Page 1

Deployment Guide for the Polycom® CX700 IP Phone
R2 | July 2010 | 1725-31424-001 Rev. A
Page 2

Trademark Information
POLYCOM®, the Polycom “Triangles” logo and the names and marks associated with Polycom’s products are
trademarks and/or service marks of Polycom, Inc. and are registered and/or common law marks in the United States
and various other countries. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners. No portion hereof may be
reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, for any purpose other than the recipient’s personal use, without
the express written permission of Polycom.
Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, Windows Server, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Office Communications Server, Office
Communicator, and Office Live Meeting are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries.
Patent Information
The accompanying product is protected by one or more U.S. and foreign patents and/or pending patent applications
held by Polycom, Inc. and/or one or more of its licensors.
Disclaimer
Some countries, states, or provinces do not allow the exclusion or limitation of implied warranties or the limitation of
incidental or consequential damages for certain products supplied to consumers, or the limitation of liability for personal
injury, so the above limitations and exclusions may be limited in their application to you. When the implied warranties
are not allowed to be excluded in their entirety, they will be limited to the duration of the applicable written warranty. This
warranty gives you specific legal rights which may vary depending on local law.
Copyright Notice
The software contained in this product may be copyrighted by Polycom and/or one or more of its licensors.
Copyright © 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 2009 Polycom, Inc.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDNG BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE
LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR
OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER
DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
© 2010 Polycom, Inc. All rights reserved.
Polycom, Inc.
4750 Willow Road
Pleasanton, CA 94588-2708
USA
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for
any purpose, without the express written permission of Polycom, Inc. Under the law, reproducing includes translating
into another language or format.
As between the parties, Polycom, Inc., retains title to and ownership of all proprietary rights with respect to the software
contained within its products. The software is protected by United States copyright laws and international treaty
provision. Therefore, you must treat the software like any other copyrighted material (e.g., a book or sound recording).
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this manual is accurate. Polycom, Inc., is not responsible
for printing or clerical errors. Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
ii
Page 3

About This Guide
Thank you for choosing the Polycom® CX700 IP phone which enables a new
era in unified communications currently unavailable with traditional desktop
phones. Connecting a Polycom CX700 to Microsoft® Office Communications
Server 2007 R2 allows you to place regular and Voice over Internet Protocol
(VoIP) calls, answer calls, forward calls, keep a record of all calls, start a
conference call, and click to call from a list of your personal contacts through
integration with Microsoft’s Active Directory and Microsoft Exchange Server.
Using your Polycom CX700 lets you take advantage of Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 R2 without needing access to a computer. For
more information on what’s new in Microsoft Office Communications Server
2007 R2, refer to
http://www.microsoft.com/communicationsserver/en/us/whats-new.aspx
This Deployment Guide provides everything you need to deploy the Polycom
CX700 in a standard Microsoft environment. Verify that the network is
prepared for deploying the Polycom CX700 IP phones with Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 R2, and your network is correctly configured.
Review the Polycom CX700 Quick Start Guide before you attempt to deploy the
phones. This information can also be found at
http://www.polycom.com/voicedocumentation/.
iii
Page 4

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
iv
Page 5

Contents
About This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iii
1 Deploying Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment . . . . . . . . . . . .1
DHCP and the Polycom CX700 IP Phone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
DHCP Search Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
DNS and the Polycom CX700 IP Phone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Polycom CX700 Phone Querying . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Exchange Server 2007 Autodiscover Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Polycom CX700 Phone Querying of Exchange Server 2007 . . . . . . . . . . 5
NTP and the Polycom CX700 IP Phone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
NTP Time Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Server Security Framework Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Root CA Certificate for the Polycom CX700 Phone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2 Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment . . . . . . . . . . .11
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Assumptions and Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Background . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Polycom CX700 Phone Upgrade Steps - Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Polycom CX700 Phone Upgrade Steps - Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Step 1 - Set Environmental Dependencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Step 2 - Upgrade Polycom CX700 Phones from 1.0.199.123 to
1.0.522.101 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Step 3 - Upgrade Polycom CX700 Phones from 1.0.522.101 to
3.5.6907.35 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3 Troubleshooting the Polycom CX700 Phone . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Logs Used for Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
When to Use DHCP Option 119 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
v
Page 6

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
Configuring Windows Server as an NTP Time Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Enabling Automatic Certificate Enrollment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Making the Root CA Certificate Available to a Polycom CX700 Phone . . 48
Installing a Public Root CA Certificate on a Polycom CX700 Phone . . . . . 49
Confirming the Current Software Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
vi
Page 7

Deploying Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
The Polycom® CX700 IP phone running Microsoft® Office Communicator
2007 R2 Phone Edition is an intelligent IP phone that is designed to get the
most out of the Microsoft unified communication platform. The Polycom
CX700 phone combines network voice, user-driven design, up-time reliability,
quality audio, and the improved communication and collaboration of
Microsoft® Office Communications Server 2007 R2.
1
To deploy and upgrade Polycom CX700 phones, you must:
• Configure a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server
• Configure a Domain Name Service (DNS) and add DNS SRV records
• Configure a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server
• Configure certificates for the phones
• Configure Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2
Topics in this section include:
• DHCP and the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
• DHCP Search Options
• DNS and the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
• NTP and the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
• Server Security Framework Overview
1
Page 8

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
For the most up-to-date version of the Deploying Microsoft Office Communicator
2007 R2 Phone Edition documentation and the complete set of the Microsoft®
Office Communications Server 2007 R2 online server and client documentation,
see the Office Communications Server TechNet Library at
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=132106.
DHCP and the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
All computers that are on a TCP/IP network must have an IP address for the
network to work correctly. Generally, you can manually configure IP
addresses at each computer, or you can install a Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) server that automatically assigns IP addresses to each client
computer or device on the network. The Polycom CX700 phone is no exception
and therefore can receive only DHCP-assigned IP addresses and requires no
configuration on the device.
A DHCP client is any network-enabled device that enables you to
communicate with a DHCP server to obtain dynamic, leased IP configuration
and related optional information. The Polycom CX700 phone is a DHCP client.
DHCP Search Options
To complete unqualified domain name system (DNS) names that will be used
to search and submit DNS queries at the client for resolution, you must have a
list of DNS suffixes that can be appended to these DNS names. For DHCP
clients, this can be set by assigning the DNS domain name option (Option 15)
and providing a single DNS suffix for the client to append and use in searches.
In some circumstances it is preferable that a DHCP client be configured by
using multiple DNS suffixes, supported with the use of DHCP Search Option
119.
DHCP Search Option 119 is passed from the DHCP server to the DHCP client
to specify the domain search list used when resolving hostnames with DNS.
DHCP Search Option 119 applies only to DNS and does not apply to other
name resolution mechanisms.
DHCP Option Description
015 Specifies the connection-specific DNS domain suffix to
119 DNS Domain Search List option to specify the domain
be used by the DHCP client.
search list used when resolving hostnames with DNS.
2
Page 9

Deploying Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
To enable search option 119 for Windows Server 2003 DHCP server:
1. Open DHCP. (To open DHCP, click Start, point to Settings, click Control
Panel, double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click DHCP.)
2. In the console tree, click the applicable DHCP server.
3. On the Action menu, click Set Predefined Options.
4. In Predefined Options and Values, click Add (Option Class Standard),
and then click OK.
5. In Name, type the string DNS Search List.
6. Set Code to 119 and Data Type string (it is not an array), and then click
OK.
7. Right-click Scope Options, select Configure Options, and then select 119
DNS Search List.
8. Enter a list of domain suffixes in your organization, delimited by a
semicolon (for example,
contoso.com;dev.contoso.com;corp.microsoft.com).
9. Click OK.
DNS and the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
The Polycom CX700 phone will process a number of DNS records in order to
locate the Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2.
Topics in this section include:
• Polycom CX700 Phone Querying
• Exchange Server 2007 Autodiscover Service
• Polycom CX700 Phone Querying of Exchange Server 2007
Polycom CX700 Phone Querying
The Polycom CX700 phone uses the following DNS domains when querying
information in DNS.
• SIP domain = Right side of sign-in address
• SMTP domain = Right side of primary e-mail address
If the query fails, the Polycom CX700 phone tries to look up the same record
with DNS suffix(es) appended.
• host.<SIP domain>
• host.<SIP domain>.<DNS suffix>
3
Page 10

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
When the Polycom CX700 phone connects to the Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 R2, it queries in the following order.
1. Hosts and port pointed to by these SRV records
— _sipinternaltls._tcp.<SIP domain>
— _sip._tls.<SIP domain>
— _sipinternal. tcp.<SIP domain>
2. sipinternal.<SIP domain>:5061
3. sipinternal.<SIP domain>:443
4. sip.<SIP domain>:5061
5. sip.<SIP domain>:443
6. sipexternal.<SIP domain>:5061
7. sipexternal.<SIP domain>:443
Exchange Server 2007 Autodiscover Service
Microsoft® Exchange Server 2007 includes a new Exchange service named the
Autodiscover service. The Autodiscover service configures client computers
that are running Microsoft® Office Outlook 2007. The Autodiscover service
can also configure supported mobile devices. The Autodiscover service
provides access to Exchange features for Outlook 2007 clients that are
connected to an Exchange messaging environment. The Autodiscover service
must be deployed and configured correctly for Outlook 2007 clients to
automatically connect to Exchange features, such as the offline address book,
the Availability service, and Unified Messaging (UM).
For more information, see the Exchange Server TechCenter topic How to
Configure Exchange Services for the Autodiscover Service at
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=141087.
Retrieving Outlook Contacts, Call Logs, and Voice Mail
The Polycom CX700 phone retrieves Outlook contacts, call logs, and voice
mails and displays them on the device. The Polycom CX700 phone does this
by accessing the Exchange Server 2007 Client Access Server (CAS) and
retrieving the information by using Exchange Web Services (EWS). The
Polycom CX700 phone locates the Exchange Server 2007 CAS by using an A
record that is in DNS. It uses the SMTP domain of the primary e-mail address
for the user to locate the A record. The primary e-mail address is sent to the
device during the sign-in process through in-band provisioning. The A record
it is querying is in the following order.
https://<SMTP domain>/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml,
https://autodiscover.<SMTP domain>/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml,
and http/ https redirect
4
Page 11

