Page 1

Page 2

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Trademarks
Copyright © PLANET Technology Corp. 2015.
Contents are subject to revision without prior notice.
PLANET is a registered trademark of PLANET Technology Corp. All other trademarks belong to their respective owners.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications, and makes no
warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for
a particular purpose. PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User's Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability
for any inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User's Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of
PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User's Manual. PLANET makes
no commitment to update or keep current the information in this User's Manual, and reserves the right to make improvements to
this User's Manual and/or to the products described in this User's Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your comments and
suggestions.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated
in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the Instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at his own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the user may be
required to take adequate measures.
Energy Saving Note of the Device
This power required device does not support Standby mode operation. For energy saving, please remove the power cable to
disconnect the device from the power circuit. In view of saving the energy and reducing the unnecessary power consumption, it
is strongly suggested to remove the power connection for the device if this device is not intended to be active.
WEEE Warning
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the presence of hazardous
substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of electrical and electronic equipment should
understand the meaning of the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of WEEE as unsorted
municipal waste and have to collect such WEEE separately.
Revision
PLANET GS-4210 Series User's Manual
FOR MODEL: GS-4210-8P2S / GS-4210-8P2T2S / GS-4210-24P4C / GS-4210-24PL4C / GS-4210-48T4S / GS-4210-48P4S
REVISION: 1.2 (April, 2015)
Part No: EM-GS-4210-series_v1.2
2
Page 3

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................. 10
1.1 Packet Contents .........................................................................................................................................10
1.2 Product Description ................................................................................................................................... 11
1.3 How to Use This Manual ............................................................................................................................14
1.4 Product Features........................................................................................................................................15
1.5 Product Specifications ..............................................................................................................................18
2. INSTALLATION ................................................................................................................... 27
2.1 Hardware Description ................................................................................................................................27
2.1.1 Switch Front Panel ..............................................................................................................................................27
2.1.2 LED Indications ...................................................................................................................................................29
2.1.3 Switch Rear Panel ...............................................................................................................................................33
2.2 Installing the Switch...................................................................................................................................35
2.2.1 Desktop Installation .............................................................................................................................................35
2.2.2 Rack Mounting.....................................................................................................................................................36
2.2.3 Installing the SFP transceiver ..............................................................................................................................38
3. SWITCH MANAGEMENT .................................................................................................... 41
3.1 Requirements..............................................................................................................................................41
3.2 Management Access Overview.................................................................................................................42
3.3 Administration Console.............................................................................................................................43
3.4 Web Management.......................................................................................................................................44
3.5 SNMP-based Network Management .........................................................................................................45
3.6 PLANET Smart Discovery Utility ..............................................................................................................45
4. WEB CONFIGURATION...................................................................................................... 48
4.1 Main Web Page ...........................................................................................................................................51
4.1.1 Save Button .........................................................................................................................................................52
4.1.2 Configuration Manager ........................................................................................................................................53
4.1.2.1 Saving Configuration .................................................................................................................................54
4.2 System.........................................................................................................................................................55
3
Page 4

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
4.2.1 System Information..............................................................................................................................................55
4.2.2 IP Configurations .................................................................................................................................................56
4.2.3 IPv6 Configuration ...............................................................................................................................................58
4.2.4 User Configuration...............................................................................................................................................60
4.2.5 Time Settings.......................................................................................................................................................61
4.2.5.1 System Time..............................................................................................................................................61
4.2.5.2 SNTP Server Settings ...............................................................................................................................64
4.2.6 Log Management.................................................................................................................................................65
4.2.6.1 Local Log...................................................................................................................................................65
4.2.6.2 Local Log...................................................................................................................................................66
4.2.6.3 Remote Syslog ..........................................................................................................................................67
4.2.6.4 Log Message.............................................................................................................................................69
4.2.7 SNMP Management ............................................................................................................................................71
4.2.7.1 SNMP Overview ........................................................................................................................................71
4.2.7.2 SNMP System Information ........................................................................................................................72
4.2.7.3 SNMP View ...............................................................................................................................................72
4.2.7.4 SNMP Access Group.................................................................................................................................74
4.2.7.5 SNMP Community.....................................................................................................................................76
4.2.7.6 SNMP User................................................................................................................................................77
4.2.7.7 SNMPv1, 2 Notification Recipients............................................................................................................79
4.2.7.8 SNMPv3 Notification Recipients................................................................................................................80
4.2.7.9 SNMP Engine ID .......................................................................................................................................81
4.2.7.10 SNMP Remote Engine ID........................................................................................................................82
4.3 Port Management .......................................................................................................................................84
4.3.1 Port Configuration................................................................................................................................................84
4.3.2 Port Counters ......................................................................................................................................................86
4.3.3 Bandwidth Utilization ...........................................................................................................................................91
4.3.4 Port Mirroring.......................................................................................................................................................92
4.3.5 Jumbo Frame ......................................................................................................................................................94
4.3.6 Port Error Disabled Configuration........................................................................................................................95
4.3.7 Port Error Disabled ..............................................................................................................................................97
4.3.8 Protected Ports....................................................................................................................................................97
4.3.9 EEE ...................................................................................................................................................................100
4.3.10 SFP Module Information ..................................................................................................................................101
4.3.10.1 SFP Module Status................................................................................................................................101
4.3.10.1 SFP Module Detail Status...................................................................................................................... 103
4.4 Link Aggregation......................................................................................................................................104
4.4.1 LAG Setting .......................................................................................................................................................106
4.4.2 LAG Management .............................................................................................................................................107
4
Page 5

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
4.4.3 LAG Port Setting................................................................................................................................................108
4.4.4 LACP Setting ..................................................................................................................................................... 110
4.4.5 LACP Port Setting.............................................................................................................................................. 111
4.4.6 LAG Status ........................................................................................................................................................112
4.5 VLAN..........................................................................................................................................................115
4.5.1 VLAN Overview .................................................................................................................................................115
4.5.2 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ........................................................................................................................................... 116
4.5.3 Management VLAN ...........................................................................................................................................120
4.5.4 Create VLAN .....................................................................................................................................................121
4.5.5 Interface Settings...............................................................................................................................................122
4.5.6 Port to VLAN......................................................................................................................................................126
4.5.7 Port VLAN Membership.....................................................................................................................................127
4.5.8 Protocol VLAN Group Setting ............................................................................................................................128
4.5.9 Protocol VLAN Port Setting ...............................................................................................................................130
4.5.10 GVRP Setting ..................................................................................................................................................131
4.5.11 GVRP Port Setting...........................................................................................................................................133
4.5.12 GVRP VLAN ....................................................................................................................................................134
4.5.13 GVRP Statistics ...............................................................................................................................................135
4.5.14 VLAN setting example: ....................................................................................................................................137
4.5.14.1 Two separate 802.1Q VLANs ................................................................................................................137
4.5.14.2 VLAN Trunking between two 802.1Q aware switches ...........................................................................140
4.6 Spanning Tree Protocol ...........................................................................................................................143
4.6.1 Theory ...............................................................................................................................................................143
4.6.2 STP Global Settings ..........................................................................................................................................150
4.6.3 STP Port Setting................................................................................................................................................152
4.6.4 CIST Instance Setting........................................................................................................................................155
4.6.5 CIST Port Setting...............................................................................................................................................157
4.6.6 MST Instance Configuration ..............................................................................................................................159
4.6.7 MST Port Setting ...............................................................................................................................................161
4.6.8 STP Statistics ....................................................................................................................................................163
4.7 Multicast ....................................................................................................................................................164
4.7.1 Properties ..........................................................................................................................................................164
4.7.2 IGMP Snooping .................................................................................................................................................165
4.7.2.1 IGMP Setting ........................................................................................................................................... 169
4.7.2.2 IGMP Querier Setting ..............................................................................................................................171
4.7.2.3 IGMP Static Group...................................................................................................................................172
4.7.2.4 IGMP Group Table...................................................................................................................................173
4.7.2.5 IGMP Router Setting ...............................................................................................................................174
4.7.2.6 IGMP Router Table..................................................................................................................................175
5
Page 6

