Page 1

WGD-800
User's Manual
8-Port 10/100Mbps
Managed Ethernet Switch
Page 2
Trademarks
Copyright © PLANET Technology Corp. 2005.
Contents subject to which revision without prior notice.
PLANET is a registered trademark of PLANET Technology Corp. All other trademarks belong to their respective
owners.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications,
and makes no warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to the quality, performance,
merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User's Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability for any
inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User's Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User's
Manual. PLANET makes no commitment to update or keep current the information in this User's Manual, and
reserves the right to make improvements to this User's Manual and/or to the products described in this User's
Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your
comments and suggestions.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the Instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at whose own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the
user may be required to take adequate measures.
WEEE Warning
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the
presence of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of
electrical and electronic equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out
wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to
collect such WEEE separately.
Revision
PLANET Ethernet Switch User's Manual
FOR MODEL: WSD-800
Part No. 2081-A92310-001
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................................6
1.1 PACKET CONTENTS ......................................................................................................................... 6
1.2 HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL .............................................................................................................6
1.3 PRODUCT FEATURE......................................................................................................................... 6
1.4 PRODUCT SPECIFICATION ................................................................................................................ 7
2. INSTALLATION ..................................................................................................................................9
2.1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION .................................................................................................................. 9
2.1.1 Product Overview..................................................................................................................9
2.1.2 Switch Front Panel................................................................................................................9
2.1.3 LED Indications.....................................................................................................................9
2.1.4 Switch Rear Panel...............................................................................................................10
2.2 INSTALL THE SWITCH ..................................................................................................................... 10
2.2.1 Desktop Installation.............................................................................................................10
2.2.2 Rack Mounting ....................................................................................................................11
3. CONSOLE MANAGEMENT.............................................................................................................12
3.1 CONNECTING TO THE SWITCH ........................................................................................................12
3.2 LOGIN IN THE CONSOLE INTERFACE................................................................................................ 12
3.3 CONSOLE MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................................... 13
3.4 TELNET LOGIN ............................................................................................................................... 14
3.5 COMMANDS .................................................................................................................................. 14
3.5.1 First level commands ..........................................................................................................14
3.5.2 Privileged Command...........................................................................................................15
4. WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT.........................................................................................................22
4.1 ABOUT WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT................................................................................................. 22
4.2 PREPARING FOR WEB MANAGEMENT..............................................................................................22
4.3 SYSTEM LOGIN.............................................................................................................................. 22
4.4 SYSTEM ........................................................................................................................................ 23
4.4.1 IP Configuration...................................................................................................................23
4.4.2 SNMP..................................................................................................................................24
4.4.2.1 Theory ..............................................................................................................................24
4.4.3 Password.............................................................................................................................27
4.4.4 CONSOLE...........................................................................................................................28
4.4.5 System Upgrade..................................................................................................................28
4.4.6 Saving Parameters..............................................................................................................29
4.4.7 Parameters Backup & Recovery.........................................................................................29
Page 4

4.4.8 Load Default........................................................................................................................30
4.4.9 Reboot.................................................................................................................................30
4.5 PORT MANAGEMENT......................................................................................................................30
4.5.1 Port Configuration ...............................................................................................................30
4.5.2 Port Statistics.......................................................................................................................31
4.5.3 Port Band Restrict...............................................................................................................31
4.6 REDUNDANCY ...............................................................................................................................32
4.6.1 Spanning Tree.....................................................................................................................32
4.6.2 Spanning Tree Configuration...............................................................................................38
4.6.3 Link Aggregation..................................................................................................................40
4.7 SECURITY ..................................................................................................................................... 41
4.7.1 VLAN...................................................................................................................................41
4.7.2 MAC Address Bind..............................................................................................................50
4.7.3 MAC Address Filtering.........................................................................................................51
4.7.4 MAC Address Learning.......................................................................................................52
4.7.5 MAC Address Aging Time ...................................................................................................53
4.7.6 802.1X Port-Based Network Access Control.......................................................................54
4.8 QOS............................................................................................................................................. 67
4.8.1 Understand QOS.................................................................................................................67
4.8.2 QOS Configuration..............................................................................................................68
4.9 MULTICAST ...................................................................................................................................73
4.9.1 IGMP Snooping...................................................................................................................73
4.9.2 Static Routing Port...............................................................................................................75
4.10 PORT ANALYSIS........................................................................................................................... 75
4.10.1 Port Analysis......................................................................................................................75
4.10.2 Port Mirror..........................................................................................................................76
4.11 STORM CONTROL ........................................................................................................................77
4.12 IP STAC KING ...............................................................................................................................78
5. TROUBLE SHOOTING.....................................................................................................................83
5.1 INCORRECT CONNECTIONS............................................................................................................. 83
5.1.1 Faulty or loose cables .........................................................................................................83
5.1.2 Non-standard cables...........................................................................................................83
5.1.3 Improper Network Topologies..............................................................................................83
5.2 DIAGNOSING LED INDICATORS....................................................................................................... 83
5.2.1 Cabling ................................................................................................................................83
6. APPENDIX........................................................................................................................................85
6.1 CONSOLE PORT PIN ASSIGNMENTS................................................................................................85
Page 5

6.2 100BASE-TX/10BASE-T PIN ASSIGNMENTS ................................................................................ 86
7. APPENDIX-B....................................................................................................................................87
802.1Q VLAN MULTI-UNTAGGED VLAN SETTING SAMPLE 1 ....................................................87
Page 6

1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Packet Contents
Check the contents of your package for following parts:
▫ Ethernet Switch x1
▫ CD-ROM user's manual x1
▫ Quick installation guide x1
▫ 19" rack mounting kit x1
▫ Power cord x1
▫ Rubber feet x 4
If any of these are missing or damaged, please contact your dealer immediately, if possible, retain the carton
including the original packing material, and use them against to repack the product in case there is a need to
return it to us for repair.
1.2 How to Use This Manual
This User Manual is structured as follows:
Chapter 2, INSTALLATION
The chapter explains the functions of the Switch and how to physically install the Switch.
Chapter 3, CONSOLE MANAGEMENT
The chapter explains how to manage the switch by Console interface.
Chapter 4, WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT
The chapter explains how to manage the switch by Web interface.
Chapter 5, TROUBLE SHOOTING
The chapter explains how to trouble shooting of the Switch.
Chapter 6, APPENDIX
The chapter contains cable information of the Switch.
In the following section, terms "SWITCH" with upper case denotes the WSD-800 Ethernet switch. Terms with
lower case "switch" means any Ethernet switches.
1.3 Product Feature
▫ 8-Port 10/100Mbps TP interfaces
▫ Complies with IEEE802.3, 10Base-T, IEEE802.3u, 100Base-Tx
▫ High back-plane bandwidth 1.6Gbps
Page 7
▫ Console/Web/SNMP management
▫ Configuration backup and recovery
▫ Per port Ingress/Egress bandwidth restriction
▫ 802.1d Spanning tree, 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree
▫ Configurable spanning tree aging time, STP port configuration
▫ 4 trunk groups, up to 4 ports per trunk
▫ Port-based/802.1Q VLAN with 4K VLAN ID
▫ MAC Binding/Filtering/Learning, configurable MAC Aging time
▫ 8 mappings ID to 4 priority queues, Support MAC/VLAN/802.1p/Port to CoS mapping
▫ IGMP snooping and IGMP Query mode for Multi-media application
▫ Statistic Routing Port
▫ 1 to many Ingress/Egress Port mirror and Port analysis
▫ Broadcast/Multicast/Flooded storm control
▫ 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
▫ IP Stack Technology supports up to 8unit switch stack for centralize management
1.4 Product Specification
Hardware Specification
Network Connector 8-Port RJ-45 for 10/100Base-TX
RS-232 connector One RS-232 DB-9 male connector for switch management
Switch architecture Store and forward switch architecture.
Switch Fabric Back-plan up to 1.6Gbps
MAC address 8K MAC address table with Auto learning function
Shared Buffer 512K byte
Power requirement 90~240V AC, 50/60Hz,
Operating environment 0~50 degree C, 5%~90%RH
Storage environment -20~70 degree C, 5%~90%RH
Dimension (W x D x H) 280×173×44 mm
Switch Specification
Spanning Tree 802.1d, 802.1w
Link Aggregation 4 groups, up to 4 ports per group
Priority Queue 802.1p Class of Service (4 Queues)
Port Mirror RX/TX/Both
Bandwidth Control Yes, per port per 64kbps, up to 80Mbps
Strom Control Per 64kbps, up to 80Mbps
IGMP Snooping v1, v2
MAC Filtering Yes
VLAN Port-Based/ 802.1q, 4K VLAN ID, 256 groups
Port Analysis Yes
Static Routing Port Yes
Security 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
Management Function
Page 8

