Page 1

PowerLogic® COM128
RS-232 to RS-485 Converter
Installation and Operation Guide
August 2006
Page 2

Page 3

Conventions
Throughoutthisoperationmanual,thefollowingmethodsareusedtohighlight
importantinformation.
NOTE
Describesimportantconsiderationsrelatedtoadevicesetup,featureor
application.
CAUTION
Alertsyoutoaconditionwhichcouldpotentiallycausedamagetothedeviceor
otherexternalequipment.
WARNING or DANGER
Warnsyoutoavoidconditionsthatcouldpotentiallycauseserious
and/orequipmentdamage.
personalinjury
Page 4

Table of Contents
COM128 FEATURES ................................................................................................. 1
1 INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................................ 2
2 Physical Features ..................................................................................................... 3
2.1 RS-232 Panel ............................................................................................................. 3
2.2 RS-485 Panel ............................................................................................................. 3
3 CONFIGURATION ...................................................................................................... 4
3.1 Configuration Switches ............................................................................................... 4
3.2 Mode Descriptions ...................................................................................................... 4
3.2.1 RS-485 Flow Control ................................................................................... 4
3.2.2 Speed Compensation ................................................................................. 5
3.2.3 RTS / CTS Flow Control ............................................................................. 5
3.2.4 RS-485 Data Buffering ................................................................................ 6
3.2.5 Repeater ..................................................................................................... 6
4 INSTALLATION ......................................................................................................... 7
4.1 DC Supply Connections.............................................................................................. 7
4.2 RS-232 Connection & Configuration ........................................................................... 7
4.2.1 RS-232 Cable ............................................................................................. 7
4.2.2 Direct Connection to a Computer ................................................................7
4.2.3 Connection to a Modem .............................................................................. 8
4.3 RS-485 Bus Connections ........................................................................................... 9
4.3.1 Convertor Connections ............................................................................... 9
4.3.2 General Bus Wiring Considerations ............................................................ 9
4.3.3 Recommended Topologies ......................................................................... 9
5 SUPPLYING POWER TO THE RS-232 DTR PIN .................................................... 11
6 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS .............................................................................. 13
7 COM128 OPTIONS .................................................................................................. 14
7.1 -UNI Option .............................................................................................................. 14
7.2 -IND Option .............................................................................................................. 14
Page 5

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
TM
COM128
MULTI-PORT RS-232 TO RS-485 CONVERTER
•
Connects one RS-232 line to four RS-485 buses.
•
Automatic baud rate detection supporting data
rates of 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, and 19200 baud.
• DTE or DCE operation allows connection to
computers or modems without the need for null
modem adapters.
• RS-485 transmit enable may be controlled
automatically, or by the RS-232 RTS line.
• RTS/CTS handshaking capability for use with radio
modems.
FEA TURES
• Compatible with short-haul modems and line
drivers that are powered by the RS-232 line.
• Works directly with M-SCADA, L-SCADA
and PowerView software, or with other
proprietary software.
• Full electrical isolation between RS-232 and RS485 to 750 VDC
• Microprocessor control allows for future
enhancements by firmware upgrade.
1
Page 6

