Page 1

2005 Pontiac Pursuit Owner Manual M
Seats and Restraint Systems
Front Seats
Rear Seats
Safety Belts
Child Restraints
Airbag System
Restraint System Check
Features and Controls
Keys
Doors and Locks
Windows
Theft-Deterrent Systems
Starting and Operating Your Vehicle
Mirrors
®
OnStar
Storage Areas
Sunroof
Instrument Panel
Instrument Panel Overview
Climate Controls
Warning Lights, Gages, and Indicators
Driver Information Center (DIC)
Audio System(s)
............................................... 1-2
.............................................. 1-10
............................................. 1-11
....................................... 1-30
......................................... 1-48
........................................................ 2-2
....................................... 2-7
................................................. 2-11
.................................................... 2-29
System
.................................................. 2-34
...................................... 2-31
......................................... 2-33
............................................. 3-1
...................................... 3-18
....................................... 3-43
........................... 1-1
............................ 1-56
..................................... 2-1
............................ 2-13
.......................... 3-4
........... 2-15
........ 3-21
.................. 3-33
Driving Your Vehicle
Your Driving, the Road, and Your Vehicle
Towing
Service and Appearance Care
Service
Fuel
Checking Things Under the Hood
Headlamp Aiming
Bulb Replacement
Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement
Tires
Appearance Care
Vehicle Identification
Electrical System
Capacities and Specifications
Maintenance Schedule
Maintenance Schedule
Customer Assistance and Information
Customer Assistance and Information
Reporting Safety Defects
Index
................................................... 4-36
..................................................... 5-3
......................................................... 5-5
...................................................... 5-45
................................................................ 1
....................................... 4-1
.......................... 5-1
............... 5-10
..................................... 5-37
.................................... 5-40
..................................... 5-71
................................. 5-80
...................................... 5-81
..................... 5-87
..................................... 6-1
................................ 6-2
........................... 7-10
..... 4-2
......... 5-44
.............. 7-1
........... 7-2
Page 2
Canadian Owners
A French language copy of this manual can be obtained
from your dealer or from:
Helm, Incorporated
P.O. Box 07130
Detroit, MI 48207
GENERAL MOTORS, GM, the GM Emblem, PONTIAC,
and the PONTIAC Emblem are registered trademarks;
and the name PURSUIT is a trademark of General
Motors Corporation.
This manual includes the latest information at the time it
was printed. We reserve the right to make changes
after that time without further notice. For vehicles first
sold in Canada, substitute the name “General Motors of
Canada Limited” for Pontiac Division whenever it
appears in this manual.
Keep this manual in the vehicle, so it will be there if it
is needed while you are on the road. If the vehicle
is sold, leave this manual in the vehicle.
Litho in U.S.A.
Part No. 05PURSUIT B First Edition
ii
How to Use This Manual
Many people read the owner manual from beginning to
end when they first receive their new vehicle. If this
is done, it can help you learn about the features
and controls for the vehicle. Pictures and words work
together in the owner manual to explain things.
Index
A good place to quickly locate information about the
vehicle is the Index in the back of the manual. It is an
alphabetical list of what is in the manual and the
page number where it can be found.
©
2004 General Motors Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3
Safety Warnings and Symbols
There are a number of safety cautions in this book.
We use a box and the word CAUTION to tell about
things that could hurt you if you were to ignore
the warning.
{CAUTION:
These mean there is something that could hurt
you or other people.
In the caution area, we tell you what the hazard is.
Then we tell you what to do to help avoid or reduce
the hazard. Please read these cautions. If you do not,
you or others could be hurt.
You will also find a circle
with a slash through it in
this book. This safety
symbol means “Do Not,”
“Do Not do this” or “Do Not
let this happen.”
iii
Page 4

Vehicle Damage Warnings
Vehicle Symbols
Also, in this manual you will find these notices:
Notice: These mean there is something that could
damage your vehicle.
A notice tells about something that can damage the
vehicle. Many times, this damage would not be covered
by your vehicle’s warranty, and it could be costly. But
the notice will tell what to do to help avoid the damage.
When you read other manuals, you might see
CAUTION and NOTICE warnings in different colors
or in different words.
There are also warning labels on the vehicle.
They use the same words, CAUTION or NOTICE.
iv
The vehicle has components and labels that use
symbols instead of text. Symbols are shown along with
the text describing the operation or information
relating to a specific component, control, message,
gage, or indicator.
If you need help figuring out a specific name of a
component, gage, or indicator, reference the following
topics:
• Seats and Restraint Systems in Section 1
• Features and Controls in Section 2
• Instrument Panel Overview in Section 3
• Climate Controls in Section 3
• Warning Lights, Gages, and Indicators in Section 3
• Audio System(s) in Section 3
• Engine Compartment Overview in Section 5
Page 5
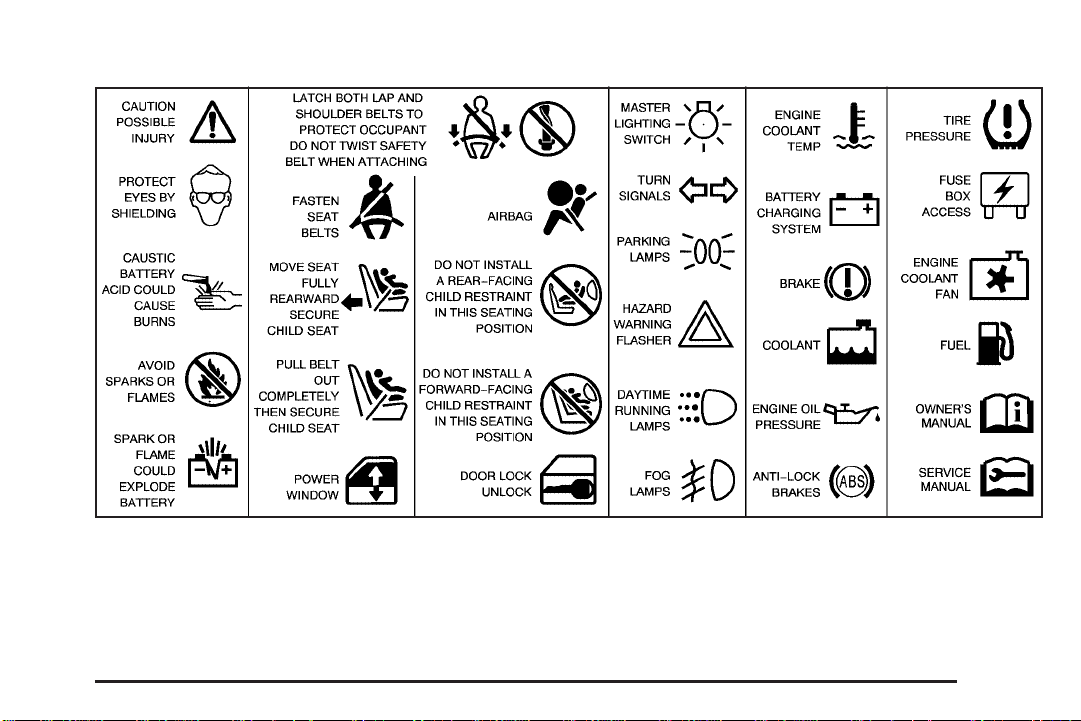
These are some examples of symbols that may be found on the vehicle:
v
Page 6

