Page 1

Internet Telephony Gateway
VIP-050 / VIP-450
User’s Manual
Rev 2.0
Page 2

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
ii
FCC Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communication. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at the user’s own
expense.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments
and applications, and makes no warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with
respect to the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User’s Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability for any inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on the part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies
that may be contained in this User’s Manual. PLANET makes no commitment to update or
keep current the information in this User’s Manual, and reserves the right to make improvements to this User’s Manual and/or to the products described in this User’s Manual, at any time
without notice. If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete,
we would appreciate your comments and suggestions.
CE Declaration of conformity
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility, EN
55022 class A for ITE and EN 50082-1. This meets the essential protection requirements of the
European Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the Member
States relating to electromagnetic compatibility.
Trademarks
All brand, company and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Revision
PLAENT VIP-050 / VIP-450 User’s Manual
Revision: 2.0
Nov. 2004
Part No. EM-VIPSV2
Preface
Page 3

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
iii
How to Use This Manual
This manual was designed for the technical and non-technical users of PLANET Internet telephony
gateway VIP-050 / VIP-450. It contains information about the functions of VIP and instructions for
its installation, basic configuration and operation in related chapters, and introduces more advanced
command line interface, firmware upgrade and appendix information. Read this section carefully for
important information about the manual’s organization.
Chapter 1: Overview
This chapter provides conceptual overview and description of VIP, explanation of how VIP interacts
with each for enabling VoIP services, and an overview of the required tasks
Chapter 2: Installing VIP
This chapter describes required steps to properly and safely install and configure VIP on your network
Chapter 3: VIP Concepts
This chapter gives information about VIP technology and describes basic concepts using VIP for
providing telephony services over IP network
Chapter 4: Configuring VIP from Web Browser
This chapter explains procedures for configuring VIP from a web browser
Chapter 5: Making a Call with VIP
This chapter explains how to make Internet calls from telephony devices connected to VIP directly
or indirectly.
Chapter 6: Command Line Interface
This chapter describes how to access the command line interface. It also contains information about
the commands used to configure VIP.
Chapter 7: Upgrading VIP
This chapter explains how to download new revision software and upgrade VIP.
Appendix A: Technical Specifications
This appendix lists VIP specifications and the assignment of pins of all the interface ports.
Appendix B: CLI Commands
This appendix provides a short description of each CLI command with a reference to the pages that
contain detailed information on the command.
Appendix C: Factory Default Settings
This appendix lists factory settings of VIP.
Preface
Page 4
SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
iv
Important Safety Instructions
Before plugging VIP into an electrical outlet, carefully read all the installation instructions in Chapter
2.
For your own safety and the safety of your equipment, always take the following precautions:
Follow instructions and warnings in the documentation.
·
Never push any object through the fan vent or other openings in the equipment. Such
·
action may produce a short circuit, causing fire, electric shock, or equipment damage.
Keep VIP away from all chemicals and sources of liquids.
·
Warning
Connection of the RJ45 connector from a VIP to TNV circuits can cause permanent damage to
·
VIP.
Incorrectly connecting telephony devices to the RJ11 port on the Telephony Interface
·
Module can cause permanent damage to the module.
Documentation Abbreviations
Throughout this guide, the user will come across a number of abbreviations that are common
throughout the industry. The user should be familiar with the following abbreviations:
ATPM
CLI
DSP
DTMF
E&M
FXO
FXS
SIP
ICMP
IMTC
IP
ITG
KTS
Address Translation and Parsing Manager
Command Line Interface
Digital Signal Processor
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency
Ear & Mouth
Foreign Exchange Office
Foreign Exchange Subscriber
ITU specification for multimedia transmission over IP networks
Internet Control Message Protocol
International Multimedia Telecommunications Consortium
Internet Protocol
Internet Telephony Gateway
Key Telephone System
LAN
NVS
Preface
Local Area Network
Non-Volatile Storage
Page 5

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
LED
PBX
PSTN
RTP
SIP
TCID
TFTP
TIM
TNV
UDP
UTP
VAD
WAN
Light Emitting Diode
Private Branch Exchange
Public Switched Telephone Network
Real-Time Transport
Session Initialization Protocol
Telephony Channel Identifier
Trivial File Transfer Protocol
Telephony Interface Modules
Telephone Network Voltage
User Datagram Protocol
Unshielded Twisted Pair
Voice Activity Detection
Wide Area Network
Notation Conventions
Throughout this guide, different type styles and characters are used. These serve a variety of purposes as described below:
Convention Description
boldface
courier Messages that VIP CLI displays are in plain courier font.
{ x | y | z } Alternative but required elements are grouped in braces ({ }) and sepa-
[ x | y | z ] Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets ([ ]) and separated
string A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the
Commands and keywords are in
italic Arguments for which you supply values are in italics.
[ ] Elements in square brackets are optional.
rated by vertical bars ( | ).
by vertical bars ( | ).
string or the string will include the quotation marks.
boldface.
Preface
v
Page 6

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
vi
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Overview 1
1.1 Features 1
1.2 Networking Protocols 1
1.3 Package Contents 2
1.4 Front Panel
1.5 Rear Panel 3
2
Chapter 2 Installing VIP 5
2.1 Network Requirements 5
2.2 Installing VIP 5
2.3 Connecting to the telephony devices 5
2.4 Connecting to the Network 5
2.5 Providing Power to VIP 6
2.6 Assigning IP address to VIP 6
Chapter 3 VIP Concepts 7
3.1 How VIP Operates 7
3.2 ATPM 7
3.3 Destination 7
3.4 Hunt Group 8
3.5 Dial Plan 8
3.6 DTMF Relay 9
3.7 Voice Codecs 9
Chapter 4 Configuring VIP from a Web Browser 11
4.1 Http setting mode 11
4.1.1 Dial Plan/ Dial Settings 13
4.1.2 Clear DialPlan 19
4.1.3 Restore DialPlan 20
4.1.4 Save to NVRAM 20
4.2 View System Configurations 21
4.2.1 Firmware Version Information 21
4.2.2 SIP Parameters 21
4.2.3 Voice Coder Type 22
4.2.4 Voice Coder Information 22
Preface
Page 7

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
4.2.5 Channel Parameters 23
4.2.6 Network Connection 24
4.3 Configure System Settings 28
4.3.1 IP Settings 30
4.3.2 SIP Parameters 30
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting Tips 34
Chapter 6 Command Line Interface 35
6.1 Connection through Serial Port 35
6.2 Connection through Telnet 35
6.3 Command Help 36
6.4 Designating IP Address 36
6.5 Designating Port Number 36
6.6 Command Reference 37
6.7 Utility Commands 38
6.8 Network Commands 39
6.9 Configuration Management Commands 44
6.10 Voice Coding Profile Configuration Commands 48
6.10.1 Common Coding Profile Configuration Commands 48
6.10.2 Voice Coding Profile Configuration Commands 49
6.11 Dial Plan Management Commands 52
6.12 Tel Commands 57
Chapter 7 Upgrading and resetting VIP 59
7.1 Firmware upgrade 59
7.2 CLI Commands in Download Mode 64
7.3 Restore default configuration 65
Appendix A Technical Specifications 69
A.1 VIP Technical Specifications 69
A.2 Console Port 70
A.3 LAN Port 70
A.4 FXO Port Pin Assignments 71
A.5 FXS Port Pin Assignments 71
Appendix B CLI Commands 73
B.1 Normal Mode Commands 73
Preface
vii
Page 8

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
viii
B.2 Download Mode Commands 74
Appendix C Factory Default Settings 75
Preface
Page 9

VIP User’s Manual
enable IP protocol, VIP must have a static IP address, subnet,
Voice over IP Protocol
Chapter 1 Overview
This chapter illustrates an overview of PLANET Internet Telephony Gateway Family –
VIP-050 / VIP-450 and a detailed product description of features and capabilities.
1.1 Features
Via growth of Internet technology, Internet telephony service plays and turns into a cost-effective
and highly reliable substitution system of the old-time traditional PBX system. PLANET VoIP (Voice
over IP) system – VIP-050 / VIP-450 offer toll quality voice and real-time fax data over IP networks.
With optimized SIP architecture, PLANET VIP series are ideal solution for various VoIP applications
such as Headquarter and Branch Office communication, and IDD cost-effective solution. With its
intuitive user-friendly interface, PLANET VIP series may be installed easily conveniently, and
dramatically down cost the huge amount of IDD fee.
With embedded, efficient Real-Time Operating System, VIP series provides efficiency and feature
enhancement capabilities; being programmed with updated firmware users may have the most
flexibility and functionality to meet different kind of application requirement. It comes equipped with
remote management capabilities, configurable signaling to work with PBX, KTS, and/or telephone.
Building on state-of-the-art advanced VoIP related technology. PLANET VVIP series offers various
features: echo cancellation, Voice Activity Detection (VAD) , Comfort Noise Generation (CNG) , lost
packet recovery algorithms and optimized voice and FAX coders to bring users superior voice quality, and best compatibility with major Internet telephony service providers.
1.2 Networking Protocols
VIP supports several industry-standard networking protocols required for voice communication. The
following table describes these protocols.
Networking Protocol Description
Internet Protocol (IP) IP is a messaging protocol that addresses and sends packets across the
network. To
and gateway assigned to it.
VoIP enables VIP to transfer voice communications over an IP network.
(VoIP)
Trivial File Transfer
Protocol (TFTP)
Real-Time Transport
(RTP)
VIP employs ITU-T SIP protocol for setting up call with one another.
TFTP allows you to transfer files over the network. VIP implements a
TFTP client allowing you to download new revision firmware from a TFTP
server. The TFTP client requires a TFTP server in your network.
RTP is a standard for transporting real-time data over IP network. VIP
uses RTP protocol to send digitized and compressed voice packets.
Overview 1
Page 10

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
2
1.3 Package Contents
The contents of your product should contain the following items:
VIP-050
2-slot Internet Telephony Gateway
l
Power cord
l
9-pin straight through RS-232 cable
l
Quick Installation Guide
l
l User’s Manual CD
l Rack mount Accessories
VIP-450
4-port Internet Telephony Gateway
l
Power cord
l
9-pin straight through RS-232 cable
l
Quick Installation Guide
l
User’s Manual CD
l
1.4 Front Panel
The front panel of VIP contains a RJ-45 Ethernet port, one DB9 RS-232 interface port, a push button and 16 LED indicators. The following figure illustrates the front panel of VIP.
Figure 1-1 VIP-050 Front Panel
Figure 1-2 VIP-450 Front Panel
LED Indicators
The LED indicators on the front panel display the current status of VIP as described in the following
table:
Indicator Color Activity Indication
Overview
Page 11

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
3
PWR Green On Power is supplied to the gateway.
SYSTEM Green Blinking The system is running. (Heartbeat LED)
LAN
ACT
Ÿ
100M
Ÿ
LNK
Ÿ
COL
Ÿ
Slot A/B
Channels
1-4
Green
Green
Green
Green
Green Off
On
On
Off
On
On
On
Blinking
Data is presented on LAN.
The gateway is connected to LAN at 100Mb/s.
The gateway is connected to LAN at 10Mb/s.
The gateway is connected to LAN.
Data collision is occurring on the network connection.
The line is idle.
The line is being used.
The line is ringing.
Ports
VIP is equipped with an Ethernet interface with 10/100 Mbps auto-negotiation capability. The
Ethernet interface port is located on the front panel. In addition to the Ethernet interface port, there
is a 9-pin RS-232 interface port on the front panel. Their functions are described below:
Port Label Function
RJ45 LAN Connecting VIP to a 10/100 Mbps Ethernet network
9-pin RS-232
User Console Connecting VIP to a VT-100 terminal or terminal emulator for con-
figuring VIP
Reset Button
There is a push button located behind a small hole next to the SYSTEM LED. This button allows
you to reset VIP or force VIP to enter firmware upgrade mode.
Reset
Push a small, stiff object into the hole until the SYSTEM LED stops blinking, then release the button.
Force firmware download mode:
Powering on the gateway while pressing down the button for 5 seconds forces VIP to enter
download mode
1.5 Rear Panel
The rear panel of VIP-050 has two slots allowing the installation of up to two Telephony-InterfaceModule (TIM) . Each module is equipped with 4 telephony interface ports. Depending on the type of
the telephony interface module, the telephony interface ports may be connected to telephony devices, such as PBX, KTS, and telephone sets of central office. VIP-450 equips with two FXO and
two FXS ports. In addition to the TIM slots (ports), there is an AC power receptacle and a power
switch (power adapter: VIP-450) on the rear panel.
Overview
Page 12

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
4
1 2 2 1
50~60H
Slot A Slot B
90~240VA
SLOT A
ELITE-FXO
SLOT B
ELITE-FXS
4 3
VIP-050 Rear Panel
VIP-450 Rear Panel
Note: For VIP-050, three modules available, VIP-FXS, VIP-FXO and VIP-E&M. Modules are not
included, please consult your local dealer for the information of the modules.
Overview
Page 13

