Page 1

User Manual
V2IU 4350 Converged
Network Appliance
V7.2.2 — May 2007
Page 2

Trademark Information
Polycom®, the Polycom logo design, [and others that appear in your document] are registered trademarks of Polycom,
Inc. [List other trademarks]™ are trademarks of Polycom, Inc. in the United States and various other countries. All other
trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
© 2007 Polycom, Inc. All rights reserved.
Polycom Inc.
4750 Willow Road
Pleasanton, CA 94588-2708
USA
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for
any purpose, without the express written permission of Polycom, Inc. Under the law, reproducing includes translating
into another language or format.
As between the parties, Polycom, Inc. retains title to, and ownership of, all proprietary rights with respect to the software
contained within its products. The software is protected by United States copyright laws and international treaty
provision. Therefore, you must treat the software like any other copyrighted material (e.g. a book or sound recording).
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this manual is accurate. Polycom, Inc. is not responsible
for printing or clerical errors. Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
2 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2–1
The V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
T1 Wide Area Network (WAN) Access Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
VoIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Quality of Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Call Quality Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Future-proof Scalability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Feature Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Front Panel LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
Back Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–4
Physical Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Required Tools and Materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Desktop Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Wall-Mount Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Rack-Mount Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–3
Connecting the Power and Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–4
Administration of the 4350 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–4
3 Configuring the V2IU 4350 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
Configuration Guide For IP Centrex Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–2
Configuration Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–3
Configuration Guide For Station Side IP PBX Applications . . . . . . . . . . . 3–4
Configuration Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–5
Configuration Guide For Trunk Side IP PBX Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–6
Configuration Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–7
Configuration Guide For Hosted Video Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–8
Configuration Guide For Enterprise Video Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–10
1
Page 4

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–12
Configure the LAN Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–12
Configuring VLANs in the 4350 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–13
Modify an Existing VLAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–15
Delete an Existing VLAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–15
Assign the 4350’s ALG to your Priority VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–16
Configure the WAN Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–16
Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–18
Frame Relay Mode and DLCI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–18
Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–19
Payload Loopback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–19
Configure the DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–19
Delete a DHCP IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–21
Disable The DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–21
Configure Hostname, SNMP and Remote Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–22
Configure SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–22
Disable SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–23
Configure Remote System Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–23
Disable Remote System Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–23
Configure a local Hostname . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–24
Enable Mean Opinion Scoring (MOS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–24
Set MOS Threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–24
Change the Administration Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–24
Read-only User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–25
Enabling a Read-only User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–25
Subinterfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–26
How Subinterfaces Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–26
Configuring Subinterfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–27
ToS Byte Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–28
How the ToS Byte Setting Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–28
Viewing or Changing the ToS Byte Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–28
H.323 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–30
H.323 Activity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–35
H.323 Alias Manipulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–35
H.323 Neighboring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–37
Regular Expressions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–39
Forwarding Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–40
How Forwarding Rules Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–40
Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–40
Configuring Forwarding Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–41
Peering Proxy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–43
How Peering Proxy Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–43
2
Page 5

Contents
Configuring Peering Proxy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–47
Adding an H.323 Prefix Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–48
Clients List Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–49
Enabling the Clients List Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–50
H.323 Activity Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–51
Type of Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–52
Call Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–52
Call Termination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–54
Viewing the H.323 Activity Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–55
VoIP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–56
Configure the VoIP ALG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–57
Configure VoIP Subnet Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–59
Enter a VoIP Subnet Route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–60
Delete a VoIP Subnet Route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–60
Configure IP Phones, IADs or Softphones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–61
Data Networking Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–62
NAT for Data Traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–62
Configure Dynamic NAT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–63
Configure Static NAT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–63
Delete a Static NAT entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–64
Static IP routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–64
Configure the static route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–64
Delete the static route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–65
Firewall Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–65
Enable or disable the firewall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–66
Configure Basic settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–66
Configure Advanced Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–66
Remove Advanced Setting Entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–68
Traffic Management Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–68
Enable Traffic Shaping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–69
Optionally enable priority IP addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–70
Enable CAC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–70
Determining the maximum number of concurrent calls . . . . . . 3–71
Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–71
A Closer Look at Traffic Management in the 4350 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–71
Classifying . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–72
Upstream Traffic Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–72
Priority classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–72
Scheduler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–72
Traffic shaper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–72
Downstream Traffic Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–73
3
Page 6

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
4 System Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–1
Viewing Software Version, Hardware Platform and the LAN MAC Address
4–1
Viewing the ALG registration code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–2
Enter the Registration Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–2
Viewing Networking Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–2
Routing Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–3
Link Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–3
Interface Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–3
Viewing Advanced System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–4
System Uptime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–4
Process Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–4
Memory Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–4
System Logging Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–5
Passive Voice Call Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–5
Accessing Troubleshooting Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–5
Verify Registered Voice and Video Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–6
Performing a Ping Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–7
Performing a Traceroute Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–7
Restarting Networking Processes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–8
Rebooting the 4350 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–8
5 Saving and Restoring the V2IU 4350 Configuration . . . . . . 5–1
The ewn Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–1
Create a Backup File and Save in Local Flash . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
Copy a Backup File to a Remote TFTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
Download a Backup File from a Remote TFTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
List the Available Backup Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
Delete a Backup File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–3
Load a Backup File so that it Becomes the Running Configuration . 5–3
6 Upgrading the V2IU 4350 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–1
Upgrade Procedure for Software Revision 1.3.11 or Later . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–1
Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Appendix–1
Troubleshooting Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Appendix–1
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Appendix–2
Regulatory Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Regulatory Notices–1
END-USER LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR POLYCOM® SOFTWARE .
Regulatory Notices–1
4
Page 7

Contents
FCC PART 68 NOTICE TO USERS OF DIGITAL SERVICE Regulatory
Notices–10
INDUSTRY CANADA (IC) NOTICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . Regulatory Notices–11
5
Page 8

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
6
Page 9

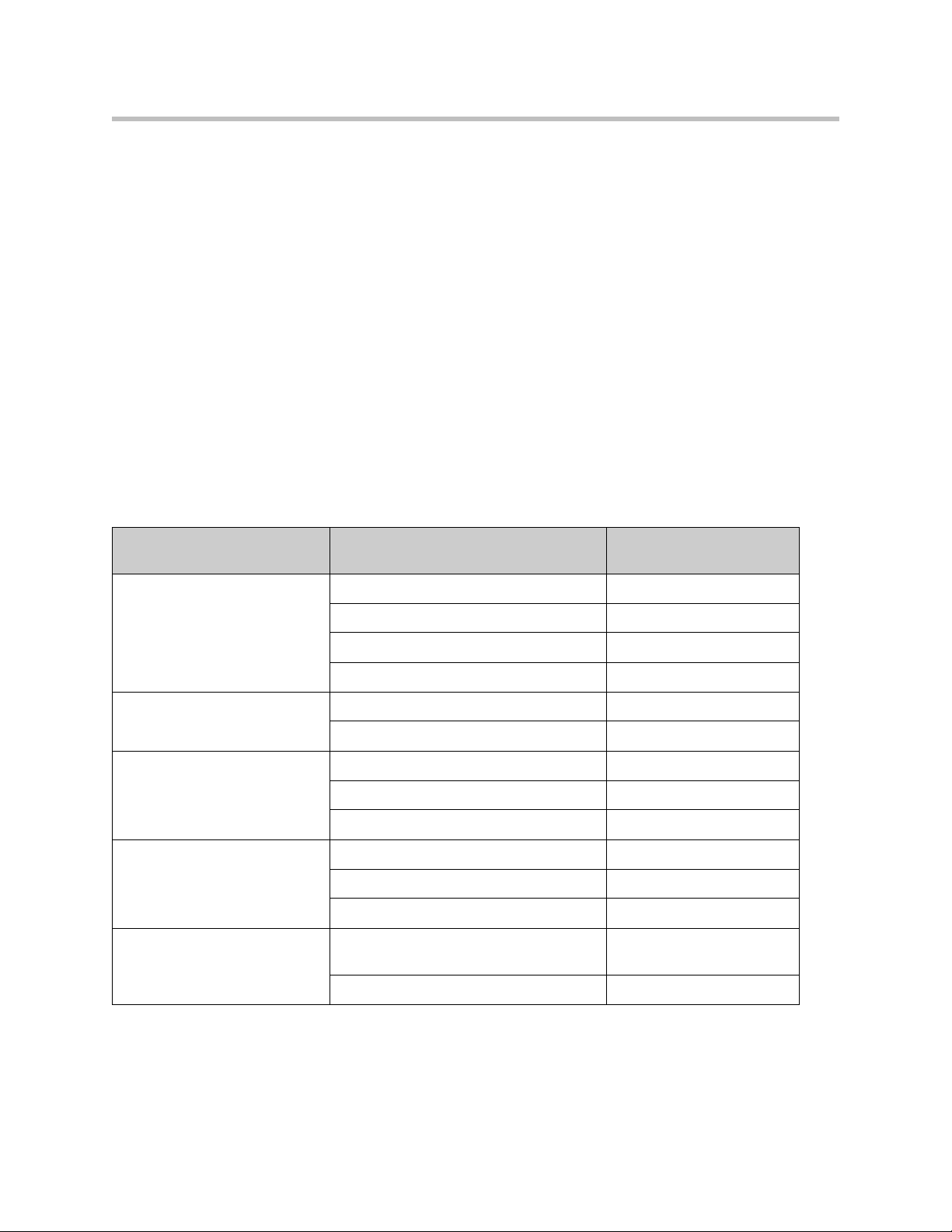
Introduction
The V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
The V2IU 4350 is an intelligent, all-in-one networking solution for enterprises
and service providers. It reduces costs by simplifying the deployment,
management and security of converged voice, video and data networks. The
4350 provides the following important functions for converged networks:
T1 Wide Area Network (WAN) Access Router
The 4350 provides an integrated T1 CSU/DSU for small and medium office
connectivity.
1
Note
The 4350E is designed for use in Australia, New Zealand, Korea and Japan. The
T1 port on the 4350E is functionally disabled through software. The T1 port should
not be connected to the telco network.
• Fully integrated CSU/DSU
• T1 support
• Fractional T1 support
• Layer 2 protocol support for: HDLC, Cisco HDLC (cHDLC), PPP, MLPPP,
MLPPPoFR, Frame Relay
• On-board RJ-48 connector for easy direct connection
• T1/E1 framer and transceiver
— B8ZS/HDB3 zero suppression
— Response to Inband Loop codes (ANSI)
— Manual payload loop through the GUI
• External transmit clock input and receive clock output headers
• Timing: internal or external (loop times from the network)
• Provides long haul CSU or short haul DSU signaling
1 - 1
Page 10

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
• Meets FCC part 68 protection requirements
Security
A stateful packet inspection firewall is used in combination with a VoIP
application layer gateway to provide comprehensive “media-aware” security.
The 4350 also supports IPSec for secure site-to-site networking.
VoIP
The 4350 resolves NAT/FW traversal problems for SIP, MGCP and H.323
traffic. It allows a single public IP address to be used for multiple VoIP clients.
Quality of Service
The 4350 maximizes WAN link utilization while optimizing voice quality
using prioritization and shaping.
Call Quality Monitoring
Passive call quality monitoring for each SIP or MGCP voice call includes
statistics needed to enforce SLAs and resolve networking problems that
negatively affect call quality.
Future-proof Scalability
The 4350 is a powerful, flexible platform that can be deployed initially as a
low-cost WAN access router and then licensed through software for more
advanced VoIP features and increased call performance. It is the ideal
platform for service providers offering DIA, hosted VoIP and managed
security services or enterprises migrating to converged voice and data
networks.
Feature Summary
• VoIP
— SIP, MGCP (for voice) and H.323 (for video) application layer gateway
enables a single public IP address to be used for multiple VoIP
endpoints
1 - 2
• QoS
— Class based queuing/prioritization
Page 11
Introduction
— Diffserv marking and policing
— Traffic shaping
— VoIP call admission control prevents oversubscription of priority
queue
• Security
— Stateful packet inspection firewall
— VoIP aware firewall dynamically provisions and closes UDP ports
used for VoIP calls
— IPSec: 3DES, SHA-1
— NAT/PAT server hides enterprise LAN topology
• Passive Call Quality Monitoring
— Per call statistics include mean opinion score (average and minimum),
jitter, latency, packet loss and much more
— Alarms for poor MOS scores
— Active call count indicators
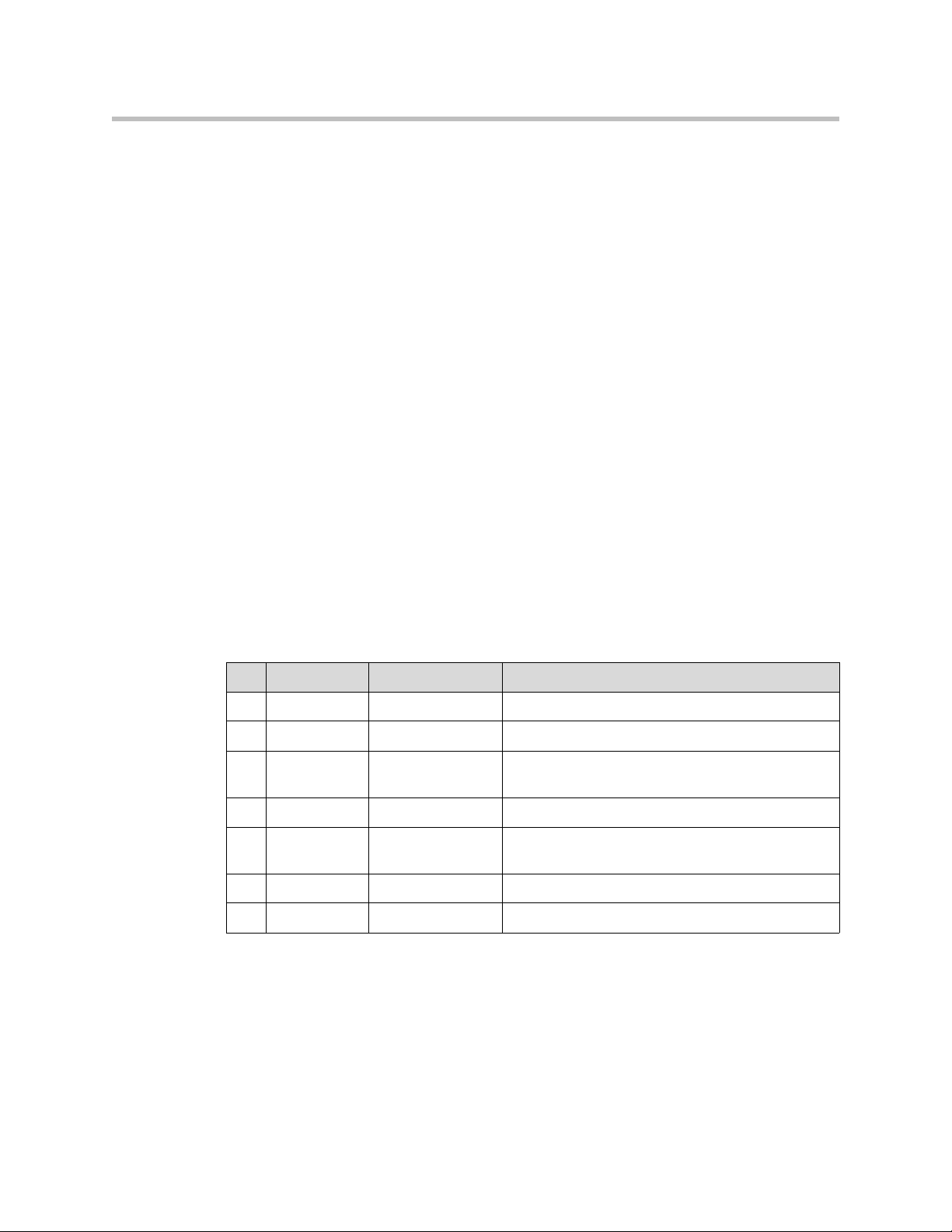
Front Panel LEDs
LED Label Activity Description
A Power Off Power switch is off (or no power from the AC outlet)
B Status Off The unit could not boot up because of self test
C T1 Off The T1 is in an alarm state and not synchronized
The LEDs display real-time information for key functions of the 4350. They are
as follows:
Green Power is supplied to the unit
failure
Green Self test passed
Flashing Green Configuration is being written to permanent storage
or an upgrade is in progress
Green T1 is in sync and no alarms are reported
1 - 3
Page 12
User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
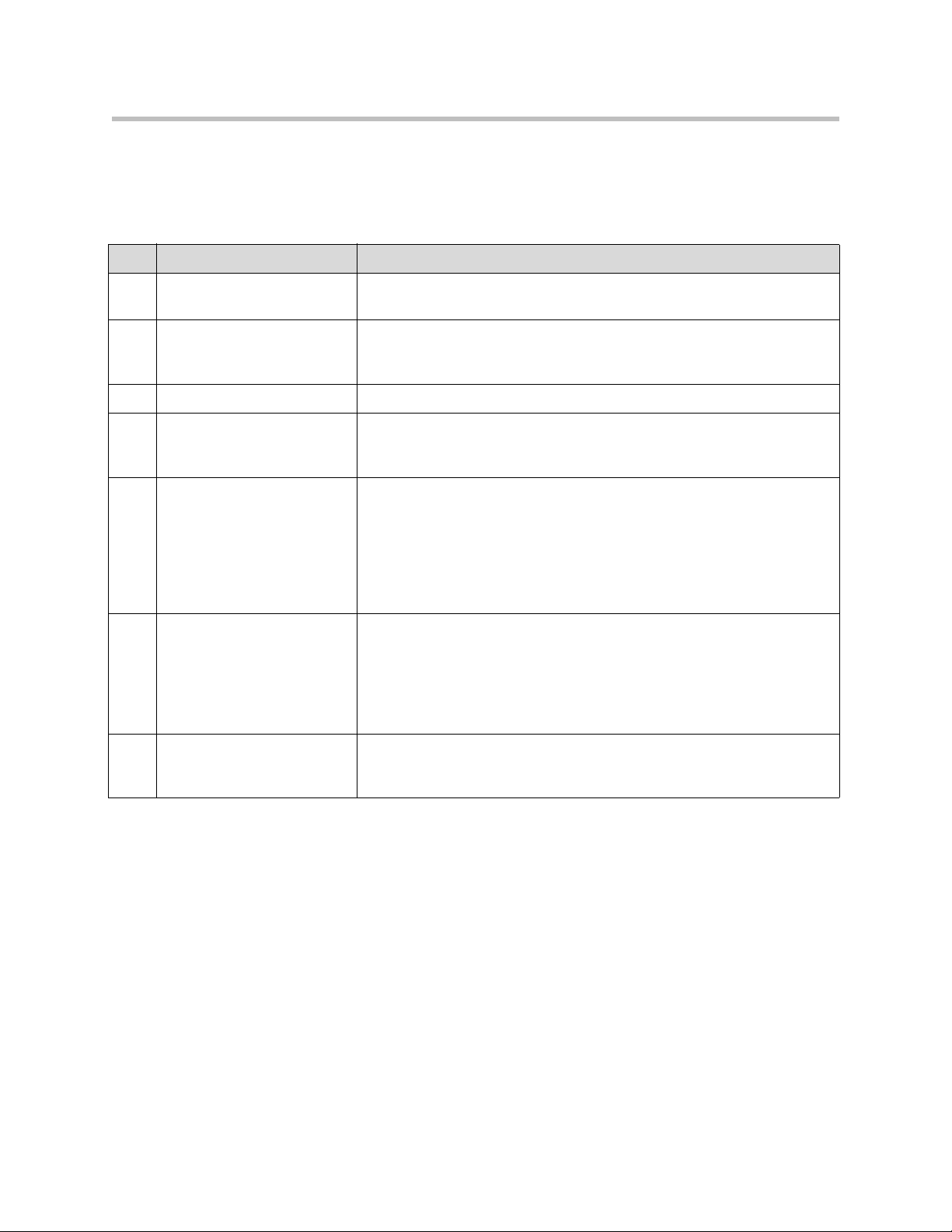
Back Panel
The back panel of the 4350E contains the following connections:
Name Description
A Power Connector Accepts the plug from the supplied power cord to connect the unit to an AC
power source
B 10/100 Mbps LAN Ports 4 x Local Area Network (LAN) ports to connect the IP phones or an
Ethernet switch. Unit can also be configure through any of these ports using
the web interface
C USB Ports 2 x USB ports (Not Used)
D Ethernet WAN Port Can be used as an alternative to the T1 WAN ports. This port is typically
used when connecting the 4350 to an existing T1/E1 WAN router, cable or
xDSL modem.
E Management Console Port This port is used to establish a local console session with the 4350 using a
VT100 terminal or emulation program. The cable required is a
straight-through 8-wire cable. The serial port uses a baud rate of 9600, 8
data bits, 1 stop bit and no parity.
This port is used for debug or local diagnostic purposes only. Primary
configuration of the 4350 is performed from a web browser as covered in
VOS User Manual
F Erase Button Press the Erase button twice in quick succession to reset the CLI password
to the factory default.
Press the Erase button three times in quick succession to reset the
Polycom V2IU 4350 to the factory default. This will reset all passwords and
erase all prior configurations.The default LAN address will now be
192.168.1.1.
G T1/E1 W AN T1/E1 port is used to connect to a data T1 line. The device at the far end of
the line is a router or other device expecting TCP/IP data. Individual DS-0
channels on T1 are not used to carry uncompressed voice.
1 - 4
Page 13

