RD7
®
TOPSwitch-II
PC Standby Reference Design Board
90 to 375 VDC Input, 3.5 W Output
Product Highlights
Low Cost Production Worthy Reference Design
• Up to 3.5 W of output power
• Meets Blue Angel requirements (5 W)
• Single sided board
• Low cost through-hole components
• Fully assembled and tested
• Easy to evaluate and modify
• Extensive performance data
• Light weight - no heat sink required for TOPSwitch-II
• Non-isolated +12 V output option
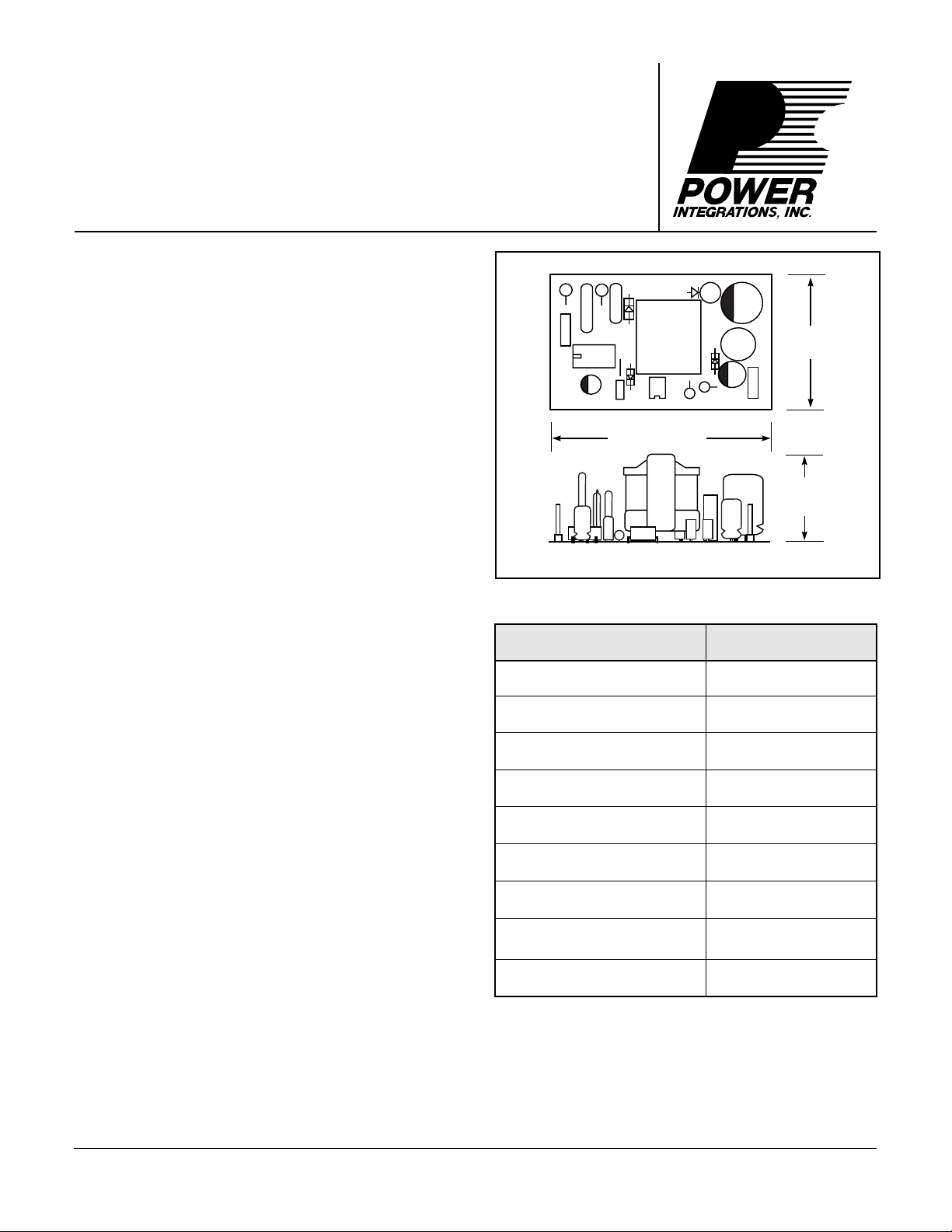
2 in. (48 mm)
®
1.19 in.