VIP User’s Guide
Chapter 2 Installing VIP
This chapter gives information on how to install VIP.
2.1 Network Requirements
For VIP successfully operate in your network, your network must meet the following requirements:
1. A working 10/100 Base-T Ethernet. VIP connects to Internet via an Ethernet LAN.
2. IP network that supports gateway, and subnet mask. You’ll need one static IP address to assign VIP.
2.2 Installing VIP
VIP can be used in a desktop configuration. Ensure that VIP is placed in a clean, well-ventilated,
and vibration-free environment.
When VIP is placed on a desktop, be certain that the unit is placed on a sturdy, flat surface, near a
grounded power outlet. At least three inches of clearance must be provided on both sides of VIP
for well ventilation.
2.3 Connecting to the telephony devices
VIP-050 supports three types of TIM. One is FXO, FXS and the other is E&M. Each module has
four ports for connecting to telephony devices. VIP-450 equips two FXO and two FXS interfaces to
have the great flexibility of PBX connection (FXO), and telephone or FAX machine connection
(FXS).
VIP-FXO module is designed for connecting to PBXs (extension line) or central office switches (CO
line).
VIP-FXS module is designed for connecting to analog telephone sets or G3 fax machines.
Connecting the telephony devices to the appropriate RJ11 ports on the TIM.
Warning:
damage to the TIM and/or VIP.
connection of incorrect telephony devices to the ports on the TIM can cause permanent
2.4 Connecting to the Network
The RJ45 network port on the front panel supports 10/100 Mbps half-duplex connection to Ethernet
Network. You can use either category 3 or 5 straight-through UTP cable for 10 Mbps connections,
but use Category 5 for 100 Mbps connections. To connect to Ethernet, insert one end of the
Ethernet cable to the RJ45 port on the front panel of VIP and other end of the cable to an Ethernet
switching hub or repeater hub.
Installing VIP
5
Page 14

VIP User’s Manual
2.5 Providing Power to VIP
To provide AC power to VIP complete the following steps:
1. Turn the power switch on the rear panel of VIP to the off position.
2. Connect one end of the power cord that came with VIP to the power receptacle on the rear
panel.
3. Connect the other end of the power cord to an AC power outlet.
4. Turn the power switch on. VIP will perform power on self-test. After completing the self-test,
the SYSTEM LED blinks continuously and the TIM indicators on the front panel will turn on.
2.6 Assigning IP address to VIP
The IP address is the unique logical address identifying each IP node, such as VIP, on an IP network. An IP address is a 32-bit number expressed as four decimal numbers from 0 to 255 separated by periods. VIP needs a static IP address and be aware of the subnet mask and default
gateway (typically a router) of your network to be able to send to and receive data from the IP network. Consult your network manager to obtain a unique and static IP address for VIP, the IP subnet
mask and default gateway of your network, and fill out the work sheet in Appendix D before configuring the gateway. Procedures for assigning IP address, default gateway and subnet mask is available in Chapter 4.
Installing VIP
6
Page 15

VIP User’s Manual
Chapter 3 VIP Concepts
VIP enables the transmission of voice and fax traffic over any IP network by digitizing voice and fax
signals, encapsulating the information within IP packets, and then sending the packets across the
IP network
3.1 How VIP Operates
1. The TIM inside VIP digitizes analog voice signals at 8 Kbps.
2. VIP system software handles the:
Capture of telephone number presented as DTMF tones.
Ÿ
Mapping the telephone number to the IP address of remote VIP.
Ÿ
Setting up calls with remote VIPs utilizing SIP call control protocol.
Ÿ
Digitizing, compressing and encapsulating the voice into IP packets and transmission of the
Ÿ
IP packets onto the Ethernet LAN.
3. A router attached to the LAN forwards the IP packets across the WAN, where they will be received by another VIP at the remote.
4. The process is reversed at the remote VIP.
3.2 ATPM
To allow you to easily dial a telephone or fax on the network, VIP maps a series of dialed digits to
the IP address of the remote VIP whose phone or fax you are calling. This mapping information is
contained in a database inside each VIP called the dial plan.
Based on the dial plan the Address Translation and Parsing Manager (ATPM) inside VIP translates
telephony numbers to IP addresses of remote VIPs. The ATPM collects telephone number dialed
by users, decides whether the dial string is part of the dial plan and, if it is, maps it a remote VIP.
When the call is set up to the destination, a substring of the original dial string will be sent along to
the remote VIP.
3.3 Destination
The destination is where a call is terminated. Typically, for inbound calls from IP network, VIP terminals the call at one of the telephony ports. The destination for the call is the telephony port where
the call terminated. For calls initiated from telephony ports, VIP forward the call to a remote VIP via
IP network, and the remote VIP terminal the call. The destination of the call is the remote VIP.
VIP Concepts 7
Page 16
VIP User’s Manual
8
3.4 Hunt Group
Instead of directly mapping a phone number to a destination, the ATPM first maps the phone number to a group of destinations known as a Hunt Group. A hunt group is a group of destinations that
are equivalent. For example, the customer support group of a company might have 20 peo-
ple who can handle support calls. Access to customer support is through a single phone
number but the next available support person is actually connected upon each incoming
call. These 20 phones would be configured as a hunt group. A hunt group consists of a
phone number and a list of destinations (members of the group). When an incoming phone
number matches the phone number of the hunt group, VIP attempts to terminate the call at each of
the destinations in the hunt group, one at a time until a call is successfully completed.
Every destination that can be reached by dialing a phone number is a member of at least one hunt
group. When an address is presented to ATPM for lookup, the output is a hunt group ID number.
As a second step, the hunt group ID is presented to ATPM to get the list of members. To effectively
bypass the hunt group feature, simply make a unique hunt group for each destination and one
member in each hunt group.
3.5 Dial Plan
The dial plan is a database inside VIP for the ATPM to map telephony numbers users dialed to the
IP address of remote VIPs. The dial plan consists of the destination table, hunt group table and the
address table. Users need to setup these tables, so that VIP knows how to setup calls with remote
VIPs.
Address Table
The address table maps a phone number to a hunt group. The table contains entries that specify
the following information:
Telephone number
·
The hunt group the phone number maps to.
·
The minimum number of digits to collect before the ATPM starting address lookup.
·
The maximum number of digits the ATPM collects before it considers the dial string is
·
complete.
Number of digits forward to the destination.
·
Address table sample:
Address Entry Hunt Grp_Id Min. Digits Max. Digits Prefix strip Prefix Address
200 1 3 3 0 None
201 3 3 3 0 None
899 11 3 3 0 None
8 11 3 3 0 None
0 5 1 1 0 None
03 5 10 10 2 “0”
VIP Concepts
Page 17

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
9
Hunt Group Table
The hunt group table maps a hunt group to a list of destinations.
Hunt group sample
Group id Type #Members Member ids
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 2 1 1
3 2 1 2
5 2 1 4
11 2 1 11
Destination Table
The destination table maps a destination to a telephony port or the IP address of a remote VIP.
Destination table sample
Dest id Mode Destination
------------------------------------------------------ 1 Local PORT = 0
3 Local PORT = 2
5 Local PORT = 4
11 SIP Dest = 192.168.0.55/ 5060
12 DNS Dest = planetvip.dyndns.org /5060
3.6 DTMF Relay
Voice from PSTN is compressed by VIP before sending across the IP network and then decompressed by the destination VIP. The voice coders supported by VIP are designed for ideally compressing and decompressing human voice. If the compression / decompression process is performed on DTMF tone which needs to be conveyed across IP network, distortion might be too significant to be not cognizable in the receiving end. To overcome the shortcoming that the voice coders cannot perfectly encode DTMF tone, VIP encodes DTMF tone into special packets. The packets are then sent to the destination VIP via a separate IP connection. The destination VIP decodes
the packets, generates the DTMF tone, and then sends the tone to the PSTN. The way VIP handles DTMF tone is so called DTMF relay.
VIP handles DTMF relay per SIP specifications. Certain third party VoIP devices may handle DTMF
relay per IMTC standard. For VIP to interoperate with those VoIP devices, users need to specify
which remote VoIP devices uses IMTC conforming DTMF relay technique. Refer to CLI command
for detailed information on how to select DTMF relay mode.
3.7 Voice Codecs
Voice codecs supported by VIP include G.711, G.723.1 5.3kbps, G.723.1 6.3kbps and G.729 AB.
When setting up a call, two VIP automatically negotiate with each other until an agreed upon codec
is determined.
VIP Concepts
Page 18

