Page 1

1-port H.323/SIP E1/T1
Trunk Gateway
VIP-2100
Page 2

CONTENTS
Chapter 1 VIP-2100 Introduction.................................................................1
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION....................................................................................1
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION..............................................................................2
AUDIO FEATURE.............................................................................................2
VIP-2100 DETAIL SPECIFICATIONS..................................................................4
VIP-2100 APPEARANCE DESCRIPTION...........................................................10
Chapter 2 Logon VIP-2100.........................................................................11
LOGON VIP-2100........................................................................................11
NETWORK CONFIGURATION...........................................................................12
SYSTEM TIME CONFIGURATION......................................................................13
ACCOUNT MANAGER.....................................................................................14
RELOGIN .....................................................................................................16
Chapter 3 H.323 Gatekeeper and SIP Proxy Mode Configuration..........17
ENVIRONMENT USED IN THIS CHAPTER............................................................17
INTERFACE CONFIGURATION..........................................................................18
T1/E1 TRUNK CONFIGURATION .....................................................................19
H.323 CONFIGURATION ................................................................................21
SIP CONFIGURATION....................................................................................22
DIGIT MANIPULATION ....................................................................................23
Chapter 4 Call Flow Editor.........................................................................27
CONFIGURATION MANAGER...........................................................................39
APPLY CHANGE ............................................................................................42
Chapter 5 Peer to Peer Mode Configuration............................................43
ENVIRONMENT USED IN THIS CHAPTER............................................................43
NETWORK CONFIGURATION...........................................................................43
ACCOUNT MANAGER.....................................................................................43
INTERFACE CONFIGURATION..........................................................................43
H.323 CONFIGURATION ................................................................................44
SIP CONFIGURATION....................................................................................44
ADDRESS BOOK ...........................................................................................45
DIGIT MANIPULATION ....................................................................................46
CALL FLOW EDITOR......................................................................................46
CONFIGURATION MANAGER...........................................................................47
APPLY CHANGE ............................................................................................48
Chapter 6 SIP to H.323 Mode Configuration.............................................49
ENVIRONMENT USED IN THIS CHAPTER............................................................49
NETWORK CONFIGURATION...........................................................................49
ACCOUNT MANAGER.....................................................................................49
INTERFACE CONFIGURATION..........................................................................49
H.323 CONFIGURATION ................................................................................49
SIP CONFIGURATION....................................................................................49
ADDRESS BOOK ...........................................................................................50
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 1 -
Page 3

DIGIT MANIPULATION ....................................................................................50
CALL FLOW EDITOR......................................................................................50
CONFIGURATION MANAGER...........................................................................50
APPLY CHANGE ............................................................................................51
Chapter 7 Advance Configuration Reference..........................................52
CONFIGURATION...........................................................................................52
System Configuration.............................................................................52
Interface Configuration...........................................................................53
Dial Plan Configuration...........................................................................55
T1/E1 Trunk Configuration......................................................................55
Rest Configuration..................................................................................59
H.323 Configuration...............................................................................59
SIP Configuration...................................................................................62
Access Control.......................................................................................68
Number Replace....................................................................................71
Routing Plan...........................................................................................71
Radius Setting........................................................................................73
Apply Change.........................................................................................75
Chapter 8 System Control.........................................................................76
SYSTEM.......................................................................................................76
SYSTEM TIME...............................................................................................76
NETWORK....................................................................................................78
SNMP........................................................................................................78
PROMPT MANAGER ......................................................................................79
CALL FLOW EDITOR......................................................................................85
ACCOUNT MANAGER.....................................................................................85
UPGRADE ....................................................................................................85
RELOGIN .....................................................................................................86
Chapter 9 System Monitor........................................................................87
LINE SUMMARY STATUS ................................................................................87
LINE DETAIL.................................................................................................88
EVENT LOG..................................................................................................88
DEBUG INFO ................................................................................................90
PING ...........................................................................................................90
Chapter 10 Telnet & RS-232 Configuration...............................................91
LOGON VIP-2100 BY TELNET........................................................................91
Chapter 11 LCD Display Configuration.....................................................97
Appendix 1 Call Flow Example................................................................100
ONE STAGE DIALING (GATEKEEPER MODE)..................................................100
ONE STAGE DIALING (SIP PROXY MODE).....................................................102
ONE STAGE DIALING (PEER TO PEER MODE)................................................104
TWO STAGE DIALING (VOIP, PSTN MIXED CALL)..........................................106
TWO STAGE DIALING WITH AAA (IP SIDE AAA)............................................109
Appendix 2 Java plug-in Installation......................................................113
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 2 -
Page 4

Appendix 4 Interface LED Description..................................................116
Appendix 5 Build-in Voice Prompt Index................................................117
Appendix 6 Timezone to Country Mapping List......................................118
Appendix 7 IP Bandwidth Requirement...................................................120
Appendix 8 Release Complete Cause Code............................................121
Appendix 9 RADIUS Format Attributes....................................................124
Appendix 10 Quick Start Check List.......................................................128
VIP-2100 FAQ.............................................................................................132
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 3 -
Page 5

VIP-2100 User’s manual - 4 -
Page 6

Chapter 1 VIP-2100 Introduction
System Description
VIP-2100 is a cost effective solution for VoIP trunk gateway supporting one-,
port T1/E1 VoIP trunks that provides voice and fax over IP network. It
supports ITU-T H.323 V3, SIP RFC 2543/3261, SNMP V2, Call Detail Record,
WEB management and other useful functions to meet customer requirements.
The built-in enhanced IVR (Interactive Voice Response) and Billing Service
of VIP-2100 is suitable for prepaid and postpaid service. It can rapidly provide
value added service for customers.
VIP-2100 Features:
- Dual SIP/H.323 co-existing
- ITU-T H.323 v3 and H.450 compliance
- SIP RFC 2543/3261 standard compliance
- PSTN signaling: ISDN/PRI, CAS (MFC R2, MFC R1, E&M), QSIQ
- Mixed SIP, Gatekeeper and P2P calls
- Support H.323 Gatekeeper register, direct and route calls
- Support SIP outbound proxy, redirect and register server
- Redundant SIP Proxy/Outbounbd Proxy Server Support (Outbond
Active/Active fail over, Register A/A no fail over)
- Support SIP Overload Redirect
- SIP supplemental service - on Hold, Call Transfer (Transferred)
- Built-in phone book and prefix routing for SIP and H.323 P2P calls
- Support H.323 fast connect, early H.245 and H.245 tunneling
- Support H.323 and SIP early media
- VoIP to VoIP calls support – SIP to H.323, SIP to SIP, H.323 to H.323
- Global Trunk-Channel Block out: 0xffffffff (busy block out)
- Intelligent PSTN call routing and in-trunk hunting: reverse rotary, channel
mask (default:0xffffffff), ANI prefix match
- Reset a channel/trunk on the fly
- Flexible digit manipulation plan
- Support RADIUS Authentication, Authorization and Accounting
- Support access control by ANI, DNIS, IP, Gatekeeper only, proxy only or
RADIUS
- SIP UDP/TCP support
- Behind NAT friendly for SIP calls
- Inbound and out of band DTMF transmission
- SIP/H.323 T.38 fax relay up to 14400 bps
- Dynamic call treatment based on DNIS, ANI or collected DTMF
- Grouping DNIS/ANI Number Replacement
- Built-in IVR & call-flow controller for PSTN / VoIP side
- CISCO compatible
- Web-based graphic announcement edit and management
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 1 -
Page 7

- Multiple configuration saving
- Provides CDR (Call Detail Record)
- Built-in internal user authentication for prepaid & postpaid users
Technical Specification
Interface
- Two 10/100MB Ethernet Ports (Host & VoIP stream)
- 1 xT1/E1 (120 Ohm-RJ48C connectors)
75 Ohm needs external 3rd party BNC/RJ-48C adapter cables
Protocol and Standard
- ITUT H.323 v3 and H.450 compliance
- SIP RFC 2543/3261 compliance
Audio Feature
- Codec -- G.711 A/μ-Law, G.723.1 (5.3K/6.3K), G.729A, G.729
- Support G.168 echo cancellation
- Configurable audio payload size & adaptive jitter buffer
- Support silent suppression for G.729A, G.723, G.729
- VAD (Voice Activity Detection)
- CNG (Comfort Noise Generation)
DTMF Transmission
- Transparent
- H.245 signal/alphanumeric
- H.323 Q.931
- RFC 2833
- SIP INFO
FAX Support
- Automatic voice/fax detection
- T.38 fax relay based on H.323 Annex D
- SIP T.38 fax relay
- Up to G3 fax
- ECM support
- Redundant T.38 packet (0-2)
- CISCO compatible
Built-in IVR & call-flow controller
- Web-based GUI Drag and Drop interface
- Full control of call behavior (one-stage or two-stage dialing)
- IVR functions
- Support time duration play back (Chinese & English)
- Power call information branch
- Collected information validation
- Active disconnect & reconnect without hang up
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 2 -
Page 8

