Page 1

WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
User’s Manual
24-Port 10/100/1000Mbps
Layer 2 Managed Switch
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
24-Port 10/100/1000Mbps
Layer 2 Managed Stackable Switch
1
Page 2
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Trademarks
Copyright © PLANET Technology Corp. 2008.
Contents subject to which revision without prior notice.
PLANET is a registered trademark of PLANET Technology Corp. All other trademarks belong to their respective owners.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications, and makes no
warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for
a particular purpose. PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User's Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability
for any inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User's Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of
PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User's Manual. PLANET makes
no commitment to update or keep current the information in this User's Manual, and reserves the right to make improvements to
this User's Manual and/or to the products described in this User's Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your comments and
suggestions.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated
in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the Instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at whose own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the user may be
required to take adequate measures.
WEEE Warning
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the presence of
hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of electrical and electronic
equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of
WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to collect such WEEE separately.
Revision
PLANET 24-Port 10/100/1000Mbps with 4 Shared SFP Combo Managed Switch User's Manual
FOR MODELS: WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R / SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
REVISION: 1.0 (AUGUEST.2008)
Part No: EM-WGSW-24040_SGSW-24040 (2080-A93070-000)
2
Page 3

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
TABLE OF CONETNTS
1. INTRODUTION .................................................................................................................... 12
1.1 Packet Contents .........................................................................................................................................12
1.2 Product Description ...................................................................................................................................12
1.3 How to Use This Manual ............................................................................................................................14
1.4 Product Features........................................................................................................................................15
1.5 Product Specification ................................................................................................................................17
2. INSTALLATION ................................................................................................................... 19
2.1 Hardware Description ................................................................................................................................19
2.1.1 Switch Front Panel ..............................................................................................................................................19
2.1.2 LED Indications ...................................................................................................................................................21
2.1.3 Switch Rear Panel ...............................................................................................................................................23
2.2 Install the Switch ........................................................................................................................................26
2.2.1 Desktop Installation .............................................................................................................................................26
2.2.2 Rack Mounting.....................................................................................................................................................27
2.2.3 Installing the SFP transceiver ..............................................................................................................................28
2.2.4 Connecting DC Power Supply .............................................................................................................................31
2.3 Stack Installation ........................................................................................................................................32
2.3.1 Connecting Stacking cable ..................................................................................................................................33
2.3.2 Management Stacking .........................................................................................................................................33
3. SWITCH MANAGEMENT .................................................................................................... 36
3.1 Requirements..............................................................................................................................................36
3.2 Management Access Overview.................................................................................................................37
3.3 Administration Console.............................................................................................................................37
3.4 Web Management.......................................................................................................................................39
3.5 SNMP-Based Network Management.........................................................................................................40
3.6 Protocols.....................................................................................................................................................40
3.6.1 Virtual Terminal Protocols....................................................................................................................................40
3.6.2 SNMP Protocol ....................................................................................................................................................41
3.6.3 Management Architecture....................................................................................................................................41
3
Page 4

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4. WEB CONFIGURATION...................................................................................................... 42
4.1 Main WEB PAGE.........................................................................................................................................45
4.2 System.........................................................................................................................................................47
4.2.1 System Information..............................................................................................................................................48
4.2.2 IP Configuration...................................................................................................................................................50
4.2.3 User Authentication .............................................................................................................................................51
4.2.4 SNTP Configuration.............................................................................................................................................52
4.2.5 WEB Firmware Upgrade......................................................................................................................................53
4.2.6 TFTP Firmware Upgrade .....................................................................................................................................54
4.2.7 Configuration Save ..............................................................................................................................................56
4.2.8 Configuration Upload...........................................................................................................................................57
4.2.9 Factory Default ....................................................................................................................................................59
4.2.10 System Reboot ..................................................................................................................................................60
4.3 Simple Network Management Protocol....................................................................................................65
4.3.1 SNMP Overview ..................................................................................................................................................65
4.3.2 SNMP System Configuration ...............................................................................................................................65
4.3.3 SNMP System Information Configuration ............................................................................................................67
4.3.4 SNMP Trap Configuration....................................................................................................................................67
4.3.5 SNMPv3 Configuration ........................................................................................................................................69
4.3.5.1 SNMPv3 Accesses Configuration ...........................................................................................................69
4.3.5.2 SNMPv3 Communities Configuration......................................................................................................70
4.3.5.3 SNMPv3 Groups Configuration...............................................................................................................71
4.3.5.4 SNMPv3 Users Configuration .................................................................................................................72
4.3.5.5 SNMPv3 Views Configuration .................................................................................................................73
4.4 Port Management .......................................................................................................................................77
4.4.1 Port Configuration................................................................................................................................................77
4.4.2 Port Statistics Overview.......................................................................................................................................79
4.4.3 Detailed Port Statistics.........................................................................................................................................80
4.4.4 Port Mirroring Configuration.................................................................................................................................82
4.5 Link Aggregation........................................................................................................................................85
4.5.1 Static Aggregation Configuration .........................................................................................................................87
Hash Code Contributors ........................................................................................................................................87
Static Aggregation Group Configuration ................................................................................................................87
4.5.2 LACP Configuration.............................................................................................................................................89
4.5.3 LACP System Status ...........................................................................................................................................90
4.5.4 LACP Port Status.................................................................................................................................................90
4.5.5 LACP statistics.....................................................................................................................................................92
4
Page 5

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.6 VLAN............................................................................................................................................................93
4.6.1 VLAN Overview ...................................................................................................................................................93
4.6.2 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN .............................................................................................................................................94
4.6.3 VLAN Basic Information.......................................................................................................................................98
4.6.4 VLAN Port Configuration .....................................................................................................................................99
4.6.5 VLAN Membership Configuration ......................................................................................................................102
4.6.6 Private VLAN Configuration...............................................................................................................................103
4.7 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol ................................................................................................................105
4.7.1 RSTP System Configuration.............................................................................................................................. 111
4.7.2 RSTP Bridge Status........................................................................................................................................... 112
4.7.3 RSTP Port Configuration ................................................................................................................................... 113
4.7.4 RSTP Port Status............................................................................................................................................... 116
4.7.5 RSTP Port Statistics .......................................................................................................................................... 11 7
4.8 Quality of Service ..................................................................................................................................... 118
4.8.1 Understand QOS ............................................................................................................................................... 11 8
4.8.2 QoS Control List Configuration .......................................................................................................................... 11 9
4.8.2.1 QoS Control Entry Configuration .............................................................................................................120
4.8.3 Port QoS Configuration......................................................................................................................................121
4.8.4 QCL Configuration Wizard.................................................................................................................................123
4.8.4.1 Set up Policy Rules...............................................................................................................................123
4.8.4.2 Set up Typical Network Application Rules.............................................................................................125
4.8.4.3 Set up ToS Precedence Mapping..........................................................................................................127
4.8.4.4 Set up VLAN Tag Priority Mapping........................................................................................................128
4.8.5 QoS Statistics ....................................................................................................................................................129
4.8.6 Bandwidth Control .............................................................................................................................................130
4.8.7 Storm Control Configuration ..............................................................................................................................131
4.9 Multicast ....................................................................................................................................................132
4.9.1 IGMP Snooping .................................................................................................................................................132
4.9.2 IGMP Snooping Configuration ...........................................................................................................................136
4.9.3 IGMP Port Related Configuration ......................................................................................................................137
4.9.4 IGMP Snooping Status ......................................................................................................................................138
4.9.5 Multicast Address Table .....................................................................................................................................139
4.10 IEEE 802.1X Network Access Control ..................................................................................................140
4.10.1 Understanding IEEE 802.1X Port-Based Authentication..................................................................................141
4.10.2 802.1X System Configuration..........................................................................................................................144
4.10.3 802.1X and MAC-Based Authentication Port Configuration.............................................................................146
4.10.4 802.1X Port Status...........................................................................................................................................149
5
Page 6

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.10.5 802.1X and MAC-Based Authentication Statistics ...........................................................................................150
4.10.6 Windows Platform RADIUS Server Configuration ...........................................................................................154
4.10.7 802.1X Client Configuration.............................................................................................................................156
4.11 Access Control Lists..............................................................................................................................159
4.11.1 Access Control List Configuration ....................................................................................................................159
4.11.2 ACE Configuration ...........................................................................................................................................161
4.11.3 ACL Configuration wizard.................................................................................................................................168
4.11.3.1 Set up Policy Rules .............................................................................................................................169
4.11.3.2 Set up Port Policies .............................................................................................................................170
4.11.3.3 Set up Typical Network Application Rules ...........................................................................................171
4.11.3.4 Set up Source MAC and Source IP Binding ........................................................................................174
4.11.3.5 Set up DoS Attack Detection Rules .....................................................................................................175
4.11.3.6 Set up DoS Attack Detection Rules .....................................................................................................176
4.11.4 ACL Rate Limiter Configuration........................................................................................................................178
4.11.5 ACL Ports Configuration...................................................................................................................................179
4.12 Address Table .........................................................................................................................................181
4.12.1 MAC Address Table Configuration ...................................................................................................................181
4.12.2 Static MAC Table Configuration ....................................................................................................................... 182
4.12.3 MAC Address Table Status ..............................................................................................................................183
MAC Table Columns............................................................................................................................................183
4.13 Port Security ...........................................................................................................................................185
4.14 LLDP ........................................................................................................................................................187
4.14.1 Link Layer Discovery Protocol .........................................................................................................................187
4.14.2 LLDP Configuration .........................................................................................................................................188
4.14.3 LLDP Neighbor ................................................................................................................................................191
4.14.4 LLDP Statistics.................................................................................................................................................192
4.15 Network Diagnastics ..............................................................................................................................194
4.15.1 Cable Diagnostics............................................................................................................................................194
4.15.2 Ping .................................................................................................................................................................195
4.16 Stacking...................................................................................................................................................196
4.16.1 Stack................................................................................................................................................................198
4.16.1.1 Switch IDs...........................................................................................................................................198
4.16.1.2 Master Election ...................................................................................................................................199
4.16.1.3 Stack Redundancy..............................................................................................................................199
4.16.1.4 Shortest Path Forwarding ...................................................................................................................200
4.16.2 Stack Configuration .........................................................................................................................................201
4.16.3 Stack Information.............................................................................................................................................202
6
Page 7

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.16.4 Stack Port State Ovewview..............................................................................................................................204
4.16.5 Stack Example.................................................................................................................................................205
5. COMMAND LINE INTERFACE.......................................................................................... 208
5.1 Accessing the CLI ....................................................................................................................................208
Logon to the Console ..........................................................................................................................................208
Configure IP address...........................................................................................................................................209
5.2 Telnet login................................................................................................................................................211
6. Command Line Mode ....................................................................................................... 212
6.1 System Command ....................................................................................................................................212
System Configuration ..........................................................................................................................................212
System Reboot....................................................................................................................................................213
System Restore Default.......................................................................................................................................213
System Name......................................................................................................................................................214
System Prompt....................................................................................................................................................214
System Password................................................................................................................................................215
System SNTP......................................................................................................................................................215
System Timezone................................................................................................................................................216
System Firmware Load........................................................................................................................................216
IP Configuration...................................................................................................................................................218
IP DHCP..............................................................................................................................................................218
IP Setup...............................................................................................................................................................219
IP Ping.................................................................................................................................................................219
6.2 Port Management Command...................................................................................................................221
Port Configuration ...............................................................................................................................................221
Port State.............................................................................................................................................................221
Port Mode............................................................................................................................................................222
Port Flow Control.................................................................................................................................................222
Port Maximum Frame..........................................................................................................................................223
Port Power...........................................................................................................................................................224
Port Excessive.....................................................................................................................................................224
Port Statistics.......................................................................................................................................................225
Port VeriPHY .......................................................................................................................................................225
Port Numbers ......................................................................................................................................................226
Mirror Configuration.............................................................................................................................................227
Mirror Port ...........................................................................................................................................................227
Mirror SID ............................................................................................................................................................227
7
Page 8

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Mirror Mode .........................................................................................................................................................228
6.3 Link Aggregation Command ...................................................................................................................229
Aggregation Configuration...................................................................................................................................229
Aggregation Add..................................................................................................................................................229
Aggregation Delete..............................................................................................................................................230
Aggregation Lookup ............................................................................................................................................230
Aggregation Mode ...............................................................................................................................................231
LACP Configuration.............................................................................................................................................232
LACP Mode .........................................................................................................................................................233
LACP Key............................................................................................................................................................233
LACP Role...........................................................................................................................................................234
LACP Status ........................................................................................................................................................234
LACP Statistics....................................................................................................................................................235
6.4 VLAN Configuration Command ..............................................................................................................237
VLAN Configuration.............................................................................................................................................237
VLAN Mode .........................................................................................................................................................237
VLAV PVID ..........................................................................................................................................................238
VLAN Frame Type...............................................................................................................................................238
VLAN Ingress Filter .............................................................................................................................................239
VLAN Link Type...................................................................................................................................................239
VLAN Q-in-Q Mode .............................................................................................................................................240
VLAN Ethernet Type............................................................................................................................................240
VLAN Add............................................................................................................................................................241
VLAN Delete........................................................................................................................................................241
VLAN Lookup ......................................................................................................................................................242
PVLAN Configuration ..........................................................................................................................................243
PVLAN Isolate .....................................................................................................................................................243
6.5 Spanning Tree Protocol Command ........................................................................................................244
RSTP Configuration.............................................................................................................................................244
RSTP SysPrio .....................................................................................................................................................244
RSTP Age............................................................................................................................................................245
RSTP Delay.........................................................................................................................................................245
RSTP Version......................................................................................................................................................246
RSTP Mode.........................................................................................................................................................246
RSTP Cost ..........................................................................................................................................................247
RSTP Priority.......................................................................................................................................................247
RSTP Edge .........................................................................................................................................................248
RSTP P2P ...........................................................................................................................................................248
RSTP Status........................................................................................................................................................249
8
Page 9

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
RSTP Statistics....................................................................................................................................................250
RSTP mCheck.....................................................................................................................................................250
6.6 Multicast Configuration Command ........................................................................................................251
IGMP Configuration.............................................................................................................................................251
IGMP Mode .........................................................................................................................................................251
IGMP State ..........................................................................................................................................................252
IGMP State ..........................................................................................................................................................252
IGMP Querier ......................................................................................................................................................253
IGMP Fast Leave.................................................................................................................................................253
IGMP Router .......................................................................................................................................................254
IGMP Flooding ....................................................................................................................................................255
IGMP Groups.......................................................................................................................................................255
IGMP Status ........................................................................................................................................................255
6.7 Quality of Service Command ..................................................................................................................257
QoS Configuration...............................................................................................................................................257
QoS Classes .......................................................................................................................................................257
QoS Default.........................................................................................................................................................257
QoS Tag Priority ..................................................................................................................................................258
QoS QCL Port .....................................................................................................................................................258
QoS QCL Add......................................................................................................................................................259
QoS QCL Delete..................................................................................................................................................260
QoS QCL Lookup ................................................................................................................................................260
QoS Mode ...........................................................................................................................................................261
QoS Weight .........................................................................................................................................................261
QoS Rate Limiter.................................................................................................................................................261
QoS Shaper.........................................................................................................................................................262
QoS Unicast ........................................................................................................................................................263
QoS Multicast ......................................................................................................................................................263
QoS Broadcast ....................................................................................................................................................264
6.8 802.1x Port Access Control Command ..................................................................................................265
Dot1x Configuration.............................................................................................................................................265
Dotx1 Mode .........................................................................................................................................................265
Dot1x Status........................................................................................................................................................266
Dot1x Server .......................................................................................................................................................266
Dot1x Secret........................................................................................................................................................267
Dot1x Authenticate ..............................................................................................................................................267
Dot1x Re-authentication......................................................................................................................................268
Dot1x Period........................................................................................................................................................268
Dot1x Timeout .....................................................................................................................................................269
9
Page 10