✍ NOTES
vi
Page 7

Section 1 Seats and Restraint Systems
Front Seats ......................................................1-2
Manual Seats ................................................1-2
Driver Seat Height Adjuster ..............................1-3
Manual Lumbar ..............................................1-3
Heated Seats .................................................1-4
Reclining Seatbacks ........................................1-5
Head Restraints .............................................1-7
Passenger Folding Seatback ............................1-8
Rear Seats .....................................................1-10
Split Folding Rear Seat .................................1-10
Safety Belts ...................................................1-11
Safety Belts: They Are for Everyone ................1-11
Questions and Answers About
Safety Belts ..............................................1-16
How to Wear Safety Belts Properly .................1-16
Driver Position ..............................................1-17
Shoulder Belt Height Adjustment .....................1-23
Safety Belt Use During Pregnancy ..................1-23
Right Front Passenger Position .......................1-24
Rear Seat Passengers ..................................1-24
Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides for
Children and Small Adults ..........................1-27
Safety Belt Pretensioners ...............................1-29
Safety Belt Extender .....................................1-29
Child Restraints .............................................1-30
Older Children ..............................................1-30
Infants and Young Children ............................1-33
Child Restraint Systems .................................1-36
Where to Put the Restraint .............................1-39
Top Strap ....................................................1-39
Top Strap Anchor Location .............................1-41
Lower Anchorages and Top Tethers for
Children (LATCH System) ...........................1-41
Securing a Child Restraint Designed for
the LATCH System ....................................1-43
Securing a Child Restraint in a
Rear Seat Position ....................................1-43
Securing a Child Restraint in the
Right Front Seat Position ............................1-45
Airbag System ...............................................1-48
Where Are the Airbags? ................................1-50
When Should an Airbag Inflate? .....................1-52
What Makes an Airbag Inflate? .......................1-54
How Does an Airbag Restrain? .......................1-54
What Will You See After an Airbag Inflates? ........1-54
Servicing Your Airbag-Equipped Vehicle ...........1-56
Restraint System Check ..................................1-56
Checking the Restraint Systems ......................1-56
Replacing Restraint System Parts
After a Crash ............................................1-57
1-1
Page 8
Front Seats
Manual Seats
{CAUTION:
You can lose control of the vehicle if you try to
adjust a manual driver’s seat while the vehicle
is moving. The sudden movement could startle
and confuse you, or make you push a pedal
when you do not want to. Adjust the driver’s
seat only when the vehicle is not moving.
Your vehicle has manual seats. Lift the bar located under
the front of the seat to unlock it. Slide the seat to where
you want it and release the bar. Try to move the seat with
your body to be sure the seat is locked in place.
1-2
Page 9
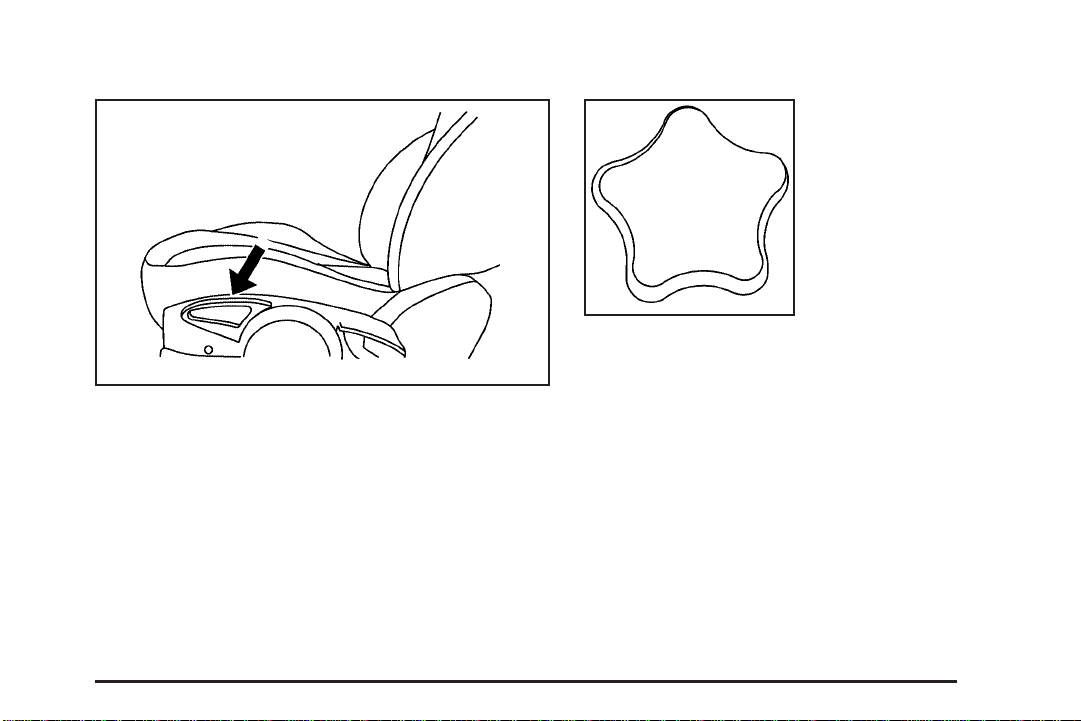
Driver Seat Height Adjuster
The driver’s seat height adjuster is located on the
outboard side of the seat.
To raise the seat, move the lever upward repetitively
until the seat is at the desired height. To lower the seat,
move the lever downward repetitively until the seat is
at the desired height.
Manual Lumbar
If your vehicle has this feature, the knob is located on
the front of the driver seat lower cushion.
Turn the knob clockwise or counterclockwise to increase
or decrease the lumbar support.
1-3
Page 10
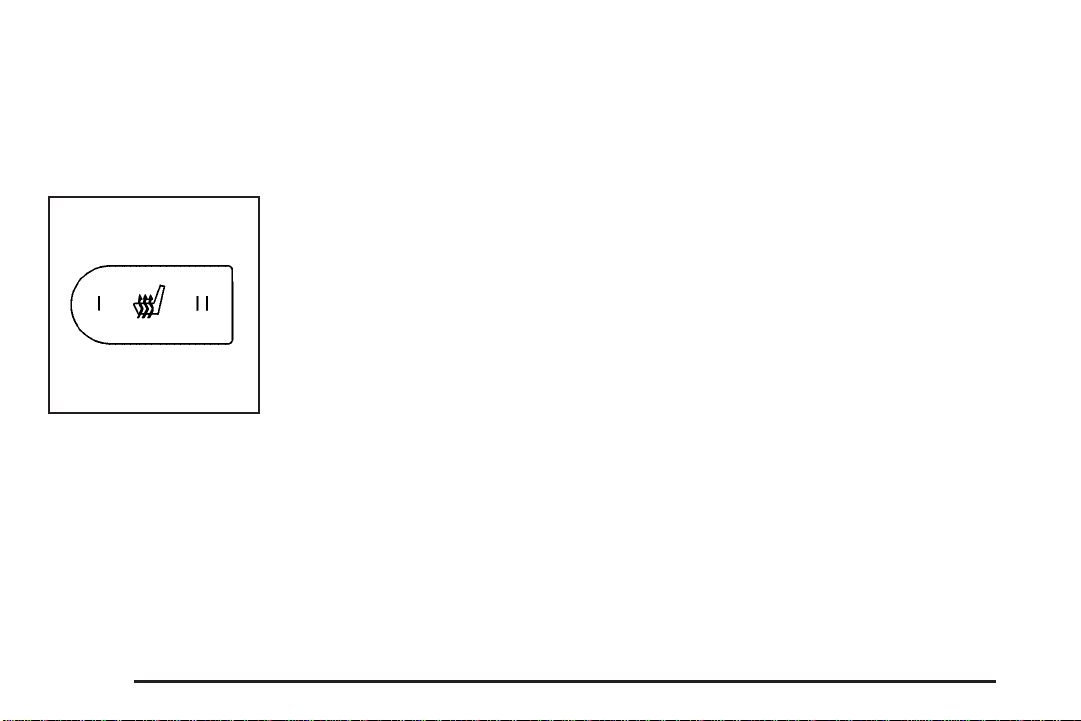
Heated Seats
Your vehicle may have heated front seats. This feature
heats the seat cushions. The switches are located
on the instrument panel above the climate
control system.
Press the side of the
switch with the double
indicator lights to turn on
the heated seat at the
highest setting.
Driver’s Side Switch,
Passenger’s Side
Similar
Both indicator lights will be lit to indicate that the setting
is on high. Press the side of the switch with the single
indicator light to go to the low setting. The indicator light
will be lit to indicate that the setting is on low. Return
the switch to the center to turn off the heated seat.
If your vehicle has been turned off, the last heated
seat setting will be retained when the vehicle is
started again.
1-4
Page 11
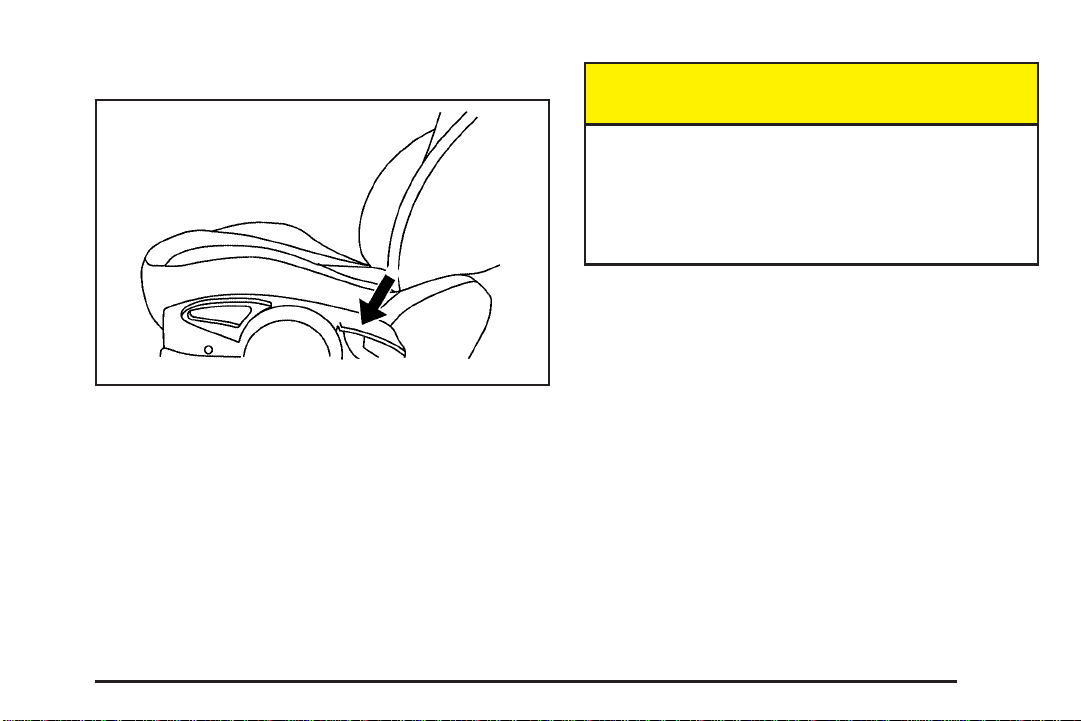
Reclining Seatbacks
Your vehicle has reclining seatbacks. The lever is
located on the outboard side of the seats. Lift the lever
to release the seatback. Move the seatback to where
you want it and release the lever to lock the seatback in
place. Press rearward on the seatback to be sure it is
locked into place.
{CAUTION:
If the seatback is not locked, it could move
forward in a sudden stop or crash. That could
cause injury to the person sitting there. Always
press rearward on the seatback to be sure it
is locked.
1-5
Page 12
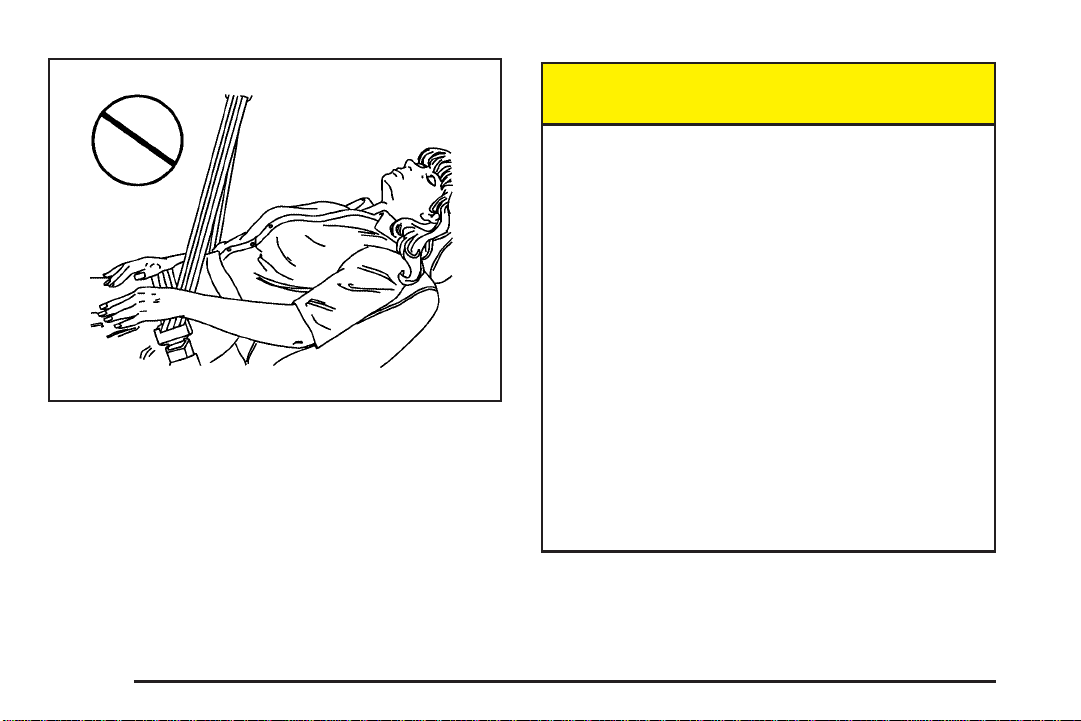
But do not have a seatback reclined if your vehicle
is moving.
{CAUTION:
Sitting in a reclined position when your vehicle
is in motion can be dangerous. Even if you
buckle up, your safety belts cannot do their
job when you are reclined like this.
The shoulder belt cannot do its job because it
will not be against your body. Instead, it will be
in front of you. In a crash you could go into it,
receiving neck or other injuries.
The lap belt cannot do its job either. In a crash
the belt could go up over your abdomen. The
belt forces would be there, not at your pelvic
bones. This could cause serious internal
injuries.
For proper protection when the vehicle is in
motion, have the seatback upright. Then sit
well back in the seat and wear your safety belt
properly.
1-6
Page 13
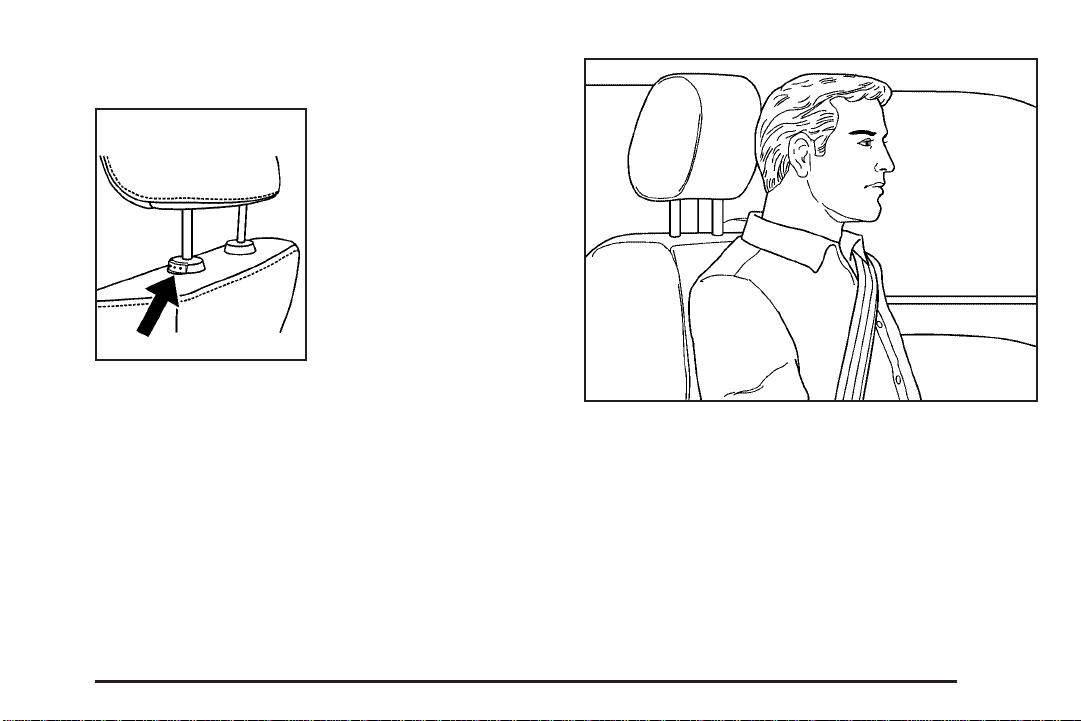
Head Restraints
Press the button on the
side of the head restraint
to adjust it.
Adjust your head restraint so that the top of the restraint
is closest to the top of your head. This position
reduces the chance of a neck injury in a crash.
1-7
Page 14
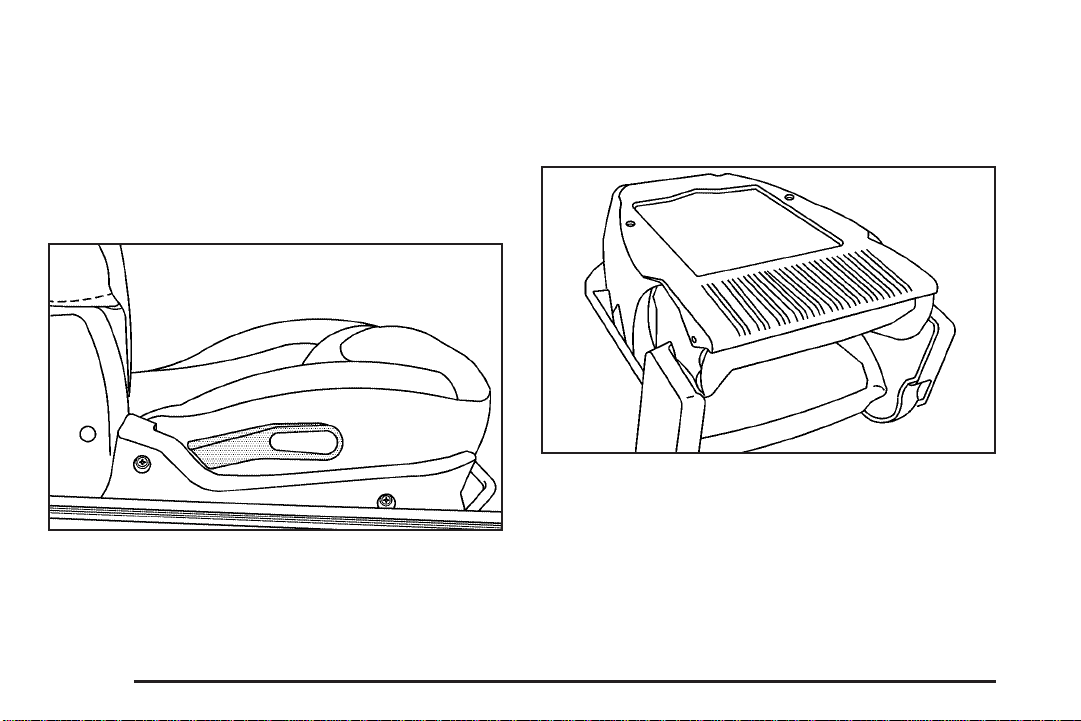
Passenger Folding Seatback
Your vehicle may have a passenger seat that folds flat.
To fold the seatback, do the following:
1. Lift the bar under the seat to unlock it.
2. Slide the seat as far back as it will go and release
the bar. Try to move the seat with your body to
make sure it is locked into place.
3. Lift the recliner lever, located on the outboard side
of the seat, and fold the seat forward until the
seatback disengages. Continue to fold the seat
forward until it locks in the folded position. Pull up
on the seatback to be sure it is locked.
1-8
Page 15
{CAUTION:
{CAUTION:
If you fold the seatback forward to carry longer
objects, such as skis, be sure any such cargo
is not near an airbag. In a crash, an inflating
airbag might force that object toward a person.
This could cause severe injury or even death.
Secure objects away from the area in which an
airbag would inflate. For more information, see
Where Are the Airbags? on page 1-50 and
Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-30.
Things you put on this seatback can strike and
injure people in a sudden stop or turn, or in a
crash. Remove or secure all items before
driving.
1-9
Page 16
Rear Seats
Split Folding Rear Seat
You can fold either side of the rear seatback down for
more cargo space.
To lower the rear seatback, follow these steps:
1. Open the trunk and pull one or both of the small
handles located in the center of the trunk.
2. Once the handle is pulled, the seatback can be
pushed open through the trunk, or pulled open
from the inside of the vehicle.
1-10
Page 17
To raise the rear seatback, lift it up and push rearward
until you hear a click. Push and pull on the seatback
to be sure it is locked into place.
Safety Belts
Safety Belts: They Are for Everyone
{CAUTION:
If the seatback is not locked, it could move
forward in a sudden stop or crash. That could
cause injury to the person sitting there. Always
pull forward on the top of the seatback at the
area of the latch to be sure it is locked.
{CAUTION:
A safety belt that is improperly routed, not
properly attached, or twisted will not provide
the protection needed in a crash. The person
wearing the belt could be seriously injured.
After raising the rear seatback, always check
to be sure that the safety belts are properly
routed and attached, and are not twisted.
This part of the manual tells you how to use safety
belts properly. It also tells you some things you should
not do with safety belts.
{CAUTION:
Do not let anyone ride where he or she can not
wear a safety belt properly. If you are in a
crash and you are not wearing a safety belt,
your injuries can be much worse. You can hit
things inside the vehicle or be ejected from it.
You can be seriously injured or killed. In the
same crash, you might not be, if you are
buckled up. Always fasten your safety belt,
and check that your passengers’ belts are
fastened properly too.
1-11
Page 18

{CAUTION:
It is extremely dangerous to ride in a cargo
area, inside or outside of a vehicle. In a
collision, people riding in these areas are more
likely to be seriously injured or killed. Do not
allow people to ride in any area of your vehicle
that is not equipped with seats and safety
belts. Be sure everyone in your vehicle is in a
seat and using a safety belt properly.
Your vehicle has a light
that comes on as a
reminder to buckle up. See
Safety Belt Reminder
Light on page 3-23.
In most states and in all Canadian provinces, the law
says to wear safety belts. Here is why: They work.
You never know if you will be in a crash. If you do have
a crash, you do not know if it will be a bad one.
A few crashes are mild, and some crashes can be so
serious that even buckled up, a person would not
survive. But most crashes are in between. In many of
them, people who buckle up can survive and sometimes
walk away. Without belts they could have been badly
hurt or killed.
After more than 30 years of safety belts in vehicles, the
facts are clear. In most crashes buckling up does
matter...a lot!
1-12
Page 19
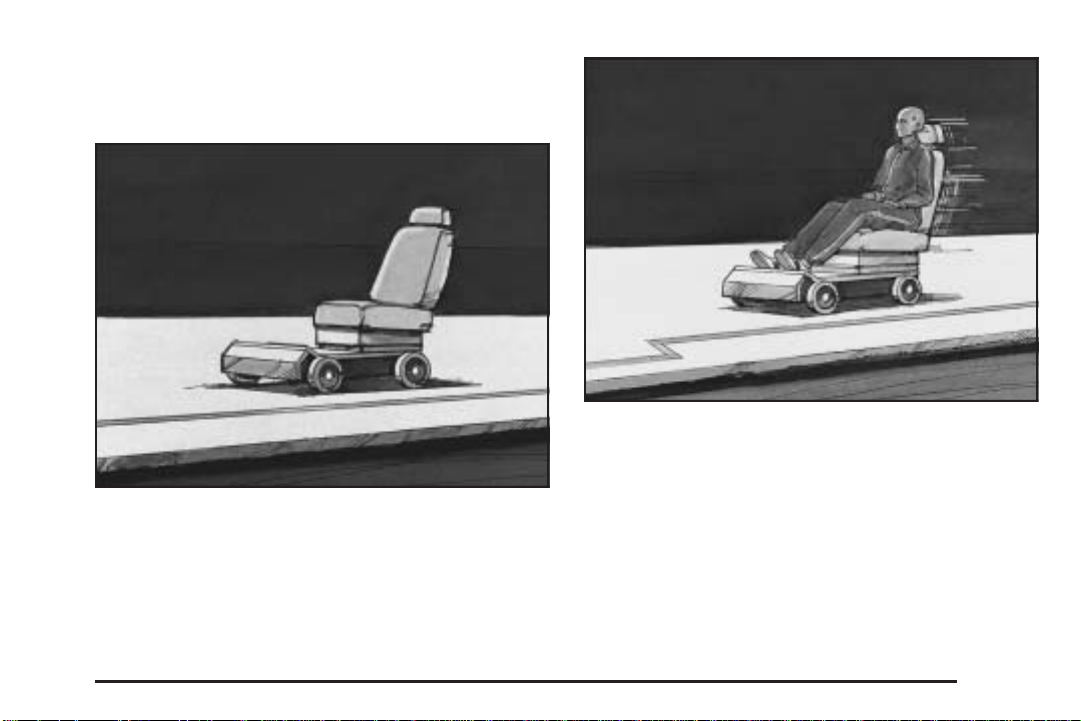
Why Safety Belts Work
When you ride in or on anything, you go as fast as
it goes.
Take the simplest vehicle. Suppose it is just a seat
on wheels.
Put someone on it.
1-13
Page 20

Get it up to speed. Then stop the vehicle. The rider
does not stop.
1-14
The person keeps going until stopped by something.
In a real vehicle, it could be the windshield...
Page 21

or the instrument panel... or the safety belts!
With safety belts, you slow down as the vehicle does.
You get more time to stop. You stop over more distance,
and your strongest bones take the forces. That is why
safety belts make such good sense.
1-15
Page 22