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
1 INTRODUCTION
The COM128 is used to interface a single RS-232 communications line to up to four RS-485 communications buses.
The RS-485 standard restricts each RS-485 bus to supporting
32 or fewer devices connected to it. The standard also dictates
a 4000 foot (1219 m) maximum overall cable length on an RS485 bus. The COM128 is ideal for installations that contain
more than 32 remote devices, or that have devices positioned at
distances greater than could be reached with a 4000 foot cable.
The COM128 has four physically independent RS-485 ports,
allowing communications with up to 128 devices. Data is
transmitted to all four RS-485 ports simultaneously (ie. the
ports are not addressable).
The COM128 provides many features which make it flexible,
easy to use, and reliable:
TWO METHODS OF RS-485 BUS CONTROL
RS-232 is a duplex communications standard, allowing signals
to be transmitted and received simultaneously. RS-485 is half
duplex standard, allowing only one device connected to an RS485 bus to transmit at any given time.
The COM128 has two ways to determine whether it should be
transmitting onto the RS-485 buses, or listening to them:
1) The COM128 can use the RTS signal generated by a
computer or other device connected to the RS-232 port.
When the RTS line is asserted, the COM128 will convert
the RS-232 data stream to RS-485 signal levels and
transmit onto the RS-485 buses. When the RTS signal is
de-asserted, the COM128 will listen for data on the RS485 bus and pass it through to the RS-232 port.
2) Some types of modems and computer hardware/software
do not support RTS line operation. For these applications,
the COM128 has an Auto RTS mode which monitors the
RS-232 bus for data signals. When data is present, the
COM128 automatically enables the RS-485 transmit mode
and begins to transmit onto the RS-485 buses.
DTE OR DCE OPERATION
The COM128 is switch-selectable to act in DTE or
DCE mode. An RS-232 port is provided for each mode,
eliminating the need for null-modems.
In DTE mode, the COM128 supports a CTS-WAIT mode in
which received RS-485 packets will be buffered until the CTS
line indicates the RS-232 device is ready to receive the data.
This feature is useful when interfacing radio modems or slow
data logging equipment to RS-485 devices.
AUTOMATIC BAUD RATE DETECTION
The microprocessor within the COM128 continuously monitors
the data being received on its RS-232 port, and determines the
correct baud rate. No jumper or switch settings are required.
HIGH ELECTRICAL ISOLATION
RS-485 buses are generally quite long, and are often run
through electrically noisy environments. The risk of exposure to
transient voltage surges and spikes on an RS-485 line is
substantially higher than on an RS-232 line. The COM128 uses
optical isolation between RS-485 and RS-232 sections to
provide 750 VDC electrical isolation, and includes transient
suppression circuitry on its RS-485 ports.
MICROPROCESSOR CONTROL
Unlike most converters, the COM128 is controlled by a
microprocessor. COM128 features are determined by the
processor, not by its electrical circuitry. As new features
become available, they can be added to the COM128 by a
simple firmware upgrade. This process requires the replacement of a single chip, allowing upgrades to be performed in the
field in a matter of minutes.
LINE DRIVER COMPATIBILITY
Short-haul modem/line drivers, such as the Gandalf mLDS,
draw their power from the RS-232 DTR line. The COM128 will
support these devices by means of a simple process that
requires the movement of a jumper within the COM128 case.
The process requires only a screwdriver and should take no
more than a few minutes to perform. Please refer to Chapter 5
(Page 12) "Supplying Power to the RS-232 DTR Pin" for details.
2
Page 7
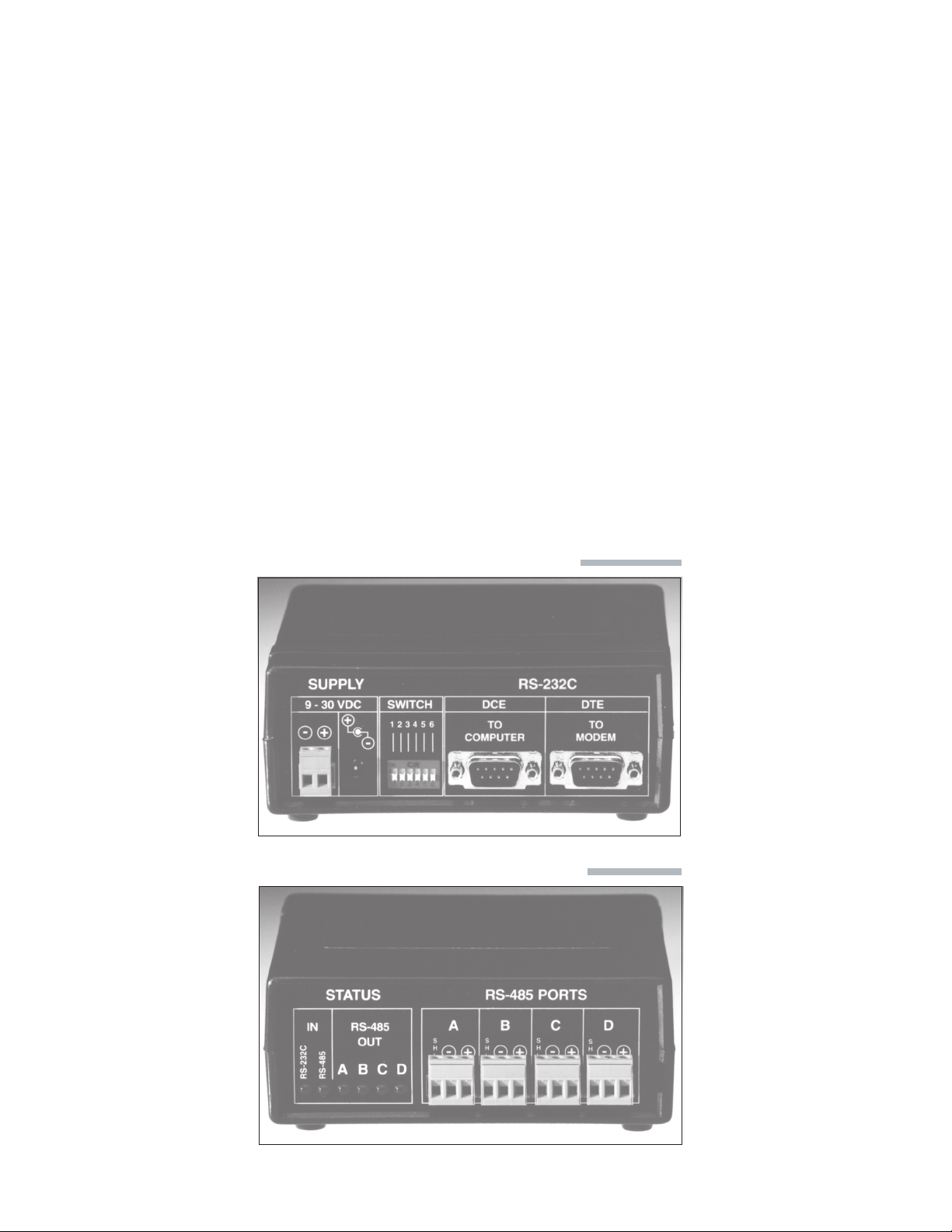
COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
2 PHYSICAL FEATURES
2.1 RS-232 PANEL
The RS-232 panel of the COM128 is illustrated in Figure 2.1.1.
DC SUPPLY CONNECTORS
These connections allow the COM128 to be powered from a
wide range of DC voltage sources, including the supplied
adapter. See Chapter 4 for additional information.
RS-232 PORTS
These ports provide connection to either a computer (DCE) or
a modem (DTE) See Chapter 3 for configuration. See
Chapter 4 for connections.
SWITCH
The 6-position switch is used to configure the operation of the
COM128. See Chapter 3 for additional details.
2.2 RS-485 PANEL
The RS-485 panel of the COM128 is illustrated in Figure 2.2.1.
RS-485 PORTS
These four ports connect the COM128 to the four
RS-485 buses. Four pluggable 3-pin terminal blocks are
provided.
STATUS INDICATORS
A. IN (RS-232)
This LED will flash to indicate that data is being passed
from the connected RS-232 port to the RS-485 ports.
B. IN (RS-485)
This LED will flash to indicate that data is being passed
from one of the four RS-485 ports to the connected RS232 port.
C. RS-485 OUT (A, B, C, D)
For each corresponding RS-485 port these LED’s indicate
if the port is in receive or transmit mode. If the LED is
on, the corresponding port is listening for data from the
RS-485 bus. If the LED is off, the corresponding port is
transmitting data to the RS-485 bus.
Figure 2.1.1 RS-232 Connection Panel
Figure 2.2.1 RS-485 Connection Panel
3
Page 8

