
Version 1.0
for
Color Flatbed Scanners
1

All trademarks and brand names mentioned in this publication are property of their
respective owners.
2000. All rights are reserved. No portion of this document may be reproduced
without permission.
2

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION.........................................................................................................................................1
OW TO USE THIS GUIDE
H
ONVENTIONS OF THIS GUIDE
C
OTE ABOUT ICONS
A N
CHAPTER I. THE TWAIN INTERFACE..................................................................................................2
NTRODUCTION TO
AN I
NSTANT DESCRIPTIONS
I
HOOSING
C
TWAIN D
DVANCED SETTINGS WINDOW
A
Preferences Window..............................................................................................................................8
DVANCED WINDOWS FOR COLOR CORRECTION
A
Color Channels.................................................................................................................................... 12
Histogram ............................................................................................................................................12
Tone Map.............................................................................................................................................14
Image Gamma......................................................................................................................................16
CANNING TIPS
S
TWAIN .....................................................................................................................................3
IALOG BOX FEATURES
..........................................................................................................................................17
............................................................................................................................1
.....................................................................................................................1
................................................................................................................................1
TWAIN...................................................................................................................2
OOL TIPS
: “T
”.........................................................................................................3
................................................................................................................3
..................................................................................................................7
......................................................................................12
CHAPTER II. THE SCANNER SOFTWARE.........................................................................................18
VERVIEW
O
HE FAX UTILITY
T
About the Fax Utility............................................................................................................................ 19
Using Fax Utility..................................................................................................................................20
Fax Utility Settings ..............................................................................................................................21
HE E-MAIL UTILITY
T
About the E-mail Utility.......................................................................................................................22
Using the E-mail Utility.......................................................................................................................22
E-mail Utility Settings..........................................................................................................................23
HE IMAGE EDITOR
T
Opening the Program ..........................................................................................................................24
Acquiring an Image from the Scanner.................................................................................................24
Basic Image Adjustments.....................................................................................................................25
Using Editing Tools.............................................................................................................................25
Saving Images...................................................................................................................................... 25
Printing Images....................................................................................................................................26
Scanning Tip: Monitor Gamma...........................................................................................................26
For Additional Help.............................................................................................................................26
HE COPY UTILITY
T
About the Copy Utility .........................................................................................................................27
Using the Copy Utility .........................................................................................................................27
.................................................................................................................................................18
......................................................................................................................................19
.................................................................................................................................22
ICTURE PUBLISHER
- P
....................................................................................................................................27
................................................................................................24

Copy Utility Settings............................................................................................................................28
HE
T
To Use OCR via Action Manager 32...................................................................................................29
To Use OCR Directly from TextBridge Program.................................................................................30
To Use OCR Directly from Your Word Processor...............................................................................32
Some key points about OCR.................................................................................................................33
CONTACTING PLUSTEK........................................................................................................................35
OCR P
ROGRAM
EXTBRIDGE CLASSIC
– T
..........................................................................................29
Introduction
How to Use This Guide
This Software User’s Guide provides instructions and illustrations on how to use
your scanner. This guide assumes the user is familiar with the Microsoft Windows. If
this is not the case, we suggest you learn more about Microsoft Windows by referring
to your Microsoft Windows manual before using your scanner.
Chapter I discusses the scanner’s TWAIN interface.
Chapters II provides an overview of the software bundled with your scanner and
is a useful companion to the help menus found within the software applications
themselves.
Conventions of this Guide
1. Bold — Important note or first use of an important term in a chapter.
2. ALL CAPS — Represents commands or contents on your computer screen.
A Note About Icons
This guide uses the following icons to point out information that deserves special
attention.
Danger
Caution
Attention
Danger
accidents.
Caution
damage to the product.
Pay Special Attention
may prevent mistakes.
A procedure that must be followed carefully to prevent injury, or
. Information that, if not followed, may result in data loss or
. Instructions that are important to remember and
1
e
Chapter I. The TWAIN Interface
An Introduction to TWAIN
The TWAIN program is a very important piece of software that comes with
your scanner. This program acts as an interface between the scanner hardware and the
image-editing software you are using to view and edit images. The TWAIN program
allows you to adjust a number of settings to define the quality of the scanned image.