Questions and Answers About Safety Belts
Q: Will I be trapped in the vehicle after an accident
if I am wearing a safety belt?
A: You could be — whether you are wearing a safety
belt or not. But you can unbuckle a safety belt,
even if you are upside down. And your chance of
being conscious during and after an accident,
so you can unbuckle and get out, is much greater if
you are belted.
Q: If I am a good driver, and I never drive far from
home, why should I wear safety belts?
A: You may be an excellent driver, but if you are in an
accident — even one that is not your fault — you
and your passengers can be hurt. Being a good
driver does not protect you from things beyond your
control, such as bad drivers.
Most accidents occur within 25 miles (40 km) of
home. And the greatest number of serious injuries
and deaths occur at speeds of less than 40 mph
(65 km/h).
Safety belts are for everyone.
Q: If my vehicle has airbags, why should I have to
wear safety belts?
A: Airbags are in many vehicles today and will be in
most of them in the future. But they are
supplemental systems only; so they work with
safety belts — not instead of them. Every airbag
system ever offered for sale has required the use of
safety belts. Even if you are in a vehicle that has
airbags, you still have to buckle up to get the most
protection. That is true not only in frontal collisions,
but especially in side and other collisions.
1-16
How to Wear Safety Belts Properly
This part is only for people of adult size.
Be aware that there are special things to know about
safety belts and children. And there are different
rules for smaller children and babies. If a child will be
riding in your vehicle, see Older Children on page 1-30
or Infants and Young Children on page 1-33. Follow
those rules for everyone’s protection.
First, you will want to know which restraint systems your
vehicle has.
We will start with the driver position.
Page 23
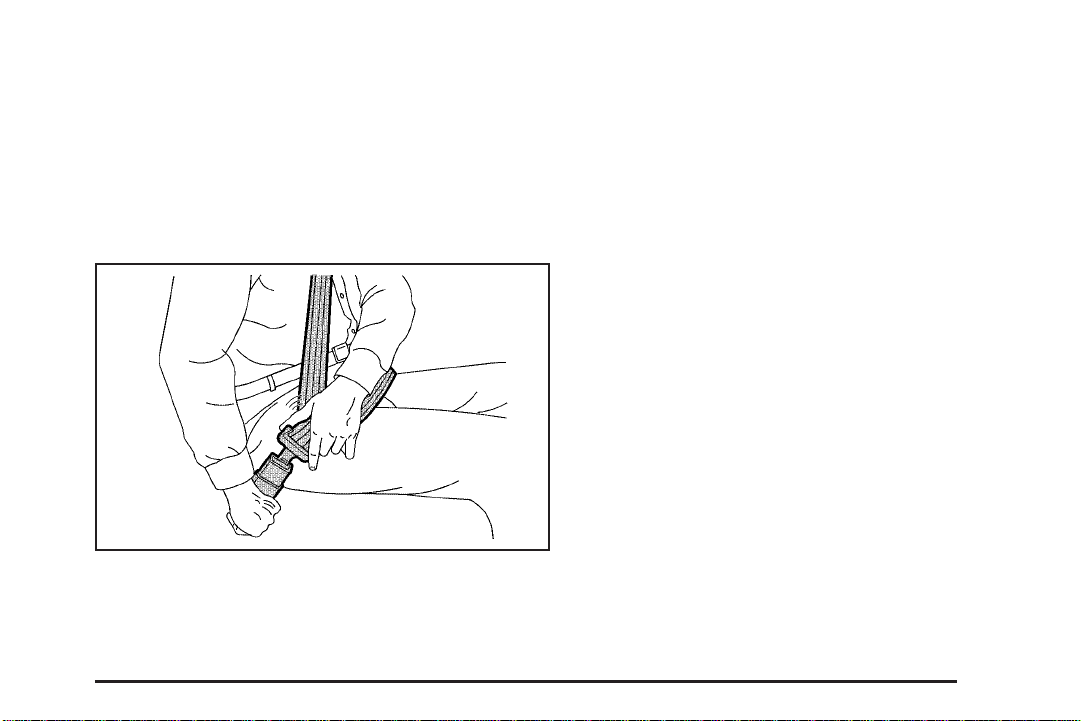
Driver Position
Lap-Shoulder Belt
The driver has a lap-shoulder belt. Here is how to wear
it properly.
1. Close and lock the door.
2. Adjust the seat so you can sit up straight. To see
how, see “Seats” in the Index.
3. Pick up the latch plate and pull the belt across you.
Do not let it get twisted.
The shoulder belt may lock if you pull the belt
across you very quickly. If this happens, let the belt
go back slightly to unlock it. Then pull the belt
across you more slowly.
4. Push the latch plate into the buckle until it clicks.
Pull up on the latch plate to make sure it is secure.
If the belt is not long enough, see Safety Belt
Extender on page 1-29.
Make sure the release button on the buckle is
positioned so you would be able to unbuckle the
safety belt quickly if you ever had to.
5. Move the shoulder belt height adjuster to the height
that is right for you. See Shoulder Belt Height
Adjustment on page 1-23.
1-17
Page 24
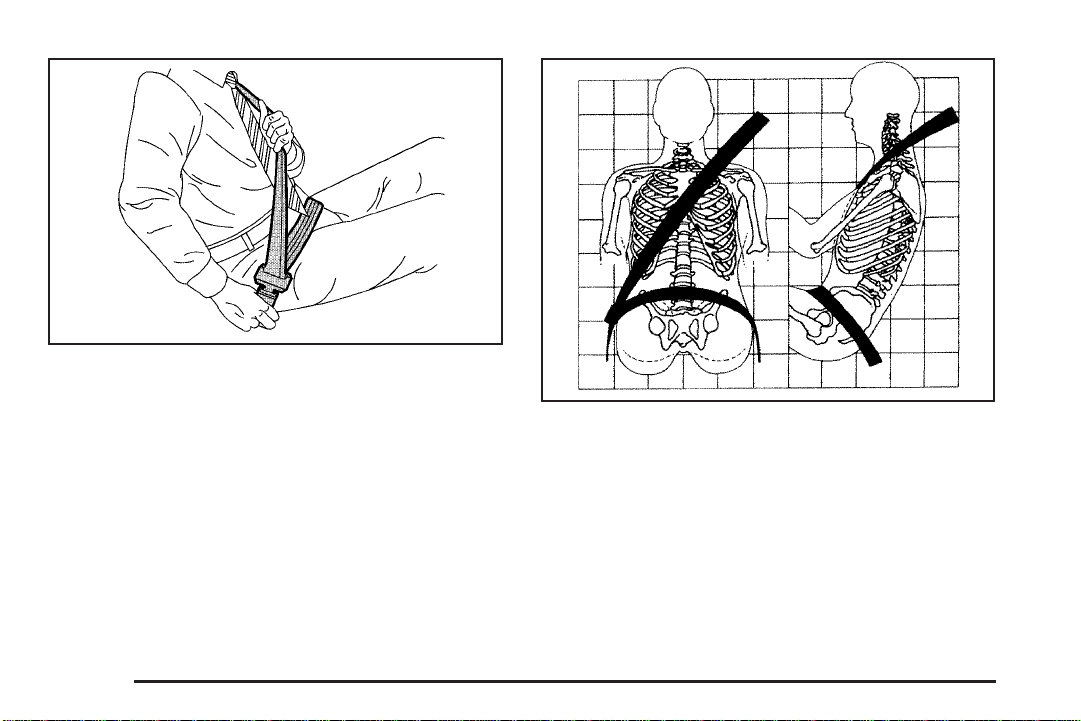
6. To make the lap part tight, pull down on the buckle
end of the belt as you pull up on the shoulder belt.
1-18
The lap part of the belt should be worn low and snug on
the hips, just touching the thighs. In a crash, this
applies force to the strong pelvic bones. And you would
be less likely to slide under the lap belt. If you slid
under it, the belt would apply force at your abdomen.
This could cause serious or even fatal injuries. The
shoulder belt should go over the shoulder and across
the chest. These parts of the body are best able to take
belt restraining forces.
The safety belt locks if there is a sudden stop or crash,
or if you pull the belt very quickly out of the retractor.
Page 25
Q: What is wrong with this?
A: The shoulder belt is too loose. It will not give nearly
as much protection this way.
{CAUTION:
You can be seriously hurt if your shoulder belt
is too loose. In a crash, you would move
forward too much, which could increase injury.
The shoulder belt should fit against your body.
1-19
Page 26
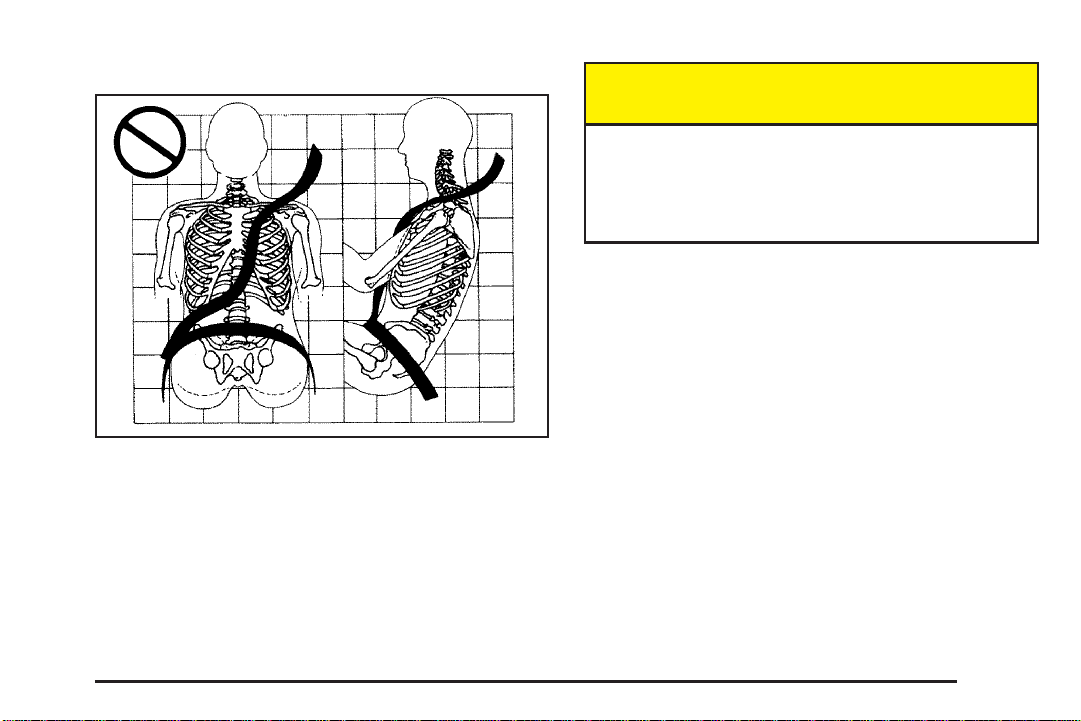
Q: What is wrong with this?
A: The belt is buckled in the wrong place.
{CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured if your belt is
buckled in the wrong place like this. In a crash,
the belt would go up over your abdomen. The
belt forces would be there, not at the pelvic
bones. This could cause serious internal
injuries. Always buckle your belt into the
buckle nearest you.
1-20
Page 27
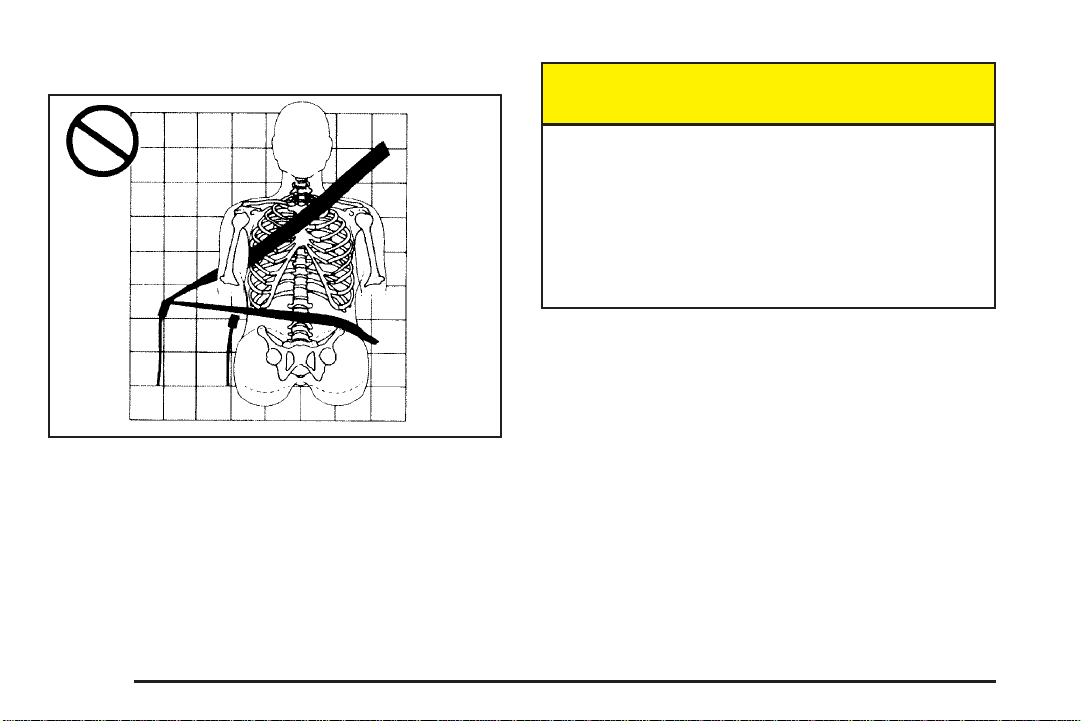
Q: What is wrong with this?
A: The shoulder belt is worn under the arm. It should
be worn over the shoulder at all times.
{CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured if you wear the
shoulder belt under your arm. In a crash, your
body would move too far forward, which would
increase the chance of head and neck injury.
Also, the belt would apply too much force to
the ribs, which are not as strong as shoulder
bones. You could also severely injure internal
organs like your liver or spleen.
1-21
Page 28
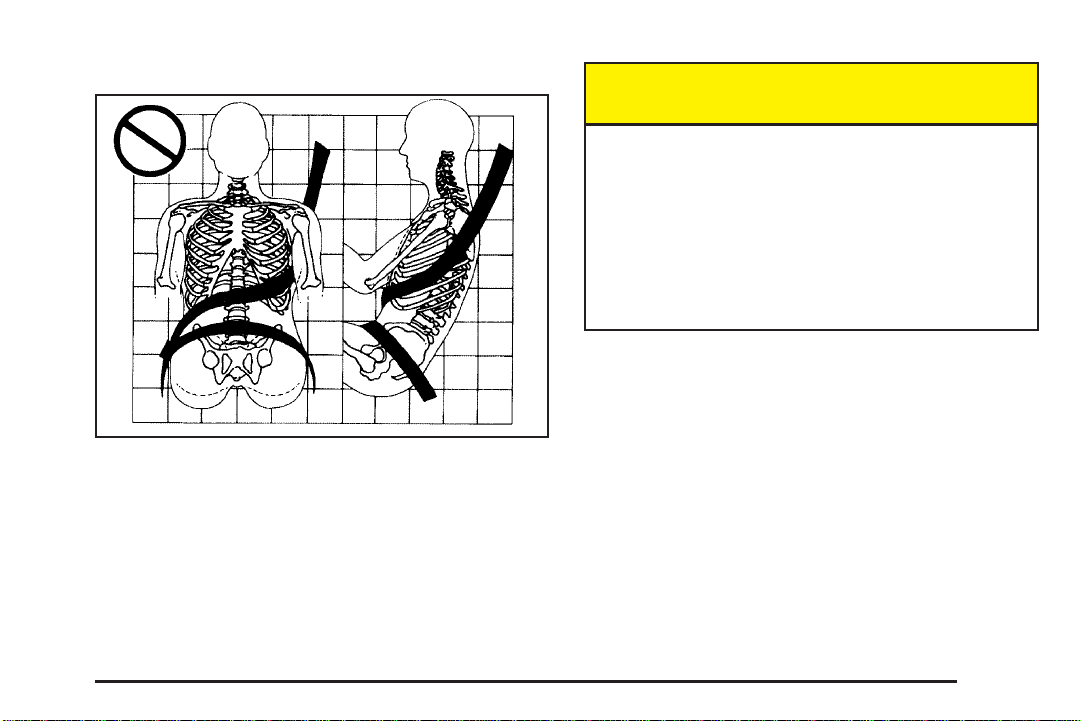
Q: What is wrong with this?
A: The belt is twisted across the body.
{CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured by a twisted belt.
In a crash, you would not have the full width of
the belt to spread impact forces. If a belt is
twisted, make it straight so it can work
properly, or ask your dealer to fix it.
To unlatch the belt, just push the button on the buckle.
The belt should go back out of the way.
1-22
Page 29
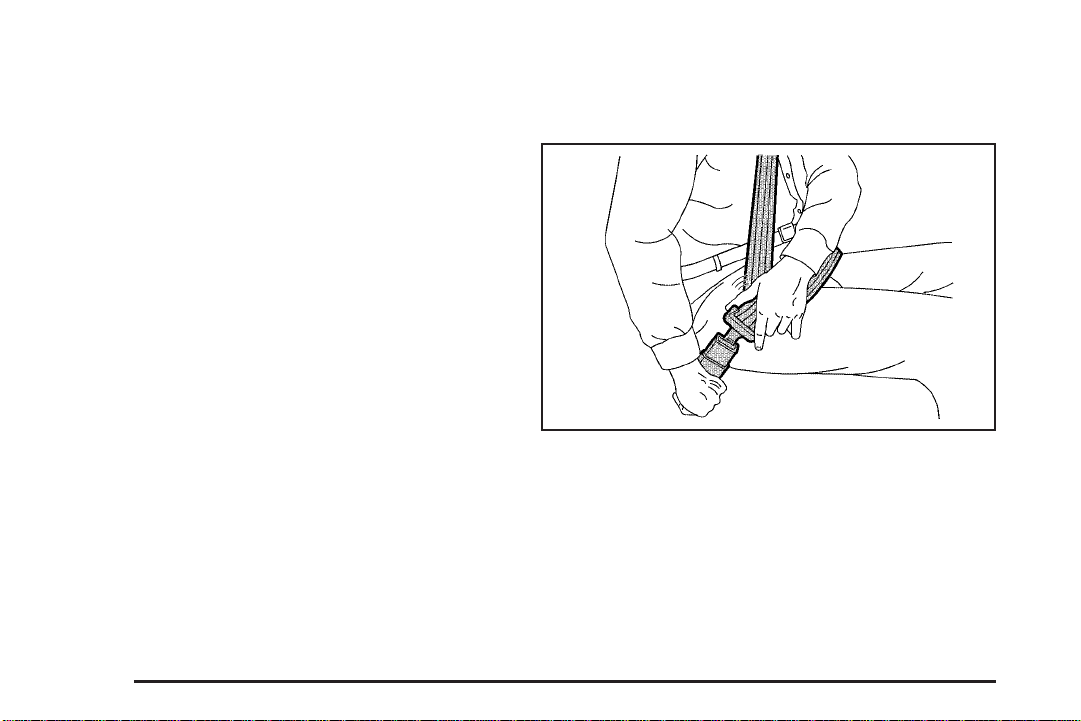
Before you close the door, be sure the belt is out of the
way. If you slam the door on it, you can damage
both the belt and your vehicle.
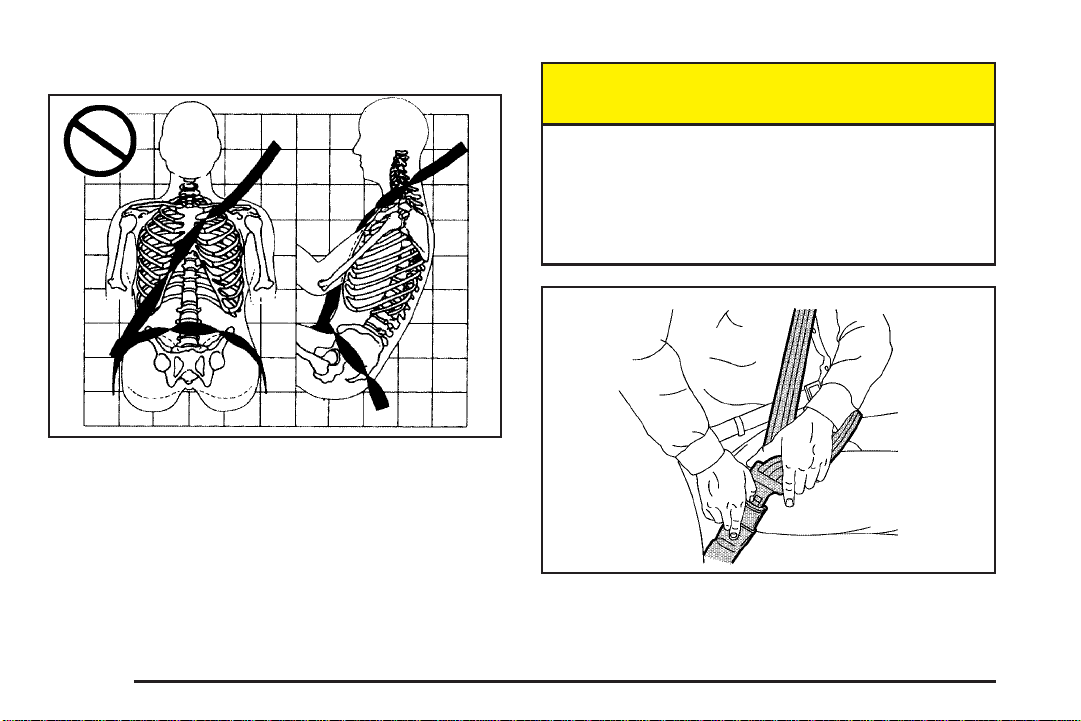
Shoulder Belt Height Adjustment
Before you begin to drive, move the shoulder belt height
adjuster to the height that is right for you.
Adjust the height so that the shoulder portion of the belt
is centered on your shoulder. The belt should be away
from your face and neck, but not falling off your shoulder.
To move it down, press the
release button (A) and
move the height adjuster to
the desired position. You
can move the height
adjuster up just by
pushing up on the
shoulder belt guide.
After you move the height adjuster to where you want it,
try to move it down without pressing the release
button to make sure it has locked into position.
Safety Belt Use During Pregnancy
Safety belts work for everyone, including pregnant
women. Like all occupants, they are more likely to be
seriously injured if they do not wear safety belts.
A pregnant woman should wear a lap-shoulder belt, and
the lap portion should be worn as low as possible,
below the rounding, throughout the pregnancy.
The best way to protect the fetus is to protect the
mother. When a safety belt is worn properly, it is more
likely that the fetus will not be hurt in a crash. For
pregnant women, as for anyone, the key to making
safety belts effective is wearing them properly.
1-23
Page 30
Right Front Passenger Position
To learn how to wear the right front passenger’s safety
belt properly, see Driver Position on page 1-17.
The right front passenger’s safety belt works the
same way as the driver’s safety belt — except for
one thing. If you ever pull the shoulder portion of the
belt out all the way, you will engage the child restraint
locking feature. If this happens, just let the belt go back
all the way and start again.
Rear Seat Passengers
It is very important for rear seat passengers to buckle
up! Accident statistics show that unbelted people in
the rear seat are hurt more often in crashes than those
who are wearing safety belts.
Rear passengers who are not safety belted can be
thrown out of the vehicle in a crash. And they can strike
others in the vehicle who are wearing safety belts.
Lap-Shoulder Belt
All rear seat positions have lap-shoulder belts. Here is
how to wear one properly.
1. Pick up the latch plate and pull the belt across you.
Do not let it get twisted.
The shoulder belt may lock if you pull the belt
across you very quickly. If this happens, let the belt
go back slightly to unlock it. Then pull the belt
across you more slowly.
1-24
Page 31