(29 mm)
Fully Protected by
• Primary safety current limit
• Output short circuit protection
• Thermal shutdown protects entire supply
Designed for World Wide Operation
• Designed for IEC/UL safety requirements
• Designed for wide range of input voltage
Typical Applications
• Desktop PC stand-by power supply (PS98, ATX, NLX,
SFX, Micro ATX)
• Consumer stand-by supply (e.g. TV, VCR, DVD)
TOPSwitch-II
Description
The RD7 reference design board is an example of a very low
cost production worthy DC input standby power supply design
using the TOPSwitch-II family of Three-terminal Off-line
PWM switchers. The reference design board is intended to help
TOPSwitch-II users quickly develop their products. It provides
a basic design that can be easily modified to fit a particular
application. The RD7 operates from a rectified and filtered AC
mains voltage and provides 3.5 W output at 5 V. Features such
as a 12 V non-isolated output or tighter output voltage tolerance
may be implemented by changing only a few components (See
Figure 4).
.75 in.
(18 mm)
Figure 1. RD7 Overall Physical Dimensions.
PARAMETER
Input Voltage Range 90 to 375 VDC
Temperature Range 0 to 50° C
Output Voltage (I = 0.7 A)
Output Power (continuous) 3.5 W
Line Regulation (90-375VDC) ± 1.0%
Load Regulation (10%-100%) ± 1.0%
Efficiency (At full load) 72%
Output Ripple Voltage ± 50 mV
Safety IEC950/UL1950
Table 1. Table of Key Electrical Parameters.
o
LIMITS
5 V ± 5%
PI-2271-062998
April 1999
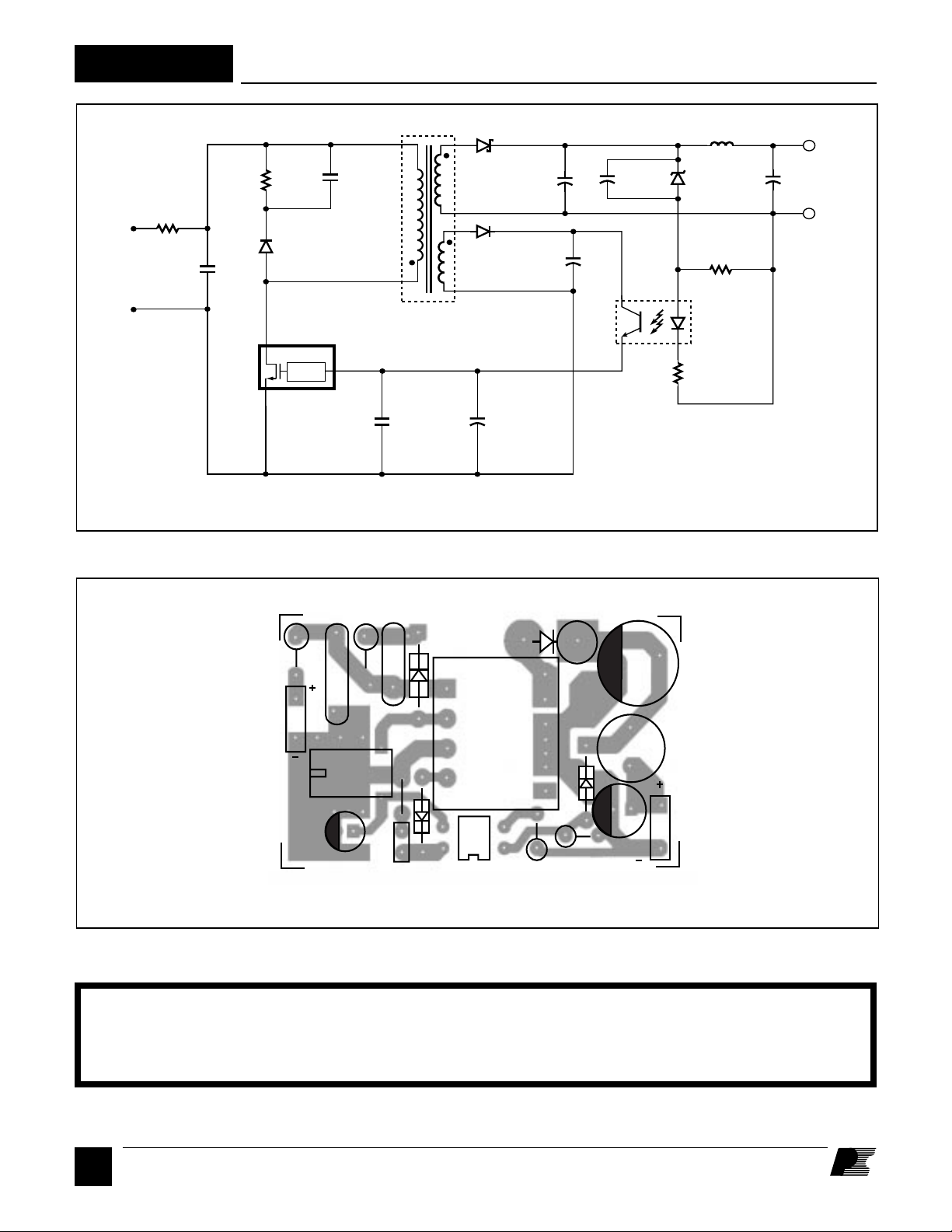
RD7
R1
C1
47 kΩ
D1
UF4005
+
90-375 VDC
Input
RF1
1
Ω
Fusible
10 nF
1 KV
-
D
TOPSwitch-II
CONTROL
S
TOP221P
U1
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the RD7.
