PMDG Boeing 737 NG User Manual

1
By Chuck
FSX GUIDE
PMDG BOEING 737-800 NG
LAST UPDATED: 04/10/2018

TABLE OF CONTENT
• PART 1 – INTRODUCTION
• PART 2 – COCKPIT LAYOUT
• PART 3 – FLIGHT PLANNING
• PART 4 – START-UP PROCEDURE
• PART 5 – TAXI
• PART 6 – TAKEOFF, CLIMB & CRUISE
• PART 7 – AUTOPILOT
• PART 8 – APPROACH & LANDING
2

3
PART 1
–
CONTROLS SETUP
PART 1
–
INTRODUCTION
The Boeing 737 is a short- to medium-range twinjet narrow-body airliner developed and
manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States. Originally developed
as a shorter, lower-cost twin-engine airliner derived from the 707 and 727, the 737 has
developed into a family of ten passenger models with capacities from 85 to 215
passengers. The 737 is Boeing's only narrow-body airliner in production, with the 737
Next Generation (-700, -800, and -900ER) and the re-engined and redesigned 737
MAX variants currently being built.
The 737 was originally envisioned in 1964. The initial 737-100 made its first flight in April
1967, and entered airline service in February 1968 at Lufthansa. Next, the lengthened
737-200 entered service in April 1968. In the 1980s, Boeing launched the longer −300,
−400, and −500 models, subsequently referred to as the Boeing 737 Classic series and
featuring CFM56 turbofan engines along with wing improvements.
The 737 Next Generation (also known as “NG” or “Next Gen”) was introduced in the
1990s in response to the A320, with a redesigned, increased span laminar flow wing,
upgraded "glass" cockpit, and new interior. The 737 Next Generation comprises the four
−600, −700, −800, and −900 models, with lengths ranging from 102 to 138 ft (31.09 to
42.06 m). Boeing Business Jet versions of the 737 Next Generation are also produced. The
737 was revised again in the 2010s for greater efficiency, with the 737 MAX series
featuring CFM International LEAP-1B engines and improved winglets. The 737 MAX
entered service in 2017.
Systems wise, the 737 has a lot of parts that were certified in the 1960/70' and had no
inherent reason to change over time. Hence this is why you will find a mix of technology
throughout the aircraft. The aerospace industry has the saying “if it isn’t broken, don’t fix
it”.
PMDG simulates the 737 NG “X” for variants -800 and -900 in the base package and the
-600 and -700 in an expansion pack.

4
IXEG Boeing 737-300 Classic (X-Plane 11)
PART 1
–
INTRODUCTION
FlyJSim Boeing 737-200 (X-Plane 11)

5
PMDG Boeing 737-800 NG (FSX)
PART 1
–
INTRODUCTION
Boeing 737 MAX 8

6
PART 1
–
INTRODUCTION
Before you even step foot in your virtual cockpit, you need to know where you are, where you are going, how you will
get there, what you need to get there. This document is structured like a short tutorial flight.
The flight tutorial is structured as follows:
• Familiarize yourself with the cockpit layout
• Plan your flight
• Determine the flight route, fuel & cargo loads
• Spawn the aircraft and set it in a Cold & Dark state
• Provide aircraft with power
• Begin navigation system alignment phase
• Program the FMC (Flight Management Computer)
• Start–up the aircraft and make it ready for flight
• Taxi
• Takeoff
• Climb and cruise
• Explore autopilot capabilities
• Approach and land
TUTORIAL STRUCTURE

7
PART 1
–
INTRODUCTION
BEST RESOURCES
DISCLAIMER: Do not use this guide for real life flying. I mean it.
Boeing B737.UK.ORG Website
http://www.b737.org.uk/
Mahmoud Abdellatief Youtube Tutorial Playlist
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLN9OFdlZ4OCVte0Puy6y3OvxEwCKazx3U
Matt Davies Youtube Channel
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gj_0GBNUAYU&list=UU7SryNncikhgt5tp3rPn0RQ
Noble Air Tutorial
http://www.nobleair.net/library/manuals/737NGX_Tutorial.pdf