- Selected disconnect cause code & behavior
Management Feature
- OS and program upgradeable
- Console port: RS-232 port
- TELNET
- Full Web management interface & real time monitor
- Front panel LCD
- SNMP v2 (H.341) and SNTP v4 support
- User account management
- Time zone and day light saving support
- Support fixed IP and DHCP
- Support DNS and dynamic DNS
LED indicators for system status
- Power/Storage access indicators
lines
- Front panel LCD (2
x 16) status display
Power
- 90~240V auto switch
Environmental
- Operation temp: 0° C to 60° C
- Relative humidity: 5% to 95%
Dimension
- 483mm (L) x 450 mm (W) x 44mm(H)
Certification
- CE, FCC, EMI
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 3 -
Page 9
10/100MB Ethernet ports *2 (host &
VIP-2100 Detail Specifications
Feature VIP-2100
Physical Dimension
1 Width
2 Height
3 Depth
4 Industrial rack mount
5 Color
6 Weight
Power / Environmental
1 Power
2 Operating temperature
3 Relative humidity
Processors & Storage
1 DSP vendor
2 Operation System
3 RAM
4 Program/Data Storage
5 OS Upgradeable
7 Program Upgradeable
Front Panel Display
1 LED status
2 LCD status
LAN Interface
483mm
44mm
450mm
Yes
Black
8Kg
90-240V auto switch
0~60 C
5%~95%
Intel Pentium, AudioCodes DSP
XP Embedded
512 MB
256 MB DOM
Yes
Yes
Power/DOM/System
Yes
1 10/100 Base Ethernet
2 IP Address Required
PSTN Interface
Customizable E1/T1 CAS
1
E1 CAS DTMF
2
E1 CAS R2 MF
3
E1 ISDN PRI Support
4
5 E1/T1 Interface Selectable
PCM law Support
6
RTP)
Yes
Loop Start FXO Hot-Line
Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile,
China, Czech-Republic, Egypt,
India, Indonesia, Israel, ITU, Korea,
Malaysia, Mexico, Philippines,
Thailand, Uruguay, Venezuela,
RomTelcom
Euro, Australia, Hong Kong, Korea,
New Zealand, QSIC
Alaw/Mulaw selectable
2
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 4 -
Page 10
E&M Bell Core Feature Group D,
Wink Start, E&M Delay Start, E&M
Feature Group A Immediate Start,
E&M Feature Group B Wink Start,
E&M Feature Group D Wink
T1 CAS DTMF/R1MF
Start(ANI B4 ADDR), E&M Feature
Group D Wink Start, E&M
Immediate Start, E&M Wink Start,
GroundStart FXO, GroundStart
FXS, Loop Start FXO, Loop Start
7
FXS, Loop Start FXO Hot-Line
NI2 ISDN,5ESS 10 ISDN,DMS100
T1 ISDN PRI Support
8
Trunk Spans
9
Default Trunk Channel Mask
10
PSTN Line Hunting
11
PSTN Line Hunting Channel Selection
12
On the Fly Reset Channel/Trunk
13
ISDN, NTT ISDN (INS-1500), Hong
Kong, QSIC
1 (T1/E1s) per chassis
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Audio Codec Support
1 G.711 A-law
2 G.711 u-law
3 G.723.1
4 G.729A
5 Selectable Payload Size - G.711
6 Selectable Payload Size - G.723
7 Selectable Payload Size - G.729
Yes
Yes
Yes (5.3/6.3K)
Yes
20, 40, 60 ms
30, 60, 90 ms
20, 40, 60 ms
Fax Transmission
1 Bypass mode
2 CISCO Compatible
3 ECM Support
4 FAX auto-detection
5 H.323 Annex D Support
6 SIP- T.38 Reinvite
7 T.38 During fast connect
8 T.38 Redundant Packet
9 Transparent mode
10 Up to G3 FAX
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
0-2
Yes
Yes (up to 14400 bps)
DTMF Transmission
1 RFC 2833
2 H.245 Alphanumeric mode
3 H.245 Signal mode
Yes
Yes
Yes
4 Q.931 UUI Yes
5 SIP INFO Yes
6 Transparent mode Yes
Voice Quality & Echo Cancellation
1 Adaptive Jitter Buffer
2 CNG
Yes
Yes
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 5 -
Page 11
3 G.168 (Echo Cancellation)
4
Gain Control Yes
5 Improved Echo Tail Suppression
6 Silence Suppression
VAD
7
Maintenance
1 Administrative Log
2 Auto Daylight Saving
3 Customizable Time Zone
4 Front Panel LCD Setup
5 FTP Server
6 HTTP server
7 HTTP SSL support
8 Multiple configuration
9 NTP time synchronization
10 Password Security
11 RS232
12 System Event Log
13 Telnet
14 Time Zone Support
15 User Account Manager
16 Web-based GUI
17 Web-based Real Time Monitor
18 Web-based Voice File Management
Network Management
1 DHCP
2 Fixed IP
3 DNS
4 Dynamic DNS
5 Ping
6 TOS field setting
7 SNMP V2 MIB I & II
8 SNMP get command
9 SNMP set command
10 SNMP Trap
11 H.341 MIB Support
12 SysLog Support
H.323 Protocol Support
1 H.323 V3
2 H.323 ID
3 E.164 ID
4 Fast Connect
5 H.450
6 H.245 Tunneling
7 Early H.245
8 Cause Code Mapping
Yes (32ms)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes (SNTP V4)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes (RTP only)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes (selectable for
incoming/outgoing)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 6 -
Page 12
SIP Protocol Support
1 Cause Code Mapping
2 HTTP Digest Authentication
3 SIP Call on Hold
4 SIP Early Media
5 SIP Overload Redirect
6 SIP Transfer (unattend)
7 SIP Transfer (attend)
8 SIP/TCP
9 SIP/UDP
10 SIP-180/SDP
11 SIP-183/SDP
12 SIP-PRACK
13 SIP-RFC 3261
14 SIP-RFC 3264 (Offer/Answer)
H.323 Gatekeeper Support
1 Gatekeeper Register
2 Direct call
3 Routed call
4 Light weight RRQ
5 IRQ: IRR sequence
6 Gatekeeper Call only
SIP Proxy Sever Support
1 SIP Outbound Proxy Support
2 SIP Redirect Server Support
3 SIP Registar Server Support
4 Redundant SIP Proxy Server
5 Auto Fail Over
Dial Plan
1 P2P H.323/SIP Call
2 GK Call
3 SIP Call
4 PSTN Call
5 Mixed SIP, P2P, GK call
6 Build-in Phone Book
7 P2P Prefix Routing
8 Digits Manipulation
9 ISDN Dial Plan by Prefix
Call Type Support
1 Call Decision
2 H.323 to H.323 Call
3 H.323 to H.323 Fax Realy
4 H.323 to PSTN Call
5 H.323 to SIP Call
6 H.323 to SIP FAX Relay
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes (Source & Destination)
Dynamic Decided by Call Flow
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 7 -
Page 13
stage dialing), IVR functions,
7 H.323 to SIP FAX Relay
7 PSTN to H.323 Call
8 PSTN to PSTN Call
9 PSTN to SIP Call
10 SIP to H.323 Call
11 SIP to PSTN Call
12 SIP to SIP Call
13 SIP to SIP Fax Relay
14 VoIP to VoIP RTP unRouted
15 VoIP to VoIP RTP Routed
Enhance Service
1 ANI Access List
2 DNIS Access List
3 DID/DOD
4 PSTN Two Stage Dialing
5 VoIP Two Stage Dialing
6 Intelligent PSTN Call Routing
7 In-trunk hunting method
8 Ring Back Tone Generation
9 Call Progress Tone Support
10 Web-based Call Flow GUI
11 Play Credit Time Duration
12 Play Credit Balance
13 Almost-time-expired notify tone
14 IVR for PSTN
15 IVR for SIP
16 IVR for H.323
17 IP Access List
18 ANI Replacement
19 DNSI Replacement
AAA
1 Call detail record (CDR)
2 RADIUS Authentication
2 RADIUS Authorization
3 RADIUS Accounting
4 Redundant RADIUS Server Support
5 PSTN Prepaid Support
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes (Random, Round Robin,
Priority)
Cyclic, random, rotary, reverse
cyclic, reverse rotary
Yes (per trunk enable/disable)
Yes
Drag and Drop interface, Full
control of call behavior (one-stage
or twoSupport time duration play back
(Chinese & English), Power call
information branch, Collected
information validation, Active
disconnect & reconnect without
hang up, Selected disconnect
cause code & behavior
Yes (Chinese & English)
Yes (Chinese & English)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes, Active/Standby/Auto Failover
Yes
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 8 -
Page 14
6 VoIP Prepaid Support
Embedded AAA
1 Embedded Prepaid Service
2 Embedded Postpaid Service
3 Point/second Calculation
4 Second/point calculation
5 Auto Disable/Clean User
6 PSTN Prepaid Support
7 VoIP Prepaid Support
System Limitation
1 Max DM
2 Max IP ACL
3 Max DNIS ACL
4 Max ANI ACL
5 Max User ACL
6 Max Phone Book Entries
7 Max Call Flow Component
8 Max CDR Keep Days
9 Max Voice File Storage
Manual
1 English User Guide
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
4096
2048
4096
4096
20000
10000
256
5
10 hours
Yes
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 9 -
Page 15

1
2
3 4 5 7 6
10
1
2 3 7 4 5 8 6
VIP-2100 Appearance Description
VIP-2100 Front Panel:
Functions:
1: Power LED
2: Network1 Interface LED
3: Network2 Interface LED (not used)
4: H/D LCD
5: Power Switch
6: System Status LED
7: LCD Panel
8: LCD Touch Panel
VIP-2100 Rear Panel:
Functions:
1: Electric Fan
2: AC Power outlet
3: AC Power switch (Keep on)
4: Trunk E1/T1 port
5: VoIP Ethernet port
6: Keyboard/Mouse
7: Com1 port
8: Ethernet port
9: VGA
10: print port (not available)
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 10 -
8
9
Page 16

Chapter 2 Logon VIP-2100
After connected E1/T1 & Ethernet cables into the VIP-2100, turned on
the power. The first step is to logon the system and set up the IP address.
Before you can use the Browser to setup VIP-2100, you need to have
Java Standard Runtime (1_4_1_02) to make it work. Please refer to
Appendix 2 Java plug-in Install for detail.
Logon VIP-2100
Setp1: Start IE5.0 (or later version) to navigate VIP-2100 Management
System by typing the default IP address (the default URL is
http://192.168.111.111:10087). The screen will display User ID and
Password as figure 2.1-1.
Figure 2.1-1
☻Note: The default network IP address is 192.168.111.111 and subnet
mask is
255.255.0.0
Step 2: Enter log user name and password (the default user id is root and
user password is root). You can manage your user account via web
(refer to Section “Account Manager”) later.
Figure 2.1-2
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 11 -
Page 17

Step 3: The screen shows the Home Page of VIP-2100 as figure 2.1-3.
Figure 2.1-3
Network Configuration
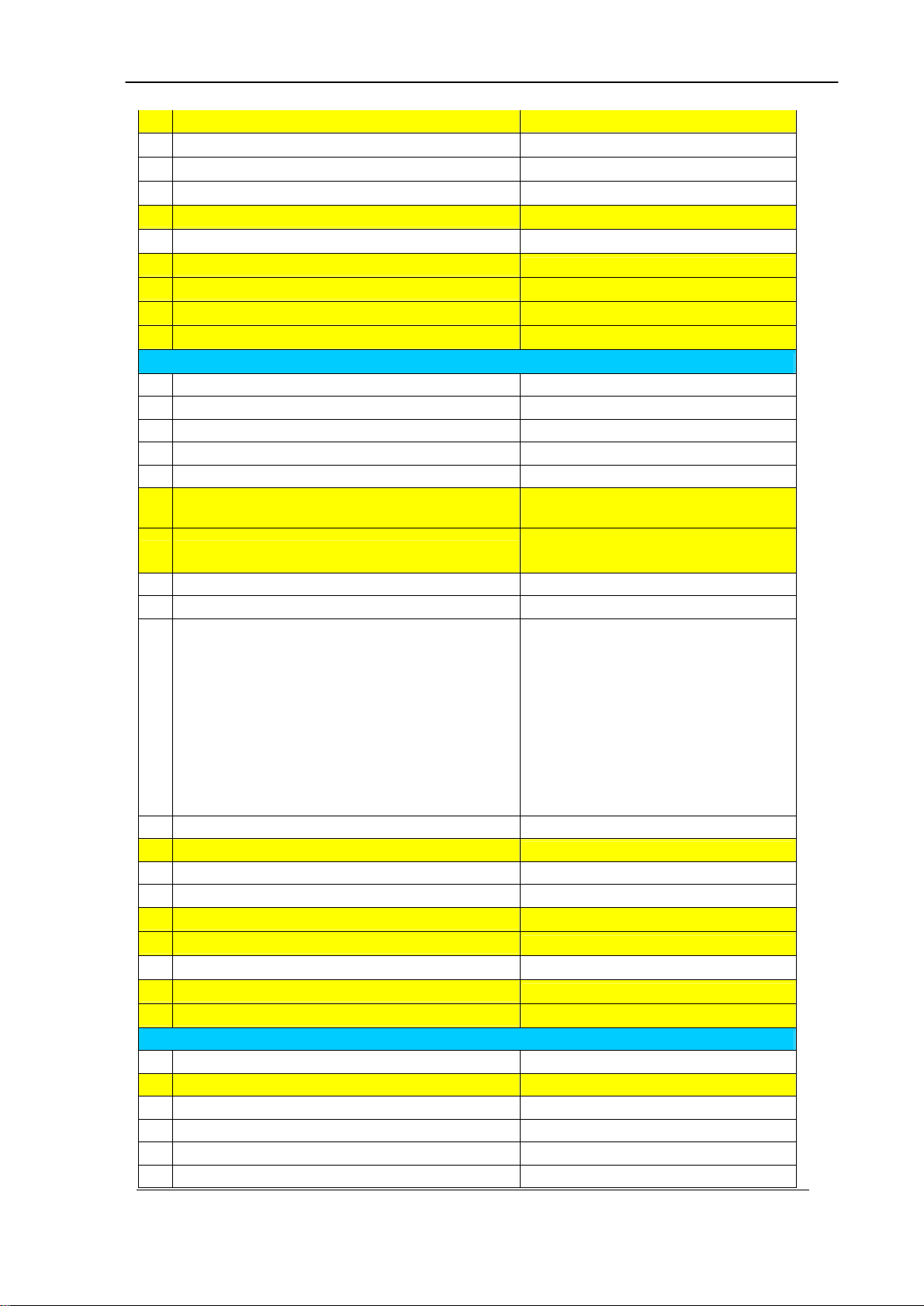
Step 1: After successfully logon to the system, we need to change the
network configuration. Click Control→Network to setup the network
parameters as figure 2.2-1.
Figure 2.2-1
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 12 -
Page 18
Step 2: Enter the deserved IP address, Submask and default gateway. Apply
the change by clicking apply button as figure 2.2-2.
Figure 2.2-2
Step 3: When screen shows “Setup network configuration successfully!”
It means the IP Network setting is successfully changed as figure 2.2-
3.
Figure 2.2-3
☻Note: “Network Control” takes around 5-second to apply the new
network configuration. Please logon again with new IP address
after 5 seconds.
System Time Configuration
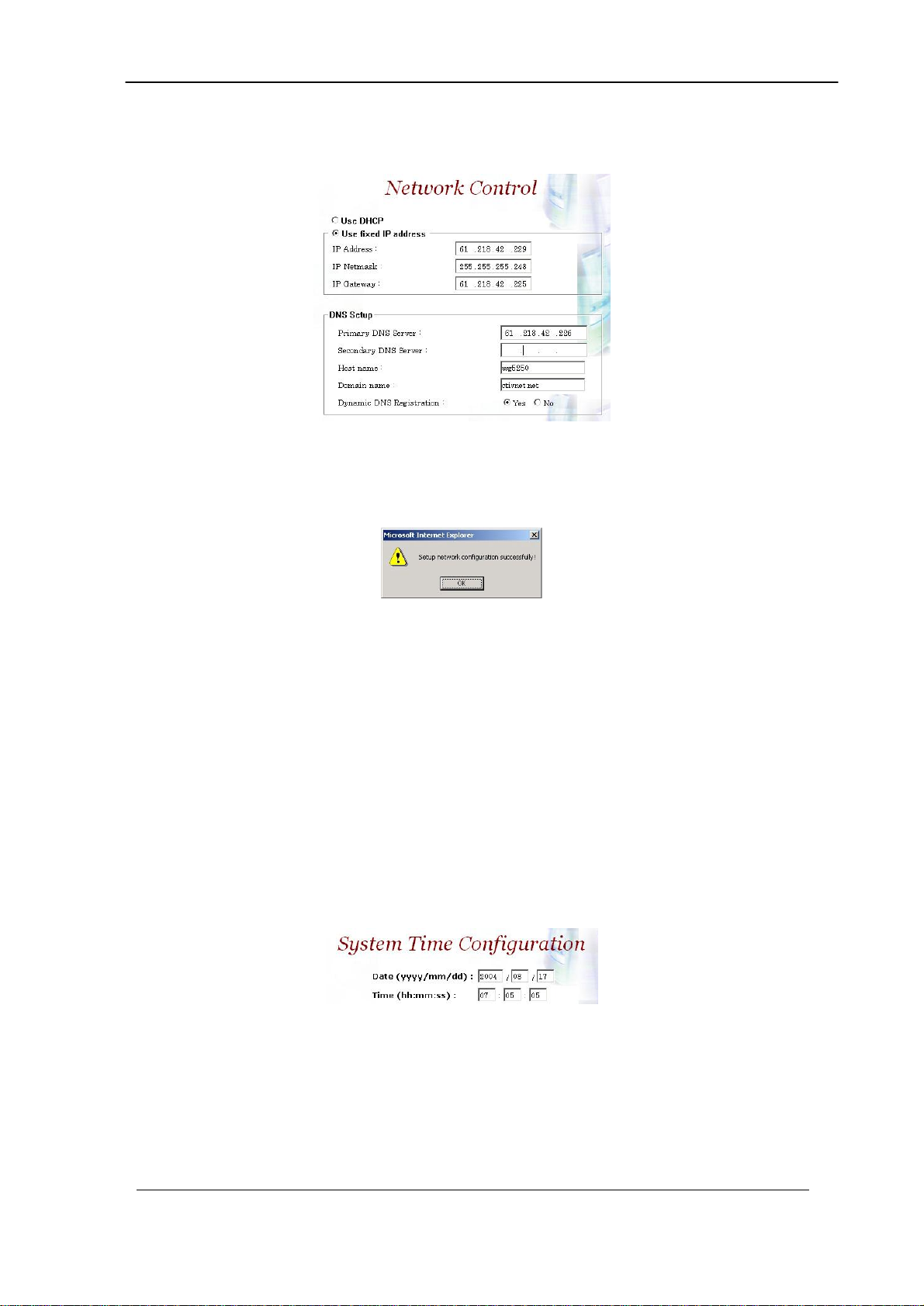
Step 1: When re-logon to the new IP address; the next is to setup the system
time zone. Click Control→System Time Zone to setup the system
as figure 2.3-1.
Figure 2.3-1
Step 2: After apply the new time zone, click Back to adjust the date and time
as figure 2.3-2.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 13 -
Page 19

