Page 1

Page 2
Trademarks
Copyright PLANET Technology Corp. 2002.
Contents subject to revision without prior notice.
PLANET is a registered trademark of PLANET Technology
Corp. All other trademarks belong to their respective owners.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with
the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of
the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the Instruction manual, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in
which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Before Starting
In this User's Manual "Fast Ethernet Switch" is used for
any/all of the PLANET Switch models of Ethernet Switches
listed on the title page. Important differences between
models will be specified.
Reversion
PLANET Fast Ethernet Switch User's Manual
FOR MODELS: FNSW-1601, FNSW-2401
Part No.: 2010- 000007- 002
Page 3
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 UNPACKING INFORMATION...........................1
CHAPTER 2 PRODUCT INTRODUCTION.............................3
2.1 K
2.2 F
EY FEATURES
RONT PANEL
.............................................................3
..............................................................4
2.2.1 Ports Speed........................................................4
2.2.2 Cabling................................................................4
2.2.3 Status LEDs........................................................5
2.3 T
HE REAR PANEL
.........................................................6
2.3.1 Power Connector................................................6
CHAPTER 3 INSTALLATION.................................................7
3.1 R
3.2 D
ACK-MOUNT INSTALLATION
ESKTOP INSTALLATION
.........................................7
................................................7
CHAPTER 4 OPTIMIZING CONFIGURATION.......................9
4.1 P
4.2 H
4.3 F
4.4 A
RIOR TO INSTALLATION
ALF- AND FULL-DUPLEX
AST ETHERNET
UTO-NEGOTIATION
4.5 MAC A
4.6 S
AMPLE APPLICATION
........................................................ 10
DDRESS TABLE
...............................................9
..............................................9
.................................................. 10
............................................... 11
................................................ 12
CHAPTER 5 TROUBLESHOOTING ................................... 13
CHAPTER 6 PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS....................... 15
CHAPTER 7 RJ-45 PIN ASSIGNMENT .............................. 17
7.1 S
TRAIGHT-THROUGH/CROSSOVER CABLE
....................... 17
- 1 -
Page 4
This page intentionally left blank!
Page 5
CHAPTER 1 UNPACKING INFORMATION
Thank you for purchasing a PLANET Fast Ethernet Switches.
Before continuing, please check the contents of the product
package. This product package should contain the following
items:
One Fast Ethernet Switch
One Power Cord
Two Rack-Mounting Brackets with Attachment Screws
This User’s Manual
Please inform your local dealer/supplier immediately if any item
is found to be defective, damaged or missing. Retain the
original packaging (carton), including the packing materials,
and use them to re-pack the product in the unlikely event there
is a need to return it to us for repair.
- 1 -
Page 6
This page intentionally left blank!
- 2 -
Page 7
CHAPTER 2 PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
Fast Ethernet Switches are multi-speed, versatile network devices combining both standard and "Big-Pipe" ports under the
same hood.
2.1 Key Features
Compliant with IEEE802.3 and 802.3u standards for
100Base-TX
16/24-port Fast Ethernet Switch, pure 10/100Base-TX
Wire-speed "Store-and-Forward" filtering/forwarding
eliminates bad data packets with minimal delay
100Base-TX ports automatically sense and set optimal
line speed from 10/20, 100/200Mbps, All 100Base-TX
port support Auto-Negotiation function
Shared buffer memory and up to 8K entry MAC source
address table make for fast handling of data packets
Flow control to eliminate packets loss
Internal, full-range power supply suitable for worldwide
use
Auto MDI/MDIX on each port for easy switch/hub cas-
cading
- 3 -
Page 8