Management Interface Console/Web/Telnet/SNMP
SNMP Version v1, v2c
Support MIB Support SNMP MIBⅡ(RFC 1213),
Bridge MIB (RFC 1493),
RMON group 1,2,3,9
Enterprise private MIB
Standard Compliance
Network Standard IEEE802.3 10Base-T
IEEE802.3u 100Base-TX
IEEE802.3x Flow Control and Back pressure
IEEE802.3ad Port trunk with LACP
IEEE802.1d Spanning tree protocol
IEEE802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree
IEEE802.1p Class of service
IEEE802.1Q VLAN Tagging
IEEE802.1X Network Access Control
EMI FCC Class A, CE
Page 9
2. INSTALLATION
This section describes the functionalities of the Switch's components and guides how to install it on the desktop or
shelf. Basic knowledge of networking is assumed. Please read this chapter completely before continuing.
2.1 Product Description
2.1.1 Product Overview
With 8-Port 10/100Mbps TP, the PLANET WSD-800 boasts a high performance switch architecture that is capable
of providing non-blocking switch fabric and wire-speed throughput as high as 1.6Gbps.
The IEEE 802 standard-based firmware provides a rich set of features and ensures interoperability with equipment
from other vendors. Additionally, the firmware includes advanced features such as IGMP snooping, broadcast
storm control, and MAC address filtering, to enhance security and bandwidth utilization.
With its built-in web-based management, the PLANET WSD-800 offers an easy-to-use, platform-independent
management and configuration facility. The PLANET WSD-800 supports standard Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP) and can be managed via any standard-based management software. For text-based
management, the WSD-800 can also be accessed via Telnet and the console port.
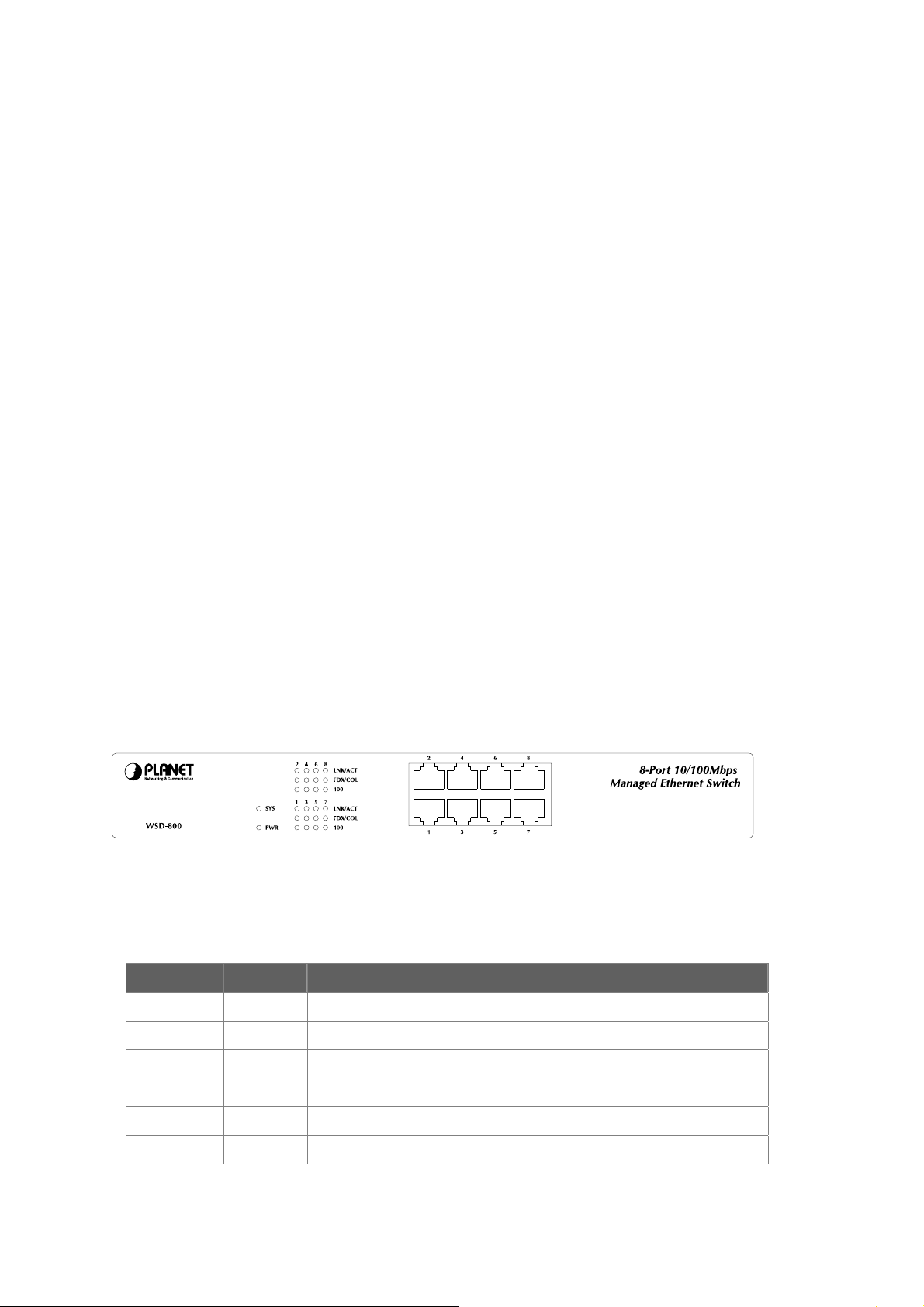
2.1.2 Switch Front Panel
Figure 2-1 shows the front panel of the switch.
Figure 2-1 WSD-800 front panel.
2.1.3 LED Indications
Network:
LED Color Function
PWR Green Lights to indicate that the Switch is powered on.
SYS Green Lights to indicate the system is working.
LNK/ACT Orange Blink to indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over
that port.
FDX/COL Green Lights to indicate the link through that port is in duplex mode.
100 Green Lights to indicate the port is acting in 100Mbps speed.
Page 10
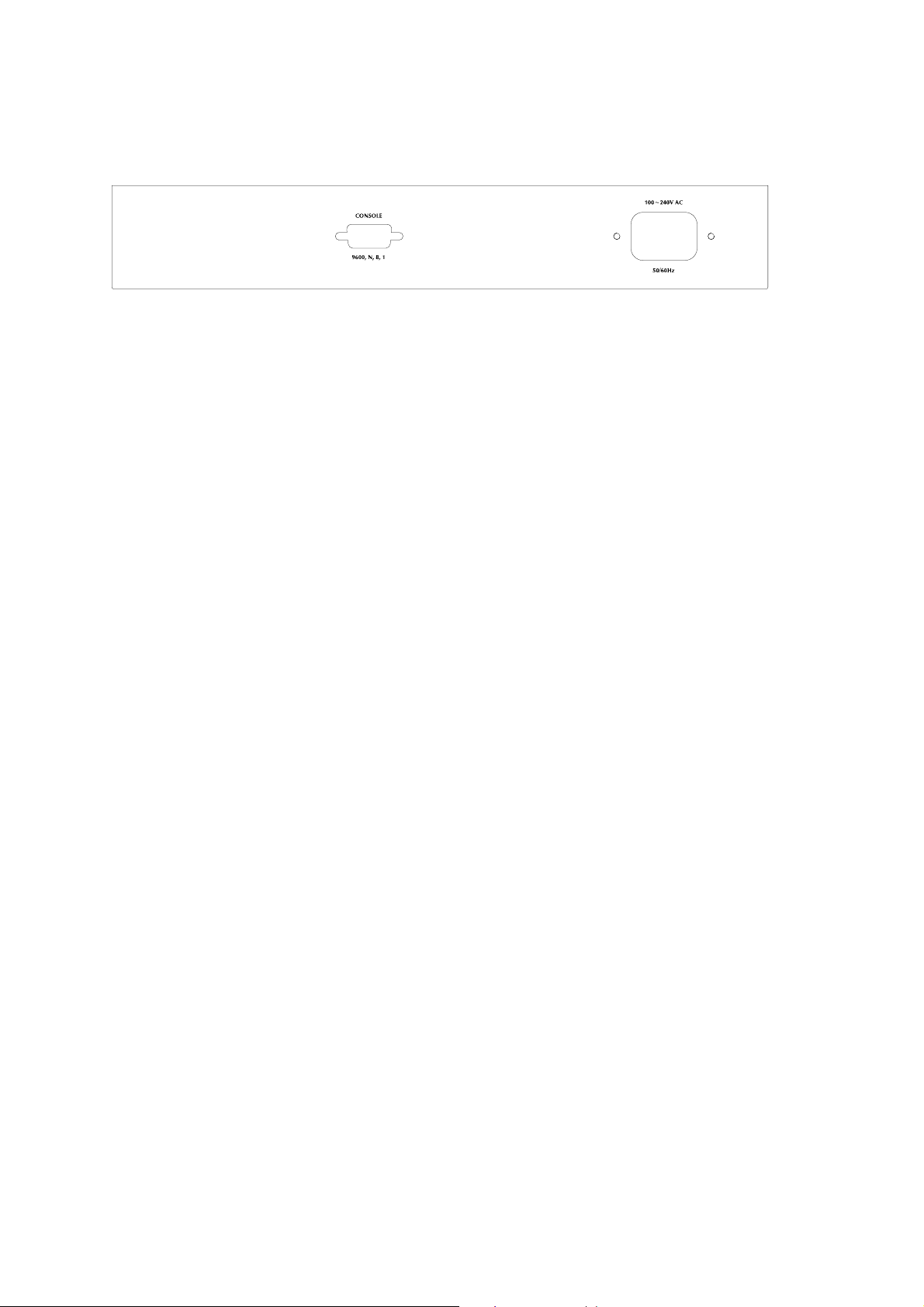
2.1.4 Switch Rear Panel
Figure 2-2 shows the rear panel of the switch
Figure 2-2 WSD-800 rear panel.
Power Notice:
1. The device is a power-required device, it means, it will not work till it is powered. If your networks should
active all the time, please consider using UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply) for your device. It will prevent
you from network data loss or network downtime.
2. In some area, installing a surge suppression device may also help to protect your switch from being damaged
by unregulated surge or current to the Switch or the power adapter.
2.2 Install the Switch
This section describes how to install the Ethernet Switch and make connections to it. Please read the following
topics and perform the procedures in the order being presented.
2.2.1 Desktop Installation
To install the Switch on desktop or shelf, please follows these steps:
Step1: Attach the rubber feet to the recessed areas on the bottom of the switch.
Step2: Place the switch on the desktop or the shelf near an AC power source.
Step3: Keep enough ventilation space between the switch and the surrounding objects.
"Note: When choosing a location, please keep in mind the environmental restrictions discussed in Chapter 1,
Section 4, in Specification.
Step4: Connect the Switch to network devices.
A. Connect one end of a standard network cable to the 10/100/1000 RJ-45 ports on the front of the Switch
B. Connect the other end of the cable to the network devices such as printer servers, workstations or
routers…etc.
"Note: Connection to the Switch requires UTP Category 5 network cabling with RJ-45 tips. For more
information, please see the Cabling Specification in Appendix A.
Step5: Supply power to the switch.
A. Connect one end of the power cable to the switch.
B. Connect the power plug of the power cable to a standard wall outlet.
Page 11
When the switch receives power, the Power LED should remain solid Green.
2.2.2 Rack Mounting
To install the switch in a 19-inch standard rack, please follows the instructions described below.
Step1: Place the switch on a hard flat surface, with the front panel positioned towards the front side.
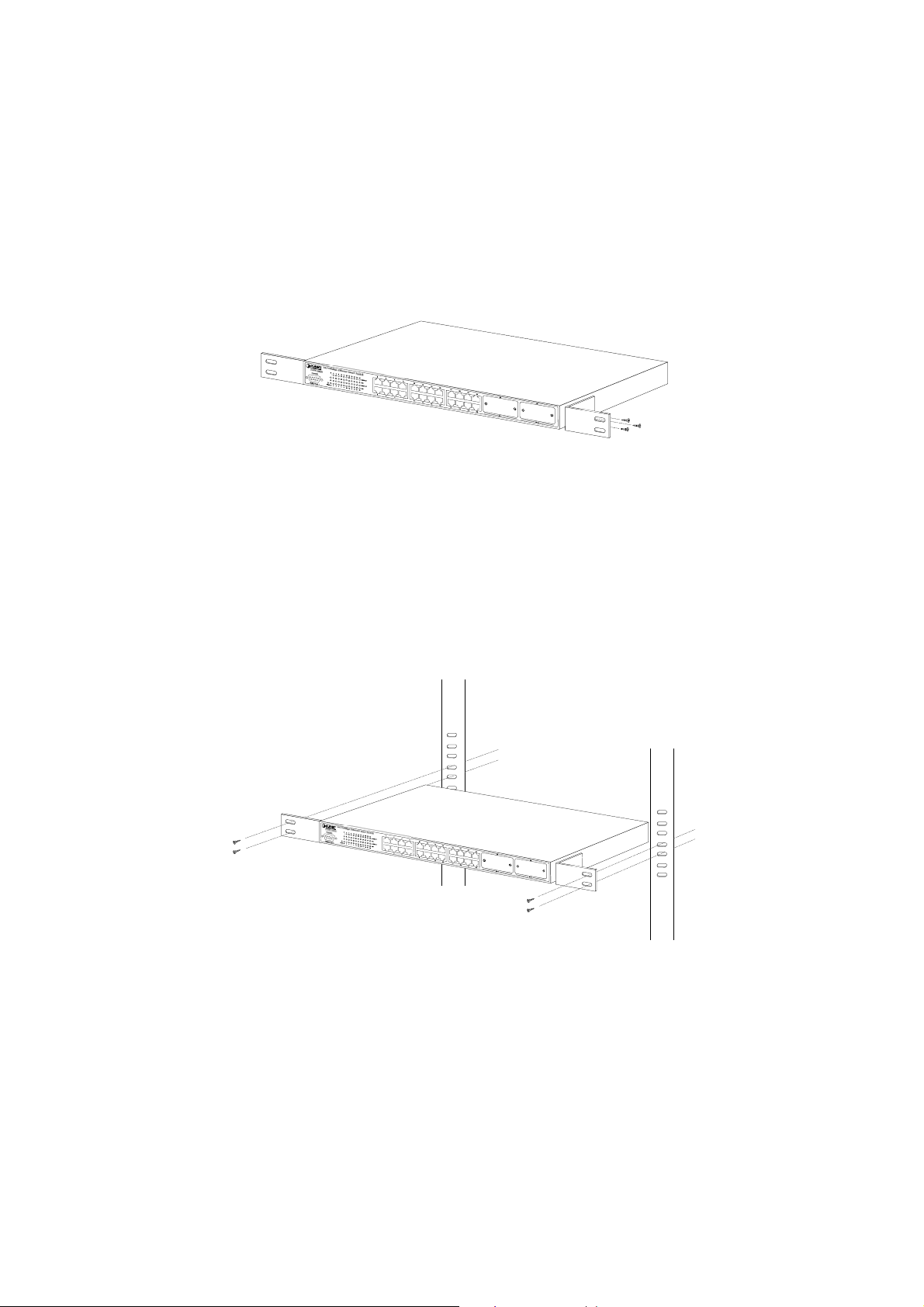
Step2: Attach the rack-mount bracket to each side of the switch with supplied screws attached to the package.
Figure 2-5 shows how to attach brackets to one side of the switch.
Figure 2-5 Attach brackets to the switch.
Caution:
You must use the screws supplied with the mounting brackets. Damage caused to the parts by using incorrect
screws would invalidate the warranty.
Step3: Secure the brackets tightly.
Step4: Follow the same steps to attach the second bracket to the opposite side.
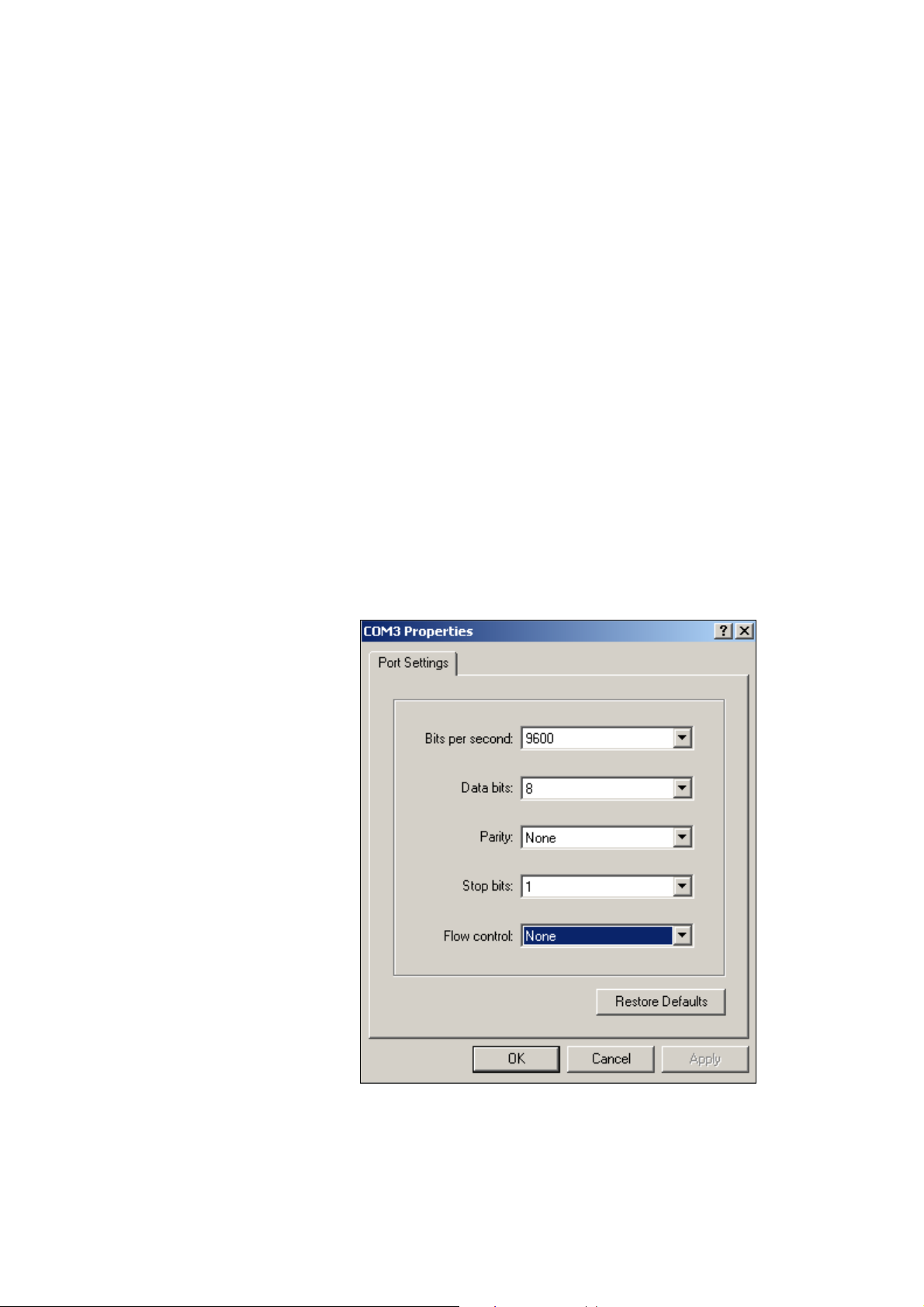
Step5: After the brackets are attached to the Switch, use suitable screws to securely attach the brackets to the
rack, as shown in Figure 2-6
Figure 2-6 Mounting the Switch in a Rack
Step6: Proceeds with the steps 4 and steps 5 of session 2.2.1 Desktop Installation to connect the network cabling
and supply power to the switch.
Page 12
3. CONSOLE MANAGEMENT
3.1 Connecting to the Switch
The console port is a female DB-9 connector that enables a connection to a PC or terminal for monitoring and
configuring the Switch. Use the supplied RS-232 cable with a male DB-9 connector to connect a terminal or PC to
the Console port. The Console configuration (out of band) allows you to set Switch for remote terminal as if the
console terminal were directly connected to it.
3.2 Login in the Console Interface
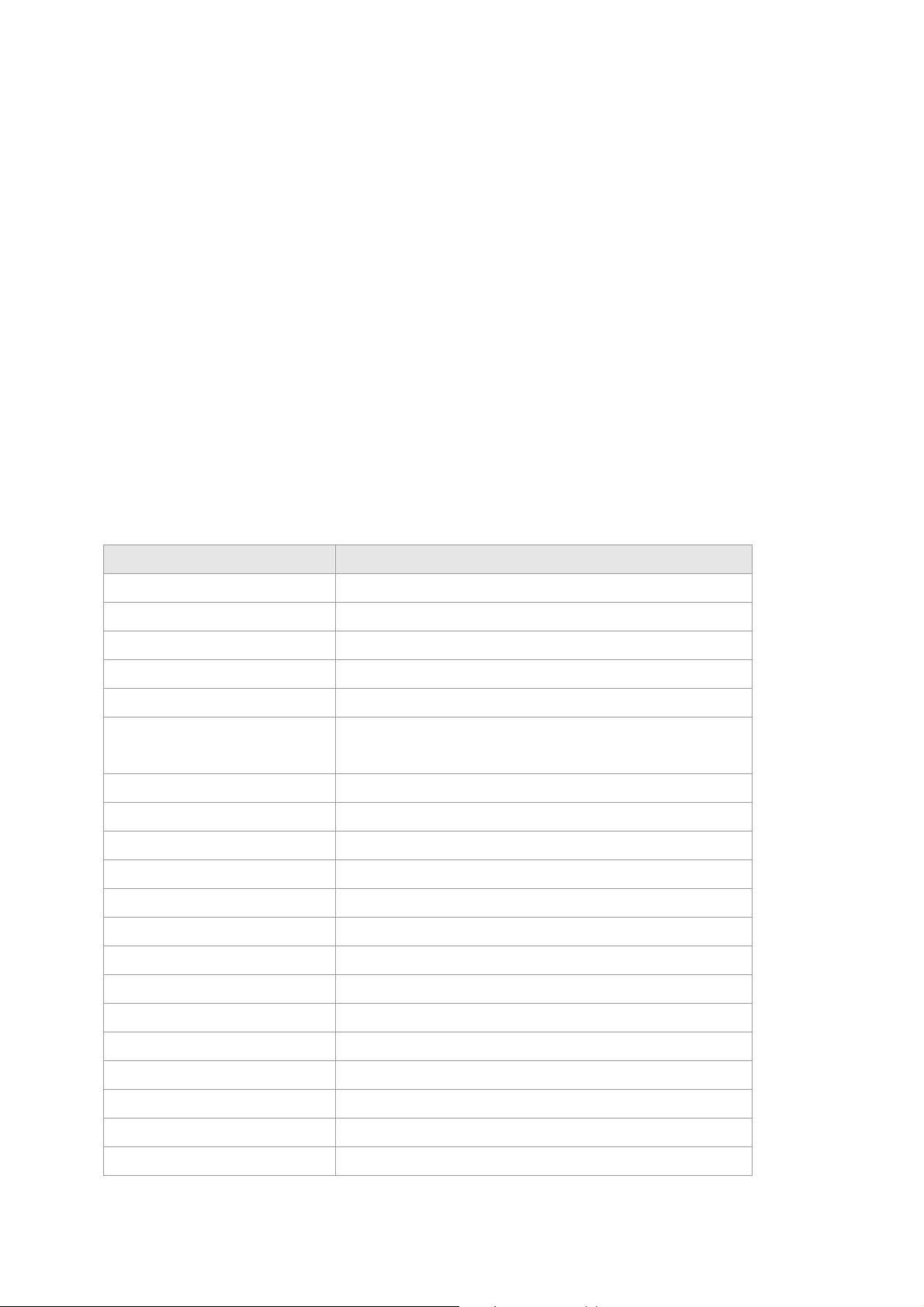
When the connection between Switch and PC is ready, turn on the PC and run a terminal emulation program or
Hyper Terminal and configure its communication parameters to match the following default characteristics of the
console port:
Baud Rate: 9600 bps
Data Bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop Bit: 1
Flow control: None
After finished the parameter settings, click “OK“. When the prompt shows “switch>”, type “?” for help or type
The settings of communication parameters
Page 13

