Page 1
NOVASwitch Series
FNSW-8086F
FNSW-8088F
Fast Ethernet Fiber-optic Switch
Page 2
Trademarks
Copyright PLANET Technology Corp. 2002.
PLANET is a registered tra demark of PLANET Technolo gy
Corp. The information in this manual is subject to change
without notice. All other trademarks belong to their
respective owners.
Contents subject to revision without prior notice.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with
the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuan t to Part 15 of
the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environmen t. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radi ate radio f requency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
Instruction manual, may caus e harmful interferenc e to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in
which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at his own expense.
Reversion
This user's manual is for PLANET NOVASwitch Series
model -- FNSW-8086F / FNSW-8088F
Rev: 2.0 (Feb, 2002)
Part No: EM-8088fv2
ii
NOVASwitch Series
Page 3
Preface
This manual describes how to install a nd use the pr ovided
Fast Ethernet Switch, which features eight ports
100BASE-FX Multi-mode fiber ports, six ports 100BASEFX plus two ports 10/100BASE-TX switching is also
available for this product series.
To get the most out of this manual, you should have an
understanding of networking concepts such as bridging,
IEEE 802.3 Ethernet and 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet,
and local area networks (LANs).
For more information about these topics, please refer to
the Appendix.
Chapter Overview
Introduction
A general overview of switching benefits and the
features of the Switch this manual accompanied with.
Installation
Everything you need to know to install and configure th e
Switch with your network.
Specifications
The Switch’s specifications at a glance.
Connector Pinouts
See Appendix A for more information.
Introduction to LAN & Ethernet Technologies
See Appendix B for more information.
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
iii
Page 4
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION.................................................5
B
ENEFITS OF SWITCHING
E
IGHT PORTS FIBER-OPTIC ETHERNET SWITCH
P
RODUCT FEATURES
P
ACKING LIST
F
RONT PANEL
Ports............................................................................................8
LED Indication.........................................................................10
CHAPTER 2. INSTALLATION ................................................13
S
ELECTING A SITE FOR THE SWITCH
C
ONNECTING TO POWER
C
ONNECTING TO YOUR NETWORK
CHAPTER 3. SPECIFICATIONS.............................................16
APPENDIX A - CONNECTOR PINOUTS..............................18
APPENDIX B – INTRODUCTION TO LAN & ETHERNET
.................................................................................8
.................................................................................8
TECHNOLOGIES .........................................19
...............................................................5
...........................6
......................................................................7
............................................13
..............................................................14
..............................................14
iv
NOVASwitch Series
Page 5
Chapter 1. Introduction
Benefits of Switching
Ethernet switching technology has dramatically boosted
the total bandwidth of a network. It puts configuration
flexibility and bandwidth adaptability into the local
workgroups where the majority of work is generated.
It further eliminates congestion problems inherent to the
CSMA/CD protocol and improves predictable response
time under heavy network loads. Expensive routing
equipment was used in the pas t to reduce the congestion
under heavy loads.
The new wave of object-oriented client and server
applications demands higher bandwidth and tighter
integration of client work stations with servers. The old
shared-access Ethernet technology provides neither
enough bandwidth nor predictable response time for this
new wave of workgroup computing.
Fast Ethernet switching not only satisfies both technical
and business requirements, but also p reserves the user’s
existing investment in the huge 10BASE-T Ethernet
installed base.
This compatibility ensures a path for users to add, c hange ,
and migrate to Fast Ethernet as demands emerge. It also
provides a low cost and flexible bandwidth so lution dire ctly
to local workgroups where the majority of work is
generated, reducing the need for expensive network
equipment.
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
5
Page 6
Eight Ports Fiber-Optic Ethernet Switch
The FNSW-8088F has eight multi-mode fiber ports. And
for FNSW-8086F, it has 6-port 100BASE-FX ports and 2port 10/100BASE-TX ports.
This switch makes it possible to join a 100Mbps Fast
Ethernet network to an existing 1 0Mbps Ethernet network
(FNSW-8086F). Its internal cache buffers the traffic from
the higher bandwidth 100Mbps segment to the 10Mbps
segment. If you later decide to make both segments
100Mbps Fast Ethernet, the ports of the switch will
automatically sense the change and adjust to 100Mbps
operation.
