Page 1

Administrator’s Guide
for the V500 System
December 2004 Edition
3725-21743-003/B
V500 Version 7.5
VideoVoiceDataWeb
Connect. Any Way You Want.
Page 2

Trademark Information
Polycom® and the Polycom logo design are registered trademarks of Polycom, Inc. V500™, Global
Management System™, People+Content IP™, Pro-Motion™, and Siren™ are trademarks of Polycom, Inc. in
the United States and various other countries. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Patent Information
The accompanying product is protected by one or more U.S. and foreign patents and/or pending patent
applications held by Polycom, Inc.
© 2004 Polycom, Inc. All rights reserved.
Polycom Inc.
4750 Willow Road
Pleasanton, CA 94588-2708
USA
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written permission of Polycom, Inc. Under the law,
reproducing includes translating into another language or format.
As between the parties, Polycom, Inc. retains title to , and ownership of, all proprietary rights with respect to the
software contained within its products. The software is protected by United States copyright laws and
international treaty provision. Therefore, you must treat the software like any other copyrighted material (e.g.
a book or sound recording).
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this manual is accurate. Polycom, Inc. is not
responsible for printing or clerical errors. Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Page 3

About this Guide
The Administrator’s Guide for the V500™ System is for administrators of the
V500 system who need to:
❑ Configure the system for use in the network environment
❑ Customize the behavior and appearance of the system
❑ Obtain information about calls
❑ Gather network usage and performance data
❑ Troubleshoot any issues
Other documents available for the V500 system include:
❑ Setting Up the System, which describes how to set up the hardware
❑ Getting Started Guide for the V500 System, which describes how to perform
video conferencing tasks
❑ Setup Sheets, which describe how to install optional hardware
❑ Release Notes
For support or service, please contact your Polycom® distributor or go to Polycom
Support at www.polycom.com/support.
Polycom recommends that you record the serial number and option key of your
V500 system here for future reference. The serial number for the system is printed
on the unit.
System Serial Number: ____________________________________________
Option Key: ____________________________________________________
© Polycom, Inc. iii
Page 4

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
iv www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 5

Chapter 1 - Introducing the V500 System
Key Features ..........................................................................................................................................1 - 2
Industry-Leading Audio and Video Quality .............................................................................1 - 2
Rich Conference Experience .........................................................................................................1 - 2
Enhanced User Experience ........................................................................................................... 1 - 2
Easy Installation ............................................................................................................................. 1 - 3
Security and Network Management ...........................................................................................1 - 3
Standard System Components ............................................................................................................ 1 - 4
Optional System Components ............................................................................................................1 - 5
Chapter 2 - Setting Up Your System Hardware
Positioning the System .........................................................................................................................2 - 2
Connecting the Monitor ....................................................................................................................... 2 - 2
Connecting the System to the Network .............................................................................................2 - 3
Connecting the LAN Cable ..........................................................................................................2 - 3
Connecting the BRI Network Interface ......................................................................................2 - 4
Connecting Headphones .....................................................................................................................2 - 4
Installing Batteries in the Remote Control ........................................................................................2 - 5
Connecting Power ................................................................................................................................2 - 5
Contents
Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
Using the Setup Wizard .......................................................................................................................3 - 2
Establishing an Administrator Password ..................................................................................3 - 2
Running the Setup Wizard ...........................................................................................................3 - 2
Configuring Your IP Connection ........................................................................................................ 3 - 3
Configuring LAN Properties .......................................................................................................3 - 3
Setting Up Your IP Network Connection ..................................................................................3 - 5
Calling Within an Intranet ....................................................................................................3 - 5
Calling Through a Cable or DSL Modem ...........................................................................3 - 6
Calling Through a Network Router .....................................................................................3 - 6
Calling Through a Router, Using a DMZ .........................................................................3 - 12
Configuring IP Network Support .............................................................................................3 - 13
Configuring H.323 Settings .................................................................................................3 - 13
Configuring SIP Settings ..................................................................................................... 3 - 16
Configuring Quality of Service (QOS) ..............................................................................3 - 17
Configuring Your ISDN Connection ...............................................................................................3 - 18
Preparing Your ISDN Network .................................................................................................3 - 18
Configuring the ISDN Network Interface ................................................................................3 - 18
Configuring Call Preferences ............................................................................................................3 - 20
Configuring the Global Directory ....................................................................................................3 - 22
Configuring the Directory Server Settings ...............................................................................3 - 22
Setting the Dialing Rules ............................................................................................................3 - 23
Placing a Test Call ...............................................................................................................................3 - 23
© Polycom, Inc. v
Page 6

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Checking System Status ..................................................................................................................... 3 - 24
Keeping your Software Current ....................................................................................................... 3 - 25
Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
Managing User Access to Settings and Features ............................................................................. 4 - 2
Setting the Admin Password .......................................................................................................4 - 2
Screens that Require the Admin Password for Access ............................................................ 4 - 3
Letting Users Customize the Workspace ................................................................................... 4 - 4
Limiting What Users Can Do With the System ........................................................................ 4 - 5
Using the System for Specialized Applications ........................................................................ 4 - 5
Designing Video Behaviors ................................................................................................................. 4 - 5
Configuring Camera Settings ...................................................................................................... 4 - 6
Configuring the TV Monitor ........................................................................................................ 4 - 7
Using Dual Monitor Emulation ...................................................................................................4 - 8
Adjusting the Monitor’s Color Balance ...................................................................................... 4 - 9
Displaying Content with People+Content IP ............................................................................ 4 - 9
Designing Audio Behaviors ..............................................................................................................4 - 11
Designing General System Behaviors .............................................................................................. 4 - 12
Configuring Call Settings ........................................................................................................... 4 - 12
Configuring Remote Control Behavior .................................................................................... 4 - 13
Configuring Directory Settings .................................................................................................4 - 13
Setting the Call Answering Mode ............................................................................................. 4 - 14
Enabling AES Encryption ........................................................................................................... 4 - 14
Setting Passwords and Security Options ................................................................................. 4 - 15
Setting Date, Time, and Location .............................................................................................. 4 - 16
Customizing the Workspace Appearance ...................................................................................... 4 - 17
Designing the Home Screen ....................................................................................................... 4 - 18
Adding Sites to the Home Screen ............................................................................................. 4 - 20
Adding On-screen Instructions ................................................................................................. 4 - 20
Using Marquee Text ............................................................................................................ 4 - 20
Using Screen Saver Text ...................................................................................................... 4 - 21
Changing System Appearance .................................................................................................. 4 - 21
Setting Ring Tones and Alert Tones ......................................................................................... 4 - 22
Configuring Closed Captioning ....................................................................................................... 4 - 22
Audio Options for Closed Captioners ..................................................................................... 4 - 23
Options for Supplying Closed Captions to Conferences ....................................................... 4 - 23
Providing Captions Via the V500 Web Interface .............................................................4 - 23
Providing Captions Via a Telnet Session .......................................................................... 4 - 24
Getting Started with Calling ............................................................................................................. 4 - 25
Chapter 5 - Managing the System Remotely
Using the V500 Web Interface ............................................................................................................ 5 - 2
Accessing the V500 Web Interface .............................................................................................. 5 - 2
Room Monitoring with the V500 Web Interface ....................................................................... 5 - 3
Managing System Profiles with the V500 Web Interface ........................................................ 5 - 4
Managing Directories with the V500 Web Interface ................................................................ 5 - 5
Configuring Global Services ............................................................................................................... 5 - 6
Viewing the Management Servers List ...................................................................................... 5 - 6
Requiring an Account Number for Calls ................................................................................... 5 - 6
vi www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 7

Adding My Information ...............................................................................................................5 - 7
Requesting Technical Support from the Global Management System Administrator .......5 - 8
Setting Up SNMP ..................................................................................................................................5 - 9
Downloading MIBs .......................................................................................................................5 - 9
Configuring for SNMP Management ....................................................................................... 5 - 10
Chapter 6 - System Usage and Statistics
Call Summary ........................................................................................................................................6 - 2
Call Statistics ..........................................................................................................................................6 - 3
Call Status ..............................................................................................................................................6 - 4
Recent Calls ............................................................................................................................................6 - 5
Call Detail Report .................................................................................................................................6 - 6
Information in the Call Detail Report .........................................................................................6 - 6
Call Detail Report Archives .........................................................................................................6 - 9
Chapter 7 - Diagnostics and General Troubleshooting
Sending a Message ................................................................................................................................7 - 2
System Screens Quick Reference ........................................................................................................7 - 2
Diagnostic Screens ................................................................................................................................7 - 3
General Troubleshooting ..................................................................................................................... 7 - 8
Power and Start-up .......................................................................................................................7 - 8
Remote Control .............................................................................................................................. 7 - 9
Access to Screens and System ......................................................................................................7 - 9
Calling ...........................................................................................................................................7 - 11
Display ..........................................................................................................................................7 - 13
Audio .............................................................................................................................................7 - 15
Error Indications .......................................................................................................................... 7 - 17
System Lights ...............................................................................................................................7 - 18
Network Interface Lights ............................................................................................................ 7 - 18
How to Contact Technical Support ..................................................................................................7 - 19
By Telephone ................................................................................................................................7 - 19
By Internet ....................................................................................................................................7 - 19
Appendix
Cable Descriptions and Drawings.......................................................................................Appendix - 1
LAN Cable ......................................................................................................................Appendix - 2
Composite Video Cable ................................................................................................ Appendix - 2
Port Usage .............................................................................................................................. Appendix - 3
Q.850 Cause Codes ............................................................................................................... Appendix - 4
Safety and Legal Notices
Index
© Polycom, Inc. vii
Page 8

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
viii www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 9

1
Introducing the V500 System
Your V500 video conferencing system is a state-of-the-art visual collaboration tool.
With crisp, clean video and crystal-clear sound, your V500 system provides the
essential tools your home or small business needs for video conferencing over
broadband networks.
When you use a V500 system for meetings, you can exchange ideas and share
documents with people anywhere in the world, as if they were all in the room with
you. Everyone’s productivity increases, without any travel required.
What’s in this Chapter? Page
Key Features 1-2
Standard System Components 1-4
Optional System Components 1-5
© Polycom, Inc. 1 - 1
Page 10

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Key Features
Industry-Leading Audio and Video Quality
❑ Best-in-class video algorithms — The H.264 video algorithm provides
smooth, natural TV-like video.
❑ State-of-the-art audio quality — The V500 system offers Polycom Siren™ 14,
a 14 kHz frequency response that delivers CD-quality sound.
❑ Video error concealment — The H. 264 video error concealment feature
enhances your video experience by minimizing the chance that the display
will freeze, concealing errors, and reducing full-frame refreshes.
❑ Higher call speed — The maximum call speed on the V500 is now 768 Kbps.
This is up from 512 Kbps in previous releases.
Rich Conference Experience
❑ Content display — Install the optional People+Content™ IP feature on your
PC or laptop, and then use the V500 system to show content (such as
spreadsheets and video clips) to other sites in the video conference.
❑ Split-screen viewing — Use Dual Monitor Emulation (split-screen viewing) to
see more even when you only have room for one monitor.
❑ Language independence — Use the V500 system user interface, remote
control, and web interface in any of twelve languages.
Enhanced User Experience
❑ Customizable home screen — Customize the home screen to support
different types of users:
• Novice users — Offer just a few options, so users need little or no training.
• Advanced users — Provide a wide range of video conferencing features.
❑ Customizable look and feel — Set up the workspace to suit your
environment.
❑ Easy-to-use remote control — Navigate through the configuration screens and
place calls easily using the color-coded remote control buttons.
1 - 2 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 11

Easy Installation
Chapter 1 - Introducing the V500 System
❑ Many ways to use the directory — Find information in the directory using the
method you find most convenient.
❑ Call Scheduler — Use the calendar and call scheduling feature to schedule
video conferences. The system automatically calls the site you selected on the
date and time you specified. For recurring calls, you can indicate whether you
want the system to automatically make the call daily, weekly, or monthly.
❑ Firewall (UPnP™) support — The V500 system offers support for routers that
support UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) NAT traversal, making video
conferencing setup easier for users in homes and small offices.
❑ IP or ISDN calling — The V500 system has a built-in 10/100 Mb Ethernet port
for IP calls. Add the optional single BRI network interface to make calls over
your ISDN telephone lines.
❑ Easy configuration wizard — The system setup wizard detects your network
connections and guides you through configuring the system to work on an IP
network or ISDN.
❑ Fully broadband capable — The standards-compliant V500 system works
with any other H.323 system.
❑ Auto-sensing power supply — The system automatically adjusts for line
voltages from 90 to 260 V and line frequencies from 47 to 63 Hz.
Security and Network Management
❑ AES encryption — Enable the integrated AES encryption to automatically
encrypt calls to other AES-capable systems, without external encryption
equipment.
❑ Remote access — Configure, manage, and monitor the system from a remote
computer using the V500 web interface (the system’s web interface), the
Polycom Global Management
choose not to allow remote management.
❑ Secure system management — Use the local administrator’s password on the
system to prevent others from changing system configuration while allowing
yourself to manage the system.
™
System, or SNMP. Alternatively, you can
© Polycom, Inc. 1 - 3
Page 12

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
❑ Room monitoring — Monitor rooms in or out of a call using the Web Director
feature, accessible through the V500 web interface.
❑ Call Detail Reports — Access the system’s call history from the V500 web
interface. You can download the data to a spreadsheet application for sorting
and formatting.
❑ Remote diagnostics — Identify and correct issues that affect the video
conferencing experience using tools in the V500 web interface.
❑ SNMP reporting — Receive SNMP traps that can indicate a total of 35
conditions.
Standard System Components
This section describes the standard components that come with the V500 system.
Two models of the V500 system are available — IP only, and IP with ISDN.
Name Component Description
V500 system The V500 system delivers high-quality,
face-to-face video communication in a
sleek package that includes the camera
and microphone.
Remote control The remote control is designed to make
it easy to set up and operate the system
— color-coded buttons correspond to
system features.
Composite video
cable
LAN cable The LAN cable connects the system to
BRI cable
(IP with ISDN
model only)
The composite video cable is a triple
RCA cable with S-video that connects
the V500 system to a monitor.
the IP network.
The BRI cable connects the system to
the ISDN.
1 - 4 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 13

Name Component Description
Power supply The power supply connects power to
Documentation Read Me First
Optional System Components
To extend what you do with your V500 system, the following additional options
are available.
Chapter 1 - Introducing the V500 System
the system.
Setting Up the V500 System
V500 system documentation CD
❑ Single BRI network interface — Connect to ISDN with your V500 system.
❑ Headphone — Listen privately by adding your own headphone using the
3.5 mm stereo mini jack.
For more information about ordering these options, please contact your Polycom distributor .
© Polycom, Inc. 1 - 5
Page 14

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
1 - 6 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 15

2
Setting Up Your System Hardware
This chapter describes detailed system setup information. You can also refer to the
system setup document that was provided with your system.
For optional components, refer to the setup sheet that was shipped with the
component.
What’s in this Chapter? Page
Positioning the System 2-2
Connecting the Monitor 2-2
Connecting the System to the Network 2-3
Connecting Headphones 2-4
Installing Batteries in the Remote Control 2-5
Connecting Power 2-5
© Polycom, Inc. 2 - 1
Page 16