8
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT

9
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Front Flight Deck

10
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
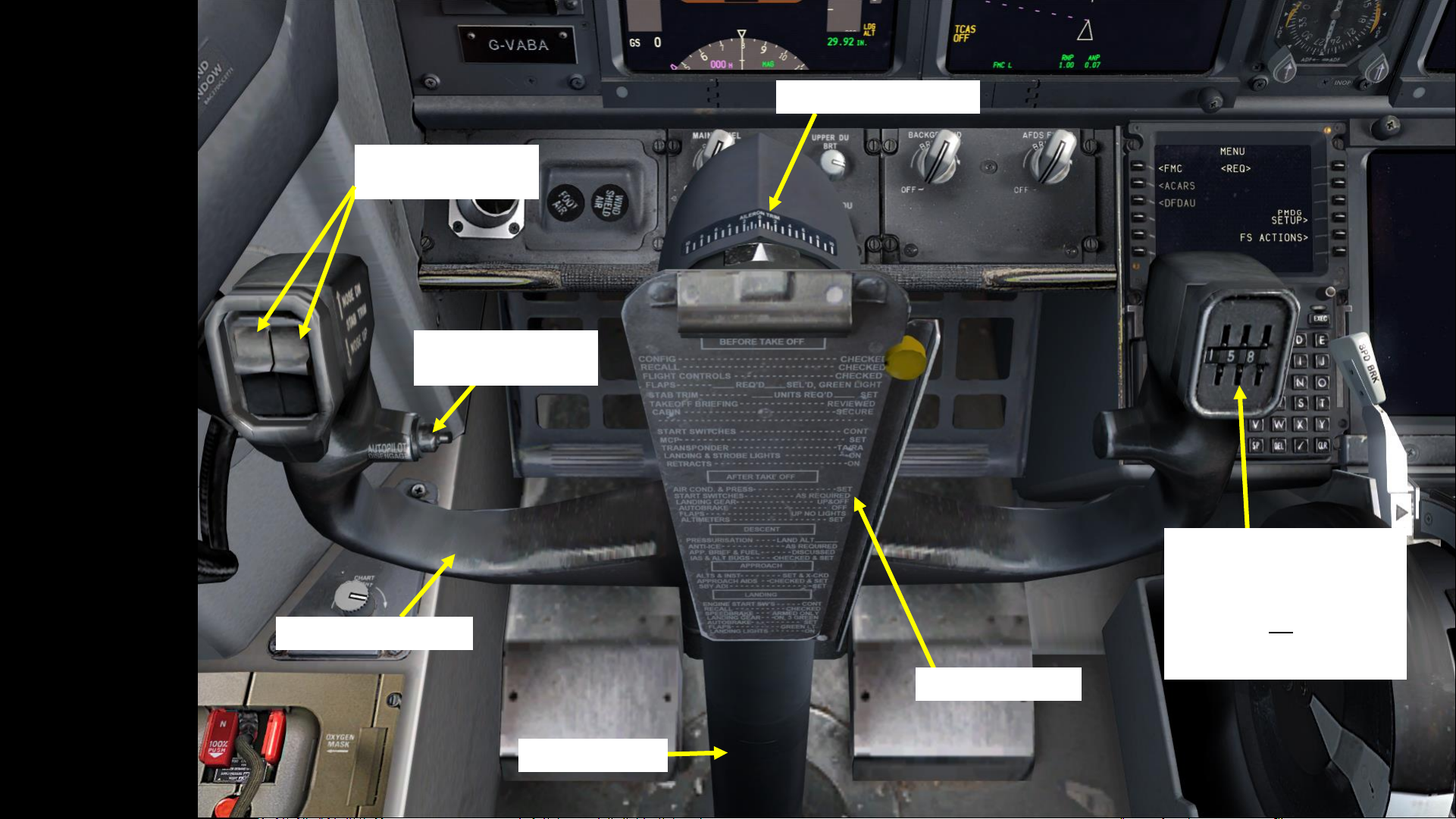
Nose Wheel Steering Tiller
(used to steer aircraft on the ground)
Chart Light Control
Oxygen Mask
Oxygen Mask
Test Switch
Map Light Control

11
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Cockpit window handle
12
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Stabilizer Trim (Nose
Up / Nose Down)
Autopilot Disengage
Button
Control Wheel / Yoke
Checklist Reminder
Memory Device Dials for
Flight Number
Note: rotate these dials to the last
three digits of your flight number
(i.e. Flight 1158) in order to
remember it when talking to the
ATC (Air Traffic Controller).
Aileron Trim Indicator
Control Column

