POWEREX PS12013-A Datasheet
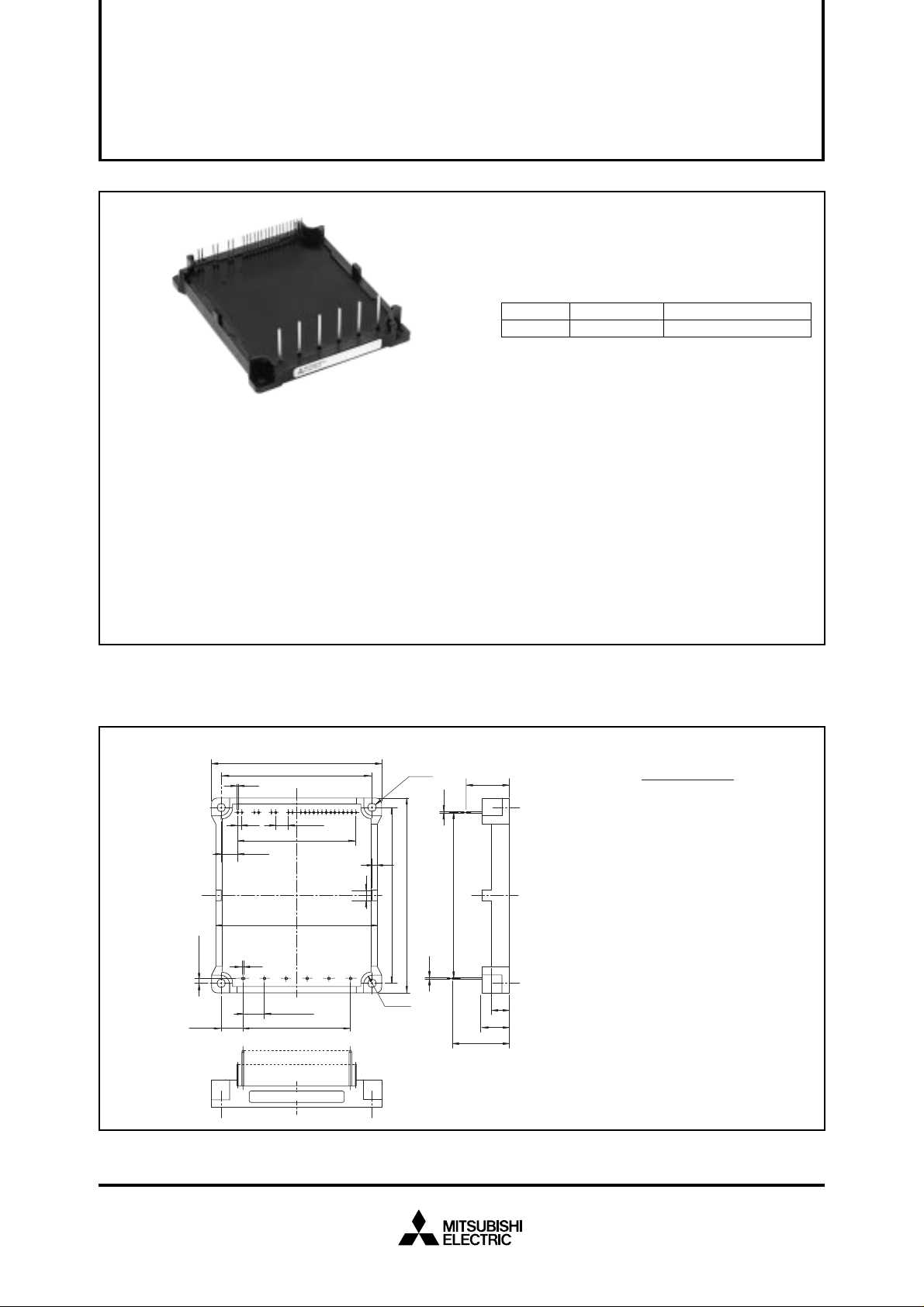
MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Application Specific Intelligent Power Module>
MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Application Specific Intelligent Power Module>
PS12013-A
FLA T-BASE TYPE
FLA T-BASE TYPE
INSULA TED TYPE
INSULA TED TYPE
PS12013-A
PS12013-A
INTEGRATED FUNCTIONS AND FEATURES
• 3-Phase IGBT inverter bridge configured by the latest 3rd.
generation IGBT and diode technologies.
• Circuit for dynamic braking of motor regenerative energy.
• Inverter output current capability Io (Note 1) :
Type Name
PS12013-A
100% load
1.8A (rms)
150% over load
2.7A (rms), 1min
(Note 1) : The inverter output current is assumed to be sinu-
soidal and the peak current value of each of the
above loading cases is defined as : Iop = Io ✕ √2
INTEGRATED DRIVE, PROTECTION AND SYSTEM CONTROL FUNCTIONS:
• For P-Side IGBTs : Drive circuit, High-speed photo-couplers, Short circuit protection (SC),
• For N-Side IGBTs : Drive circuit, Short-circuit protection (SC), Control supply Under voltage and Over voltage protection (OV/UV),
• For Brake circuit IGBT : Drive circuit.
