Page 1

22Mbps Wireless Broadband Router
WRT-405
User’s Manual
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright 2002 by PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may
be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language
or computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical,
chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of PLANET.
PLANET makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or implied, with respect to the
contents hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness for any particular
purpose. Any software described in this manual is sold or licensed "as is". Should the programs
prove defective following their purchase, the buyer (and not this company, its distributor, or its dealer)
assumes the entire cost of all necessary servicing, repair, and any incidental or consequential
damages resulting from any defect in the software. Further, this company reserves the right to revise
this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof without obligation to
notify any person of such revision or changes..
All brand and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks and/or registered trademarks
of their respective holders.
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
3. Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
4.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio technician for help.
FCC Caution:
To assure continued compliance.(example-use only shielded interface cables when connecting to
computer or peripheral devices). Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the Following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2 ) this Device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Page 3

Federal Communication Commission (FCC) Radiation Exposure
Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure set forth for an uncontrolled environment. In
order to avoid the possibility of exceeding the FCC radio frequency exposure limits, human proximity
to the antenna shall not be less than 20 cm(8 inches) during normal operation.
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of DIRECTIVE 1999/5/CE OF THE EUROPEAN
PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL OF 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunication
terminal Equipment and the mutual recognition of their conformity (R&TTE)
The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC (Telecommunications Terminal
Equipment and Satellite Earth Station Equipment) As of April 8,2000.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it. However,
special attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when working with
electrical equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacture must therefore be allowed
at all times to ensure the safe use of the equipment.
Revision
User’s Manual for PLANET Wireless Broadband Router
Model: WRT-405
Rev: 1.0 (November. 2002)
Part No. EM-WRT405v1
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION..............................................................................................1
ACKAGE CONTENTS
1.1 P
YSTEM REQUIREMENTS
1.2 S
EATURES
1.3 F
PECIFICATION
1.4 S
1.5 LED I
.....................................................................................................................1
NDICATORS
.....................................................................................................1
................................................................................................1
..............................................................................................................2
...........................................................................................................3
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION...........................................................................3
ARDWARE CONNECTION
2.1 H
...............................................................................................3
CHAPTER 3 CONFIGURE THROUGH WEB BROWSER.....................................................5
AIN
3.1 M
............................................................................................................................5
3.1.1 LAN & DHCP Server............................................................................................5
3.1.2 WAN.....................................................................................................................6
3.1.3 Password.............................................................................................................7
3.1.4 Time.....................................................................................................................8
IRELESS
3.2 W
.....................................................................................................................9
3.2.1 Basic....................................................................................................................9
3.2.2 WEP.....................................................................................................................9
3.2.3 Advanced...........................................................................................................10
TATUS
3.3 S
.......................................................................................................................11
3.3.1 Device Information..............................................................................................11
3.3.2 Log.....................................................................................................................12
3.3.3 Log Settings.......................................................................................................12
3.3.4 Statistic..............................................................................................................13
3.3.5 Wireless.............................................................................................................14
OUTING
3.4 R
....................................................................................................................14
3.4.1 Static..................................................................................................................14
3.4.2 Dynamic.............................................................................................................15
3.4.3 Routing Table.....................................................................................................16
CCESS
3.5 A
......................................................................................................................17
3.5.1 User Group.........................................................................................................17
3.5.2 Protocol Filter.....................................................................................................17
3.5.3 IP Filter...............................................................................................................19
3.5.4 Virtual Server......................................................................................................19
3.5.5 Special AP..........................................................................................................20
3.5.6 DMZ...................................................................................................................21
Page 5

3.5.7 Firewall Rule......................................................................................................22
ANAGEMENT
3.6 M
.............................................................................................................23
3.6.1 SNMP................................................................................................................23
3.6.2 Remote Management.........................................................................................24
OOLS
3.7 T
........................................................................................................................24
3.7.1 Restart...............................................................................................................24
3.7.2 Settings..............................................................................................................25
3.7.3 Firmware............................................................................................................26
3.7.4 Ping Test............................................................................................................27
CHAPTER 4 TROUBLESHOOTING....................................................................................28
REQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
4.1 F
4.2 G
LOSSARY
..................................................................................................................29
..................................................................................28
Page 6

as
Chapter 1 Introduction
Thank you for purchasing WRT-405. This device features the latest innovation wireless technology
making the wireless networking world happened. This manual guides you on how to install and properly
use the WRT-405 in order to take full advantage of its features.
1.1 Package Contents
Make sure that you have the following items:
• One WRT-405
• One AC Power Adapter
• One User’s Manual CD
• One Quick Installation Guide
Note:
1.2 System Requirements
Before installation, please check the following requirements with your equipment.
If any of the above items are missing, contact your supplier as soon
possible.
• Pentium Based (And Above) IBM-Compatible PC System
• CD-ROM drive
• Windows 98/ME/NT/2000/XP Operating System with TCP/IP protocol
1.3 Features
• Utilize Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) Technology and support the modulation
of Packet Binary Convolutional Code (PBCC) mode to provide robust,
interference-resistant solution in a multi-user environment
• Wireless LAN IEEE802.11b compliant
• Auto Fall-Back Data Rate for Long-Distance Communication and Noisy Environments
• High-Speed Data Transmitter Rate Up to 22 Mbps
• Features Roaming, Best Access Point Selection, and Network Traffic Filtering
• 64bit, 128bit and 256bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
• Web Configuration provide a user friendly interface for the user to configure through web
browser
• Support DHCP Server
• Support MAC Filter
• Support telnet and SNMP
• Build-in 4 -port switch
• Provides Setup Wizard for the user to configure easily in the first time
- 1 -
Page 7

1.4 Specification
Standard IEEE 802.11b Compliant
Signal Type DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum)
Modulation QPSK / BPSK / CCK / PBCC
Port Five 10/100Base-TX (WAN*1,LAN*4)
Antenna Dual Dipole Antenna
Data Encryption 64 bit / 128 bit / 256bit WEP encryption
Frequency 2.4GHz - 2.484GHz
Sensitivity -78dBm (@PER8%, 22Mbps)
Channel 11 Channels (FCC / US, Canada)
13 Channels (ETSI / urope)
14 Channels (TELEC / Japan)
Data Rate Up to 22Mbps (with automatic scale back)
LED Indicators WLAN Act, Dial, Power
LAN: Link/Act * 4, Full/Col * 4, 100Mbps * 4
WAN: Link/Act * 1, Full/Col * 1, 100Mbps * 1
Power
Requirement
Power
Consumption
Temperature Operating :0 ~ 55 degree C
Humidity Operating: 0 ~ 95%
Dimensions 200 x 150 x 60 mm
Output Power 15dBm
5V DC, 2.5A
TX power consumption: <650mA
RX power consumption <350mA
Sleep Mode power consumption: 20mA
Storage: -20 ~ 70 degree C
Storage: 0 ~ 95% Non-Condensing
- 2 -
Page 8