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
1.
Positioning the System
The V500 system is designed for homes, home offices, and small- to medium-sized
businesses.
To position the system:
>> Place the V500 system on top of your TV monitor. For optimal audio and video
performance, locate the monitor within 5 to 10 feet (1.52 to 3.05 meters) away
from the people in the call.
5'-10'
Connecting the Monitor
You must connect a television monitor to the V500 system. This may be an NTSC
or PAL monitor, depending on your system.
To connect a monitor to the system:
1. Connect the monitor to the S-video or composite video outputs on the back of
the V500 system.
You must use the same type of connector on the monitor as on the system. For
example, if you use the S-video connector on the monitor, use the S-video
connector on the system.
S-video output
(preferred)
DC IN 12V
BRI
Composite video output
LAN
2 - 2 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 17

Chapter 2 - Setting Up Your System Hardware
S-video provides superior video quality, and is recommended.
2. Connect the system’s audio outputs to the monitor’s audio inputs using the
red and white connectors on the monitor cable.
After you have finished setting up the system, you will need to configure the
monitor’s behavior. You can find information on how to do this in Configuring
the TV Monitor on page 4-7.
Connecting the System to the Network
This section tells you how to physically connect the system to the LAN or to ISDN
(if you purchased the optional BRI network interface).
However, before you can use the LAN or any networking capabilities, you must
configure your system for network use. Follow the steps in the remaining sections
of this chapter to finish physically connecting your system. Then, proceed on to the
next chapter, Configuring Network Use, to get information about network
configuration.
Connecting the LAN Cable
The V500 system comes standard with a LAN cable.
To connect the system to the LAN:
1. Connect the LAN cable to the LAN connector on the back of the system.
DC IN 12V
BRI
LAN connector
2. Connect the other end of the LAN cable to the LAN.
© Polycom, Inc. 2 - 3
LAN
Page 18

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Connecting the BRI Network Interface
The V500 system is available with the optional BRI network interface, which
allows you to make ISDN calls.
You may need an NT-1 device if your site does not use an internal telephone
system (PBX). A PBX or an NT-1 device provides the S/T interface that the
system’s BRI network interface requires.
To install the BRI network interface:
1. Make sure the system is powered off.
2. Connect the BRI cable from the BRI connector on the back of the system to
ISDN or to your NT-1 device, as appropriate.
BRI
DC IN 12V
LAN
3. If you are using an NT-1 device, connect it to the ISDN.
Connecting Headphones
You can connect optional headphones to the V500 system to listen to your calls
privately.
To connect headphones to the system:
>> Connect the headphone cable to the headphone jack on the back of the system.
BRI
BRI connector
Headphone jack
DC IN 12V
LAN
2 - 4 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 19

Chapter 2 - Setting Up Your System Hardware
Installing Batteries in the Remote Control
The remote control uses three AAA batteries, which are included with the system.
To install batteries in the remote control:
1. Remove the battery cover from the back of the remote control.
2. Refer to the diagram inside the remote control, and install the batteries in the
orientation shown.
3. Reinstall the battery cover on the remote control.
Connecting Power
The V500 system has an external power supply.
Do not use a power supply other than the one supplied with your V500 system. Using the
wrong power supply will void the warranty and may damage your system.
To connect power and power on the system:
1. Connect the power supply to the power connector on the back of the system.
2. Connect the power cord to the power supply.
Do not connect the V500 system power cord to a wall outlet until you have connected all
equipment to the system.
3. Press the power switch located at the back of the system.
DC IN 12V
BRI
LAN
Power switchPower connector
© Polycom, Inc. 2 - 5
Page 20

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
2 - 6 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 21

3
Configuring Network Use
The V500 system is factory configured to enable you to easily and quickly make
video calls in most network situations. In many cases, you simply need to
physically connect the system as described in Chapter 2, power it on, and follow
the setup wizard.
However, because networks vary from business to business and home to home,
you may need to change some of the default settings or perform other network
configuration. For example, if you’re using a router, you need to configure that
router to allow video calls.
This chapter begins by helping you determine which type of network
configuration you have. It then provides you with the steps you need to take to
prepare your particular network for video calling. It also describes the various IP
and ISDN settings, and which of these you may need to change for your network
environment. For example, if you have a gatekeeper and gateway, this chapter
describes how to configure those.
Once you have done this, you can set your call preferences and, if you choose, set
up your system to use the global directory. Then you’re ready to place your first
test call. This chapter describes how to perform all of these tasks, so that you can
successfully enjoy video calling with your V500 system.
What’s in this Chapter? Page
Using the Setup Wizard 3-2
Configuring Your IP Connection 3-3
Configuring Your ISDN Connection 3-18
Configuring Call Preferences 3-20
Configuring the Global Directory 3-22
Placing a Test Call 3-23
Checking System Status 3-24
Keeping your Software Current 3-25
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 1
Page 22

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Using the Setup Wizard
When you power on the system for the first time, a setup wizard begins to run. The
setup wizard automatically detects your system’s IP and ISDN connections, and it
leads you through the minimum steps you need to take to place a video call.
As you go through the setup wizard, you may need additional information or you
may want to change a default setting. If this is your situation, refer to the rest of
this chapter. You will find information there about how to configure your IP and
ISDN connections for your particular network environment.
Establishing an Administrator Password
The setup wizard enables you to set an administrator password, which allows you
to limit access to the Admin Settings. The administrator password may contain
letters and numbers, but no other characters. The default administrator password
is the system’s serial number.
If you change the password, make sure y ou remember it. If you forget the passw ord, you will
have to reset the system, delete the system files, and run the setup wizard again in order to
access the Admin Settings and reset the password. You cannot set the administrator
password from a remote location.
Note that if you establish an administrator’s password during the setup wizard,
you will need to enter it each time you wish to change advanced settings.
Running the Setup Wizard
You can run the setup wizard in either of these two ways.
❑ Directly on the system — Use the remote control to navigate the screens and
enter information. You can use the number pad on the remote control to enter
text just like you can with a cell phone.
❑ From a remote location — Use a web browser to access the V500 web interface.
To do this, your network must be set up and you need to know the IP address
of the system; therefore, this may not be an option if you are installing your
system for the first time in a new location. For more information about remote
management, refer to Managing the System Remotely on page 5-1.
3 - 2 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 23

Configuring Your IP Connection
To configure your IP network connection, you need to:
❑ Configure LAN properties
❑ Set up your IP network connection
❑ Configure IP network support
Configuring LAN Properties
The first step in setting up your IP connection is to configure the LAN properties.
If you are connecting your V500 system directly to a cable or DSL modem, before
you begin you need to know the public IP address assigned to your system by your
Internet Service Provider (ISP). Your ISP will provide you with one of these IP
addresses:
❑ Static IP address – This address is reserved for your system and will not
change. When you configure the LAN properties of the system, choose the
Enter IP Address Manually option.
Your ISP should also provide you with the DNS server address, default
gateway address, subnet mask, and WINS server IP address.
Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
❑ Dynamic IP address – This address is obtained from your ISP’s DHCP server,
and therefore may change. When you configure the LAN properties of the
system, choose the Obtain IP Address Automatically option.
When you choose this option, the DNS server address, default gateway
address, and other settings should fill in automatically.
To configure LAN properties:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > LAN Properties.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 3
Page 24
Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
2. Configure these settings:
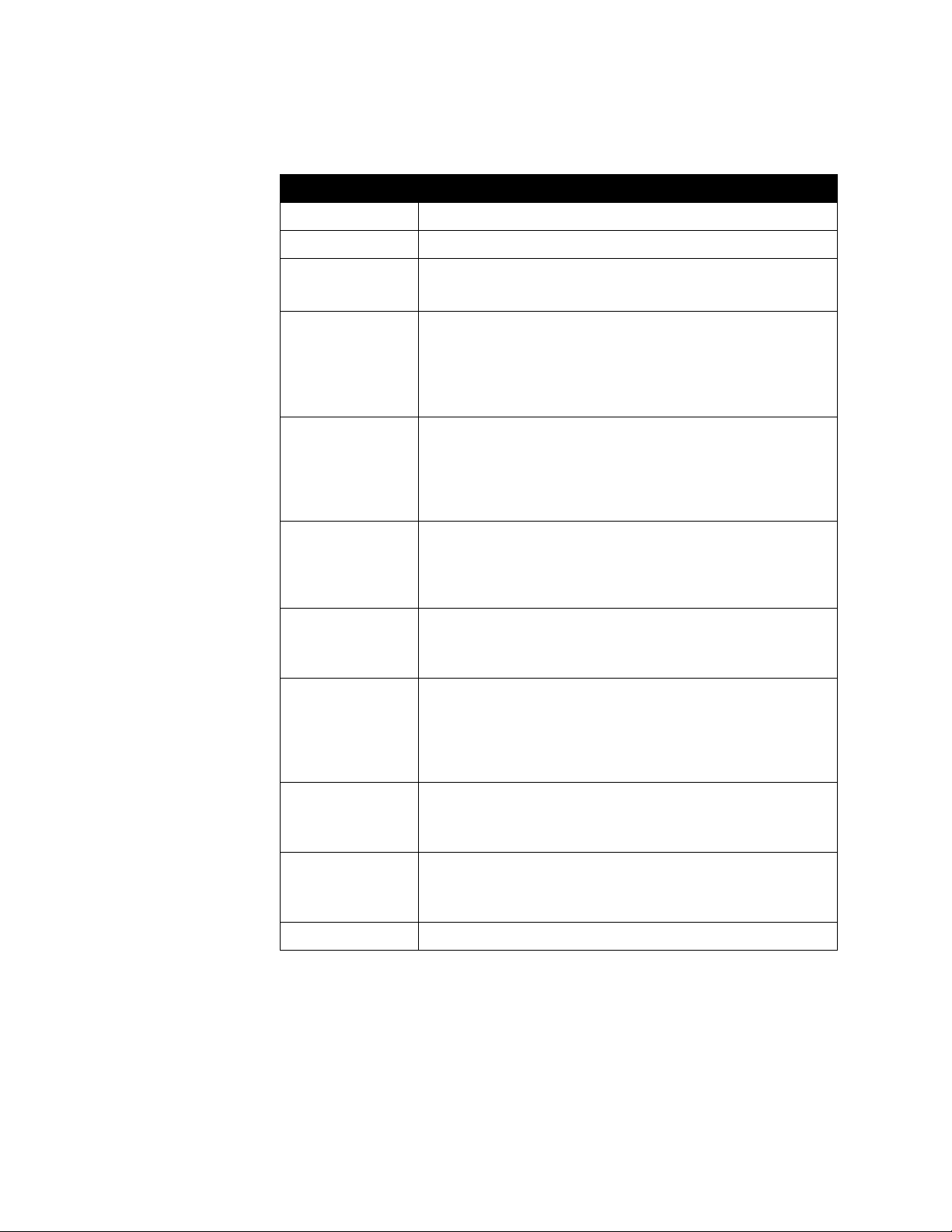
Setting Description
Connect to my LAN Check this to specify whether the system is part of the LAN.
Allow IP Calls Check this to enable the system to make and receive IP calls.
Host Name Indicates the system’s DNS name.
IP Address Specify how the system obtains an IP address:
If you change the Host Name, the system restarts.
• Obtain IP Address Automatically — Select this if the system
gets an IP address from the DHCP server on the LAN.
• Enter IP Address Manually — Select this if the IP address will
not be assigned automatically.
Your IP Address is
or
Use the Following
IP Address
If the system obtains its IP address automatically, this field
automatically displays the IP address currently assigned to the
system.
If you selected Enter IP Address Manually, enter the IP address
here.
Domain Name Displays the domain name currently assigned to the system if the
system is a member of a corporate domain.
If the system does not automatically obtain a domain name, enter
one here if needed for your corporate network.
DNS Servers Displays the DNS servers currently assigned to the system.
If the system does not automatically obtain a DNS server address,
enter up to four DNS servers here.
Default Gateway Displays the gatewa y currently assigned to the system. (If you are
using a router for Internet access, the Default Gateway will be the
router’s internal address.)
If the system does not automatically obtain a gateway IP address,
enter one here.
Subnet Mask Displays the subnet mask currently assigned to the system.
If the system does not automatically obtain a subnet mask, enter
one here.
WINS Server Displays the WINS server currently assigned to the system.
If the system does not automatically obtain a WINS server IP
address, enter one here.
WINS Resolution Sends a request to the WINS server for WINS name resolution.
3 - 4 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 25
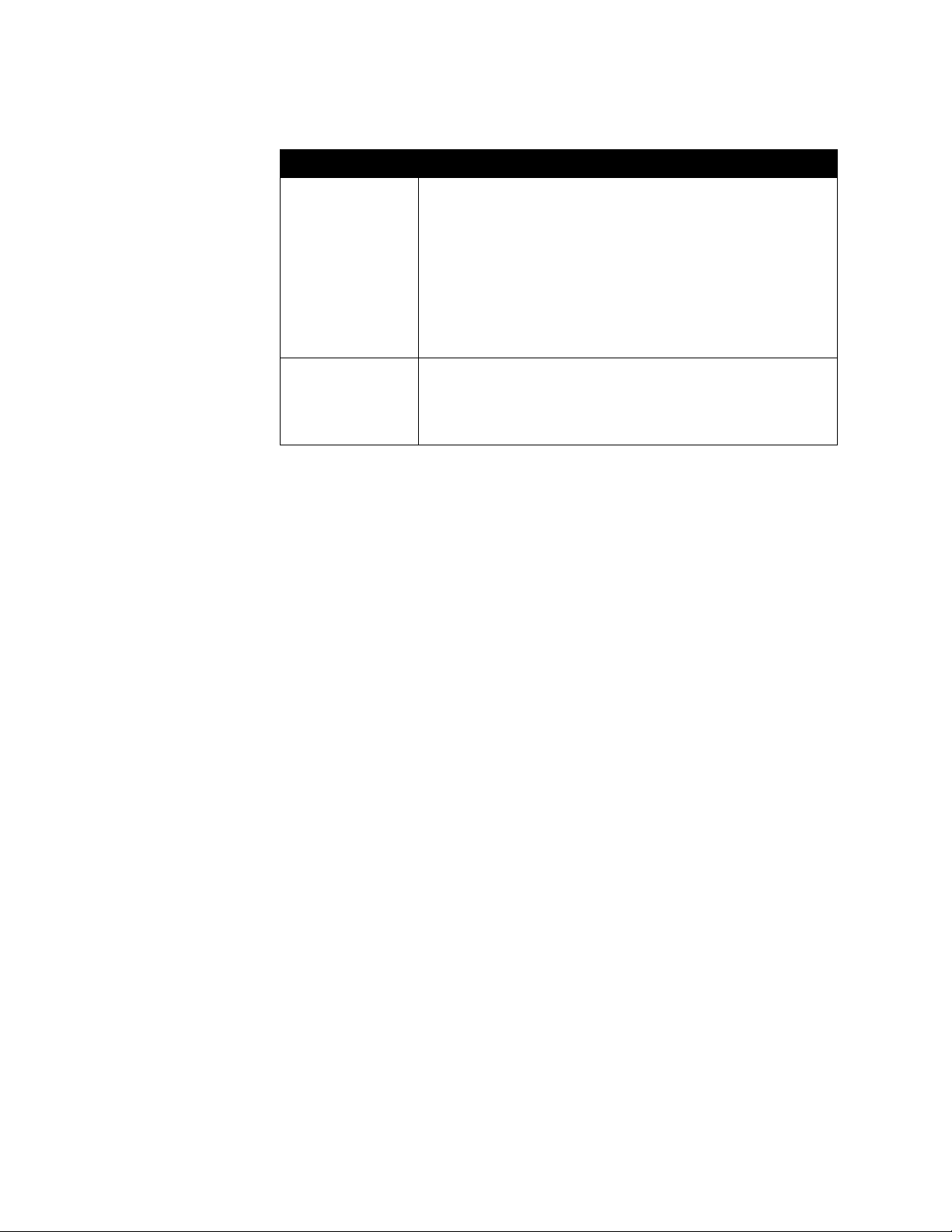
Setting Description
LAN Speed Specify the LAN speed to use. Note that the speed you choose
must be supported by the switch.
Choose Auto to have the switch negotiate the speed
automatically. If you choose 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps, you must also
select a duplex mode.
Note: The LAN speed setting for the V500 and the switch must
match. Polycom strongly recommends that you do not select Auto
for either only the V500 or only the router; the settings for both
must be the same. Typically, selecting Auto for both is sufficient.
Duplex Mode Specify the Duplex mode to use. Note that the Duplex mode you
choose must be supported by the switch.
Choose Auto to have the network switch negotiate the Duplex
mode automatically.
Setting Up Your IP Network Connection
The following is a list of the common ways you can connect your V500 to an IP
network so that you can make video calls. Pick out the IP network connection type
that most closely resembles how you plan to make your calls, then read the section
that corresponds to that connection type. If you need help determining how your
V500 connects to the network, contact your network administrator, network
service provider, or Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
❑ If you’re limiting your calls to other systems within your company’s intranet,
refer to Calling Within an Intranet on page 3-5.
❑ If your V500 system plugs directly into a cable or DSL modem, without a
router in between, refer to Calling Through a Cable or DSL Modem on
page 3-6.
❑ If your V500 system connects to the network through a router, with or without
a firewall or Network Address Translator (NAT), refer to Calling Through a
Network Router on page 3-6.
❑ If your V500 system is set up in a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), refer to Calling
Through a Router, Using a DMZ on page 3-12.
Calling Within an Intranet
An intranet is a private network within a company or organization. Calls within
an intranet don’t access the Internet, so security isn’t an issue. Even if your
company has a firewall, intranet calls remain within the firewall, so you can easily
communicate with anyone within your office network.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 5
Page 26