T1
C2
2.2 nF
1 KV
C
C
C
0.1 µF
*
D2
1N5822
D3
1N4148
C3
270 µF
25 V
0.1 µF
50 V
C5
47 µF
10 V
* optional component, not populated
C6
L1
3.3 µH
*
C
ss
VR1
IN5228C
C4
100 µF
25 V
+
5 V – 5%
0.7 A
-
R3
100 Ω
U2
PC817A
R2
10 Ω
PI-2187-062998
RF1
J1
U1
C5
Figure 3. RD7 Pinout and Component Legend.
The RD7 is designed for DC input. Please observe the proper polarity when applying power to this board.
Applying reverse polarity or AC power to the input terminals of the board can damage the TOPSwitch.
D2
U2
R1
C1
C6
S/N
C2
D1
JP1
D3
COMPONENT SIDE SHOWN
CAUTION
R2
R3
T1
VR1
C3
C4
L1
J2
PI-2269-070298
B
2
4/99

Component Listing
Reference Value Part Number Manufacturer
C1 10 nF, 1 KV, Disc 5GAS10 Cera-Mite
C2 2.2 nF 1 KV, Disc DD222 Philips
C3 270 µF 25 V ECA-1EFQ271 Panasonic
C4 100 µF 25 V ECE-A1EGE101 Panasonic
C5 47 µF, 10 V ECE-A1AGE470 Panasonic
C6 0.1 µF, 50 V ECU-S1H104MEA Panasonic
Cc* 0.1 µF, 50 V ECU-S1H104MEA Panasonic
Css*
D1 600 V, 1A, UFR UF4005 General Instrument
D2 40 V, 3 A, Schottky 1N5822 General Instrument
D3 75 V, Switching 1N4148 Liteon
L1 3.3 µH, 5 A 622LY-3R3M Toko
RF1 1 Ω Fuse Resistor 1/2 W BW1/2F 1 Ω 5% RCD
R1 47 K, 1/2 W 5053CX47K00J Philips
R2 10 Ω, 1/4 W 5043CX10R00J Philips
R3 100 Ω, 1/4 W 5043CX100R0J Philips
T1** TRD7 Custom
U1 TOP221P or TOP221G*** Power Integrations
U2 Optocoupler, Controlled CTR LTV817A Liteon
VR1 3.9 V, Zener, 2% 1N5228C APD
RD7
Table 2. Parts List For the RD7. (* Optional, for Css values see Figure 9. **T1 is available from Premier Magnetics (714) 362-4211 as P/N
TDS-1185-9818, and from Coiltronics (561) 241-7876 as P/N CTX14-14193-X1. *** TOP221G can be used with layout modifications.)
General Circuit Description
The RD7 is a low-cost, flyback switching power supply using
the TOP221P. The circuit shown in Figure 2 provides a nominal
output power of 3.5 W at 5 VDC output. The power supply
operates from a DC voltage of 90 to 375 VDC. In a typical
application this DC voltage is derived from a rectified and
filtered AC main voltage of 85 to 265 VAC. The 5 V output is
directly sensed by optocoupler U2 and Zener diode VR1. The
output voltage is determined by the Zener diode (VR1) voltage
and the voltage drop across the optocoupler (U2) LED and
resistor R2. Other output voltages are possible by adjusting the
transformer turns ratios and the value of the Zener diode VR1.