13
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
HUD (Heads-Up Display) Brightness
HUD (Heads-Up Display) screen
(click to stow or deploy)
14
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
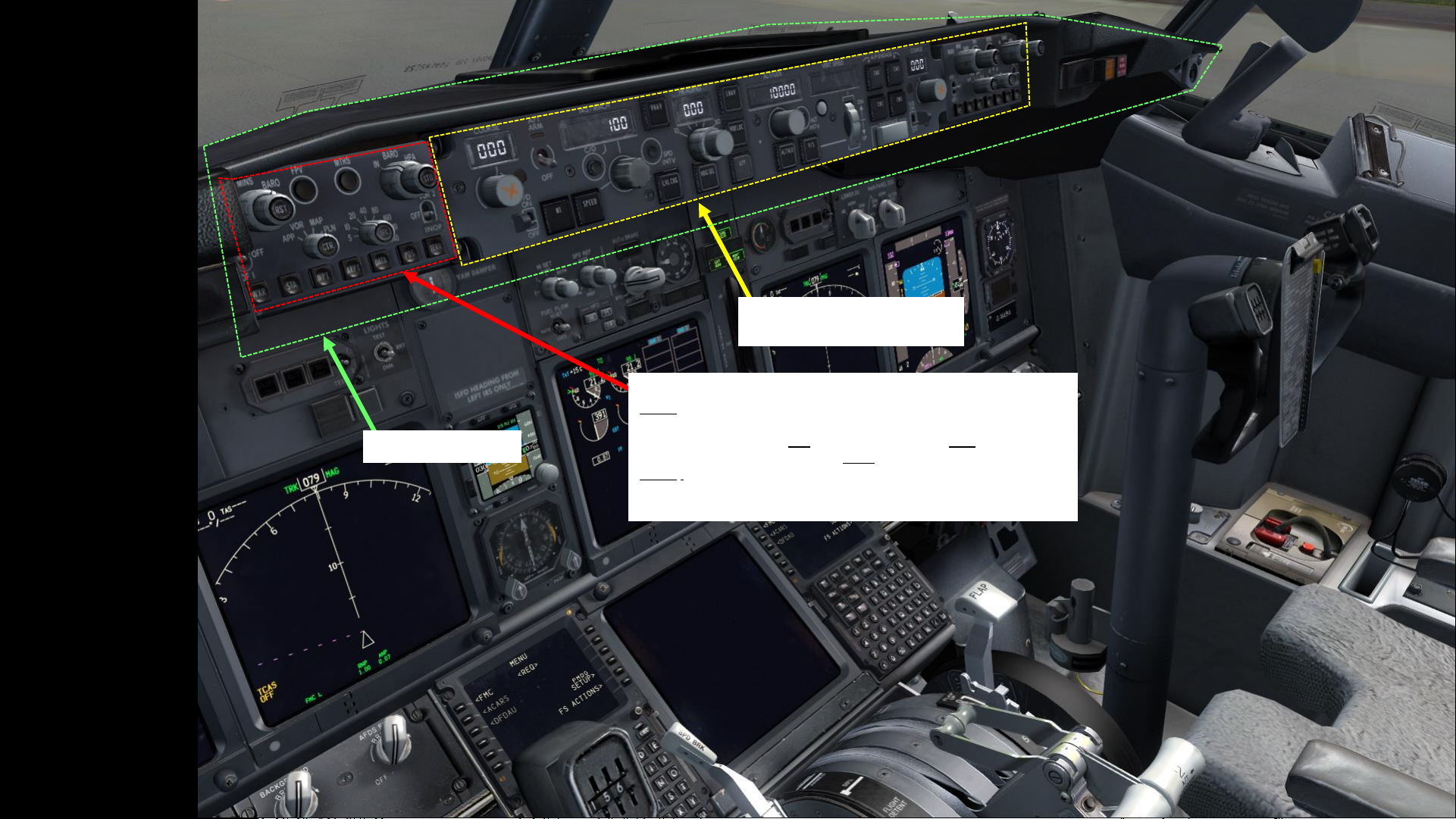
MCP (Mode Control Panel)
Autopilot controls
Glareshield Panel
EFIS (Electronic Flight Instrument System) Control Panel
Note 1: The EFIS is a flight deck instrument display system that displays flight
data electronically rather than electromechanically. An EFIS normally consists
of a primary flight display (PFD), multi-function display (MFD), and an engine
indicating and crew alerting system (EICAS) display.
Note 2: The complex electromechanical attitude director indicator (ADI)
and horizontal situation indicator (HSI) were the first candidates for
replacement by EFIS.