Figure 2.3-2
Step 3: Enter current date and time. Apply the change by clicking Apply
button as figure 2.3-3.
Figure 2.3-3
Step 4: The screen will shows “Setup system time successfully!” It means
the System Time setting is successfully changed as figure 2.3-4.
Figure 2.3-4
Step 5: If you would like to use SNTP to sync time with a SNTP V4 Server,
click Time Sync button to setup it as figure 2.3-5.
Figure 2.3-5
Account Manager
Step 1: You can manage your user account by click Control→Account
Manager. Add a new user account, Click New button as figure 2.4-1.
Figure 2.4-1
Step 2: Enter the new user ID, password, user role and description, as you
need. Apply the change as figure 2.4-2.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 14 -
Page 20

Figure 2.4-2
Field Description:
• User ID: Login User ID
• Password: Login Password
• Confirm Password: Confirm new password again
Step 3: When screen shows “Create user account successfully!” It means
user account setting is successfully created as figure 2.4-3
Figure 2.4-3
☻Note: The system provides 2 USER ID by default:
User 1: “root” Password: “root”
User 2: “admin” Password: “admin”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 15 -
Page 21

Relogin
Step 1: Click Control→Relogin to relogon by another user account as figure
2.5-1.
Figure 2.5-1
Step 2: Enter new User ID and Password to relogon the VIP-2100 as figure
2.5-2.
Figure 2.5-2
Step 3: The screen shows the Home Page of VIP-2100 as figure 2-5-3.
Figure 2.5-3
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 16 -
Page 22
H.323 GK
and
SIP Proxy Mode
H323 VoIP
SIP VoIP
work
H323
Phone
SIP
Phone
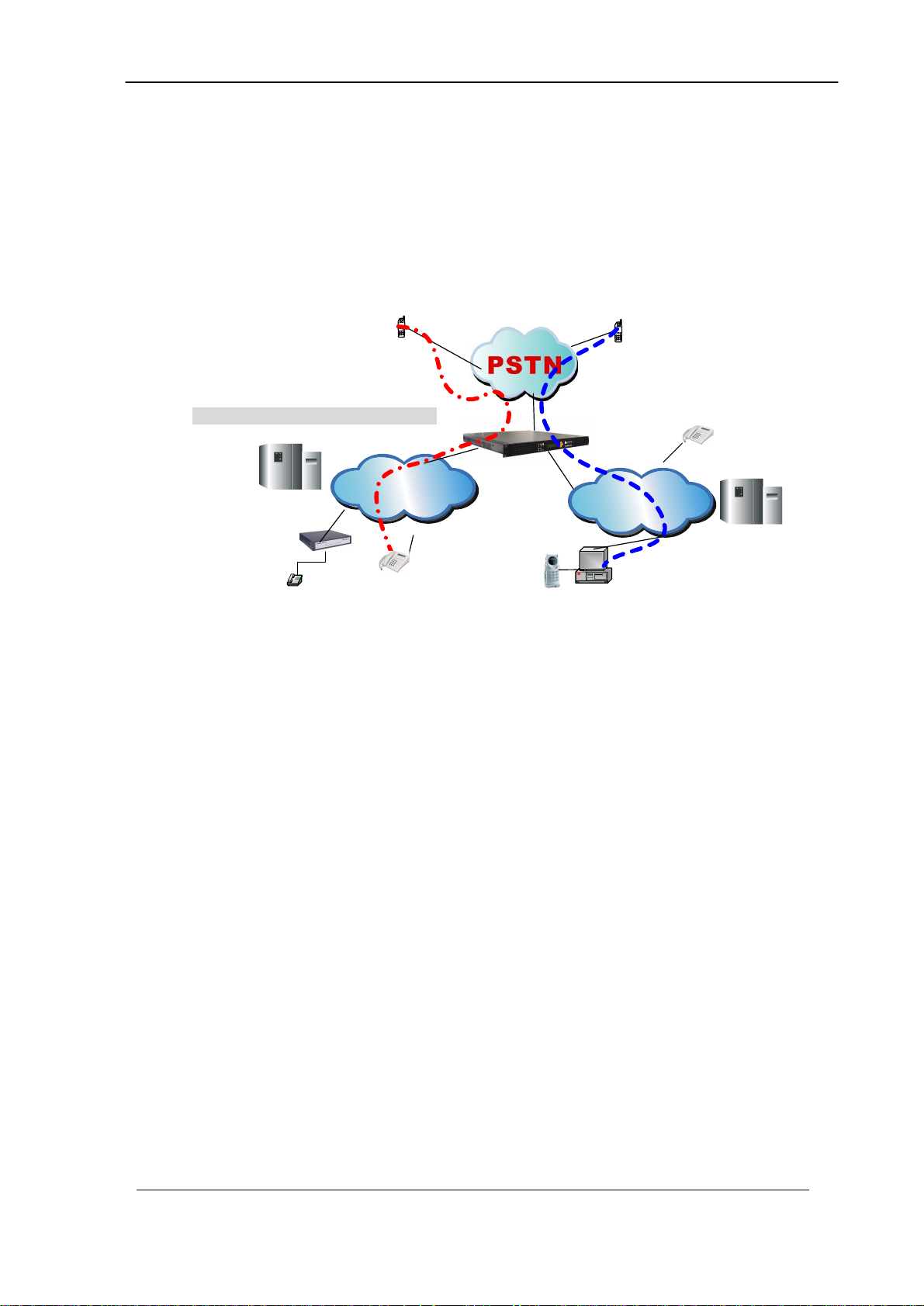
Chapter 3 H.323 Gatekeeper and SIP Proxy
Mode Configuration
Environment used in this chapter
Process:
PSTN → H.323 Call: DNIS (1001) → Make H.323 - Gatekeeper Call (1001)
→ SIP Call: DNIS (8888) → Make SIP – SIP Proxy Call (8888)
H.323 → DNIS (5932111222) → DM (H.323_in_drop) → Make Call
(0932111222)
SIP → DNIS (11382265699) → DM (SIP_in_drop) → Make Call
(82265699)
Gatekeeper
H.323
Gateway
Phone 1001
Network
Net
Proxy Server
SIP USB Phone 8888
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 17 -
Page 23

Interface Configuration
This section is going to setup the VoIP interface.
Step 1: Now we are going to setup the VoIP interface, click Configuration→
Interface to setup VoIP T1/E1 interface as figure 3.1-1.
Figure 3.1-1
Step 2: Double-click the installed interface (i.e Interface ID:0) to config it as
figure 3.1-2.
Figure 3.1-2
Step 3: Modify the VoIP Interface parameters (i.e. IP Address, Protocol Tag,
Subnet Mask and Default gateway) and apply the change by clicking
Apply as figure 3.1-3.
Figure 3.1-3
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 18 -
Page 24

Frequency changed parameters: (Refer to section “Interface
Configuration” for more detail)
• IP Address: 192.168.19.174
• Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
• Default Gateway: 192.168.19.254
• PCM Type: A-law or Mulaw
☻Caution: Subnet Mask does not support Supernet.
Step 4: After successfully to change the Interface configuration, the screen
come back the page of Interface Configuration as figure 3.1-4.
Figure 3.1-4
T1/E1 Trunk Configuration
This section is going to setup the PSTN trunk parameters.
Step 1: Select the installed interface to modify the trunk parameter by click
Detail button as figure 3.2-1.
Figure 3.2-1
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 19 -
Page 25

Step 2: Select the trunk to be modified, and click Modify button as figure 3.2-
2.
Figure 3.2-2
Step 3: Modify the trunk parameters (i.e. Trunk Type, Termin Side, Trunk
Mode, Protocol Tag, Line Code) and apply the change by clicking
Apply as figure 3.2-3.
Figure 3.2-3
Frequency Changed Parameters:
• Trunk Type: E1 or T1
• Termin Type: User Side or Network Side
• Trunk Mode: Normal
• Protocol Tag: ISDN protocol used
• Line Code: T1 or E1 line code used
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 20 -
Page 26

Step 4: After modifications are made to the Trunk Configuration, the screen
comes back the page of Trunk Configuration as figure 3.2-4.
Figure 3.2-4
H.323 Configuration
This section is going setup the H.323 parameter. If you only need SIP
calls, you can skip it.
Step 1: Click Configuration→H.323 to setup the H.323 parameters for
Gatekeeper related information as figure 3.3-1.
Figure 3.3-1
Frequency used parameters:
• Register to Gatekeeper: Yes
• Gatekeeper IP: 192.168.5.1
• E.164 Tel: 113
• Register H.323 ID: 113
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 21 -
Page 27

Step 3: You can see the screen display the new configuration of the H.323
Configuration as figure 3.3-3.
Figure 3.3-3
SIP Configuration
This section is going setup the SIP parameter. If you only need H.323
calls, you can skip it.
Step 1: Click Configuration→SIP to setup the SIP parameters for SIP Proxy
Server related information as figure.3.4-1.
Figure 3.4-1
Frequency used parameters:
• SIP Register: Yes
• Primary Registar Server: 192.168.19.150
• Primary Registar Port: 5060
• Primary Registar User: 173
• Primary Registar Password: 173
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 22 -
Page 28

• Primary Outbound Proxy Server: 192.168.19.150
• Primary Outbound Proxy Port: 5060
• Primary Outbound Proxy User: 173
• Primary Outbound Password: 173
Step 3: You can see the screen display the new configuration of the SIP
Configuration as figure 3.4-2.
Figure 3.4-2
Digit Manipulation
The purpose of “Digit Manipulation” is to add or drop dialed digits for
PSTN or IP side (Interface configuration for PSTN side & H.323 Configuration
for IP side) at the selected interface in order to meet local PSTN dialing
requirement. It can also be used in Call Flow Edit for flexible usage.
Step 1: We introduced the group and interface dependent digital manipulation
to meet the customer’s requires. Click Digit Manipulation to add a
new Digit Manipulation Group, add as figure 3.5-1.
Figure 3.5-1
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 23 -
Page 29

Step 2: Enter the related parameters and click Apply button as figure 3.5-2.
Figure 3.5-2
Field Description:
• Group ID: 0 (DM Group identify)
• Description: H.323: H323 In Drop
SIP: SIP In Drop
Step 3: Click the New created DM and Detail button to add digits setting as
figure 3.5-3.
Figure 3.5-3
Step 4: Click New button to add a new DM rule as figure 3.5-4.
Figure 3.5-4
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 24 -
Page 30

Step 5: Create a new H.323 DM Group “1” and DM detail is show as follows:
Figure 3.5-5
H.323 Incoming Call DM Setting:
• Matched Pattern: 5 (pattern to be matched)
• Group ID: 1-H323 In Drop (belong to this DM group)
• Drop: 5 (drop digits)
H.323 incoming call
↓
Dialed number: 582265699
↓
Match the pattern 5
↓
Delete 5 (Drop)
↓
New dialed number becomes 82265699
Step 5: Also create a new SIP DM Group ‘2” and DM detail is show as follows:
Figure 3.5-6
SIP Incoming Call DM Setting:
• Matched Pattern: 113 (pattern to be matched)
• Group ID: 1-SIP In Drop (belong to this DM group)
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 25 -
Page 31

• Drop: 113 (drop digits)
SIP incoming call
↓
Dialed number: 11307688222
↓
Match the pattern 11307
↓
Delete 113 (Drop)
↓
New dialed number becomes 07688222
Step 6: Create a PSTN incoming call DM Group “3” and DM detail is show as
follows:
Figure 3.5-7
PSTN DM Setting:
• Matched Pattern: 0282265699 (pattern to be matched)
• Group ID: PSTN In Drop (belong to this group id)
• Drop: 0282265699 (drop digits)
PSTN incoming call (DNIS mode)
↓
Dialed number: 02822656991001
↓
Match the pattern 0282265699
↓
Delete 0282265699 (Drop)
↓
New dialed number becomes 1001
☻Note: Digit Manipulation have to tapped for PSTN Side (Trunk
Outbound/Inbound DM Group), VoIP Side (VoIP
→
→
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 26 -
Page 32

