Page 1

4/8-Port H.323/SIP VoIP Gateway
VIP-480/VIP-880 Series
User’s manual
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright (C) 2006 PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved.
The products and programs described in this User’s Manual are licensed products of PLANET Technology, This
User’s Manual contains proprietary information protected by copyright, and this User’s Manual and all
accompanying hardware, software, and documentation are copyrighted.
No part of this User’s Manual may be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any electronic
medium or machine-readable form by any means by electronic or mechanical. Including photocopying, recording,
or information storage and retrieval systems, for any purpose other than the purchaser's personal use, and without
the prior express written permission of PLANET Technology.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications,
and makes no warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to the quality, performance,
merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User’s Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability for any
inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User’s
Manual. PLANET makes no commitment to update or keep current the information in this User’s Manual, and
reserves the right to make improvements to this User’s Manual and/or to the products described in this User’s
Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your
comments and suggestions.
CE mark Warning
The is a class B device, In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the
user may be required to take adequate measures.
WEEE Warning
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the presence of
hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of electrical and electronic
equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of
WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to collect such WEEE separately.
Trademarks
The PLANET logo is a trademark of PLANET Technology. This documentation may refer to numerous hardware
and software products by their trade names. In most, if not all cases, their respective companies claim these
designations as trademarks or registered trademarks.
2
Page 3

Revision
User’s Manual for PLANET 4/8-Port H.323/SIP VoIP Gateway:
Model: VIP-480/VIP-480FS/VIP-480FO/VIP-880/VIP-882/VIP-880FO
Rev: 10 (September, 2006)
Part No. EM-VIP480_880V1
3
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1 Introduction ......................................................................... 6
Overview............................................................................................................................6
Package Content ............................................................................................................... 8
Physical Details ................................................................................................................. 8
Front Panel LED Indicators & Rear Panels..............................................................10
Chapter 2 Preparations & Installation ............................................... 12
Physical Installation Requirement ................................................................................12
LAN/WAN Interface quick configurations...............................................................13
LAN IP address configuration via web configuration interface...............................13
WAN IP address configuration via web configuration interface ..............................14
Chapter 3 Network Service Configurations ...................................... 15
Configuring and monitoring your VoIP Gateway from web browser .......................15
Overview on the web interface of VoIP Gateway.....................................................15
Manipulation of VoIP Gateway via web browser .....................................................15
Wizard Setup for Quick Start........................................................................................16
1. WAN Port Type Setup (Setup First) .....................................................................16
2. Configuring NAT or Bridge setting:..................................................................... 18
3. VoIP Call Protocol Setup ......................................................................................18
Chapter 4 System Configurations..................................................... 21
Advance Setup of Network Setup .................................................................................21
WAN Setting.............................................................................................................21
LAN Setting.............................................................................................................. 23
Virtual Server............................................................................................................ 24
Dynamic DNS ..........................................................................................................25
Netwrok Management ..............................................................................................26
Advance Setup of VoIP Setup ........................................................................................27
VoIP Basic Configuration to H.323 protocol............................................................ 28
Dialing Plan to H.323 protocol.................................................................................30
Advance Setting to H.323 protocol ..........................................................................34
VoIP Basic Configuration to SIP Protocol................................................................38
Dialing Plan to SIP protocol..................................................................................... 40
Advance Setting to SIP protocol...............................................................................43
Port Status.................................................................................................................47
Chapter 5 System Administrations ................................................... 48
Management....................................................................................................................48
Save Configuration...................................................................................................48
4
Page 5

Access Control.......................................................................................................... 49
Set To Default Configuration.................................................................................... 49
Backup/Restore Configuration to a File ...................................................................50
System Information Display Function...................................................................... 50
SNTP Setting Function............................................................................................. 51
Syslog setting............................................................................................................ 51
Capture packetackets Function................................................................................. 52
Appendix A.......................................................................................... 53
FAQ .................................................................................................................................. 53
Appendix B ......................................................................................... 54
Voice communications ....................................................................................................54
Concepts: Voice Port.................................................................................................54
H.323 VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode ...................................................................... 56
SIP VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode...........................................................................68
Appendix C ......................................................................................... 79
VIP-480 series Specifications................................................................................... 79
VIP-880 series Specifications................................................................................... 80
5
Page 6

1
Chapter 1 Introduction
Overview
With years of Internet telephony and router manufacturing experience, PLANET proudly introduces the
newest member of the PLANET VoIP gateway family: the VIP-480/VIP-880 series.
The PLANET VoIP Gateway is fully both SIP and H.323 standard compliant residential gateway that
provides a total solution for integrating voice-data network and the Public Switched Telephone Network
(PSTN), not only provides quality voice communications, but also offers secure, reliable Internet
sharing capabilities for daily voice and Internet communications.
With advanced DSP processor (TI) and cutting edge VoIP technology, the PLANET VoIP Gateway is
capable of handling both SIP and the H.323 calls. Up to 4/8 registrations to the SIP proxy or H.323
Gatekeeper, the VoIP Gateway are able to make calls to either H.323 or SIP voice communication
environment. The VoIP Gateway is equipped with LAN port Ethernet switch and built-in NAT router
function that provides Internet access using only one IP address; with these features, users may now
enjoy high quality voice calls and secure Internet access without interfering with routine activities.
Meanwhile, the PLANET VoIP Gateway is designed for comfort, ease-of-use with a sophisticated, and
satisfaction from customers, VoIP Gateway not only inherits traditions of quality voice communications
and real-time fax data over IP networks, but VoIP Gateway also eliminates the human resource VoIP
network deployment. With optimized H.323/SIP architecture, PLANET VoIP Gateway is the ideal
choices for P2P voice chat, ITSP cost-saving solution, but also provide network-converting feature to
translate the packet network into traditional PBX system.
With built-in PPPoE/DHCP/DDNS clients, up to 4/8 concurrent connections in VoIP Gateway, voice
communications can be established from anywhere around the world. PLANET VoIP Gateway comes
with intuitive user-friendly, yet powerful management interface (web/telnet), that can dramatically
reduce IT personnel resource, and complete VoIP deployment in a short time, plus remote
management capability, VoIP administrators can monitor machine/network status, or proceed
maintenance/trouble-shooting service via Internet browser or telnet session.
Besides, it provides voice channels status display and optimized packet voice streaming over managed
and public (Internet) IP networks.
6
Page 7

There are models for VIP-480/VIP-880 and there are:
4-port model, VIP-48nxx:
VIP-480 equips two FXO and two FXS interfaces to have the great flexibility of PBX connection
(FXO), and telephone or FAX machine connection (FXS).
VIP-480FS equips four FXS interfaces telephone set or FAX machine connections (FXS).
VIP-480FO equips four FXO interfaces to have the great flexibility of PBX connection (FXO).
8-port mode, VIP-88nxx:
VIP-880 equips four FXO and four FXS interfaces to have the great flexibility of PBX connection
(FXO), and telephone or FAX machine connection (FXS).
VIP-880FO equips eight FXO interfaces to have the great flexibility of PBX connection (FXO).
VIP-882 equips six FXS and two FXO interfaces to have the great flexibility of telephone or FAX
machine connection (FXS), and PBX connection (FXO).
In the following section, unless specified, VIP-480/VIP-880 will represent the famaily of products.
Network Feature
• Network Address Translation (NAT):
NAT allows multiple PCs to connect to an Internet Service Provider (ISP) using a single Internet access
account.
• Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) Client Support:
If you are a DSL user, the router has a built-in PPPoE client for establishing a DSL link connection with
the ISP. There is no need to install a further PPPoE driver on your computers.
• Smart QoS
The smart QoS provide stable voice quality while user access internet from private LAN to internet at
thesame time. This device would start suppressing throughput automatically when VoIP call proceed
and keep full speed access when there is no VoIP traffic.
• DDNS(Dynamic Domain Name Server)
DDNS is a service that maps Internet domain names to IP addresses. It allows you to provide Internet
users with a domain name (instead of an IP Address) to access your Virtual Servers.
• Virtual Server
Remote Users can access services such as the Web or FTP at your local site via public IP addresses
can be automatically redirected to local servers configured with private IP addresses.
7
Page 8

