Page 1

Integrators’
Reference Manual
For
ViewStation®EX,
ViewStation®FX,
and VS4000
March 2003 Edition
3725-20771-001
Revision A
Page 2

Trademark Information
Polycom® and the Polycom logo design are registered trademarks of Polycom Inc. ARENA™, Global Management
System™, ImageShare™, iPower™, LimeLight™, MGC Manager™, PathNavigator™, Polycom Office™, Polycom
OneDial™, ViewStation™, ViaVideo™, Visual Concert DC™, Visual Concert FX™, Visual Concert PC™,
WebOffice™, and WebCommander™ are trademarks of Polycom, Inc. in the United States and various other
countries.
Internet Explorer™, NetMeeting®, Windows®, and Windows NT® are either registered trademarks or trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Intel®, Pentium®, and Celeron® are registered trademarks and TeamStation™ is a trademark of Intel Corporation.
Adobe® Acrobat® is a registered trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
ADTRAN® is a registered trademark of ADTRAN, Inc.
QuickTime™ is a trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.
Netscape® Navigator® is a registered trademark of Netscape Communications Corporation.
IP/TV® is a registered trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Every effort has been made to ensure that the
information in this manual is accurate. Polycom, Inc. is not responsible for printing or clerical errors. Information in
this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2003 Polycom, Inc. All rights reserved.
Polycom Inc.
4750 Willow Road
Pleasanton, CA 94588-2708
USA
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
for any purpose, without the express written permission of Polycom, Inc. Under the law, reproducing includes
translating into another language or format.
As between the parties, Polycom, Inc. retains title to, and ownership of, all proprietary rights with respect to the
software contained within its products. The software is protected by United States copyright laws and international
treaty provision. Therefore, you must treat the software like any other copyrighted material (e.g. a book or sound
recording).
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this manual is accurate. Polycom, Inc. is not responsible
for printing or clerical errors. Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 - About this Manual ................................................ 1
Conventions Used in this Manual....................................................................................2
Glossary................................................................................................................................2
Chapter 2 - Technical Information.......................................... 11
System Descriptions .........................................................................................................12
Technical Specifications............................................................................................12
RS-232 Interface..........................................................................................................20
Quad BRI Network Interface Module.....................................................................22
Indicators on the Quad BRI Network Interface Module ..............................22
Quad BRI Cabling...............................................................................................23
NT-1 Information................................................................................................24
ISDN Switches.....................................................................................................25
Automatic Quad BRI Software Update...........................................................25
PRI Network Interface Module for ViewStation FX and VS4000.......................26
Indicators on the PRI Network Interface Module .........................................27
PRI Cabling..........................................................................................................29
Channel Selection ...............................................................................................30
PRI E1 Channel Information.............................................................................30
Dedicated Full PRI T1 or E1 Line.....................................................................30
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module.................................................31
Indicators on the V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module........... 31
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Cabling ...........................................................................32
Serial Interface Control Signals ........................................................................38
State Machine ......................................................................................................39
Crypto Resync.....................................................................................................44
Other Elements of a Typical Deployment.....................................................................45
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy.............................................. 47
Predeployment Overview................................................................................................48
Video Network Security...................................................................................................49
Best Practices .....................................................................................................................50
Predeployment Planning .................................................................................................51
LAN/WAN Considerations.....................................................................................52
© Polycom, Inc. i
Page 4

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Capacity Planning ..................................................................................................... 53
Call Processing Considerations...............................................................................54
Gatekeeper Identifier......................................................................................... 55
Default Gatekeeper ............................................................................................ 55
Call Routing Mode............................................................................................. 55
Developing the Dial Plan................................................................................................. 55
Services ................................................................................................................ 57
Administration, Policies, and Routing............................................................58
Network Topology............................................................................................. 59
Neighbor gatekeepers........................................................................................ 59
Addressing ................................................................................................................. 60
Zones and Zone Prefixes................................................................................... 60
Entity Addressing .............................................................................................. 61
Rules for Assigning Prefixes and Numeric Aliases ...................................... 62
Service Plans ....................................................................................................... 62
System Services ..................................................................................................63
ISDN Requirements.......................................................................................................... 63
ISDN PRI..................................................................................................................... 63
Determining Usage ............................................................................................ 65
PBX Network Configuration ............................................................................65
ISDN BRI..................................................................................................................... 65
DCP (Digital Communication Port) On Lucent Definity ECS............................ 68
Network Configuration..................................................................................... 68
Installation........................................................................................................... 68
Configuration...................................................................................................... 69
Site Considerations........................................................................................................... 72
Predeployment Worksheet.............................................................................................. 74
Chapter 4 - Installing Videoconferencing Systems.................. 77
The Deployment Process.................................................................................................78
Installation Procedures .................................................................................................... 79
Installing Network Interface Modules ................................................................... 79
Quad BRI Network Interface Module.................................................................... 79
NT-1 Device ........................................................................................................ 80
Cables Used with the Quad BRI Network Interface Module ...................... 80
Installation........................................................................................................... 80
Installing a PRI Network Interface Module ..........................................................81
External Power Supply...................................................................................... 81
Channel Service Unit ......................................................................................... 82
ADTRAN Atlas 800 Plus E1 Module............................................................... 82
If You Are Connecting to a PBX....................................................................... 83
Cables Used with the PRI Network Interface Module ................................. 83
ii www.polycom.com
Page 5

Contents
Installation...........................................................................................................84
Installing a V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module ............................85
Cables Used with the V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module ...85
Installation...........................................................................................................86
Network Configuration....................................................................................................88
On a PRI T1 Network: Configuring the CSU.........................................................88
Firewall and NAT Issues ..........................................................................................89
Configuring the System to Operate Behind a Firewall.................................89
Configuring the System to Operate Behind a NAT.......................................90
Connecting the System to a PC.......................................................................................91
PC Requirements ................................................................................................91
Connecting the PC to the LAN Through the ViewStation EX,
ViewStation FX, or VS4000.............................................................................92
Connecting the System to a PC off the LAN ..................................................94
Placing Test Calls ..............................................................................................................96
Chapter 5 - Supporting Advanced Users................................ 97
Multiple-Monitor Mode...................................................................................................98
RS-232 Interface...............................................................................................................105
RS-232 Control Mode.......................................................................................105
RS-232 Pass-Thru Mode...................................................................................105
Flow Control......................................................................................................106
Configure the System for RS-232 Operation........................................................107
Command Line Interface (CLI)..............................................................................107
Chapter 6 - Testing and Troubleshooting ............................. 109
Indicator Lamps ..............................................................................................................109
Indicator Lamps on the PRI Network Interface Module ...................................110
Indicator Lamps on the Quad BRI Network Interface Module ........................111
Indicator Lamps on the V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module.....112
Fault Isolation..................................................................................................................113
ISDN Error Codes ...........................................................................................................114
Appendix A - System Interoperability................................. 121
Appendix B - ViewStation Series Cables............................. 125
Board Room and Custom Room Systems.....................................................125
© Polycom, Inc. iii
Page 6

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Medium and Large Room Systems ...............................................................128
Small Room Systems........................................................................................ 130
Safety and Legal Notices..................................................... 133
Index................................................................................. 135
iv www.polycom.com
Page 7

List of Figures
Figure 2-1. RS-232 Cable for ViewStation EX and FX ....................................................... 20
Figure 2-2. RS-232 Cable for VS4000.................................................................................... 21
Figure 2-3. Keyed RJ-45 Cable, System to Network Interface Module........................... 23
Figure 2-4. Standard RJ-45 Cable, Network Interface Module to Network................... 24
Figure 2-5. Keyed RJ-45 Cable, System to Network Interface Module........................... 29
Figure 2-6. Standard RJ-45 Cable, Network Interface Module to Network................... 29
Figure 2-7. HD-44M to RS-366/V.35 “Y” Cable Diagram ................................................ 32
Figure 2-8. Pinout to the HD-44M to RS-366/V.35 “Y” Cable ........................................ 33
Figure 2-9. HD-44M to RS-449/RS-422 “Y” Cable Diagram ............................................ 34
Figure 2-10. Pinout to the HD-44M to RS-449/RS-422 “Y” Cable .................................... 35
Figure 2-11. Ascend HD-44M to HD-44M Cable Diagram................................................. 36
Figure 2-12. Pinout for the Ascend HD-44M to HD-44M Cable ....................................... 36
Figure 2-13. RS-530 Cable Diagram and Pinout................................................................... 37
Figure 3-1. The Predeployment Process.............................................................................. 48
Figure 3-2. Network Configuration (No PBX) ................................................................... 66
Figure 3-3. Network Configuration (Behind PBX) ............................................................ 66
Figure 4-1. The Deployment Process................................................................................... 78
Figure 4-2. Installing Network Interface Modules ............................................................ 79
Figure 4-3. Quad BRI Network Interface Module (Peripheral Side)............................... 80
Figure 4-4. Quad BRI Network Interface Module (Network Side) ................................. 81
Figure 4-5. PRI Network Interface Module (Peripheral Side).......................................... 84
Figure 4-6. PRI Network Interface Module (Network Side) ............................................ 84
Figure 4-7. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module (Peripheral Side) ........... 86
Figure 4-8. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module (Network Side).............. 86
© Polycom, Inc. v
Page 8

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
vi www.polycom.com
Page 9

List of Tables
Table 2-1. Electrical and Physical Specifications.............................................................. 12
Table 2-2. Connectivity ........................................................................................................ 13
Table 2-3. Video Standards Supported.............................................................................. 14
Table 2-4. Video Signal Formats......................................................................................... 14
Table 2-5. Video Input/Output Electrical Specifications................................................ 15
Table 2-6. Video Resolution, Frame Rate, and Error Correction ................................... 15
Table 2-7. Cameras and Displays ....................................................................................... 16
Table 2-8. Audio Input/Output Electrical Characteristics............................................. 16
Table 2-9. Audio Features.................................................................................................... 17
Table 2-10. Microphone Pods................................................................................................ 17
Table 2-11. Call Capabilities.................................................................................................. 18
Table 2-12. User Interface...................................................................................................... 19
Table 2-13. Quad BRI Indicator Lamps ............................................................................... 22
Table 2-14. Sample NT-1 Settings......................................................................................... 24
Table 2-15. ISDN Switch Types and SPID Allocations...................................................... 25
Table 2-16. PRI T1 and E1 Network Interface Modules.................................................... 26
Table 2-17. PRI Network Side Indicator Lamps................................................................. 27
Table 2-18. PRI Peripheral Side Indicator Lamps .............................................................. 28
Table 2-19. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Peripheral Side Indicators........................................... 31
Table 2-20. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Side Indicator Lamps .................................. 32
Table 2-21. Serial Interface Control Signals ........................................................................ 38
Table 2-22. Dial-Out State Machine...................................................................................... 39
Table 2-23. Inbound Call State Machine ............................................................................. 40
Table 2-24. Non-Dialed User-Initiated Call State Machine ............................................. 42
Table 2-25. Non-dialed Network-Initiated Call State Machine ....................................... 43
Table 3-1. Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss........................................................................ 50
Table 3-2. Bandwidth Requirements.................................................................................. 53
Table 3-3. Zone Identifiers and Neighbor Gatekeepers.................................................. 61
Table 3-4. ISDN PRI Requirements .................................................................................... 64
Table 3-5. Example Configuration, Data Module 1......................................................... 70
Table 3-6. Example Configuration: Channel 1, Secondary Data Module 2.................. 70
Table 3-7. Site Considerations............................................................................................. 72
Table 4-1. Firewall Ports to Open for Videoconferencing............................................... 89
Table 5-1. Expected Display for Each Monitor................................................................. 98
Table 5-2. RS-232 Control and Pass-Thru Modes........................................................... 106
Table 6-1. PRI indicator lamps - Network side .............................................................. 110
Table 6-2. PRI indicator lamps - Peripheral side ............................................................ 111
Table 6-3. Quad BRI Indicator Lamps ............................................................................. 111
© Polycom, Inc. vii
Page 10

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Table 6-4. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Indicator Lamps - Network Side...............................112
Table 6-5. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Indicator Lamps - Peripheral Side ............................112
Table 6-6. Fault Isolation ....................................................................................................113
Table 6-7. ISDN Call Status Codes....................................................................................114
Table A-1. H.320 Endpoints................................................................................................121
Table A-2. H.323 Endpoints................................................................................................122
Table A-3. H.323 MCU Interoperability............................................................................123
Table A-4. Gateway/Gatekeeper Interoperability ..........................................................123
Table A-5. NAT and Firewall Interoperability.................................................................124
Table B-1. Cables for VS4000..............................................................................................125
Table B-2. Cables for ViewStation EX and ViewStation FX...........................................126
Table B-3. Cables for Upgrades to ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000.... 126
Table B-4. Cables for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 Accessories .....127
Table B-5. Additional Cables for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 ......127
Table B-6. Cables for ViewStation H.323..........................................................................128
Table B-7. Cables for ViewStation MP..............................................................................129
Table B-8. Cables for ViewStation MP DCP.....................................................................129
Table B-9. Cables for Upgrading ViewStation Models (Except FX).............................130
Table B-10. Cables for ViewStation SP 128.........................................................................130
Table B-11. Cables for ViewStation 128..............................................................................131
Table B-12. Cables for ViewStation SP 384.........................................................................131
viii www.polycom.com
Page 11

1
About this Manual
This chapter provides information to help you use the rest of the
manual.
This manual covers the following topics:
Topic Page
Technical Information 11
Before You Deploy 47
Installing Videoconferencing Systems 77
Supporting Advanced Users 97
Testing and Troubleshooting 109
© Polycom, Inc. 1
Page 12

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Conventions Used in this Manual
The following typographic conventions are used in this manual:
❑ Links that allow you to jump to other sections of this manual are
blue
.
❑ File path names and commands you type in command lines are
shown in
this font.
❑ Screen names and elements are shown in bold type.
❑ Navigation through sequences of screens or menu selections is
shown in this form: First selection > second selection > third
selection.
Glossary
4CIF 4 x CIF (Common Intermediate Format). A video
format providing resolution of 704 x 576 pixels.
See also CIF, QCIF, 16CIF.
16CIF 16 x CIF (Common Intermediate Format). A video
format providing resolution of 1408 x 1152 pixels.
See also CIF, 4CIF, QCIF.
ADSL Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line. Used to
transmit digital data over telephone wires at up to
six megabits per second.
AIS Alarm Indication Signal. This indicates that there
is a problem upstream.
Analog Line A telephone line that transmits and receives
analog signals. An analog signal is a true electrical
representation of the original source audio.
2 www.polycom.com
Page 13