Page 19
VIP User’s Manual
Chapter 4 Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
This chapter explains procedures for configuring VIP from the web browser.
4.1 Http setting mode
This section describes the processes for setting up Internet Telephony Gateway once it has been installed. Microsoft Explorer version 4 or higher, or Navigator version 4.5 or higher can be used in this
section to view and change parameters.
PC Setup
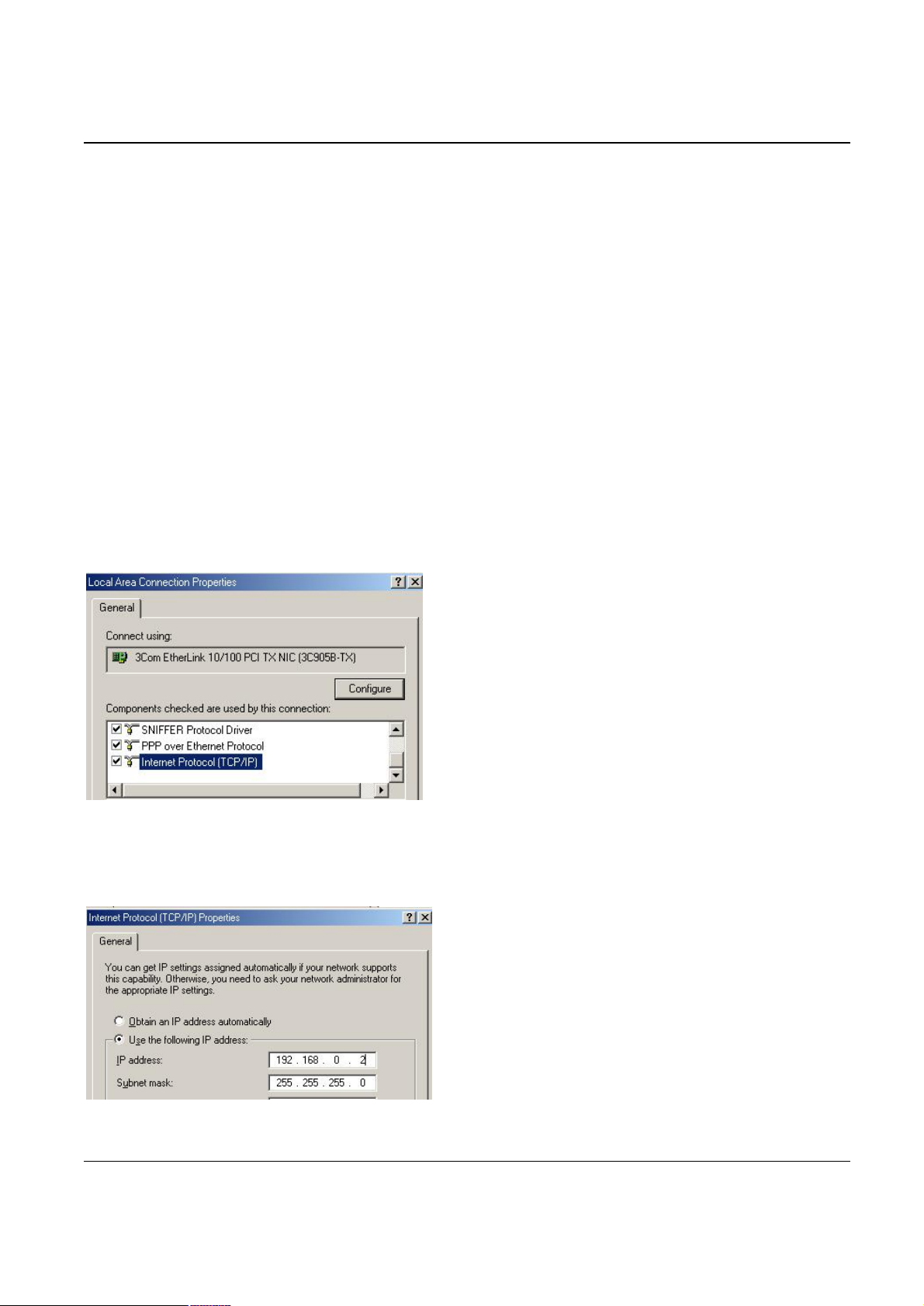
In order to configure VIP, PC needs to have TCP/IP protocol and a compatible IP Address.
1. Connect VIP to network with a RJ-45 UTP cable. Power it on.
2. Find a PC, for example, Windows 2000. Under Windows 2000, select the Network Neighborhood
icon on the desktop, then select Properties. We will see a screen like below:
3. If a line like the one highlighted ("TCP/IP -> Network Card”) is not listed , select Add-Protocol-
Microsoft-TCP/IP-OK to add it.
4. Select Properties for the “TCP / IP -> Network card” entry. You will see a screen like the following:
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
11
Page 20
VIP User’s Manual
12
5. On the IP Address table, enter values as follows:
Specify an IP address set ON.
·
IP Address: 192.168.0.2
·
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
·
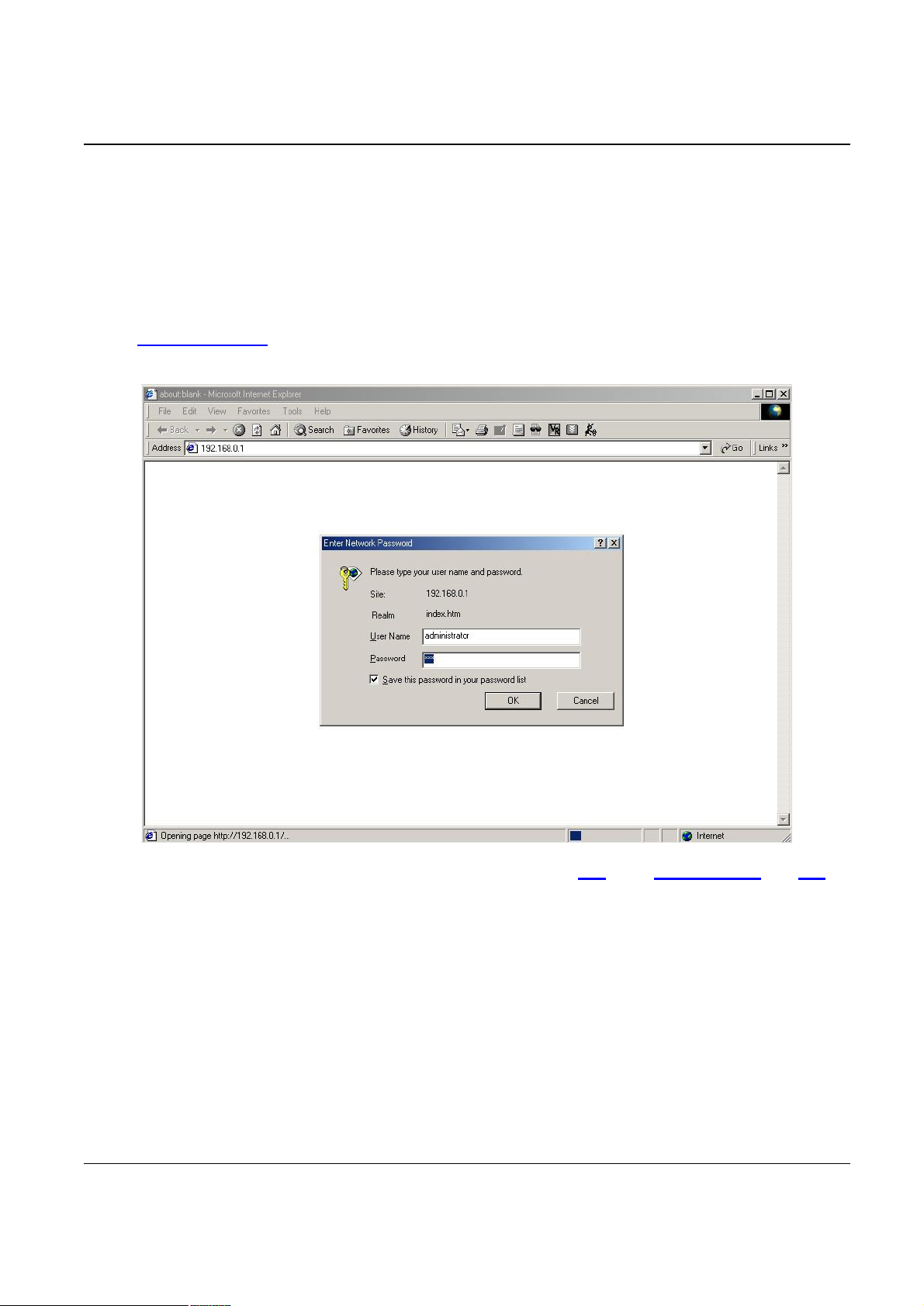
Restart your PC and Start your WEB browser.
6. In the Address box, enter the following:
http://192.168.0.1 (default IP address of the Voice Gateway)
7. Press enter to confirm and you should find the screen below.
8. The User Name is administrator (all lower case). Password is 123. Both administrator and 123
are default strings from factory). For security reasons, please change and memorize the new password after this first setup.
9. Click “OK”. The main screen will appear as below.
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 21

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
13
which allows one to
4.1.1 Dial Plan/ Dial Settings
Main Menu Function Briefings
1.Dial Plan Settings, which helps you configure the dial plan. You should complete the dial plan work
sheets before working on this menu.
2.View System Configurations, which includes the specific information related to version, network,
SIP, coder, and the channel of the gateway you are using.
3.Configure System Settings, which allows you to modify the system parameters as you wish.
Select Main Menu\Dial Plan Settings, we can find the following Dial Plan Menu.
Dial Settings
Common Dial
Parameters
Clear Dial Plan
Restore Dial
Plan
Store to
NVRAM
The Setup screen of the Dial Plan including:
· Telephone Settings
Add, Delete, Find, or List telephone numbers.
· Hunt Group Settings
Add, Delete, Find, or List hunt group settings
· Destination Settings
Add, Delete, Find, or List destination settings
Defines the desired total dial time, first digit wait
time, inter-digit wait time, and the termination digit
Clears all telephone numbers, hunt groups, and
destinations settings, for both old and new ones
Retrieves all dial plan settings from the flash while
temporary settings will be cleared
Stores all settings that you have specified permanently
, which allows one to
,
, which allows one to
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 22

VIP User’s Manual
14
fore the ATPM starting matching the dial string
4.1.1.1 Phone number
Please select Main Menu\Dial Plan\Phone/Hunt Group/Destination Settings, we can find
Phone/Hunt Group/Dest. Setting Menu. We are doing VIP telephone address table manage-
ment.
We can add (delete, find or list) desired telephone number mapping to hunt group at this menu.
Telephone
Number
Hunt
Group ID
Min. Digits
Max. Digits
Strip
Length
Append
Prefix
Telephone number to match. This is only part
of the total dialed string.
For each hunt group ID, you need to assign it
a unique identifier between 0 and 99.
Minimum number of digits to be collected be-
with entries in the address table.
Maximum number of digits to be collected before the ATPM starting matching the dialed
string with entries in the address table.
The number of digits to be stripped at the beginning of the collected dial string before forwarding the string to the destination.
(Optional) Digit to be added before the beginning of the collected dial string before forwarding it to the destination.
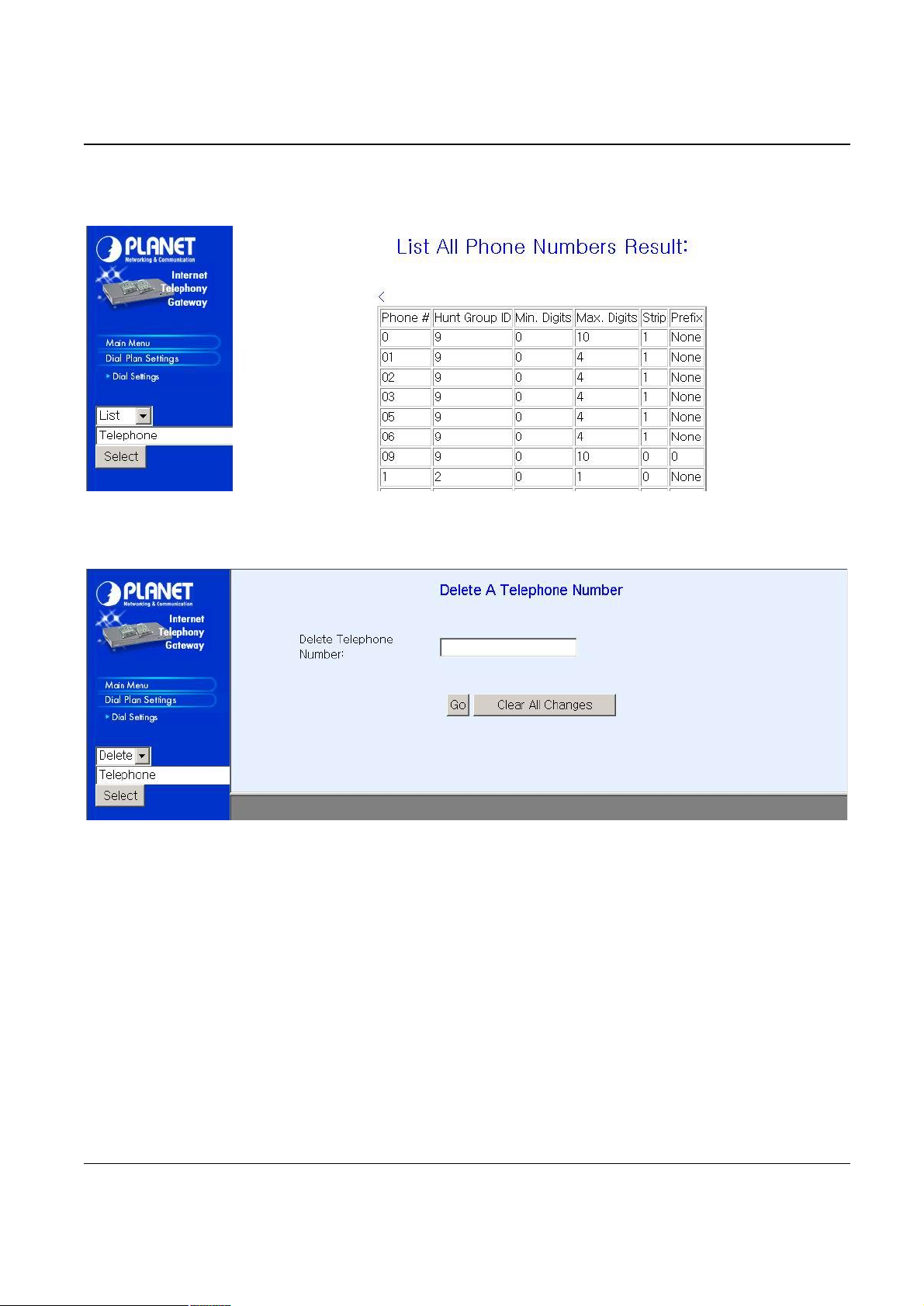
To list the phone numbers, click on “List” and select “Telephone”, the screen will displayed as below:
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 23
SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
15
To delete / find a Telephone, select the option and telephone, you can key in the phone number to find
or delete. The right bottom screen will show the result.
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 24
VIP User’s Manual
16
4.1.1.2 Hunt Group
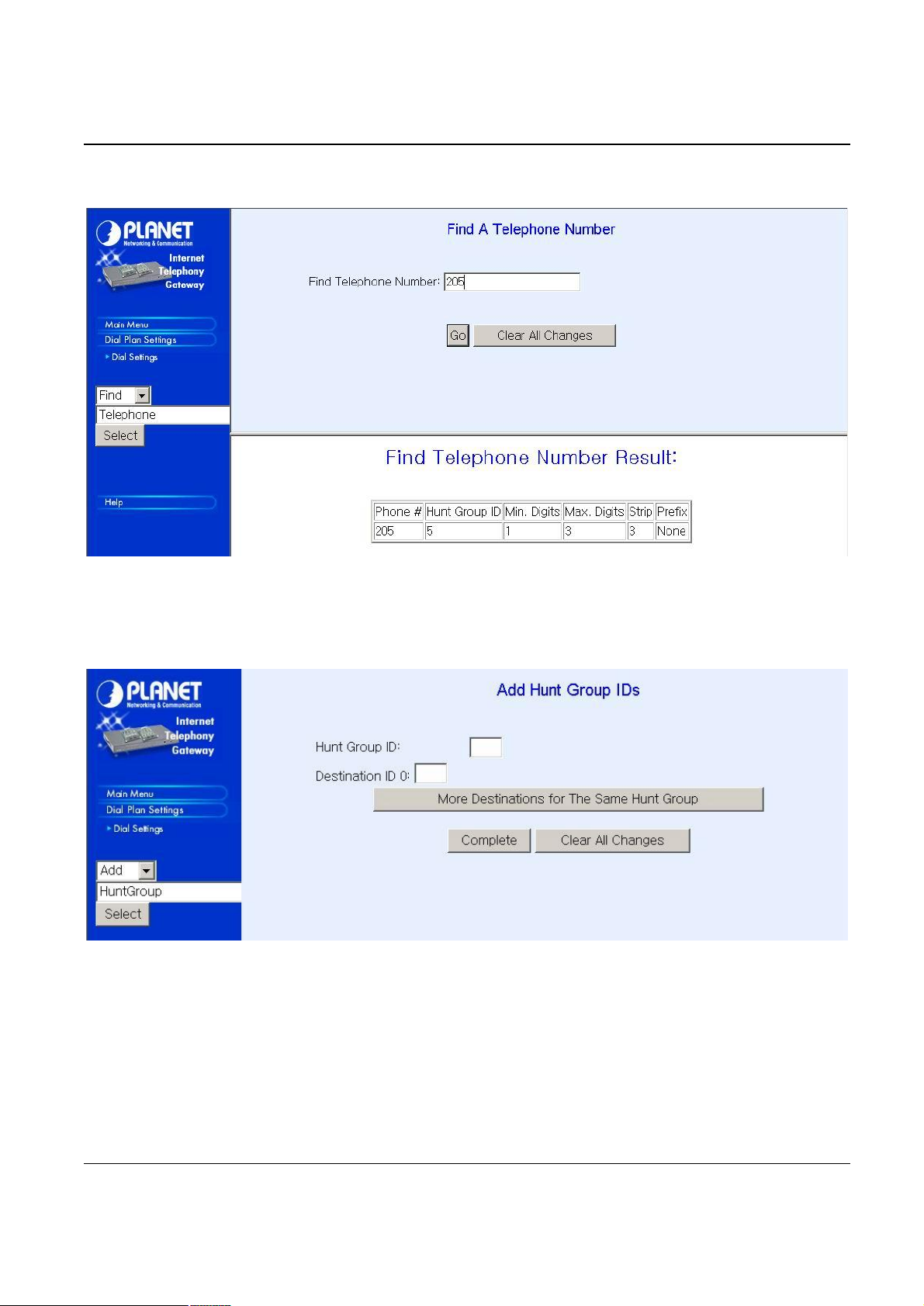
Please select Main Menu\Dial Plan\Phone/Hunt Group/Destination Settings, we can find
Phone/Hunt Group/Dest. Setting Menu. We are doing VIP hunt group table management.
We can add (delete, find or list) desired hunt group ID mapping to destination ID at this menu. If you
want to make the port calls to the secondary receiver, you can click one “More Destinations” you can
then add the second, third receiver if the desired port/phone is busy.
We can add (delete, find or list) desired hunt group ID mapping to destination ID at this menu.
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 25
SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
17
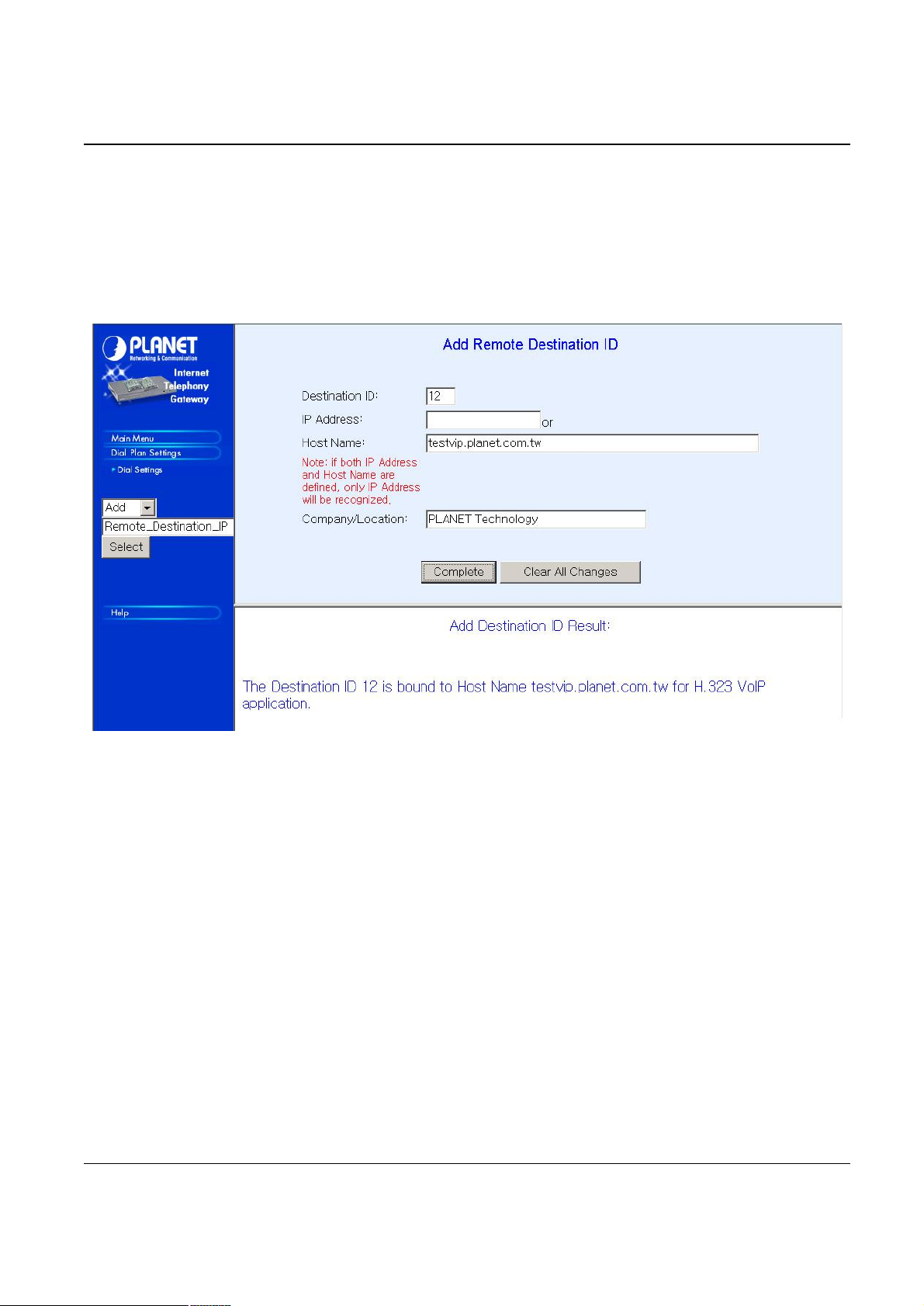
4.1.1.3 Destination IP/ Destination Channel
Please select Main Menu\Dial Plan\Phone/Hunt Group/Destination Settings, we can find
Phone/Hunt Group/Dest. Setting Menu.
Remote Destination IP, one is Remote Host Name and the other is Local Destination Channel.
We are doing VIP destination table management. One is
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 26

