OFF: With burner operating,
press TIMER button. Then press or
to change to the scheduled time,
then press the TIMER button again,
the TIMER starts timing and the
TIMER will flash. Burner will automati-
cally shut off at the desired time.
LOCKING TOUCH-PAD
(childproof)
A. Key-press locking: Press LOCK
button on the operating panel,
a symbol will appear on the LCD.
B. Key-press unlocking: Press ,
then press LOCK button to unlock.
1.Press the IGN/OFF button on the
touch pad.
2.Set the ON/OFF switch to OFF posi-
tion on top panel.
If the manual control knob points to
ELECTRIC position, press in the con-
trol knob and turn counter clockwise
to OFF position.
4. Wait five (5) minutes to clear any
gas. Then smell for gas, including
near the floor. If you smell gas,
STOP! Follow “B” in the safety in-
formation on page11. If you do not
smell gas, go to the next step.
5. Push in gas control knob slightly
and turn counterclockwise to
PILOT/IGN and depress for five(5)
seconds. NOTE:The first time the
heater is operated after connecting
the gas supply, the control knob
should be depressed for about
thirty(30) seconds. This will allow
air to exit the gas system.
6. With control knob pressed, push
and release ignitor button. This
will light the pilot. If needed, keep
pressing ignitor button until pilot
lights.
7. Keep control knob depressed for
ten (10) seconds after lighting
pilot. If pilot goes out, repeat steps
5,6 and 7.
8. Rotate counterclockwise to
ON position to light burner. Do not
operate between locked positions.
NOTE: Wait one minute to light
again after shutting off heater.
MANUAL OPERATING
INSTRUCTIONS
TO TURN OFF GAS TO
HEATER
MAN: Blower operates continuously.
OPERATING BLOWER
Press BLOWER button, for desired
blower operation.
OFF: Blower is off.
AUTO: Blower will come on several
minutes after burner comes on and
will go off several minutes after burner
goes off.
1. STOP! Read the safety information
on page11 before lighting.
3. Remove round access door of right
side panel. Push in control knob
slightly and turn clockwise to the
OFF position.
We provide the manual control
system just in case of power
shortage. Install battery for Manual
Ignitor:
1. Unscrew the ignitor cap.
2. Insert a AAA type battery with its an-
ode (“+”) pointing out.
3. Screw the ignitor back cap.
Note: We recommend that the battery
be taken out of the ignitor when the
power supply gets right.
2. Check that gas supply to the heater
is on.
Control Knob
Ignitor Button
Page 13

13
Figure 15- Manual Control
Push in gas control knob slightly
and turn clockwise to OFF.
Do not use force. NOTE: Wait one
(1) minute with control knob in OFF
position before operating heater.
9. When electric power is available
and elelectronic operation is
desired, turn clockwise to
OFF positon for one minute. Then
pressdown knob and rotate
clockwise to ELECTRIC
position. Do not operate between
locked positions.
1. Remove lower front panel.
2. Follow steps 1 through 5 under
Manual Operatting
Instructions on page 12.
3. With control knob pressed in, strike
match. Hold match to pilot until pilot
lights.
MANUAL LIGHTING
PROCEDURE
INSPECTING BURNER
Check pilot flame pattern and burner
flame pattern often.
MANUAL OPERATING
INSTRUCTIONS
continued
4. Keep control knob pressed in for 30
seconds after lighting pilot.
5. Rotate counterclockwise to ON po-
sition to light burner. Do not oper-
ate between looked positions.
4. Replace lower front panel.
TO TURN OFF GAS TO
APPLIANCE
(Match Light)
l turn heater off (see page 11)
l see Troubleshooting, pages 17
through 19.
Figure 16- Correct Pilot Flame
Pattern
BURNER FLAME PATTERN
Figure 18 shows a correct burner
flame pattern. Figure 19 shows an
incorrect burner flame pattern. If
burner flame pattem is incorrect,
as shown in Figure 19.
l turn heater off (see page 11 ).
l see Troubleshooting. pages 17
through 19.
PILOT FLAME PATTERN
Figure 16 shows a correct pilot flame
pattern. The incorrect pilot flame is
not touching hermocouple. This will
cause the thermocouple to cool.
When the thermocouple cools, the
healer will shut down. If pilot flame
pattern is incorrect, as shown in Fig-
ure 17.
Figure 17 - Incorrect Pilot Flame
Pattern
Figure 18 - Correct Burner Flame
Pattern
Figure 19 - Incorrect Burner
Flame Pattern
Page 14