Getting Started
Physical Installation
The V2IU 4350 is designed for desktop, rack or wall-mount installation. Please
observe the following guidelines when installing the system:
• Never assume that the AC cord is disconnected from a power source.
Always check first.
• Always connect the AC power cord to a properly grounded AC outlet to
avoid damage to the system or injury.
Ensure that the physical location of the installation has adequate air circulation
and meets the minimum operating conditions as provided in the
environmental specifications for the system.
2
Warning
Secure the power supply using a fastener or nearby shelf so that it does not hang
from the power connector.
Required Tools and Materials
The following items are required:
• If the unit is to be mounted on the wall:
— 1 Flat or Phillips screw driver
— 2 round or flat head Phillips or slotted screws - 1 ½ inch long
— 2 hollow wall anchors
• If the unit will be mounted in a shelf:
— 1 Flat or Phillips screw driver
2 - 1
Page 14
User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
• If the T1/E1 port will be used to connect to WAN:
— T1 cable to connect the T1/E1 port to a T1 line.
Warning
To reduce the risk of fire, use only 26 AWG or larger wire (e.g. 24, 22, 20, etc.) to
connect the T1 port on your unit to an RJ-45 jack.
• Ethernet cables to connect the LAN ports to LAN switches or to individual
Desktop Installation
1. Remove the 4350 and accessories from the shipping container.
2. Place the 4350 on a flat, dry surface such as a desktop, shelf or tray.
3. Connect the power and network cables to the appropriate ports on the
Caution
To reduce the risk of fire, use only 26 AWG or larger wire (e.g. 24, 22, 20, etc.) to
connect the T1 port on your unit to an RJ-45 jack.
Wall-Mount Installation
1. The 4350 can be wall-mounted using the two mounting brackets on the
IP phones. They can also be used to connect the Ethernet WAN port to a
WAN router, a Cable Modem or a DSL Modem, if T1/E1 port is not being
used to connect to the WAN.
back of the system.
bottom of the appliance. We recommend using two round or pan head
screws.
2 - 2
2. Install two screws 5.9" (150 mm) horizontally apart on a wall or other
vertical surface. The screws should protrude from the wall so that you
can fit the appliance between the head of the screw and the wall. If you
install the screws in drywall, use hollow wall anchors to ensure that the
unit does not pull from the wall due to prolonged strain from the cable
and power connectors.
3. Remove the 4350 and accessories from the shipping container.
Page 15

4. Mount the 4350 on the wall as shown below.
Do not mount the 4350 on the wall as shown below.
Getting Started
1. Connect the power and network cables to the appropriate ports on the
Warning
Caution
Secure the power supply using a fastener or nearby shelf so that it does not hang
from the power connector.
To reduce the risk of fire, use only 26 AWG or larger wire (e.g. 24, 22, 20, etc.) to
connect the T1 port on your unit to an RJ-45 jack.
Rack-Mount Installation
You can mount the 4350 in a shelf by using the rack-mount kit supplied with
the product.
1. Attach the ear mounts to both sides of 4350 with the screws.
2. Attach the 4350 with the ear mounts to the shelf by screwing the ear
back of the system.
mounts to the shelf with screws.
2 - 3
Page 16

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Connecting the Power and Cables
The 4350 comes with an AC power cord and power adapter for connecting the
unit to the AC outlet.
Warning
Caution
Always connect the AC power cord to an AC outlet suitable for the power supply
that came with the unit in order to reduce the risk of damage to it.
• Connect one end of the AC power cord to the power adapter and the other one
to the AC outlet.
• Connect plug from the power adapter to the Power Connector on the 4350.
Sometimes a little force is necessary to get the plug properly positioned
Secure the power adapter using a fastener or tie wrap to nearby shelf so that it
does not hang from the power connector.
If you are connecting to the WAN using the T1, then connect the T1 cable to
the T1/E1 port and the other end of the cable to the T1 line. Enable the T1 port
from the Network Configuration Menu. In this case, the Ethernet WAN port
will not be available.
If you are connecting to a WAN router, cable modem or DSL modem, then
connect the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet WAN port on 4350 and the other end
to the WAN device.
Administration of the 4350
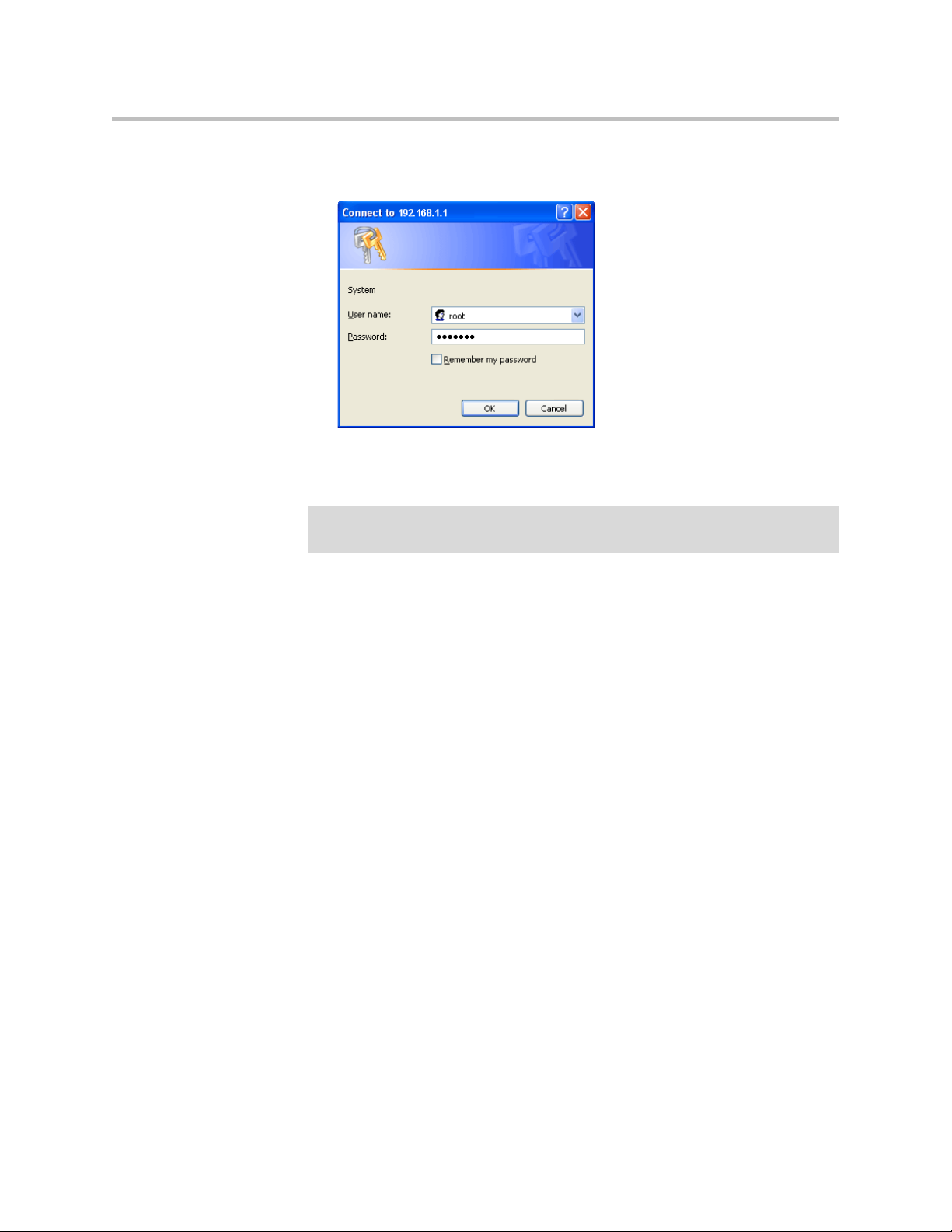
2 - 4
The 4350 is configured using a web browser such as Internet Explorer or
Netscape Navigator. The 4350 is shipped with a pre-configured IP address for
its LAN port of 192.168.1.1. To connect to the 4350, do the following:
1. Connect a PC using an IP address of 192.168.1.2 and subnet mask of
255.255.255.0 to LAN port 4 of the 4350.
Page 17
Getting Started
2. Launch a web browser on the PC and enter the URL string: 192.168.1.1.
Press Return.
3. Enter the username root and the password default to log into the system.
The 4350 main configuration menu appears.
Note
For secure management of your network, be sure to change the default userid and
password as described under Change the Administration Password.
4. Configure the system using the information provided in Chapter 3.
2 - 5
Page 18