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
4.7.2.7 IGMP Forward All ....................................................................................................................................176
4.7.3 IGMP Snooping Statics......................................................................................................................................177
4.7.4 MLD Snooping...................................................................................................................................................179
4.7.4.1 MLD Setting.............................................................................................................................................179
4.7.4.2 MLD Static Group ....................................................................................................................................181
4.7.4.3 MLD Group Table ....................................................................................................................................182
4.7.4.4 MLD Router Setting .................................................................................................................................182
4.7.4.5 MLD Router Table....................................................................................................................................184
4.7.4.6 MLD Forward All......................................................................................................................................185
4.7.5 MLD Snooping Statics .......................................................................................................................................186
4.7.6 Multicast Throttling Setting ................................................................................................................................188
4.7.7 Multicast Filter ...................................................................................................................................................189
4.7.7.1 Multicast Profile Setting ...........................................................................................................................190
4.7.7.2 IGMP Filter Setting ..................................................................................................................................191
4.7.7.3 MLD Filter Setting....................................................................................................................................192
4.8 Quality of Service .....................................................................................................................................194
4.8.1 Understanding QoS ...........................................................................................................................................194
4.8.2 General..............................................................................................................................................................195
4.8.2.1 QoS Properties........................................................................................................................................195
4.8.2.2 QoS Port Settings....................................................................................................................................196
4.8.2.3 Queue Settings........................................................................................................................................197
4.8.2.4 CoS Mapping...........................................................................................................................................198
4.8.2.5 DSCP Mapping........................................................................................................................................200
4.8.2.6 IP Precedence Mapping ..........................................................................................................................201
4.8.3 QoS Basic Mode................................................................................................................................................203
4.8.3.1 Global Settings ........................................................................................................................................203
4.8.3.2 Port Settings............................................................................................................................................204
4.8.4 Rate Limit ..........................................................................................................................................................205
4.8.4.1 Ingress Bandwidth Control ......................................................................................................................205
4.8.4.2 Egress Bandwidth Control ....................................................................................................................... 206
4.8.4.3 Egress Queue .........................................................................................................................................207
4.8.5 Voice VLAN .......................................................................................................................................................208
4.5.8.1 Introduction to Voice VLAN......................................................................................................................208
4.8.5.2 Properties ................................................................................................................................................ 209
4.8.5.3 Telephony OUI MAC Setting....................................................................................................................210
4.8.5.4 Telephony OUI Port Setting .....................................................................................................................212
4.9 Security .....................................................................................................................................................214
4.9.1 802.1X ...............................................................................................................................................................214
4.9.1.1 Understanding IEEE 802.1X Port-based Authentication..........................................................................215
6
Page 7

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
4.9.1.2 802.1X Setting.........................................................................................................................................218
4.9.1.3 802.1X Port Setting .................................................................................................................................219
4.9.1.4 Guest VLAN Setting ................................................................................................................................221
4.9.1.5 Authenticated Host ..................................................................................................................................223
4.9.2 RADIUS Server .................................................................................................................................................224
4.9.3 TACACS+ Server...............................................................................................................................................227
4.9.4 AAA ...................................................................................................................................................................229
4.9.4.1 Login List .................................................................................................................................................230
4.9.4.2 Enable List...............................................................................................................................................231
4.9.5 Access ...............................................................................................................................................................232
4.9.5.1 Telnet.......................................................................................................................................................232
4.9.5.2 SSH .........................................................................................................................................................233
4.9.5.3 HTTP .......................................................................................................................................................235
4.9.5.4 HTTPs .....................................................................................................................................................236
4.9.6 Management Access Method ............................................................................................................................237
4.9.6.1 Profile Rules ............................................................................................................................................237
4.9.6.2 Access Rules...........................................................................................................................................239
4.9.7 DHCP Snooping ................................................................................................................................................240
4.9.7.1 DHCP Snooping Overview ......................................................................................................................240
4.9.7.2 Global Setting..........................................................................................................................................241
4.9.7.3 DHCP Snooping VLAN Setting................................................................................................................242
4.9.7.4 Port Setting..............................................................................................................................................244
4.9.7.5 Statistics ..................................................................................................................................................246
4.9.7.6 Database Agent.......................................................................................................................................247
4.9.7.7 Rate Limit ................................................................................................................................................249
4.9.7.8 Option82 Global Setting ..........................................................................................................................250
4.9.7.9 Option82 Port Setting ..............................................................................................................................251
4.9.7.10 Option82 Circuit-ID Setting....................................................................................................................253
4.9.8 Dynamic ARP Inspection ...................................................................................................................................254
4.9.8.1 Global Setting..........................................................................................................................................254
4.9.8.2 VLAN Setting...........................................................................................................................................255
4.9.8.3 Port Setting..............................................................................................................................................256
4.9.8.4 Statistics ..................................................................................................................................................258
4.9.8.5 Rate Limit ................................................................................................................................................259
4.9.9 IP Source Guard................................................................................................................................................260
4.9.9.1 Port Settings............................................................................................................................................261
4.9.9.2 Binding Table...........................................................................................................................................263
4.9.10 Port Security ....................................................................................................................................................264
4.9.11 DoS.................................................................................................................................................................. 266
4.9.11.1 Global DoS Setting ................................................................................................................................266
7
Page 8

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
4.9.11.2 DoS Port Setting ....................................................................................................................................269
4.9.12 Storm Control...................................................................................................................................................270
4.9.12.1 Global Setting........................................................................................................................................270
4.9.12.2 Port Setting............................................................................................................................................271
4.10 ACL ..........................................................................................................................................................273
4.10.1 MAC-based ACL..............................................................................................................................................274
4.10.2 MAC-based ACE .............................................................................................................................................275
4.10.3 IPv4-based ACL...............................................................................................................................................278
4.10.4 IPv4-based ACE ..............................................................................................................................................279
4.10.5 IPv6-based ACL...............................................................................................................................................284
4.10.6 IPv6-based ACE ..............................................................................................................................................285
4.10.7 ACL Binding .....................................................................................................................................................290
4.11 MAC Address Table................................................................................................................................291
4.11.1 Static MAC Setting...........................................................................................................................................292
4.11.2 MAC Filtering ...................................................................................................................................................293
4.11.3 Dynamic Address Setting.................................................................................................................................294
4.11.4 Dynamic Learned.............................................................................................................................................295
4.12 LLDP ........................................................................................................................................................297
4.12.1 Link Layer Discovery Protocol .........................................................................................................................297
4.12.2 LLDP Global Setting ........................................................................................................................................298
4.12.3 LLDP Port Setting............................................................................................................................................300
4.12.4 LLDP Local Device ..........................................................................................................................................303
4.12.5 LLDP Remove Device .....................................................................................................................................305
4.12.6 MED Network Policy........................................................................................................................................306
4.12.7 MED Port Setting.............................................................................................................................................310
4.12.8 LLDP Overloading ...........................................................................................................................................313
4.12.9 LLDP Statistics.................................................................................................................................................314
4.13 Diagnostics .............................................................................................................................................316
4.13.1 Cable Diagnostics............................................................................................................................................316
4.13.2 Ping .................................................................................................................................................................318
4.13.3 Ping Test..........................................................................................................................................................318
4.13.4 IPv6 Ping Test..................................................................................................................................................319
4.13.5 Trace Router.................................................................................................................................................... 320
4.14 RMON.......................................................................................................................................................321
4.14.1 RMON Statistics ..............................................................................................................................................321
4.14.2 RMON Event ...................................................................................................................................................323
4.14.3 RMON Event Log ............................................................................................................................................324
4.14.4 RMON Alarm ...................................................................................................................................................325
8
Page 9

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
4.14.5 RMON History .................................................................................................................................................328
4.14.6 RMON History Log ..........................................................................................................................................329
4.15 Power over Ethernet ..............................................................................................................................330
4.15.1 Power over Ethernet Powered Device.............................................................................................................331
4.15.2 System Configuration ......................................................................................................................................332
4.15.3 Power over Ethernet Configuration..................................................................................................................333
4.15.4 PoE Schedule..................................................................................................................................................336
4.15.5 PoE Alive Check Configuration........................................................................................................................339
4.16 Maintenance............................................................................................................................................341
4.16.1 Factory Default ................................................................................................................................................341
4.16.2 Reboot Switch .................................................................................................................................................341
4.16.3 Backup Manager .............................................................................................................................................342
4.16.4 Upgrade Manager............................................................................................................................................342
4.16.5 Dual Image ......................................................................................................................................................344
5. SWITCH OPERATION ....................................................................................................... 346
5.1 Address Table...........................................................................................................................................346
5.2 Learning ....................................................................................................................................................346
5.3 Forwarding & Filtering .............................................................................................................................346
5.4 Store-and-Forward ...................................................................................................................................346
5.5 Auto-Negotiation ......................................................................................................................................347
6. TROUBLESHOOTING....................................................................................................... 348
APPENDIX A Switch's RJ45 Pin Assignments................................................................... 350
A.1 1000Mbps, 1000BASE-T..........................................................................................................................350
A.2 10/100Mbps, 10/100BASE-TX..................................................................................................................350
9
Page 10
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
1. INTRODUCTION
Thank you for purchasing PLANET GS-4210 Managed Switch series, which comes with multiple Gigabit Ethernet copper and
SFP fiber optic connectibility and robust layer 2 and layer 4 features. The description of this model is shown below:
GS-4210-8P2S
8-Port 10/100/1000T 802.3at PoE + 2-Port 100/1000X SFP Managed Switch
GS-4210-8P2T2S
GS-4210-24P4C
GS-4210-24PL4C
GS-4210-48T4S
GS-4210-48P4S
“Managed Switch” is used as an alternative name in this user’s manual.
8-Port 10/100/1000BASE-T 802.3at PoE Plus + 2-Port 10/100/1000BASE-T + 2-Port 100/1000BASE-X
SFP Managed Switch (240W)
24-Port 10/100/1000BASE-T PoE Plus Plus + 4-Port Gigabit TP/SFP Combo Managed Switch (220W)
24-Port 10/100/1000BASE-T PoE Plus Plus + 4-Port Gigabit TP/SFP Combo Managed Switch (440W)
48-Port 10/100/1000BASE-T + 4-Port 100/1000BASE-X SFP Managed Gigabit Switch
48-Port 10/100/1000T 802.3at PoE + 4-Port 100/1000BASE-X SFP Managed Switch (440W)
1.1 Packet Contents
Open the box of the Managed Switch and carefully unpack it. The box should contain the following items:
Model Name
Item
The Managed Switch
GS-4210-8P2S GS-4210-8P2T2S
■ ■ ■ ■
GS-4210-24P4C
GS-4210-24PL4C
GS-4210-48T4S
GS-4210-48P4S
Quick Installation Guide
RS-232 to RJ45 Console Cable
Rubber Feet
Two Rack-mounting Brackets
with Attachment Screws
Power Cord
SFP Dust Caps
If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact your local reseller for replacement.
■ ■ ■ ■
x
■ ■ ■ ■
■ ■ ■ ■
■ ■ ■ ■
2 2 4 4
■ ■
10
x
Page 11