VoIP Functions
• H.323 / SIP dual mode communication
• SIP 2.0 (RFC3261), H.323v4 compliant
• Peer-to-Peer / H.323 GK / SIP proxy calls
• Voice codec support: G.711(A-law /-law), G.729 AB, G.723 (6.3 Kbps / 5.3Kbps)
• Voice processing: Voice Active Detection, DTMF detection, G.165/G.168 compliant echo canceller,
silence detection, FAX (T.38 / T.30) Mode Option.
• Built in adaptive buffer that helps to smooth out the variations in delay (jitter) for voice traffic.
• Voice channels status display: This function display each port status likes as on-hook, off-hook,
calling number called number, talk duration, codec.
• Life line support for co-existing FXO-FXS port of VIP-480, VIP-880 and VIP-882 while power down.
Package Content
The contents of your product should contain the following items:
VoIP Gateway
Power adapter
Quick Installation Guide
User’s Manual CD
RJ-45 cable x 1
Physical Details
The following figure illustrates the front/rear panel of VIP-480/VIP-880 series.
Front Panel of VIP-480
Front Panel of VIP-480FS
8
Page 9
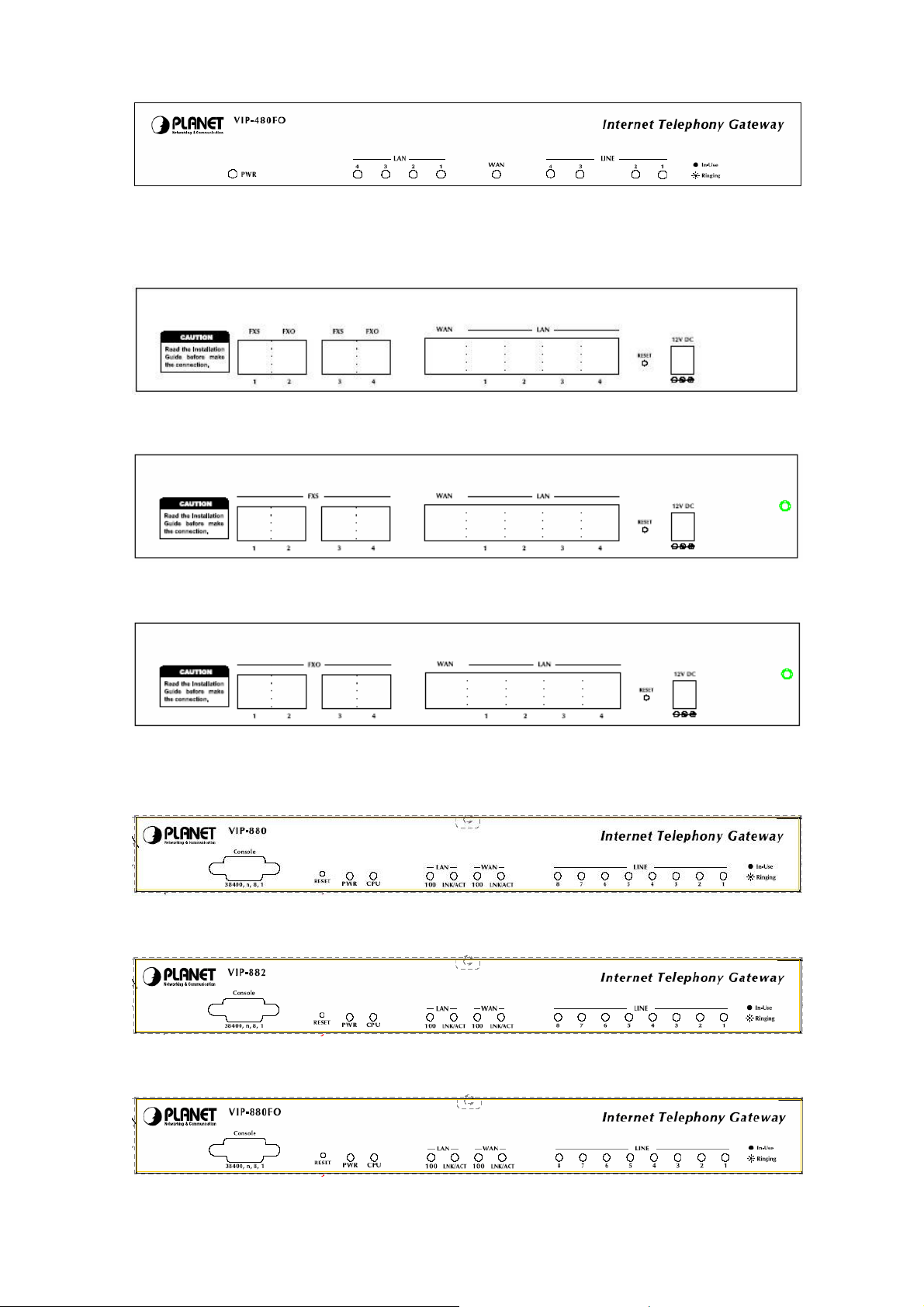
Front Panel of VIP-480FO
Rear Panel of VIP-480
Rear Panel of VIP-480FS
Rear Panel of VIP-480FO
Front Panel of VIP-880
Front Panel of VIP-882
Front Panel of VIP-880FO
9
Page 10
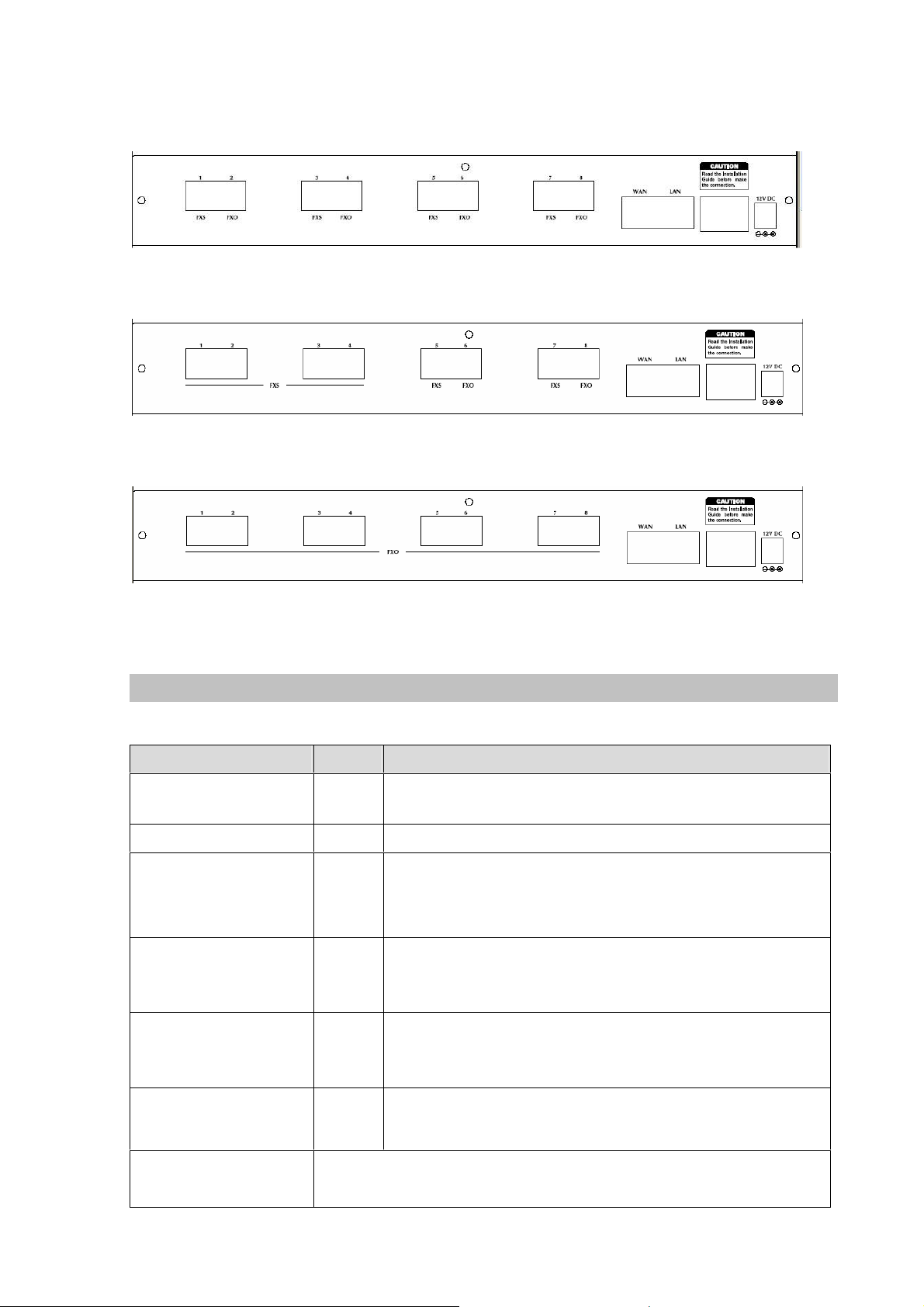
Rear Panel of VIP-880
Rear Panel of VIP-882
Rear Panel of VIP-880FO
Front Panel LED Indicators & Rear Panels
Front Panel LED State Descriptions
PWR
CPU
WAN Port
LAN Port
FXS
FXO
On
Off
Flashing
ON
Flashing
Off
ON
Flashing
Off
ON
Flashing
Off
On
Off
GW is power ON
GW is power Off
The system is running
GW network connection established
Data traffic on cable network
Waiting for network connection
LAN is connected successfully
Data is transmitting
Ethernet not connected to PC
Telephone Set is On-Hook
Ring Indication
Telephone Set is Off-Hook
Line is busy
Line is not enabled
9-pin RS-232
(VIP-880 series only)
10
Connecting VIP to a terminal emulator for configuring VIP
Page 11

NOTE: System initialization will turn some LEDs ON for a few seconds.
gh a
. Press RESET button
on rear panel over 5 seconds will reset the VoIP Gateway
Username/Password
Incorrectly connecting telephony devices to the RJ11 port
on the Telephony Interface can cause permanent damage to
Rear Panel Descriptions
WAN
LAN
(VIP-880 series)
LAN 1 ~ LAN 4
(VIP-480 series)
Reset
Power
FXS
FXO
Warning
The WAN port supports auto negotiating Fast Ethernet 10/100Base-T
networks. This port allows your voice gateway to be connected to an
Internet Access device, e.g. router, cable modem, ADSL modem, throu
CAT.5 twisted pair Ethernet cable.
The LAN port supports 4 10/100Base-T switch hub networks. These 4
ports allow your PC or Switch/Hub to be connected to the voice gateway
through a CAT.5 twisted pair Ethernet cable.
The reset button, when pressed, resets the cable voice gateway without
the need to unplug the power cord.
The supplied power adapter connects here.
FXS port was connected to your telephone sets or Trunk Line of PBX.
FXO port was connected to the extension port of a PBX or directly
connected to a PSTN line of carrier.
the VoIP Gateway
Note
The Default LAN IP is http://192.168.0.1
to this default LAN/WAN IP address and
function.
11
Page 12

Chapter 2
2
Preparations & Installation
Physical Installation Requirement
This chapter illustrates basic installation of VIP-480/VIP-880 series
• Network cables. Use standard 10/100BaseT network (UTP) cables with RJ45 connectors.
• TCP/IP protocol must be installed on all PCs.
For Internet Access, an Internet Access account with an ISP, and either of a DSL or Cable modem (for
WAN port usage)
Administration Interface
PLANET VIP-480/VIP-880 provides GUI (Web based, Graphical User Interface) for machine
management and administration.
Web configuration access
To start VIP-480/VIP-880 web configuration, you must have one of these web browsers
installed on computer for management
• Netscape Communicator 4.03 or higher
•
Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.01 or higher with Java support
Default LAN interface IP address of VIP-480/VIP-880 is 192.168.0.1. You may now open your
web browser, and insert 192.168.0.1 in the address bar of your web browser to logon
VIP-480/VIP-880 web configuration page.
VIP-480/VIP-880 will prompt for logon username/password, please enter: admin / 123 to continue
machine administration.
:
Page 13
. If you’re not familiar with
TCP/IP, please refer to related chapter on user’s manual
CD or consult your network administrator for proper network
In general cases, the LAN IP address is the default gateway
of LAN side workstations for Internet access, and the WAN
the IP address for remote calling party
Note
Please locate your PC in the same network segment
(192.168.0.x) of VIP-480/880
configurations.
LAN/WAN Interface quick configurations
Nature of PLANET VIP-480/VIP-880 is an IP Sharing (NAT) device, it comes with two default IP
addresses, and default LAN side IP address is “192.168.0.1”, default WAN side IP address is
“172.16.0.1”. You may use any PC to connect to the LAN port of VIP-480/VIP-880 to start machine
administration.
Hint
IP of VIP-480/880 are
to connect with.
LAN IP address configuration via web configuration interface
Execute your web browser, and insert the IP address (default: 192.168.0.1) of VIP in the adddress bar.
After logging on machine with username/password (default: admin / 123), browse to “Advance Setup”
--> “LAN setting” configuration menu:
13
Page 14