“enable” for further configuration. The system needs password for further configuration. After the “enable”
command, the system asks for password, please enter “admin” for the default password. As shows in the
following screen:
Console login screen
3.3 Console Management
Entering a question mark "?" at the prompt displays the list of commands available for command mode.
As shows in the following screen:
The question mark “?” command
Page 14
3.4 Telnet login
The switch also supports telnet for remote management. The switch asks for user name and password for remote
login when using telnet, please use “admin” for username and “admin” for password.
3.5 Commands
There are two levels for console commands. The first level provides commands to show system informations and
current configurations. The second level (privileged mode) provides commands to set, clear and show the
configuration.
3.5.1 First level commands
The follow table lists the first commands and the equivalent usages.
Command Description
enable Enable privileged mode
show channel Show channel information
show console-info Show console-info
show dow1x local-userInfo Show dot1x local user information
show dot1x state Show dot1x information
show igmp-snooping group
number
show igmp-snooping group policy Show igmp snooping group policy
show igmp-snooping info Show igmp snooping information
show igmp-snooping policy deny Show igmp snooping policy deny
show ip http server Show http server information
show ip telnet server Show telnet server information
show ipstack info Show ip stack information
show mirror Show mirror information
show multicast router Show multicast router port information
show port counter Show port counter information
show port dot1x Show port dot1x information
show igmp snooping group-limit
show port mac-learning Show MACs on certain port
show port rate-shaping Show port ingress and egress rate-shaping
show port rstp-extension Show port RSTP port role and protocol mode
show port spantree Show spantree information on ports
Page 15
show port state Show port infomation
show port storm-limit Show port storm limit mode and rate
show qos map cos-queue-map Show qos map cos-queue-map
show qos map dot1p-cos-map Show qos map cos-queue-map
show qos map mac-cos-map Show qos map mac-cos-map
show qos map port-cos-map Show each port's cos
show qos map vlan-cos-map Show qos map vlan-cos-map
show qos queue egress-policy Show qos queue egress-policy
show radius Show radius information
show security MAC-aging Show MAC aging time
show security filter-MAC Show MAC filter entry
show security mac-learning Show port security status
show security static-MAC Show static mac table information
show snmp Show snmp information
show snmp rmon Show snmp rmon state
show spantree Show spanning tree information
show syntax Show basic help infomation
show system Show system information
show trunk Show trunk information
show version Get last software version
show vlan Show vlan information
show vlan type Show current vlan type
3.5.2 Privileged Command
To access to the second level, enter the “enable” command in the first level. The sysem then prompt for a
password. Please enter “password” for the password.
The promt then changes to “Switch\enable>”. Entering a question mark "?" at the prompt displays the list of
commands available for command mode.
3.5.2.1 Clear command
Clear command is to clear the parameter. The follow table lists the clear commands and the equivalent usages.
Command Description
clear channel Clear member from channel
clear dot1x local-userInfo Clear igmp-snooping group policy
clear igmp-snooping policy deny Clear igmp snooping policy deny
clear mirror monitored-port egress Clear egress monitored port for mirror
Page 16

clear mirror monitored-port ingress Clear ingress monitored port for mirror
clear multicast router Clear router port
clear port counters Clear port statistics counter
clear port rate-shaping Clear rate-shaping of all ports
clear port spantree portcost Restore spanning tree port cost to default value
clear port spantree portpri Restore spanning tree port priority to default value
clear port storm-limit Clear strom limit of all ports
clear qos map cos-queue-map Reset cos-queue map to default
clear qos map dot1p-cos-map Reset dot1p_cos map to default
clear qos map mac-cos-map Clear qos map mac-cos-map
clear qos map vlan-cos-map Clear qos map vlan-cos-map
clear radius key Clear radius share key
clear security filter-MAC Clear MAC filter entry
clear security static-MAC Clear static MAC entry
clear snmp community Clear snmp community entry
clear snmp trap Clear snmp trap management host
clear spantree root Restore spanning tree parameters
clear trunk Clear trunk port from vlans
clear vlan Clear member from vlan
copy config flash Copy system configuration parameters to default value
clear port storm-limit Clear strom limit of all ports
clear qos map cos-queue-map Reset cos-queue map to default
clear qos map dot1p-cos-map Reset dot1p_cos map to default
clear qos map mac-cos-map Clear qos map mac-cos-map
clear qos map vlan-cos-map Clear qos map vlan-cos-map
clear security filter-MAC Clear MAC filter entry
clear security static-MAC Clear static MAC entry
clear snmp community Clear snmp community entry
clear snmp trap Clear snmp trap management host
clear spantree root Restore spanning tree parameters
clear trunk Clear trunk port from vlans
clear vlan Clear member from vlan
3.5.2.2 Copy command
Once the configuration is changed, it remains the original after a reboot unless the configuration is saved. Copy
command is to save the current configuration to the flash, this saves the configuration to next reboot.
Command Description
Page 17
copy config flash Copy system configuration parameters to flash
3.5.2.3 Disable command
Disable command is to exit the privileged mode and back to the first level of command line interface.
Command Description
Disable Disable privileged mode
3.5.2.4 Reboot command
Reboot command is to reboot the switch, please beware to check if the configuration is saved..
Command Description
Reboot Reboot system
3.5.2.5 Set command
Set command is to change the parameter of the switch functions. The follow table lists the set commands and the
equivalent usages.
Command Description
set channel Set ports to be channel
set default Set system load default parameters
set dot1x auth mode Set dot1x auth mode
set dot1x auth-ctrl disable Disable dot1x
set dot1x auth-ctrl enable Enable dot1x
set dot1x local-userInfo Set dot1x local user information
set dot1x max-req Max times of re-transmit EAP request to Supplicant
set dot1x quiet-period Quiet-period in secondst
set dot1x reauth-max
set dot1x reauth-mode Enable or Disable reauthentication
set dot1x reauth-period Period for automatic re-authentication
set dot1x servertimeout Authentication server timeout
set dot1x supptimeout Timeout for supplicant
set dot1x tx-period Set dot1x server timeout
Max times of re-transmit Request/ID before port become
Unauthorized
set enable password Set the password for the privileged level of the CLI
set igmp-snooping disable Disable igmp snooping
set igmp-snooping enable Enable igmp snooping
set igmp-snooping forward-all-leave
Disable/Enable forward all-leave when fastleave is
disabled
Page 18

set igmp-snooping group number Set number of goups that a port can join in
set igmp-snooping group policy Set igmp-snooping group policy
set igmp-snooping immediate-leave Disable & Enable igmp snooping immediate-leave
set igmp-snooping policy deny Set igmp snooping policy deny
set ip http server disable Disable http server
set ip http server enable Enable http server
set ip telnet server disable Disable telnet server
set ip telnet server enable Enable telnet server
set ipstack enable Set ipstack enable
set ipstack disable Set ipstack disable
set ipstack group Set ipstack group STR
set ipstack mac-addr Set ipstack mac-addr
set ipstack mode Set ipstack mode master/client
set ipstack system-priority Set ipstack system-priority
set mirror Enable/Disable mirror function
set mirror capture-port Set a port to capture traffic
set mirror monitored-port egress Capture egress traffic
set mirror monitored-port ingress Capture ingress traffic
set multicast router Set multicst router port
set password Set the password for telnet
set port disable Disable a port
set port duplex Set port transmission type
set port enable Enable a port
set port flow-control Set port traffic flowcontrol
set port mcheck-rstp Set port mcheck
set port point-to-point Set port point-to-point admin value
set port rate-shaping egress Set port egress rate-shaping rate
set port rate-shaping ingress Set port ingress rate-shaping rate
set port rate-shaping egress Set port egress rate-shaping rate
set port rate-shaping ingress Set port ingress rate-shaping rate
set port spantree <port_num> portco Set spanning tree port cost
set port spantree <port_num> portfa Set spanning tree PortFast feature
set port spantree <port_num> portpr Set spanning tree port priority
set port speed Set port transmission speed
set port storm-limit mode Set port storm limit mode
set port storm-limit rate Set port storm limit rate
set port vlan-type Set port vlan-type
Page 19

set qos map cos-queue-map Set the queue number of each cos
set qos map dot1p-cos-map Set the cos value of each dot1p priority
set qos map mac-cos-map Set MAC based qos
set qos map port-cos-map Set port's cos
set qos map vlan-cos-map Set vlan based qos
set qos queue egress-policy Set the egress policy
set radius key Set share key for radius server
set radius server Set radius server parameters
set rstp force-version Set RSTP force version
set security MAC-aging Set MAC aging time
set security filter-MAC Create MAC filter entry
set security mac-learning Set port leanrning MAC (enable|disable)
set security static-MAC Create static MAC entry
set snmp Enable/Disable snmp agent
set snmp community Set snmp community string
set snmp rmon Enable/Disable rmon state
set snmp trap Set snmp trap receive host
set spantree disable Disable spanning tree
set spantree enable Enable spaning tree
set spantree fwddelay Set the forward delay for the spanning tree
set spantree hello Set the hello interval for the spanning tree
set spantree maxage Set the max age interval for the spanning
set spantree priority Set the bridge priority for the spanning tree
set system contact Set system contact
set system default-gateway Set default gateway
set system ip Set system ip mask
set system location Set system location
set system mac Set system mac address
set system management-vlan Specify a vlan for system management
set system name Set system name
set trunk Set vlan trunk port
set vlan <vid> name Set vlan name
set vlan <vlan id> <portlist> Set vlan members
set vlan port-mode Set vlan port-mode
set vlan type port-based Set system be port-based vlan
set vlan type dot1q-based Set system be dot1q-based vlan
set snmp rmon Enable/Disable rmon state
Page 20
set snmp trap Set snmp trap receive host
set spantree disable Disable spanning tree
3.5.2.6 Show command
Show command is to display the current parameter of the switch functions. The follow table lists the show
commands and the equivalent usages.
Command Description
show channel Show channel information
show console-info Show console-info
show dot1x local-userInfo Show dot1x local user information
show dot1x state Show dot1x information
show igmp-snooping group number Show igmp-snooping group-limit
show igmp-snooping group policy Show igmp-snooping group policy
show igmp-snooping info Show igmp snooping information
show igmp-snooping policy deny Show igmp snooping policy deny
show igmp-snooping Show igmp snooping information
show ip http server Show http server information
show ip telnet server Show telnet server information
show ipstack info Show ipstack info
show mirror Show mirror information
show multicast router Show multicast router port information
show port counter Show port counter information
show port dot1x Show dot1x information
show port mac-learning Show MACs on certain port
show port rate-shaping Show port ingress and egress rate-shaping
show port spantree Show spantree information on ports
show port state Show port infomation
show port storm-limit Show port storm limit mode and rate
show qos map cos-queue-map Show qos map cos-queue-map
show qos map dot1p-cos-map Show qos map cos-queue-map
show qos map mac-cos-map Show qos map mac-cos-map
show qos map port-cos-map Show each port's cos
show qos map vlan-cos-map Show qos map vlan-cos-map
show qos queue egress-policy Show qos queue egress-policy
show radius Show radius information
show security MAC-aging Show MAC aging time
show security filter-MAC Show MAC filter entry
Page 21

show security mac-learning Show port security status
show security static-MAC Show static mac table information
show snmp Show snmp information
show snmp rmon Show snmp rmon state
show spantree Show spanning tree information
show syntax Show basic help infomation
show system Show system information
show trunk Show trunk information
show version Get last software version
show vlan Show vlan information
show vlan type Show current vlan type
Page 22

4. WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT
This section introduces the configuration and functions of the Web-Based management.
4.1 About Web-based Management
The switch offers management features that allow users to manage the switch from anywhere on the network
through a standard browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer.
The Web-Based Management supports Internet Explorer 5.0. It is based on Java Applets with an aim to reduce
network bandwidth consumption, enhance access speed and present an easy viewing screen.
Note: By default, IE5.0 or later version does not allow Java Applets to open sockets. The user has to explicitly
modify the browser setting to enable Java Applets to use network ports.
4.2 Preparing for Web Management
Before use web management, you can use console to login the Switch checking the default IP of the Switch.
Please refer to Console Management Chapter for console login. If you need change IP address in first time, you
can use console mode to modify it. The default value is as below:
IP Address: 192.168.0.100
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.0.254
User Name: admin
Password: admin
4.3 System Login
1. Launch the Internet Explorer.
2. Enter the IP address of the switch.
3. When the login screen appears, use admin/admin as the default username/password respectively to login.
4. The main web page of the Web-based management appears. As shows in the following screen.
Page 23

WSD-800 Web Management Interface
4.4 System
4.4.1 IP Configuration
The switch can be managed by the Web/Telnet/SNMP interfaces. Administrators can access the management
interface via the IP address of the switch. The default IP address of the switch is 192.168.0.100. You can change
the IP address to be in the same IP segment as your LAN network for convinence.
To change the IP address, click on the System/IP Address menu button. The IP address configuration screen
then shows in the main page on the web. Enter the new IP address, Submask and Gateway then click on the OK
button to change.
NOTE:
IP Address Configuration
Page 24