Outbound/Inbound DM Group) or Call Flow (refer to section “Call
Flow Editor”) to take effect.
Chapter 4 Call Flow Editor
Call Flow Editor is used to control the call behavior including voice
prompt, AAA, DM…etc. It requires Java run time to run.
Step 1: Click Control→Call Flow Editor to create a Call Flow, click
button to activate IVR Tool as figure 4-1
Figure 4-1
Component Description:
• New: Create a new call flow
• Load Call Flow: Load call flow from VIP-2100
• Save: Save a call flow in VIP-2100
• Cut: Cut a component
• Copy: Copy a component
• Paste: Paste a component
• Delete: Delete a component
• Line: Connecting 2 components together
• Select: Select the component at call flow workspace
• Scroll: Scroll the call flow workspace
• Zoom: Zoom in or zoom out the workspace
• View Grid: View or not
• Show Component Table: Show all component table
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 27 -
Page 33

Step 2: Drag and prop the required component icon into the workspace as
figure 4-2.
Figure 4-2
Right click the component to bring up the component propriety to
setup parameter:
• AAA: Send Authorization or Authentication for validation
o Type: AAA type selection
- Authorization: Send RADIUS Authorization packet out
- Authentication: Send RADIUS Authentication packet out
Success To: Success to component
Failed other to: Failed to component
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 28 -
Page 34

o Failed Reason: Return code from RADIUS server
o Line Propriety:
- Invalid Account
- Account In Use
- Zero Balance
- Account Expired
- Over Credit Limit
- Number of Retries Exceeded
- Insufficient Balance
J Note: Detail response attributes, please refer RADIUS Format
Attributes
• Answer: Answer incoming call (PSTN only)
• Branch: Play an announcement and branch into different route
o Voice File: Voice prompt file (“. raw” format) to be playing
o DTMF Length: Number of DTMF to be receiving
o Others: Default flow if not match
o DTMF: DTMF match pattern
o Goto: The next component if matched
o Line Propriety:
-Branch Line: DTMF branch line setting
• CDV: Collected Digit Validation
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 29 -
Page 35

o Check Parameter: Check parameter type (DNIS, ANI….)
o Digit From: Start digit from
o Digit To: End digit to
o Valid To: If the checked variable is success to validate
o Invaried To: If the checked variable is not success to validate
• CIB: Call Information Branch
o Info Type: Information type selection
- ANI: Calling Number
- DNIS: Called Number
- IP: IP Address or network (e.g. 192.168.0.0)
- PSTN: E1/T1 trunk and channel filter, format: interface id-
trunk id- trunk start- trunk stop
- Prefix: The prefix to be match
0-1-17-31:
0: Interface ID (Always 0)
1: Trunk ID: 1
17: Start from B Channel 17
31: Stop from B Channel 31
o Goto: The component to run next
o Call Info Branch Line: ANI, DNIS, IP or PSTN goto setting
• CIV: Call Information Validation, the user need setup the ACL for
DNIS and IP TO take effect
o Info Type: The infor type to be validation
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 30 -
Page 36

-DNIS: Called number
-ANI: Calling number
-IP: In coming IP address
-User: User ID
o Allow To: If it is met the ACL defined
o Disallow To: If it is not met the ACL defined
• CTB: Call Type Branch
o PSTN To: Route for PSTN call
o H.323 To: Route for H.323 call
o SIP To: Route for SIP call
• Cut Rule: Cut a system variable into different parts
o Cut From: Cut start digit from (start from 1)
o Cut To: Cut end digit to
o Assign To: Store the cutted result into
• Disconnect: Disconnect the call
• DM: Digit Manipulation
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 31 -
Page 37

o DM Parameter: Manipulation ANI or DNIS
o DM Group ID: Apply to DM group
• MakeCall: Make Call to PSTN or H.323/SIP site
o Route Mode: Gatekeeper Call or P2P Call or PSTN…etc. (for PSTN
incoming call, please select the Gatekeeper, P2P Call, or SIP Proxy
call TA; for H.323/SIP incoming call, please select the PSTN call)
o Transport Address: When used for “H.323 TA” routing mode, the
format used is “Ipaddr:port” (e.g. 192.168.111.50:1720)
o Active Disconnect: Enable PSTN user can actively disconnect the
call or not
o Active Disconnect Digit: The DTMF digit to be tread as the
disconnect trigger. Only can be used “Active Disconnect” enable
o Active Disconnect To: The next component when active disconnect
is occurred
o Inter Digit Timeout: The max time to in seconds to wait between two
digits.
o RTP Route: Voice RTP routing over VIP-2100 or not, for VoIP to
VoIP call
o Finish To: Successfully connect to remote site
o Failed Other to: The next component when default failed call
o Failed Reason: Failed reason selection
o Failed To: When the failed reason occurred go to
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 32 -
Page 38

o Line Propriety:
-PSTN: PSTN disconnect reason code:
-Normal Call Clear
-User Busy
-No User Response
-No Answer
-Call Reject
- VoIP: VoIP disconnect reason code:
-User Busy
-No Answer
-Unreachable
-Other
• PA: Play Announcement
o Dynamic Play: Dynamic play voice file by combine prefix and
variable as the file name
o Enable: Combine prefix to variable as the voice file to play
-Prefix: Voice file prefix (e.g. prefix: WT, variable: user1 (contact
201, played voice file is “WT201.raw”)
-Variable: Variable to be appending as the voice file name
o Disable: Use filter voice prompt file
-Voice File: Voice prompt file
o Interrupted: Voice can be interrupted or not
• PB: Play Balance for prepaid purpose
o Voice File: Voice prompt file
o Language: Play balance language section
-English
-Chinese.
o Interrupted: Voice can be interrupted or not
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 33 -
Page 39

• PCUI: Prompt and Connect User Information
o Play Type: Dial tone or voice prompt selection
o Voice File: Voice prompt file
o Max DTMF: Maxtor of DTMF to be received.
o Assign To: Result (received DTMF) will be assign to
o End of DTMF: The digit to indicate dial end.
o Interrupted: Voice can be interrupted or not
• PD: Play Duration for prepaid purpose
o Voice File: Leading voice prompt file
o Language: Play duration language section
-English
-Chinese
o Interrupted: Voice can be interrupted or not
☻Note: The RADIUS servers need to be setup to send H.323/SIP
credit time or internal RADIUS must be used.
• PSTN L.H: PSTN Line Hunting
o Success To: If fine an available channel by system setup (call
hunting)
o Failed To: If not fine an available channel by system setup (call
hunting)
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 34 -
Page 40

• Set Data: Assign value to a variable
o Assign To: Assigned variable
o Use SysParam: Use system parameter to replace or not
o Value: ANI, DNIS, User ID or other digits
• Start: Call flow start
o Next Component
• Quit: Disconnect calls
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 35 -
Page 41

Example Call Flow as figure 4-3.
Example Description:
Components Contents
Start
Next Component: 1001
Component ID:
1000
PSTN To: 1011
CTB
H.323 To: 1009
SIP To: 1008
Component ID:
1001
Info Type: ANI
CIB
Component ID:
Prefix: 1 goto: 1010 (H.323 GK call)
Prefix: 8 goto: 1004 (SIP Proxy call)
1011
1011 Route for PSTN call
Route Mode: Gatekeeper
MakeCall
Finish To: 1005
Failed Other To: 1005
Component ID:
1010
Route Mode: SIP Proxy Call
MakeCall
Finish To: 1005
Failed Other To: 1005
Component ID:
1004
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 36 -
Page 42

Next Component: 1006
Disc
Component ID:
1005
Quit
Component: 1006
1001 Route for H.323Gatekeeper call
DM Parameter: DNIS
DM
DM Group ID: H.323 In Drop
Next Component: 1007
Component ID:
1009
Route Mode: PSTN
MakeCall
Finish To: 1005
Failed Other To: 1005
Component ID:
1007
Next Component: 1006
Disc
Component ID:
1005
Quit
Component: 1006
1001 Route for SIP Proxy call
DM Parameter: DNIS
DM
DM Group ID: SIP In Drop
Next Component: 1007
Component: 1008
Route Mode: PSTN
MakeCall
Finish To: 1005
Failed Other To: 1005
Component ID:
1007
Next Component: 1006
Disc
Component ID:
1005
Quit
Component: 1006
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 37 -
Page 43

Example Used Call Flow:
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 38 -
Page 44

to 1009
H.323 in
to 1008
SIP in
Start:1000
CTB:1001
PSTN to:1011
H323 to: 1009
SIP to: 1008
1011
PSTN in
DM: 1009
Call to PSTN
Make Call: 1007
Call to PSTN
Finish to
Failed other to
DM: 1008
Call to PSTN
Disc: 1005
Disconnect
Quit: 1006
Disconnect
1
Make Call: 1010
Make Gatekeeper
call to H.323
Success /Failed to
CIB: 1011
Info Type: DNIS
Prefix: 1 goto: 1010
Prefix: 8 goto: 1004
8
Make Call: 1004
Make SIP Proxy
call to SIP
Success /Failed to
Configuration Manager
Configuration Management provides a way to save and reload the
system configuration for future use.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 39 -
Page 45

Load a Configuration:
Step 1: When you need to load a saved configuration, click a saved
configuration (i.e. 04/26/2004 Loading Test) item to load it back as figure
4.1-1.
Figure 3.7-1
Step 2: When screen shows “Current configuration will lost! Are you sure
to load this configuration?” click on OK button to load he saved
configuration to the working configuration as figure 4.1-1.
Figure 3.8-2
JNote: It is need to restart the system to take effect of the new-loaded
working configuration.
Save the working Configuration:
Step 3: To save the current configuration, select a new created configuration
and click Save button, when screen shows “Description”, please
enter the configuration description (i.e. Billing Test) for the saved
configuration as figure 4.2-2.
Figure 3.8-3
Step 4: You can see the screen display the changes as figure 4.2-4.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 40 -
Page 46

Figure 3.8-4
Backup the working configurations:
Step 5: To backup the running configuration, click on Backup button, to back
up local hard disk. The whole running configuration will be compress
into a zip file (file name: export.zip) and transfer back to local as figure
4.2-2.
Figure 3.8-5
Restore configuration:
Step 6: To restore the backup configuration file, click on Restore button,
when screen shows “Import Configuration file”, select backup file
(i.e. c:\export.zip) click on Import button to restore the configuration to
the working configuration as figure 4.2-2.
Figure 3.8-6
Compact the database file:
Step 7: In order to optimize the system performance, you can optional
compact the database by click Compact button as figure 4.1-2.
Figure 3.8-7
J Note: Please make sure that there is no others person to use database
concurrently.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 41 -
Page 47

Apply Change
When you load a new working configuration, the system must be
restarted to take effect.
Step 1: Click Configuration→Apply Change, the screen show “ The
change you mode need to restart the system for apply please
confirm to restart or do it later.” Click on OK/Cancel to restart the
system or not as figure 4.3-1.
Figure 4.3-1
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 42 -
Page 48

H323 VoIP
Peer to Peer
SIP VoIP
work
H323
Phone
SIP
Phone
Chapter 5 Peer to Peer Mode Configuration
Environment used in this chapter
H.323
Gateway
Phone 1001
Process:
PSTN → H.323 Call: DNIS (822656991001) → DM (PSTN In Drop) →Make
H.323 - Peer to Peer Call (1001)
→ SIP Call: DNIS (822656998888) → DM (PSTN In Drop) →Make
SIP - Peer to Peer Call (8888)
H.323 → DNIS (50932123321) → DM (H.323_in_drop) → Make Call
(0932123321)
SIP → DNIS (1130028610825123) → DM (SIP_in_drop) → Make Call
(0028610825123)
☺Digit Manipulation: Please refer section “Digit Manipulation”
Network
Net
SIP USB Phone 8888
Network Configuration
Please refer to section “Network Configuration”
Account Manager
Please refer to section “Account Manager”
Interface Configuration
Please refer to section “Interface Configuration”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 43 -
Page 49

H.323 Configuration
Step 1: Change Register To Gatekeeper to “No” to enable peer to peer
mode as
figure 5.1-1.
Figure 5.1-1
Frequency used parameters:
• Register to Gatekeeper: No
SIP Configuration
Step 1: Change SIP Register to “No” to enable peer to peer mode as figure
5.2-1.
Figure 5.2-1
Frequency used parameters:
• Primary SIP Register: No
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 44 -
Page 50

Address Book
For making a Peer-to-Peer call, the IP device must has an address
record in the phone book for routing.
Step 1: Click Address Book adds a new address book for the peer to peer
calls, New to add as figure 5.3-1.
Figure 5.3-1
Step 2: Enter the related parameters and click Apply button as figure 5.3-2.
Figure 5.3-2
Field Description:
• Name: H.323 IP Phone or SIP-Cisco
• Tel/Prefix: 1002
• Trans Address:
- H.323 Call: 192.168.5.102 or 192.168.5.102:1720
- SIP Call: sip:8001@192.168.5.61 or sip:8001@192.168.5.61:5060 or
sip:8001@ctivnet.net
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 45 -
Page 51