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Dot1x Statistics....................................................................................................................................................269
Dot1x Clients .......................................................................................................................................................270
Dot1x Agetime .....................................................................................................................................................270
Dot1x Holdtime....................................................................................................................................................271
6.9 Access Control List Command ...............................................................................................................272
ACL Configuration ...............................................................................................................................................272
ACL Action...........................................................................................................................................................272
ACL Policy...........................................................................................................................................................273
ACL Rate.............................................................................................................................................................273
ACL Add ..............................................................................................................................................................274
ACL Delete..........................................................................................................................................................275
ACL Lookup.........................................................................................................................................................276
ACL Lookup.........................................................................................................................................................276
6.10 MAC Address Table Command .............................................................................................................277
MAC Configuration ..............................................................................................................................................277
Mac Add ..............................................................................................................................................................277
MAC Delete .........................................................................................................................................................278
MAC Lookup........................................................................................................................................................278
MAC Age Time ....................................................................................................................................................279
MAC Learning .....................................................................................................................................................279
MAC Dump..........................................................................................................................................................280
MAC Statistics .....................................................................................................................................................280
MAC Flash...........................................................................................................................................................281
6.11 LLDP Command......................................................................................................................................282
LLDP Configuration .............................................................................................................................................282
LLDP Mode .........................................................................................................................................................282
LLDP Optional TLV..............................................................................................................................................283
LLDP Interval.......................................................................................................................................................283
LLDP Hold ...........................................................................................................................................................284
LLDP Delay .........................................................................................................................................................284
LLDP Reinit .........................................................................................................................................................285
LLDP Information ................................................................................................................................................285
LLDP Statistics ....................................................................................................................................................286
6.12 Stack Management Command ..............................................................................................................287
Stack List.............................................................................................................................................................287
Stack List.............................................................................................................................................................287
Stack Master Reelect...........................................................................................................................................287
Stack Select.........................................................................................................................................................288
10
Page 11

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Stack SID Swap...................................................................................................................................................288
Stack SID Delect .................................................................................................................................................288
Stack SID Asign...................................................................................................................................................289
7. SWITCH OPERATION ....................................................................................................... 290
7.1 Address Table...........................................................................................................................................290
7.2 Learning ....................................................................................................................................................290
7.3 Forwarding & Filtering .............................................................................................................................290
7.4 Store-and-Forward ...................................................................................................................................290
7.5 Auto-Negotiation ......................................................................................................................................291
8. TROUBLE SHOOTING...................................................................................................... 293
APPENDEX A ........................................................................................................................ 295
A.1 Switch's RJ-45 Pin Assignments ...........................................................................................................295
A.2 10/100Mbps, 10/100Base-TX...................................................................................................................295
APPENDEX B : GLOSSARY................................................................................................. 297
11
Page 12

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
1. INTRODUTION
The PLANET Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Switch series - WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R / SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R are all
multiple ports Gigabit Ethernet Switched with SFP fiber optical connective ability and robust layer 2 features; the description of
these models as below:
WGSW-24040 :
WGSW-24040R :
SGSW-24040 :
SGSW-24040R :
Terms of “Managed Switch” means the Switches mentioned titled in the cover page of this User’s manual, i.e.WGSW-24040
and SGSW-24040.
24-Port 10/100/1000Base-T with 4 Shared SFP Managed Gigabit Switch
24-Port 10/100/1000Base-T with 4 Shared SFP Managed Gigabit Switch / Redundant Power
24-Port 10/100/1000Base-T with 4 Shared SFP Managed Stackable Switch
24-Port 10/100/1000Base-T with 4 Shared SFP Managed Stackable Switch / Redundant Power
1.1 Packet Contents
Open the box of the Managed Switch and carefully unpack it. The box should contain the following items:
Check the contents of your package for following parts:
; The Managed Switch
; User’s manual CD
; Quick installation guide
; 19” Rack mount accessory kit
x1
x1
x1
x1
; Power cord
; Rubber feet
; RS-232 DB9 male Console cable
; CB-STX50 – 50cm stack cable
(SGSW-24040/24040R only)
If any of these are missing or damaged, please contact your dealer immediately, if possible, retain the carton including the
original packing material, and use them against to repack the product in case there is a need to return it to us for repair.
x1
X4
x1
x1
1.2 Product Description
High-Performance / Cost-effective / Telecom class Gigabit solution for Enterprise backbone and Data
Center Networking
The PLANET Managed Switch is a L2/L4 Managed Gigabit Switch. Since Gigabit network interface had become the basic
equipment and requirement of Enterprise and Network Servers, with 48Gbps switching fabric, the MANAGED SWITCH can
handle extremely large amounts of data in a secure topology linking to a backbone or high capacity servers. The powerful
12
Page 13

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
QoS and Network Security features make it to meets the needs of effective data traffic control for both Campus and Enterprise,
such VoIP, video streaming and multicast application.
High Performance
The Managed Switch provides 24 10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet ports with 4 shared Gigabit SFP slots. It boasts a high
performance switch architecture that is capable of providing non-blocking switch fabric and wire-speed throughput as high as
48Gbps, which greatly simplifies the tasks of upgrading the LAN for catering to increase bandwidth demands.
Robust Layer 2 Features
The Managed can be programmed for basic switch management functions such as port speed configuration, Port aggregation,
VLAN, Spanning Tree protocol, QoS, bandwidth control and IGMP Snooping. The WGSW-24040 provides 802.1Q Tagged
VLAN, Q-in-Q VLAN trunning and private VLAN, the VLAN groups allowed on the WGSW-24040 will be maximally up to 4k.
Via supporting port aggregation, the Managed Switch allows the operation of a high-speed trunk combining multiple ports, up
to eight groups of maximum to 8-ports for trunking, and it supports fail-over as well.
Excellent Traffic Control
PLANET WGSW-24040 is loaded with powerful traffic management and QoS features to enhance services offered by
telecoms. The functionality includes QoS features such as wire-speed Layer 4 traffic classifiers and bandwidth limiting that
are particular useful for multi-tenant unit, multi business unit, Telco, or Network Service Provide applications. It also
empowers the enterprises to take full advantages of the limited network resources and guarantees the best performance at
VoIP and Video conferencing transmission.
Efficient Management
For efficient management, the series of Managed Switch is equipped with console, WEB and SNMP management interfaces.
With its built-in Web-based management, it offers an easy-to-use, platform-independent management and configuration
facility. The Managed Switch supports standard Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and can be managed via any
standard-based management software. For text-based management, it can also be accessed via Telnet and the console port.
Powerful Security
The Managed Switch offers comprehensive Access Control List (ACL) for enforcing security to the edge. Its protection
mechanisms also comprise of port-based 802.1x and MAC-based user and device authentication. The port-security is
effective in limit the numbers of clients pass through, so that network administrators can now construct highly secured
corporate networks with time and effort considerably less than before.
Flexibility and Extension solution
The 4 mini-GBIC slots are compatible with 1000Base-SX/LX and WDM SFP(Small Factor Pluggable) fiber-optic modules. The
distance can be extended from 550 meters (Multi-Mode fiber) up to above 10/50/70/120 kilometers (Single-Mode fiber or
WDM fiber). They are well suited for using within the enterprise data centers and distributions.
13
Page 14

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Reliability Stacking Management
The SGSW Series Managed Switch provides a switch stacking function to manage up to 16 switches using a single IP
address. That helps network managers to easily configure switches via one single IP address instead of connecting and
setting each unit one by one. Through its high bandwidth tunnel and stacking technology, it gives enterprise, service
provider and telcom flexible control over port density, uplinks and switch stack performance.
Ethernet ports can be managed by a stacking group and you can add ports and functionality as needed. The stacking
Up to 384 Gigabit
technology also enables the advantages of chassis-based switches to be integrated into SGSW Series Managed
Switch, but without the expensive up-front cost.
AC / DC Power Redundant to ensure continuous operation
The R series Managed Switch equip with one 100~240V AC power supply unit and one DC -48V power supply unit on its
standard package, it provides redundant power supply installation. A redundant power system is also provided to enhance the
reliability with either 100~240V AC power supply unit or DC -48V power supply unit. The continuous power systems are
specifically designed to handle the demands of high tech facilities requiring the highest power integrity available.
1.3 How to Use This Manual
This User Manual is structured as follows:
Section 2, INSTALLATION
The section explains the functions of the Switch and how to physically install the Managed Switch.
Section 3, SWITCH MANAGEMENT
The section contains the information about the software function of the Managed Switch.
Section 4, WEB CONFIGURATION
The section explains how to manage the Managed Switch by Web interface.
Section 5, COMMAND LINE INTERFACE
The section describes how to use the Command Line interface (CLI).
Section 6, CLI CONFIGURATION
The section explains how to manage the Managed Switch by Command Line interface.
Section 7, SWITCH OPERATION
The chapter explains how to does the switch operation of the Managed Switch.
Section 8, TROUBSHOOTING
The chapter explains how to trouble shooting of the Managed Switch.
Appendix A
The section contains cable information of the Managed Switch.
14
Page 15
1.4 Product Features
¾ Physical Port
WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
24-Port 10/100/1000Base-T Gigabit Ethernet RJ-45
4 mini-GBIC/SFP slots, shared with Port-21 to Port-24
RS-232 DB9 console interface for Switch basic management and setup
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
24-Port 10/100/1000Base-T Gigabit Ethernet RJ-45
4 mini-GBIC/SFP slots, shared with Port-21 to Port-24
RS-232 DB9 console interface for Switch basic management and setup
2 High-performance 5GbE Stacking interface
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
¾ Layer 2 Features
Complies with the IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.3ab, IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet standard
Supports Auto-negotiation and half duplex/full duplex modes for all 10Base-T/100Base-TX and 1000Base-T ports.
Auto-MDI/MDI-X detection for each RJ-45 port
Prevents packet loss with back pressure (Half-Duplex) and IEEE 802.3x PAUSE frame flow control (Full-Duplex)
High performance of Store-and-Forward architecture, broadcast storm control and runt/CRC filtering eliminates
erroneous packets to optimize the network bandwidth
8K MAC address table, automatic source address learning and ageing
1392Kbytes embedded memory for packet buffers
Support VLAN
− IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN
− Up to 4041 VLANs groups, out of 4041 VLAN IDs
− Provider Bridging (VLAN Q-in-Q) support (IEEE 802.1ad)
− Private VLAN Edge (PVE)
Support Spanning Tree Protocol
− STP, IEEE 802.1d (Spanning Tree Protocol)
− RSTP, IEEE 802.1w (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol)
Support Link Aggregation
− 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
− Cisco ether-channel (Static Trunk)
− Maximum 8 trunk groups, up to 8 ports per trunk group
− Up to 16Gbps bandwidth(Duplex Mode)
Provide Port Mirror (many-to-1)
Port Mirroring to monitor the incoming or outgoing traffic on a particular port
15
Page 16

¾ Quality of Service
4 priority queues on all switch ports.
Supports for strict priority and weighted round robin (WRR) CoS policies
Ingress Shaper and Egress Rate Limit per port bandwidth control
Traffic-policing policies on the switch port
¾ Multicast
Supports IGMP Snooping v1, v2 and v3
Querier mode support
¾ Security
IEEE 802.1x Port-Based / MAC-Based network access authentication
IP-Based Access Control List (ACL)
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
MAC-Based Access Control List
Port Security
¾ Management
WEB-based, Telnet, Console Command Line management
Accesses through SNMPv1, v2c and v3 security set and get requests.
Built-in Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) client
BOOTP and DHCP for IP address assignment
Firmware upload/download via HTTP / TFTP
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol)
LLDP Protocol
¾ Stacking
Hardware stack up to 16 units and 384 ports
Stacking architecture supports Chain and Ring mode
Mirror across stack
Link Aggregation groups spanning multiple switches in a stack
Hardware learning with MAC table synchronization across stack
¾ Redundant Power System (WGSW-24040R / SGSW-24040R)
100~240V AC / 48V DC Dual power redundant
Active-active redundant power failure protection
Backup of catastrophic power failure on one supply
Fault tolerance and resilience.
16
Page 17
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
1.5 Product Specification
Product WGSW-24040 WGSW-24040R SGSW-24040 SGSW-24040R
Hardware Specification
Copper Ports
SFP/mini-GBIC Slots
Stacking Ports
Switch Fabric
Address Table
Share data Buffer
Switch Processing Scheme
Flow Control
Jumbo Frame
LED
Power Consumption
Power Requirement – AC
24 10/ 100/1000Base-T RJ-45 Auto-MDI/MDI-X ports
4 SFP interfaces, shared with Port-21 to Port-24
--- 2 5GbE / Cross-HDMI interface
48Gbps / non-blocking 68Gbps
8K entries
1392 kilobytes
Store-and-Forward
IEEE 802.3x Pause Frame for Full-Duplex
Back pressure for Half-Duplex
10Kbytes
Power, Link/Act and speed per Gigabit
port
Max. 30 watts /
102 BTU
AC 100~240V,
50/60Hz
Max. 30 watts /
102 BTU
AC : 100~240V,
50/60Hz
Power, Stack Master, Stack Port LNK,
Link/Act and speed per Gigabit port
Max. 30.2 watts /
102.98 BTU
AC 100~240V,
50/60Hz
Max. 30.2 watts /
102.98 BTU
AC : 100~240V,
50/60Hz
Power Requirement – DC
Stacking Numbers
Stacking Bandwidth
Stack ID Display
Layer 2 function
System Configuration
Port configuration
Port Status
VLAN
---
Console, Telnet, Web Browser, SNMPv1, v2c and v3
Port disable/enable.
Auto-negotiation 10/100/1000Mbps full and half duplex mode selection.
Flow Control disable / enable.
Bandwidth control on each port.
Display each port’s speed duplex mode, link status, Flow control status. Auto
negotiation status, trunk status.
802.1Q Tagged Based VLAN ,up to 4K VLAN groups
Q-in-Q
Private VLAN
-48V DC @ 0.6A
---
Range: -30 ~ -60V
--- 16
--- 10Gbps Full-Duplex
--- 7-Segment LED Display (1~9, A~F,0)
-48V DC @ 0.6A
Range: -30 ~ -60V
17
Page 18