1. The Switch’s factory-default IP address is 192.168.0.100 with Submask 255.255.255.0 and a default
gateway of 192.168.0.254
2. The changed IP address take effect immediately after click on the OK button, you need to use the new
IP address to access the Web interface.
3. The changed IP address remains the original after reboot the switch unless the configuration is saved.
To save the changed IP address, please move to System/Saving Parameters menu.
4.4.2 SNMP
4.4.2.1 Theory
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of
management information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol suite. SNMP enables network administrators to manage network performance, find and
solve network problems, and plan for network growth.
An SNMP-managed network consists of three key components: Network management stations (NMSs), SNMP
agents, Management information base (MIB) and network-management protocol:
。 Network management stations (NMSs):Sometimes called consoles, these devices execute management
applications that monitor and control network elements. Physically, NMSs are usually engineering
workstation-caliber computers with fast CPUs, megapixel color displays, substantial memory, and abundant
disk space. At least one NMS must be present in each managed environment.
。 Agents:Agents are software modules that reside in network elements. They collect and store management
information such as the number of error packets received by a network element.
。 Management information base (MIB):A MIB is a collection of managed objects residing in a virtual
information store. Collections of related managed objects are defined in specific MIB modules.
。 network-management protocol:A management protocol is used to convey management information
between agents and NMSs. SNMP is the Internet community's de facto standard management protocol.
SNMP Operations
SNMP itself is a simple request/response protocol. NMSs can send multiple requests without receiving a
response.
。 Get -- Allows the NMS to retrieve an object instance from the agent.
。 Set -- Allows the NMS to set values for object instances within an agent.
。 Trap -- Used by the agent to asynchronously inform the NMS of some event. The SNMPv2 trap message is
designed to replace the SNMPv1 trap message.
SNMP community
An SNMP community is the group that devices and management stations running SNMP belong to. It helps define
where information is sent. The community name is used to identify the group. A SNMP device or agent may belong
to more than one SNMP community. It will not respond to requests from management stations that do not belong
Page 25
to one of its communities. SNMP default communities are:
。 Write = private
。 Read = public
4.2.2.2 SNMP Configuration
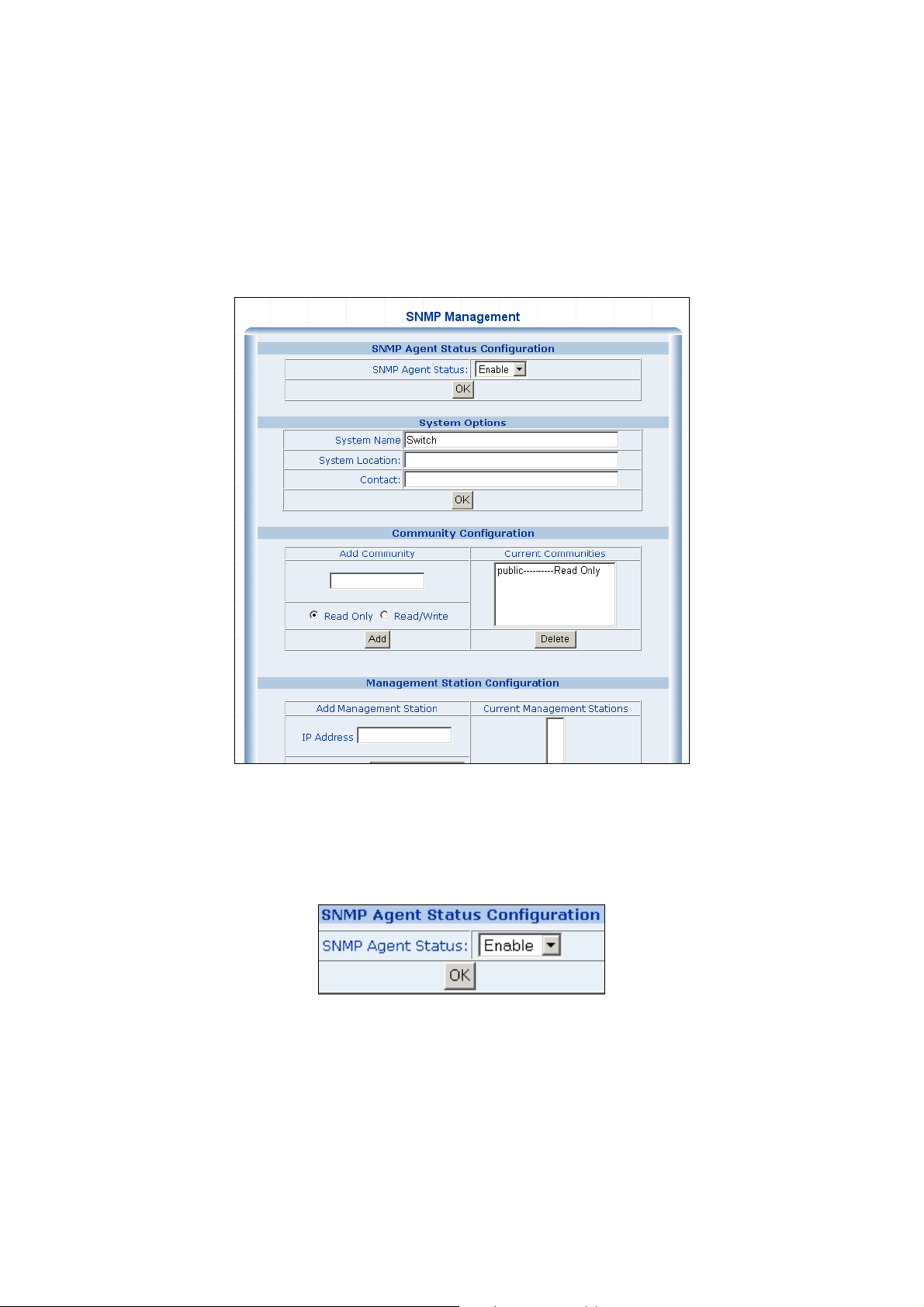
To configure SNMP management, click on System/SNMP menu button, and the web main page changes to the
SNMP Management function, as shows in the following:
The followings are the description of the sub-table.
1. SNMP Agent Status Configuration
This block enables to turn on SNMP Agent.
Enabled / Disabled: To turn on or turn off the SNMP function on the Switch.
2. System Options
This table is to define the system name, system location and the contact person of the switch. These informations
show in the SNMP software of the management workstation which helps to identify the switch that is looking into.
There are three fields in the “system options” configuration block:
。 System Name: The system name of the switch which would show in the SNMP software.
。 System Location: The system location of the switch which would show in the SNMP software.
Page 26
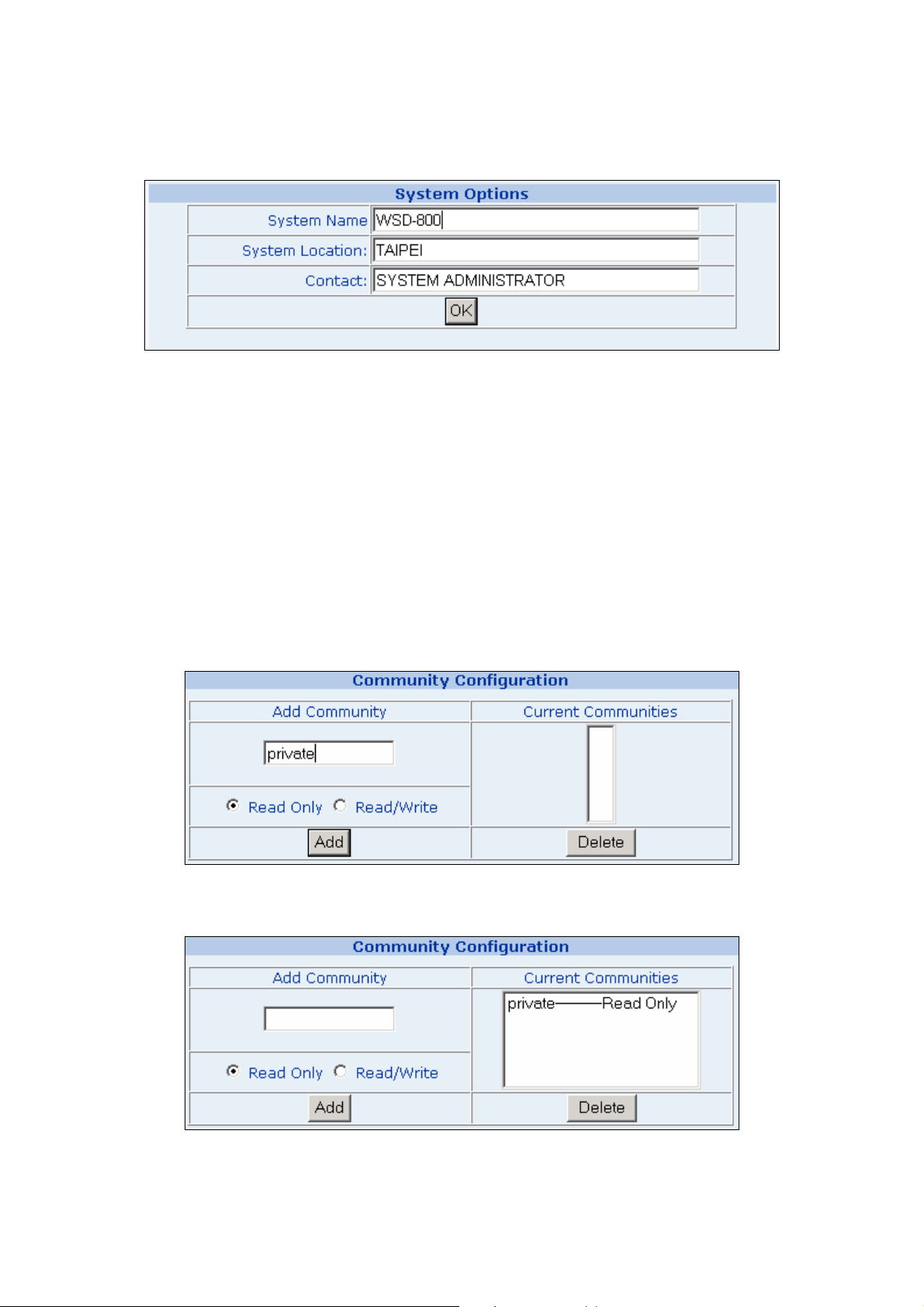
。 Contact: The contact person of the switch which would show in the SNMP software.
Fill the fileds and click on the “OK” button to save.
3. Community Configuration
Use this table to configure the SNMP community strings and define the policy of the relative string. The community
string acts like a password to permit access to the agent on the Switch. One or more of the following
characteristics can be associated with the community string:
。 Add Community: enter private or public
。 Chooses community strings for the Switch management access: read only or read/write
Read only: Enables requests accompanied by this string to display MIB-object information.
Read/Write: Enables requests accompanied by this string to display MIB-object information and to set MIB
objects.
Complete the above steps and click on the “Add” button.
The added string then shows in the Current Communities field.
z Current Communities: show the list in input field
4. Management Station Configuration
Page 27
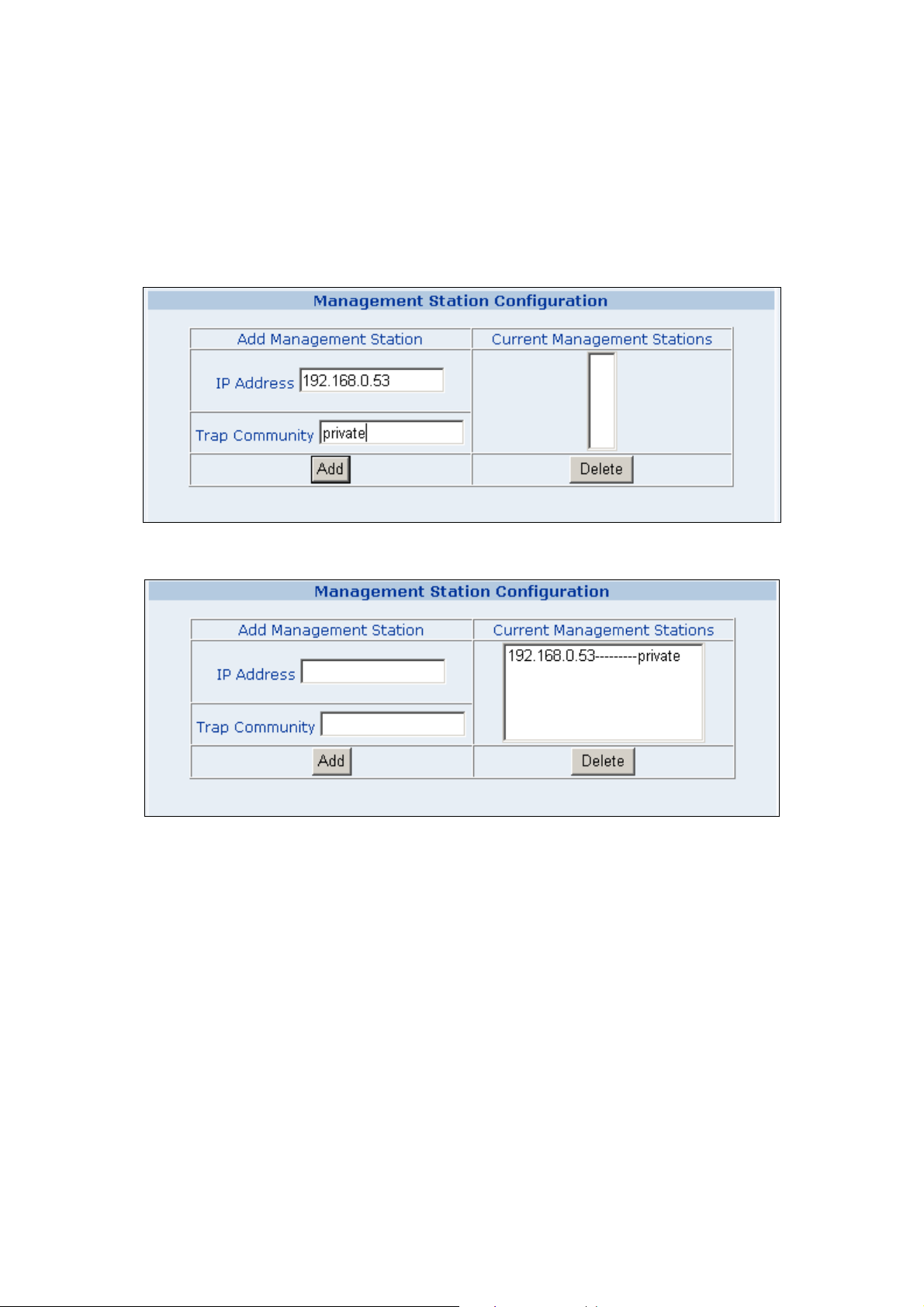
A trap manager is a management station (SNMP application) that receives traps (the system alerts generated by
the switch). If no trap manager is defined, no traps are issued. Create a trap manager by entering the IP address
of the station and a community string.
。 Enter Network management stations IP address: 192.168.0.53 (for example)
。 Trap Community: must be the same string as “Add community”
Then click on “Add” button.
The “Current Management Stations” field shows the trap list.
4.4.3 Password
The Password management menu is to set or change the password of the Web Management Interface.
Click on System/Password menu button, and the Modify Password table shows in the main web page.
Enter “old password “, “new password”, “confirm password” Click “OK” to change the password.
Page 28

4.4.4 CONSOLE
This function shows the connection parameters for the Console Management Interface. Click on the
System/CONSOLE menu button, and the following table shows in the main page of the web.
4.4.5 System Upgrade
This function allows performing firmware update from the web interface.
Click on the System/System Upgrade menu button, and the following table shows in the main page of the web.
Click on the “Browse” button of the main page, the system would pop up the file selection menu to choose
firmware. Select on the firmware, and the Update Status would show the file upload status.
Page 29

CAUTION: Do not power off the switch until the update progress is complete.
4.4.6 Saving Parameters
It takes effect immediately when you change the parameters of the management function when the switch is
running. But the parameters would not be saved after reboot the swith. To keep the changed parameters, Click on
the System/Saving Parameters menu button, and click on the “Save” button on the web main page as show in
the following.
4.4.7 Parameters Backup & Recovery
This function is to backup the running configuration to the workstation and to restore the configuration you had
saved in the workstation.
Click on the System/Backup & Recovering menu button, and the following table shows in the web main page.
To backup the running configuration, click on the “Backup the system’s parameters” link, and a pop up window
shows to save the configuration of the switch to your workstation.
To recover a saved configuration, click on the “Browse” button in the Parameters Recovery table. A pop up
window would direct you to upload the configuration file.
Page 30