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
1.2 Product Description
Perfect Managed PoE+ Switch with Full PoE+ Power Budget
PLANET GS-4210 PoE series is the new generation of PLANET Managed Gigabit PoE+ Switch featuring PLANET intelligent
PoE functions to improve the availability of critical business applications. It provides a quick, safe and cost-effective Power over
Ethernet network solution to IP security surveillance for small businesses and enterprises.
Built-in Unique PoE Functions for Powered Devices Management
As a managed PoE Switch for surveillance, wireless and VoIP networks, the GS-4210 PoE series features special PoE
Management functions:
PD Alive Check
Scheduled Power Recycling
PoE Schedule
PoE Usage Monitoring
Intelligent Powered Device Alive Check
The GS-4210 PoE series can be configured to monitor connected PD (Powered Device) status in real time via ping action. Once
the PD stops working and responding, the GS-4210 PoE series will resume the PoE port power and bring the PD back to work.
It will greatly enhance the network reliability through the PoE port resetting the PD’s power source and reducing administrator
management burden.
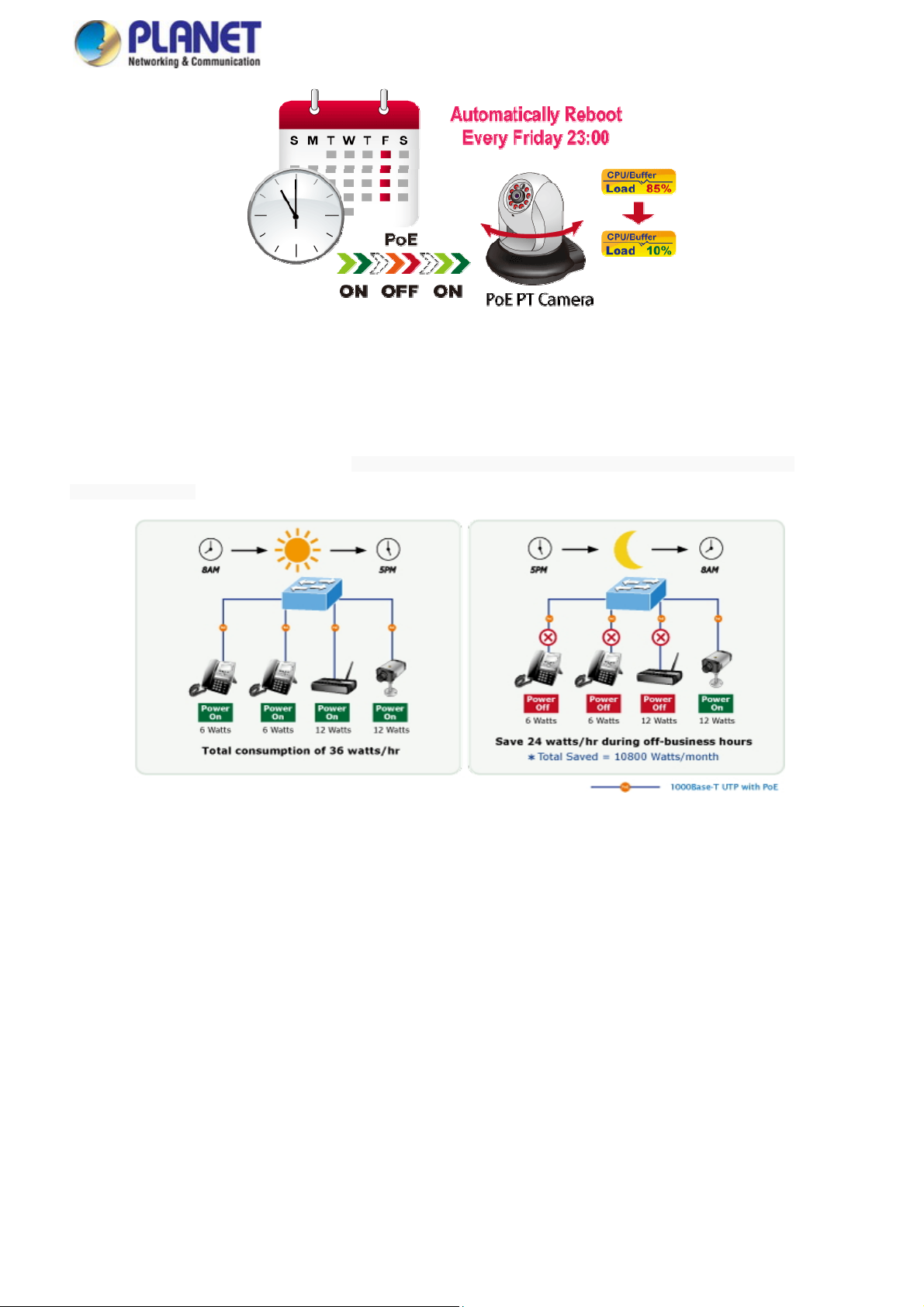
Scheduled Power Recycling
The GS-4210 PoE series allows each of the connected PoE IP cameras or PoE wireless access points to reboot at a specific
time each week. Therefore, it will reduce the chance of IP camera or AP crash resulting from buffer overflow.
11
Page 12
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
PoE Schedule for Energy Saving
Under the trend of energy saving worldwide and contributing to environmental protection, the GS-4210 PoE series can
effectively control the power supply besides its capability of giving high watts power. The “PoE schedule” function helps you to
enable or disable PoE power feeding for each PoE port during specified time intervals and it is a powerful function to help SMBs
or enterprises save power and money. It also increases security by powering off PDs that should not be in use during
non-business hours.
PoE Usage Monitoring
Via the power usage chart in the web management interface, the GS-4210 PoE series enables the administrator to monitor the
status of the power usage of the connected PDs in real time. Thus, it greatly enhances the management efficiency of the
facilities.
Environment-friendly, Smart Fan Design for Silent Operation
The GS-4210 series features a desktop-sized metal housing, a low noise design and an effective ventilation system. It supports
the smart fan technology to automatically control the speed of the built-in fan to reduce noise and maintain the temperature of
the PoE switch for optimal power output capability. The GS-4210 series is able to operate reliably, stably and quietly in any
environment without affecting its performance.
IPv6 / IPv4 Dual Stack
Supporting both IPv6 and IPv4 protocols, the GS-4210 series helps the SMBs to step in the IPv6 era with the lowest investment
as its network facilities need not to be replaced or overhauled if the IPv6 FTTx edge network is set up.
12
Page 13

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Robu
st Layer 2 Features
The GS-4210 series can be programmed for advanced switch management functions such as dynamic port link aggregation,
802.1Q VLAN and Q-in-Q VLAN, Multiple Spanning Tree protocol (MSTP), Loop and BPDU Guard, IGMP Snooping, and
MLD Snooping. Via the link aggregation, the GS-4210 series allows the operation of a high-speed trunk to combine with
multiple ports such as a 16Gbps fat pipe, and supports fail-over as well. Also, the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is the
Layer 2 protocol included to help discover basic information about neighboring devices on the local broadcast domain.
Efficient Traffic Control
The GS-4210 series is loaded with robust QoS features and powerful traffic management to enhance services to business-class
data, voice, and video solutions. The functionality includes broadcast / multicast storm control, per port bandwidth control, IP
DSCP QoS priority and remarking. It guarantees the best performance for VoIP and video stream transmission, and empowers
the enterprises to take full advantage of the limited network resources.
Powerful Security
PLANET GS-4210 series offers comprehensive IPv4 / IPv6 Layer 2 to Layer 4 Access Control List (ACL) for enforcing
security to the edge. It can be used to restrict network access by denying packets based on source and destination IP address,
TCP/UDP ports or defined typical network applications. Its protection mechanism also comprises 802.1X port-based user and
device authentication, which can be deployed with RADIUS to ensure the port level security and block illegal users. With the
Protected Port function, communication between edge ports can be prevented to guarantee user privacy. Furthermore, Port
Security function allows to limit the number of network devices on a given port.
Advanced Network Security
The GS-4210 series also provides DHCP Snooping, IP Source Guard and Dynamic ARP Inspection functions to prevent IP
snooping from attack and discard ARP packets with invalid MAC address. The network administrators can now construct highly
secured corporate networks with considerably less time and effort than before.
Friendly and Secure Management
For efficient management, the GS-4210 series is equipped with console, Web, Tel net and SNMP management interfaces. With
the built-in Web-based management interface, the GS-4210 series offers an easy-to-use, platform-independent management
and configuration facility. By supporting the standard Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), the switch can be
managed via any standard management software. For text-based management, the switch can be accessed via Telnet and the
console port. Moreover, the GS-4210 series offers secure remote management by supporting SSH, SSL and SNMPv3
connections which encrypt the packet content at each session.
13
Page 14