14
CLEANING AND
MAINTENANCE
DISCONNECT WIRING ON CONTROL
MODULE
1. Remove two screws from the lower
front panel , put the lower front panel
forward the down take out thermostat
sensing bulb from the clip, then disco-
nnect the wires to from control
module .
Note: Do not confuse the mark on
each wire.
2. Remove two screws and hex nuts,
take out the control module. When
installing , reverse the steps above.
(See Figure 20, 23 and 24)
Figure 20 Control Model Access
DISCONNECT FAN
1.Remove screws from the fan
bracket panel, pull the fan bracket
panel out to remove. Disconnect
two wires two wires of temperature
sensor.
2.Mark or tag each wire removed for
its exact reconnection. Remove
the four screws from the fan .
When installing , reverse the
steps above.(See Figures 21, 23
and 24)
CAUTION: You must keep
control areas, burner, and circulat-
ing air passageways of heater
clean. Inspect these areas of
heater before each use. Have
heater Inspected yearly by a quali-
fied service person. Heater may
need more frequent cleaning due
to excessive lint from carpeting,
bedding material, pet hair, etc.
Figure 21- Fan Access
CLEANING BURNER AND PILOT
AIR INLET HOLE
We recommend that you clean
the unit every 2,500 hours of
operation or every three months.
We also recommend that you keep
the burner tube and pilot assembly
clean and free of dust and dirt.
CLEANING ODS/PILOT AND BURNER
l Use a vacuum cleaner,pressurized
air. or small, soft bristled brush
to clean.
Clean the pilot assembly also. A
yellow tip on the pilot flame indi-
cates dust and dirt in the pilot
assembly. There is a small pilot air
inlet hole about two inches from
where the pilot flame comes out of
the pilot assembly (see Figure 22).
With the unit off, lightly blow air through
the air inlet hole. You may blow through
a drinking straw if compressed air is
not available.
WARNING: Failure to keep
the primary air opening(s) of the
burner(s) clean may result in soot-
ing and property damage.
CAUTION: Label all wires
prior to disconnection when servic-
ing controls.Wiring errors can
cause improper and dangerous
operation. Verify proper operation
after servicing.
To clean these parts we recom-
mend using compressed air no
greater than 30 PSl.
Your local computer store, hardware
store, or home center may carry
compressed air in a can. You can
use a vacuum cleaner in the blow
position. If using compressed air in
a can, please follow the directions
on the can. If you don’t follow direc-
tions on the can, you could damage
the pilot assembly.
1. Shut off the unit, including the
pilot. Allow the unit to cool for
at least thirty minutes.
2. Inspect burner, pilot for dust
and dirt.
3. Blow air through the ports/slots
and holes in the burner.
CLEANING HEATER CABINET
Air Passageways
l Use a vacuum cleaner or
pressurized air to clean.
Exterior
l Use a soft cloth dampened with
a mild soap and water mixture.
Wipe the cabinet to remove dust.
Figure 22 - Pilot Inlet Air Hole
WARNING: Disconnect
power before attempting any main-
tenance or cleaning to reduce the
risk of fire , electric shook or per-
sonal injury. Turn off heater and let
cool before cleaning.
Page 15