VIP User’s Manual
18
We can add (delete, find or list) desired destination ID mapping to Remote Destination IP, Domain
Name or Local Destination Channel at this menu.
Please back to Dial Plan Menu.
4.1.1.4 Common Parameter
Please select Main Menu\Dial Plan\Common Parameter Settings
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 27

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
19
This Common Parameter Settings is the same as previous ATPM system parameters description. .
4.1.2 Clear DialPlan
Please select Main Menu\Dial Plan\Clear All Dial Plan Settings
Clear All Dial Plan Settings will clear all the settings you made before
only temporary if you do not store to the Flash Memory afterwards.
That is, to restore all the settings from the Flash Memory, you need only to click on the 'Restore All En-
tries' on the left frame, or to reboot the system (the settings can be restored ONLY IF YOU DID NOT
STORE the entries).
. However, the 'Clear All' is
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 28

VIP User’s Manual
20
4.1.3 Restore DialPlan
Please select Main Menu\Dial Plan\Restore All Dial Plan Settings
Retrieve all dial plan settings from the flash memory. All temporary settings will be cleared.
4.1.4 Save to NVRAM
Please select Main Menu\Dial Plan\ Save to NVRAM
Ready to store Dial Plan settings to Flash Memory
Please Back To Main Menu
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 29

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
21
4.2 View System Configurations
Please select Main Menu\View System Config.
View System Config. Function Briefings.
1.Firmware Version Information, which shows the versions of each firmware component
2.Network Settings, which shows the IP-related settings, and the status of associated management
tools
3.SIP Parameter Settings, which shows the SIP-related parameters associated with the gateway
4.Coding Profile Information, which shows the configurations related to a specific coding profile
5.Channel Settings, which shows the configurations associated with a specific channel
6.Network Connection, which shows type of connection enabled in VIP
Six options available
4.2.1 Firmware Version Information
Please select Main Menu\View System Config.\Firmware Version Info.
This will show current VIP firmware version information.
Firmware Information:
Internet Telephony Gateway (PLA) Version: s1.0
Boot Loader Version: 4.13
RTOS Version: 2.5.0/BE
SIP Stack Version: 2.1.1.4
DSP image Version: 8.1.2.1.
TSG Version: R8.0 Gateway (Build 4)
4.2.2 SIP Parameters
Please select Main Menu\View System Config.\SIP Parameter Settings
The SIP Parameters Settings:
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 30

VIP User’s Manual
22
SIP Addr Configuration:
UDP ctl addr = 192.168.0.99/5060
RTP data addr = 192.168.0.99/2070
Domain name server = 168.95.192.1
Info switch is off
nat_call is on
auto_reg is off
outboundproxy : None
4.2.3 Voice Coder Type
Please select Main Menu\View System Config.\Coder Type
The Voice Coder For Each Line Module:
Voice coder is G.723 for Line Module 1.
4.2.4 Voice Coder Information
Please select Main Menu\View System Config.\Coder Information
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 31

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
23
4.2.5 Channel Parameters
Please select Main Menu\View System Config.\Channel Parameters
This command can show the desired channel setting of VIP.
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 32

VIP User’s Manual
24
4.2.6 Network Connection
Please select Main Menu\View System Config\Network Connection
This command can display the type of connection currently enabled in VIP.
4.2.6.1 DHCP Settings
Display current DHCP status in VIP
Command Line Interface reference:
net set dhcp
net set dhcp command configures VIP to be DHCP client in order to obtain TCP/IP related pa-
rameters from ISP while VIP is deployed in DHCP environment.
Syntax Description
on
off
If DHCP client is enabled/disabled, VIP has to be rebooted to make the DHCP service
started/stopped.
Turn on DHCP client
Turn off DHCP client
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 33

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
25
4.2.6.2 PPPoE Settings
Display current PPPoE status in VIP
Command Line Interface reference:
net set pppoe
The net set pppoe command configures PPPoE related parameters while VIP is deployed in
PPPoE environment.
Syntax Description
on
off
username
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Turn on PPPoE client
Turn off PPPoE client
PPPoE connection username provided by ISP
Page 34

VIP User’s Manual
26
password
fix_ip
PPPoE connection password provided by ISP
Fixed IP address provided by ISP
If PPPoE client is enabled/disabled, VIP has to be rebooted to make the PPPoE service
started/stopped.
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 35

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
27
4.2.6.3 DDNS Settings
Display current DDNS status in VIP
Command Line Interface reference:
net set dyndns
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 36

VIP User’s Manual
28
DDNS service can help users to find each other in dynamic/static IP environment, and enable two
VIPs call each other with registered host names. To be fully functional, DNS server MUST be
added into SIP configuration while DDNS service is enabled.
DDNS clients supported in VIP are www.dyndns.org and www.dtdns.com currently.
If VIP DDNS client is enabled, users MUST register a DDNS name from the sites listed above before proceeding any further.
Syntax Description
on
off
If DDNS client is enabled, VIP has to be rebooted to make the DDNS service effective.
sub commands:
set dyndns add [serv_name] [host_name] [user_name] [password]
Adding applied DDNS name into VIP database.
Note: if multiple DDNS names are inserted, only the first one will be updated.
Syntax Description
serv_name
host_name
user_name
password
set dyndns delete [host_name]|all
Turn on DDNS client
Turn off DDNS client
DDNS service server (MUST be “dyndns” or “dtdns” for now)
DDNS name registered from DDNS service provider
Username used to update DDNS account
Password used to update DDNS account
Delete specified or all DDNS name(s) configured in VIP.
DDNS related parameters must be saved via commands: “config activate, config store” in
order to be effective.
4.3 Configure System Settings
Please select Main Menu\Configure System Settings
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 37

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
29
System Config. Settings Function Briefings
1. IP Settings, which allows one to set the gateway's IP address, its subnet mask, and its Default
Gateway IP address.
2. SIP Parameter Settings, which allows one to set the SIP parameters, such as communication
ports, SIP registration settings, outbound proxy server settings …… etc.
3. Channel Parameter Settings, which allows one to set parameters associated with each port, such
as transmission/receive gains, comfort noise level, etc.
4. Voice Coder Type Selection, which allows one to set the desired coder type, such as G.711,
G.723 or G.729A, in a per line module base.
5. Network Connection, which allows user to buildup Internet connection according to different connection type, currently connection types supported in VIP are DHCP, PPPoE connections.
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 38