2. Push the latch plate into the buckle until it clicks.
Pull up on the latch plate to make sure it is secure.
When the shoulder belt is pulled out all the way,
it will lock. If it does, let it go back all the way and
start again.
If the belt is not long enough, see Safety Belt
Extender on page 1-29.
Make sure the release button on the buckle is
positioned so you would be able to unbuckle the
safety belt quickly if you ever had to.
3. To make the lap part tight, pull down on the buckle
end of the belt as you pull up on the shoulder part.
1-25
Page 32

The lap part of the belt should be worn low and snug on
the hips, just touching the thighs. In a crash, this
applies force to the strong pelvic bones. And you would
be less likely to slide under the lap belt. If you slid
under it, the belt would apply force at your abdomen.
This could cause serious or even fatal injuries. The
shoulder belt should go over the shoulder and across
the chest. These parts of the body are best able to take
belt restraining forces.
The safety belt locks if there is a sudden stop or a
crash, or if you pull the belt very quickly out of
the retractor.
{CAUTION:
You can be seriously hurt if your shoulder belt
is too loose. In a crash, you would move
forward too much, which could increase injury.
The shoulder belt should fit against your body.
1-26
To unlatch the belt, push the button on the buckle.
Page 33

Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides for Children and Small Adults
Rear shoulder belt comfort guides will provide added
safety belt comfort for older children who have outgrown
booster seats and for small adults. When installed on
a shoulder belt, the comfort guide better positions
the belt away from the neck and head.
There is one guide for each outside passenger position
in the rear seat. To provide added safety belt comfort
for children who have outgrown child restraints and
booster seats and for smaller adults, the comfort guides
may be installed on the shoulder belts. Here is how
to install a comfort guide and use the safety belt:
1. Pull the elastic cord out from between the edge of
the seatback and the interior body to remove the
guide from its storage clip.
1-27
Page 34

2. Slide the guide under and past the belt. The elastic
cord must be under the belt. Then, place the guide
over the belt, and insert the two edges of the
belt into the slots of the guide.
1-28
3. Be sure that the belt is not twisted and it lies flat.
The elastic cord must be under the belt and the
guide on top.
Page 35

4. Buckle, position and release the safety belt as
described in Rear Seat Passengers on page 1-24.
Make sure that the shoulder belt crosses the
shoulder.
To remove and store the comfort guides, squeeze the
belt edges together so that you can take them out of the
guides. Pull the guide upward to expose its storage
clip, and then slide the guide onto the clip. Turn
the guide and clip inward and in between the seatback
and the interior body, leaving only the loop of elastic
cord exposed.
Safety Belt Pretensioners
Your vehicle has safety belt pretensioners for the driver
and right front passenger. Although you cannot see
them, they are located on the retractor part of the safety
belts. They help the safety belts reduce a person’s
forward movement in a moderate to severe frontal or
near frontal crash.
Pretensioners work only once. If they activate in a
crash, you will need to get new ones, and probably other
new parts for your safety belt system. See Replacing
Restraint System Parts After a Crash on page 1-57.
Safety Belt Extender
If the vehicle’s safety belt will fasten around you, you
should use it.
But if a safety belt is not long enough, your dealer will
order you an extender. It is free. When you go in to
order it, take the heaviest coat you will wear, so
the extender will be long enough for you. To help avoid
personal injury, do not let someone else use it, and
use it only for the seat it is made to fit. The extender has
been designed for adults. Never use it for securing
child seats. To wear it, just attach it to the regular safety
belt. For more information, see the instruction sheet
that comes with the extender.
1-29
Page 36

Child Restraints
Older Children
Older children who have outgrown booster seats should
wear the vehicle’s safety belts.
Q: What is the proper way to wear safety belts?
A: If possible, an older child should wear a
lap-shoulder belt and get the additional restraint a
shoulder belt can provide. The shoulder belt
should not cross the face or neck. The lap belt
should fit snugly below the hips, just touching the
top of the thighs. It should never be worn over
the abdomen, which could cause severe or even
fatal internal injuries in a crash.
Accident statistics show that children are safer if they
are restrained in the rear seat.
In a crash, children who are not buckled up can strike
other people who are buckled up, or can be thrown
out of the vehicle. Older children need to use safety
belts properly.
1-30
Page 37

{CAUTION:
Never do this.
Here two children are wearing the same belt.
The belt can not properly spread the impact
forces. In a crash, the two children can be
crushed together and seriously injured. A belt
must be used by only one person at a time.
Q: What if a child is wearing a lap-shoulder belt,
but the child is so small that the shoulder belt
is very close to the child’s face or neck?
A: If the child is sitting in a seat next to a window,
move the child toward the center of the vehicle.
Also see Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides for
Children and Small Adults on page 1-27. If the child
is sitting in the center rear seat passenger
position, move the child toward the safety belt
buckle. In either case, be sure that the shoulder belt
still is on the child’s shoulder, so that in a crash
the child’s upper body would have the restraint that
belts provide.
1-31
Page 38

{CAUTION:
Never do this.
Here a child is sitting in a seat that has a
lap-shoulder belt, but the shoulder part is
behind the child. If the child wears the belt in
this way, in a crash the child might slide under
the belt. The belt’s force would then be applied
right on the child’s abdomen. That could cause
serious or fatal injuries.
Wherever the child sits, the lap portion of the belt
should be worn low and snug on the hips, just touching
the child’s thighs. This applies belt force to the child’s
pelvic bones in a crash.
1-32
Page 39

Infants and Young Children
Everyone in a vehicle needs protection! This includes
infants and all other children. Neither the distance
traveled nor the age and size of the traveler changes
the need, for everyone, to use safety restraints. In fact,
the law in every state in the United States and in
every Canadian province says children up to some age
must be restrained while in a vehicle.
Every time infants and young children ride in vehicles,
they should have the protection provided by appropriate
restraints. Young children should not use the vehicle’s
adult safety belts alone, unless there is no other choice.
Instead, they need to use a child restraint.
{CAUTION:
People should never hold a baby in their arms
while riding in a vehicle. A baby does not
weigh much — until a crash. During a crash a
baby will become so heavy it is not possible to
hold it. For example, in a crash at only 25 mph
(40 km/h), a 12 lb (5.5 kg) baby will suddenly
become a 240 lb (110 kg) force on a person’s
arms. A baby should be secured in an
appropriate restraint.
1-33
Page 40

{CAUTION:
Children who are up against, or very close to,
any airbag when it inflates can be seriously
injured or killed. Airbags plus lap-shoulder
belts offer protection for adults and older
children, but not for young children and
infants. Neither the vehicle’s safety belt system
nor its airbag system is designed for them.
Young children and infants need the protection
that a child restraint system can provide.
Q: What are the different types of add-on child
restraints?
A: Add-on child restraints, which are purchased by the
vehicle’s owner, are available in four basic types.
Selection of a particular restraint should take
into consideration not only the child’s weight, height
and age but also whether or not the restraint will
be compatible with the motor vehicle in which it will
be used.
For most basic types of child restraints, there are
many different models available. When purchasing a
child restraint, be sure it is designed to be used
in a motor vehicle. If it is, the restraint will have a
label saying that it meets federal motor vehicle
safety standards.
The restraint manufacturer’s instructions that come
with the restraint, state the weight and height
limitations for a particular child restraint. In addition,
there are many kinds of restraints available for
children with special needs.
1-34
Page 41

{CAUTION:
{CAUTION:
Newborn infants need complete support,
including support for the head and neck.
This is necessary because a newborn infant’s
neck is weak and its head weighs so much
compared with the rest of its body. In a crash,
an infant in a rear-facing seat settles into
the restraint, so the crash forces can be
distributed across the strongest part of an
infant’s body, the back and shoulders. Infants
always should be secured in appropriate infant
restraints.
The body structure of a young child is quite
unlike that of an adult or older child, for whom
the safety belts are designed. A young child’s
hip bones are still so small that the vehicle’s
regular safety belt may not remain low on the
hip bones, as it should. Instead, it may settle
up around the child’s abdomen. In a crash, the
belt would apply force on a body area that is
unprotected by any bony structure. This alone
could cause serious or fatal injuries. Young
children always should be secured in
appropriate child restraints.
1-35
Page 42

Child Restraint Systems
An infant car bed (A), a special bed made for use in a
motor vehicle, is an infant restraint system designed
to restrain or position a child on a continuous flat
surface. Make sure that the infant’s head rests toward
the center of the vehicle.
A rear-facing infant seat (B) provides restraint with the
seating surface against the back of the infant. The
harness system holds the infant in place and, in a crash,
acts to keep the infant positioned in the restraint.
1-36
Page 43

A forward-facing child seat (C-E) provides restraint for
the child’s body with the harness and also sometimes
with surfaces such as T-shaped or shelf-like shields.
A booster seat (F-G) is a child restraint designed to
improve the fit of the vehicle’s safety belt system. Some
booster seats have a shoulder belt positioner, and some
high-back booster seats have a five-point harness. A
booster seat can also help a child to see out the window.
1-37
Page 44

Q: How do child restraints work?
A: A child restraint system is any device designed for
use in a motor vehicle to restrain, seat, or position
children. A built-in child restraint system is a
permanent part of the motor vehicle. An add-on
child restraint system is a portable one, which
is purchased by the vehicle’s owner.
For many years, add-on child restraints have used
the adult belt system in the vehicle. To help
reduce the chance of injury, the child also has to be
secured within the restraint. The vehicle’s belt
system secures the add-on child restraint in the
vehicle, and the add-on child restraint’s harness
system holds the child in place within the restraint.
One system, the three-point harness, has straps
that come down over each of the infant’s shoulders
and buckle together at the crotch. The five-point
harness system has two shoulder straps,
two hip straps and a crotch strap. A shield may
take the place of hip straps. A T-shaped shield has
shoulder straps that are attached to a flat pad
which rests low against the child’s body. A shelf- or
armrest-type shield has straps that are attached
to a wide, shelf-like shield that swings up or to
the side.
When choosing a child restraint, be sure the child
restraint is designed to be used in a vehicle. If it is, it
will have a label saying that it meets federal motor
vehicle safety standards.
Then follow the instructions for the restraint. You may
find these instructions on the restraint itself or in a
booklet, or both. These restraints use the belt system or
the LATCH system in your vehicle, but the child also
has to be secured within the restraint to help reduce the
chance of personal injury. When securing an add-on
child restraint, refer to the instructions that come with the
restraint which may be on the restraint itself or in a
booklet, or both, and to this manual. The child restraint
instructions are important, so if they are not available,
obtain a replacement copy from the manufacturer.
Keep in mind that an unsecured child restraint can move
around in a collision or sudden stop and injure people
in the vehicle. Be sure to properly secure any child
restraint in your vehicle – even when no child is in it.
1-38
Page 45

Where to Put the Restraint
Accident statistics show that children are safer if they
are restrained in the rear rather than the front seat. We,
therefore, recommend that child restraints be secured
in a rear seat, including an infant riding in a rear-facing
infant seat, a child riding in a forward-facing child
seat and an older child riding in a booster seat. Never
put a rear-facing child restraint in the front passenger
seat. Here is why:
{CAUTION:
A child in a rear-facing child restraint can be
seriously injured or killed if the right front
passenger’s airbag inflates. This is because
the back of the rear-facing child restraint
would be very close to the inflating airbag.
Always secure a rear-facing child restraint in a
rear seat.
If you need to secure a forward-facing child
restraint in the right front seat, always move
the front passenger seat as far back as it will
go. It is better to secure the child restraint in a
rear seat.
Wherever you install a child restraint, be sure to secure
the child restraint properly.
Keep in mind that an unsecured child restraint can
move around in a collision or sudden stop and injure
people in the vehicle. Be sure to properly secure
any child restraint in your vehicle — even when no child
is in it.
Top Strap
Some child restraints have a top strap, or “top tether.” It
can help restrain the child restraint during a collision.
For it to work, a top strap must be properly anchored to
the vehicle. Some top strap-equipped child restraints
are designed for use with or without the top strap being
anchored. Others require the top strap always to be
anchored. Be sure to read and follow the instructions for
your child restraint. If yours requires that the top strap
be anchored, do not use the restraint unless it is
anchored properly.
If the child restraint does not have a top strap, one can
be obtained, in kit form, for many child restraints.
Ask the child restraint manufacturer whether or not a kit
is available.
1-39
Page 46