405. Otherwise, the product may be
ngs, press and hold the Reset button over 5
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
Before you proceed with the installation, it is necessary that you have enough information about the
WRT-405.
2.1 Hardware Connection
1. Locate an optimum location for the WRT-405. The best place for your WRT-405 is usually at
the center of your wireless network, with line of sight to all of your mobile stations.
2. Adjust the antennas of WRT-405. Try to adjust them to a position that can best cover your
wireless network. The antenna’s position will enhance the receiving sensitivity.
3. Connect RJ-45 cable to WRT-405 LAN port. Connect one of the LAN ports on WRT-405 to your
LAN switch/hub with a RJ-45 cable.
4. Connect RJ-45 cable to WRT-405 WAN port. Connect ADSL/Cable Modem to the WAN port on
WRT-405. Use the cable supplied with your modem. If no cable was supplied with your modem,
please use a RJ-45 Ethernet cable
5. Plug in power adapter and connect to power source. After power on, WRT-405 will start to
operate.
Note: ONLY use the power adapter supplied with the WRT-
damaged.
Note: If you want to reset WRT-405 to default setti
seconds. And then wait for 10 seconds for WRT-405 restart.
2.2 LED Indicators
- 3 -
Page 9

LED STATE MEANING
Green WLAN link status is on WLAN ACT
Blinking Green WLAN activity
Diag Green Indicates a connection error
Green Device power on PWR
Off Device power off
LNK/ACT
FDX/COL
100 Green Port works on 100Mbps
Green Link is established
Blinking Green Packets are transmitting or receiving
Off Not connected
Green Full-duplex mode
Blinking Orange Collision has occurred
Off Half-duplex mode
- 4 -
Page 10
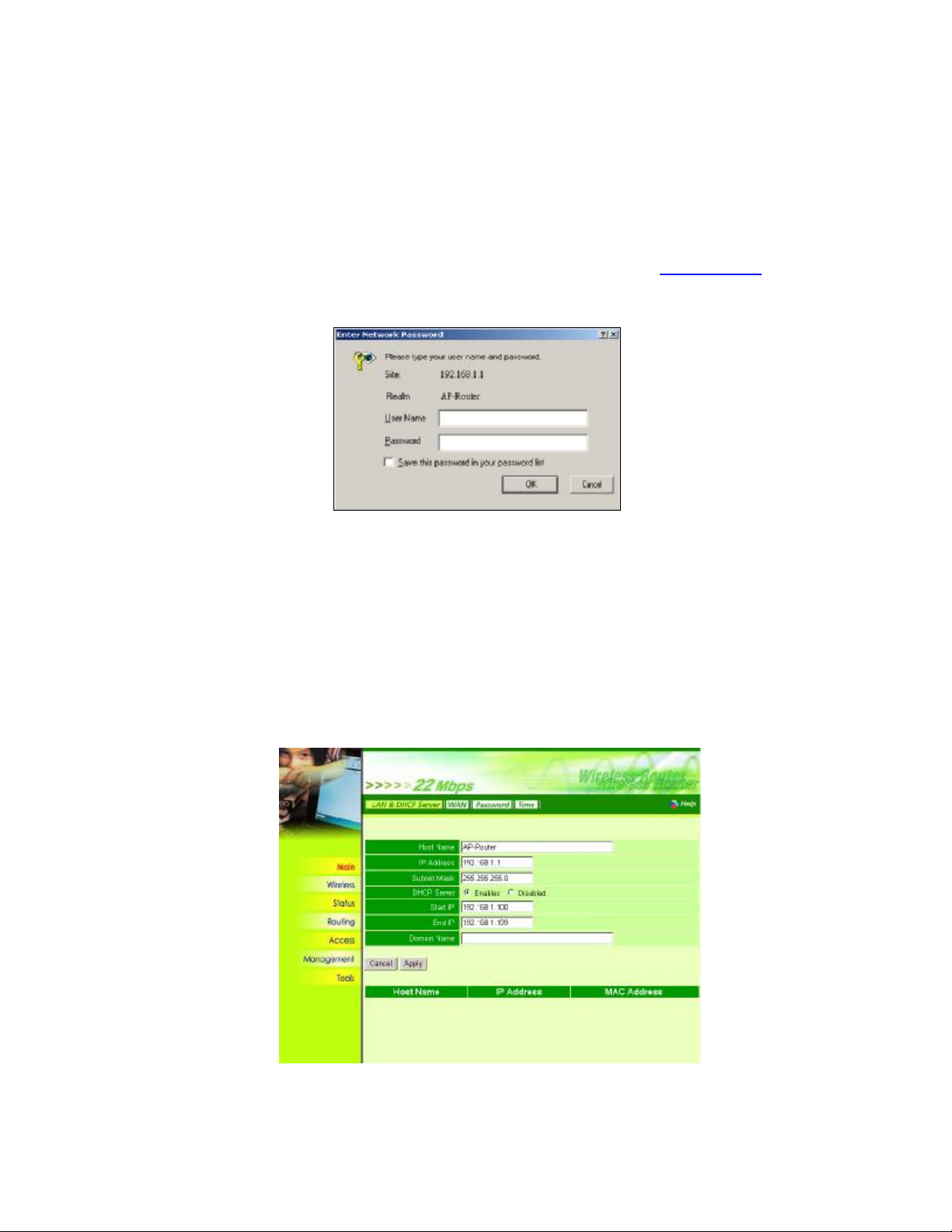
Chapter 3 Configure through Web Browser
Web configuration provides a user-friendly graphical user interface (web pages) to manage your
WRT-405. A WRT-405 with an assigned IP address will allows you to monitor and configure via web
browser (e.g., MS Internet Explorer or Netscape).
1. Open your web browser.
2. Enter the IP address of your WRT-405 in the address field (default IP address is http://192.168.1.1).
3. A User Name and Password dialog box will appear. Please enter your User Name and Password here.
Default User Name and Password is “admin”. Click OK.
4. Then you will see the WRT-405 web configuration page.
5. If this is your first time to configure WRT-405, we will suggest you refer to our Quick Installation Guide
to use the Setup Wizard to configure. Setup Wizard will guide you to complete the configuration step