Parameter Description
It is suggested to keep the DHCP server related parameters
Please consult your ISP personnel to obtain proper PPPoE/IP
If Internet connection cannot be established, please check
the physical connection or contact the ISP service staff
LAN IP address of VIP-480/VIP-880
IP address
Subnet Mask
Default: 192.168.0.1
LAN IP address of VIP-480/VIP-880
Default: 255.255.255.0
Hint
in default state to keep machine in best performance.
After confirming the modification you’ve done, Please click on the Apply button to macke the changes
effective, and click “
Save Configuration”
to save configuration.
WAN IP address configuration via web configuration interface
Execute your web browser, and insert the IP address (default: 172.16.0.1) of VIP in the adddress bar.
After logging on machine with username/password (default: admin / 123), browse to “WAN Setting”
configuration menu, you will see the configuration screen below:
Connection Type Data required.
Static IP The ISP will assign IP Address, and related information.
DHCP
Get WAN IP Address automatically; it is no need to configure the
DHCP settings.
PPPoE
Hint
14
address related information, and input carefully.
for support information.
The ISP will assign PPPoE username / password for Internet
access,
Page 15
3
Chapter 3
Network Service Configurations
Configuring and monitoring your VoIP Gateway from web browser
The VIP-480/VIP-880 integrates a web-based graphical user interface that can cover most
configurations and machine status monitoring. Via standard, web browser, you can configure and
check machine status from anywhere around the world.
Overview on the web interface of VoIP Gateway
With web graphical user interface, you may have:
More comprehensive setting feels than traditional command line interface.
Provides user input data fields, check boxes, and for changing machine configuration settings
Displays machine running configuration
To start VIP-320 web configuration, you must have one of these web browsers installed on computer for
management
Netscape Communicator 4.03 or higher
Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.01 or higher with Java support
Manipulation of VoIP Gateway via web browser
Log on VoIP Gateway via web browser
After TCP/IP configurations on your PC, you may now open your web browser, and input
http://192.168.0.1 to logon VoIP gateway web configuration page.
VoIP gateway will prompt for logon username/password: admin / 123
VIP-480/VIP-880 log in page
15
Page 16

VIP-480/VIP-880 main page
Wizard Setup for Quick Start
Wizard Setup
After finishing the authentication, the Main menu will display 3 parts of configuration, please click
“Wizard Setup” to enter quick start:
1. WAN Port Type Setup (Setup First)
For most users, Internet access is the primary application. The Gateway support the WAN interface for
Internet access and remote access. The following sections will explain more details of WAN Port
Internet access and broadband access setup. When you click “WAN Port Type Setup” from within the
Wizard Setup, the following setup page will be show.
Three methods are available for Internet Access
Fixed IP User
IP Address
Netmask
Default Gateway
16
If you are a leased line user with a fixed IP address, fill out the
following items with the information provided by your ISP.
check with your ISP provider
check with your ISP provider
check with your ISP provider
Page 17

ADSL Dial-Up User (PPPoE Enable)
Some ISPs provide DSL-based service and use PPPoE to establish communication link with end-users.
If you are connected to the Internet through a DSL line, check with your ISP to see if they use PPPoE. If
they do, you need to select this item.
Three methods are available for Internet Access
User Name
Password
Retype Password
Enter User Name provided by your ISP
Enter Password provided by your ISP
Enter Password to confirm again
DHCP Client (Dynamic IP): (Get WAN IP Address automatically)
IP Address: If you are connected to the Internet through a Cable modem line then a dynamic IP
address will be assigned.
17
Page 18
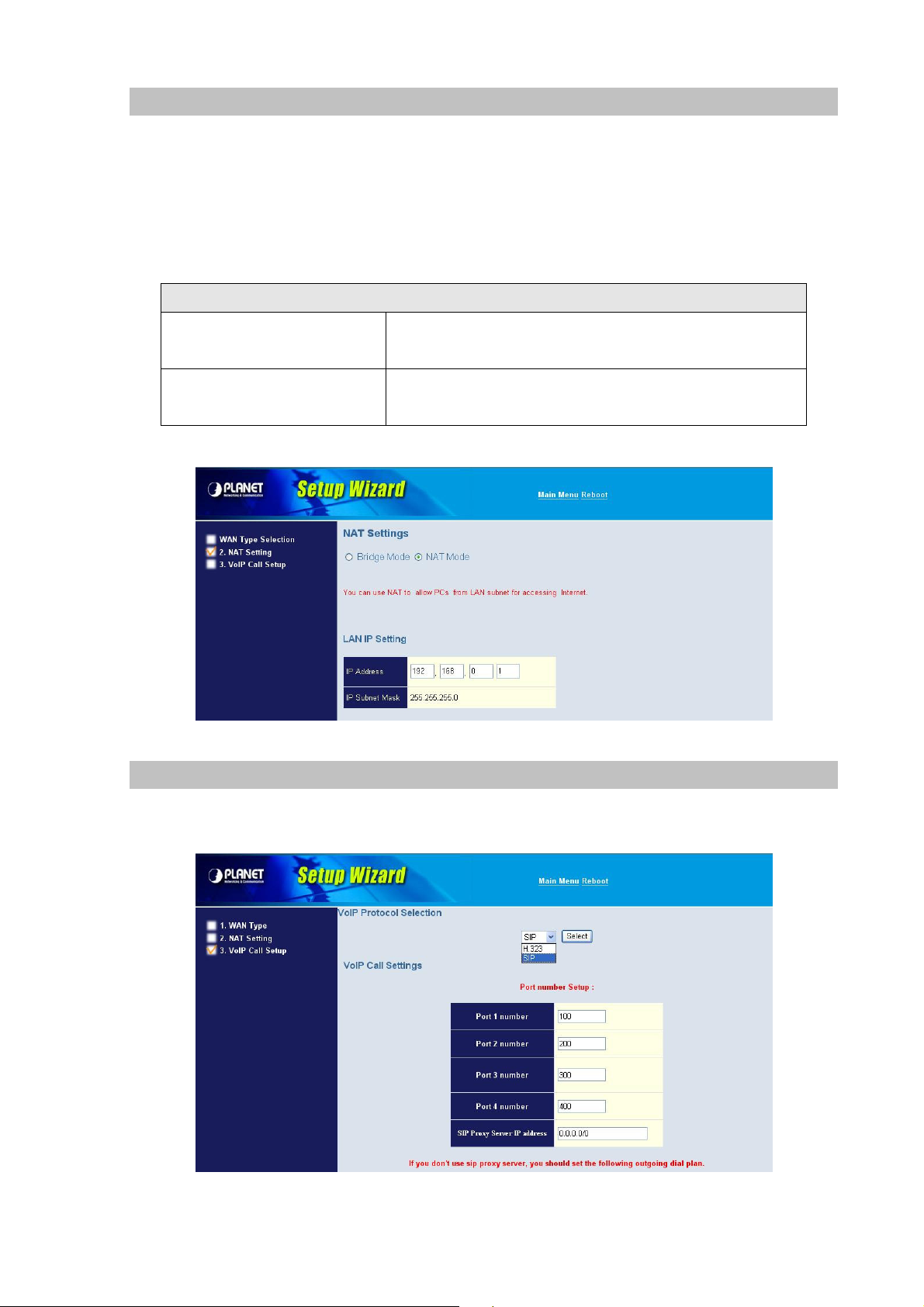
2. Configuring NAT or Bridge setting:
Bridge Mode:
When working on Bride Mode, the VoIP gateway will use only the LAN setting IP, The VoIP gateway will
use the same LAN IP setting as WAN IP. That means, when Bride mode enable, the WAN connection
setting will be ignored.
NAT mode:
LAN IP Network Configuration
IP Address
Subnet Mask
3. VoIP Call Protocol Setup
Private IP address for connecting to a local private network
(Default: 192.168.0.1)
Netmask for the local private network
(Default: 255.255.255.0)
STEP1 : Configure VoIP Call Signal Protocols :
User could select either H.323 or SIP Protocol, and click “select”
18
Page 19
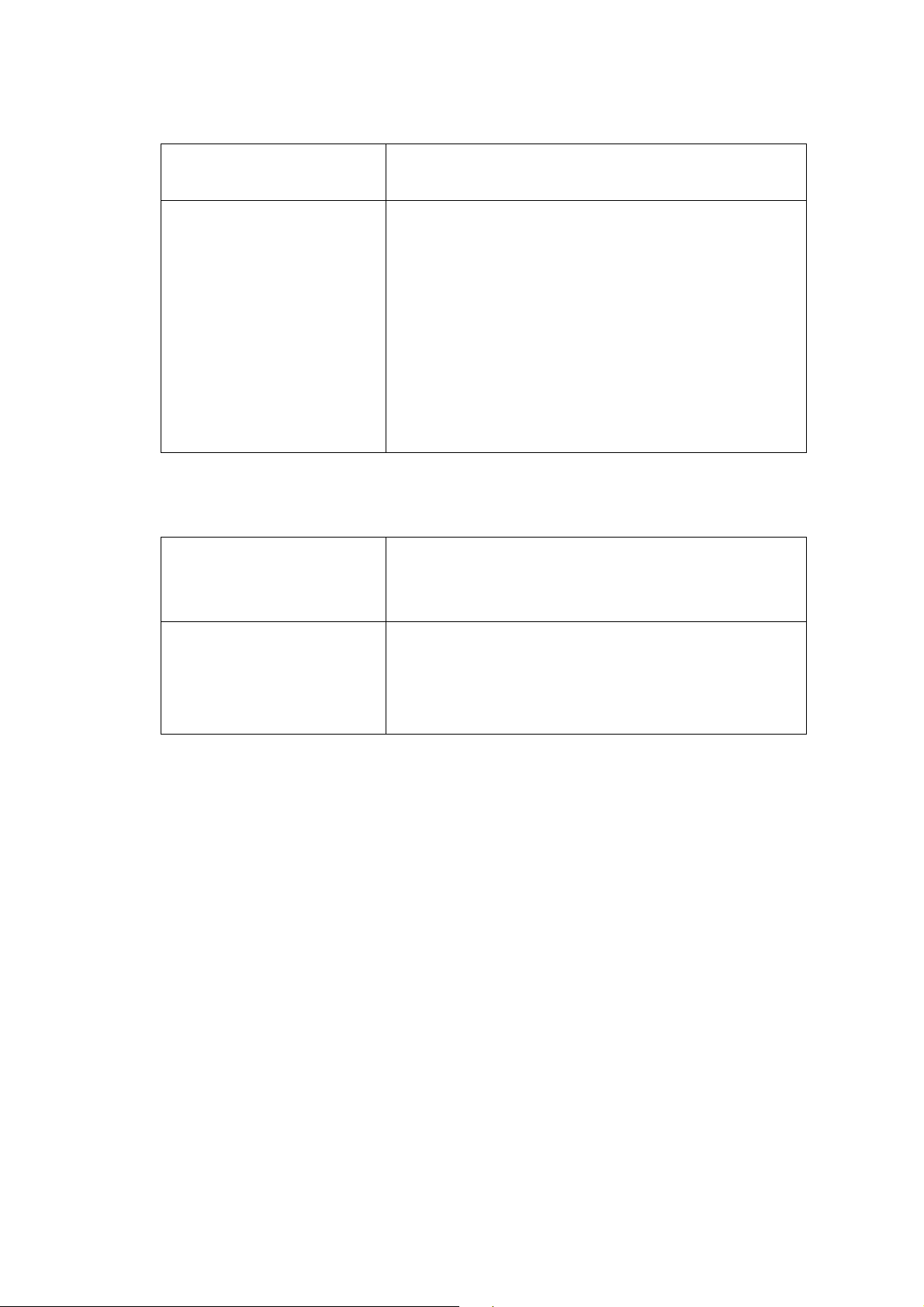
STEP2 : configure the numbering with phone/line ports.
Phone Number
telephone that is connected to Phone port
Line ports are connected to the extension ports of the PBX
system or the PSTN line. They have a common Line
Hunting Group Number. When this number is dialed, the
Gateway system will find a free FXO line connected to
The representation number is the phone number of the
Line Number
PBX. This hunting will skip all busy lines and absent lines
and find only the idle line to the PBX. After the available
line is found, you can hear the dial tone from PBX. After
that, you can dial the needed phone number out through
PBX
STEP3: Let GW Register to Gatekeeper/SIP Proxy Server
(If user does not have Gatekeeper/SIP Proxy Server, Please go to STEP 4: Outgoing Dialing Plan)
There is a gatekeeper address fields. If this gateway does
Gatekeeper IP address
not want to register to any gatekeeper, just set value
0.0.0.0 to the primary gatekeeper address.
There is a SIP Proxy Server address fields. If this gateway
SIP Proxy Server IP
addresses
does not want to register to any SIP Proxy Server, just set
value 0 .0.0.0 to the sip proxy server address.
STEP 4: Outgoing Dialing Plan
The purpose of “Outgoing Direct Call” setting is to let user create a proprietary dialing plan when this
Gateway is not registered to any H.323 Gatekeeper or any SIP Proxy Server. This setting can also
assign some dialing plan to local ports (including prefix strip, prefix addition).
Through this setting, user can directly map a number to a specific gateway (IP address).
19
Page 20