Step 3: You can see the screen displays the new Address Book as figure 5.3-
3.
Figure 5.3-3
☻Note: You must apply the change to take effect for the change.
Digit Manipulation
Please refer to section “Digit Manipulation”
Call Flow Editor
Please refer to section “Call Flow Editor”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 46 -
Page 52

Call Flow (P2P Mode):
to 1009
H.323 in
Start:1000
CTB:1001
PSTN to:1011
H323 to: 1009
SIP to: 1008
1011
PSTN in
DM: 1009
Call to PSTN
Make Call: 1007
Call to PSTN
Finish to
Failed other to
to 1008
SIP in
DM: 1013
Call to PSTN
DM: 1008
Call to PSTN
Make Call: 1004
Make Peer to Peer
call to SIP
Success /Failed to
Disc: 1005
Disconnect
Quit: 1006
Disconnect
Configuration Manager
Please refer to section “Configuration Manger”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 47 -
Page 53

Apply Change
Please refer to section “Apply Change”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 48 -
Page 54

H323 VoIP
SIP to H.323
SIP VoIP
work
H323
Phone SIP USB
Phone
8888 SIP
Phone
Chapter 6 SIP to H.323 Mode Configuration
Environment used in this chapter
H.323
Gateway
Process:
SIP → H.323 Call: DNIS (8861001) → DM (SIP In Drop) →Make H.323
H.323 → SIP (8868888) → DM (H.323_in_drop) → Make Call (8888)
☺Digit Manipulation: Please refer section “Digit Manipulation”
Network
Net
(1001)
Network Configuration
Please refer to section “Network Configuration”
Account Manager
Please refer to section “Account Manager”
Interface Configuration
Please refer to section “Interface Configuration”
H.323 Configuration
Please refer to section “H323 Configuration”
SIP Configuration
Please refer to section “SIP Configuration”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 49 -
Page 55

Address Book
Please refer to section “Address Book”
Digit Manipulation
Please refer to section “Digit Manipulation”
Call Flow Editor
Please refer to section “Call Flow Editor”
Call Flow (P2P Mode):
Start:1000
1009
H.323 in
Make Call: 1002
Make Peer to Peer
Call to SIP / H323
Finish to
Failed other to
1008
SIP in
CTB:1001
PSTN:1010
H323: 1009
SIP: 1008
Disc: 1003
Disconnect
1010
PSTN in
Make Call: 1010
Make
Gatekeeper
call to H.323
Success to
Quit: 1004
Quit
Configuration Manager
Please refer to section “Configuration Manger”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 50 -
Page 56

Apply Change
Please refer to section “Apply Change”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 51 -
Page 57

Chapter 7 Advance Configuration Reference
Configuration
System Configuration
Start Path: Configuration→System
Figure 7.1-1
Parameter Description:
• CDR Mode: Call detail record generating mode (Refer to “Appendix 3
Retrieve CDR Information” for detail file description)
o File Only: Log CDR into the file only. It can be retrieved by ftp
(directory c:\cd cdr).
o Radius Start/Stop: Log CDR into the file and send RADIUS start/stop
billing message out.
- VoIP: enable VoIP site RADIUS billing message or not.
- PSTN: enable PSTN site RADIUS billing message or not.
o Radius Stop: Log CDR into the file and send RADIUS stop billing
message out.
- VoIP: enable VoIP site RADIUS billing message or not.
- PSTN: enable PSTN site RADIUS billing message or not.
• CDR Keepdays: CDR system keeping days
• Hot Swappable: Hot swappable support (reserved)
• First Digit Timeout: The max to time (in second) waits for receiving the
first digit entered (5~20 sec).
• Inter Digit Timeout: The max to time (in second) waits for the between
two digits (5~20 sec).
• Debug Level:
o Critical: Show critical error messages only
o Warring: Show warring and critical error message only
o Information: Show information, warring and critical message only
o Debug: Show all debug messages
o Full Trace: Show all status and debug messages
☻Note: Please set to “Critical” only, or the whole system performance
will be hitted.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 52 -
Page 58

• Time Expired Notify: Seconds to be notifying caller before
communication expired. This function is used for Pre-Paid calling card
service and must cooperate with RADIUS Server.
• Almost Expired Tone: Communication expired notice tone selection
• Fast Response Timeout: The maximum times to wait for response. It’s
depended on the network speed.
• No Answer Timeout: The maximum the (in second) to wait the remote
party answer (pick up phone)
o Notify Tone#1:
o Notify Tone#2:
• Authentication Mode: Authentication by VIP-2100 or RADIUS
o Internal: Authentication building User ACL
o External: Authentication by RADIUS
o Ext. AAA Failure Opt: Bypass or disconnect incoming calls when
external
• Version: 5.1
Interface Configuration
Start Path: Configuration→Interface
Figure 7.2-1
Basic Parameter Description:
• Interface ID: System parameter
• Card slot: System parameter
• Interface Type: System parameter
• Description: System parameter
• Serial No: System parameter
• License Key: System parameter
• IP Address: IP address used for voice RTP stream
• Subnet Mask: Submask (doesn’t support super class)
• Default Gateway: Default gateway for routing
• PCM Type: PCM type encoding, E1 A-law; T1 u-law
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 53 -
Page 59

Advance Interface Configuration:
Start Path: Configuration→Interface →Advance
Figure 7.2-2
Advance Parameter Description:
• Interface ID: System parameter
• UDP Port Base: UDP port used for RTP stream, each channel needs 3
RTP ports and must be started by a multiple of 10
• IP Precedence: Voice package priority setting
o Routine Precedence
o Priority Precedence
o Immediate Precedence
o Flash Precedence
o Flash Override Precedence
o Critical Precedence
o Internetwork Precedence
o Network Precedence
• IP TOS: Top of Service with the following priority selection
o Normal Service
o Minimize Monetary
o Maximize Reliability
o Maximize Thought
o Minimize Delay
• PCM Idle Pattern: This pattern will be sending on each B channel PCM
time slot when the channel is idle (not connected). The default value
for A-Law is 0xff and for Mu-Law is 0x55. You only change it when
SWITCH need.
• CAS Idle Pattern: When channel is idle, ABCD (CAS) pattern to be
applied CAS signaling bus
• Jitter Min Delay: The minimum delay time of Jitter buffer. The range is 0
to 150ms. Default value is 150ms. Which has better voice quality but
the delay time will be long.
• Jitter Opt Factor: Jitter buffer optimization factor from 0 to 12. The
default value is 7. Set to 0 will have lowest voice delay but have bad
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 54 -
Page 60

voice quality. Set to 12 will have long voice delay but with better voice
quality
• EC Tail Length: Echo Cancellation Length, default value is 25ms
• Silence Compress: Enable silence compress or not
• TDM Bus Clock: TDM Bus clock source
o Internal: derived from internal oscillator
o External: derived from external PSTN E1/T1 clock
Dial Plan Configuration
Dial Plan can be used to assign the ISDN number plan based on prefix
setting.
Start Path: Configuration→Interface→Dial Plan
Figure 7.3-1
Basic Parameter Description:
• Prefix: Called party number prefix
• Src Num Plan: ISDN Source number plan
• Src Num Type: ISDN Source number type
• Dest Num Plan: ISDN destination number plan
• Dest Num Type: ISDN destination number type
• ApplyTo: Trunks apply to
T1/E1 Trunk Configuration
Start Path: Configuration→Interface→Trunk
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 55 -
Page 61

Figure 7.3-1
Basic Parameter Description:
• Interface ID: System parameter
• Trunk ID: System parameter
• Trunk Type: T1or E1 selection
• Description: Description for this trunk ID
• Termin Side: Network site or User Site (normally, you set to “user site”
when connect to switch)
o User Side
o Network Side
• Trunk Mode: Trunk operation mode
o Disable: Disable the trunk
o Normal: Accept PSTN and VoIP calls
o PSTN incoming only: Allow the PSTN incoming calls only
o H.323 incoming only: Allow the H.323 incoming calls only
• Hunting Method: PSTN trunk hunting method for available channel
o Random: Hunt randomly
o Cyclic: Initial hunt (after power-up/reboot) begins with B channel 1;
subsequent hunts begin with position following last successfully
allocated resource
o Rotary: Hunt always begins with B channel 1
o Reverser Rotary: Hunt always begins with B channel 31
o Reverser Cyclic: Initial hunt (after power-up/reboot) begins with B
channel 31, follows next available channel in reverser order
• CAS Variance: CAS counting variance
• Framing Method:
o For T1
- super frame
- 4-frame multi-frame
- 12 frame multi-frame (D4)
- extend super frame without CRC6
- extend super frame with CRC6
- 72-Frame Multi-Frame
o For E1:
- Automatic CRC4 or Double Frame selection
- Double Frame Format
- CRC4 multi-frame
- CRC4 extend multi-frame
• Protocol Tag: supported protocol on T1/E1 interface with PSTN switch
o For T1:
- T1 CAS
- T1 RAW CAS
- T1 NI2 ISDN
- T1 4ESS ISDN
- T1 5ESS 9 ISDN
- T1 5ESS 10 ISDN
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 56 -
Page 62

- T1 DMS100 ISDN
- T1 NTT ISDN: used to connect NTT INS-1500 ISDN standard (Japan
Only)
- T1 HKT ISDN
- T1 QSIG
- T1 EURO ISDN
- T1 DMS100 MERIDIAL ISDN
- T1 NI1 ISDN
o For E1:
- E1 EURO ISDN: used for most of European ISDN standard
- E1 MFCR2
- E1 CAS
- E1 RAW CAS
- E1 AUSTEL ISDN: Australia E1 ISDN Variance
- E1 HKT ISDN: Hong E1 ISDN Kong Variance
- E1 KOR ISDN: Korea E1 ISDN Variance
- QSIO
- E1 TNZ ISDN
• Line Code: T1: you can choose AMI, B8ZS; E1: you can choose AMI,
HDB3
• PSTN Trace: PSTN layer debug trace. It will generate a debug trace file
for tracing purpose. Only enables it under Welltech technical supports
instruction and disable it when complete the debug
• Inbound DM Group: Digit Manipulation group used for incoming calls
associated to this trunk
• Outbound DM Group: Digit Manipulation group used for outgoing calls
• Local Ring Back: Provide ring back tone for PSTN or not. It only works
when VoIP outgoing Fast Start is disabled.
• Channel Mask: Channel mask for incoming or outgoing calls (default:
0xffffffff)
Start from MSB each bit, indicate a time, slot a trunk (e.g. 0x0000ffff:
0~15 B channel mask, 17~31 B channel free)
• Clock Master: PSTN trunk clock source
Advance Trunk Configuration:
Start Path: Configuration→Interface →Trunk →Advance
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 57 -
Page 63

Figure 7.3-2
Advance Parameter Description:
• Interface ID: System parameter
• Trunk ID: System parameter
• Src Num Plan: ISDN source number plan
• Dest Num Plan: ISDN destination number plan
• Src Num Type: ISDN source number type
• Dest Num Type: ISDN destination number type
• Src Num Presen: ISDN source number presentation
• Src Num Screen: ISDN source number display
• Input Gain: Voice Gain from IP to PSTN side (default: 0 db)
• Output Gain: Voice Gain from PSTN to IP side (default: 0 db)
• Q.931 General Opt.: used for Q.931 general behavior.
o 0x0001: No Status message send for unknown facility IE if it is set
o 0x0002: No Status message send for invalid content of a valid
facility IE if it is set
o 0x0080: Send Connect Ack message when receive Connect
message if it is set, you can OR the required option together
• Q.931 Incoming Opt.: used for Q.931 incoming call behavior
o 0x0800: include Channel-ID IE in the first reply message (e.g. Call
Proceeding or Alerting)
o 0x2000: enable the system to include Channel-ID IE in the Call
Proceeding message, you can OR the required option together
• Q.931 Outgoing Opt.: used for Q.931 outgoing behavior
o 0x0010: use Mu-law if this bit is set, or A-law will be used. Apply
only for Korea variance, you can OR the required option together
• Trans Cap: Transfer Capability
o Voice Service
o Data Service
o Modem Service
• CallID Transfer Type: Call ID transfer type
o Disable Caller ID: default parameter
o Transparent Caller ID
o Relay Caller ID
o Bypass Caller ID
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 58 -
Page 64

Rest Configuration
Reset a channel or a trunk idle state.
Start Path: Configuration→Interface→Detail→Reset
Figure 7.4-1
Start Path: Configuration→Interface→Detail→Reset
Figure 7.4-2
Basic Parameter Description:
• Trunk: Reset trunk ID
• Channel: Rest channel selection
- All Channel: Reset all channel
- 0~31: Reset 0~30 logical channel to reset
H.323 Configuration
Start Path: Configuration→H.323
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 59 -
Page 65