• Warning and Fault signaling :
F
F
F
CL : Warning for inverter current overload condition
• For system feedback control : Analogue signal feedback reproducing actual inverter output phase current (3φ).
• Input Interface : 5V CMOS/TTL compatible, Schmitt trigger input, and Arm-Shoot-Through interlock protection.
Bootstrap circuit supply scheme (Single drive power supply ) and Under-voltage protection (UV).
System Over temperature protection (OT), Fault output signaling circuit (Fo), and Current-Limit warning signal output (CL).
O1 : Short circuit protection for lower-leg IGBTs and Input interlocking against spurious arm shoot-through.
O2 : N-side control supply abnormality locking (OV/UV)
O3 : System over-temperature protection (OT).
APPLICATION
Acoustic noise-less 0.4kW/AC400V Class 3 Phase inverter and other motor control applications.
PACKAGE OUTLINES
2.45 ± 0.3
(10.35)
80.5 ± 1
71.5 ± 0.5
0.5
2
± 0.3
(7.75)
1.2
31 32 34 35 36
6 ± 0.3
56 ± 0.8
76.5
33
10.16 ± 0.3
50.8 ± 0.8
LABEL
± 1
4-φ4
231
2.5
5
92.5 ± 1
83.5 ± 0.5
4-R4
20.4 ± 1
0.5
78.75
0.6
8.5
13
27 ± 1
Terminals Assignment:
1 CBU+
2 CBU–
3 CBV+
4 CBV–
5 CBW+
6 CBW–
7 GND
8 VDL
9 VDH
10 CL
11 FO1
12 FO2
13 FO3
14 CU
15 CV
16 CW
17 UP
18 VP
19 WP
20 UN
21 VN
22 WN
23 Br
31 P
32 B
33 N
34 U
35 V
36 W
(Fig. 1)
Jan. 2000
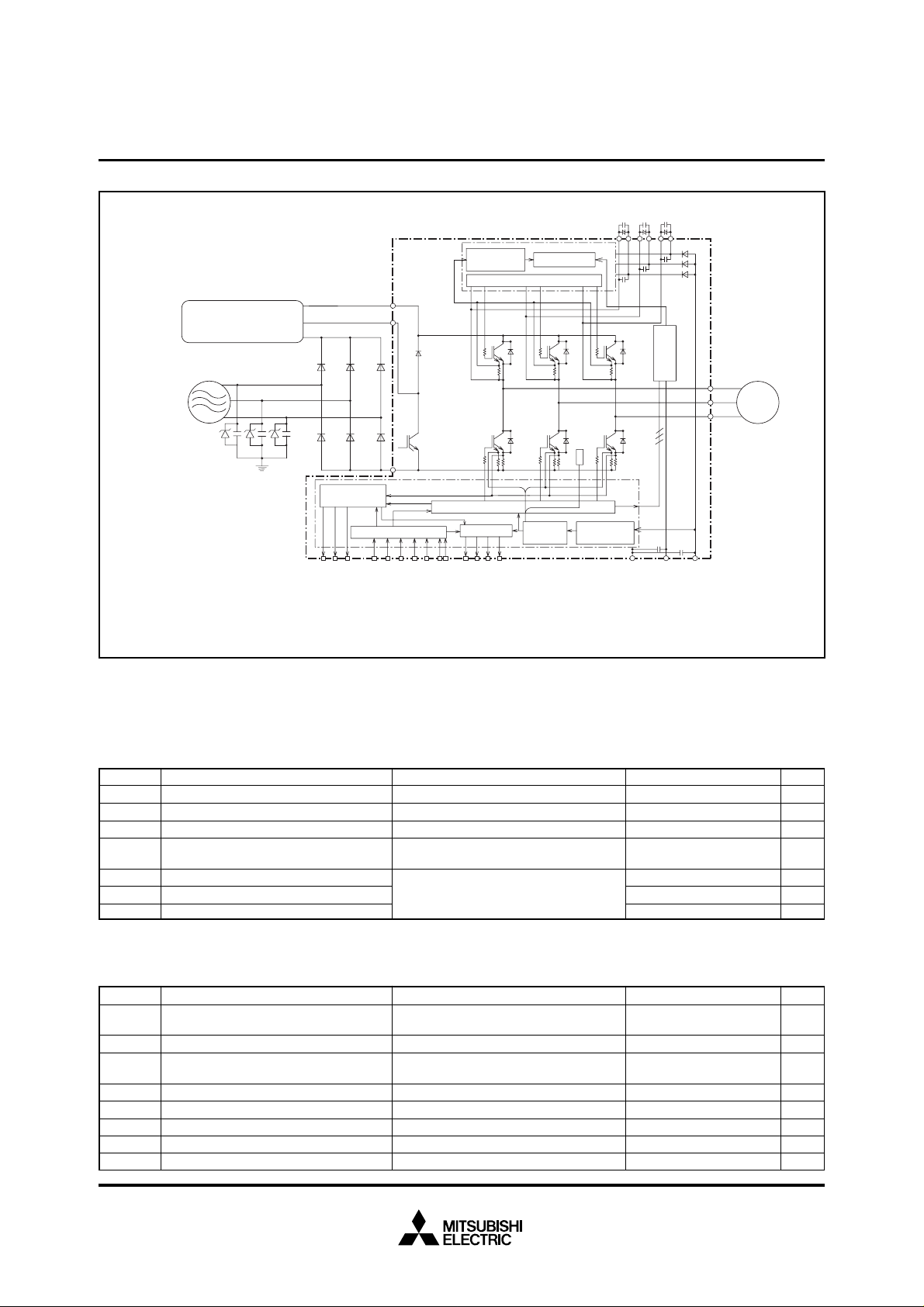
MITSUBISHI SEMICONDUCTOR <Application Specific Intelligent Power Module>
PS12013-A
FLA T-BASE TYPE
INSULA TED TYPE
INTERNAL FUNCTIONS BLOCK DIAGRAM
Brake resistor connection,
Inrush prevention circuit,
etc.