15
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Master Fire Warning Light
Windshield Wiper
Master Caution Warning Light
Master Recall Panel (“six pack”)
System faults annunciations are displayed
on this panel. They tell you where to look
for the problem.
EFIS (Electronic Flight Instrument System) Control Panel
MINS (Minimums) Reference Selector
Outer knob selects RADIO or BAROMETRIC altitude reference for minimums
Middle knob adjusts radio or barometric altitude value
Inner reset pusher resets minimum
FPV (Flight Path Vector) switch
Displays the flight path vector on the attitude indicator.
MTRS (Meters) switch
Displays the altitude in meters instead of feet.
BARO (Barometric) Reference
Selector
Outer knob selects units in Hg or HPa
Middle knob adjusts barometric altitude value
Inner STD pushbutton sets standard 29.92 in Hg

16
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
EFIS (Electronic Flight Instrument System) Control Panel
Note 1: The EFIS is a flight deck instrument display system that displays flight
data electronically rather than electromechanically. An EFIS normally consists
of a primary flight display (PFD), multi-function display (MFD), and an engine
indicating and crew alerting system (EICAS) display.
Note 2: The complex electromechanical attitude director indicator (ADI)
and horizontal situation indicator (HSI) were the first candidates for
replacement by EFIS.
VOR / ADF 1 (VHF Omnidirectional Range or
Automatic Direction Finder) selector switch
Navigation Display MAP buttons
WXR: Weather Radar
STA: Station, displays all FMC data base navigation aids
WPT: displays waypoints in FMC data base
ARPT: displays airports in FMC data base
DATA: displays altitude constraint and estimated time of arrival for each active route waypoint
POS: displays VOR and ADF bearing vectors (position)
TERR: displays GPWS (Ground Proximity Warning System) generated terrain data
Navigation Display (ND) Mode Selector
APP (Rotate): displays localizer and glideslope information
VOR (Rotate): displays VOR navigation information
MAP (Rotate): displays FMC generated route and MAP information
PLAN (Rotate): displays a non-moving, true north up, route depiction
CTR (Push): Displays full compass rose (center) for APP, VOR & MAP modes
Navigation Display (ND) Display Range Selector
(nautical miles)
Outer knob: sets range in nm
TFC (Push): Displays TCAS (Traffic Collision and Avoidance System) info
VOR / ADF 2 (VHF Omnidirectional
Range or Automatic Direction
Finder) selector switch

17
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Autopilot Course Setter
Autothrottle (A/T) Arming Switch
Changeover (C/O) switch
Switches between IAS and Mach
Autopilot Speed (IAS or Mach) Selected Indicator
Autopilot Course Selected Indicator
Autothrottle N1 Mode pushbutton
Maintains thrust at engine N1 limit selected from FMC CDU
Autothrottle Speed Mode pushbutton
Maintains airspeed selected
Autopilot Speed (IAS or Mach) Selector
Flight Director (F/D) Switch
Speed Intervention Switch
MCP (Mode Control Panel)

18
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Autopilot VNAV (Vertical
Navigation) pushbutton
Autopilot LNAV (Lateral
Navigation) pushbutton
Autopilot Selected Heading Indicator
Autopilot Selected Altitude Indicator (ft)
Autopilot Altitude Selector
Autopilot Heading Selector
Autopilot Level Change pushbutton
Autopilot Heading Selected pushbutton
Autopilot VOR/LOC pushbutton
Autopilot Approach pushbutton
Autopilot Altitude Hold pushbutton
Autopilot Vertical Speed pushbutton
Autopilot Selected Vertical Speed
Indicator (ft/min)
Altitude Intervention Switch
Autopilot Vertical Speed
thumbwheel selector
Autopilot Bank Angle Limit Selector

19
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Autopilot Engage Command
Button (A/P A)
Autopilot Engage Command
Button (A/P A B)
Autopilot Control Wheel
Steering Engage Button (A/P A)
Autopilot Control Wheel
Steering Engage Button (A/P B)
Autopilot Disengage Switch
Flip bar UP to disengage A/P