Deploying Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
Outlook 2007 uses Active Directory Service Connections Points (SCP) and
DNS SRV records to locate Exchange Server 2007 CAS. However, the device
does not support these additional methods.
The Autodiscover service finds and presents the various URLs that are used to
interact with Exchange Web Services and information about how to connect
Outlook 2007 to Exchange Server 2007. The device uses those URLs to retrieve
the Outlook contacts, call logs, and voice mails from Exchange Server 2007.
Polycom CX700 Phone Querying of Exchange Server 2007
The device must be able to resolve to the Exchange Web Services URL and
connect to it using HTTP or HTTPS.
If HTTPS is enabled, the certificate must be trusted by the device.
The Polycom CX700 phone tries to connects to the Exchange Server 2007
Autodiscover service in the following order:
• https://<SMTP domain>/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
• https://autodiscover.<SMTP domain>/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
• http -> https redirect
On successful response, the Polycom CX700 phone connects to the Exchange
Web Service URL in the Autodiscover response XML.
The certificate from Exchange Server 2007 must be trusted.
NTP and the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is the default time synchronization protocol
that is used by the Windows Time service in Windows Server 2003. NTP is a
fault-tolerant, highly scalable, time protocol that is used most frequently for
synchronizing computer clocks. It does this by using a designated time
reference. The Polycom CX700 phone requires NTP to set the correct time and
date for the Polycom CX700 phone.
NTP Time Provider
The NTP provider is the standard time provider that is included with
Windows Server 2003. The NTP provider in the Windows Time service
consists of the following two parts:
• NtpServer output provider. This is a time server that responds to client
time requests on the network.
• NtpClient input provider. This is a time client that obtains time
information from another source, either a hardware device or an NTP
server, and can return time samples that are useful for synchronizing the
local clock.
5
Page 12

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
Although the actual operations of these two providers are closely related, they
appear independent to the time service. By default, when a computer that is
running Windows Server 2003 is connected to a network, it is configured as an
NTP client.
The Polycom CX700 phone searches for a NTP server in DNS as follows:
• NTP SRV record (UDP port 123)
— _ntp._udp.<SIP domain> pointing to NTP server
If it cannot find the NTP SRV record, it will try to use windows.com as an NTP
server:
• NTP A record
— time.windows.com
To set Group Policy for Windows Time Service global configuration settings:
1. From the MMC, click Active Directory Users and Computers.
2. Right-click the domain that contains the NTP server, and then select
Properties.
3. Click the Group Policy tab, make sure that the Default Domain Policy is
highlighted, and then click Edit.
4. Click Computer Configuration, click Administrative Templates, click
System, and then click Windows Time Service.
5. Click Time Providers and in the right pane, double-click Enable
Windows NTP Server, select the Enabled button, and then click OK.
6. From the Group Policy Object Editor menu, select File, and then click
Exit.
Server Security Framework Overview
The following section summarizes the elements that form the security
framework for Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2. It is helpful
to understand how these elements work together when you deploy the
Polycom CX700 phone in your organization.
These security elements are as follows:
• Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) provides a single trusted,
back-end repository for user accounts and network resources.
• PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) uses certificates that are issued by trusted
CAs (certificate authorities) to authenticate servers and to help ensure data
integrity.
6
Page 13

Deploying Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
• TLS (Transport Layer Security) and MTLS (Mutual Transport Layer
Security) enable endpoint authentication and instant messaging (IM)
encryption. Media streams are encrypted by using Secure Real-time
Transport Protocol (SRTP).
These fundamental elements work together to define trusted users, servers,
and connections. The resulting trust relationships provide the foundation on
which the complete Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 security
framework is built.
Root CA Certificate for the Polycom CX700 Phone
Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 relies on certificates to
authenticate servers and to establish a chain of trust between clients and
servers and among the different server roles. By default, communication
between the Polycom CX700 phone and Office Communications Server 2007
R2 is encrypted by using TLS and SRTP. Therefore, the device must be able to
trust certificates presented by Office Communications Server 2007 R2 servers.
A means must always exist for the VoIP client to create the TLS secured
connection that is required for audio communication on the network.
Publicly Hosted Certificate Authority Solution
If Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 servers use public
certificates, the certificates will most likely be automatically trusted by the
device, because the device contains the same list of trusted CAs as Windows
CE. The table at the end of this topic lists the public certificates that are trusted
by the Polycom CX700 phone.
Privately Hosted Certificate Authority Solution
Most Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 deployments use
internal certificates for the internal Office Communications Server 2007 R2
server roles. In these types of deployments, the Root CA certificate must be
installed from the internal CA to the device. Because you cannot manually
install the Root CA certificate on the device, the certificate must be
downloaded to the device through the network.
The Polycom CX700 phone downloads the certificate using the following
methods:
1. The device searches for Active Directory directory objects of category
certificationAuthority. If the search returns any objects, the device will
use the attribute caCertificate. This attribute is assumed to hold the
certificate and the device will install the certificate.
The Root CA certificate must be published in the caCertificate for the
Polycom CX700 phone. To place the Root CA certificate in the caCertificate
attribute, use the following command:
certutil -f -dspublish <Root CA certificate in .cer file> RootCA.
7
Page 14

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
2. If the search for Active Directory objects of category
CertificationAuthority does not return any objects, or if the objects have
empty caCertificate attributes, the device searches for Active Directory
objects of category pKIEnrollmentService in the configuration naming
context. Such objects exist if certificate AutoEnrollment was enabled in
Active Directory. If the search returns any objects, it will use the
dNSHostName attribute returned to reference the CA and it will then use
the Web interface of the Microsoft Certificates Service to retrieve the Root
CA certificate by using the HTTP GET command
http://<dNSHostname>/certsrv/certnew.p7b?ReqID=CACert&Renewa
l=-1&Enc=b64
If neither of these methods succeeds, the device displays the error message
“Cannot validate server certificate” and the user is unable to use the device.
Polycom CX700 Phone Certificates
The following is a list of considerations for issuing certificates to the Polycom
CX700 phone.
• By default, the uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Real-time
Transport Protocol (SRTP).
.
— Requirement: Trust certificates presented by Office Communications
Server 2007 R2 and Exchange Server 2007 server.
— Requirement: Root certification authority (CA) chain certificate
resides on the device.
• No manual installation of certificate on device is possible.
• Options:
— Use public certificates
— Preloaded public certificates on device
— Use of enterprise certificates
— Receive the Root CA chain from the network
Enterprise Root CA Chain
The Polycom CX700 phone can find the certificate by using either the public
key infrastructure (PKI) PKI auto-enrollment object in Active Directory
Domain Services or through a well-known distinguished name (DN).
• Enable PKI auto-enrollment through Enterprise CA.
— Device makes an LDAP request to find pKIEnrollmentService/CA
server address and eventually download the certificate over HTTP to
Windows CA /certsrv site by using the users credentials.
• Use certutil -f -dspublish .cer file location" RootCA to upload certificates
to the Configuration NC.
8
Page 15
Deploying Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
— Cn=Certificate Authorities, cn=Public Key Services, CN=Services,
cn=Configuration, dc=<AD Domain>
The LDAP request is BaseDN: CN=Configuration, dc= <Domain> Filter:
(objectCategory=pKIEnrollmentService) and searched for attribute is
dNSHostname. Be aware that the device downloads the certificate by using
HTTP get http://<dNSHostname>/certsrv/certnew.p7b?ReqID=CACert&Renewal=-1
&Enc=b64.
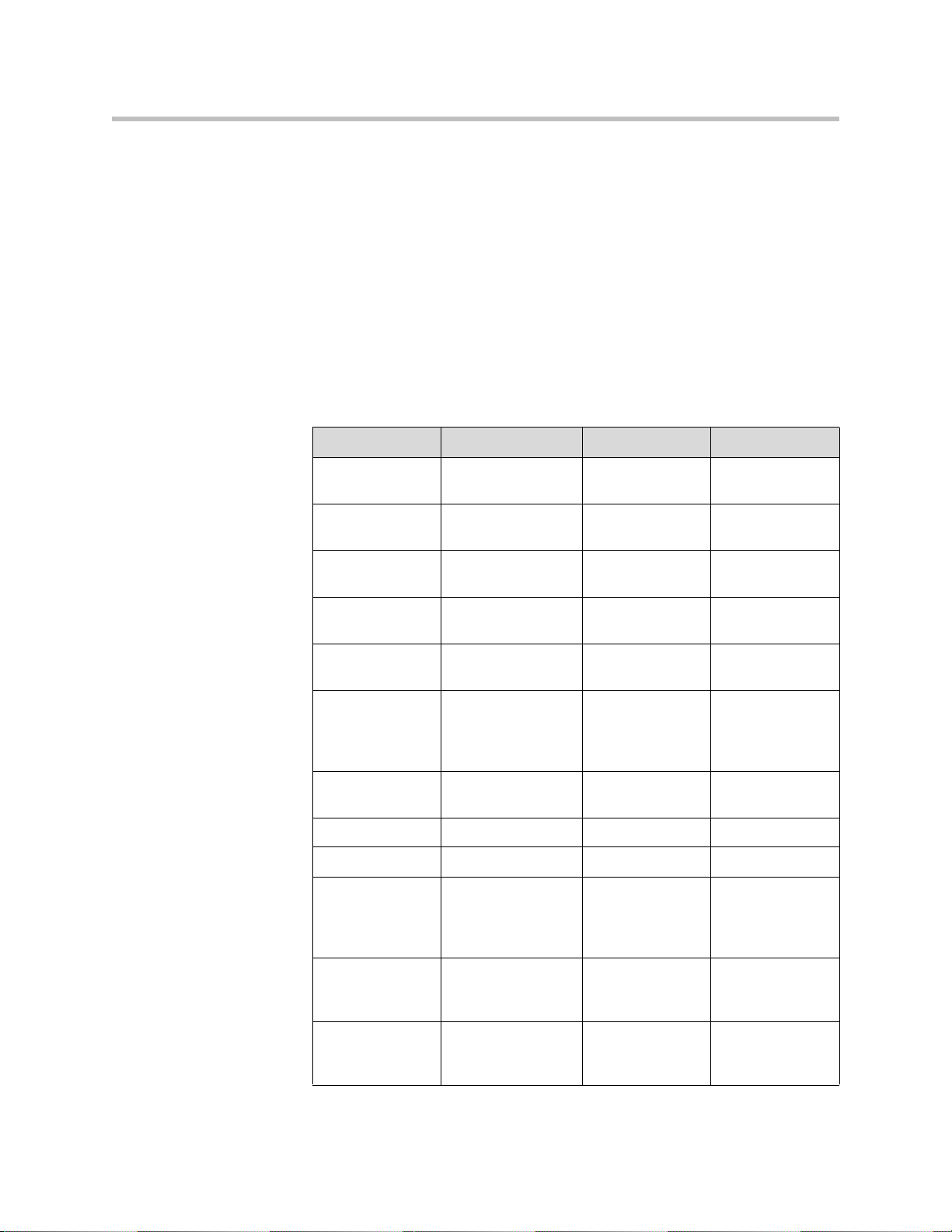
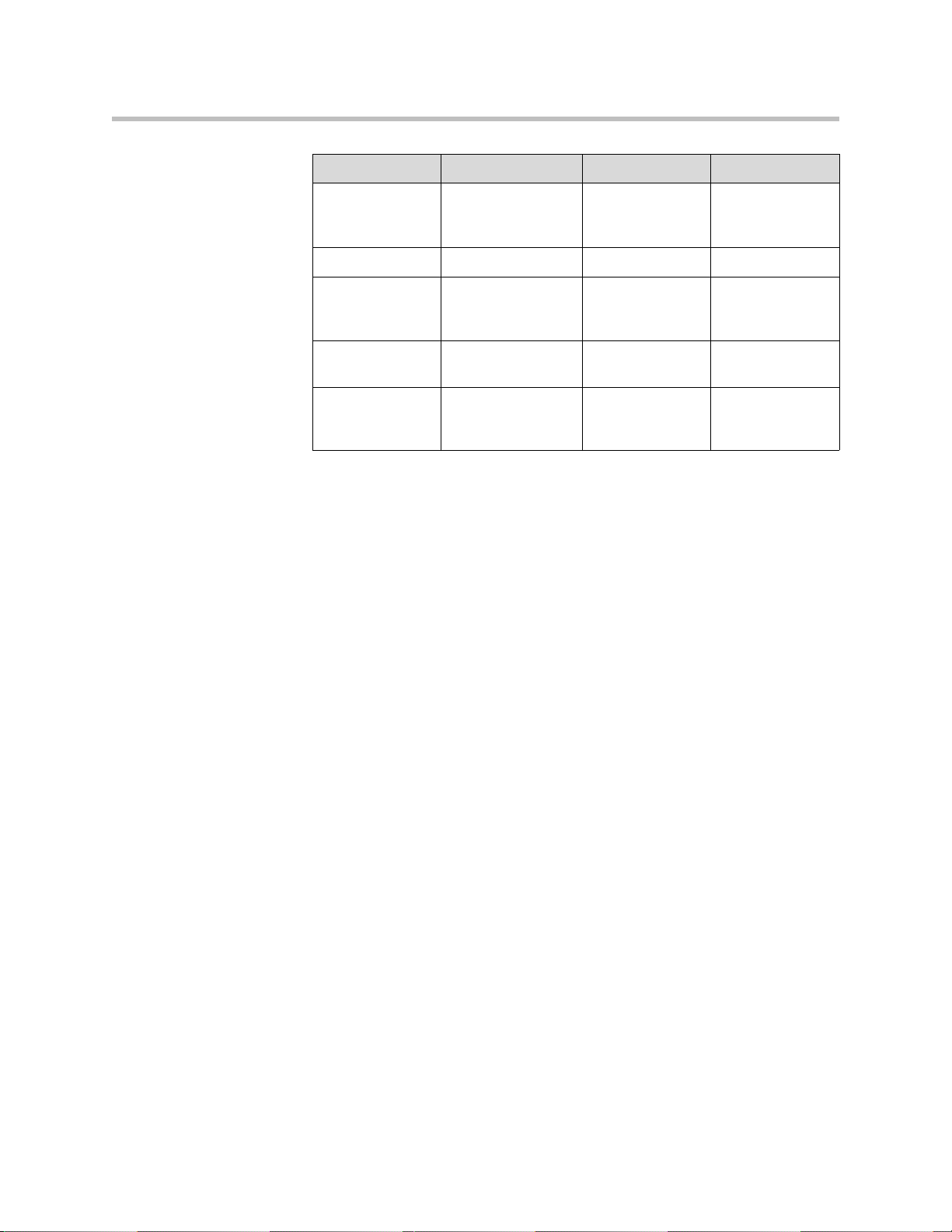
Trusted Authorities Cache
The following table lists the public certificates that are trusted by the Polycom
CX700 phone.
Vendor Certificate Name Expiry Date Key Length
Comodo AAA Certificate
Services
Comodo AddTrust External
CA Root
Cybertrust Baltimore
CyberTrust Root
Cybertrust GlobalSign Root
CA
Cybertrust GTE CyberTrust
Global Root
VeriSign Class 2 Pub lic
Primary
Certification
Authority
VeriSign Thawte Premium
Server CA
VeriSign Thawte Server CA 12/31/2020 1024
VeriSign Comodo 1/7/2010 1000
VerSign Class 3 Public
Primary
Certification
Authority
12/31/2020 2048
5/30/2020 2048
5/12/2025 2048
1/28/2014 2048
8/13/2018 1024
8/1/2018 1024
12/31/2020 1024
8/1/2028 1024
Entrust Entrust.net
Certification
Authority (2048)
Entrust Entrust.net Secure
Server Certification
Authority
9
12/24/2019 2048
5/25/2019 1024
Page 16
Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
Vendor Certificate Name Expiry Date Key Length
Equilax Equifax Secure
8/22/2018 1024
Certification
Authority
GeoTrust GetTrust Global CA 5/20/2022 2048
GoDaddy GoDaddy Class 2
6/29/2034 2048
Certification
Authority
GoDaddy http//www.valicert.c
6/25/2019 1024
om/
GoDaddy Starfield Class 2
6/29/2034 2048
Certification
Authority
10
Page 17