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Flexibilit
The GS-4210 series provides Gigabit TP/SFP interfaces supporting 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 copper to connect with
surveillance network devices such as NVR, Video Streaming Server or NAS to facilitate surveillance management. Or through
these dual-speed fiber SFP slots, it can also connect with the 100BASE-FX / 1000Base-SX/LX SFP (Small Form-factor
Pluggable) fiber transceiver and then to backbone switch and monitoring center over a long distance. The distance can be
extended from 550 meters to 2 kilometers (multi-mode fiber) and up to 10/20/30/40/50/70/120 kilometers (single-mode fiber or
WDM fiber). They are well suited for applications within the enterprise data centers and distributions.
y and Extension Solution
Intelligent SFP Diagnosis Mechanism
The GS-4210 series supports SFP-DDM (Digital Diagnostic Monitor) function that greatly helps network administrator to
easily monitor real-time parameters of the SFP, such as optical output power, optical input power, temperature, laser bias
current and transceiver supply voltage.
1.3 How to Use This Manual
This User Manual is structured as follows:
Section 2, INSTALLATION
The section explains the functions of the Switch and how to physically install the Managed Switch.
Section 3, SWITCH MANAGEMENT
The section contains the information about the software function of the Managed Switch.
Section 4, WEB CONFIGURATION
The section explains how to manage the Managed Switch by Web interface.
Section 5, SWITCH OPERATION
The chapter explains how to do the switch operation of the Managed Switch.
Section 6, TROUBLESHOOTING
The chapter explains how to troubleshoot the Managed Switch.
Appendix A
The section contains cable information of the Managed Switch.
14
Page 15

1.4 Product Features
Physical Port
■ 10/100/1000BASE-T Gigabit RJ45 copper
■ 100/1000BASE-X mini-GBIC/SFP slots.
■ RJ45 console interface for switch basic management and setup
Power over Ethernet (GS-4210 PoE Series)
■ Complies with IEEE 802.3at High Power over Ethernet End-Span PSE
■ Complies with IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet End-Span PSE
■ IEEE 802.3af / 802.3at devices powered
■ Supports PoE Power up to 30.8 watts for each PoE port
■ Auto detects powered device (PD)
■ Circuit protection prevents power interference between ports
■ Remote power feeding up to 100 meters
■ PoE Management
Total PoE power budget control
Per port PoE function enable/disable
PoE Port Power feeding priority
Per PoE port power limitation
PD classification detection
PD alive check
PoE schedule
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Layer 2 Features
■ Prevents packet loss with back pressure (half-duplex) and IEEE 802.3x pause frame flow control (full-duplex)
■ High performance Store and Forward architecture, broadcast storm control, runt/CRC filtering eliminates erroneous
packets to optimize the network bandwidth
■ Supports VLAN
- IEEE 802.1Q tagged VLAN
- Provider Bridging (VLAN Q-in-Q) support (IEEE 802.1ad)
- Protocol VLAN
- Voice VLAN
- Private VLAN
- Management VLAN
- GVRP
■ Supports Spanning Tree Protocol
- STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
- RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol)
- MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol)
- STP BPDU Guard, BPDU Filtering and BPDU Forwarding
■ Supports Link Aggregation
IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
Cisco ether-channel (static trunk)
15
Page 16

Maximum 8 trunk groups, up to 8 ports per trunk group
■ Provides port mirror (many-to-1)
■ Loop protection to avoid broadcast loops
Quality of Service
■ Ingress / Egress Rate Limit per port bandwidth control
■ Storm Control support
Broadcast / Unknown unicast / Unknown multicast
■ Traffic classification
- IEEE 802.1p CoS
- TOS / DSCP / IP Precedence of IPv4/IPv6 packets
■ Strict priority and Weighted Round Robin (WRR) CoS policies
Multicast
■ Supports IGMP Snooping v2 and v3
■ Supports MLD Snooping v1, v2
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
■ IGMP Querier mode support
■ IGMP Snooping port filtering
■ MLD Snooping port filtering
Security
■ Authentication
IEEE 802.1X Port-based network access authentication
Built-in RADIUS client to co-operate with the RADIUS servers
RADIUS / TACACS+ login user access authentication
■ Access Control List
IPv4 / IPv6 IP-based ACL
MAC-based ACL
■ MAC Security
Static MAC
MAC Filtering
■ Port Security for Source MAC address entries filtering
■ DHCP Snooping to filter distrusted DHCP messages
■ Dynamic ARP Inspection discards ARP packets with invalid MAC address to IP address binding
■ IP Source Guard prevents IP spoofing attacks
■ DoS Attack Prevention
■ SSH/SSL
16
Page 17

Management
■ IPv4 and IPv6 dual stack management
■ Switch Management Interface
- Web switch management
- Telnet Command Line Interface
- SNMP v1, v2c and v3
- SSH / SSL secure access
■ User Privilege Levels Control
■ Built-in Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) client
■ BOOTP and DHCP for IP address assignment
■ System Maintenance
- Firmware upload/download via HTTP / TFTP
- Configuration upload / download through Web interface
- Dual Images
- Hardware reset button for system reboot or reset to factory default
■ SNTP Network Time Protocol
■ Cable Diagnostics
■ Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Protocol and LLDP-MED
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
■ SNMP trap for interface Link Up and Link Down notification
■ Event message logging to remote Syslog server
■ Four RMON groups (history, statistics, alarms, and events)
■ PLANET Smart Discovery Utility
■ Smart fan with speed control
17
Page 18

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
1.5 Product Specifications
GS-4210-8P2S / GS-4210-8P2T2S
Product GS-4210-8P2S GS-4210-8P2T2S
Hardware Specifications
Copper Ports
SFP/mini-GBIC Slots
PoE Injector Port
Console ---
Switch Architecture Store-and-Forward
Switch Fabric 20Gbps / non-blocking 24Gbps / non-blocking
Switch Throughput@64Bytes 14.88Mpps 17.76Mpps
Address Table 8K entries
Shared Data Buffer 4.1 megabits
Flow Control
8 x 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45
Auto-MDI/MDI-X ports
2 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP interfaces with
Port-9 to Port-10.
Supports 100/1000Mbps dual mode and
DDM
8 ports with 802.3at / af PoE injector
function with Port-1 to Port-8
IEEE 802.3x pause frame for full-duplex
Back pressure for half-duplex
10 x 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45
Auto-MDI/MDI-X ports
2 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP interfaces
with Port-11 to Port-12.
Supports 100/1000Mbps dual mode
and DDM
8 ports with 802.3at / af PoE injector
function with Port-1 to Port-8
1 x RS-232-to-RJ45 serial port (115200,
8, N, 1)
Jumbo Frame
Reset Button
LED
Smart Fan
Dimensions (W x D x H) 330 x 155 x 43.5 mm, 1U high 330 x 200 x 44.5 mm, 1U height
Weight 1687g 2kg
Power Requirements AC 100~240V, 50/60Hz, auto-sensing
ESD Protection 2KV DC 6KV DC
Power Consumption /
Dissipation
Enclosure Metal
Power over Ethernet
PoE Standard IEEE 802.3af / 802.3at PoE / PSE
PoE Power Supply Type End-span
PoE Power Output Per Port 52V DC, 36 watts (max.) Per Port 54V DC, 36 watts (max.)
10K bytes
< 5 sec: System reboot
> 5 sec: Factory default
PWR, Fan Alert, LNK/ACT, PoE In-Use,
1000
1 1
165 watts (max.) /
563 BTU
PWR, SYS, LNK/ACT, PoE In-Use, 1000
320 watts (max.) /
1091.8 BTU
Power Pin Assignment 1/2(+), 3/6(-)
18
Page 19

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
PoE Power Budget
PoE Ability PD @ 9 watts 8 units 8 units
PoE Ability PD @ 15 watts 8 units 8 units
PoE Ability PD @ 30 watts 4 units 8 units
Layer 2 Functions
Port Mirroring
VLAN
Link Aggregation
Spanning Tree Protocol STP / RSTP / MSTP
120 watts (max.) @ 25 degrees C
100 watts (max.) @ 50 degrees C
TX / RX / both
Many-to-1 monitor
802.1Q tagged-based VLAN
Up to 256 VLAN groups, out of 4094 VLAN IDs
802.1ad Q-in-Q tunneling
Voice VLAN
Protocol VLAN
Private VLAN (Protected port)
GVRP
IEEE 802.3ad LACP and static trunk
Supports 8 groups of 8-port trunk
240 watts (max.) @ 25 degrees C
200 watts (max.) @ 50 degrees C
IGMP Snooping
MLD Snooping
Access Control List
QoS
Security
IGMP (v2/v3) Snooping
IGMP Querier
Up to 256 multicast groups
MLD (v1/v2) Snooping, up to 256 multicast groups
IPv4/IPv6 IP-based ACL / MAC-based ACL
8 mapping ID to 8 level priority queues
- Port number
- 802.1p priority
- 802.1Q VLAN tag
- DSCP field in IP packet
Traffic classification based, strict priority and WRR
IEEE 802.1X – Port-based authentication
Built-in RADIUS client to co-operate with RADIUS server
RADIUS / TACACS+ user access authentication
IP-MAC port binding
MAC filter
Static MAC address
DHCP Snooping and DHCP Option82
STP BPDU guard, BPDU filtering and BPDU forwarding
DoS attack prevention
ARP inspection
IP source guard
Management Functions
Basic Management Interfaces
Web browser / Telnet / SNMP v1, v2c
Firmware upgrade by HTTP / TFTP protocol through Ethernet network
Remote / Local Syslog
19
Page 20