{CAUTION:
Each top tether bracket is designed to anchor
only one child restraint. Attaching more than
one child restraint to a single bracket could
cause the anchor to come loose or even break
during a crash. A child or others could be
injured if this happens. To help prevent injury
to people and damage to your vehicle, attach
only one child restraint per bracket.
In Canada, the law requires that forward-facing child
restraints have a top strap, and that the strap be
anchored. In the United States, some child restraints
also have a top strap. If your child restraint has a
top strap, it should be anchored.
If the position you are using has a head restraint, route
the top strap over it. See Head Restraints on page 1-7.
Anchor the top strap to an anchor point specified in
Top Strap Anchor Location on page 1-41. Be sure to use
an anchor point located on the same side of the
vehicle as the seating position where the child restraint
will be placed.
1-40
Once you have the top strap anchored, you will be
ready to secure the child restraint itself. Tighten the top
strap when and as the child restraint manufacturer’s
instructions say.
Page 47

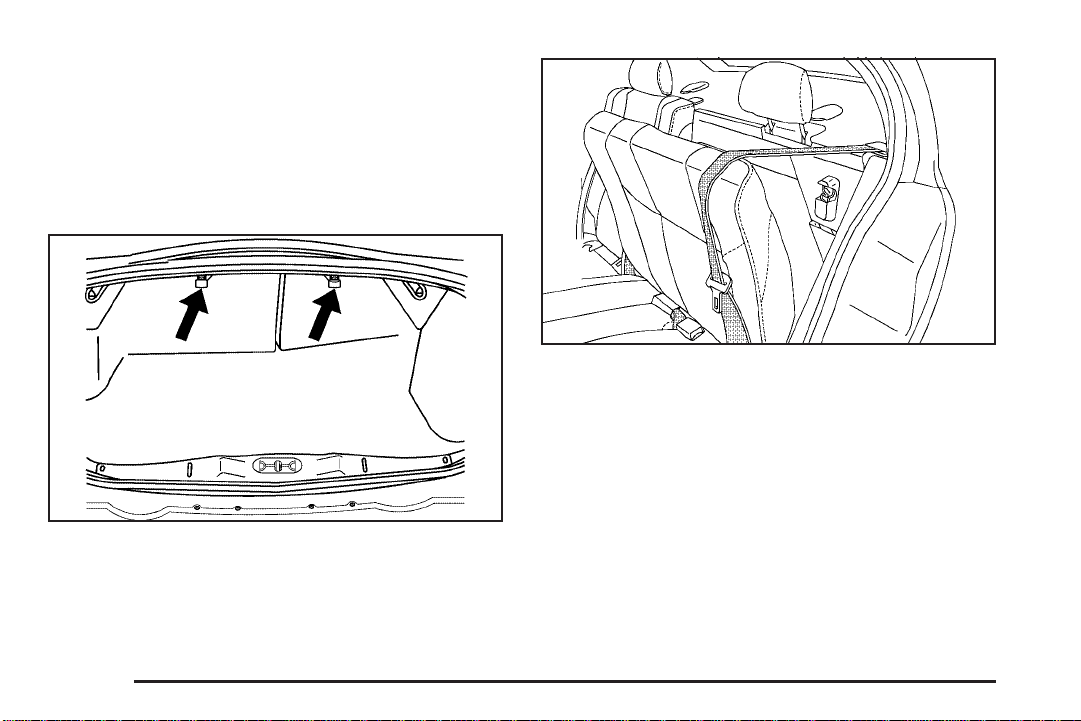
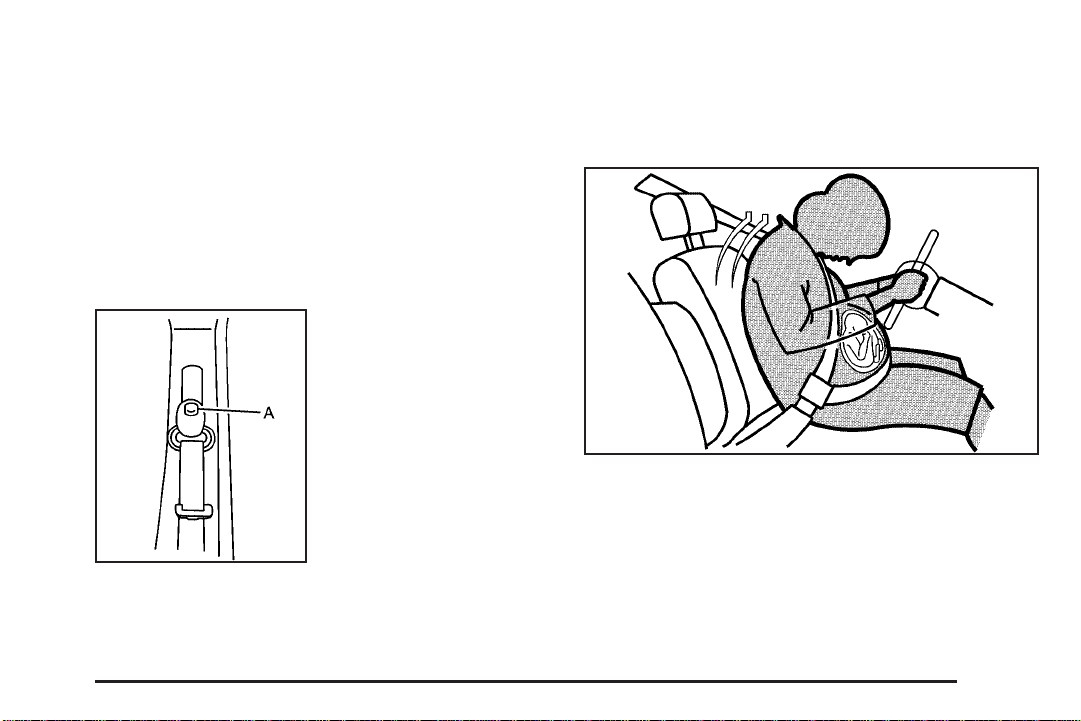
Top Strap Anchor Location
Your vehicle has top strap anchors (A) for the rear
seating positions. The anchors are located behind the
rear seat on the filler panel.
Do not secure a child restraint in the right front
passenger’s position if a national or local law requires
that the top strap be anchored, or if the instructions that
come with the child restraint say that the top strap
must be anchored. There is no place to anchor the top
strap in this position.
Lower Anchorages and Top Tethers for Children (LATCH System)
Your vehicle has the LATCH system. There are anchors
for each rear seating position.
This system, designed to make installation of child
restraints easier, does not use the vehicle’s safety belts.
Instead, it uses vehicle anchors and child restraint
attachments to secure the restraints. Some restraints
also use another vehicle anchor to secure a top
tether strap.
A. Lower Anchorage
B. Lower Anchorage
C. Top Tether
1-41
Page 48

A. Lower Anchorage
B. Lower Anchorage
In order to use the LATCH system in your vehicle, you
need a child restraint designed for that system.
To assist you in locating the lower anchorages for this
child restraint system, each seating position with
the LATCH system has visible metal anchors in the seat
where the seatback meets the seat cushion.
{CAUTION:
If a LATCH-type child restraint is not attached
to its anchorage points, the restraint will not
be able to protect the child correctly. In a
crash, the child could be seriously injured or
killed. Make sure that a LATCH-type child
restraint is properly installed using the
anchorage points, or use the vehicle’s safety
belts to secure the restraint, following the
instructions that came with that restraint, and
also the instructions in this manual.
1-42
Page 49

Securing a Child Restraint Designed for the LATCH System
Securing a Child Restraint in a Rear Seat Position
1. Find the LATCH anchorages for the seating
position you want to use, where the bottom of the
seatback meets the back of the seat cushion.
See Lower Anchorages and Top Tethers for
Children (LATCH System) on page 1-41.
2. Put the child restraint on the seat.
3. Attach and tighten the LATCH attachments on the
child restraint to the LATCH anchorages in the
vehicle. The child restraint instructions will show
you how.
4. If the child restraint is forward-facing, attach and
tighten the top tether to the top tether anchorage.
The child restraint instructions will show you
how. Also see Top Strap on page 1-39.
5. Push and pull the child restraint in different
directions to be sure it is secure.
To remove the child restraint, simply unhook the top
tether from the top tether anchorage and then
disconnect the LATCH attachments from the LATCH
anchorages.
If your child restraint is equipped with the LATCH
system, see Lower Anchorages and Top Tethers for
Children (LATCH System) on page 1-41. See Top Strap
on page 1-39 if the child restraint has one.
If your child restraint does not have the LATCH system,
you will be using the lap-shoulder belt to secure the
child restraint in this position. Be sure to follow the
instructions that came with the child restraint. Secure
the child in the child restraint when and as the
instructions say.
1. Put the child restraint on the seat.
2. Pick up the latch plate, and run the lap and shoulder
portions of the vehicle’s safety belt through or
around the restraint. The child restraint instructions
will show you how.
1-43
Page 50

3. Buckle the belt. Make sure the release button is
positioned so you would be able to unbuckle the
safety belt quickly if you ever had to.
1-44
4. Pull the rest of the shoulder belt all the way out of
the retractor to set the lock.
Page 51

5. To tighten the belt, push down on the child restraint,
pull the shoulder portion of the belt to tighten the
lap portion of the belt and feed the shoulder
belt back into the retractor. If you are using a
forward-facing child restraint, you may find it helpful
to use your knee to push down on the child
restraint as you tighten the belt.
6. Push and pull the child restraint in different
directions to be sure it is secure.
To remove the child restraint, just unbuckle the vehicle’s
safety belt and let it go back all the way. The safety
belt will move freely again and be ready to work for an
adult or larger child passenger.
Securing a Child Restraint in the Right Front Seat Position
If your child restraint is equipped with the LATCH
system, see Lower Anchorages and Top Tethers for
Children (LATCH System) on page 1-41.
There is no top strap anchor in the right front
passenger’s position. Do not secure a child seat in this
position if a national or local law requires that the
top strap be anchored, or if the instructions that come
with the child restraint say that the top strap must
be anchored. See Top Strap on page 1-39 if the child
restraint has one.
1-45
Page 52

Your vehicle has a right front passenger airbag.
Never put a rear-facing child restraint in this seat. Here
is why:
{CAUTION:
A child in a rear-facing child restraint can be
seriously injured or killed if the right front
passenger’s airbag inflates. This is because
the back of the rear-facing child restraint
would be very close to the inflating airbag.
Always secure a rear-facing child restraint in a
rear seat.
A rear seat is a safer place to secure a forward-facing
child restraint. If you need to secure a forward-facing
child restraint in the right front seat, you will be using the
lap-shoulder belt to secure the restraint in this position.
Be sure to follow the instructions that came with the
child restraint. Secure the child in the child restraint
when and as the instructions say.
1. Because your vehicle has a right front passenger
airbag, always move the seat as far back as it will
go before securing a forward-facing child restraint.
See Manual Seats on page 1-2.
2. Put the child restraint on the seat.
3. Pick up the latch plate, and run the lap and shoulder
portions of the vehicle’s safety belt through or
around the restraint. The child restraint instructions
will show you how.
4. Buckle the belt. Make sure the release button is
positioned so you would be able to unbuckle the
safety belt quickly if you ever had to.
1-46
Page 53

5. Pull the rest of the shoulder belt all the way out of
the retractor to set the lock.
6. To tighten the belt, push down on the child restraint,
pull the shoulder portion of the belt to tighten the
lap portion of the belt and feed the shoulder
belt back into the retractor. You may find it helpful
to use your knee to push down on the child
restraint as you tighten the belt.
7. Push and pull the child restraint in different
directions to be sure it is secure.
To remove the child restraint, just unbuckle the vehicle’s
safety belt and let it go back all the way. The safety
belt will move freely again and be ready to work for an
adult or larger child passenger.
1-47
Page 54

Airbag System
Your vehicle has a frontal airbag for the driver and
another frontal airbag for the right front passenger. Your
vehicle may also have roof mounted side impact
airbags. Roof mounted side impact airbags are available
for the driver and the passenger seated directly behind
the driver and for the right front passenger and the
passenger seated directly behind that passenger.
If your vehicle has side impact airbags, the word
AIRBAG will appear on the airbag covering on the
garnish trim near ceiling and the side windows.
Frontal airbags are designed to help reduce the risk of
injury from the force of an inflating frontal airbag.
But these airbags must inflate very quickly to do their
job and comply with federal regulations.
Here are the most important things to know about the
airbag system:
{CAUTION:
You can be severely injured or killed in a crash
if you are not wearing your safety belt — even
if you have airbags. Wearing your safety belt
CAUTION: (Continued)
CAUTION: (Continued)
during a crash helps reduce your chance of
hitting things inside the vehicle or being
ejected from it. Airbags are “supplemental
restraints” to the safety belts. All airbags are
designed to work with safety belts but do not
replace them.
Frontal airbags for the driver and right front
passenger are designed to deploy in moderate
to severe frontal and near frontal crashes.
They are not designed to inflate in rollover,
rear or low-speed frontal crashes, or in many
side crashes. And, for some unrestrained
occupants, frontal airbags may provide less
protection in frontal crashes than more
forceful airbags have provided in the past. The
roof-mounted side impact airbags are designed
to inflate in moderate to severe crashes where
something hits the side of your vehicle. They
are not designed to inflate in frontal, in rollover
or in rear crashes. Everyone in your vehicle
should wear a safety belt properly — whether
or not there is an airbag for that person.
1-48
Page 55

{CAUTION:
CAUTION: (Continued)
Both frontal and side impact airbags inflate
with great force, faster than the blink of an
eye. If you are too close to an inflating airbag,
as you would be if you were leaning forward, it
could seriously injure you. Safety belts help
keep you in position for airbag inflation before
and during a crash. Always wear your safety
belt even with frontal airbags. The driver
should sit as far back as possible while still
maintaining control of the vehicle. Occupants
should not lean on or sleep against the door.
{CAUTION:
Anyone who is up against, or very close to,
any airbag when it inflates can be seriously
injured or killed. Airbags plus lap-shoulder
CAUTION: (Continued)
belts offer the best protection for adults, but
not for young children and infants. Neither the
vehicle’s safety belt system nor its airbag
system is designed for them. Young children
and infants need the protection that a child
restraint system can provide. Always secure
children properly in your vehicle. To read how,
see Older Children on page 1-30 or Infants and
Young Children on page 1-33.
There is an airbag
readiness light on
the instrument panel
cluster, which shows the
airbag symbol.
The system checks the airbag electrical system for
malfunctions. The light tells you if there is an electrical
problem. See Airbag Readiness Light on page 3-24
for more information.
1-49
Page 56

Where Are the Airbags?
The driver’s airbag is in the middle of the
steering wheel.
The right front passenger’s airbag is in the instrument
panel on the passenger’s side.
1-50
Page 57

If your vehicle has a side impact airbag for the driver
and the person seated directly behind the driver, it
is located in the ceiling above the side windows.
If your vehicle has a side impact airbag for the right
front passenger and the person directly behind
that passenger, it is located in the ceiling above
the side windows.
1-51
Page 58

{CAUTION:
If something is between an occupant and an
airbag, the bag might not inflate properly or it
might force the object into that person causing
severe injury or even death. The path of an
inflating airbag must be kept clear. Do not put
anything between an occupant and an airbag,
and do not attach or put anything on the
steering wheel hub or on or near any other
airbag covering. And, if your vehicle has
roof-mounted side impact airbags, never secure
anything to the roof of your vehicle by routing
the rope or tiedown through any door or window
opening. If you do, the path of an inflating side
impact airbag will be blocked. The path of an
inflating airbag must be kept clear.
When Should an Airbag Inflate?
The driver’s and right front passenger’s frontal airbags
are designed to inflate in moderate to severe frontal
or near-frontal crashes. But they are designed to inflate
only if the impact exceeds a predetermined deployment
threshold. Deployment thresholds take into account
a variety of desired deployment and non-deployment
events and are used to predict how severe a crash
is likely to be in time for the airbags to inflate and help
restrain the occupants. Whether your frontal airbags
will or should deploy is not based on how fast your
vehicle is traveling. It depends largely on what you hit,
the direction of the impact and how quickly your
vehicle slows down.
In addition, your vehicle has “dual-stage” frontal airbags,
which adjust the restraint according to crash severity.
Your vehicle is equipped with electronic frontal sensors
which help the sensing system distinguish between a
moderate frontal impact and a more severe frontal
impact. For moderate frontal impacts, these airbags
inflate at a level less than full deployment. For
more severe frontal impacts, full deployment occurs. If
the front of your vehicle goes straight into a wall
that does not move or deform, the threshold level for
the reduced deployment is about 12 to 16 mph
(19 to 26 km/h), and the threshold level for a full
deployment is about 18 to 24 mph (29 to 38.5 km/h).
1-52
Page 59

The threshold level can vary, however, with specific
vehicle design, so that it can be somewhat above
or below this range.
Frontal airbags may inflate at different crash speeds.
For example:
• If the vehicle hits a stationary object, the airbags
could inflate at a different crash speed than if the
object were moving.
• If the vehicle hits an object that deforms, the
airbags could inflate at a different crash speed than
if the object does not deform.
• If the vehicle hits a narrow object (like a pole) the
airbags could inflate at a different crash speed
than if the vehicle hits a wide object (like a wall).
• If the vehicle goes into an object at an angle the
airbags could inflate at a different crash speed
than if the vehicle goes straight into the object.
Frontal airbags (driver and right front passenger) are not
intended to inflate during vehicle rollovers, rear
impacts, or in many side impacts.
Your vehicle may or may not have side impact airbags.
See Airbag System on page 1-48. Side impact
airbags are intended to inflate in moderate to severe
side crashes. A side impact airbag will inflate if the crash
severity is above the system’s designed threshold
level. The threshold level can vary with specific vehicle
design. Side impact airbags are not intended to
inflate in frontal or near-frontal impacts, rollovers or rear
impacts. A side impact airbag is intended to deploy
on the side of the vehicle that is struck.
In any particular crash, no one can say whether an
airbag should have inflated simply because of the
damage to a vehicle or because of what the repair costs
were. For frontal airbags, inflation is determined by
the angle of the impact and how quickly the vehicle
slows down in frontal or near-frontal impacts. For side
impact airbags, inflation is determined by the location
and severity of the impact.
1-53
Page 60