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
This chapter detailed instructions on how to upgrade Polycom CX700 IP
Phone. Due to a number of issues, the upgrade may be a two-step process,
which includes a hard reset of the phone to remove any pre-existing phone
credentials, certificates chains, and URLs.
2
Topics in this chapter include:
• Introduction
• Polycom CX700 Phone Upgrade Steps - Summary
• Polycom CX700 Phone Upgrade Steps - Details
A list of frequency asked questions can be found in Troubleshooting the
Polycom CX700 Phone on page 3-39.
11
Page 18

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
Introduction
The Polycom® CX700 IP Phone may contain one of the following software
releases:
Software Releases
1.0.199.123 OCS 2007 (R1)—software on phones
1.0.522.101 OCS 2007 (R1)—download from
3.5.6907.35 OCS 2007 (R2)—download from
This section will focus on upgrading the Polycom CX700 phone from
1.0.199.123 to 1.0.522.101 and then to 3.5.6907.35 using an Office
Communications Server 2007 R2 Device Update service.
If any of the Polycom CX700 phones are running a software release earlier than
1.0.199.123, it may be necessary to install an R1 Update Server to update to
1.0.199.123. If the phone is already running 1.0.199.123, the upgrade process to
1.0.522.101,and then 3.5.6907.35 can be performed using an Office
Communications Server 2007 R2 Device Update service only. It is not possible to
upgrade directly from 1.0.199.123 to 3.5.6907.35—due to 1.0.199.123 software
limitations.
Corresponding Microsoft Office
Communications Server (OCS) 2007
Microsoft web site
Microsoft web site
The Polycom CX700 phone software updates behaves differently in terms of
environmental dependencies and how the device locates firmware updates.
Version 1.0.199.123 is the least tolerant of variations in the environment.
Topics in this section include:
• Assumptions and Terminology
• Background
Assumptions and Terminology
Terminology
When referring to signing in to the Polycom CX700 phone, the following
format will be used:
Sign-in address: userAlias@SIPDomain
Domain\User name: DomainFQDN\userAlias
For example:
12
Page 19

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
Sign-in address: ocstest1@fabrikam.com(fabrikam.com represents
<SIPDomain> in this document)
Domain\User name: contoso.com\ocstest1(contoso.com represents
<DHCPDomain> in this document)
<SIPDomain> and <DHCPDomain> are used as placeholders to distinguish
between the domain used in the Sign-in address: list box and the domain
specified in the Domain\User name: list box:
• <SIPDomain>
This is the SIP domain of the user that’s signing into the OCPE device and
is the same one they use when signing into their MOC client.
• <DHCPDomain>
This is the domain assigned by DHCP Option 015 DNS Domain Name and
is usually the NetBIOS name of the domain containing the pool running
the Device Update service. Domain\User name is analogous to the
account the user signs in to Active Directory with.
In some environments the <SIPDomain> and <DHCPDomain> values will be the
same but they are purposely kept different in the examples used here to highlight
the issues that arise as a result of them being different.
For example; depending on the firmware version, a phone will look in <SIPDomain>
for the _ntp._udp SRV record but in <DHCPDomain> for locating a domain
controller to use for LDAP queries. And to make it more confusing, and the phone
will occasionally query DNS using a combination of <SIPDomain>.<DHCPDomain>
(e.g., _sipinternal._tcp.fabrikam.com.contoso.com) as sort of a catchall query.
Although some phone queries concatenate <SIPDomain> and <DHCPDomain> It
is not necessary to create any corresponding concatenated DNS records in order to
upgrade a Polycom CX700 phone. Refer to the table in Step 1.2 - Configure DNS
on page 2-24 for external DNS requirements.
13
Page 20

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
The Polycom CX700 phone reset options are as follows:
• Power cycle— Reboot the phone by removing and then reapplying power
• Soft Reset—Press the reset button on the back of the phone just long
enough to reset it
• Hard Reset - Unplug the phone, use a paper clip to press and hold the reset
button (small hole on back between USB and Headphone jack), reapply
power (while continuing to hold down the reset button) until the scroll bar
on the display goes all the way across the screen. Then release the reset
button and within 30 to 120 seconds, the display should change to the
white calibration screen with the large plus sign in the center.
This process removes any credentials, certificate chains and XML
configuration files and restores the phone to factory defaults.
The first time a user powers up the phone and signs in, the phone gets in-band
provisioning information from the server or Enterprise pool hosting the user's
account. The information contains the internal and external URL of the server
running Device Update Service.
For example, this is the payload from a packet returned by the pool indicating
the location of the cpe.nbt file for both internal and external phones (some code
has been removed for clarity):
Http: Response, HTTP/1.1, Status Code = 200, URL:
/RequestHandler/ucdevice.upx
ProtocolVersion: HTTP/1.1
+ Element: XmlElement:<FileName> - CPE.nbt
+ Element: XmlElement:<SignatureFileName> - CPE.cat
+ Element: XmlElement:<DescriptFile> - CPE_desc.xml
+ Element: XmlElement:<BaseURL> -
14
Page 21