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
3 CONFIGURATION
3.1 CONFIGURATION SWITCHES
These six switches are used to configure the COM128 for the
desired operation (see Figure 3.1.1). A switch is ON when it is
in the UP position. The following is a description of each mode
of operation. A list of switch settings for the different modes
follows each mode description. The configuration switches are
only read when control power is initally applied to the
COM128. To re-configure the COM128, the control power
must be removed and re-applied.
3.2 MODE DESCRIPTIONS
3.2.1 RS-485 FLOW CONTROL
FUNCTION
This mode is used to convert the RS-232 signals from either a
DTE or DCE device to RS-485 signals. The COM128 makes the
signal conversion and provides the timing control signals for
the RS-485 ports. No data buffering takes place. Timing can be
set for a fixed baud rate or the COM128 is able to do automatic baud rate detection on the incoming RS-232 data. Either
the DTE or DCE port can be programmed. When the DTE port
of the COM128 is selected in automatic baud rate detection
mode, the input CD (Carrier Detect) signal from the DCE
device can be used to control the transmission of RS-232 data
from the COM128 to the DCE device.
For applications where a DTE device uses the RS-232 RTS
signal for flow control the COM128 can be programmed to use
the RTS signal to control the RS-485 ports.
Figure 3.1.1 COM128 Configuration Switches
SWITCHES
SW2
SW1
ON
1 2 3 4 5 6
OFF
Setting the Configuration Switches to an
undefined value will cause the COM128 to
continually reset.
SW3
NOTE
SW4
SW5
SW6
Mode Port Baud SW1 SW2 SW3 SW4 SW5 SW6
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DT E 1200 OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DT E 2400 ON OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DT E 4800 OFF ON OFF OFF ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DT E 9600 ON ON OFF OFF ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DT E 19,200 OFF OFF O N OFF ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DCE 1200 ON OFF ON OFF ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DCE 2400 OFF ON ON OFF ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DCE 4800 ON ON ON OFF ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DCE 9600 OFF OFF OFF ON ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control @ fixed Baud Rate DCE 19,200 ON OFF OFF ON ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control with Auto Baud Rate Detect DCE NA OFF O N OFF O N ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control with Auto Baud Rate Detect DT E N A ON O N OFF O N ON OFF
RS-485 Flow Control with Auto Baud Rate Detect and Carrier Detect Required DT E N A OFF OFF ON O N O N OFF
RS-485 Flow Control with Hardware RTS DCE NA O N OFF O N O N ON OFF
4
Page 9