Port trunking
QoS
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
IEEE 802.3ad LACP / Static Trunk
Support 8 groups of 8-Port trunk support
Traffic classification based, Strict priority and WRR
4-level priority for switching
- Port Number
- 802.1p priority
IGMP Snooping
Access Control List
SNMP MIBs
Standards Conformance
- DS/TOS field in IP Packet
IGMP (v1/v2) Snooping, up to 8K multicast Groups
IGMP Querier mode support
IP-Based ACL / MAC-Based ACL
Up to 256 entries
RFC-1213 MIB-II
IF-MIB
RFC-1493 Bridge MIB
RFC-1643 Ethernet MIB
RFC-2863 Interface MIB
RFC-2665 Ether-Like MIB
RFC-2737 Entity MIB
RFC-2618 RADIUS Client MIB
RFC-2933 IGMP-STD-MIB ()
RFC3411 SNMP-Frameworks-MIB
IEEE802.1X PAE
LLDP
MAU-MIB
Regulation Compliance
Standards Compliance
FCC Part 15 Class A, CE
IEEE 802.3 10Base-T
IEEE 802.3u 100Base-TX/100BASE-FX
IEEE 802.3z Gigabit SX/LX
IEEE 802.3ab Gigabit 1000T
IEEE 802.3x Flow Control and Back pressure
IEEE 802.3ad Port trunk with LACP
IEEE 802.1d Spanning tree protocol
IEEE 802.1w Rapid spanning tree protocol
IEEE 802.1p Class of service
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Tagging
IEEE 802.1x Port Authentication Network Control
IEEE 802.1ab LLDP
18
Page 19

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
2. INSTALLATION
This section describes the hardware features and installation of the Managed Switch on the desktop or rack mount. For easier
management and control of the Managed Switch, familiarize yourself with its display indicators, and ports. Front panel
illustrations in this chapter display the unit LED indicators. Before connecting any network device to the Managed Switch, please
read this chapter completely.
2.1 Hardware Description
2.1.1 Switch Front Panel
The unit front panel provides a simple interface monitoring the switch. Figure 2-1 and 2-2 shows the front panel of the Managed
Switches.
WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040RFront Panel
Figure 2-1 WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R front panel.
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R Front Panel
Figure 2-2 SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R front panel.
■ Gigabit TP interface
10/100/1000Base-T Copper, RJ-45 Twist-Pair: Up to 100 meters.
■ Gigabit SFP slots
1000Base-SX/LX mini-GBIC slot, SFP (Small Factor Pluggable) transceiver module: From 550 meters (Multi-mode fiber),
up to 10/30/50/70/120 kilometers (Single-mode fiber).
■ Console Port
The console port is a DB9, RS-232 male seria port connector. It is an interface for connecting a terminal directly. Through
the console port, it provides rich diagnostic information includes IP Address setting, factory reset, port management, link
status and system setting. Users can use the attached RS-232 cable in the package and connect to the console port on the
device. After the connection, users an run any terminal emulation program (Hyper Terminal, ProComm Plus, Telix, Winterm
and so on) to enter the statup screen of the device.
19
Page 20

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
■ Reset button
At the left of front panel, the reset button is designed for reboot the Managed Switch without turn off and on the power. The
following is the summary table of Reset button functions:
Reset Button Pressed and Released Function
About 1~3 second Reboot the Managed Switch
Reset the Managed Switch to Factory Default configuration.
The Managed Switch will then reboot and load the default
settings as below:
Until the PWR LED lit off
■ Stack ID
SGSW-24040 and SGSW-24040R only
。 Default Password: admin
。 Default IP address: 192.168.0.100
。 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
。 Default Gateway: 192.168.0.254
Each SGSW Managed Stackable Switch on a stack must have a unique “Stack ID”. There are 16 degrees (0~9, A~F) in the
rotary switch. The Stack ID is configured via Web or CLI management interface. Use the Stack ID to identify the localtion of
the real device.
Stack ID is not equals to the Master Priority that configured in the management interface.
■ Master LED
SGSW-24040 and SGSW-24040R only
If master switch is fail or disconnected to the switch by stack port, the switch with least switch ID will become master.
20
Page 21

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
2.1.2 LED Indications
The front panel LEDs indicates instant status of port links, data activity, system operation, Stack status and system power, helps
monitor and troubleshoot when needed.
WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R LED indication
Figure 2-3 WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R LED panel
■ System
LED Color Function
PWR Green
■ 10/100/1000Base-T interfaces
LED Color Function
1000
Green
LNK/ACT
Lights to indicate that the Switch is powered on.
Blink to indicate the System is running under booting procedure.
Lights:
Blink:
Off:
Lights:
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established with speed
1000Mbps
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
If L10/100 NK/ACT LED light-> indicate that the port is operating at 10Mbps or
100Mbps
If LNK/ACT LED Off -> indicate that the port is link down
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established with speed
10/100
LNK/ACT
Orange
Blink:
Off:
10Mbps or 100Mbps
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
If 1000 LNK/ACT LED light-> indicate that the port is operating at 1000Mbps
If 1000 LNK/ACT LED Off -> indicate that the port is link down
21
Page 22

■ 1000Base-SX/LX SFP interfaces (Shared Port-21~Port-24)
LED Color Function
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Lights:
1000
Green
LNK
Off:
To indicate the link through that SFP port is successfully established with
speed 1000Mbps
To indicate that the SFP port is link down
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R LED indication
Figure 2-4 SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R LED panel
■ System
LED Color Function
PWR Green
Master Green
STX1 Green
STX2 Green
■ 10/100/1000Base-T interfaces
LED Color Function
1000
Green
LNK/ACT
Lights to indicate that the Switch is powered on.
Blink to indicate the System is running under booting procedure.
Lights to indicate that the Switch is the Master of the stack group
Lights to indicate the stacking link through that port is successfully established.
Lights to indicate the stacking link through that port is successfully established.
Lights:
Blink:
Off:
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established with speed
1000Mbps
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
If L10/100 NK/ACT LED light-> indicate that the port is operating at 10Mbps or
100Mbps
If LNK/ACT LED Off -> indicate that the port is link down
22
Page 23
Lights:
10/100
Orange
LNK/ACT
■ 1000Base-SX/LX SFP interfaces (Shared Port-21~Port-24)
LED Color Function
Blink:
Off:
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established with speed
10Mbps or 100Mbps
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
If 1000 LNK/ACT LED light-> indicate that the port is operating at 1000Mbps
If 1000 LNK/ACT LED Off -> indicate that the port is link down
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Lights:
1000
Green
LNK
■ 7-Segment LED Display
Stack ID (1~9, A~F, 0): To indicate the Switch ID of each SGSW Managed Switch. Switch IDs are used to uniquely identify
the Managed Switches within a stack. The Switch ID of each Managed Switch is shown on the display on the front of the
Managed Switch and is used widely in the web pages as well as in the CLI commands of the Stack group.
Stack ID 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A. B. C. D. E. F. 0
Switch ID 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Off:
To indicate the link through that SFP port is successfully established with
speed 1000Mbps
To indicate that the SFP port is link down
2.1.3 Switch Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Managed Switch indicates an AC inlet power socket, which accept input power from 100 to 240V AC,
50-60Hz. Figure 2-5 to Figure 2-8 shows the rear panel of these Managed Switches
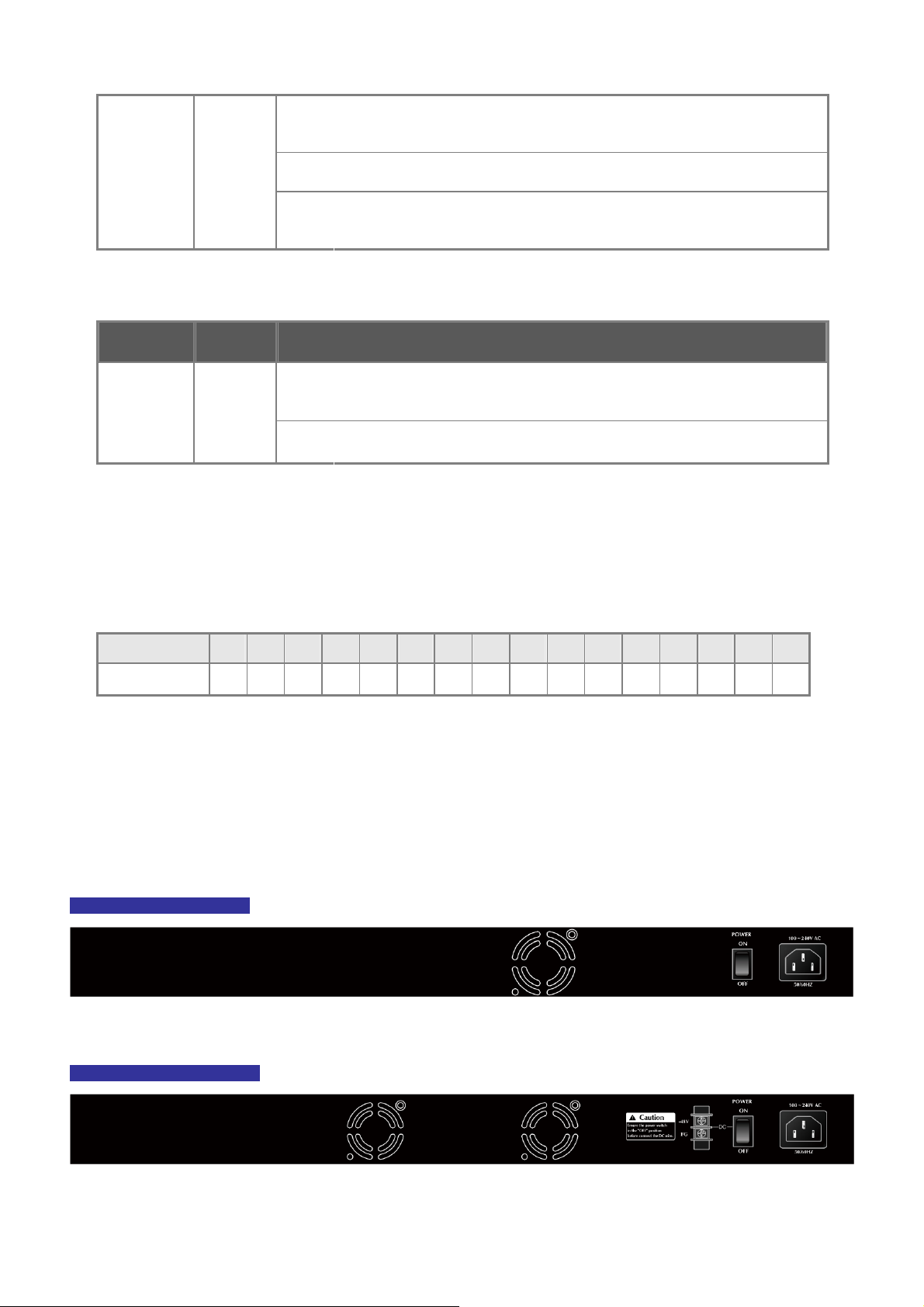
WGSW-24040 Rear Panel
Figure 2-5 Rear panel of WGSW-24040
WGSW-24040R Rear Panel
Figure 2-6 Rear panel of WGSW-24040R
23
Page 24

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 Rear Panel
Figure 2-7 Rear panel of SGSW-24040
SGSW-24040R Rear Panel
Figure 2-8 Rear panel of SGSW-24040R
■ AC Power Receptacle
For compatibility with electric service in most areas of the world, the Managed Switch’s power supply automatically adjusts
to line power in the range 100-240VAC and 50/60 Hz.
Plug the female end of the power cord firmly into the receptalbe on the rear panel of the Managed Switch. Plug the other
end of the power cord into an electric service outlet then the power will be ready.
The device is a power-required device, it means, it will not work till it is powered. If your networks should
active all the time, please consider using UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply) for your device. It will
Power Notice:
■ Stack ports
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
There are two High-Performance stack ports on the rear panel. One is STX1 / Cascade Down and the other is STX2 /
Cascade UP.
• When stacked, the STX1 / Cascade Down port should connect to the other switch’s STX2 / Cascade UP port and the
STX2 / Cascade UP port should connect to other switch’s STX1 / Cascade Down out.
prevent you from network data loss or network downtime.
In some area, installing a surge suppression device may also help to protect your Managed Switch from
being damaged by unregulated surge or current to the Switch or the power adapter.
• You can just use attached PLANET CB-STX50 or longer stack cable CB-STX200 connector to stack.
• The CB-STX50 and CB-STX200 are Cross-Overed HDMI cables, only attached PLANET stack cable can be used.
• Plug-and-play connection.
24
Page 25

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 2-9 SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R Stack Ports
■ DC Power Connector
The rear panel of the WGSW-24040R and SGSW-24040R contains a power switch and a DC power connector, which
accepts DC power input voltage from -30V to -60V DC. Connect the power cable to the Managed Switch at the input
terminal block. The size of the two screws in the terminal block is M3.5.
Warning:
Figure 2-10 Rear Panel of WGSW-24040R / SGSW-24040R
Before connect the DC power cable to the input terminal block of WGSW-24040R or SGSW-24040R,
ensure that the power switch in the “OFF” position and the DC power is OFF
25
Page 26
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
2.2 Install the Switch
This section describes how to install your Managed Switch and make connections to the Managed Switch. Please read the
following topics and perform the procedures in the order being presented. To install your Managed Switch on a desktop or shelf,
simply complete the following steps.
2.2.1 Desktop Installation
To install the Managed Switch on desktop or shelf, please follows these steps:
Step1: Attach the rubber feet to the recessed areas on the bottom of the Managed Switch.
Step2: Place the Managed Switch on the desktop or the shelf near an AC power source, as shown in Figure 2-10.
Figure 2-10 Place the Managed Switch on the desktop
Step3: Keep enough ventilation space between the Managed Switch and the surrounding objects.
When choosing a location, please keep in mind the environmental restrictions discussed in Chapter
1, Section 4, and Specification.
Step4: Connect the Managed Switch to network devices.
Connect one end of a standard network cable to the 10/100/1000 RJ-45 ports on the front of the Managed Switch
Connect the other end of the cable to the network devices such as printer servers, workstations or routers…etc.
Connection to the Managed Switch requires UTP Category 5 network cabling with RJ-45 tips. For
more information, please see the Cabling Specification in Appendix A.
26
Page 27