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
http://POOL01.contoso.com/DeviceUpdateFiles_Int/UCPhone/Polycom/CX
700/A/ENU/1.0.522.101/CPE
+ Element: XmlElement:<ExternalBaseURL> https://ocsrp.fabrikam.com/DeviceUpdateFiles_Ext/UCPhone/Polycom/C
X700/A/ENU/1.0.522.101/CPE
Scenario
The upgrade instructions in this document assume the following conditions:
• Starting state for a Polycom CX700 phone is software release 1.0.199.123
• Test account is OCSTest1 (for example, ocstest1@fabrikam.com)
• Pool running Device Update Service is pool01.contoso.com
• Test Device is Tanjay01
• Domain Controller is dc01.contoso.com
• DHCP / DNS / WINS / Certificate Authority / NTP run on the domain
controller
• There is an internal DNS zone called fabrikam.com (i.e., the
<SIPDomain>) created manually and populated with autodiscover
(pointed to Exchange UM) and sip A records. It also contains
_sipinternaltls._tcp and _ntp._udp SRV records.
Background
• There is an Active Directory DNS zone called contoso.com (i.e., the
<DHCPDomain>) and created automatically during setup. It will contain
the pool and ucupdates-r2 A records at a minimum. It also hosts all
machine accounts.
• There are corresponding external DNS zones for contoso.com and
fabrikam.com.
• There is a reverse proxy that is publishing the pool locations for
DeviceUpdateFiles_Ext and RequestHandlerExt (refer to Device Update
File Storage on page 2-16).
• Software release 1.0.522.101 is set to “Approved” and software release
3.5.6907.35 is set to “Pending”. To upgrade from 1.0.522.101 to 3.5.6907.35,
the phones are added to the Test Devices tab to limit the upgrade to just
the targeted devices.
When trying to figure out why one or more steps in the upgrade process are
not working, it is helpful to know how it is supposed to work. This section
provides a brief explanation of the components involved and how a Polycom
CX700 phone interacts with DNS, Pool, Web Components service and the
Device Update service.
15
Page 22

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
Device Update File Storage
During Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 installation, Device
Update Service is automatically installed on all servers running the Web
Components Server role. You do not need to plan for additional servers to
support Device Update Service.
Device Update Service uses a number of files that must be stored on a file
system. The location is different, depending on which edition of Office
Communications Server 2007 R2 you are running.
• Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Enterprise Edition.
Before running the Create Enterprise Pool wizard during deployment,
you must create a shared folder for both client and device update files.
Device Update Service creates folders within this shared folder in which
to store update image files, log files, and configuration files. The shared
folder will also be used by Office Communications Server for storing
Office Communicator update files. During installation you will need to
provide the UNC path of this folder.
For example, if you specified Pool01Data during setup, the path would be:
C:\Pool01Data\ClientUpdateStore\DeviceUpdates
• Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Standard Edition. The
installer automatically creates the DeviceUpdateFiles folder in the Web
Components folder under the Office Communications Server 2007 R2
installation folder on the local computer. This folder is not shared, and it
inherits the permissions of the installation folder. Device Update Service
creates folders within the DeviceUpdateFiles folder in which to store
update image files, log files, and configuration files.
16
By default:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
R2\Web Components\DeviceUpdateFiles\DeviceUpdates
Two virtual directories in Internet Information Services (IIS) refer to these
folders:
• The DeviceUpdateFiles_int virtual directory points internal devices to the
updates folder.
• The DeviceUpdateFiles_ext virtual directory points external devices to the
updates folder.
By default, the built in group Users (for example,
Pool01\Users
) is issued
Read & execute, List folder contents and Read access to the
DeviceUpdateFiles_Int and DeviceUpdateFiles_Ext virtual directories (and
everything below) in IIS 7.0.For more information, refer to Logs Used for
Troubleshooting on page 3-40.
Page 23

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
How Polycom CX700 Phones Connect to the Device Update Service
At a high level, a Polycom CX700 phone using the default configuration
connects to the Microsoft Office Communications Server (OCS) 2007 R2 Device
Update Service in the following way:
1. When a user signs in to an OCPE device, the device contacts the server or
pool hosting the corresponding user account to obtain in-band
provisioning information that includes the internal and external URL of
the IIS server running the Device Update Service.
If the device is turned on, but no user signs on, and no user has ever
previously signed on to the device (or a hard reset is performed) AND it's
running either version 1.0.522.101 or 3.5.6907.35; the device sends a DNS
lookup request to ucupdates-r2.<DHCPDomain> to obtain the FQDN of
the pool server running Device Update Service.
Software release 1.0.199.123 does not check for a DNS A record called
“ucupdates.<DHCPDomain>”. The check was disabled for this particular software
release so the only option for obtaining the FQDN of the Device Update service is
via in-band provisioning; which only occurs by signing in to the phone.
Thereafter, when the phone is turned on or every 24 hours by default, the
phone queries DNS for ucupdates-r2.<DHCPDomain> and sends an
HTTP POST request over port 80 to the IP Address returned. The request
(for example, http://192.168.7.81/RequestHandler/ucdevice.upx) is sent
to the Web Components Server hosting the Device Update Service and
includes the MAC address and serial number of the phone issuing the
request.
If you sign in to the phone, this will be a DNS query for an A record called
ucupdates-r2.<DHCPDomain> which returns the pool IP address.
1. The Microsoft Office Communications Server (OCS) 2007 R2 Device
Update Service returns a response containing one of the following:
• If no updates exists for the current version, the response contains
downloads=0. For test devices, updates must be “Pending” rather than
“Approved” for this to occur.
• If an approved update exists for the current version, the response contains
an internal and external URL for Device Update Service. For test devices,
updates must be “Pending” rather than “Approved” for this to occur.
In the latter case, the phone sends an HTTP update request over port 80 to
the Device Update Service unless the device is remote; in that case HTTPS
over port 443 is used.
17
Page 24

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
2. If the phone determines it is running a down level version of firmware it
issues either an HTTP or HTTPS GET request to the pool hosting the
Device Update Service:
http://192.168.7.81/DeviceUpdateFiles_Int/UCPhone/Polycom/CX700
/A/ENU/1.0.522.101/CPE/CPE.nbt
https://63.123.155.6/DeviceUpdateFiles_Int/UCPhone/Polycom/CX70
0/A/ENU/1.0.522.101/CPE/CPE.nbt
Where 192.168.7.81 is the internal pool IP address and 63.123.155.6 is the
reverse proxy address defined in WMI as the ExternalBaseURL value.
3. The image is downloaded to the device using HTTP (80) internally or
HTTPS (443) externally.
4. The phone waits for five minutes of idle activity, and then restarts.
5. When restart is complete, the phone is updated but will need to be
recalibrated before use.
Detailed Polycom CX700 Phone Upgrade Sequence When Running Software
Release 1.199.123
The following steps occur when you sign in to a Polycom CX700 phone
running software release 1.199.123. This assumes that the Sign-in address: value
is ocstest1@fabrikam.com and the Domain\User Name: value is
contoso.com\ocstest1 .
Action Examples / Comments
1. Obtain DHCP address
2. Query DNS for time.windows.com and
time.windows.com.<DHCPDomain> A records
3. Polycom CX700 phone sends it’s time to NTP
server time.windows.com
4. DHCP server confirms lease
5. Polycom CX700 phone queries DNS for
_ntp._udp.<SIPDomain> SRV record
6. Polycom CX700 phone queries DNS for DC
(specified in DHCP DomainNameServer attrib.)
dc01.<DHCPDomain> A record
7. Polycom CX700 phone queries DNS for SRV / A
records in this order (returns Success or Name
Error for each query)
(time.windows.com.contoso.com)
(_ntp._udp.fabrikam.com)
(dc01.contoso.com)
• Query DNS for _sipinternaltls._tcp. <SIPDomain>
SRV record
• Query DNS for pool01.<DHCPDomain> A record (pool01.contoso.com) / _sipinternaltls points to
18
(_sipinternaltls._tcp.fabrikam.com)
pool01
Page 25

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
• Query DNS for _sipinternal._tcp. <SIPDomain>
SRV record
• Query DNS for _sipinternal._tcp.
<SIPDomain>.<DHCPDomain> SRV record
• Query DNS for _sip._tls. <SIPDomain> SRV
record
• Query DNS for _sip._tls.
<SIPDomain>.<DHCPDomain> SRV record
• Query DNS for _sip._tcp. <SIPDomain> SRV
record
• Query DNS for _sip._tcp.
<SIPDomain>.<DHCPDomain> SRV record
• Query DNS for sip.<SIPDomain> A record; IP
address of pool is returned
8. Polycom CX700 phone queries DNS for
poolFQDN and is returned the pool’s IP address
9. Polycom CX700 phone initiates TLS connection
to pool IP Address specifying which Ciphers are
supported
10. Pool responds with Certificate detail; they
exchange keys if handshake is OK
(_sipinternal._tcp.fabrikam.com)
(_sipinternal._tcp.fabrikam.com.contoso.com)
(_sip._tls.fabrikam.com)
(_sip._tls.fabrikam.com.contoso.com)
(_sip._tcp.fabrikam.com)
(_sip._tcp.fabrikam.com.contoso.com)
(sip.fabrikam.com)
(Client Hello)
(Note: SHA2 is not supported)
(Server Hello) Note: TLS connection is not
established yet.
11. Polycom CX700 phone queries <DHCPDomain>
for AD LDAP service using DC provided by
DHCP
12. Polycom CX700 phone binds to AD and looks for
RootCA in <DHCPDomain>
13. DC responds with RootCA details. If the Pool cert
was issued by the RootCA returned, we proceed.
14. Polycom CX700 phone queries DNS for
<DHCPDomain> and is returned the domain’s IP
address
•Note: this is why we sign in as
contoso.com\userAlias instead of just
contoso\userAlias.
• This step must return a valid IP in order to find a
DC again and download the certificate chain.
15. Polycom CX700 phone locates RootCA again in
<DHCPDomain>
16. Polycom CX700 phone attempts HTTP request
to download RootCA cert chain using NTLM
(_ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.contoso.com)
(OCPE binds using Auth type SASL)
(contoso.com)
(contoso.com)
(NTLM Auth fails)
19
Page 26