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
If, therefore, you’re limiting your calls to other systems within your intranet, you
don’t need to perform any additional network configuration to use your V500.
Simply go on to the next section, Configuring IP Network Support on page 3-13.
Calling Through a Cable or DSL Modem
You can access the network and make video calls by directly connecting your V500
to a cable modem or Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) modem, without using a
network router.
If you have a DSL connection and you are in a home environment or your DSL
modem does not maintain a connection state automatically, Polycom recommends
that you use a network router.
Directly connecting your V500 to the network with a cable or DSL modem does not
provide you with a security barrier between your home or business network and
the Internet; however, it is an easy way to set up your V500 network connection.
Systems set up outside a firewall are potentially vulnerable to unauthorized access. Visit the
Polycom Security Center at www.polycom.com for timely security information. You can also
register to receive periodic email updates and advisories.
If your V500 system is directly connected to a cable or DSL modem, you don’t need
to perform any additional network configuration to use your V500. Simply go on
to the next section, Configuring IP Network Support on page 3-13.
Calling Through a Network Router
Network routers let you connect more than one computer, video conferencing
system, or other device to your cable or DSL modem so that they all can share the
same high-speed network connection. This is accomplished by using Network
Address Translation (NAT) services. Routers also often offer firewall protection.
❑ In a typical IP network, all the devices within the network have their own
unique IP address, which is available for everyone in or outside the network
to access. With a NAT, each device within the network retains its own IP
address, but the NAT presents a single IP address to the outside world. This
provides an extra level of security because devices inside the network are
masked behind that single, external IP address.
3 - 6 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 27

Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
❑ A firewall acts as a security barrier between one network and another. Often
that barrier is between a smaller network, like you might have at your home
or business, and an exterior network, such as the Internet. The firewall
prevents unsolicited external network traffic from accessing your internal
network.
Because NATs and firewalls provide security for your network, they limit outside
access to your internal network. Some access, however, is necessary for video
communications. To enable your V500 to freely place and receive calls with the
outside world, while still maintaining protection for your network, you must open
ports in the firewall. This process is known as port forwarding or pinholing.
The following sections describe the steps you need to take to place video calls
through a network router, including:
❑ Configuring router port forwarding
❑ Configuring firewall and NAT properties on the V500
Configuring Router Port Forwarding
To make video calls with your V500 system when you have a router, you must
open and assign ports in the firewall. This section describes how to do that with
the most common routers from NetGear®, Linksys®, and D-Link®. Most other
routers require similar procedures.
Before you can change your router configuration, you must know:
❑ The IP address of your router, which you can find in your router’s
documentation. (Note that many routers use the default address 192.168.1.1.)
❑ Your router’s administrator name and password, which you can find in your
router’s documentation. (Note that many routers use the default user name
admin and the password blank or password.)
❑ The IP address that has been assigned to your system if you’re using DHCP,
which you can find on the LAN Properties screen. (See Configuring LAN
Properties on page 3-3 for more information.)
With any router brand or model, you must open the ports listed here:
Port Function TCP or UDP
1720 H.323 call setup TCP
3230-3235 Signaling and control for audio, call,
video, and data/FECC
3230-3253 Audio and video R T P media streams UDP
1503 (optional) T.120 data collaboration TCP
TCP
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 7
Page 28

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Refer to the Port Usage section in Appendix if you want advanced port
configuration information.
NetGear Routers
The following procedure applies to NetGear MR814v2 and RP614v2 routers. If you
have a different NetGear model, the settings may vary slightly. This procedure
assumes that your router is correctly configured and connected to the Internet and
that your network is operational.
To configure a NetGear router:
1. In a browser such as Internet Explorer, type the IP address of your router,
which you can find in your router’s documentation.
2. Log in to your router setup using the user name and password, which you can
find in your router’s documentation.
3. From the Advanced menu on the left of the page, select Port Forwarding.
4. On the Port Forwarding page, select Add Custom Service.
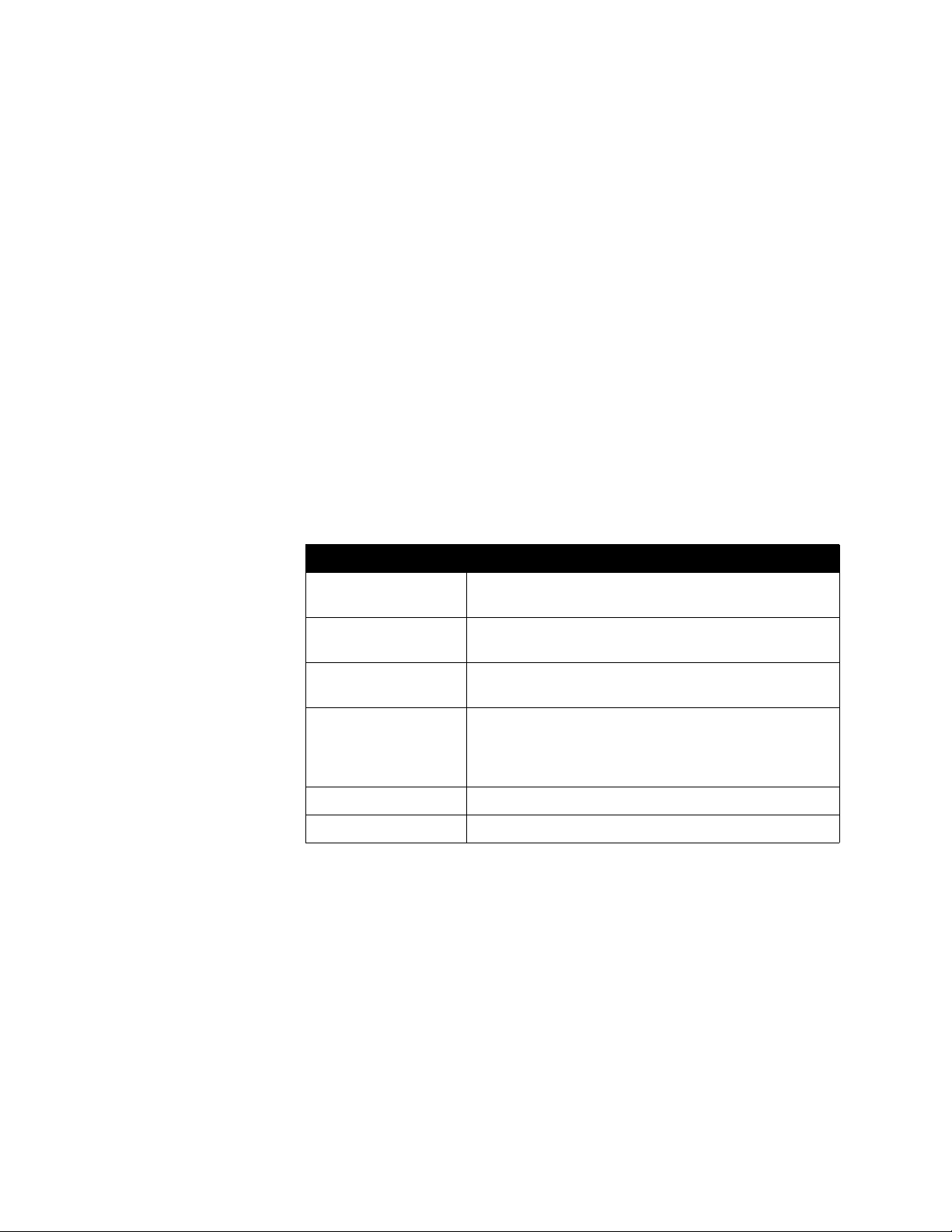
5. On the Ports-Custom Services page, enter this information for the first port
you need to open (such as port 1720):
Setting Description
Service Name Any unique identifier (for example, you can use the text
from the Function column in the table on page 3-7).
Start Port The specific port or the starting value of the range of ports
(see the table on page 3-7 for the list of ports).
End Port The specific port or the ending value of the range of ports
(see the table on page 3-7 for the list of ports).
Server IP Address The IP address that the NA T has assigned to your system.
NetGear routers automatically pass TCP and UDP traffic through the same port. Y ou do
not have to designate TCP or UDP when you open ports.
6. Click Apply.
7. Repeat Steps 4 through 6 of this procedure for the remaining ports that you
need to open. (For the list of ports that you need to open, refer to the table on
page 3-7.)
8. When you have opened and assigned all of the ports listed in the table on page
3-7, review the Port Forwarding page. Check that all the ports are correct,
enabled, and assigned to the correct Server IP (internal) Address.
3 - 8 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 29
Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
Linksys Routers
The following procedure applies to the Linksys BEFSX41 router. If you have a
different Linksys model, the settings may vary slightly. This procedure assumes
that your router is correctly configured and connected to the Internet and that your
network is operational.
To configure a Linksys router:
1. In a browser such as Internet Explorer, type the IP address of your router,
which you can find in your router’s documentation.
2. Log in to your router setup using the user name and password, which you can
find in your router’s documentation.
3. Locate the Port Range Forwarding page.
Depending on your router model, the Port Range Forwarding page may be
listed in the Advanced menu or the Applications and Gaming menu.
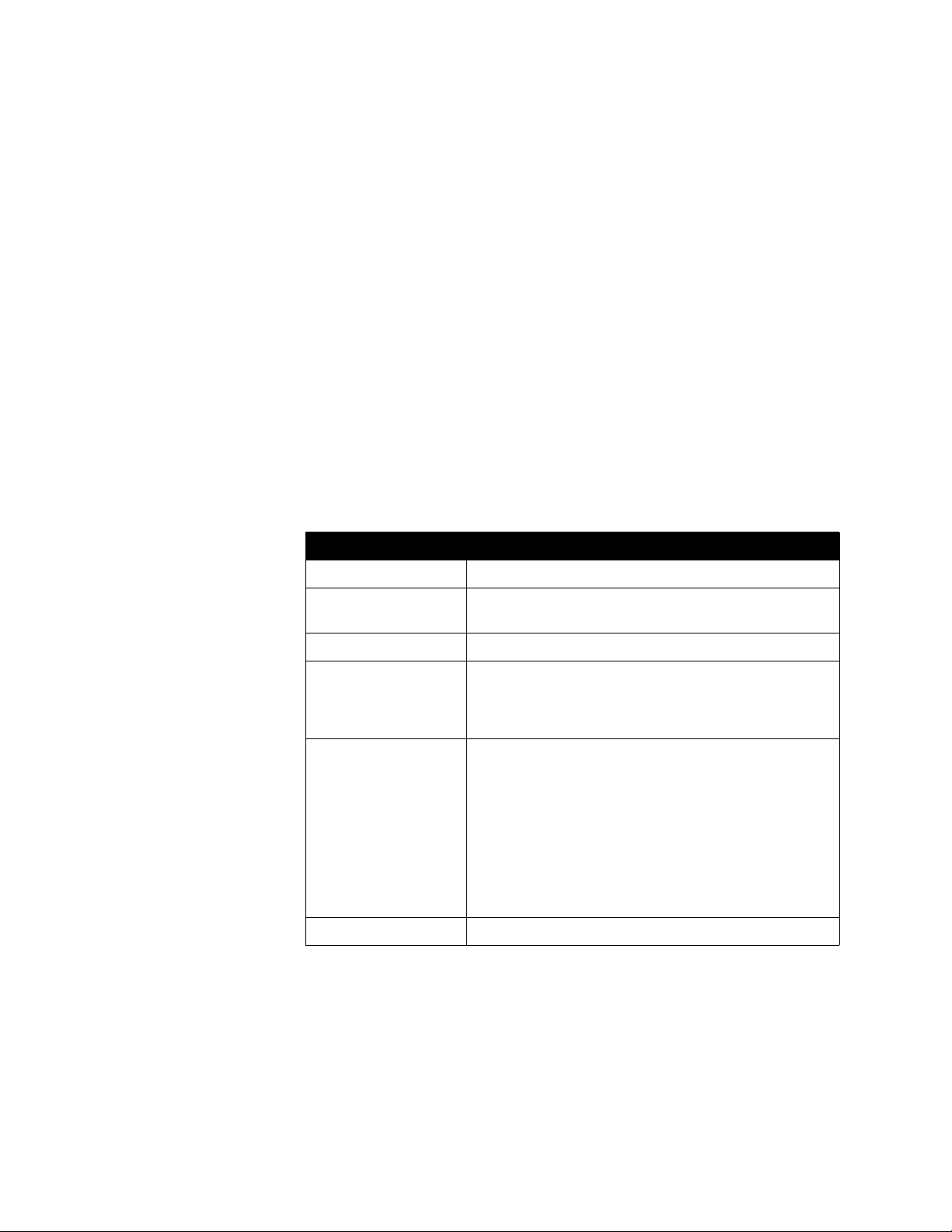
4. On the Port Range Forwarding page, enter this information for the first port
you need to open (such as port 1720):
Setting Description
Application Any unique identifier (for example, you can use the text
from the Function column in the table on page 3-7).
Start The specific port or the starting value of the range of ports
(see the table on page 3-7 for the list of ports).
End The specific port or the ending value of the range of ports
(see the table on page 3-7 for the list of ports).
TCP/UDP Either TCP or UDP, whichever is listed in the tab le on page
3-7 for that particular port or range of ports. If the table lists
both TCP and UDP, enter the Appl ication twice: once as
TCP and once as UDP.
IP Address The IP address that the NA T has assigned to your system.
Enabled Check this box.
5. Repeat Step 4 of this procedure for the remaining ports that you need to open.
(For the list of ports that you need to open, refer to the table on page 3-7.)
6. When you have opened and assigned all of the ports listed in the table on page
3-7, review the Port Range Forwarding list. Check that all the ports are correct,
enabled, and assigned to the correct IP (internal) Address.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 9
Page 30
Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
D-Link Routers
The following procedure applies to the D-Link DI-604 router. If you have a
different D-Link model, the settings may vary slightly. This procedure assumes
that your router is correctly configured and connected to the Internet and that your
network is operational.
To configure a D-Link router:
1. In a browser such as Internet Explorer, type the IP address of your router,
which you can find in your router’s documentation.
2. Log in to your router setup using the user name and password, which you can
find in your router’s documentation.
3. Select the Advanced tab.
4. Click the Firewall button.
5. On the Firewall page, enter this information for the first port you need to open
(such as port 1720):
Setting Description
Enabled Click this radio button.
Name Any unique identifier (for example, you can use the text
from the Function column in the table on page 3-7).
Action Click Allow.
Source Interface: WAN
IP Range Start: *
IP Range End: (blank)
Destination Interface: LAN
IP Range Start: The IP address (internal) that the NA T has
assigned to your system.
IP Range End: (blank)
Protocol: TCP, UDP, or * for both
Port Range: The specific port or the starting and ending
value of the range of ports (see the table on page 3-7 for
the list of ports).
Schedule Always (or select a time for the port to be open).
6. When you have opened and assigned all of the ports listed in the table on page
3-7, review the Firewall Rules list. Check that all the ports are correct, enabled,
and assigned to the correct IP (internal) Address.
3 - 10 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 31

Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
Configuring Firewall and NAT Properties
Once you’ve set up your router, you must configure the V500 system so that it
works with the firewall and NAT.
Before making changes on the Firewall screen, you should know whether or not
your firewall device is H.323 compatible. Firewall devices that are H.323
compatible have been programmed with logic that can detect H.323 video
conferencing traffic as it passes between the LAN and WAN. Because of this, they
are able to open the necessary ports dynamically as needed, on a call-by-call basis.
Some firewall devices can even insert the NAT Public WAN Address automatically
during the H.323 call. For these devices, it is not necessary to configure the
V500 system with fixed ports or even, in some cases, with NAT. Check with the
manufacturer of your device to see if it supports H.323 compatibility.
To set up the V500 system to work with a firewall and NAT:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Network > IP > Firewall.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Fixed Ports Specify whether to define the TCP and UDP ports.
If you select Fixed Ports, the V500 system will restrict its port
usage to the range of TCP and UDP port s you specify. (The
system defaults to a range beginning with port 3230 for both
TCP and UDP.) If you do not select Fixed Ports, the system
will dynamically allocate ports on a call-by-call basis.
• If the firewall is not H.323 compatible, enable this option.
• If the firewall is H.323 compatible or if the system is not
behind a firewall, you may not need to enable this option.
TCP Ports
UDP Ports
Specify the range of TCP and UDP ports used by the system.
Note: The TCP and UDP port ranges you open here must
match those that you opened for your router (including TCP
port 1720, which allows H.323 traffic). Refer to the previous
section, Configuring Router Port Forwarding on page 3-7, for
information about opening ports for your router .
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 11
Page 32

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Setting Description
NAT Configuration Specify whether the system should attempt to determine the
NAT Public WAN Address automatically.
• If the system is behind a NA T that allows HTTP traffic, select
Auto. The system will attempt to automatically discover the
NAT Public WAN Address.
• If the system is behind a NAT that does not allow HTTP
traffic or if Auto fails to discover the NAT Public WAN
address, select Manual.
• If the system is not behind a NAT, select Off.
• If the system is behind a firewalled NAT router that is
UPnP™ (Universal Plug and Play) certified, select UPnP.
Many routers used in homes and small businesses support
UPnP NAT traversal. If this is your situation, try selecting
UPnP first. If this selection does not work for your router,
select Auto or Manual.
NAT Public (WAN)
Address
NAT is H.323
Compatible
Address Displayed in
Global Directory
Displays the address that callers from outside the LAN use to
call your system.
If you chose to configure the NAT manually, enter the NAT
Public WAN Address here. You can obtain this address by
looking at your router configuration or by asking your network
service provider.
Specify whether the system is behind a NAT that is capable of
translating H.323 traffic.
Specify whether to display this system’s public or private
address in the Global Directory.
Calling Through a Router, Using a DMZ
A Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) is a way to configure a network so that the device
that is in the DMZ (such as the V500) is served by the router, but is outside the
firewall. Depending on your router, configuring the V500 system to be in the DMZ
may affect its ability to communicate locally with other devices on the internal
LAN.
With a DMZ, no unauthorized external connections are allowed with the devices
inside the firewall, but the V500 is allowed free access to the Internet. Therefore,
this configuration leaves the V500 without protection from external sources.
Systems deployed outside a firewall are potentially vulnerable to unauthorized access. Visit
the Polycom Security Center at www.polycom.com for timely security information. You can
also register to receive periodic email updates and advisories.
3 - 12 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 33

Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
There are two types of DMZs:
❑ Virtual DMZ — With a virtual DMZ, all ports through the router are opened
for the device in the DMZ (in this case, the V500). This has the affect of placing
the V500 on the outside of the router’s firewall. Keep in mind, however, that
the V500 may still be protected by some global firewall securities, which may
adversely affect video conferencing.
❑ Physical DMZ — With a physical DMZ, there is an actual, physical port on
your router, usually labeled DMZ, into which you plug your V500 LAN cable.
This port places the V500 physically outside of the firewall, which is usually
less restrictive, but is also less secure.
Typically, you should only use a DMZ when other configurations fail to allow
H.323 traffic to flow through unobstructed. If you do choose to place your V500 in
a DMZ, you must:
1. Make sure your router’s firewall software provides a DMZ.
2. Assign the internal IP address of the V500 to the DMZ.
For more information about how to perform these steps, refer to the
documentation that came with your router.
Configuring IP Network Support
After you have configured LAN properties and set up your IP network connection,
you may need to configure IP network support, depending on your network setup.
The only setting that you must set for making IP video calls is Enable IP H.323 on
the H.323 Settings screen. Settings for gateways, gatekeepers, SIP, and QOS are
optional depending on your network infrastructure. For example, if your network
does not have a gatekeeper or if you are not using SIP, you do not need to change
either of these settings.
Configuring H.323 Settings
H.323 settings enable you to allow IP dialing, as well as set up gatekeepers and
gateways:
❑ A gatekeeper supervises network traffic and manages functions such as
bandwidth control and admission control. The gatekeeper also handles
address translation, which allows you to make calls using static aliases instead
of IP addresses that can change each day.
❑ A gateway performs code and protocol conversion between IP networks and
ISDN, so that users on different networks can call one another. If the system is
configured to use a gateway, you must also configure it to use a gatekeeper.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 13
Page 34

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
To configure H.323 settings:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Network > IP > H.323 Settings.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Enable IP H.323 Check this to allow IP dialing.
Display H.323
Extension
H.323 Name This is the name that gatekeepers and gateways can use to
H.323 Extension
(E.164)
Check this if you want to place gatewa y calls by entering the H.323
extension separately from the gateway ID.
If you do not check this box, you can make gateway calls by
entering the call information in this format:
gateway ID + TCS4 delimiter + extension
To determine your TCS4 delimiter, ask with your network provider.
identify this system. Y ou can mak e point-to-point calls using H.323
names if both systems are registered to a gatekeeper.
The H.323 Name is the same as the System Name, unless you
change it. Your dial plan may define the names you can use.
You can place point-to-point calls using the extension if both
systems are registered with a gatekeeper.
The default H.323 Extension is based on the system serial
number, but you can change it. Your dial plan may define the
extensions you can use.
3. If you have a gatekeeper, select and configure these settings:
Setting Description
Use Gatekeeper Select one of the following, but keep in mind that gateways and
gatekeepers are required for calls between ISDN and IP networks:
• Off — Calls do not use a gatekeeper.
•Auto — System automatically finds an available gatekeeper.
• Specify — Calls use the specified gatekeeper. Enter the
gatekeeper’s IP address or name (for example,
gatekeeper.companyname.usa.com or 255.255.255.255).
H.323 Name This is the name that gatekeepers and gateways use to identify
this system. You can make point-to-point calls using H.323 names
if both systems are registered to a gatekeeper.
The H.323 Name is the same as the System Name, unless you
change it. Your dial plan may define the names you can use.
H.323 Extension
(E.164)
3 - 14 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
You can place point-to-point calls using the extension if both
systems are registered with a gatekeeper.
The default H.323 Extension is based on the system serial
number, but you can change it. Your dial plan may define the
extensions you can use.
Page 35

Setting Description
Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
Outbound Call
Route
Gatekeeper IP
Address
Alternate
Gatekeeper
If your system uses a gatekeeper, you can specify whether
outbound ISDN calls are routed through an IP-to-ISDN gateway or
through an ISDN line directly connected to the V500 system.
If you chose to use an automati cally selected gatekeeper , this fiel d
automatically displays the gatekeeper’s IP address.
If you chose to specify a gatekeeper, enter the IP address of the
gatekeeper here.
If your H.323 network infrastructure has been configured to use an
alternate gatekeeper when the primary ga tekeeper is not
available, the alternate gatekeeper is displayed in this field.
Alternate gatekeeper support is configured on the primary
gatekeeper, and the V500 is notified of this configuration when it
registers to the gatekeeper on startup.
4. If you have a gateway, select and configure these settings:
Setting Description
Country Code Enter the country code for the system’s location.
Area Code Enter the area or city code for the system’s location.
Number Enter the gateway’s number.
H.323 Extension
(E.164)
You can place point-to-point calls using the extension if both
systems are registered with a gatekeeper.
The default H.323 Extension is based on the system serial
number, but you can change it. Your dial plan may define the
extensions you can use.
Gateway Number
Type
Number of Digits in
DID Number
Number of Digits in
Extension
Select the number type users must enter to call this system:
• Direct Inward Dial (DID) — Users enter an internal extensi on
to call this system directly.
Note: If you choose this option, you must also register the
number with the gatekeeper as an E.164 alias.
• Number + Extension — Users enter the gateway number and
the system’s extension to call this system.
Enter the number of digits in the DID number.
The national or regional dialing plan for your location determines
the standard number of digits. For instance, the US standard is 7
digits.
If you selected Number + Extension , you m ust enter the number
of digits in the extension.
Your organization’s dial plan determines this number.
5. Select and enter a prefix or suffix for each bandwidth you want to allow
for gateway calls.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 15
Page 36

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Be sure to configure the gateway to use the same prefixes and suffixes you define for
the system.
Configuring SIP Settings
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol for Internet
conferencing.
If you are unfamiliar with SIP, Polycom recommends that you do not change the
default settings.
To configure the SIP settings if your network supports SIP:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Network > IP > SIP Settings.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Enable SIP Check this to allow the system to make calls using SIP.
Transport Protocol Select the protocol the system uses for SIP signalling.
The SIP network infrastructure in which your V500 system is
operating determines which protocol you should choose. For
example, if your V500system is operating in a Microsoft Live
Communication Server (LCS) SIP network, choose TCP. If your
V500 system is operating in a Nortel Multimedia Communication
Server (MCS) SIP network, choose UDP.
Password Enter the password that authenticates the system to the Registr ar
Server.
User Name Enter the system’s SIP name or leave this field blank if you want
to use the system’s IP address as the SIP user name.
Proxy Server Enter the DNS name or IP address of the SIP Proxy Server, or
leave this field blank if no proxy server is used.
By default, the SIP signalling is sent to port 5060 on the proxy
server. To specify a different port, add it to the address as shown
here:
255.255.255.255:5070
Registrar Server Enter the name or IP address of the SIP Registrar Server.
By default, the SIP signalling is sent to port 5060 on the registrar
server. To specify a different port, add it to the address as shown
here:
255.255.255.255:5070
3 - 16 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 37

Configuring Quality of Service (QOS)
If your network is configured to recognize and prioritize network traffic using
QOS, you can configure the V500 system to mark IP packets with the values
recognized by your network. Keep in mind that enabling QOS on the V500 is not
enough; all devices in the network path must also be configured for QOS.
If you are unfamiliar with QOS, Polycom recommends that you do not change the
default settings.
To configure the Quality of Service (QOS) options:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Network > IP > Quality of Service.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Type of Service Select your service type:
• IP Precedence — Lets you specify the priority of IP packets
sent to the system. The value, which you enter in the Type of
Service Value field, can be between 0 and 5.
• DiffServ —Lets you specify a priority level between 0 and 63.
Enter the value in the Type of Service Value field.
Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
Type of Service
Value
Enable PVEC Check this if you want the system to use PVEC (Polycom Video
Dynamic
Bandwidth
Maximum Transmit
Bandwidth
Maximum Receive
Bandwidth
Specify the IP Precedence or Diffserv value for Video, A udio, and
Far-Site Camera Control.
Error Concealment) if packet loss occurs.
Check this if you want the V500 system to dynamically scale the
bandwidth to best suit the network conditions.
Specify the maximum transmit line speed between 48 Kbps and
512 Kbps.
Since DSL and cable modems typically allow for faster download
(receive) speeds compared to upload (transmit) speeds, this
setting enables you to regulate differences.
Specify the maximum receive line speed between 48 Kbps and
512 Kbps.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 17
Page 38

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Configuring Your ISDN Connection
If you have the ISDN option, you can connect your V500 through ISDN as well as
through one of the IP network connections described earlier in this chapter.
Preparing Your ISDN Network
Before you set up your connection using ISDN:
1. Refer to the Preparing Your Network for Collaboration document, available at
www.polycom.com/videodocumentation.
This document contains information you need to get your network ready, such
as worksheets that will help you order ISDN. Note that this document may not
pertain to all countries.
2. Obtain this information from your ISDN service provider:
• ISDN address
• SPIDs (in North America only)
• ISDN switch protocols
Configuring the ISDN Network Interface
To configure the ISDN network interface settings:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Network > ISDN.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Enable ISDN H.320 Check this to allow your system to make H.320 (ISDN) calls.
Outside Line
Dialing Prefix
ISDN Switch
Protocols
Enter the ISDN dialing prefix used to call outside the network.
Enter the protocol used by your network’s switch.
3 - 18 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 39