What Makes an Airbag Inflate?
In an impact of sufficient severity, the airbag sensing
system detects that the vehicle is in a crash. For
both frontal and side impact airbags, the sensing system
triggers a release of gas from the inflator, which
inflates the airbag. The inflator, airbag, and related
hardware are all part of the airbag modules inside the
steering wheel and in the instrument panel in front of the
right front passenger. For vehicles with side impact
airbags, the airbag modules are located in the ceiling of
the vehicle, near the side windows.
frontal or near frontal collisions, rollovers, and rear
impacts, primarily because an occupant’s motion is not
toward those airbags. Airbags should never be
regarded as anything more than a supplement to safety
belts, and then only in moderate to severe frontal or
near-frontal collisions for the driver’s and right front
passenger’s frontal airbags, and only in moderate to
severe side collisions for side impact airbags.
What Will You See After an Airbag
Inflates?
How Does an Airbag Restrain?
In moderate to severe frontal or near frontal collisions,
even belted occupants can contact the steering wheel or
the instrument panel. In moderate to severe side
collisions, even belted occupants can contact the inside
of the vehicle. The airbag supplements the protection
provided by safety belts. Airbags distribute the force of
the impact more evenly over the occupant’s upper
body, stopping the occupant more gradually. But the
frontal airbags would not help you in many types
of collisions, including rollovers, rear impacts, and many
side impacts, primarily because an occupant’s motion
is not toward the airbag. Side impact airbags would not
help you in many types of collisions, including many
1-54
After an airbag inflates, it quickly deflates, so quickly
that some people may not even realize the airbag
inflated. Some components of the airbag module — the
steering wheel hub for the driver’s airbag, the
instrument panel for the right front passenger’s bag or
the garnish trim and ceiling of your vehicle near the side
windows — will be hot for a short time. The parts of
the bag that come into contact with you may be warm,
but not too hot to touch. There will be some smoke
and dust coming from the vents in the deflated airbags.
Airbag inflation does not prevent the driver from
seeing or being able to steer the vehicle, nor does it
stop people from leaving the vehicle.
Page 61

{CAUTION:
When an airbag inflates, there is dust in the
air. This dust could cause breathing problems
for people with a history of asthma or other
breathing trouble. To avoid this, everyone in
the vehicle should get out as soon as it is safe
to do so. If you have breathing problems but
cannot get out of the vehicle after an airbag
inflates, then get fresh air by opening a
window or a door. If you experience breathing
problems following an airbag deployment, you
should seek medical attention.
Your vehicle has a feature that will automatically unlock
the doors and turn the interior lamps on when the
airbags inflate (if battery power is available). You can
lock the doors again and turn the interior lamps off
by using the door lock and interior lamp controls.
In many crashes severe enough to inflate an airbag,
windshields are broken by vehicle deformation.
Additional windshield breakage may also occur from the
right front passenger airbag.
• Airbags are designed to inflate only once. After an
airbag inflates, you will need some new parts for
your airbag system. If you do not get them,
the airbag system will not be there to help protect
you in another crash. A new system will include
airbag modules and possibly other parts. The
service manual for your vehicle covers the need to
replace other parts.
• Your vehicle is equipped with a crash sensing and
diagnostic module which records information after
a crash. See Vehicle Data Collection and Event
Data Recorders on page 7-9.
• Let only qualified technicians work on your airbag
system. Improper service can mean that your
airbag system will not work properly. See your
dealer for service.
Notice: If you damage the covering for the driver’s
or the right front passenger’s airbag, or the side
impact airbag covering on the garnish trim and
ceiling near the side windows, the airbag may not
work properly. You may have to replace the
airbag module in the steering wheel, both the airbag
module and the instrument panel for the right
front passenger’s airbag, or side impact airbag
module, garnish trim and ceiling covering for
roof-mounted side impact airbags. Do not open or
break the airbag coverings.
1-55
Page 62

Servicing Your Airbag-Equipped Vehicle
Airbags affect how your vehicle should be serviced.
There are parts of the airbag system in several places
around your vehicle. You do not want the system to
inflate while someone is working on your vehicle. Your
dealer and the service manual have information
about servicing your vehicle and the airbag system. To
purchase a service manual, see Service Publications
Ordering Information on page 7-11.
{CAUTION:
For up to 10 minutes after the ignition key is
turned off and the battery is disconnected, an
airbag can still inflate during improper service.
You can be injured if you are close to an
airbag when it inflates. Avoid yellow
connectors. They are probably part of the
airbag system. Be sure to follow proper
service procedures, and make sure the person
performing work for you is qualified to do so.
The airbag system does not need regular maintenance.
Restraint System Check
Checking the Restraint Systems
Now and then, make sure the safety belt reminder light
and all your belts, buckles, latch plates, retractors
and anchorages are working properly. Look for any other
loose or damaged safety belt system parts. If you see
anything that might keep a safety belt system from doing
its job, have it repaired.
Torn or frayed safety belts may not protect you in a
crash. They can rip apart under impact forces. If a belt
is torn or frayed, get a new one right away.
Also look for any opened or broken airbag covers, and
have them repaired or replaced. (The airbag system
does not need regular maintenance.)
1-56
Page 63

Replacing Restraint System Parts After a Crash
{CAUTION:
A crash can damage the restraint systems in
your vehicle. A damaged restraint system may
not properly protect the person using it,
resulting in serious injury or even death in a
crash. To help make sure your restraint
systems are working properly after a crash,
have them inspected and any necessary
replacements made as soon as possible.
If you have had a crash, do you need new belts or
LATCH system parts?
After a very minor collision, nothing may be necessary.
But if the belts were stretched, as they would be if
worn during a more severe crash, then you need
new parts.
If the LATCH system was being used during a more
severe crash, you may need new LATCH system parts.
If belts are cut or damaged, replace them. Collision
damage also may mean you will need to have LATCH
system, safety belt or seat parts repaired or replaced.
New parts and repairs may be necessary even if the belt
or LATCH system was not being used at the time of
the collision.
If an airbag inflates, you will need to replace airbag
system parts. See the part on the airbag system earlier
in this section.
If the frontal airbags inflate you will also need to replace
the driver and front passenger’s safety belt retractor
assembly. Be sure to do so. Then the new retractor
assembly will be there to help protect you in a collision.
After a crash you may need to replace the driver and
front passenger’s safety belt retractor assemblies, even
if the frontal airbags have not deployed. The driver
and front passenger’s safety belt retractor assemblies
contain the safety belt pretensioners. Have your
safety belt pretensioners checked if your vehicle has
been in a collision, or if your airbag readiness light stays
on after you start your vehicle or while you are driving.
See Airbag Readiness Light on page 3-24.
1-57
Page 64

✍ NOTES
1-58
Page 65

Section 2 Features and Controls
Keys ...............................................................2-2
Remote Keyless Entry System .........................2-3
Remote Keyless Entry System Operation ...........2-4
Doors and Locks .............................................2-7
Door Locks ....................................................2-7
Power Door Locks ..........................................2-7
Delayed Locking .............................................2-8
Automatic Door Locks .....................................2-8
Programmable Automatic Door Unlock ...............2-8
Rear Door Security Locks ................................2-8
Lockout Protection ..........................................2-9
Trunk ............................................................2-9
Windows ........................................................2-11
Manual Windows ..........................................2-11
Power Windows ............................................2-12
Sun Visors ...................................................2-13
Theft-Deterrent Systems ..................................2-13
Content Theft-Deterrent .................................2-13
Passlock
®
....................................................2-15
Starting and Operating Your Vehicle ................2-15
New Vehicle Break-In ....................................2-15
Ignition Positions ..........................................2-16
Retained Accessory Power (RAP) ...................2-18
Starting the Engine .......................................2-18
Engine Coolant Heater ..................................2-19
Automatic Transaxle Operation .......................2-20
Manual Transaxle Operation ...........................2-23
Parking Brake ..............................................2-24
Shifting Into Park (P) (Automatic Transaxle) ......2-25
Shifting Out of Park (P)
(Automatic Transaxle) ................................2-26
Parking Your Vehicle .....................................2-27
Parking Over Things That Burn .......................2-27
Engine Exhaust ............................................2-28
Running the Engine While Parked ...................2-28
Mirrors ...........................................................2-29
Manual Rearview Mirror .................................2-29
Automatic Dimming Rearview Mirror ................2-29
Outside Manual Mirror ...................................2-29
Outside Remote Control Mirror .......................2-30
Outside Power Mirrors ...................................2-30
Outside Convex Mirror ...................................2-31
®
OnStar
Storage Areas ................................................2-33
System .............................................2-31
Glove Box ...................................................2-33
Cupholder(s) ................................................2-33
Center Console Storage Area .........................2-33
Driver’s Storage Compartment ........................2-33
Convenience Net ..........................................2-33
Sunroof .........................................................2-34
2-1
Page 66

Keys
{CAUTION:
Leaving children in a vehicle with the ignition
key is dangerous for many reasons. They could
operate the power windows or other controls or
even make the vehicle move. The children or
others could be badly injured or even killed.
Do not leave the keys in a vehicle with children.
2-2
Page 67

One key is used for the
ignition, the doors and all
other locks.
When a new vehicle is delivered, the dealer removes
the key tag from the key and gives it to the first owner.
Each tag has a code on it that tells your dealer or a
qualified locksmith how to make extra keys. Keep the
tag in a safe place. If you lose your key, you will be able
to have a new one made easily using the tag.
If you need a new key, contact your dealer who can
obtain the correct key code. See Roadside Assistance
Program on page 7-6 for more information.
Notice: If you ever lock your keys in your vehicle,
you may have to damage the vehicle to get in.
Be sure you have spare keys.
If your vehicle is equipped with the OnStar
an active subscription and you lock your keys inside
the vehicle, OnStar
®
may be able to send a command to
®
system with
unlock your vehicle. See OnStar®System on page 2-31
for more information.
Remote Keyless Entry System
If equipped, the keyless entry system operates on a
radio frequency subject to Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) Rules and with Industry Canada.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device.
This device complies with RSS-210 of Industry Canada.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device.
2-3
Page 68

Changes or modifications to this system by other than
an authorized service facility could void authorization to
use this equipment.
At times you may notice a decrease in range. This is
normal for any remote keyless entry system. If the
transmitter does not work or if you have to stand closer
to your vehicle for the transmitter to work, try this:
• Check the distance. You may be too far from your
vehicle. You may need to stand closer during
rainy or snowy weather.
• Check the location. Other vehicles or objects may
be blocking the signal. Take a few steps to the
left or right, hold the transmitter higher, and
try again.
• Check to determine if battery replacement is
necessary. See “Battery Replacement” under
Remote Keyless Entry System Operation on
page 2-4.
• If you are still having trouble, see your dealer or a
qualified technician for service.
Remote Keyless Entry System Operation
If your vehicle has this feature, the vehicle’s doors
can be locked and unlocked, and the trunk can
be unlocked from about 3 feet (1 m) up to 60 feet (18 m)
away with the remote keyless entry transmitter.
If you notice a decrease in the operating range of the
transmitter, see Remote Keyless Entry System on
page 2-3 for information regarding conditions which may
affect the transmitter’s performance.
The following functions are
available with the remote
keyless entry system.
2-4
Page 69

Q (Lock): Press the lock button to lock all the doors.
If enabled through the Driver Information Center
(DIC), the remote lock feedback can be programmed to
have the horn chirp and/or the parking lamps flash
when the remote keyless entry transmitter is used to
lock the vehicle’s doors. See “LOCK HORN” and
“LIGHT FLASH” under DIC Vehicle Personalization on
page 3-38 for more information.
Pressing the lock button may arm the content
theft-deterrent system. See Content Theft-Deterrent
on page 2-13.
" (Unlock): Press the unlock button one time to unlock
the driver’s door. Press the unlock button again within
five seconds to unlock the other doors. The interior
lamps will come on and stay on for 20 seconds or until
the ignition is turned on. If enabled through the DIC,
the remote unlock feedback can be programmed to have
the horn chirp and/or the parking lamps flash when
the remote keyless entry transmitter is used to unlock
the vehicle’s doors. See “UNLOCK HORN” and
“LIGHT FLASH” under DIC Vehicle Personalization
on page 3-38 for more information.
If enabled through the DIC, and it is dark enough
outside, the vehicle’s high-beam headlamps, parking
lamps, and back-up lamps will come on each time
the unlock button on the transmitter is pressed.
These exterior lamps will stay on for 20 seconds, or
until a door is opened. See “EXT (Exterior) LIGHTS”
under DIC Vehicle Personalization on page 3-38.
Pressing the unlock button on the remote keyless entry
transmitter will disarm the content-theft deterrent
system. See Content Theft-Deterrent on page 2-13
for more details.
V (Remote Trunk Release): The trunk will open
when this button on the transmitter is pressed and held
for approximately one second. You can open the
trunk with the transmitter when the vehicle is stationary.
L (Vehicle Locator/Panic Alarm): This button
may be used to help locate your vehicle. The horn will
sound three times and the headlamps and parking
lamps will flash three times. Press and hold the button
for three seconds to sound the panic alarm. The horn
will sound and the headlamps and parking lamps
will flash for 30 seconds. Press the button again to
cancel the panic alarm.
2-5
Page 70

Matching Transmitter(s) to Your Vehicle
Each remote keyless entry transmitter is uniquely coded
to prevent another transmitter from unlocking the
vehicle. If a transmitter is lost or stolen, a replacement
can be purchased through your GM dealer. Remember
to bring any additional transmitters with you when
you go to your dealer. The vehicle can have a maximum
of four transmitters matched to it.
Battery Replacement
Under normal use, the battery in the remote keyless
entry transmitter should last about four years.
You can tell the battery is weak if the transmitter will
not work, at the normal range, in any location.
If you have to get close to your vehicle before the
transmitter works, it is probably time to change the
battery. The KEY FOB BATT LOW message in the
vehicle’s DIC will display, if the remote keyless entry
transmitter battery is low.
Notice: When replacing the battery, use care not to
touch any of the circuitry. Static from your body
transferred to these surfaces may damage the
transmitter.
To replace the battery do the following:
1. Insert a flat object with a thin edge into the notch,
located below the Vehicle Locator/Panic Alarm
button, and pry the front and back apart.
2. Remove the old battery, but do not use a metal
object to do this.
3. Slide the new battery into the transmitter with the
positive side of the battery facing up. Use a type
CR2032 battery, or equivalent type.
4. Snap the front and the back of the transmitter
together.
5. Test the operation of the transmitter with the
vehicle.
2-6
Page 71

Doors and Locks
Door Locks
{CAUTION:
Unlocked doors can be dangerous.
• Passengers — especially children — can
easily open the doors and fall out of a
moving vehicle. When a door is locked,
the handle will not open it. You increase
the chance of being thrown out of the
vehicle in a crash if the doors are not
locked. So, wear safety belts properly and
lock the doors whenever you drive.
• Young children who get into unlocked
vehicles may be unable to get out. A child
can be overcome by extreme heat and can
suffer permanent injuries or even death
from heat stroke. Always lock your vehicle
whenever you leave it.
• Outsiders can easily enter through an
unlocked door when you slow down or
stop your vehicle. Locking your doors
can help prevent this from happening.
There are several ways to lock and unlock your vehicle.
To lock the driver’s door from the outside, turn the
key clockwise. To unlock the door, turn the key
counterclockwise.
You can also use the remote keyless entry transmitter
to lock and unlock the doors.
From the inside, use the manual lock knobs on each
door or the power door lock switch to lock and unlock
all doors.
Power Door Locks
Your vehicle may have
power door locks. If so,
they are located on
the driver’s and front
passenger’s door armrest.
Press the right side of the switch with the lock symbol to
lock the doors. Press the left side of the switch with
the unlock symbol to unlock the doors.
2-7
Page 72

Delayed Locking
The delayed locking feature will delay the actual locking
of the doors for up to five seconds after exiting the
vehicle when the power door lock switch or remote
keyless entry transmitter is used to lock the vehicle.
If any door is open when locking the vehicle, three
chimes will sound signaling that the delayed locking
feature is active. Five seconds after the last door
is closed, all of the doors will lock and the turn signal
lamps will flash. To cancel the delay and lock the doors
immediately, press the lock button a second time.
If the key is in the ignition this feature will not lock
the doors.
You can disable this function through the Driver
Information Center (DIC). See DIC Vehicle
Personalization on page 3-38.
Automatic Door Locks
With this feature, the doors will automatically lock when
the shift lever is moved out of PARK (P) for a vehicle
with an automatic transmission, or the speed is greater
than 5 mph (8 km/h) for a vehicle with a manual
transmission.
The automatic door locking feature cannot be disabled.
Programmable Automatic Door Unlock
Your vehicle can be programmed through the Driver
Information Center (DIC) to automatically unlock several
ways. See DIC Vehicle Personalization on page 3-38
for more information.
Rear Door Security Locks
Your vehicle has rear door security locks that prevent
passengers from opening the rear doors from the inside.
The rear door security
locks are located on the
inside edge of each
rear door. You must
open the rear doors to
access them.
2-8
Page 73