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Step5: Supply power to the Managed Switch.
Connect one end of the power cable to the Managed Switch.
Connect the power plug of the power cable to a standard wall outlet.
When the Managed Switch receives power, the Power LED should remain solid Green.
2.2.2 Rack Mounting
To install the Managed Switch in a 19-inch standard rack, please follows the instructions described below.
Step1: Place the Managed Switch on a hard flat surface, with the front panel positioned towards the front side.
Step2: Attach the rack-mount bracket to each side of the Managed Switch with supplied screws attached to the package.
Figure 2-11 shows how to attach brackets to one side of the Managed Switch.
Figure 2-11 Attach brackets to the Managed Switch.
You must use the screws supplied with the mounting brackets. Damage caused to the parts by
using incorrect screws would invalidate the warranty.
Step3: Secure the brackets tightly.
Step4: Follow the same steps to attach the second bracket to the opposite side.
Step5: After the brackets are attached to the Managed Switch, use suitable screws to securely attach the brackets to the rack,
as shown in Figure 2-12.
27
Page 28
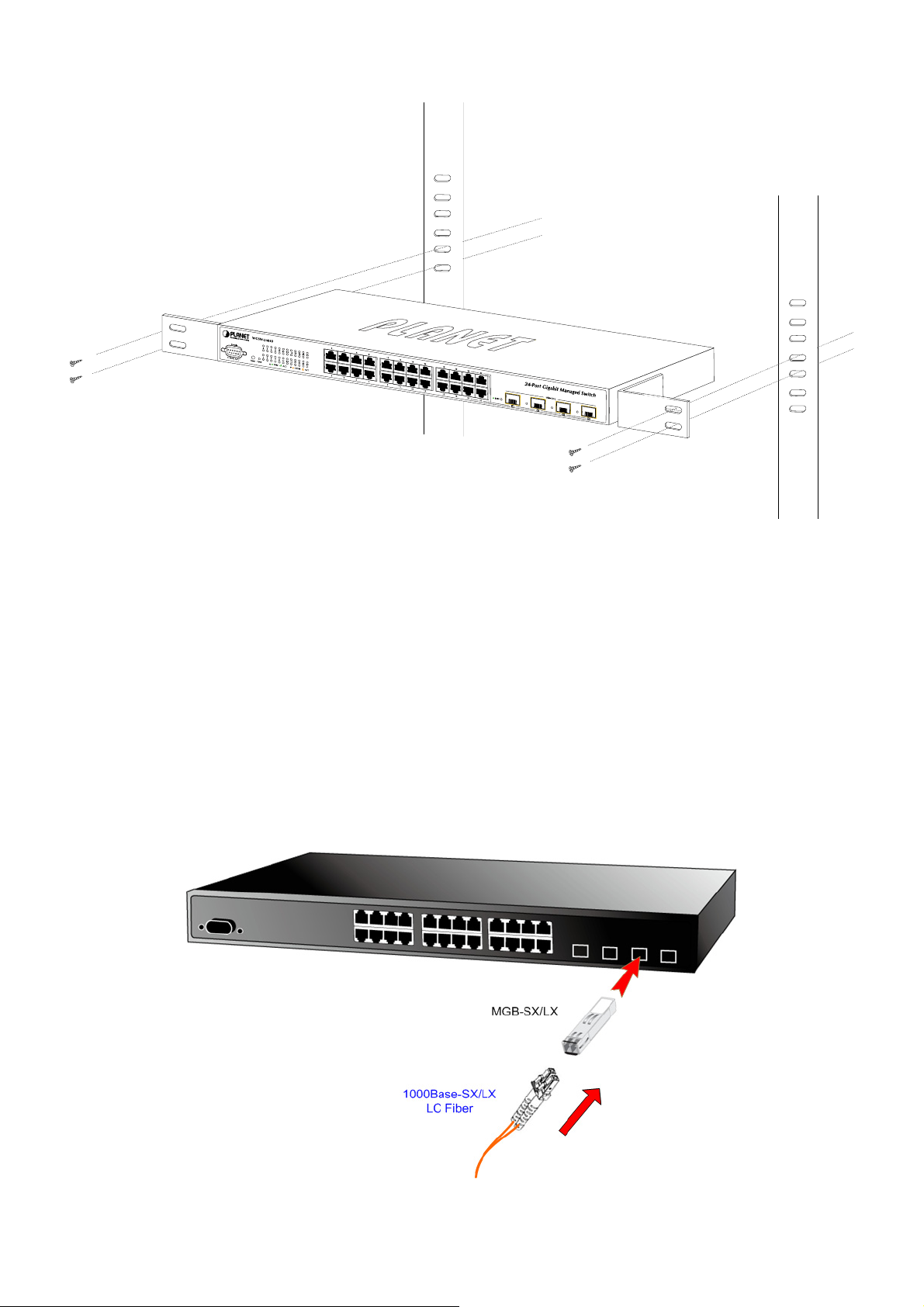
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 2-12 Mounting SGSW-2840 in a Rack
Step6: Proceeds with the steps 4 and steps 5 of session 2.2.1 Desktop Installation to connect the network cabling and supply
power to the Managed Switch.
2.2.3 Installing the SFP transceiver
The sections describe how to insert an SFP transceiver into an SFP slot.
The SFP transceivers are hot-pluggable and hot-swappable. You can plug-in and out the transceiver to/from any SFP port
without having to power down the Managed Switch. As the Figure 2-13 appears.
Figure 2-13 Plug-in the SFP transceiver
28
Page 29

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Approved PLANET SFP Transceivers
PLANET Managed Switch supports both Single mode and Multi-mode SFP transceiver. The following list of approved PLANET
SFP transceivers is correct at the time of publication:
■ MGB-SX SFP (1000BASE-SX SFP transceiver / Multi-mode / 850nm / 220m~550m)
■ MGB-LX SFP (1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver / Single mode / 1310nm / 10km)
■ MGB-L30 SFP (1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver / Single mode / 1310nm / 30km)
■ MGB-L50 SFP (1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver / Single mode / 1310nm / 50km)
■ MGB-LA10 SFP (1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver / WDM Single mode / TX: 1310nm, RX: 1550nm/ 10km)
■ MGB-LB10 SFP (1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver / WDM Single mode / TX: 1550nm, RX: 1310nm / 10km)
It recommends using PLANET SFPs on the Managed Switch. If you insert a SFP transceiver that is
not supported, the Managed Switch will not recognize it.
Before connect the other Managed Switches, workstation or Media Converter.
1. Make sure both side of the SFP transceiver are with the same media type, for example: 1000Base-SX to 1000Base-SX,
1000Bas-LX to 1000Base-LX.
2. Check the fiber-optic cable type match the SFP transceiver model.
¾ To connect to 1000Base-SX SFP transceiver, use the Multi-mode fiber cable- with one side must be male duplex LC
connector type.
¾ To connect to 1000Base-LX SFP transceiver, use the Single-mode fiber cable-with one side must be male duplex LC
connector type.
Connect the fiber cable
1. Attach the duplex LC connector on the network cable into the SFP transceiver.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to a device – switches with SFP installed, fiber NIC on a workstation or a Media
Converter..
3. Check the LNK/ACT LED of the SFP slot on the front of the Managed Switch. Ensure that the SFP transceiver is operating
correctly.
4. Check the Link mode of the SFP port if the link failed. Co works with some fiber-NICs or Media Converters, set the Link
mode to “1000 Force” is needed.
Remove the transceiver module
1. Make sure there is no network activity by consult or check with the network administrator. Or through the management
interface of the switch/converter (if available) to disable the port in advance.
2. Remove the Fiber Optic Cable gently.
3. Turn the handle of the MGB module to horizontal.
4. Pull out the module gently through the handle.
29
Page 30

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 2-14 Pull out the SFP transceiver
Never pull out the module without pull the handle or the push bolts on the module. Direct pull
out the module with violent could damage the module and SFP module slot of the Managed
Switch.
30
Page 31

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
2.2.4 Connecting DC Power Supply – WGSW-24040R / SGSW-24040R
The WGSW-24040R and SGSW-24040R support -48VDC power input, connect the power cable to the switch at the input
terminal block.
1. The size of the two screws in the terminal block is M3.5.
2. The terminals are marked “-48V”, “FG“.
3. Loosen the two screws so you can slide the DC cable beneath it. Insert the DC cable into the connector first, and screw it
down tight.
4. Connect the power cable to the DC power supply. After power up or reset, the Managed Switch performs a cold start
procedure.
Warning:
Figure 2-15 -48VDC connector
Before connect the DC power cable to the input terminal block of Managed Switch, ensure that the
power switch in the “OFF” position and the DC power is OFF
31
Page 32

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
2.3 Stack Installation
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
The SGSW-24040 series Managed Switch provides a switch stacking function to manage up to 16 switches using a single IP
address. And up to 384 Gigabit Ethernet ports can be managed by a stacking group and you can add ports and functionality as
needed. You can add SGSW-24040 series switches as needed to support more network clients, knowing that your switching
fabric will scale to meet increasing traffic demands.
Two types of stack topologies are supported by the SGSW-24040 series:
Chain topology (same as a disconnected ring)
Ring topology
Please find the following picture for sample connection.
Figure 2-16 Chain Stack topology
Figure 2-17 Ring Stack topology
32
Page 33

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
2.3.1 Connecting Stacking cable
Before attempting to connect stacking ports, verify that you have the required stack cables. The following cables are used to
connect stacked switches:
• CB-STX50: 50cm, Short stack cable –used to connect adjacent SGSW switches.
• CB-STX200: 200cm, Long / Redundant stack cable – used to connect the top and bottom SGSW switches of a stack.
There are two high-performance HDMI-like Stack ports on the rear panel for proprietary management stack. Only attached
PLANET CB-STX50 and CB-STX200 cross-overed HDMI cable can be used.
STEP-1: Plug one end of the cable in the “STX1 / Cascade Down” port and the other end to the ”STX2 / Cascade UP” port of
next device.
STEP-2: Repeat the step for every device in the stack cluster, then ending at last switch.
Figure 2-18 Stacking connection
STEP-3: If you wish to implement stack redundancy, use the long stack cable –CB-STX200 to connect the stack port marked
“STX1 / Cascade Down” on the bottom switch to the port marked “STX2 / Cascade Up” on the top switch of the stack.
The stack port is for management and data packets to be transmitted between other SGSW stackable
switches, the stack ports can’t be configured with Layer 2 features via management interface.
STEP-4: Power up the stack switches.
2.3.2 Management Stacking
The stack operation of the SGSW Managed Switch supports Plug and Play Stacking connection and auto stack configuration.
33
Page 34

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
STEP-5: Once the stack start operation, the Stack master be automatically elected without any configure. The Stack master is
indicated by a lit green “Master” LED on the front panel. As the Figure 2-19 appears.
Master LED
Figure 2-19 Stack Master with “Master” LED lit
Stack ID
STEP-6: When a SGSW Switch is added to the stack, a Switch ID is automatically assigned to the SGSW Switch. The
automatic SID assignment can be modified by choosing a different Switch ID on the Stack Configuration page. This
method allows Switch IDs to be assigned so that it is easier for the user to remember the ID of each switch.
STEP-7: Connect the RS-232 serial cable to the console port on the front of the stack master, then loin the SGSW Switch to
start the switch management. Or you can use the PLANET Smart Discovery Utility to displayt the IP address of the
stack and Web login the stack with this IP address. The default IP address of the SGSW Switch is 192.168.0.100.
Figure 2-20 Use PLANET Smart Discovery Utility to display the IP address of stack master
34
Page 35

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
1. The stack switch with least priority ID or MAC Address number will become Master. Only Master
switch’s management interface (console, telnet, web and SNMP) is accessible.
2.
It’s allow to build a stack of up to 16 PLANET SGSW Switches. If there is the space limitation or power issue and you wish to
stack all the switches in different racks, use long stack cables “CB-STX200” to connect two stacks.
2m stack cable CB-STX200 2m stack cable CB-STX200
Figure 2-21 Separated Stack connection
CB-STX50
35
Page 36

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
3. SWITCH MANAGEMENT
This chapter explains the methods that you can use to configure management access to the Managed Switch. It describes the
types of management applications and the communication and management protocols that deliver data between your
management device (work-station or personal computer) and the system. It also contains information about port connection
options.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Requirements
Management Access Overview
Administration Console Access
Web Management Access
SNMP Access
Standards, Protocols, and Related Reading
3.1 Requirements
Workstations of subscribers running Windows 98/ME, NT4.0, 2000/XP, MAC OS9 or later, Linux, UNIX or other
platform compatible with TCP/IP protocols.
Workstation installed with Ethernet NIC (Network Interface Card)
Serial Port connect (Terminal)
• Above PC with COM Port (DB-9 / RS-232) or USB-to-RS-232 converter
Ethernet Port connect
• Network cables - Use standard network (UTP) cables with RJ45 connectors.
Above Workstation installed with WEB Browser and JAVA runtime environment Plug-in
It is recommended to use Internet Explore 6.0 or above to access Managed Switch.
36
Page 37

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
3.2 Management Access Overview
The Managed Switch gives you the flexibility to access and manage it using any or all of the following methods:
An administration console
Web browser interface
An external SNMP-based network management application
The administration console and Web browser interface support are embedded in the Managed Switch software and are
available for immediate use. Each of these management methods has their own advantages. Table 3-1 compares the three
management methods.
Method Advantages Disadvantages
Console
Web Browser
SNMP Agent
• No IP address or subnet needed
• Text-based
• Telnet functionality and HyperTerminal
built into Windows
95/98/NT/2000/ME/XP operating
systems
• Secure
• Ideal for configuring the switch remotely
• Compatible with all popular browsers
• Can be accessed from any location
• Most visually appealing
• Communicates with switch functions at
the MIB level
• Based on open standards
• Must be near switch or use dial-up connection
• Not convenient for remote users
• Modem connection may prove to be unreliable
or slow
• Security can be compromised (hackers need
only know the IP address and subnet mask)
• May encounter lag times on poor connections
• Requires SNMP manager software
• Least visually appealing of all three methods
• Some settings require calculations
• Security can be compromised (hackers need
only know the community name)
Table 3-1 Management Methods Comparison
3.3 Administration Console
The administration console is an internal, character-oriented, and command line user interface for performing system
administration such as displaying statistics or changing option settings. Using this method, you can view the administration
console from a terminal, personal computer, Apple Macintosh, or workstation connected to the switch's console (serial) port.
There are two ways to use this management method: via direct access or modem port access. The following sections describe
these methods. For more information about using the console, refer to Chapter 5 Command Line Interface Console
Management.
37
Page 38

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 3-1 Console management
Direct Access
Direct access to the administration console is achieved by directly connecting a terminal or a PC equipped with a
terminal-emulation program (such as HyperTerminal) to the Managed Switch console (serial) port.
When using this management method, a straight DB9 RS-232 cable is required to connect the switch to the PC. After
making this connection, configure the terminal-emulation program to use the following parameters:
The default parameters are:
115200 bps
8 data bits
No parity
1 stop bit
Figure 3-2 Terminal parameter settings
You can change these settings, if desired, after you log on. This management method is often preferred because you can
remain connected and monitor the system during system reboots. Also, certain error messages are sent to the serial port,
regardless of the interface through which the associated action was initiated. A Macintosh or PC attachment can use any
terminal-emulation program for connecting to the terminal serial port. A workstation attachment under UNIX can use an emulator
such as TIP.
38
Page 39

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
3.4 Web Management
The Managed Switch offers management features that allow users to manage the Managed Switch from anywhere on the
network through a standard browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer. After you set up your IP address for the switch, you can
access the Managed Switch's Web interface applications directly in your Web browser by entering the IP address of the
Managed Switch.
Figure 3-3 Web management
You can then use your Web browser to list and manage the Managed Switch configuration parameters from one central location,
just as if you were directly connected to the Managed Switch's console port. Web Management requires either Microsoft
Internet Explorer 6.0 or later, Safari or Mozilla Firefox 1.5 or later.
Figure 3-4 Web main screen of Managed Switch
39
Page 40