20
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Clock
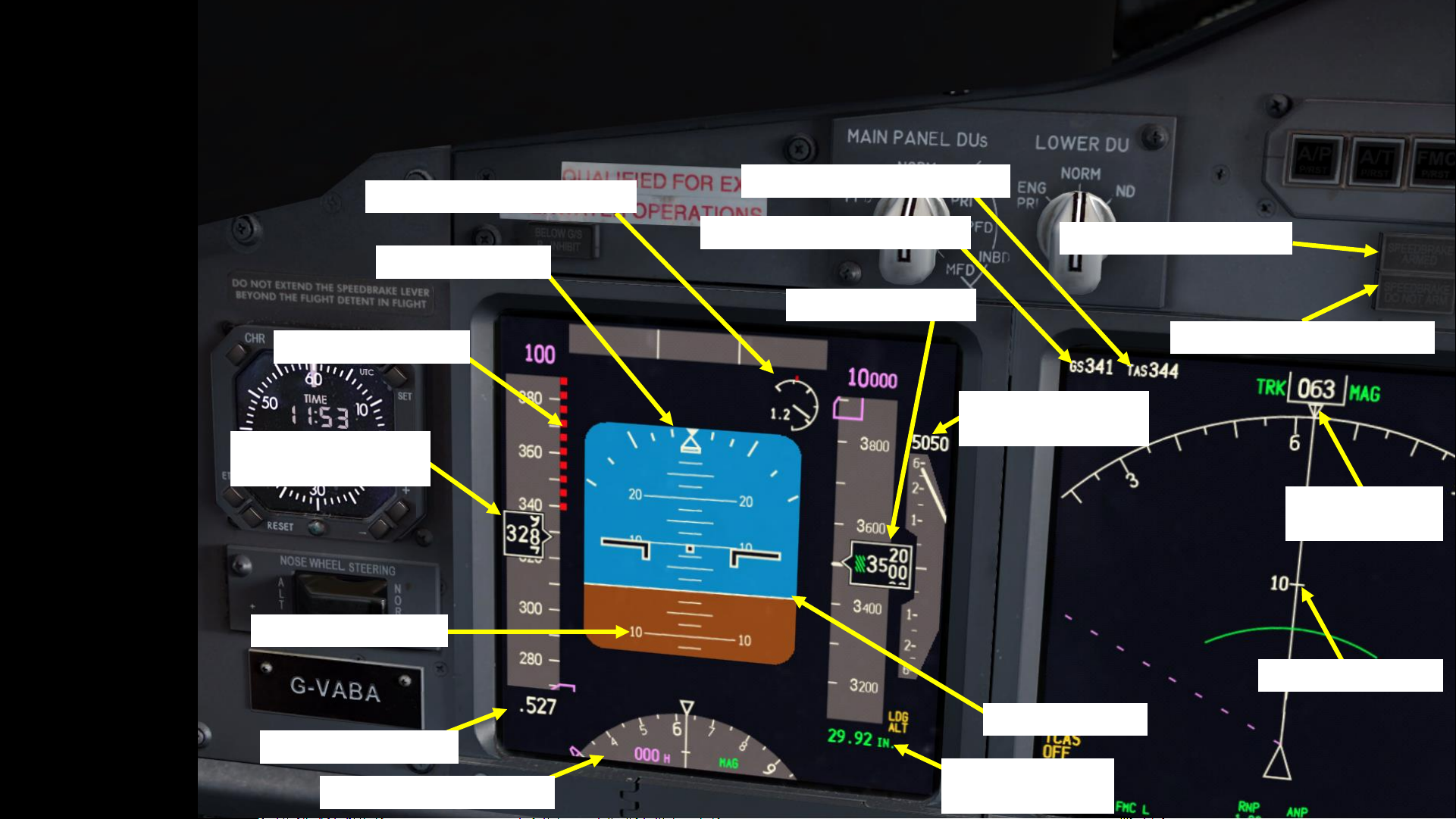
Nosewheel Steering Switch
NORM: uses hydraulic System A
ALT: uses alternate hydraulic System B
BELOW G/S PUSH-INHIBIT light
Illuminates when flying below a
safe glide slope except when flying
under 1000 ft
Main Panel DUs (Display Units) selector
Outboard PFD (Primary Flight Display)
Normal – PFD on OUTBD, ND on INBD
Inboard PFD (Primary Flight Display)
Inboard MFD (Multifunction Display)
Lower Panel DU (Display Unit) selector
ENG PRI: Engine Primary
Normal
ND: Navigation Display
PFD (Primary Flight
Display) screen
ND (Navigation Display)
screen
Master Lights Test and Dim switch
Test / Bright / Dim
Autopilot (A/P) Disengage Light
Autothrottle (A/T) Disengage Light
FMC P/RST (Flight Management
Computer, Push-to-Reset) Alert Light
A/T & FMC Disengage Test Switch
21
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Speed Brake Armed Light
Speed Brake Do Not Arm Light
ND True Airspeed Indication (kts)
ND Ground Speed Indication (kts)
Bank Angle Scale
Maximum Speed (kts)
AoA (Angle of Attack) Indicator
Calibrated Airspeed
Indicator (kts)
Attitude Indicator
Altitude Indicator (ft)
Vertical Speed
Indicator (ft/min)
Barometric Pressure
(inches of Hg)
Heading and Track Indicator
Mach Number Indicator
Range (nautical miles)
Heading Indicator
(Triangle)
Pitch Angle Scale (deg)