4.4.8 Load Default
This function is to reset the configuration of switch to the factory default. Click on the System/Load Default menu
button, and the following table shows in the web main page.
CAUTION: This operation will result in all the parameters losing.
4.4.9 Reboot
This function is to reboot the system.
4.5 Port Management
4.5.1 Port Configuration
This function is to configure and to view the configured port management status, port negotiation mode and the
port flow control function.
。 Management Status: Display port status: Enable or Disable. Disable is to turn off the port.
。 Link Status: “Up” to indicate the port is linked while “Down” to indicate the port is not connectd.
。 Speed: Shows the negotiation mode and the running speed on the port.
。 Duplex: Displays full-duplex or half-duplex mode.
。 Flow Control: Display Flow status of port: Enable or Disable, Disable indicates Flow control is off.
。 Auto: Display which mode the port is auto-negotiated
。 Config: (configured) Displays the state defined by the user.
。 Atual: Displays the negotiation result.
Page 31

4.5.2 Port Statistics
The Port Statistics page provides a view of the current status of every port on the Switch.
Pressing the “Reset” button will reset all port counters to zero.
4.5.3 Port Band Restrict
The function provides the In-Band and Out-Band connection speed restriction on the ports. The Band of the
connection speed rangs from 64Kbps to 80000Kbps.
Ingress Port List/Egress Port List field can be filled in distinct number or a port range. For example, you can fill
with “1, 3” for port 1 and port 3 and “3-5” for port 3 to port 5.
Band(64~80000Kbps) field can be filled with any number between 64 and 80000.
Page 32

Due to the Chipset limition, set the band rate large then 500Kbps at In-Band Restrict field.
NOTICE:
If this value is less than 500Kbps and the packet will drop on that time.
And please also be remined, enable flow control at specific port is required.
4.6 Redundancy
4.6.1 Spanning Tree
1. Spanning Tree Protocol
The IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol and IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol allow for the blocking
of links between switches that form loops within the network. When multiple links between switches are detected,
a primary link is established. Duplicated links are blocked from use and become standby links. The protocol allows
for the duplicate links to be used in the event of a failure of the primary link. Once the Spanning Tree Protocol is
configured and enabled, primary links are established and duplicated links are blocked automatically. The
reactivation of the blocked links (at the time of a primary link failure) is also accomplished automatically without
operator intervention.
This automatic network reconfiguration provides maximum uptime to network users. However, the concepts of the
Spanning Tree Algorithm and protocol are a complicated and complex subject and must be fully researched and
understood. It is possible to cause serious degradation of the performance of the network if the Spanning Tree is
incorrectly configured. Please read the following before making any changes from the default values.
The Switch STP performs the following functions:
Page 33

。 Creates a single spanning tree from any combination of switching or bridging elements.
。 Creates multiple spanning trees – from any combination of ports contained within a single switch, in user
specified groups.
。 Automatically reconfigures the spanning tree to compensate for the failure, addition, or removal of any
element in the tree.
。 Reconfigures the spanning tree without operator intervention.
Bridge Protocol Data Units
For STP to arrive at a stable network topology, the following information is used:
。 The unique switch identifier
。 The path cost to the root associated with each switch port
。 The por tidentifier
STP communicates between switches on the network using Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs). Each BPDU
contains the following information:
。 The unique identifier of the switch that the transmitting switch currently believes is the root switch
。 The path cost to the root from the transmitting port
。 The port identifier of the transmitting port
The switch sends BPDUs to communicate and construct the spanning-tree topology. All switches connected to the
LAN on which the packet is transmitted will receive the BPDU. BPDUs are not directly forwarded by the switch, but
the receiving switch uses the information in the frame to calculate a BPDU, and, if the topology changes, initiates a
BPDU transmission.
The communication between switches via BPDUs results in the following:
。 One switch is elected as the root switch
。 The shortest distance to the root switch is calculated for each switch
。 A designated switch is selected. This is the switch closest to the root switch through which packets will be
forwarded to the root.
。 A port for each switch is selected. This is the port providing the best path from the switch to the root switch.
。 Ports included in the STP are selected.
Creating a Stable STP Topology
It is to make the root port a fastest link. If all switches have STP enabled with default settings, the switch with the
lowest MAC address in the network will become the root switch. By increasing the priority (lowering the priority
number) of the best switch, STP can be forced to select the best switch as the root switch.
When STP is enabled using the default parameters, the path between source and destination stations in a
switched network might not be ideal. For instance, connecting higher-speed links to a port that has a higher
number than the current root port can cause a root-port change.
STP Port States
The BPDUs take some time to pass through a network. This propagation delay can result in topology changes
where a port that transitioned directly from a Blocking state to a Forwarding state could create temporary data
Page 34

loops. Ports must wait for new network topology information to propagate throughout the network before starting to
forward packets. They must also wait for the packet lifetime to expire for BPDU packets that were forwarded based
on the old topology. The forward delay timer is used to allow the network topology to stabilize after a topology
change. In addition, STP specifies a series of states a port must transition through to further ensure that a stable
network topology is created after a topology change.
Each port on a switch using STP exists is in one of the following five states:
。 Blocking – the port is blocked from forwarding or receiving packets
。 Listening – the port is waiting to receive BPDU packets that may tell the port to go back to the blocking
state
。 Learning – the port is adding addresses to its forwarding database, but not yet forwarding packets
。 Forwarding – the port is forwarding packets
。 Disabled – the port only responds to network management messages and must return to the blocking state
first
A port transitions from one state to another as follows:
。 From initialization (switch boot) to blocking
。 From blocking to listening or to disabled
。 From listening to learning or to disabled
。 From learning to forwarding or to disabled
。 From forwarding to disabled
。 From disabled to blocking
Switch
Blocking
Listening
Learning
Disable
Forwarding
STP Port State Transitions
You can modify each port state by using management software. When you enable STP, every port on every switch
in the network goes through the blocking state and then transitions through the states of listening and learning at
Page 35

power up. If properly configured, each port stabilizes to the forwarding or blocking state. No packets (except
BPDUs) are forwarded from, or received by, STP enabled ports until the forwarding state is enabled for that port.
2. STP Parameters
STP Operation Levels
The Switch allows for two levels of operation: the switch level and the port level. The switch level forms a spanning
tree consisting of links between one or more switches. The port level constructs a spanning tree consisting of
groups of one or more ports. The STP operates in much the same way for both levels.
NOTICE: On the switch level, STP calculates the Bridge Identifier for each switch and then sets the
Root Bridge and the Designated Bridges.
On the port level, STP sets the Root Port and the Designated Ports.
The following are the user-configurable STP parameters for the switch level:
Parameter Description Default Value
Bridge Identifier(Not user
configurable
except by setting priority
below)
Priority
Hello Time
Maximum Age Timer
Forward Delay Timer
A combination of the User-set priority and
the switch’s MAC address.
The Bridge Identifier consists of two parts:
a 16-bit priority and a 48-bit Ethernet MAC
address 32768 + MAC
A relative priority for each switch – lower
numbers give a higher priority and a greater
chance of a given switch being elected as
the root bridge
The length of time between broadcasts of
the hello message by the switch
Measures the age of a received BPDU for a
port and ensures that the BPDU is discarded
when its age exceeds the value of the
maximum age timer.
The amount time spent by a port in the
learning and listening states waiting for a
32768 + MAC
32768
2 seconds
20 seconds
15 seconds
The following are the user-configurable STP parameters for the port or port group level:
Variable Description Default Value
BPDU that may return the port to the
blocking state.
Page 36

Port Priority
A relative priority for each
32768
port –lower numbers give a higher priority
and a greater chance of a given port being
elected as the root port
Port Cost
Default Spanning-Tree Configuration
User-Changeable STA Parameters
The Switch’s factory default setting should cover the majority of installations. However, it is advisable to keep the
A value used by STP to evaluate paths –
STP calculates path costs and selects the
path with the minimum cost as the active
path
Feature Default Value
Enable state STP enabled for all ports
Port priority 128
Port cost 19
Bridge Priority 32,768
19-100Mbps Fast Ethernet ports
4-1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet ports
default settings as set at the factory; unless, it is absolutely necessary. The user changeable parameters in the
Switch are as follows:
Priority – A Priority for the switch can be set from 0 to 65535. 0 is equal to the highest Priority.
Hello Time – The Hello Time can be from 1 to 10 seconds. This is the interval between two transmissions of
BPDU packets sent by the Root Bridge to tell all other Switches that it is indeed the Root Bridge. If you set a Hello
Time for your Switch, and it is not the Root Bridge, the set Hello Time will be used if and when your Switch
becomes the Root Bridge.
NOTICE: The Hello Time cannot be longer than the Max. Age. Otherwise, a configuration error will
occur.
Max. Age – The Max Age can be from 6 to 40 seconds. At the end of the Max Age, if a BPDU has still not been
received from the Root Bridge, your Switch will start sending its own BPDU to all other Switches for permission to
become the Root Bridge. If it turns out that your Switch has the lowest Bridge Identifier, it will become the Root
Bridge.
Forward Delay Timer – The Forward Delay can be from 4 to 30 seconds. This is the time any port on the
Switch spends in the listening state while moving from the blocking state to the forwarding state.
NOTICE: Observe the following formulas when setting the above parameters:
Max. Age _ 2 x (Forward Delay - 1 second)
Page 37

Max. Age _ 2 x (Hello Time + 1 second)
Port Priority – A Port Priority can be from 0 to 255. The lower the number, the greater the probability the port will
be chosen as the Root Port.
Port Cost – A Port Cost can be set from 0 to 65535. The lower the number, the greater the probability the port will
be chosen to forward packets.
3. Illustration of STP
A simple illustration of three switches connected in a loop is depicted in Figure 5-7. In this example, you can
anticipate some major network problems if the STP assistance is not applied. If switch A broadcasts a packet to
switch B, switch B will broadcast it to switch C, and switch C will broadcast it to back to switch A ... and so on. The
broadcast packet will be passed indefinitely in a loop, potentially causing a network failure. In this example, STP
breaks the loop by blocking the connection between switch B and C. The decision to block a particular connection
is based on the STP calculation of the most current Bridge and Port settings. Now, if switch A broadcasts a packet
to switch C, then switch C will drop the packet at port 2 and the broadcast will end there. Setting-up STP using
values other than the defaults, can be complex. Therefore, you are advised to keep the default factory settings and
STP will automatically assign root bridges/ports and block loop connections. Influencing STP to choose a
particular switch as the root bridge using the Priority setting, or influencing STP to choose a particular port to block
using the Port Priority and Port Cost settings is, however, relatively straight forward.
LAN 1
Portcast = 19
Port 3
A
Bridge ID = 15
Port 2
Portcast = 4
Portcast = 4
C
Port 2
Port 1
Bridge ID = 20
Port 3
B
Port 2
Port 1
Bridge ID = 30
Portcast = 4
Portcast = 4
Port 3
Port 1
Portcast = 19
Portcast = 19 Portcast = 19
LAN 2 LAN 3
Before Applying the STA Rules
In this example, only the default STP values are used.
Page 38

A
LAN 1
Port 3
Root Bridge
Blocked
Port 2
Designated Port
Root Port
C
Designated Bridge
Port 2
Port 1
Port 3
Port 1
Designated Port
Root Port
Port 1
B
Port 2
Port 3
LAN 2 LAN 3
After Applying the STA Rules
The switch with the lowest Bridge ID (switch C) was elected the root bridge, and the ports were selected to give a
high port cost between switches B and C. The two (optional) Gigabit ports (default port cost = 4) on switch A are
connected to one (optional) Gigabit port on both switch B and C. The redundant link between switch B and C is
deliberately chosen as a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet link (default port cost = 19). Gigabit ports could be used, but the
port cost should be increased from the default to ensure that the link between switch B and switch C is the blocked
link.
4.6.2 Spanning Tree Configuration
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) operates on two levels: On the switch level, the settings are globally
implemented. On the port level, the settings are implemented on a. per user-defined Group of ports.
1. Spanning Tree Configuration
The “Rapid Spanning Tree Bridge Configure” table allows configuring the spanning tree parameters.
Rapid Spanning Tree Status: The spanning tree function of the switch is default disabled. This field enables to
turn on the spanning tree on the switch.
Force Protocol Version: 0 for IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree, 2 for IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree
Max Age: (6 - 40 sec) the default setting is 20
Hello Time: (1 - 10sec) the default setting is 2
Forward Delay: (4 -30 sec) the default setting is 15
Bridge Priority: (0 - 61440) the default setting is 32768
Page 39

2. Bridge Information
The informations of the STP Root show in the Bridge Information table.
3. STP Port Configuration
On the STP port configuration, the settings are implemented on a. per user-defined Group of ports.
The following fields can be set for STP port configuration:
Edge Port: Defines if this port connected directly to a single workstation, or this port that is directly connected to a
LAN segment where a loop cannot be created. For example, this port is connected to a PC, Print-Server, IP
camera or any other network end-node device. Since end nodes cannot cause forwarding loops, they can pass
directly through to the spanning tree forwarding state.
There are two selections for this function:
。 True - This port connected directly to a end-node device or LAN segment where a loop cannot be
created
。 F alse – This port connected to one or more LAN segments – maybe a ethernet switch or HUB, that a
loop might be occured
P2P Status: Enables or disables the device to establish a point-to-point link, or specifies for the device to
automatically establish a point-to-point link. A P2P port is also capable of rapid transition. P2P ports may be used
Page 40

to connect to other bridges. Under RSTP, all ports operating in full-duplex mode are considered to be P2P ports,
unless manually overridden through configuration.
The link type attached to this port could be selected as following:
。 Auto - The switch automatically determines if the interface is attached to a point-to-point link or to shared
media
。 True – A connection to exactly one other bridge.
。 False - A connection to two or more bridges.
Port Priority: Defines if this port is more or less likely to become the root port. The range is from 0 to 255, the
default setting is 128.The lower number has the highest priority.
Path Cost: Specifies the path cost of the port. The switch uses this parameter to help determine which port will
become a forwarding port. Lower numbers will be used as forwarding ports first. The range is from 0 to 65535. The
default values based on IEEE802.1D are: 10Mb/s = 50-600, 100Mb/s = 10-60, 1000Mb/s = 3-10
4.6.3 Link Aggregation
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a standardized means for exchanging information
between Partner Systems that require high speed redundant links. Link aggregation lets you group up to eight
consecutive ports into a single dedicated connection. This feature can expand bandwidth to a device on the
network. LACP operation requires full-duplex mode, more detail information refer to the IEEE 802.3ad standard.
Link aggregation can be used to increase the bandwidth of a network connection or to ensure fault recovery. Link
aggregation lets you group up consecutive ports into a single dedicated connection between any two of the
Switches or other Layer 2 switches. However, before making any physical connections between devices, use the
Link Aggregation menu to specify the link aggregation on the devices at both ends. When using a port link
aggregation, note that:
。 The ports used in a link aggregation must all be of the same media type (RJ-45, 100 Mbps fiber).
。 The ports that can be assigned to the same link aggregation have certain other restrictions (see below).
。 Ports can only be assigned to one link aggregation.
。 The ports at both ends of a connection must be configured as link aggregation ports.
。 None of the ports in a link aggregation can be configured as a mirror source port or a mirror target port.
。 All of the ports in a link aggregation have to be treated as a whole when moved from/to, added or deleted
from a VLAN.
。 The Spanning Tree Protocol will treat all the ports in a link aggregation as a whole.
。 Enable the link aggregation prior to connecting any cable between the switches to avoid creating a data
loop.
。 Disconnect all link aggregation port cables or disable the link aggregation ports before removing a port link
aggregation to avoid creating a data loop.
Page 41