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
System log
LLDP protocol
SNTP
Secure Management Interfaces
SNMP MIBs
Standards Conformance
Regulation Compliance
Standards Compliance
Environment
Operating
Storage
SSH, SSL, SNMP v3
RFC 1213 MIB-II
RFC 1215 Generic Traps
RFC 1493 Bridge MIB
RFC 2674 Bridge MIB Extensions
RFC 2737 Entity MIB (Version 2)
RFC 2819 RMON (1, 2, 3, 9)
RFC 2863 Interface Group MIB
RFC 3635 Ethernet-like MIB
FCC Part 15 Class A, CE
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX/100BASE-FX
IEEE 802.3z Gigabit SX/LX
IEEE 802.3ab Gigabit 1000T
IEEE 802.3x flow control and back pressure
IEEE 802.3ad port trunk with LACP
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1p Class of Service
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging
IEEE 802.1x Port Authentication Network Control
IEEE 802.1ab LLDP
IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet
IEEE 802.3at High Power over Ethernet
RFC 768 UDP
RFC 793 TFTP
RFC 791 IP
RFC 792 ICMP
RFC 2068 HTTP
RFC 1112 IGMP version 1
RFC 2236 IGMP version 2
RFC 3376 IGMP version 3
RFC 2710 MLD version 1
RFC 3810 MLD version 2
Temperature: 0 ~ 50 degrees C
Relative Humidity: 5 ~ 95% (non-condensing)
Temperature: -20 ~ 70 degrees C
Relative Humidity: 5 ~ 95% (non-condensing)
20
Page 21

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
GS-4210-24P4C / GS-4210-24PL4C
Product GS-4210-24P4C GS-4210-24PL4C
Hardware Specifications
Copper Ports 28 x 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 auto-MDI/MDI-X ports
SFP/mini-GBIC Slots
PoE Injector Port 24 ports with 802.3at / af PoE injector function with Port-1 to Port-24
Console 1 x RS-232-to-RJ45 serial port (115200, 8, N, 1)
Switch Architecture Store-and-Forward
Switch Fabric 56Gbps / non-blocking
Switch Throughput@64Bytes 41.67Mpps
Address Table 8K entries
Shared Data Buffer 4.1 megabits
Flow Control
Jumbo Frame
Reset Button
LED
Smart Fan
Dimensions (W x D x H) 440 x 300 x 44.5 mm, 19-inch, 1U height
4 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP interfaces shared with Port-25 to Port-28.
Supports 100/1000Mbps dual mode and DDM
IEEE 802.3x pause frame for full-duplex
Back pressure for half-duplex
10K bytes
< 5 sec: System reboot
> 5 sec: Factory default
PWR, SYS, LNK/ACT, PoE-in-Use, 1000, FAN 1 Alert, FAN 2 Alert, PoE PWR Alert
2 3
Weight 4.214kg 4.814kg
Power Requirements AC 100~240V, 50/60Hz, auto-sensing
ESD Protection 2KV DC
Power Consumption /
Dissipation
Enclosure Metal
Power over Ethernet
PoE Standard IEEE 802.3af / 802.3at PoE / PSE
PoE Power Supply Type End-span
PoE Power Output Per Port 52V DC, 30.8 watts (max.)
Power Pin Assignment 1/2(+), 3/6(-)
PoE Power Budget
PoE Ability PD @ 9 watts 24 units
PoE Ability PD @ 15.4 watts 14 units 24 units
PoE Ability PD @ 30 watts 7 units 14 units
Layer 2 Functions
275 watts (max.) /
938.3 BTU
220 watts (max.) @ 25 degrees C
190 watts (max.) @ 50 degrees C
544 watts (max.) /
1856.2 BTU
440 watts (max.) @ 25 degrees C
380 watts (max.) @ 50 degrees C
21
Page 22

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Port Mirroring
VLAN
Link Aggregation
Spanning Tree Protocol STP / RSTP / MSTP
IGMP Snooping
MLD Snooping
Access Control List
TX / RX / both
Many-to-1 monitor
802.1Q tagged-based VLAN
Up to 256 VLAN groups, out of 4094 VLAN IDs
802.1ad Q-in-Q tunneling
Voice VLAN
Protocol VLAN
Private VLAN (Protected port)
GVRP
IEEE 802.3ad LACP and static trunk
Supports 8 groups of 8-port trunk
IGMP (v2/v3) Snooping
IGMP Querier
Up to 256 multicast groups
MLD (v1/v2) Snooping, up to 256 multicast groups
IPv4/IPv6 IP-based ACL / MAC-based ACL
QoS
Security
Management Functions
Basic Management Interfaces
8 mapping ID to 8 level priority queues
- Port number
- 802.1p priority
- 802.1Q VLAN tag
- DSCP field in IP packet
Traffic classification based, strict priority and WRR
IEEE 802.1X – Port-based authentication
Built-in RADIUS client to co-operate with RADIUS server
RADIUS / TACACS+ user access authentication
IP-MAC port binding
MAC filter
Static MAC address
DHCP Snooping and DHCP Option82
STP BPDU guard, BPDU filtering and BPDU forwarding
DoS attack prevention
ARP inspection
IP source guard
Web browser / Telnet / SNMP v1, v2c
Firmware upgrade by HTTP / TFTP protocol through Ethernet network
Remote / Local Syslog
System log
LLDP protocol
SNTP
Secure Management Interfaces
SNMP MIBs
SSH, SSL, SNMP v3
RFC 1213 MIB-II
RFC 1215 Generic Traps
RFC 1493 Bridge MIB
22
Page 23

Standards Conformance
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
RFC 2674 Bridge MIB Extensions
RFC 2737 Entity MIB (Version 2)
RFC 2819 RMON (1, 2, 3, 9)
RFC 2863 Interface Group MIB
RFC 3635 Ethernet-like MIB
Regulation Compliance
Standards Compliance
Environment
Operating
Storage
FCC Part 15 Class A, CE
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX/100BASE-FX
IEEE 802.3z Gigabit SX/LX
IEEE 802.3ab Gigabit 1000T
IEEE 802.3x flow control and back pressure
IEEE 802.3ad port trunk with LACP
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1p Class of Service
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging
IEEE 802.1x Port Authentication Network Control
IEEE 802.1ab LLDP
IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet
IEEE 802.3at High Power over Ethernet
RFC 768 UDP
RFC 793 TFTP
RFC 791 IP
RFC 792 ICMP
RFC 2068 HTTP
RFC 1112 IGMP version 1
RFC 2236 IGMP version 2
RFC 3376 IGMP version 3
RFC 2710 MLD version 1
RFC 3810 MLD version 2
Temperature: 0 ~ 50 degrees C
Relative Humidity: 5 ~ 95% (non-condensing)
Temperature: -20 ~ 70 degrees C
Relative Humidity: 5 ~ 95% (non-condensing)
23
Page 24

GS-4210-48T4S
Product GS-4210-48T4S
Hardware Specifications
Copper Ports 48 x 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 Auto-MDI/MDI-X ports
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
SFP/mini-GBIC Slots
Switch Architecture Store-and-Forward
Switch Fabric 104Gbps / non-blocking
Switch Throughput@64Bytes 77.38Mpps @64Bytes
Address Table 16K entries
Share Data Buffer 12Mbit SRAM Packet Buffer
Flow Control
Jumbo Frame
Reset Button
LED
4 100/1000BASE-X SFP interfaces,
Supports 100/1000Mbps dual mode and DDM
IEEE 802.3x pause frame for full-duplex
Back pressure for half-duplex
10K bytes
< 5 sec: System reboot
> 5 sec: Factory default
System:
PWR(Power) (Green)
SYS(System) (Green)
10/100/1000T RJ45 Interfaces (Port 1 to Port 48):
1000Mbps (Orange), LNK/ACT (Green)
10/100Mbps (None), LNK/ACT (Green)
100/1000Mbps SFP Interfaces (Port 49 to Port 52):
1000Mbps, LNK/ACT (Green)
100Mbps, LNK/ACT (Orange)
Thermal Fan Fanless design (no fan)
Power Requirements AC 100~240V, 50/60Hz, auto-sensing.
ESD Protection 6KV DC
Power Consumption /
Dissipation
Dimensions (W x D x H) 440 x 300 x 44.5 mm, 1U height
Weight 3.7 kg
Enclosure Metal
Layer 2 Functions
Port Mirroring
VLAN
34 watts / 116 BTU
TX / RX / Both
Many-to-1 monitor
802.1Q tagged-based VLAN
Up to 256 VLAN groups, out of 4094 VLAN IDs
802.1ad Q-in-Q tunneling (VLAN stacking)
Voice VLAN
Protocol VLAN
Private VLAN (Protected port)
24
Page 25