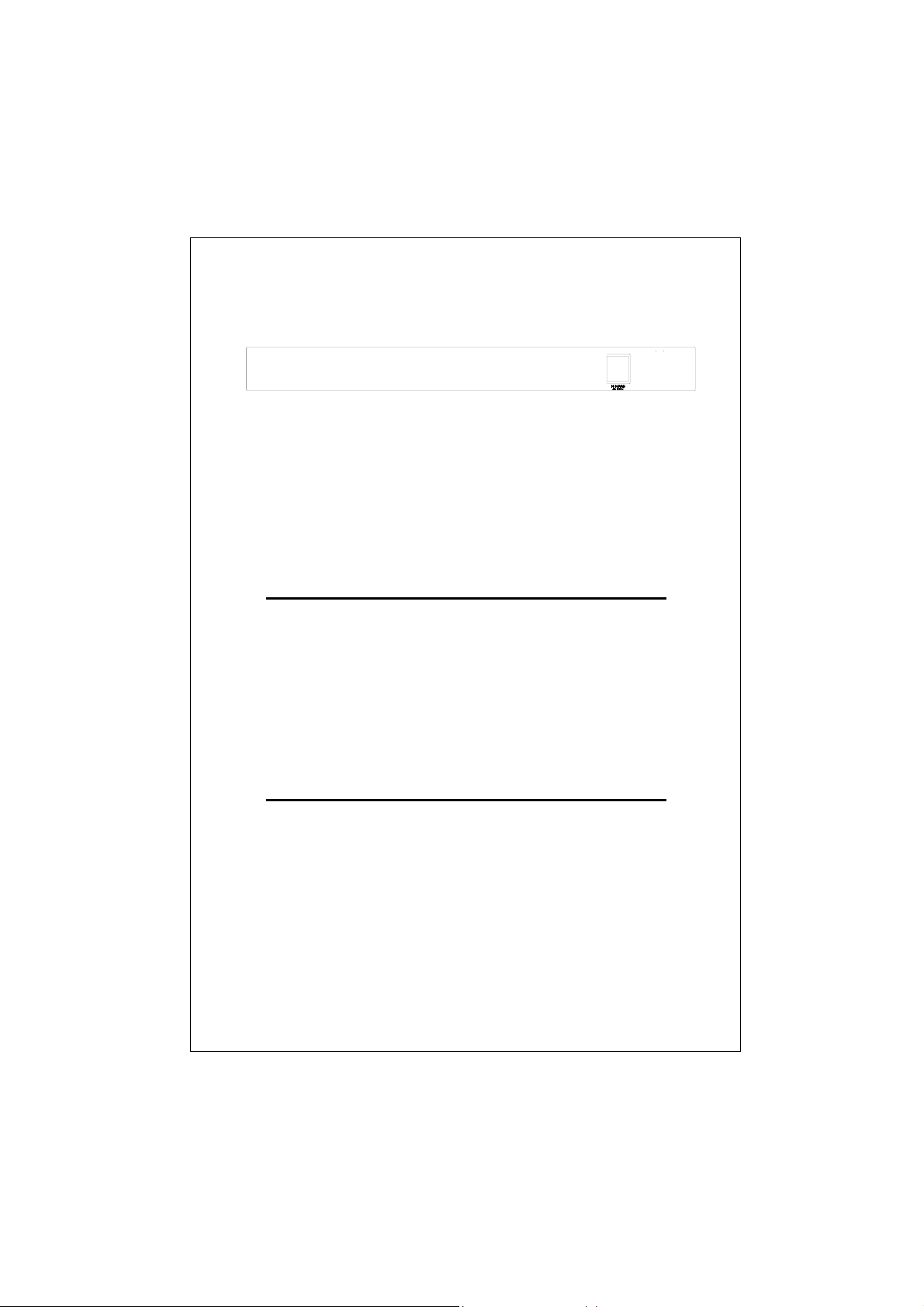
2.2 Front Panel
Figure 1: Front View of the FNSW-1601
Figure 2: Front View of the FNSW-2401
2.2.1 Ports Speed
100Base-TX
All 100Base-TX ports come with auto-negotiation capability.
They automatically support 100Base-TX and 10Base-T
networks. Users only need to plug a working network device
into one of the 100Base-TX ports, then turn on the hub. The
port will automatically runs in 10Mbps, 20Mbps, 100Mbps or
200Mbps after the negotiation with the connected device.
2.2.2 Cabling
Fast Ethernet Switch 100Base-TX ports use RJ-45 sockets -similar to phone jacks -- for connection of unshielded
twisted-pair cable (UTP). The IEEE 802.3u Fast Ethernet
standard requires Category 5 UTP for 100Mbps
100Base-TX. 10Base-T networks can use Cat.3, 4, or 5 UTP
(see table A)
Port Type Cable Type Connector
10Base-T
100Base-TX
Cat 3, 4, 5 RJ-45
Cat.5/5e UTP RJ-45
Table A: Supported port list
- 4 -
Page 9