Figure 7.5-1
Basic Parameter Description:
• Register To Gatekeeper: Register to Gatekeeper or not
o Yes: Register to GK
o No: Not register to GK
• Gatekeeper IP: Gatekeeper IP Address
• Gatekeeper RAS: UDP Port number listened on Gatekeeper (default:
1719)
• E.164 Tel: Telephone number to be registered to Gatekeeper
• Register H.323 ID: H.323 alias name to be registered to Gatekeeper
• Register Time To Live (sec): The registration maximum time to live
setting when registered to the Gatekeeper
• Response Timeout (Q.931)(sec): The maximum time to wait for
response from sending call setup signal out
• Connect Timeout (Q.931)(sec): The maximum time to wait for
connection (answer) from dialing out the destination number
• DTMF Relay: DTMF transfer type selection
o RTP relay (RFC 2833): DTMF relay via RTP packet (RFC2833
standard)
o DTMF transparent: transmitter DTMF over voice channel
o H.245 Signal input: DTMF relay via H.245 user signal input
o H.245 Alphanumeric: DTMF relay via H.245 Alphanumeric signal
o Q.931 User Information: DTMF relay via Q.931 User to user
information
• Fax Transport: Fax transport type selection
o Transparent mode: Transparent mode (by voice packet)
o T.38 Fax Relay (H.245 mode): T.38 Fax relay (H.323 Annex D)
o T.38 Fax Relay (Propriety mode): T.38 Fax Relay (propriety mode)
o FRF11 Fax Relay (Propriety mode): FRF11 Fax Relay (propriety
mode)
• Fast Connect Mode: Connection of H.323 call fast mode
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 60 -
Page 66

o Disable: Don’t use Fast Start.
o Enable Fast Start Both Site: Use Fast Start for incoming call and
outgoing H.323 calls
o Fast Start-H.323 incoming only: Enable Fast Start for H.323
incoming calls only
o Fast Start-H.323 outgoing only: Enable Fast Start for H.323
outgoing calls only.
o Early H.245: Use Early H.245
• H.245 Tunneling: Transfer the H.245 message over the Q.931 channel
• H.450 Service: Enable the H.450 calls transfer service
• FS Enable 1-6 (Codec Priority 1-6): Enable Fast Start codec selection
for each codec
• Inbound DM Group: Digit Manipulation Group for H.323 incoming calls
• Outbound DM Group: Digit Manipulation Group for H.323 outgoing
calls
Advance H.323 Configuration:
Start Path: Configuration→H.323 →Advance
Figure 7.5-2
Advance Parameter Description:
• RAS Multicast IP: RAS multicast IP for Gatekeeper searching
• RAS Multicast Port: RAS multicast Port for Gatekeeper searching
• Max Call: The maximum H.323 calls
• Max Channel: The maximum channel of each H.323 call
• RAS Port: Local RAS port (default: 1719)
• Q.931 Port: Local TCP port number of Q.931
• T.38 ECM Mode: T.38 Error Correction Mode
o T.38 ECM Interoperable mode
o T.38 ECM Backward Compatible Mode
• FAX Rdepth: T.38 relay redundancy packet depth for high-speed mode.
• H.245 Option: Separate the H.245 channel in the call of the Fast Start
mode or not.
• G.723 Psize: G.723 transmission packet size in ms (default: 30ms)
• G.729 Psize: G.729 transmission packet size in ms (default: 20ms)
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 61 -
Page 67

• G.711 Psize: G.711 transmission packet size in ms (default: 20ms)
SIP Configuration
Start Path: Configuration→SIP
Figure 7.6-1
Basic Parameter Description:
• Primary SIP Register: Register to SIP proxy server or not
o Yes: Register to proxy server
o No: Not register to proxy server
• Primary Register Server: SIP register proxy server IP Address
• Primary Register Port: SIP register proxy server port number (default:
1719)
• Primary Register User: SIP register proxy server User ID
• Primary Register Password: SIP register proxy server User Password
• Primary Register TTL: The registration maximum time to live setting
when registered to the SIP proxy server
• Secondary SIP Register: Register to SIP proxy server or not
o Yes: Register to proxy server
o No: Not register to proxy server
• Secondary Register Server: SIP register proxy server IP Address
• Secondary Register Port: SIP register proxy server port number
(default: 1719)
• Secondary Register User: SIP register proxy server User ID
• Secondary Register Password: SIP register proxy server User
Password
• Secondary Register TTL: The registration maximum time to live setting
when registered to the SIP proxy server
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 62 -
Page 68

• Primary Outbound Proxy Server: The IP address of an outbound Proxy
the SIP Stack uses.
• Primary Outbound Proxy Port: The port of an outbound Proxy the SIP
Stack uses
• Primary Outbound Proxy User: The User ID of an outbound Proxy the
SIP Stack uses.
• Primary Outbound Proxy Password: The password of an outbound
Proxy the SIP Stack uses.
• Secondary Outbound Proxy Server: The IP address of an outbound
Proxy the SIP Stack uses.
• Secondary Outbound Proxy Port: The port of an outbound Proxy the
SIP Stack uses
• Secondary Outbound Proxy User: The User ID of an outbound Proxy
the SIP Stack uses.
• Secondary Outbound Proxy Password: The password of an outbound
Proxy the SIP Stack uses.
• Codec Selection Policy: Selection order to match the remote SDP for
codec selection.
o Local SDP Order: Use local SDP order to match codec
o Remote SDP Order: Use Remote SDP order to match codec
• Local Codec 1~4: Codec selection priority (1 to 4) (1: highest, 4: lowest)
• G.723 Bit Rate Used: G.723.1 high bits rate (6.3k) or low bit rate (5.3k)
is used
• 180 SDP: Set SDP for 180 ring message
• 183 SDP: Set SDP for 183 call progress indication.
• DTMF Relay Method: DTMF transport type selection
o Transparent: transmit DTMF over audio channel
o SIP INFO: Use SIP INFO Message to relay DTMF
o RFC2833: Use RFC2833 for DTMF over RTP packet
- RFC2800 Payload Type: RTP payload type used for RFC2833
DTMF relay
• Fax Transmission: Fax transparent type selection
o T.38 Fax Relay: T.38 fax relay
o Transparent: Transparent mode (by voice packet)
• Accept Proxy Call Only:
o Yes: Only call from outbound proxy server is allowed
o NO: Accept any SIP calls
• Inbound DM Group: Digit Manipulation Group for SIP incoming calls
• Outbound DM Group: Digit Manipulation Group for SIP outgoing calls
Advance SIP Configuration:
Start Path: Configuration→SIP →Advance
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 63 -
Page 69

Figure 7.6-2
Advance Parameter Description:
• TCP Enable: Receive SIP TCP call or not.
• Max TCP Connection: Max Call: The maximum SIP TCP calls.
• Outbound Use TCP: Use SIP TCP for outbound call or not. If it set to
no, UDP is used.
• Register Use TCP: Use SIP/TCP to register to SIP register.
• TCP Port: The local TCP port on which the SIP Stack listens.
• UDP Port: The local UDP port on which the SIP Stack listens.
• Reliable Provision: Support PRACK or not (100rel)
• Max Call Leg: The maximum number of call-legs the SIP Stack
allocates. You should set this value to the maximum number of call
your expect the SIP Stack to handle simultaneously.
• Max Transaction: The maximum number of transactions the SIP Stack
allocates. You should set this value to the maximum number of call
your expect the SIP Stack to handle simultaneously.
• Max Register Client: The maximum number of Register-Clients the SIP
Stack allocates. You should set this value to the maximum number of
call your expect the SIP Stack to handle simultaneously.
• Send Receive Buffer Size: The buffer size used by SIP Stack for
receiving and sending SIP messages.
• Reject Unsupported Extension: Yes or No
• Message Pool Page Size: Used to hold and process all incoming and
outgoing message in the from of encoded messages or message
objects. It is recommended that you configure the page size to the
average message size your system is expected to message.
• General Pool Page Size: Used by SIP Stack objects, such as call-legs
and transaction, to store the internal fields. For example, the call-legs
object will store the To, From and Call-ID headers and the local and the
remote contact addresses on the general pool pages. The general pool
is also used from other activities that demand memory allocation.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 64 -
Page 70

• Application Pool Page Size: The size of page in the application pool
• Retransmission T1: T1 determines several timer as defined in
RFC3261. For example, When an unreliable transport protocol is used,
a Client Invite transaction retransmits requests at an interval that start
at T1 seconds and doubles after every retransmission. A Client General
transaction retransmits requests at an interval that starts at T1 and
doubles until it reaches T2. (Default Value: 500)
• Retransmission T2: Determines the maximum retransmission interval
as defined in RFC3261. For example, when an unreliable transport
protocol is used, general requests are retransmitted at an interval
which starts at T1 and doubles until reaches T2. If a provisional
response is received, retransmission continue but at an interval of T2.
(Default Value: 4000)
• Retransmission T4: T4 represents the amount of time the network
takes to clear message between client and server transactions as
defined in RFC3261. For example, when working with an unreliable
transport protocol, T4 determines the time that UAS waits after
receiving an ACK message and before terminating the transaction.
(Default Value: 5000)
• Invite Linger Timer: After sending an ACK for an INVITE final response,
a client cannot be sure that the server has received the ACK message;
the client should be able to retransmit the ACK upon receiving
retransmissions of the final response for inviteLingerTimer milliseconds.
• General Linger Timer: After a server sends a final response, the server
cannot be sure that the client has received the response message. The
server should be able to retransmit the response upon receiving
retransmissions of the request for generalLingerTimer milliseconds.
(Default Value: 32000)
• Provisional Timer: When a client receives a provisional response, it
continues to retransmit the request, but with an interval of
provisionalTimer milliseconds.
• Cancel General No Response Timer: When sending a CANCEL
request on a General transaction, the User Agent waits
cancelGeneralNoResponseTimer milliseconds before timeout
termination if there is no response for the cancelled transaction.
• Cancel Invite No Response Timer: When sending a CANCEL request
on a Invite transaction, the User Agent waits
cancelInviteNoResponseTimer milliseconds before timeout termination
if there is no response for the cancelled transaction.
• General Request Timeout Timer: After sending a General request, the
User Agent waits for a final response generalRequestTimeoutTimer
milliseconds before timeout termination (in this time the User Agent
retransmits the request every T1, 2*T1,…T2,…milliseconds)
• 183 to Alerting: When receive a SIP 183 message from remote site,
send Alerting in stead of Call Progress Indicator
• AutoSend 183: VIP-2100 always send Call Progress Indicator (SIP 183)
to VoIP party. It can be used for CAS protocol to enable early media.
• Behind NAT: Does VIP-2100 is located behind NAT or not
• Public Signal IP: The static mapped IP for SIP signal
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 65 -
Page 71

• Public Signal Port: The static mapped Port for RTP stream
• Public RTP IP: The static mapped RTP IP
• Public RTP Port: The static mapped RTP starting port
• Public RTP Port Interval: The VIP-2100 has at least 30 RTP channels.
Each channel needs 3 ports mapping on NAT Server. The interval is
used to caculate the right port for each channel.
• Overload Redirect: SIP overload redirect when VIP-2100 is not able for
service the call
• Redirect Host: Redirect host URI (format: user@siphost, siphost)
• Redirect Port: Redirect port number
• Send 487 When Recv CANCEL: When receive CANCEL form remote
site, send “487 Request canceled” or not
• Caller ID Mode:
o Local: use VIP-2100 proxy user id
o Caller: use SIP calling party ANI
• Receive Hold music source:
o Auto: Auto determinate to play hold tone based on SIP signaling.
o Local: Play hold tone locally.
• On Hold music: Hold tone music file name
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 66 -
Page 72

Behind NAT Example 1:
VIP-2100 NAT Server Setting
One-by-One Static
IP Mapping
192.168.111.112 210.59.163.11
Static Port Mapping 192.168.111.111:5060 210.59.163.10:10000
VIP-2100 NAT Enable Setting:
Public Signal IP: 210.59.163.10
Public Signal Port: 10000
Public RTP IP: 210.59.163.11
Public RTP base port: 4000 (same as “Interface→Advance’s Config”)
Public RTP Port Interval: 10
Behind NAT Example 2:
VIP-2100 NAT Server Setting
Static Port Mapping 192.168.111.111:5060 210.59.163.10:5060
RTP Channel 01 192.168.111.112:4000
4001
4002
RTP Channel 02 192.168.111.112:4010
4011
4012
.
.
.
.
.
.
RTP Channel 30 192.168.111.112:4310
4311
4312
210.59.163.10:10000
10001
10002
210.59.163.10:10003
10004
10005
.
.
.
210.59.163.10:10357
10358
10359
VIP-2100 NAT Enable Setting:
Public Signal IP: 210.59.163.10
Public Signal Port: 5060
Public RTP IP: 210.59.163.10
Public RTP base port: 10000 (same as “Interface→Advance’s Config”)
Public RTP Port Interval: 0
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 67 -
Page 73

Access Control
Access Control list can be used to filter the calls forms the IP Network,
DNIS, and ANI. It must be used in call flow edit to take effect.
IP ACL
Start Path: Configuration→Access Control→IP ACL
Figure 7.7-1
Parameters:
• IP Network: IP Address or prefix used to be filtered
• Access Mode:
o Allow: the inputs IP Network are allowed for calls.
o Disallow: The inputs IP Network are disallowed for calls.
☻Note: If in the system has both allowance and disallowance setup, the
system will check allowance first and disallowance later. If only
disallowance inputted all IP will allow to work except disallowed
network. If only allowance inputted, only those IP from
allowance list will work.
ANI ACL
ANI ACL
Start Path: Configuration→Access Control→ANI ACL
Figure 7.7-2
Parameters:
• ANI: Calling party number used to filter
• Access Mode:
o Allow: the calling numbers are allowed for calls
o Disallow: The calling numbers are disallowed for calls
☻Note: If in the system has both allowance and disallowance setup, the
system will check allowance first and disallowance later. If only
disallowance inputted all ANI will allow to work except
disallowed ANI. If only allowance inputted, only those ANI from
allowance list will work.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 68 -
Page 74