The positive rail of the high voltage DC input is connected to
one side of the primary winding of T1. Capacitor C1 filters the
high voltage supply, and is necessary only if the connections
between the high voltage DC supply and the RD7 are long. The
other side of the transformer primary is driven by the integrated,
high-voltage MOSFET inside the TOP221. D1, R1, and C2
clamp voltage spikes caused by transformer leakage inductance
to a safe value and reduce ringing at the DRAIN of U1.
The secondary winding is rectified and filtered by D2 and C3
to generate a 5 V output. L1 and C4 provide additional filtering
to reduce high frequency ripple voltage. R3 and VR1 provide
a slight pre-load on the 5 V output to improve load regulation
at light loads. R3 also provides bias current for Zener VR1 to
improve regulation.
Soft start can be added to eliminate turn-on overshoot. With C
placed across VR1, the optocoupler current is increased during
turn-on time. This increased current limits the duty cycle and
slows down the rising output voltage (See Figure 9). The bias
winding output is rectified and filtered by D3 and C6 to provide
a bias voltage for U2. C5 filters internal MOSFET gate drive
charge current spikes on the CONTROL pin, determines the
auto-restart frequency, and compensates the control loop. Cc is
needed when the supply is operating in a noisy environment
(e. g. when the power supply is sharing the same input rectifier
and filter capacitor with another power supply). Cc filters high
frequency noise.
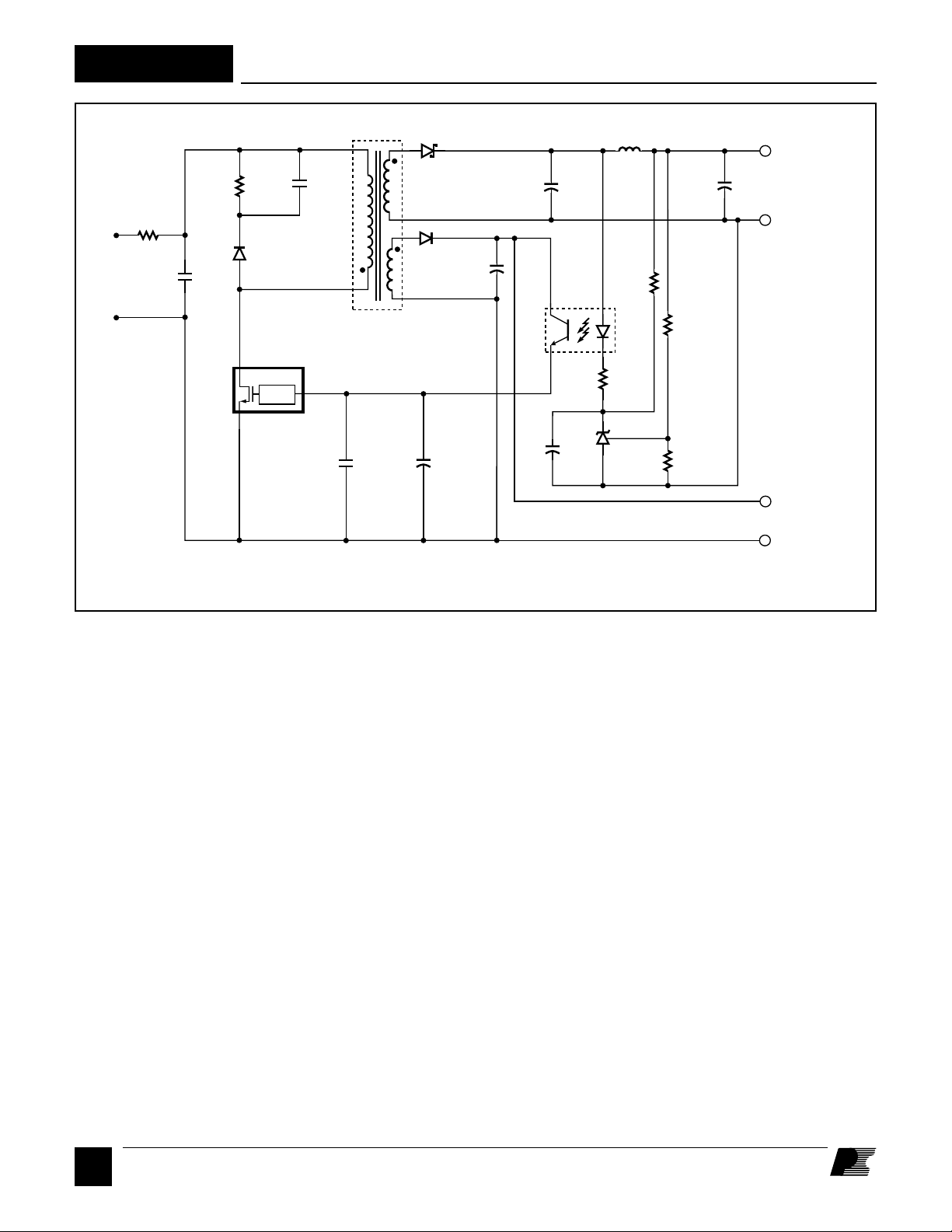
The schematic of Figure 4 shows an enhanced version of the
RD7. The circuit comprising R2, R3, R4, R5 and U3 improves
overall output regulation to ±2%. Optional soft start capacitor
Css is used to eliminate turn-on overshoot. The bias supply
output can be used to provide a +12 V, non-isolated output by
changing C6 to 100 µF as shown in Figure 4. C6 is added to
reduce output ripple to a primary load.