In the “Outgoing Dial Plan” settings:
“Leading Number” is the leading digits of the dialing number.
“Min Length” and “Max Length” is the min/max allowed length you can dial.
“Strip Length” is the number of digits that will be stripped from beginning of the dialed number.
“Prefix Number” is the digits that will be added to the beginning of the dialed number.
“Destination” is the IP address of the destination Gateway that owns this phone number.
STEP 5: Finishing the Wizard Setup
After completing the W izard Setup, please click “Finish” bottom. The VoIP Gateway will save the
configuration and rebooting Gateway automatically. After 20 Seconds, you could re-login the Gateway.
20
Page 21

Chapter 4
4
System Configurations
Advance Setup of Network Setup
In Advanced Setup, GW provides user two major parts function to configure:
One is “Network Setup”, the other one is “VoIP Call Setup”
Network Setup Label
WAN Setting
LAN Setting
Virtual Server
Dynamic DNS
Network Parameters
Sets/changes the WAN port Type like “Fixed IP”, “DHCP
Client” or ”PPPoE”.
Modifies the IP address of the LAN port and setting DHCP
Server parameters.
Remote user can access server such as Web or FTP at
you local site via public IP address can be automatically
redirected to local servers configured with private IP
address.
Dynamitic DNS allows you to provide Internet users with a
domain name to access your server.
Network Parameter allows you to modify the access port of
gateway.
WAN Setting
For most users, Internet access is the primary application. The VIP-480/VIP-880 series Gateway
support the WAN interface for Internet access and remote access. The following sections will explain
more details of WAN Port Internet access and broadband access setup. When you click “WAN Setting”,
21
Page 22

the following setup page will be shown.Three methods are available for Internet Access.
You are a leased line user with a fixed IP address; fill out
Static IP
IP Address
Netmask
Default Gateway
PPPoE for ADSL
the following items with the information provided by your
ISP.
check with your ISP provider
check with your ISP provider
check with your ISP provider
Some ISPs provide DSL-based service and use PPPoE to establish communication link with end-users.
If you are connected to the Internet through a DSL line, check with your ISP to see if they use PPPoE. If
they do, you need to select this item.
User Name
Password
Retype Password
Enter User Name provided by your ISP
Enter Password provided by your ISP.
Enter Password to confirm again.
22
Page 23
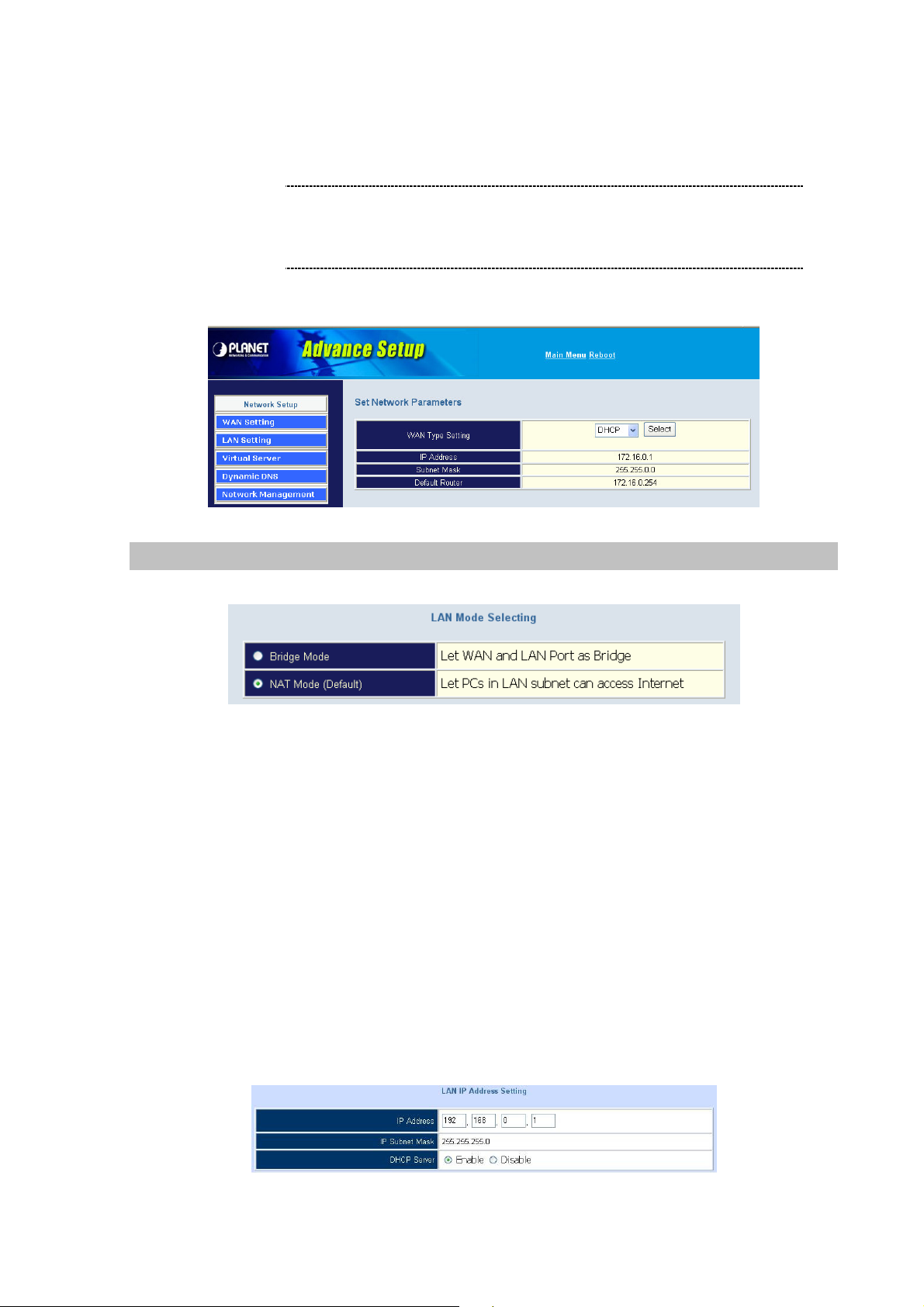
DHCP Client (Dynamic IP): (get WAN IP address automatically)
WAN port display the IP address, Subnet Mask and Default
IP Address: If you are connected to the Internet through a Cable modem line then a dynamic IP
address will be assigned.
Note
gateway IP address if DHCP client is successful
LAN Setting
There are two kinds of network feature to configure: Bridge Mode and NAT Mode
Bridge Mode:
Select this Gateway as Bridge. (WAN Port and LAN Port use the same IP address)
NAT Mode:
Each of the VoIP Gateway has two Ethernet interfaces, one is for connecting to local network users,
and the other is for connecting to an external broadband device (i.e. DSL modem/router or Cable
modem). The LAN port is connected to the local Ethernet network. WAN is connected to the external
broadband device. The LAN IP address/netmask is for private users or NAT users, and the WAN IP
address/netmask is for public users.
LAN IP Network Configuration
IP Address: Private IP address for connecting to a local private network (Default: 192.168.0.1).
Subnet Mask: Netmask for the local private network (Default: 255.255.255.0).
23
Page 24

DHCP Server Configuration
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It can automatically dispatch related IP
settings to any local user configured as a DHCP client. The DHCP server supports up to 253 users
(PCs) on Yes: Enables the DHCP server. No: Disables the DHCP server.
Start IP Address
End IP Address
DNS Server IP Address
Primary IP Address
Secondary IP Address
Sets the start IP address of the IP address pool.
Sets the end of IP address in the IP address pool.
DNS stands for Domain Name System. Every Internet
host. must have a unique IP address, also they may have a
human friendly, easy to remember name such as
www.yahoo.com. The DNS server converts the human
friendly name into it’s equivalent IP address.
Sets the IP address of the primary DNS server.
Sets the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
Virtual Server
“Natural firewall” allows requests for Internet access from the local network. However, any request from
the Internet to the local network is blocked. By setting the Virtual Server function, computers outside
the Intranet are allowed to access specific ports of local client. The Virtual Server Port Table may be
used to expose internal servers to the public domain or open a specific port number to internal hosts.
Internet hosts can use the WAN IP address to access internal network services, such as FTP, WWW,
and Telnet etc.
How to set a Virtual Server
The following example shows how an internal FTP server is exposed to the public domain. The internal
FTP server is running on the local host addressed as 192.168.0.100.
24
Page 25

Public Port
Private IP
Private Port
Apply
Specifies which port should be redirected to the internal
host.
Specifies the private IP address of the internal host offering
the service.
Specifies the private port number of the service offered by
the internal host.
Click here to add the port-mapping entry and enable the
service.
Dynamic DNS
DDNS is a service that maps Internet domain names to IP addresses. DDNS serves a similar
purpose to DNS: DDNS allows anyone hosting a Web or FTP server to advertise a public nam
e to prospective users. Unlike DNS that only works with static IP addresses, DDNS works with
dynamic IP addresses, such as those assigned by an ISP or other DHCP server. DDNS is po
pular with home network, who typically receive dynamic, frequently-changing IP addresses from
their service provider. To use DDNS, one simply signs up with a provider and installs network
software on their host to monitor its IP address.
25
Page 26