Setting Description
Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
ISDN Voice
Algorithm
Auto BRI
Configuration
Enter which voice algorithm (Alaw or uLaw) you want to use for
ISDN voice calls.
Do not change this setting unless you experience audio issues in
all ISDN voice calls.
Check this to allow the NI-1 switch to automatically configure the
directory numbers and SPIDs.
This setting is only available if you have selected the NI-1 switch
protocol.
3. Select and configure these settings:
Setting Description
Area Code Enter the area code for this system’s location.
Directory Numbers Enter the numbers assigned to the B1 and B2 channels for the
BRI line.
The two numbers for a line may be the same or different,
depending on the switch protocol in use.
Enable Check this to enable the ISDN line.
If you selected the Standard ETSI Euro ISDN protocol, you must
enable the BRI line.
The ISDN BRI Numbers screen also displays the country selected as the
system’s location and the Country Code used for international calls to the
system. To specify the system’s location, go to System > Admin Settings >
General Settings > Location. The system automatically supplies the country
code when you specify the country.
4. If you have configured
the ISDN switch protocol to be AT&T 5ESS Multipoint,
NI-1, or Nortel DMS-100, select and enter the ISDN BRI SPIDs provided
by your service provider.
After you enter the SPIDs, the system verifies them. If the system is unable to
verify the SPIDs, make sure the system is connected and that the ISDN
numbers you entered are correct.
If you do not have the SPIDs from your service provider, you can click Start to
Auto-Detect SPIDs.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 19
Page 40

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Configuring Call Preferences
Call preferences help you manage the network bandwidth used for calls. For
example, you can specify the default and optional call settings for outgoing calls,
and limit the call speeds for incoming calls.
If you have just set up your network, use the screens described in this section to
specify your call settings. If your network has been set up for some time, but you
notice that your call quality is not optimal, you may want to change some of these
call preference settings to increase the quality of your calls.
To configure your call preferences:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Network > Call Preference.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Enable H.329 Check this to specify standards-based People+Content data
collaboration.
Note: Not all H.323 devices recognize this new standard. You can
try disabling this option if you suspect a compatibility issue.
Enable IP H.323 Check this to allow the system to make IP calls.
Enable SIP Check this to allow the system to use SIP when connecting IP
calls.
Enable ISDN H.320 If you have the ISDN option, check this to allow the system to
make ISDN calls.
Enable Voice Over
ISDN
If you have the ISDN option, check this to allow the system to
make voice-only calls to phones connected to an ISDN network,
such as an organization’s PBX.
3. If you have the ISDN option, select to go to the Network Dialing screen
and specify the dialing order preference between IP and ISDN.
3 - 20 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 41

Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
4. Select to go to the Preferred Speeds screens and configure these settings:
Setting Description
Preferred Speed for
Placing Calls
Maximum Speed
for Receiving Calls
Enter the speed that will be used for calls placed from this system
in either of these cases:
• When Call Quality is set to Auto on the home screen and
Directory screen
• When the Call Quality option is not available for users
If the far-site system does not support the speed you select, the
system automatically negotiates a lower speed.
Note: Cable and DSL modems typically have bandwidth
restrictions for upload (transmit) and download (receive).
Therefore, if you’re making calls through a cable or DSL modem,
you need to find out what your upload and download capabilities
are in order to select the correct speed for your system. If you
don’t know, ask your ISP.
If you want to restrict the bandwidth used when receiving calls,
enter the speed here. For example, if y ou hav e a DSL connection
that it is limited to 384 Kbps upload and 1.5 MB download, you
should restrict your calls to 384 Kbps or less for better call results.
If the far site attempts to call the system at a higher speed than
selected here, the call is re-negotiated at the speed specified in
this field.
One way to determine what your optimal call speeds should be is to select the lowest call
speed for each direction: upload and download. Try the call at that speed and see how it
looks. You can then keep increasing the call speeds and checking the results until you find
your optimal call speed for each direction.
Keep in mind, howev er, that optimal call speeds may vary at different times of day depending
on the traffic on the network. Also, if another system in the video call cannot upload at the
speed you specified, the call may suffer from poor video quality or you may not be able to
view video at all (black screen). Call speeds also do not reflect additional IP overhead (such
as timestamps) of approximately 20%.
5. Select to go to the Call Speeds screen and specify the call speeds to make
available to users, if you are allowing them to choose speeds on a call-by-call
basis.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 21
Page 42

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Configuring the Global Directory
If you use the Polycom Global Management System, you can configure your
system to use the Global Directory. The Global Directory provides a list of other
systems that are registered with the Global Directory Server and are available for
calls. The other systems appear in the Directory, allowing you to place calls to other
users by selecting their names.
Configuring the Directory Server Settings
To configure the Directory Server settings:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Global Services > Directory Servers.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Global Directory
(GDS)
Register Registers this system with the Global Directory Server.
Password Lets you enter the Global Directory password, if there is one.
Display Global
Addresses
Display Name in
Global Directory
Save Global
Directory to System
Specifies the IP address or DNS address of the Global Directory
Server. You can enter up to five addresses.
Displays other registered systems in the Global Directory.
Specifies whether to display the system’s name in the Global
Directories of other registered systems.
Copies the Global Directory to this local system.
3 - 22 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 43

Setting the Dialing Rules
If your system is connected to a private network and also to a public network, you
may need to specify the codes and prefixes necessary for dialing other systems.
To set the dialing rules:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Global Services > Dialing Rules.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
Always Dial Area
Code
Dial 1+ for all USA
calls
Placing a Test Call
When you finish configuring the system, you can use one of the sample numbers
in the directory to test your setup.
To place a test call:
1. On the Place a Call screen, select Directory.
2. Select Category.
3. Select Sample Sites and highlight a location.
4. Press Call on the remote control.
Specifies that calls to sites in the same area code must include
the area code.
Specifies that calls to systems in the United States must include
a “1” before the area code.
You can also find a list of worldwide numbers that you can use to test your V500 system at
www.polycom.com/videotest.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 23
Page 44

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
If you have trouble making video calls:
❑ Make sure the number you dialed is correct, then try the call again. For
example, you may need to dial 9 for an outside line or include a long distance
access code or country code.
❑ To find out if the problem exists in your system, ask the person you were trying
to reach to call you instead.
❑ Find out if the system you are calling has its power turned on and is
functioning properly.
❑ If you can make calls but not receive them, make sure that your system is
configured with the correct number.
Checking System Status
The System Status screen provides detailed information about system settings, IP
and ISDN connections, time server connections, and other information that is
important to the functioning of the system. For an explanation of any of the status
items, select the item and press on the remote.
When there is a change in system status that is a potential problem, you see an alert
at the bottom of the Place a Call screen.
To view System Status information:
>> Go to System > Diagnostics > System Status.
To get information about a status message:
>> Select the status message and press or on the remote control.
3 - 24 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 45

Keeping your Software Current
If you have Internet access and a software key, you can use the web-based
Softupdate application to upgrade the V500 software. If you do not have Internet
access, your reseller can supply you with the V500 software update on CD-ROM.
To upgrade your software via the Internet:
1. Before you begin, read the Release Notes, available at the Polycom Resource
Center at www.polycom.com, for information about the latest software
version.
2. Find your product page at the Polycom Product Resource Center, and
download the V500 software update file in .zip format.
3. Double-click the software.zip file to extract the file.
4. Double-click Softupdate.exe to run the update program.
Chapter 3 - Configuring Network Use
Do not power off the system during the software update process. If the update is interrupted,
the system reverts to its original software version.
© Polycom, Inc. 3 - 25
Page 46

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
3 - 26 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 47

4
Designing the User Experience
Everybody who uses the Polycom V500 system has different needs. That’s why
your system has a customizable user interface. You can design the video
conferencing experience to meet your needs and the needs of any other users who
use the system.
You can customize the behavior of the system, and then build in various access
levels for the different users, depending on how much or how little you want them
to change system behaviors.
When you set up the system for the first time, the system is configured with the
most commonly used settings. If you need to change any of these initial settings,
you can adjust the screen settings as described in this chapter.
If you established an administrator’s password during the initial configuration,
you must enter it each time you change advanced settings.
What’s in this Chapter? Page
Managing User Access to Settings and Features 4-2
Designing Video Behaviors 4-5
Designing Audio Behaviors 4-11
Designing General System Behaviors 4-12
Customizing the Workspace Appearance 4-17
Configuring Closed Captioning 4-22
Getting Started with Calling 4-25
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 1
Page 48

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Managing User Access to Settings and Features
You can manage access to various settings and features by using passwords and by
configuring the system to show only those options you want other users to see.
To maintain this
security level: You can allow users to:
High
(Kiosk mode)
Medium Place calls using the restrictions you specify for length of call,
Low Configure user settings.
Very low Configure all system settings.
Setting the Admin Password
Set an administrator’s password to restrict who can:
❑ Make changes other than those in the User Settings screen
❑ Update the software
❑ Perform remote management using the V500 web interface
Call only the numbers you specify on the home screen.
See Using the System for Specialized Applications on
page 4-5 and Designing the Home Screen on page 4-18.
type of call, and use of the directory.
See Limiting What Users Can Do With the System on
page 4-5.
See Letting Users Customize the Workspace on page 4-4.
To set or change the Admin Password:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Security.
2. Enter or change the password.
4 - 2 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 49

Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
To reset a forgotten Admin Password:
1. Get the system’s serial number from the system or from the System
Information screen.
2. Go to System >Diagnostics > Reset System.
3. Enter the system’s serial number and select Delete System Settings.
4. Select Reset System.
When the system completes the reset, it leads you through the setup wizard. You
can enter a new Admin Password when you set up the system.
Screens that Require the Admin Password for Access
The following diagram shows top-level system screens. All screens within Admin
Settings require the administrator’s password.
Admin Settings Diagnostics
General Settings Network LAN PropertiesAudioCameraMonitor Global Services
System Settings
Home Screen Settings
Security
Location
IP
ISDN
Call Preference
Recent Calls
H.323 Settings
SIP Settings
Quality of Service
Firewall
System Information Utilities
User Settings
Directory Servers
Dialing Rules
SNMP
Management Servers
Account Validation
My Information
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 3
Page 50

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Letting Users Customize the Workspace
You can allow other users of the V500 system to change common user preferences
by providing access to the User Settings screen.
To allow users to customize the workspace:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Security.
2. Check the Allow Access to User Settings option to make the User Settings
button available to users on the System screen.
User Settings contains the following options:
❑ Backlight Compensation
❑ Camera Brightness
❑ Meeting Password
❑ Auto-Answer Point to Point
❑ Mute Auto-Answer Calls
❑ PIP
❑ Keypad Audio Confirmation
❑ Color Scheme
❑ Far Site Name Display Time
❑ Dual Monitor Emulation
❑ Allow Video Display on Web
These options are also available to the administrator on the Admin Settings screens.
4 - 4 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 51

Limiting What Users Can Do With the System
You can limit what you allow other users to do with the system by configuring the
following:
❑ Maximum Time in Call — If you want to specify the maximum time a call can
last, go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > System Settings >
Call Settings and enter the maximum call length allowed.
❑ Allow Directory Changes — If you do not want anyone to save changes to the
local directory of the system, go to System > Admin Settings > General
Settings > System Settings > Directory and clear this option.
Using the System for Specialized Applications
You can customize the system to show only a specific set of numbers to call. This
mode, also known as “kiosk mode,” can be used for specialized applications, such
as customer query stations or systems used for calling the same numbers on a
regular basis. Kiosk mode requires little or no training and instructions can be
incorporated into the screen design.
Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
See Designing the Home Screen on page 4-18 for more details about the kiosk
mode and its applications.
Designing Video Behaviors
You can configure the following video behaviors to accommodate your
environment:
❑ Camera Settings
❑ TV Monitor
❑ Dual Monitor Emulation
❑ Monitor’s Color Balance
❑ People+Content IP
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 5
Page 52

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Configuring Camera Settings
The Camera screen lets you specify camera settings.
To configure camera settings:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Camera.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Backlight
Compensation
Camera
Brightness
Power Frequency Synchronizes the screen display with the local electrical power
Specifies whether to have the camera automatically adjust for a
light background. Backlight compensation is best used in
situations where the subject appears darker than the background.
Specifies how much light is let into the camera’s iris. A low n umber
allows in less light; a high number allows in more light.
frequency in order to eliminate video flicker. Typically, the default
setting is correct for your system and location. However, if your
system experiences video flicker, you may want to change the
setting:
•60 Hz — Select this if the power frequency in your location is 60
Hz, but you have a PAL system.
•50 Hz — Select this if the power frequency in your location is 50
Hz, but you have an NTSC system.
4 - 6 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 53

Configuring the TV Monitor
The V500 system allows you to customize the display to suit your room and
equipment configuration.
To configure the TV monitor:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Monitor.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Monitor Spec if ie s th e mo ni to r’s aspect ratio:
Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
•4:3 — Select if you are using a regular TV monitor.
•16:9 — Select if you are using a wide screen monitor and
configuring for dual-monitor emulation.
You can set a wide-screen monitor to 16:9 to resize the UI screens
even if you do not configure it for dual-monitor emulation. The
far-site video is displayed in the same way for both settings.
Note: If you select 16:9, you will also need to set up the monitor for
full-screen display. In the monitor’s setup menu, choose the setting
that stretches the picture uniformly without clipping the edges.
Use this setting: Not this setting:
PIP Specifies PIP (Picture-in-Picture) behavior:
•On — The PIP window stays on for the duration of the call.
•Off — The PIP window is not displayed during the call.
•Auto — The PIP window is displayed when a user picks up the
remote.
Note: PIP settings are also available in the User Settings screen.
Users can turn the PIP on or off and change its location on the
screen using the PIP button on the remote control.
Display Icons in a
Call
Snapshot
Timeout
Dual Monitor
Emulation
Specifies whether to display all on-screen graphics, including icons
and help text, during calls.
Lets you choose whether to have snapshots time out after a period
of four minutes, after which the system returns to live video.
If you want to return to live video before four min utes hav e elapsed,
press the Near button on the remote control twice.
Specifies whether both sites are displayed in a split-screen mode
when using one monitor.
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 7
Page 54

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Using Dual Monitor Emulation
With Dual Monitor Emulation, you see both near and far sites on one TV monitor in two
different views. During presentations, you see content and the near and far site s.
Setting Up On the monitor’s setup menu, select the full-screen setting that
Using in a Call
Near and far site are the same size
and appear side by side.
stretches the picture uniformly, without clipping.
On the TV Monitor screen:
1. If you are using a wide screen monitor, set Monitor to 16:9.
Otherwise, set Monitor to 4:3.
2. Select Dual Monitor Emulation.
Call connects
Far site Near site
Near site presses PIP
Size of far site window increases.
Far site presents to near site
Content, near site, and far site are displayed in
Dual Monitor Emulation mode.
4 - 8 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 55