Chapter 1 - About this Manual
ARJ H.323 Admission Reject Message. This message is
from the Gatekeeper, rejecting the endpoint’s
request to connect to another endpoint.
ARQ H.323 Admission Request Message. This message
is from an endpoint to the Gatekeeper requesting
a connection to another endpoint.
Automatic
Voice Tracking
A feature on Polycom ViewStation
allows the camera to point toward the person
®
systems that
speaking.
B channel Bearer channel. B channels carry audio and video.
Bandwidth The data-carrying capacity of a network
connection, given in terms of speed. For example,
an Ethernet link is capable of moving 10 million
bits of data per second. A Fast Ethernet link can
move 100 million bits of data per second – it has 10
times more bandwidth.
Bonding Calls In ISDN BRI and PRI transmissions, bonding
refers to joining two or more B channels together
to get one channel whose bandwidth is equal to
the sum of the bonded channels’ bandwidths.
Using a Quad BRI interface, up to 8 channels may
be bonded. T1 allows up to 23 channels to be
bonded, and E1 allows up to 30.
BRI ISDN Basic Rate Interface. Provides two B
channels and one 16 Kbps D channel (2B+D) for a
total of 144 Kbps, 128Kbps of which is available
for the audio and video content of the call.
Bridge A device that passes packets between network
segments that use the same communications
protocol. If a packet’s destination is within the
sender’s own network segment, the bridge keeps
the packet local. Otherwise, the bridge passes the
packet to the network backbone. Also, in
videoconferencing, a Multipoint Control Unit. See
MCU.
Broadcast A one-to-many transmission that can be received
by anyone connected to the network.
© Polycom, Inc. 3
Page 14

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
CIF Common Intermediate Format, also called FCIF.
A video format providing resolution of 352 x 288
pixels. See also QCIF, 4CIF, 16CIF.
Client A networked PC or terminal that shares services
with other PCs. These services are provided by a
server.
Conference
Call
Any call that establishes all-way communication
between three or more endpoints.
CPE Customer Premises Equipment.
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check.
CSU Channel Service Unit.
D channel Data channel. The D channel carries the call
protocol signals.
Data
Conferencing
Enables people in different locations to work on
the same document via networked computers.
Also called collaborative computing.
DB-25 The standard 25-pin connector used for RS-232
serial data communications.
DCE Data Communications Equipment.
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. DHCP
servers permit multiple devices to share a group
of IP addresses, assigning IP addresses to specific
devices as needed.
DID Direct Inward Dial.
Digital Line A telephone line that carries audio encoded as a
digital signal, which must be decoded to analog at
the destination. ISDN uses digital signaling.
Downstream Closer to the endpoint. For example, the
peripheral side of a network interface module is
downstream of the network side.
DSL Digital Subscriber Line. Uses existing copper
telephone lines and connects to the telephone
company’s central office. See also ADSL.
4 www.polycom.com
Page 15

Chapter 1 - About this Manual
Endpoint A site, videoconferencing system, gateway, or
MCU.
Ethernet 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps LAN technology based on
CSMA/CD.
Far End The party or parties to whom you place a call.
Fast Ethernet 100 Mbps LAN technology based on CSMA/CD.
FCIF Full CIF. See CIF.
Firewall A network node set up as a boundary to prevent
traffic from one segment to cross over into
another.
fps Frames per second. Note that there are two fields
per frame.
FTP File Transfer Protocol. A part of the chief Internet
protocol stack or group (TCP/IP) used for
transferring files.
Full Duplex Transmission in two directions at once
(bidirectional communication). In a full-duplex
call, all participants can both talk and hear others
at the same time.
Gatekeeper An H.323 device that provides address
translation, control access, and bandwidth
management to the LAN.
Gateway An H.323 device that provide real-time, two-way
communication between dissimilar (H.323 and
H.320) endpoints operating across dissimilar
networks.
GUI Graphical User Interface. A user interface that
incorporates icons, command menus, and other
graphical elements. GUI-based software requires
the use of a mouse, touch-screen, or other pointing
device.
H.320 ITU-T videoconferencing standards for ISDN.
© Polycom, Inc. 5
Page 16

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
H.323 ITU-T videoconferencing standard for IP. H.323
includes the H.225, H.245, G.711, G.722, G.723.1,
G.728, and G.729 standards.
IMUX Inverse Multiplexer. See Quad BRI network
interface module.
IP Internet Protocol. A unique IP address identifies
every computer connected to the Internet. IP
addresses take the form
of the four numbers is in the range 0 to 255.
IP Precedence Audio, video and far end camera control packets
may be assigned a higher priority than other
network traffic. Precedence 4 is recommended for
multimedia data. By default, IP precedence is
disabled by most routers and is not enabled on the
Internet.
ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network. Digital
telephone service, available at 128 Kbps (BRI),
1.544 Mbps (PRI), and Broadband ISDN (2 Mbps 600 Mbps).
255.255.255.255; each
ISP Internet Service Provider.
LAN Local Area Network. A network that serves users
within a confined geographical area. It includes
servers, workstations, a network operating
system and a communications link.
LED Light-Emitting Diode. An indicator lamp.
MCU Multipoint Conferencing Unit or Multi Control
Unit. Hardware that allows three or more
videoconferencing systems to participate in an
interactive multi-way conference.
Multicast A one-to-many transmission that goes to
designated recipients only.
Multipoint call A call in which more than two sites participate.
Near End Your end or local end site of the videoconference.
Network side The portion of a network interface module that
connects to the network. See also Upstream.
6 www.polycom.com
Page 17

Chapter 1 - About this Manual
NFAS Non-Facility Associated Signalling.
NT-1 Network Termination type 1. The device that
converts the ISDN BRI U interface from the
telecommunications service provider to the S/T
interface used by ISDN products and systems.
Pan Move the camera to the left or right.
PBX Private Branch eXchange. A private telephone
switching system connected to common lines
from one or more central offices. Most PBXs allow
analog extensions on the system, allowing access
to special features such as conferencing and
transferring to analog devices. If you are using a
telephone connected to a PBX, typically you will
be required to dial 9 to gain access to an outside
line.
Peripheral
side
The portion of a network interface module that
connects to the videoconferencing system. See
also Downstream.
Point-to-point
A call between two sites.
call
POTS Plain Old Telephone Service. See PSTN.
PRI Primary Rate Interface.
Private Branch
See PBX.
Exchange
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network. The voice
telephone network accessible to all those with
telephones and access privileges.
PTZ Pan/Tilt/Zoom. Describes the cameras supplied
as part of the ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX,
and VS4000 systems.
QCIF Quarter CIF (Common Intermediate Format). A
video format providing resolution of 176 x 144
pixels. See also CIF, 4CIF, 16CIF.
© Polycom, Inc. 7
Page 18

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
QoS Quality of Service. This allows guaranteed
bandwidth and packet delivery between
endpoints over a packet network.
RAI Remote Alarm Indication.
RJ-11 A six-conductor modular jack. RJ-11 connectors
are used on all standard telephones in the US for
connecting to the PSTN.
RJ-45 An eight-conductor modular jack commonly used
for data lines such as LAN connections.
RJ-9 A four-conductor modular jack commonly used
for telephone handsets. Polycom uses RJ-9
connectors for all of the Extension microphone
connections.
Router A networking device with ports for connection to
hubs and switches. It provides central
connectivity and security for multiple
workgroups and LANs.
Server A computer or software that provides services to
clients — for example, file storage (file server),
programs (application server), or printer sharing
(print server). See also client.
Site A location or a system; the term implies that rooms
and people are also included. Two sites participate
in a point-to-point call. Multiple sites participate in
a multipoint call.
Streaming A technology that allows an audio or video file to
start playing on your computer before the entire
file has finished downloading.
Tilt Move the camera up or down.
UI User Interface. The controls that let you interact
with equipment or software. See also GUI.
UPS Uninterruptable Power Supply.
Upstream Farther from the endpoint. For example, the
network side of a network interface module is
upstream of the peripheral side.
8 www.polycom.com
Page 19

Chapter 1 - About this Manual
WAN Wide Area Network. Business with LANs at more
than one location may use the public carrier
network to carry data between these locations.
Typical WAN services provided by the pubic
carrier are Frame Relay, X.25, and ISDN for
carrying data.
Whiteboard Software that allows you to share and annotate
images.
Zoom Adjust the area shown on the screen using the
camera’s telephoto and wide-angle capabilities.
© Polycom, Inc. 9
Page 20

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
10 www.polycom.com
Page 21

2
Technical Information
This chapter provides descriptions and technical information about
the ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 systems.
This chapter covers the following topics.
Topic Page
System Descriptions 12
Other Elements of a Typical Deployment 45
© Polycom, Inc. 11
Page 22