15
Figure 23-
Figure 24- Double Control Systems Diagram
(Model MN200EHBC MN300EHBC)
(Model MN200EBC MN300EBC)
Page 16

16
Note: Dimensions listed are outer most points on the heater
(includes grill).
* For purposes of input adjustment.
MN200EBC(MN200EHBC)
20,000
Natural Gas Only
Automatic(Automatic/Electric)
120 V
20 W
3" W.C.
10.5"
4"
23 5/8×19 5/8×9
27 1/2×22×10 1/8
33(34)
38(39)
REPLACEMENT PARTS
Use only original replacement parts.
This will protect your warranty
coverage for parts replaced under
warranty.
PARTS NOT UNDER
WARRANTY
Contact authorized dealers of this
product. If they can’t supply original
replacement part(s), call PRO-COM’s
phone number (877)886-5989.
TECHNICAL SERVICE
You may have further questions
about installation, operation, or
troubleshooting. If so, contact
PRO-COM’S phone number (877)
886-5989.
FLOOR MOUNTING STAND
For locating heater on the floor,
away from a wall. Complete installation instructions provided with floor
mounting base stand.
FLOOR STAND MODEL: PF0920C
EQUIPMENT SHUTOFF VALVE
For all models. Equipment shutoff
valve with 1/8" NPT tap. This part
should be purchased.
ACCESSORIES
Purchase these heater accessories from your local dealer. If they
l your name
l your address
l model and serial numbers of
your heater
l how heater was malfunctioning
l type of gas used (Propane/LP or
Natural gas)
l purchase date
l warranty card
Usually, we will ask you to return the
defective part to the factory.
If they are unable to supply
original replacement part(s), call
the number on the front of manual. When contacting your dealer or
PRO-COM, have ready:
PARTS UNDER WARRANTY
Contact authorized dealer from
whom you purchased this product.
SPECIFICATIONS
BTU/Hr
Gas Type
Ignition
Volts
Watts
Manifold Pressure
Inlet Gas Pressure
(inches of water)
Maximum
Minimum
Dimensions, Inches (HxWxD)
Heater
Carton
Weight (pounds)
Heater
Shipping
can not supply these accessories,
contact PRO-COM for information. You
can also write to the address
listed on the front of this manual.
MN300EBC(MN300EHBC)
30,000
Natural Gas Only
Automatic(Automatic/Electric)
120 V
27 W
3" W.C.
10.5"
4"
23 5/8×27 1/16×9
27 1/2×29 7/16×11 1/8
40(41)
45(46)
Page 17

17
TROUBLESHOOTING
POSSIBLE CAUSE
1. No power to heater
2. ON/off swith not ON
3. Wire is damaged or loose
4. Pilot electrude position is not correct
5. Touch pad cable is not connected
6. System halt
1. Gas supply turned off or equipment
shut off valve closed
2. Air in gas lines when installed
3. Depleted gas supply
4. ODS/pilot is clogged
5. Gas inlet supply pressure not correct
6. Wire is damaged or loose
7. Pilot electrude position is not correct
8. Gas valve or regulator is damage
1. Equipment shutoff valve is not
fully open
2. Thermocouple connection
loose at control module
3 Low gas pressure
4. Dirt or partially clogged ODS/pilot
5. Thermocouple damaged
6. Gas valve or regulator damaged
WARNING: If you smell gas
l Shut off gas supply.
l Do not try to light any appliance.
l Do not touch any electrical switch; do not use any phone in your building.
l Immediately cal l your gas supplier from a neighbor ’s phone. Follow the gas
supplier’s instructions.
l If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the fire department.
IMPORTANT: Operating heater where impurities in air exist may create odors.
Cleaning supplies, paint, paint remover, cigarette smoke, cements and glues, new
carpet or textiles, etc., create fumes. These fumes may mix with combustion air
and create odors.
Warning : Make sure that power
is turned off before proceeding.
CAUTION: Never use a wire,
needle, or similar object to clean
ODS/pilot. This can damage
ODS/pilot unit.
OBSERVED PROBLEM
When ignition button is pressed,
there is no spark at ODS/pilot.
When IGN/OFF is pressed
Spark at ODS/pilot but no ignition.
ODS/pilot has flame, but continues
to spark.
WARNING: Turn off and let cool
before servicing. Only a qualified
service person should service and
repair heater.
Page 18