User Name
Password
Domain Name
DNS Server IP
Input your DDNS User Name
Input your DDNS Password
Input you set from your DDNS
Input your DNS Server IP
Netwrok Management
Network Parameter allows you to modify the access port of gateway.
For example:
Setting HTTP port: 80
Setting TELNET port: 23
26
Page 27

Advance Setup of VoIP Setup
In Advanced Setup, GW provides user two major parts function to configure:
One is “Network Setup”, the other one is “VoIP Call Setup”
VoIP Setup Label
The S Series Gateway support 4 / 8 phone/line for SIP and
VoIP Basic
Dialing Plan
Advanced Setting
Hot Line Setting
Port Status
H.323 VoIP call applications. You can configure these
ports from this menu.
Users could apply any dial policy by setting Dial Plan
including outgoing dial plan and incoming dial plan.
VoIP Gateway support for silence compression, DTMF
Relay, Codec Selection, FAX mode Option,
H323 Register Type and H.323 Fast-Start/Normal-Start
function.
FXO AC impedance, Volume Adjustment, RRQ TTL,
RFC2833 Payload, IP TOS,..etc
Let user can set up “hotline” to dial the phone number
automatically.
Display the telephone interface status
27
Page 28

VoIP Basic Configuration to H.323 protocol
VoIP Basic Configuration: (Configure the VoIP protocol to H.323 Protocol)
Configure the numbering with FXS / FXO ports. (Depending on model)
FXS Number:
The representation number is the phone number of the telephone that is connected to FXS
port.
FXO Number:
FXO ports are connected to the extension ports of the PBX system or the PSTN line. They
have a common Line Hunting Group Number. When this number is dialed, the Gateway system
will find a free FXO line connected to PBX. This hunting will skip all busy lines and absent lines
and find only the idle line to the PBX. After the available line is found, you can hear the dial tone
from PBX. After that, you can dial the needed phone number out through PBX.
Configure the ANI (Answer Number Indication) / Caller ID of the FXS/FXO ports.
ITSP needs ANI for authorization when gateway calls Off-Net call to PSTN number or mobile phone
number.
Register to H.323 Gatekeeper
(If user does not have Gatekeeper, Please go to H.323 Dialing Plan Policy for mour undrestaindgins)
28
Page 29

H.323 Parameters Label
H.323 ID
Primary Gatekeeper IP
Address
Secondary Gatekeeper IP
Address
Primary Gatekeeper Domain
Name
Secondary Gatekeeper
Domain Name
H.323 Gatekeeper ID
Sets the unique name of this Gateway, that is
communicated as part of H.323 messaging.
There are two gatekeeper address fields, one is primary,
the other secondary. If this gateway does not want to
register to any gatekeeper, just set value 0 to the primary
gatekeeper address. If the primary gatekeeper address is
not 0, the gateway will register to the primary gatekeeper. If
the second gatekeeper is not 0, the gateway will try to
register to the second gatekeeper when failed to register to
primary gatekeeper, i.e. if both the primary gatekeeper and
second gatekeeper
Let user use Domain Name of H.323 Gatekeeper.
The Gatekeeper ID; usually do not need to set this field
unless the gatekeeper must need this value.
Voice Cap Prefix
Let user set prefix number in RRQ nonstandard voicecap
entry.
In H.323 standard the RAS default port number is 1719.
The VoIP gateway provides user to change RAS port
RAS Port Adjustment
number to meet the network environment.(Some area
carrier blocks or forbidden the default port number)
In H.323 standard the default Q.931 port number is 1720.
The VoIP gateway provides user to change Q.931 port to
Q.931 Port Adjustment
meet the network environment. (Some area carrier blocks
or forbidden the default port number)
29
Page 30

H.323 Call Pass through NAT
H.323 ID
H.323 Pass Through NAT
method
Sets the unique name of this Gateway, that is
communicated as part of H.323 messaging.
1. Disable : The Gateway operates in public IP address
2. Auto Detection: When the Gateway register to GNU
Gatekeeper, please select this option.
3. Manual Setting: When the Gateway registers to H.323
Gatekeeper and operate under NAT (enable DMZ), please
select this option and key in IP address.
Dialing Plan to H.323 protocol
The “Dialing plan” needs setting when the user uses the method of Peer-to-Peer H.323 VoIP call or
registering H.323 Gatekeeper Mode. The H.323 Dialing Plan has three kinds of directions: Outgoing
(call out) and Incoming (call in) and PSTN route.
Outgoing Dial Plan:
Peer-to-Peer Call Mode: Effective
Registering to H.323 Gatekeeper Mode: Effective
Incoming Dial Plan
PSTN Route Dial Plan
In the “Outgoing Dial Plan Configurations” settings: Maximum Entries : 50
“Outbound number” is the leading digits of the call out dialing number.
“Length of Number” has two text fields need filled: “Min Length” and “Max Length” is the min/max
allowed length you can dial.
“Delete Length” is the number of digits that will be stripped from beginning of the dialed number.
“Add Digit Number” is the digits that will be added to the beginning of the dialed number.
“Destination IP Address / Domain Name” is the IP address / Domain Name of the destination
Gateway that owns this phone number.
Peer-to-Peer Call Mode: Effective
Registering to H.323 Gatekeeper Mode:
The leading number would register to H.323 Gatekeeper
Peer-to-Peer Call Mode: The same as the Incoming Dial
Plan
Registering to H.323 Gatekeeper Mode: The leading
number would NOT register to H.323 Gatekeeper
30
Page 31

Example1: Normally Dial
001x leading call out, call to Destination IP address: 172.16.0.100
002x leading call out, call to Destination Domain Name: h323gw.test.com
Example2: Speed Dial
If user dial “101”,
Gateway automatically dials “1234567890” to Destination IP address: 172.16.0.101
If user dial “202”
Gateway automatically dials “0987654321” to Destination IP address: 172.16.0.202
In the “Incoming Dial Plan Configurations” settings: Maximum Entries : 50
“Inbound number” is the leading digits of the dialing number.
“Length of Number“ has two text fields need filled: “Min Length” and “Max Length” is the min/max
allowed length you can dial.
“Delete Length” is the number of digits that will be stripped from beginning of the dialed number.
“Add Digit Number” is the digits that will be added to the beginning of the dialed number.
“Destination Tele port” is “Tel-port”; this is for local dial plan setting phone number.
Example1: Hunting for FXS Port
Port 1: FXS
Port 2: FXS
Port 3: FXS
Port 4: FXS
H.323 number “123” call incoming, Port 1 will be ringing.
If Port 1 is busy, Port will be ringing.
31
Page 32

If Port 1 and 2 are busy, Port 3 will be ringing.
If Port 1, Port 2 and Port 3 are busy, Port 4 will be ringing.
Note: “123” will be register to H.323 Gatekeeper if “Register to GK” was enabled, show
as below:
Example2: Hunting for FXO Port
Port 1: FXO was connected to PSTN.
Port 2: FXO was connected to PSTN.
Port 3: FXO was connected to PSTN.
Port 4: FXO was connected to PSTN.
H.323 number “123” call incoming, Port 1 will be off-hook and hear the Dial Tone from PSTN.
If Port 1 is busy, Port will be will be off-hook and hear the Dial Tone from PSTN.
If Port 1 and 2 are busy, Port 3 will be off-hook and hear the Dial Tone from PSTN.
If Port 1, Port 2 and Port 3 are busy, Port 4 will be off-hook and hear the Dial Tone from PSTN.
Note: “123” will be register to H.323 Gatekeeper if “Register to GK” was enabled, show as below:
32
Page 33

Example3: Termination Call to FXO for One-Shoot Call
Port 1: FXO was connected to PSTN (area code is 81xxxxxxxx).
H.323 leading number “081x”incoming, and delete the first one digit “0”, and call to PSTN number.
Note: “081x” will be registered to H.323 Gatekeeper if “Register to GK” was enabled,
show as below:
Example4: Termination Call to FXO
Port 1: FXS
Port 1: FXO was connected to PSTN (area code is 92xxxxxxxx).
Port 1 FXS call to “092x” to PSTN, FXO port will delete the first one digit “0” and call to PSTN
number.
(Note: “092x” will be NOT register to H.323 Gatekeeper when Gateway when Registering H.323
Gatekeeper Mode)
33
Page 34

Advance Setting to H.323 protocol
In Advanced Setting , GW provides user three major parts function to configure:
One is “VoIP Advance”, the other one is “Telephone Advance” and “Network Advance”
H.323 VoIP Advance Configurtion
If this function is enabled, when VoIP call is occurred, the
Smart-QoS
DTMF Relay for H.323
H.323 Start Mode
other data will be automatically reduced traffic which
across the internet in order to guarantee the voice
bandwidth.
After the VoIP call is connected, when you dial a digit, this
digit is sent to the other side by DTMF tone. There are two
methods of sending the DTMF tone. The first is “in band”,
that is, sending the DTMF tone in the voice packet. The
other is “out band”, that is, sending the DTMF tone as a
signal. Sending DTMF tone as a signal could tolerate more
packet loss caused by the network. If this selection is
enabled, the DTMF tone will be sent as a signal.
This selection could force the Gateway to use normal start
mode (default mode) or fast start mode when establishing
a VoIP call. Many other gateways only support normal start
mode, enable this selection when it is necessary. The
default is disabled (using fast start mode).
This selection could force the Gateway to use normal start
mode (default mode) or fast start mode when establishing
H.323 H.245 Tunneling
34
a VoIP call. Many other gateways only support normal start
mode, enable this selection when it is necessary. The
default is disabled (using fast start mode).
Page 35

T.30/T.38 real-time FAX compliant Voice/FAX auto-switch.
FAX Mode Option
H.323 RRQ TTL
H.323 Registration type
H.323 Telephone Advance Configuration
Silence Compression
The T.38 is a “Real Time Group 3 Fax Communication over
IP network” format. That’s meaning it’s a protocol for Fax
over IP. You have to enable this function.
This command configures the number of seconds that the
gateway should be considered active by the H.323
gatekeeper. The gateway transmits this value in the RRQ
message to the gatekeeper.The default value is “0”.
There are 2 choices for this setting. “Gateway” means it will
act as the VoIP gateway. “Terminal” means it will act as the
IP phone terminal.
If this function is enabled, when silence is occurred for a
period of time, no data will be sent across the network
during this period in order to save bandwidth.
Dial Complete Tone
Disable / Enable dialing complete tone.
The Codec is used to compress the voice signal into data
Voice Codec option
packets. Each Codec has different bandwidth requirement.
There are four kinds of Codec, G.723, G.729AB, G.711_u
and G.711_A. The default value is G.723.
FXS Impedance
FXO AC Impedance
Phone (Line) in/out volume
FXO Tx/Rx Gain
UK PSTN release tone
detection
The FXS provides 600/900 OHM impedances for selection.
The FXO provides wild and complex ac termination
impedances for selection.
You can adjust the Phone (Line) in/out volume, range from
-9db to 9db.
You can adjust the FXO Tx/Rx Gain , range from -6db to
6db.
When you use the Gateway to UK, you can Enable this
selection to detection release tone.
Scenario : Flash detection and generation duration
1. PSTN Call from PSTN to Office PBX and dial the extension 102 go to Gateway.
2. Call to Gateway of Home by Hotline.
3. Home user needs call transfer to extension number 101.
4. Dial Flash and Gateway FXS detect and generate the Flash to PBX in Office.
Flash Detection: Let you change flash detection (milliseconds) of Gateway when phone
generate flash to FXS.
Flash Generation: Let you change flash generation time (milliseconds) for PBX detection.
35
Page 36