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
System Descriptions
The Polycom ViewStation EX and ViewStation FX systems are
set-top videoconferencing systems designed for conference rooms.
The Polycom VS4000 system is a rack-mounted videoconferencing
system designed for large conference rooms or board rooms. These
systems may be purchased with the following optional network
interface modules:
❑ Quad BRI : allows up to four ISDN lines to be multiplexed
together to create a higher-bandwidth connection to the far-site
device. Each ISDN line adds 128 Kbps to the available data rate.
❑ V.35/RS-449/RS-530: supports V.35, RS-449, and RS-530
protocols, depending on the cable used. This interface module
allows you to connect the system to third-party network
interfaces.
In addition, a PRI network interface module is available with the
ViewStation FX and VS4000 systems. This module allows you to
make video calls over ISDN T1 and E1 lines.
Technical Specifications
The following table gives electrical and physical specifications for
the ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 systems.
Table 2-1. Electrical and Physical Specifications
Parameter ViewStation EX and FX VS4000
Power supply type Auto-sense
Line voltage 90 to 260 VAC continuous
Line frequency 47 to 63 Hz continuous
Power consumption 40 W
Case style Set-top Rack-mount
Physical dimensions 33 x 20 x 15 cm
(13 x 8 x 6 in.)
Weight 2.7 kg (6 lbs) 4.7 kg (10.3 lbs)
12 www.polycom.com
46.7 x 43.8 x 8.8 cm
(18.4 x 17.2 x 3.5 in.)
Page 23
Chapter 2 - Technical Information
The following table describes the network interfaces available.
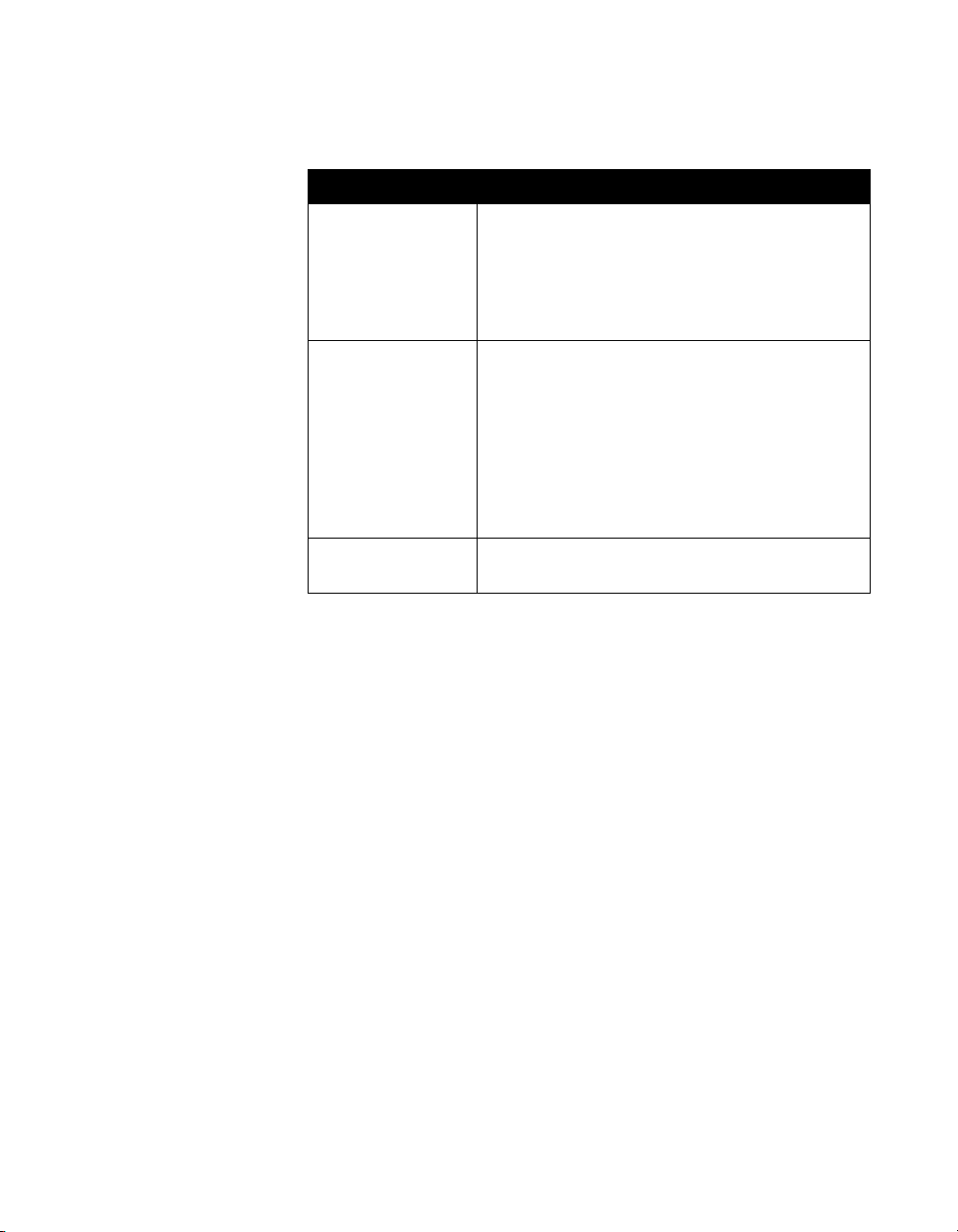
Table 2-2. Connectivity
Network interface Connectivity provided
LAN/WAN Supports—TCP/IP, DNS, WINS, SNMP, DHCP,
ARP, WWW, FTP, Telnet
(2) 10/100 Mbps Ethernet ports
T.120 interface with ShowStation® IP,
WebStation™ and Microsoft ® NetMeeting®
Telephony Quad BRI (Basic Rate Interface)
PRI (Primary Rate Interface) T1 — not available
for ViewStation EX
PRI E1 — not available for ViewStation EX
V.35/RS449/RS-530; support direct connect or
RS-366 dialing
Supports H.331 broadcast mode
Data port RS-232 control port/data communications port
(1200 baud to 115 K baud asynchronous)
ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 are Cisco AVVID
certified.
© Polycom, Inc. 13
Page 24
Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
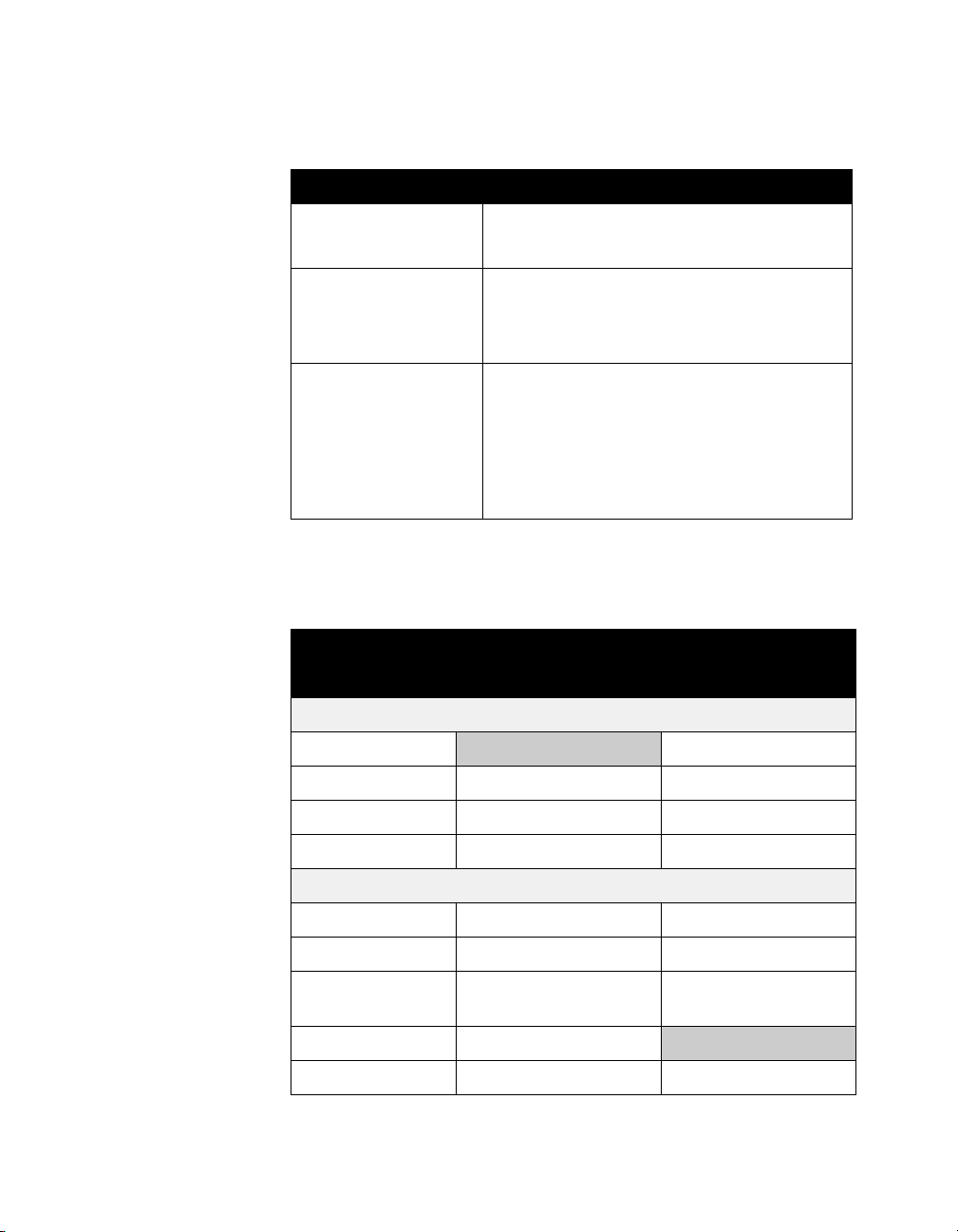
The following table lists the supported video standards.
Table 2-3. Video Standards Supported
Standard Supported
Videoconferencing H.320 p x 64
H.323
Video standards H.261 + Annex D
H.263 + Annexes F, I, J, L, T, U, u
ITU 60 fields/sec
Other ITU standards H.221
BONDING, mode 1
H.225, H.245
H.281 far-end camera control
H.331 broadcast mode
The following table gives information about the video signal
formats.
Table 2-4. Video Signal Formats
Input/Output Signal format
ViewStation EX and FX VS4000
Video inputs (NTSC or PAL)
Main camera S-video and composite
Second camera S-video S-video and composite
Document camera S-video S-video and composite
VCR (playback) Composite Composite
Video outputs (NTSC or PAL)
Main display S-video and composite S-video and composite
Additional displays S-video S-video and composite
VCR out
(recording)
VGA out Up to 1280 x 1024
SXGA out Up to 1280 x 1024 Up to 1280 x 1024
14 www.polycom.com
Composite Composite
Page 25
Chapter 2 - Technical Information
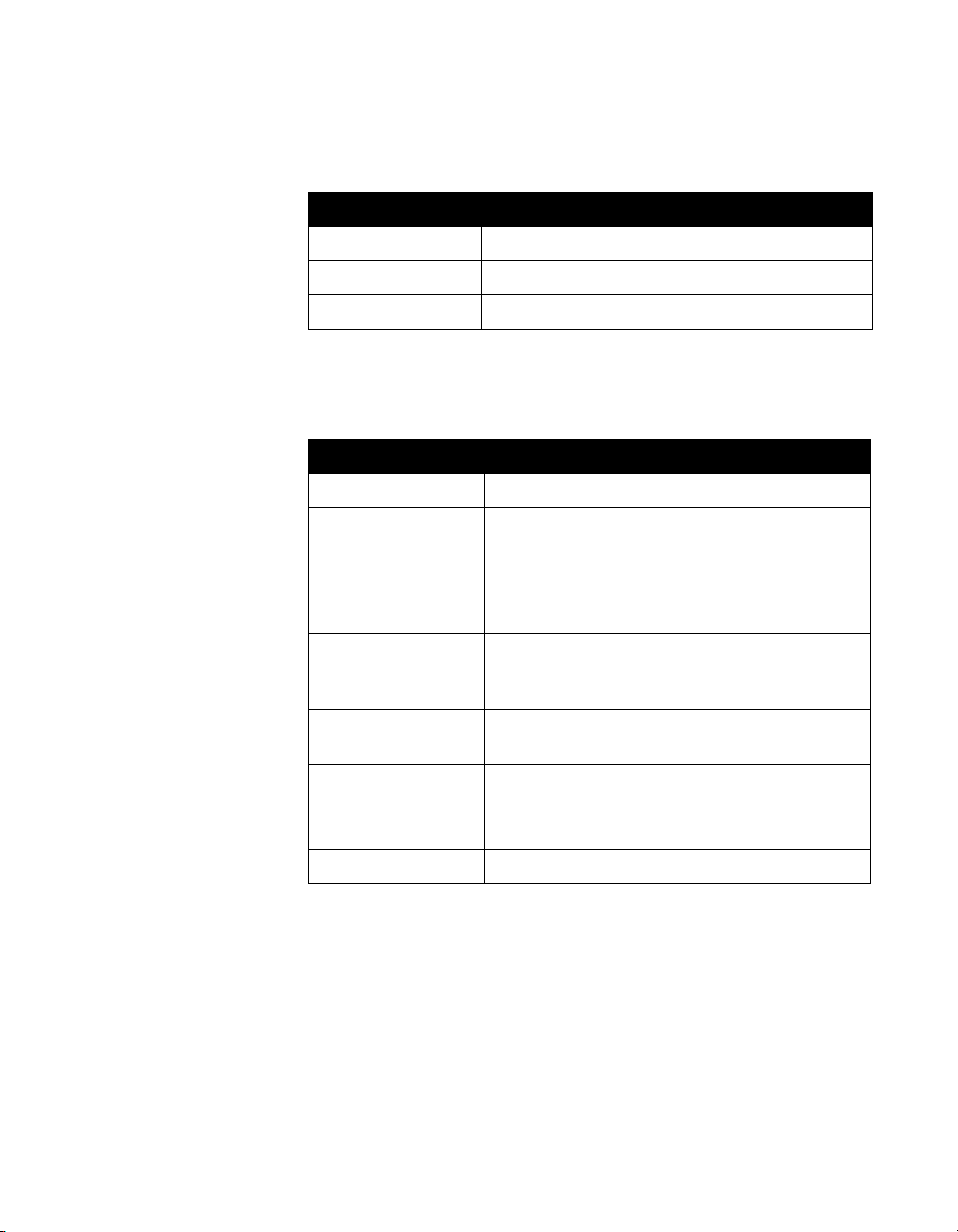
The following table gives electrical specifications for the video
inputs and outputs.
Table 2-5. Video Input/Output Electrical Specifications
Parameter Value/format
Impedance 75 Ω
Signal amplitude 1.0 Vpp typical
Coupling DC
The following table gives other video specifications for the
ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 systems.
Table 2-6. Video Resolution, Frame Rate, and Error Correction
Parameter Value/format
Video format NTSC or PAL
Video resolutions QCIF (176 x 144)
CIF (352 x 288)
4CIF (704 x 576)
TV-quality wide-screen (letterbox)
Graphics
resolutions, slide
transmission
Graphics resolution,
H.261 mode: 4CIF (704 x 576)
H.263 mode: 16CIF (1408 x 1152)
up to 1280 x 1024
local display
Frame rate NTSC: 30 frames/second
(60 fields/second)
PAL: 25 frames/second (50 fields/second)
Error correction Polycom Video Error Concealment (PVEC)
a
a. PVEC is activated and deactivated automatically, as needed.
Video quality degradation with the PVEC feature active may
indicate that your IP network is not functioning properly. At the time
of publication, PVEC is not available in dual stream mode or
standards-based 60-field video.
© Polycom, Inc. 15
Page 26
Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
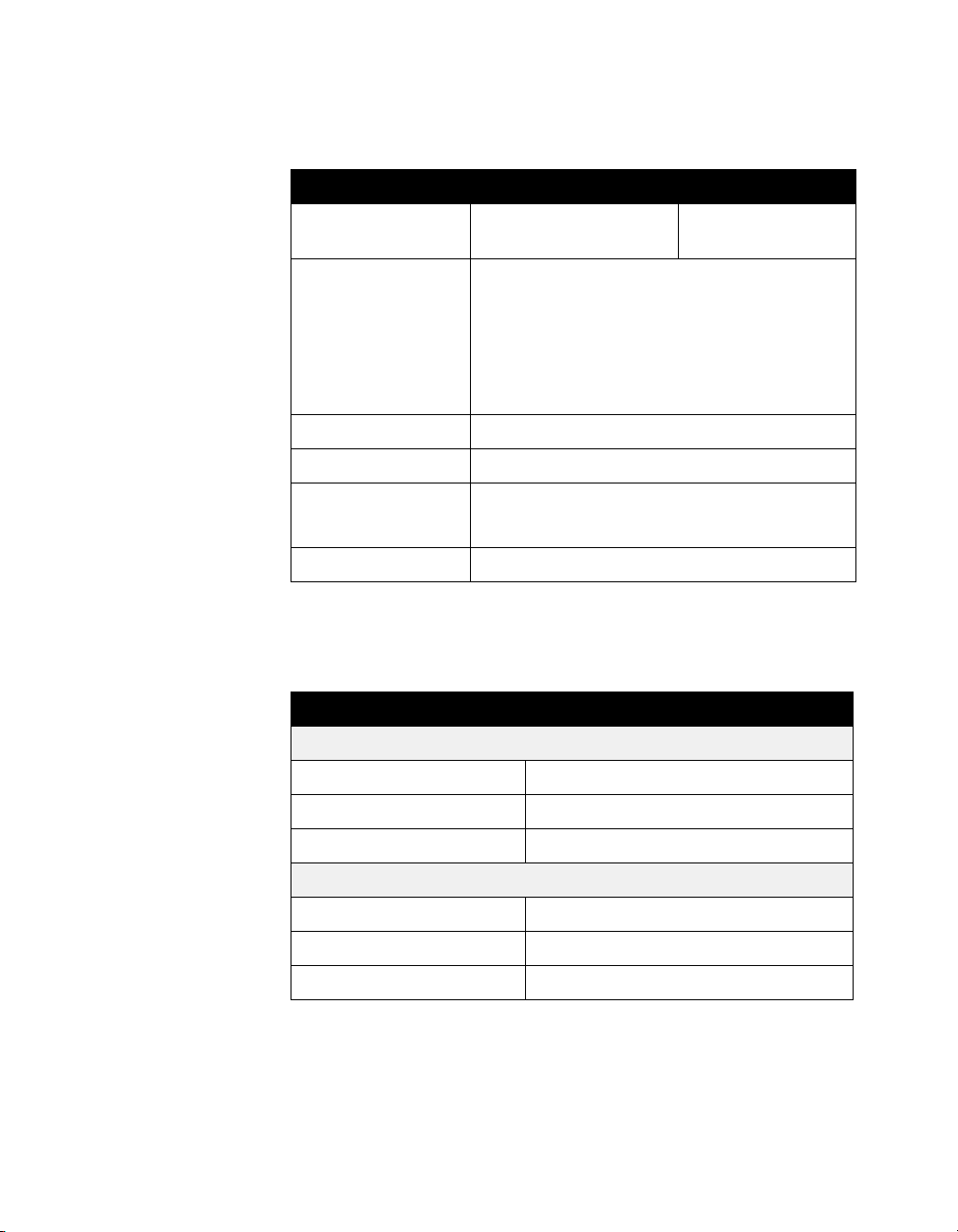
The following table gives camera and display information.
Table 2-7. Cameras and Displays
Parameter ViewStation EX and FX VS4000
Main camera Integrated Sony EVI-10 External Sony
EVI-D10
Main camera
features
Main camera presets 10
Far camera presets 10
Tracking Voice tracking
Auto-PIP system Auto-on, auto-swap, auto-off
65° field of view
12 x Zoom; f=4.2 to 42 mm
F=1.85 to 2.9 mm
Auto focus
Automatic white balance
Track to presets
The following table gives electrical specifications for the audio
inputs and outputs.
Table 2-8. Audio Input/Output Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Value/format
Input
Impedance 10 KΩ minimum
Signal amplitude 1.0 Vpp full-scale (expected)
Coupling AC
Output
Impedance 800 Ω maximum
Signal amplitude 1.0 Vpp full-scale (typical)
Coupling AC
16 www.polycom.com
Page 27
Chapter 2 - Technical Information
The following table gives information about audio features.
Table 2-9. Audio Features
Parameter Value/format
Audio codecs
a
G.711, G.722, G.722.1b, G.728
Mode Full duplex
Gain control Automatic
Noise suppression Automatic
Echo cancellation Instant adaptation
a. The protocol used depends on the protocols supported by the
opposite endpoint and on the line rate. Audio protocol is selected
automatically to provide optimum audio clarity.
b. Provides enhanced frame loss compensation.
The following table gives information about the microphone pods
supplied with the ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
systems.
Table 2-10. Microphone Pods
Parameter Value/description
Pick-up elements 3 hypercardioid pressure-zone microphones
Coverage 360°
Placement Minimum 6 ft (1.8 m) from speakers
Minimum 15 ft (4.6 m) from any other microphone
© Polycom, Inc. 17
Page 28
Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
The following table gives information about multipoint calling.
Table 2-11. Call Capabilities
Feature Capability
Maximum data rate ViewStation EX: 768 Kbps
ViewStation FX and VS4000: 2 Mbps
Local plus three other sites ViewStation FX and VS4000: 384 Kbps
ViewStation EX: 256 Kbps
Local plus two other sites ViewStation FX and VS4000: 512 Kbps
ViewStation EX: 384 Kbps
Cascading (H.320 only) Up to 10 sites at 384 Kbps each, plus
audio only to four other sites
Mixed-protocol dialing
(H.320 and H.323)
Local plus three other sites, through
internal MCU
Inbound calling Sites using either H.320 (ISDN) or H.323
(IP) can dial in to an existing call
Integrated speakerphone
(where approved)
Third-party audio add-in
Point-to-point calling
Multipoint calling
Video streaming Live multicast to Cisco IP/TV® viewer or
®
Apple QuickTime
player
Start and stop the stream using Polycom
browser interface
18 www.polycom.com
Page 29
Chapter 2 - Technical Information
The following table gives information about the systems’ user
interfaces.
Table 2-12. User Interface
Feature Capability
Languages English, French, German, Spanish, Italian,
Portuguese, Norwegian, Chinese, Japanese
Control system Hand-held, ergonomically designed remote control
Infrared receiver (external unit for VS4000,
integrated in ViewStation EX and FX)
On-screen graphical user interface
Web browser interface (requires Microsoft Internet
Explorer® or Netscape Navigator®)
Closed caption
Three lines of text
support
Presentation
and
collaboration
tools
Collaboration
accessories
PolycomSNAP™ screen capture tool
pcPresent™ conversion tool for Microsoft
PowerPoint® files
Visual Concert FX™
Visual Concert PC™
API ARENA™ API (Enables custom integration with
remote devices such as touchscreen panels through
RS-232 or Telnet interfaces)
© Polycom, Inc. 19
Page 30
Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
RS-232 Interface
The RS-232 interface allows users to connect a ViewStation EX,
ViewStation FX, or VS4000 to a PC. This provides a means of access
to the ARENA API, which allows users to automate some of the
systems’ control features. Refer to the ViewStation EX, ViewStation
FX, and VS4000 ARENA API Programmer’s Guide for information
about this API.
The RS-232 interface also makes it possible to use the system as a
peripheral device for an RS-232 host.
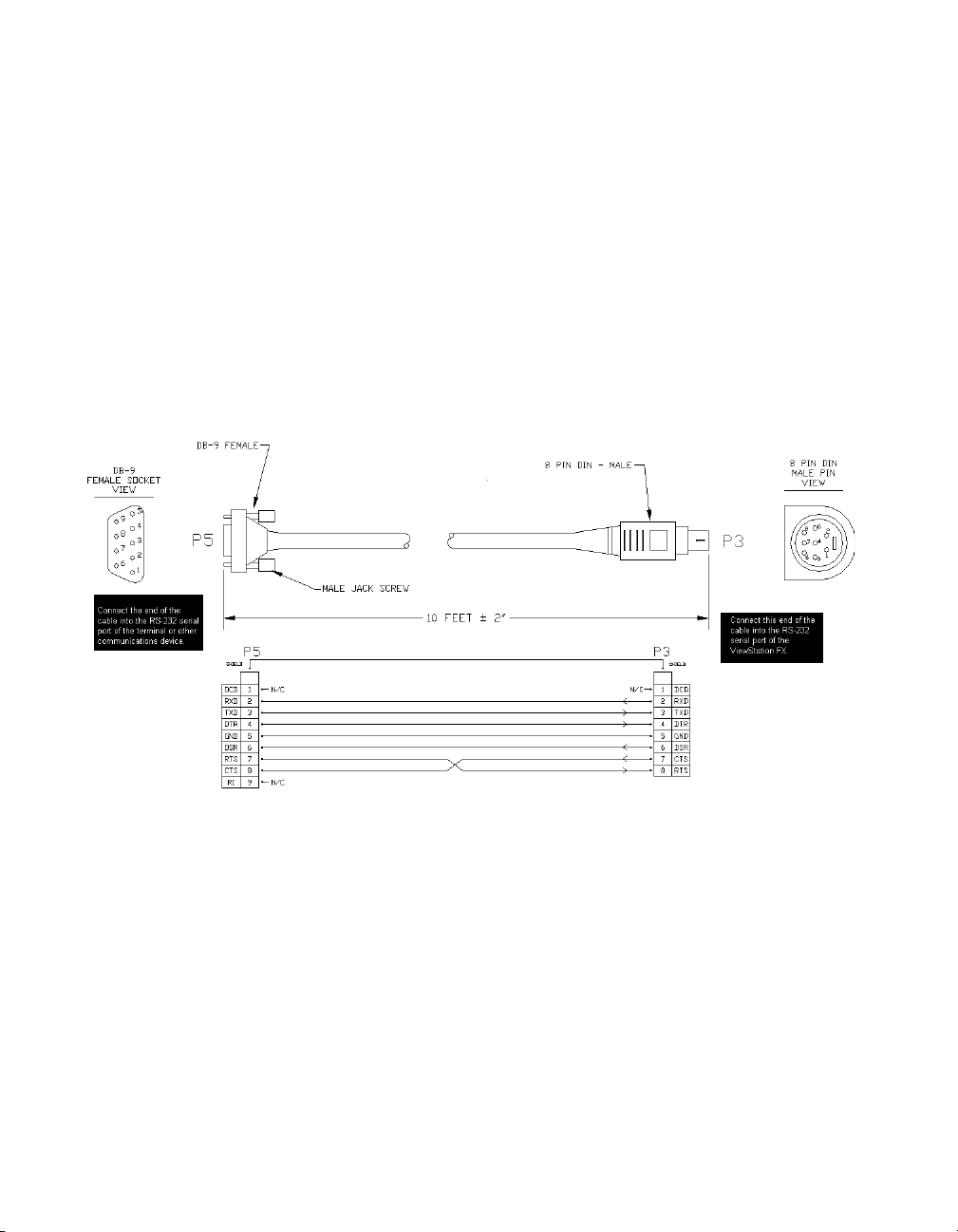
Figure 2-1 shows the RS-232 cable for the ViewStation EX and
Viewstation FX systems.
Figure 2-1. RS-232 Cable for ViewStation EX and FX
20 www.polycom.com
Page 31

Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Figure 2-2 shows the RS-232 cable for the VS4000 system.
Figure 2-2. RS-232 Cable for VS4000
© Polycom, Inc. 21
Page 32

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Quad BRI Network Interface Module
The following paragraphs provide technical information about the
Quad BRI network interface module available with the
ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 systems.
If you do not connect the system to an internal telephone system
(PBX), you must use a network termination (NT-1) device between
the Quad BRI and the ISDN connection at the wall outlet.
Note
Outside the United States or Canada, service providers or public
telephone utilities generally provide the NT-1 device.
Indicators on the Quad BRI Network Interface Module
Table 2-13 shows the indicator lamp (LED) activity on the Quad BRI
network interface module.
Table 2-13. Quad BRI Indicator Lamps
Indication Meaning
Green LED Off = no connection to the switch, or no clock.
On = clock is synchronized with the switch.
Yellow LED Off = in reset mode, booting
On = active
Both LEDs on Normal operation
Note
The indicators do not show whether the SPIDs, switch type, and
ISDN numbers have been correctly entered into the endpoint
equipment.
22 www.polycom.com
Page 33

Quad BRI Cabling
The Quad BRI network interface module connects to the endpoint
using a cable with one keyed RJ-45 connector and one standard
RJ-45 connector. Figure 2-3 shows this cable. Because it uses a
non-standard connector, Polycom Inc. does not support cables of
this type that are fabricated by other vendors.
Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Figure 2-3. Keyed RJ-45 Cable, System to Network Interface Module
© Polycom, Inc. 23
Page 34

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Standard RJ-45 to RJ-45 cables connect the Quad BRI to the network.
Figure 2-4 shows this type of cable.
Figure 2-4. Standard RJ-45 Cable, Network Interface Module to Network
NT-1 Information
Following are sample NT-1 settings. For more detailed diagnostic
information, see the manual that was shipped with your particular
NT-1 device.
Table 2-14. Sample NT-1 Settings
Make and model Switch Indicator
ADTRAN NT-1 ACE Ready = ON
Error = OFF
Power = ON
Motorola NT1D 1 = ON
2 = ON
3 = ON
4 = ON
Alpha Telecom (AT1)
UT620F
24 www.polycom.com
1 = ON
2 = ON
3 = OFF
4 = ON
SC = ON
ACT = ON
LB = OFF
LP= ON
RP = OFF
RPR = OFF
Power = ON
ST&U = OFF
Back = OFF
Page 35

ISDN Switches
Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Depending on the type of ISDN lines you are using, your service
provider may assign zero, one, or two SPIDs per line. Refer to
Table 2-15 below.
Table 2-15. ISDN Switch Types and SPID Allocations
Switch Type SPIDs Allocated
AT&T 5ESS Custom None
AT&T 5ESS NI-1 1 per B-channel
NT DMS-100 NI-1 1 per B-channel
NI-2 1 per device
Siemens EWSD NI-1 1 per B-channel
Siemens EWSD NI-2 1 per device
International (outside United States or
Canada)
Automatic Quad BRI Software Update
The Quad BRI is expected to have a software version at least as
recent as that of the system to which it is connected. If, upon reboot,
the system detects an older software version on the Quad BRI, it
automatically updates the Quad BRI software. The download is
accompanied by an explanatory message.
Do not turn off your system during the download process.
None
Caution
© Polycom, Inc. 25
Page 36

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
PRI Network Interface Module for ViewStation FX and VS4000
The following paragraphs provide technical information about the
T1 and E1 PRI network interface modules available with the
ViewStation FX and VS4000. This network interface module is not
available with the ViewStation EX.
Table 2-16. PRI T1 and E1 Network Interface Modules
Parameter PRI T1 PRI E1
Areas where used North America,
Japan, Hong Kong,
Taiwan
B channels 23 30
D channels 1 1
Total data capacity 1472 Mbps
(23 x 64 Kbps)
Power source VS4000/ViewStation
FX, via peripheral
cable
External power supply
available (required if
not using external
CSU)
Clock source Network Network
Keep-alive signal Yes No
Switch protocol AT&T 5ESS
AT&T 4ESS
Nortel DMS
NI-2
Europe, other areas
where T1 is not used
1920 Mbps
(30 x 64 Kbps)
VS4000/ViewStation
FX, via peripheral
cable
External power supply
available
NET5/CTR4
Line signalling ESF/B8ZS CRC4/HDB3
HDB3
H0 and other
higher-bandwidth
channels
26 www.polycom.com
Not supported
Page 37

Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Table 2-16. PRI T1 and E1 Network Interface Modules (Continued)
Parameter PRI T1 PRI E1
Non-Facility
Associated Signaling
(NFAS)
Special services
(Caller ID, call
blocking, etc.)
Not supported
Not supported
Indicators on the PRI Network Interface Module
The tables below describe the expected behavior of the indicator
lamps on the PRI network interface module. On the network side,
the expected behavior depends on whether it is a T1 module or an
E1 module.
Table 2-17. PRI Network Side Indicator Lamps
Indication PRI T1 PRI E1
Red LED blinking Not connected to the network, or no power to the
upstream equipment
Red LED on Connected to the network, but no clock sync
Yellow LED blinking Receiving clock and
frame sync; receiving
RAI from the network
with CRC errors
Yellow LED on Receiving clock and
frame sync, waiting for
a timer to elapse
Red and yellow
LEDs on
Green LED on Synchronized with the network and ready to use
© Polycom, Inc. 27
Receiving clock and
frame sync; receiving
Remote Alarm
Indication (RAI) from
the network with no
Cyclic Redundancy
Check (CRC) errors
Receiving clock sync;
receiving AIS Alarm
Indication Signal
(unframed all-ones)
Page 38

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Indicator lamps on the peripheral side of the PRI network interface
module have the same meanings for both the T1 and E1 models.
Table 2-18. PRI Peripheral Side Indicator Lamps
Indication Meaning
Amber LED onThe PRI network interface module is in boot mode.
a
Amber and
New software is being burned into flash.
green LEDs
on
Green LED on The PRI network interface module is fully booted.
a. If this LED stays on for more than a minute, new microcode is
being uploaded from the system to DRAM.
b. If the PRI network interface module is connected to an external
power source, the green LED turns on after several seconds, even
if the peripheral link cable is not connected.
b
28 www.polycom.com
Page 39

PRI Cabling
Chapter 2 - Technical Information
The peripheral side of the PRI network interface module connects to
the endpoint using a cable with keyed RJ-45 connectors. Figure 2-5
shows this cable. Because it uses a non-standard connector, Polycom
Inc. does not support cables of this type that are fabricated by other
vendors.
Figure 2-5. Keyed RJ-45 Cable, System to Network Interface Module
A standard RJ-45 to RJ-45 cables connects the PRI to the network.
This is the same cable used by the Quad BRI network interface.
Figure 2-6 shows this type of cable.
Figure 2-6. Standard RJ-45 Cable, Network Interface Module to Network
© Polycom, Inc. 29
Page 40

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Channel Selection
For outgoing calls, the system uses the lowest-numbered available
channel (1-23 for a PRI T1 and 1-30 for a PRI E1). If an additional
channel is needed, the system chooses the next higher-numbered
channel. For example, if channels 1 through 7 are unavailable, but 8
is avail able, the sys tem use s channel 8 to pla ce an ou tgoing c all. If an
additional channel is needed, the system will use the next available
active channel in the range (which could be 9, and so on).
For incoming calls, the system uses the highest numbered channel
that is available. If another channel is needed, the next lower
channel number is used.
PRI E1 Channel Information
The PRI Status screen for E1 shows 30 channels. However, E1 trunk
lines have 32 timeslots, numbered 0 - 31. Timeslot 0 is used for
framing, and timeslot 16 is used for call signaling (the D channel).
The remaining 30 timeslots are used as bearer (data) channels.
In call signaling between Polycom equipment and the switch, these
channels are numbered 1-15, 17-31. But the PRI Status screen
numbers these channels in the range 1-30. On the PRI Status screen,
channels 1-15 control the status of timeslots 1-15, and channels 16-30
control the status of timeslots 17-31.
Dedicated Full PRI T1 or E1 Line
All channels should be active for a full T1 or E1 line dedicated to
your ViewStation FX or VS4000.
30 www.polycom.com
Page 41