Adjusting the Monitor’s Color Balance
In most cases, the monitor you connect to your system provides natural color
without any adjustment. Depending on your environment as well as the model of
monitor, however, the video may exhibit one of these problems:
❑ Picture is too dark
❑ Colors appear faded
❑ Picture has too much of one color — for example, the picture may appear
greenish
If you notice any of these, the monitor needs to be adjusted.
To adjust the monitor for natural color:
1. Go to System > Diagnostics > Video.
2. Select the Color Bars icon to display the color bar test screen.
3. Adjust the color using the monitor’s controls for color, contrast, and
brightness. Your monitor may also have controls for tint and temperature.
Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
4. When the colors look right on the test screen, press the Near button on the
remote control to stop the Color Bars test and show video of the room.
5. If the color appears natural, you do not need to make further adjustments.
If the color still needs adjustment, use the monitor’s controls to make small
adjustments until the picture appears natural.
Displaying Content with People+Content IP
People+Content IP is an optional software application available for the
V500 system. It enables a presenter to show content from a computer to other sites
in a video conference using only an IP network connection.
The presenter can show PowerPoint® slides, video clips, spreadsheets, or any
other type of content that runs on a computer. Supported resolutions include CIF,
SIF, 4CIF, 4SIF, VGA, SVGA, and XGA.
Before a presenter can use a computer to show content with People+Content IP,
you need to:
❑ Enable People+Content IP on the V500 system.
When you purchase this option, you receive a software activation key. This key
allows you to enable People+Content IP on a V500 system.
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 9
Page 56

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
❑ Install People+Content IP on the computer(s) that the presenter will use to
show content.
You don’t need to change the computer resolutions and you don’t need special
cables or hardware, but the computer(s) must meet these requirements:
• Operating System: Windows 2000, Windows XP Home, or Windows XP
• Minimum computer: 500 MHz Pentium® III (or equivalent); 256 MB
Note that, although you can install People+Content IP on only one video
conferencing system, you can install it on an unlimited number of computers.
❑ Connect the computer(s) to the IP network.
For information about purchasing the People+Content IP option, please contact your
Polycom distributor.
Professional
memory
Recommended computer: 1 GHz Pentium III (or equivalent); 500 MB
memory
To enable People+Content IP on a V500 system:
1. On a computer, open a web browser and go to the Polycom Resource Cneter
Video Downloads page at http://extranet.polycom.com.
2. Enter the license number you received when you purchased the
People+Content IP option.
3. Enter the serial number of the V500 system onto which you want to install
People+Content IP.
You will then receive a People+Content IP software activation key.
4. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Options on the
V500 system.
5. Enter the People+Content IP software activation key.
To install People+Content IP on a computer:
1. On the computer, open a web browser and go to the Polycom Resource Center
Video Downloads page at http://extranet.polycom.com.
2. Locate the People+Content IP application and click the link to download the
file locally.
3. Double-click setup.exe.
4 - 10 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 57

4. When prompted, download the file locally.
5. Follow the steps in the Setup Wizard to finish installing the application on the
computer.
Anyone using that computer can then double-click on the People+Content IP
icon to present content during video conferences using the V500 system.
Make the application available to all users in your organization by downloading the setup.ex e
file to a local location that everyone can access.
Designing Audio Behaviors
This section describes how to configure the audio behaviors of the V500 system.
Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
To configure general audio settings:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Audio.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Master Audio V olume Sets the volume level for audio from the far site.
Sound Effects
Volume
Incoming Video Call Specifies the ring tone used for incoming calls.
User Alert Tones Specifies the tone used for user alerts.
Bass Sets the volume level f or the lower frequencies without changing
Treble Sets the volume level f or the higher frequencies without
Mute Auto-Answer
Calls
Enable Internal
Ringer
Sets the volume level of the ring tone and user alert tones.
the master audio volume.
changing the master audio volume.
Specifies whether to mute incoming calls.
If you select this option, incoming calls are muted until you press
the Mute button on the remote control.
Specifies an additional ring tone when receiving an incoming
call.
The ringer is built into the system and will alert you to incoming
calls even if the TV monitor connected to the system is powered
off.
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 11
Page 58

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Designing General System Behaviors
You can configure the following general system behaviors to accommodate the
needs of your organization:
❑ Call Settings
❑ Remote Control Behavior
❑ Directory Settings
❑ Call Answering Mode
❑ AES Encryption
❑ Passwords and Security Options
❑ Date, Time, and System Location
Configuring Call Settings
The Call Settings screens provide access to high-level options for the entire system.
For convenience, some of the User Settings options are repeated on these screens.
To configure call settings:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > System Settings > Call
Settings.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Maximum Time in
Call
Auto-Answer Point
to Point
Display Time in Call Specifies whether to display the elapsed time or the local time
Call Detail Report Specifies whether to generate a report of all calls made with the
Enter the maximum number of minutes allowed for call length.
When that time has expired, you see a message asking you if you
want to hang up or stay in the call. If you do not answer within one
minute, the call automatically disconnects. If you choose to stay
in the call at this time, you will not be prompted again.
Specifies whether to answer incoming point-to-point calls
automatically.
during a call. You can also choose not to display the time.
system. When selected, details for all calls can be viewed via the
V500 web interface and downloaded as a .csv file.
4 - 12 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 59

Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
Setting Description
Recent Calls Specifies whether to display the Recent Calls button on the home
screen. The Recent Calls screen lists the site number or name,
the date and time, and whether the call was incoming or outgoing.
Note: If the Call Detail Report option is not selected, the Recent
Calls option is not available.
Far Site Name
Display Time
Specifies the time period the far-site name appears on screen
when calls first connect.
Configuring Remote Control Behavior
You can customize the behavior of the remote control to support the your
environment.
To configure remote control behavior:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > System Settings >
Remote Control.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Keypad Audio
Confirmation
Remote Control
Keypad
Specifies whether to play a voice confirmation of numbers
selected with the remote control.
Specifies whether the camera creates DTMF tones when the
remote control keypad buttons are pressed.
Configuring Directory Settings
You can customize the behavior of the Directory on the Directory screen.
To configure system settings:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > System Settings >
Directory.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
System Name Enter or change the system name in this field. This name appears
on the screen for the far site when you are making calls.
Allow Directory
Changes
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 13
Specifies whether you can save changes you make to the
directory.
Page 60

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Setting Description
Confirm Directory
Additions
Confirm Directory
Deletions
Specifies whether you are prompted to confirm new directory
entries when saving the information for the last site called.
Specifies whether you are prompted to confirm deletions of
directory entries.
Setting the Call Answering Mode
You can choose to answer calls automatically or manually, or you can set the
system to automatically refuse any incoming calls.
To set the call answering mode:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > System Settings > Call
Settings.
2. Select Auto-Answer Point to Point.
3. Select one of the following:
•Yes – Answers calls automatically.
•No – Enables you to answer calls manually.
•Do Not Disturb – Refuses incoming calls automatically. The caller receives
a message that the site is unavailable.
Automatically answering calls is convenient, but keep in mind that an unexpected caller
could interrupt you or see and hear you without your knowledge. If you still want to
automatically answer calls but you want to pre vent incoming callers from seeing and hearing
you, you can choose to mute all automatically answered calls and mak e sure your lens cover
is closed.
Enabling AES Encryption
AES encryption is a standard feature on every V500 system.
To enable AES encryption:
>> Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Security and select AES
Encryption.
4 - 14 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 61

Setting Passwords and Security Options
You can enter or change the administrator and meeting passwords as well as
specify whether to allow remote access to the system.
To set passwords and security options:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Security.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Admin Password Enter or change the Admin password.
When the Admin password is set, you must enter this password
to:
• Make configuration changes not in the User Settings screen.
• Update the software.
• Manage the system using the V500 web interface.
Meeting Password Enter or change the meeting password, if any.
Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
Allow Access to
User Settings
AES Encryption Specifies whether to encrypt calls with other sites that suppor t
Enable Remote
Access
Web Access Port Specifies the port to use when accessing the system using the
Allow Video Display
on Web
Specifies whether the User Settings screen is accessible to users
via the System screen.
Uncheck this option if you do not want users to change
environmental settings.
AES encryption.
Specifies whether to allow remote access to the system by:
• FTP
• Web
• Telnet
• SNMP
You may select any of these, or an y combination of them.
Note: The system reboots if you change the remote access
settings.
V500 web interface.
If you change this from the default (port 80), you will need to
include the port number with the IP address when you use the
V500 web interface to access the system. This makes
unauthorized access more difficult.
Specifies whether to allow administrators who use the V500 web
interface to view the room where the system is located.
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 15
Page 62

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Setting Date, Time, and Location
You can update the system with regional settings, including the location-specific
language and calling parameters.
To set the date, time, and location:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Location.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Country Specifies the country where the system is located.
Changing the country automati cally adjusts the country code
associated with your system number.
Language Sets the language for the user interface .
Country Code Specifi es the country code for the system location.
Area Code Required Specifies if an area code is required to place ISDN calls in the
specified country.
ISDN International
Access
Room Telephone
Number
Specifies the international code required for placing ISDN calls
from the system location to another country.
Indicates the telephone number of the room where the system is
located.
3. Select and configure these settings:
Setting Description
Date Format and
Time Format
Daylight Saving Time Specifies whether it is daylight saving time.
Time Difference from
GMT
Display Time in Call Specifies the time display in a call:
Time Server Specifies connection to a time server for automatic system time
Specifies your format preference for the date and time display
and lets you enter your local date and time.
Specifies the time difference between GMT (Greenwich Mean
Time) and your location.
•Elapsed Time – Displays the amount of time in the call.
•Local Time – Displays the local time on the screen during a
call.
•Off – Time is not displayed.
settings.
4 - 16 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 63

Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
Customizing the Workspace Appearance
You can customize the V500 system workspace appearance to suit your
environment functionally and aesthetically.
For example, by customizing the home screen into kiosk mode, anyone who uses
the system only has to select a site and press the Call button on the remote
control to place a call.
Use the following sections to configure the general appearance of the system:
❑ Designing the Home screen
❑ Adding Sites to the Home screen
❑ Adding On-screen Instructions
❑ Changing Color Schemes
❑ Setting Ring Tones and Alert Tones
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 17
Page 64

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Designing the Home Screen
Customize the system functionality according to your needs, skill level, and environment.
Use the marquee to
add instructions
Infrequent Users (Kiosk Mode)
Provide a simple workspace so no training is
needed:
• Let users make calls to pre-defined
numbers with one button click.
• Include instructions on screen.
New Users
Provide more options but keep it simple:
• Dialing entry field
• Directory numbers
• Recent Calls
Include a short
list of specific
items for users
to select
Add features
for users
as needed
Advanced Users
Provide additional options for advanced video
conferencing users:
• Call Quality
• User Settings, Diagnostics, and System
Information
• Speed Dial list of frequently called sites
4 - 18 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Add more
features as
users gain
experience
Page 65

Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
To design the home screen:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Home Screen Settings.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Dialing Display Specifies which dialing option to display:
• Dialing entry field — Allows users to enter numbers manually.
• Display marquee — Displays text in the dialing entry field. Can
be used to display user instructions. Users cannot enter numbers
manually when this option is selected.
•None — Removes the dialing entry field from the screen.
Call Quality Allows users to select the bandwidth for calls.
H.323 Extension
(E.164)
Directory Allows users to access the directory.
System Allows users to access the System screen, which includes User
If you remove the System button, you can still access the System screen by navigating to
the home screen, pressing Help on the remote, and selecting System.
Allows users to enter extensions on the home screen.
Settings, Diagnostics, and System Information.
3. Select and configure these settings:
Setting Description
System Name Specifies whether to display the name of the system on the home
screen above the PIP window.
IP or ISDN
Information
Local Date and
Time
Do Not Disturb
Icon
Specifies whether to display the system’s IP address, ISDN number ,
or both on the home screen.
Specifies whether to display the local date and time on the home
screen.
Allows users to set the system to automatically accept or ignore
incoming calls using the Do Not Disturb button on the home screen.
Call Detail Report Specifies whether to generate a report of all calls made with the
system. When selected, all calls can be viewed through the V500
web interface and downloaded as a .csv file.
Recent Calls Allows users to access a list of recent calls made with the system by
displaying the Recent Cal ls button on the home screen.
If the Call Detail Report option is not selected, the Recent Calls
option is not available.
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 19
Page 66

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
4. Select and configure these settings:
Setting Description
Sites Allows users to access any pre-defined sites from a My
Contacts/Speed Dial list on the home screen.
Last Number
Dialed
Specifies whether to display the last number dialed or clear the
address box on the home screen.
Adding Sites to the Home Screen
Creating Site buttons on the home screen makes it easy for you to place calls to sites
that you call on a regular basis.
Sites can appear as individual buttons or as part of a list called Speed Dial or My
Contacts.
You must enter the site information in the directory before creating specific Site buttons for
the home screen.
To add sites on the Home screen:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Home Screen Settings.
2. Select three times to access the Sites screen.
3. Select Add and choose the sites to add from the directory.
4. Select either Speed Dial or Contacts as the name you want to appear on the
button.
Adding On-screen Instructions
Using Marquee Text
You can create marquee text to display in the dialing entry field on the home
screen. You can create context-specific instructions or, if the home screen has Site
buttons, the marquee text can provide information that helps other users choose
which site to call.
Marquee text does not support double-byte characters.
4 - 20 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 67

To enter marquee text:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Home Screen Settings.
2. In Dialing Display, select Display Marquee and enter the text.
You can also add marquee text through the V500 web interface.
Using Screen Saver Text
You can customize the V500 system to display text when the system is in sleep
mode. For instance, you can display on-screen instructions.
To enter screen saver text:
1. On a PC, open a web browser.
2. In the browser address line, enter the system’s IP address (for example,
http://255.255.255.255) to go to the V500 web interface.
Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
3. Enter your user name and the password, if a password has been established.
4. Click System Setup > Utilities > Screen Saver and enter:
• Text — Appears as scrolling text when the system is in sleep mode. You
can use this scrolling text to provide instructions or next steps for users of
the system.
• Logo Text — Appears underneath the logo before the system goes into
sleep mode.
5. Click Update.
Changing System Appearance
Different user interface color schemes are available, allowing you to coordinate the
system interface with the room décor.
To change the color scheme:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > System Settings >
Appearance.
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 21
Page 68

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Color Scheme Customizes the look of your system with different color schemes.
Screen Saver Wait
Time
You can allow users to change color schemes by allowing user access to the User
Settings screen.
Specifies how long the system remains awake during periods of
inactivity. The default is 3 minutes.
Setting Ring Tones and Alert Tones
To set ring tones and alert tones:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Audio.
2. Select a tone, as desired.
To set the V500 system internal ringer:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Audio.
2. Select Enable Internal Ringer to specify an additional ring tone when
receiving an incoming call.
The ringer is built into the system and will alert you to incoming calls even if the TV
monitor connected to the system is powered off.
Configuring Closed Captioning
You can provide real-time text transcriptions or language translations of the video
conference by displaying closed captions on your system. When you provide
captions for a conference, the captioner uses a web browser to listen to the
conference audio and enter the caption text in the system’s web interface. When
the captioner sends a unit of text, all sites see it on the main monitor for 15 seconds.
The text then disappears automatically.
4 - 22 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 69

Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
Audio Options for Closed Captioners
When you provide captions for a conference, the captioner may be present, or may
use a telephone or web browser to listen to the conference audio.
The captioner must receive audio from the conference in one of these ways:
• Attending one of the conferences sites
• Listening to the conference via the V500 web interface
• Listening to the conference via a speakerphone in the room at one of the
sites
Options for Supplying Closed Captions to Conferences
Captions can be provided in any language that uses the Latin alphabet.
The captioner can enter caption text in one of these ways:
• In the room or remotely, using the V500 web interface
• In the room or remotely, using a Telnet session
Providing Captions Via the V500 Web Interface
Closed captioners can provide captions from inside the conference room, or from
a remote location, by entering the captions directly into the V500 web interface, as
shown in the diagram below.
V500 web interface
To supply closed captions for a conference using the V500 web interface:
1. On a PC, open a web browser.
2. In the browser address line, enter the IP address of the system (for example,
http://255.255.255.255) to go to the V500 web interface.
LAN
V500 System
LAN
port
3. Go to System Setup > Utilities > Closed Caption.
4. Enter your user name and the password, if a password has been established.
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 23
Page 70

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
5. In the Closed Caption screen, type the caption text into the text field. Text
wraps to the next line after 59 characters.
6. Press Enter to send the text to the sites in the conference.
Providing Captions Via a Telnet Session
Closed captioners can provide captions from inside the conference room, or from
a remote location, by entering captions via a Telnet session, as shown in the
diagram below.
Telnet session
LAN
V500 System
LAN
port
To supply closed captions for a conference using a Telnet session:
1. On a PC, open a command line interface.
2. Start a Telnet session using the V500 system IP address and port 24 (for
example,
3. Enter the command
telnet 255.255.255.24).
cc to start captioning.
4. Press Enter to send the text.
5. To stop sending closed captions, press Ctrl-Z.
4 - 24 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 71

Getting Started with Calling
The system is installed and you’ve finished the network configuration and
designed the behaviors. Now it’s time for you to start placing calls. You may want
to spend time becoming familiar with basic calling tasks.
The following resources are available:
❑ V500 System Getting Started Guide — This guide is for all users, from beginners
to the more experienced. It covers meeting basics, different ways to place calls,
how to use the remote control, and how to deliver presentations.
It is included on the V500 system documentation CD and is also available on
the web.
❑ Screen Help — The home and Directory screens have context-specific help.
Users can press Help on the remote control to access help topics.
❑ www.polycom.com/videodocumentation — Refer to the video
documentation page on the Polycom website for the latest documents
supporting these products.
Chapter 4 - Designing the User Experience
© Polycom, Inc. 4 - 25
Page 72

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
4 - 26 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 73

5
Managing the System Remotely
You configure, manage, and monitor the system from a remote computer using the
V500 web interface (the system’s web interface), the Polycom Global Management
System, or SNMP.
Your choice of management tool depends on your network environment:
❑ V500 web interface requires only a web browser to control the system.
❑ Polycom Global Management System requires the Global Management System
application to be installed on your network.
❑ SNMP requires network management software on your network management
station.
What’s in this Chapter? Page
Using the V500 Web Interface 5-2
Configuring Global Services 5-6
Setting Up SNMP 5-9
© Polycom, Inc. 5 - 1
Page 74

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Using the V500 Web Interface
You can use the V500 web interface to perform most of the calling and
configuration tasks you can perform on the local system.
Accessing the V500 Web Interface
To configure your browser to use the V500 web interface:
1. Be sure that you use Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or later as your web
browser.
2. Configure these settings:
• Allow cookies: Enabled
• Force pages to reload on every visit to a page: Enabled
To access the system using the V500 web interface:
1. On a PC, open a web browser.
2. In the browser address line, enter the system’s IP address (for example,
http://255.255.255.255) to go to the V500 web interface.
3. Enter admin as the user name, and the password, if a password has been
established.
You can use the V500 web interface to configure all of the system settings except the remote
management settings. For security reasons, these settings must be configured on the local
system by an administrator.
5 - 2 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 75

Room Monitoring with the V500 Web Interface
The Web Director feature within the V500 web interface allows administrators of
the V500 system to monitor a call or the room where the system is installed.
For security reasons, this feature can only be enabled on the local system by an
administrator.
To enable room monitoring:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > General Settings > Security.
2. Select Allow Video Display on Web to allow the room to be viewed remotely.
To view a room:
1. On a PC, open a web browser.
Chapter 5 - Managing the System Remotely
2. In the browser address line, enter the system’s IP address (for example,
http://255.255.255.255) to go to the V500 web interface.
3. Go to System Setup > Utilities > Web Director.
4. Perform any of the following tasks:
• Place or end a call
• View near and far sites
• Adjust system volume settings
• Mute and unmute the microphone
© Polycom, Inc. 5 - 3
Page 76

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Managing System Profiles with the V500 Web Interface
The customization options for V500 systems have been extended with the ability
to store your system settings as separate profiles. Profiles can be stored on your PC
as a .csv file using the V500 web interface. There is no limit to the number of
profiles you can save.
This is particularly useful if you are managing systems that support multiple
applications. Changing the interface and behaviors of the V500 system can be done
quickly and easily.
The following settings are included in a profile:
• Home Screen settings
• User access levels
• Icon selections
• Option keys
• System behaviors
Polycom recommends using profiles as a way to bac k up system settings. Attempting to edit
a stored profile or upload it to a different system can result in unexpected problems.
To store a profile:
1. In the V500 web interface, go to System Setup > Utilities > Profile Center.
2. Click V500 -> PC to download the .csv file from the V500 system.
3. Save the file to a location on your PC.
To upload a profile:
1. In the V500 web interface, go to System Setup > Utilities > Profile Center.
2. Click Browse and browse to the location of the .csv file on your PC.
3. Click PC -> V500 to upload the .csv file to your system.
5 - 4 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 77

Chapter 5 - Managing the System Remotely
Managing Directories with the V500 Web Interface
The V500 web interface import/export directory feature allows you to efficiently
maintain consistency of V500 system directories. It is particularly useful if you are
managing multiple systems that call the same locations. You can:
❑ Transfer existing directory entries between V500 systems
❑ Develop directory entries on one system, save them to your PC, and then
distribute them to other systems
Only local directories can be downloaded. The directory file is in .csv format.
To download a V500 system directory to your PC:
1. In the V500 web interface, go to System Setup > Utilities > Import Directory.
2. Click V500 -> PC to download the .csv file from the V500 system.
3. Save the file to a location on your PC.
To upload V500 system directory entries:
1. In the V500 web interface, go to System Setup > Utilities > Import Directory.
2. Click PC -> V500.
3. Click Browse and browse to the location of the .csv file on your PC.
4. Click Export Directory to upload the .csv file to the V500 system.
© Polycom, Inc. 5 - 5
Page 78

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Configuring Global Services
If you use the Polycom Global Management System, you can configure, manage,
and monitor the V500 system using the Global Management System server. The
Global Management System is a web-based client/server software tool that allows
administrators to manage a network of video conferencing systems.
To use global services for the system, configure the following:
❑ Management Servers
❑ Account Numbers
❑ My Information
Viewing the Management Servers List
On networks managed by the Global Management System, several Global Servers
may be configured to manage this system remotely. The system also has a primary
Global Management System server that performs account validation. You can view
information about these servers, but this information can only be changed by the
Global Management System Administrator.
To view the management servers list:
>> Go to System > Admin Settings > Global Services > Management Servers.
Requiring an Account Number for Calls
If your system is set up for use with the Global Management System, the system
can prompt you to enter an account number before placing a call. The account
number is added to the Global Management System’s Call Detail Record (CDR),
and this information can be used for call tracking and billing purposes. The
account number is also added to the system’s local CDR file (localcdr.csv).
If you configure the system to validate the account number, calls placed without a
valid account number are not completed. If you do not configure the system to
validate account numbers, calls are completed regardless of whether the account
number is valid. Account numbers are set up in the Global Management System
by the Global Management System administrator
For more information about account validation, please contact your Global
Management System administrator.
.
5 - 6 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 79

To require an account number for calls:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Global Services > Account Validation.
2. Specify whether to require an account number for placing calls and whether
that number should be validated by the Global Management System server.
Adding My Information
If your system is managed by the Global Management System, you can configure
the V500 system so that you can request help from the Global Management System
administrator.
To add information for the Global Management System administrator:
1. Go to System > Admin Settings > Global Services > My Information.
2. Enter the contact information for the Global Management System
administrator for technical support.
The following section illustrates the interaction between Global Management
System and the system you are configuring.
Chapter 5 - Managing the System Remotely
© Polycom, Inc. 5 - 7
Page 80

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Requesting Technical Support from the Global Management System
Administrator
1. From the Place A Call screen, press on the remote.
2. Select Support and press on the remote.
You see the f ollowing message:
Tech Support will be alerted to phone you at the
following number. Continue?
Enter your contact telephone number.
The V500 system sends your information to the
Global Management System administrator.
You see the following message:
Tech Support has been alerted. You can also call
this number for assistance.
The message displays the telephone number you
entered for Tech Support on the My Information screen.
The V500 system displays the message from Global
Management System:
Your request for help has been acknowledged.
5 - 8 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
The Global Management System
administrator opens the alert
message containing your teleph one
number.
Global Management System sends
a message to your V500 system.
The Global Management System
administrator calls you.
Page 81

Setting Up SNMP
The V500 system sends SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) reports to
indicate a total of 31 conditions, including the following:
• All alert conditions found on the V500 system’s alert page
• Details of jitter, latency, and packet loss
• Low battery power is detected in the remote control
• A system powers on after a long period powered off
• Administrator logon is successful or unsuccessful
• A call fails for a reason other than a busy line
• A user requests help
• A telephone or video call connects or disconnects
Downloading MIBs
Chapter 5 - Managing the System Remotely
In order to allow your SNMP management console application to resolve SNMP
traps and display text descriptions for those traps, you need to install Polycom
MIBs on the computer you intend to use as your network management station.
The MIBs are available for download from the V500 web interface.
To download the Polycom MIBs:
1. On a PC, open a web browser.
2. In the browser address line, enter the IP address of the system (for example,
http://255.255.255.255) to go to the V500 web interface.
3. Go to System Setup > Admin Settings > Global Services > SNMP.
4. Click Download MIB and follow the onscreen instructions.
© Polycom, Inc. 5 - 9
Page 82

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Configuring for SNMP Management
To configure the V500 system for SNMP management:
1. Access the SNMP configuration screen either in the V500 web interface or on
the V500 system:
• In the V500 web interface, go to System Setup > Admin Settings > Global
Services > SNMP.
• On the V500 system, go to System > Admin Settings > Global Services >
SNMP.
2. Configure these settings:
Setting Description
Enable SNMP Allows administrators to manage the system remotely using
SNMP.
Community Specifies the SNMP management community in which you want
to enable this system. The default community is public.
Contact Name Specifies the name of the person responsible for remote
management of this system.
Location Name Specifies the location of the system.
System Description Specifies the type of video conferencing device.
Console IP Address Specifies the IP address of the computer you intend to use as
your network management station and to which SNMP traps will
be sent.
5 - 10 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 83

6
System Usage and Statistics
The V500 system provides various screens that allow you to review information
about calls made by the system and to review network usage and performance.
What’s in this Chapter? Page
Call Summary 6-2
Call Statistics 6-3
Call Status 6-4
Recent Calls 6-6
Call Detail Report 6-6
© Polycom, Inc. 6 - 1
Page 84

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Call Summary
The Call Summary screen provides details about the calls placed by the system,
including:
❑ Duration of the last call
❑ Total number of calls placed and received
❑ Number, total time, and percentage of IP calls
❑ Number, total time, and percentage of ISDN calls
To view the Call Summary screen:
>> Go to System > Diagnostics > Call Statistics and then select three times.
You can view Call Statistics and Call Summary during a call by pressing Help on the
remote control.
6 - 2 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 85

Call Statistics
Chapter 6 - System Usage and Statistics
The two Call Statistics screens provide information about the call in progress,
including:
This screen: Displays this information:
Call Statistics (1) • Call speed (transmit and receive)
• Video protocol, annexes, and format in use (transmit and
receive). The video protocol is shown in green if the system
is currently using error concealment.
• Audio protocol in use (transmit and receive)
• Number of packets lost and percentage packet loss (transmit
and receive) in IP calls
• Encryption type, key exchange algorithm type, and key
exchange check code (if the encryption option is enabled and
the call is encrypted)
• Far site details and call type
Call Statistics (2) • Audio and video data rates specified (transmit and receive)
• Video data rate and frame rate in use (transmit and receive)
• Video packet loss and jitter in IP calls
• Audio packet loss and jitter in IP calls
• Far site details and call type
To view the Call Statistics screen:
>> Go to System > Diagnostics > Call Statistics and then select .
You can view Call Statistics and Call Summary during a call by pressing Help on the
remote control.
© Polycom, Inc. 6 - 3
Page 86

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Call Status
The Call Status screen provides call connection information. The spheres on the
screen provide details for each line. When you place a call, you’ll see the status
change as the call connects.
To view the Call Status screen:
>> Go to System > Diagnostics > Call Statistics.
You can highlight the spheres on this screen to see the number dialed, the relevant
status code, and details of any errors.
You can view Call Status during a call by pressing Help on the remote control.
6 - 4 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 87

Recent Calls
Chapter 6 - System Usage and Statistics
Recent Calls shows a list of up to 99 calls made by the system. It includes the
following information:
❑ Site name or number
❑ Date
❑ Time
❑ Call In or Out
The Recent Calls list shows incoming and outgoing calls that connect, as well as
outgoing calls that do not connect.
If Do Not Disturb has been enabled, any incoming calls attempted by other sites
will not be listed.
The Home screen can be configured to include Recent Calls. For more information about
including the Recent Calls list on the home screen, see Designing the Home Screen on
page 4-18.
To view the Recent Calls screen:
>> Go to System > Admin Settings > Network > Recent Calls.
You can see more detail about any call by highlighting an entry and pressing
Help on the remote control. Information includes the far site’s number and name,
and the type, speed (bandwidth), and duration of the call.
You can call any site on the Recent Calls list by highlighting the entry and pressing
Call or Select on the remote control to place the call.
If you need even more detail about calls, you can download the Call Detail Report (CDR)
from the V500 web interface. For more information about the CDR, see Call Detail Repor t
on page 6-6.
© Polycom, Inc. 6 - 5
Page 88

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Call Detail Report
The Call Detail Report (CDR) provides the system’s call history. You can view the
CDR from the V500 web interface, and you can download the data in CSV format
for sorting and formatting.
CSV stands for Comma Separated V alue. CSV files can be imported into spreadsheet and
database programs.
Every call that connects is added to the CDR, whether it is a call that you make or
that you receive. If a call does not connect, the report shows the reason.
The CDR does not include incoming calls that the V500 system does not answer, so
if calls were missed while Do Not Disturb was enabled, details will not be included
in the CDR.
To view and download the CDR via the V500 web interface:
1. On a PC, open a web browser.
2. In the browser address line, enter the system’s IP address (for example,
http://255.255.255.255) to go to the V500 web interface.
3. Enter admin as the user name, and the admin password, if a password has
been established.
4. Click System Setup > Utilities > Call Detail Report to view the details of the
file.
5. Click Save and then specify a location on your computer to save the file.
Information in the Call Detail Report
The following table describes the data fields in the CDR.
Data Description
Row ID Each call is logged on the first available row.
Start Date The call start date, in the format dd-mmm-yyyy.
Start Time The call start time, in the 24-hour format hh:mm:ss.
End Date The call end date.
End Time The call end time.
6 - 6 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 89