Ring Frequency
You can configure how long the Ring Frequency do you
FXO Battery Reverse
FXO Answer Mode
want to use.
Enable battery reverse to detect polarity from PSTN line.
The PSTN line can send H.323 case: Sending the Q.931
connect signal to caller when detecting polarity reverse
from PSTN Line.
When user calls the PSTN line which was connected with
the FXO port, there are three answer mode for user to
configure.
1. Ringing Answer Mode (Default Setting): FXO answer
the call once the ring coming from PSTN line.
2. Connecting Answer Mode:
Case A: “Hot Line Number” was NOT assigned in the
FXO port. FXO answer the call once the ring comes
from PSTN line.
Case B: “Hot Line Number” was assigned and the Hot
line number belongs to remote VoIP device.
In this case, FXO port will not answer (off-hook) the
PSTN till the user picks up the call.
(Note: This case can avoid charging for the Local
PSTN call when the remoting VoIP devic still ring.)
Case C: “Hot Line Number” was setting and the Hot
line number was assigned to another FXS port in
same Gateway. FXO port will not answer (off-hook) till
the Phone (connected to the FXS port) was picked up
by user.
(Note: This case can avoid the Local PSTN charge
when the FXS port still ring.)
36
Page 37

3. Non Answer Mode: FXO will NOT answer the call in
any time.
(Note: Some ITSP only let the FXO for termination
function, they do not user use the FXO port for
origination)
H.323 Call Connecting Answer Mode
Case B: Hot Line Number” was assigned and the Hot line number belongs to remote H.323
device.
(Note: The remote H.323 device need Disable the “Auto Answer”)
1. When the call com from PSTN to FXO, FXO start the Hot line dialing to remote H.323
gateway
2. The phone of remote H.323 gateway start ring.
3. When the phone was picked up, the remote H.323 Gateway send “Q.931 connects”
signal to FXO port.
4. Once FXO port receives the “Q.931 connects” signal, FXO port would off-hook to
answer the PSTN call.
Case C: “Hot Line Number” was setting and the Hot line number was assigned to another
FXS port in same Gateway.
When the call com from PSTN to FXO, FXO start the Hot line dialing to FXS port.
The phone start ring.
Once the phone was picked up, FXO port would off-hook to answer the PSTN call.
37
Page 38

H.323 Netwrok Advance Configuration
If this function is enabled, when VoIP call is occurred, the
Smart-QoS
Bandwidth control
G.723/G.729 Bandwidth
IP TOS
other data will be automatically reduced traffic which
across the internet in order to guarantee the voice
bandwidth.
You can configure your bandwidth what the Max byte of
download and upload of ADSL modem rate.
Enable / Disable Type of Service in IP packets.
VoIP Basic Configuration to SIP Protocol
Select “SIP Protocol”
SIP number (username) and Password Setting: Please fill out the SIP account including username /
password from ITSP.
(Note: now only support digits type for SIP number / username)
38
Page 39

SIP Hunting Table: This allows gateway can answer SIP call from internet by Hunting. For example:
Port 1and Port 2 is hunting for the Port 1 SIP account. Then when port 1 are on call, the other one SIP
call from internet will ring port 2.
SIP Proxy Server Setting
SIP Proxy Server Setting
Enter the SIP service IP address or domain name in this
field (the domain name that comes after the @ symbol i n a
full SIP URI).
Use Net2Phone Service Provider
SIP Domain
Enter the SIP realm in this field
This field sets how long an entry remains registered with
the SIP register server. The register server can use a
Register Interval Setting
different time period. The Gateway sends another
registration request after half of this configured time period
has expired.
Enable or Disable MD5 Authentication with SIP Proxy
SIP Authentication
Server.
The Outbound Proxy method is just very like the Proxy
Outbound Proxy Support
server built-in NAT pass-through solution, except that the
packets need to pass through the Outbound proxy server.
39
Page 40

SIP NAT Traversal Method
NAT Traversal Method: STUN Client / Symmetric RTP
Dialing Plan to SIP protocol
The “Dialing plan” needs setting when the user uses the method of Peer-to-Peer SIP VoIP call or
registering SIP Proxy Server Mode. The SIP Dialing Plan has two kinds of directions: Outgoing (call out)
and Incoming (call in).
Outgoing Dial Plan:
Incoming Dial Plan
Peer-to-Peer Call Mode: Effective
Registering to SIP Proxy Server Mode: Effective
Peer-to-Peer Call Mode: Effective
Registering to SIP Proxy Server Mode:
The leading number would register to SIP Proxy Server
Peer-to-Peer Call Mode: The same as the Incoming Dial
PSTN Route Dial Plan
Plan
Registering to SIP Proxy Server Mode: The leading
number would NOT register to SIP Proxy Server
In the “Outgoing Dial Plan Configurations” settings: Maximum Entries: 50
“Outbound number” is the leading digits of the call out dialing number.
“Length of Number” has two text fields need filled: “Min Length” and “Max Length” is the min/max
allowed length you can dial.
“Delete Length” is the number of digits that will be stripped from beginning of the dialed number.
“Add Digit Number” is the digits that will be added to the beginning of the dialed number.
“Destination IP Address / Domain Name” is the IP address / Domain Name of the destination
Gateway that owns this phone number.
40
Page 41

Example1: Normally Dial
2290x leading call out, call to Destination Domain Name: sipgw.test.com
221 leading call out, call to Destination IP Address: 172.16.0.100
Example2: Speed Dial
If user dial “101”,
Gateway automatically dials “1234567890” to Destination IP address: 172.16.0.101
If user dial “202”
Gateway automatically dials “0987654321” to Destination IP address: 172.16.0.202
In the “Incoming Dial Plan Configurations” settings: Maximum Entries: 50
“Inbound number” is the leading digits of the dialing number.
“Length of Number“has two text fields need filled: “Min Length” and “Max Length” is the min/max
allowed length you can dial.
“Delete Length” is the number of digits that will be stripped from beginning of the dialed number.
“Add Digit Number” is the digits that will be added to the beginning of the dialed number.
“Destination Tele port” is “Tel-port”; this is for local dial plan setting phone number.
41
Page 42

Example1: Hunting for FXS Port
Port 1: FXS
Port 2: FXS
Port 3: FXS
Port 4: FXS
H.323 number “123”call incoming, Port 1 will be ringing.
If Port 1 is busy, Port will be ringing.
If Port 1 and 2 are busy, Port 3 will be ringing.
If Port 1, Port 2 and Port 3 are busy, Port 4 will be ringing.
(Note: “123” will be NOT register to SIP Proxy Server when Gateway is Registering SIP Proxy
Server Mode)
Example2: Hunting for FXO Port
Port 1: FXO was connected to PSTN.
Port 2: FXO was connected to PSTN.
Port 3: FXO was connected to PSTN.
Port 4: FXO was connected to PSTN.
H.323 number “123”call incoming, Port 1 will be off-hook and hear the Dial Tone from PSTN.
If Port 1 is busy, Port will be will be off-hook and hear the Dial Tone from PSTN.
If Port 1 and 2 are busy, Port 3 will be off-hook and hear the Dial Tone from PSTN.
If Port 1, Port 2 and Port 3 are busy, Port 4 will be off-hook and hear the Dial Tone from PSTN.
(Note: “123” will be NOT register to SIP Proxy Server when Gateway is Registering SIP Proxy
Server Mode)
Example3: Termination Call to FXO for One-Shoot Call
Port 1: FXO was connected to PSTN (area code is 81xxxxxxxx).
H.323 leading number “081x”incoming, and delete the first one digit “0”, and call to PSTN number.
42
Page 43

(Note: “081x” will be NOT register to SIP Proxy Server when Gateway is Registering SIP Proxy
Server Mode)
Advance Setting to SIP protocol
In Advanced Setting , GW provides user three major parts function to configure:
One is “VoIP Advance”, the other one is “Telephone Advance” and “Network Advance”
SIP VoIP Advance Configurtion
DTMF Method for SIP
FAX Mode Option
After the VoIP call is connected, when you dial a digit, this
digit is sent to the other side by DTMF tone. There are
three methods of sending the DTMF tone. The first one is
“in band”, that is, sending the DTMF tone in the voice
packet. The second one is “RFC2833”, that is, sending the
DTMF tone as a RTP payload signal. The third one is “SIP
Info”, that is, sending the DTMF tone as a SIP signal.
Sending DTMF tone as a signal could tolerate more packet
loss caused by the network. If this selection is enabled, the
DTMF tone will be sent as a signal.
T.30/T.38 real-time FAX compliant Voice/FAX auto-switch.
The T.38 is a “Real Time Group 3 Fax Communication over
IP network” format. That’s meaning it’s a protocol for Fax
over IP. You have to enable this function.
43
Page 44
SIP Telephone Advance Configuration
Silence Compression
Dial Complete Tone
Voice Codec option
FXS Impedance
FXO AC Impedance
Phone (Line) in/out volume
FXO Tx/Rx Gain
UK PSTN release tone
If this function is enabled, when silence is occurred for a
period of time, no data will be sent across the network
during this period in order to save bandwidth.
Disable / Enable dialing complete tone.
The Codec is used to compress the voice signal into data
packets. Each Codec has different bandwidth requirement.
There are four kinds of Codec, G.723, G.729AB, G.711_u
and G.711_A. The default value is G.723.
The FXS provides 600/900 OHM impedances for selection.
The FXO provides wild and complex ac termination
impedances for selection.
You can adjust the Phone (Line) in/out volume, range from
-9db to 9db.
You can adjust the FXO Tx/Rx Gain , range from -6db to
6db.
When you use the Gateway to UK, you can Enable this
detection
selection to detection release tone.
Scenario : Flash detection and generation duration
5. PSTN Call from PSTN to Office PBX and dial the extension 102 go to Gateway.
6. Call to Gateway of Home by Hotline.
7. Home user needs call transfer to extension number 101.
8. Dial Flash and Gateway FXS detect and generate the Flash to PBX in Office.
Flash Detection: Let you change flash detection (milliseconds) of Gateway when phone
generate flash to FXS.
Flash Generation: Let you change flash generation time (milliseconds) for PBX detection.
44
Page 45