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
3.5 SNMP-Based Network Management
You can use an external SNMP-based application to configure and manage the Managed Switch, such as SNMPc Network
Manager, HP Openview Network Node Management (NNM) or What’s Up Gold. This management method requires the SNMP
agent on the switch and the SNMP Network Management Station to use the same community string. This management
method, in fact, uses two community strings: the get community string and the set community string. If the SNMP Net-work
management Station only knows the set community string, it can read and write to the MIBs. However, if it only knows the get
community string, it can only read MIBs. The default gets and sets community strings for the Managed Switch are public.
Figure 3-4 SNMP management
3.6 Protocols
The Managed Switch supports the following protocols:
Virtual terminal protocols, such as Telnet
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
3.6.1 Virtual Terminal Protocols
A virtual terminal protocol is a software program, such as Telne t, that allows you to establish a management session from a
Macintosh, a PC, or a UNIX workstation. Because Telnet runs over TCP/IP, you must have at least one IP address configured on
the Managed Switch before you can establish access to it with a virtual terminal protocol.
Terminal emulation differs from a virtual terminal protocol in that you must connect a terminal directly
to the console (serial) port.
To access the Managed Switch through a Telnet session:
1. Be Sure of the Managed Switch is configured with an IP address and the Managed Switch is reachable from a PC.
40
Page 41

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
2. Start the Telnet program on a PC and connect to the Managed Switch.
The management interface is exactly the same with RS-232 console management.
3.6.2 SNMP Protocol
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is the standard management protocol for multi-vendor IP networks. SNMP
supports transaction-based queries that allow the protocol to format messages and to transmit information between reporting
devices and data-collection programs. SNMP runs on top of the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), offering a connectionless-mode
service.
3.6.3 Management Architecture
All of the management application modules use the same Messaging Application Programming Interface (MAPI). By unifying
management methods with a single MAPI, configuration parameters set using one method (console port, for example) are
immediately displayable by the other management methods (for example, SNMP agent of Web browser).
The management architecture of the switch adheres to the IEEE open standard. This compliance assures customers that the
Managed Switch is compatible with, and will interoperate with other solutions that adhere to the same open standard.
41
Page 42

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4. WEB CONFIGURATION
This section introduces the configuration and functions of the Web-Based management.
About Web-based Management
The Managed Switch offers management features that allow users to manage the Managed Switch from anywhere on the
network through a standard browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer.
The Web-Based Management supports Internet Explorer 6.0. It is based on Java Applets with an aim to reduce network
bandwidth consumption, enhance access speed and present an easy viewing screen.
By default, IE6.0 or later version does not allow Java Applets to open sockets. The user has to
explicitly modify the browser setting to enable Java Applets to use network ports.
The Managed Switch can be configured through an Ethernet connection, make sure the manager PC must be set on same the
IP subnet address with the Managed Switch.
For example, the default IP address of the WGSW / SGSW Managed Switch is 192.168.0.100, then the manager PC should be
set at 192.168.0.x (where x is a number between 1 and 254, except 100), and the default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
If you have changed the default IP address of the Managed Switch to 192.168.1.1 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 via console,
then the manager PC should be set at 192.168.1.x (where x is a number between 2 and 254) to do the relative configuration on
manager PC.
Figure 4-1-1 Web Management
42
Page 43

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Logging on the switch
1. Use Internet Explorer 6.0 or above Web browser. Enter the factory-default IP address to access the Web interface. The
factory-default IP Address as following:
http://192.168.0.100
2. When the following login screen appears, please enter the default username "admin" with password “admin” (or the
username/password you have changed via console) to login the main screen of Managed Switch. The login screen in
Figure 4-1-2 appears.
Figure 4-1-2 Login screen
Default User name: admin
Default Password: admin
After entering the username and password, the main screen appears as Figure 4-1-3.
43
Page 44

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 4-1-3 Default main page
Now, you can use the Web management interface to continue the switch management or manage the Managed Switch by Web
interface. The Switch Menu on the left of the web page let you access all the commands and statistics the Managed Switch
provides.
1. It is recommended to use Internet Explore 6.0 or above to access Managed Switch.
2. The changed IP address take effect immediately after click on the Save button, you need to
use the new IP address to access the Web interface.
3. For security reason, please change and memorize the new password after this first setup.
4. Only accept command in lowercase letter under web interface.
44
Page 45

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.1 Main WEB PAGE
The WGSW / SGSW Managed Switch provides a Web-based browser interface for configuring and managing it. This interface
allows you to access the Managed Switch using the Web browser of your choice. This chapter describes how to use the
Managed Switch’s Web browser interface to configure and manage it.
Main Functions Menu SFP Port Link Status
Copper Port Link Status
Main Screen
Figure 4-1-4 Main Page
Panel Display
The web agent displays an image of the Managed Switch’s ports. The Mode can be set to display different information for the
ports, including Link up or Link down. Clicking on the image of a port opens the Port Statistics page.
The port states are illustrated as follows:
Help Button
State Disabled Down Link
RJ-45 Ports
SFP Ports
Stack Ports
45
Page 46

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Main Menu
Using the onboard web agent, you can define system parameters, manage and control the Managed Switch, and all its ports, or
monitor network conditions. Via the Web-Management, the administrator can setup the Managed Switch by select the functions
those listed in the Main Function. The screen in Figure 4-1-5 appears.
Figure 4-1-5 WGSW/SGSW Managed Switch Main Funcrions Menu
46
Page 47

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.2 System
Use the System menu items to display and configure basic administrative details of the Managed Switch. Under System the
following topics are provided to configure and view the system information: This section has the following items:
■ System Information Provides basic system description, including contact information
■ IP Configuration Sets the IP address for management access
■ User Authentication
■ SNTP Configuration Simple Network Time Protocol. Configures SNTP client settings, including
■ Web Firmware Upgrade Upgrade the firmware via Web browser
■ TFTP Firmware Upgrade Upgrade the firmware via TFTP server
■ Configuration Save
■ Configuration Upload
■ Factory Default
■ System Reboot Restarts the switch
Allows to configure the system password required to access the web pages
or log in from CLI.
broadcast mode or aspecified list of servers
Save/view the switch configuration to remote host
Upload the switch configuration from remote host
Reset the configuration of the Managed Switch
47
Page 48

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.2.1 System Information
The System Info page provides information for the current device information. System Info page helps a switch administrator to
identify the hardware MAC address, software version and system uptime. The screen in Figure 4-2-1 appears.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Contact
• Name
• Location
• MAC Address
• System Date
• System Uptime
• Switch ID
• Software Version
Figure 4-2-1 System Information page screenshot
The system contact configured in SNMP \ System Information \ System Contact.
The system name configured in SNMP \ System Information \ System Name.
The system location configured in SNMP \ System Information \ System Location
The MAC Address of this switch.
The current (GMT) system time and date. The system time is obtained through
the configured SNTP Server
The period of time the device has been operational.
The switch ID. (SGSW-Series Only)
The software version of the switch.
, if any.
• Software Date
Buttons
Auto-refresh : Check this box to enable an automatic refresh of the page at regular intervals.
The date when the switch software was produced.
48
Page 49

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
: Click to refresh the page; any changes made locally will be undone.
For the SGSW series stackable switch, the System Information page add additional column to identify the current switch ID of
stack member switches in a stack group. The screen as below appears:
49
Page 50

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.2.2 IP Configuration
The IP Configuration includes the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway. The Configured column is used to view or change the
IP configuration.Fill up the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway for the device. The screen in Figure 4-2-2 appears.
Figure 4-2-2 IP Configuration page screenshot
The Current column is used to show the active IP configuration.
Object Description
• DHCP Client
• IP Address
• IP Mask
• IP Router
• SNTP Server
• VLAN ID
Enable the DHCP client by checking this box. If DHCP fails and the configured IP
address is zero, DHCP will retry. If DHCP fails and the configured IP address is
non-zero, DHCP will stop and the configured IP settings will be used. The DHCP
client will announce the configured System Name as hostname to provide DNS
lookup.
Provide the IP address of this switch in dotted decimal notation
Provide the IP mask of this switch dotted decimal notation
Provide the IP address of the router in dotted decimal notation
Provide the IP address of the SNTP Server in dotted decimal notation
Provide the managed VLAN ID. The allowed range is 1 through 4095.
.
.
.
.
Buttons
• Timezone Offset
Provide the timezone offset relative to UTC/GMT.
The offset is given in minutes east of GMT. The valid range is from -720 to 720
minutes.
50
Page 51

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
: Click to save changes.
: Click to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously saved values.
4.2.3 User Authentication
This page allows you to configure the system password required to access the web pages or log in from CLI. After setup
completed, please press “Save” button to take effect. Please login web interface with new password, the screen in Figure 4-2-3
appears.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Old Password
• New Password
• Confirm New
Password
Figure 4-2-3 User Authentication page screenshot
Enter the current system password. If this is incorrect, the new password will not
be set.
The system password. The allowed string length is 0 to 31, and the allowed
content is the ASCII characters from 32 to 126. It will not display as it is typed,
only asterisks (*) will show. Passwords are alpha numeric characters in length,
and are case sensitive.
The new password must be entered twice to catch typing errors. To confirm that
you entered it correctly, this field will not display, but will show asterisks (*)
After change the default password, if you forget the password. Please press the “Reset” button
in the front panel of the Managed Switch over 10 seconds and then release, the current setting
includes VLAN, will be lost and the Managed Switch will restore to the default mode.
51
Page 52

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.2.4 SNTP Configuration
In the System sub-function menu, you can see the SNTP Configuration (see Figure 4-4), by which you can configure the time
settings for the Managed Switch. You can specify SNTP Servers and set GMT Timezone. The SNTP Configuration screen in
Figure 4-2-4 appears.
Figure 4-2-4 SNTP Configuration page screenshot
The Time page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• SNTP Server
• Timezone Offset
• System Date
Provide the IP address of the SNTP Server in dotted decimal notation.
Enter a user-defined SNTP server IP addresses or hostname. This is a text string
of up to 64 characters containing the encoded unicast IP address or hostname of
a SNTP server. Unicast SNTP requests will be sent to this address. If this
address is a DNS hostname, then that hostname should be resolved into an IP
address each time a SNTP request is sent to it.
Provide the timezone offset relative to UTC/GMT.
The offset is given in minutes east of GMT.
The valid range is from -720 to 720 minutes.
Display the current local date and time (UTC) of the last SNTP request or receipt
of an unsolicited message. The field format is Year-Month-Day HH : MM : SS.
For example, 2008-08-20 21:15:03
• System Uptime
The device supports the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP). SNTP assures accurate
network device clock time synchronization up to the millisecond. Time synchronization is
performed by a network SNTP server. SNTP operates only as a client, and cannot provide time
services to other systems.
Display the time passed since the device boot up.
52
Page 53

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
It is recommended that you research any time server selection to ensure that it can meet your
specific time server requirements. Any NTP time server selection should be evaluated to
determine if the server in question meets your specific time server requirements.
For more detail about the Time Server and Time Server List, please refer to the following URL:
http://ntp.isc.org/bin/view/Servers/WebHome
http://ntp.isc.org/bin/view/Servers/NTPPoolServers
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/262680/en-us
4.2.5 WEB Firmware Upgrade
The Web Firmware Upgrade page contains fields for downloading system image files from the Local File browser to the device.
The Web Firmware Upgrade screen in Figure 4-2-5 appears.
Figure 4-2-5 Web Firmware Upgrade page screenshot
To open Firmware Upgrade screen perform the folling:
1. Click System -> Web Firmware Upgrade.
2. The Firmware Upgrade screen is displayed as in Figure 4-2-5.
3. Click the “Browse” button of the main page, the system would pop up the file selection menu to choose firmware.
4. Select on the firmware then click “Upload”, the Software Upload Progress would show the file upload status.
5. Once the software be loaded to the system successfully. The following screen appears. Click the “Yes” button to activate
the new software immediately. The system will load the new software after reboot.
Figure 4-2-6 Software successfully loaded notice screen
53
Page 54

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.2.6 TFTP Firmware Upgrade
The Firmware Upgrade page provides the functions to allow a user to update the Managed Switch firmware from the TFTP
server in the network. Before updating, make sure you have your TFTP server ready and the firmware image is on the TFTP
server. The screen in Figure 4-2-7 appears.
Figure 4-2-7 TFTP Firmware Update page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• TFTP Server IP
• Filename
• Upgrade button
To open Firmware Upgrade screen perform the folling:
1. Click System -> TFTP Firmware Upgrade.
2. The Firmware Upgrade screen is displayed as in Figure 4-2-7.
Fill in your TFTP server IP address.
The name of firmware image.
(Maximum length : 24 characters)
Press the button for upgrade the switch firmware.
3. Fill in the TFTP server IP Address and the firmware file name, click the “Upgrade” button of the main page, the system
would pop up the confirm message
.
54
Page 55

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 4-2-8 TFTP Firmware upgrade pop-up message
Figure 4-2-9 Firmware Upgrade pop-up message
4. Click “OK”, the Switch will start the TFTP upgrade procedure.
5. Please check your TFTP server application to confirm the TFTP file is well transmit to the Switch.
6. The Switch will reboot then, and It will cost 2 to 3 minutes for the TFTP firmware upgrade and reboot procedure. Please
wait for the process complete.
7. Once the new software is loaded to the system successfully, the Login screen appears. Enter the user name and password
to login the Switch.
DO NOT Power OFF the switch until the update progress is complete.
Do not quit the Firmware Upgrade page without press the “OK” button - after the image be
loaded. Or the system won’t apply the new firmware. User has to repeat the firmware
upgrade processes again.
55
Page 56

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.2.7 Configuration Save
This function allows backup and reload the current configuration of the Managed Switch to the local management station. The
screen in Figure 4-2-10 appears.
Figure 4-2-10 Configuration Save page screenshot
Configuration Download: Download the current configuration file of the switch to the local machine.
Configuration Download
1. Press the “Download” button to save the current configuration in manager workstation. The following screens in Figure
4-2-11 and 4-2-12 appear
Figure 4-2-11 File Download screen
2. Chose the file save path in management workstation.
56
Page 57

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 4-2-12 File save screen
4.2.8 Configuration Upload
This function allows backup and reload the current configuration of the Managed Switch to the local management station. The
screen in Figure 4-2-13 appears.
Figure 4-2-13 Configuration Upload page screenshot
Configuration Upload: Upload the existed configuration file to the Managed Switch. The configuration file had been
saved at the local machine already.
Configuration Upload
1. Click the “Browse” button of the main page, the system would pop up the file selection menu to choose saved
configuration.
57
Page 58

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 4-2-14 Windows file selection menu popup
2. Select on the configuration file then click “Upload”, the bottom of the browser shows the upload status.
3. After down, the main screen appears “Transfer Completed”.
58
Page 59

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.2.9 Factory Default
The Factory Reset button can reset the VDSL2 Switch back to the factory default mode. Be aware that the entire configuration
will be reset; include the IP address of the VDSL2 Switch. Once the Factory Reset item is pressed, the screen in Figure 4-2-15
appears.
Figure 4-2-15 Factory Default Reset screen
After the “Factory” button be pressed and rebooted, the system will load the default IP settings as following:
。 Default IP address: 192.168.0.100
。 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
。 Default Gateway: 192.168.0.254
。 The other setting value is back to disable or none.
To reset the VDSL2 Switch to the Factory default setting, you can also press the hardware reset
button at the front panel about 10 seconds. After the device be rebooted. You can login the
management WEB interface within the same subnet of 192.168.0.xx.
Hardware Reset button
59
Page 60