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
GVRP
Management VLAN
Link Aggregation
Spanning Tree Protocol
IGMP Snooping
MLD Snooping
Access Control List
QoS
IEEE 802.3ad LACP and static trunk
Supports 8 groups of 8-port trunk
STP, IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
RSTP, IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
MSTP, IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
STP BPDU Guard, BPDU Filtering and BPDU Forwarding
IGMP (v2/v3) snooping
IGMP querier
Up to 256 multicast groups
IPv6 MLD (v1 / v2) snooping, up to 256 multicast groups
IPv4/IPv6 IP-based ACL / MAC-based ACL
IPv4/IPv6 IP-based ACE / MAC-based ACE
8 mapping ID to 8 level priority queues
- Port Number
- 802.1p priority
- DSCP / IP Precedence of IPv4 / IPv6 packets
Traffic classification based, strict priority and WRR
Ingress / Egress Rate Limit per port bandwidth control
Security
Management Functions
Basic Management Interfaces
IEEE 802.1X port-based authentication
Built-in RADIUS client to co-operate with RADIUS server
RADIUS / TACACS+ authentication
IP-MAC port binding
MAC filtering
Static MAC address
DHCP snooping and DHCP Option82
STP BPDU guard, BPDU filtering and BPDU forwarding
DoS attack prevention
ARP inspection
IP source guard
Storm control support
- Broadcast / Unknown-Unicast / Unknown-Multicast
Web browser / Telnet / SNMP v1, v2c, v3
Firmware upgrade by HTTP / TFTP protocol through Ethernet network
Configuration upload / download through HTTP / TFTP
Remote / Local Syslog
System log
LLDP protocol
SNTP
PLANET Smart Discovery Utility
Secure Management Interfaces
SSH, SSL, SNMP v3
25
Page 26

SNMP MIBs
Standards Conformance
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
RFC 3635 Ethernet-like MIB
RFC 2863 Interface Group MIB
RFC 2819 RMON (1, 2, 3, 9)
RFC 1493 Bridge MIB
Regulation Compliance
Standards Compliance
Environment
Operating
Storage
FCC Part 15 Class A, CE
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX / 100BASE-FX
IEEE 802.3z Gigabit SX/LX
IEEE 802.3ab Gigabit 1000BASE-T
IEEE 802.3x flow control and back pressure
IEEE 802.3ad Port Trunk with LACP
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1p Class of Service
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Tagging
IEEE 802.1x Port Authentication Network Control
IEEE 802.1ab LLDP
RFC 768 UDP
RFC 793 TFTP
RFC 791 IP
RFC 792 ICMP
RFC 2068 HTTP
RFC 1112 IGMP version 1
RFC 2236 IGMP version 2
RFC 3376 IGMP version 3
RFC 2710 MLD version 1
RFC 3810 MLD version 2
Temperature: 0 ~ 50 degrees C
Relative Humidity: 5 ~ 95% (non-condensing)
Temperature: -20 ~ 70 degrees C
Relative Humidity: 5 ~ 95% (non-condensing)
26
Page 27

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
2. INSTALLATION
This section describes the hardware features and installation of the Managed Switch on the desktop or rack mount. For easier
management and control of the Managed Switch, familiarize yourself with its display indicators and ports. Front panel
illustrations in this chapter display the unit LED indicators. Before connecting any network device to the Managed Switch, please
read this chapter completely.
2.1 Hardware Description
2.1.1 Switch Front Panel
The front panel provides a simple interface monitoring of the Managed Switch. Figure 2-1-1a~ Figure 2-1-1d show the front
panel of the Managed Switch.
GS-4210-8P2S Front Panel
GS-4210-8P2T2S Front Panel
GS-4210-24P4C Front Panel
GS-4210-24PL4C Front Panel
Figure 2-1-1a GS-4210-8P2S Front Panel
Figure 2-1-1b GS-4210-8P2T2S Front Panel
Figure 2-1-1c GS-4210-24P4C Front Panel
GS-4210-48T4S Front Panel
Figure 2-1-1d GS-4210-24PL4C Front Panel
Figure 2-1-1e GS-4210-48T4S Front Panel
27
Page 28

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
■ Gigabit TP Interface
10/100/1000BASE-T Copper, RJ45 Twisted-pair: Up to 100 meters.
■ 100/1000BASE-X SFP Slots
Each of the SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) slots supports dual-speed, 1000BASE-SX / LX or 100BASE-FX
- For 1000BASE-SX/LX SFP transceiver module: From 550 meters (multi-mode fiber) to 10/30/50/70/120 kilometers
(single-mode fiber).
- For 100BASE-FX SFP transceiver module: From 2 kilometers (multi-mode fiber) to 20/40/60 kilometers (single-mode
fiber).
■ Console Port
The console port is an RJ45 port connector. It is an interface for connecting a terminal directly. Through the console port, it
provides rich diagnostic information including IP address setting, factory reset, port management, link status and system
setting.
Users can use the attached DB9 to RJ45 console cable in the package and connect to the console port on the device.
After the connection, users can run any terminal emulation program (Hyper Terminal, ProComm Plus, Telix, Winterm
and so on) to enter the startup screen of the device.
■ Reset Button
On the left of the front panel, the reset button is designed to reboot the Managed Switch without turning off and on the
power. The following is the summary table of Reset button functions:
Reset Button Pressed and Released Function
< 5 sec: System Reboot Reboot the Managed Switch.
Reset the Managed Switch to Factory Default configuration.
The Managed Switch will then reboot and load the default
settings shown below:
> 5 sec: Factory Default
。 Default username: admin
。 Default password: admin
。 Default IP address: 192.168.0.100
。 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
。 Default gateway: 192.168.0.254
28
Page 29

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
2.1.2 LED Indications
The front panel LEDs indicate instant status of port links, data activity and system power; it helps monitor and troubleshoot when
needed. Figure 2-1-2a~2-1-2c show the LED indications of these Managed Switches.
GS-4210-8P2S LED Indication
■ System
LED Color Function
PWR Green
FAN Orange
■ 10/100/1000BASE-T interfaces
LED Color Function
LNK/ACT Green
1000 Green
Lights to indicate that the Switch has power.
Lights to indicate that the FAN is down.
Lights:
Blinks:
Lights: To indicate that the port is operating at 1000Mbps.
Off: If LNK/ACT LED light-> indicate that the port is operating at 10/100Mbps
Figure 2-1-2a GS-4210-8P2S LED Panel
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established.
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
■ 100 / 1000BASE-X SFP interfaces
LED Color Function
LNK/ACT Green
1000 Green
Lights:
Blinks:
Lights: To indicate that the port is operating at 1000Mbps.
Off: If LNK/ACT LED is lit, it indicates that the port is operating at 100Mbps
If LNK/ACT LED Off -> indicate that the port is link down
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established.
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
If LNK/ACT LED is off, it indicates that the port is link down
29
Page 30

GS-4210-8P2T2S LED Indication
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
■ System
LED Color Function
PWR Green
SYS Green
■ 10/100/1000BASE-T interfaces
LED Color Function
LNK/ACT Green
1000 Orange
Lights to indicate that the Switch has power.
Lights to indicate the system is working.
Blinks to indicate the system is booting.
Lights:
Blinks:
Lights: To indicate that the port is operating at 1000Mbps.
Off: If LNK/ACT LED light-> indicate that the port is operating at 10/100Mbps
Figure 2-1-2b GS-4210-8P2T2S LED Panel
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established.
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
If LNK/ACT LED Off -> indicate that the port is link down
■ 100 / 1000BASE-X SFP interfaces
LED Color Function
LNK/ACT Green
1000 Orange
Lights:
Blinks:
Lights: To indicate that the port is operating at 1000Mbps.
Off: If LNK/ACT LED is lit, it indicates that the port is operating at 100Mbps
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established.
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
If LNK/ACT LED is off, it indicates that the port is link down
30
Page 31

GS-4210-24P (L) 4C LED Indication
Figure 2-1-2c GS-4210-24P (L) 4C LED Panel
■ System / Alert
LED Color Function
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
PWR Green
SYS Green
FAN 1 Red
FAN 2 Red
PoE PWR Red
■ 10/100/1000BASE-T interfaces (Port-1 to Port-24)
LED Color Function
LNK/ACT Green
PoE Orange
■ 10/100/1000BASE-T interfaces (Port-25 to Port-28)
Lights to indicate that the Switch has power.
Lights to indicate the system is working.
Off to indicate the system is booting.
Lights to indicate that the FAN1 is down.
Lights to indicate that the FAN2 is down.
Lights to indicate that the PoE power is down.
Lights:
Blinks:
Lights:
Off:
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established.
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
To indicate the port is providing 56V DC in-line power.
To indicate the connected device is not a PoE Powered Device (PD)
LED Color Function
LNK/ACT Green
1000 Orange
■ 100/1000BASE-SX/LX SFP interfaces (Port-25 to Port-28)
LED Color Function
LNK/ACT Green
1000 Orange
Lights:
Blinks:
Lights: To indicate that the port is operating at 1000Mbps.
Off: If LNK/ACT LED is lit, it indicates that the port is operating at 10/100Mbps.
Lights:
Blinks:
Lights: To indicate that the port is operating at 1000Mbps.
Off: If LNK/ACT LED is lit, it indicates that the port is operating at 100Mbps.
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established.
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
If LNK/ACT LED is off, it indicates that the port is link down.
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established.
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
If LNK/ACT LED is off, it indicates that the port is link down.
31
Page 32