by step.
3.1 Main
3.1.1 LAN & DHCP Server
You can configure WRT-405’s IP settings and DHCP server function in this screen. When
configuration is completed, please click “Apply” to save and restart WRT-405.
This page enables you to set LAN and DHCP properties, such as the host name, IP address, subnet
mask, and domain name. LAN and DHCP profiles are listed in the DHCP table at the bottom of the
screen.
- 5 -
Page 11
Host Name: Type the host name in the text box. The host name is required by some ISPs.
The default host name is "AP-Router."
IP Address: This is the IP address of the router. The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
Subnet Mask: Type the subnet mask for the router in the text box. The default subnet
mask is 255.255.255.0.
DHCP Server: Enables the DHCP server to allow the router to automatically assign IP
addresses to devices connecting to the WLAN or LAN. DHCP is enabled by default. All
DHCP client computers are listed in the table at the bottom of the page, providing the host
name, IP address, and MAC address of the client.
Start IP: Type an IP address to serve as the start of the IP range that DHCP will use to
assign IP addresses to all LAN devices connected to the WRT-405.
End IP: Type an IP address to serve as the end of the IP range that DHCP will use to
assign IP addresses to all LAN devices connected to the WRT-405.
Domain Name: Type the local domain name of the network in the text box. This item is
optional.
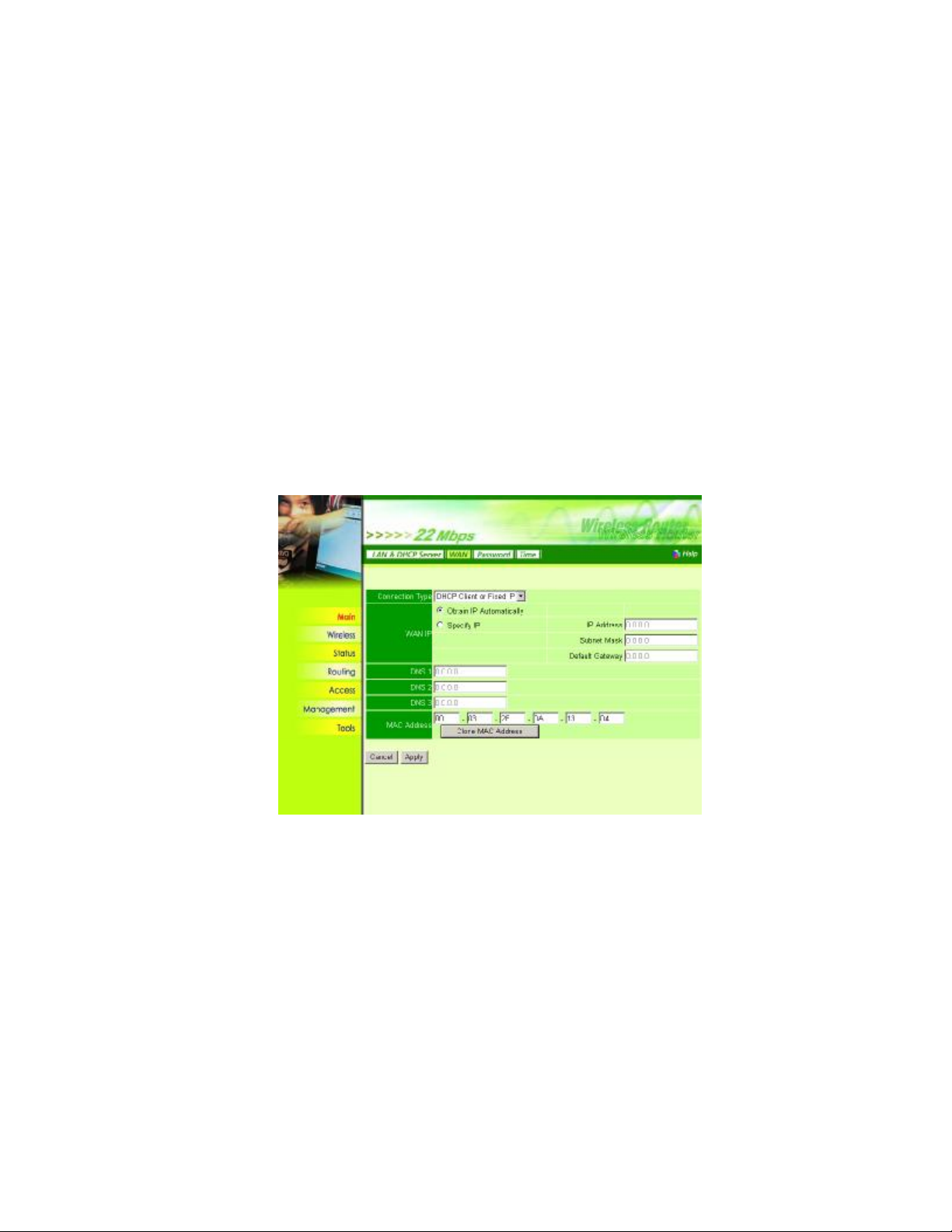
3.1.2 WAN
Please refer to your Internet connection method to select the Connection Type. And please configure
those settings per the information your ISP provides.
Connection Type: Select the connection type, either DHCP client/Fixed IP or PPPoE from
the drop-down list.
When using DHCP client/Fixed IP, enter the following information in the fields (some information are
provided by your ISP):
WAN IP: Select whether you want to specify an IP address manually, or want DHCP to
obtain an IP address automatically. When “Specify IP” is selected, type the IP address,
subnet mask, and default gateway in the fields. Your ISP will provide you with those
informations.
DNS 1/2/3: Type up to three DNS numbers in the fieldes. Your ISP will provide you with this
DNS information.
MAC Address: If required by your ISP, type the MAC address for the WRT-405 WAN
interface in this field. You can also copy the MAC address of your PC’s network card to
the WRT-405 WAN interface by clicking “Clone MAC address”.
- 6 -
Page 12