Chapter 2 - Technical Information
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module
The following paragraphs provide technical information about the
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 network interface module available with the
ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000.
The system’s V.35/RS-449/RS-530 network interface module is not
interchangeable with the previous V.35 network interface module.
The new module uses HD-44F connectors for ports 1 and 2, and uses
a keyed RJ-45 connector for the serial link to the back panel of the
ViewStation FX or VS4000. The cable used with the
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 network interface module is the same as is
used for the PRI network interface module. It is shown in Figure 2-5.
An HD-44M to DB-25F adapter cable is available to connect existing
ViewStation DB-25 interface module V.35 network cables.
“Common speeds” are divisible by both 56 and 64. The
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 network interface module supports the
following common speeds:
❑ 448 Kbps
❑ 896 Kbps
❑ 1344 Kbps (E1 only)
Indicators on the V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module
The following tables describe the behavior of the indicator lamps on
the V.35/RS-449/RS-530 network interface module.
Table 2-19. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Peripheral Side Indicators
Indication Meaning
Amber LED and
green LED flash once
Amber LED off No communication between endpoint and
Amber LED on Communication established between endpoint
Amber LED and
green LED on
© Polycom, Inc. 31
Power-up test
network interface module
and network interface module
Communication established with network
Page 42

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Table 2-20. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Side Indicator Lamps
Indication Meaning
Amber LED on Network interface module is connected to the
network and receiving a clock signal
Green LED on System is in a call
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Cabling
This section provides cable drawings and pinouts for the three
cables that you can use with the V.35/RS-449/RS-530 network
interface module. All are common to the ViewStation EX,
ViewStation FX, and VS4000.
Figure 2-7. HD-44M to RS-366/V.35 “Y” Cable Diagram
32 www.polycom.com
Page 43

Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Figure 2-8. Pinout to the HD-44M to RS-366/V.35 “Y” Cable
© Polycom, Inc. 33
Page 44
Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Figure 2-9. HD-44M to RS-449/RS-422 “Y” Cable Diagram
34 www.polycom.com
Page 45

Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Figure 2-10. Pinout to the HD-44M to RS-449/RS-422 “Y” Cable
© Polycom, Inc. 35
Page 46

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Figure 2-11. Ascend HD-44M to HD-44M Cable Diagram
Figure 2-12. Pinout for the Ascend HD-44M to HD-44M Cable
36 www.polycom.com
Page 47

Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Figure 2-13. RS-530 Cable Diagram and Pinout
© Polycom, Inc. 37
Page 48

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Serial Interface Control Signals
If you need to customize your V.35/RS-449/RS-530 interface, use
the signal information in Table 2-21 below in addition to the
information provided by your network equipment vendor.
Table 2-21. Serial Interface Control Signals
Signal
(Pin) In/Out Description Configuration Option
ST
(TC/TT)
RT (RC) IN Receive
RTS
(RTS)
DCD
(DCD)
CTS
(CTS)
DTR
(DTR)
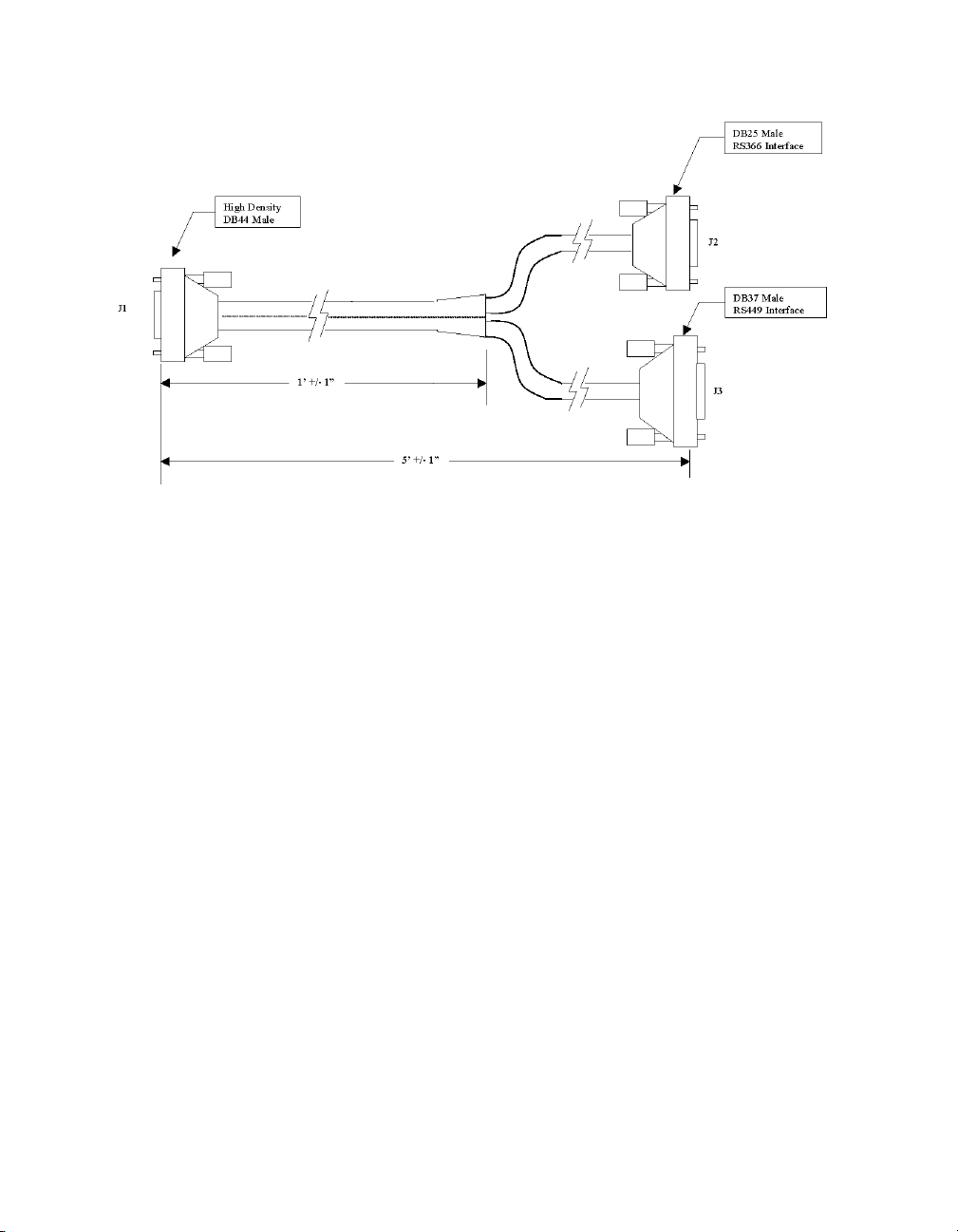
DSR
(DSR)
OUT Send Timing
(clock)
Timing (clock)
OUT Request To
Send
IN Data Carrier
Detect
IN Clear To Send Normal: high is logic 1
OUT Data Terminal
Ready
IN Data Set
Ready
Normal: falling edge sends data
Inverted: rising edge sends data
Normal: rising edge receives
data
Inverted: falling edge receives
data
Normal: high is logic 1
Inverted: low is logic 1
Normal: high is logic 1
Inverted: low is logic 1
Filter: allow DCD to drop for 60
seconds before changing call
state
Inverted: low is logic 1
Normal: high is logic 1
Inverted: low is logic 1
On: signal remains higha
Normal: high is logic 1
Inverted: low is logic 1
Answer: Use DSR as a Ring-In
indication
b
a. If set to ON, inverted is not an option.
b. DSR is not used as a ring-in indication if it is set to ANSWER in
the V.35 Advanced Setup screen.
38 www.polycom.com
Page 49

State Machine
Chapter 2 - Technical Information
The V.35/RS-449/RS-530 state machine controls how the
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 interface signals handshake with the network
interface equipment while the call is being established. The
following tables describe the machine states.
Table 2-22. Dial-Out State Machine
ViewStation or
State
VS4000 Signals Network Signals
1 Initial State:
DTR = 0a
RTS = 0
b
CRQ = 0
USER INITIATES
Initial State:
RI = 0
DLO = 0
ACR = 0
DSR = 0
CALL
2 DTR = 1a
3 Wait 10 ms
4 CRQ = 1
5 PND = 1
6 Set Digit
(NB1,NB2,NB3,NB4)
7 DPR = 1
8 PND = 0
9 DPR = 0
10 If not last digit, go to
state 4; else continue
11 Call connects on
network
12 DSR = 1 AND/OR
DCD = 1
(AND/OR DSR = 1
c
13 RTS = 1b
14 DATA FLOW STARTS DATA FLOW STARTS
User Hang-up Far end hang-up
© Polycom, Inc. 39
Page 50

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Table 2-22. Dial-Out State Machine (Continued)
ViewStation or
State
15 RTS = 0
VS4000 Signals
b
DTR = 0
a
CRQ = 0
All signals go low if Far
End or User hang up
is detected
Network Signals
DSR = 1 to 0, OR DCD
= 1 to 0
A falling edge on DSR
or DCD are interpreted
by the ViewStation FX
or VS4000 as a
hang-up
16 IDLE
DTR = 0
RTS = 0
CRQ = 0
a
b
IDLE
RI = 0
DLO = 0
ACR = 0
DSR = 0
a. DTR does not act as shown but remains high if DTR is set to ON
in the V.35 Advanced Setup screen.
b. RTS does not act as shown but acts as a resync pulse if
Security/Crypto-Resync is set to ON.
c. DSR is used as a ring-in indicate if DSR is set to ANSWER in the
V.35 Advanced Setup screen.
Table 2-23. Inbound Call State Machine
ViewStation FX or
State
1 Initial State:
VS4000 Signals Network Signals
Initial State:
DTR = 0
RTS = 0
CRQ = 0
a
b
RI = 0
DLO = 0
ACR = 0
DSR = 0
REMOTE USER
INITIATES CALL
2 RI= 0 to 1, or DCD= 0
c
3 Notify user of ring-in
to 1, or DSR= 0 to 1
d
4 System accepts call
40 www.polycom.com
Page 51

Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Table 2-23. Inbound Call State Machine (Continued)
ViewStation FX or
State
VS4000 Signals
Network Signals
5 DTR = 1
6 RTS = 1
b
7 Wait for DSR high
8 DSR = 1 AND/OR
DCD = 1 (AND/OR
DSR = 1c)
9 Go to connected state
10 DATA FLOW STARTS DATA FLOW STARTS
11 User Hang-up Far End Hang-up
12 RTS = 0
DTR = 0
CRQ = 0
All signals go low if Far
End or User hang up
is detected
b
a
DSR= 1 to 0, OR
DCD= 1 to 0 OR CTS=
1 to 0
A falling edge on DSR
or DCD or CTS is
interpreted by the
FX/VS4000 as a
hang-up
e
13 IDLE
DTR = 0
RTS = 0
CRQ = 0
a
b
IDLE
RI = 0
DLO = 0
ACR = 0
DSR = 0
a. DTR does not act as shown but remains high if DTR is set to ON
in the V.35 Advanced Setup screen.
b. RTS does not act as shown but acts as a resync pulse if
Security/Crypto Resync is set to ON.
c. DSR is used as a ring-in indicate if DSR is set to ANSWER in the
V.35 Advanced Setup screen.
d. If RS-366 Dialing is not enabled, auto answer must be enabled.
If auto answer is not enabled, ring-in will be ignored when in
non-dialed mode.
e. If DCD filter is set to ON in the V.35 Advanced Setup screen,
the system will not react to a low DCD until DCD has been low for
60 seconds.
© Polycom, Inc. 41
Page 52

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Table 2-24. Non-Dialed User-Initiated Call State Machine
ViewStation FX or
State
VS4000 Signals Network Signals
1 Initial State:
DTR = 0
RTS = 0
a
b
CRQ = 0
Initial State:
RI = 0
DLO = 0
ACR = 0
DSR = 0
USER INITIATES
CALL
2 DTR = 1
3 RTS = 1
a
b
4 DCD = 0 to 1
5 DATA FLOW STARTS DATA FLOW STARTS
User Hang-up Far end hang-up
6 RTS = 0
DTR = 0
CRQ = 0
All signals go low if far
end or User hang up is
detected
7 IDLE
DTR = 0
RTS = 0
CRQ = 0
b
a
DSR= 1 to 0, OR
DCD= 1 to 0
A falling edge on DSR
or DCD is interpreted
by the FX/ VS4000 as
a hang-up
c
IDLE
a
b
RI = 0
DLO = 0
ACR = 0
DSR = 0
a. DTR does not act as shown but remains high if DTR is set to ON
in the V.35 Advanced Setup screen.
b. RTS does not act as shown but acts as a resync pulse if
Security/Crypto Resync is set to ON.
c. If DCD filter is set to ON in the V.35 Advanced Setup screen,
the system does not react to a low DCD until DCD has been low
for 60 seconds.
42 www.polycom.com
Page 53

Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Table 2-25. Non-dialed Network-Initiated Call State Machine
ViewStation FX or
State
VS4000 Signals Network Signals
1 Initial State:
DTR = 0
RTS = 0
a
b
CRQ = 0
Initial State:
RI = 0
DLO = 0
ACR = 0
DSR = 0
USER INITIATES
CALL
2 DCD = 0 to 1
3 DTR = 1
4 RTS = 1
a
b
5 DATA FLOW STARTS DATA FLOW STARTS
User hang-up Far end hang-up
6 RTS = 0
DTR = 0
CRQ = 0
All signals go low if far
end or User hang up is
detected
7 IDLE
DTR = 0
RTS = 0
CRQ = 0
b
a
DSR= 1 to 0, or DCD=
1 to 0
A falling edge on DSR
or DCD is interpreted
by the FX/ VS4000 as
a hang-up
DCD= 0
c
IDLE
a
b
RI = 0
DLO = 0
ACR = 0
DSR = 0
a. DTR does not act as shown but remains high if DTR is set to ON
in the V.35 Advanced Setup screen.
b. RTS does not act as shown but acts as a resync pulse if
Security/Crypto Resync is set to ON.
c. If DCD filter is set to ON in the V.35 Advanced Setup screen,
the system does not react to a low DCD until DCD has been low
for 60 seconds.
© Polycom, Inc. 43
Page 54

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Crypto Resync
If a cryptographic encoder/decoder is connected between the
system and the network, it may require a resynchronization signal
from the system. This is a signal indicating that the system has lost
video synchronization due to a network problem and requires that
the cryptographic encoder/decoder resync with the equipment at
the other end of the connection.
To use this feature, select System Info > Admin Setup > Security.
When you select the Crypto Resync option, the Crypto Resync
Pulse screen appears.
On this screen you can enable crypto resync, set the time between
pulses (in seconds), and set the pulse width (in milliseconds).
If the system loses H.320 synchronization while in a call, it sends the
resynchronization pulses at the specified rate until H.320 regains
synchronization.
The resync pulse is output on the RTS signal. If this feature is
enabled, the RTS signal no longer functions as the Ready-To-Send
signal.
Most installations that use encryption equipment require a custom
cable. The cable should route the RTS signal from the system to the
appropriate resync input on the encryption equipment. The
encryption equipment can get its RTS input from the
videoconferencing system's DTR output or by tying this input high.
In this non-dialed mode, the DTR output and RTS output act alike.
44 www.polycom.com
Page 55