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
17. Polycom CX700 phone attempts HTTP request
to download RootCA cert chain using Kerberos
(SPNEGO)
18. Polycom CX700 phone attempts HTTP request
to download RootCA cert chain using Kerberos
(SPNEGO) w/different key
19. DC streams Base64 certificate chain to Polycom
CX700 phone via HTTP
20. Polycom CX700 phone initiates a TLS
connection to the pool’s IP address with the
Ciphers it supports
21. Pool responds with negotiated Cipher spec to
complete the TLS handshake
22. Polycom CX700 phone queries DNS for
autodiscover.<SIPDomain> A record
23. Polycom CX700 phone initiates TLS connection
with Exchange 2007 CAS
24. Polycom CX700 phone sends HTTP 80 POST to
pool.<DHCPDomain> for
/RequestHandler/ucdevice.upx
•Note: This would be an HTTPS 443 POST to
pool.<DHCPDomain> for
/RequestHandlerExt/ucdevice.upx for an external
OCPE device
(Kerberos Auth fails)
(Kerberos Auth succeeds)
(URL: /certsrv/certnew.p7b, Using SPNEGO
Authentication)
(Client Hello) Note: SHA2 is not supported
(Server Hello) Note: TLS connection is now
established.
(fabrikam.com) Returns IP address of Exchange CAS
if configured.
(Used for missed call notification)
(Payload contains phone vendor info)
25. Pool responds with current firmware upgrade
version and Internal / External file path info
(These values are blank if WMI settings were not
populated)
• <BaseURL> http://pool01.contoso.com/DeviceUpdateFiles_Int/UCPhone/Polycom/CX700/A/ENU/1.0.522.101/CPE
• <ExternalBaseURL> https://ocsrp.fabrikam.com/DeviceUpdateFiles_Ext/UCPhone/Polycom/CX700/A/ENU/1.0.522.101/CPE
26. Polycom CX700 phone issues an HTTP GET for CPE file if it’s newer than the currently installed version
• (HTTP:Request, GET
/DeviceUpdateFiles_Int/UCPhone/Polycom/CX700/A/ENU/1.0.522.101/CPE/CPE.nbt)
27. Pool begins streaming CPE.nbt to Polycom
(You will see a lot of TCP traffic)
CX700 phone as a binary/octet-stream (approx.
15MB)
28. Polycom CX700 phone issues one last HTTP Get
(Success!!)
and the pool responds with 200 to indicate
download is complete
20
Page 27

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
When looking through a NetMon trace from an upgrade to 1.0.522.101, you may
notice that the DNS query for ucupdates-r2.<DHCPDomain> does not occur until
the CPE.NBT file had already started streaming to the OCPE device. This happens
when you sign into the phone prior to the upgrade starting; if you do not sign in, the
DNS query would have occurred at the beginning of the trace.
Polycom CX700 Phone Upgrade Steps - Summary
If your environmental dependencies are close to being set and you just want a
high level checklist of the steps involved in configuring Microsoft Office
Communications Server (OCS) 2007 R2 to upgrade from release 1.0.199.123 to
1.0.522.101 and then to 3.5.6907.35, the following is a summary of the steps. For
more details, refer to the next section, Polycom CX700 Phone Upgrade Steps -
Details.
1. Set Environmental Dependencies
a Configure DHCP
— Set Option 006 = the IP Address of internal DNS server
— Set Option 015 = the <DHCPDomain> (contoso.com is used in the
example)
— Optional; set Option 119 = FQDN of any domain containing users that
may connect using and Polycom CX700 phone as well as the domain
containing the pool running Device Updater
b Configure DNS for <SIPDomain> (fabrikam.com is used in the
example)
Add A records for:
— autodiscover.fabrikam.com pointed to the IP address or the
Exchange CAS server used by OCS
— sip.fabrikam.com pointed to the IP address of the pool running
Device Updater
Add SRV records for:
— _sipinternaltls._tcp .fabrikam.com pointed to the FQDN of pool
running Device Update service on port 5061
— _ntp._udp. fabrikam.com pointed to the FQDN of NTP server
(typically time.windows.com but can be any NTP server FQDN)
on port 123
If upgrading Polycom CX700 phones remotely, refer to the table in Step 1.2 -
Configure DNS on page 2-24 for external DNS requirements.
21
Page 28

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
c Configure DNS for <DHCPDomain> (contoso.com is used in the
example)
Add A records for:
— yourPoolName.contoso.com pointed to the IP address of the pool
— ucupdates-r2.contoso.com pointed to the IP address of the pool
Add SRV records for
— No SRV records required
If upgrading Polycom CX700 phones remotely, refer to the table in Step 1.2 -
Configure DNS on page 2-24 for external DNS requirements.
d Configure Certificates
running Device Update service
running Device Update service. If you currently have a
ucupdates.<DHCPDomain> A record, it can be deleted if all your
Polycom CX700 phones are release 1.0.199.123 or later.
— If using a W2K8 / W2K3 Enterprise CA, the RootCA certificate chain
should already be published but you can confirm that using the steps
in Enabling Automatic Certificate Enrollment on page 3-45.
— If using a W2K8 / W2K3 Standard CA, use certutil -f to upload
certificate chain and then confirm that it was successfully published it
is present using the steps in Enabling Automatic Certificate
Enrollment on page 3-45. Or alternatively, you can enable Auto
Enrollment.
2. Configure Microsoft Office Communications Server (OCS)
On the pool running the Device Update service:
— Modify the Client Version filter to allow “OCPhone” devices equal to
or greater than (=>) release 1.0.199.* .
If you get the error "Cannot sign in. You do not have the necessary permissions.
Contact your system administrator." when trying to authenticate it is probably
related to the Client Version filter not being set properly.
— Modify Device Update Service External URLs (required even if
upgrading Polycom CX700 phones internally).
3. Upgrade Polycom CX700 phone from release 1.0.199.123 to 1.0.522.101
22
— Download the latest build 522 ucupdates.exe file
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=eeb
1b339-df7e-486f-a47a-23d7ed8be6fd&DisplayLang=en, expand the
CAB file, upload and approve it using Device Updater.
Page 29

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
— Performs a hard reset, and then recalibrate the phone.
— Sign-in to the Polycom CX700 phone using your SIP URI for the
Sign-in Address value and your domain FQDN for the Domain\User
name value (e.g., ocstest1@fabrikam.com and contoso.com\ocstest1
respectively).
4. Upgrade Polycom CX700 phone from release from 1.0.522.101 to
3.5.6907.35
— Download the latest build 6907 ucupdates.exe file
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=5655
95be-6cf3-4a61-a1e4-12555749ca64&displaylang=en&tm, expand the
CAB file, upload and leave it as “Pending” using Device Updater.
— Add the MAC address of the phone you are upgrading to release
3.5.6907.35 . (Later you can make 3.5.6907.35 approved but there may
be existing phones with release 1.0.522.101 that you do not want
upgraded to 3.5.6907.35 and this approach allows you to control
which phones are upgraded.)
— When upgrading from 1.0.199.123 to 1.0.522.101, a ucupdates.XML file
is copied to the Polycom CX700 phone and it should not be necessary
to sign back in, but you will want to power cycle the phone to start the
upgrade.
if you do a hard reset, you will wipe the ucupdates.xml file and will need to sign in to
the Polycom CX700 phone to trigger the upgrade to 3.5.6907.35 . You may also
have to wait 15 minutes for the update to begin.
— If you do sign-in to the Polycom CX700 phone, use your SIP URI for
the Sign-in Address value and your domain FQDN for the
Domain\User name value (for example, ocstest1@fabrikam.com and
contoso.com\ocstest1 respectively).
— The Polycom CX700 phone should upgrade to 3.5.6907.35 at this point.
Polycom CX700 Phone Upgrade Steps - Details
Use the detailed steps in this section if you are just getting started with
configuring Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 to upgrade
Polycom CX700 phones.
Step 1 - Set Environmental Dependencies
Prior to upgrading the Polycom CX700 phone’s software, there are certain
environmental dependencies that must be in place. Some dependencies are
only required for upgrading from 1.0.199.123 to 1.0.522.101 or are considered
optional and will be noted as such.
23
Page 30

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
Step 1.1 - Configure DHCP
The first step is to make sure the Polycom CX700 phone can get an IP address
and the necessary DNS (and potentially WINS) information it needs to locate
a time service, certificate chain and pool running the Device Update service.
The figure below shows both WINS and DHCP Option 119 configured but
typically you will only configure Option 119 and leave the WINS scope
options out.
Polycom CX700 phones look for a WINS entry matching the NetBIOS name of
<DHCPDomain> (for example, CONTOSO or CONTOSO.COM if you sign in using
the domain FQDN in the Domain\User name: field). All examples in this document
were done using the domain FQDN (so WINS was not used).
If the <SIPDomain> value that users sign in to their Polycom CX700 phones
with is different than the domain where their domain controller is located, you
can configure DHCP Option 119 to include a list of all the domains to check for
a DC. For instructions on configuring Option 119, refer to How to Configure
DHCP Option 119 on page 3-43.
Step 1.2 - Configure DNS
The following DNS records are required for upgrading but some are only
required for a specific phase (for example, ucupdates-r2 is only used from
1.0522.101 to 3.5.6907.35):
24
Page 31

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
DNS Type Name Port IP Address / FQDN
Internal Zone
<SIPDomain>
Internal Zone
<DHCPDomain>
External Zone
<SIPDomain>
A sip.<SIPDomain> N/A IP/VIP of Pool running Device
Update.
A autodiscover.<SIPDomain> N/A Internal IP/VIP of Exchange
server running CAS role. Note:
this assumes SIP URI matches
the user’s Primary SMTP
address in Exchange.
SRV _sipinternaltls._tcp.<SIPDomain> 5061 FQDN of Pool containi n g user(s)
signing into the OCPE device
being upgraded.
SRV _ntp._udp.<SIPDomain> 123 time.windows.com or FQDN of
internal or external time source
A ucupdates-r2.<DHCPDomain> N/A IP/VIP of Pool running Device
Update.
A poolName.<DHCPDomain> N/A IP/VIP of Pool running Device
Update.
A sip.<SIPDomain> N/A External IP/VIP of Access Edge
server.
A autodiscover.<SIPDomain> N/A External IP/VIP of Exchange
server running CAS role. Note:
this assumes SIP URI matches
the user’s Primary SMTP
address in Exchange.
External Zone
<DHCPDomain>
A reverseProxyFQDN.<SIPDomain> N/A IP of reverse proxy specified in
the ExternalBaseURL WMI
setting.
SRV _sip._tls.<SIPDomain> 443 FQDN of Access Edge server.
SRV _ntp._udp.<SIPDomain> 123 time.windows.com or FQDN of
external time source
A ucupdates-r2.<DHCPDomain> N/A IP of reverse proxy specified in
the ExternalBaseURL WMI
setting.
Polycom CX700 phones running release 1.0.199.123 look for time.windows.com by
default and use it if it's reachable. If not, they append <DHCPDomain> to
time.windows.com and try again (e.g. time.windows.com.contoso.com).
Polycom CX700 phones running 3.5.6907.35 use SRV records to locate a time
source but also checks for a time.windows.com A record for reporting its time back
to the pool (applies to 1.0.199.123 and 1.0.522.101 also).
25
Page 32