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
3.2.2 SPEED COMPENSATION
APPLICATION
For use with DCE devices that require very accurate baud rate
input. Typical uses are with high speed dial up modems.
This mode can be programmed to either ignore the Carrier
Detect (CD) input of its RS-232 DTE port or require that CD
be asserted by the DCE device before data is transmitted by
the COM128 to the DCE device.
Mode Port Baud SW1 SW2 SW3 SW4 SW5 SW6
Speed Compensation w/o Carrier Detect DT E 1200 OFF ON ON OFF O FF OFF
Speed Compensation w/o Carrier Detect DT E 2400 ON ON ON OF F OFF O FF
Speed Compensation w/o Carrier Detect DT E 4800 OFF OF F OFF O N OFF OF F
Speed Compensation w/o Carrier Detect DT E 9600 ON OFF OF F ON O FF OFF
Speed Compensation w/o Carrier Detect DT E 19,200 OFF ON OFF ON OFF OFF
Speed Compensation with Carrier Detect DTE 1200 ON ON O FF ON OF F OFF
Speed Compensation with Carrier Detect DTE 2400 OF F OFF O N ON OFF OF F
Speed Compensation with Carrier Detect DTE 4800 ON OFF ON ON OFF O FF
Speed Compensation with Carrier Detect DTE 9600 OF F ON O N ON OFF OF F
Speed Compensation with Carrier Detect DTE 19,200 ON ON ON ON OFF OFF
3.2.3 RTS / CTS FLOW CONTROL
APPLICATION
This mode is used in conjunction with DCE devices which
require hardware RTS / CTS handshaking. Typical uses are
radio modems and multi-drop lease line modems with
switched carriers.
RS-232 TO RS-485 DATA FLOW
The COM128 detects the start bit, or falling edge, of the first
byte received by the RS-232 DTE port and sets all 4 RS-485
ports into Transmit mode. The COM128 continues to
monitor the RS-232 DTE port for data and continues to pass
data to the RS-485 port until there is no data coming in the
RS-232 port.
RS-485 TO RS-232 DATA FLOW
The COM128 detects data received on any of the 4 RS-485
ports. The first byte is stored in an internal memory buffer
and the Request To Send (RTS) output signal of the DTE RS232 port is asserted. The buffer size is 256 bytes. The
COM128 continues to buffer bytes received from the RS-485
port and scans the RS-232 DTE ports' input signal Clear To
Send (CTS). When the COM128 detects that CTS has been
asserted it starts to transmit the buffered data out the RS-232
DTE port. After the last byte in the buffer has been transmitted out the RS-232 DTE port the COM128 de-asserts the RTS
signal and returns to the Idle State.
If CTS is not asserted after 256 bytes have been received from
the RS-485 port a buffer overflow will occur. The COM128 deasserts RTS and clears the buffer.
If CTS is not asserted within 256 byte times after the first byte
has been received from the RS-485 port a time-out will occur.
The COM128 de-asserts RTS and clears the buffer.
If CTS is de-asserted before the entire contents of the buffer
have been transmitted out the RS-232 DTE port the COM128
de-asserts RTS and clears the buffer.
When in the RS-485 to RS-232 Data flow state the COM128
ignores any data received from its' RS-232 DTE port.
Mode Port Baud SW1 SW2 SW3 SW4 SW5 SW6
RTS / CTS Flow control DT E 1200 ON OF F O FF OF F OFF OF F
RTS / CTS Flow control DT E 2400 OFF ON O FF OF F O FF OF F
RTS / CTS Flow control DT E 4800 ON ON OFF O FF OF F O FF
RTS / CTS Flow control DT E 9600 OFF OFF O N OF F OFF O FF
RTS / CTS Flow control DT E 19,200 ON OFF ON OFF OFF OFF
5
Page 10