In addition to the benefits of integrating 10Mbps and
100Mbps networks through TP ports, this switch is also
useful for segmenting networks that is bogged down with
excess traffic as a fiber-optic switching backbone. By
splitting a network into several segments and bridging
them, you can cut the traffic load on your network and
reduce collisions on each segment, especially if you can
minimize intersegment traffic by placing users and devices
that normally talk to each other on the same segment.
This switch fully complies with IEEE802.3u, 100BASE-TX,
100BASE-FX, and IEEE802.3, 10BASE-T standards. It
features "wire-speed” switching mechanisms as well as
the ability to filter local traffic, collisions, and error pack ets
to maximize network performance.
This eight-port switch also facilitates an affordable and
efficient migration path to 100Mbps Fast Ethernet and can
continue to enhance your network's performance even if
6
NOVASwitch Series
Page 7
you upgrade your existing network with standar d Ethernet
applications, internetworking systems and client-side
adapters to minimize migration costs.
Product Features
This eight-port switch provides the following features:
♦ FNSW-8088F provide eight 100BASE-FX switching
ports (ST Interface)
♦ FNSW-8086F provide two-port 10/100BASE-TX,
with six-port 100BASE-FX for multiple choice of TP
wiring
♦ Full-duplex support on each port (default) for up to
2Km wiring
♦ DIP Switch for Full- and Half-Duplex setting on
Fiber ports.
♦ Designed in compliance with IEEE 802.3,
10BASE-T and IEEE802.3u, 100BASE-TX and
100BASE-FX standards.
♦ Comprehensive array of LED indicators that
communicate the status of the switch and
troubleshooting information.
♦ Dynamic learning mode that automatically adjusts
to the network configuration.
♦ Runt and CRC filtering eliminates erroneous
packets to optimize network bandwidth.
♦ Full compatibility with standard Ethernet
applications, internetworking systems and
client-side adapters to minimize migration costs.
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
7
Page 8

Packing List
When you unpack the switch, you should find the items
listed below. Please inspect the conten ts, and report any
apparent damage or missing items immediately to your
authorized reseller.
The Eight-port Switch
●
Users Manual
●
AC power cord
●
Rack Mount Ears with Screws
●
Front Panel
The front panel of the switch has eight ports and an array
of LED indicators to provide you with instant feedback on
the status of the switch.
Figure 1: Front Panel of FNSW-8086F/ FNSW-8088F
Ports
Ports of this switch are capable of accepting 100BASE-FX
with ST interface connections. For FNSW-8086 F, the two
TP ports support 10/100BASE-TX with Cat. 3, 4, 5
(100Mbps) twisted pairs connection.
8
NOVASwitch Series
Page 9

When connects to a 100BASE-TX network, the ports
operate at 100Mbps in half-duplex mo de and 200Mbps in
full-duplex mode. When connects to a 10BASE-T network,
the ports operate at 10Mbps in half-duplex mode and
20Mbps in full-duplex mode. With the fiber-optic port ,
when it connects to a 100BASE-FX network, the ports
operate at 100Mbps in half-duplex mo de and 200Mbps in
full-duplex mode (default).
The maximum range of a 100BASE-TX network
connected to the switch is 100 meters with Category 5
shielded twisted-pair and unshielded twisted-pair
(STP/UTP) cable. A 10BASE-T network may range up to
100 meters with Category 3, 4, or 5 STP/UTP cable.
As for the length of FX fiber link between a switch and
Data Terminal Equipment, FX is capable to span at most 2
Kilometers using 62.5/125-micron fiber-optic cable.
The following table summarizes the port and cable
specifications for this switch.