When using PPPoE, enter the following information in the fields (some information are provided by your
ISP):
WAN IP: Select whether you want the ISP to provide the IP address automatically, or
whether you want to assign a static IP address to the WRT-405 WAN interface. When
“Specify IP” is selected, type the PPPoE IP address in the field. Your ISP will provide you
with this information.
DNS 1/2/3: Type up to three DNS numbers in the fieldes. Your ISP will provide you with this
DNS information.
User Name: Type your PPPoE user name.
Password: Type your PPPoE password.
Connect on Demand: Enables or disables the connect on demand function, which enables
WRT-405 to initiate a connection with your ISP when an Internet request is made to the
WRT-405. When enabled, the WRT-405 automatically connects to the Internet when you
open your browser.
Idle Time Out: Specify the time that will elapse before the WRT-405 times out of a
connection.
MTU: Type the MTU value in the field.
3.1.3 Password
You can change the Administrator and User’s password in this screen. These passwords are used to
gain access to the router interface. When you login with user name “User”, you don’t have permission to
configure WRT-405.
- 7 -
Page 13

Administrator: Type the password the Administrator will use to login to the system. The
password must be typed again for confirmation.
User: Users can type a password to be used for logging in to the system. The password
must be typed again for confirmation.
3.1.4 Time
This screen enables you to set the time and date for the router's real time clock, select your time zone,
specify an NTP server, and enable or disable daylight saving.
Local Time: Displays the local time and date.
Time Zone: Select your time zone from the pull-down list.
Default NTP Server: Type the NTP server IP address in the field to enable the WRT-405 to
automatically set the time from the Internet NTP server.
Set the Time: Select the date and time from the pull-down lists, and click “Set Time” to set
the WRT-405's internal clock to the correct date and time.
Daylight Saving: Enables you to enable or disable daylight saving time. When enabled,
select the start and end date for daylight saving time.
- 8 -
Page 14

3.2 Wireless
3.2.1 Basic
This page enables you to enable and disable the wireless LAN function, enter a SSID, and set the
channel for wireless communications.
Enable/Disable: Enable or disable wireless LAN via the WRT-405.
SSID: Type an SSID in the field. The SSID of any wireless device must match the SSID
typed here in order for the wireless device to access the LAN and WAN via the WRT-405.
Channel: Select a work channel for wireless communications. The channel of any wireless
device must match the channel selected here in order for the wireless device to access the
LAN and WAN via the WRT-405.
3.2.2 WEP
This screen enables you to set WEP parameters for secure wireless communications.
- 9 -
Page 15

Mode: Select the key code you want to use for WEP Key. HEX or ASCII. When Hex is
selected, you may enter alphanumeric characters in the range of “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” in the
WEP Key entry field. Alternatively, you may enter digit hexadecimal values in the range of
“a-z”, “A-Z” and “0-9”.
WEP Key: Select the level of encryption you want from the drop-down list. WRT-405
supports 64, 128 and 256-bit encryption.
Key 1 ~ Key 4: There are 4 keys available, please ensure you have enter correct number
for the key values with different Key Length and coding (Hex or ASCII) as 64bit (10 Hex
digit / 5 ASCII), 128bit (26 Hex digit / 13 ASCII) or 256bit (58 Hex digit / 29 ASCII), please
select one of them and enter the key you want to use. Click “Clear” to erase key values.
Note: 128 and 256bit WEP encryption will require more system resources than 64bit encryption. Use
64-bit encryption for better performance.
3.2.3 Advanced
This screen enables you to configure advanced wireless functions.
Firmware Version: Displays the wireless firmware version. The wireless firmware is
updated when you update the WRT-405 firmware.
Beacon Interval: Type the beacon interval in the field. You can specify a value from 1 to
1000. The default beacon interval is 100.
RTS Threshold: Type the RTS (Request-To-Send) threshold in the field. This value
stabilizes data flow. If data flow is irregular, choose values between 256 and 2432 until data
flow is normalized.
Fragmentation Threshold: Type the fragmentation threshold in the field. If packet transfer
error rates are high, choose values between 256 and 2432 until packet transfer rates are
minimized. Please note that setting the fragmentation threshold value may diminish
system performance.
DTIM Interval: Type a DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) interval in the field. You
can specify a value between 1 and 65535. The default value is 3.
Basic Rates (MBps): Select one of the wireless LAN receive rates.
TX Rates (MBps): Select one of the wireless communications transfer rates, based upon
the speed of wireless adapters connected to the WLAN.
- 10 -
Page 16

Preamble Type: There is the “Long” or “Short” selection to ensure that systems receiving
the information correctly interpret when the data transmission starts. To select “Short”
Preamble may be used to minimize overhead and “Long” to maximize the network
reliability. The default value will be set for “Long”.
Authentication Type: Select the authentication type. Open System allowss public access
to the WRT-405 via wireless communications. Shared Key requires the user to set a WEP
key to exchange data with other wireless clients that have the same WEP key.
SSID Broadcast: Enable or disable a Service Set Identifier broadcast. When enabled, the
SSID of the WRT-405 is sent to wireless enabled devices on the area. Set the WRT-405's
SSID in the Basic screen. Enabling this function may cause unauthorized user to connect
your wireless networks.
3.3 Status
3.3.1 Device Information
This screen enables you to view the router LAN, wireless LAN, and WAN configuration.
Firmware Version: Displays the latest build of the WRT-405 firmware interface. After
upgrading the firmware in Tools -> Firmware, check this to ensure that your firmware was
successfully upgraded.
LAN: This field displays the WRT-405 LAN interface MAC address, IP address, subnet
mask, and DHCP server status. Click “DHCP Table” to view a list of client stations currently
connected to the WRT-405 LAN interface.
Wireless: Displays the WRT-405 wireless connection information, including the WRT-405
wireless interface MAC address, connection status, SSID status, which channel is being
used and whether WEP is enabled or not.
WAN: This field displays the WRT-405 WAN interface MAC address, DHCP client status,
IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS.
Click “DHCP Release” to release IP addresses get from ISP for the WAN port. Click “DHCP
Renew” to get a new IP addresses from ISP for the WAN port.
- 11 -
Page 17

3.3.2 Log
This screen will show you a running log of system statistics, events and activities. The log displays up to
200 entries. Older entries are overwritten by new entries. You can save logs via the Log Settings option
-> “Send to”. The Log screen commands and informations meaning are as follows
First Page: View the first page of the log message list.
Last Page: View the last page of the log message list.
Previous Page: View the page just before the current page.
Next Page: View the page just after the current page.
Clear Log: Delete the contents of the log and begin a new log.
Refresh: Renew log statistics.
Time: Displays the time and date that the log entry was created.
Message: Displays summary information about the log entry.
Source: Displays the source of the communication.
Destination: Displays the destination of the communication.
Note: Displays the IP address of the communication.
3.3.3 Log Settings
This screen allows you to set WRT-405 logging parameters.
- 12 -
Page 18