To set the locks, do the following:
1. Insert the key into the security lock slot and turn it
so the slot is in the horizontal position.
2. Close the door.
When you want to open a rear door when the security
lock is on, do the following:
1. Unlock the door using the remote keyless entry
transmitter, the power door lock switch, or by
lifting the rear door manual lock.
2. Open the door from the outside.
To cancel the rear door security lock, do the following:
1. Unlock the door and open it from the outside.
2. Insert the key into the security lock slot and turn it
so the slot is in the vertical position.
Lockout Protection
If you press the power door lock switch when the key is
in the ignition and any door is open, all the doors will
lock and the driver’s door will unlock. Be sure to remove
the key from the ignition when locking your vehicle.
The lockout protection can be overridden by pressing
and holding the power door lock in the lock position for
three seconds.
Trunk
To release the trunk lid from the outside, use the key or
the remote keyless entry transmitter.
{CAUTION:
It can be dangerous to drive with the trunk lid
open because carbon monoxide (CO) gas can
come into your vehicle. You cannot see or
smell CO. It can cause unconsciousness and
even death. If you must drive with the trunk lid
open or if electrical wiring or other cable
connections must pass through the seal
between the body and the trunk lid:
• Make sure all other windows are shut.
• Turn the fan on your heating or cooling
system to its highest speed and select the
control setting that will force outside air
into your vehicle. See Climate Control
System in the Index.
• If you have air outlets on or under the
instrument panel, open them all the way.
See Engine Exhaust on page 2-28.
2-9
Page 74

Remote Trunk Release
To open the trunk from
inside the vehicle, press
the remote trunk release
button located inside
the driver’s storage
compartment located on
the lower left side of
the instrument panel.
See Instrument Panel Overview on page 3-4 or Driver’s
Storage Compartment on page 2-33.
The remote trunk release will only work when either the
ignition is in OFF or ACC, or the vehicle speed is
less than 2 mph (3 km/h).
Emergency Trunk Release Handle
Notice: Do not use the emergency trunk release
handle as a tie-down or anchor point when securing
items in the trunk as it could damage the handle.
The emergency trunk release handle is only
intended to aid a person trapped in a latched trunk,
to open the trunk from the inside.
There is a glow-in-the-dark emergency trunk release
handle located on the inside of the trunk lid of your
vehicle. This handle will glow following exposure to light.
Pull the release handle and push the trunk lid open
from the inside to open the trunk.
2-10
Page 75

Windows
{CAUTION:
Leaving children, helpless adults, or pets in a
vehicle with the windows closed is dangerous.
They can be overcome by the extreme heat
and suffer permanent injuries or even death
from heat stroke. Never leave a child,
a helpless adult, or a pet alone in a vehicle,
especially with the windows closed in warm
or hot weather.
Manual Windows
If your vehicle has manual windows, use the window
crank to open and close each window.
2-11
Page 76

Power Windows
If your vehicle has power windows, the switches on the
driver’s door armrest control each of the windows.
In addition, each passenger’s door has a window switch
that controls that door’s window. Press the front of
the switch to open the window. Pull up the switch to
close it.
Express-Down Window
The driver’s window switch has an express-down
feature which allows the window to be lowered fully
without continuously pressing the switch. This switch is
labeled AUTO. Press the front of the switch to the
first position, and the driver’s window will open a small
amount. Press the switch down fully and the window
will go all the way down.
To stop the window while it is lowering, pull the front of
the switch.
Window Lockout
(Window Lockout): The driver’s window controls
o
also include a lockout switch. Press the right side of the
switch to prevent the rear passengers from using
their window switches. The driver can still control all the
windows with the lockout on. Press the switch to the
left to return to normal window operation. A red bar on
the right side of the switch indicates that the lockout
feature is off.
2-12
Page 77

Sun Visors
To block out glare, swing down the visor(s). The visors
can also be detached from the center mount and
swung to the side to cover the windows.
Visor Vanity Mirror
Your vehicle may have a driver’s side vanity mirror.
Swing down the sun visor and lift the cover to expose
the mirror.
Theft-Deterrent Systems
Vehicle theft is big business, especially in some cities.
Although your vehicle has a number of theft-deterrent
features, we know that nothing we put on it can make it
impossible to steal.
Content Theft-Deterrent
Your vehicle may have a
content theft-deterrent
alarm system.
Arming the System
With the ignition off, you can arm the system by doing
any one of the following:
• Press the remote keyless entry transmitter
lock button.
• Press the power door lock switch while the driver’s
door is open.
The system will arm after either of these things occur:
• Thirty seconds after all the doors are closed.
• Sixty seconds with any door open.
If you press the lock button on the transmitter a second
time while all the doors are closed, the system will
arm immediately. The system will still arm in 60 seconds
if a door is open. When the open door is closed, it will
also become armed.
The security light, located on the instrument panel
cluster, will turn on to indicate that arming has been
initiated. Once the system is armed, the security light
will flash once every three seconds.
If the security light is flashing twice per second,
this means that a door is open.
If you do not want to arm the system, you may lock the
car with the manual lock knobs on the doors.
2-13
Page 78

Disarming the System
You can disarm the system by doing any one of the
following:
• Press the remote keyless entry transmitter unlock
button.
• Turn the ignition on.
If the system is armed and the trunk is opened using
the trunk release button on the transmitter, the system
will temporarily disarm itself and re-arm when the
trunk has been closed. This allows the you to exit the
vehicle, lock the doors using the transmitter, and
open the trunk using the transmitter without having to
disarm and re-arm the system.
Once the system is disarmed, the security light will
stop flashing.
How the System Alarm is Activated
If the system is armed, it can be activated by either:
• Opening the driver’s door or trunk. This will cause
a ten second pre-alarm chirp followed by a
thirty second full alarm of horn and lights.
• Opening any other door. This will immediately
cause a full alarm of horn and lights for
thirty seconds.
When an alarm event has finished, the system will
re-arm itself automatically.
How to Turn Off the System Alarm
To turn off the system alarm, do one of the following:
• Press the lock button on the remote keyless
entry transmitter. The system will then re-arm itself.
• Press the unlock button on the remote keyless entry
transmitter. This will also disarm the system.
• Insert the key in the ignition and turn it on. This will
also disarm the system.
Simulated Armed Mode
If you choose not to arm the system or if proper arming
cannot be completed, the Content Theft Deterrent
system will flash the security light once every
three seconds after a one minute delay with all the
doors closed. This flashing serves as a visual deterrent;
however, the system is not armed.
How to Detect a Tamper Condition
If you hear three chirps when you press the unlock,
lock, or trunk release buttons on the remote keyless
transmitter, it means that the content theft security
system alarm was activated previously.
Passive Arming
If passive arming is enabled through the Driver
Information Center (DIC), the system will arm itself
60 seconds after cycling the ignition off and closing
all doors.
2-14
Page 79

Passlock
Your vehicle is equipped with the Passlock
theft-deterrent system.
Passlock
enables fuel if the ignition lock cylinder is turned with
a valid key. If a correct key is not used or the ignition
lock cylinder is tampered with, fuel is disabled.
During normal operation, the security light will go off
approximately three seconds after the key is turned to
RUN following an engine start. The security light is
located on the instrument panel cluster. See Instrument
Panel Cluster on page 3-22.
If the engine stalls and the security light flashes, wait
until the light stops flashing before trying to restart
the engine. Remember to release the key from START
as soon as the engine starts.
If the engine is running and the security light comes on,
you will be able to restart the engine if you turn the
engine off. However, your Passlock
not working properly and must be serviced by your
dealer. Your vehicle is not protected by Passlock
time. See your dealer for service. Or see Roadside
Assistance Program on page 7-6 for more information.
You may also want to check the fuses. See Fuses
and Circuit Breakers on page 5-81.
®
®
®
is a passive theft-deterrent system. Passlock
®
system is
®
at this
Starting and Operating Your Vehicle
®
New Vehicle Break-In
Notice: Your vehicle does not need an elaborate
break-in. But it will perform better in the long run if
you follow these guidelines:
• Do not drive at any one speed, fast or slow,
for the first 500 miles (805 km). Do not make
full-throttle starts.
• Avoid making hard stops for the first 200 miles
(322 km) or so. During this time your new brake
linings are not yet broken in. Hard stops with new
linings can mean premature wear and earlier
replacement. Follow this breaking-in guideline
every time you get new brake linings.
• Do not tow a trailer during break-in. See Towing a
Trailer (Manual Transaxle) on page 4-38 or
Towing a Trailer (Automatic Transaxle) on
page 4-38 for more information.
2-15
Page 80

Ignition Positions
With the key in the ignition switch, you can turn it to
four different positions.
Notice: Using a tool to force the key from the
ignition switch could cause damage or break the
key. Use the correct key and turn the key only with
your hand. Make sure the key is all the way in.
If it is, turn the steering wheel left and right while
you turn the key hard. If none of this works,
then your vehicle needs service.
9(LOCK): This position locks your steering column. It
is a theft-deterrent feature. You will only be able to
remove your key when the ignition is turned to LOCK.
If you have an automatic transaxle, the ignition
switch cannot be turned to LOCK unless the shift lever
is in PARK (P).
{CAUTION:
If you have a manual transaxle removing the key
from the ignition switch will lock the steering
column and result in a loss of ability to steer the
vehicle. This could cause a collision. If you
need to turn the engine off while the vehicle
is moving, turn the key to ACC.
ACC (ACCESSORY): This position operates some of
your electrical accessories. It unlocks the steering wheel
and ignition.
R (RUN): This is the position the switch returns to after
you start your engine and release the switch. The switch
stays in the RUN position when the engine is running.
But even when the ignition is not running, you can
use RUN to operate your electrical accessories and to
display some warning and indicator lights.
/ (START): This position starts the engine. When the
engine starts, release the key. The ignition switch will
return to RUN for normal driving.
A warning tone will sound if you open the driver’s door
when the key has not been removed from the ignition.
2-16
Page 81

Shift Lock Release
The following procedure allows the ignition to be turned
to LOCK and for ignition key removal in case of a
dead battery or low voltage battery.
1. Make sure the shift lever is in PARK (P).
2. Using a tool, pry off the cover from the bottom of
the steering column.
3. Place your finger into the access hole and locate
the plunger.
4. Press and hold the plunger toward the driver’s
door while turning the ignition key to LOCK.
Remove the key.
Have your vehicle serviced at your GM dealer as soon
as possible.
2-17
Page 82

Retained Accessory Power (RAP)
Your vehicle is equipped with a Retained Accessory
Power (RAP) feature which will allow the radio, power
windows and sunroof to continue to work up to
10 minutes after the ignition is turned off.
Your vehicle’s radio will work when the ignition key is in
RUN or ACC. Once the key is turned off, the radio,
power windows and sunroof will continue to work for up
to 10 minutes or until any door is opened.
Starting the Engine
Automatic Transaxle
Move your shift lever to PARK (P) or NEUTRAL (N).
Your engine will not start in any other position — that is
a safety feature. To restart when you are already
moving, use NEUTRAL (N) only.
Notice: Shifting into PARK (P) with the vehicle
moving could damage the transaxle. Shift into
PARK (P) only when your vehicle is stopped.
Manual Transaxle
The shift lever should be in NEUTRAL and the parking
brake engaged. Hold the clutch pedal to the floor
and start the engine. Your vehicle will not start if the
clutch pedal is not all the way down — that is a safety
feature.
Starting Procedure
1. With your foot off the accelerator pedal, turn your
ignition to START. When the engine starts, let go
of the key. The idle speed will go down as your
engine gets warm.
Notice: Holding your key in START for longer than
15 seconds at a time will cause your battery to
be drained much sooner. And the excessive heat
can damage your starter motor. Wait about
15 seconds between each try to help avoid draining
your battery or damaging your starter.
2. If it does not start, wait about 15 seconds and try
again to start the engine by turning the ignition to
START. Wait about 15 seconds between each try.
When your engine has run about 10 seconds to
warm up, your vehicle is ready to be driven. Do not
run your engine at high speed when it is cold.
If the weather is below freezing (32°F or 0°C),
let the engine run for a few minutes to warm up.
2-18
Page 83

3. If your engine still will not start, or starts but then
stops, it could be flooded with too much gasoline.
Try pushing your accelerator pedal all the way to the
floor and holding it there as you hold the key in
START for about three seconds. If the vehicle starts
briefly but then stops again, do the same thing,
but this time keep the pedal down for five or
six seconds. This clears the extra gasoline from
the engine.
Notice: Your engine is designed to work with the
electronics in your vehicle. If you add electrical
parts or accessories, you could change the way the
engine operates. Before adding electrical equipment,
check with your dealer. If you do not, your engine
might not perform properly. Any resulting damage
would not be covered by your vehicle’s warranty.
Engine Coolant Heater
Your vehicle has this feature, in very cold weather
0°F (−18°C) or colder, the engine coolant heater can
help. You will get easier starting and better fuel economy
during engine warm-up. Usually, the coolant heater
should be plugged in a minimum of four hours prior to
starting your vehicle. At temperatures above 32°F (0°C),
use of the coolant heater is not required.
To Use the Engine Coolant Heater
1. Turn off the engine.
2. Open the hood and unwrap the electrical cord.
The electrical cord is located in front of the
engine coolant surge tank on the passenger’s side.
3. Plug it into a normal, grounded 110-volt AC outlet.
{CAUTION:
Plugging the cord into an ungrounded outlet
could cause an electrical shock. Also, the
wrong kind of extension cord could overheat
and cause a fire. You could be seriously
injured. Plug the cord into a properly grounded
three-prong 110-volt AC outlet. If the cord will
not reach, use a heavy-duty three-prong
extension cord rated for at least 15 amps.
4. Before starting the engine, be sure to unplug and
store the cord as it was before to keep it away
from moving engine parts. If you do not, it could
be damaged.
2-19
Page 84

How long should you keep the coolant heater plugged
in? The answer depends on the outside temperature, the
kind of oil you have, and some other things. Instead
of trying to list everything here, we ask that you contact
your dealer in the area where you will be parking
your vehicle. The dealer can give you the best advice
for that particular area.
PARK (P): This position locks your front wheels. It is
the best position to use when you start your engine
because your vehicle cannot move easily.
{CAUTION:
Automatic Transaxle Operation
If your vehicle is equipped with an automatic transaxle,
the shift lever is located on the console between
the seats.
There are several different positions for your shift lever.
2-20
It is dangerous to get out of your vehicle if the
shift lever is not fully in PARK (P) with the
parking brake firmly set. Your vehicle can roll.
Do not leave your vehicle when the engine is
running unless you have to. If you have left the
engine running, the vehicle can move suddenly.
You or others could be injured. To be sure your
vehicle will not move, even when you are on
fairly level ground, always set your parking
brake and move the shift lever to PARK (P).
See Shifting Into Park (P) (Automatic Transaxle)
on page 2-25. If you are pulling a trailer, see
Towing a Trailer (Manual Transaxle) on
page 4-38 or Towing a Trailer (Automatic
Transaxle) on page 4-38.
Page 85

Ensure the shift lever is fully in PARK (P) before
starting the engine. Your vehicle has an automatic
transaxle shift lock control system. You have to
fully apply your regular brakes before you can shift
from PARK (P) when the ignition key is in RUN. If you
cannot shift out of PARK (P), ease pressure on the shift
lever by pushing the shift lever all the way into
PARK (P), or by releasing the shift lever button on floor
shift console models as you maintain brake application.
Then move the shift lever into the gear
you want. Press the shift lever button before
moving the shift lever. See Shifting Out of Park (P)
(Automatic Transaxle) on page 2-26.
REVERSE (R): Use this gear to back up.
Notice: Shifting to REVERSE (R) while your vehicle
is moving forward could damage the transaxle.
The repairs would not be covered by your warranty.
Shift to REVERSE (R) only after your vehicle is
stopped.
To rock your vehicle back and forth to get out of snow,
ice or sand without damaging your transaxle, see
If Your Vehicle is Stuck in Sand, Mud, Ice or Snow on
page 4-29.
NEUTRAL (N): In this position, your engine does not
connect with the wheels. To restart when you are
already moving, use NEUTRAL (N) only. Also, use
NEUTRAL (N) when your vehicle is being towed.
{CAUTION:
Shifting into a drive gear while your engine is
running at high speed is dangerous. Unless
your foot is firmly on the brake pedal, your
vehicle could move very rapidly. You could
lose control and hit people or objects. Do not
shift into a drive gear while your engine is
running at high speed.
Notice: Shifting out of PARK (P) or NEUTRAL (N)
while the engine is running at high speed may
damage the transaxle. The repairs would not be
covered by your warranty. Be sure the engine is not
running at high speeds when shifting your vehicle.
2-21
Page 86

AUTOMATIC OVERDRIVE (D): This position is for
normal driving with the automatic transaxle. If you need
more power for passing, and you are:
• Going less than about 35 mph (55 km/h), push your
accelerator pedal about halfway down.
• Going about 35 mph (55 km/h), push your
accelerator all the way down.
SECOND (2): This position is also used for normal
driving. However, it offers braking from the engine for
slight downgrades where the vehicle would otherwise
accelerate due to steepness of grade. If repetitive shifts
occur between third and fourth gears on steep uphills,
this position can be used to prevent repetitive shifting.
Fuel economy will be lower than AUTOMATIC
OVERDRIVE (D). Here are some times you might
choose SECOND (2) instead of AUTOMATIC
OVERDRIVE (D):
• When driving on hilly, winding roads.
• When towing a trailer, so there is less shifting
between gears.
FIRST (1): This position holds you in the lowest gear
possible for the given vehicle speed. It provides
more engine braking but lower fuel economy than
SECOND (2). You can use it on very steep hills as a
brake assist, or in deep snow or mud.
Notice: Spinning the tires or holding the vehicle
in one place on a hill using only the accelerator
pedal may damage the transaxle. If you are stuck,
do not spin the tires. When stopping on a hill,
use the brakes to hold the vehicle in place.
2-22
Page 87