Ring Frequency
You can configure how long the Ring Frequency do you
FXO Battery Reverse
want to use.
Enable battery reverse to detect polarity from PSTN line.
The PSTN line can send SIP case: Sending the 200 OK
connect signal to caller when detecting polarity reverse
from PSTN Line.
When user calls the PSTN line which was connected with
the FXO port, there are three answer mode for user to
configure.
4. Ringing Answer Mode (Default Setting): FXO answer
the call once the ring coming from PSTN line.
5. Connecting Answer Mode:
Case A: “Hot Line Number” was NOT assigned in the
FXO port. FXO answer the call once the ring comes
from PSTN line.
Case B: “Hot Line Number” was assigned and the Hot
line number belongs to remote VoIP device.
In this case, FXO port will not answer (off-hook) the
FXO Answer Mode
PSTN till the user picks up the call.
(Note: This case can avoid charging for the Local
PSTN call when the remoting VoIP devic still ring.)
Case C: “Hot Line Number” was setting and the Hot
line number was assigned to another FXS port in
same Gateway. FXO port will not answer (off-hook) till
the Phone (connected to the FXS port) was picked up
by user.
(Note: This case can avoid the Local PSTN charge
when the FXS port still ring.)
6. Non Answer Mode: FXO will NOT answer the call in
any time.
(Note: Some ITSP only let the FXO for termination
function, they do not user use the FXO port for
origination)
SIP Call Connecting Answer Mode
Case B: Hot Line Number” was assigned and the Hot line number belongs to SIP device.
1. When the call com from PSTN to FXO, FXO start the Hot line dialing to remote SIP
gateway
2. The phone of remote SIP gateway start ring.
3. When the phone was picked up, the remote SIP Gateway sends “SIP 200 OK” signal to
FXO port.
45
Page 46

4. Once FXO port receives the “SIP 200 OK” signal, FXO port would off-hook to answer the
PSTN call.
Case C: “Hot Line Number” was setting and the Hot line number was assigned to another
FXS port in same Gateway.
1. When the call com from PSTN to FXO, FXO start the Hot line dialing to FXS port.
2. The phone start ring.
3. Once the phone was picked up, FXO port would off-hook to answer the PSTN call.
46
Page 47

SIP Netwrok Advance Configuration
If this function is enabled, when VoIP call is occurred, the
Smart-QoS
Bandwidth control
G.723/G.729 Bandwidth
IP TOS
other data will be automatically reduced traffic which
across the internet in order to guarantee the voice
bandwidth.
You can configure your bandwidth what the Max byte of
download and upload of ADSL modem rate.
Enable / Disable Type of Service in IP packets.
Port Status
Port Status Display: This selection will display concurrent call status of this Gateway. The status
information of each voice channel includes codec, dialing number and destination IP address. The
status is refreshed every 3 seconds.
47
Page 48

Chapter 5 System Administrations
5
Management
Management Label
You can save configuration and restart the gateway with
Save Configuration
Access Control
Set to Default
Backup/Restore
Configuration
System Information
SNTP Setting
Syslog Setting
Capture Packets
the default configuration or with the current running
configuration.
Users can Sets/changes the administrator password...
You can restart the gateway with the default configuration.
User can backup the configuration file of Gateway to PC or
Restore the configuration file from PC.
Display Software version, WAN Type, VoIP Status, VoIP
Codec, Phone Interface and System Tim.
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) Configuration for
synchronizing gateway clocks in the global Internet.
Gateway can sends log information to Syslog Server by
UDP ports 514.
The gateway supports packets capture and save the
packets to your PC.
Save Configuration
This page allows you to click “Save Configuration and Reboot” to save configuration and begin to
restart.
48
Page 49

Access Control
Changing the Administrator/Guest Password
For security reasons, we strongly recommend that you set an administrator/password for the router. On
first setup the router requires no password. If you don’t set a password the router is open and can be
logged into and settings changed by any user from the local network or the Internet.
Click Access Control Setup, the following screen will open.
Set To Default Configuration
If you want to reboot the router using factory default configuration, click “Apply” then reset the
router’ s settings to default values.
49
Page 50

Backup/Restore Configuration to a File
User can backup the configuration to a File at Microsoft Operation System. And also restore the
configuration file to the GW from PC.
System Information Display Function
Click System Information Display to open the Online Status page. In the example, on the foll
owing page, both PPPoE connections is up on the WAN interface, H323/SIP Status, MAC addr
ess, Register Status.., etc.
50
Page 51

SNTP Setting Function
Click SNTP setting to open the Online Status page. In the example, on the following page,
.
Use SNTP Setting— when checked, Gateway uses a Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) to set the
date and time. The Gateway synchronizes the Gateway’s time after you select the time zone. Use
SNTP Setting; Select the time zone which Gateway was at.
Syslog setting
Use Syslog server to record your Gateway log file. You can set you syslog server IP address for this
function.
51
Page 52

Capture packetackets Function
Use “Capturer Packets” to record Gateway packets. You can start and stop the capture then save the
file to PC. Use the Ethereal Tool (www.ethereal.com) to analyze the packets.
52
Page 53

Appendix A
FAQ
Q: What is the default administrator password to login to the gateway?
A: By default, your default username is “admin”, default password is “123” to login to the
router. For security, you should modify the password to protect your gateway against hacker
attacks.
Q: I forgot the administrator password. What should I do?
A: Press the Reset button on the rear panel for over 5 seconds to reset all settings to default
values.
Q: What is the default IP address of the router?
A: The default WAN IP address is 172.16.0.1 with subnet mask 255.255.0.0.
The default LAN IP address is 192.168.0.1 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
Q: Why is it that I can ping to outside hosts, but not access Internet
Web sites?
A: Check the DNS server settings on your PC. You should get the DNS servers settings
from your ISP. If your PC is running a DHCP client, remove any DNS IP address setting. As
the router will assign the DNS settings to the DHCP-client-enabled PC.
Q: 5. What is the maximum number of IP addresses that the DHCP server of the
gateway can assign to local PCs?
A: The built-in DHCP server can support 253 IP addresses for local network usage.
53
Page 54

Appendix B
node like telephone or fax machine (since
vide a number!). If you connect those to FXO port, you will hear
FXO
Voice communications
The chapter shows you the concept and command to help you configure your VoIP gateway through
sample configuration. And provide several ways to make calls to desired destination in
VIP-480/VIP-880. In this section, we’ll lead you step by step to establish your first voice communication
via web browsers operations.
Concepts: Voice Port
There are two type of the voice port, FXO (Foreign exchange Office) and FXS. (Foreign exchange
Station) On the printing of the RJ-11 port, you should find that.
FXO (Foreign exchange Office) port
The FXO port allows the connection with a device that already has a fixed number; say 222, or
412-1111. So the only connections for FXO port will be to your local PSTN or one of your extension-line
from your PBX system.
With your FXO connect to PSTN; the Internet Voice can then have a local call through this line/number
(412-1111). Or, locally, you can have an Internet Call through the line 412-1111
The same to PBX system, you are required to know with which extension number to the FXO port. Your
PBX users will need to know this number in the future.
Hint
FXO port cannot connect to an end-
they do not pro
nothing once you pick up the handset.
54
Page 55

PBX extension line or PSTN line. This may make the FXS port or your PBX
222
FXS (Foreign exchange Station) port
The FXS port allows the connection to an end node, like telephone, fax machine, or out-line of PBX
system.
FXS port is as like your local phone service provider who provides a number to you. It is easy to tell that
after you have connected an end-device to FXS port and you will hear the dial-tone from FXS port once
the hand set off-hook.
Caution
FXS
412-1111
The FXS port is with voltage and current. DO NOT connects the port to any
extension port malfunction.
55
Page 56

H.323 VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
801
WAN
Scenario 1: H.323 VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
Gateway 1 to Gateway 2 PLAR connection
H.323 Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode)
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3 |Des: GW1 IP address
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
Digit: Digit Length min~ max
Gateway#1
901
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
Gateway#2
801
901
56
Page 57

Scenario 2: H.323 VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
609, 601
801
WAN
Gateway 1 (with PBX) to Gateway 2 PLAR connection
H.323 Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) with PBX: Call PBX Extension
Method 1: Two-Stage-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW2 IP address
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
Gateway#1
Extension 609
901
Extension 601
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
No: 6x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
Gateway#2
801
57
Page 58

Scenario 3: H.323 VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
801
609, 0,
12345678
WAN
Gateway 1 (with PBX/PSTN) to Gateway 2 PLAR connection
Call Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
H.323 Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) with PBX: Remote Call PSTN number
Method 1: Two-Stages-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
X: wild card
Des: Destination IP
Digit: Digit Length min~ max
Extension 609
Trunk-Line
02-12345678
Gateway#1
901
Extension 601
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
Gateway#2
801
58
Page 59

Scenario 4: H.323 VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
WAN
Des:
Destination IP
Extension 609
Extension 601
Gateway 1 (with PBX/PSTN) to Gateway 2 PLAR connection
Call Method: One-Shot-Dialing
H.323 Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) with PBX: Remote Call PSTN number
Method 2: One-Shot-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3 |Des:GW2 IP address
Incoming Dial Plan
x: wild card
Trunk-Line
02-12345678
Gateway#1
901
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
No: 6x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
Gateway#2
801
801
02-12345678
59
Page 60

Scenario 5: H.323 VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
801
02-12345678
WAN
Digit:
Di
git Length min~ max
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number) PLAR connection
Call Method: One-Shot-Dialing
H.323 Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) : Remote Call PSTN number
Method: One-Shot-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3, Des | GW2 IP address
Incoming Dial Plan
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
FXO
02-12345678
Gateway#1
901
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
No: 6x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
Gateway#2
801
60
Page 61

Scenario 6: H.323 VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
Gateway#2
Incoming Dial Plan
No: 02x| Digit: 3~10 | Des: GW 1 IP
56785678
, 02
-
12345678
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number) PLAR connection
Call Method: One-Shot-Dialing
H.323 Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) : PSTN Call PSTN number
Method: One-Shot-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW2 IP address
No: 04x | Digit: 3~10 | Des: GW2 IP address
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
02-87654321
FXO
02-12345678
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
No: 6x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
Gateway#1
901
WAN
04-12341234
04-56785678
FXO
801
04-12341234
61
Page 62

Scenario 7: H.323 VoIP Call: Register to Gatekeeper
901
801
Gateway 1 to Gateway 2 PLAR connection
H.323 Call (GK Mode)
Register Number List
GW1: 801
GW2: 901
GK
WAN
Gateway#1
Gateway#2
801
901
62
Page 63

Scenario 8: H.323 VoIP Call: Register to Gatekeeper
Gateway#2
801
Extension 609
Extension 601
901
GK
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Call PBX extension number) PLAR connection
Call Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
H.323 Call (GK Mode) with PBX: Call PBX Extension
Method 1: Two-Stage-Dialing
Register Number List
GW1: 801
x: wild card
Gateway#1
WAN
801
609, 601
63
Page 64