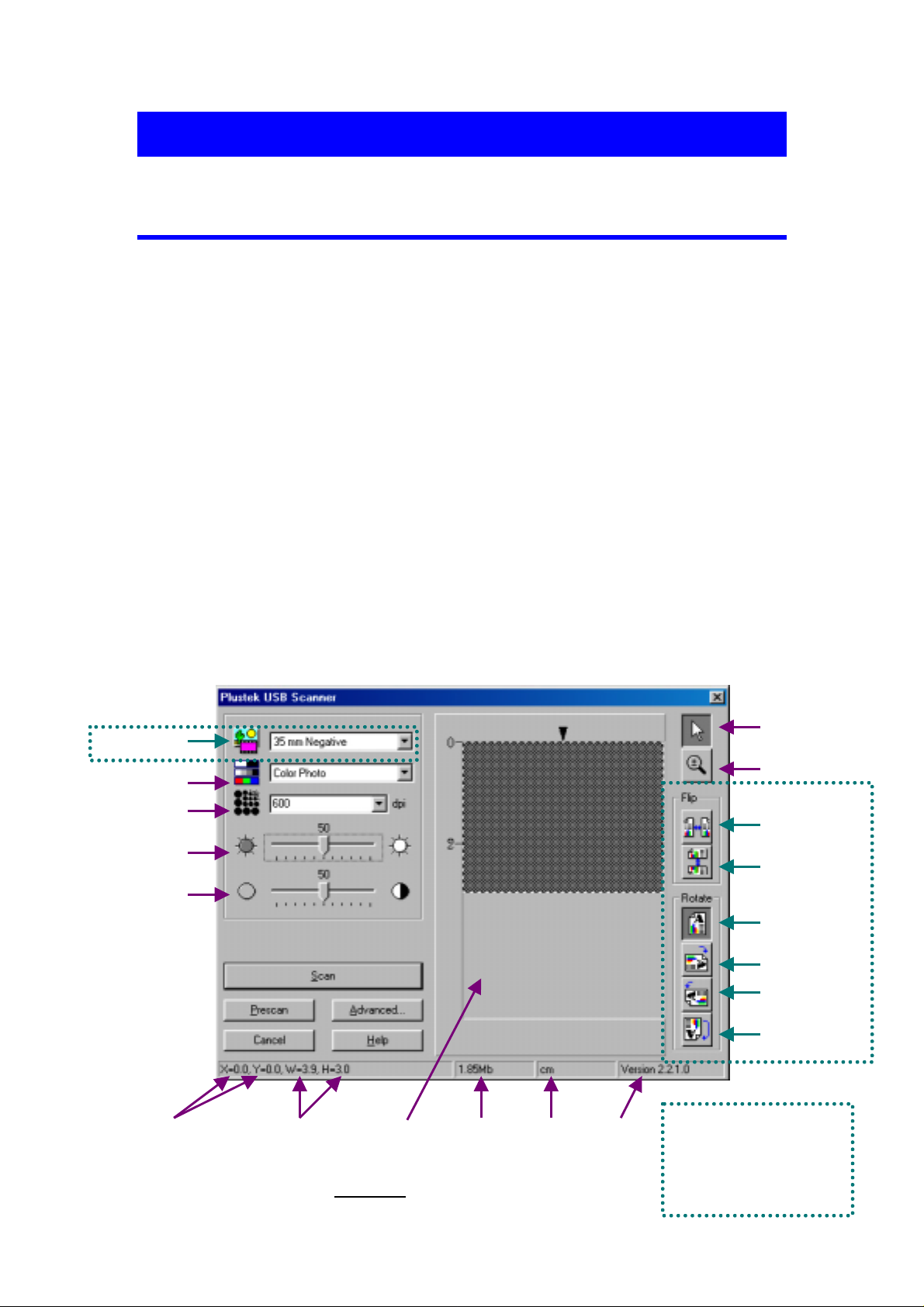
The following chapter describes the TWAIN interface (see Figure 1) which
automatically opens when you click SCAN, or ACQUIRE from within a TWAIN
compatible scanning program or image-editing application.