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
Step 1.3 - Configure Certificates
Two approaches to configure certificates are provided. By default, a Windows
2008 / 2003 Enterprise Certificate Authority (CA) will publish the trusted root
certificate chain in Active Directory automatically.
To determine whether you need to run certutil, you can confirm that the
certificate chain is present by running ADSIedit.msc to check the
Configuration naming context for the following entry under CN=Certification
Authorities (you should see your Enterprise CA listed with a Class type of
certificationAuthority).
26
Once you’ve determined that your Enterprise CA is listed, you can confirm
that the Trusted Root certificate chain actually uploaded by double-clicking on
your Enterprise CA (CN=ContosoCA in the example) and look for the
cACertificate attribute. It should be populated because this is the data
(basically .CER file) that the Polycom CX700 phone pulls down from Active
Directory to populate its Trusted Root Certificate cache in order to trust the
pools internally issued certificate (refer to the following figure).
Page 33

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
Do one of the following:
• Upload certificate chain
If for some reason the cACertificate attribute is not populated, or you want
to make sure that it contains the information you want, you can run
certutil with the -f option to force an override as shown.
On a domain controller, open cmd.exe and run the following command:
certutil -f -dspublish ".CER file location" RootCA
For example:
certutil -f -dspublish "c:\certs\ContosoCARootChain.cer"
RootCA
• Enable Auto Enrollment
As an alternative to running certutil and uploading the Trusted Root
Certificate Chain into Active Directory, you can enable the domain for
certificate auto enrollment. For instructions, refer to Enabling Automatic
Certificate Enrollment on page 3-45.
Step 1.4 - Configure Microsoft Office Communications Server
Modify client version filter
On the Pool running the Device Update service, confirm that Client Version
control is either turned off or the filter is set to a value that will allow OCPhone
(Polycom CX700 phone) devices that are version 1.0.199.* or higher as shown
in the figure below. There is also a client version filter on the Edge so if you
plan to upgrade external Polycom CX700 phones as well, be sure to make the
same adjustment on your Edge server (set to 1.0.522.* by default).
27
Page 34

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
Modify Device Update Service External URLs (required even if upgrading
OCPE devices internally)
There are two URLs used by external Polycom CX700 phones for downloading
updates; the DownloadURL and StoreURL. If there are Polycom CX700
phones that need to upgrade remotely, then use either the Automatic or
Manual method to configure the DownloadURL / StoreURL values using
WMI.
In some cases, the URLs already contain the correct values and may not need
modification. You can confirm this by running steps 1 - 5 only of the Manual
approach described below.
Use the Automated Method:
1. Create a VBS file, ConfigureExternalDownloadURLs, that you can use to
modify the client version filter and automate the creation of the
DownloadURL and StoreURL WMI entries.
2. From a command prompt on a front end server in the pool running the
Device Update service, run cscript
ConfigureExternalDownloadURLs.vbs
3. The script will populate the DownloadURL / StoreURL values with the
FQDN of the reverse proxy server that is publishing the URLs from
which remote Polycom CX700 phones will download updated image files
from (e.g. ocsrp.fabrikam.com) and update the client version filter.
4. If you plan to upgrade external Polycom CX700 phones, open a browser
from outside the corporate firewall, connect to
https://ReverseProxyFQDN/RequestHandler/ucdevice.upx and
download cpe.nbt to confirm that remote OCPE devices will be able to
download firmware updates.
Use the Manual Method:
1. Click Start, click Run, and then type wbemtest to open Window
Management Instrumentation Tester.
2. Click Connect. For Name space, type root\cimv2, and then click Connect.
This enables all the buttons on the wbemtest user interface.
3. Click Query, and type the following query:
select * from MSFT_SIPUpdatesServerSetting where
backend='$poolbackend$'
where $poolbackend$ is the backend database of the pool in
instance\database format.
28
Page 35

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
To determine the correct syntax for the DB to connect to you can look at the Pool,
Database tab; the value listed for Database Instance Name: is the value you
substitute for $poolbackend$. Also, double quotes work as well as single quotes
Also, you have to add a second backslash to existing backslash separating
the instance name from the database name as shown (for example,
'(local)\\rtc'):
4. This query opens one instance of this class. Double-click the instance.
29
Page 36

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
5. Double-click the ExternalUpdatesDownloadURL and
ExternalUpdatesStoreURL properties to edit them, and type the values
for each property as follows:
For ExternalUpdatesDownloadURL, type
https://ReverseProxyFQDN/RequestHandlerExt/ucdevice.upx
6. Click Save Property.
For ExternalUpdatesStoreURL, type
https://ReverseProxyFQDN/DeviceUpdateFiles_Ext
30
7. Click Save Property and then Save Object to save the instance.
8. Click Close.
9. Verify that the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) values are
updated by querying the class as described in step 3. The
ExternalUpdatesDownloadURL and ExternalUpdatesStoreURL
properties should be set to a non-NULL value.
10. Click Exit to close wbemtest.
Verify Internal and External Download URLs
Confirm that internal and external Polycom CX700 phones will be able to
download firmware updates.
Page 37

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
• Internal
— Using a browser from inside the corporate firewall, connect to:
http://FQDNofPoolRunningDeviceUpdateService/DeviceUpdateFil
es_Int/OCInterim/ENU/cpe.nbt and verify that you can download
the file. If you can, chances are the Polycom CX700 phone can.
The CPE files stored in the OCInterim directory are for build 522.103. If you have
used the Device Update service to upload 1.0.522.101 then you would connect to
something like:
http://pool01.contoso.com/DeviceUpdateFiles_Int/UCPhone/Polycom/CX700/A/EN
U/1.0.522.101/CPE.
— Using a browser from inside the corporate firewall, connect to:
http://FQDNofPoolRunningDeviceUpdateService/RequestHandler
/ucdevice.upx and confirm the version
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
- <Response>
<NumOfFiles>0</NumOfFiles>
<CurrentTime>2009-06-04T06:22:03</CurrentTime>
<ServerVersion>3.5.6907.0</ServerVersion>
<ServiceVersion>3.5.6907.0</ServiceVersion>
</Response>
• External
— Using a browser from outside the corporate firewall, connect to:
http://ReverseProxyFQDN/DeviceUpdateFiles_Ext/OCInterim/E
NU/cpe.nbt and verify that you can download the file. If you can,
chances are the Polycom CX700 phone can.
The CPE files stored in the OCInterim directory are for build 522.103. If you have
used the Device Update service to upload 1.0.522.101 then you would connect to
something like:
http://pool01.contoso.com/DeviceUpdateFiles_Int/UCPhone/Polycom/CX700/A/EN
U/1.0.522.101/CPE.
— Using a browser from outside the corporate firewall, connect to
https://ReverseProxyFQDN/RequestHandlerExt/ucdevice.upx and
download cpe.nbt
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
- <Response>
<NumOfFiles>0</NumOfFiles>
<CurrentTime>2009-06-04T06:22:03</CurrentTime>
<ServerVersion>3.5.6907.0</ServerVersion>
<ServiceVersion>3.5.6907.0</ServiceVersion>
</Response>
31
Page 38

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
For details on Verifying External Device Access refer to the Microsoft Office
Communications Server (OCS) 2007 R2 product documentation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd572289(office.13).aspx
In previous releases of OCS 2007, Polycom CX700 phones operating outside the
firewall connected to the update service by using anonymous access. In this
release, to enhance security, Polycom CX700 phones by default must use NTLM
authentication. This means that a user must be logged on to the device with a valid
user account in order for an external device to connect to Device Update service
and receive updates.
If your organization has external Polycom CX700 phones that were deployed with
the previous version of OCS 2007, and you want to use OCS 2007 R2 to update
them, you must enable Anonymous access for the RequestHandlerExt virtual
directory in Internet Information Services (IIS). For security reasons, once all
previously deployed devices have been updated, you should disable anonymous
access on this virtual directory. OCS 2007 R2 Polycom CX700 phones can be
updated without Anonymous access.
Step 1.5 - Configure a Time Source
This step is optional.
If you are not using time.windows.com as your time source, you can configure
a Windows 2008 / 2003 domain member server as an NTP server. For more
information, refer to Configuring Windows Server as an NTP Time Source on
page 3-43.
Once configured, modify the _ntp._udp.<SIPDomain> SRV record to point to
the FQDN of the internal NTP server. In some cases, this may require creating
DNS zone for <SIPDomain>.
Step 2 - Upgrade Polycom CX700 Phones from 1.0.199.123 to 1.0.522.101
Once the environmental dependencies are in place, the next step in the process
is to upgrade the Polycom CX700 phone’s software from release 1.0.199.123 to
1.0.522.* (either .101 or .103). (The reason you cannot directly from 1.0.199.123
to 3.5.6907.35 is because the 1.0.199.123 software does not recognize builds
greater than 1.0.522.*).
Step 2.1 - Prepare Software Update Files
There are three basic steps to this process:
1. Download the UCUpdates files and uncompress them to CAB files
2. Upload the CAB files to the pool and uncompress them further to CPE
files
32
3. Approve the CPE files
Page 39

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
To prepare the software update files:
1. Download the Microsoft Office Communications Server (OCS) 2007
1.0.522.101 Polycom CX700 phone software release (UCUpdates.exe) here
and store it on a Pool Front End server (for example,
c:\UCUpdates\522.101
).
2. Open a CMD window, change to the directory where you downloaded
the 1.0.522.101 version of UCUpdates and run the ucupdates.exe file.
Extract the CAB file to a directory (for example, use the same directory
that ucupdates.exe is in).
3. From the Pool Front End server, click Start, Administrative Tools, Office
Communications Server R2.
4. Right-click on the Pool and click Device Updater. Select Tools, Upload
.cab File.
5. Navigate to the directory where you extracted the CAB file (for example,
c:\UCUpdates\522.101), click on UCUpdates and click Open.
This will extract the 3 CPE.* files from the CAB file and make them
available for Approval / Rollback.
6. Click the Pending Updates tab and ensure that 1.0.522.101 is in the
“Pending” state. Do not change it at this time.
7. Click the Test Devices tab and add the Polycom CX700 phone to be
upgraded (no spaces / dashes in the MAC address).
Step 2.2 - Upgrade the Polycom CX700 Phone from 1.0.199.123 to
1.0.522.101
Now that the necessary CPE files have been installed and a test device created,
it is time to upgrade the Polycom CX700 phone (test device) to release
1.0.522.101.
To upgrade the phone to release 1.0.522.101:
1. With the power off, connect the Polycom CX700 phone that you
configured as a “Test Device” in the step 2.1 to the same network subnet
as the Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 pool containing
the Device Update service.
2. Perform a hard reset—hold down the reset button on the back of the
phone using a paper clip through the small hole near the headset plug
in— while keeping the reset button depressed, plug in the power supply.
When the scroll bar goes all the way across the screen, let go of the reset
button and wait approximately 15 seconds for the white calibration screen.
3. Calibrate the phone by clicking the plus signs and then press the button
in the center of the scroll wheel.
33
Page 40