VIP User’s Manual
30
4.3.1 IP Settings
Please select Main Menu\Configure System Settings\IP Settings
This screen can setup your VIP IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default IP Gateway Address. These
values will be valid after VIP reboot.
4.3.2 SIP Parameters
Please select Main Menu\Configure System Settings\SIP Parameter Settings
There are SIP Configuration Settings, Registration Server Settings, Outbound Proxy Sever configurations, Domain name server configurations, and Other settings..
4.3.2.1 SIP Configuration Settings
Please select Main Menu\Configure System Settings\SIP Parameter Settings\SIP Configuration
Settings
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 39

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
31
4.3.2.2 SIP Registration Server settings
Please select Main Menu\Configure System Settings\SIP Parameter Settings\SIP Registration
Server Settings
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 40

VIP User’s Manual
32
4.3.2.2 SIP Outbound Proxy Server Settings
Please select Main Menu\Configure System Settings\SIP Parameter Settings\SIP Outbound
Proxy Server Settings
4.3.2.3 SIP Domain Name Server Settings
Please select Main Menu\Configure System Settings\SIP Parameter Settings\SIP Domain Name
Server Settings
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 41

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
33
4.3.2.4 Other SIP Settings
Configuring VIP from a Web Browser
Page 42

VIP User’s Manual
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting Tips
This section provides solutions for problems you may possibly encounter while installing and connecting your Internet Telephony Gateway.
Power (PWR) LED is not illuminate
1. Check the power adapter connection.
2. If the power adapter or power cord is connected to the gateway, check that the cord is securely
plugged into the power socket on the rear of the console.
3. Check that the other end of the power adapter or power cord is securely plugged into the power
outlet.
4. If both ends of the power cord are properly connected and there is still no power, the gateway
might have a faulty power outlet, power adapter, or power cord.
5. Change to another power outlet or obtain another power adapter or power cord.
LNK LED is not illuminate
1. Check VIP was connected correctly:
a. Powered on
b. Correctly connected
2. Check if the cable connect to an end device is a standard straight through network Ethernet cable.
3. Make sure connectors at both end are securely seated.
4. Check VIP IP setting is correct
There is no dial tone when pick up the phone
1. Check line module port LED illuminate
2. Check the RJ11 telephone line is connected correctly between phone set and line module port
There is an out-of-service tone when dialing destination phone number
1. Check the dial plan setting (address table, hunt group table and destination table) at the destination
phone number
There is no connected tone when dialing destination phone number
1. Check the IP network (Ethernet cable, Ethernet port and GW IP setting) is connected correctly
2. Check the destination VIP and phone is available
Final Steps
If the procedures in this section have not solved the problem, reset the gateway several times by turning the power on and off. If the problem still exists, contact customer support.
Command Line Interface
34
Page 43

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
35
Chapter 6 Command Line Interface
VIP has a built-in command line interpreter and provides users a Command Line Interface (CLI).
You can configure VIP by entering commands from the CLI.
You can access the CLI from a VT-100 terminal or terminal emulator connected to the RS-232 port
on the front panel or through a Telnet session.
6.1 Connection through Serial Port
The serial port of VIP is fixed at the following settings:
Baud rate
Number of data bit
Parity check
Number of stop bit
Flow control
To access VIP through the RS-232 serial port, follow the steps below:
1. Insert one end of the serial cable that came with VIP into the 9-pin RS-232 port (labeled User
Console) on the front panel.
Insert the other end of the cable into your terminal’s serial port.
2.
Configure the terminal so that settings for baud rate, number of data bit, parity check, number
3.
of stop bit and flow control capability exactly match VIP’s serial interface. (Refer to you terminal
documentation for more information about setting up these features).
4. Press <Return> from the terminal.
5. VIP displays the following prompts on the terminal and you are ready to access the CLI then.
EVIP>
19,200
8
None
1
None
6.2 Connection through Telnet
To use Telnet, you must have previously set the IP address using the net set ip command for VIP.
Refer to the section describing the net set command later in this chapter for information about setting the IP address. Up to two sessions through Telnet are possible. To access VIP from a remote
host with Telnet, perform the following tasks:
Command Line Interface
Page 44

VIP User’s Manual
36
command later in this
Task Prompt Type
From the remote host, enter the telnet command
followed by the IP address of VIP you want to access.
None
telnet ip_addr
When VIP prompts “Login:”, enter the user name
“administrator”
When VIP prompts “Password:”, enter the password. The default password is “123” unless a
password was previously established using the
net set user_pw command (Refer to the section
describing net set user_pw
chapter for details about the setting password).
Upon successfully entered the password, VIP displays greeting message and the following prompts
and you are ready to access the CLI commands.
ITG>
Login:
Password: password
administrator
6.3 Command Help
Help for commands is provided by the CLI. Type help to see a listing of the top-level commands.
On most cases, if you enter a command using the wrong number of arguments or inappropriate arguments, the CLI will give further usage.
6.4 Designating IP Address
Some commands require an IP address, which must be designated in a standard format. The IP
address format is 32 bits, written as four octets separated by periods (dotted decimal format) that
are made up of a network section, an optional subnet section, and a host section, as shown in the
following example:
192.168.0.1
6.5 Designating Port Number
Some commands require a telephony port number. VIP designates the first port telephony interface
as port number 0, the 2nd port as port number 1 and so on.
Command Line Interface
Page 45

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
37
6.6 Command Reference
The following table list the CLI command in alphabetic order.
Command
Description
atpm Dial plan management command
clrscr Clear screen
config Configuration management command
download Download new revision code image from TFTP server
help Display help screen
net Set or display network parameters
ping Ping another Internet host
set Set system configuration
tel Set or display telephony port options
For the ease of understanding and explaining these commands, the commands are categorized
into the following command sets and the following sections explaining each set of the commands.
Command Set
Utility clrscr
Commands Function
General purpose utility commands
download
help
ping
Network net Commands for setting or displaying network
related parameters
Configuration
management
Dial plan
menagement
Telephony tel Commands for setting or displaying telephony
config
show
Commands for configuring VIP or displaying
configuration
set
atpm Commands for setting or displaying dial plan
related options
Command Line Interface
Page 46

VIP User’s Manual
38
Causes ping to send one datagram per second, printing one line of
6.7 Utility Commands
clrscr
The clrscr command to clear the screen
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords
download
Use the download command to enter download mode for reading code image from a TFTP server
and program it to flash memory. Refer to 0 for detailed information on how to upgrade the system
software.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords
Note
This command in available from serial interface. It is not available from Telnet unless the TFTP
loader is version 3.00 or higher.
help
The help command lists the top-level commands.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords
ping
The ping command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets to another node on the network.
ping host_ip_addr
ping -s host_ip_addr count/timeout
Syntax description
-s
host_ip_addr
count
timeout
output for every response received.
The IP address or IP alias of the host.
(Optional) The number of packets to send
(Optional) Timeout value for the ping in millisecond
Command Line Interface
Page 47

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
39
gateway. IP address of 0.0.0.0 stands for no default
6.8 Network Commands
net reset
Use the net reset command to reset VIP. The CLI will prompt you to confirm the command before resetting VIP.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords
net set gateway
Use the net set gateway command to assign a default gateway (router) for VIP. The default
gateway routes packet data outside or your IP subnet.
Syntax description
ip_addr
Note
The new setting will not take effect until VIP is reset.
ip_addr
The IP address of the default
gateway.
net set http {on|off}
VIP allows you enable of disable its built-in HTTP server. Use the net set http command to enable or disable the HTTP server.
Syntax description
on
off
Enable HTTP server. This allows users to access VIP from web browser.
Disable HTTP server.
net set telnet {on|off}
VIP allows you enable of disable its built-in Telnet server. Use the net set telnet command to
enable or disable the Telnet server.
Syntax description
on
off
net set ip
Use the net set ip command to assign an static IP address to VIP.
Syntax description
Note
Command Line Interface
ip_addr
ip_addr
Enable Telnet server. This allows users to access VIP from web browser.
Disable Telnet server.
The IP address of VIP.
Page 48

VIP User’s Manual
40
The new IP address will not take effect until VIP is reset.
net set ip_preced
VIP allows you to set the 8-bit Service Type field in the IP header for all the voice packets it sends
out. The Service Type field is broken down into five subfields, among which four subfileds are user
configurable. This command is used to set these subfields.
net set ip_preced ip_preced [d] [t] [r]
Syntax description
ip_preced
d
t
r
Default
ip_preced: 0
d: 0
t: 0
r: 0
Notes
The new setting will not take effect until the VIP is reset.
ip_preced
The 3-bit PRECEDENCE subfiled ranging from 0 through 7.
The D bit subfield, either 0 or 1.
The T bit subfield, either 0 or 1.
The R bit subfield, either 0 or 1.
net set mask
Use the net set mask command to set the IP subnet mask for VIP.
Syntax description
ip_mask
Note
The new setting will not take effect until VIP is reset.
ip_mask
The subnet mask of your network.
net set speed {10|100|auto}
VIP allows you set the link speed for its Ethernet interface. Use the net set speed command to set
the Ethernet link speed.
Syntax description
10
100
Command Line Interface
Fixed the Ethernet speed at 10 Mbps
Fixed the Ethernet speed at 100 Mbps
Page 49

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
41
auto
Enable the 10/100 Mbps auto-negoriation capablity.
net set user_pw
password password
Use the net set user_pw command to change the password for Telnet user.
Syntax description
The new password. The password must be equal to or less than 7
password
alphanumeric characters. It must be identically typed twice for VIP to
be certain about the new password.
net show
The net show command displays all the network settings.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords
Example
The following example shows how to display network settings:
ITG> net show <Enter>
******************* Net Parameters *******************
PPPoE = disabled
DYN DNS = enabled
DHCP client = disabled
Configured IP address = 192.168.0.99.
Configured IP subnet mask = 255.255.255.0.
Default gateway IP address = 192.168.0.253.
Current active IP address = 192.168.0.99.
Current active subnet mask = 255.255.255.0.
IP precedence = 0 0 0 0
Ethernet MAC address = 00-30-4f-00-29-20
Ethernet speed setting = 10/100 Mbps auto-negotiation
USER password = 123
HTTP server = enabled
Telnet server = enabled
Ethernet speed setting = 10/100 Mbps auto-negotiation
USER password = 123
Command Line Interface
Page 50

VIP User’s Manual
42
HTTP server = enabled
Telnet server = enabled
******************************************************
ITG>
net show hwstat
The net show hwstat command displays the hardware configuration of VIP.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords
Example
The following example shows how to display hardware configuration:
ITG>net show hwstat <Enter>
****************** Hardware Configuration ******************
Flash: type-MX29L1611 32 sectors 64 KB/sector
RAM: 8 MB 512K x 16
LAN: 100 Mbps half duplex. Link UP
TIM slot A: type-FXO2S2 DSP-C5409 codec-PEB2466 Diag-OK
************************************************************
ITG>
net set pppoe
The net set pppoe command configures PPPoE related parameters while VIP is deployed in
PPPoE environment.
Syntax Description
on
off
username
password
fix_ip
Turn on PPPoE client
Turn off PPPoE client
PPPoE connection username provided by ISP
PPPoE connection password provided by ISP
Fixed IP address provided by ISP
net set dhcp
net set dhcp command configures VIP to be DHCP client in order to obtain TCP/IP related pa-
rameters from ISP while VIP is deployed in DHCP environment.
Syntax Description
Command Line Interface
Page 51

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
43
on
off
Turn on DHCP client
Turn off DHCP client
net set dyndns
DDNS service can help users to find each other in dynamic/static IP environment, and enable two
VIPs call each other with registered host names. To be fully functional, DNS server MUST be
added into SIP configuration while DDNS service is enabled.
DDNS clients supported in VIP are www.dyndns.org and www.dtdns.com currently.
If VIP DDNS client is enabled, users MUST register a DDNS name from the sites listed above before proceeding any further.
Syntax Description
on
off
sub commands:
set dyndns add [serv_name] [host_name] [user_name] [password]
Adding applied DDNS name into VIP database.
Note: if multiple DDNS names are inserted, only the first one will be updated.
Turn on DDNS client
Turn off DDNS client
Syntax Description
serv_name DDNS service server (MUST be “dyndns” or “dtdns” for now)
host_name
user_name
password
set dyndns delete [host_name]|all
Delete specified or all DDNS name(s) configured in VIP.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
DDNS name registered from DDNS service provider
Username used to update DDNS account
Password used to update DDNS account
Command Line Interface
Page 52