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
9
Page 10
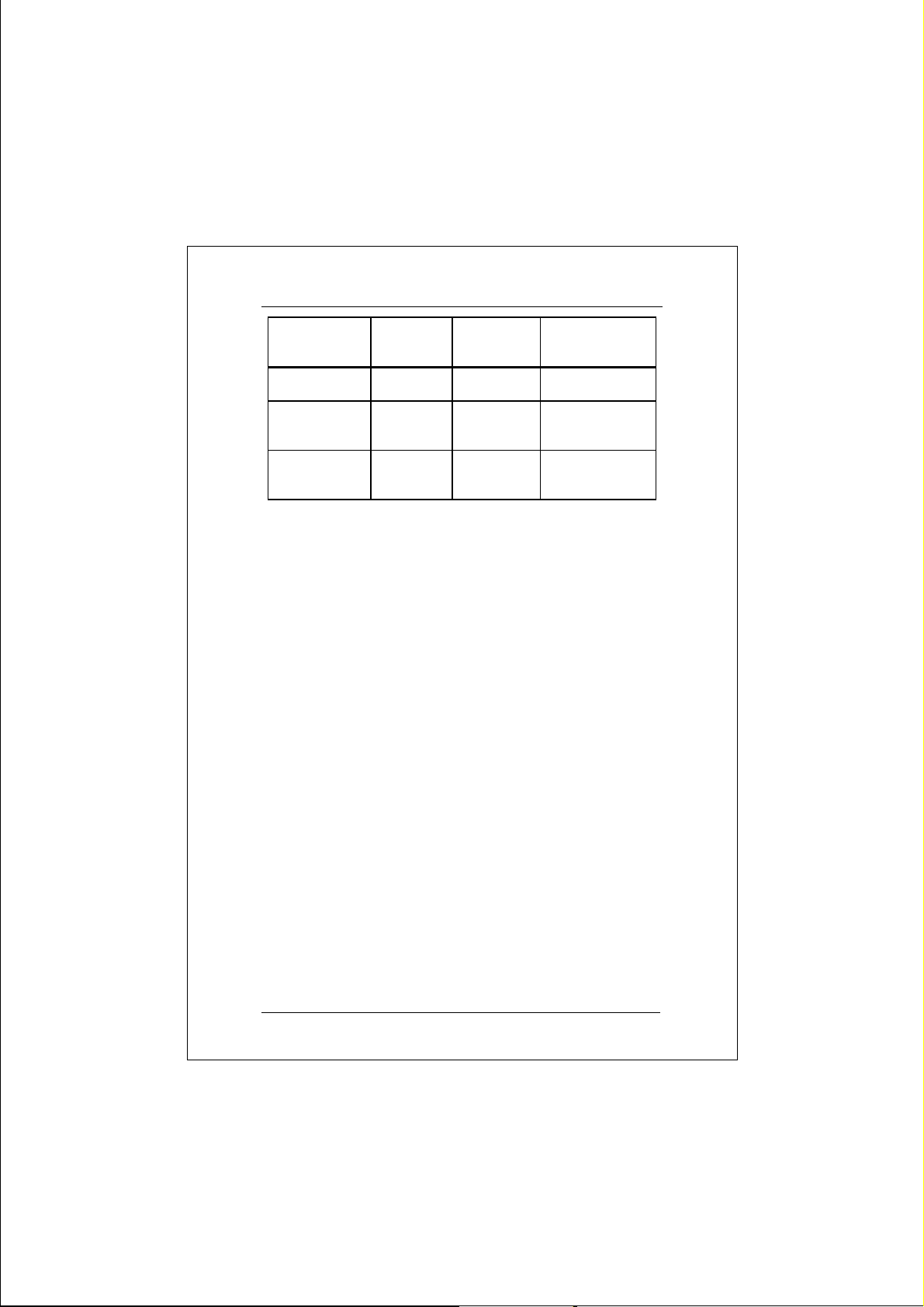
Speed Connector Port Speed
Half/Full
Duplex
100BASE-TX RJ-45 100/200
Mbps
10BASE-T RJ-45 10/20 Mbps 100M, Category
100BASE-FX Straight-tip
(ST)
100/200
Mbps
Cable
100M, Category
5 STP/UTP
3, 4, or 5
STP/UTP
50/125,62.5/125
micron fiberoptic cable
LED Indication
The array of LED indicators on the front panel conveys
status and configuration information to help you monitor
and troubleshoot the switch.
Port Status
n
Each port has an array of three LEDs to show status
information. The LEDs are identified by a corresponding
array of captions located below the LEDs on the front
panel.
LNK/ACT: The link indicator is the top-left LED. it is
illuminated whenever the port is connected
to another working networked device.
The LED flashes when the port is
transmitting or receiving data.
100: The middle LED shines whenever the
switch detects that the corresponding port
is connected to a 100BASE-TX or
100BASE-FX segment.
10
NOVASwitch Series
Page 11

FDX/ COL: The lower LED is illuminated when the port
is operating in full-duplex mode. When this
LED is off, the port is operating in
half-duplex mode.
The LED flashes when the switch detects
packet collisions on the port.
o
Power
This LED comes on when the switch is connected to a
power supply and turned on.