The TWAIN interface allows you to make important adjustments before
scanning. For example, you can scan in different modes: black and white, grayscale or
color; increase or decrease the resolution (dots per inch of an image), and adjust the
brightness and/or contrast. The Prescan option allows you to adjust the borders of the
scan area by increasing or decreasing the size of the crop box located inside the
Prescan Area. The TWAIN interface also provides you with statistics such as how
large an image will be after scanning, in terms of both file size and physical
dimensions.
Sourc
Scan Mode
Resolution
Brightness
Contrast
Scan Area
Coordinates
Scan Area
Dimensions
Scan Area
Borders
Prescan
Area
Figure 1. TWAIN Window
Image
Size
Units Version
Pointer
Note: Apply for the
scanner model built
with a transparency
adapter only.
Magnifying
Glass
Horizontal
Vertical
None
90°°°° Right
90°°°° Left
180°°°°
2

Instant Descriptions: “Tool Tips”
Let the mouse pointer rest over any item within the TWAIN dialog box and a
description of the item will instantly appear. However, for more information about the
use and function of specific items, you can refer to the on-line TWAIN Help by
clicking on the Help button towards the bottom of the window.
Choosing TWAIN
To select the TWAIN interface: From your TWAIN compatible program, locate
the scanner setup or TWAIN source option usually listed under the FILE menu and
choose the appropriate TWAIN source for your scanner.
TWAIN Dialog Box Features
This section describes all of the options available in the TWAIN interface. It is
very important to correctly configure the first two items (Source and Scan Mode) in
order to successfully perform a scan. All other items are optional and allow you to
tailor the characteristics of the scanned image.
Source - This option is available only for scanners built with a
transparency adapter. There are three possible sources listed:
• Normal - Use this setting to scan normal sheets of paper or any non-
transparent material.
• 35mm Slide - Use this mode for scanning slides.
• 35mm Negative - Use this mode for scanning negatives.
Scan Mode - There are three settings to choose from:
• Text - scans in black and white and is suitable for scanning text.
• B/W Photo (grayscale) - scans in 256 shades of gray, giving black and
white images or photos depth and shadow.
• 16-bit B/W Photo (grayscale) – scans in more than 65,000 shades of gray,
improving the realism of b/w images.
• Color Photo - scans in millions of colors for photo-realism. Choose this
mode when scanning color pictures or graphics.
3

• 48-bit Color Photo – scans in billions of colors for professional imaging
requiring precise uniformity of color.
Resolution - Resolution is measured in dots per inch (dpi). The higher the
resolution, the more detailed the image, and the more memory and drive space
the image will use.
Brightness - This is the amount of light that is concentrated onto a document
while it is being scanned.
Contrast - Contrast adjusts the tonal range of an image by lowering mid-tone
values and increasing values for high and low tones.
Flip Horizontally - This option will only appear when scanning
transparencies or negatives, if your scanner is built with a transparency
adapter. It will flip the scanned image around the central vertical axis. This
feature will not show up on the prescanned image, but will only affect the final
scanned image.
Flip Vertically - This option will only appear when scanning
transparencies or negatives, if your scanner is built with a transparency
adapter. It will flip the scanned image around the central horizontal axis. This
feature will not show up on the prescanned image, but will only affect the final
scanned image.
Rotate 90°°°° Clockwise - This option will only appear when scanning
transparencies or negatives, if your scanner is built with a transparency
adapter. It will rotate the scanned image 90°clockwise. This feature will not
show up on the prescanned image, but will only affect the final scanned image.
Rotate 180° - This option will only appear when scanning transparencies
or negatives, if your scanner is built with a transparency adapter. It will
rotate the scanned image 180°. This feature will not show up on the prescanned
image, but will only affect the final scanned image.
4
Rotate 90°°°° counter-clockwise - This option will only appear when
scanning transparencies or negatives, if your scanner is built with a
transparency adapter. It will rotate the scanned image 90° counter-
clockwise. This feature will not show up on the prescanned image, but will
only affect the final scanned image.