22
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Yaw Damper Indicator
ISFD (Integrated Standby
Flight Display) Indicator
Standby RMI (Radio
Magnetic Indicator)
Displays magnetic heading and
VOR/ADF bearing to the station
MFD (Multi-function Display)
Displays either ENG or SYS pages.
ENG shows engine parameters.
SYS shows brake temperature
and control surfaces positions.
Fuel Quantity (x 1000 lbs)
Fuel Flow Indication
(x 1000 lbs/hour)
EGT (Exhaust Gas Temperature)
Indication (deg C)
N1 (Fan Speed/Low Pressure Compressor Speed) Indication (%RPM)
Total Air Temperature (TAT) (deg C)
Thrust Mode Display
(G/A = Go-Around)
Engine Crew Alerts
i.e. START VALVE OPEN, OIL FILTER
BYPASS, LOW OIL PRESSURE, etc.
EICAS (Engine Indicating
and Crew Alerting System)
(Airbus Equivalent: ECAM )

23
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
N1 Set
Outer Knob: AUTO displays both N1 bugs set by FMC, while BOTH displays
both N1 bugs manually set by turning the N1 Set Inner Knob
Inner Knob: positions reference N1 bugs and readouts when outer knob is
set to BOTH.
SPD REF: Speed Reference Selector
Outer Knob: AUTO sets reference airspeed bugs from the FMC, V1 sets decision speed manually, VR
sets rotation speed manually, WT sets reference gross weight, VREF sets landing reference speed, and
SET removes digital readout above Mach/airspeed indicator.
Inner Knob: manually sets appropriate reference airspeed or gross weight
Fuel Flow Indication Selector switch (Reset/Rate/Used)
Auto Brake select switch
OFF: deactivates autobrake system
1, 2, 3 or MAX: selects desired deceleration rate for landing (switch must be pulled out to select MAX decel)
RTO (Rejected Takeoff): automatically applies maximum brake pressure when thrust levers are retarded to idle at or above 90 kts
Auto Brake Disarm Light
Antiskid Inoperative
Light
LE (Leading Edge) Flaps In
Transit light
LE (Leading Edge) Flaps
Extended light
Flaps Indicator (degrees)
MFD (Multi-function Display) page selector
Displays either ENG or SYS pages.
Pressing ENG changes engine parameter display mode on lower and
upper DU (Display Unit) to display more or less information about
engine parameters.
Pressing SYS shows brake temperature and control surfaces
positions on lower DU on the center pedestal.

24
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
ENG page
SYS page
ENG page
MFD (Multi-function Display) page selectors
N2 (High Pressure Compressor
Speed) Indication (%RPM)
Fuel Flow (x 1000
lbs/hour)
Oil Pressure (PSI)
Oil Temperature (deg C)
Oil Quantity (%)
Engine Vibration Level
Hydraulic System Fluid
Quantity & Pressure
Brake Temperature
Flight Control Position