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
2 - 6
Page 19
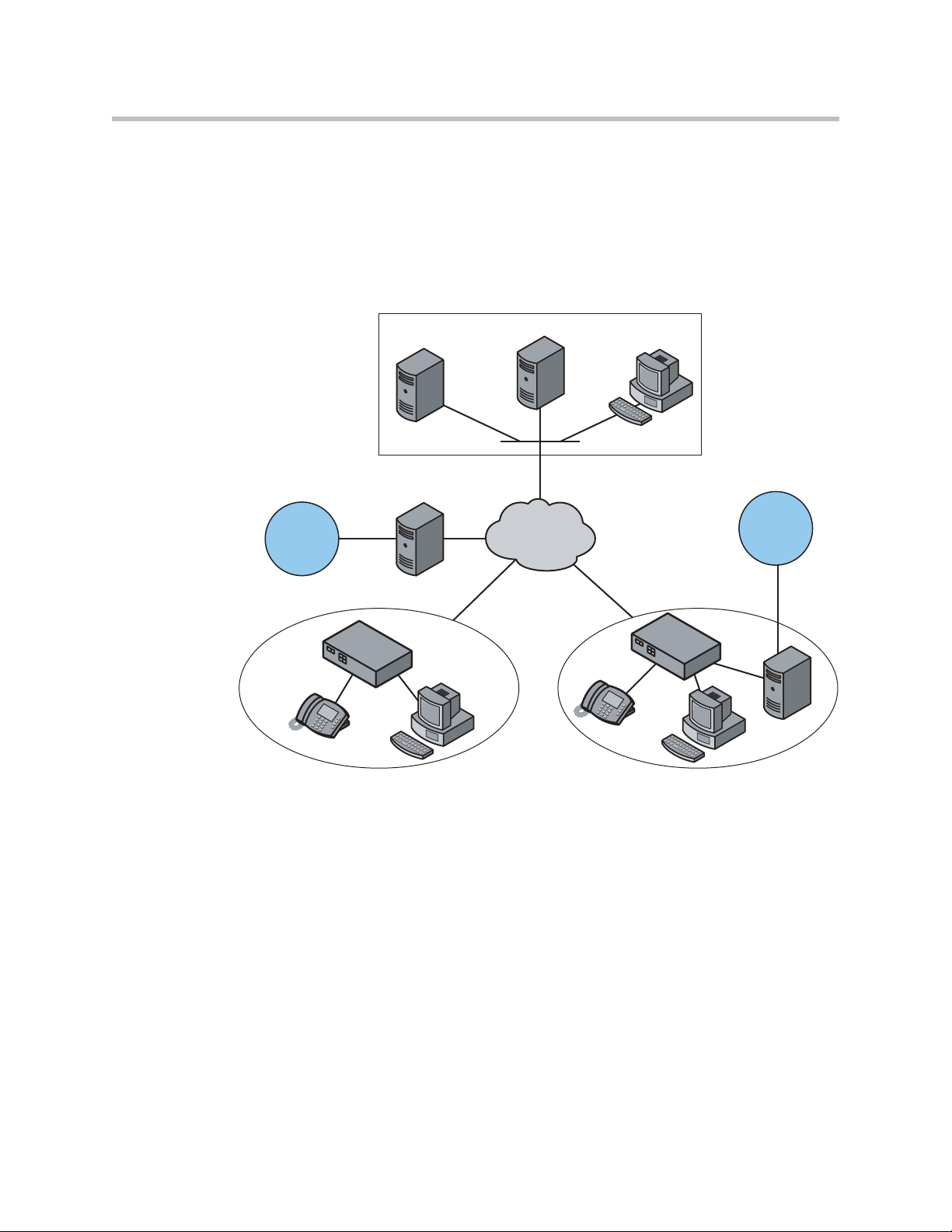
Configuring the V2IU 4350
The V2IU 4350 is a flexible, easy to use converged network appliance that
provides many critical networking functions for IP based voice, video and
data. It can be installed in several different topologies:
• At the customer premise for IP Centrex and hosted video applications
• At the station side of enterprise IP PBXs
• At the trunk side of enterprise IP PBXs
• At the public/private IP address boundary for enterprise video
applications
Most users will follow the steps provided in the “Configuring The Systems
Settings” section of this manual to initially connect the 4350 into their IP
network. The remainder of the configuration can be different based on the
application, VoIP topology and presence of other networking equipment such
as firewalls or DHCP servers. In general, however, the steps used to configure
the 4350 are:
3
Step Task
1 System configuration
2 VoIP configuration
3 Data networking configuration
4 Firewall configuration
5 Traffic management configuration
Some of the steps are optional depending on your particular application. We
have provided configuration guidelines below for each of the application
types supported by the 4350.
3 - 1
Page 20
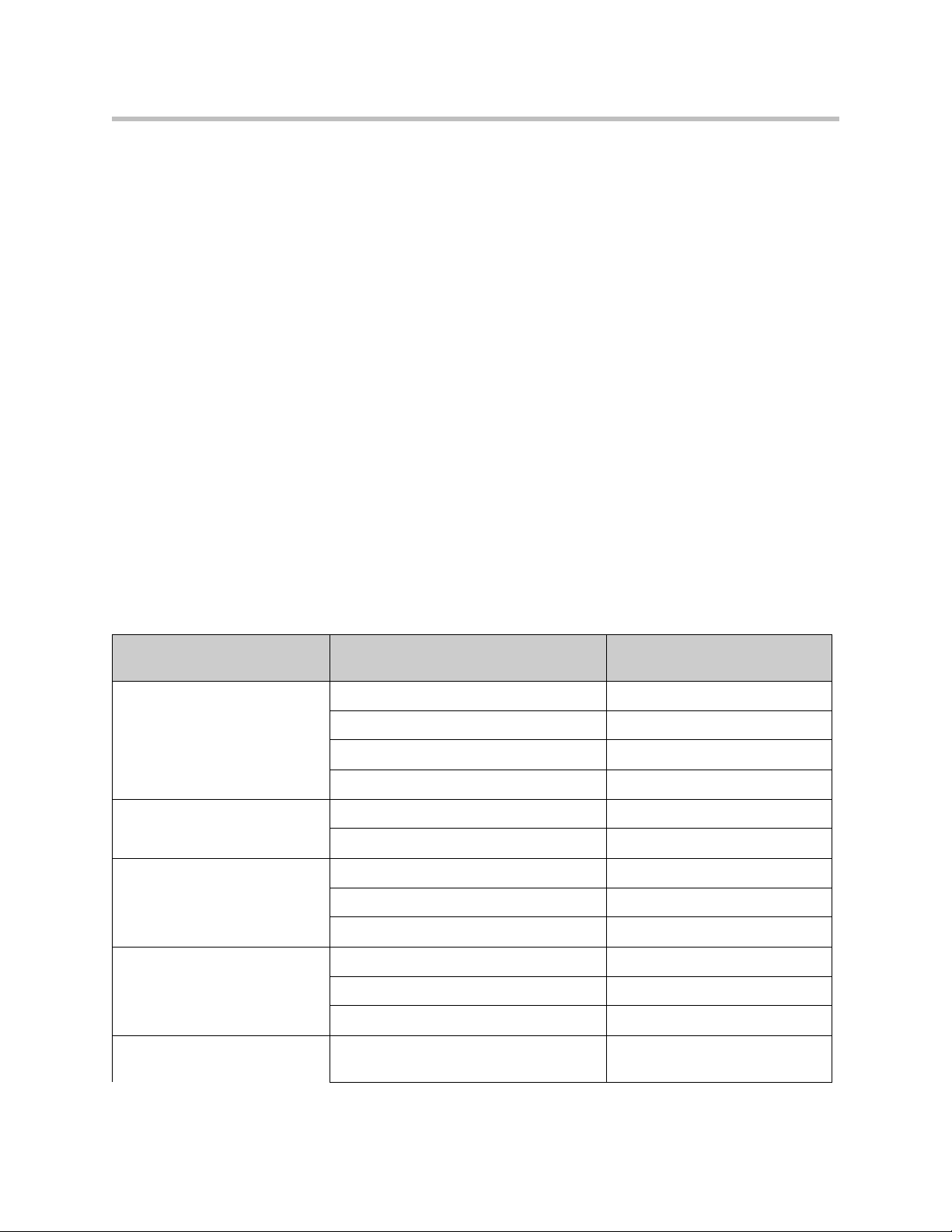
User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Application Server
Softswitch
Gateway
Gateway
4300T
4300T
PSTN
PSTN
NMS
EM003
VoIP Operations Center
Enterprise Enterprise
T1
T1/FT1 T1/FT1
4350
4350
Configuration Guide For IP Centrex Applications
A typical 4350 installation for an IP Centrex application requires no external
router or firewall. The 4350 WAN port is connected directly to the T1/E1 line
and the LAN port(s) are connected directly to enterprise devices and/or
Ethernet switches.
VoIP signaling is performed in the service provider network via a softswitch
and the 4350 acts as a proxy for the voice devices installed in the enterprise
LAN. In this configuration a single public IP address is used to proxy for all of
the IP phones and to route to multiple PC’s installed on the LAN.
The 4350 performs the following functions in this application:
• WAN/LAN IP routing.
• Traffic shaping and priority queuing to guarantee high quality voice
traffic. These mechanisms protect voice and data traffic from contending
for the same network resources to guarantee low latency and the highest
call quality possible for VoIP traffic. At the same time they ensure the best
utilization of WAN bandwidth by enabling data traffic to burst up to full
3 - 2
line rate in the absence of voice calls. Precedence is automatically given to
traffic coming from IP phones and other devices using the 4350’s
Application Layer Gateway function.
Page 21
Configuring the V2IU 4350
• NAT/PAT translation for IP phones and PC’s. This allows a single public
IP address to be used on the WAN link to represent all of the private IP
addresses assigned to the LAN IP phones and PC’s.
• Static NAT entries. This enables the customer to use a WAN public IP
address for data servers (web, mail, ftp, etc.) connected behind the 4350.
These servers can then be configured with private IP addresses for
additional security.
• A “VoIP” aware firewall. A full Layer 7 gateway for voice traffic and a
stateful packet inspection firewall for data traffic.
• Call Admission Control (CAC). CAC uses a deterministic algorithm to
decide when there are insufficient network resources available to
adequately support new calls and then return the equivalent of a “fast
busy” to new call requests.
• DHCP server and TFTP relay. These features are used to simplify and
expedite the IP configuration of phones and PC’s. This also includes VoIP
signaling gateway information (MGCP, SIP, and H.323.
• Call quality monitoring (using MOS, jitter, latency, packet loss and much
more) and test tools.
Configuration Outline
Configure For IP Centrex
Task Subtask
System Configuration configure LAN/WAN interface Yes
set ethernet link rate Optional
enable the DHCP server Optional but recommended
configure SNMP Optional
VoIP Configuration enable the VoIP ALG Yes
configure a VoIP subnet route Optional
Data Networking Configuration dynamic NAT Optional but recommended
static NAT Optional
static IP routing Optional
Firewall Configuration enable the data firewall Yes
configure basic settings Optional
configure advanced settings Optional
Traffic Management
Configuration
enable traffic shaping Yes
Application?
3 - 3
Page 22
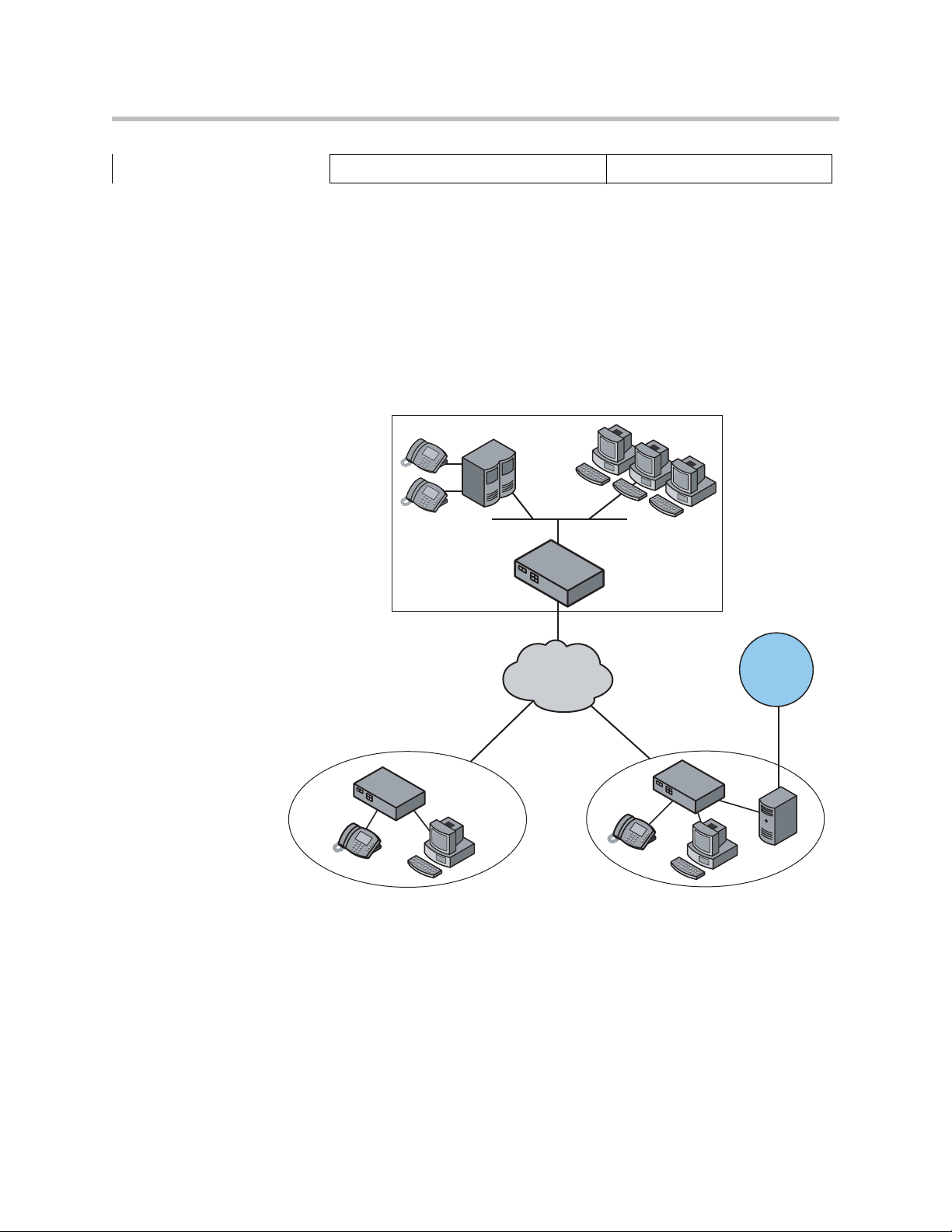
User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
4350
4350
4350
enable Call Admission Control Optional
Configuration Guide For Station Side IP PBX Applications
Most private enterprise VoIP networks use an IP PBX at the corporate
headquarters location to provide voice switching between headquarters,
branch offices and the PSTN. The 4350 is used in these environments to
securely connect branch office employees to the IP PBX installed in the
corporate headquarters location.
Headquarters
IP PBX
4300T
T1
PSTN
Branch Office Branch Office
4300T
T1/FT1 T1/FT1
4300T
Gateway
EM004
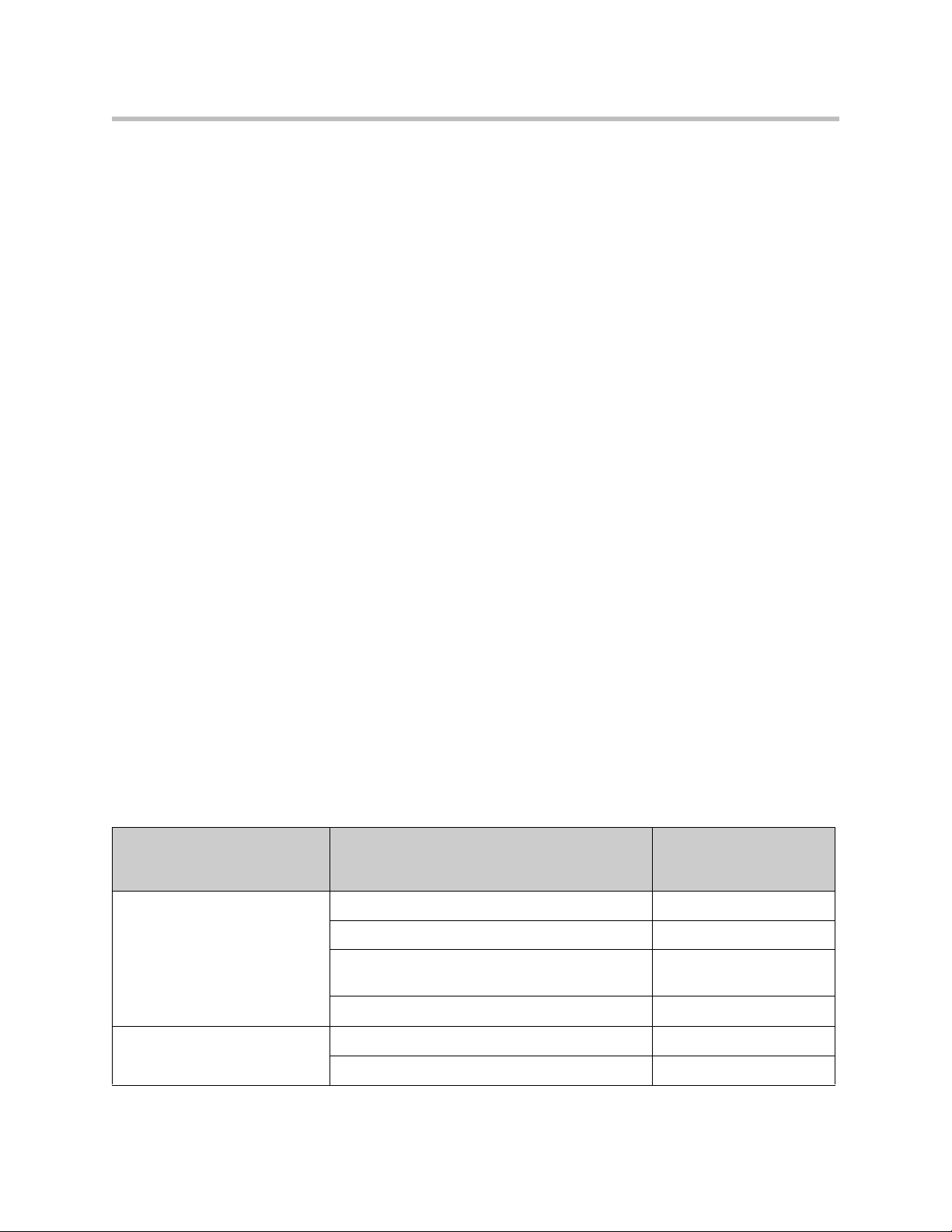
The installation of an 4350 on the station side of an enterprise IP PBX is very
similar to the IP Centrex application above. The branch office is connected to
the corporate network using a private T1/E1 link connected directly to the
WAN port of the 4350. The LAN port(s) of the 4350 are connected directly to
enterprise devices and/or Ethernet switches.
3 - 4
Page 23
Configuring the V2IU 4350
The IP PBX in the corporate headquarters location performs VoIP signaling
and the 4350 acts as a proxy for the voice devices installed at the branch office.
Please note that in the configuration the 4350 located at the Headquarters
location is acting as a WAN router only. The 4350s installed at the brand offices
perform the following functions in this application:
• WAN/LAN IP routing.
• Traffic shaping and priority queuing to guarantee high quality voice
traffic. These mechanisms protect voice and data traffic from contending
for the same network resources to guarantee low latency and the highest
call quality possible for VoIP traffic. At the same time they ensure the best
utilization of WAN bandwidth by enabling data traffic to burst up to full
line rate in the absence of voice calls. Precedence is automatically given to
traffic coming from IP phones and other devices using the 4350’s
Application Layer Gateway function.
• NAT/PAT translation for IP phones and PC’s. This allows a single IP
address to be used on the WAN link to represent all of the private IP
addresses assigned to the LAN IP phones and PC’s.
• A “VoIP” aware firewall. A full layer 7 gateway for voice traffic and a
stateful packet inspection firewall for data traffic.
• Call Admission Control (CAC). CAC uses a deterministic algorithm to
decide when there are insufficient network resources available to
adequately support new calls and then return the equivalent of a “fast
busy” to new call requests.
• DHCP server and TFTP relay. These features are used to simplify and
expedite the IP configuration of phones and PC’s. This also includes VoIP
signaling gateway information (MGCP, SIP, and H.323).
• Call quality monitoring and test tools.
Configuration Outline
Configure For Station
Side IP PBX
Task Subtask
System Configuration configure LAN/WAN interface Yes
set ethernet link rate Optional
enable the DHCP server Optional but
configure SNMP Optional
Application?
recommended
VoIP Configuration enable the VoIP ALG Yes
configure a VoIP subnet route Optional
3 - 5
Page 24
User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
4350
4350
4350
Data Networking Configuration dynamic NAT Optional but
recommended
static NAT Optional
static IP routing Optional
Firewall Configuration enable the data firewall Yes
configure basic settings Optional
configure advanced settings Optional
Traffic Management
enable traffic shaping Yes
Configuration
enable Call Admission Control Optional
Configuration Guide For Trunk Side IP PBX Applications
Companies with existing IP-based WAN links for inter-office voice and data
communications can use the 4350 as a traffic shaper to meet the stringent jitter,
latency and packet loss requirements for toll quality voice. The 4350 is
deployed at the edge of the WAN in both headquarters and branch office
locations, as shown below.
Branch Office
Headquarters
IP PBX
4300T
Frame Relay
Or
IP Network
4300T
T1/E1
Branch Office
T1/E1
4300T
IP PBX
3 - 6
IP PBX
EM005
The 4350 performs WAN/LAN IP routing and traffic management functions
in this application. In particular, it provides prioritization to ensure voice
packets are not delayed or dropped while allowing data traffic to use all
remaining bandwidth.
Page 25
Configuration Outline
Task Subtask
System Configuration configure LAN/WAN interface Yes
set ethernet link rate Optional
enable the DHCP server Not required
configure SNMP Optional
VoIP Configuration enable the VoIP ALG Not required
configure a VoIP subnet route Not required
Configuring the V2IU 4350
Configure For Trunk Side IP
PBX Application?
Data Networking
Configuration
static NAT Not required
static IP routing Not required
Firewall Configuration enable the data firewall Not required
configure basic settings Not required
configure advanced settings Not required
Traffic Management
Configuration
enable Call Admission
dynamic NAT Not required
enable traffic shaping Yes
Not required
Control
3 - 7
Page 26
User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
4350
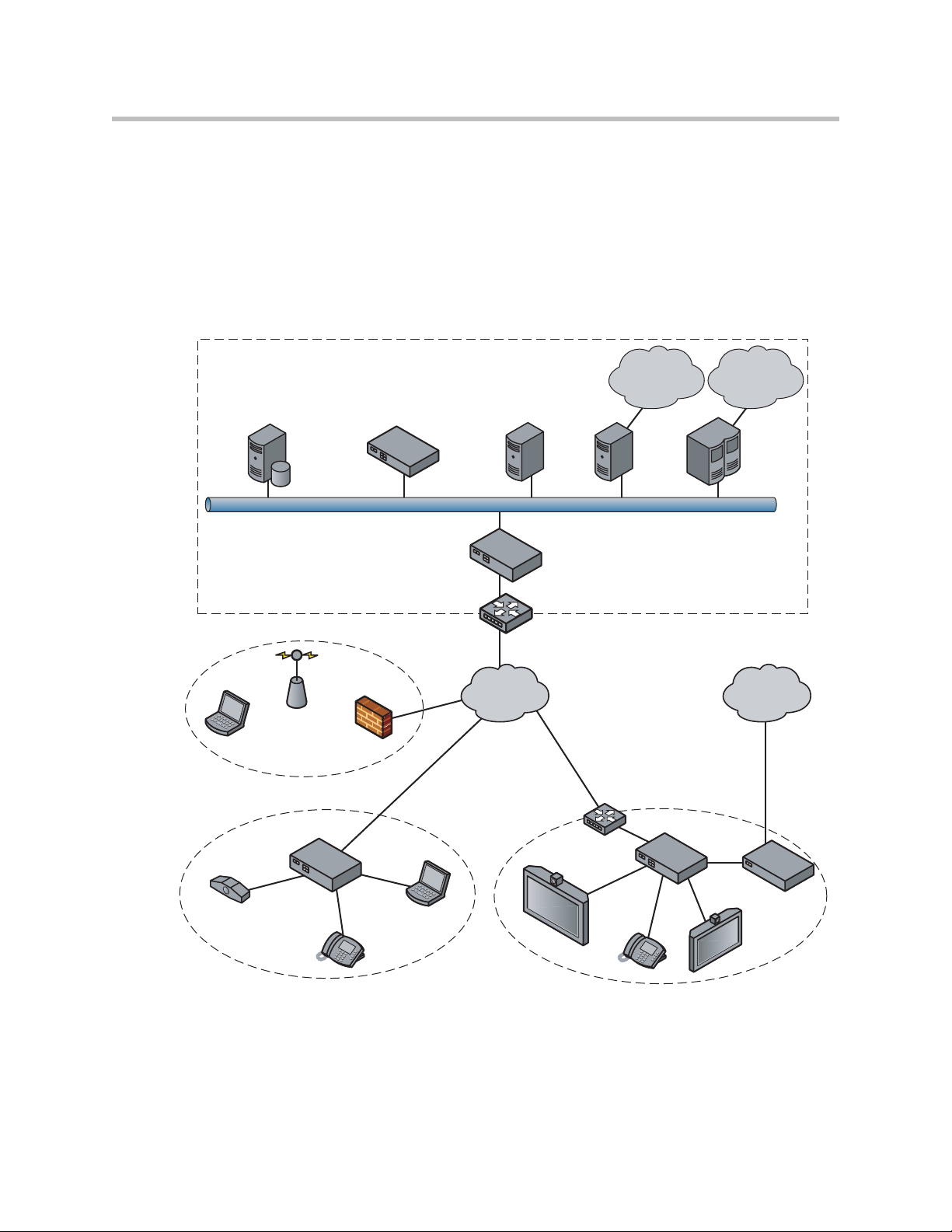
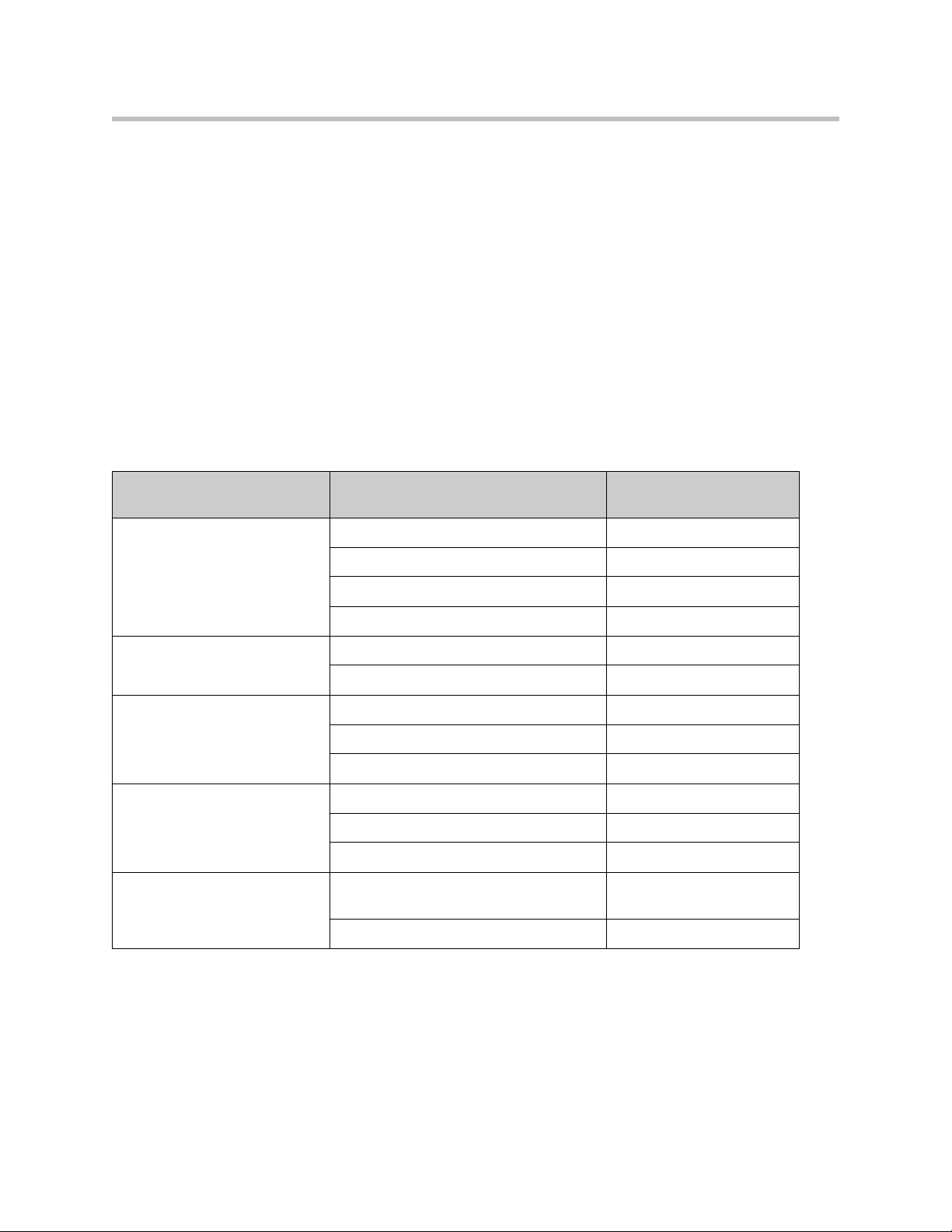
Configuration Guide For Hosted Video Applications
A typical 4350 installation for hosted video applications is depicted in the
diagram below. In this scenario, the 4350s are used to connect all of the video
endpoints to the Gatekeeper. The video endpoints should be configured to
point to the LAN address of the 4350 as the Gatekeeper and the 4350 will proxy
RAS and call setup messages to the Gatekeeper
Service Provider
H.323
Gatekeeper
SIP Voice
V500
NMS
Hotspot
NAT/Firewall
User
T-1/E-1 NxT-1/E-1
Company A Company B
4300T
IP
Phone
Laptop
Softswitch
Public IP
Network
Aggregation
Gateway MCU
5300-S
Aggregation Router
Router
H.323 Video
Endpoint
IP
Phone
PSTN
ISDN,
PSTN Network
PSTN
5300-E
Gateway
H.323 Video
Endpoint
3 - 8
EM008B
The 4350 is installed at the customer premises and is used as a demarcation
point for the video service by providing the following functions:
• WAN/LAN IP routing.
Page 27
• Traffic shaping and priority queuing to guarantee high quality video
traffic. These mechanisms protect video and data traffic from contending
for the same network resources to guarantee low latency and the highest
call quality possible for voice and video traffic. At the same time they
ensure the best utilization of WAN bandwidth by enabling data traffic to
burst up to full line rate in the absence of video calls. Precedence is
automatically given to traffic coming from video endpoints and other
devices using the 4350’s Application Layer Gateway function.
• Video NAT/PAT translation for video endpoints and PC’s. This allows a
single IP address to be used on the WAN link to represent all of the private
IP addresses assigned to the LAN video endpoints and PC’s.
• A video aware firewall. A full layer 7 gateway for video traffic and a
stateful packet inspection firewall for data traffic
• Call Admission Control (CAC). CAC uses a deterministic algorithm to
decide when there are insufficient network resources available to
adequately support new video calls and then return the equivalent of a
“fast busy” to new call requests.
Task Subtask
Configuring the V2IU 4350
Configure For Hosted
Video Applications?
System Configuration configure LAN/WAN interface Yes
set ethernet link rate Optional
enable the DHCP server Optional
configure SNMP Optional
VoIP Configuration enable the VoIP ALG Yes
configure a VoIP subnet route Optional
Data Networking Configuration dynamic NAT Optional but recommended
static NAT Optional
static IP routing Optional
Firewall Configuration enable the data firewall Yes
configure basic settings Optional
configure advanced settings Optional
Traffic Management
Configuration
enable Call Admission Control Optional
enable traffic shaping Yes
3 - 9
Page 28
User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
NMS
PC PC
PC
IP Phone
IP PhoneIP Phone
5300-E
PC
H.323
Endpoint
5300-S 5300-E
IP
Network
PSTNPSTN
Aggregation Router
Aggregation
Router
4300T
Gateway
H.323
Laptop
IP Phone
IP Phone
Headquarters
Branch Office Company B
T-1/E-1 NxT-1/E-1
H.323
Gatekeeper
PSTN
Gateway
Application
Server
Softswitch
Gateway
EM009A
4350
Configuration Guide For Enterprise Video Applications
A typical 4350 installation for enterprise video applications is depicted in the
diagram below. In this scenario, the 4350s are used to connect all of the video
endpoints to the Gatekeeper. The video endpoints should be configured to
point to the LAN address of the 4350 as the Gatekeeper and the 4350 will proxy
RAS and call setup messages to the Gatekeeper.
The 4350 is installed at the private/public IP address boundary and provides
the following functions:
3 - 10
• WAN/LAN IP routing.
• Traffic shaping and priority queuing to guarantee high quality video
traffic. These mechanisms protect video and data traffic from contending
for the same network resources to guarantee low latency and the highest
Page 29
call quality possible for voice and video traffic. At the same time they
ensure the best utilization of WAN bandwidth by enabling data traffic to
burst up to full line rate in the absence of video calls. Precedence is
automatically given to traffic coming from video endpoints and other
devices using the 4350’s Application Layer Gateway function.
• Video NAT/PAT translation for video endpoints and PC’s. This allows a
single IP address to be used on the WAN link to represent all of the private
IP addresses assigned to the LAN video endpoints and PC’s.
• A video aware firewall. A full layer 7 gateway for video traffic and a
stateful packet inspection firewall for data traffic
• Call Admission Control (CAC). CAC uses a deterministic algorithm to
decide when there are insufficient network resources available to
adequately support new video calls and then return the equivalent of a
“fast busy” to new call requests.
Configure For Hosted
Task Subtask
System Configuration configure LAN/WAN interface Yes
Video Applications?
Configuring the V2IU 4350
set ethernet link rate Optional
enable the DHCP server Optional
configure SNMP Optional
VoIP Configuration enable the VoIP ALG Yes
configure a VoIP subnet route Optional
Data Networking Configuration dynamic NAT Optional but recommended
static NAT Optional
static IP routing Optional
Firewall Configuration enable the data firewall Yes
configure basic settings Optional
configure advanced settings Optional
Traffic Management
Configuration
enable Call Admission Control Optional
enable traffic shaping Yes
3 - 11
Page 30