It allows a maximum of four ports to be aggregated at the same time and up to 4 groups. If the group is defined as
a LACP static link aggregationing group, then any extra ports selected are placed in a standby mode for
redundancy if one of the other ports fails. If the group is defined as a local static link aggregationing group, then
the number of ports must be the same as the group member ports.
4.7 Security
4.7.1 VLAN
4.7.1.1 Theory
Understanding IEEE 802.1p Priority
Priority tagging is a function defined by the IEEE 802.1p standard designed to provide a means of managing traffic
on a network where many different types of data may be transmitted simultaneously. It is intended to alleviate
problems associated with the delivery of time critical data over congested networks. The quality of applications
that are dependent on such time critical data, such as video conferencing, can be severely and adversely affected
by even very small delays in transmission.
Network devices that are in compliance with the IEEE 802.1p standard have the ability to recognize the priority
level of data packets. These devices can also assign a priority label or tag to packets. Compliant devices can also
strip priority tags from packets. This priority tag determines the packet's degree of expeditiousness and
determines the queue to which it will be assigned.
Priority tags are given values from 0 to 7 with 0 being assigned to the lowest priority data and 7 assigned to the
highest. The highest priority tag 7 is generally only used for data associated with video or audio applications,
which are sensitive to even slight delays, or for data from specified end users whose data transmissions warrant
Page 42

special consideration.
The Switch allows you to further tailor how priority tagged data packets are handled on your network. Using
queues to manage priority tagged data allows you to specify its relative priority to suit the needs of your network.
There may be circumstances where it would be advantageous to group two or more differently tagged packets into
the same queue. Generally, however, it is recommended that the highest priority queue, Queue 1, be reserved for
data packets with a priority value of 7. Packets that have not been given any priority value are placed in Queue 0
and thus given the lowest priority for delivery.
A weighted round robin system is employed on the Switch to determine the rate at which the queues are emptied
of packets. The ratio used for clearing the queues is 4:1. This means that the highest priority queue, Queue 1, will
clear 4 packets for every 1 packet cleared from Queue 0.
Remember, the priority queue settings on the Switch are for all ports, and all devices connected to the Switch will
be affected. This priority queuing system will be especially beneficial if your network employs switches with the
capability of assigning priority tags.
VLAN Description
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network topology configured according to a logical scheme rather than
the physical layout. VLAN can be used to combine any collection of LAN segments into an autonomous user
group that appears as a single LAN. VLAN also logically segment the network into different broadcast domains so
that packets are forwarded only between ports within the VLAN. Typically, a VLAN corresponds to a particular
subnet, although not necessarily.
VLAN can enhance performance by conserving bandwidth, and improve security by limiting traffic to specific
domains.
A VLAN is a collection of end nodes grouped by logic instead of physical location. End nodes that frequently
communicate with each other are assigned to the same VLAN, regardless of where they are physically on the
network. Logically, a VLAN can be equated to a broadcast domain, because broadcast packets are forwarded to
only members of the VLAN on which the broadcast was initiated.
NOTICE:
1. No matter what basis is used to uniquely identify end nodes and assign these nodes VLAN
membership, packets cannot cross VLAN without a network device performing a routing function
between the VLAN.
2. The Switch supports Port-based VLAN and IEEE 802.1Q VLAN. The port untagging function can
be used to remove the 802.1 tag from packet headers to maintain compatibility with devices that
are tag-unaware.
3. The Switch's default is to assign all ports to a single 802.1Q VLAN named DEFAULT_VLAN. As
new VLAN is created, the member ports assigned to the new VLAN will be removed from the
Page 43

DEFAULT_ VLAN port member list. The DEFAULT_VLAN has a VID = 1.
Port-based VLAN
Port-based VLAN limit traffic that flows into and out of switch ports. Thus, all devices connected to a port are
members of the VLAN(s) the port belongs to, whether there is a single computer directly connected to a switch, or
an entire department.
On port-based VLAN.NIC do not need to be able to identify 802.1Q tags in packet headers. NIC send and receive
normal Ethernet packets. If the packet's destination lies on the same segment, communications take place using
normal Ethernet protocols. Even though this is always the case, when the destination for a packet lies on another
switch port, VLAN considerations come into play to decide if the packet is dropped by the Switch or delivered.
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
IEEE 802.1Q (tagged) VLAN are implemented on the Switch. 802.1Q VLAN require tagging, which enables them
to span the entire network (assuming all switches on the network are IEEE 802.1Q-compliant).
VLAN allow a network to be segmented in order to reduce the size of broadcast domains. All packets entering a
VLAN will only be forwarded to the stations (over IEEE 802.1Q enabled switches) that are members of that VLAN,
and this includes broadcast, multicast and unicast packets from unknown sources.
VLAN can also provide a level of security to your network. IEEE 802.1Q VLAN will only deliver packets between
stations that are members of the VLAN. Any port can be configured as either tagging or untagging. The untagging
feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN allows VLAN to work with legacy switches that don't recognize VLAN tags in packet
headers. The tagging feature allows VLAN to span multiple 802.1Q-compliant switches through a single physical
connection and allows Spanning Tree to be enabled on all ports and work normally.
Any port can be configured as either tagging or untagging. The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN allow
VLAN to work with legacy switches that don’t recognize VLAN tags in packet headers. The tagging feature allows
VLAN to span multiple 802.1Q-compliant switches through a single physical connection and allows Spanning Tree
to be enabled on all ports and work normally.
Some relevant terms:
Tagging - The act of putting 802.1Q VLAN information into the header of a packet.
Untagging - The act of stripping 802.1Q VLAN information out of the packet header.
802.1Q VLAN Tags
The figure below shows the 802.1Q VLAN tag. There are four additional octets inserted after the source MAC
address. Their presence is indicated by a value of 0x8100 in the Ether Type field. When a packet's Ether Type field
is equal to 0x8100, the packet carries the IEEE 802.1Q/802.1p tag. The tag is contained in the following two octets
and consists of 3 bits of user priority, 1 bit of Canonical Format Identifier (CFI - used for encapsulating Token Ring
packets so they can be carried across Ethernet backbones), and 12 bits of VLAN ID (VID). The 3 bits of user
Page 44

priority are used by 802.1p. The VID is the VLAN identifier and is used by the 802.1Q standard. Because the VID
is 12 bits long, 4094 unique VLAN can be identified.
The tag is inserted into the packet header making the entire packet longer by 4 octets. All of the information
originally contained in the packet is retained.
802.1Q Tag
User Priority CFI VLAN ID (VID)
3 bits 1 bits 12 bits
TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier) TCI (Tag Control Information)
2 bytes 2 bytes
Preamble Destination
Address
Source
Address
VLAN TAG Ethernet
Type
Data FCS
6 bytes 6 bytes 4 bytes 2 bytes 46-1517 bytes 4 bytes
The Ether Type and VLAN ID are inserted after the MAC source address, but before the original Ether
Type/Length or Logical Link Control. Because the packet is now a bit longer than it was originally, the Cyclic
Redundancy Check (CRC) must be recalculated.
Adding an IEEE802.1Q Tag
Dest. Addr. Src. Addr. Length/E. type Data Old CRC
Original Ethernet
Dest. Addr. Src. Addr. E. type Tag Length/E. type Data New CRC
Priority CFI VLAN ID
New Tagged Packet
Port VLAN ID
Packets that are tagged (are carrying the 802.1Q VID information) can be transmitted from one 802.1Q compliant
network device to another with the VLAN information intact. This allows 802.1Q VLAN to span network devices
(and indeed, the entire network – if all network devices are 802.1Q compliant).
Every physical port on a switch has a PVID. 802.1Q ports are also assigned a PVID, for use within the switch. If no
VLAN are defined on the switch, all ports are then assigned to a default VLAN with a PVID equal to 1. Untagged
packets are assigned the PVID of the port on which they were received. Forwarding decisions are based upon this
PVID, in so far as VLAN are concerned. Tagged packets are forwarded according to the VID contained within the
tag. Tagged packets are also assigned a PVID, but the PVID is not used to make packet forwarding decisions, the
VID is.
Page 45

Tag-aware switches must keep a table to relate PVID within the switch to VID on the network. The switch will
compare the VID of a packet to be transmitted to the VID of the port that is to transmit the packet. If the two VID
are different the switch will drop the packet. Because of the existence of the PVID for untagged packets and the
VID for tagged packets, tag-aware and tag-unaware network devices can coexist on the same network.
A switch port can have only one PVID, but can have as many VID as the switch has memory in its VLAN table to
store them.
Because some devices on a network may be tag-unaware, a decision must be made at each port on a tag-aware
device before packets are transmitted – should the packet to be transmitted have a tag or not? If the transmitting
port is connected to a tag-unaware device, the packet should be untagged. If the transmitting port is connected to
a tag-aware device, the packet should be tagged.
Default VLANs
The Switch initially configures one VLAN, VID = 1, called "default." The factory default setting assigns all ports on
the Switch to the "default". As new VLAN are configured in Port-based mode, their respective member ports are
removed from the "default."
VLAN and Trunk Groups
In order to use VLAN segmentation in conjunction with port trunk groups, you can first set the port trunk group(s),
and then you may configure VLAN settings. If you wish to change the port trunk grouping with VLAN already in
place, you will not need to reconfigure the VLAN settings after changing the port trunk group settings. VLAN
settings will automatically change in conjunction with the change of the port trunk group settings
4.7.1.2 VLAN Configuration
Port-based VLAN Configuration
Packets can only be broadcast among other members of the same VLAN group. Note all unselected ports are
treated as belonging to the default system VLAN. If port-based VLAN are enabled, then VLAN-tagging is ignored.
1. On VLAN Configuration table, choose Port-based VLAN. Click on the “OK” button.
2. The main page then change to Port-base VLAN table, click on the “Add/Modify” button to create a new VLAN
group.
Page 46

3. The Port-base VLAN Confirutation table then pops up, enter the VLAN group ID, VLAN name and select the
member ports for the VLAN.
4. Click the “OK” button to add the VLAN.
5. Select the ports in the Port List field and click on the Add button to add the member ports to the VLAN. The
selected VLAN member then shows in the VLAN Member field.
6. Click on the “Close” button and back to the Port-based VLAN main page.
The “Show VLAN Member” button is to list the valid VLANs. You can also remove the added VALN by click on
this button.
Page 47

802.1Q VLAN Configuration
There are up to 256 configurable VLAN groups. By default when 802.1Q is enabled, all ports on the switch belong
to default VLAN (VID 1). The default VLAN cannot be deleted.
Understand nomenclature of the S witch
Tagging and Untagging
Every port on an 802.1Q compliant switch can be configured as tagging or untagging.
。 Tagging: Ports with tagging enabled will put the VID number, priority and other VLAN information into the
header of all packets that flow into those ports. If a packet has previously been tagged, the port will not alter
the packet, thus keeping the VLAN information intact. The VLAN information in the tag can then be used by
other 802.1Q compliant devices on the network to make packet-forwarding decisions.
。 Untagging: Ports with untagging enabled will strip the 802.1Q tag from all packets that flow into those ports.
If the packet doesn't have an 802.1Q VLAN tag, the port will not alter the packet. Thus, all packets received
by and forwarded by an untagging port will have no 802.1Q VLAN information. (Remember that the PVID is
only used internally within the Switch). Untagging is used to send packets from an 802.1Q-compliant
network device to a non-compliant network device.
Frame Income
Frame Leave
Leave port is tagged Frame remains tagged Tag is inserted
Leave port is untagged Tag is removed Frame remain untagged
Here pay attention to the explainion of “Access”, ”Alwa y s Untag”and “Trunk”.
。 Access: Ports will strip the 802.1Q tag from all packets that out of those ports. If the packet doesn’t have an
802.1Q VLAN tag, the port will not alter the packet. Thus, all packets received by and forwarded by an
untagging port will have no 802.1Q VLAN information. Untagging is used to send packets from an
802.1Q-compliant network device to a non-compliant network device.
Ports with “Access” mode belong to a single untagged VLAN.
。 Trunk: Ports with tagging enabled will put the VID number, priority and other VLAN information into the
header of all packets that out of those ports. If a packet has previously been tagged, the port will not alter the
packet, thus keeping the VLAN information intact. The VLAN information in the tag can then be used by
other 802.1Q compliant devices on the network to make packet forwarding decisions.
。 Always Untag: The port belongs to VLANs, and each VLAN is user-defined as tagged or untagged (full
Income Frame is tagged Income Frame is untagged
802.1Q mode). Ports will strip the 802.1Q tag from all packets that out of those ports.
Page 48

。
Port Mode VLAN Membership Frame Leave
Access Belongs to a single untagged VLAN
Always Untag
Trunk
Port VID (PVID)
Set the port VLAN ID that will be assigned to untagged traffic on a given port. This feature is useful for
accommodating devices that you want to participate in the VLAN but that don’t support tagging. The Switch allows
each port to set one PVID, the range is 1~255, default PVID is 1. The PVID must be the same as the VLAN ID that
the port was defined as belonging to in the VLAN group, or the untagged traffic will be dropped.
1. Select 802.1Q VLAN in the VLAN Type field and click on the “OK” button.
Allowed to belongs to multiple untagged
VLANs at the same time
Allowed to belongs to multiple Tagged
VLANs at the same time
(Tag=PVID or Original VID be remained)
( Tag=PVID be removed)
Untagged
Untagged
(Tag=PVID be removed)
Tagged
The main page then changes to the 802.1Q VLAN table which displays the VLAN configuration of each port.
2. If you want to configure port #2 to be in a VLAN other than default VLAN. Double click on “port2” to enter into
VLAN port configuration window.
Page 49

3. Choose the Link Type in the drop drop down menu: Access , Always Untag or Trunk.
Note that if the Access type is chosen, it will strip the 802.1Q tag from all packets that out of this port. On the other
hand, if the Trunk type is chosen, it will put the VID number, priority and other VLAN information into the header of
all packets that out of this port. And if the Always Untag type is chosen, it will strip the 802.1Q tag from all packets
that out of the port. But the port can be assigned to more than one VLAN group.
4. Define the PVID for the port
Set the port VLAN ID that will be assigned to untagged traffic on a given port. This feature is useful for
accommodating devices that you want to participate in the VLAN but that don’t support tagging.
5. Trunk configuration: If the Trunk type is chosen, please follow the steps to set the Trunk of the port.
5.1 Add and define the names and VIDs for new VLANs. The VID number ranges from 2 to 4094. Fill the VID field
and the VLAN Name field in the Set VLAN’s VID & Name table and click on the “Add/Modify” button to save.
5.2 The added new VLAN then shows the the VLAN Table field in the Set Trunk Port for VLAN table.
Page 50