25
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Nose Landing Gear In Transition Indication (Red when not Down & Locked )
Nose Landing Gear Deployed Indication (Green when Down & Locked )
Right Landing Gear In Transition Indication (Red when not Down & Locked )
Left Landing Gear In
Transition Indication
(Red when not Down &
Locked )
Left & Right Landing
Gear Deployed
Indication (Green
when Down & Locked )
Landing Gear Lever
UP: Landing Gear Retracted
MIDDLE: OFF (Hydraulic Pressure is removed from landing gear system)
DOWN: Landing Gear Deployed
Landing Gear Hydraulic Pressure Indicator
26
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
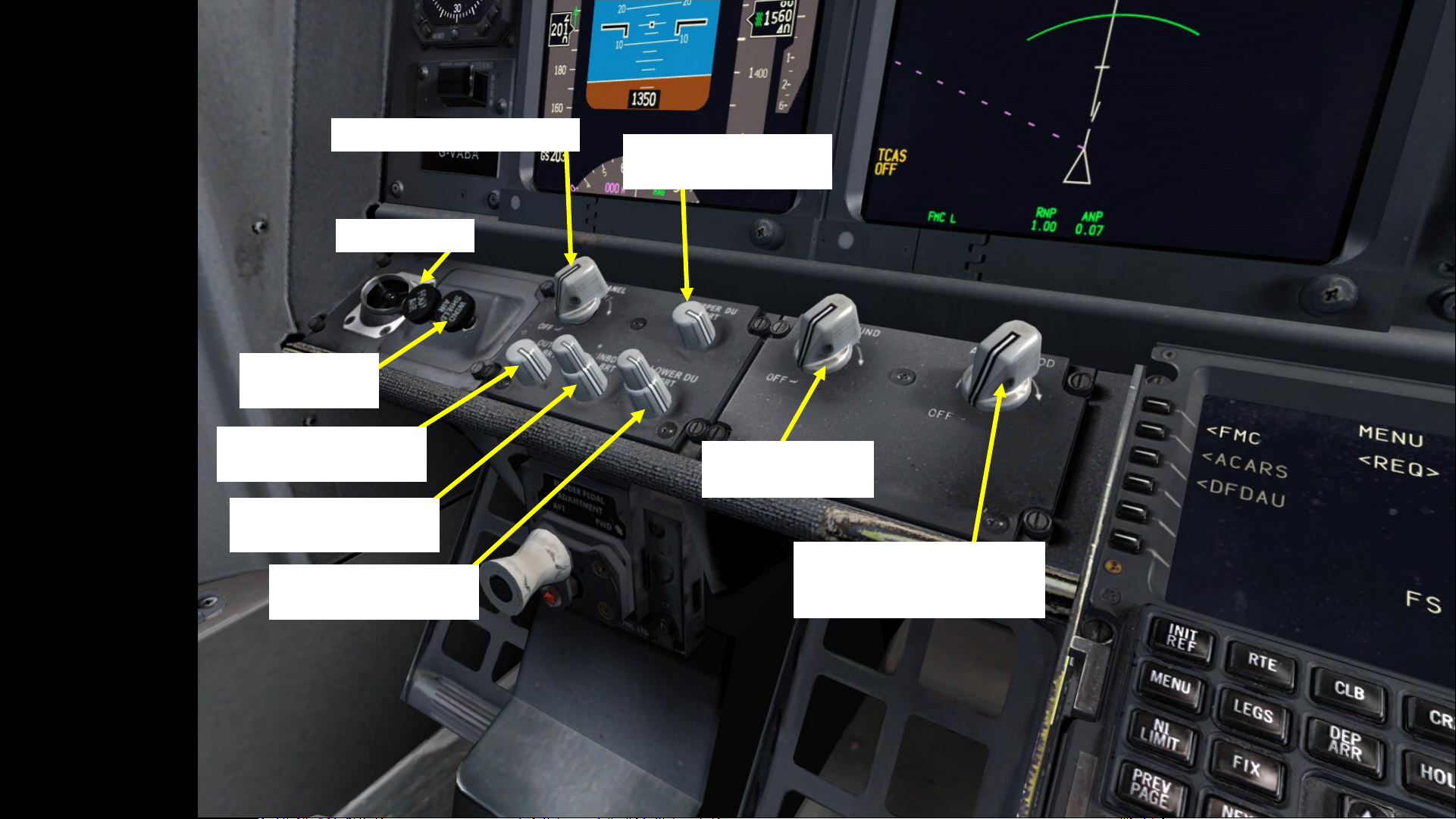
Foot Air Control
Windshield Air
Control
Outboard Display Unit
(DU) Brightness Control
Inboard Display Unit (DU)
Brightness Control
Lower Display Unit (DU)
Brightness Control
Upper Display Unit (DU)
Brightness Control
Main Panel Brightness Control
Background Light
Brightness Control
AFDS (Autopilot Flight Director
System) Panel Flood Lights
Brightness Control

27
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
FMS (Flight Management System) CDU (Control Display Unit)
• An FMS is a specialized computer system that automates a wide variety of
in-flight tasks, reducing the workload on the flight crew to the point that
modern civilian aircraft no longer carry flight engineers or navigators. A
primary function is in-flight management of the flight plan.
• The FMS is controlled through the CDU physical interface.
• The FMS sends the flight plan for display to the Electronic Flight Instrument
System (EFIS), NavigationDisplay (ND),or Multifunction Display (MFD).