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
System Configuration
This section explains how to configure the 4350 to function in your IP network.
You will configure the T1/E1 WAN interface, Ethernet interfaces, network
addresses, DNS settings, default gateway, SNMP settings and change the
administrative password.
1. Physically connect to the 4350 as described in Administration of the 4350
on page 2-4.
A browser-based configuration GUI should appear, as shown here.
2. Select the Network entry in the Configuration Menu.
Configure the LAN Interface
The 4350 provides an integrated 4 port 10/100 Mbps ethernet switch that can
be optionally configured to support 802.1q VLANs. Integrated VLAN support
simplifies the integration of the 4350 with existing VLAN-based networks. The
4350 is able to receive 802.1q-tagged packets from a downstream VLAN switch
and appropriately route and process them per its firewall rules. Packets
received from the WAN are placed in the appropriate VLAN based on IP
address routing.
By default VLANs are not enabled and a single IP address is used for all 4
ethernet ports. The configuration of this address is as follows:
1. Enter the IP Address.
2. Enter the Subnet Mask (e.g. 255.255.255.0).
3 - 12
Page 31
Configuring the V2IU 4350
4350
3. Press Submit.
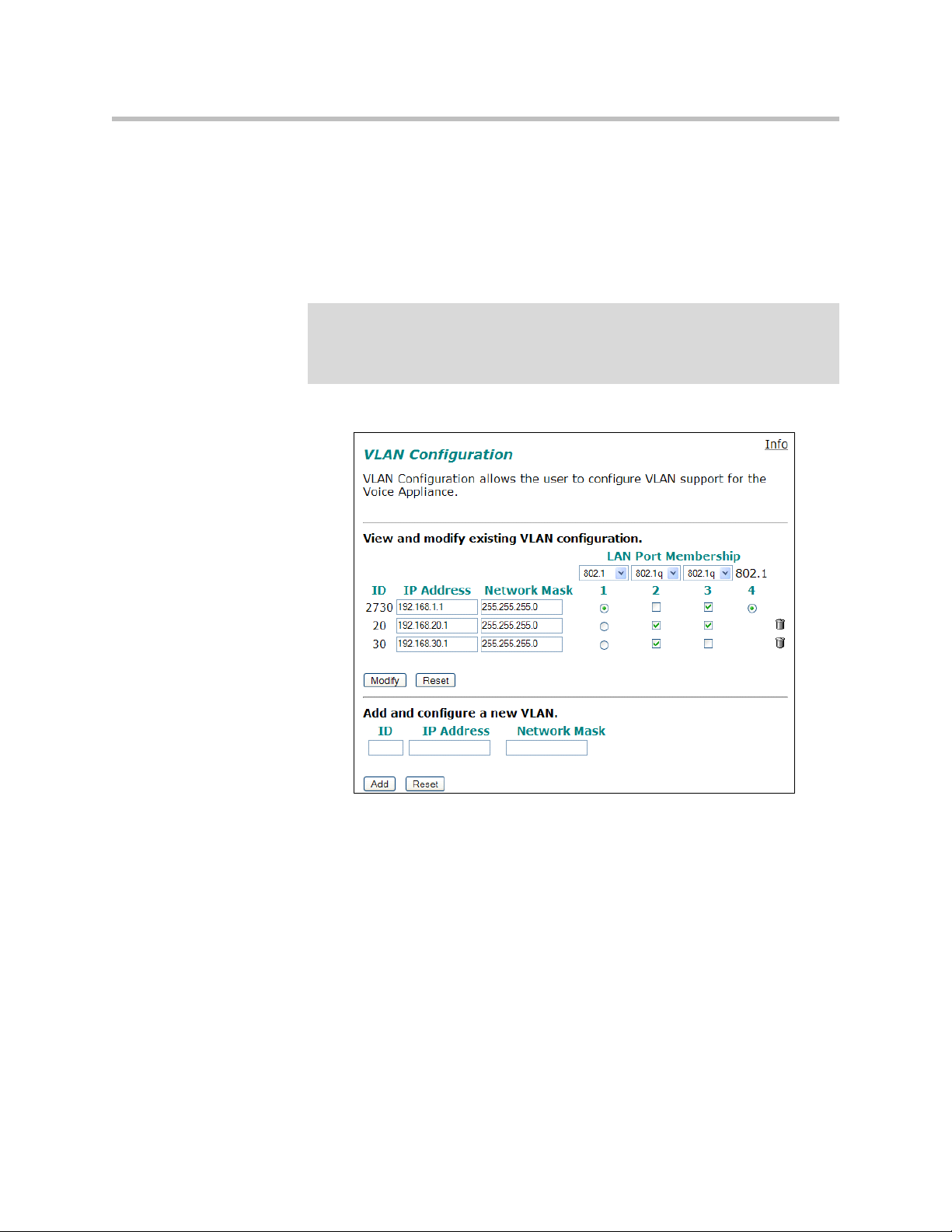
Configuring VLANs in the 4350
As depicted in the diagram below, VLANs are used to connect the 4350 to an
Ethernet switch that has been configured to use VLANs.
VLANid 1/2
VLANid 1/3 VLANid 1/2/3
VLANid 1/2/3
802.1
VLAN
Switch
(VLANid 16)
4300T
P1
P2
P3
P4
WAN
EM006
Typically, all VoIP devices are placed in the same VLAN while data devices
are placed in a different VLAN. This is to ensure priority treatment of the VoIP
traffic on the LAN. Note that the 4350 does not require VLANs to prioritize
VoIP traffic; prioritization is determined by the VOS Application Layer
Gateway, regardless of VLAN. Some important notes about VLANs:
• A physical LAN port will operate in either 802.1 or 802.1q mode, not both
simultaneously
• The 4350 supports up to 16 VLANs
• A unique IP Subnet is assigned to each VLAN
• You can associate one or more VLANs to each LAN port operating in
802.1q mode
• Traffic within a VLAN is switched among all ports with membership
• Traffic between VLANs is routed by the 4350
• The 4350 ALG can only be assigned to one VLAN id
— Only ALG traffic is prioritized over the WAN
— Other non-VoIP traffic in the same VLAN will not receive priority
treatment
• A DHCP server can be enabled/disabled per VLAN
• Cisco Discovery Protocol is not supported
3 - 13
Page 32
User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
• 802.1p is not currently supported
1. Select the Network link.
2. Select Enable VLAN support.
3. Press Submit.
Caution
Be careful when changing a port from 802.1 to 802.1q mode. Any 802.1 devices
connected to that port (such as your management PC!) will loose access to the
4350. Port 4 is only able to receive 802.1 frames, so a PC can always be connected
to this port if the configuration of the other ports is unknown.
3 - 14
4. Select System.
5. Select VLAN Configuration.
6. Adjust LAN Port Membership drop-down boxes to specify 802.1 or
802.1q mode, as desired. Press Modify.
If changing modes, the radio-buttons or checkboxes will change from one
style to the other.
7. Under Add and configure a new VLAN enter a new VLAN ID, the 4350’s
IP address within this VLAN, and the Network Mask. Press Add.
A new VLAN entry will be added to the VLAN Configuration above.
8. Depending on the mode of a physical port, assign it to one or more
VLANs:
Page 33

Configuring the V2IU 4350
— 802.1 mode: Assign the port to any ONE VLAN.
— 802.1q mode: Assign the port to any number of VLANs
Perform steps 1 through 6 above for each VLAN you wish to create.
Modify an Existing VLAN Configuration
1. Select the Network link.
2. Select VLAN Settings.
3. Change the desired settings.
4. Press the Modify to modify the VLAN. The Reset button will restore the
input area being modified to its previous value.
Delete an Existing VLAN Configuration
1. Select the Network link.
2. Select VLAN Settings.
3. Press the trash can icon next to the VLAN you wish to delete.
3 - 15
Page 34

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Assign the 4350’s ALG to your Priority VLAN
Once you have completed your VLAN configuration you must assign the 4350
ALG to the VLAN containing your VoIP phones.
1. Select the VoIP ALG from the main configuration menu.
2. Use the drop down menu to assign the ALG to the VLAN ID containing
your VoIP phones.
3. Press Submit.
Configure the WAN Interface
The 10/100 Ethernet WAN port is configured as follows:
1. Select ADSL-PPPoE if you want to connect to Internet using ADSL and
your ISP has given PPPoE username and password. Press Submit. You
will be prompted to enter username and password, enter these and press
Submit again.
2. Select DHCP if you want to get WAN side IP address using DHCP server
available in WAN side of the network. Press Submit.
3. Select Static IP address if you want to manually assign the IP address
configuration to the ethernet WAN interface.
4. Enter the IP Address.
5. Enter the Subnet Mask (e.g. 255.255.255.0).
3 - 16
Page 35

Configuring the V2IU 4350
6. Enter the Default Gateway. This is usually the upstream router’s IP
address. Packets destined for IP networks not known to the 4350 are
forwarded to the default gateway for handling.
7. Enter the Primary DNS Server. The DNS server is used by the 4350 to
resolve domain names to IP addresses. The value entered into this field is
provided to IP devices that use the 4350 as a DHCP server. The 4350 VoIP
ALG also uses it if domain names are used instead of IP addresses to
identify signaling and/or TFTP servers (see the section entitled
“Configuring the VoIP ALG” for more details).
8. Enter the Secondary DNS Server. This server will be used in the event
that the primary DNS server is not reachable.
9. Press Submit.
To enable the T1 interface:
1. Select Network.
2. Select the T1 radio button.
3. Select Submit.
To configure the T1 parameters:
1. Select Network.
2. Select the T1 link next to the radio button to proceed to the T1
Configuration page.
The T1 Configuration menu will display, as shown here.
The 4350 supports a wide range of T1/E1 Layer 2 configuration parameters.
The specific values you will need must be supplied by the WAN provider.
Each of the 4350’s configurable parameters are described below.
3 - 17
Page 36

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Protocol
Display and set the T1 Layer 2 protocol. Supported protocols are:
• HDLC
• Cisco HDLC
• PPP
• ANSI (Frame Relay)
• CCITT (Frame Relay)
1. Select the desired T1 protocol.
2. Press Submit.
Frame Relay Mode and DLCI
When the Protocol is one of ANSI or CCITT, then additional Frame Relay
configuration parameters are required.
The Frame Relay Mode is usually set to DTE for the customer premises.
The Frame Relay DLCI is set by the WAN provider and identifies the far-end
device across the Frame Relay network. This DLCI can also be used to carry
voice traffic only by enabling the Secondary DLCI for data.
Most installations will use a single DLCI for both voice and data traffic.
However, in instances where the network will provide a different quality of
service based on DLCI number it is desirable to place all voice traffic on one
DLCI and then configure a second DLCI for data. In this case, the Secondary
DLCI is configured as follows:
1. Select Network.
2. Select the T1 link next to the radio button to proceed to the T1
configuration page.
3. Select Enable in the Frame Relay Secondary Settings section of the page.
4. Enter the Secondary DLCI, IP Address, Network Mask and Gateway for
the data traffic using the Secondary DLCI.
3 - 18
Page 37

Configuring the V2IU 4350
Timing
Display and set the clock timing source for the T1/E1 interface. The timing can
be either derived from the network (External) or provided to the T1 interface
by the V
2
IU (Internal). With a carrier-provided T1, the timing is usually
derived from the network (External, the default setting).
Warning
Mismatched timing modes can result in WAN connectivity but with intermittent data
loss.
Payload Loopback
Display and set the loopback setting. During T1 line testing the local interface
can be set to Loopback to allow the network provider to verify connectivity
and line quality. For normal operation the setting should always be No
Loopback (the default setting).
Configure the DHCP Server
The 4350 can act as a DHCP server granting IP addresses to PCs, workstations,
servers or voice devices (IP phones, IADs or softphones) connected to its LAN
interfaces. DHCP is a protocol that enables IP devices to obtain temporary or
permanent IP addresses (out of a pool) from centrally administered servers.
The user can configure blocks of IP addresses, a default gateway, DNS servers,
NTP server address, Time offset from NTP value, WINS address and
TFTP/FTP server name that can be served to the requesting IP devices.
3 - 19
Page 38

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
In addition the 4350 will provide its LAN IP address in DHCP user options 150
and 151 for use by IP phones. Some IP phones use these values for
configuration of their TFTP server and MGCP control server addresses.
Note
The DHCP server in the 4350 should not be used if a DHCP server already exists in
the same subnet as the 4350. Also, it is recommended that you assign static IP
addresses for common-access devices such as network printers or fax machines.
You can also enable or disable the 4350 DHCP server on a per VLAN basis.
1. Select DHCP Server.
2. If you are using VLANs select the desired VLAN ID from the drop down
menu.
3. The default value for the DHCP server is disabled. Click the top checkbox
to enable or disable the internal DHCP server (default is disabled). If you
are using VLANs select the desired VLAN ID.
4. Enter the Lease Duration.
The lease duration is the amount of time in days that an IP device may use
an assigned IP address before requesting that it be renewed. The default
value is 7 days and the valid range of input is 1 to 30 days.
5. Enter the Subnet Mask.
This is the subnet mask that will be sent via DHCP to the requesting IP
devices.
6. Enter the DHCP IP Addresses.
This is the pool of IP addresses that will be provided to the requesting IP
devices. You can enter both individual IP addresses or a range of
addresses using the following format:
3 - 20
Note
192.168.1.2 (single address)
192.168.1.4-10 (address range 192.168.1.4 through 192.168.1.10)
The range format can only be used for class C addresses (those with a subnet
mask of 255.255.255.0).
7. Enter the Time Offset (DHCP user option 2).
8. Set the time offset in hours from UTC for your local location. This value is
optional; if supplied, it will be delivered to clients.
9. Enter the NTP Server Address (DHCP user option 42).
This is the IP address of a Network Time Server. This value is optional; if
supplied, it will be delivered to clients.
10. Enter the WINS Address.
Page 39