VIP User’s Manual
44
6.9 Configuration Management Commands
The configuration management commands allow the user to set values for system configuration parameters. In addition, it provides mechanisms to allow a user to control when new parameter values are put in use.
The CLI maintains three areas where the parameters are stored:
Temporary
Ÿ
Active
Ÿ
Non-volatile Storage (NVS)
Ÿ
When a set command is entered and processed, it changes the parameter value in the Temporary
area. This does not affect current operation of VIP, which is using the values in the Active area.
The config activate command moves configuration data from the Temporary area to the Active
area, where it can actually be used. Thus a user can make multiple changes in the Temporary
area using set commands, then put them into use with a single config activate command. (Note
that the config activate command may only be used between calls, and will usually tear down any
in-progress calls when invoked.)
Configuration data in the Active area is only available while VIP remains in operation. If VIP is reset, the Active area is reloaded from the data stored in NVS. Data in the Active area may be saved
to NVS by entering the config store command.
For most of the SIP parameter, settings won’t take effect until VIP reset. To ensure the SIP setting
to take effect, it is recommended to reset VIP after changing the settings using the set command.
In summary:
Use set commands to make configuration parameters changes in the Temporary area
Ÿ
Use the config activate command to move the new values into the Active area, available for
Ÿ
use
Use the config store command to save the new Active values in NVS
Ÿ
Reset VIP after changing SIP settings and storing the setting to NVS.
Ÿ
config {activate|store|erase}
Use the activate command to manage the configuration data. A sequence of set command is typically preceded by and/or followed by the config command for the set command to become active.
Syntax description
activate
store
erase
Move the configuration from temporary area to active area.
Store the active configuration data into non-volatile storage.
Erase the configuration from non-volatile storage.
SIP related commands
Command Line Interface
Page 53

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
45
show sip
The show SIP command displays the settings of the parameter that are related to SIP signaling
protocol.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords
Example
The following example shows how to display the SIP parameters:
ITG>show sip
SIP Addr Configuration:
UDP ctl addr = 192.168.0.99/5060
RTP data addr = 192.168.0.99/2070
Domain name server = 168.95.192.1
Info switch is off
nat_call is on
auto_reg is off
outboundproxy : None
show sip reg
- Displays the information of registration
show sip cfg
- Displays the configuration of registration
show sip proxy
- Displays the configuration of proxy server
show sip dns_ip
- Displays the configuration of DNS server
show sip info_sw
- Displays the information switch
show sip auto_reg
- Displays auto-registration on/off when reboot
Command Line Interface
Page 54

VIP User’s Manual
46
show sip nat_call
- Displays nat_call switch
show sip outboundproxy
- Displays the outbound proxy
set sip reg add
- used to add registration information
set sip reg add [
Syntax description
reg_num
expires how long the reg_num is to re-register
registrar
#
ip IP of the registrar
port
port of the registrar
name
passwd
reg_num] [expires] [#registrar] [ip] [port] {name | 0} {passwd | 0} {ip port …}
the phone number to be registered
the number of registrar
[the name for authentication | 0 for no authentication]
[the password for authentication | 0 for no authentication]
set sip reg del
- used to delete registration information
set sip reg del [reg_num]
Syntax description
reg_num the phone number to be deleted
set sip cfg
- used to set the configuration of sip
set sip cfg
Syntax description
udp_ctl_port
rtp_data_port
set sip proxy
- used to set the configuration of sip
set sip proxy
Syntax description
[udp_ctl_port] [rtp_data_port]
<udp control port>|( 0 : default port will be used)
<rtp data port>|( 0 : default port will be used)
[#proxy_svr] [ proxy svr-1 nwa ] { proxy svr-2 nwa }…
#proxy_svr number of proxy server | 0 to remove existing server
Command Line Interface
Page 55

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
47
proxy svr nwa <ip> <port>
set sip actreg
set sip actreg
- used to send out the registration
set sip dns_ip
used to set the domain name server. The IP domain should be in
-
numerical format
set sip dns_ip [ip]
Syntax description
ip
<x.x.x.x> | 0 to remove dns ip
set sip info_sw
- used to set the sip process information switch
set sip info_sw [on/off]
set sip auto_reg
- used to set registration auto start when reboot in the condition of registration server is set
set sip auto_reg [on/off]
set sip nat_call
- used to set nat_call switch on/off whether the gateway in public IP is to receive calls from the
private IP or not. The default value is on.
set sip outboundproxy add
- used to add outbound proxy
set sip nat_call [on/off]
set sip outboundproxy add [ip/hostname] [port]
set sip outboundproxy del
- used to delete outbound proxy
set sip outboundproxy del
set sip name [Registrar_ID] [name]
- used to setup SIP Caller ID information. You may use "show sip reg" to show the Registrar ID
and setup the corresponding Caller ID parameter. The Caller ID is the [name] field.
Command Line Interface
Page 56

VIP User’s Manual
48
6.10 Voice Coding Profile Configuration Commands
Coding profile is used to store coding parameters for voice and fax coding p that can be used by telephony port on VIP. VIP has built-in coding profiles, each having a unique profile ID and parameters for specific voice, fax or modem coder. Among these coding profiles, there are five may be
used for voice or fax applications. The following table summarizes coding profiles available for
voice and fax applications.
Coding profile ID Coder
0 G.723 6.3 kbps voice coder
1 G.729ab voice coder
2 G723 5.3 kbps voice coder
5 Proprietary fax coder
6
10 Standard T.38 fax coder
This session will introduce commands for setting the parameters for a particular coding profile. All
the commands in this session are of the same syntax as follows:
G.711 μ-law voice coder
set coding profile_id option [option] . . .
Syntax for the profile_id is as follows:
profile_id
ID of the coding profile to be modified.
6.10.1 Common Coding Profile Configuration Commands
set coding
Syntax description
coding_type
profile_id
Parameter Description
g711_mu
g723_53
g723_63
g729ab
fax_t38
coding_type
Type of the codcc as defined in the following table.
G.711 PCM u-law coding
G.723.1 5.3 kbps coding
G.723.1 6.3 kbps coding
G.729 annex A, annex B 8kbps coding
Fax Relay in T.38 mode
Note: Modification will not take effect till save and next reboot.
coding_type
Command Line Interface
Page 57

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
49
set coding
This command is used to specify a secondary level of control of call progress tone detection. If the
call progress detection control for a telephony port is set to "As per coding profile" (refer to command “set port port cp_tone_det_ctrl”), this parameter determines if detection is to be enabled or
not.
Syntax description
set coding
This command is used to specify a secondary level of control of V.21 fax tone detection. If the fax
tone detection control for a telephony port is set to "As per coding profile" (refer to command “set
port port fax_tone_det_ctrl”), this parameter determines if detection is to be enabled or not. For a
voice coder, fax tone detection has to be enabled, otherwise, telephony port never switches to fax
mode while the voice coder is active. For a fax profile it does not matter if the fax tone detection is
enabled or disabled.
Syntax description
profile_id
on
off
profile_id
on
off
cp_tone_detect {on | off}
Enable call progress tone detection.
Disable call progress tone detection.
fax_tone_detect {on | off}
Enable V.21 fax tone detection.
Disable V.21 fax tone detection.
set coding
Syntax description
Voice
Fax
profile_id
The coding profile is allowed, if the parameter that follows is “on”, for being used
as voice coder.
The coding profile is not allowed, if the parameter that follows is “off”, for being
used as voice coder.
The coding profile is allowed, if the parameter that follows is “on”, for being used
as fax coder.
The coding profile is not allowed, if the parameter that follows is “off”, for being
used as fax coder.
usage {voice | fax} {on | off}
6.10.2 Voice Coding Profile Configuration Commands
set coding
VIP has built-in voice packet buffer, which allows VIP to remove packet jitter from the incoming
packet stream. VIP also implements an adaptive voice packet playback.This command is used to
enable/disable the adaptive playback function for a voice coding profile.
Syntax description
profile_id
adaptive_playout
{on | off}
Command Line Interface
Page 58

VIP User’s Manual
50
on
off
set coding
Enable adaptive playback.
Disable adaptive playback.
profile_id
dtmf_relay {on | off}
VIP supports DTMF Relay, in which DTMF tones are detected during voice processing, encoded into
SIP-UserInformation packets and conveyed to the remote VIP via the SIP call control band. This command is used to enable or disable the DTMF Relay feature.
Syntax description
on
off
set coding
Detect DTMF tones while voice session is on-going, and send detected
DTMF digits to remote gateway via the SIP call control band.
Do not detect DTMF tones. DTMF tones are compressed and send to
remote gateway the same as regular voice frame.
profile_id
max_delay
Voice packets from network may have traversed variable path and each packets have experienced different propagation delay. To ease this phenomenon, VIP has a built-in voice packet buffer, which
stores voice packets received from the network. The effect of non-uniform delay among packets is
known as jitter. The voice buffer allows VIP to remove the packet jitter from the incoming packet
stream before decompressing and sending the packet to telephony port for playing out. This command
is used to set the size of voice buffer.
Syntax description
delay
Value in milliseconds.
Notes
The maximum delay should be at least 2 packet times greater than the nominal delay. Refer to
1.
command
set coding profile_id nom_delay
“
for details about setting nominal delay.
”
2. The maximum delay for each coder is shown in the following table:
Coding Type Maximum Delay
G.711 μ-law
145 ms
G.723 500 ms
G.729AB 500 ms
set coding
profile_id
min_delay
This command is used to set the time each voice packet is stored in the voice packet buffer before VIP
playing out the packet. It is only meaningful when the adaptive playback feature is disabled. Refer to
“set coding profile_id adaptive_playout” for details about adaptive playback feature.
Syntax description
delay
Value in milliseconds.
Command Line Interface
Page 59

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
51
On
Off
profile_id
Value in milliseconds.
profile_id
Enable VAD.
Disable VAD.
profile_id
profile_id
nom_delay
{on | off}
vad
vad_thresh
Value in dBm, ranging from –20 to +10.
vif
set coding
Syntax description
Delay
set coding
This command is used to enable/disable the Voice Activity Detector (VAD) for a coding profile.
Syntax description
set coding
This command is used to set threshold level for the VAD for a coding profile.
Syntax description
threshold
set coding
This command is used to set the size of the Voice Information Field (VIF), in bits, for a voice coder.
Syntax description
Coding type Sampling time VIF
G.711 μ-law
20 ms 1,280
30 ms 1,920
G.723 30 ms 192
60 ms 384
G.729AB 10 ms 80
20 ms 160
30 ms 240
40 ms 320
50 ms 400
60 ms 480
Note:
Command Line Interface
10 ms 640
Page 60

VIP User’s Manual
52
Size of the Voice Information Field (VIF), in bits, for a voice coder are related to the coding type and
the rate the voice coder samples a voice frame (the packet time), as shown in the table above. VIF
sizes of a coder of values other than those shown in the table are not valid.
6.11 Dial Plan Management Commands
Among the command sets supported by the CLI, the dial plan management commands are the
most sophisticated. Some of the dial plan management commands are only allowed when VIP is in
the atpm table update state. For ease of explaining, this command set is further categorized into
several sub command sets.
Sub command set
Database update
control
Instruct VIP to start or stop
Ÿ
atpm table update state.
Store/restore atpm tables
Ÿ
Purposes
to/from non-volatile storage
Purge atpm tables
Ÿ
Erase dial plan database
Ÿ
from non-volatile storage
Destination table
Manage atpm destination table atpm dadd
management
Hunt group table
Manage atpm hunt group table atpm hadd
management
Address table
Manage atpm address table atpm aadd
management
System Manage atpm system configura-
tion
Commands
atpm req
atpm done
atpm restore
atpm store
atpm purge
atpm erase
atpm ddel
atpm dfind
atpm dlist
atom hdel
atpm hfind
atpm hlist
atpm adel
atpm afind
atpm alist
atpm slist
atpm sys
atpm table up-
date state re-
quired?
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
Yes
The following sections describe each sub command set and the commands.
Command Line Interface
Page 61

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
53
Database Update Control Commands
atpm done
The atpm done command ends the atpm table update session and re-enables the address translation.
Syntax description
This command has no arguments or keywords
atpm erase
The
atpm erase
Syntax description
This command has no arguments or keywords
command erases the dial plan database from the non-volatile memory.
atpm purge {all|addr|dest|hunt}
Use the
atpm purge
command to delete all entries from the atpm tables.
Syntax description
all
addr
dest
hunt
Delete all entries from atpm ddress, destination and hunt group tables.
Delete all entries from atpm address table.
Delete all entries from atpm destination table.
Delete all entries from atpm hunt group table.
atpm req
The atpm req command starts the atpm table update session. Upon starting the atpm table update
session, the ATPM address translation is disabled, hence no phone call can be made, until a atpm
done command is issued.
Syntax description
This command has no arguments or keywords
atpm restore
The atpm restore command restores the whole dial plan from non-volatile storage to the atpm address, destination and hung group tables.
Syntax description
This command has no arguments or keywords
Command Line Interface
Page 62