Auto MDI-X
p
If connecting to an uplink port of a hub or another
switch, any of the switch’s RJ-45 ports can be used.
There is no auto MDI -X for fiber 100BASE-FX ports; thus
the auto MDI -X status does not apply to 100BASE-FX
ports.
q
DIP Switch
Full-Duplex: Toggle on to enable Full-Duplex mode for
100BASE-FX ports (Default setting).
Half-Duplex: Toggle down to enable Half-Duplex mode
for 100BASE-FX ports.
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
11
Page 12
This page intentionally left blank!
12
NOVASwitch Series
Page 13
Chapter 2. Installation
This chapter presents step-by-step installa tion instructions
for this eight-port Fiber-optic Fast Ethernet Switch.
Selecting a Site for the Switch
As with any electronic device, you should place the Switch
where it will not be subjected to extreme temperatures,
humidity, or electromagnetic interference. Specifically, the
site you select should meet the following requirements:
♦ The room temperature should be between 0 and 50
degrees Celsius.
♦ The relative humidity should be less than 90 percen t,
non-condensing.
♦ Surrounding electrical devices should not exceed
the electromagnetic field (RFC) standards for IEC
801-3, Level 2 (3V/M) field strength.
♦ Make sure that the switch receives adequate
ventilation. Do not block the ventilation holes on the
side of the switch or the fan exhaus t port on the rear
of the switch.
♦ The power outlet should be within 1 .8meter (6 feet)
of the switch.
Detailed specifications may be found on page 17 and 18.
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
13
Page 14

Connecting to Power
Connect the supplied AC power cord to the receptacle on
the back of the switch, and then plug the cord into a
standard AC outlet with a vo ltage range from 100 to 240
VAC.
Turn the Ethernet switch on by flip ping the ON/OF F switch
on the rear of the unit to the I (ON) position. The O position
is OFF.
Connecting to Your Network
10/100BASE-TX TP Ports
Connect cables to computers or network segments into the
RJ-45 ports on the front of this switch. It does not matter
which port you select. All the non-fiber ports support
10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX with full or half duplex.
Use the uplink port with the uplink button pressed down
for connecting to a regular (i.e. non-uplink) por t o f a hu b or
another switch. If connecting to an uplink port of a hub or