Configuring the V2IU 4350
Note
If you are not using WINS leave this field blank.
The Windows Internal Naming Service (WINS) is a service that keeps a
database of computer name-to-IP address mappings so that computer
names used in Windows environments can be mapped to IP addresses.
The WINS Address is the IP address of the WINS server in your network.
This value will be delivered to clients.
1. Enter the TFTP/FTP Server Name (DHCP user option 66).
Some IP phones use this setting to locate the TFTP or FTP servers which
contain the phone software image used during boot. By default this option
is the same as the TFTP server on the VoIP ALG page.
2. Primary and Secondary DNS
The primary and secondary DNS values come from those set under the
WAN interface configuration, see Configure the WAN interface. These
values will be delivered to clients.
3. Default Gateway
The default gateway is automatically set to the 4350’s LAN address, see
Configure the LAN interface. This value will be delivered to clients.
4. Press Submit.
Delete a DHCP IP Address
1. Select DHCP Server.
2. To delete an IP address or a range of IP addresses highlight an entry or
range of entries in the DHCP IP Addresses list and press the Delete key
on your keyboard.
3. Press Submit.
Disable The DHCP Server
4. Select DHCP Server.
5. Uncheck\ the Enable DHCP Server checkbox.
6. Press Submit.
3 - 21
Page 40

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Configure Hostname, SNMP and Remote Logging
The 4350 can be managed remotely by an SNMP network management system
such as HP Openview. The 4350 supports SNMPv1 or SNMPv3 and MIB-II
(RFC1213). All MIB-II variables are read only. The MIB variables sysContact
and sysLocation are set by the web GUI.
3 - 22
Messages generated by the 4350 can be sent to a remote log server.
The configuration screen is reached through the Configuration Menu:
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Services Configuration.
Configure SNMP
1. Select the Enable SNMP v1 or v3 checkbox. If using SNMPv1 enter the
Read-Only Community. If using SNMPv3 enter the User Name,
Passphrase and Security method.
Page 41

Configuring the V2IU 4350
2. Enter the System Location.
This is a comment string that can be used to indicate the physical location
of the 4350. By default, no value is set.
3. Enter the System Contact.
This is the administrative contact information for the 4350. By default, no
value is set.
4. Enter the SNMP Port.
This is the port that the 4350 uses for SNMP communications with the
network management system. The default is 161.
5. Press Submit.
Disable SNMP
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Services Configuration.
4. Uncheck the Enable SNMP checkbox.
5. Press Submit.
Configure Remote System Logging
The 4350 can be configured to log system messages to an external syslog
server.
1. Select the Enable Remote System Logging checkbox.
2. Enter the IP address of the Remote Syslog Host.
By default messages are sent to the remote host on port 514. This port can
be changed by using the syntax ADDRESS:PORT.
3. Press Submit.
Disable Remote System Logging
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Services Configuration.
4. Uncheck the Enable Remote System Logging checkbox.
5. Press Submit.
3 - 23
Page 42

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Configure a local Hostname
A locally configured hostname is useful for remote management. This name
can appear as the identifier string for the 4350 on a system management
console.
>>
Enter a host name in the field provided.
Enable Mean Opinion Scoring (MOS)
The 4350 produces useful statistics on a per call basis that can be written to
syslog. These include MOS, jitter, latency, packet loss and much more.
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Services Configuration.
4. Select Enable MOS.
Set MOS Threshold
You can define a minimum MOS value in the 4350 such that a message will be
sent to syslog when the measured MOS value drops below the minimum. This
is useful when for monitoring a particular location for call quality problems
and enables pro-active resolution of problems that negatively affect call
quality.
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Services Configuration.
4. Enter the minimum MOS threshold in the Set MOS threshold field.
5. Press Submit
Change the Administration Password
We strongly recommend that you change the default password for the root
administrative account using the following steps:
3 - 24
Page 43

Configuring the V2IU 4350
Note
The new password must be between 6 and 20 characters in length. Any
combination of alpha and numeric characters is accepted.
1. Enter the password you chose in step C again in the Confirm Password to
ensure that there were no mistakes in the initial entry.
2. Press Submit.
Read-only User
This feature works by creating a new user with read-only access to the system.
All information is displayed in a non-changeable form. Information changed
in entry boxes cannot be submitted. In fact, most Submit and OK buttons are
not visible.
Note: You must have administrator privileges and log in as an administrator
to change read-only user.
Enabling a Read-only User
To enable a read-only user, use the following steps:
1. Using the configuration graphical user interface, from the Configuration
Menu on the left-hand side, click Network.
Note: You must have administrator access and log in as an administrator
to change read-only user.
2. Scroll down to the area of the screen shown below.
3. Click changed. The following window screen appears:
3 - 25
Page 44

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Note: All open web browsers must be closed when you change between
administrative user “root” and read-only “rouser.”
4. Enter a new password. The password must be a minimum of six
characters long.
4. Re-enter the new password to confirm it.
5. Click Submit.
No w when you ac cess the s ystem usin g thi s use r name (rou ser) a nd pa sswor d,
all fields are read-only.
Subinterfaces
The Subinterfaces feature allows a system administrator to assign additional
IP addresses to interfaces. These are sometimes referred to as aliases or
loopback interfaces. An additional address may be assigned to the system’s
WAN interface to support, for example, another management IP address.
How Subinterfaces Works
A common use for subinterfaces is forwarding a public subnet. A subinterface
may be created to support a subnet forwarded through the Polycom V
4350. When forwarding a subnet through the Polycom V
necessary to assign an address for this subnet to the system to act as the
subnet's gateway. To configure forwarding rules, use the Forwarding Rules
submenu under the Firewall configuration link.
2
IU 4350, it is
2
IU
3 - 26
When applied to the WAN/Provider interface, these addresses are protected
by the same firewall policy that is applied to the WAN/Provider address.
Several other features in the system automatically create Subinterfaces. VRRP
(if supported) and Static NAT automatically create Subinterfaces.
Page 45

When viewing the Network Information page, Subinterfaces are designated in
the Interface Information section with the device name and number, separated
by a colon (for example, eth0:100).
Configuring Subinterfaces
To configure subinterfaces, use the following steps:
1. Using the configuration graphical user interface, from the Configuration
Menu on the left-hand side, click Network.
2. Click Subinterfaces. The window shown below opens.
Configuring the V2IU 4350
3. On this screen, complete the following information:
• IP Address is the address to be assigned to the subinterface.
•Netmask is the network mask to use for the address. If several addresses
are applied to an interface and these addresses are in a common network,
they must use a common subnet. The system does not support
supernetting.
• Interface is the port where the subinterfaces will be configured.
4. When you have finished entering this information, click Add. The
following popup appears:
5. Click OK. The new subinterfaces entry appears on the Subinterfaces
window in the list area.
3 - 27
Page 46

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
ToS Byte Setting
Since the Internet itself has no direct knowledge of how to optimize the path
for a particular application or user, the IP protocol provides a limited facility
for upper layer protocols to convey hints to the Internet Layer about how the
trade-offs should be made for the particular packet. This facility is the “Type
of Service” or ToS facility.
ToS settings allow the service provider to prioritize time sensitive traffic, such
as voice plus video to ensure minimized packet loss and delay through their
network. When providing end-to-end QOS, it is important that the voice plus
video traffic be placed in the correct queues to deliver a higher QOS than
regular traffic. Regular traffic, that is not time sensitive, can be delayed with
little or no indication to the user, while the slightest delay in voice plus video
can cause auditable differences. The ToS byte setting helps prioritize traffic
going to the WAN so a provider can prioritize the traffic correctly in its
network.
Although the ToS facility has been a part of the IP specification since the
beginning, it has been little used in the past. However, the Internet host
specification now mandates that hosts use the ToS facility. Additionally,
routing protocols (including OSPF and Integrated IS-IS) have been developed
which can compute routes separately for each type of service. These new
routing protocols make it practical for routers to consider the requested type
of service when making routing decisions.
How the ToS Byte Setting Works
For all RTP traffic (voice and video), the Polycom V2IU 4350 marks the ToS
byte in the IP header as “High Priority,” and strips (set to 0) the ToS byte for
all other traffic. Unchecking the “Enable ToS Byte Stripping” option means
that the ToS byte will not be stripped from non-RTP traffic, but will remain
unchanged.
Note: For most situations, you should leave this setting as it is. Only change it
if your provider indicates that you should do so.
Viewing or Changing the ToS Byte Setting
To view or change the ToS byte setting, use the following steps:
1. Using the configuration graphical user interface, from the Configuration
Menu on the left-hand side, click Traffic Shaper.
2. Scroll down the area of the screen shown below.
3 - 28
Page 47

Configuring the V2IU 4350
3. For most situations, you should leave this setting as it is. Only change it if
your provider indicates that you should do so. If your provider indicates
that you need to change the ToS byte setting, that provider should also
provide the other parameters required on this screen.
4. If you have changed the values, click Submit to activate the new settings.
3 - 29
Page 48

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
H.323 Configuration
To access the H.323 Settings page, select VoIP ALG > H.323 in the Configuration Menu.
3 - 30
Page 49

Configuring the V2IU 4350
The H.323 Settings page has the following areas:
• Gatekeeper Mode
• WAN/Provider-side gatekeeper mode settings
• LAN/Subscriber-side gatekeeper mode settings
• Embedded gatekeeper mode settings
• LRQ Size
• Default Alias
• Stale Time
• Multicast Messages
3 - 31
Page 50

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
• H.460.18 Support
• Alias Restrictions
In the Gatekeeper mode area, select one of the following modes:
Item Description
None H.323 is disabled.
WAN/Provider-side
gatekeeper mode
LAN/Subscriber-side
gatekeeper mode
Peering-Proxy mode Allows calls to be forwarded to other endpoints based on
Embedded gatekeeper
mode
Specifies that the system will forward all client RAS
messages to the gatekeeper. If this is selected, you must
configure the settings in the WAN/Provider-side
gatekeeper mode settings area.
Specifies that the system will act as a gatekeeper. If this
option is selected, you must configure the settings in the
LAN/Subscriber-side gatekeeper mode settings area.
the information sent from the endpoints. All the
information about routing the call must be sent as part of
the request or prefixes must be configured.
Provides gatekeeper functions and accepts endpoint
registrations. If this option is selected, you must configure
the settings in the Embedded gatekeeper mode settings
area.
If WAN/Provider-Side Gatekeeper mode is selected, you must configure the
following parameters:
Item Description
WAN/Provider-side GK
address
Modify Time-To-Live Allows you to override the value for time-to-live returned
New Time-To-Live Specifies how long an endpoint's registration should be
Specifies the IP address of the gatekeeper
by the gatekeeper before forwarding the response to the
endpoint.
valid.
3 - 32
Page 51

Configuring the V2IU 4350
If LAN/Subscriber-Side Gatekeeper mode is selected, you must configure the
following parameters:
Item Description
LAN/Subscriber-side GK
address
Allow public IP in LCF Select the checkbox if the gatekeeper has been deployed
Enter the IP address of the gatekeeper.
with multiple outbound proxies and must decide which
proxy to use based on the IP address returned in the LCF .
This is an advanced configuration option and should
usually not be selected.
If Embedded Gatekeeper is selected, you must configure the following
parameters:
Item Description
Time-to-Live(s) Enter a time in seconds. This setting controls how
long an endpoint’s registration should be valid. At
the end of this period the endpoint sends another
registration request.
Prevent calls from
unregistered endpoints:
Blocks unregistered LAN-side endpoints from
making calls through the device.
In the LRQ Size area, you can limit the number of source aliases in a
forwarded LRQ message to a maximum of two to allow interoperability with
gatekeepers that cannot handle more than two source aliases.
In the Default Alias area, you can specify a default alias to be added to incoming calls without a destination message in the Q.931 Setup message. This alias
allows the embedded gatekeeper or a LAN/Subscriber-side gatekeeper to
route the call to a default endpoint. Enter a default alias and select one of the
following types:
• E.164
• H.323
In the Stale Time area, you can arrange to delete clients that have not sent any
registration requests for the specified interval. This area includes the
following configurable parameters:
Item Description
Delete stale clients Select this checkbox to enable the stale timer feature.
Stale time (m) Specify the length of the interval in minutes.
3 - 33
Page 52

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Some RAS messages can be multicast in order to automatically detect gatekeepers. In the Multicast Messages area, you can enable listening to multicast
messages. This area includes the following configurable parameter:
Item Description
Listen to multicast
messages
In the H.460.18 Support area, you can configure H.460.18 support. This allows
the system to do NAT/Firewall traversal for clients behind NAT or firewall
devices. This area includes the following configurable parameters:
Item Description
Disabled Disables H.460.18 support.
Enabled Enables H.460.18 support.
Keep-alive time(s) Specifies the keep-alive time if H.460.18 support is
Select this checkbox to enable listening to multicast
messages.
enabled.
In the Alias Restrictions area, you can set a limit on the number of aliases that
are allowed to register with the system. If this number is exceeded when a client tries to register, the registration is rejected. This area includes the following parameter:
Item Description
Max Aliases Enter the maximum number of allowed aliases. If the value is set
to 0, the maximum is not enforced.
The H.323 Settings page includes the following two buttons:
Item Description
Submit Applies the settings configured on this page.
Reset Clears all fields and selections and allows you to enter new
information.
3 - 34
Page 53

H.323 Activity
Configuring the V2IU 4350
To access the H.323 Activity page, select VoIP ALG > H.323 Activity in the
Configuration Menu.
The H.323 Activity page is a read-only page that shows the following information:
• Current time
• WAN Gatekeeper status
• Current payload bandwidth
• Estimated total bandwidth
• Activity log of recent H.323 events
H.323 Alias Manipulation
Alias manipulation is performed immediately when a message (such as an
ARQ, LRQ or a Setup) is received. Any matching pattern is replaced with the
specified string, allowing you to replace characters or strings that are hard or
impossible to dial on certain endpoints. Normal call look-up is performed
following alias manipulation.
3 - 35
Page 54

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
To access the H.323 Alias Manipulation page, select VoIP ALG > H.323
>Alias Manipulation in the Configuration Menu.
This page includes the following areas:
Item Description
Destination
H323-ID or
E.164 Alias
Modification
table
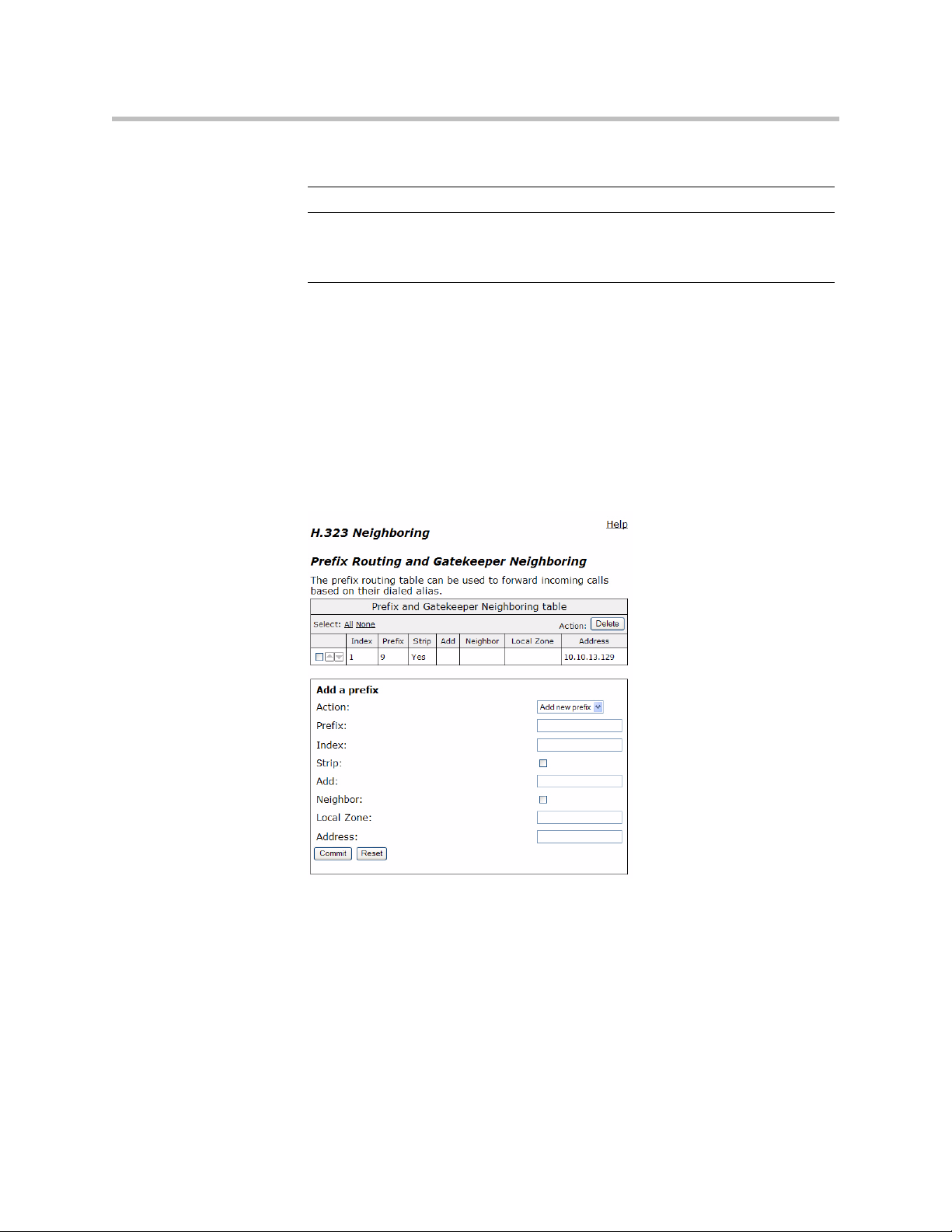
Add a rule Allows you to add new prefixes to the Prefix Routing and
Item Description
Action Indicates whether the rule is to be added or edited.
Pattern Specifies the pattern to be matched. See <l_link>“Regular
Index Determines the order in which the rule is scanned in the
Replace Specifies the string that will replace the matched pattern.
Lists alias manipulation rules.
Rules are executed in the order in which they are listed. Use the
arrows to move entries up and down, or use the Index field to
specify where a new or edited rule falls in the list.
Gatekeeping Neighboring table.
Expressions” on page 39 for details on valid patterns.
Destination H323-ID or E.164 Alias Modification table. To add a
rule between two rules with consecutive indexes (n and m), use
the higher index (m).
3 - 36
Page 55
H.323 Neighboring
Configuring the V2IU 4350
The H.323 Alias Manipulation page includes the following buttons:
Item Description
Commit Applies the settings configured on this page.
Reset Clears all fields and selections and allows you to enter new
information.
Neighboring and prefix routing can be used to route calls based on a matching prefix in the destination alias of the call. The call decision is made following alias manipulation and acts on the modified string, similar to other call
lookup processes such as registered client look-up. Each prefix is associated
with a domain name or IP address that is used in the event that the prefix
matches.
To access the H.323 Neighboring page (formerly the Prefix Routing page),
select VoIP ALG > H.323 > Neighboring in the Configuration Menu.
3 - 37
Page 56

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
This page includes the following areas:
Item Description
Prefix Routing
and
Gatekeeper
Neighboring
table
Lists rules for forwarding incoming calls based on their dialed
alias.
Rules are executed in the order in which they are listed. Use the
arrows to move entries up and down, or use the Index field to
specify where a new or edited rule falls in the list.
Add a prefix Allows you to add new prefixes to the Prefix Routing and
Gatekeeper Neighboring table.
Item Description
Action Indicates whether the rule is to be added or edited.
Prefix Specifies the prefix pattern to be matched against the dialing
string. See
<l_link>“Regular Expressions” on page 39 for details
on valid patterns.
Index Determines the order in which the rule is scanned in the Prefix and
Gatekeeper Neighboring table. To add a rule between two rules
with consecutive indexes (n and m), use the higher index (m).
Strip Indicates whether the matching prefix is stripped from the dialing
string.
Add Specifies a string to be prepended to the dialing string.
Neighbor Determines whether a location request (LRQ) is sent when this
prefix matches.
• If enabled, the prefix becomes a neighboring statement.
• If disabled, the incoming Q.931 Setup is forwarded to the given
address without a preceding LRQ.
This field is used for interoperability with other ga tekeepers that
may not accept a Setup without a preceding LRQ.
3 - 38
Local Zone Provides compatibility with remote gatekeepers that are
configured to accept LRQs only from sources that match its
configured remote zone. If a gatekeeper is configured to accept
requests only from a known source, enter the zone in this field.
Address Specifies the IP address or domain name of the device to which
the call is to be forwarded.
The H.323 Neighboring page includes the following buttons:
Item Description
Commit Applies the settings configured on this page.
Reset Clears all fields and selections and allows you to enter new
information.
Page 57