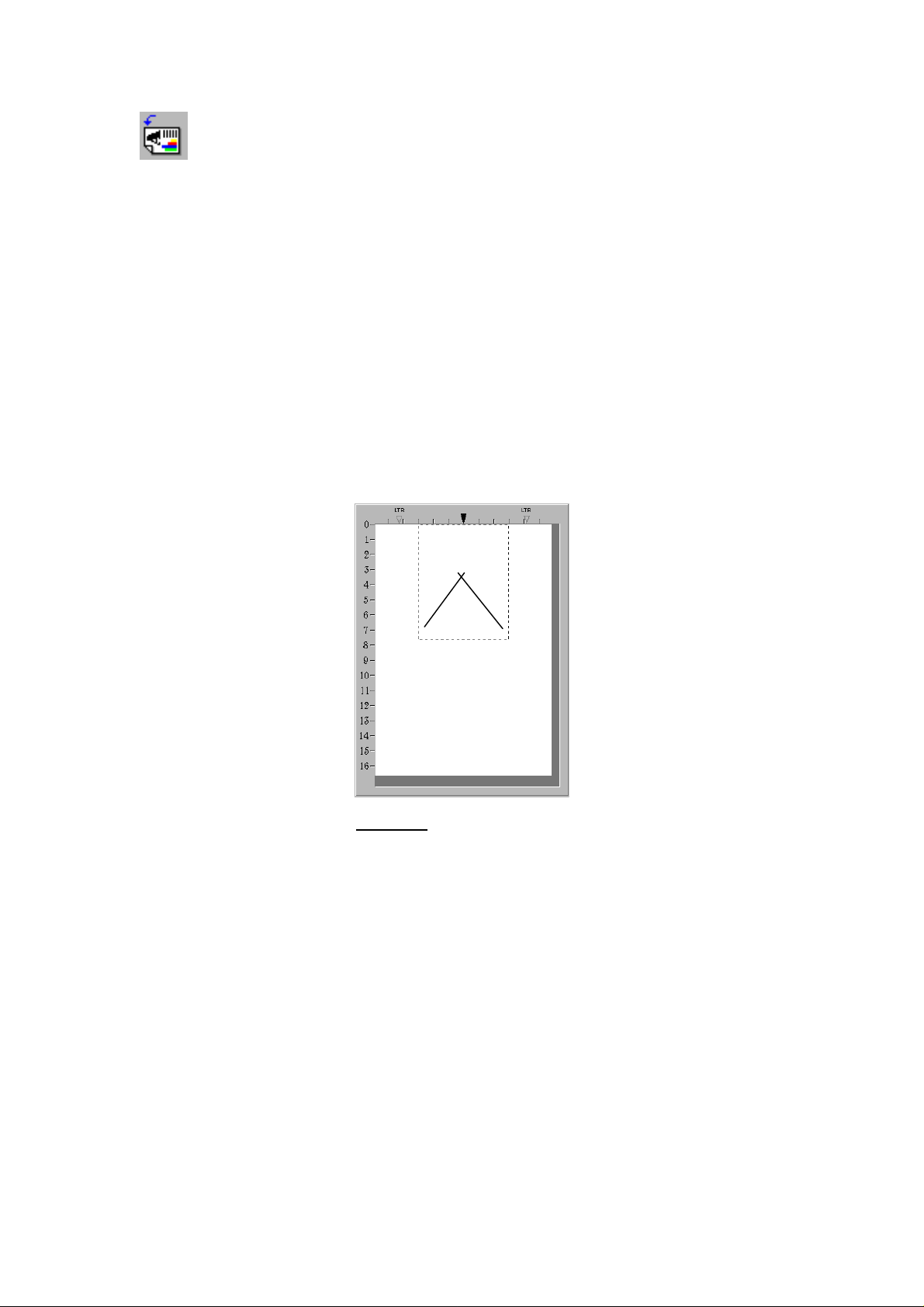
Prescan Window - The Prescan Window (figure 2) is the large white area in the
middle of the TWAIN window. Documents or images that are prescanned will
be displayed there.
Prescanning images is very useful as it gives you an idea of how a document or
image will look after it is scanned. You can use the Magnifying Glass to zoom
the view of the prescanned image by clicking on the magnifying glass button
towards the upper right of the TW AIN window and then clicking on the part of
the image you wish to view in detail.
Scan Area
Borders
Figure 2. Prescan Window
If you change any settings either in the TWAIN window or in any of the
Advanced windows, the effects of the changes (except for Flip, Rotate, Filter
and Descreen) will immediately appear on the prescanned image in the Prescan
Area. This allows you to instantly judge the effects of almost any setting you
change.