Chapter 2 - Technical Information
Other Elements of a Typical Deployment
A typical deployment includes some of the following Polycom
equipment and software in addition to videoconferencing
endpoints:
❑ MGC Manager™
❑ Global Management System™
❑ WebCommander™
❑ PathNavigator™
For more information, please refer to the documentation supplied
with the products deployed within your organization, or see
www.polycom.com.
© Polycom, Inc. 45
Page 56

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
46 www.polycom.com
Page 57

3
Before You Deploy
This chapter provides a summary of the deployment process, and
describes what you must do to prepare for installation.
This chapter covers the following topics.
Topic Page
Predeployment Overview 48
Video Network Security 49
Best Practices 50
Predeployment Planning 51
Developing the Dial Plan 55
ISDN Requirements 63
Site Considerations 72
Predeployment Worksheet 74
© Polycom, Inc. 47
Page 58

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Predeployment Overview
The diagram below gives an overview of the tasks involved in
predeployment planning.
Document the network:
LANs
Subnets
WAN links
Determine network capacity
requirements
Specify call processing
considerations:
Define CPS architecture
Identify gatekeepers
Specify the default
gatekeeper for each endpoint
or group of endpoints
Specify direct or routed calls
as default mode
Create the dial plan:
Define service plan
Define routing tables
Define policies
Define zones
Define the entity addressing
scheme
Verify appropriateness of the
hardware that will host Polycom
Office software
Start deployment
Figure 3-1. The Predeployment Process
48 www.polycom.com
Page 59

Video Network Security
Polycom recommends the following general precautions to keep
your video network secure:
❑ Deploy IP endpoints behind a firewall.
❑ If your deployment seldom requires centralized management
capabilities, disable all endpoints’ remote management
capabilities.
❑ If your deployment does not ever require centralized
management capabilities, consider an ISDN-only deployment.
For detailed discussions of how to secure specific models of
videoconferencing equipment, please refer to the documents
available at Polycom’s Security Center,
http://www.polycom.com/securitycenter.
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
© Polycom, Inc. 49
Page 60

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Best Practices
Polycom recommends the following as best practices when
deploying Polycom IP voice and video applications.
❑ Consider latency, jitter, and packet loss. All are obstacles to
high quality audio and video. Table 3-1 below recommends
maximum values for these parameters.
Table 3-1. Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss
Parameter Maximum recommended value
Latency less than 150 ms one way; 300 ms end to end
Jitter 50 ms or less
Packet loss 1% or less
❑ Consider system requirements. Be sure to meet the minimum
server hardware requirements of all software-based products.
❑ Consider network requirements. Building an end-to-end H.323
video network requires an infrastructure based on layer 2 and
layer 3 switches and routers.
When planning the deployment of multimedia communication
applications, ensure that switches and routers can handle more
than one queue and are enabled to process applications with
different requirements relating to latency, jitter, and loss
characteristics.
❑ Set IP precedence appropriately (if applicable). Some Polycom
systems can set the precedence level for use in Quality of Service
(QoS) enabled networks.
❑ Determine bandwidth requirements. Consider the total
amount of bandwidth associated with video sessions prior to
deployment. It is recommended that all H.323 video endpoints,
CPSs, gateways, and MCUs be connected to a dedicated 10/100
switched-Ethernet port.
50 www.polycom.com
Page 61

Older Polycom ViewStation systems and the RADVision MCUs
and gateways both support 10 Mbps half duplex only.
There are known issues with some older Cisco Catalyst 10/100
switches and video endpoints negotiating half/full duplex. If
the negotiation fails, the endpoint will still function, but the
system will experience video freezing every 3 to 5 seconds.
Predeployment Planning
The main factors to consider in planning the deployment are:
❑ LAN/WAN considerations — document the LANs, subnets,
and WAN links involved in the deployment.
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
Notes
❑ Capacity planning — assess the bandwidth requirements for
the deployment.
❑ Call processing considerations — define call processing
architecture and identify gatekeepers, define registration policy
and call policy.
❑ Dial plan — define details of services, routing, policies, zones,
and addressing.
❑ Server requirements — verify that all management software
will be installed on suitable equipment.
© Polycom, Inc. 51
Page 62

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
LAN/WAN Considerations
You will need to develop a network topology checklist that includes
the following information:
❑ List of Networks: To take advantage of least cost routing and
alternate routing, you must define the topology of the Local area
networks (LANs) that each gatekeeper serves, as well as the
LANs that are logically connected to these but served by other
gatekeepers. This allows the gatekeeper to determine how IP
traffic is routed from one endpoint to the next. PathNavigator
uses the network topology to determine when resources are
unavailable so that an alternate (ISDN) path can be determined.
❑ Subnets within each network and subnet IP address: A
network address is the equivalent of a subnet. You will need to
define all subnet addresses within your LAN. If this information
is not available to the gatekeeper, calls may be rejected because
no route can be determined.
❑ WAN links: These are logical connections from one LAN to
another LAN within the WAN cloud, or logical connections
from one network to another network outside of the
organization. The two types of WAN links are the dedicated
WAN link, which is a logical connection via a dedicated link,
leased line, frame relay or though an ATM network; and the
WAN link to other networks through a VPN tunnel, which
connects one network to another through a secure connection
over the Internet.
❑ Network Diagram describing how networks are connected and
bandwidth capacity on each WAN link.
Each gatekeeper will need information about its neighbor
gatekeepers to be able to communicate with them. Neighbor
gatekeepers manage other H.323 zones within an organization and
allow the network’s workload to be distributed across logical
boundaries within the organization. This enables more efficient use
of the network by limiting communication between zones (across
WAN links). When a call originates with one gatekeeper's zone and
that zone's gatekeeper is unable to resolve the dialed address, it will
be forwarded to the neighbor gatekeepers for resolution. The port
used for gatekeeper-to-gatekeeper communication is usually 1719.
52 www.polycom.com
Page 63

Capacity Planning
H.323 traffic uses more bandwidth than the selected call quality or
H.320 equivalent. Polycom recommends that you allow 20%
overhead for the H.323 signaling traffic. ISDN networks do not
include signaling in the payload calculations, but in TCP/IP
networks all signaling must also be accounted for. For example, a
384-Kbps video call would require approximately 384 Kbps + 20% =
460 Kbps of bandwidth on a TCP/IP network. These figures assume
a full-duplex network.
If H.323 traffic starts out on a half-duplex network segment, it will
require twice the bandwidth indicated by the bandwidth
calculations described above. It will, however, take advantage of
full-duplex segments as soon as it reaches them. For full-duplex
segments, the calculations above remain valid. WAN segments (T1,
Frame Relay, ATM) are typically full-duplex.
The following equations will help in determining the bandwidth
required for H.323 traffic across various network segments:
❑ Full-duplex Ethernet = (Call Speed + 20%) x 1
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
❑ Half-duplex Ethernet = (Call Speed + 20%) x 2
❑ Wide Area Network = (Call Speed + 20%) x 1
❑ ATM (Using LANE) = (Call Speed + 35%) x 1
The table below provides a comparison between H.320 and H.323
point-to-point calls.
Table 3-2. Bandwidth Requirements
Call Quality
(Speed)
128 Kbps 1 Basic Rate ISDN (BRI) line 153 Kbps
256 Kbps 2 BRI lines 307 Kbps
384 Kbps 3 BRI lines 460 Kbps
512 Kbps 4 BRI lines 614 Kbps
768 Kbps Fractional T1 or full Primary
© Polycom, Inc. 53
Bandwidth Required over
ISDN (H.320)
Rate ISDN (PRI) line
Bandwidth Required
over IP (H.323)
922 Kbps
Page 64

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Table 3-2. Bandwidth Requirements
1.5 Mbps 1 PRI line 1.843 Mbps
2.0 Mbps Multiplea PRI lines or E1 line
(Europe)
a. Requires a third-party inverse multiplexer. Inverse multiplexers
provide inverse multiplexing to transmit a single high-speed data
channel over one or many T1 (PRI) or E1 links.
Keep in mind that the examples given here discuss only a single
point-to-point call. Your capacity planning calculations must take
into account the total number of calls that you expect the network to
handle at one time, including multipoint calls. In addition, you will
need to factor in the requirements for any other traffic that the
network must handle.
For detailed information about capacity planning, please refer to the
Polycom white paper, H.323 Bandwidth Considerations, available
at www.polycom.com.
Call Processing Considerations
After documenting your network topology, you will need to define:
❑ Call processing architecture
2.4 Mbps
❑ Gatekeeper identifier
❑ Default gatekeeper
❑ Call routing mode
Defining the call processing architecture is outside the scope of this
document. Please refer to the PathNavigator Deployment Guide in
the Documentation section at www.polycom.com for detailed
information on this topic.
54 www.polycom.com
Page 65

Gatekeeper Identifier
You will need to specify the gatekeeper identifier for each
gatekeeper being deployed. You must also define the maximum
number of endpoints that may be registered to each gatekeeper and
the maximum number of calls that each gatekeeper may handle at
one time.
Default Gatekeeper
An endpoint may register to a gatekeeper automatically or
manually. If endpoint registration is automatic, the registration
policy must specify a default gatekeeper — more than one
gatekeeper may exist on the network.
The registration policy defines the endpoints that may register to the
gatekeeper. It may allow any endpoint to register, or it may restrict
registration to specific endpoints or endpoints on specific networks.
Call Routing Mode
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
The default call mode may be direct or routed. In direct call mode,
the gatekeeper allows endpoints to send messages directly to each
other — the calls do not need to be routed through the gatekeeper.
If direct call mode is used, gatekeeper functionality (such as
simplified dialing, Conference on Demand, and alternate routing) is
not available, because the call bypasses the gatekeeper.
Developing the Dial Plan
The final element of the predeployment preparations is the dial
plan.
The dial plan defines how you set numeric aliases and service
prefixes. Numeric aliases look like telephone numbers. They allow
people to dial a short string of numbers like a telephone extension
or local telephone number instead of entering a full IP address.
© Polycom, Inc. 55
Page 66

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Service prefixes are short numeric strings that identify the services
being requested, such as call speed and zone.
An H.323 dial plan allows you to associate a numeric alias to the
network address of each H.323 entity. This is the calling plan that
you develop for H.323 deployments.
In large deployments, the dial plan also helps to manage resources
by segmenting user populations.
The dial plan defines the following elements of the deployment:
❑ Services — these include system services, gateway and MCU
services.
❑ Routing and policies — these include the default group policy
and least-cost routing tables.
❑ Network topology — includes private numbering plans (E.164
provisioning) or a public dialing plan (ISDN alias assignment).
❑ Neighbor gatekeepers — these are gatekeepers that manage
other H.323 zones within an organization.
❑ Addressing — specifies the requirements for assigning zone
and service prefixes and endpoint addresses.
Before you design a dial plan, you should document:
❑ Current telephone number dialing patterns
❑ Planned router locations
❑ Traffic routing requirements
Because no standard protocol defines the dynamic routing of E.164
addresses, H.323 dial plans must be configured statically and
managed on gateway and gatekeeper platforms.
To reduce the complexity of the configuration, confine H.323
addresses to one portion of the dial plan.
56 www.polycom.com
Page 67

Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
A well-designed dial plan distributes the dial plan logic among the
gateways and gatekeepers. Try to keep the dial plan logic at the
highest component level — for example, allow the gatekeeper to
handle routing and fail-over decisions. This allows individual zones
to be added or modified without affecting other zones, so the
deployment is very scalable.
To assign gateways and gatekeepers:
1. Determine the area that your dial plan covers.
2. Determine what calling area(s) each gateway and gatekeeper
will be responsible for.
3. Determine the peak traffic volume, and determine how many
gateways will be required to handle anticipated increases in this
peak volume.
4. Logically group the gateways into zones to determine how
many gatekeepers you need. A zone can have one or many
gateways. The number of zones you define depends on the
gateways’ capacity and traffic.
5. Determine which gatekeeper should administer each zone.
Services
System services are defined within PathNavigator. They include
many of the functions that simplify the user’s interaction with the
Polycom Office. System services only work within a zone.
PathNavigator’s gateway and MCU services make it simple for the
user to dial out through a gateway or dial into a conference. For
these services to be effective, the gateway service information such
as call speed, service and zone prefixes, and device capabilities must
be registered with PathNavigator.
Gateway and MCU services are defined in both PathNavigator and
the MGC platform itself. It is critical that the prefixes are exactly the
same in each system.
© Polycom, Inc. 57
Page 68

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Administration, Policies, and Routing
Administration Plan
The videoconferencing administration plan allows the system
administrator to manage user permissions and network policies.
Your plan should define:
❑ Superusers
❑ Administrators
❑ Permissions for groups and for individuals
❑ Policies such as bandwidth allocation per user
Default Group Policy
A group policy allows you to define dialing properties, services, and
bandwidth management parameters for all members of a defined
group without having to configure these individually for each user.
The default group is normally all users, and the policy settings for
this group are the default group policy. The administrator sets
policy, services, and other settings for this and other groups.
Least-Cost Routing
Least-cost routing enables calls that originate inside the
organization to be routed in the manner that incurs the lowest
expense. In order for least-cost routing to be implemented, the
network topology must be defined — the gateways on each
network, WAN link capacities, and other factors.
Each gateway has an associated least-cost routing table which is
created by the administrator. The table consists of dial string entries
(country code, area/city code, etc.) and cost. For calls between
networks, the tables are compared to identify the least-cost route for
the call. Least-cost routing will not be used if the least-cost route
cannot be identified, if the required resources are unavailable, or if
bandwidth limitations exist on the WAN link.
58 www.polycom.com
Page 69

If your organization has special rate plans, those should be
incorporated into the least-cost routing tables.
Network Topology
You will need the network topology information described in
LAN/WAN Considerations
plan and configure PathNavigator to manage your video network.
If the network is physically changed, you will need to update
PathNavigator’s network information so that it can manage the
video network effectively.
PathNavigator provides the means for you to assign ISDN numbers
to endpoints. The way numbers are assigned depends on your
network:
❑ E.164 provisioning — Choose E.164 provisioning if you are
using private numbers.
❑ ISDN alias assignment — If you assign ISDN numbers to
endpoints, then the ISDN ranges need to be provided to the
gatekeeper. These numbers must be coordinated with your local
ISDN provider as these numbers cannot be self-populated.
Assigning numbers that are not in your domain will result in
failed calls when users outside the organization try to access
users within the organization with self-populated numbers.
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
on page 52 when you design your dial
❑ Automatically assigned numbers — PathNavigator can
automatically assign direct inward dial (DID) numbers or
gateway extensions. You cannot automatically assign both
types of numbers on the same network.
Neighbor gatekeepers
Neighbor gatekeepers allow for the distribution of the workload
across logical boundaries within the organization. This enables
more efficient use of the network by limiting communication across
WAN links. When a call originates in one gatekeeper’s zone and that
gatekeeper is unable to resolve the dialed address, it will be
forwarded to the neighbor gatekeepers for resolution.
© Polycom, Inc. 59
Page 70