SMTP Server: Type the SMTP server address for the email that the log will be sent to in
the next field.
Send to: Type an email address for the log to be sent to. Click “Email Log Now” to send the
current log immediately.
Syslog Server: Type the IP address of the Syslog Server if you want the WRT-405 to listen
and receive incoming SysLog messages.
Log Type: Select what items will be included in the log:
w System Activity: Displays information related to WRT-405 operation.
w Debug Information: Displays information related to errors and system
malfunction.
w Attacks: Displays information about any malicious activity on the network.
w Dropped Packets: Displays information about packets that have not been
transferred successfully.
w Notice: Displays important notices by the system administrator.
3.3.4 Statistic
This screen displays a table that shows the rate of packet transmission via the WRT-405 LAN, WLAN
and WAN ports (in bytes per second).
- 13 -
Page 19

Click “Reset” to erase all statistics and begin logging statistics again.
Utilization: Separates packet transmission statistics into send and receive categories.
Peak indicates the maximum packet transmission recorded since logging began, while
Average indicates the average of the total packet transmission since recording began.
3.3.5 Wireless
This screen will show you which wireless devices that are connected to this WRT-405 via wireless
interface.
Connected Time: Displays how long the wireless device has been connected to the LAN
via the WRT-405.
MAC Address: Displays the devices wireless LAN interface MAC address.
3.4 Routing
3.4.1 Static
You can set parameters by which the WRT-405 forwards data to its destination if your network has a
static IP address.
- 14 -
Page 20

Network Address: Type the static IP address your network uses to access the Internet.
Your ISP or network administrator provides you with this information.
Network Mask: Type the network (subnet) mask for your network. If you do not type a
value here, the network mask defaults to 255.255.255.255. Your ISP or network
administrator provides you with this information.
Gateway Address: Type the gateway address of your network. Your ISP or network
administrator provides you with this information.
Interface: Select the interface WAN or LAN that you will use to connect to the Internet.
Metric: Select which metric you want to apply to this configuration.
Add: Click to add a configuration to the static IP address table at the bottom of this page.
Update: Select one of the entries in the static IP address table at the bottom of the page
and, after changing parameters, click “Update” to confirm the changes.
Delete: Select one of the entries in the static IP address table at the bottom of the page and
click “Delete” to remove the entry.
New: Click “New” to clear the fieldes and add required information to create a new entry.
3.4.2 Dynamic
This screen allows you to set the NAT parameters.
- 15 -
Page 21

NAT: Select the button to enable or disable NAT.
Transmit: Select the button to set the desired transmit parameters. Disabled, RIP 1 or RIP
2.
Receive: Select the button to set the desired transmit parameters. Disabled, RIP 1 or RIP
2.
3.4.3 Routing Table
This screen will show you the routing table of WRT-405. The routing table is a database created by
the WRT-405 that displays the network interconnection topology.
Network Address: Displays the network IP address of the connected node.
Network Mask:
Gateway Address: Displays the gateway address of the connected node.
Interface:
Metric: Displays the metric of the connected node.
Displays whether the node has a static or dynamic IP address.
Type:
Displays the network (subnet) mask of the connected node.
Displays whether the node is connected via a WAN or LAN.
- 16 -
Page 22

3.5 Access
3.5.1 User Group
This screen enables you to allows and deny user access based upon a user list you create.
MAC Filter: By default is disabled. You can use this function to allows or deny the users
access to this WRT-405.
Disabled: Disable MAC Filter function.
Allows: All users in all groups except for those you have assigned to Deny in the
User Table are allowed Internet access.
Deny: All users are allowed Internet access except those users you have assigned to
Groups 1 to 4 in the User Table are allowed Internet access.
User Table: Use this section to create a user profile to which Internet access is denied or
allowed. The user profiles are listed in the table at the bottom of the page.
Note: When selecting items in the table at the bottom, click anywhere in the item. The line is
selected, and the fields automatically load the item's parameters, which you can edit.
Name: Type the name of the user to be permitted/denied access.
MAC Address: Type the MAC address of the user's network interface.
Connection Type: Select whether the user's access is via a wired Ethernet, or a
wireless LAN connection.
Group: Select a group from the pull-down list to apply this user to.
Add: Click to add the user to the list at the bottom of the page.
Update: Click to update information for the user, if you have changed any of the
fields.
Delete: Select a user from the table at the bottom of the list and click “Delete” to
remove the user profile.
New: Click “New” to erase all fields and enter new information.
3.5.2 Protocol Filter
This screen enables you to allows or deny access based upon a communications protocol list you create.
The protocol filter profiles are listed in the table at the bottom of the page.
- 17 -
Page 23

Note: When selecting items in the table at the bottom, click anywhere in the item. The line is
selected, and the fields automatically load the item's parameters, which you can edit.
Protocol Filter: Enables you to allow or deny Internet access to users based upon the
communications protocol of the origin. Click the radio button next to Disabled to disable the
protocol filter.
Allows: All protocols in the list are allowed to connect to the Internet via the LAN.
(Create list items in section under Add Protocol Filter.)
Deny: All protocols in the list are not allowed to connect to the Internet via the LAN.
(Create list items in section under Add Protocol Filter.)
Add Protocol Filter: Use this section to create a profile for the protocol you want to permit
or deny Internet access to.
Enable: Click to enable or disable the protocol filter.
Name: Type a descriptive name for the protocol filter.
Protocol: Select the protocol (TCP, UDP or ICMP) you want to allows/deny Internet
access to from the pull-down list.
Port Range: If you are creating a profile for ICMP, type a minimum and maximum
port range in the two fields.
Apply to Group: Select which user group you want to apply the profile to. You can
define the user groups in the User Group screen.
Add: Click to add the protocol filter to the list at the bottom of the page.
Update: Click to update information for the protocol filter, if you have changed any of
the fields.
Delete: Select a filter profile from the table at the bottom of the list and click Delete to
remove the profile.
New: Click “New” to erase all fields and enter new information.
- 18 -
Page 24