Manual Transaxle Operation
This is your shift pattern.
Here is how to operate your manual transaxle:
FIRST (1): Press the clutch pedal and shift into
FIRST (1). Then, slowly let up on the clutch pedal as
you press the accelerator pedal.
You can shift into FIRST (1) when you are going less
than 20 mph (32 km/h). If you have come to a complete
stop and it is hard to shift into FIRST (1), put the shift
lever in NEUTRAL and let up on the clutch. Press
the clutch pedal back down. Then shift into FIRST (1).
SECOND (2): Press the clutch pedal as you let up on
the accelerator pedal and shift into SECOND (2).
Then, slowly let up on the clutch pedal as you press the
accelerator pedal.
THIRD (3), FOURTH (4) and FIFTH (5): Shift into
THIRD (3), FOURTH (4) and FIFTH (5) the same way
you do for SECOND (2). Slowly let up on the clutch
pedal as you press the accelerator pedal.
To stop, let up on the accelerator pedal and press the
brake pedal. Just before the vehicle stops, press the
clutch pedal and the brake pedal, and shift to NEUTRAL.
NEUTRAL: Use this position when you start or idle
your engine.
REVERSE (R): To back up, press down the clutch
pedal and shift into REVERSE (R). Let up on the clutch
pedal slowly while pressing the accelerator pedal.
Notice: Shifting to REVERSE (R) while your vehicle
is moving forward could damage the transaxle.
The repairs would not be covered by your warranty.
Shift to REVERSE (R) only after your vehicle is
stopped.
Also, use REVERSE (R), along with the parking brake,
for parking your vehicle.
2-23
Page 88

Parking Brake
Manual Shift
Automatic Shift
The parking brake lever is located between the
front seats.
For vehicles equipped with an armrest, lift the console
armrest in order to access the parking brake lever.
2-24
Page 89

To set the parking brake, Hold the brake pedal down
and pull up on the parking brake lever. If the ignition
is on, the brake system warning light will come on.
See Brake System Warning Light on page 3-25.
To release the parking brake, hold the brake pedal
down. Pull the parking brake lever up until you can press
the release button. Hold the release button in as you
move the brake lever all the way down.
If you forget to release your parking brake, a chime will
sound and a warning light will flash when the parking
brake is applied and the vehicle is moving faster
than 5 mph (8 kph). See DIC Warnings and Messages
on page 3-36.
Notice: Driving with the parking brake on can
overheat the brake system and cause premature
wear or damage to brake system parts. Verify that
the parking brake is fully released and the brake
warning light is off before driving.
Shifting Into Park (P) (Automatic Transaxle)
{CAUTION:
It can be dangerous to get out of your vehicle
if the shift lever is not fully in PARK (P) with
the parking brake firmly set. Your vehicle can
roll. If you have left the engine running, the
vehicle can move suddenly. You or others
could be injured. To be sure your vehicle will
not move, even when you are on fairly level
ground, use the steps that follow. If you are
pulling a trailer, see Towing a Trailer (Manual
Transaxle) on page 4-38 or Towing a Trailer
(Automatic Transaxle) on page 4-38.
Hold the brake pedal down and set the parking brake.
1.
2. Move the shift lever into PARK (P) by holding the
button on the shift lever and pushing the lever all
the way toward the front of the vehicle.
3. Turn the ignition key to LOCK.
4. Remove the key and take it with you. If you can
leave your vehicle with the ignition key in your
hand, your vehicle is in PARK (P).
2-25
Page 90

Leaving Your Vehicle With the
Engine Running
{CAUTION:
It can be dangerous to leave your vehicle with
the engine running. Your vehicle could move
suddenly if the shift lever is not fully in
PARK (P) with the parking brake firmly set.
And, if you leave the vehicle with the engine
running, it could overheat and even catch fire.
You or others could be injured. Do not leave
your vehicle with the engine running.
If you have to leave your vehicle with the engine
running, be sure your vehicle is in PARK (P) and your
parking brake is firmly set before you leave it. After you
have moved the shift lever into PARK (P), hold the
regular brake pedal down. Then, see if you can move
the shift lever away from PARK (P) without first pushing
the button. If you can, it means that the shift lever
was not fully locked into PARK (P).
Torque Lock
If you are parking on a hill and you do not shift your
transaxle into PARK (P) properly, the weight of the
vehicle may put too much force on the parking pawl in
the transaxle. You may find it difficult to pull the shift
lever out of PARK (P). This is called “torque lock.”
To prevent torque lock, set the parking brake and then
shift into PARK (P) properly before you leave the
driver’s seat. To find out how, see Shifting Into Park (P)
(Automatic Transaxle) on page 2-25.
When you are ready to drive, move the shift lever out of
PARK (P) before you release the parking brake.
If torque lock does occur, you may need to have another
vehicle push yours a little uphill to take some of the
pressure from the parking pawl in the transaxle, so you
can pull the shift lever out of PARK (P).
Shifting Out of Park (P) (Automatic Transaxle)
This vehicle is equipped with an electronic shift lock
release system. The shift lock release is designed to:
• Prevent ignition key removal unless the shift lever
is in PARK (P) with the shift lever button fully
released, and
• prevent movement of the shift lever out of PARK (P)
unless the ignition is in a position other than LOCK.
2-26
Page 91

The shift lock release is always functional except in
the case of a an uncharged or low voltage (less than
9 volt) battery.
If your vehicle has an uncharged battery or a battery
with low voltage, try charging or jump starting the
battery. See Jump Starting on page 5-33 for more
information.
If you still cannot move the shift lever from PARK (P),
consult your dealer or a professional towing service.
Parking Your Vehicle
Before leaving your vehicle, fully press the clutch pedal
in, move the shift lever into REVERSE (R), and firmly
apply the parking brake. Once the shift lever has
been placed in REVERSE (R) with the clutch pedal
pressed in, you can turn the ignition key to LOCK,
remove the key and release the clutch. See Manual
Transaxle Operation on page 2-23.
Parking Over Things That Burn
{CAUTION:
Things that can burn could touch hot exhaust
parts under your vehicle and ignite. Do not
park over papers, leaves, dry grass or other
things that can burn.
2-27
Page 92

Engine Exhaust
{CAUTION:
Running the Engine While Parked
It is better not to park with the engine running. But if you
ever have to, here are some things to know.
Engine exhaust can kill. It contains the gas
carbon monoxide (CO), which you cannot see or
smell. It can cause unconsciousness and death.
You might have exhaust coming in if:
• Your exhaust system sounds strange or
different.
• Your vehicle gets rusty underneath.
• Your vehicle was damaged in a collision.
• Your vehicle was damaged when driving
over high points on the road or over
road debris.
• Repairs were not done correctly.
• Your vehicle or exhaust system had been
modified improperly.
If you ever suspect exhaust is coming into your
vehicle:
• Drive it only with all the windows down to
blow out any CO; and
• Have your vehicle fixed immediately.
2-28
{CAUTION:
Idling the engine with the climate control
system off could allow dangerous exhaust into
your vehicle. See the earlier caution under
Engine Exhaust on page 2-28.
Also, idling in a closed-in place can let deadly
carbon monoxide (CO) into your vehicle even if
the climate control fan is at the highest setting.
One place this can happen is a garage.
Exhaust — with CO — can come in easily.
NEVER park in a garage with the engine
running.
Another closed-in place can be a blizzard. See
Winter Driving on page 4-25.
Page 93

{CAUTION:
It can be dangerous to get out of your vehicle
if the shift lever is not fully in PARK (P) with
the parking brake firmly set. Your vehicle can
roll. Do not leave your vehicle when the engine
is running unless you have to. If you have left
the engine running, the vehicle can move
suddenly. You or others could be injured. To
be sure your vehicle will not move, even when
you are on fairly level ground, always set your
parking brake and move the shift lever to
PARK (P).
Follow the proper steps to be sure your vehicle will not
move. See Shifting Into Park (P) (Automatic Transaxle)
on page 2-25.
If you are parking on a hill and if you are pulling a
trailer, also see Towing a Trailer (Manual Transaxle) on
page 4-38 or Towing a Trailer (Automatic Transaxle)
on page 4-38.
Mirrors
Manual Rearview Mirror
To reduce glare from lamps behind you, move the lever
toward you to the night position.
Automatic Dimming Rearview Mirror
The automatic dimming rearview mirror automatically
dims to the proper level to minimize glare from
lights behind you after dark.
Outside Manual Mirror
Adjust your outside mirror so you can just see the side
of your vehicle and have a clear view of objects behind
you. The mirror can be folded in to enter narrow areas.
2-29
Page 94

Outside Remote Control Mirror
Outside Power Mirrors
Adjust the driver’s outside
mirror with the control
lever located on the
driver’s door.
Adjust the outside mirrors so that the side of the vehicle
can be seen while sitting in a comfortable driving
position.
To adjust the passenger’s outside mirror, sit in the
driver’s seat and have a passenger adjust the mirror
for you. The mirror is a manual fold design.
2-30
The controls for the
outside power mirrors,
are located on the driver’s
door armrest.
Move the selector switch located below the four-way
control pad to the left or right to choose either the
driver’s side or passenger’s side mirror. To adjust a
mirror, use the arrows located on the four-way control
pad to move the mirror in the desired direction.
Adjust each outside mirror so that a little of the vehicle
and the area behind it can be seen while sitting in a
comfortable driving position. Keep the selector switch
in the center position when not adjusting either
outside mirror.
Page 95

Both mirrors can manually be folded by pulling them
toward the vehicle. This feature may be useful
when going through a car wash or a confined space.
Push the mirrors away from the vehicle, to the normal
position, before driving.
Outside Convex Mirror
{CAUTION:
A convex mirror can make things (like other
vehicles) look farther away than they really are.
If you cut too sharply into the right lane, you
could hit a vehicle on your right. Check your
inside mirror or glance over your shoulder
before changing lanes.
The passenger’s side mirror is convex. A convex
mirror’s surface is curved so more can be seen from
the driver’s seat. It also makes things appear farther
away than they really are.
OnStar®System
OnStar®uses global positioning system (GPS) satellite
technology, wireless communications, and call centers
to provide you with a wide range of safety, security,
information, and convenience services.
A complete OnStar
conditions of the OnStar®Subscription Service
Agreement are included in the vehicle’s glove box
literature. For more information, visit www.onstar.com
or www.onstarcanada.com. Contact OnStar
1-888-4-ONSTAR (1-888-466-7827), or press the
®
OnStar
24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
Terms and conditions of the Subscription Service
Agreement can be found at www.onstar.com or
www.onstarcanada.com.
button to speak to an OnStar®advisor
OnStar®Services
For new vehicles equipped with OnStar®, the Safe and
Sound Plan is included for the first year. You can
extend this plan beyond the first year, or upgrade to the
Directions and Connections Plan to meet your needs.
For more information, press the OnStar
with an advisor.
®
user’s guide and the terms and
®
at
®
button to speak
2-31
Page 96

Safe and Sound Plan
•
Advanced Automatic Collision Notification
• Automatic Notification of Airbag Deployment
• Emergency Services
• Roadside Assistance
• Stolen Vehicle Tracking
• AccidentAssist
• Remote Door Unlock/Vehicle Alert
• Remote Diagnostics
• Online Concierge
Directions and Connections Plan
•
All Safe and Sound Plan Services
• Driving Directions
• RideAssist
• Information and Convenience Services
OnStar®Personal Calling
As an OnStar®subscriber, the Personal Calling
capability is an available hands-free wireless phone that
is integrated into the vehicle. Calls can be placed
nationwide using simple voice commands with no
additional contracts and no additional roaming charges.
To find out more about OnStar
refer to the OnStar®user’s guide in the vehicle’s glove
box or visit www.onstar.com or www.onstarcanada.com;
or speak with an OnStar
®
OnStar
(1-888-466-7827).
button or by calling 1-888-4-ONSTAR
OnStar®Virtual Advisor
Virtual Advisor is a feature of OnStar®Personal Calling
that uses minutes to access up-to-date weather and
traffic reports for your area, news and sports updates,
stock quotes, entertainment and more. Customize
your information profile at www.myonstar.com.
See the OnStar
®
user’s guide for more information.
®
Personal Calling,
®
advisor by pressing the
2-32
Page 97

Storage Areas
Glove Box
Open the glove box by lifting up on the lever. Close the
glove box with a firm push.
Cupholder(s)
There are two cupholders located at the front of the
center console, in front of the shift lever. There are also
cupholder for the rear seat passengers located at the
rear of the center console.
Center Console Storage Area
Your vehicle may have a center console armrest with
storage area. Use the lever on the front of the console
to open it.
Driver’s Storage Compartment
The driver’s storage compartment is located near the
left side of the steering column on the bottom of the
instrument panel. It can be used to store small items and
contains the remote trunk release switch. For more
information, see Remote Trunk Release under Trunk on
page 2-9.
Convenience Net
Your vehicle may have a convenience net. You will see
it inside the back wall of the trunk. Put small loads
behind the net. It can help keep them from falling over
during sharp turns or quick starts and stops.
Unclip a corner of the convenience net to fit larger
objects behind the net, then reclip it to secure them
in place. The net is not for larger, heavier loads.
Store them in the trunk as far forward as you can.
You can unhook the net so that it will lie flat when you
are not using it.
2-33
Page 98

Sunroof
Your vehicle may be
equipped with a power
sunroof. The switch
that operates it is located
on the headliner.
To open or close the sunroof, the ignition must be on,
or turned to ACC, or Retained Accessory Power (RAP)
must be active. See Retained Accessory Power (RAP)
on page 2-18.
Press and hold the switch rearward to open the glass
panel to the vent position. Press and hold the switch
rearward a second time to open the sunroof. If the
sunshade is closed, it will open automatically with
the sunroof.
To close the sunroof, press the switch forward and
hold it until the sunroof is closed. The sunroof will stop
if the switch is released. The sunshade must be
closed manually.
The sunroof glass panel cannot be opened or closed if
the vehicle has an electrical failure.
Notice: If you force the sunshade forward of the
sliding glass panel, damage will occur and the
sunroof may not open or close properly. Always
close the glass panel before closing the sunshade.
2-34
Page 99

Section 3 Instrument Panel
Instrument Panel Overview ...............................3-4
Hazard Warning Flashers ................................3-6
Other Warning Devices ...................................3-6
Horn .............................................................3-6
Tilt Wheel .....................................................3-6
Turn Signal/Multifunction Lever .........................3-7
Turn and Lane-Change Signals ........................3-8
Headlamp High/Low-Beam Changer ..................3-8
Flash-to-Pass .................................................3-8
Windshield Wipers ..........................................3-9
Windshield Washer .......................................3-10
Cruise Control ..............................................3-10
Headlamps ..................................................3-13
Wiper Activated Headlamps ............................3-14
Headlamps on Reminder ................................3-14
Daytime Running Lamps (DRL) .......................3-14
Fog Lamps ..................................................3-15
Instrument Panel Brightness ...........................3-15
Dome Lamp .................................................3-15
Entry/Exit Lighting .........................................3-16
Mirror Reading Lamps ...................................3-16
Battery Run-Down Protection ..........................3-16
Accessory Power Outlets ...............................3-16
Ashtrays and Cigarette Lighter ........................3-17
Climate Controls ............................................3-18
Climate Control System .................................3-18
Outlet Adjustment .........................................3-21
Warning Lights, Gages, and Indicators ............3-21
Instrument Panel Cluster ................................3-22
Speedometer and Odometer ...........................3-23
Tachometer .................................................3-23
Safety Belt Reminder Light .............................3-23
Airbag Readiness Light ..................................3-24
Charging System Light ..................................3-25
Brake System Warning Light ..........................3-25
Anti-Lock Brake System Warning Light .............3-26
Enhanced Traction System Warning Light .........3-27
Engine Coolant Temperature Warning Light ......3-28
Malfunction Indicator Lamp .............................3-28
Oil Pressure Light .........................................3-31
Security Light ...............................................3-32
Fog Lamp Light ............................................3-32
Highbeam On Light .......................................3-32
Fuel Gage ...................................................3-32
Driver Information Center (DIC) .......................3-33
DIC Operation and Displays ...........................3-34
DIC Warnings and Messages .........................3-36
DIC Vehicle Personalization ............................3-38
3-1
Page 100

Section 3 Instrument Panel
Audio System(s) .............................................3-43
Setting the Time for Radios without
Radio Data Systems (RDS) ........................3-44
Setting the Time for Radios with
Radio Data Systems (RDS) ........................3-44
Radio with CD (Base Level) ...........................3-45
Radio with CD (Up Level) ..............................3-49
Radio with CD (MP3) ....................................3-59
3-2
Theft-Deterrent Feature ..................................3-73
Audio Steering Wheel Controls .......................3-74
Radio Reception ...........................................3-74
Care of Your CDs .........................................3-75
Care of the CD Player ...................................3-75
Fixed Mast Antenna ......................................3-75
XM™ Satellite Radio Antenna System .............3-75
 Loading...
Loading...