GS-4210-48T4S LED Indication
Figure 2-1-2d GS-4210-48T4S LED Panel
■ System
LED Color Function
PWR Green Lights to indicate that the Switch has power.
SYS Green Lights to indicate the system is working.
■ Per 10/100/1000Mbps RJ45 interfaces (Port-1 to Port-48)
LED Color Function
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Speed
LNK/ACT Green Blinks: Indicates that the Switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
■ Per 100/1000Mbps SFP Interface (Port-49 to Port-52)
LED Color Function
LNK/ACT
Orange Indicates the link through that port is successfully established at 1000Mbps.
None Indicates the link through that port is successfully established at 10/100Mbps.
Lights: Indicates the link through that port is successfully established at 1000Mbps.
Green
Blinks: Indicates that the Switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
Lights: Indicates the link through that port is successfully established at 100Mbps.
Orange
Blinks: Indicates that the Switch is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
32
Page 33

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
2.1.3 Switch Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Managed Switch indicates an AC inlet power socket, which accepts input power from 100 to 240V AC,
50-60Hz. Figures 2-1-3a~2-1-3d show the rear panel of these Managed Switches
GS-4210-8P2S Rear Panel
Figure 2-1-3a Rear Panel of GS-4210-8P2S
GS-4210-8P2T2S Rear Panel
GS-4210-24P4C Rear Panel
GS-4210-24PL4C Rear Panel
GS-4210-48T4S Rear Panel
Figure 2-1-3b Rear Panel of GS-4210-8P2T2S
Figure 2-1-3c Rear Panel of GS-4210-24P4C
Figure 2-1-3d Rear Panel of GS-4210-24PL4C
Figure 2-1-3e Rear Panel of GS-4210-48T4S
■ AC Power Receptacle
For compatibility with electric service in most areas of the world, the Managed Switch’s power supply automatically adjusts
to line power in the range of 100-240V AC and 50/60 Hz.
33
Page 34

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Plug the female end of the power cord firmly into the receptacle on the rear panel of the Managed Switch. Plug the other
end of the power cord into an electrical outlet and the power will be ready.
The device is a power-required device, which means it will not work till it is powered. If your networks
Power Notice:
Power Notice:
should be active all the time, please consider using UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply) for your device.
It will prevent you from network data loss or network downtime.
In some areas, installing a surge suppression device may also help to protect your Managed Switch
from being damaged by unregulated surge or current to the Managed Switch.
34
Page 35

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
2.2 Installing the Switch
This section describes how to install your Managed Switch and make connections to the Managed Switch. Please read the
following topics and perform the procedures in the order being presented. To install your Managed Switch on a desktop or shelf,
simply complete the following steps.
2.2.1 Desktop Installation
To install the Managed Switch on desktop or shelf, please follow these steps:
Step 1: Attach the rubber feet to the recessed areas on the bottom of the Managed Switch.
Step 2: Place the Managed Switch on the desktop or the shelf near an AC power source, as shown in Figure 2-1-4.
Figure 2-1-4 Place the Managed Switch on the desktop
Step 3: Keep enough ventilation space between the Managed Switch and the surrounding objects.
When choosing a location, please keep in mind the environmental restrictions discussed in Chapter 1,
Section 4, and specifications.
Step 4: Connect the Managed Switch to network devices.
Connect one end of a standard network cable to the 10/100/1000 RJ45 ports on the front of the Managed Switch.
Connect the other end of the cable to the network devices such as printer server, workstation or router.
Connection to the Managed Switch requires UTP Category 5 network cabling with RJ45 tips. For more
information, please see the Cabling Specification in Appendix A.
35
Page 36

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Step 5: Supply power to the Managed Switch.
Connect one end of the power cable to the Managed Switch.
Connect the power plug of the power cable to a standard wall outlet.
When the Managed Switch receives power, the Power LED should remain solid Green.
2.2.2 Rack Mounting
To install the Managed Switch in a 19-inch standard rack, please follow the instructions described below.
Step 1: Place the Managed Switch on a hard flat surface, with the front panel positioned towards the front side.
Step 2: Attach the rack-mount bracket to each side of the Managed Switch with supplied screws attached to the package.
Figure 2-1-5 shows how to attach brackets to one side of the Managed Switch.
Figure 2-1-5 Attach Brackets to the Managed Switch.
You must use the screws supplied with the mounting brackets. Damage caused to the parts by
using incorrect screws would invalidate the warranty.
Step 3: Secure the brackets tightly.
Step 4: Follow the same steps to attach the second bracket to the opposite side.
Step 5: After the brackets are attached to the Managed Switch, use suitable screws to securely attach the brackets to the rack,
as shown in Figure 2-1-6.
36
Page 37

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Figure 2-1-6 Mounting Managed Switch in a Rack
Step 6: Proceed with Steps 4 and 5 of session 2.2.1 Desktop Installation to connect the network cabling and supply power to the
Managed Switch.
37
Page 38

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
2.2.3 Installing the SFP transceiver
The sections describe how to insert an SFP transceiver into an SFP slot. The SFP transceivers are hot-pluggable and
hot-swappable. You can plug in and out the transceiver to/from any SFP port without having to power down the Managed Switch,
as the Figure 2-1-7 shows.
Figure 2-1-7 Plug in the SFP transceiver
Approved PLANET SFP Transceivers
PLANET Managed Switch supports both single mode and multi-mode SFP transceivers. The following list of approved PLANET
SFP transceivers is correct at the time of publication:
Gigabit SFP Transceiver Modules
MGB-GT
MGB-SX
MGB-LX
MGB-L50
MGB-L70
MGB-L120
MGB-LA10
MGB-LA20
MGB-LB20
SFP-Port 1000BASE-T Module
SFP-Port 1000BASE-SX mini-GBIC module
SFP-Port 1000BASE-LX mini-GBIC module
SFP-Port 1000BASE-LX mini-GBIC module – 50km
SFP-Port 1000BASE-LX mini-GBIC module – 70km
SFP-Port 1000BASE-LX mini-GBIC module – 120km
SFP-Port 1000BASE-LX (WDM,TX:1310nm) – 10km
SFP-Port 1000BASE-LX (WDM,TX:1310nm) – 20km
SFP-Port 1000BASE-LX (WDM,TX:1550nm) – 20km
MGB-LA40
MGB-LB40
SFP-Port 1000BASE-LX (WDM,TX:1310nm) – 40km
SFP-Port 1000BASE-LX (WDM,TX:1550nm) – 40km
Fast Ethernet SFP Transceiver Modules
MFB-FX
SFP-Port 100BASE-FX Transceiver – 2km
38
Page 39

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
MFB-F20
MFB-F60
MFB-FA20
MFB-FB20
1. Before we connect Managed Switch to the other network device, we have to make sure both sides of the SFP
transceivers are with the same media type, for example: 1000BASE-SX to 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX to
1000BASE-LX.
SFP-Port 100BASE-FX Transceiver – 20km
SFP-Port 100BASE-FX Transceiver – 60km
SFP-Port 100BASE-BX Transceiver (WDM,TX:1310nm) – 20km
SFP-Port 100BASE-BX Transceiver (WDM,TX:1550nm) – 20km
It is recommended to use PLANET SFP on the Managed Switch. If you insert an SFP transceiver
that is not supported, the Managed Switch will not recognize it.
In the installation steps below, this Manual uses Gigabit SFP transceiver as an example. However,
the steps for Fast Ethernet SFP transceiver are similar.
2. Check whether the fiber-optic cable type matches with the SFP transceiver requirement.
To connect to 1000BASE-SX SFP transceiver, please use the multi-mode fiber cable with one side being the male
duplex LC connector type.
To connect to 1000BASE-LX SFP transceiver, please use the single-mode fiber cable with one side being the male
duplex LC connector type.
Connect the Fiber Cable
1. Insert the duplex LC connector into the SFP transceiver.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to a device with SFP transceiver installed.
3. Check the LNK/ACT LED of the SFP slot on the front of the Managed Switch. Ensure that the SFP transceiver is operating
correctly.
4. Check the Link mode of the SFP port if the link fails. To function with some fiber-NICs or media converters, user has to set
the port Link mode to “1000 Force” or “100 Force”.
Remove the Transceiver Module
1. Make sure there is no network activity anymore.
2. Remove the fiber-optic cable gently.
3. Lift up the lever of the MGB module and turn it to a horizontal position.
4. Pull out the module gently through the lever.
39
Page 40

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Figure 2-1-8 How to Pull Out the SFP Transceiver
Never pull out the module without lifting up the lever of the module and turning it into a horizontal
position. Directly pulling out the module could damage the module and the SFP module slot of the
Managed Switch.
40
Page 41