3.5.3 IP Filter
This screen enables you to define a minimum and maximum IP address range filter; all IP addresses
falling in the range are not allowed Internet access.
The IP filter profiles are listed in the table at the bottom of the page.
Note: When selecting items in the table at the bottom, click anywhere in the item. The line is
selected, and the fields automatically load the item's parameters, which you can edit.
Enable: Click to enable or disable the IP address filter.
Range Start: Type the minimum address for the IP range. IP addresses falling between
this value and the Range End are not allowed to access the Internet.
Range End: Type the minimum address for the IP range. IP addresses falling between this
value and the Range Start are not allowed to access the Internet.
Add: Click to add the IP range to the table at the bottom of the screen.
Update: Click to update information for the range if you have selected a list item and have
made changes.
Delete: Select a list item and click Delete to remove the item from the list.
New: Click New to erase all fields and enter new information.
3.5.4 Virtual Server
This screen enables you to create a virtual server via the WRT-405. If the WRT-405 is set as a virtual
server, remote users requesting Web or FTP services through the WAN are directed to local servers in
the LAN. The WRT-405 redirects the request via the protocol and port numbers to the correct LAN server.
The Virtual Sever profiles are listed in the table at the bottom of the page.
- 19 -
Page 25

Enable: Click to enable or disable the virtual server.
Name: Type a descriptive name for the virtual server.
Protocol: Select the protocol (TCP or UDP) you want to use for the virtual server.
Private Port: Type the port number of the computer on the LAN that is being used to act as
a virtual server.
Public Port: Type the port number on the WAN that will be used to provide access to the
virtual server.
LAN Server: Type the LAN IP address that will be assigned to the virtual server.
Add: Click to add the virtual server to the table at the bottom of the screen.
Update: Click to update information for the virtual server if you have selected a list item and
have made changes.
Delete: Select a list item and click Delete to remove the item from the list.
New: Click “New” to erase all fields and enter new information.
3.5.5 Special AP
This screen allowss you to specify special applications, such as games, that require multiple connections
that are inhibited by NAT.
The special applications profiles are listed in the table at the bottom of the page.
- 20 -
Page 26

Enable: Click to enable or disable the application profile. When enabled, users will be able
to connect to the application via the WRT-405 WAN connection. Click Disabled on a profile
to prevent users from accessing the application on the WAN.
Name: Type a descriptive name for the application.
Trigger: Defines the outgoing communication that determines whether the user has
legitimate access to the application.
Protocol: Select the protocol (TCP, UDP or ICMP) that can be used to access the
application.
Port Range: Type the port range that can be used to access the application in the
fields.
Incoming: Defines which incoming communications users are permitted to connect with.
Protocol: Select the protocol (TCP, UDP or ICMP) that can be used by the incoming
communication.
Port: Type the port number that can be used for the incoming communication.
Add: Click to add the special application profile to the table at the bottom of the screen.
Update: Click to update information for the special application if you have selected a list
item and have made changes.
Delete: Select a list item and click Delete to remove the item from the list.
New: Click New to erase all fields and enter new information.
3.5.6 DMZ
This screen enables you to create a DMZ for those computers that cannot access Internet applications
properly through the WRT-405 and associated security settings.
- 21 -
Page 27

Enable: Click to enable or disable the DMZ.
DMZ Host IP: Type a host IP address for the DMZ. The computer with this IP address acts
as a DMZ host with unlimited Internet access.
Apply: Click to save the settings.
Note: Any clients added to the DMZ exposes the clients to security risks such as viruses and
unauthorized access.
3.5.7 Firewall Rule
This screen enables you to set up the firewall. The WRT-405 provides basic firewall functions, by filtering
all the packets that enter the WRT-405 using a set of rules. The rules are in an order sequence list-the
lower the rule number, the higher the priority the rule has.
The rule profiles are listed in the table at the bottom of the page.
Enable: Click to enable or disable the firewall rule profile.
Name: Type a descriptive name for the firewall rule profile.
- 22 -
Page 28

Action: Select whether to allow or deny packets that conform to the rule.
Inactive Timeout: Type the number of seconds of network inactivity that elapse before the
WRT-405 refuses the incoming packet.
Source: Defines the source of the incoming packet that the rule is applied to.
Interface: Select which interface (WAN or LAN) the rule is applied to.
IP Range Start: Type the start IP address that the rule is applied to.
IP Range End: Type the end IP address that the rule is applied to.
Destination: Defines the destination of the incoming packet that the rule is applied to.
Interface: Select which interface (WAN or LAN) the rule is applied to.
IP Range Start: Type the start IP address that the rule is applied to.
IP Range End: Type the end IP address that the rule is applied to.
Protocol: Select the protocol (TCP, UDP or ICMP) of the destination.
Port Range: Select the port range.
Apply to Group: Select which user group you want to apply the profile to. You define the
user groups in the User Group screen.
Add: Click to add the rule profile to the table at the bottom of the screen.
Update: Click to update information for the rule if you have selected a list item and
changed.
Delete: Select a list item and click “Delete” to remove the item from the list.
New: Click “New” to erase all fields and enter new information.
Priority Up: Select a rule from the list and click “Priority” Up to increase the priority of the
rule.
Priority Down: Select a rule from the list and click “Priority Down” to decrease the priority
of the rule.
Update Priority: After increasing or decreasing the priority of a rule, click “Update Priority”
to save the changes.
3.6 Management
3.6.1 SNMP
This screen allows you to configure SNMP.
Enabled/Disabled: Click to enable or disable SNMP. By default is disabled.
- 23 -
Page 29

System Name: Displays the name given to the WRT-405.
System Location: Displays the location of the WRT-405 (normally, the DNS name).
System Contact: Displays the contact information for the person responsible for the
WRT-405.
Community: SNMP system name for exchanging SNMP community messages. The name
can be used to limit SNMP messages passing through the network. The default name is
“public”.
Trap Receiver: Type the name of the destination PC that will receive trap messages.
3.6.2 Remote Management
This screen enables you to set up remote management. Using remote management, the WRT-405 can
be configured through the WAN via a Web browser. A user name and password are required to perform
remote management.
HTTP: Enables you to set up HTTP access for remote management.
Enable: Click to enable or disable HTTP access for remote management.
Remote IP Range: Type the range of IP addresses that can be used for remote
access.
Telnet: Enables you to set up Telnet access for remote management.
Enable: Click to enable or disable Telnet access for remote management.
Remote IP Range: Type the range of IP addresses that can be used for remote
access.
Allows to Ping WAN Port: This function allows remote users to ping WRT-405 WAN port
IP address.
Enable: Click to enable or disable WAN port pinged function.
Remote IP Range: Type the range of IP addresses that can ping from remote
locations.
3.7 Tools
3.7.1 Restart
Click Restart to restart the system in the event the system is not performing correctly.
- 24 -
Page 30