Regular Expressions
Configuring the V2IU 4350
Alias manipulation patterns and prefixes use regular expressions to match a
string in the destination alias. A regular expression can be a string of literal
characters to match or a set of special expressions.
Alias manipulation patterns can match a sub-string at any location and
number of times within the alias. Prefixes are always searched from the left of
the alias and cannot match a middle part or the end of the alias.
Regular expressions are listed in <l_link>Table 1 and <l_link>Table 2 lists
some example expressions.
Table 1 Regular Expressions
Symbol Description
. Matches any single character.
[] Matches any single character listed between the []. For example,
[abc], [123]. If the characters are separated by a -, all characters
between the two are matching, e.g. [a-z], [0-9]
() Matches the literal string given, e.g. (abc)
| Matches the block on either side of the |, e.g. a|b.
? Matches 0 or 1 of the preceding block.
* Matches 0 or more of the preceding block.
+ Matches 1 or more of the preceding block.
\ Escapes the special meaning of the next character.
{a} Matches exactly 'a' numbers of the preceding block.
{a,} Matches 'a' or more of th e preceding block.
{a,b} Matches between 'a' and 'b' (inclu si ve ) of th e pr eceding block.
Table 2 Example Regular Expressions
Expression Description
100 Matches the string 100.
(555)?123 Matches 555123 or 123.
(408|555) Matches 408 or 555.
555[0-9]{3} Matches 555 followed by exactly 3 digits.
# Matches the character '#'.
\* Matches the character '*'. Note that '*' by itself is a regular
expression and must therefore be escaped with a '\' to match the
character itself.
3 - 39
Page 58

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Forwarding Rules
Forwarding Rules allows a system administrator to forward data traffic for a
subnet from one interface to another, overriding the Firewall’s default drop
rules.
Allowing a subnet to be forwarded is commonly used when servers with
public addresses are placed behind the system. Configuring the network in
this way allows the system to manage and prioritize bandwidth, sharing it
between the VoIP services and the servers.
How Forwarding Rules Works
When forwarding, one address from the forwarded range of addresses must
be assigned to the rule's output interface. The Polycom V
address to act as a gateway router for the subnet. The address may be
assigned using the Subinterfaces page.
Note: The subnet and forwarded addresses are not protected by the firewall.
A similar method for forwarding traffic is provided by Proxy ARP. Proxy ARP
is used to “bridge” addresses within a single subnet range from one interface
to another. Often this is used to bridge and forward a public address to the
protected side of the system without having to subnet the public address
range. Proxy ARP does not require an additional gateway address on the system for the subnet, but does not allow port and protocol filtering for forwarded data.
2
IU 4350 uses this
Example
In this example:
• The ISP has supplied two separate subnets to the customer:
— A small one (2 hosts) for the WAN link
— A large one (254 hosts) for a bank of servers
• 67.40.41.2 is the WAN IP address for the Polycom V2IU 4350
• NAT is a private IP range of 192.168.1.xxx using the WAN address for PCs
and Phones
• On the LAN side of the Polycom V2IU 4350 are the following:
— Private IP subnet (192.168.1.xxx)
— Public IP subnet (67.40.40.xxx)
This is shown below.
3 - 40
Page 59

Configuring the V2IU 4350
Configuring Forwarding Rules
To configure address forwarding rules, use the following steps:
1. Using the configuration graphical user interface, from the Configuration
Menu on the left-hand side, click Firewall.
2. Click Forwarding Rules. The window shown below opens.
3 - 41
Page 60

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
3 - 42
3. On this screen, complete the following information:
• IP Subnet: The subnet to be forward through the firewall from the Input
Interface to the Output Interface.
•Netmask: The network mask to apply to the IP Subnet to create the range
of IP addresses that are forwarded through the firewall.
• Input Interface: The interface where data is received that is destined for
the forwarded subnet (destination address(es)).
• Output Interface: The interface where data is received that is sent from the
forwarded subnet (source address(es)).
•Protocol: The following protocols are used:
— UDP: for the specified network, allows the specified UDP port or port
range to pass through the system
— TCP: for the specified network, allows the specified TCP port or port
range to pass through the system
Page 61

Peering Proxy
Configuring the V2IU 4350
— Any: for the specified network, allows all ports and protocols through
the system. No ports are required because not all protocols support
the concept of ports.
• Port or Port Range: The port number or port range allowed through the
system when UDP or TCP are selected. A port range is specified by
separating the starting and ending ports with a colon ':' (for example,
22:80). The ports parameter is not supported when you select Any
protocol because not all protocols support the concept of ports.
4. When you have finished entering this information, click Add.
5. Click OK. The new forwarding entry appears on the Forwarding Rules
window in the list area.
H.323 prefixes can be used to route calls based on a matching prefix in the
destination alias of the call. Each prefix is associated with a domain name or IP
address to send the call to in case the prefix matches.
The prefixes are searched in order, that is, the first prefix is tried first, and then
the next one on the list until the system finds a matching prefix. This means
that if there are multiple matching prefixes, the first one is used.
How Peering Proxy Works
The Polycom V2IU 4350 supports the concept of an H.323 Peering Proxy. This
function provides advanced security layers or peering points within the
network where a security layer is needed. Peering Proxy allows network
providers to add internetworking connections between their “trusted”
network and an unknown network. This topology hides their trusted network
and the Stateful packet inspection Firewall provides the policies to ensure
security. You can add Peering Proxies in series with one another to push the
core H.323 networking infrastructure to meet individual security
requirements.
The illustration below shows a sample diagram with dial plan and call flow
examples. It is a snapshot of how the Peering Proxy can be deployed. Peering
Proxy however, is not limited to this specific scenario, so contact your Polycom
representative to discuss specific network requirements for full Peering Proxy
support.
3 - 43
Page 62

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Note: A minimum configuration for Peering Proxy would be for inbound only
prefixes, since there may be many endpoints to statically route calls to. There
might also be a master gatekeeper to which all endpoints are registered. In this
case, you would only need 1 prefix pointing to the master gatekeeper and let
that gatekeeper signal the other endpoints directly.
3 - 44
In the example above, the Polycom V2IU 4350 Peering Proxy is installed in
“Private Video Network A and B,” a peering point into this network. This
network could have additional peering points to allow topology spreading of
network resources. However, this example shows only a single point. Peering
Page 63

Configuring the V2IU 4350
Proxy provides an access point into this network and is responsible for the
E.164 dial plan using NANP (North American Numbering Plans or NAP’s).
The NAP’s in this case are 831 and 408.
Dial plan integrity is required to insure proper routing of prefix's. This means
that if users are to dial into your network, they could be required to enter a
“Prefix” on their V
2
IU with a corresponding destination IP. If the user was to
dial another user NOT destined to your network with the same beginning
prefix, the prefix configured on this V
2
IU would create a prefix match and the
call would route incorrectly. The call routes to the destination defined in the
prefix and not to the intended endpoint. The example shows “Private Video
Network A's Peering Proxy” with an inbound prefix defined as 8315…… Any
inbound call that matches 8315 with any 6 digits creates a prefix match and
sends the call to 10.10.11.1. Refer to “Regular Expressions” in the Info button
on the GUI interface for information on all the methods for defining prefixes.
Private Video Network A is one example of a V
2
IU configured in “LAN Side
Gatekeeper” mode with an ANNEX O dial method to dial “Off Net.” Internal
“On Net” endpoints registered to the LAN Side Gatekeeper will dial E.164
only. This allows any location to place calls to any location with an ANNEX O
dial plan, that is, E.164@WAN_IP or other V
2
IU's deployed on the network. In
this example a Peering Proxy has been deployed to allow dialing ingress and
egress to the Public Internet. At each V
2
IU location required to egress, the
Public Internet requires a “Prefix” to be configured. This allows that location's
endpoint to dial “Off Net” to the Public Internet. This prefix can be configured
to any digit and may be part of the externally dialed E.164 in the
E.164@WAN_IP, that is, to reach site A by dialing 4155551000@66.20.20.4
where the prefix is defined as 415* or 415……. In this example, a “9” was
chosen. The prefix is then mapped to the LAN interface of the Peering Proxy
10.10.11.1. The dial string is now 94155551000@66.20.20.4 and a strip rule for
the prefix is applied. This is needed to route the call at the destination
correctly. If the Site C V
2
IU does not strip the “9”, the destination V2IU fails the
call with a “No Registered Client” message (call failures can be viewed under
the “H323 Activity” page in the GUI), since the “9” becomes part of the E.164.
If you choose a prefix that matches the destination E.164, set Site A’s V
2
IU to
NOT strip matching prefixes.
NOTE: In this illustration E.164@WAN_IP was used as an example. Peering
Proxy and all V
2
IU's support user@host ANNEX O dialing methods, for
example 123@1.1.1.1 or abc@1.1.1.1 or abc@abc.com with a DNS SRV record
configured to point to an A record for the WAN IP of the V
2
IU.
The following sections demonstrate the Dial Plan for ingress and egress calls
to Private Video Network A as shown in the illustration.
Outbound from Site C to Site A
Site C dials an endpoint located at Site A: 94155551000@66.20.20.4. The
PathNavigator receives the call and generates a Q.931setup to the V
subnet. The V
2
V
IU looks for a prefix match. In this case, the “9” creates a match. The “Strip
2
IU processes the Q.931 setup from the calling endpoint. The
Matching Prefix” rule is applied, the “9” is stripped, and the call is routed to
2
IU for that
3 - 45
Page 64

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
the Peering Proxy IP 10.10.10.1. The Peering Proxy applies the same rule set, in
this case, NO matching prefix is found and ANNEX O dialing is applied. The
call is now routed to Site A's V
PathNavigator where the registered client with the E.164 of 4155551000 is
located and the call is gatekeeper routed to the called endpoint.
Inbound from Site A to Site C
Site A dials: 8315551000@67.40.40.4. (The destination IP is the Peering Proxy
WAN IP address.) The Peering Proxy is configured with prefix 8315……and is
mapped to the WAN IP of the V
could be 831* or 83…… and so on, depending upon dial plan requirements.
The PathNavigator receives the Q.931setup from the endpoint and forwards
the call to the V
calling endpoint. The V
and ANNEX O dialing is applied. The call is now routed to the Peering Proxy
IP 67.40.40.4. The Peering Proxy receives the Q.931 setup and looks for a prefix
match, in this case “8315” creates a match. The Peering Proxy now changes the
destination IP to 10.10.11.1 and routes the call to Site A’s V
is forwarded to the LAN Side PathNavigator where the registered client with
the E.164 of 8315551000 is located, and the call is gatekeeper routed to the
called endpoint.
2
IU. The call is forwarded to the LAN Side
2
IU 10.10.11.1. As explained earlier, the prefix
2
IU for that subnet. The V2IU receives the Q.931 setup from the
2
IU looks for a prefix match, finds NO matching prefix,
2
IU. The Q.931 setup
Outbound from Site C to Site D
Site C dials an endpoint located at Site D: 95125551000@68.30.30.4. The
PathNavigator receives the call and generates a Q.931 setup to the V
that subnet. The V
2
V
IU looks for a prefix match, in this case the “9” creates a match. The “Strip
2
IU processes the Q.931 setup from the calling endpoint. The
Matching Prefix” rule is applied, the “9” is striped, and the call is routed to the
Peering Proxy IP 10.10.10.1. The Peering Proxy applies the same rule set, in this
case NO matching prefix is found, and ANNEX O dialing is applied. The call
is now routed to the Peering Proxy for “Private Video Network B” IP
68.30.30.4. The Peering Proxy receives the Q.931 and looks for a prefix match.
In this case, “5125” creates a match. The Peering Proxy now changes the
destination IP to 172.16.2.1 and routes the call to Site D's V
2
IU. The V2IU is
configured for Embedded Gatekeeper Mode. In this mode, the endpoint is
directly registered and an E.164 registered client match is made. The call is
then routed to the called endpoint.
2
IU for
Outbound from Site D to Site B
Site D dials an endpoint located at Site B: 95105551000@65.10.10.4. The V2IU
Embedded Gatekeeper is configured with a prefix of “9” to point to Peering
Proxy 172.16.1.1. The V
a match. The “Strip Matching Prefix” rule is applied, the “9” is striped, and the
call is routed to Peering Proxy IP 172.16.1.1. The Peering Proxy applies the
same rule set. In this case NO matching prefix is found and ANNEX O dialing
is applied. The call is now routed to Site B. The V
2
IU looks for a prefix match. In this case, the “9” creates
2
IU is configured for
3 - 46
Page 65

Configuring the V2IU 4350
Embedded Gatekeeper Mode. In this mode, the endpoint is directly registered,
an E.164 registered client match is made, and the call is routed to the called
endpoint.
Outbound from Site C to Public IP Endpoint
Site C dials the public endpoint: 9@61.10.10.4. The PathNavigator receives the
call and generates a Q.931 setup to the V
the Call setup from the calling endpoint, and the V
In this case, the “9” creates a match. The “Strip Matching Prefix” rule is
applied, the “9” is striped, and the call is routed to the Peering Proxy IP
10.10.10.1. The Peering Proxy applies the same rule set, in this case NO
matching prefix is found, and direct IP dialing is applied.
Inbound from Public IP Endpoint to Site C
Public IP endpoint is NOT registered to a gatekeeper and must dial an IP+EXT
to reach Site A’s endpoint,. In this case, the IP address is 67.40.40.4 and EXT
8315551000. The Peering Proxy receives the call and looks for a prefix match.
In this case “8315” creates a match. The Peering Proxy now changes the
destination IP to 10.10.11.1 and routes the call to Site A’s V
is forwarded to the LAN Side PathNavigator where the registered client with
the E.164 of 8315551000 is located, and the call is gatekeeper routed to the
called endpoint.
Configuring Peering Proxy
To configure peering proxy, use the following steps:
2
IU for that subnet. The V2IU receives
2
IU looks for a prefix match.
2
IU. The Q.931 setup
1. Using the configuration graphical user interface, from the Configuration
Menu on the left-hand side, click VoIP ALG.
2. Click H.323. The window shown below opens.
3 - 47
Page 66

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
3. On this screen, check “Peering-Proxy mode”.
4. Scroll to the bottom of the window and click Submit.
Adding an H.323 Prefix Entry
You can add prefixes by entering the prefix string and the target address.
To add an H.323 prefix entry, use the following steps:
1. Using the configuration graphical user interface, from the Configuration
Menu on the right-hand side, click VoIP ALG.
2. Click H.323 Prefixes. The window shown below opens.
3 - 48
Page 67
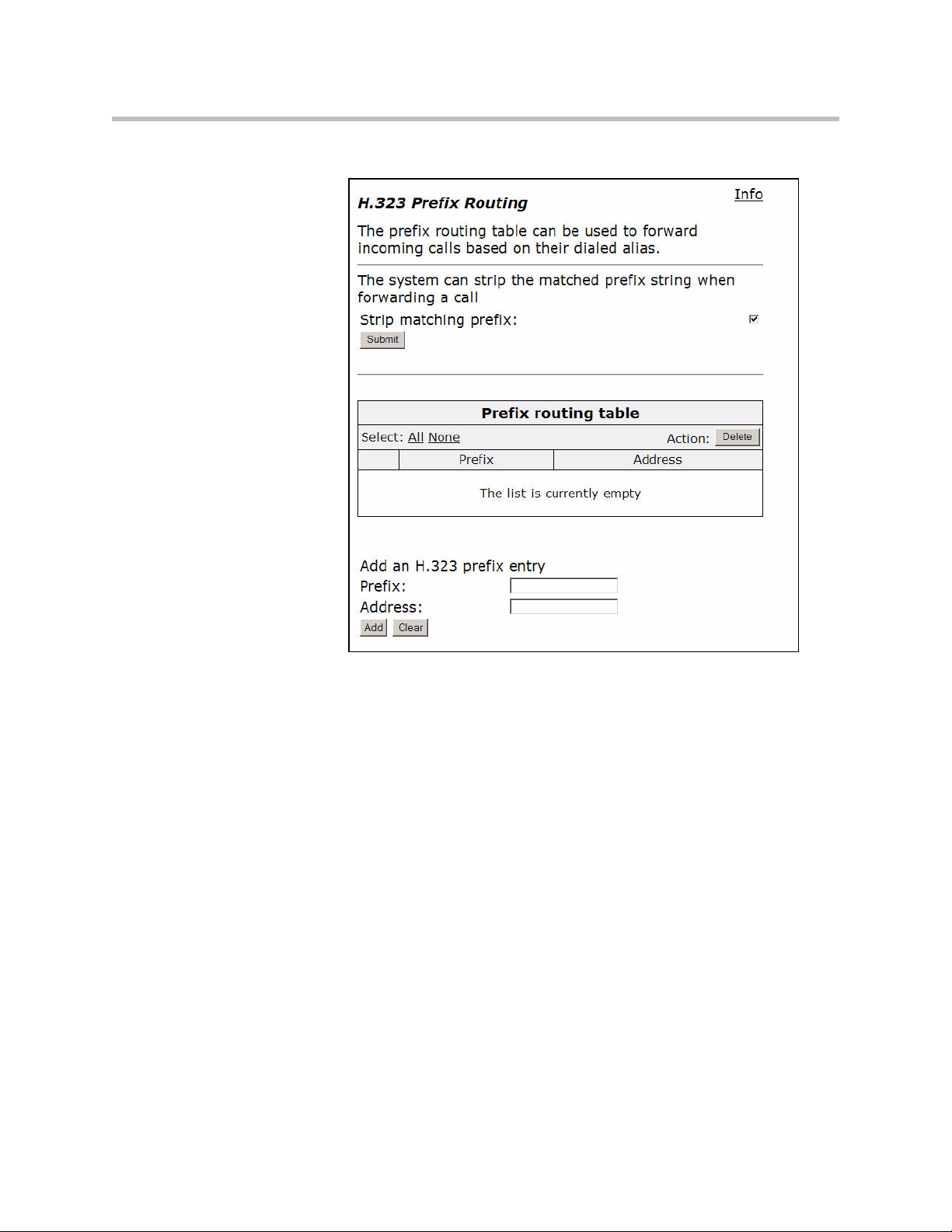
Configuring the V2IU 4350
3. To strip a matching prefix, select the checkbox and click Submit.
4. To add an entry, enter the prefix and the address.
5. Click Add. The new entry appears in the table.
Clients List Lock
Client List lockdown allows you to prevent new clients from registering. This
is done as follows:
• Creating a client, as follows:
The prefix routing table shows all currently configured prefixes. The
prefixes are searched in the order they are entered. Each prefix can be
moved up or down in the list. You can select and delete prefixes.
If you enable this, all matching prefixes are stripped from the destination
alias before the call is forwarded.
The prefix string can be a regular expression as described above. The
target address can be a domain name or an IP address.
3 - 49
Page 68