The circuit performance data shown in Figures 5 to 12 was
ss
4/99
B
3
RD7
RF1
1
+
Fusible
90-375 VDC
Input
-
T1
*
D2
1N5822
D3
1N4148
C6
100 µF
35 V
C5
47 µF
10 V
R1
47 kΩ
Ω
D1
UF4005
C1
10 nF
1 KV
D
TOPSwitch-II
CONTROL
S
TOP221P
U1
C2
2.2 nF
1 KV
C
C
C
0.1 µF
C3
270 µF
25 V
C
*
SS
U2
PC817A
L1
3.3 µH
R3
75 Ω
R2
150 Ω
U3
TL431
C4
100 µF
25 V
R4
10 kΩ
R5
10 kΩ
+
5 V – 2%
0.6 A
-
+
12 V
Non-isolated
50 mA
-
*
optional component, not populated
PI-2189-071098
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the RD7 with 12V Non-isolated output.
measured with DC voltage applied to RD7.
Load Regulation (Figure 5(a) and 5(b)) - The amount of change
in the DC output voltage for a given change in output current is
referred to as load regulation. The 5 V output stay within
±1.0% when the output current is between 0% to 100% of rated
load current at the 5 V output. The TOPSwitch-II overtemperature protection circuit will safely shut down the power
supply under prolonged overload conditions. When the output
load is disconnected, R3 acts as a preload and the output stays
in regulation.
Line Regulation (Figure 6(a) and 6(b)) - The amount of change
in DC output voltage for a given change in the DC input voltage
is called line regulation. The maximum change in output
voltage is within ±1%.
Efficiency (Line Dependent). Efficiency is the ratio of output
power to the input power. The curve in Figure 7 shows how the
efficiency changes with input voltage using a 3.5 W load. The
efficiency is greater than 72% throughout the input range.
Efficiency (Load Dependent). The curves in Figure 8 show
how the efficiency changes with output power at 155 and 310
VDC inputs. The efficiency is greater than 70% for loads
greater than 2.5 W.
Power Supply Turn On Sequence. An internal switched, high
voltage current source provides the initial bias current for
TOPSwitch when power is first applied. The waveforms shown
in Figure 8 illustrates the timing relationship between the high
voltage DC bus and 5 V output voltage for the RD7 circuit.
Capacitor C1 charges to the DC input voltage before TOPSwitch
turns on. The delay of 130 ms (typical) is caused by the time
required to charge the auto-restart capacitor C5 to 5.7 V. At this
point the power supply turns on as shown.
Figure 10 shows the output voltage turn on transient as well as
a family of curves associated with the additional soft-start
capacitor Css. The soft-start capacitor is placed across VR2 and
can range in value from 10 µF to 47 µF as shown.
Switching frequency ripple voltage is shown in Figure 11 for
the RD7 circuit at 155 VDC input and 3.5 W output. Peak to
peak ripple is less than 50 mV at 3.5 W.
The RD7 power supply transient response to a step load change
from 0.52 A to 0.75 A (75% to 100%) is shown in Figure 12.
The response is quick and well damped.
The RD7 is designed to meet worldwide safety specifications.
B
4
4/99
 Loading...
Loading...