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Addressing
The addressing components of an H.323 dial plan are:
❑ Gatekeeper zone identifiers or prefixes
❑ Entity addressing
❑ Terminal aliases (include numeric and alphabetic aliases)
❑ System Services
❑ MCU service prefixes
❑ Gateway service prefixes
Ea ch H.32 3 entit y mus t have a t least one network address (transport
address). The network address uniquely identifies the H.323 entity
on the network. It is typically a TCP/IP address.
If the entity is a terminal, it may also have one or more alias
addresses associated with it.
Zones and Zone Prefixes
A zone is the collection of all terminals, gateways, and MCUs
managed by a single gatekeeper. A zone may be independent of
network topology, and may include multiple network segments
which are connected by routers and other devices.
When using multiple zones (multiple gatekeepers), zone identifiers
must be used. Zone identifiers are analogous to area codes.
Specifying local zone prefixes enables the gatekeeper to resolve
addresses sent by neighbor gatekeepers. The local zone prefix
identifies this gatekeeper. Some gatekeepers do not strip prefixes
before the address when sending out a request for address
resolution. These addresses cannot be resolved without the local
zone prefix. The local zone prefix needs to be removed from the
dialed address in order to match the address to a registrant.
60 www.polycom.com
Page 71

Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
Table 3-3. Zone Identifiers and Neighbor Gatekeepers
Milpitas
Prefix
Local zone prefix 408 512 770
Neighbor gatekeeper 1 prefix 512 408 408
Neighbor gatekeeper 2 prefix 770 770 512
gatekeeper
Austin
gatekeeper
Atlanta
gatekeeper
If the local zone prefixes are configured, requests from neighbor
gatekeepers with prefixes that match the local zone prefix will be
resolved. All other calls will be rejected.
Entity Addressing
An entity must have a network address and may have alias
addresses. These are defined as follows:
❑ Network address: This address relates to network transport. It
is usually a TCP/IP address. This address can either be
automatically issues via dynamic host configuration protocol
(DHCP), or statically assigned by the administrator from a pool
of available addresses.
❑ Alias address: This may be a telephone number (private
number or public E.164 address) or an H.323 identifier, which is
an alphabetic string such as a username, email-like address, or
H.323 URL.
❑ LAN host name: Any system connected to a LAN must have a
LAN host name (netBIOS name) defined. This is sometimes
called the computer name.
An alias address may represent a terminal or it may represent a
conference. Alias addresses must be unique within a zone. For
example, within a zone there may only be one entity that uses the
alias 3721005.
© Polycom, Inc. 61
Page 72

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Rules for Assigning Prefixes and Numeric Aliases
In assigning prefixes and numeric aliases, it is critically important to
observe certain rules:
❑ MCUs and gateways provide services, so they must have
service prefixes assigned to them. Each service must have its
own prefix. For example, an MCU or gateway will have a
separate service prefix for each call speed that it provides.
❑ MCU and gateway services work across zones only if used in
conjunction with a manually entered zone prefix.
❑ If the system uses more than one gatekeeper, each gatekeeper
must have a zone identifier prefix.
❑ The numeric aliases for terminals and conferences may begin
with the same initial digit(s) as any service prefix or zone
identifier prefix. This is because PathNavigator’s parsing rule is
that aliases are checked first and service prefixes are checked
last.
❑ The numerals used for service prefixes may not start with an
existing service prefix. Example: If 9 is selected as your access
simplified dialing system service, then you may not create MCU
or gateway service prefixes that begin with 9.
❑ Local zone prefixes are not considered local service prefixes.
Therefore, if you have a local zone prefix of 408, you may still
use 40 to designate a service.
Service Plans
A service plan assigns numeric prefixes to services on the network.
Gatekeepers use service prefixes to route terminal requests to the
appropriate provider of services. Services on the network are
processed by media processors on the network. Within H.323,
media processors are MCUs, gateways, and proxies. A service prefix
is analogous to the digit 9 that you must dial to request an outside
line from a PBX system; the system’s response of connecting you to
the requested outside line would be the service in this example.
62 www.polycom.com
Page 73

System Services
System services include the following:
❑ Conference on demand
❑ Call forwarding: set forward busy, set forward no answer, and
❑ Access simplified dialing
❑ Join or leave hunt group
System services only work within a zone. They do not work across
zones.
Gateway and MCU services are defined in both PathNavigator and
the MGC platform itself. It is critical that the prefixes are exactly the
same in each system.
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
set forward unconditional.
ISDN Requirements
The following paragraphs describe the requirements for ISDN PRI
and BRI interfaces.
ISDN PRI
The PRI network interface is available for the ViewStation FX and
VS4000.
Note
Polycom ISDN PRI modules include an internal CSU for the PRI
interface. The system’s internal CSU can be disabled via the Admin
Setup.
© Polycom, Inc. 63
Page 74

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
The PRI T1 needs to be provisioned for the ViewStation FX and
VS4000 systems as follows:
Table 3-4. ISDN PRI Requirements
Line settings ESF/B8ZS (default)
Extended Super Frame B8ZS is modem standard for
T1/PRI line encoding and framing
Line termination
type
CPE (user side) only
The required termination is built into the system and
most access switches
Supported PRI
switch protocols
AT&T 4ESS, AT&T 5ESS, NI-1, NI-2, Siemens,
Nortel DMS 100, and Nortel 250
These are standard protocols for North America
Number of
channels
23 B-channels dialable at 64 or 56 Kbps, and one D
channel
Ensure that you have 64 Kbps clear channel service
Number of
1 (single PRI)
network
interfaces
Line build-out
modes
DSU+CSU (0 to –22.5dB attenuation), DSU-only
(DSX 0-665 feet)
Physical distance is offset by the settings in the user
interface
Clocking Must be derived from the external network or the
PBX
Terminal
Endpoint ID
(TEI)
0-63
This identifies the PRI endpoint; the common default
is 0
Numbering One local directory number per interface (23
channels)
D-channel slot
number
24
Included to verify where the D channel is; this is
where additional diagnostic information resides
Call-by-call
service codes
64 www.polycom.com
Values 0-31 service codes for GVPN/PN/UPN
network-specific services
Page 75

The PRI direct from the telephone service provider should support
both data and voice for Polycom’s voice add-on capability of
systems.
Determining Usage
To get the best rate of return from PRI lines, they should be used as
much as possible. To do this, look at the data and video traffic as a
whole. Establish a reasonable ratio between the total bandwidth
required if every device is in use and the number of lines provided.
A ratio of 10:1 is fair for general use. If you use a PBX, access switch,
or other data communications unit, the total number of lines into
your customer premise equipment (CPE) can be allocated by
channel to your equipment, according to the bandwidth required at
any given time.
PBX Network Configuration
The PBX or other CPE that will be providing the ISDN PRI interface
to the system must be able to provide a clock signal.
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
Other than the clocking requirement, the rest of the ISDN PRI
provisioning on the PBX is very similar to what would be requested
of an outside ISDN provider.
ISDN BRI
All Polycom ISDN BRI interfaces are S/T-loop. ISDN BRI lines
coming direct from a Telco are U-loop, so if your system is not
behind a PBX or other private network, you must connect the BRI
interface to BRI line(s) through an NT1 device capable of supporting
multiple BRI lines.
NT1 Devices that you may order through Polycom:
❑ Single NT1 (2200-08406-001 or NT1)
❑ Triple NT1 (2200-08406-003)
❑ Quad NT1 (2200-08406-004 or NT1-QUAD)
© Polycom, Inc. 65
Page 76
Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Peripheral Link
ISDN BRI
S/T-loop
Quad BRI
Quad NT 1
(May not be needed)
Figure 3-2. Network Configuration (No PBX)
ISDN BRI
U-loop
ISDN
Peripheral Link
ISD N B R I
Quad BRI
S/T-loop
Quad NT1
(May not be needed)
ISD N BRI
U-loop
PBX
ISD N PRI or
Multiple BRI
ISD N
Figure 3-3. Network Configuration (Behind PBX)
For ISDN BRI lines to be used from a PBX to a videoconferencing
system, you must do these things in addition to meeting the other
requirements.
❑ Determine the interface type of the ISDN BRI network module
in the PBX (U-loop or S/T-loop). This will determine whether or
66 www.polycom.com
Page 77

Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
not you need an NT1 device between the PBX and the ISDN BRI
interface of the videoconferencing system.
❑ If the ISDN BRI network module in the PBX is S/T-loop, there
is a 500-foot limitation with S/T-loop ISDN. The module may
still require a special jack with a resistor.
❑ Ensure that the ISDN PRI or multiple BRI lines, on the public
side (from the Telco) are provisioned to carry data traffic as if it
was connected directly to the videoconferencing systems as
discussed in the appropriate sections above. Voice can be added
but is not required. Items such as switch protocol, numbering
plans, etc. are not necessary as those are determined by the PBX
connecting to the ISDN lines from the Telco side.
❑ Ensure that the ISDN BRI lines’ channels that connect to the
videoconferencing systems are mapped appropriately to the
channels on the public network side of the PBX that connects to
the Telco’s ISDN cloud. This is critical also for the success of the
inbound calls from systems outside the company to ensure that
the ISDN number, provided to the videoconferencing system by
the PBX, is routable in the public ISDN cloud and through the
PBX to the appropriate videoconferencing system.
❑ The ISDN BRI lines between the PBX or other CPE and the
videoconferencing system(s) should be provisioned in the same
way as ISDN BRI lines that would be connected the system(s)
directly from a Telco, as described below.
The following requirements are common to all BRI deployments.
❑ ISDN BRI lines need to be configured in the same way as one of
the following two Bell Core equivalents:
Capability Package R: Circuit Switched Data on 2 B channels.
Data capabilities include Calling Number Identification. No
voice capabilities are provided.
Capability Package S (recommended if system is not behind a
PBX): Alternate Voice/Circuit Switched Data on 2 B channels.
Data and voice capabilities include Calling Number
Identification.
❑ Both B channels must carry circuit-switched videoconferencing
data (voice can be added but is not required).
© Polycom, Inc. 67
Page 78

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
❑ The ISDN BRI service must allow videoconferencing calls to be
dialed on either B channel or on both simultaneously.
❑ The D channel should not permit X.25 packet data.
❑ The ISDN BRI service must be configured as Terminal Type A.
❑ The ISDN BRI service must support automatic Terminal
Endpoint Identifiers (TEIs).
❑ The ISDN BRI service must be tariffed and available from the
customer’s local central office.
DCP (Digital Communication Port) On Lucent Definity ECS
Network Configuration
The Lucent Definity G3 supports DCP connectivity on V2 and
later. ViewStation DCP-based systems support the Lucent Definity
DCP 2-wire configuration, and requires the DCP ports to be
programmed as PDM. No NT1 devices are required with
DCP-based systems.
Typically, 4-pair Cat-5 cabling is used between the Definity ECS and
the network interface module of the ViewStation, terminated on
RJ-45 jacks.
Installation
You can install ViewStation systems in the same room as the Quad
BRI network interface module, or you can connect to the Quad BRI
network interface module through the building’s wiring.
You can locate the system up to 250 feet away from the Quad BRI
network interface module, with the following provisions:
❑ If the distance from the system to the Quad BRI network
interface module is less than 50 feet, no additional power is
required.
68 www.polycom.com
Page 79

Configuration
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
❑ If the distance is between 50 and 250 feet, you must use a 9-volt
AC/DC transformer to boost power (such as the Digi-Key
#T405-ND). Connect the transformer to the Quad BRI network
interface module.
❑ RJ-45 jacks, connected to 110 blocks or 66 blocks, should be
installed in the wiring closet. You can then connect these jacks
to the Quad BRI network interface module with the supplied
RJ-45 cables.
The Polycom DCP-based systems connect to the Definity
Communications server through 2-wire digital communications
ports (DCP).
Note
Digital Trunk Services are required.
DCP-based systems require up to four 2-wire DCP ports on the
Definity server. These ports should reside on the same digital
station card in the system. These DCP ports are set up as personal
data modules (PDMs).
© Polycom, Inc. 69
Page 80

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
The following tables show how the data modules should be
configured in the Lucent Definity PBX administrative console. Ports
3 and 4 are configured identically with unique extensions for each
module, and different port numbers.
Table 3-5. Example Configuration, Data Module 1
Data Extension 6761
Type pdm
Port 01A0001
ITC unrestricted
Name Polycom Channel 1
COS 1
COR 40
TN 1
BCC 1
Remote Loop-Around Test? n
Secondary data module? n
Connected to dte
Table 3-6. Example Configuration: Channel 1, Secondary Data Module 2
Data Extension 6762
Type pdm
Port 01A0001
ITC unrestricted
Name Polycom Channel 1
COS 1
COR 40
TN 1
BCC 1
Remote Loop-Around Test? n
70 www.polycom.com
Page 81

Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
Table 3-6. Example Configuration: Channel 1, Secondary Data Module 2
Secondary data module? n
Connected to dte
Next, you must configure any required hunt groups with a direct
inward dialing (DID) numbers, or local directory numbers. This
enables other systems to call your system.
Once you have configured the hunt groups, hook up the DCP ports
to the system and follow the appropriate system installation
procedures. Use the data module extension numbers for the port
configurations on the system, and the DID/LDN number for the
system’s main number.
Note
If you use Equal Access and a long distance reseller, the long
distance reseller is probably not providing full 64 KBPS connectivity
on long distance calls. In this case, you must set up the Definity to
send long distance video calls through a long distance carrier that
provides full-bandwidth connections.
You must configure a special COR for the system that uses a
different ARS partition group. The ARS partition group will direct
all long distance calls through separate routing patterns that have a
KICK code configured. This KICK code tells the local carrier which
long distance reseller to use and direct the call accordingly.
© Polycom, Inc. 71
Page 82

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Site Considerations
When you select a site for videoconferencing equipment, consider
the following factors:
Table 3-7. Site Considerations
Factor For best results
Access to
required
connections
Room lighting Ensure that the camera will normally point toward an
Room color
and decor
Items in
camera range
Ensure that the equipment will be within 6 feet (1.8 m)
of power and network connections.
Ensure that cables are routed in a way that does not
inconvenience people who use the room.
area that is well-lit but not exceptionally bright. Lighting
should be diffuse to prevent harsh shadows.
If there is a window in the room, ensure that the camera
does not normally point toward it. Backlighting makes
the speaker appear in silhouette.
The camera will perform best if the room furnishings
are medium to dark in color and do not have polished
or reflective surfaces.
Ensure that the camera normally points toward an area
that is of a medium shade and does not contain
detailed, patterned, or brightly-colored elements. For
example, a blue or gray wall provides a more effective
backdrop than a bright painting.
To prevent autofocus problems, place an object
somewhere near the center of the camera’s default
position.
Ensure that no confidential material can be
inadvertently disclosed to callers. For example, ensure
that white boards in the conference room are not used
for engineering sketches.
72 www.polycom.com
Page 83