2.2.3 Status LEDs
One green LED to show power On/Off is on the front panel. Also,
each port has three status LED indicators, as shown below.
Label
Status /
Color
Meaning Description
OWER
L
ROW
IDDLE
M
ROW
PPER
U
ROW
Steady
Green
Blink
Green
Steady
Green
Link Lit to indicate a valid physical
UTP/STP connection exists
Active Blink to indicate the port is
receiving data packets
100M Lit to indicate that a valid
physical UTP/STP connection
exists on that port runs in
100Mbps
Steady
Orange
Blink Orange
Full-Duplex
Collision
Lit to indicate Full-Duplex
mode detected on that port
Blinks if a collision is detected
when the port is in Half-Duplex
mode
Table B: The Switch's Port-LED Functions
- 5 -
Page 10
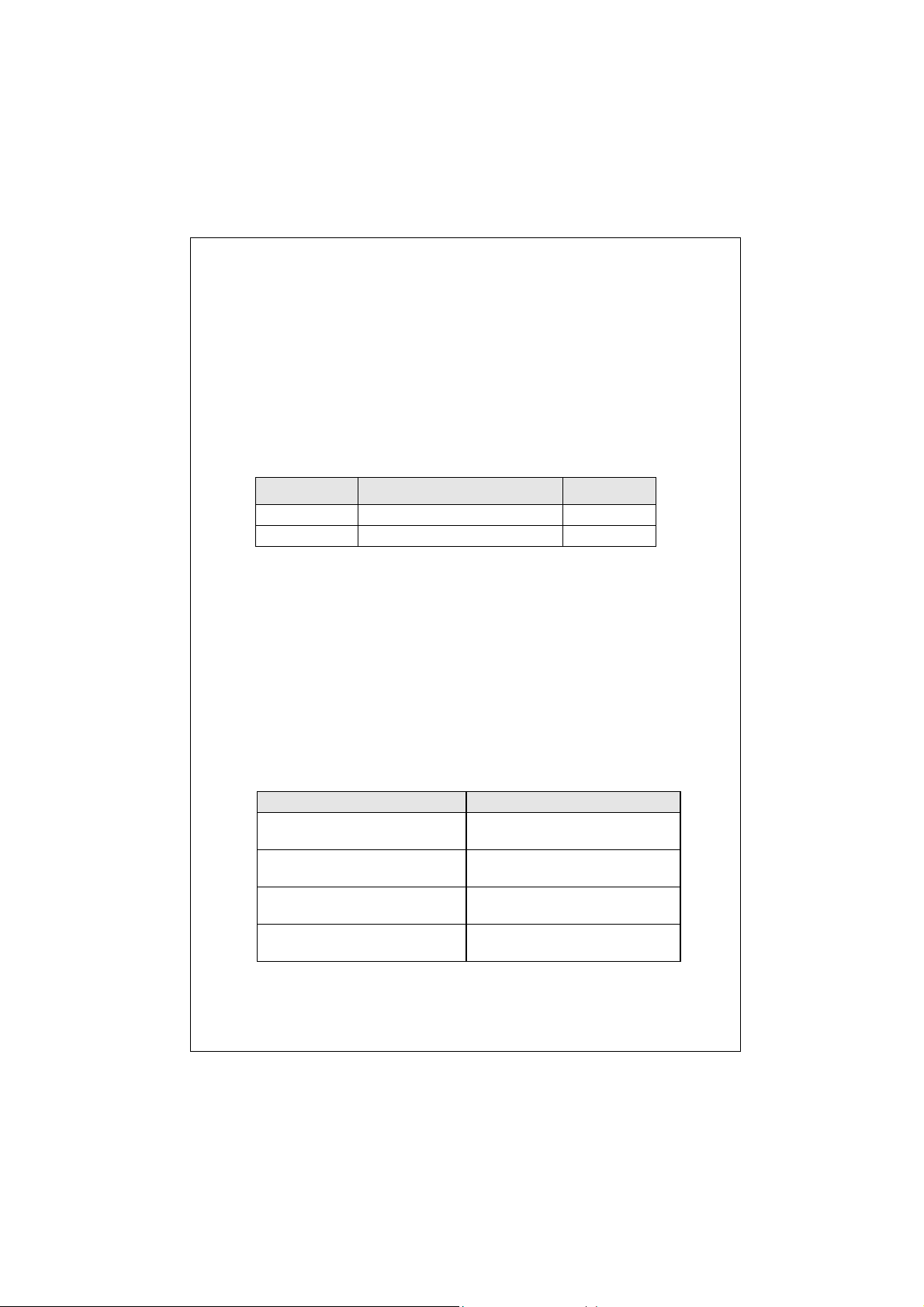
2.3 The Rear Panel
AC inlet
Figure 3: Rear View for the Switch
2.3.1 Power Connector
The Power Connector is designed to be used with the power
cord included in the product package. Attach the female end
of the cord to the power connector and the male end of the
cord to a grounded power outlet. The accepted power range
is from 100VAC to 240VAC, 50/60Hz.
Note:
The Switch is a power-required device, it means, the
Switch will not work until it is powered. If your networked
PCs will need to transmit data all the time, please consider
use an UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply) for your
Switch. It will prevent you from network data loss.
In some area, installing a surge suppression device may
also help to protect your Switch from being damaged by
unregulated surge or current to the Switch or the power
adapter
- 6 -
Page 11