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
3.2.4 RS-485 DATA BUFFERING WITH
TRANSMISSION DELAY AFTER RTS
ASSERTION
APPLICATION
This mode is very similar to the RTS / CTS mode. The
COM128 buffers data from the RS-485 ports, asserts its RTS
output then transmits data out of the DTE port after a
programmable time delay. This mode is used in conjunction
with DCE devices which require hardware flow control
(handshaking) but do not provide a CTS signal back to the
COM128. Typical uses are radio modems and multi-drop
lease line modems with switched carriers.
monitor the RS-232 DTE port for data and continues to pass
data to the RS-485 port until there is no data coming into the
RS-232 port.
RS-485 TO RS-232 DATA FLOW
The COM128 detects data received on any of the 4 RS-485
ports. The first byte is stored in an internal memory buffer
and the Request To Send (RTS) output signal of the DTE RS232 port is asserted and an internal timer is started. The
buffer size is 256 bytes. The COM128 continues to buffer
bytes received from the RS-485 port. When the COM128's
internal timer has elapsed it starts to transmit the buffered
data out the RS-232 DTE port. After the last byte in the
buffer has been transmitted out the RS-232 DTE port the
RS-232 TO RS-485 DATA FLOW
The COM128 detects the start bit, or falling edge, of the first
byte received by the RS-232 DTE port and sets all 4 RS-485
ports into Transmit mode. The COM128 continues to
Mode Port Baud SW1 SW2 SW3 SW4 SW5 SW6
RS-485 Data Buffering with 20 mSe c transmission delay after RTS assertion DT E 1200 O FF O FF O FF O FF OFF O N
RS-485 Data Buffering with 50 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion DTE 1200 ON OFF O FF O FF OFF ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 100 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion D TE 1200 O FF O N OFF OF F OF F ON
COM128 de-asserts the RTS signal and returns to the Idle
State.
When in the RS-485 to RS-232 Data flow state the COM128
ignores any data received from its' RS-232 DTE port.
RS-485 Data Buffering with 20 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion DTE 2400 ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 50 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion DTE 2400 OF F OF F ON OFF O FF O N
RS-485 Data Buffering with 100 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion D TE 2400 O N OFF ON OF F OF F ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 20 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion DTE 4800 OF F ON ON OFF OFF ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 50 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion DTE 4800 ON ON O N OFF OF F ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 100 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion D TE 4800 O FF OFF OFF ON OF F ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 20 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion DTE 9600 ON OFF O FF O N OFF ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 50 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion DTE 9600 OF F ON OFF O N OFF ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 100 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion D TE 9600 O N ON OF F ON O FF O N
RS-485 Data Buffering with 20 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion DTE 19,200 OFF OFF ON ON OFF ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 50 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion DTE 19,200 ON OFF ON ON OFF ON
RS-485 Data Buffering with 100 mSec transmission delay after RTS assertion D TE 19,200 OFF ON ON ON OFF ON
3.2.5 REPEATER
For use as a RS-485 repeater. It is a 1 to 3 repeater with Port
A as a "master" port and Ports B, C, and D as slaves. Ports
B, C, and D do not share data. The RS-232 ports are not
used. That is, port A can transmit to B, C, and D, and ports
Mode Port Baud SW1 SW2 SW3 SW4 SW5 SW6
Repeater NA 1200 ON ON O FF OFF ON O N
Repeater NA 2400 OFF OF F ON OFF ON ON
Repeater NA 4800 ON OFF O N OFF ON O N
Repeater NA 9600 OFF ON O N OFF ON O N
B or C or D can transmit to A.
6
Page 11

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
4 INSTALLATION
4.1 DC SUPPLY CONNECTIONS
The COM128 is shipped with a 9 VDC adapter which plugs
into the adapter receptacle. Use only the adapter provided
with the COM128 for this particular powering application.
Alternatively, any DC power supply capable of supplying
from 9 to 30 VDC at 500 mA (minimum) can be used to
power the COM128. Connect the (+) and (-) outputs from
the power supply to the corresponding terminals of the
removable 2-pin terminal block connector supplied with the
COM128 (See Chapter 2, Figure 2.1.1).
4.2 RS-232 CONNECTIONS
& CONFIGURATION
Sections 4.2.2 and 4.2.3 discuss RS-232 port connections
when connecting to a computer or modem. The COM128
configuration switches are used to select which port is active.
Note that the COM128 can also be used in other applications
by selecting the appropriate port and modes as described in
Chapter 3. For configuration switch settings, refer to section
3.2, 'Mode Descriptions'.
4.2.2 DIRECT CONNECTION
TO A COMPUTER
PORT SELECTION
An IBM-compatible PC acts as a DTE (Data Terminal
Equipment) RS-232 device. Therefore, the computer’s RS-232
port should be connected to the DCE port on the COM128.
Refer to Figure 4.2.2.
SWITCH SETTINGS
To properly communicate with the computer, the COM128
must be configured as a DCE (Data Communications
Equipment) RS-232 device (see subsection 3.2.1, 'RS-485 Flow
Control').
4.2.1 RS-232 CABLE
A standard RS-232 serial communications cable should be
used. The COM128 end must be a female DB9 connector for
direct connection, or a male DB25 for connection via the
supplied adapter plug. Maximum cable length is 50 feet
(15.2 m).
Figure 4.2.2 RS-232 Direct Connection to Computer
DCE
RS-232 Cable
50 ft. max.
PORT
DTE
PORT
RS-232 to RS-485 Converter
RS-232
COM128
PORT D
PORT C
RS-485
PORT B
PORT A
SHLD
To
RS-485
Bus
RS-485 Cable
AWG 22 shielded twisted pair.
Total length: 4000 ft. maximum.
IBM PC
7
Page 12