Table 3-7. Site Considerations (Continued)
Factor For best results
Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
Acoustics and
background
noise
Microphone
placement
Ensure that there is no audible echo in the room where
the camera and microphone(s) will be installed.
Carpeting, drapery, and upholstered furniture all help
to reduce echo problems. Non-rectangular rooms have
less echo than standard conference rooms.
Refer to the documentation for the specific equipment
model for information on where to place the
microphone(s).
© Polycom, Inc. 73
Page 84

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Predeployment Worksheet
This worksheet will help you get the information you need to install
videoconferencing systems on your company’s LAN computer
network. Complete this worksheet before you start the installation.
Once you have this information, refer to this worksheet as needed.
To use your system for LAN-based system management and
LAN-based software upgrades you need to know the type of
addressing your network uses:
• DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) (Recommended for LAN
calls)
• Fixed IP address (Recommended for LAN calls)
IP address for the system _______._______._______.______
Subnet Mask _______._______._______.______
LAN Gateway _______._______._______.______
Check the type of configuration the system uses. Check only one:
•
Use DNS Server Configuration
• Use WINS Server Configuration
Host
Domain
PrimaryWINS _______._______._______.______
Primary DNS _______._______._______.______
Secondary WINS _______._______._______.______
Secondary DNS _______._______._______.______
To ready your system for LAN-based videoconferencing, you also
need to know:
Gatekeeper DNS name or IP
address (if necessary)
Alias for the videoconferencing
system
74 www.polycom.com
Page 85

Chapter 3 - Before You Deploy
Extension (Terminal ID or E.164
number) for the
videoconferencing system
SNMP Information (if necessary)
If you intend to ready your system for remote management via Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP), you also need to know:
IP address for the network
_______._______._______._______
management station
SNMP community string
Dialing Directory Information (if
necessary)
If you intend to use central dialing directories with your
videoconferencing system(s), you need to know:
Central Directory (LDAP) Server
URL or IP address
Port number (default is 389)
Directory service root
Server type
Account password (if you want to
auto-publish the account name)
Document Server (if necessary)
If you intend to use the Document Server option, you need to know:
DNS name or IP address
© Polycom, Inc. 75
Page 86

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
76 www.polycom.com
Page 87

4
Installing Videoconferencing
Systems
This chapter provides installation instructions for the
ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 and their network
interface modules.
This chapter covers the following topics.
Topic Page
The Deployment Process 78
Installation Procedures 79
Network Configuration 88
Connecting the System to a PC 91
Placing Test Calls 96
© Polycom, Inc. 77
Page 88

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
The Deployment Process
The diagram below summarizes the tasks involved in the
deployment process. This chapter assumes that the appropriate
products have been ordered, and that you have done the
appropriate predeployment tasks.
Pre-deployment Deployment
Identify the site's
communication needs
Determine the site's...
Network topology
Bandwidth
requirements
Policies
Dial plan (includes
services plan)
Install PathNavigator and
configure it without
configuring MGC services
and DID
Install MGCManager and
use it to configure MGC
In PathNavigator, configure
MGC services and DID
Install GMS with GDS
Install WebCommander
Configure GMS and
WebCommander
Post-deployment
Place test calls:
IP to IP
IP to ISDN
ISDN to IP
ISDN to ISDN
Install and configure
endpoints
Figure 4-1. The Deployment Process
This chapter discusses installing and configuring endpoints.
78 www.polycom.com
Page 89

Chapter 4 - Installing Videoconferencing Systems
Installation Procedures
For basic system installation, please refer to the installation
instructions in the appropriate User Guide and the QuickStart cards.
Installing Network Interface Modules
The ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 may be
purchased with either of these network interface modules:
❑ Quad BRI
❑ V.35/RS-449/RS-530
In addition, PRI T1 and E1 network interface modules are available
with the ViewStation FX and VS4000.
The diagram below shows a general view of how network interface
modules are installed.
ViewStation EX,
ViewStation FX,
or VS4000
Network
interface
module
External power
supply
(if using PRI)
Figure 4-2. Installing Network Interface Modules
Auxiliary device
(such as NT-1 if
using Quad BRI,
CSU if using PRI)
UPS
ISDN
network
Power
source
Quad BRI Network Interface Module
This section provides information about installing the Quad BRI
network interface module. For performance specifications, cable
diagrams and pinouts, and other technical information, please refer
to Technical Information
© Polycom, Inc. 79
, on page 11.
Page 90

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
NT-1 Device
The Quad BRI network interface module requires an S/T interface.
If your site does not use an internal telephone system (PBX), you
must connect the Quad BRI module to the ISDN line(s) through a
network termination (NT-1) device, which provides the S/T
interface.
Cables Used with the Quad BRI Network Interface Module
The network cables are standard CAT5 cables. If you are connecting
to a PBX, you may need a crossover cable.
Installation
To connect the Quad BRI network interface module to the
system:
1. Make sure your system is turned off.
2. Connect the peripheral side of the Quad BRI network interface
module to the system using the supplied network interface
cable. This cable is color-coded blue on one end, green on the
other.
Figure 4-3. Quad BRI Network Interface Module (Peripheral Side)
80 www.polycom.com
Page 91

Chapter 4 - Installing Videoconferencing Systems
3. Connect the network side of the Quad BRI network interface
module to the NT-1 device or to the ISDN network, as
appropriate.
Figure 4-4. Quad BRI Network Interface Module (Network Side)
4. If you are using an NT-1 device, connect it to the ISDN network.
You are now ready to power on and configure the system.
Installing a PRI Network Interface Module
This section provides information about installing the PRI network
interface module. This module is available for the ViewStation FX
and VS4000.
For performance specifications, cable diagrams and pinouts, and
other technical information, please refer to Technical Information
on page 11.
External Power Supply
If the PRI network interface module loses power, it creates an alarm
condition that may result in the service provider disabling the line.
The PRI network interface must be connected to the external 12-volt
DC power supply so that it does not lose power when the system is
powered off. Connect the external power supply to an
uninterruptable power supply (UPS) if possible.
The external power supply is mandatory for installations in Europe
and is strongly recommended where not mandatory.
© Polycom, Inc. 81
,
Page 92

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
You must use an external power supply if you use the internal CSU
capability of the PRI T1 network interface module.
Channel Service Unit
In North America, the PRI T1 network interface module can be
connected to an external Channel Service Unit (CSU). The CSU
isolates the PRI from the network, and continues to transmit a signal
to the network even if the PRI network interface module loses
power or is disconnected. This prevents the line from being
deactivated. A CSU is normally used only when the PRI network
interface module is connected directly to a telephone company
switch, not a PBX.
Outside North America, CSUs are not used with PRI network
interface modules.
If you use an external CSU, connect an RJ-45 cable from the CPE
equipment side of the CSU to the PRI network interface module.
ADTRAN Atlas 800 Plus E1 Module
Firmware
If you are using an ADTRAN Atlas 800 Plus E1 Module, it must use
firmware version G03b or later.
Channel Restarts
Wait two to three minutes after the endpoint has been powered on
and the PRI status icon has turned green before making or receiving
calls with the ADTRAN Atlas 800 Plus. This allows time for channel
restarts on the ADTRAN Atlas 800 Plus E1 module. If you place a
call before channel restarts are complete, a Network Congestion
message appears on the system. Incoming calls during this time will
receive a Far Site Busy message.
82 www.polycom.com
Page 93

Chapter 4 - Installing Videoconferencing Systems
If You Are Connecting to a PBX
❑ Some PBXs require a crossover cable.
❑ The PBX must provide the clock signal and act as the network
side for layers 1, 2, and 3.
❑ QSIG signaling (PSS1) is not supported. However, a PRI
network interface module can be connected to a PISN through a
gateway using ETSI DSS1 signaling.
Cables Used with the PRI Network Interface Module
The following cables may be used with the PRI network interface
module.
❑ Peripheral link cable: The peripheral link cable does not fit into
a standard RJ-45 network port. You can, however, use it to
connect any Polycom network interface module to the system.
❑ PBX crossover cable: An RJ-45 crossover cable may be required
when connecting the PRI network interface module to a PBX or
other third-party network access device.
❑ PRI Cable extension: You can purchase a cable adapter kit to
extend the distance between your system and the PRI network
interface module.
❑ 75 Ω coaxial adapter: The PRI E1 line termination is 120 Ω. In
some areas, however, the E1 network connection is via a 75 Ω
coaxial cable. The PRI network interface module does not
directly support this, but you can obtain passive adapter
devices from various vendors.
© Polycom, Inc. 83
Page 94

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Installation
To install the PRI network interface module:
1. Ensure that the system is powered off.
2. Connect peripheral side of the PRI network interface module to
the system using the supplied cable. Figure 4-5 shows the
peripheral side of the PRI network interface module.
Port
(not used)
Figure 4-5. PRI Network Interface Module (Peripheral Side)
Input Port
LEDs
3. Connect the 12-volt DC power supply to the PRI network
interface module and then to the UPS or wall outlet.
4. Connect the PRI network interface module to the ISDN
network.
Network
Connector
LEDs
Figure 4-6. PRI Network Interface Module (Network Side)
You are now ready to power on and configure the system.
84 www.polycom.com
Page 95

Chapter 4 - Installing Videoconferencing Systems
Installing a V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module
Cables Used with the V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module
The network interface module connects to the system using a cable
that is not interchangeable with standard RJ-45 to RJ-45 cables.
The following optional cables used to connect the
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 module to the DCE are available from the
Polycom Web store:
❑ V.35 “Y” cable—HD-44M to DB-25M/RS-366 and M34
“Winchester” V.35
❑ RS-449/422 “Y” cable—HD-44M to DB-25M/RS-366 and
DB-37M/RS-449/422
❑ Ascend cable—HD-44M to HD-44M
Cable for Direct Connect. Direct Connect users can choose to have
the local system answer a video call when it detects data from a
remote site, or hang up when it detects lack of data from the remote
si te. Th is Direc t Connec t signa l lead would be in additio n to ex isting
V.35/RS-449/RS-530 signal leads that control answer/hang up call
states.
© Polycom, Inc. 85
Page 96

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
s
Installation
To install V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module:
1. Make sure the system is turned off.
2. Connect the peripheral side of the network interface module to
the system. Refer to Figure 4-7.
12 VDC Connector
(not used)
Figure 4-7. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module (Peripheral
Side)
Port (not used)
Input Port
LEDs
3. Connect the network side of the network interface module to
the DCE, shown in Figure 4-8 below. If you have only one cable,
connect it to port 1.
LED
Figure 4-8. V.35/RS-449/RS-530 Network Interface Module (Network Side)
86 www.polycom.com
Page 97

Chapter 4 - Installing Videoconferencing Systems
Note
If your DCE does not use dialing, do not use the RS-366 (DB-25M)
connector.
© Polycom, Inc. 87
Page 98

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Network Configuration
The following paragraphs give information about configuring the
ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000 systems for the ISDN
network.
On a PRI T1 Network: Configuring the CSU
If you use an external CSU, you must specify the following
information on the PRI Setup screen (System Info > Admin Setup
> Video Network > IMUX > PRI Network > PRI Setup):
1. In the CSU field, select External.
2. In the Line Buildout field, select the length of the cable that
connects the PRI network interface module to the CSU.
You can also configure the T1 PRI network interface module to act
as a CSU. To do this, the external power supply must be connected.
To use the T1 PRI network interface module as an internal CSU, you
must specify the following information on the PRI Setup screen
(System Info > Admin Setup > Video Network > IMUX > PRI
Network > PRI Setup):
1. In the CSU field, select Internal.
2. In the Line Buildout field, select an appropriate dB setting. The
telephone company usually determines the dB value by
measuring the characteristics of the line. If an external CSU was
previously used, use the setting selected for that CSU.
Otherwise, start with 0.
88 www.polycom.com
Page 99

Firewall and NAT Issues
A firewall protects an organization’s network by controlling data
traffic from outside the network. Different types of firewalls use
different techniques to provide network security, but unless the
firewall is designed to work with H.323 videoconferencing
equipment, it will prevent successful videoconferencing because it
is designed to prevent unsolicited data from entering the network.
From a functional perspective, it blocks incoming calls, and it
prevents outgoing calls by blocking the call signalling from the
external endpoint when the two endpoints begin the signal
transaction required to set up the call.
Network Address Translation (NAT) network environments use
internal IP addresses for the devices within the network, while
using one external IP address to communicate with the outside
world (Wide Area Network). The NAT router accepts incoming data
and forwards it to the appropriate endpoint. This provides a degree
of network security, as the internal IP addresses do not provide
access from outside the network.
Firewalls and NAT are often used together.
Chapter 4 - Installing Videoconferencing Systems
Configuring the System to Operate Behind a Firewall
To make calls through a firewall, you must open the following ports
and assign them to the videoconferencing system:
Table 4-1. Firewall Ports to Open for Videoconferencing
Port Used for
389 (TCP) ILS registration
1503 (TCP) Microsoft NetMeeting T.120 data sharing
1718 (UDP) Gatekeeper discovery
1719 (UDP) Gatekeeper RAS (must be bidirectional)
1720 (TCP) H.323 call set-up (must be bidirectional)
1731 (TCP) Audio call control (must be bidirectional)
3230-3235
(TCP/UDP)
3603 (TCP) Web interface
© Polycom, Inc. 89
Signalling and control for audio, call, video, and
data/FECC
Page 100

Integrators’ Reference Manual for ViewStation EX, ViewStation FX, and VS4000
Configuring the System to Operate Behind a NAT
The System is behind a NAT option allows the user make calls
outside the internal network.
At this time, it is not possible to make videoconferencing calls
within the internal network when the System is behind a NAT
option is selected. To make videoconferencing calls within the
network, users must deselect the System is behind a NAT option
before making the call.
1. Determine the NAT’s external (WAN) IP address.
2. Determine the IP address of the system. This can be found in the
System Information screen.
3. Go to Quality of Service and Firewalls screen (System Info >
Admin Setup > LAN/H.323 > H.323 > QOS).
4. Select Use Fixed Ports.
5. Select System is behind a NAT.
6. Enter the NAT’s external IP address into the NAT outside
(WAN) address field.
7. Write down the Fixed TCP and UDP port numbers displayed on
this screen. The default values are:
TCP: 3230 to 3231
UDP: 3230 to 3235
8. Reset the firewall’s fixed ports from step 4 to be permanently
open, and redirect them to the IP address of your system.
9. To accept incoming calls, open and redirect port 1720 to the IP
address of your system.
90 www.polycom.com
 Loading...
Loading...