18
TROUBLESHOOTING
Continued
OBSERVED PROBLEM
ODS/pilot has flame, but burner(s)
does not light
Delayed ignition of burner(s)
Burner backfiring during combustion
Burner Plaque(s) does not glow
Slight smoke or odor during
initial operation
Heater produces a clicking/ticking
noise just after burner is lit or
shut off
White powder residue forming
within burner box or on adjacent
walls or furniture
POSSIBLE CAUSE
1. Burner injector is clogged
2. Inlet gas pressure is too low
3. Thermoocouple leads discon
nected or improperly connected
4. Batteries weak
1. Manifold pressure is too low.
2. Burner injector is clogged
1. Burner injector is clogged or
damaged
2. Burner is damaged.
3. Excessive supply pressure
damaged regulator
1. Plaque damaged
2. Inlet gas pressure is too low
1. Residues from manufacturing
processes
1. Metal expanding while heating or
contracting while cooling
1. Heated vapors from furniture
polish, wax, carpet cleaners,
etc. turn into white powder
residue
REMEDY
1. Clean burner injector (see Cleaning
and Maintenance, Page14) or
replace burner injector
2. Contact local natural gas company
3. Reconnect leads (See wiring
diagram)
4. Replace batteres
1. Contact local natural gas company.
2. Clean burner (see Cleaning and
Maintenance, Page 14) or replace
burner injector
1. Clean burner injector (see Cleaning
and Maintenance, Page 14) or
replace burner injector(s)
2. Replace burner
3. Replace gas regulator
1. Replace burner
2. Contact local natural gas
company.
1. Problem will stop after a few hours
of operation
1. This is common with most
heaters. If noise is excessive,
contact qualified service person
1. Turn heater off when using furniture
polish, wax, carpet cleaner, or
similar products
Page 19

19
TROUBLESHOOTING
Continued
REMEDY
1. Ventilate room. Stop using odor
causing products while heater
is running
2. Locate and correct all leaks(see
Checking Gas Connections,
Page 10)
1. Open window and/or door for,
ventilation
2. Contact local natural gas
company.
3. Clean ODS/pilot (see Cleaning
Page 14)
1. Locate and correct all leaks(see
Checking Gas Connections,
Page 10)
1. Remove foreign matter.
2. Locate and correct all leaks
(see Checking Gas
Connections, Page 10)
1. Refer to Air for Combustion and
Ventilation requirements , Page
5
POSSIBLE CAUSE
1. Heater is burning vapors from
paint, hair spray, glues, etc.
(See IMPORTANT statement
at beginning of troubleshooting)
2. Gas leak. See WARNING
Statement at begining of
troubleshooting
1. Not enough fresh air is available.
2. Low line pressure
3. ODS/pilot is partially clogged
1. Gas leak. See WARNING
Statement at begining of trouble
shooting
1. Foreign matter between control
valve and burner
2. Gas leak See WARNING
Statement at begining of
troubleshooting
1. Not enough combustion/
ventilation air
OBSERVED PROBLEM
Heater produces unwanted odors
Heater shuts off in use (ODS
perates)
Gas odor exists even when heater is
shut off
Gas odor during combustion
Moisture/condensation on windows
NOTE: BEFORE YOU SWITCH TO “ELECTRIC” CONTROL LEVEL FROM MANUAL CONTROL, YOU NEED
TO TURN THE KNOB TO “OFF” LEVEL FIRST AND WAIT FOR ONE MINUTE, THEN TURN THE KNOB TO
“ELECTRIC”.
IN CASE OF “ELECTRONIC” CONTROL LEVEL DOES NOT WORK, PLEASE TURN THE CONTROL KNOB
COUNTERCLOCKWISE TO “OFF” LEVEL AND WAIT FOR ONE MINUTE.
Page 20