CHAPTER 3 INSTALLATION
The Fast Ethernet Switch do NOT require software configuration. Users can immediately use any of the features of this
product simply by attaching the cables and turning on the
power.
To get the best use of these Fast Ethernet Switch models,
many things need to be considered first. See Section 4,
OPTIMIZING CONFIGURATION for details.
3.1 Rack-Mount Installation
Most users prefer to attach the power cord to the hub before
installation in a network rack. Do not plug the other end of the
cord into a power outlet until after the Switch is installed.
For mounting the Fast Ethernet Switch
attach the rack-mount brackets to the side of the hub with
screws. (Both brackets and screws are included in the product
package.) Slide the hub into the rack and align the holes in the
bracket with the corresponding holes in the network rack. Attach the bracket to the rack with the enclosed screws.
in a network rack, first
3.2 Desktop Installation
To locate the Fast Ethernet Switch models on a desktop, first
attach the four rubber feet to the bottom of the hub, one in each
corner. Place the hub on a clean, flat desk or table-top close to
a power outlet. Make sure there is no hindrance behind the fan
of the hub
Plug in all network connections and then turn the switch on via
plug in the power cord.
- 7 -
Page 12

This page is intentionally left blank
- 8 -
Page 13

CHAPTER 4 OPTIMIZING
CONFIGURATION
4.1 Prior to Installation
Before installing the Fast Ethernet Switch models and connecting network devices, it is important to plan the new network
layout. Consider:
Dedicated Bandwidth:
high-traffic hardware can improve if they have their own
direct connection with dedicated 10 or 100Mbps bandwidth.
Full-Duplex:
from a Full Duplex connection and check that they
support it.
Fast Ethernet:
different rules for cable and distance. Make sure these
are followed.
Auto-Negotiation:
be easily swapped when the other end of the cable is
fixed to a port with auto-negotiation.
Determine which devices would benefit
100Base-TX and 100Base-FX have
File servers and other
Devices with different speeds may
4.2 Half- and Full-Duplex
The Fast Ethernet Switch supports both Half- and Full-Duplex
modes for 10Base-T and 100Base-TX. Half-Duplex mode is the
traditional data transfer mode: one station sends data while
other devices wait for the first to finish.
Full-Duplex is the simultaneous transmission and receiving of
data. It is only possible between two devices with a dedicated
link (e.g., switch-to-switch, switch-to-PC). Both of the devices
must be capable of, and set to, Full-Duplex
100Base-TX ports use auto-negotiation to detect and set the
line's operating mode.
- 9 -