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.2.10 System Reboot
The Reboot page enables the device to be rebooted from a remote location. Once the Reboot button is pressed, user have to
re-login the WEB interface about 60 seconds later, the screen in Figure 4-2-16 appears.
Figure 4-2-16 System Reboot page screenshot
You can also check the SYS LED at the front panel to identify the System is load completely or not. If the SYS LED is blinking,
then it is in the firmware load stage; if the SYS LED light on, you can use the WEB browser to login the Switch.
60
Page 61

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Example 1: Save Current Configuration setting
To save all applied changes and set the current configuration as startup configuration. The startup-configuration file will be load
automatically across a system reboot.
1. Click System, File Management, Copy Operation.
2. Select “running-config to startup-config” as the file transfer method.
3. Select the startup file name used for startup on the Managed Switch to overwrite or specify a new file name, then click
Apply.
Figure 4-2-17 Configuration saving screenshot
You can also select any configuration file as the start-up configuration by using the
System/File Management /Set Start-Up page.
4. If you specify a new file name to startup-config, click System \ File Management \ Set Start-up to check the specified file be
set to “Y” in the “Startup” column.
Figure 4-2-18 Set Start-up screenshot
61
Page 62

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Example 2: Downloading System Software from a Server
When downloading runtime code, you can specify the destination file name to replace the current image, or first download the
file using a different name from the current runtime code file, and then set the new file as the startup file.
1. Click System, File Management, Copy Operation.
2. Select “tftp to file” as the file transfer method, enter the IP address of the TFTP server.
3. Set the file type to “opcode,” enter the file name of the software to download, select a file on the Managed Switch to
overwrite or specify a new file name and click Apply.
4. If you replaced the current firmware used for startup and want to start using the new operation code, reboot the system via
the System/Reset menu.
Figure 4-2-19 Download system software screenshot
Figure 4-2-20 TFTP Server system software transmit screenshot
62
Page 63

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
• If you download to a new destination file, go to the System / File / Set Start-Up menu, mark the operation code file used at
startup, and click Apply.
• To start the new firmware, reboot the system via the System / Reset menu.
• To delete a file, select System / File Management File / Delete. Select the file name from the given list by checking the tick
box and click Apply. Note that the file currently designated as the startup code cannot be deleted.
1. Up to two copies of the system software (i.e., the runtime firmware) can be stored in the
file directory on the Managed Switch.
2. The currently designated startup version of this file cannot be deleted.
The file name should not contain slashes (\ or /), the leading letter of the file name should
not be a period (.), and the maximum length for file names on the TFTP server is 127
characters or 31 characters for files on the switch. (Valid characters: A-Z, a-z, 0-9, ".", "-",
"_")
Example 3: Downloading Configuration Settings from a Server
You can download the configuration file under a new file name and then set it as the startup file, or you can specify the current
startup configuration file as the destination file to directly replace it.
1. Click System / File Management / Copy Operation.
2. Select “tftp to startup-config” as the file transfer method, enter the IP address of the TFTP server.
3. Enter the file name of the configuration file to download, select a file on the Managed Switch to overwrite or specify a new
file name and click Apply.
4. Reboot the system via the System / Reset menu.
Figure 4-2-21 Download system configuration screenshot
If you download to a new file name using “tftp to startup-config” or “tftp to file,” the file is automatically set as the start-up
63
Page 64

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
configuration file. To use the new settings, reboot the system via the System / Reset menu.
Example 4: Saving or Restoring Configuration Settings
You can upload/download configuration settings to/from a TFTP server. The configuration files can be later downloaded to
restore the Managed Switch’s settings.
1. Click System / File Management / Copy Operation.
2. Select “running-config to tftp” or “startup-config to tftp” as the file transfer method, enter the IP address of the TFTP
server.
3. Enter a new file name for the configuration to upload, and click Apply.
Figure 4-2-22 Upload system configuration screenshot
1. The file “Factory_Default_Config.cfg” can be copied to the TFTP server, but cannot
be used as the destination on the Managed Switch.
2. The maximum number of user-defined configuration files is limited only by available
flash memory space.
64
Page 65

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.3 Simple Network Management Protocol
4.3.1 SNMP Overview
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management
information between network devices. It is part of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol suite.
SNMP enables network administrators to manage network performance, find and solve network problems, and plan for network
growth.
An SNMP-managed network consists of three key components: Network management stations (NMSs), SNMP agents,
Management information base (MIB) and network-management protocol:
。 Network management stations (NMSs):Sometimes called consoles, these devices execute management applications
that monitor and control network elements. Physically, NMSs are usually engineering workstation-caliber computers with
fast CPUs, megapixel color displays, substantial memory, and abundant disk space. At least one NMS must be present in
each managed environment.
。 Agents:Agents are software modules that reside in network elements. They collect and store management information
such as the number of error packets received by a network element.
。 Management information base (MIB):A MIB is a collection of managed objects residing in a virtual information store.
Collections of related managed objects are defined in specific MIB modules.
。 network-management protocol:A management protocol is used to convey management information between agents
and NMSs. SNMP is the Internet community's de facto standard management protocol.
SNMP Operations
SNMP itself is a simple request/response protocol. NMSs can send multiple requests without receiving a response.
。 Get -- Allows the NMS to retrieve an object instance from the agent.
。 Set -- Allows the NMS to set values for object instances within an agent.
。 Trap -- Used by the agent to asynchronously inform the NMS of some event. The SNMPv2 trap message is designed to
replace the SNMPv1 trap message.
SNMP community
An SNMP community is the group that devices and management stations running SNMP belong to. It helps define where
information is sent. The community name is used to identify the group. A SNMP device or agent may belong to more than one
SNMP community. It will not respond to requests from management stations that do not belong to one of its communities. SNMP
default communities are:
。 Write = private
。 Read = public
4.3.2 SNMP System Configuration
Configure SNMP on this page.
65
Page 66

The SNMP System Configuration screen in Figure 4-3-1 appears.
Figure 4-3-1 SNMP System Configuration page screenshot
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Object Description
• Mode
• Version
• Read Community
Indicates the SNMP mode operation. Possible modes are:
• Enabled: Enable SNMP mode operation.
• Disabled: Disable SNMP mode operation.
Indicates the SNMP supported version. Possible versions are:
• SNMP v1: Set SNMP supported version 1.
• SNMP v2c: Set SNMP supported version 2c.
• SNMP v3: Set SNMP supported version 3.
Indicates the community read access string to permit access to SNMP agent.
The allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed content is the ASCII
characters from 33 to 126. The field only suits to SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c.
SNMPv3 is using USM for authentication and privacy and the community string
will associated with SNMPv3 communities table.
• Write Community
Indicates the community write access string to permit access to SNMP agent.
The allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed content is the ASCII
characters from 33 to 126. The field only suits to SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c.
SNMPv3 is using USM for authentication and privacy and the community string
will associated with SNMPv3 communities table.
• Engine ID
Indicates the SNMPv3 engine ID. The string must contain an even number
between 10 and 64 hexadecimal digits, but all-zeros and all-'F's are not allowed.
Change of the Engine ID will clear all original local users.
66
Page 67

4.3.3 SNMP System Information Configuration
The switch system information is provided here.
The System Information Configuration screen in Figure 4-3-2 appears.
Figure 4-3-2 System Information Configuration page screenshot
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• System Contact
• System Name
• System Location
The textual identification of the contact person for this managed node, together
with information on how to contact this person. The allowed string length is 0 to
255, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 32 to 126.
An administratively assigned name for this managed node. By convention, this is
the node's fully-qualified domain name. A domain name is a text string drawn
from the alphabet (A-Za-z), digits (0-9), minus sign (-). No space characters are
permitted as part of a name. The first character must be an alpha character. And
the first or last character must not be a minus sign. The allowed string length is 0
to 255.
The physical location of this node(e.g., telephone closet, 3rd floor). The allowed
string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 32
to 126.
4.3.4 SNMP Trap Configuration
Configure SNMP trap on this page.
The SNMP Trap Configuration screen in Figure 4-3-3 appears.
67
Page 68

Figure 4-3-3 SNMP Trap Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Object Description
• Trap Mode
Indicates the SNMP trap mode operation. Possible modes are:
• Enabled: Enable SNMP trap mode operation.
• Disabled: Disable SNMP trap mode operation.
• Trap Version
• Trap Community
Indicates the SNMP trap supported version. Possible versions are:
• SNMP v1: Set SNMP trap supported version 1.
• SNMP v2c: Set SNMP trap supported version 2c.
• SNMP v3: Set SNMP trap supported version 3.
Indicates the community access string when send SNMP trap packet. The
allowed string length is 0 to 255, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters
from 33 to 126.
• Trap Destination
Indicates the SNMP trap destination address.
Address
• Trap Authentication
Failure
Indicates the SNMP entity is permitted to generate authentication failure traps.
Possible modes are:
• Enabled: Enable SNMP trap authentication failure.
• Disabled: Disable SNMP trap authentication failure.
• Trap Inform Mode
• Trap Inform Timeout
Indicates the SNMP trap inform mode operation. Possible modes are:
• Enabled: Enable SNMP trap inform mode operation.
• Disabled: Disable SNMP trap inform mode operation.
Indicates the SNMP trap inform timeout. The allowed range is 0 to 2147.
(seconds)
• Trap Inform Retry
Indicates the SNMP trap inform retry times. The allowed range is 0 to 255.
Times
68
Page 69

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
• Trap Probe Security
Indicates the SNMP trap probe security engine ID mode of operation. Possible
Engine ID
• Trap Security Engine
ID
• Trap Security Name
4.3.5 SNMPv3 Configuration
values are:
• Enabled: Enable SNMP trap probe security engine ID mode of operation.
• Disabled: Disable SNMP trap probe security engine ID mode of operation.
Indicates the SNMP trap security engine ID. SNMPv3 sends traps and informs
using USM for authentication and privacy. A unique engine ID for these traps and
informs is needed. When "Trap Probe Security Engine ID" is enabled, the ID will
be probed automatically. Otherwise, the ID specified in this field is used. The
string must contain an even number between 10 and 64 hexadecimal digits, but
all-zeros and all-'F's are not allowed.
Indicates the SNMP trap security name. SNMPv3 traps and informs using USM
for authentication and privacy. A unique security name is needed when traps and
informs are enabled.
4.3.5.1 SNMPv3 Accesses Configuration
Configure SNMPv3 accesses table on this page. The entry index key are Group Name, Security Model and Security Level.
The SNMPv3 Accesses Configuration screen in Figure 4-3-4 appears.
Figure 4-3-4 SNMPv3 Accesses Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Delete
• Group Name
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
A string identifying the group name that this entry should belong to. The allowed
string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 33
69
Page 70

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
to 126.
• Security Model
• Security Level
• Read View Name
• Write View Name
Indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possible security
models are:
• any: Accepted any security model (v1|v2c|usm).
• v1: Reserved for SNMPv1.
• v2c: Reserved for SNMPv2c.
• usm: User-based Security Model (USM)
Indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possible security
models are:
• NoAuth, NoPriv: None authentication and none privacy.
• Auth, NoPriv: Authentication and none privacy.
• Auth, Priv: Authentication and privacy.
The name of the MIB view defining the MIB objects for which this request may
request the current values. The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed
content is the ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
The name of the MIB view defining the MIB objects for which this request may
potentially SET new values. The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed
content is the ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
4.3.5.2 SNMPv3 Communities Configuration
Configure SNMPv3 communities table on this page. The entry index key is Community.
The SNMPv3 Communities Configuration screen in Figure 4-3-5 appears.
Figure 4-3-5 SNMPv3 Communities Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Delete
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
70
Page 71

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
• Community
Indicates the community access string to permit access to SNMPv3 agent. The
allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters
from 33 to 126.
• Source IP
• Source Mask
Indicates the SNMP access source address.
Indicates the SNMP access source address mask.
4.3.5.3 SNMPv3 Groups Configuration
Configure SNMPv3 groups table on this page. The entry index key are Security Model and Security Name.
The SNMPv3 Groups Configuration screen in Figure 4-3-6 appears.
Figure 4-3-6 SNMPv3 Groups Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Delete
• Security Model
• Security Name
• Group Name
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
Indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possible security
models are:
• v1: Reserved for SNMPv1.
• v2c: Reserved for SNMPv2c.
• usm: User-based Security Model (USM).
A string identifying the security name that this entry should belong to.
The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the ASCII
characters from 33 to 126.
A string identifying the group name that this entry should belong to.
The allowed string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the ASCII
71
Page 72

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
characters from 33 to 126.
4.3.5.4 SNMPv3 Users Configuration
Configure SNMPv3 users table on this page. The entry index key are Engine ID and User Name.
The SNMPv3 Users Configuration screen in Figure 4-3-7 appears.
Figure 4-3-7 SNMPv3 Users Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Delete
• Engine ID
• User Name
• Security Level
Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
A octet string identifying the engine ID that this entry should belong to. The string
must contain an even number between 10 and 64 hexadecimal digits, but
all-zeros and all-'F's are not allowed.
A string identifying the user name that this entry should belong to. The allowed
string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 33
to 126.
Indicates the security model that this entry should belong to. Possible security
models are:
• NoAuth, NoPriv: None authentication and none privacy.
• Auth, NoPriv: Authentication and none privacy.
• Auth, Priv: Authentication and privacy.
The value of security level cannot be modified if entry already exist. That
means must first ensure that the value is set correctly.
• Authentication
Protocol
Indicates the authentication protocol that this entry should belong to. Possible
authentication protocol are:
• None: None authentication protocol.
• MD5: An optional flag to indicate that this user using MD5 authentication
72
Page 73

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
protocol.
• SHA: An optional flag to indicate that this user using SHA authentication
protocol.
The value of security level cannot be modified if entry already exist. That
means must first ensure that the value is set correctly.
• Authentication
Password
• Privacy Protocol
• Privacy Password
A string identifying the authentication pass phrase. For MD5 authentication
protocol, the allowed string length is 8 to 32. For SHA authentication protocol, the
allowed string length is 8 to 40. The allowed content is the ASCII characters from
33 to 126.
Indicates the privacy protocol that this entry should belong to. Possible privacy
protocol are:
• None: None privacy protocol.
• DES: An optional flag to indicate that this user using DES authentication
A string identifying the privacy pass phrase. The allowed string length is 8 to 32,
and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 33 to 126.
4.3.5.5 SNMPv3 Views Configuration
protocol.
Configure SNMPv3 views table on this page. The entry index key are View Name and OID Subtree.
The SNMPv3 Views Configuration screen in Figure 4-3-8 appears.
Figure 4-3-8 SNMPv3 Views Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Delete • Check to delete the entry. It will be deleted during the next save.
• View Name
A string identifying the view name that this entry should belong to. The allowed
string length is 1 to 32, and the allowed content is the ASCII characters from 33
to 126.
73
Page 74

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
• View Type
Indicates the view type that this entry should belong to. Possible view type are:
• included: An optional flag to indicate that this view subtree should be
included.
• excluded: An optional flag to indicate that this view subtree should be
excluded.
General, if a view entry's view type is 'excluded', it should be exist another view
entry which view type is 'included' and it's OID subtree overstep the 'excluded'
view entry.
• OID Subtree
================================================================================================
The OID defining the root of the subtree to add to the named view. The allowed
OID length is 1 to 128. The allowed string content is digital number or asterisk(*).
EXAMPLE: Add a new SNMPv3 user
In the New User page, define a name and assign it to a group, then click Add to save the configuration and return to the
User Name list.
74
Page 75