5.3 Select on the VLAN chich you want to tag with in the VLAN Table field and click on the “Add” button to add.
This will add the VLAN in to the VLAN with The Trunk Port field.
5.4 Click on the “close” button to close the VLAN port configuration table of port #2, and back to the 802.1Q main
page.
5.5 Click on the “Show VLAN Members” button to show the VLAN members.
5.6 As shows in the following screen:
4.7.2 MAC Address Bind
This function is based upon for the switch security. When you add one MAC Address is bind with one port. It
remains in the switch's address table, regardless of whether the device is physically connected to the switch. This
saves the switch from having to re-learn a device's MAC address after it has been disconnected or powered-off
Page 51

from the network, and then reconnected at some time later. If the Network station is connected with one port want
to control the switch, the station’s MAC Address must be the same as one MAC Address
To bind the MAC Address, click on the Security/MAC Address Binding menu button, the main web page then
shows the MAC Address Bind function table.
1. Fill the MAC Address field with MAC address in the format “xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx “ and choose the port to bind
the MAC Address in the Port field.
2. Click on the “Add” button.
3. To remove the MAC Address binded by the port. Simply click on the “Delete” button of the MAC Address in the
Show MAC Address Table.
4.7.3 MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering allows the switch to drop unwanted traffic. Traffic is filtered based on the destination
addresses.
To filter the MAC Address, click on the Security/MAC Address Filtering menu button, the main web page then
shows the MAC Address Filtering function table.
1. Fill the MAC Address field with MAC address in the format “xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx “.
2. Click on the “Add” button to add.
3. To remove the MAC Address filtered by the port. Simply click on the “Delete” button of the MAC Address in the
Page 52

Current Filtering MAC Tab le .
4.7.4 MAC Address Learning
The switch is able to disable MAC Address learning function on ports.
1. Fill the Port List field in the MAC Address Learning table and select Enable/Disable in the MAC Address
Learning field.
2. Click on the “OK” button to save.
Page 53

4.7.5 MAC Address Aging Time
The Aging Time affects the learning process of the Switch. Dynamic forwarding table entries, which are made up
of the source and destination MAC addresses and their associated port numbers, are deleted from the table if they
are not accessed within the aging time.
The aging time can be from 30 to 1,000,000 seconds with a default value of 300 seconds. A very long aging time
can result in dynamic forwarding table entries that are out-of-date or no longer exist. This may cause incorrect
packet forward indecisions by the Switch.
If the Aging Time is too short however, many entries may be aged out too soon. This will result in a high
percentage of received packets whose source addresses cannot be found in the forwarding table, in which case
the switch will broadcast the packet to all ports, negating many of the benefits of having a switch.
Static forwarding entries are not affected by the aging time.
To set the Aging Time, enter the number in the MAC Address Aging Time field, and click on the “OK” button to
save. The valid range is 30~1000 seconds. Default is 300 seconds.
Page 54

4.7.6 802.1X Port-Based Network Access Control
4.7.6.1 Theory
Understanding IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
The IEEE 802.1X standard defines a client-server-based access control and authentication protocol that restricts
unauthorized clients from connecting to a LAN through publicly accessible ports. The authentication server
authenticates each client connected to a switch port before making available any services offered by the switch or
the LAN.
Until the client is authenticated, 802.1X access control allows only Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN
(EAPOL) traffic through the port to which the client is connected. After authentication is successful, normal traffic
can pass through the port.
This section includes this conceptual information:
•
Device Roles
• Authentication Initiation and Message Exchange
• Ports in Authorized and Unauthorized States
Device Roles
With 802.1X port-based authentication, the devices in the network have specific roles as shown below.
Client—the device (workstation) that requests access to the LAN and switch services and responds to
z
requests from the switch. The workstation must be running 802.1X-compliant client software such as that
offered in the Microsoft Windows XP operating system. (The client is the
specification.)
supplicant in the IEEE 802.1X
Page 55

Authentication server—performs the actual authentication of the client. The authentication server
z
validates the identity of the client and notifies the switch whether or not the client is authorized to access
the LAN and switch services. Because the switch acts as the proxy, the authentication service is
transparent to the client. In this release, the Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS)
security system with Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) extensions is the only supported
authentication server; it is available in Cisco Secure Access Control Server version 3.0. RADIUS operates
in a client/server model in which secure authentication information is exchanged between the RADIUS
server and one or more RADIUS clients.
Switch (802.1X device)—controls the physical access to the network based on the authentication status
z
of the client. The switch acts as an intermediary (proxy) between the client and the authentication server,
requesting identity information from the client, verifying that information with the authentication server, and
relaying a response to the client. The switch includes the RADIUS client, which is responsible for
encapsulating and decapsulating the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) frames and interacting
with the authentication server. When the switch receives EAPOL frames and relays them to the
authentication server, the Ethernet header is stripped and the remaining EAP frame is re-encapsulated in
the RADIUS format. The EAP frames are not modified or examined during encapsulation, and the
authentication server must support EAP within the native frame format. When the switch receives frames
from the authentication server, the server's frame header is removed, leaving the EAP frame, which is
then encapsulated for Ethernet and sent to the client.
Authentication Initiation and Message Exchange
The switch or the client can initiate authentication. If you enable authentication on a port by using the dot1x
port-control auto interface configuration command, the switch must initiate authentication when it determines
that the port link state transitions from down to up. It then sends an EAP-request/identity frame to the client to
request its identity (typically, the switch sends an initial identity/request frame followed by one or more requests for
authentication information). Upon receipt of the frame, the client responds with an EAP-response/identity frame.
However, if during bootup, the client does not receive an EAP-request/identity frame from the switch, the client
can initiate authentication by sending an EAPOL-start frame, which prompts the switch to request the client's
identity
NOTICE:
If 802.1X is not enabled or supported on the network access device, any EAPOL frames from the client are
Page 56

dropped. If the client does not receive an EAP-request/identity frame after three attempts to start
authentication, the client transmits frames as if the port is in the authorized state. A port in the authorized
state effectively means that the client has been successfully authenticated.
When the client supplies its identity, the switch begins its role as the intermediary, passing EAP frames between
the client and the authentication server until authentication succeeds or fails. If the authentication succeeds, the
switch port becomes authorized. For more information, see the
section
The specific exchange of EAP frames depends on the authentication method being used. “Figure 2-43” shows a
message exchange initiated by the client using the One-Time-Password (OTP) authentication method with a
RADIUS server.
"Ports in Authorized and Unauthorized States"
Ports in Authorized and Unauthorized States
The switch port state determines whether or not the client is granted access to the network. The port starts in the
unauthorized state. While in this state, the port disallows all ingress and egress traffic except for 802.1X protocol
packets. When a client is successfully authenticated, the port transitions to the authorized state, allowing all traffic
for the client to flow normally.
Page 57

If a client that does not support 802.1X is connected to an unauthorized 802.1X port, the switch requests the
client's identity. In this situation, the client does not respond to the request, the port remains in the unauthorized
state, and the client is not granted access to the network.
In contrast, when an 802.1X-enabled client connects to a port that is not running the 802.1X protocol, the client
initiates the authentication process by sending the EAPOL-start frame. When no response is received, the client
sends the request for a fixed number of times. Because no response is received, the client begins sending frames
as if the port is in the authorized state
If the client is successfully authenticated (receives an Accept frame from the authentication server), the port state
changes to authorized, and all frames from the authenticated client are allowed through the port. If the
authentication fails, the port remains in the unauthorized state, but authentication can be retried. If the
authentication server cannot be reached, the switch can retransmit the request. If no response is received from
the server after the specified number of attempts, authentication fails, and network access is not granted.
When a client logs off, it sends an EAPOL-logoff message, causing the switch port to transition to the
unauthorized state.
If the link state of a port transitions from up to down, or if an EAPOL-logoff frame is received, the port returns to the
unauthorized state.
Page 58

4.7.6.2 802.1X Configuration
This switch has two 802.1X Mode: Radius Server & Local Authenticate, choose one you need
● Local Authenticate — In this situation, do not need Radius server in the network, all authentication completed
by 802.1x Switch,the normal topologies as below
1. Enter“802.1X Port Status Configuration", there are 3“Authenticate authorization” states
。 Auto: enables 802.1X authentication and causes the port to begin in the unauthorized state, allowing only
Page 59

EAPOL frames to be sent and received through the port. It’s a default status
。 Force authorized: disables 802.1X authentication and causes the port to transition to the authorized state
without any authentication exchange required. The port transmits and receives normal traffic without
802.1X-based authentication of the client. This is the default setting.
。 Force unauthorized: causes the port to remain in the unauthorized state, ignoring all attempts by the client
to authenticate. The switch cannot provide authentication services to the client through the interface.
。 Maximum account number: the biggest user's quantity of passing authentication under this port, set 1,
Only one user can pass this authentication,The second user is unable to carry on authentication on this
port。The max value is 32
。 Current account number: show the current user who passed authentication under one port.
2. Enter”802.1X Local Authenticate” to set legitimate user information: In the local server model, the need
for each port through the establishment of the legitimate user authentication information available. As
Figure2-45
"
3. “Other configuration”: only choose “Local Authenticate” mode is available. If you not have good
experiences please keep the default value.
Page 60

● Radius Server — In this situation, need a Radius server in the network, the normal topologies as below
1. Select the “Radius Server” mode.
2. The RADIUS Server configuration table includes the following fields:
Page 61

• RADIUS Server IP
Address
• Authentication
Port(1-65535)
• Account
Port(1-65535)
• Share Key
3. Setup the RADIUS server and assign the client IP address to the Web-Smart switch. In this case, field in
the default IP Address of the Web-Smart switch with 192.168.0.100. And also make sure the shared secret
key is as same as the one you had set at the switch RADIUS server – 12345678 at this case.
The IP address of the RADIUS server being added.
The UDP port used by this server. The valid range is 0 - 65535.
The default UDP Port No. is
The UDP port used by accounting server. The valid range is 0 -
65535.
The default UDP Port No. is
Indicates if the shared secret for this server has been
configured.
1812
1813
Page 62

4. Configure ports attribute of 802.1X, the same as “802.1X Port Status Configuration”.
NOTE: Set the Ports Authenticate Status to “Force Authorized” if the port is connected to the RADIUS
server or the port is a uplink port that is connected to another switch. Or once the 802.1X stat
to work, the switch might not be able to access the RADIUS server.
5. Create user data. That step are different of “Local Authenticate”, the establishment of the user data needs
Page 63

to be created on the Radius Server PC. For example, the Radius Server founded on Win2000 Server, and
then:
Enter ” Active Directory Users and Computers”, create legal user data, the next,
right-click a user what you created to enter properties, and what to be noticed:
Page 64

6. The last, run your 802.1X Client
4.7.6.3 802.1X Client Configuration
Windows XP is originally 802.1X support. As to other operating systems (windows 98SE, ME, 2000), an 802.1X
client utility is needed. The following procedures show how to configure 802.1X Authentication in Windows XP.
Please note that if you want to change the 802.1x authentication type of a wireless client, i.e. switch to EAP-TLS
from EAP-MD5, you must remove the current existing wireless network from your preferred connection first, and
add it in again.
• Configure Sample: EAP-MD5 Authentication
1. Go to Start > Control Panel, double-click on “Network Connections”.
2. Right-click on the Local Network Connection.
3. Click “Properties” to open up the Properties setting window.
Page 65

4. Select “Authentication” tab.
5. Select “Enable network access control using IEEE 802.1X” to enable 802.1x authentication.
6. Select “MD-5 Challenge” from the drop-down list box for EAP type.
7. Click “OK”.
8. When wireless client has associated with WGSW-2840/5240, a user authentication notice appears in system
tray. Click on the notice to continue.
Page 66

9. Enter the user name, password and the logon domain that your account belongs.
10. Click “OK” to complete the validation process.
Page 67

4.8 QoS
4.8.1 Understand QOS
Quality of Service (QoS) is an advanced traffic prioritization feature that allows you to establish control over
network traffic. QoS enables you to assign various grades of network service to different types of traffic, such as
multi-media, video, protocol-specific, time critical, and file-backup traffic.
QoS reduces bandwidth limitations, delay, loss, and jitter. It also provides increased reliability for delivery of your
data and allows you to prioritize certain applications across your network. You can define exactly how you want the
switch to treat selected applications and types of traffic.
You can use QoS on your system to:
。 Control a wide variety of network traffic by:
。 Classifying traffic based on packet attributes.
。 Assigning priorities to traffic (for example, to set higher priorities to time-critical or business-critical
applications).
。 Applying security policy through traffic filtering.
。 Provide predictable throughput for multimedia applications such as video conferencing or voice over IP by
minimizing delay and jitter.
。 Improve performance for specific types of traffic and preserve performance as the amount of traffic grows.
。 Reduce the need to constantly add bandwidth to the network.
。 Manage network congestion.
QoS Terminology
Classifier-classifies the traffic on the network. Traffic classifications are determined by protocol, application,
source, destination, and so on. You can create and modify classifications. The Switch then groups classified traffic
in order to schedule them with the appropriate service level.
DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) - is the traffic prioritization bits within an IP header that are encoded by certain
applications and/or devices to indicate the level of service required by the packet across a network.
Service Level-defines the priority that will be given to a set of classified traffic. You can create and modify
service levels.
Policy-comprises a set of “rules” that are applied to a network so that a network meets the needs of the business.
That is, traffic can be prioritized across a network according to its importance to that particular business type.
QoS Profile-consists of multiple sets of rules (classifier plus service level combinations). The QoS profile is
assigned to a port(s).
Rules-comprises a service level and a classifier to define how theSwitch will treat certain types of traffic. Rules
are associated with a QoS Profile (see above).
To implement QoS on your network, you need to carry out the following actions:
Page 68

1. Define a service level to determine the priority that will be applied to traffic.
2. Apply a classifier to determine how the incoming traffic will be classified and thus treated by the Switch.
3. Create a QoS profile which associates a service level and a classifier.
4. Apply a QoS profile to a port(s).
4.8.2 QOS Configuration
QoS settings allow customization of packet priority in order to facilitate delivery of data traffic that might be affected
by latency problems. The IEEE 802.1p Priority specification uses 8 priority levels to classify data packets. In
802.1p compliant devices, a tag inserted into the packet header is used to identify the priority level of data packets.
The Switch supports four kinds of Traffic classifiers: 802.1P/ Port/MAC/VLANs and four queues.
NOTE: COS: Priority classifiers of the Switch forward packet. COS range is from 0 to 7. Seven is the
high class. Zero is the less class. The user may configure the mapping between COS and Traffic classifiers.
1. MAC-COS Mapping
QoS settings allow customization of MAC address to Traffic classifiers.
1. Fill the MAC Address field in the MAC-CoS Mapping Configuration Table in the In the format
“xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx “.
2. Fill the mapping number in the CoS (0-7) field.
3. Click on the “OK” button to save.
4. To remove the MAC-CoS mapping item, simply click on the “Delete” button in the Show MAC-CoS Mapping
table.
Page 69

2. VLAN-COS Mapping
QoS settings allow customization of VLAN ID to Traffic classifiers
1. Fill the VID (1-2094) field in the VLAN-CoS Mapping Table.
2. Fill the mapping number in the CoS (0-7) field.
3. Click on the “OK” button to save.
4. To remove the VLAN-CoS mapping item, simply click on the “Delete” button in the Show VLAN-CoS
Mapping table.
Page 70

3. 802.1p-CoS Mapping
QoS settings allow customization of packet priority in order to facilitate delivery of data traffic that might be affected
by latency problems. The IEEE 802.1p Priority specification uses 8 priority levels to classify data packets. In
802.1p compliant devices, a tag inserted into the packet header is used to identify the priority level of data packets.
1. Fill the 802.1p Priority (0-7) field in the 802.1p-priority-CoS Mapping Configuration Table.
2. Fill the mapping number in the CoS (0-7) field.
3. Click on the “OK” button to save.
Page 71

4. Port-COS Mapping
QoS settings allow customization of VLAN ID to Traffic classifiers
1. Fill the Port List (e.g. 1-3,7) field in the port-based QoS Configuration Table.
2. Fill the mapping number in the CoS (0-7) field.
3. Click on the “OK” button to save.
5. COS-Queue Mapping
1. Fill the CoS (0-7) field in the CoS-Queue Mapping Configuration Table.
2. Fill the mapping number in the Queue (0-3) field.
3. Click on the “OK” button to save.
Page 72