Page 14
4.3 Fast Ethernet
100Base-TX and 100Base-FX are called "Fast Ethernet." This
is because they use the Ethernet CSMA/CD access rules and
data packet structure, but data travels ten times faster
(100Mbps) than traditional 10Mbps Ethernet.
Below is a list of the cable types and connectors that supported
by Fast Ethernet
100Base-FX networks.
PORT TYPE Cables Type Connector
Switch models for 10Base-T, 100Base-TX, and
ASE
100B
10B
-TX
ASE
-T
Table C: Cables & Connectors Supported by the Switch
Cat. 5 UTP only RJ-45
Cat.3, 4, 5 UTP RJ-45
In many cases, 10Base-T LANs can quickly and easily upgrade
to 100Base-TX networks.
4.4 Auto-Negotiation
The 100Base-TX ports on the Fast Ethernet Switch have
built-in "Auto-Negotiation". This technology automatically sets
the best possible bandwidth when a connection is established
with another network device (usually at Power On or Reset).
This is done by detect the mode and speed at the second device is capable of. The 100Base-TX devices can connect with
the 100Base-TX port in either Half- or Full-Duplex mode.
If attached device is: 100Base-TX port will set to:
100Mbps, no auto-negotiation 100Mbps
(100Base-TX, Half-Duplex)
100Mbps, with auto-negotiation 200Mbps
(100Base-TX, Full-Duplex)
10Mbps, no auto-negotiation 10Mbps
(10Base-T, Half-Duplex)
10Mbps, with auto-negotiation 20Mbps
(10Base-T, Full-Duplex)
Table D: Speed & Duplex mode detected by the switch
- 10 -
Page 15

4.5 MAC Address Table
This 6-byte ID is called the MAC (Media Access Control) Address. Every Ethernet data packet includes both source and
destination addresses.
These Fast Ethernet Switch models can automatically learn
and store up to 8K MAC addresses. The MAC address table is
volatile: it disappears when the switch is powered off or reset.
Note: When the network needs reconfiguration, we
recommend turning off the power first. After all
nodes have been moved, power on the switch to
rebuild the internal MAC address table.
- 11 -
Page 16

4.6 Sample Application
The optimal application for the Fast Ethernet Switch, no matter
with the extension module or not, is as a "big pipe" backbone
interconnecting file servers with bandwidth-hungry workgroups,
departments, and offices.
In the figure, the first FNSW-1601(or FNSW-2401) links to another hub‘s Uplink (MDI-II) port, some ports connect to
100Mbps Workstations, and attached to file servers at
200Mbps.
FNSW-2401
Server Farm
Ethernet/Fast Ethernet Hubs
Server Farm
DH-1601
200Mbps
FNSW-1601
200Mbps
200Mbps
100Mbps
10/100Mbps
Workgroup
FNSW-2401
10Mbps
E H - 1 6 0 2 R
1 0 M b p s
Figure 5: Sample Application
200Mbps
1 0 M b p s
E H - 3 2 0 0
10/20Mbps
Workgroups
20Mbps
FSD-1600 -
2 0 M b p s
- 12 -
Page 17