Chapter 6 - System Usage and Statistics
Data Description
Call Duration The length of the call.
Account Number If Require Account Number to Dial is enabled on the system, the
value entered by the user is displayed in this field.
Remote System
The far site’ s system name.
Name
Call Field Number 1The number dialed from the first call field, not necessarily the
transport address.
For incoming calls — The caller ID information from the first
number received from a far site.
Call Field Number
2 (if applicable for
call)
For outgoing calls — The number dialed from the second call field,
not necessarily the transport address.
For incoming calls — The caller ID information from the second
number received from a far site.
Transport Type The type of call — Either H.320 (ISDN) or H.323 (IP).
Call Rate The bandwidth negotiated with the far site.
System
Manufacturer
The name of the system manufacturer, model, and software
version, if they can be determined.
Call Direction In — For calls received.
Out — For calls placed from the system.
Conference ID A number given to each conference.
Call ID Identifies individual calls within the same conference.
Total H.320
The total number of ISDN B channels used in the call.
Channels Used
Endpoint Alias The alias of the far site .
Endpoint
An additional alias of the far site.
Additional Alias
Endpoint Type Terminal, gateway, or MCU.
Endpoint
Transport Address
Audio Protocol
The actual address of the far site (not necessarily the address
dialed).
The audio protocol transmitted to the far site, such as G.728.
(Tx)
Audio Protocol
(Rx)
Video Protocol
(Tx)
Video Protocol
(Rx)
The audio protocol received from the far site, such as G.728 or
G.722.
The video protocol transmitted to the far site, such as H.263 or
H.264.
The video protocol received from the far site, such as H.261 or
H.263.
Video Format (Tx) The video format transmitted to the far site, such as CIF or SIF.
© Polycom, Inc. 6 - 7
Page 90

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Data Description
Video Format (Rx) The video format received from the far site, such as CIF or SIF.
Disconnect
Reason
Q.850 Cause
The description of the Q.850 (ISDN) cause code showing how the
call ended.
The Q.850 cause code showing how the call ended.
Code
Total H.320 Errors The number of errors dur ing an H.320 call.
Aver age Percent of
Packet Loss (Tx)
The combined average of the percentage of both audio and video
packets transmitted that were lost during the 5 seconds preceding
the moment at which a sample was taken. This value does not
report a cumulative average for the entire H.323 call. However, it
does report an average of the sampled values.
Aver age Percent of
Packet Loss (Rx)
The combined average of the percentage of both audio and video
packets received that w ere lost during the 5 seconds preceding the
moment at which a sample was taken. This value does not report
a cumulative average for the entire H.323 call. However, it does
report an average of the sampled values.
Average Packets
Lost (Tx)
Average Packets
Lost (Rx)
Average Latency
(Tx)
The number of packets transmitted that were lost during an H.323
call.
The number of packets from the far site that were lost during an
H.323 call.
The average latency of packets transmitted during an H.323 call
based on round-trip delay , calculated from sample tests done once
per minute.
Average Latency
(Rx)
The average latency of packets received during an H.323 call
based on round-trip delay , calculated from sample tests done once
per minute.
Maximum Latency
(Tx)
The maximum latency for pac kets tra nsmitted during an H .323 call
based on round-trip delay , calculated from sample tests done once
per minute.
Maximum Latency
(Rx)
The maximum latency for packets received during an H.323 call
based on round-trip delay , calculated from sample tests done once
per minute.
Average Jitter (Tx) The average jitter of packets transmitted during an H.323 call,
calculated from sample tests done once per minute.
Average Jitter (Rx) The average jitter of packets received during an H.323 call,
calculated from sample tests done once per minute.
Maximum Jitter
(Tx)
Maximum Jitter
(Rx)
6 - 8 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
The maximum jitter of packets transmitted during an H.323 call,
calculated from sample tests done once per minute.
The maximum jitter of packets received during an H.323 call,
calculated from sample tests done once per minute.
Page 91

Call Detail Report Archives
Calls are added to the CDR until the file size reaches 50 KB, which is equivalent to
about 150 calls. The system then automatically archives the CDR and creates a new
CDR file. If an archive is already present, the new archive overwrites it.
Each CDR starts with Row 1, but the conference numbers continue from the file
most recently archived. Conference numbering restarts at 1 after the system
assigns conference number 100,000.
To get an archived CDR:
1. From your computer, open an FTP client.
2. FTP into the V500 system.
3. Enter this FTP command:
GET localcdr_archive.csv
4. Close your FTP session.
Chapter 6 - System Usage and Statistics
© Polycom, Inc. 6 - 9
Page 92

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
6 - 10 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 93

7
Diagnostics and General
Troubleshooting
This chapter covers the diagnostic screens of the V500 system. It is organized by
category to help you troubleshoot any issue.
Diagnostic tools are available via the system itself and the V500 web interface. To
connect to the V500 web interface, enter your system’s IP address in a web browser
and browse to the required diagnostic tool.
What’s in this Chapter? Page
Sending a Message 7-2
System Screens Quick Reference 7-2
Diagnostic Screens 7-3
General Troubleshooting 7-8
How to Contact Technical Support 7-19
© Polycom, Inc. 7 - 1
Page 94

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Sending a Message
If you are experiencing difficulties with connectivity or audio, you may want to
send a message to the V500 system.
Only the near site can see the message; it is not broadcast to the far site in the call.
To send a message via the V500 web interface:
1. On a PC, open a web browser.
2. In the browser address line, enter the system’s IP address (for example,
http://255.255.255.255) to go to the V500 web interface.
3. Enter admin as the user name, and the password, if a password has been
established.
4. Go to System Setup > Diagnostics > Send a Message.
5. In the Send a Message page, enter a message (up to 100 characters in length),
then click Send Message.
The message is displayed for 15 seconds on the screen of the system.
System Screens Quick Reference
These screens allow you to view information about the system, configure the
system, and diagnose performance issues if they arise. They are available on the
system and through the V500 web interface.
To view information about the system, go to the home screen and select System.
Then choose the type of information you need:
This choice: Presents this information or capability:
Admin Settings User interface customization, system customization, security,
dialing requirements and network configuration, key-enabled
options, Global Management System information.
Diagnostics System status and performance and system tests. The V500
web interface also offers the Send Message function and
provides access to the Call Detail Report.
System Information Identifying information.
Utilities C all scheduler and calendar.
User Settings System behavior and appearance.
7 - 2 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 95

Diagnostic Screens
You can view network statistics and perform diagnostic tests from the
V500 system’s Diagnostics screens.
To access the Diagnostics screens on the system:
>> Go to System > Diagnostics.
To access the Diagnostics screens from the V500 web interface:
1. On a PC, open a web browser.
2. In the browser address line, enter the system’s IP address (for example,
http://255.255.255.255) to go to the V500 web interface.
3. Enter admin as the user name, and the password, if a password has been
established.
4. Go to System Setup > Diagnostics.
Chapter 7 - Diagnostics and General Troubleshooting
The following diagnostic screens and tools are available:
Call Status Tools
Diagnostic Tool In the system’s user interface In the V500 web interface
System Status screen
Displays system status information,
including auto-answer point to point,
remote control battery , time server , Global
Directories, IP network, gatekeeper,
UPnP, and ISDN BRI line.
Call Summary screen
Displays calling information, such as time
spent in calls, total number of IP and ISDN
calls, and percentage of time spent in IP
and ISDN calls.
On the Diagnostics screen, select
System Status.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select System Status.
2. Select to go to the Call
Summary screen.
For more information about this screen, see Call Summary on
page 6-2.
Select Diagnostics > System
Status.
Select Diagnostics > System
Status > Call Summary.
© Polycom, Inc. 7 - 3
Page 96

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Call Status Tools
Diagnostic Tool In the system’s user interface In the V500 web interface
Call Status screen
Displays call type, data speed, and
number dialed for t h e current call.
In ISDN calls, this screen also displays
connection status for each channel.
Selecting a channel call progress indicator
displays its ISDN number.
Call Statistics screen
Displays call speed, audio and video
protocols, annexes, and error count for the
call in progress.
Call Detail Report screen
Displays the current Call Detail Report
(CDR) and provides access to the
archived CDR.
On the Diagnostics screen, select
Call Statistics.
1. Select Diagno stics > Call
Statistics.
2. Select twice.
For more information about this screen, see Call Status on page 6-4.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select Call Statistics.
2. Select
to go to the Call
Select Diagnostics > Call
Statistics.
Statistics screen.
For more information about this screen, see Call Statistics on page 6-3.
Not available. Select Utilities > Call Detail
Report.
For more information about this screen, see Call Detail Report on
page 6-6.
7 - 4 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 97

Chapter 7 - Diagnostics and General Troubleshooting
Network Tools
Diagnostic Tool In the system’s user interface In the V500 web interface
Near End Loop test
T ests whether y our system is able to make
IP calls successfully.
Monitor 1 displays the video and plays the
audio that would be sent to the far site in a
call.
This test is not available when you are in
an IP call.
PING test
Tests whether the system can establish
contact with a far-site IP address that you
specify.
Trace Route test
Tests the routing path between the local
system and the IP address entered.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select Network.
2. Select Near End Loop to start
the test.
3. Press any b utton on the remote
control to stop the test.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select Network > PING.
2. Enter the IP address that you
wish to test.
3. Select Start.
If the test is successful, the
system displays a message
indicating that the IP address
under test is available.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select Network > Trace Route.
2. Enter the IP address that you
wish to trace.
3. Select Start.
If the test is successful, the
system lists the hops between
the system and the IP address
you entered.
1. Select Diagnostics > Network
> Near End Loop.
2. Click the Near End Loop icon.
3. Clic k Near End Loop again to
end the test.
1. Select Diagnostics > Network
> PING.
2. Enter the IP address that you
wish to test.
3. Click the PING icon.
If the test is successful, the
system displays a message
indicating that the IP address
under test is available.
1. On the Diagnostics menu,
select Netw ork > T race Route.
2. Enter the IP address that you
wish to trace.
3. Click the Trace Route icon.
If the test is successful, the
system lists the hops between
the system and the IP
address you entered.
Error Log files
Created if the system restarts due to
problems. Thes e fi l es co nt ai n information
that can be used by Polycom Support
Not available. A Polycom Support
representative will provide
instructions if the error log is
needed.
personnel to troubleshoot system issues.
© Polycom, Inc. 7 - 5
Page 98

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
Video and Audio Tools
Diagnostic Tool In the system’s user interface In the V500 web interface
Color Bar test
T e sts the color settings of your monitor for
optimum picture quality.
If the color bars generated during the test
are not clear, or the colors do not look
correct, the monitor needs to be adjusted.
Speaker test
Tests the audio cable connections. A
400 Hz audio tone indicates that the local
audio connections are correct.
Speaker test
Tests the audio cable connections. A
400 Hz audio tone indicates that the local
audio connections are correct.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select Video.
2. Select the Color Bars icon.
3. Press any b utton on the remote
control to stop the test.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select Audio > Speaker Test.
2. Select the Speaker Test icon.
3. Press any b utton on the remote
control to stop the test.
If you are in a call, the far site will
also hear the tone.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select Audio > Speaker Test.
2. Select the Speaker Test icon.
3. Press any b utton on the remote
control to stop the test.
If you are in a call, the far site will
also hear the tone.
1. Select Diagno s t ic s > Video.
2. Click the Color Bars icon.
3. Click the Color Bars icon
again to stop the test.
1. Select Diagnostics > Audio >
Speaker Test.
2. Click the Spea ker Test icon.
3. Click the Spea ker Test icon
again to stop the test.
The people at the site you are
testing will hear the tone, but you
will not. You can send a message
to tell them how to notify you
when they hear the speaker test.
1. Select Diagnostics > Audio >
Speaker Test.
2. Click the Spea ker Test icon.
3. Click the Spea ker Test icon
again to stop the test.
The people at the site you are
testing will hear the tone, but you
will not. You can send a message
to tell them how to notify you
when they hear the speaker test.
Audio Meter screen
Measures the strength of audio signals
from the system’s microphone.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select Audio.
2. Select Audio Meter.
The audio meter should
Select Diagnostics > A u dio >
Audio Meter to start the test.
The audio meter should register
between 0 and 15 dB.
register between 0 and 15 dB
for each active input.
3. To check the microphone,
speak into the microphone.
4. To check far-site audio, ask a
person at the far site to speak.
7 - 6 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
Page 99

Chapter 7 - Diagnostics and General Troubleshooting
Reset
Diagnostic Tool In the system’s user interface In the V500 web interface
Reset System
Cycles power to the system.
When you reset the system using the
remote control, the system’s user interf ace
allows you to:
• Keep your system settings (such as
system name and network
configuration) or restore factory
settings.
• Keep or delete the directory stored on
the system.
1. On the Diagnostics screen,
select Reset System.
2. Enter the system’s serial
number.
3. If you wish to restore the
original factory settings, select
Delete System Settings.
This deletes the
administrator’s password,
CDR, and CDR archive along
with the other system settings.
Y o u may wish to download the
CDR and CDR archive before
you reset the system. See Call
Detail Report on page 6-6. If
you delete system settings,
the setup wizard will lead you
through the initial
configuration after the system
restarts.
4. If you wish to remove the
directory, select Delete
Directory Entries.
This only deletes the system’s
local directory. System reset
does not affect the Global
Directory.
5. Select Reset System.
1. Select Diagnostics > Reset
System.
2. Click the Reset System icon.
© Polycom, Inc. 7 - 7
Page 100

Administrator’s Guide for the V500 System
General Troubleshooting
This section presents problems, likely causes, and corrective actions. Problems are
grouped as follows:
❑ Power and Start-up
❑ Remote Control
❑ Access to Screens and System
❑ Calling
❑ Display
❑ Audio
❑ Error Indications
❑ System Lights
❑ Network Interface Lights
Power and Start-up
Symptom Problem Corrective action
The system does not
start or respond in any
way
The system starts in the
software update screen
The system restarts over
and over
The power switch is off. Turn on the power switches for the system and any
equipment connected to it.
The power cord is not
connected.
The power outlet is not
active, or the system’s
power supply is not
operating properly.
The system software is
corrupted or not loaded
properly.
The power supply is bad. Return the system for service.
The socket is corroded. Unplug and resea t the power plug 5 times.
Make sure the power pack is connected to a power outlet,
and that its power cords are seated securely.
Check the power outlet by unplugging the system and
plugging in a lamp, radio, or other small appliance. If it
does not operate, the outlet is not active — connect the
system to a different outlet.
If the outlet is active, the problem is in the system’ s po wer
supply. In this case, call Polycom Technical Support and
arrange to return the system for service.
Load the system software from your PC. For instructions
on how to do this, refer to K eeping y our Softw are Current
on page 3-25.
7 - 8 www.polycom.com/videodocumentation
 Loading...
Loading...