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
— Manually entering all clients that are allowed to use the system
— Running the system without the Client List lockdown feature until all
desired clients have registered
• Enabling this feature.
This feature is useful for lists involved with 911 usage.
When this feature is in effect, any message from an unauthorized SIP client
will be rejected with a “403 Forbidden” response. MGCP messages will be
discarded.
Enabling the Clients List Lock
To configure clients list lock, use the following steps:
6. Using the configuration graphical user interface, from the Configuration
Menu on the left-hand side, click VoIP ALG. The following window
appears.
3 - 50
3. On this screen, check “Enable Client List lockdown”.
4. Scroll to the bottom of the window and click Submit.
Page 69

H.323 Activity Monitor
The H.323 Activity Monitor shows any recent H.323 events that may be of
interest to the administrator of the system. The information appears in three
columns:
• Event/Time
• Source
• Destination
Following this information are a number of lines with event specific information such as call-id, duration, call-status, and so on.
Abnormal events have their event specific information listed in red.
Configuring the V2IU 4350
3 - 51
Page 70

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Type of Events
The events that may currently be listed in the activity monitor are as follows:
• Bandwidth change - the endpoint requested a change of the bandwidth
used for its call, only sent if the bandwidth management is enabled.
• Call Setup – Only sent if the call was ‘successfully’ established. A call is
successfully established if the H.245 media negotiation connection was
established.
• Call Termination – Sent when a call terminates. You can have a call
termination event without a call setup event, for example, a failed call that
doesn’t reach the H.245 established state will not cause a call setup event,
but only a call termination event.
• Registration Reject – Sent when a registration was rejected. This includes
the authority that rejected the registration (our side or the gatekeeper (only
in WAN GK mode) as well as a text reason for the rejection.
• Gatekeeper reachability changed (only in WAN GK mode). Gatekeeper
status toggled from reachable to unreachable or vice versa.
• Location Request – Received a location request from a neighboring
gatekeeper.
Call Status
• Location Confirm – Sent, or forwarded, a location confirm to a previous
request.
• Location Reject - Sent, or forwarded, a location reject to a previous
request.
The call status shows the last state of the call at the time of the event. Each call
progresses through a number of states when being established. If a call fails,
the call-status in the call termination event can help trouble-shoot the cause of
the call failure. For example, if the call fails at the “Caller/Callee admission
request received” state, there may be a problem communicating with the
gatekeeper, whereas if the call fails at the “Attempting to establish outgoing
Q.931 TCP connection” state, the remote endpoint may not be reachable.
The following are call status messages:
• “Caller admission request received”
Received an admission request from the source endpoint and forwarded it to
the gatekeeper.
• “Caller admission response received”
Received an admission response (either confirm or reject) from the gatekeeper
and forwarded it to the source endpoint.
• “Incoming Q.931 TCP connection established”
Received an incoming Q.931 TCP connection from the source.
3 - 52
Page 71

Configuring the V2IU 4350
• “Attempting to establish outgoing Q.931 TCP connection”
Successfully resolved the destination of the call and attempting to establish an
outgoing Q.931 TCP connection to the destination.
• “Q.931 signaling received and forwarded”
Both Q.931 TCP connections have been successfully established and Q.931
signaling has been received and forwarded.
• “Callee admission request received”
Received an admission request from the destination endpoint and forwarded
it to the gatekeeper.
• “Callee admission response received”
Received an admission response (either confirm or reject) from the gatekeeper
and forwarded it to the destination endpoint.
• “Incoming H.245 TCP connection established”
Received an incoming H.245 TCP connection from the source.
• “Attempting to establish outgoing H.245 TCP connection”
Attempting to establish an outgoing H.245 TCP connection to the destination.
• “H.245 signaling received and forwarded”
Both H.245 TCP connections have been successfully established and H.245
signaling has been received and forwarded. At this point, the call is considered established, even though no media channels have been opened up yet.
• “Outgoing media channel established”
An outgoing media channel (from the LAN/subscriber side to the WAN/provider side) has been opened.
• “Incoming media channel established”
An incoming media channel (from the WAN/provider side to the LAN/subscriber side) has been opened.
• “Bidirectional media channels established”
Media channels have been opened in both directions. This is a normal call
where media is being sent in both directions.
3 - 53
Page 72

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Call Termination
The call termination cause may also give some information about why the call
terminated or failed to be established.
• “Out of system resources”
The call could not be completed because the system was out of system
resources.
• “Client owning the call has been deleted”
The call could not be completed because the client that made this call was
deleted during the call setup.
• “Connection to destination could not be established”
A TCP connection to the destination could not be established.
• “Connection refused by destination”
The call could not be completed because the destination refused the incoming
TCP connection.
• “No route to destination”
A TCP connection to the destination could not be established because the destination could not be reached. This could happen if there is no route to the
destination or, if the destination is on the same subnet, the destination does
not answer to ARP requests.
• “Connection to destination timed out”
The TCP connection attempt to the destination timed out before it could be
established.
• “Call ended by source”
The call was gracefully terminated by H.323 signaling from the source. This
usually indicates that the endpoint intended to terminate the call.
• “Call ended by destination”
The call was gracefully terminated by H.323 signaling from the destination.
This usually indicates that the endpoint intended to terminate the call.
• “Connection terminated by source”
The call was terminated because the source terminated the TCP connection
without prior call termination signaling.
• “Connection terminated by destination”
The call was terminated because the destination terminated the TCP connection without prior call termination signaling.
• “No admission confirm received”
The call could not be established because the admission response was not
received from the gatekeeper.
• “Cannot resolve destination”
The call could not be established because the destination could not be
resolved.
3 - 54
• “At maximum bandwidth usage”
Page 73

The call could not be established because the system already is at the maximum allowed bandwidth.
• “Received admission reject”
The call was terminated because an admission reject was received from the
gatekeeper.
• “Received disengage request”
The call was terminated because the endpoint requested to tear down the call.
• “Received invalid data”
The call could not be established because the system received invalid data on
the signaling channel.
• “Cannot find client”
The call could not be established because the called client could not be found.
Viewing the H.323 Activity Monitor
To configure the H.323 Activity Monitor, use the following steps:
5. Using the configuration graphical user interface, from the Configuration
Menu on the left-hand side, click VoIP.
Configuring the V2IU 4350
6. Click H.323 Activity. The window shown below opens.
2. On this screen, the event list contains three columns:
— The Event/Time field - shows the type of event and the time that it
occurred.
— The Source field - shows the source of the event as an IP address and
an alias (when available).
— The Destination field - shows the destination of the event as an IP
address and an alias (when available).
3 - 55
Page 74

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
VoIP Configuration
The 4350 provides a VoIP application layer gateway (ALG) for the SIP, MGCP,
and H.323 protocols. The ALG proxies the connection between the VoIP
softswitch, IP PBX or gatekeeper and voice and video devices such as IP
phones, IADs or softphones. By acting as a proxy the 4350 is able to provide
several important functions for IP based voice and video:
• Provide NAT/PAT services for voice and video traffic. NAT/PAT for
VoIP enables you to use a single public IP address on the WAN interface
of the 4350 to represent multiple private IP addresses assigned to voice or
video devices on the LAN. The NAT function maps both IP address and
IP port number between the public and private addresses so that all
signaling and VoIP media packets are translated. A single public IP
address can support up to 253 voice and video devices.
• Provide security services for voice and video traffic.
— NAT/PAT services hide enterprise LAN topology from hackers.
— The ALG acts as a “voice and video aware” firewall and ensures only
authenticated voice traffic enters the enterprise LAN. This is
accomplished by the dynamic provisioning of signaling and media
ports for authenticated voice devices. The implementation is stateful
and open ports are closed automatically when no longer required to
support the voice or video call.
• Enable mobility in the enterprise LAN for voice devices. This is useful, for
example, when using WiFi or moving office locations. In these instances
the IP address of the voice and video device may be changed.
3 - 56
Page 75

Configure the VoIP ALG
In order to configure the VoIP ALG the 4350 must be told where to reach the
signaling servers and TFTP server on behalf of the voice devices.
Configuring the V2IU 4350
1. Select VoIP ALG.
2. If using VLANs assign the ALG to a specific VLAN id using the drop
down menu.
3. If you are using MGCP enter the MGCP Server IP Address, MGCP Media
Gateway Port and MGCP Notified Entity Port.
4. If you are using SIP enter the SIP Server IP Address and SIP server port.
The SIP server port is the port used by the SIP registrar. The default value
is port 5060.
5. If you are using H.323 enter the H.323 Gatekeeper IP Address.
6. Enter the TFTP Server Address. This address is used to identify the TFTP
server that contains the images used by IP phones at boot up. The 4350
performs a TFTP server relay function.
3 - 57
Page 76

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Note
It is not necessary to program in an FTP server address if your IP phones use the
FTP protocol instead of TFTP to retrieve their images. A relay function is not
needed for FTP as the 4350 will forward FTP traffic to the destination server as
programmed in your IP phone.
7. Automatic MGCP Re-registration is used to re-register MGCP endpoints
every time the network or system restarts. Enable this feature to
automatically synchronize the softswitch and phones immediately after a
restart. The default is Enabled.
8. The MGCP Re-registration Rate is used to set the number of MGCP RSIP
messages to send per second to the Media Gateway Controller when
re-registration is needed. If the MGCP Re-registration Rate needs to be
changed, enter a value between 1 and 5. Generally, this value does not
need to be modified. The default value is 5 msg/second.
9. The system re-registers clients when it starts up. If any of these
re-registration requests fail, the system will wait for the configured
number of seconds and then retry the re-registration for the clients that
failed. The system will make at most 10 re-registration requests for failed
attempts. If the MGCP Re-registration Retry Delay needs to be changed,
enter a value between 30 and 60 seconds. Generally, this value does not
need to be modified. The default value is 30 seconds.
10. The H.323 TerminalType is used to specify the type of terminal that the
Voice Appliance should use. It can be either endpoint or gateway. The
Maximum Bandwidth specifies the bandwidth to allow for H.323 calls.
The bandwidth is specified in kbps and if it is set to 0, bandwidth
management is not enforced. Only calls with media traversing the 4350 is
counted towards the bandwidth maximum.
3 - 58
Page 77

11. The Current payload bandwidth calculates the current video traffic,
without IP overhead, traversing the Appliance. The Estimated total
bandwidth calculates the total video traffic, plus IP overhead, traversing
the Appliance.
12. The H.323 Max Aliases limits the number of aliases that are allowed to
register with the Voice Appliance. If this number is exceeded when a
client tries to register, the registration will be rejected. If the value is set to
0, the maximum is not enforced.
13. The SIP LAN Side Gateway is used to configure a LAN side SIP gateway
to which calls that are not for a registered phone can be sent. The name of
the gateway is the name that is configured for the gateway in the
soft-switch and the IP address is the address where the gateway can be
reached.
14. Press Submit.
Configure VoIP Subnet Routing
It is not necessary to configure VoIP subnet routing if all of your voice and
video devices are installed on the same IP subnet as the 4350. In some
installations the voice and video devices are located in different subnets than
the 4350 and connected via intermediate routers. In these instances it is
necessary to configure a return path in the 4350 by specifying the intermediate
router who knows how to reach the voice devices. This router must be
reachable by the 4350.
Configuring the V2IU 4350
WAN
V2IU
IP Phones
Router
Subnet BSubnet B
EM007B
3 - 59
Page 78

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Note
VoIP Subnet Routing is separate and independent from static data routes (see
Static IP routing). VoIP subnet routes must be configured for each LAN subnet that
contains devices making use of the 4350’s Application Layer Gateway (ALG).
These entries tell the ALG that the identified subnet is allowed to make use of its
services and what router the ALG should use to reach that subnet.
Enter a VoIP Subnet Route
1. Select System.
Note
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select VoIP Subnet Routing.
4. Enter the IP Network (e.g. 10.10.12.0).
This is the IP address of the remote subnet containing the voice devices.
5. Enter the Netmask (e.g. 255.255.255.0).
This is the mask of the IP address of the subnet containing the voice
devices.
6. Enter the Gateway (e.g. 10.10.10.2).
This is the IP address of the intermediate router that knows the return path
to the remote subnet from the 4350.
7. Press Submit.
Perform steps 1 through 7 for each remote subnet containing the voice devices.
The 4350 is limited to a total of 20 different VoIP subnets.
Delete a VoIP Subnet Route
1. Select System.
3 - 60
Page 79

Configuring the V2IU 4350
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select VoIP Subnet Routing.
4. Enter the IP Network (e.g. 10.10.12.0).
This is the IP address of the remote subnet containing the voice devices.
5. Enter the Netmask (e.g. 255.255.255.0).
This is the mask of the IP address of the subnet containing the voice
devices.
6. Enter the Gateway (e.g. 10.10.10.2).
7. This is the IP address of the intermediate router that knows the return
path to the remote subnet from the 4350.
8. Select the Delete Subnet checkbox.
9. Press Submit.
Perform steps 1 through 8 for each remote subnet that you wish to delete.
Configure IP Phones, IADs or Softphones
After configuring the 4350 VoIP ALG the voice devices must be configured to
point to the LAN interface of the 4350 as their signaling gateway and
optionally as their TFTP server (if they use the TFTP protocol to retrieve their
software images). The steps required to setup these devices differ from vendor
to vendor. Using the DHCP server included in the 4350 will significantly
simplify the setup of these devices if they are able to obtain their IP
configuration via DHCP. Please consult the applicable users guide of each
device for detailed instructions.
3 - 61
Page 80

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Data Networking Configuration
The 4350 provides static IP routing and two types of Network Address
Translation (NAT) functions for data traffic. This section describes the use and
configuration of these features.
NAT for Data Traffic
Note
3 - 62
NAT allows hosts on a private internal network (the LAN side of the 4350) to
anonymously communicate with devices on an external network (the WAN
side of the 4350). The 4350 with NAT enabled will re-write outbound packet
headers using public IP addresses in place of private IP addresses so that the
private IP addresses are not exposed to the external network. Additionally, the
ports used by the IP addresses are also changed as they traverse the 4350. This
is known as Port Address Translation (PAT) and provides an additional
security measure. The 4350 maintains a table of these mappings so that return
packets can be forwarded to the correct host on the private network.
The 4350 provides two types of NAT functions: dynamic NAT and static NAT.
Dynamic NAT allows many private IP addresses to be mapped to a single
public IP address (using different port numbers of the public IP address).
Static NAT maps private IP addresses and port. For example, mapping a
public IP address to a specific machine on the private network responsible for
receiving email.
The 4350 ALG automatically handles NAT for voice devices.
Page 81

Configuring the V2IU 4350
Configure Dynamic NAT
Use Dynamic NAT when you have multiple PCs installed on the LAN side of
the 4350 that require Internet or WAN access. Once Dynamic NAT is enabled
the 4350 will automatically perform an address translation for all packets
to/from the LAN side PCs.
1. From the Configuration Menu select NAT.
2. Use the Enable Lan NAT checkbox to enable or disable dynamic NAT.
The default value for dynamic NAT is enabled.
3. Press Submit.
Configure Static NAT
Use Static NAT when a server or PC located in the private network needs to be
accessible from the external network. Some examples include a corporate web
server, a mail server or an FTP server. In these instances, the 4350 statically
maps the public IP address of each server to the actual private IP address of
the server.
Note
In order for Static NAT to function dynamic NAT must be enabled.
1. Select NAT.
2. Enter the public and private IP addresses and ports to be mapped in
Static NAT Client Entries using the following format:
Protocol;PublicIPAddress/netmask-port>PrivateIPAddress-port
For example, the entry “tcp;198.66.203.19-80>192.168.1.3-8080” will map
all web traffic destined to public IP address 198.66.203.19 to the private
webserver 192.168.1.3 port 8080. The public IP address of 198.66.203.19 is
automatically created as a “subinterface” or “secondary address” on the
WAN interface of the 4350 so that external hosts can reach the web server.
Each entry should be placed on a new line.
3. Press Submit.
3 - 63
Page 82

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Delete a Static NAT entry
1. Select NAT.
2. To delete an IP address or a range of IP addresses highlight the entry in
the Static NAT Client Entries list and press the Delete key on your
keyboard.
3. Press Submit.
Static IP routing
In addition to locally connected IP networks the 4350 can forward traffic for a
remote data network by configuring a static route entry. Any packets destined
for the remote data network will be forwarded to the specified gateway
address in the entry.
Configure the static route
1. Select System.
3 - 64
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Route.
Page 83

Configuring the V2IU 4350
4. Select the Apply Route checkbox.
5. Enter the IP Network address. This address is the remote data network
you would like the 4350 to forward to the gateway. The hosts portion of
the IP address should be set to “0”. For example, 10.10.20.0
6. Enter the Netmask of the remote data network. For example,
255.255.255.0
7. Enter the Gateway IP address of the interface that will receive all packets
destined for the remote data network.
8. Press Submit.
Delete the static route
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Route.
4. Remove the check in the Apply Route checkbox.
5. Press Submit.
Firewall Configuration
3 - 65
Page 84

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
The 4350 uses a Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) firewall to protect data devices
installed behind the LAN interface. Voice devices are protected by the 4350
Application Layer Gateway (ALG) as described in VoIP Configuration.
The firewall is enabled by default. The default behavior of the firewall is to:
• deny all traffic originating from the WAN
• allow all traffic originating from the LAN
• allow only return traffic for connections that originated from the LAN
• deny all traffic originating from the WAN to the 4350 itself
• allow all traffic originating from the LAN to the 4350
The default behavior can be modified using the basic and advanced settings
fields on the firewall configuration page. We recommend that you use the 4350
firewall, however it can be disabled if the 4350 is installed behind an existing
legacy firewall.
Enable or disable the firewall
1. Select Firewall.
Warning
2. Use the Enable Firewall checkbox to either enable or disable the firewall.
3. Select Submit.
Configure Basic settings
To allow or deny HTTP, Telnet and SSH traffic originating from the WAN to
the 4350 simply use the checkboxes provided in the basic settings area of the
firewall configuration page. By default, access from the WAN into the 4350 is
disabled.
Denying HTTP, Telnet or SSH traffic from the WAN may result in losing
management connectivity to the 4350 if you are configuring the system remotely
using the WAN link.
1. Select Firewall.
2. Use the three Allow access from WAN side checkboxes to enable or
disable HTTP, Telnet, and/or SSH access from IP devices on the WAN
side of the 4350.
3. Select Submit.
Configure Advanced Settings
3 - 66
A comprehensive security policy can be created using the advanced settings of
the 4350 firewall. The policy actions that can be taken on any packet processed
by the 4350 are summarized in the following table:
Page 85

Action Description Input format
Configuring the V2IU 4350
Allow TCP Port Allows traffic with the
specified TCP port to
terminate on the 4350.
Allow UDP Port Allows traffic with the
specified UDP port to
terminate on the 4350.
Deny Hosts (IP) Denies all traffic with the
source IP address
matching the specified
hosts
Deny Hostwise
TCP (IP-Port)
Denies all traffic
matching the specified
TCP port numbers and
the specified source IP
addresses
Deny Hostwise
UDP (IP-Port)
Denies all traffic
matching the specified
UDP port numbers and
the specified source IP
addresses
*Valid values ra ng e from 1 through 65535. *Multiple
entries are separated by a space
*Range value specified by the : character. For example,
25:50 means perform the action on ports 25 through 50
*Valid values ra ng e from 1 through 65535. *Multiple
entries are separated by a space
*Range value specified by the : character. For example:
25:50 means perform the action on ports 25 through 50
*Multiple entries are separated by a space
*Classful IP addresses are assumed by default. For
example: 192.168.3.1 uses a class c mask. Subnets can
be specified using the / notation. E.g. 192.168.3.1/24
*Multiple entries are separated by a space
*Port are specified using a - character. For example:
192.168.3.1-23 for Telnet.
*Port ranges are specified using a : character. For
example: 192.168.3.1-23:50 means port 23 through 50
*Classful IP addresses are assumed by default. For
example: 192.168.3.1 uses a class c mask. Subnets can
be specified using the / notation. E.g. 192.168.3.1/24
*Multiple entries are separated by a space
*Port are specified using a - character. For example:
192.168.3.1-23 for Telnet.
*Port ranges are specified using a : character. For
example: 192.168.3.1-23:50 means port 23 through 50
*Classful IP addresses are assumed by default. For
example: 192.168.3.1 uses a class c mask. Subnets can
be specified using the / notation. E.g. 192.168.3.1/24
Allow Hostwise
TCP (IP-Port)
Allows all traffic matching
the specified TCP port
numbers and the
specified source IP
addresses
*Multiple entries are separated by a space
*Port are specified using a - character. For example:
192.168.3.1-23 for Telnet.
*Port ranges are specified using a : character. For
example: 192.168.3.1-23:50 means port 23 through 50
*Classful IP addresses are assumed by default. For
example: 192.168.3.1 uses a class c mask. Subnets can
be specified using the / notation. E.g. 192.168.3.1/24
3 - 67
Page 86