another switch, any of the eight ports can be used. To
connect two regular RJ-45 ports between any two switches
or hubs, you need a cross-wire cable.
The cable must be a Category 5 shielded twisted-pair or
unshielded twisted-pair (STP/UTP) cable for 100BASE-TX,
or Category 3, 4, or 5 STP/UTP cable for 10BASE-T.
100BASE-FX Fiber-optic ports
Prepare a pair of fiber optic cables with ST type connectors
at both ends.
14
NOVASwitch Series
Page 15

If you are making a connection to a server or workstation,
be sure that it has a properly installed 100BASE-FX
network interface card. Connect the Rx/Tx jacks on the
target device to the Tx/Rx jacks on the switch.
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
15
Page 16
This page intentionally left blank!
16
NOVASwitch Series
Page 17
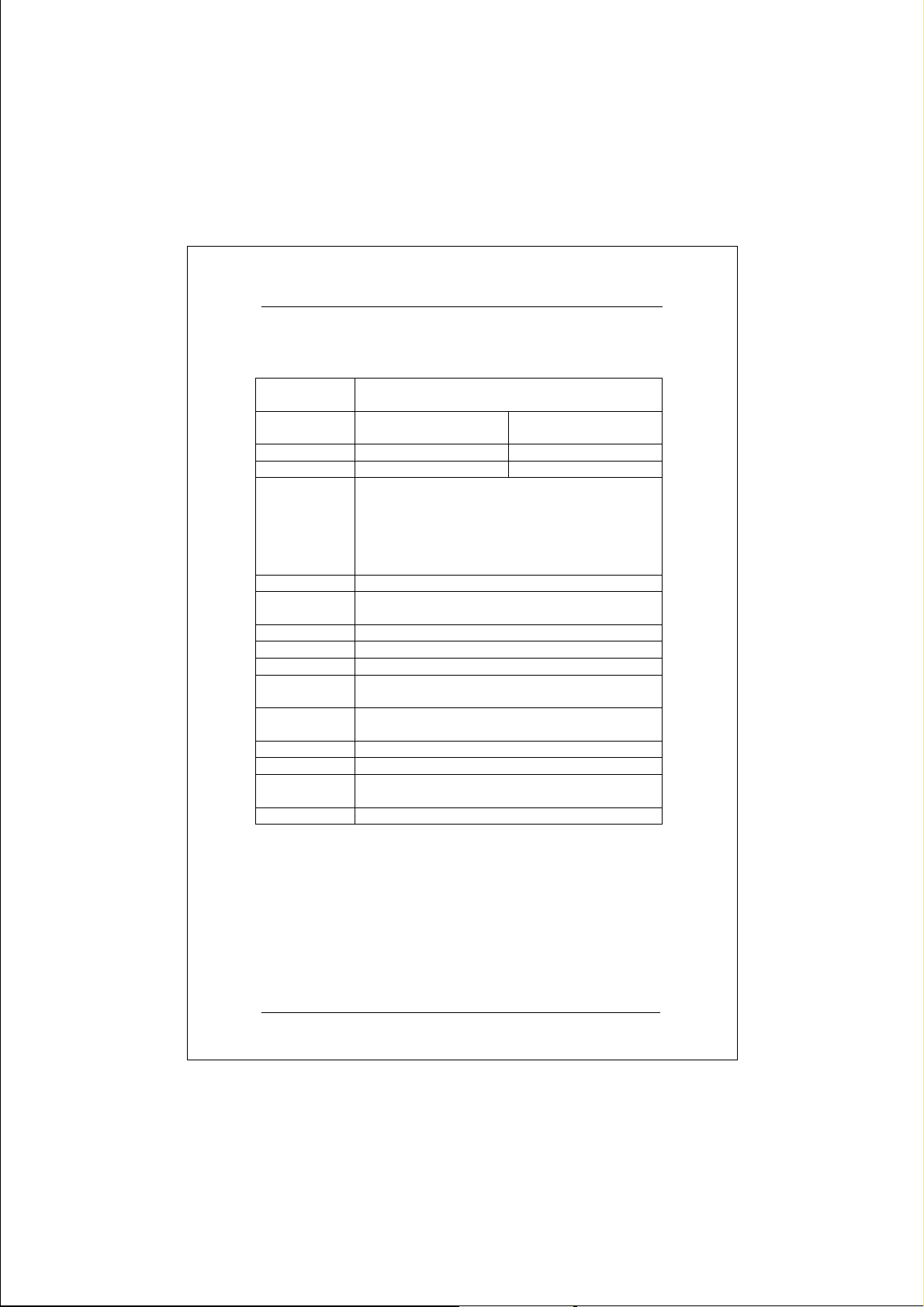
Chapter 3. Specifications
Applicable
Standards
Ports 10/100BASE-TX Auto-
FNSW-8086F 2 6
FNSW-8088F 0 8
Speed 100BASE-TX: 200Mbps full-duplex
Performance 148,800pps forwarding rate per port.
Switch LED
Indicators
Dimensions 440 X 205 X 45mm Rack-mount size
Weight 2.5kg
Power Input 100 ~ 250 VAC, 47/63 Hz, 2A
Power
Consumption
Operating
Temperature
Humidity 10 ~ 90%, non-condensing
Altitude 10,000 ft (3048 m)
Emissions FCC part 15 Class A, CISPR Class A, CE Mark,
Safety UL, CSA, TUV/GS
10BASE-T, IEEE 802.3
100BASE-TX, IEEE 802.3u
100Base-FX Ports
sensing Ports
100Mbps half-duplex
10BASE-T: 20Mbps full-duplex
10Mbps half-duplex
100BASE-FX: 200Mbps full-duplex
100Mbps half-duplex
Power
LNK/ACT, 100, FDX/COL for each port
12 W, 41BTU
0 ~ 50 degrees C
VCCI-I
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
17
Page 18

Appendix A - Connector Pinouts
Figure 6: RJ-45 Connector and Cable Pins
The following table lists the pinout of the switch’s
10/100BASE-T/TX ports.
Pin Regular Ports Uplink port
1 Input Receive Data + Output Transmit Data +
2 Input Receive Data - Output Transmit Data 3 Output Transmit Data + Input Receive Data +
4 NC NC
5 NC NC
6 Output Transmit Data - Input Receive Data 7 NC NC
8 NC NC
18
NOVASwitch Series
Page 19

Appendix B – Introduction to LAN &
Ethernet Technologies
In the last ten years, as communication and business
applications become increasingly complex, computer
network has evolved as a very important part of the
enterprise infrastructure. Communication systems like
Local Area Network (LANs) have grown into a
sophisticated, powerful, yet flexible technology today.