6. Queue Management
There are two rules for the Priority Queue: Weighted Round Robin (WRR) and Always Hight.
To configure Queue Rule, select the Queue Policy drop down menu in the Queue Rule Configuration table. And
Click on the “OK” button to save.
If the WRR was chosen as the Queue Policy, the page would show in the main page.
Page 73

4.9 Multicast
4.9.1 IGMP Snooping
Theory
Computers and network devices that want to receive multicast transmissions need to inform nearby routers that
they will become members of a multicast group. The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used to
communicate this information. IGMP is also used to periodically check the multicast group for members that are no
longer active. In the case where there is more than one multicast router on a sub network, one router is elected as
the ‘queried’. This router then keeps track of the membership of the multicast groups that have active members.
The information received from IGMP is then used to determine if multicast packets should be forwarded to a given
sub network or not. The router can check, using IGMP, to see if there is at least one member of a multicast group
on a given subnet work. If there are no members on a sub network, packets will not be forwarded to that sub
network.
IGMP Versions 1 and 2
Multicast groups allow members to join or leave at any time. IGMP provides the method for members and
multicast routers to communicate when joining or leaving a multicast group.
IGMP version 1 is defined in RFC 1112. It has a fixed packet size and no optional data.
The format of an IGMP packet is shown below:
IGMP Message Format
Octets
0 8 16 31
Type Response Time
Group Address (all zeros if this is a query)
The IGMP Type codes are shown below:
Type Meaning
0x11 Membership Query (if Group Address is 0.0.0.0)
0x11 Specific Group Membership Query (if Group Address is Present)
0x16 Membership Report (version 2)
Checksum
0x17 Leave a Group (version 2)
0x12 Membership Report (version 1)
IGMP packets enable multicast routers to keep track of the membership of multicast groups, on their respective
sub networks. The following outlines what is communicated between a multicast router and a multicast group
member using IGMP.
Page 74

A host sends an IGMP “report” to join a group
A host will never send a report when it wants to leave a group (for version 1).
A host will send a “leave” report when it wants to leave a group (for version 2).
Multicast routers send IGMP queries (to the all-hosts group address: 224.0.0.1) periodically to see whether any
group members exist on their sub networks. If there is no response from a particular group, the router assumes
that there are no group members on the network.
The Time-to-Live (TTL) field of query messages is set to 1 so that the queries will not be forwarded to other sub
networks.
IGMP version 2 introduces some enhancements such as a method to elect a multicast queried for each LAN, an
explicit leave message, and query messages that are specific to a given group.
The states a computer will go through to join or to leave a multicast group are shown below:
Non-Member
Leave Group
(Stop Timer)
Delaying Member Idle Member
Join Group
(Send Report,
Start Timer)
Query Received
(Start Timer)
Report Received
(Stop Timer)
Timer Expried
(Send report)
Leave Group
IGMP State Transitions
IGMP Snooping Configuration
The default status of the IGMP Snooping function is disabled. To turn on the IGMP Snooping, select “Enable” of
the IGMP Snooping Status field and click on the “OK” button to save.
Page 75

4.9.2 Static Routing Port
This function is to configure ports to be the member of IGMP Groups in VLANs.
To do this, fill the Port List field and the VID field for the static routing and click on the “Add” button to save.
4.10 Port Analysis
4.10.1 Port Analysis
This function shows the statistical information of each port, it helps to diagnose the network malfunction.
The following example shows the statistic table of port #6.
Page 76

4.10.2 Port Mirror
Port Mirroring is a method of monitoring network traffic that forwards a copy of each incoming and/or outgoing
packet from one port of a network switch to another port where the packet can be studied. It enables the manager
to keep close track of switch performance and alter it if necessary.
Configuring the port mirroring by assigning a source port from which to copy all packets and a sniffer port where
those packets will be sent.
Capture Port: Use this option to select the destination port for monitored traffic. This is the port that your network
analyzer would be connected to.
Ingress Port: Duplicate the date transmitted from the source port and forward it to the Capture port.
Egress Port: Duplicate the data sent to the source and forward it to the Capture port.
Page 77

4.11 Storm Control
This function is to control the Braodcast Storm, Multicast Storm and Flooded Storm packet on each port.
To configure the Storm Control, click on the Storm Control menu button. The web main page then shows the
Strom Restricting function table.
1. Fill the Port List field in the Broadcast Storm Restricting table, select the type in the Restricting T ype drop
down menu and enter the packet size in the Flow field.
2. Click on the “OK” button to save.
3. To remove the Storm Restricting function on the port, simpy click on the “Delete” button in the Show Port
Restricting Table table.
Page 78

4.12 IP Stacking
4.12.1 About IP Stacking
IP Stacking function enables you to use a single IP address and standard network cabling to manage a group of
up to 8 PLANET WSW-2401A/WGSW-2840/5240 switches in the same IP subnet (broadcast domain).
Once one switch had been operated as the Master of a stack, additional switches can join the IP stack by manual
methods to setting with the same group name. After a switch becomes a Client and stack group member, you can
work through the Master switch to further configure the Member switch as necessary for all of the IP Stack
features available in the switch.
4.12.2 IP Stacking Configuration
Before the IP Stacking Configuration, the network manager have to identify the roles of the stackable switches –
the Master mode and Client mode. At a IP stacking group domain, there is only one Master switch and many
Client switches. If there’re more than one switch be configured to the Master mode, the it will depends on the
“System Priority” to elect a active Master. The others with Master mode would be Backup Master.
To join a IP Stack group, both the Master and Client have to be assigned with the same string at “IP Stacking
Group” filed.
Once the switch be assigned as a Client switch, it’s not allowed to management the Client switch with its original
system IP address. That is, the administrator has to configure the Client switch via the Master switch
mamagement UI.
The following fields can be set for IP Stacking configuration:
Current mode: Display the current mode of IP Stacking, there’re three possible statuses:
• Disable – The IP Stacking function is disabled.
Page 79

• Master – The IP Stacking Management status is enabled and the current switch is a Master switch at this
IP Stack Group.
• Client.- The IP Stacking Management status is enabled and the current switch is a Client switch at this IP
Stack Group.
Manamement status: This filed is to Enable or Disable the IP Stack function.
Management mode: Identify the management mode of the current switch. There’re two possible selections:
• Master – The switch plays as a Master of the IP Stack Group.
• Client - The switch plays as a Client of the IP Stack Group.
IP Stacking group: This filed effects if the switches be joined to the same IP Stack group. With the same “string”
entry, both the Master and Client will be assigned to the same IP Stack group. If not, the switches will not be the IP
Stack group members.
System priority: If there’re more than one switch be configured to the Master mode, the it will depends on the
“System Priority” to elect a active Master. The others with Master mode would be Backup Master. If there is no
other Master switch, it’s no need to modify this value.
IPStacking MAC: The Master will base on the MAC address to find out the Cleint switches. Generally the entry
would be the burn-in MAC address of the switch.
Stack name: Identify the name at a IP Stack group. The entry will be displayed at the Master switch management
UI for Master and Client switches identify.
Following we’ll show you how to configure the Master switch and Client switch.
• Master Switch configuration
1. Please enter into switch web main screen and choose “Enable” in Management status field. It will enable the
stack function of the switch and the following screen appears.
Page 80

2. Then assign a role to the WGSW-2840 as Master in Management mode field, the following screen appears.
3. Enter a string in the “IP Stacking Group” field; the default string of the WGSW-2840/5240 is “planet_switch”.
This string must be the same with the Client switches that to be assigned to the same IP Stack group.
4. Modify the “System priority” and “Stack name” if necessary. At this sample we change the Stack name of the
Master to “Switch-1”
5. Click “OK” if the configuration is down.
• Client Switch configuration
6. Please enter into Client switch web main screen and choose “Enable” in Management status field. It will
enable the stack function of the switch.
7. Then assign a role to the WGSW-2840 as Client in Management mode field, the following screen appears.
Page 81

8. Enter a string in the “IP Stacking Group” field; the default string of the WGSW-2840/5240 is “planet_switch”.
This string must be the same with the Master switch that to be assigned to the same IP Stack group.
9. Modify the “System priority” and “Stack name” if necessary. At this sample we change the Stack name of
the Client to “Switch-2”
10. Click “OK” if the configuration is down.
11. Please use a UTP cable to uplink together through its Ethernet interface
12. Back to login the WEB main screen of Master switch- then you can see two WGSW-2840 stacks together
from its web interface. The following screen appears.
Page 82

13. After setup complete, please go to system and choose “Saving parameters” to save current configuration.
The following screen appears.
NOTE: Please do not assign role for whole stack member Switch as client, it cannot detect the Master
device with minimum MAC address.
Page 83

5. TROUBLE SHOOTING
This section is intended to help you solve the most common problems on the WSD-800 Managed Ethernet Switch
5.1 Incorrect connections
The switch port can auto detect straight or crossover cable when you link switch with other Ethernet device. For
the RJ-45 connector should use correct UTP or STP cable, 10/100Mbps port use 2 pairs twisted cable. If the
RJ-45 connector is not correct pin on right position then the link will fail. For fiber connection, please notice that
fiber cable mode and fiber module should be match.
5.1.1 Faulty or loose cables
Look for loose or obviously faulty connections. If they appear to be OK, make sure the connections are snug. IF
that does not correct the problem, try a different cable.
5.1.2 Non-standard cables
Non-standard and miss-wired cables may cause numerous network collisions and other network problem, and can
seriously impair network performance. A category 5-cable tester is a recommended tool for every 100Base-T
network installation.
5.1.3 Improper Network Topologies
It is important to make sure that you have a valid network topology. Common topology faults include excessive
cable length and too many repeaters (hubs) between end nodes. In addition, you should make sure that your
network topology contains no data path loops. Between any two ends nodes, there should be only one active
cabling path at any time. Data path loops will cause broadcast storms that will severely impact your network
performance.
5.2 Diagnosing LED Indicators
The Switch can be easily monitored through panel indicators to assist in identifying problems, which describes
common problems you may encounter and where you can find possible solutions.
IF the power indicator does turn on when the power cord is plugged in, you may have a problem with power outlet,
or power cord. However, if the Switch powers off after running for a while check for loose power connections,
power losses or surges at power outlet. IF you still cannot resolve the problem, contact your local dealer for
assistance.
5.2.1 Cabling
RJ-45 ports: use unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) or shield twisted-pair (STP) cable for RJ-45 connections: 100Ω
Page 84

Category 3, 4 or 5 cable for 10Mbps connections or 100Ω Category 5 cable for 100Mbps connections. Also be
sure that the length of any twisted-pair connection does not exceed 100 meters (328 feet).
Page 85

6. APPENDIX
6.1 Console Port Pin Assignments
The DB-9 serial port on the front panel is used to connect to the switch for out-of-band console configuration. The
console menu-driven configuration program can be accessed from a terminal or a PC running a terminal emulation
program. The pin assignments used to connect to the serial port are provided in the following tables.
DB-9 Console Port Pin Numbers
DB-9 Port Pin Assignments
CCITT
EIA Circuit
Signal
BB 104 RxD (Received Data) 2 2
BA 103 TxD (Transmitted Data) 3 3
AB 102 SGND (Signal Ground) 5 5
Console Port to 9-Pin DTE Port on PC
Switch’s 9-Pin Serial Port CCITT Signal PC’s 9-Pin DTE Port
2 RXD <---------RXD ------------ 3 TxD
3 TXD -----------TXD ----------> 2 RxD
5 SGND -----------SGND ---------- 5 SGND
Cable Types and Specifications
Description
Switch’s DB9 DTE
Pin #
PC DB9
DTE Pin #
Cable Type Max. Length Connector
Page 86

10BASE-T Cat. 3, 4, 5100-ohm UTP 100 m (328 ft) RJ-45
100BASE-TX Cat. 5 100-ohm UTP 100 m (328 ft) RJ-45
100BASE-FX
50/125 or 62.5/125 micron
core multimode fiber (MMF)
2 km (1.24 miles) SC or ST
6.2 100BASE-TX/10BASE-T Pin Assignments
With 100BASE-TX/10BASE-T cable, pins 1 and 2 are used for transmitting data, and pins 3 and 6 for receiving
data.
RJ-45 Pin Assignments
Pin Number Assignment
1 Tx+
2 Tx-
3 Rx+
6 Rx-
Note: "+" and "-" signs represent the polarity of the wires that make up each wire pair.
All ports on this switch support automatic MDI/MDI-X operation, you can use straight-through cables for all
network connections to PCs or servers, or to other switches or hubs. In straight-through cable, pins 1, 2, 3, and 6,
at one end of the cable, are connected straight through to pins 1, 2, 3 and 6 at the other end of the cable. The table
below shows the 10BASE-T/ 100BASE-TX MDI and MDI-X port pin outs.
Pin MDI-X Signal Name MDI Signal Name
1 Receive Data plus (RD+) Transmit Data plus (TD+)
2 Receive Data minus (RD-) Transmit Data minus (TD-)
3 Transmit Data plus (TD+) Receive Data plus (RD+)
6 Transmit Data minus (TD-) Receive Data minus (RD-)
Page 87

7. APPENDIX-B
802.1Q VLAN Multi-Untagged VLAN setting sample 1
The version V.1.4.27 of WGSW-2840 had added the multiple untagged VLAN function on a port. The function
could be applied at if the members of two or more different VLAN groups all have to access the same
server/AP/Printer. But the two VLAN groups are separated and can’t access to each other. The graphic in Figure
7-1 appears.
Figure 7-1 Overlap VLAN graphic
The next will be a configure sample- how to setup the WGSW-2840 802.1Q VLAN with a multiple untagged port.
1. At the menu bar ,click “Security” > “ VLAN”
2. After the VLAN configuration page appear, select “802.1Q VALN“ and clink “OK” to apply. Then the following
screen in Figure 7-2 appears.
Page 88

Figure 7-2 802.1Q VLAN page screen
3. Move the mouse course to the port, which had be assigned to be connect to the server/AP/printer, then click
on the port. For this case, we set the Port-1 to be the multiple untagged port. The screen in Figure 7-3
appears.
4. At the Link Type, select “Always Untag” at the draw bar. Click “OK” to apply.
Figure 7-3 802.1Q VLAN Port Configuration – Port1 screen
5. Click the “Add/Modify” button to create new VLAN groups with VID=2 and VID=3.
Page 89

6. At the Port 1-VLAN Port configuration page, select VLAN 2 and VLAN 3 to add to the Port 1. The right
information window at this table shows the status. The screen in Figure 7-4 appears.
Figure 7-4 Assign Port-1 to be VLAN 2 and VLAN 3 member.
7. After the down the Port 1 VLAN configuration, press “close” to back to the 802.1Q VLAN main screen. And
check if the setting be applied to Port 1 at the “Egress Policy” column. The screen in Figure 7-5 appears.
Figure 7-5 Port 1 VLA N status
8. Assign the VLAN 2 and VLAN 3 group member. At this case, Port 2 had been assigned to as VLAN 2 group
member and Port 3 be assigned to as VLAN 3 group member.
9. Repeat step 2 to step 7, expect that :
• Configure the Port 2 with PVID=2, Port 3 with PVID=3.
• The link type of both Port-2 and Port 3 are “Always Untag”.
Page 90

• And both Port 2 and Port 3 are VLAN 1 members.
10. After properly configure the 802.1Q VLAN per port setting, it should be as the screen in Figure 7-6 appears.
Figure 7-6 Port 1, Port 2 and Port 3 VLAN configuration
Although Port 2 and Port 3 are VLAN 1 members, with different PVID setting, the two ports are not able to access
each other. But they all can access with the server/AP/Printer which connect to the Port 1 now.
Part No. 2081-A92310-001
 Loading...
Loading...