CHAPTER 5 TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom Link LED does not lit after cable is connected to
the port.
Checkpoint Verify that the other end of the cable is connected
to a device that is powered on and on-line.
For UTP cable connection to another hub, verify
that only one end of the cable is connected to a
“MDI-II” Uplink port.
Symptom 100Base-TX port Link LED is lit, Collision LED is
blinking, but traffic is irregular.
Checkpoint Check that the attached device is not set to
dedicated full-duplex. (Some devices use a
physical or software switch to change duplex
modes. Auto-negotiation may not recognize this
type of full-duplex setting.
ALWAYS CHECK THAT THE CABLE, LINK DISTANCES,
AND OVERALL NETWORK DIAMETER ARE WITHIN SPEC.
FOR THE NETWORK TYPE.
- 13 -
Page 18

This page is intentionally left blank
- 14 -
Page 19

CHAPTER 6 PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
RODUCT
P
PORTS
FNSW-1601 FNSW-2401
16 24
10/10/Base-TX RJ-45 10/100Base-TX RJ-45
DDRESSES
MAC A
ANDWIDTH
B
F
R
ILTER
ATE
/ F
ORWARD
LEDs
EDIA SUPPORT
M
OWER SUPPLY
P
OWER
P
ONSUMPTION
C
NVIRONMENT
E
IMENSIONS
D
TANDARD COMPLIANCE
S
ETWORK
N
EMISSION
AFETY
S
8K-entry 8K-entry
100Base-TX, 200/100/20/10Mbps, Auto-Negotiation
148,800 packets/second per port @ 100Mbps, max.
1 for Power On/Off
3 per port for 100Mbps, Full-Duplex/Collision, Act/Link
100Base-TX Cat. 5 UTP, RJ-45
10Base-T Cat. 3, 4, 5 UTP RJ-45
Auto-switching. Input voltage: 100~240 VAC, 50 ~ 60Hz
6 watt / 20 BTU 8 watt / 27 BTU
Operating Temp: 0 ~ 50°C (32 ~ 122°F)
Storage Temp: -30 ~ 70°C (-22 ~ 158°F)
Humidity 0 ~ 90% non-condensing
440 x 200 x 44 mm
IEEE802.3 (10Base-T), IEEE802.3u (100Base-TX)
IEEE802.3x (Flow-Control)
FCC Class A, CE
UL, TUV/GS (EN60950)
Table E: Product Specifications
- 15 -
Page 20

This page is intentionally left blank
- 16 -
Page 21

CHAPTER 7 RJ-45 PIN ASSIGNMENT
Pin
Numbered Ports
(MDI-X port)
Uplink Port (MDI-II port)
1 Input Receive Data + Output Transmit Data+
2 Input Receive Data - Output Transmit Data3 Output Transmit Data+ Input Receive Data +
6 Output Transmit Data- Input Receive Data -
4,5,7,8 Not used Not used
Schematics for both straight and crossover twisted-pair cable
are shown below. (Note that crossover cable is only required if
you cascade hubs via the RJ-45 station ports; i.e. the Uplink
port is not used.)
7.1 Straight-Through/Crossover Cable
The pin assignment of the cables both ends should be as below:
Straight-through Crossover
Hub (MDI-X) Adapter(MDI-II) Hub (MDI-X) Hub (MDI-X)
Pin 1 Pin 1 Pin 1 Pin 3
Pin 2 Pin 2 Pin 2 Pin 6
Pin 3 Pin 3 Pin 3 Pin 1
Pin 6 Pin 6 Pin 6 Pin 2
2 1 3 6
2 1 3 6
6
3
1 2
- 17 -
Page 22

2010-000007-002
 Loading...
Loading...