Among different types of Local Area Networks, such as
FDDI, ATM, Token Ring and Apple Talk, Et hernet strikes a
good balance between speed, price, ease of installation,
and supportability.
This primer helps to explain this most popular technology
and its associated products such as Ethernet hubs and
switches.
LAN
In order to reduce the expense on compu t er hardware and
software and to easily share information, LAN technologies
were developed for people to share distribu ted computing
resources. LAN connects independent computers, file
servers, printers, etc. together within a confined geographic
area, usually a single building or a college campus. As
LAN expands to link hundreds and thousands of
computers, various network protocols and media have
developed to meet the organization’s different
requirements. At times, multiple LANs that are
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
19
Page 20
geographically dispersed may need to
become so called Wide Area Network (WAN).
connect together and
Ethernet Technologies
More than 80 percent of all Local Area networks are
installed with Ethernet. The Institute of Electrical and
Electronic Engineers (IEEE) define the standard of
Ethernet as IEEE 802.3. The IEEE 802.3 provides rules
for configuring Ethernet LANs, specifies how elements
should interact with one another, and different types of
media that can be used, as well as data rate (10Mbps) of
Ethernet. Ethernet supports just about all kinds of popular
network protocols. It is one of the most ideal networking
technologies today.
Fast Ethernet
For networks that need higher transmission speeds, IEEE
has also established the standard 802 .3u, which raises the
Ethernet speed limit from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps. This
allows a network device to transmit data through media
such as category 5 UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cable
or fiber optic cable at the rate of 100 Mbps instead of 10
Mbps. A number of other high-speed LAN technologies
are also available for high bandwidth and good client
server response time. However, Fast Ethernet offers the
best solution that provides smooth migration from 10Ba seT technology to 100 Base-TX. It requires only minimal
changes with existing cabling infrastructur e. Fast Ether net
and its successors have been said to be the most cost
20
NOVASwitch Series
Page 21
effective and high-performance networking solutions of th e
future.
The Fast Ethernet contains three different cabling
schemes. 100Base-TX for use with category 5 UPT/STP
cable, 100Base-FX for use with Multi-mode fiber-optic
cable, and 100Base-T4 for use with cable 3,4,or 5 UPT
cable. Among three of them, 100Base-TX is most
compatible to 10Base-T. It allows users to retain the
existing 10Base-T cabli ng infrastructure, thus becomes the
most popular Fast Ethernet technolog y. Gigabit Ethernet
is still in the process of development. Other than supports
higher data transfer speed, this techn ology also promises
for an easy migration path.
Ethernet Products
Hub
Hub is a central connection point for wiring the network. It
connects two or more Ethernet segments of any media
type. When transmitting signal begins to deteriorate, which
is caused by the limitation of media length, hub simply
takes the incoming signal and repeats or amplifies it out to
all ports connected. Hub, also called repeater, on ly allows
users to share Ethernet. Individuals of a shared network
can only get a percentage of the available network
bandwidth, therefore, a network of repeaters also named
Shared Ethernet”.
“
FNSW-8086 / 8088F User's Manual
21
Page 22
Switches
The function of a switch is to connect separate ne tworks
together. A Switch maps the Ethernet addresses of the
nodes residing on each network segment and then allows
only the necessary traffic to pass through. When a pac ket
is received by the switch, the switch determines the
destination and source segments of a packet and forward
it to the right direction or drop it if the destination and the
source are originated from the same network. Switches
also prevent bad or misaligned packets from spreading
into the rest of network, thus increasing efficiency of the
network transmission.
There are two basic architectures of LAN switches, cutthrough and store-and-forward. Cu t-through switches only
examine the destination address before forwarding it on to
its destination segment. A store-and-forward switch
accepts and analyzes the entire packet before forwarding it
to its destination. It allows the switch to catch certain
packet errors and keep them from propagating through the
network. Today there are a large number of hybrid
switches available that mix both cut through and store-andforward architectures.
22
NOVASwitch Series
Page 23

Part No:
EM-8088FV2
ISO9002
 Loading...
Loading...