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
3. SWITCH MANAGEMENT
This chapter explains the methods that you can use to configure management access to the Managed Switch. It describes the
types of management applications and the communication and management protocols that deliver data between your
management device (workstation or personal computer) and the system. It also contains information about port connection
options.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Requirements
Management Access Overview
Administration Console Access
Web Management Access
SNMP Access
Standards, Protocols, and Related Reading
3.1 Requirements
Workstations running Windows 2000/XP, 2003, Vista/7/8, 2008, MAC OS9 or later, Linux, UNIX or other platforms
are compatible with TCP/IP protocols.
Workstation is installed with Ethernet NIC (Network Interface Card).
Serial Port connect (Terminal)
The above PC comes with COM Port (DB9 / RS-232) or USB-to-RS-232 converter
Ethernet Port connection
Network cables -- Use standard network (UTP) cables with RJ45 connectors.
The above Workstation is installed with Web browser and Java runtime environment plug-in.
It is recommended to use Internet Explore 8.0 or above to access Managed Switch.
41
Page 42

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
3.2 Management Access Overview
The Managed Switch gives you the flexibility to access and manage it using any or all of the following methods:
An administration console
Web browser interface
An external SNMP-based network management application
The administration console and Web browser interfaces are embedded in the Managed Switch software and are available for
immediate use. Each of these management methods has their own advantages. Table 3-1 compares the three management
methods.
Method Advantages Disadvantages
Console
Web Browser
SNMP Agent
No IP address or subnet needed
Text-based
Telnet functionality and HyperTerminal
built into Windows
95/98/NT/2000/ME/XP operating
systems
Secure
Ideal for configuring the switch remotely
Compatible with all popular browsers
Can be accessed from any location
Most visually appealing
Communicates with switch functions at
the MIB level
Based on open standards
Must be near the switch or use dial-up
connection
Not convenient for remote users
Modem connection may prove to be unreliable
or slow
Security can be compromised (hackers need
to only know the IP address and subnet mask)
May encounter lag times on poor connections
Requires SNMP manager software
Least visually appealing of all three methods
Some settings require calculations
Security can be compromised (hackers need
to only know the community name)
Table 3-1 Comparison of Management Methods
42
Page 43

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
3.3 Administration Console
The administration console is an internal, character-oriented, and command line user interface for performing system
administration such as displaying statistics or changing option settings. Using this method, you can view the administration
console from a terminal, personal computer, Apple Macintosh, or workstation connected to the Managed Switch's console port.
Figure 3-1-1: Console Management
Direct Access
Direct access to the administration console is achieved by directly connecting a terminal or a PC equipped with a
terminal-emulation program (such as HyperTerminal) to the Managed Switch console (serial) port. When using this
management method, a straight RS-232 to RJ45 cable is required to connect the switch to the PC. After making this
connection, configure the terminal-emulation program to use the following parameters:
The default parameters are:
115200 bps
8 data bits
No parity
1 stop bit
Figure 3-1-2: Terminal Parameter Settings
43
Page 44

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
You can change these settings, if desired, after you log on. This management method is often preferred because you can
remain connected and monitor the system during system reboots. Also, certain error messages are sent to the serial port,
regardless of the interface through which the associated action was initiated. A Macintosh or PC attachment can use any
terminal-emulation program for connecting to the terminal serial port. A workstation attachment under UNIX can use an emulator
such as TIP.
Console interface is not available for the GS-4210-8P2S, GS-4210-48T4S and GS-4210-48P4C.
3.4 Web Management
The Managed Switch offers management features that allow users to manage the Managed Switch from anywhere on the
network through a standard browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer. After you set up your IP address for the switch, you can
access the Managed Switch's Web interface applications directly in your Web browser by entering the IP address of the
Managed Switch.
Figure 3-1-3 Web Management
You can then use your Web browser to list and manage the Managed Switch configuration parameters from one central location,
just as if you were directly connected to the Managed Switch's console port. Web Management requires either Microsoft
Internet Explorer 8.0 or later, Google Chrome, Safari or Mozilla Firefox 1.5 or later.
44
Page 45

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Figure 3-1-4 Web Main Screen of Managed Switch
3.5 SNMP-based Network Management
You can use an external SNMP-based application to configure and manage the Managed Switch, such as SNMPc Network
Manager, HP Openview Network Node Management (NNM) or What’s Up Gold. This management method requires the SNMP
agent on the switch and the SNMP Network Management Station to use the same community string. This management
method, in fact, uses two community strings: the get community string and the set community string. If the SNMP Network
management Station only knows the set community string, it can read and write to the MIBs. However, if it only knows the get
community string, it can only read MIBs. The default gets and sets community strings for the Managed Switch are public.
Figure 3-1-5 SNMP Management
3.6 PLANET Smart Discovery Utility
For easily listing the Managed Switch in your Ethernet environment, the Planet Smart Discovery Utility from user’s manual
CD-ROM is an ideal solution. The following installation instructions are to guide you to running the Planet Smart Discovery
Utility.
45
Page 46

1. Deposit the Planet Smart Discovery Utility in administrator PC.
2. Run this utility as the following screen appears.
User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Figure 3-1-6: Planet Smart Discovery Utility Screen
If there are two LAN cards or above in the same administrator PC, choose a different LAN card
by using the “Select Adapter” tool.
3. Press “Refresh” button for the currently connected devices in the discovery list as the screen shows below:
Figure 3-1-7: Planet Smart Discovery Utility Screen
1. This utility shows all necessary information from the devices, such as MAC Address, Device Name, firmware version and
Device IP Subnet address. It can also assign new password, IP Subnet address and description to the devices.
46
Page 47

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
2. After setup is completed, press “Update Device”, “Update Multi” or “Update All” button to take effect. The meaning of
the 3 buttons above are shown below:
Update Device: use current setting on one single device.
Update Multi: use current setting on multi-devices.
Update All: use current setting on whole devices in the list.
The same functions mentioned above also can be found in “Option” tools bar.
3. To click the “Control Packet Force Broadcast” function, it allows you to assign a new setting value to the Web Smart
Switch under a different IP subnet address.
4. Press “Connect to Device” button and the Web login screen appears in Figure 3-1-4.
5. Press “Exit” button to shut down the Planet Smart Discovery Utility.
47
Page 48

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
4. WEB CONFIGURATION
This section introduces the configuration and functions of the Web-based management.
About Web-based Management
The Managed Switch offers management features that allow users to manage the Managed Switch from anywhere on the
network through a standard browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer.
The Web-based Management supports Internet Explorer 8.0. It is based on Java Applets with an aim to reduce network
bandwidth consumption, enhance access speed and present an easy viewing screen.
By default, IE8.0 or later version does not allow Java Applets to open sockets. The user has to
explicitly modify the browser setting to enable Java Applets to use network ports.
The Managed Switch can be configured through an Ethernet connection, making sure the manager PC must be set on the same
IP subnet address as the Managed Switch.
For example, the default IP address of the Managed Switch is 192.168.0.100, then the manager PC should be set at
192.168.0.x (where x is a number between 1 and 254, except 100), and the default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
If you have changed the default IP address of the Managed Switch to 192.168.1.1 with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 via console,
then the manager PC should be set at 192.168.1.x (where x is a number between 2 and 254) to do the relative configuration on
manager PC.
Figure 4-1-1 Web Management
Logging on the switch
1. Use Internet Explorer 8.0 or above Web browser. Enter the factory-default IP address to access the Web interface. The
factory-default IP address is as follows:
http://192.168.0.100
48
Page 49

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
2. When the following login screen appears, please enter the default username "admin" with password “admin” (or the
username/password you have changed via console) to login the main screen of Managed Switch. The login screen in
Figure 4-1-2 appears.
Figure 4-1-2 Login screen
Default User Name: admin
Default Password: admin
After entering the username and password, the main screen appears as Figure 4-1-3.
49
Page 50

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
Figure 4-1-3 Default Main Page
Now, you can use the Web management interface to continue the switch management or manage the Managed Switch by Web
interface. The Switch Menu on the left of the web page lets you access all the commands and statistics the Managed Switch
provides.
It is recommended to use Internet Explore 8.0 or above to access Managed Switch.
The changed IP address takes effect immediately after clicking on the Save button. You need to
use the new IP address to access the Web interface.
For security reason, please change and memorize the new password after this first setup.
Only accept command in lowercase letter under Web interface.
50
Page 51

User’s Manual of GS-4210 Series
4.1 Main Web Page
The Managed Switch provides a Web-based browser interface for configuring and managing it. This interface allows you to
access the Managed Switch using the Web browser of your choice. This chapter describes how to use the Managed Switch’s
Web browser interface to configure and manage it.
Main Functions Menu SFP Port Link Status
Main Screen
Copper Port Link Status
Figure 4-1-4 Main Page
Panel Display
The Web agent displays an image of the Managed Switch’s ports. The Mode can be set to display different information for the
ports, including Link up or Link down. Clicking on the image of a port opens the Port Statistics page.
The port states are illustrated as follows:
State Disabled Down Link
RJ45 Ports
SFP Ports
Main Menu
Using the onboard Web agent, you can define system parameters, manage and control the Managed Switch, and all its ports, or
monitor network conditions. Via the Web-Management, the administrator can set up the Managed Switch by selecting the
functions those listed in the Main Function. The screen in Figure 4-1-5 appears.
51
 Loading...
Loading...