3.7.2 Settings
This screen allows you to save settings as a profile and load profiles for different circumstances. You can
also load the factory default settings, and run a setup wizard to configure the WRT-405 and WRT-405
interface.
Save Settings: Click to save the current configuration as a profile that you can load when
necessary.
Load Settings: Click Browse and go to the location of a stored profile. Click Load to load
the profile's settings.
Restore Factory Default Settings: Click to restore the default settings. All configuration
changes you have made will be lost.
Setup Wizard: The setup wizard enables you to configure the WRT-405 quickly and
conveniently. Click “Run Wizard” button, the window below will appear. Please click
“Next>” and follow the steps to configure WRT-405.
- 25 -
Page 31

:
1. You are prompted to select a password. Type a password in the text box, and then
type it again for verification. Click Next.
2. Select your time zone from the drop-down list. Click Next.
3. Type the LAN IP address in the text box. The default IP address 192.168.1.1.
4. Type the subnet mask in the text box.
5. Enable DHCP Server if you want DHCP to automatically assign IP addresses.
Type a beginning IP address and an end IP address for the DHCP server to use in
assigning IP addresses.
6. Click Next. Select how the router will set up the Internet connection. If you have
enabled DHCP server, choose "Obtain IP automatically (DHCP client)" to have the
router assign IP addresses automatically.
7. Click to enable or disable wireless LAN. If you enable the wireless LAN, type the
SSID in the text box and select a communications channel. The SSID and channel
must be the same as wireless devices attempting communication to the router.
8. Click Next. You are prompted to restart save the settings and restart the router
interface. Click Restart to complete the wizard.
3.7.3 Firmware
You can upgrade your WRT-405 with new firmware in this screen. Please follow these instructions:
1. Download the latest firmware from PLANET's website, and save it to your disk.
2. Click “Browse” and find out the location of the downloaded file.
3. Select the file and click “Upgrade” to update WRT-405 to the latest firmware.
- 26 -
Page 32

3.7.4 Ping Test
You can ping an IP address or host which is present on the Internet. Type the IP address or host name in
the field and click Ping.
- 27 -
Page 33

Chapter 4 Troubleshooting
This chapter provides solutions to problems usually encountered during the installation and operation of
the Wireless Broadband Router. Read the description below to solve your problems.
4.1 Frequently Asked Questions
Can I run an application from a remote computer over the wireless network?
This will depend on whether or not the application is designed to be used over a network. Consult
the application’s user guide to determine if it supports operation over a network.
Can I play games with other members of the wireless network?
Yes, as long as the game supports multiple plays over a LAN (local area network). Refer to the
game’s user guide for more information.
What is the IEEE 802.11b standard?
The IEEE 802.11b Wireless LAN standards subcommittee, which is formulating a standard for the
industry. The objective is to enable wireless LAN hardware from different manufactures to
communicate.
What IEEE 802.11 features are supported?
The product supports the following IEEE 802.11 functions:
• CSMA/CA plus Acknowledge protocol
• Multi-Channel Roaming
• Automatic Rate Selection
• RTS/CTS feature
• Fragmentation
• Power Management
What is PBCC?
This new products use the ACX100 chip from Texas Instruments. In addition to meeting the existing
standard, the chip also supports a new modulation scheme developed by TI, called Packet Binary
Convolution Code (PBCC). It's this scheme that gives the products the extra kick: Even at lower
speeds, PBCC provides better performance at greater distances, and it can also work at 22 Mbps.
What is Ad-hoc?
An Ad-hoc integrated wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN adapter, connected
as an independent wireless LAN. Ad hoc wireless LAN is applicable at a departmental scale for a
branch or SOHO operation.
- 28 -
Page 34

What is Infrastructure?
An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure configuration. Infrastructure is
applicable to enterprise scale for wireless access to central database, or wireless application for
mobile workers.
What is Roaming?
Roaming is the ability of a portable computer user to communicate continuously while moving
freely throughout an area greater than that covered by a single Wireless Network Access Point.
Before using the roaming function, the workstation must make sure that it is the same channel
number with the Wireless Network Access Point of dedicated coverage area.
4.2 Glossary
ACCESS POINT
Access points are way stations in a wireless LAN that are connected to an Ethernet hub or server. Users
can roam within the range of access points and their wireless device connections are passed from one
access point to the next.
AUTHENTICATION
Authentication refers to the verification of a transmitted message's integrity.
DMZ
DMZ (DeMilitarized Zone) is a part of an network that is located between a secure LAN and an insecure
WAN. DMZs provide a way for some clients to have unrestricted access to the Internet.
BEACON INTERVAL
Refers to the interval between packets sent sent by access points for the purposes of synchronizing
wireless LANs.
DHCP
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) software automatically assigns IP addresses to client
stations logging onto a TCP/IP network, which eliminates the need to manually assign permanent IP
addresses.
DNS
DNS stands for Domain Name System. DNS converts machine names to the IP addresses that all
machines on the net have. It translates from name to address and from address to name.
DOMAIN NAME
The domain name typically refers to an Internet site address.
DTIM
DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) provides client stations with information on the next
opportunity to monitor for broadcast or multicast messages.
FILTER
Filters are schemes which only allow specified data to be transmitted. For example, the router can filter
- 29 -
Page 35

specific IP addresses so that users cannot connect to those addresses.
FIREWALL
Firewalls are methods used to keep networks secure from malicious intruders and unauthorized access.
Firewalls use filters to prevent unwanted packets from being transmitted. Firewalls are typically used to
provide secure access to the Internet while keeping an organization's public Web server separate from
the internal LAN.
FIRMWARE
Firmware refers to memory chips that retain their content without electrical power (for example, BIOS
ROM). The router firmware stores settings made in the interface.
FRAGMENTATION
Refers to the breaking up of data packets during transmission.
FTP
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is used to transfer files over a TCP/IP network, and is typically used for
transferring large files or uploading the HTML pages for a Web site to the Web server.
GATEWAY
Gateways are computers that convert protocols enabling different networks, applications, and operating
systems to exchange information.
HOST NAME
The name given to a computer or client station that acts as a source for information on the network.
HTTP
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) is the communications protocol used to connect to servers on the
World Wide Web. HTTP establishes a connection with a Web server and transmits HTML pages to client
browser (for example Windows IE). HTTP addresses all begin with the prefix 'http://' prefix (for example,
http://www.yahoo.com).
ICMP
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a TCP/IP protocol used to send error and control messages
over the LAN (for example, it is used by the router to notify a message sender that the destination node is
not available).
IP
IP (Internet Protocol) is the protocol in the TCP/IP communications protocol suite that contains a network
address and allows messages to be routed to a different network or subnet. However, IP does not ensure
delivery of a complete message—TCP provides the function of ensuring delivery.
IP ADDRESS
The IP (Internet Protocol) address refers to the address of a computer attached to a TCP/IP network.
Every client and server station must have a unique IP address. Clients are assigned either a permanent
address or have one dynamically assigned to them via DHCP. IP addresses are written as four sets of
numbers separated by periods (for example, 211.23.181.189).
ISP
An ISP is an organization providing Internet access service via modems, ISDN (Integrated Services
Digital Network), and private lines.
- 30 -
Page 36