The Scan Area Border, designated by the dotted box in the Prescan Area, can
be resized and moved. This is very important for keeping the image size (in
terms of computer memory) as small as possible. To do this, first prescan the
document or image you wish to scan by loading it in the scanner and clicking
on the Prescan Button. After it appears in the Prescan Area, resize and move
the dotted box so it fits snugly around the edges of the prescanned image.
5

Placing the mouse pointer INSIDE the Scan Area Border box will change the
cursor as shown to the left and allows you to move the entire frame by
dragging the mouse.
Placing the mouse pointer at the EDGE of any side of the margin will change
the cursor as shown to the left and allows you to reduce or expand the frame
around the image.
Pointer - Changes the cursor from magnifying glass to pointer. The pointer
must be used to adjust the Scan Area Border or change settings.
Magnifying Glass - Clicking on the magnifying glass button changes the
cursor to a magnifying glass and lets you easily zoom in and out of the
prescanned image in the Prescan Window.
To zoom in, click the left mouse button. To zoom out, click the right mouse
button. To stop zooming in and out of the image, click on the Pointer button
just above the Magnifying Glass button.
Note: The magnifying glass only affects the view of the prescanned image
in the prescan area and in no way affects the scanning process or
the final scanned image.
Scan Button - Accepts all settings and begins scanning.
Prescan Button - By clicking on the Prescan button, you can scan the source
document into the Prescan Area in the middle of the TWAIN window. This
allows you to modify the scan area (for smaller images such as photographs)
and gives you a rough idea of what the scanned image will look like before you
scan.
Advanced Button - Advanced controls for precision scans. See below for detailed
explanations about the Advanced Settings window that appears when you click
on this button.
Cancel - Clicking on the Cancel button saves your current settings and closes the
TWAIN window
Help - Clicking on this button runs the on-line help program
6

Attention
Status Bar - The status bar (figure 3) contains important information about the
settings in the TWAIN window.
Figure 3. Status Bar
Scan Area Coordinates shows the position of the Scan Area Border in terms of X
and Y coordinates.
Scan Area Dimension shows the exact width and height of the Scan Area Border.
Image Size displays the amount of memory your image will use. The larger the image
size, the longer it takes to actually scan the image. Larger images, due to their
memory requirements, will also take longer for your image-editing applications
to process when making any corrections.
Tips for reducing the file size of an image:
• Change the scan mode – Color mode collects the most amount of
information and therefore requires more memory than grayscale or black
and white.
• Reduce the resolution –See S canning Tips later in this chapter for detailed
information about selecting the proper amount of resolution.
• Reduce the scan area - When scanning images that are smaller than a full
page, make sure you prescan the image and adjust the scan area borders in
the Prescan Area window.
• Some file formats such as GIF and JPEG can compress image data, greatly
reducing the amount of space an image takes up on your hard drive.
Units shows the measurement units used i n the Prescan Area. The measurement uni ts
can be changed by clicking on the Advanced button.
Version displays the version of the TWAIN program you are using.
Advanced Settings Window
The Advanced Settings window (figure 4) has 4 tabs running along the top Preferences, Histogram, Tone Map and Gamma, all of which will be explained in
detail below. Click on one of the tabs to display settings. For additional instructions
click on the Help button at the bottom-right of the window to view the on-line
TWAIN help.