AC 400V class line input
Z
Z : Surge absorber.
C : AC filter (Ceramic condenser 2.2~6.5nF)
[Note : Additionally an appropriate Line-to line
surge absorber circuit may become necessary
depending on the application environment].
Note 1) To prevent chances of signal oscillation, a series resistor (1kΩ) coupling at each output is recommended.
Note 2) By virtue of integrating a photo-coupler inside the module, direct coupling to CPU, without any extemal opto or transformer isolation is possible.
Note 3) All outputs are open collector type. Each signal line should be pulled up to plus side of the 5V power supply with approximately 5.1kΩ resistance.
Note 4) The wiring between power DC link capacitor and P/N terminals should be as short as possible to protect the ASIPM against catastrophic high surge voltage.
For extra precaution, a small film snubber capacitor (0.1~0.22µF, high voltage type) is recommended to be mounted close to these P and N DC power input pins.
R
S
T
C
Current sensing
circuit
Input signal conditioning
Analogue signal output corresponding to
each phase current (5V line) Note 1)
CU CV CW
P
B
N
UPVPWPVNWNB
U
N
PWM input
(5V line) Note 2)
Application Specific Intelligent
Power Module
Protection
Drive Circuit
Fo Logic
r
CL,FO
(5V line) Note 3)
Circuit
1
,FO2,FO
Fault output
Input Circuit
Drive Circuit
Protection
circuit
3
CBU–
CBU+
T
S
Control supply
fault sense
GND VDL VDH
CBV–
CBV+
CBW–
CBW+
Photo
Coupler
U
V
M
W
AC 400V class
line output
(Fig. 2)
MAXIMUM RATINGS (Tj = 25°C)
INVERTER PART (Including Brake Part)
VCC
VCC(surge)
VP or VN
VP(S) or
N(S)
V
±Ic(±Icp)
Ic(Icp)
I
F(IFP)
Item
Supply voltage
Supply voltage (surge)
Each output IGBT collector-emitter static voltage
Each output IGBT collector-emitter surge voltage
Each output IGBT collector current
Brake IGBT collector current
Brake diode anode current
Applied between P-N
Applied between P-N, Surge-value
Applied between P-U, V, W, Br or U, V, W, Br-N
Applied between P-U, V, W, Br or U, V, W, Br-N
TC = 25°C
Note : “( )” means IC peak value
ConditionSymbol
Ratings Unit
900
1000
1200
1200
±5 (±10)
5 (10)
5 (10)
CONTROL PART
Symbol Item Ratings Unit
DH, VDB Supply voltage V20
V
DL
V
CIN
VFO
IFO
VCL
ICL
ICO
Supply voltageV
Input signal voltage
Fault output supply voltage
Fault output current
Current-limit warning output voltage
CL output current
Analogue-current-signal output current
Applied between V
C
BV+-CBV–, CBW+-CBW–
Applied between V
Applied between U
W
N · Br-GND
Applied between F
Sink current of FO1 · FO2 · FO3
Applied between CL-GND
Sink current of CL
Sink current of CU · CV · CW
Condition
DH-GND, CBU+-CBU–,
DL-GND
P · VP · WP · UN · VN ·
O1 · FO2 · FO3-GND
–0.5 ~ VDL+0.5 V
–0.5 ~ 7
15
–0.5 ~ 7
15
±1
V
V
V
V
A
A
A
V7
V
mA
V
mA
mA
Jan. 2000
 Loading...
Loading...