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Allow Hostwise
UDP (IP-Port)
Allows all traffic matching
the specified UDP port
numbers and the
specified source IP
addresses
If a given packet does not match any of the configured rules, it is dropped.
1. Select Firewall.
2. Enter the desired Advanced Settings using the table above as a guide.
3. Select Submit.
Remove Advanced Setting Entries
To remov e an a dvan ced fi rewa ll se ttin g sim ply hi ghli ght t he va lue i n the e ntry
box and delete it using the keyboard.
*Multiple entries are separated by a space
*Port are specified using a - character. For example:
192.168.3.1-23 for Telnet.
*Port ranges are specified using a : character. For
example: 192.168.3.1-23:50 means port 23 through 50
*Classful IP addresses are assumed by default. For
example: 192.168.3.1 uses a class c mask. Subnets can
be specified using the / notation. E.g. 192.168.3.1/24
1. Select Firewall.
2. Highlight the entry to be deleted in the Advanced Settings list and press
the Delete key on your keyboard.
3. Press Submit.
Traffic Management Configuration
Traffic management is required to ensure high quality voice and video calls
when voice, video, and data traffic share the same WAN link. Voice and video
traffic must be prioritized for transmission over data traffic to meet the
stringent jitter, latency and packet loss requirements for high quality voice and
video. The 4350:
• Automatically prioritizes voice and video traffic over data traffic to ensure
high quality voice and video calls.
• Maximizes WAN link utilization by allowing data traffic to burst up to full
line rate in the absence of voice and video calls.
3 - 68
Page 87

Configuring the V2IU 4350
• Controls the data transfer rate of far-end WAN TCP devices to limit WAN
link congestion.
• Supports network-based QoS applications by setting the TOS bits for all
VoIP packets sent to the WAN and the LAN. TOS bits are used so that
VoIP packets can be prioritized in the network by DiffServ enabled
routers. The TOS bit value used by the 4350 is to “minimize delay and
maximize throughput”, or 0xb8 hexadecimal. This value is set for all VoIP
packets processed by the 4350 and overwrites any specific TOS bit
configuration set by VoIP endpoints.
• Ensures that bandwidth allocated to new voice and video calls does not
adversely affect the quality of existing active calls (Call Admission Control
or CAC).
The 4350 combines sophisticated traffic management mechanisms including
classification, prioritization, queuing, rate limiting and CAC to ensure high
quality voice and video calls. Fortunately the system manages this complexity
for you and configuring traffic management is very straightforward:
1. Enable traffic shaping.
2. Specify the upstream and downstream bandwidth of your WAN link.
3. Enable CAC.
Please follow the steps below to configure and enable traffic management.
Enable Traffic Shaping
1. From the Configuration Menu, select Traffic Shaper.
2. Select the Enable traffic shaper checkbox.
3 - 69
Page 88

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
3. Specify the upstream and downstream bandwidth of your WAN link
4. Enter the WAN Downstream Bandwidth in Kbps.
5. Enter the WAN Upstream Bandwidth in Kbps.
Note
For FT1/T1/E1 links the upstream and downstream bandwidths will always be the
same value (the link is full-duplex).
Optionally enable priority IP addresses
VoIP traffic from devices that use the VoIP ALG function (phones, video
stations, softphones on Pcs, etc.) are already marked as high priority and do
not need to be manually configured in this list. This list is used to prioritize
voice traffic from trunk interfaces of IP PBXs or other high priority devices that
do not use the VoIP ALG function of the 4350.
>>
Enter the IP address of other high priority devices in the priority IP
Addresses box.
You can enter individual IP addresses or a range using by appending a
“-“character to the last octet. For example, 10.10.10.2-5 would specify
10.10.10.2, 10.10.10.3, 10.10.10.4 and 10.10.10.5 as voice devices.
Warning
Care must be taken to ensure that the IP addresses entered do not include data
devices such as PCs or workstations. Traffic from these devices will be placed in
the priority voice queue internal to the 4350 and burst up to full line rate. This will
starve actual voice devices by consuming priority bandwidth and result in dropped
calls, busy signals & poor voice quality.
Enable CAC
3 - 70
The 4350 uses CAC to limit the number of active voice calls over the WAN link.
This is necessary because a typical installation uses a ratio of 1:2 or 1:4 active
voice calls to voice devices on the assumption that 50% or 25% of all users are
on the phone at the same time. These ratios are guidelines only and at times
the number of concurrent calls may exceed the amount of WAN bandwidth
available to process the calls. In this instance existing phone calls will
experience poor quality or be dropped all together. To prevent this from
occurring a typical voice installation will set a threshold for the maximum
number of concurrent voice calls supported by the WAN access link. New call
requests in excess of this threshold will receive the equivalent of a “fast busy”
and the WAN link will not become oversubscribed.
For IP Centrex installations the maximum number of concurrent voice calls is
usually configured in the 4350 by enabling CAC. When the 4350 is deployed
in IP PBX applications the maximum number of concurrent calls could be
configured in the IP PBX. If the PBX is responsible for this setting you do not
need to configure CAC in the 4350. Please check with your IT administrator to
determine if this is the case.
Page 89

Configuring the V2IU 4350
Determining the maximum number of concurrent calls
The maximum number of concurrent calls that can be supported by the WAN
access link is calculated using the following formula:
Max calls = (Maximum WAN upstream bandwidth * .85)/VoIP codec rate
where,
Maximum WAN upstream bandwidth = value entered in step D above (in
Kbps)
VoIP codec rate = 85.6Kbps for G.711 voice devices or 29.6Kbps for G.729 voice
devices.
The maximum WAN upstream bandwidth is multiplied by .85 in the formula
above to reduce the total bandwidth available for voice calls by 15%. This
reduction is necessary because the 4350 automatically reserves 15% of the total
WAN bandwidth for low priority data traffic so that it is not starved
completely. Starving data traffic completely would increase the number of
retry attempts and exacerbate congestion on the link during periods of peak
usage.
Examples
The maximum number of G.711 voice calls supported by a T1 (1.536 Kbps)
WAN is calculated as follows:
(1.536*.85)/85.6 = 15.3 or 15 total voice calls.
The maximum number of G.711 voice calls supported by a 768Kbps fractional
T1 WAN is calculated as follows:
(768*.85)/85.6 = 7.6 or 7 total voice calls
The maximum number of G.729 voice calls supported by a 256Kbps fractional
T1 WAN is calculated as follows:
(256*.85)/29.6 = 7.4 or 7 total voice calls
After determining the maximum number of voice calls CAC is enabled as
follows:
1. Select the Enable Call Admission Control checkbox.
2. Enter Maximum number of calls allowed as calculated above.
3. Press Submit.
A Closer Look at Traffic Management in the 4350
The traffic management mechanisms provided by the 4350 are designed to
ensure high priority real-time voice and video traffic is processed before lower
priority data traffic. At the same time, bandwidth not in use by voice and video
traffic is made available so that data traffic can burst up to full line rate making
efficient use of WAN bandwidth. Traffic management mechanisms are
3 - 71
Page 90

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
applied to traffic in both the upstream (LAN to WAN) and downstream (WAN
to LAN) direction. Each direction is independent of the other and can support
different size priority queues.
Classifying
High priority voice and video traffic generated by endpoint devices is
automatically identified by the V
VoIP devices (not making use of the ALG) can be defined as high-priority by
their IP address. The user configures these addresses into the priority list in the
Traffic Shaper section of the 4350 web GUI.
As the 4350 processes packets they are identified as either high or low priority
based on this configuration. Packets identified as high priority are marked as
such in the TOS bits of their IP header, allowing prioritization by downstream
routers. The TOS field is set to 12 hexadecimal “minimize delay and maximize
throughput.” This value overwrites any prior value.
Upstream Traffic Management
The 4350 appliance uses a combination of Class Based Queuing and simple
classless queuing to send data in the upstream direction. The Class Based
Queue (CBQ) consists of two priority classes (high and low), a scheduler to
decide when packets need to be sent, and a traffic shaper to rate-limit by
delaying packets before they are sent. Each of these is described in more detail
below.
Priority classes
Voice and video traffic is placed in the high-priority queue and data traffic is
placed in the low-priority queue. The IP header TOS field of packets in the
high-priority queue is set to “minimize delay and maximize throughput”.
2
IU’s VoIP Application Layer Gateway. Other
3 - 72
Scheduler
High-priority data is polled before low priority data, thereby minimizing the
latency for voice and video traffic. High-priority data is allowed to use up to
85% of the total WAN bandwidth. Although preferential treatment is given to
high-priority data, 15% of the WAN link is always reserved so that
low-priority data is not starved.
High priority data is polled before lower priority data to reduce overall latency
for voice traffic.
Traffic shaper
To smooth bursts from high speed data links (typically from the LAN Ethernet
heading to the WAN) the 4350 appliance uses a buffer that clocks data out at
rates not exceeding automatically-calculated maximums. Low-priority data is
Page 91

clocked out at the WAN link’s full rate LESS the bandwidth currently being
used for high-priority (voice) data. High-priority data is clocked out at the
WAN’s full link rate. Any long-lasting burst condition in low-priority data will
cause these packets to be delayed and, if necessary, dropped.
Downstream Traffic Management
Since the 4350 is the final transmitting device for WAN traffic in the upstream
direction (LAN to WAN) it is easy to see how its QoS mechanisms can be
applied to traffic it is transmitting to guarantee sufficient bandwidth for voice
traffic. We have control over how packets are handed to the WAN interface.
In the downstream direction (WAN to LAN) we are installed at the receiving
end of a service provider link and therefore have no control over the amount
of voice or data traffic being sent to us over the WAN interface. How then can
we still guarantee the quality of in-bound voice traffic when it is entirely
possible for an FTP session, for example, to consume the vast majority of
downstream bandwidth?
Fortunately this is possible by shaping on both the egress LAN and egress
WAN ports of the 4350 appliance and leveraging the congestion avoidance
mechanisms built into TCP. Essentially, data packets received by the 4350’s
WAN interface at a rate that exceeds the T1’s bandwidth LESS the bandwidth
used for active voice calls are delayed (then dropped if necessary) before being
forwarding on to its LAN interface. Similarly, data traffic sent back to the 4350
for transmission to the WAN are also delayed (as described in the above
section). This results in the WAN-based devices following the rules of TCP/IP
congestion avoidance and slowing down their transmit rate. This technique is
quite effective in practice, as end stations usually reduce their transmit rate
before VoIP signaling has completed for new call setup.
Configuring the V2IU 4350
For example consider the scenario where there are no voice calls over a WAN
link and multiple FTP sessions are consuming all available bandwidth:
1. A new call request is received by the 4350 from the WAN.
2. All signaling messages for the call are classified as voice traffic and
therefore prioritized for transmission to the LAN before servicing the
inbound FTP data.
3. RTP traffic (the voice data within an ongoing VoIP session) is similarly
classified as voice traffic and treated with priority.
4. FTP data is buffered (or dropped) by the 4350 and return data, including
the FTP ACKs, are also delayed. This results in a throttling of the transmit
rate by the (far-end) FTP hosts, reducing overall WAN bandwidth
consumption.
Generally, excessive UDP traffic must be shaped in the service provider
network, as UDP does not provide congestion avoidance mechanisms. The
exception to this is in the case of RTP UDP-based messages for voice traffic.
3 - 73
Page 92

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Although RTP makes use of UDP the 4350 appliance is able to provide its own
congestion avoidance mechanism for voice traffic using Call Admission
Control (CAC).
3 - 74
Page 93

4
System Diagnostics
The V2IU 4350 provides a powerful set of diagnostic information,
troubleshooting tools and utilities for system maintenance to network
operators.
Viewing Software Version, Hardware Platform and the LAN MAC Address
The software version, hardware platform, and LAN MAC address are
common pieces of information requested by technical support and are
accessed directly through the System page of the 4350 web GUI.
4 - 1
Page 94

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Viewing the ALG registration code
You will also find a link to the ALG registration code on the System page. The
registration code enables the ALG and is pre-installed at the factory. If the
registration code is inadvertently deleted you can re-enter the code using the
following steps:
Enter the Registration Code
1. Select System.
2. Select registration code.
3. Select Edit Registration Code.
4. Enter the Registration Code.
The registration code can be found on the sticker located on the bottom of
the 4350.
5. Press Submit.
Viewing Networking Information
4 - 2
Page 95

System Diagnostics
To view the networking configuration and status of the 4350 proceed to the
Network Information page as follows:
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Network Information.
The following networking information is displayed:
Routing Information
The system routing table contains the static routes for hosts and networks that
are configured on the 4350. If just the LAN and WAN IP addresses have been
configured there will be four lines displayed:
• The private subnet will be associated with the LAN interface.
• A public subnet present for the WAN interface.
• An entry for the 4350 loopback interface
• The 4350’s default gateway forwarding to the WAN interface
Additional lines may be displayed depending on the contents of the Route and
VoIP Subnet Routing pages. Each of the entries on these pages will cause an
additional entry in the routing table.
Link Status
Link Status displays the status of the ethernet interfaces. Ethernet
autonegotiation is often unreliable, especially between different vendors or
old and new networking equipment. Failure of autonegotiation is generally
not a cause for concern. However, if the negotiated rates change intermittently
or the link is reported as down or no link, the link rate may need to be set
manually on the Set Link Rate page. Intermittent data and voice outages may
be caused by link flapping when the two endpoints of the Ethernet cable
cannot reach agreement using autonegotiation. If the link rate is set manually,
ensure that the device at the far end of the connection can communicate at the
desired rate. Incompatible rates can cause a loss of communication with the
4350.
Link status for the Ethernet ports is displayed via the LEDs adjacent to each
physical port.
Interface Information
The specific status and configuration information for the system interfaces is
displayed in the Interface Information section. HDLC0 shows the interface
statistics for the T1/E1 WAN link. ETH0 shows the interface statistics for the
internal LAN interface between the 4350 processor and the built-in LAN
switch. Interface statistics for the external LAN ports are not displayed.
4 - 3
Page 96

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
The interface statistics can point to areas of congestion in the network. If the
errors statistic is a few percent or more of the total packets sent it may be an
indication of excessive congestion on the network interface. If the congestion
is not corrected the quality of voice calls will be affected. The topology of the
network attached to the network interface with the errors should be examined
and modified to better segment and isolate network traffic.
Viewing Advanced System Information
To view advanced system information for the 4350 proceed to the System
Information page as follows:
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select System Information.
The following system information is displayed:
4 - 4
System Uptime
System Uptime displays the current time, the amount of time elapsed since the
last system reboot, and the system load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15
minutes. Uptime can help trace when a power outage may have interrupted
service. Load averages that remain greater than 2 indicate excessive system
loading. Partitioning voice traffic using a second system may be required.
Process Information
Displays the active processes in the 4350.
Memory Usage
Displays detailed memory allocation information that may be of use to
technical support.
Page 97

System Logging Messages
Displays information logged during system boot and normal operation.
Logging messages may indicate unauthorized attempts to access the 4350,
process restart messages, and excessive resource utilization messages.
Passive Voice Call Monitoring
The 4350 monitors live voice calls and performs objective speech quality
assessment. This information enables the network operator to assess voice
quality for the purposes of SLA tracking or problem isolation. Mean Opinion
Score (MOS) results for RTP streams in both directions of a VoIP call are
calculated at call completion. This information along with the IP addresses of
the VoIP endpoints supporting the call are logged locally and optionally sent
to an external syslog server (see Enable Remote System Logging <<<find this
heading>>> for instructions on enabling logging to a remote syslog server).
Additionally the 4350 will generate a real-time message for any MOS values
calculated less than 2.5 (considered poor quality) during an active call.
Voice call quality information is found locally in the System Logging Messages
section of the System Information page and a sample output is provided
below.
System Diagnostics
Accessing Troubleshooting Tools
The 4350 provides convenient test tools to facilitate problem isolation and
resolution. A network operator can use these tools to verify connectivity
to/from the 4350 as well as trace datapaths to endpoints throughout the
network.
4 - 5
Page 98

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
Verify Registered Voice and Video Devices
The 4350 maintains a list of all registered voice and video devices called a
clients list so that it can properly route voice and video calls. At startup, voice
and video devices register their IP addresses with the 4350. The 4350 then
registers on behalf of the voice and video devices by providing its own WAN
IP address to the softswitch, gatekeeper, or IP PBX. If a user or network
operator reconfigures the IP address of the voice or video device (such as an IP
phone or IAD), it will re-register the new address with the 4350. In this
instance voice and video calls may be routed improperly because the 4350
clients list contains out of date information.
To update the clients list simply highlight and delete the stale entry using the
following steps:
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Clients List.
4. Proceed to the appropriate signaling section, highlight the duplicate
entry or entries and press the delete key on the keyboard
5. Press Submit.
6. Restart the VoIP ALG by following the instructions found in Restarting
Networking Processes.
4 - 6
Page 99

System Diagnostics
Performing a Ping Test
A ping test is the most common test used to verify basic connectivity to a
networking device. Successful ping test results indicate that both physical and
virtual path connections exist between the 4350 and the test IP address.
Successful ping tests do not guarantee that all data traffic is allowed between
the 4350 and the test IP address but is useful to verify basic reachability.
The following steps are used to perform a ping test:
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Network Test Tools.
4. Enter the IP Address to Ping.
5. Press Ping.
The Network Test Tools page will be refreshed and the results of the ping test
are displayed (this may take several seconds). The Reset button is used to clear
the IP address entry used in step D above.
Performing a Traceroute Test
A traceroute test is used to track the progress of a packet through the network.
The test can be used to verify that data destined for a WAN device reaches the
remote IP address via the desired path. Similarly, internal network paths can
be traced over the LAN to verify the local network topology. The following
steps are used to perform a traceroute test:
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Network Test Tools.
4. Enter the IP address to Trace.
5. Select either the WAN or the LAN radio button
6. Press Traceroute.
4 - 7
Page 100

User Manual V2IU 4350 Converged Network Appliance
The Network Test Tools page will be refreshed and the results of the traceroute
test are displayed (this may take several seconds). The Reset button is used to
clear the IP address entry used in step D above.
Restarting Networking Processes
In extreme circumstances while troubleshooting you may be asked to restart
the networking processes including the VoIP ALG in the 4350 by technical
support. Use the following steps to restart the networking processes:
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Networking Restart.
4. Press restart.
Warning
Warning
Restarting network services will interrupt the system for up to a minute. All voice
and data sessions currently in progress will be interrupted.
Rebooting the 4350
In extreme circumstances while troubleshooting you may be asked to reboot
the 4350 by technical support. Please use the following steps to reboot the
system:
1. Select System.
2. Select System Overview.
3. Select Rebooting System.
4. Press reboot.
Alternatively a reset can be performed locally by temporarily disconnecting
the power cable from the 4350.
Rebooting the system will interrupt services for a few minutes. All voice and data
sessions currently in progress will be interrupted.
4 - 8
 Loading...
Loading...