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
4.2.3 CONNECTION TO A MODEM
PORT SELECTION
A telephone or radio modem typically acts as a DCE RS-232
device. Therefore, the modem’s RS-232 port should be
connected to the COM128’s DTE RS-232 port. Refer to Figure
4.2.3.
SWITCH SETTINGS
To properly communicate with the modem, the COM128 must
be configured as a DTE RS-232 device .
If the modem requires RTS-CTS handshaking, the RTS/CTS
Flow Control function provided by the COM128 should be
enabled. This will force the COM128 to buffer all RS-485 data
received until the modem is ready to receive the data. Most
radio modems require this mode, as do some telephone
modems. Refer to your modem’s operation manual to see if
your modem provides or requires this handshaking. .
Refer to Section 3.2, 'Mode Descriptions', for examples of
switch settings for this application.
Figure 4.2.3 RS-232 Connection to Modem
RS-232 Cable
50 ft. max.
Telephone, Radio, or
Fibre Optic Modems
IBM PC
RS-232
Cable
50 ft. max.
DCE
PORT
DTE
PORT
RS-232
PORT D
PORT C
RS-485
PORT B
PORT A
COM128
RS-232 to RS-485 Converter
Telephone
Network, Radio or
Fibre Optic Link
SHLD
To
RS-485
Bus
RS-485 Cable
22 AWG shielded twisted pair.
Total length: 4000 ft. maximum.
8
Page 13

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
4.3 RS-485 BUS CONNECTIONS
4.3.1 CONVERTOR CONNECTIONS
The RS-485 port of the COM128 provides screw down,
captured wire type terminal blocks that unplug from the main
chassis to simplify wiring.
Refer to the following sections for detailed information on
wiring requirements and recommended topologies.
4.3.2 GENERAL BUS WIRING
CONSIDERATIONS
Up to 32 devices can be connected on a single RS-485 bus. The
overall length of the RS-485 cable connecting all devices cannot
exceed 4000 ft. (1219 m).
Devices connected on the bus, including convertor(s) and other
instrumentation, must be wired as follows:
a. Use a good quality shielded twisted pair cable for each
RS-485 bus. It is recommended that AWG 22 (0.6 mm) or
larger conductor size be used.
b. Ensure that the polarity is correct when connecting to the
RS-485 port (+) and (-) terminals of each device.
c. The shield of each segment of the RS-485 cable must be
connected to ground at one end only.
4.3.3 RECOMMENDED TOPOLOGIES
Devices on an RS-485 bus are connected in a point-to-point
configuration, with the (+) and (-) terminals of each device
connected to the associated terminals on the next device. This
is illustrated in Figure 4.3.3a.
While there are many topologies that can be used to connect
devices on an RS-485 communication bus, the two recommended methods are the straight-line and loop topologies.
STRAIGHT-LINE TOPOLOGY
The straight-line wiring method is illustrated in Figure 4.3.3a.
Note that connections are shown for one RS-485 port only. The
COM128 supports four RS-485 buses simultaneously. The
COM128 can exist at any position on the RS-485 bus, including
an end point.
Each end point of the straight-line bus must be terminated with
a 1/4 watt resistor. These termination resistors reduce signal
reflections which may corrupt data on the bus.
Termination resistors are connected between the (+) and (-)
terminals of the device at each end of the bus. This device can
include either a convertor or any other instrument. The value
of the resistor should match the line impedance of the cable
being used. For AWG 22 shielded twisted pair cable, values
between 150 and 300 ohms are typical. Consult the cable
manufacturer’s documentation for the exact impedance of
your cable.
CAUTION
Do not connect ground to the shield at both
ends of a segment. Doing so will allow
ground loop currents to flow in the shield,
inducing noise in the communications cable.
LOOP TOPOLOGY
The loop wiring method is illustrated in Figure 4.3.3a. The
COM128 can exist at any position on the RS-485 bus.
One advantage of the loop topology is that a single open
circuit fault condition anywhere on the loop will not result in
the loss of communication between the computer station and
any of the remote devices.
d. It is recommended that an intermediate terminal strip be
used to connect each device to the bus. This will allow for
The loop topology does not require termination resistors at any
point on the bus.
easy removal of a device for servicing if necessary. The
terminal strip should be connected as shown in Figure
4.3.2.
Figure 4.3.2 RS-485 Intermediate Terminal Strip Connection
RS-485
Device
Terminal
Strip
RS-485 PORT
SHLD
RS-485 Cable
22 gauge shielded
twisted pair
SHLD
To next
device
To next
device
NOTE
Terminal strip connection
method adds 2 times
distance X to overall RS-485
cable length.
DISTANCE X
9
Page 14