LAN
LANs (Local Area Networks) are networks that serve users within specific geographical areas, such as in
a company building. LANs are comprised of servers, workstations, a network operating system, and
communications links such as the router.
MAC ADDRESS
A MAC address is a unique serial number burned into hardware adapters, giving the adapter a unique
identification.
METRIC
A number that indicates how long a packet takes to get to its destination.
MTU
MTU (Maximum Transmission/Transfer Unit) is the largest packet size that can be sent over a network.
Messages larger than the MTU are divided into smaller packets.
NAT
NAT (Network Address Translation - also known as IP masquerading) enables an organization to present
itself to the Internet with one address. NAT converts the address of each LAN node into one IP address
for the Internet (and vice versa). NAT also provides a certain amount of security by acting as a firewall by
keeping individual IP addresses hidden from the WAN.
(NETWORK) ADMINISTRATOR
The network administrator is the person who manages the LAN within an organization. The
administrator's job includes ensuring network security, keeping software, hardware, and firmware
up-to-date, and keeping track of network activity.
NTP
NTP (Network Time Protocol) is used to synchronize the realtime clock in a computer. Internet primary
and secondary servers synchronize to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
PACKET
A packet is a portion of data that is transmitted in network communications. Packets are also sometimes
called frames and datagrams. Packets contain not only data, but also the destination IP address.
PING
Ping (Packet INternet Groper) is a utility used to find out if a particular IP address is present online, and is
usually used by networks for debugging.
PORT
Ports are the communications pathways in and out of computers and network devices (routers and
switches). Most PCs have serial and parallel ports, which are external sockets for connecting devices
such as printers, modems, and mice. All network adapters use ports to connect to the LAN. Ports are
typically numbered.
PPPOE
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol Over Ethernet) is used for running PPP protocol (normally used for
dial-up Internet connections) over an Ethernet.
PREAMBLE
Preamble refers to the length of a CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) block that monitors communications
- 31 -
Page 37

between roaming wireless enabled devices and access points.
PROTOCOL
A protocol is a rule that governs the communication of data.
RIP
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a routing protocol that is integrated in the TCP/IP protocol. RIP
finds a route that is based on the smallest number of hops between the source of a packet and its
destination.
RTS
RTS (Request To Send) is a signal sent from the transmitting station to the receiving station requesting
permission to transmit data.
SERVER
Servers are typically powerful and fast machines that store programs and data. The programs and data
are shared by client machines (workstations) on the network.
SMTP
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is the standard Internet e-mail protocol. SMTP is a TCP/IP
protocol defining message format and includes a message transfer agent that stores and forwards mail.
SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a widely used network monitoring and control protocol.
SNMP hardware or software components transmit network device activity data to the workstation used to
oversee the network.
SSID
SSID (Service Set Identifier) is a security measure used in WLANs. The SSID is a unique identifier
attached to packets sent over WLANs. This identifier emulates a password when a wireless device
attempts communication on the WLAN. Because an SSID distinguishes WLANS from each other, access
points and wireless devices trying to connect to a WLAN must use the same SSID.
SUBNET MASK
Subnet Masks (SUBNETwork masks) are used by IP protocol to direct messages into a specified network
segment (i.e., subnet). A subnet mask is stored in the client machine, server or router and is compared
with an incoming IP address to determine whether to accept or reject the packet.
SYSLOG SERVER
A SysLog server monitors incoming Syslog messages and decodes the messages for logging purposes.
TCP
(Transmission Control Protocol) is the transport protocol in TCP/IP that ensures messages over the
network are transmitted accurately and completely.
TCP/IP
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is the main Internet communications protocol.
The TCP part ensures that data is completely sent and received at the other end. Another part of the
TCP/IP protocol set is UDP, which is used to send data when accuracy and guaranteed packet delivery
are not as important (for example, in realtime video and audio transmission).
The IP component of TCP/IP provides data routability, meaning that data packets contain the destination
- 32 -
Page 38

station and network addresses, enabling TCP/IP messages to be sent to multiple networks within the
LAN or in the WAN.
TELNET
Telnet is a terminal emulation protocol commonly used on the Internet and TCP- or IP-based networks.
Telnet is used for connecting to remote devices and running programs. Telnet is an integral component of
the TCP/IP communications protocol.
UDP
(User Datagram Protocol) is a protocol within TCP/IP that is used to transport information when accurate
delivery isn't necessary (for example, realtime video and audio where packets can be dumped as there is
no time for retransmitting the data).
VIRTUAL SERVERS
Virtual servers are client servers (such as Web servers) that share resources with other virtual servers
(i.e., it is not a dedicated server).
WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is the de facto security protocol for wireless LANs, providing the
"equivalent" security available in hardwired networks.
WIRELESS LAN
Wireless LANs (WLANs) are local area networks that use wireless communications for transmitting data.
Transmissions are usually in the 2.4 GHz band. WLAN devices do not need to be lined up for
communications like infrared devices. WLAN devices use access points which are connected to the
wired LAN and provide connectivity to the LAN. The radio frequency of WLAN devices is strong enough
to be transmitted through non-metal walls and objects, and can cover an area up to a thousand feet.
Laptops and notebooks use wireless LAN PCMCIA cards while PCs use plug-in cards to access the
WLAN.
WLAN
WLANs (Wireless LANs) are local area networks that use wireless communications for transmitting data.
Transmissions are usually in the 2.4 GHz band. WLAN devices do not need to be lined up for
communications like infrared devices. WLAN devices use access points which are connected to the
wired LAN and provide connectivity to the LAN. The radio frequency of WLAN devices is strong enough
to be transmitted through non-metal walls and objects, and can cover an area up to a thousand feet.
Laptops and notebooks use wireless LAN PCMCIA cards while PCs use plug-in cards to access the
WLAN.
WAN
WAN (Wide Area Network) is a communications network that covers a wide geographic area such as a
country (contrasted with a LAN, which covers a small area such as a company building).
- 33 -
 Loading...
Loading...