7
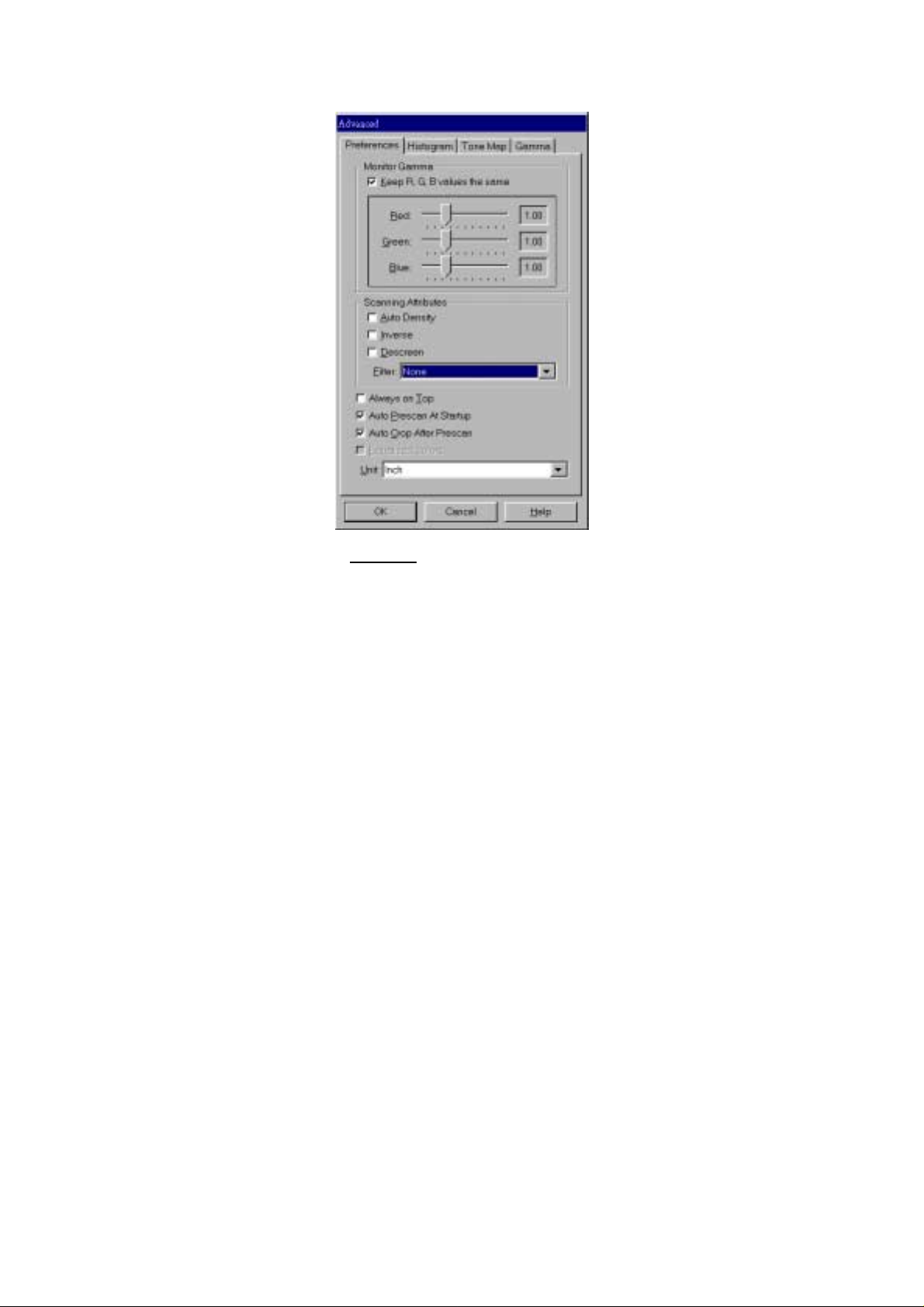
Figure 4. Advanced Settings
Most of the menu options are considered advanced features. W e strongly suggest
that you first become familiar with scanning and using the settings in the TWAIN
window before attempting to use any of the following features. Many of these
advanced features will also be available to you in your image-editing software after
you scan.
PPrreeffeerreenncceess WWiinnddooww
The Preferences window (figure 4) has a number of settings that control how the
image is scanned and how it is viewed in the Prescan Area.
MMoonniittoorr GGaammmmaa
Monitor gamma defines how the colors in an image will be displayed on your
monitor (not the color data in the image itself). The monitor gamma setting allows you
to change the gamma values for your monitor.
The monitor gamma only aff ects the prescanned image in th e prescan area.
This is because image-editing applications have their own monitor gamma settings.
The settings defined here should be exactly the same as the settings in the imageediting application you will use to view and edit the scanned image.
To correctly adjust the monitor gamma, you must first have your computer and
working environment stable. This includes the lighting in the room, and making sure
your monitor brightness, contrast and colors are properly adjusted. Next, drag the
slider bars to alter the monitor gamma. When finished, click OK to exit.
8
 Loading...
Loading...