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 4-3-9 SNMPv3 Users-NEW page screenshot
Once the new SNMPv3 user be successed add and be assign to a snmp group, this entry will shows in the users table.
Figure 4-3-10 SNMPv3 Users page screenshot
EXAMPLE: Add a new SNMPv3 Group
In the New Group page, define a name, assign a security model and level, and then select read and write views. Click Add
to save the new group and return to the Groups list.
75
Page 76

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 4-3-11 SNMPv3 Groups-NEW page screenshot
76
Page 77

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.4 Port Management
Use the Port Menu to display or configure the Managed Switch's ports. This section has the following items:
Port Configuration
Port Statistics
Mirror Port Configuration
Configures port connection settings
Lists Ethernet and RMON port statistics
Sets the source and target ports for mirroring
4.4.1 Port Configuration
This page displays current port configurations. Ports can also be configured here.
The port settings relate to the currently selected stack unit, as reflected by the page header.
The table has one row for each port on the selected switch in the stack and a number of columns, which are:
The Port Configuration screen in Figure 4-4-1 appears.
Figure 4-4-1 Port Configuration page screenshot
77
Page 78

The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
• Port
• Link
• Current Link Speed
• Configured Link Speed
• Flow Control
This is the logical port number for this row.
The current link state is displayed graphically. Green indicates the link is up and
red that it is down.
Provides the current link speed of the port.
Select any available link speed for the given switch port. Draw the menu bar to
select the mode.
• Auto Speed - Setup Auto negotiation.
• 10 half - Force sets 10Mbps/Half-Duplex mode.
• 10 Full - Force sets 10Mbps/Full-Duplex mode.
• 100 half - Force sets 100Mbps/Half-Duplex mode.
• 100 full - Force sets 100Mbps/Full-Duplex mode.
• 1000 full - Force sets 10000Mbps/Full-Duplex mode.
• Disable - Shutdown the port manually.
When Auto Speed is selected for a port, this section indicates the flow control
capability that is advertised to the link partner.
• Maximum Frame
• Excessive Collision
Mode
• Power Control
When a fixed-speed setting is selected, that is what is used.
• Current Rx column indicates whether pause frames on the port are
obeyed.
• Current Tx column indicates whether pause frames on the port are
transmitted.
The Rx and Tx settings are determined by the result of the last Auto-Negotiation.
Check the configured column to use flow control.
This setting is related to the setting for Configured Link Speed.
Enter the maximum frame size allowed for the switch port, including FCS. The
allowed range is 1518 bytes to 9600 bytes.
Configure port transmit collision behavior.
• Discard: Discard frame after 16 collisions (default).
• estart: Restart backoff algorithm after 16 collisions.
The Usage column shows the current percentage of the power consumption per
port. The Configured column allows for changing the power savings mode
parameters per port.
• Disabled: All power savings mechanisms disabled.
• ActiPHY: Link down power savings enabled.
• Dynamic: Link up power savings enabled.
78
Page 79

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
• Enabled: Link up and link down power savings enabled.
• Total Power Usage
When set each port to run at 100M Full, 100M Half, 10M Full, and 10M Half-speed modes. The
Auto-MDIX function will disable.
Total power usage in board, measured in percent.
4.4.2 Port Statistics Overview
This page provides an overview of general traffic statistics for all switch ports. The ports belong to the currently selected stack
unit, as reflected by the page header.
The Port Statistics Overview screen in Figure 4-4-2 appears.
Figure 4-4-2 Port Statistics Overview page screenshot
79
Page 80

The displayed counters are:
Object Description
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
• Port
• Packets
• Bytes
• Errors
• Drops
• Filtered
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row.
The number of received and transmitted packets per port.
The number of received and transmitted bytes per port.
The number of frames received in error and the number of incomplete
transmissions per port.
The number of frames discarded due to ingress or egress congestion.
The number of received frames filtered by the forwarding process.
4.4.3 Detailed Port Statistics
This page provides detailed traffic statistics for a specific switch port. Use the port select box to select which switch port details
to display. The selected port belong to the currently selected stack unit, as reflected by the page header.
The displayed counters are the totals for receive and transmit, the size counters for receive and transmit, and the error counters
for receive and transmit. The Detailed Port Statistics screen in Figure 4-4-3 appears.
Figure 4-4-3 Detailed Port Statistics Port 1 page screenshot
80
Page 81

The page includes the following fields:
Receive Total and Transmit Total
Object Description
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
• Rx and Tx Packets
• Rx and Tx Octets
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) packets
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) bytes. Includes FCS, but
excludes framing bits.
• Rx and Tx Unicast
• Rx and Tx Multicast
• Rx and Tx Broadcast
• Rx and Tx Pause
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) unicast packets.
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) multicast packets.
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) broadcast packets.
A count of the MAC Control frames received or transmitted on this port that have
an opcode indicating a PAUSE operation.
Receive and Transmit Size Counters
The number of received and transmitted (good and bad) packets split into categories based on their respective frame
sizes.
Receive and Transmit Queue Counters
The number of received and transmitted packets per input and output queue.
Receive Error Counters
Object Description
• Rx Drops
The number of frames dropped due to lack of receive buffers or egress
congestion.
• Rx CRC/Alignment
• Rx Undersize
• Rx Oversize
• Rx Fragments
• Rx Jabber
• Rx Filtered
The number of frames received with CRC or alignment errors.
1
The number of short
The number of long
The number of short
The number of long
frames received with valid CRC.
2
frames received with valid CRC.
1
frames received with invalid CRC.
2
frames received with invalid CRC.
The number of received frames filtered by the forwarding process.
Short frames are frames that are smaller than 64 bytes.
Long frames are frames that are longer than the configured maximum
frame length for this port.
81
Page 82

Transmit Error Counters
Object Description
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
• Tx Drops
• Tx Late/Exc. Coll.
The number of frames dropped due to output buffer congestion.
The number of frames dropped due to excessive or late collisions.
4.4.4 Port Mirroring Configuration
Configure port Mirroring on this page. This function provide to monitoring network traffic that forwards a copy of each incoming
or outgoing packet from one port of a network Switch to another port where the packet can be studied. It enables the manager to
keep close track of switch performance and alter it if necessary.
• To debug network problems, selected traffic can be copied, or mirrored, to a mirror port where a frame analyzer can be
attached to analyze the frame flow.
• The Managed Switch can unobtrusively mirror traffic from any port to a monitor port. You can then attach a protocol
analyzer or RMON probe to this port to perform traffic analysis and verify connection integrity.
Figure 4-4-4 Port Mirror application
The traffic to be copied to the mirror port is selected as follows:
• All frames received on a given port (also known as ingress or source mirroring).
• All frames transmitted on a given port (also known as egress or destination mirroring).
82
Page 83

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
Mirror Port Configuration
The Port Mirror Configuration screen in Figure 4-4-5 and Figure 4-4-6 appears.
WGSW Standalone Switch
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 4-4-5 Port Mirror Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Port to mirror to
• Port
• Mode
Frames from ports that have either source or destination mirroring enabled are
mirrored to this port. Disabled disables mirroring.
The logical port for the settings contained in the same row.
Select mirror mode.
• Rx only
• Tx only
• Disabled
• Enabled
Frames received at this port are mirrored to the mirroring port.
Frames transmitted are not mirrored.
Frames transmitted from this port are mirrored to the mirroring
port. Frames received are not mirrored.
Neither frames transmitted or frames received are mirrored.
Frames received and frames transmitted are mirrored to the
mirror port.
83
Page 84

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW Stackable Switch
The SGSW Stackable switch supports port mirror function over stack switch.
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 4-4-6 Port Mirror Configuration page screenshot
Object Description
• Switch to mirror to
Frames from ports that have either source or destination mirroring enabled are
mirrored to this switch.
84
Page 85

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.5 Link Aggregation
Port Aggregation optimizes port usage by linking a group of ports together to form a single Link Aggregated Groups (LAGs). Port
Aggregation multiplies the bandwidth between the devices, increases port flexibility, and provides link redundancy.
Each LAG is composed of ports of the same speed, set to full-duplex operations. Ports in a LAG, can be of different media types
(UTP/Fiber, or different fiber types), provided they operate at the same speed.
Aggregated Links can be assigned manually (Port Trunk) or automatically by enabling Link Aggregation Control Protocol
(LACP) on the relevant links.
Aggregated Links are treated by the system as a single logical port. Specifically, the Aggregated Link has similar port attributes
to a non-aggregated port, including auto-negotiation, speed, Duplex setting, etc.
The device supports the following Aggregation links :
Static LAGs (Port Trunk) – Force aggregared selected ports to be a trounk group.
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) LAGs - LACP LAG negotiate Aggregated Port links with other LACP
ports located on a different device. If the other device ports are also LACP ports, the devices establish a LAG
between them.
Figure 4-5-1 Link Aggregation
85
Page 86

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a standardized means for exchanging information between Partner
Systems that require high speed redundant links. Link aggregation lets you group up to eight consecutive ports into a single
dedicated connection. This feature can expand bandwidth to a device on the network. LACP operation requires full-duplex mode,
more detail information refer to the IEEE 802.3ad standard.
Port link aggregations can be used to increase the bandwidth of a network connection or to ensure fault recovery. Link
aggregation lets you group up to 4 consecutive ports into a single dedicated connection between any two the Switch or other
Layer 2 switches. However, before making any physical connections between devices, use the Link aggregation Configuration
menu to specify the link aggregation on the devices at both ends. When using a port link aggregation, note that:
• The ports used in a link aggregation must all be of the same media type (RJ-45, 100 Mbps fiber).
• The ports that can be assigned to the same link aggregation have certain other restrictions (see below).
• Ports can only be assigned to one link aggregation.
• The ports at both ends of a connection must be configured as link aggregation ports.
• None of the ports in a link aggregation can be configured as a mirror source port or a mirror target port.
• All of the ports in a link aggregation have to be treated as a whole when moved from/to, added or deleted from a VLAN.
• The Spanning Tree Protocol will treat all the ports in a link aggregation as a whole.
• Enable the link aggregation prior to connecting any cable between the switches to avoid creating a data loop.
• Disconnect all link aggregation port cables or disable the link aggregation ports before removing a port link aggregation to
avoid creating a data loop.
It allows a maximum of 16 ports to be aggregated at the same time. The Managed Switch support Gigabit Ethernet ports (up to
12 groups). If the group is defined as a LACP static link aggregationing group, then any extra ports selected are placed in a
standby mode for redundancy if one of the other ports fails. If the group is defined as a local static link aggregationing group,
then the number of ports must be the same as the group member ports.
The aggregation code ensures that frames belonging to the same frame flow (for example, a TCP connection) are always
forwarded on the same link aggregation member port. Reording of frames within a flow is therefore not possible. The
aggregation code is
based on the following information:
• Source MAC
• Destination MAC
• Source and destination IPv4 address.
• Source and destination TCP/UDP ports for IPv4 packets
• IPv6 Flow Label
Normally, all 5 contributions to the aggregation code should be enabled to obtain the best traffic distribution among the link
aggregation member ports. Each link aggregation may consist of up to 16 member ports. Any quantity of link aggregation s may
be configured for the device (only limited by the quantity of ports on the device.) To configure a proper traffic distribution, the
ports within a link aggregation must use the same link speed.
86
Page 87

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.5.1 Static Aggregation Configuration
This page is used to configure the Aggregation hash mode and the aggregation group. The aggregation hash mode settings are
global, whereas the aggregation group relate to the currently selected stack unit, as reflected by the page header.
Hash Code Contributors
Figure 4-5-2 Aggregation Mode Configuration page screenshot
Object Description
• Source MAC Address
• Destination MAC
Address
• IP Address
• TCP/UDP Port Number
The Source MAC address can be used to calculate the destination port for the
frame. Check to enable the use of the Source MAC address, or uncheck to
disable. By default, Source MAC Address is enabled.
The Destination MAC Address can be used to calculate the destination port for
the frame. Check to enable the use of the Destination MAC Address, or uncheck
to disable. By default, Destination MAC Address is disabled.
The IP address can be used to calculate the destination port for the frame. Check
to enable the use of the IP Address, or uncheck to disable. By default, IP Address
is enabled.
The TCP/UDP port number can be used to calculate the destination port for the
frame. Check to enable the use of the TCP/UDP Port Number, or uncheck to
disable. By default, TCP/UDP Port Number is enabled.
Static Aggregation Group Configuration
The Aggregation Group Configuration screen in Figure 4-5-3 appears.
87
Page 88

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Figure 4-5-3 Aggregation Group Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
.
Object Description
• Locality
• Group ID
• Port Members
Indicates the aggregation group type. This field is only valid for stackable
switches.
• Global: The group members may reside on different units in the stack. The
device supports two 8-port global aggregations.
• Local: The group members reside on the same unit. Each local
aggregation may consist of up to 16 members.
Indicates the group ID for the settings contained in the same row. Group ID
"Normal" indicates there is no aggregation. Only one group ID is valid per port.
Each switch port is listed for each group ID. Select a radio button to include a port
in an aggregation, or clear the radio button to remove the port from the
aggregation. By default, no ports belong to any aggregation group.
88
Page 89

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.5.2 LACP Configuration
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) - LACP LAG negotiate Aggregated Port links with other LACP ports located on a
different device. LACP allows switches connected to each other to discover automatically whether any ports are member of the
same LAG.
This page allows the user to inspect the current LACP port configurations, and possibly change them as well. The LACP port
settings relate to the currently selected stack unit, as reflected by the page header. The LACP Port Configuration screen in
Figure 4-5-4 appears.
Figure 4-5-4 LACP Port Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Port
• LACP Enabled
• Key
The switch port number.
Controls whether LACP is enabled on this switch port. LACP will form an
aggregation when 2 or more ports are connected to the same partner. LACP can
form max 12 LLAGs per switch and 2 GLAGs per stack.
The Key value incurred by the port, range 1-65535 . The Auto setting will set the
key as appropriate by the physical link speed, 10Mb = 1, 100Mb = 2, 1Gb = 3.
Using the Specific setting, a user-defined value can be entered. Ports with the
same Key value can participate in the same aggregation group, while ports with
different keys cannot.
The default setting is “Auto”
• Role
The Role shows the LACP activity status. The Active will transmit LACP packets
89
Page 90

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
each second, while Passive will wait for a LACP packet from a partner (speak if
spoken to).
4.5.3 LACP System Status
This page provides a status overview for all LACP instances. The LACP Status page display the current LACP aggregation
Groups and LACP Port status . The LACP System Status screen in Figure 4-5-5 appears.
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Aggr ID
• Partner System ID
• Partner Key
• Last changed
• Local Ports
Figure 4-5-5 LACP System Status page screenshot
The Aggregation ID associated with this aggregation instance.
For LLAG the id is shown as 'isid:aggr-id' and for GLAGs as 'aggr-id'
The system ID (MAC address) of the aggregation partner.
The Key that the partner has assigned to this aggregation ID.
The time since this aggregation changed.
Shows which ports are a part of this aggregation for this switch/stack.
The format is: "Switch ID:Port".
4.5.4 LACP Port Status
This page provides a status overview for LACP status for all ports.
The LACP Port Status screen in Figure 4-5-6 appears.
90
Page 91