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
Last
(End Point)
RS-485 Device
RS-485 PORT
SHLD
SHLD
Last
RS-485 Device
See Section 4.3.3.
Termination Resistor
T
R
RS-485 Cable
(End Point)
RS-485 PORT
SHLD
SHLD
See Section 4.3.3.
Termination Resistor
T
R
SHLD
RS-485 PORT
SHLD
SHLD
RS-485 PORT
SHLD
SHLD
RS-485 Cable
RS-485 PORT RS-485 PORT
RS-485 PORT RS-485 PORT
SHLD
AWG 22 shielded twisted pair. Overall length: 4000 ft. maximum.
SHLD
SHLD
PORT C
PORT B
RS-485
DTE
PORT
or Modem
PORT A
COM128
RS-232 to RS-485 Converter
RS-485 STRAIGHT-LINE TOPOLOGY
PORT D
RS-232
DCE
PORT
Computer
Figure 4.3.3a RS-485 Straight-Line and Loop Topologies
RS-485 PORT RS-485 PORT
AWG 22 shielded twisted pair. Overall length: 4000 ft. maximum.
SHLD
SHLD
PORT C
PORT D
RS-485
COM128
RS-485 LOOP TOPOLOGY
RS-232
RS-232 to RS-485 Converter
DCE
PORT
Computer
DTE
PORT
or Modem
RS-485 PORT RS-485 PORT
PORT B
SHLD
PORT A
10
Page 15

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
CALCULATING OVERALL CABLE LENGTH
When determining the overall length of an RS-485 communication straight-line or loop connection, it is important to account
for all cable segments. For example, when RS-485 connections
to the device are made via an intermediate terminal block
(Figure 4.3.2), the lengths of cable between the device and the
terminal block must be added to the total cable distance. This
length is equal to 2 times distance X in the diagram.
CONNECTION METHODS TO AVOID
Any device connection that causes a branch in the main RS-485
bus should be avoided. This includes star and tee (T) methods.
Refer to Figure 4.3.3b for examples. These wiring methods will
cause signal reflections that may cause interference.
RULE OF THUMB
At any connection point on the RS-485 bus,
no more than two (2) cables should be connected. This includes connection points on
instruments, converters, and terminal strips.
Following this guideline ensures that star
and tee connections are avoided.
5 SUPPLYING POWER TO THE
RS-232 DTR PIN
The COM128 is shipped configured for use with devices that
supply their own power.
Some RS-232 devices, such as short-haul modems and line
drivers, receive their power from the DTR pin of the RS-232
line. The COM128 can be configured to support these devices,
supplying 5 VDC @ 10 mA to the DTR pin of its DTE or DCE
port.
To configure the COM128 to supply power on the DTR pin,
follow this procedure:
1. Disconnect all power and communications connections to
the COM128.
2. Remove the two case screws, and lift the top half of the
case away from the base of the unit.
3. Locate the 3-pin jumper blocks J1 and J2. For normal use,
these are configured with pins 2 and 3 connected. Change
each jumper so that pins 1 and 2 are connected.
4. Replace the cover and re-install the screws.
11
Page 16

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
DO NOT
CONNECT
SHLD
DO NOT
CONNECT
RS-485 PORT
SHLD
RS-485 PORT
SHLD
SHLD
RS-485 PORT RS-485 PORT
SHLD
3-way star
connection
point not
allowed
SHLD
RS-485 PORT RS-485 PORT
SHLD
PORT B
PORT C
PORT D
COM128
RS-232
RS-232 to RS-485 Converter
DCE
PORT
DTE
RS-485
PORT
SHLD
RS-485 PORT RS-485 PORT
SHLD
PORT A
SHLD
RS-485 PORT RS-485 PORT
SHLD
SHLD
PORT B
PORT C
PORT D
COM128
RS-232
RS-232 to RS-485 Converter
DCE
PORT
DTE
RS-485
PORT
PORT A
Figure 4.3.3a RS-485 Topologies to Avoid
RS-485 STAR CONNECTION
12
Computer
or Modem
RS-485 T-CONNECTION
Computer
or Modem
Page 17