DNIS ACL
Start Path: Configuration→Access Control→DNIS ACL
Figure 7.7-3
Parameters:
• DNIS: Called party number used for filter
• Access Mode:
o Allow: The called numbers are allowed for calls
o Disallow: The called numbers are disallowed for calls
☻Note: If in the system has both allowance and disallowance setup, the
system will check allowance first and disallowance later. If only
disallowance inputted all DNIS will allow to work except
disallowed DNIS. If only allowance inputted, only those DNIS
from allowance list will work.
User ACL
User ACL is used to store subscriber information when internal AAA is
enabled.
Start Path: Configuration→Access Control→User ACL
Figure 7.7-4
Parameters:
• User: User ID (0~9, *#)
• Password: Password (0~9, *#)
• Prepaid Point: Allowed prepaid point (When prepaid point is used, the
system will deduct it automatically base on the rate setting.)
o Postpaid: postpaid user
• Status:
o Active: User is activeled
o Inactive: User is inactived
☻Note: 1. IP Authentication method must be set to “ internal AAA” to
talk effect.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 69 -
Page 75

New a Calling Rate: The calling rate will have different appearance for
different calling rate policy set in Radiu configuration.
Click Calling Rate button to add a new calling rate as figure 7.7-5.
Figure 7.7-5
Point per Second calling rate:
Calling rate (point per second) is used to convert prepaid point into
prepaid time in second. For example, you can set calling rate to 5 for “100”
prefix. When a caller, which has 200 prepaid point, calls “100xxxx”, the max
talk time will be 200/5=40 seconds. If a calling rate is set to “0”, it means free
charge.
New a Calling Rate (Second per Point):
Click Calling Rate button to add a new calling rate as figure 7.7-6.
Figure 7.7-6
Second per Point calling rate:
. Calling rate (Second per point) is used to convert prepaid point into
prepaid second in time. For example, you can set calling rate (Second) to 6,
charge point to 1 for “113” prefix. It means that every 6 seconds charge 1
point. When a caller, which has 200 prepaid point, calls “113xxxx”, the max
talk time, will be 200*6/1=1200 seconds.
J Note: Tel prefix * is used as a default rate, you need to create it to
work.
Search Condition:
You can search a user by User ID, Prepaid or Postpaid condition as figure
7.7-7.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 70 -
Page 76

Figure 7.7-7
Number Replace
The purpose of “Number Replace” is to replace called number or
calling number for PSTN or IP. It must be used in call flow to take effect.
Step 1: It is useful for real PSTN number to virtual VoIP number replacement.
Click Number Replace to add a new Number Replace Group, add as
figure 7.8-1.
Figure 7.8-1
Field Description:
• Group ID: 1 (Number Replace Group identify)
• Description: SIP in
Step 2: Click the New created NR and Detail button to add digits setting as
figure 7.8-2.
Figure 7.8-2
Field Description:
• Original Number: Original number filter
• Target Type: ANI or DNIS
• Target Number: The ANI or DNIS are change to target nubmer
Routing Plan
The purpose of Routing Plan is to select T1/E1 trunk and channels by
your preference when there is a call from IP side to PSTN side. The PSTN
must be used in call flow edit or line hunting component to take effect.
Hunting Group
Start Path: Configuration→Routing Plan→Hunting Group
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 71 -
Page 77

Figure 7.9-1
Parameters:
• Group ID: Hunting Group ID
• Description: Description of Hunting Group
• Hunting Method: Route selection
o Random: Random select a trunk within this hunting group
o Priority: Select a trunk by priority. (Priority 1 has lowest priority; 9
has highest priority)
o Round Robin: Call is hunting rotationally
Start Path: Configuration→Routing Plan→Hunting Group→Detail
Figure 7.9-2
Parameters:
Group: 4 Description: FET Trunk 02 and 03
• Interface ID: Interface ID
• Trunk ID: trunk id for group 4
• Priority: Trunk priority
• Channel Mask: Channel mask for incoming or outgoing calls (refer
T1/E1 Trunk Configuration)
J Note: When a Route Plan channels mask is cooperated to trunk
channel mask to decide the channel availity 17~31 channels are
available:
Example 1:
Trunk ID: 0 channel mask: 0xffffffff
Route Plan channel mask: 0x0000ffff
Available channel: 0x0000ffff (17~31) channels.
Example 2:
Trunk ID: 0 channel mask: 0xffff0000
Route Plan channel mask: 0xffc00000
Available channel: 0xffc00000 (1~9) channels.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 72 -
Page 78

Call Routing
The call routing can be used for hunting a PSTN trunk by prefix.
Start Path: Configuration→Routing Plan→Call Routing
Figure 7.9-3
Parameters:
• Group ID: Select the T1/E1 according to the selection of Hunting Group
ID when dialed number is matched
• Number To Route: The dialed telephone number to be matched
• Matched ANI Prefix: Calling party number used to filter
• Allow Use Others: To select other T1/E1 trunk when all trunk are busy
at your desired Hunting Group.
o Allowed: The call will use other T1/E1 trunks which is not belong to
the selected hunting group
o Forbad: The call will be disconnected immediately
Radius Setting
When you have an external RADIUS server to do the AAA
(Authorization, Authentication and Accounting), enter the correct parameter to
the Radius setting. It must be used in call flow to take effect.
Start Path: Configuration→Radius Setting
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 73 -
Page 79

Figure 7.10-1
Parameters:
• Auth IP: Radius Authentication Server IP address (default)
• Auth Port: Radius Authentication Server Port
• Acct IP: Radius Account Server IP address
• Acct Port: Radius Account Server Port
• Backup Auth IP: Backup Radius Authentication Server IP address
• Backup Auth Port: Back Radius Authentication Server Port
• Backup Acct IP: Back Radius Account Server IP address
• Backup Acct Port: Back Radius Account Server Port
• Secret Key: The shared secret key with RADIUS Server
• Max Retry: The maximum retry times
• Response Time (sec): The maximum wait for response time from
RADIUS Server
• Auth Retry Interval (sec): The internal to resend the Authentication
packet to RADIUS Server.
• Acc Retry Interval (sec): The internal to resend the Account packet to
RADIUS Server.
• Switch Threshold: Switch to alternate RADIUS Server when failures are
occurred more than switch threshold.
• Auto Inactive: Auto inactive an unused or not
o Disable: Don’t auto inactive
o Prepaid User: Auto inactive prepaid user only
o Postpaid User: Auto inactive postpaid user only
o All User: Auto inactive all unused user
• Inactive prepaid: The minimum credit point threshold for a prepaid user
to be inactived
• Inactive Period: The max unaccess days for a postpaid user to be
inactived
• Charge Method: Billing charge method selection
o Point per Second: Point / calling rate = seconds
o Second per Point: Point * calling rate / charge point = seconds
• Auto Clean: Auto clean the inactive user
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 74 -
Page 80

o Disable: Don’t auto clean inactive user
o Prepaid User: Auto clean prepaid user only
o Postpaid User: Auto clean postpaid user only
o All User: Auto clean inactive user
• Clean Filter: Auto clean filter
o None: Auto clean users exceed clean period without access the
network
o Inactive: Auto clean only to inactive users
• Clean Period: The maximum unaccess days to clean up. When the
clean filter is set Inactive, the unaccess day is start counting when the
user is inacived
Apply Change
1. Some of modification needs to restart system before it is effective to system
operation. “Apply the change” shows “The change you mode need to
restart the system for apply please confirm to restart or do it later?”
Click on OK button to reboot the system.
Figure 7.11-1
2. For the modification can be changed to fly, “Apply the Change” shows “Are
you sure to apply the running system?” Click on OK button to take
effecting.
Figure 7.11-2
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 75 -
Page 81

Chapter 8 System Control
System
Start path: Click Control→System
Figure 8.1-1
Parameter:
• Soft Reset: Soft Reset at VIP-2100
• Restart: Restart the VIP-2100
• Shutdown: Shutdown the VIP-2100
System Time
Timezone Setting
Step 1: If you would like to use timezone, click Timezone button to setup the
system timezone as figure 8.2-1.
Figure 8.2-1
Stardand:
Step 2: Select the Standard option to setup the system predefined time zone
as figure 8.2-2
Figure 8.2-2
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 76 -
Page 82

Parameter:
• Time Zone:
o Standard: Use a predefined standard time zone (Refer Timezone
to Country Mapping List)
o Customize: Use a user defined time zone
• Auto Daylinght Saving: Auto adjust daylinght saving time or not
User defined timezone :
Step 3: Select the Customized option and enter the time zone bias to set a
user defined timezone as figure 8.2-3
Figure 8.2-3
Parameter:
• Daylight Bias: The offset added to the Bias when the time zone is in
daylight saving time
• Daylight Start: The date that a time zone enters daylight time
o Month: 01 to 12
o Week Day: Sunday to Saturday
o Apply Week (Day:01 to 05, Specifies the occurrence of day in the
month; 01 = First occurrence of day, 02 = Second occurrence of
day, ...and 05 = Last occurrence of day)
o Hour: 00 to 23
• Standard Start: The date that a time zone enters daylight time
o Month: 01 to 12
o Week Day: Sunday to Saturday
o Apply Week (Day:01 to 05, Specifies the occurrence of day in the
month; 01 = First occurrence of day, 02 = Second occurrence of
day, ...and 05 = Last occurrence of day)
o Hour: 00 to 23
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 77 -
Page 83

Network
DNS Server Setting:
Step 1: After successfully logon to the system, we need to change the
network configuration. Click Control→Network to setup the network
parameters as figure 8.3-1.
Figure 8.3-1
Parameter:
• Primary DNS Server: Primary DNS Server IP network
• Secondary DNS Server: Secondary DNS Server IP network
• Host Name: Host name used to register to DNS Server
• Domain Name: Domain name used to
• Dynamic DNS Registration: Enable Dynamic DNS registration or not
SNMP
Start path: Click Control→SNMP→Community
Figure 8.4-1
Parameter:
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 78 -
Page 84

• Community Name: Community name for network manager system
accessing
• Access Rights: Giving access right to the community
Start path: Click Control→SNMP→Trap
Figure 8.4-2
Parameter:
• Trap Community: Trap community name for NMS
• Trap Host: Trap host IP address
JNote: It takes around 1-minute to update SNMP configuration and
display successful message.
Prompt Manager
Start path: Click Control→Prompt Manager
Figure 8.4-1
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 79 -
Page 85

☻Note:
1. You mast has a sound card in your PC to record the voice. You
need to set Network security in order to execute this recording.
Click Tool→Internet Option→Security→Custom Level.
2. Enable the following security to active setting:
Voice prompt editor:
- Download unsigned ActiveX control: Enable
- Initialize and script ActiveX control not marked as safe: Enable
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 80 -
Page 86

New, Record:
Step 1: Make sure you have installed microphone or other device when you
want to record, Click New and Record buttons to record as figure
8.4-2.
Figure 8.4-2
Stop, Pause, Play:
Step 2: Click Stop or Pause button to stop record, and click Play button to
listen the voice prompt as figure 8.4-3.
Figure 8.4-3
Save:
Step 3: Click Save button to saving the voice file at local path, and the screen
shows Please input the file path and file name!! (i.e.
c:\irene_test.raw) as figure 8.4-4.
Figure 8.4-4
Save Remote File:
Step 4: Click Save Remote File to saving the voice file at VIP-2100, and the
screen shows “please input the file path and file name!!” (i.e.
9999.raw) as figure 8.4-5
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 81 -
Page 87

Figure 8.4-5
☻Note: The file name must be “ .raw” file format.
Open Remote File:
Step 5: Click Open Remote File button to open voice file at VIP-2100 and
screen shows Voice File List as figure 8.4-6.
Figure 8.4-6
Open:
Step 6: Click Open button to open local host voice file and screen shows
Choose File as figure 8.4-7.
Figure 8.4-7
Close:
Step 7: Click Close button to close the voice file as figure 8.4-8.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 82 -
Page 88

Figure 8.4-8
Copy:
Step 8: Select the desired voice range and click Copy button as figure 8.4-9
8.4-9
Paste:
Step 9: Click Paste button to paste the voice range as figure 8.4-10.
Figure 8.4-10
Cut:
Step 10: Select the desired voice range and click Cut button as figure 8.4-11.
Figure 8.4-11
Save As: Refer the Section “Save”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 83 -
Page 89

Save Remote As: Refer the Section “Save Remote File”
Undo:
Step 13: Click Undo button to return modification, you can see the
configuration that haven’t be changed as figure 8.4-12.
Figure 8.4-12
Redo: Refer Section “Undo”
Zoom Zoom In Zoom Out:
Step 14: Select the desired voice range click Zoom button as figure 8.4-13.
Figure 8.4-13
Step 15: The screen shows the zoom out voice file range as figure 8.4-14.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 84 -
Page 90

Figure 8.4-14
Delete Remote file:
Step 16: Click Delete Remote file button to delete remote voice file as figure
8.4-15.
Figure 8.4-15
Call Flow Editor
Please refer section “Call Flow Editor”
Account Manager
Please refer section “Account Manager”
Upgrade
Step 1: Click “Control→Upgrade” to upgrade the software as figure 7.5-1.
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 85 -
Page 91

Figure 7.5-1
Field Description:
• File Name: Upload the software file name
• Upload: Remote Upload the software at VIP-2100
• Apply: Remote apply the upload at VIP-2100
Relogin
Please refer section “Relogin”
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 86 -
Page 92