VIP User’s Manual
54
atpm store [erase]
The atpm store command store all atpm tables into non-volatile memory.
Syntax description
(Optional) Erase the non-volatile before storing the dial plan data-
erase
base. This option is not recommended except the very first time you
use the atpm store command.
Hunt Group Table Management Commands
atpm hadd
Use the atpm hadd command to add an entry into the atpm hunt group table.
Syntax description
hunt_group_id
Example
The following example shows how to group destination 1, 2, 3 and 4 into a hunt group, assign it
hunt group ID 10, and specify hunt type 2 for this hunt group.
ITG>atpm hadd 10 2 1 2 3 4<Enter>
hunt_group_id
1
2
dest_id1
dest_id2
dest_id3 …
{1|2}
Hunt group ID. For each hunt group, you need to assign it a unique identifier
between 1 and 65536.
Hunt type 1. Hunt type 1 hunts destination within a hunt group starting from
the destination member just after the last used member.
Hunt type 2. Hunt type 2 hunts destination within a hunt group starting from
the first destination member.
ID of the first destination member in the hunt group.
(Optional)List of ID’s of additional destination members in the hunt group.
dest_id [desi_id2
] …
atpm hdel
The atpm hdel command deletes an entry from the atpm hunt group table.
Syntax description
hunt_group_id
atpm hfind
The atpm hfind finds and display an entry in the hunt group table.
Command Line Interface
hunt_group_id
ID of the hunt group to be deleted from the hunt group table.
hunt_group_id
Page 63

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
55
Syntax description
hunt_group_id
ID of the hunt group to be displayed.
atpm hlist
The atpm hlist display all entries in the hunt group table.
Syntax description
This command has no arguments or keywords
Example
ITG>atpm hlist
Group id Type #Members Member ids
------------------------------------------------------------------ 1 2 1 1
2 2 1 2
3 2 1 3
4 2 1 4
5 2 1 5
6 2 1 6
7 2 1 7
8 2 1 8
11 2 1 11
OK
ITG>
Address Table Management Commands
atpm aadd
Use the atpm aadd command to add an entry into the atpm address table.
Syntax description
min_digits
max_digits
hunt_group_id
fix_strip_len
Command Line Interface
tel# min_digits max_digits hunt_group_id prefix_strip_len [prefix#
tel#
pre-
prefix#
Telephone number to match. This is only part of the total dialed string.
Minimum number of digits to be collected before the ATPM starting
matching the dialed string with entries in the address table.
Maximum number of digits to be collected before the ATPM starting
matching the dialed string with entries in the address table.
Hung group ID for this telephone number
The number of digits to be stripped at the beginning of the collected dial
string before forwarding the string to the destination.
(Optional) Digit to be added before the beginning of the collected dial
string before forwarding it to the destination.
]
Page 64

VIP User’s Manual
56
atpm adel
tel#
The atpm adel command deletes an entry from the atpm address table.
Syntax description
tel#
Number of a previously added entry to be deleted from the atpm address table.
atpm afind
tel#
The atpm afind finds and display an entry in the address table.
Syntax description
tel#
Number of a previously added entry in the atpm table to be displayed.
atpm alist
The atpm alist displays all entries in the address table.
Syntax description
This command has no arguments or keywords
Example
ITG>atpm alist
Address Hunt Min Max Prefix Prefix
Entry Grp_Id Digits Digits strip Address
201 1 1 3 3 None
202 2 1 3 3 None
203 3 1 3 3 None
204 4 1 3 3 None
ITG>atpm done
OK
ITG>
System Commands
atpm slist
The atpm slist displays the atpm system table.
Syntax description
This command has no arguments or keywords
Example
Command Line Interface
Page 65

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
57
ITG>atpm slist
System Info: Total dial time = 30000ms, First digit wait = 10000ms,
Interdigit wait = 5000ms, Dial term digit = None
OK
ITG>
atpm sys
Use the atpm sys command to set the time constraints for collection of dial digits.
Syntax description
inter_digit_wait
dial_term_digitr
dial_time 1st_digit_wait inter_digit_wait
dial_time
1st_digit_wait
The maximum time, in millisecond, allowed for entry of the entire
string of dial digits. At expiration, ATPM starts address lookup.
The maximum time, in millisecond, allowed between off-hook
and when the first dial digit is entered. At expiration, ATPM considers address lookup to fail.
The maximum time allowed between entry of each digit after the
previous digit. At expiration, ATPM starts address lookup.
(Optional) End of the dial string is declared when the digit is entered.
dial_term_digit
[
]
6.12 Tel Commands
tel show pcm_gain_level
The tel show pcm_gain_level command to display the gain level setting of the PCM codec’s receive channel.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords
tel show port [
The tel show port command displays the hook state of a telephony port.
Syntax Description
port#
Default
If the port number is not specified, the CLI displays hook state of all telephony ports.
port#
]
Number of the port.
tel show ring_freq
The
tel show ring_freq
FXS ports..
Command Line Interface
command to displays the frequency of the ring signal that VIP sends to
Page 66

VIP User’s Manual
58
tel set pcm_gain_level {1|2|3|4|5}
The FXO ports might be connected to central office switch or PBX via local loop which may of as
long as several miles. For compensating signal distortion in the local loop, VIP’s PCM codec is designed in such a way that users might adjust it gain level before transmitting analog signal to the local loop. The tel set pcm_gain_level command is used to set the gain level for the PCM codec for
compensating signal loss in the local loop.
Syntax Description
1
2
3
4
5
Default
The default setting is -1 dB.
Note
The PCM gain level setting is only meaningful to FXO ports. It is not applicable to FXS ports.
Set gain level to –1 dB
Set gain level to 0 dB
Set gain level to +1 dB
Set gain level to +2 dB
Set gain level to +3 dB
tel set ring_freq {1|2|3|4}
Use the tel set ring_freq command to set the frequency of the ringer VIP uses to ring a FXS port.
Syntax Description
1
2
3
4
Set ring freq to 17 Hz
Set ring freq to 20 Hz
Set ring freq to 25 Hz
Set ring freq to 50 Hz
Command Line Interface
Page 67

VIP User’s Manual
VIP
Chapter 7 Upgrading and resetting VIP
VIP-450 is able to have system functionality enhancement via software upgrade. This must be operated in upgrade mode. In firmware upgrade mode, limited commands allow users to read new revision
codes from a remote TFTP server and write into the built-in flash non-volatile storage.
To enter download mode, either Telnet or Console (RS-232) connection can take the job, and a TFTP
server is required by VIP to complete firmware upgrade process.
7.1 Firmware upgrade
To switch from normal operation mode to download mode, use the download CLI command.
download
ITG>
<Enter>
Note:
To be able to switch to download mode from Telnet session, TFTP loader on VIP must be ver-
sion 3.00 or higher. To upgrade to firmware version 3.03 or above, bootloader version 4.01 or
above is required.
After download command is inserted, VIP will terminate all on-going calls, reset and enter firmware
download mode. If you enter download mode from Telnet session. The Telnet session will be terminated too. You need to re-connect to VIP from Telnet client to be able to access the firmware download
mode.
Before going any further, please note: NEVER, NEVER TURN OFF POWER while firmware upgrade is working in progress!! (Please ensure power supply is stable before firmware upgrade is
executed.)
TFTP server is required to complete VIP series firmware upgrade process; there are various TFTP
server software on the market, please utilize the existing software or find a new one on the net to complete upgrade process. (In this chapter, 3CDeamon TFTP server was installed for demonstration.)
TCP/IP Configuration:
Computer installed with TFTP server: 192.168.0.7
VIP: 192.168.0.1
Note: If a Telnet connection is built behind NAT environment, TCP port 69 MUST be reserved for data
communication.
(192.168.0.1)
Computer equipped with TFTP
Server IP: 192.168.0.7
Command Line Interface
Console connection
59
Page 68

VIP User’s Manual
60
TFTP server configuration
1. Execute TFTP server program, assign firmware file location, and save the path if necessary. (In this
sample datagram, the file is assigned in c:\) (This part might vary on different kind of TFTP server.)
2. Allocate VIP firmware file in the directory, and apply the modification (if required).
Note: TCP port 69 is required for TFTP access.
VIP configuration:
Telnet session
a) Under Telnet firmware download mode, the user name: eitg; password: 123 (password may
vary because of user’s configuration) is used for logging on VIP
b) Under ITG> prompt, insert command: download to enter VIP firmware upgrade mode.
c) Insert command: “start” and answer questions on screen to proceed firmware upgrade.
d) When VIP prompts downloading firmware file into EEPROM, insert “y” to continue.
e) Wait till firmware is fully loaded into VIP, insert “quit” to leave firmware upgrade mode and an-
swer “y“ to reboot machine when VIP prompts for restart.
Command Line Interface
Page 69

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
61
Application code downloaded successfully
A
ITG>download
============================== WARNING ==============================
* Entering download mode will hang up all telephone connections *
* and all the configuration settings will lose. *
* Be certain all the configuration settings have been saved. *
=======================================================================
Do you want to enter download mode now (y/n)? [n] y
Boot loader V4.12
Loading TFTP loader.....................
** Internet Telephony Gateway TFTP Loader Ver 4.10 **
EITGLoader>start
IP address of the TFTP server? [192.168.0.254] 192.168.0.7
File name?
Starting download file: xyz123.imz
.................................................................................................................................................................
..........................................
Download complete, file size = 833004
Do you want to write downloaded image to flash EEPROM (y/n)? [y]
Press <Enter> to start flash EEPROM programming
Flash EPROM programming on-going, BE CERTAIN NOT TO TURN POWER OFF...
Flash sector no. 4 write done
Flash sector no. 5 write done
Flash sector no. 6 write done
Flash sector no. 7 write done
Flash sector no. 8 write done
Flash sector no. 9 write done
Flash sector no. 10 write done
Flash sector no. 11 write done
Flash sector no. 12 write done
Flash sector no. 13 write done
Flash sector no. 14 write done
Flash sector no. 15 write done
Flash sector no. 16 write done
Flash EEPROM programming completed
ll sectors programmed successfully
Download another file (y/n)? [n]
EITGLoader>
Do you want to restart the system now (y/n)? [n]
xyz123.imz
quit
y
n
y
Command Line Interface
Page 70

VIP User’s Manual
62
Application code downloaded successfully
All sectors programmed successfully
Console session
a) Connect VIP through the 9-pin RS232 female console (No password required)
Under ITG> prompt, insert command: download to enter VIP firmware upgrade mode.
b) Insert command: “
” and answer questions on screen to proceed firmware upgrade.
start
c) When VIP prompts downloading firmware file into EEPROM, insert “y” to continue.
d) Wait till firmware is fully loaded into VIP, insert “quit” to leave firmware upgrade mode and an-
swer “y“ to reboot machine when VIP prompts for restart.
ITG>download
============================== WARNING ==============================
* Entering download mode will hang up all telephone connections *
* and all the configuration settings will lose. *
* Be certain all the configuration settings have been saved. *
=======================================================================
Do you want to enter download mode now (y/n)? [n] y
Boot loader V4.12
Loading TFTP loader.....................
** Internet Telephony Gateway TFTP Loader Ver 4.10 **
EITGLoader>start
IP address of the TFTP server? [192.168.0.254] 192.168.0.7
File name?
Starting download file: xyz123.imz
.................................................................................................................................................................
..........................................
Download complete, file size = 833004
Do you want to write downloaded image to flash EEPROM (y/n)? [y]
Press <Enter> to start flash EEPROM programming
Flash EPROM programming on-going, BE CERTAIN NOT TO TURN POWER OFF...
Flash sector no. 4 write done
Flash sector no. 5 write done
Flash sector no. 6 write done
Flash sector no. 7 write done
Flash sector no. 8 write done
Flash sector no. 9 write done
Flash sector no. 10 write done
Flash sector no. 11 write done
Flash sector no. 12 write done
Flash sector no. 13 write done
Flash sector no. 14 write done
Flash sector no. 15 write done
Flash sector no. 16 write done
Flash EEPROM programming completed
Download another file (y/n)? [n]
EITGLoader>quit
Do you want to restart the system now (y/n)? [n]
xyz123.imz
y
n
y
Command Line Interface
Page 71

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
63
Trouble Shooting Tips
If following error (TFTP timeout error) occurs:
** Internet Telephony Gateway TFTP Loader Ver 4.10 **
EITGLoader>start
IP address of the TFTP server? [192.168.0.7]
File name?
Starting download file: xyz123.imz
TFTP device open failed. Download another file (y/n)? [n]
xyz123.imz
TFTP server timeout while waiting for a response from the client.
Possibility:
a) Network connection is not correctly configured
check if cable is securely connected.
è
check if TFTP server IP address is correctly configured
è
check if TCP port 69 is available for TFTP connection
è
if firmware upgrade is processed remotely, a fast connection between VIP and TFTP server
è
is required (ping response time <300 ms)
During firmware upgrade, ”protocol error detected” displays on the screen.
** Internet Telephony Gateway TFTP Loader Ver 4.10 **
EITGLoader>start
IP address of the TFTP server? [192.168.0.7]
File name?
Starting download file: xyz123.imz
TFTP device open failed. Download another file (y/n)? [n]
xyz123.imz
Protocol error detected.
a) In most circumstances, this error occurs while requested firmware file cannot be found on TFTP
server.
Possibility:
check if the firmware file is correctly located in assigned folder.
à
check if TFTP server supports long file name format.
à
check if firmware file name is correctly inserted
à
check system log on TFTP server if there is error message for trouble shooting.
à
Command Line Interface
Page 72