20
ILLUSTRATED
PARTS BREAKDOWN
MN200EBC
MN300EBC
Page 21

21
PARTS LIST
MN200EBC
MN300EBC
This list contains replaceable parts for your heater. When ordering relacement
parts, following the instructions listed under Replacement Part on page16 of this
manual.
KEY
NO.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
9-1
9-2
10
11
12
13
14
MN200EBC
PART NO.
MCL001-02
MCL008-01
VL067-01
NAM02-00
MCL039-02
MCB29002
MCB09002
NAM03-00
ND2103X400-R
ND0803-4B
ND0807-B3
ML091-03
NRV81FIL-3
NBB20-000M1
NFHTX100-D
MCB62001
PART AVAILABLE NOT SHOWN
DESCRIPTION
Rotating cover
rotating cover dowel
ON/OFF switch
Touch pad
Glass
Grill guard ASM
Lower Front panel ASM
Control Module Asembly
ODS
Thermocouple
Electrode
Injector
Regulator
Burner
Fan Assembly
Fan temp switch bracket asm
QTY
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
MCB28001
MCL055-21
MCL046-01
MCL046-02
Hardware Assembly
CSA/AGA Decal
Lighting Instruction Plate
Warning Plate
1
1
1
1
MN300EBC
PART NO.
MCL001-01
MCL008-01
VL067-01
NAM02-00
MCL039-01
MCB29001
MCB09001
NAM03-00
ND2103X400-R
ND0803-4B
ND0807-B3
ML091-03
NRV81FIL-3
NBB30-000M1
NFHTX186-D
MCB62001
MCB28001
MCL055-11
MCL046-01
MCL046-02
Page 22

22
ILLUSTRATED
PARTS BREAKDOWN
MN200EHBC
MN300EHBC
Page 23

23
PARTS LIST
MN200EHBC
MN300EHBC
This list contains replaceable parts for your heater. When ordering replacement
parts, following the instructions listed under Replacement Part on page16 of this
manual.
KEY
NO.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
15-1
15-2
16
17
18
19
MN200EHBC
PART NO.
MCL001-02
MCL008-01
VL067-01
NAM02-00
MCL003-01B
MCL039-02
MCB29002
MCB09002
NAM03-00
NRV81FIL-3
AL092-01
MB16004
MB16005
NV2020-22
ND4703X400-RH
ND0803-4C
ND0807-C3
NBB20-000M1
ML091-03
NFHTX100-D
MCB62001
PART AVAILABLE NOT SHOWN
DESCRIPTION
Rotating cover
rotating cover dowel
ON/OFF switch
Touch pad
Right panel Door
Glass
Grill guard ASM
Lower Front panel ASM
Control Module Asembly
Regulator
Injector
Control knob ASM
Control knob pole ASM
Override control system
ODS
Thermocouple
Electrode
Burner
Injector
Fan Assembly
Fan temp switch bracket asm
MCB28001
MCL055-13
MCL046-03
MCL046-02
Hardware Assembly
CSA/AGA Decal
Lighting Instruction Plate
Warning Plate
1
1
1
1
QTY
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
MN300EHBC
PART NO.
MCL001-01
MCL008-01
VL067-01
NAM02-00
MCL003-01B
MCL039-01
MCB29001
MCB09001
NAM03-00
NRV81FIL-3
AL092-01
MB16004
MB16005
NV2020-22
ND4103X400-RH
ND0803-4C
ND0807-C3
NBB30-000M1
ML091-03
NFHTX186-D
MCB62001
MCB28001
MCL055-07
MCL046-03
MCL046-02
 Loading...
Loading...