Chapter 9 System Monitor
It provides a way to monitor the system status.
Line Summary Status
Show channel summary status.
Start Path: Monitor→Line Summary Status
Figure 9.1-1
Field Description:
• Refresh Interval (second): Refresh interval time (1, 5, 10 seconds)
• Line ID: Line ID (format: Interface: trunk: channel)
• Talk Time: Total conversation time
• Successfully calls: Total successfully calls (connected calls)
• Unsuccessfully calls: Total unsuccessfully calls (unconnected calls)
See the line detail:
Selection the line and click Detail button as figure 9.1-2.
Figure 9.1-2
Refer to line detail for field description
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 87 -
Page 93

Line Detail
Show detail channel status.
Start Path: Monitor→Line Detail
Figure 9.2-1
Field Description:
• Refresh Interval (second): Refresh interval time (1, 5, 10 seconds)
• Line ID: Line ID
• Line Status: Current time status
• Call Originate: Call originate site
• ANI String: Calling party number
• DNIS String: Called party number
• PSTN Status: PSTN site status
• VoIP Status: IP site status
• Escape Time: Talk time
Event Log
Show system log status.
Start Path: Configuration→Event Log
Figure 9.3-1
Field Description:
• Type: Event Log type
o Information
o Warring
o Error
• Date: Event created date
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 88 -
Page 94

• Time: Event created time
• Source: Executable program
• Category: Event type (none, welltech Sys…)
• Event ID: Event Log
☻Note: You can click Clear button to clear all event log.
See the detail event log:
Double click the log or select the log and click detail to see the log
detail.
Figure 9.3-2
Event Description:
Event ID
[GK]: [xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:xxxx] not found or
8003
8700 VoIP Gateway application on the fly change On the fly change (system change)
8703
9500 Gateway application started VoIP Gateway program start
9500 AAA Mgr application started AAA Manager program start
9500 TelnSvr application started Telnet Server program start
9501 VoIP Board (0) started Interface (ID:0) start
9502 H323 stack started H323 stack start
9503
9504 PSTN trunk (0) alarm clear Connect to PSTN
9505
9600 SNTP client application started Failed / Success to connect SNTP server
registered failure
[SIP Register]: [xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:xxxx] not found
or registered failure
[0]: evt: D CHANNEL STATUS: runkId=3,
Status=1, Comment='', LOS=14, LOF=0,
RAI=108, AIS=145, RAI_CRC=-1
H323 GK [xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:xxxx] found &
registered
[SIP Register]: [xxx.xxx.xxx.xxxx] Found &
Registered.
[0]: evt: D CHANNEL STATUS: TrunkId=3,
Status=0, Comment='', LOS=29, LOF=67,
RAI=31, AIS=1, RAI_CRC=-1
Event Description Description
Failed to register to H323 Gatekeeper
Failed to registered to SIP Registratar
Server
D Channel and Trunk ID (ID: 0) not available
Registered to H323 Gatekeeper
Registered to SIP Registratar Server
D Channel and Trunk ID (ID:0) available
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 89 -
Page 95

Debug Info
Start Path: Click “Monitor→Debug Info”
Figure 9.4-1
Filed Description:
• Get Log: Get debug log (-1~999)
• Search: Search debug logs
• Clear: Clear log
Ping
You can use the “Ping” to check an IP is active or not.
Start Path: Configuration→Ping
Figure 9.5-1
Field Description:
• Host IP Address: The IP address to ping
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 90 -
Page 96

Chapter 10 Telnet & RS-232 Configuration
VIP-2100 also can support to be managed by Telnet or Console port
(RS-232) for basic operations.
Interface:
v Network: TCP/IP Telnet
v RS232:
- Connect using: COM1
- Baud Rate: 9600
- Data bits: 8
- Parity: None
- Stop bits: 1
- Flow Control: None
- Wire: Null modem line (crossed)
Logon VIP-2100 by Telnet
Use Windows build-in Hyper Terminal or other telnet terminal emulator
to login (e.g. telnet 192.168.111.111:10086). User ID & password will be
required for login (default login user id: admin, password: admin & user id:
root, password: root).
Command List:
Command Description
echo Auto echo on or off
eventlog Clean or show system log message
exit Quit the current session
ipconfig Configure or show network information
ping Check an IP address is available or not
reboot Reboot
reset Soft-reset
shutdown Shutdown
time Reset or show system time.
timezone Setup or show system timezone
useradmin Manage user account.
help & ? View command list
Echo: auto echo on or not
Command Purpose
[root#]echo ?
[root#]echo on Echo is on
[root#]echo off Echo is off (default ralue)
Usage: echo on/off
Example: echo on
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 91 -
Page 97

Eventlog: show system log message
Command Purpose
[root#]eventlog ?
Usage: eventlog [-clear]
Example: eventlog
eventlog -clear
[root#]eventlog Show system eventlog:
Eventlog example:
Time: 2003-06-19 20:15:17 Event ID: 8700
Type: Warning Source : wellgate5x00
Description: [0]: evt: TRUNK ALARM: TrunkId=3
Time: 2003-06-19 20:15:17 Event ID: 8700
Type: Warning Source : wellgate5x00
Description: [0]: evt: TRUNK ALARM: TrunkId=2
Time: 2003-06-19 20:15:14 Event ID: 9501
Type: Information Source : wellgate5x00
Description: [0]: evt: BOARD STARTED: SLOT:8
Press any key to continue or press 'Q' to quit
[root#]eventlog -
Clear all event log
clear
Exit: Quit the current session
Command Purpose
[root#]exit Quit the current session
Ipconfig: Configuration or show network information
Command Purpose
[root#] ipconfig ?
Usage: ipconfig [-delete dns] [-dhcp] [-dns IPAddress1
IPAddress2 ] [-ip IPAddress -mask Mask -gateway
Gateway]
Example : ipconfig -ip 192.168.111.111 -mask 255.255.0.0
-gateway 192.168.1.254
: ipconfig -dhcp
: ipconfig -dns 192.168.1.1
: ipconfig -delete dns
[root#]ipconfig Show current network configuration
USE FIXED IP (or DHCP)
IP Address : 192.168.5.113
Subnet Mask : 255.255.0.0
Default Gateway : 192.168.1.254
DNS Servers : 192.168.5.1
168.95.1.1
[root#]ipconfig –delete
dns
Delete the DNS servers setting
USE FIXED IP
IP Address : 192.168.5.113
Subnet Mask : 255.255.0.0
Default Gateway : 192.168.1.254
DNS Servers :
[root#]ipconfig –dchp Enable DHCP
USE DHCP
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 92 -
Page 98

IP Address : 192.168.5.10
Subnet Mask : 255.255.0.0
Default Gateway : 192.168.1.254
DNS Servers : 192.168.5.1
168.95.1.1
[root#]ipconfig –ip
61.220.126 28 –mask
255.255.0.224 –gateway
61.220.126.1
[root#]ipconfig –ip
61.220.126.115
[root#]ipconfig –dns
210.59.126.53
Use fixed network configuration
USE FIXED IP
IP Address : 61.220.126.28
Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.1
Default Gateway : 61.220.126.254
DNS Servers :
Changes IP address only.
USE FIXED IP
IP Address : 61.220.126.115
Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.1
Default Gateway : 61.220.126.254
DNS Servers :
Changes DNS configuration only.
USE FIXED IP
IP Address : 61.220.126.115
Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.1
Default Gateway : 61.220.126.254
DNS Servers : 210.59.126.53
Ping: Check an IP address is available or not
Command Purpose
[root#] ping ? Usage: ping IP.
Example: ping 127.0.0.1
[root#]ping 61.220.126.1 Ping result
Reply from 61.220.126.1 bytes=64 time=1ms TTL=29
Reply from 61.220.126.1 bytes=64 time=1ms TTL=29
Reply from 61.220.126.1 bytes=64 time=1ms TTL=29
Reply from 61.220.126.1 bytes=64 time=1ms TTL=29
Reboot:
Command Purpose
[root#] reboot ? Reboot System
Are You Sure? (Y/N)
[root#]reboot
Are You Sure?(Y/N)y
VIP-2100 are rebooting
Shutdown:
Command Purpose
[root#] shutdown ? Shutdown System
Are You Sure? (Y/N)
[root#]shutdown
Are You Sure?(Y/N)y
VIP-2100 are shutting down
Reset:
Command Purpose
[root#] reset ? Soft reset System
Are You Sure? (Y/N)
[root#]reset
Are You Sure?(Y/N)y
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 93 -
Page 99

Time: Reset or show system time
Command Purpose
[root#] time ?
[root#]time
[root#]time 2003-07-29
Usage : time YYYY-MM-DD HH:NN:SS
Example : Time 2002-01-01 12:00:00
Show current time
The current time is 2003-06-20 15:17:30
Change system bios time
23:14:53
Timezone: Setup or show system timzone
Command Purpose
[root#] timezone ?
Fixed Zone List:
01. Afghanistan Standard Time
03. Arab Standard Time
05. Arabic Standard Time
07. AUS Central Standard Time
09. Azores Standard Time
11. Cape Verde Standard Time
13. Cen. Australia Standard Time
15. Central Asia Standard Time
17. Central European Standard
Time
19. Central Standard Time
21. Dateline Standard Time
23. E. Australia Standard Time
25. E. South America Standard
Time
27. Egypt Standard Time
29. Fiji Standard Time
31. GMT Standard Time
33. Greenwich Standard Time
35. Hawaiian Standard Time
37. Iran Standard Time
39. Korea Standard Time
41. Mexico Standard Time 2
43. Mountain Standard Time
45. N. Central Asia Standard
Time
47. New Zealand Standard Time
49. North Asia East Standard
Time
51. Pacific SA Standard Time
53. Romance Standard Time
55. SA Eastern Standard Time
57. SA Western Standard Time
59. SE Asia Standard Time
61. South Africa Standard Time
63. Taipei Standard Time
65. Tokyo Standard Time
67. US Eastern Standard Time
69. Vladivostok Standard Time
71. W. Central Africa Standard
Time
73. West Asia Standard Time
75. Yakutsk Standard Time
02. Alaskan Standard Time
04. Arabian Standard Time
06. Atlantic Standard Time
08. AUS Eastern Standard Time
10. Canada Central Standard
Time
12. Caucasus Standard Time
14. Central America Standard
Time
16. Central Europe Standard
Time
18. Central Pacific Standard
Time
20. China Standard Time
22. E. Africa Standard Time
24. E. Europe Standard Time
26. Eastern Standard Time
28. Ekaterinburg Standard Time
30. FLE Standard Time
32. Greenland Standard Time
34. GTB Standard Time
36. India Standard Time
38. Israel Standard Time
40. Mexico Standard Time
42. Mid-Atlantic Standard Time
44. Myanmar Standard Time
46. Nepal Standard Time
48. Newfoundland Standard
Time
50. North Asia Standard Time
52. Pacific Standard Time
54. Russian Standard Time
56. SA Pacific Standard Time
58. Samoa Standard Time
60. Singapore Standard Time
62. Sri Lanka Standard Time
64. Tasmania Standard Time
66. Tonga Standard Time
68. US Mountain Standard Time
70. W. Australia Standard Time
72. W. Europe Standard Time
74. West Pacific Standard Time
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 94 -
Page 100

[root#]timezone
Usage1 : timezone Zone (1 to 75) AutoDaylight (Y or N)
Example1 : timezone 1 Y
Usage2 : timezone -custom Bias DaylightBias DaylightStart
StandardStart
Bias : -12:00 to +13:00
DaylightBias : -12:00 to +13:00
DaylightStart :
MM (Month: 01 to 12) ;
WD (Day of week: 00 to 06)
DD (Day:01 to 05 ;Specifies the occurrence of day in the
month;
01 = First occurrence of day,
02 = Second occurrence of day, ..., 05 = Last occurrence of
day
HH (Hour:00 to 23)
StandardStart :
MM (Month: 01 to 12) ;
WD (Day of week: 00 to 06)
DD (Day:01 to 05 ;Specifies the occurrence of day in the
month;
01 = First occurrence of day,
02 = Second occurrence of day, ..., 05 = Last occurrence of
day
HH (Hour:00 to 23)
Example2 : timezone -custom +08:00 -01:00 04-00-01-02 10-0005-02
Show current timezone info
Time Zone : (40) Mexico Standard Time (GMT -06:00)
Daylight Bias : -01:00
Daylight Start : 05-00-01 02:00
Standard Start : 09-00-05 02:00
Auto Daylight : Y
[root#]timezone 40 n Use pre-defined timezone
Time Zone : (40) Mexico Standard Time (GMT -06:00)
Daylight Bias : -01:00
Daylight Start : 05-00-01 02:00
Standard Start : 09-00-05 02:00
Auto Daylight : n
[root#]timezone custom +08:00 01:00 05-00-01-03
09-00-05-03
Use customized timezone
Time Zone : (99) Customized (GMT 08:00)
Daylight Bias : -01:00
Daylight Start : 05-00-01 03:00
Standard Start : 09-00-05 03:00
Auto Daylight : Y
Please refer Timezone to Country Mapping List
Useradmin: Manager user account
Command Purpose
[root#] useradmin ?
[root#]useradmin
Usage: useradmin [-add User] [-delete User] [password User]
Example: useradmin -add irene
Show the current login user account
root
[root#]useradmin -list Show the current user account list
rdmin
VIP-2100 User’s manual - 95 -
 Loading...
Loading...