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Port
• LACP
• Key
• Aggr ID
• Partner System ID
• Partner Port
Figure 4-5-6 LACP Port Status page screenshot
The switch port number.
'Yes' means that LACP is enabled and the port link is up. 'No' means that LACP is
not enabled or that the port link is down.
The key assigned to this port.
Only ports with the same key can aggregate together.
The Aggregation ID assigned to this aggregation group.
IDs 1 and 2 are GLAGs while IDs 3-14 are LLAGs.
The partners System ID (MAC address).
The partners port number connected to this port.
91
Page 92

4.5.5 LACP statistics
This page provides an overview for LACP statistics for all ports.
The LACP statistics screen in Figure 4-5-7 appears.
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Port
• LACP Transmitted
• LACP Received
• Discarded
Figure 4-5-7 LACP Port statistics page screenshot
The switch port number.
Shows how many LACP frames have been sent from each port.
Shows how many LACP frames have been received at each port.
Shows how many unknown or illegal LACP frames have been discarded at each
port.
92
Page 93

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.6 VLAN
4.6.1 VLAN Overview
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network topology configured according to a logical scheme rather than the physical
layout. VLAN can be used to combine any collection of LAN segments into an autonomous user group that appears as a single
LAN. VLAN also logically segment the network into different broadcast domains so that packets are forwarded only between
ports within the VLAN. Typically, a VLAN corresponds to a particular subnet, although not necessarily.
VLAN can enhance performance by conserving bandwidth, and improve security by limiting traffic to specific domains.
A VLAN is a collection of end nodes grouped by logic instead of physical location. End nodes that frequently communicate with
each other are assigned to the same VLAN, regardless of where they are physically on the network. Logically, a VLAN can be
equated to a broadcast domain, because broadcast packets are forwarded to only members of the VLAN on which the
broadcast was initiated.
1. No matter what basis is used to uniquely identify end nodes and assign these nodes VLAN
membership, packets cannot cross VLAN without a network device performing a routing
function between the VLAN.
2. The Managed Switch supports IEEE 802.1Q VLAN. The port untagging function can be used
to remove the 802.1 tag from packet headers to maintain compatibility with devices that are
tag-unaware.
3. The Switch's default is to assign all ports to a single 802.1Q VLAN named DEFAULT_VLAN.
As new VLAN is created, the member ports assigned to the new VLAN will be removed from
the DEFAULT_ VLAN port member list. The DEFAULT_VLAN has a VID = 1.
This section has the following items:
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
Private VLAN
Enable IEEE 802.1Q Tag based VLAN group
Enables 802.1Q (QinQ) Tunneling
Creates/removes primary or community VLANs
93
Page 94

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.6.2 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
In large networks, routers are used to isolate broadcast traffic for each subnet into separate domains. This Managed Switch
provides a similar service at Layer 2 by using VLANs to organize any group of network nodes into separate broadcast domains.
VLANs confine broadcast traffic to the originating group, and can eliminate broadcast storms in large networks. This also
provides a more secure and cleaner network environment.
An IEEE 802.1Q VLAN is a group of ports that can be located anywhere in the network, but communicate as though they belong
to the same physical segment.
VLANs help to simplify network management by allowing you to move devices to a new VLAN without having to change any
physical connections. VLANs can be easily organized to reflect departmental groups (such as Marketing or R&D), usage groups
(such as e-mail), or multicast groups (used for multimedia applications such as videoconferencing).
VLANs provide greater network efficiency by reducing broadcast traffic, and allow you to make network changes without having
to update IP addresses or IP subnets. VLANs inherently provide a high level of network security since traffic must pass through
a configured Layer 3 link to reach a different VLAN.
This Managed Switch supports the following VLAN features:
Up to 4k VLANs based on the IEEE 802.1Q standard
Distributed VLAN learning across multiple switches using explicit or implicit tagging and GVRP protocol
Port overlapping, allowing a port to participate in multiple VLANs
End stations can belong to multiple VLANs
Passing traffic between VLAN-aware and VLAN-unaware devices
Priority tagging
1. The Managed Switch allows 4k user-manageable VLANs.
2. One other VLAN (VLAN ID 4093) is reserved for switch clustering.
■ IEEE 802.1Q Standard
IEEE 802.1Q (tagged) VLAN are implemented on the Switch. 802.1Q VLAN require tagging, which enables them to span the
entire network (assuming all switches on the network are IEEE 802.1Q-compliant).
VLAN allow a network to be segmented in order to reduce the size of broadcast domains. All packets entering a VLAN will only
be forwarded to the stations (over IEEE 802.1Q enabled switches) that are members of that VLAN, and this includes broadcast,
multicast and unicast packets from unknown sources.
VLAN can also provide a level of security to your network. IEEE 802.1Q VLAN will only deliver packets between stations that are
members of the VLAN. Any port can be configured as either tagging or untagging. The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
allows VLAN to work with legacy switches that don't recognize VLAN tags in packet headers. The tagging feature allows VLAN
to span multiple 802.1Q-compliant switches through a single physical connection and allows Spanning Tree to be enabled on all
94
Page 95

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
ports and work normally.
Any port can be configured as either tagging or untagging. The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLAN allow VLAN to work
with legacy switches that don’t recognize VLAN tags in packet headers. The tagging feature allows VLAN to span multiple
802.1Q-compliant switches through a single physical connection and allows Spanning Tree to be enabled on all ports and work
normally.
Some relevant terms:
- Tagging - The act of putting 802.1Q VLAN information into the header of a packet.
- Untagging - The act of stripping 802.1Q VLAN information out of the packet header.
■ 802.1Q VLAN Tags
The figure below shows the 802.1Q VLAN tag. There are four additional octets inserted after the source MAC address. Their
presence is indicated by a value of 0x8100 in the Ether Type field. When a packet's Ether Type field is equal to 0x8100, the
packet carries the IEEE 802.1Q/802.1p tag. The tag is contained in the following two octets and consists of 3 bits of user priority,
1 bit of Canonical Format Identifier (CFI - used for encapsulating Token Ring packets so they can be carried across Ethernet
backbones), and 12 bits of VLAN ID (VID). The 3 bits of user priority are used by 802.1p. The VID is the VLAN identifier and is
used by the 802.1Q standard. Because the VID is 12 bits long, 4094 unique VLAN can be identified.
The tag is inserted into the packet header making the entire packet longer by 4 octets. All of the information originally contained
in the packet is retained.
802.1Q Tag
User Priority CFI
VLAN ID (VID)
3 bits 1 bits 12 bits
TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier) TCI (Tag Control Information)
2 bytes 2 bytes
Preamble Destination
Address
Source
Address
VLAN TAG
Ethernet
Type
Data FCS
6 bytes 6 bytes 4 bytes 2 bytes 46-1517 bytes 4 bytes
The Ether Type and VLAN ID are inserted after the MAC source address, but before the original Ether Type/Length or Logical
Link Control. Because the packet is now a bit longer than it was originally, the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) must be
recalculated.
95
Page 96

Adding an IEEE802.1Q Tag
User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
Dest. Addr. Src. Addr. Length/E. type Data Old CRC
Dest. Addr. Src. Addr.
E. type Tag
Priority CFI VLAN ID
Length/E. type Data New CRC
Original Ethernet
New Tagged Packet
■ Port VLAN ID
Packets that are tagged (are carrying the 802.1Q VID information) can be transmitted from one 802.1Q compliant network
device to another with the VLAN information intact. This allows 802.1Q VLAN to span network devices (and indeed, the entire
network – if all network devices are 802.1Q compliant).
Every physical port on a switch has a PVID. 802.1Q ports are also assigned a PVID, for use within the switch. If no VLAN are
defined on the switch, all ports are then assigned to a default VLAN with a PVID equal to 1. Untagged packets are assigned the
PVID of the port on which they were received. Forwarding decisions are based upon this PVID, in so far as VLAN are concerned.
Tagged packets are forwarded according to the VID contained within the tag. Tagged packets are also assigned a PVID, but the
PVID is not used to make packet forwarding decisions, the VID is.
Tag-aware switches must keep a table to relate PVID within the switch to VID on the network. The switch will compare the VID of
a packet to be transmitted to the VID of the port that is to transmit the packet. If the two VID are different the switch will drop the
packet. Because of the existence of the PVID for untagged packets and the VID for tagged packets, tag-aware and tag-unaware
network devices can coexist on the same network.
A switch port can have only one PVID, but can have as many VID as the switch has memory in its VLAN table to store them.
Because some devices on a network may be tag-unaware, a decision must be made at each port on a tag-aware device before
packets are transmitted – should the packet to be transmitted have a tag or not? If the transmitting port is connected to a
tag-unaware device, the packet should be untagged. If the transmitting port is connected to a tag-aware device, the packet
should be tagged.
■ Default VLANs
The Switch initially configures one VLAN, VID = 1, called "default." The factory default setting assigns all ports on the Switch to
the "default". As new VLAN are configured in Port-based mode, their respective member ports are removed from the "default."
■ Assigning Ports to VLANs
Before enabling VLANs for the switch, you must first assign each port to the VLAN group(s) in which it will participate. By default
all ports are assigned to VLAN 1 as untagged ports. Add a port as a tagged port if you want it to carry traffic for one or more
96
Page 97

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
VLANs, and any intermediate network devices or the host at the other end of the connection supports VLANs. Then assign ports
on the other VLAN-aware network devices along the path that will carry this traffic to the same VLAN(s), either manually or
dynamically using GVRP. However, if you want a port on this switch to participate in one or more VLANs, but none of the
intermediate network devices nor the host at the other end of the connection supports VLANs, then you should add this port to
the VLAN as an untagged port.
VLAN-tagged frames can pass through VLAN-aware or VLAN-unaware network interconnection
devices, but the VLAN tags should be stripped off before passing it on to any end-node host that
does not support VLAN tagging.
■ VLAN Classification
When the switch receives a frame, it classifies the frame in one of two ways. If the frame is untagged, the switch assigns the
frame to an associated VLAN (based on the default VLAN ID of the receiving port). But if the frame is tagged, the switch uses
the tagged VLAN ID to identify the port broadcast domain of the frame.
■ Port Overlapping
Port overlapping can be used to allow access to commonly shared network resources among different VLAN groups, such as
file servers or printers. Note that if you implement VLANs which do not overlap, but still need to communicate, you can connect
them by enabled routing on this switch.
■ Untagged VLANs
Untagged (or static) VLANs are typically used to reduce broadcast traffic and to increase security. A group of network users
assigned to a VLAN form a broadcast domain that is separate from other VLANs configured on the switch. Packets are
forwarded only between ports that are designated for the same VLAN. Untagged VLANs can be used to manually isolate user
groups or subnets. However, you should use IEEE 802.3 tagged VLANs with GVRP whenever possible to fully automate VLAN
registration.
97
Page 98

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.6.3 VLAN Basic Information
The VLAN Basic Information page displays basic information on the VLAN type supported by the Managed Switch.
The VLAN Basic Information screen in Figure 4-6-1 appears.
Figure 4-6-1 VLAN Basic Information page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• VLAN Mode
• Maximum VLAN ID
• Maximum Number of
Supported VLANs
• Current number of
VLANs
• VLAN Learning
Display the current VLAN mode used by this Managed Switch
Port-Based
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
Maximum VLAN ID recognized by this Managed Switch.
Maximum number of VLANs that can be configured on this Managed Switch.
Display the current number of VLANs
Display the VLAN learning mode. The Managed Switch supports IVL (IVL
Independent vlan learning).
98
Page 99

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
4.6.4 VLAN Port Configuration
This page is used for configuring the Managed Switch port VLAN. The VLAN per Port Configuration page contains fields for
managing ports that are part of a VLAN. The port default VLAN ID (PVID) is configured on the VLAN Port Configuration page. All
untagged packets arriving to the device are tagged by the ports PVID.
Understand nomenclature of the Switch
■ IEEE 802.1Q Tagged and Untagged
Every port on an 802.1Q compliant switch can be configured as tagged or untagged.
• Tagged:
• Untagged:
Frame Leave
Leave port is tagged Frame remains tagged Tag is inserted
Leave port is untagged Tag is removed Frame remain untagged
Ports with tagging enabled will put the VID number, priority and other VLAN information into the
header of all packets that flow into those ports. If a packet has previously been tagged, the port
will not alter the packet, thus keeping the VLAN information intact. The VLAN information in the
tag can then be used by other 802.1Q compliant devices on the network to make
packet-forwarding decisions.
Ports with untagging enabled will strip the 802.1Q tag from all packets that flow into those
ports. If the packet doesn't have an 802.1Q VLAN tag, the port will not alter the packet. Thus,
all packets received by and forwarded by an untagging port will have no 802.1Q VLAN
information. (Remember that the PVID is only used internally within the Switch). Untagging is
used to send packets from an 802.1Q-compliant network device to a non-compliant network
device.
Frame Income
Income Frame is tagged Income Frame is untagged
■ IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (Q-in-Q)
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QinQ) is designed for service providers carrying traffic for multiple customers across their networks.
QinQ tunneling is used to maintain customer-specific VLAN and Layer 2 protocol configurations even when different customers
use the same internal VLAN IDs. This is accomplished by inserting Service Provider VLAN (SPVLAN) tags into the customer’s
frames when they enter the service provider’s network, and then stripping the tags when the frames leave the network.
A service provider’s customers may have specific requirements for their internal VLAN IDs and number of VLANs supported.
VLAN ranges required by different customers in the same service-provider network might easily overlap, and traffic passing
through the infrastructure might be mixed. Assigning a unique range of VLAN IDs to each customer would restrict customer
configurations, require intensive processing of VLAN mapping tables, and could easily exceed the maximum VLAN limit of
4096.
99
Page 100

User’s Manual of WGSW-24040 / WGSW-24040R
SGSW-24040 / SGSW-24040R
The Managed Switch supports multiple VLAN tags and can therefore be used in MAN applications as a provider bridge,
aggregating traffic from numerous independent customer LANs into the MAN (Metro Access Network) space. One of the
purposes of the provider bridge is to recognize and use VLAN tags so that the VLANs in the MAN space can be used
independent of the customers’ VLANs. This is accomplished by adding a VLAN tag with a MAN-related VID for frames entering
the MAN. When leaving the MAN, the tag is stripped and the original VLAN tag with the customer-related VID is again available.
This provides a tunneling mechanism to connect remote costumer VLANs through a common MAN space without interfering
with the VLAN tags. All tags use EtherType 0x8100 or 0x88A8, where 0x8100 is used for customer tags and 0x88A8 are used
for service provider tags.
In cases where a given service VLAN only has two member ports on the switch, the learning can be disabled for the particular
VLAN and can therefore rely on flooding as the forwarding mechanism between the two ports. This way, the MAC table
requirements is reduced.
The VLAN Port Configuration screen in Figure 4-6-2 appears.
Figure 4-6-2 VLAN Port Configuration page screenshot
The page includes the following fields:
Object Description
• Port
• PVID
This is the logical port number for this row.
Allow assign PVID for selected port. The range for the PVID is 1-4094.
The PVID will be inserted into all untagged frames entering the ingress port. The
PVID must as same as the VLAN ID that the port belong to VLAN group, or the
100
 Loading...
Loading...