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
4. Sign in to the Polycom CX700 phone using an account that is on the same
pool as the Device Update service.
If the Polycom CX700 phone is not picking up downloads, be sure the client version
filter is set properly and that WMI has been configured with internal (BaseURL) and
external (ExternalBaseURL values.
Also, make sure that if you have a build set to “Pending” that the corresponding
MAC address or serial number of the phone is listed on the Test Devices tab. You
can also refer to Logs Used for Troubleshooting on page 3-40 for which logs to
check to begin the troubleshooting process.
5. Perform a Reboot— power cycle the Polycom CX700 phone to force it to
look for an update and leave it alone for five to ten minutes.
The phone should reset automatically and present the calibration screen
again.
You can monitor the IIS and ImageUpdate Audit log files for progress /
status.
There is a lag between when 1.0.522.101 is available and when the phone can
access it and the system logs the attempt. Be sure to allow for that (usually less
than 5 minutes.)
6. Calibrate the phone, but do not sign in.
7. Confirm the Polycom CX700 phone is running release 1.0.522.101 by
clicking About on the main menu and checking the Version information.
Click OK to return to the Sign in screen.
At this point Step 2 is confirmed and you can do one of two things:
• Add any remaining Polycom CX700 phones still running release
1.0.199.123 as “Test Devices”, power cycle them and within five to ten
minutes they should pick up the pending 1.0.522.101 (only Polycom
CX700 phones listed on the Test Devices tab can receive Pending Updates)
OR
• If no other production Polycom CX700 phones are on a build higher than
1.0.522.101, you can use Device Updater to approve the pending updates
and finish flashing the software on the remaining phones running build
1.0.199.123.
Once all Polycom CX700 phones are running release 1.0.522.101 and have been
recalibrated, go to the next section, Step 3 - Upgrade Polycom CX700 Phones
from 1.0.522.101 to 3.5.6907.35.
34
Page 41

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
Step 3 - Upgrade Polycom CX700 Phones from 1.0.522.101 to 3.5.6907.35
This is the final step in the upgrade process and can be conducted on a one-off
basis or after all Polycom CX700 phones have been upgraded from release
1.0.522.101 to 3.5.6907.35. As in Step 2, you will want download the latest
software updates and use test devices to confirm the update works properly
before approving the build for product distribution.
Step 3.1 - Prepare Software Update Files
There are three basic steps to this process:
1. Download the UCUpdates files and uncompress them to CAB files
2. Upload the CAB files to the pool and uncompress them further to CPE
files
3. Approve the CPE files.
To prepare the software update files:
1. Download the Microsoft Office Communications Server (OCS) 2007
3.5.6907.9 Polycom CX700 phone software release (UCUpdates.exe) here
and store it on a Pool Front End server (for example,
c:\UCUpdates\
6907.9 ).
2. Open a CMD window, change to the directory where you downloaded
the 3.5.6907.9 version of UCUpdates and run the ucupdates.exe file.
Extract the CAB file to a directory (for example, use the same directory
that ucupdates.exe is in).
3. From the Pool Front End server, click Start, Administrative Tools, Office
Communications Server R2.
4. Right-click on the Pool and click Device Updater. Select Tools, Upload
.cab File.
5. Navigate to the directory where you extracted the CAB file (for example,
c:\UCUpdates\6907.9), click on UCUpdates and click Open.
This will extract the 3 CPE.* files from the CAB file and make them
available for Approval / Rollback.
35
Page 42

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
6. Click the Pending Updates tab and ensure that 3.5.6907.9 is in the
“Pending” state. Do not change it at this time.
7. If using a different Polycom CX700 phone for testing release 3.5.6907.9,
click the Test Devices tab and add the Polycom CX700 phone to be
upgraded (no spaces / dashes in the MAC address); otherwise, use the
existing test device.
Step 3.2 - Upgrade the Polycom CX700 Phone from 1.0.522.101 to 3.5.6907.*
Now that the necessary CPE files have been installed and a test device created,
it is time to upgrade the Polycom CX700 phone (test device) to release
3.5.6907.9.
To upgrade the phone to release 3.5.6907.9:
1. If the Polycom CX700 phone has not reset after 10 minutes of inactivity or
you want to expedite the process, perform a reboot—power cycle the
phone and let it sit for five to ten minutes.
You can monitor the IIS and ImageUpdate Audit log files for progress /
status.
There is a lag between when 3.5.6907.9 is available and when the phone can
access it and the system logs the attempt. Be sure to allow for that (usually less
than 5 minutes.)
The phone will reset and go to the calibration screen.
If the Polycom CX700 phone is not picking up downloads, be sure the client version
filter is set properly and that WMI has been configured with internal (BaseURL) and
external (ExternalBaseURL values.
Also, make sure that if you have a build set to “Pending” that the corresponding
MAC address or serial number of the phone is listed on the Test Devices tab. You
can also refer to Logs Used for Troubleshooting on page 3-40 for which logs to
check to begin the troubleshooting process.
36
Page 43

Upgrading Polycom CX700 Phone within a Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Environment
3. Calibrate the phone and sign in.
4. Confirm the Polycom CX700 phone is running release 3.5.6907.9 by
clicking About on the main menu and checking the Version information.
Click OK to return to the Sign in screen.
The Polycom CX700 phone is now ready to use.
37
Page 44

Deployment Guide for the Polycom CX700 IP Phone
38
Page 45

3
Troubleshooting the Polycom CX700 Phone
This chapter contains general troubleshooting information to help you solve
any problems you might encounter when you use the Polycom® CX700 Phone
in a wireless environment. The phone can provide feedback in the form of
on-screen error messages, status indicators, and log files for troubleshooting
issues.
This chapter presents frequently asked questions and corrective actions for the
Polycom CX700 phone in a Microsoft® Office Communications Server 2007 R2
environment. Issues are grouped as follows:
• Logs Used for Troubleshooting
• When to Use DHCP Option 119
• Configuring Windows Server as an NTP Time Source
• Enabling Automatic Certificate Enrollment
• Making the Root CA Certificate Available to a Polycom CX700 Phone
• Installing a Public Root CA Certificate on a Polycom CX700 Phone
• Confirming the Current Software Version
For more troubleshooting information, refer to the User Guide for the Polycom
CX700 phone, which is available at
http://www.polycom.com/support/voice/cx/communicator_cx700.html .
Review the latest Getting Started for Microsoft® Office Communications Server
2007 R2 Polycom CX700, which is available at
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd441174%28office.13%29.aspx
39
Page 46

Deployment Guide Polycom CX700
Logs Used for Troubleshooting
To confirm that a Polycom CX700 phone running release 1.0.199.123 is not
having issues locating resources, you can use a browser to FTP to the device
and copy over the Communicator and DOMO log files. Use the IP address
assigned to the device (for example, ftp://192.168.7.235). This option does not
work for releases 1.0.522.101 or later.
If the Polycom CX700 phone running release 1.0.199.123 contains a
ucupdate.xml file, you should confirm it contains the correct information for
your environment or it can cause updates to fail. Alternatively, perform a hard
reset to remove the file.
To confirm the Polycom CX700 phone connects to IIS correctly:
c:\inetpub\logs\LogFiles\W3SVC1\*_*.log (where *_* = some prefix
and the current date)
To confirm the Polycom CX700 phone runs:
>> Locate the Device Update service correctly review the Device Update
audit logs:
By default, audit logs are located in different locations depending on
Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 product type:
— For Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Standard
Edition, device update files and Device Update Service audit log files
are stored on the local computer in c:\Program Files\Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 R2\Web
Components\DeviceUpdateFiles\Logs\Server\Audit\ImageUpdat
es.
— For Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Enterprise
Edition, you can find the DeviceUpdates folder on the shared updates
folder that was created during pool setup for client and device update
files.
40
Page 47

Troubleshooting the Polycom CX700 Phone
To confirm the Polycom CX700 phone can locate / run ucdevice.upx (which in
turn locates the correct CPE.NBT file):
>> Use a browser to confirm you can access the virtual directory where the
ucdevice.upx file is located:
Internal
http://pool01.contoso.com/RequestHandler/ucdevice.upx When
hitting this link, an XML file showing the current firmware version
will be displayed if security is set properly.
External
http://ocsrp.fabrikam.com/RequestHandlerExt/ucdevice.upx
When hitting this link, an XML file showing the current software
release will be displayed if security is set properly and the reverse
proxy publishing rules map the reverse proxy FQDN to the
/RequestHandlerExt virtual directory on the pool hosting the Device
Update service.
To confirm that the Polycom CX700 phone can get to the device update files,
the following example provides instructions for a Polycom CX700 running
build 199 with planned upgrade to build 522:
Internal (assumes pool running Device Update service =
pool01.contoso.com)
http://pool01.contoso.com/DeviceUpdateFiles_Int/UCPhone/Poly
com/CX700/A/ENU/1.0.522.101/CPE/CPE.nbt When hitting this
link, you should get prompted to save cpe.nbt if security is set
properly.
External (assumes reverse proxy FQDN = ocsrp.fabrikam.com)
https://ocsrp.fabrikam.com/DeviceUpdateFiles_Ext/UCPhone/Pol
ycom/CX700/A/ENU/1.0.522.101/CPE/CPE.nbt When hitting this
link, you should get prompted to save cpe.nbt if security is set
properly and the reverse proxy publishing rules map the reverse
proxy FQDN to the /DeviceUpdateFiles_Ext virtual directory on the
pool hosting the Device Update service.
When to Use DHCP Option 119
You need to use the DHCP option 119 when you deploy the Polycom CX700
phone to find a domain controller to talk to.
You can sign in to a the Polycom CX700 phone in two different ways:
• Using NetBIOS style (<domain>\<user>)
• Using User Principal Name (UPN) style (<user>@<domain>)
41
Page 48