Scenario 9: H.323 VoIP Call: Register to Gatekeeper
Trunk
-
Line
GK
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number with PBX) PLAR connection
Call Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
H.323 Call (GK Mode) with PBX: Remote Call PSTN number
Method 1: Two-Stages-Dialing
Register Number List
GW1: 801
02-12345678
Extension 609
Gateway#1
901
Extension 601
WAN
Gateway#2
801
609, 0, 23221344
801
64
Page 65

Scenario 10: H.323 VoIP Call: Register to Gatekeeper
Extension
02-12
345678
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number with PBX) PLAR connection
Call Method: One-Shot-Dialing
H.323 Call (GK Mode) with PBX: Remote Call PSTN number
Method 2: One-Shot-Dialing
Incoming Dial Plan
No: 02x | Digit: 3~10 |Strip:2 |Prefix: 0, | fxo port
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
Digit: Digit Length min~ max
Trunk-Line
Gateway#1
Extension 601
Register Number List
GW1: 801
WAN
901
801
02-12345678
GK
Gateway#2
801
65
Page 66

Scenario 11: H.323 VoIP Call: Register to Gatekeeper
Gateway#2
Digit:
Digit Length min~ max
FXO
02-12345678
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number) PLAR connection
Call Method: One-Shot-Dialing
H.323 Call (GK Mode) : Remote Call PSTN number
Method: One-Shot-Dialing
Incoming Dial Plan
No: 02x | Digit: 3~10 |Strip:2 |fxo port
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
Register Number List
GW1: 801
Gateway#1
901
02-12345678
GK
WAN
801
801
66
Page 67

Scenario 12: H.323 VoIP Call: Register to Gatekeeper
WAN
Digit:
Digit Length min~ max
04-12341234
87654321
, 04
-
1234123
4
04-56785678
GW2: 901,609,02x, 04 xs
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number) PLAR connection
Call Method: One-Shot-Dialing
H.323 Call (GK Mode) : PSTN Call PSTN number
Method: One-Shot-Dialing
Register Number List
GW1: 801
Incoming Dial Plan
No: 02x | Digit: 3~10 |Strip:2 |fxo port
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
02-87654321
FXO
Incoming Dial Plan
No: 04x | Digit: 3~10 |Strip:2 |fxo port
GK
Gateway#1
901
Gateway#2
56785678, 02-12345678
FXO
801
67
Page 68

SIP VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
WAN
Scenario 13: SIP VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
Gateway 1 to Gateway 2 PLAR connection
SIP Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode)
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3, Des | GW1 IP address
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
Digit: Digit Length min~ max
Gateway#1
901
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3, Des | GW1 IP address
Gateway#2
801
801
901
68
Page 69

Gateway#2
801
WAN
Des:
Destination IP
Scenario 14: SIP VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Call PBX extension number) PLAR connection
Call Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
SIP Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) with PBX: Call PBX Extension
Method 1: Two-Stage-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3 |Des GW2 IP address
x: wild card
Gateway#1
Extension 609
901
Extension 601
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 |Des: GW1 IP address
801
609, 601
69
Page 70

WAN
Extension 601
Scenario 15: SIP VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number with PBX) PLAR connection
Call Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
SIP Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) with PBX: Remote Call PSTN number
Method 1: Two-Stages-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3, Des | GW2 IP address
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
Digit: Digit Length min~ max
Trunk-Line
02-12345678
Extension 609
Gateway#1
901
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3, Des | GW1 IP address
Gateway#2
801
801
609, 0, 12345678
70
Page 71

WAN
Digit:
Digit Length min~ max
Extension 601
Trunk
-
Line
Scenario 16: SIP VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number with PBX) PLAR connection
Call Method: One-Shot-Dialing
SIP Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) with PBX: Remote Call PSTN number
Method 2: One-Shot-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3, Des | GW2 IP address
Incoming Dial Plan
x: wild card
Gateway#1
Des: Destination IP
Extension 609
02-12345678
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
No: 6x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
Gateway#2
901
801
801
02-12345678
71
Page 72

801
02-12345678
WAN
Scenario 17: SIP VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number) PLAR connection
Call Method: One-Shot-Dialing
SIP Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) : Remote Call PSTN number
Method: One-Shot-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3, Des | GW2 IP address
Incoming Dial Plan
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
FXO
02-12345678
Gateway#1
901
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
No: 6x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
Gateway#2
801
72
Page 73

WAN
04-12341234
Scenario 18: SIP VoIP Call: Peer-To-Peer Mode
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (PSTN Call PSTN number) PLAR connection
Call Method: One-Shot-Dialing
SIP Call (Peer-To-Peer Mode) : PSTN Call PSTN number
Method: One-Shot-Dialing
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 8x | Digit: 3~3, Des | GW2 IP address
No: 04x| Digit: 3~10 | Des: GW2 IP address
Incoming Dial Plan
x: wild card
Des: Destination IP
02-87654321
FXO
02-12345678
56785678, 02-12345678
Outgoing Dial plan
No: 9x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
No: 6x | Digit: 3~3 | Des: GW1 IP address
No: 02x| Digit: 3~10 | Des: GW 1 IP
Gateway#1
901
04-12341234
Gateway#2
04-56785678
FXO
801
73
Page 74

Gateway#1
Gateway#2
901
801
SIP Proxy Server
Scenario 19: SIP VoIP Call: Register to SIP Proxy Server
Gateway 1 to Gateway 2 PLAR connection
SIP Call (Register to SIP Proxy Server Mode)
Register Number List
GW1: 801
GW2: 901
WAN
801
901
74
Page 75

Gate
way#1
Gateway#2
801
Extension 609
Extension 601
901
SIP Proxy Server
Scenario 20: SIP VoIP Call: Register to SIP Proxy Server
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Call PBX extension number) PLAR connection
Call Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
SIP Call (SIP Proxy Server Mode) with PBX: Call PBX Extension
Method 1: Two-Stage-Dialing
Register Number List
GW1: 801
GW2: 901,609
WAN
801
609, 601
75
Page 76

Extension 601
02-12345678
Scenario 21: SIP VoIP Call: Register to SIP Proxy Server
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number with PBX) PLAR connection
Call Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
SIP Call (SIP Proxy Server Mode) with PBX: Remote Call PSTN number
Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
Register Number List
GW1: 801
GW2: 901,609
SIP Proxy Server
Extension 609
Trunk-Line
Gateway#1
901
WAN
Gateway#2
801
801
609, 0, 12345678
76
Page 77

WAN
Scenario 22: SIP VoIP Call: Register to SIP Proxy Server
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (Remote Call PSTN number) PLAR connection
Call Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
SIP Call (SIP Proxy Server Mode) : Remote Call PSTN number
Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
Register Number List
GW1: 801
GW2: 901,904
SIP Proxy Server
Gateway#2
801
904
FXO
Gateway#1
901
801
904, 12345678
77
Page 78

901
02-12345678
04-43221344
04-56785678
804
Scenario 23: SIP VoIP Call: Register to SIP Proxy Server
Gateway 2 to Gateway 1 (PSTN Call PSTN number) PLAR connection
Call Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
SIP Call (SIP Proxy Server Mode) : PSTN Call PSTN number
Method: Two-Stages-Dialing
Register Number List
GW1: 801,804
GW2: 901,904
SIP Proxy Server
Gateway#1 Gateway#2
904
FXO
02-87654321
WAN
FXO
801
87654321, 804,
56785678,904, 12345678
78
Page 79

Appendix C
VIP-480 series Specifications
Product 4-Port H.323/SIP VoIP Gateway
Model VIP-480 VIP-480FS VIP-480FO
Hardware
WAN 1 x 10/100Mbps RJ-45 port
LAN 4 x 10/100Mbps RJ-45 port
Voice 4 x RJ-11 connection
( 2 x FXS, 2 x FXO)
Protocols and Standard
Standard H.323 v2/v3/v4 and SIP (RFC 3261) , SDP (RFC 2327), Symmetric RTP,
STUN (RFC3489), ENUM (RFC 2916), RTP Payload for DTMF Digits
(RFC2833), Outbound Proxy Support.
Voice codec G.711(A-law /u-law), G.729 AB, G.723 (6.3 Kbps / 5.3Kbps)
Fax support T.30, T.38
Voice Standard Voice activity detection (VAD)
Comfort noise generation (CNG)
G.165/G.168 Echo cancellation
Dynamic Jitter Buffer
Protocols SIP 2.0 (RFC-3261), H.323, TCP/IP, UDP/RTP/RTCP, HTTP, ICMP, ARP,
NAT, DHCP, PPPoE, DNS
Advanced Function Virtual Server, Smart QoS, IP TOS (IP Precedence) / DiffServ, Build-in NAT
router function.
Network and Configuration
Access Mode Static IP, PPPoE, DHCP
Management Web, Telnet
LED Indications System: PWR
WAN: 1, LAN/ACT
LAN: 4, LNK/ACT
Voice 4, In-Use/Ringing
Dimension (W x D x H) 260 x 135 x 35 mm
Operating Environment 0~40 degree C, 0~95% humidity
Power Requirement 12V DC
EMC/EMI CE, FCC Class B
4 x RJ-11 connection
( 4 x FXS)
4 x RJ-11 connection
( 4 x FXO)
79
Page 80

VIP-880 series Specifications
Product 8-Port H.323/SIP VoIP Gateway
Model VIP-880 VIP-882 VIP-880FO
Hardware
WAN 1 x 10/100Mbps RJ-45 port
LAN 1 x 10/100Mbps RJ-45 port
Voice 8 x RJ-11 connection
( 4 x FXS, 4 x FXO)
Protocols and Standard
Standard
Voice codec G.711(A-law /-law), G.729 AB, G.723 (6.3 Kbps / 5.3Kbps)
Fax support T.30, T.38
Voice Standard Voice activity detection (VAD)
Protocols SIP 2.0 (RFC-3261), H.323, TCP/IP, UDP/RTP/RTCP, HTTP, ICMP, ARP, NAT,
Advanced Function Virtual Server, Smart QoS, IP TOS (IP Precedence) / DiffServ, Build-in NAT router
Network and Configuration
Access Mode Static IP, PPPoE, DHCP
Management Web, RS-232 Console, Telnet
LED Indications System: 2, PWR, CPU
Dimension (W x D x H) 300 x 160 x 40 mm
Operating Environment 0~40 degree C, 0~95% humidity
Power Requirement 12V DC
EMC/EMI CE, FCC Class B
H.323 v2/v3/v4 and SIP (RFC 3261) , SDP (RFC 2327), Symmetric RTP,
STUN (RFC3489), ENUM (RFC 2916), RTP Payload for DTMF Digits (RFC2833),
Outbound Proxy Support.
Comfort noise generation (CNG)
G.165/G.168 Echo cancellation
Dynamic Jitter Buffer
DHCP, PPPoE, DNS
function.
WAN: 1, LAN/ACT
LAN: 1, LNK/ACT
Voice 8, In-Use/Ringing
8 x RJ-11 connection
( 6 x FXS, 2 x FXO)
8 x RJ-11 connection
( 8 x FXO)
80
 Loading...
Loading...