28
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
GPWS (Ground Proximity Warning
System) Inoperative Light
GPWS System Test Switch
GPWS Flap Inhibit Switch
Inhibits ground proximity TOO LOW FLAPS alert
GPWS Gear Inhibit Switch
Inhibits ground proximity TOO LOW GEAR alert
GPWS TERR (Terrain) Inhibit Switch
Inhibits look-ahead terrain alerts and terrain display

29
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Pedestal
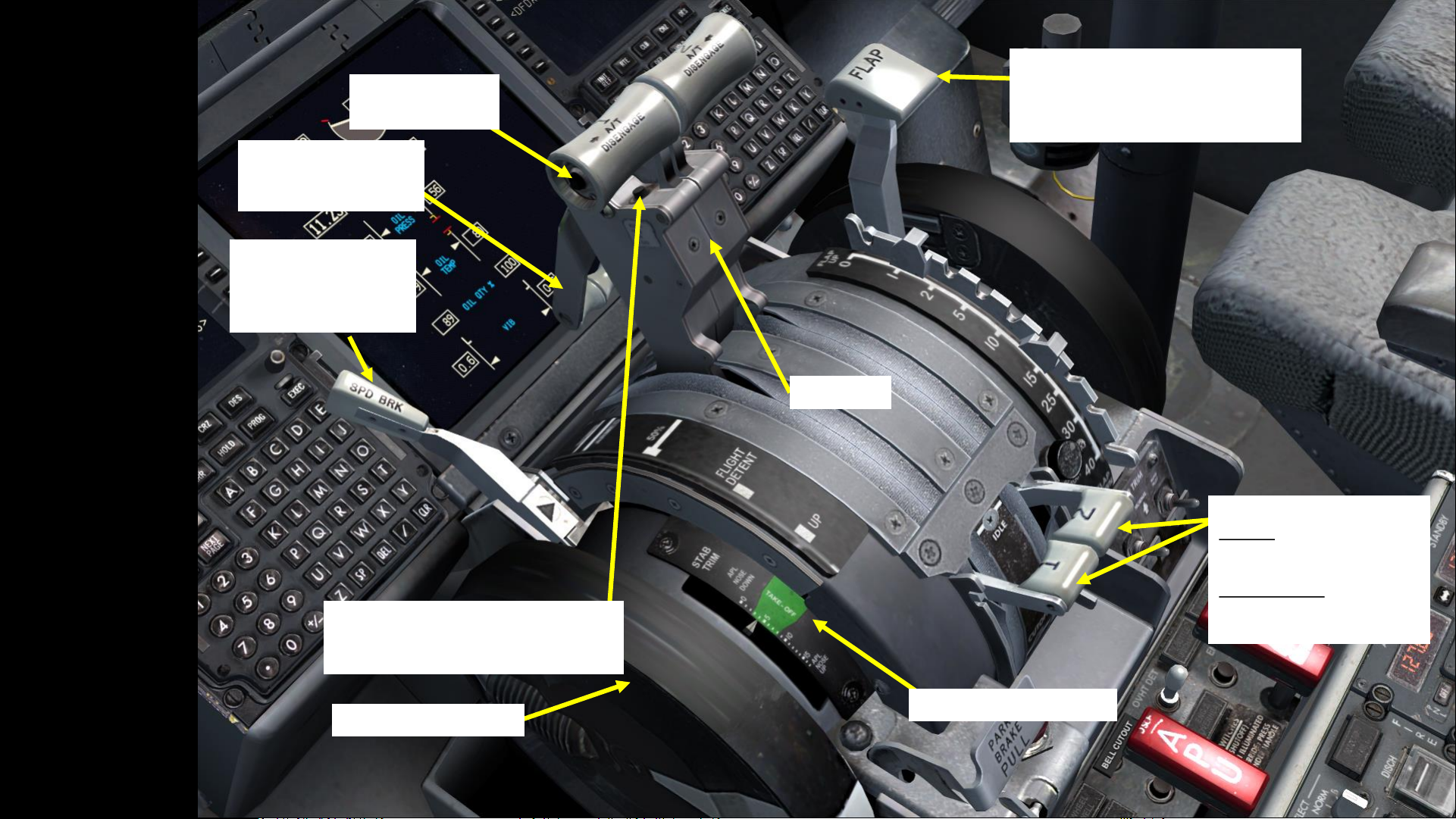
30
PART 2
–
COCKPIT LAYOUT
Autothrottle
Disengage Switch
Speed Brake Switch
(“Spoiler” control)
FWD: Retracted
AFT: Deployed
Throttles
Thrust Reverser Lever
Can only be deployed if
throttle is at IDLE.
Flap Lever
Left clicking moves it AFT (deploys flaps),
while right clicking moves it FORWARD
(retracts flaps)
Stabilizer Trim Indicator
Engine Start Levers
UP: IDLE (opens fuel shutoff
valve and energizes ignition
system)
DOWN: CUTOFF (closes fuel
shutoff valve and de-energizes
ignition system)
Stabilizer Trim Wheel
TO/GA Button
(only works if autothrottle is engaged and
N1 is greater than 40 %)
 Loading...
Loading...