VIP User’s Manual
64
7.2 CLI Commands in Download Mode
Under download mode, the CLI supports the following commands:
Command
help
quit
set
start
The following section describes each of the commands.
Display help screen
Terminate download mode, switch to normal operation mode.
Change IP parameter
Start downloading code from TFTP server
Description
help
The help command lists the top-level commands.
quit
The quit command is used to terminate the download mode and return to normal operation mode.
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords
Note
Switching mode from Telnet session will terminate current active session. You’ll need to connect to
VIP again to be able to access the CLI.
set ip
ip_addr
Use the set ip command to assign an static IP address to VIP.
Syntax description
ip_addr
Note
The new IP address will not take effect until VIP is reset.
set gateway
Use the set gateway command to assign a default gateway (router) for VIP. The default gateway
routes packet data outside or your IP subnet.
Syntax description
ip_addr
Note
The new setting will not take effect until VIP is reset.
Command Line Interface
The IP address of VIP.
ip_addr
The IP address of the default gateway. Default value: 0.0.0.0
Page 73

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
65
set mask
Use the set mask command to set the IP subnet mask for VIP.
Syntax description
Note
The new setting will not take effect until VIP is reset.
ip_mask
ip_mask
The subnet mask of your network.
start
Use the start command to start downloading code from TFTP server. VIP will prompt you for the IP
address of the TFTP server and the file to download.
7.3 Restore default configuration
If there is system re-organization, firmware upgrade or improper parameters are loaded in VIP-450,
restoring factory default settings may help you to restore initial state of machine and restart configuration.
Following are steps loading VIP series default parameters:
Note: restore process in this session only can be applied to firmware version 3.xx)
System configuration default parameters
a) Logon VIP via telnet or console connection, and insert command: config erase
b) After this command, VIP pops up a warning message and prompts for confirmation.
c) Press ”y” to erase current system configuration parameters,
d) Enter net reset to reboot and load the default system parameters into machine.
e) Log on VIP, and insert command: config store to load factory default parameters into VIP.
Command Line Interface
Page 74

VIP User’s Manual
66
Are you sure to erase it (y/n)? [n]
A sample is attached below for reference.
config erase
ITG>
The system configuration data will be erased from non-volatile storage permanently.
System configuration records erased from flash
ITG>net reset
============================== WARNING ==============================
* Restarting the system will hang up all telephone connections *
* and all the configuration settings will lose. *
* Be certain all the configuration settings have been saved. *
=======================================================================
Do you want to restart the system now (y/n)? [n] y
Boot loader V4.12
Mem 16b 16M
Loading application code.............................................................................................................
******* Internet Telephony Gateway (PLA) Version s1.0 *******
****************** Hardware Configuration ******************
Flash: type-MX29L1611 32 sectors 64 KB/sector
RAM: 8 MB 512K x 16
LAN: auto-negotiation on-going. Link DOWN
TIM slot A: type-FXO2S2 DSP-C5409 codec-PEB2466 Diag-OK
************************************************************
config store
ITG>
OK
ITG>
y
Command Line Interface
Page 75

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
67
Are you sure to erase it (y/n)? [n]
Dialplan configuration default parameters:
a) Log on VIP via telnet or console connection.
b) At the ITG prompt, insert following commands:
ITG>atpm erase
ITG>net reset (Answer ”y” to reboot machine.)
After rebooting, logon VIP. At the ITG> prompt, insert: atpm store to restore Dialplan default
value into VIP.
A sample is attached below for reference.
atpm erase
ITG>
The dial plan will be erased from non-volatile storage permanently.
Dial plan erased from flash
OK
ITG>net reset
============================== WARNING =============================
* Restarting the system will hang up all telephone connections *
* and all the configuration settings will lose. *
* Be certain all the configuration settings have been saved. *
====================================================================
Do you want to restart the system now (y/n)? [n] y
Boot loader V4.12
Mem 16b 16M
Loading application
code........................................................................................................................
******* Internet Telephony Gateway (PLA) Version s1.0 *******
****************** Hardware Configuration ******************
Flash: type-MX29L1611 32 sectors 64 KB/sector
RAM: 8 MB 512K x 16
LAN: auto-negotiation on-going. Link DOWN
TIM slot A: type-FXO2S2 DSP-C5409 codec-PEB2466 Diag-OK
************************************************************
ITG>No dial plan info can be found in the Flash, the default dial plan is used but NOT saved.
OK
atpm store
ITG>
OK
y
Command Line Interface
Page 76

Page 77

VIP User’s Manual
Appendix A Technical Specifications
A.1 VIP Technical Specifications
VIP-450: 2 ports loop start FXO, 2 ports loop start FXS
Telephony Interface
Module support
VIP-050: 4 ports loop start FXO, 4 ports loop start FXS
(Up to two modules per unit)
Network Interface Ports
Voice codec support
Fax
Fax over IP protocol
Echo cancellation
Simultaneous connection
Voice processing
Call control
Management
1 10/100Base-T, auto sensing, RJ45
G.711 PCM 64kbps (A-law and μ-law)
G.723.1A ACELP/M-MLQ (5.3, 6.3kbps)
G.729AB CS-ACELP (8kbps)
ITU-T V.21, V.27ter, V.29, V.33 and V.17
T.38 Proprietary low bandwidth protocol
G.168 compliant, 16 ms tail length
VIP-450: 4 channels voice/fax
VIP-050: 8 channels voice/fax
Voice activity detection
DTMF detection/generation
Echo cancellation
Comfort noise generation
Call progress detection
Gain control
SIP 2.0 (RFC3261)
Built HTTP server allowing management from web browser
Command line interface allowing management from VT-100 terminal
or Telnet client
Software upgrade
Power
Environmental
Dimension (L x W x D)
Technical Specifications 69
Flash memory and built-in TFTP allowing software upgrade via network
VIP-450: AC-to-DC power supply, 90-260 VAC, 50-60 Hz
VIP-050: 90-240 VAC, 20 Watts, 50-60 Hz
Operating temperature: 0o to 45o C (32o to 113o F)
Storage temperature: -10o to 65o C (-4o to 149o F)
Humidity: 10% to 85% (non-condensing)
VIP-450: 150 x 220 x 44 (mm)
VIP-000: 445 x 275 x 44 (mm)
Page 78

VIP User’s Manual
70
EMI
FCC Part 15 Class A
EN55022 Class A (CISPR-22 Class A)
VCCI Class A
Compliances
CE
Safety
UL 1950
CE
VIP-450: Desktop
Mounting
VIP-000: Desktop or 19” rack mounting
A.2 Console Port
The console port uses a DB-9 RS-232 connector. The supplied straight-through RS-232 cable connects the console port of VIP to a console PC or terminal. Pinout for the port is described in the following table.
DB-9 pin Signal
1 Not connected
2 TxD
3 RxD
4 Not connected
5 Ground
6 Not connected
7 Not connected
8 Not connected
9 Not connected
A.3 LAN Port
The 10/100 LAN port use standard RJ-45 connector and Ethernet pinouts. The following diagram
and table show the pinout on the port connector. When connecting the LAN port to switches or repeaters, you must use a straight-through cable.
RJ45 pin Signal
1 RxD+
2 RxD-
3 TxD+
4 Not connected
5 Not connected
12345678
Technical Specifications
Page 79

SIP Voice Gateway User’s Manual
71
6 TxD-
7 Not connected
8 Not connected
A.4 FXO Port Pin Assignments
The FXO Telephony Interface Module has 4 RJ11C/W modular jacks. The following diagram and
table show the assignments of the pin for the RJ11 port.
RJ-11 pin Signal
1 Not connected
2 Tip
3 Ring
4 Not connected
1234
A.5 FXS Port Pin Assignments
The FXS Telephony Interface Module has 4 RJ11C/W modular jacks. The following diagram and
table show the assignments of the pin for the RJ11 port.
RJ-11 pin Signal
1 Not connected
2 Tip
3 Ring
4 Not connected
1234
Technical Specifications
Page 80

VIP User’s Manual
72
A.6 FXO Card Technical Specifications
Signaling: Loop Start / DTMF
No. of channels: 4
Interface Connectors: 4 RJ-11 2-pin modular jacks.
Line Impedance :
Insertion Loss: 2 dB nominal.
Frequency Response: 300Hz ~ 3400Hz +/- 2dB w.r.t. 1004Hz.
Return Loss:
Input Level adjustment: -6 dB to +6 dB
Output Attenuation: 0 dB to 13 dB
Longitudinal Balance:
600 W
900 W
18 dB
³
45 dB
³
A.7 FXS Card Technical Specifications
Signaling: Loop Start / DTMF
No. of channels: 4
Interface Connectors: 4 RJ-11 2-pin modular jacks.
Line Impedance :
600 W
900 W
Insertion Loss: 2 dB nominal.
Frequency Response: 300Hz ~ 3400Hz +/- 2dB w.r.t. 1004Hz.
Return Loss:
Input Level adjustment: -6 dB to +6 dB
Output Attenuation: 0 dB to 13 dB
Longitudinal Balance:
Loop Current: 25mA nominal
Ring Voltage: 50Vrms Nominal
Ringing Tone: 16.67Hz, 20Hz(default), 25Hz or 50Hz
Technical Specifications
18 dB
³
45 dB
³
Page 81

VIP User’s Manual
Appendix B CLI Commands
B.1 Normal Mode Commands
Command Description
atpm aadd Add an entry to the address table
atpm adel Delete an entry from the address table
atpm afind Find and display an entry in the address tble
atpm alist Display all entries in the address table
atpm dadd Add an entry to the destination table
atpm ddel Delete an entry from the destination table
atpm dfind Find and display an entry in the destination atble
atpm dlist Display all entries in the address table
atpm hadd Add an entry to the hunt group table
atpm hdel Delete an entry from the hunt group table
atpm hfind Find and display an entry in the hunt group tble
atpm hlist Display all entries in the hunt group table
atpm done End the atpm table update session
atpm erase Erase all atpm tables from NVS
atpm purge Purge entries from atpm table(s)
atpm req Start atpm table update session
atpm restore Restore atpm tables from NVS
atpm store Store atpm tables into NVS
atpm slist Display atpm system parameters
atpm sys Set atpm system parameters
config activate Move the configuration from temporary area to active area.
config erase Erase the configuration from NVS
config store Store the active configuration data into NVS
clrscr Clear screen
download Switch to download mode
help Display help screen
CLI Commands 73
Page 82

VIP User’s Manual
74
net reset Reset the system
net set gateway Set default gateway’s IP address
net set http Turn on/off HTTP server
net set ip Set IP address
net set ip_preced Set IP precedence bits
net set mask Set IP subnet mask
net set speed Select Ethernet link speed
net set user_pw Set password
net show Display IP parameters
net show hwstat Display hardware status
ping Send ICMP echo request to another host
show sip Display SIP parameter settings
show version Show software versions
set sip Setup SIP related parameters
tel show
pcm_gain_level
tel show port Display hook state for a telephony port
tel show ring_freq Show ringer’s frequency
tel set pcm_gain_level Set gain level for the PCM codec’s receive channel
tel set ring_freq Set ringer’s frequency
Display gain level setting of the PCM codec’s receive channel.
B.2 Download Mode Commands
Command Description
help Display help screen
quit Switch to normal operation mode
set gateway Set default gateway ‘s IP address
set ip Set IP address
net set mask Set IP subnet mask
start Start downloading file
CLI Commands
Page 83

VIP User’s Manual
Appendix C Factory Default Settings
The following table lists the settings of certain parameters before VIP is shipped.
Parameter Default Setting
Network
IP address 192.168.0.1
IP subnet mask 255.255.255.0
Default gateway 0.0.0.0
IP precedence 0
Ethernet link speed 10/100 auto-negotiation
User ID for HTTP browser and Telnet client login administrator
Password for HTTP browser and Telnet access login 123
User name for Telnet session in download mode eitg
Password for Telnet session in download mode 123
HTTP server On
Telnet server On
Serial port (Fixed)
Baud rate 19,200
Number of data bit 8
Parity check None
Number of stop bit 1
Voice codec
Preferred voice codec G.723 6.3kbps
TxVIF size (default voice codec=g.723) 192
RxVIF size (default voice codec=g.723) 192
VAD Enabled
Playout nominal delay 120 ms
Playout maximum delay 240 ms
Playout minimum delay 0 ms
Fax tone detect Enabled
Call Progress Tone detect Enabled
Telephony
PCM codec receiver gain for FXO ports -1 dB
Ringer frequency for FXS ports 17 Hz
Index 75
 Loading...
Loading...