Deployment Guide Polycom CX700
When you use NetBIOS style, the phone needs to use the <domain> name to
find a domain controller. If WINS is configured for use by the phone (via
DHCP), it will use that. However if WINS is not configured, and the phone is
on another subnet than the domain controller, it needs to use DNS to find it.
The way it looks for a domain controller is using the DC locator SRV records
in DNS (_ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.<DNS domain>). When it looks up these
records, it uses domain information received using DHCP (option 15 and
option 119). Say we have the following situation:
• The phone receives the DNS domain fabrikam.dk in DHCP option 15
(DomainName).
• The phone receives the DNS domains fabrikam.dk and dk in DHCP
option 119 (DomainSearch).
• The domain controller is located in fabrikam.dk and can be found by
locating the SRV record _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.fabrikam.dk .
• The user signs in with Fabrikam\Jens .
The phone will try to locate the domain controller using this sequence:
• _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.fabrikam—takes the NetBIOS name directly (fails)
• _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.fabrikam.fabrikam.dk—adds the DomainName
value (fails)
• _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.fabrikam.fabrikam.dk—adds first element in
DomainSearch (fails)
• _ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.fabrikam.dk—adds second element in
DomainSearch (succeeds)
So if dk was not added to DHCP option 119, the phone would have been
unable to locate a domain controller and, therefore, the user could not sign in
and the phone would have be unable to download certificates. You need to
configure the DNS Suffix list such that the device can construct the correct
DNS domain based on the NetBIOS name used.
An alternative approach is to instruct users to sign in using UPN style, for
example, jens@fabrikam.dk, and in this way the user provides the correct
DNS domain directly at sign in.
If you have configured the NetBIOS name to be completely different to the AD
DNS domain name, for example, NetBIOS fabrikam and AD DNS domain is
contoso.net, it is not possible to use the DNS Suffix list to create the mapping.
In such a scenario the best approach is to instruct the users to use UPN style
login. Alternatively use WINS.
42
Page 49

Troubleshooting the Polycom CX700 Phone
How to Configure DHCP Option 119
To configure DHCP Option 119:
1. From DHCP Administrator, right click DHCP server name and select Set
Predefined Options.
2. Leave Option class: as DHCP Standard Options and click Add.
3. For Name:, enter DNS Search List, set Code: to 119 and Data Type to
String, leave the Array check box unchecked (it is not an array) and click
OK.
4. Right click Scope Options, select Configure Options, check Option 119
DNS Search List.
5. In the Value section in the String list box, enter a list of domain suffixes
in your organization delimited by a semi-colon.
For example, contoso.com;corp.contoso.com;fabrikam.com
6. Click OK to close the Predefined Options and Values page.
Configuring Windows Server as an NTP Time Source
For Windows 2008
To configure Windows 2008 Server as an NTP time source:
1. Click Start, Run, type regedit in the list box and click OK to open the
Registry editor.
2. To enable the Network Time Protocol; NTPserver, locate and click
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time
\TimeProviders\NtpServer\
3. In the right pane, right-click Enabled, then click Modify.
4. In the Edit DWord Value box, type 1 under Value data, then click OK.
5. Now go back and click on
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time
\Parameters\NtpServer
43
Page 50

Deployment Guide Polycom CX700
6. In the right pane, right-click NtpServer, then Modify, in the Edit
DWORD Value under Value Data type the Domain Name System (DNS),
each DNS must be unique and you must append 0×1 to the end of each
DNS name otherwise changes will not take effect.
By default this is set time.windows.com,0x9 and was changed to
contoso.com,0x1
7. Now click OK.
8. Locate and click the following
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time
\TimeProviders\NtpClient\SpecialPollInterval
9. In the right pane, right-click SpecialPollInterval, then click Modify.
10. In the Edit DWORD Value box, set Base to Decimal. In the Value data
text box type the number of seconds you want for each poll, (for example,
900 will poll every 15 minutes), then click OK.
11. Exit Registry editor.
12. Now, to restart windows time service, click Start, Run (or alternatively
use the command prompt facility) and type:
net stop w32time && net start w32time
Your time server should be now up and running.
For Windows 2003
To use an internal server as the authoritative time source as outlined in the
section “Configuring the Windows Time service to use an internal hardware
clock” in the document available at
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/816042/
Enabling the time service is done via group policy on the domain object
containing the NTP server.
To configure Windows 2003 Server as an NTP time source:
1. Open Active Directory Users and Computers.
2. Right-click on the domain containing your NTP server and select
Properties.
3. Click the Group Policy tab, make sure the Default Domain Policy is
highlighted and click the Edit button.
4. Expand Computer Configuration, Administrative Templates, System,
Windows Time Service.
5. Click on Time Providers and in the right pane double-click Enable
Windows NTP Server, confirm the Enabled radio button is selected and
click OK.
44
Page 51

6. From the Group Policy Object Editor menu, select File and click Exit.
Enabling Automatic Certificate Enrollment
For Windows 2008
Troubleshooting the Polycom CX700 Phone
To configure autoenrollment Group Policy for a domain:
1. On a domain controller running Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows
Server 2008, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click
Group Policy Management.
2. In the console tree, double-click Group Policy Objects in the forest and
domain containing the Default Domain Policy Group Policy object
(GPO) that you want to edit.
3. Right-click the Default Domain Policy GPO, and then click Edit.
4. In the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), select User
Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings, and
then click Public Key Policies.
5. Double-click Certificate Services Client - Auto-Enrollment.
6. Select Enabled from the configuration model list box.
7. Select one of the following three check boxes depending on requirements:
— Renew expired certificates, update pending certificates, and remove
revoked certificates enables autoenrollment for certificate renewal,
issuance of pending certificate requests, and the automatic removal of
revoked certificates from a user's certificate store.
— Update certificates that use certificate templates enables
autoenrollment for issuance of certificates that supersede issued
certificates.
45
Page 52

Deployment Guide Polycom CX700
— Expiration notification controls when the end user is notified that a
certificate is about to expire.
8. Click OK to accept your changes.
9. Run the following command at an elevated command prompt:
gpupdate /force
Automatic enrollment will start working in about 90 seconds for any
applicable templates.
For Windows 2003
Enabling certificate AutoEnrollment is done via group policy on the domain
object containing the Polycom CX700 phone using the following steps:
To configure autoenrollment Group Policy for a domain:
1. Open Active Directory Users and Computers.
2. Right click on the domain containing the Polycom CX700 phone and
select Properties.
3. Click the Group Policy tab, make sure the Default Domain Policy is
highlighted and click the Edit button
4. Select Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security
Settings.
5. Click on Public Key Policies and in the right pane double-click
Autoenrollment Settings, confirm the Enroll certificates automatically
radio button is selected and click OK.
46
Page 53

Troubleshooting the Polycom CX700 Phone
6. From the Group Policy Object Editor menu, select File and click Exit.
To confirm that the Certificate Authorities is set:
1. Click Start, Run, type ADSIEDIT.MSC and click OK.
2. Select Configuration [yourDC.yourDomain.com]
3. Select CN=Configuration,DC=yourDomain,DC=com
4. Select CN=Services
5. Select CN=Public Key Services and check the following two objects:
a Click CN=Certification Authorities and confirm that the name of
your internal Certificate Authority is listed in the right pane with a
Class type of certificationAuthority.
b Click CN=Enrollment Services and confirm that the name of your
internal Certificate Authority is listed in the right pane with a Class
type of pkiEnrollmentService.
6. From the ADSI Edit menu, click File, then Exit to close ADSIEDIT.MSC.
47
Page 54

Deployment Guide Polycom CX700
Making the Root CA Certificate Available to a Polycom CX700 Phone
Communication between the Polycom CX700 phone and Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 R2 is by default encrypted using TLS and SRTP.
Therefore, the device needs to trust certificates presented by Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 R2 servers. If the servers use public certificates,
they will most like be automatically trusted by the phone, since it contains the
same list of trusted certificate authorities (CAs) as Windows CE. However,
since most Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 deployments use
internal certificates for the internal Microsoft Office Communications Server
2007 R2 server roles, there is a need to install the Root CA certificate from the
internal CA to the phone. It is not possible to manually install the Root CA
certificate on the phone, so it needs to come via the network.
The Polycom CX700 phone is able to download the certificate using two
methods:
• The device will search for AD objects of category certificationAuthority. If
the search returns any objects, it will use the attribute caCertificate. That
attribute is assumed to hold the certificate and the device will install the
certificate. To get the Root CA certificate placed in the caCertificate
attribute, use the command certutil -f -dspublish <Root CA certificate in
.cer file> RootCA. This command will publish the certificate as required by
Polycom CX700 phone.
• If the search for AD objects of category certificationAuthority does not
return any or if the objects have empty caCertificate attributes, the phone
will search for AD objects of category pKIEnrollmentService in the
configuration naming context. Such objects exists if Certificate
AutoEnrollment has been enabled in Active Directory. If the search
returns any objects, it will use the dNSHostName attribute returned to
reference the CA and it will then use the Web interface of the Microsoft
Certificates Service to retrieve the Root CA certificate using the HTTP GET
command
http://<dNSHostname>/certsrv/certnew.p7b?ReqID=CACert&Renewa
l=-1&Enc=b64.
If neither of these methods succeeds, the error message “Cannot validate
server certificate” appears on the screen and the user will not be able to use the
phone.
48
Page 55

Troubleshooting the Polycom CX700 Phone
Installing a Public Root CA Certificate on a Polycom CX700 Phone
The Public Certificate you are using on your Edge server(s) is not trusted by
the Polycom CX700 phone, because its corresponding Root CA certificate is
not installed on the phone per default.
You can use the certutil mechanism to install the Public Root CA certificate.
First, you download the certificate from the CA’s web site. Then you use the
certutil command to publish the certificate to your Active Directory. It will be
added as an object under CN=Certification Authorities, CN=Public Key
Services, CN=Services, CN=Configuration, DC=<domain>, DC=<tld>. You
can add multiple Root CA certificates using this method. The phone will
download all the certificates found.
After the public Root CA certificate is published, you will have to connect the
phone once to the internal network to get the certificate downloaded. Before
you do that you need to reset the phone to clear the certificate store, since you
need the device to ask for certificates (if you do not do this, the phone will use
the currently installed certificate when challenged by your internal Microsoft
Office Communications Server 2007 R2 servers and not search for them in
Active Directory). You reset the device by inserting a paper clip in the small
hole on the back between the USB and headset connectors. Then you can
connect the device to the Internet and it will connect to the Edge server.
The above steps only work if the phone is able to get to your Active Directory
domain controller and the way it finds that is through DNS or NetBios. If you are
using UPN style username and the certificate download fails, try to use
<domain>\<username> style login
Confirming the Current Software Version
If you have not signed in, click the About menu option (bottom menu) and the
release information will be the first value displayed.
If you have signed in to Polycom CX700 phone, unlock it (if necessary) and
click the Settings icon (looks like a small sprocket on the left menu). The
release information will be the first value displayed.
In either case, the release number is displayed just to the left of the value in
parenthesis:
For example: 1.0.522.101 (1.23)
49
Page 56

Deployment Guide Polycom CX700
50
 Loading...
Loading...