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
6 TECHNICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL RATINGS
Isolation: 750 V between RS-232 and RS-
485 ports
Power Supply: Standard: 9 VDC @ 500 mA
(120 VAC adapter supplied)
Alternate: 2-pin pluggable terminal
block accepts
9-30 VDC
Power to DTR Pin: 5 VDC @ 10 mA
(jumper selectable)
Operating Temperature: 00C TO 500C (320F to 1220F)
ambient air
Storage Temperature: -300C to 700C
(-220F to + 1580F)
Humidity: 5 to 95 percent, non-
condensing
Shipping: Weight: 0.9 kg (2 lbs. 0 oz.)
Carton: 30 x 25 x 18cm
(11.8" x 9.8" x 5.9")
FEATURES
Baud Rates Supported: 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200
RS-232 Ports: One DTE (Male DB9)
One DCE (Male DB9)
RS-485 Ports: Four 3-pin, pluggable terminal
blocks, each with (+), (-), and
shield (SHLD) terminals
RS-485 port terminals all pass
ANSI/IEEE C37.90A-1989
surge withstand and fast transient tests.
Figure 6.1 COM128 Mechanical Dimensions
5.25"
(133mm)
2.13" (54
mm)
(includes rubber
feet)
5.25"
(133mm)
13
Page 18

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
7 COM128 OPTIONS
-UNI OPTION
The -UNI option is a universal power supply that allows the
COM128 to be powered from any standard international
voltage and frequency.
Specifications
Input Voltage: 90 VAC to 264 VAC
Input Frequency Range: 47 Hz to 63 Hz
Protection: Internal Fuse
Operating Temperature : 00C to 400C
320F to 1040F
Storage Temperature: -400C to 700C
-400F to 1580F
Standards Compliance
The UNI option is CSA and UL approved, and CE compliant.
-IND OPTION
The -IND option is a universal power supply that allows the
COM128 to be powered from any standard international
voltage and frequency. The power supply is designed for
industrial applications where it can be mounted on the wall or
door of a cabinet. Refer to Figure 7.2.1.
Specifications
Input Voltage: 85 VAC to 264 VAC
110 VDC to 340 VDC
Input Frequency Range: 47 Hz - 440 Hz
Protection: Internal fuse
Operating Temperature: 00C to 500C (relative humidity, non-
condensing)
320F to 1220F
Storage Temperature: -200C to 750C
-40F to 1670F
STANDARDS COMPLIANCE
The IND option is CSA, UL and VDE approved, and CE
certified.
SPECIAL CONSIDERATION
For the CE certification to be valid, the IND
power supply must be installed in accordance with all local electrical codes and
standards and must not be user-accessible
during normal operation.
Mechanical and Mounting Dimensions
Dimensions in inches except where otherwise indicated.
Connections
The -IND power supply must be connected to a dedicated
fused feed voltage source. The COM128 is connected to the
IND supply via the Phoenix 2-pin power supply connector on
the COM128 enclosure. Refer to Figure 7.2.
14
Page 19

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
Figure 7.2 Connecting the -IND Power
Supply
COM128
-
+
(see specs for
for input range)
1A Slo-Blo
-
+
AC (L)
FG
AC (N)
IND Power Supply
15
Page 20

COM128 Installation and Operation Manual Schneider Electric
Figure 7.2.1 -IND Option (Industrial P/S)
16
Page 21

Page 22

Page 23

Page 24

PowerLogic COM 128
Installation and Operation Manual
For further assistance
please contact us at:
Schneider Electric
Power Monitoring and Control
2195 Keating Cross Road
Saanichton, BC
Canada V8M 2A5
Tel: 1-250-652-7100
295 Tech Park Drive, Suite 100
Lavergne, TN 37086
USA
Tel: 1-615-287-3400
Electropole (38 EQI)
31, rue Pierre Mendès France
F - 38050 Grenoble Cédex 9
Tel : + 33 (0) 4 76 57 60 60
Getting technical support:
Contact your local Schneider Electric sales
representative for assistance or go to the
www.powerlogic.com website.
Electrical equipment should be installed, operated,
serviced, and maintained only by qualified personnel.
No responsibility is assumed by Schneider Electric for any
consequences arising out of the use of this material.
70002-0025-06
© 2006 Schneider Electric. All rights reserved.
09/2006
 Loading...
Loading...