Page 1

802.11n Wireless ADSL2/2+ Router
ADN-4102
802.11n Wireless ADSL 2/2+
Router
►ADN-4102
Page 2

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Copyright
Copyright © 2015 by PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or
computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical,
manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of PLANET.
PLANET makes no representations or warranties, either expres sed or implied, with respe ct to the contents
hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Any
software described in this manual is sold or licensed "as is". Should the progra ms prove defective following
their purchase, the buyer (and not PLANET, its distributor, or its dealer) assumes the entire cost of all
necessary servicing, repair, and any incidental or consequential damages resulting from any defect in the
software. Further, PLANET reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to
time in the contents hereof without obligation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
All brand and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of
their respective holders.
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
3. Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is conne cted.
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio technician for help.
FCC Caution
To assure continued compliance, use only shielded interface cables when connecting to computer or
peripheral devices. Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two con ditions: (1)
This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this Device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Federal Communication Commission (FCC) Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure set forth for an uncontrolled environment. In order
to avoid the possibility of exceeding the FCC radio frequency exposure limits, human proximity to the
antenna shall not be less than 20 cm (8 inches) during normal operation.
2
Page 3

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it. However,
special attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when working with
electrical equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacture must therefore be allowed at
all times to ensure the safe use of the equipment.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which
case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
WEEE Regulation
To avoid the potential effects on the en vironment an d human health as a re sult of the pre sence of
hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of electrical and
electronic equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol. Do
not dispose of WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to collect such WEEE separately.
Revision
User’s Manual of 802.11n Wireless ADSL2/2+ Router
Model: ADN-4102
Rev: 1.0 (July 2015)
Part No. EM-ADN-4102_v1.0
3
Page 4

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Contents
Chapter 1. Overview ........................................................................................................6
1.1 System Requirements ...........................................................................................9
1.2 Features ..............................................................................................................10
1.3 Specifications.......................................................................................................11
Chapter 2. Hardware Installation ..................................................................................14
Chapter 3. Web Configuration ......................................................................................15
3.1 Accessing the Router...........................................................................................15
3.2 Status...................................................................................................................16
3.2.1 Device Information .....................................................................................16
3.2.2 ADSL.......................................................................................................... 17
3.2.3 Statistics.....................................................................................................18
3.3 Wizard .................................................................................................................18
3.4 Setup...................................................................................................................25
3.4.1 WAN...........................................................................................................25
3.4.2 LAN............................................................................................................29
3.5 WLAN..................................................................................................................37
3.5.1 Security ......................................................................................................38
3.5.2 MBSSIDs....................................................................................................40
3.5.3 Access Control ...........................................................................................41
3.5.4 Advanced Settings......................................................................................42
3.5.5 WPS...........................................................................................................43
3.6 Advanced.............................................................................................................43
3.6.1 Route..........................................................................................................43
3.6.2 NAT ............................................................................................................47
3.6.3 QoS............................................................................................................55
3.6.4 CWMP (TR-069).........................................................................................56
3.6.5 Port Mapping..............................................................................................58
3.6.6. Others .......................................................................................................59
3.7 Service.................................................................................................................62
3.7.1 IGMP..........................................................................................................63
3.7.2 UPNP .........................................................................................................65
3.7.3 SNMP.........................................................................................................65
3.7.4 DNS............................................................................................................66
3.7.5 DDNS.........................................................................................................68
3.7.6 FTP Server.................................................................................................69
3.8 Firewall................................................................................................................69
3.8.1 MAC Filter ..................................................................................................70
3.8.2 IP/Port Filter ...............................................................................................71
3.8.3 URL Filter...................................................................................................73
3.8.4 ACL ............................................................................................................73
3.8.5 DoS ............................................................................................................77
4
Page 5

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.8.6 Parental Control .........................................................................................78
3.9 Maintenance........................................................................................................78
3.9.1 Update........................................................................................................79
3.9.2 Password....................................................................................................81
3.9.3 Reboot........................................................................................................82
3.9.4. Time ..........................................................................................................83
3.9.5 Log.............................................................................................................84
3.9.6 Diagnostic...................................................................................................84
Chapter 4. Q&A ..............................................................................................................92
5
Page 6
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Chapter 1. Overview
Built-in Firewall to Have Safe Internet Surfing
PLANET ADN-4102 is a Wireless ADSL 2/2+ Router compliant with 802.11n and features 1T1R MIMO
antenna technology. The ADN-4102’s built-in parental controls is to limit children’s online time – be it
computing or gaming, thus creating a safer computing environment for children. In Annex M mode, the
ADN-4102 provides transmission rates up to 24Mbps downstream and 3.5Mbps upstream with ADSL 2+
support. Through integration with single chipset to reduce boot time, the ADN-4102 brings more powerful
performance to users. The ADN-4102 also supports PPPoA (RFC 2364 -- PPP over ATM Adaptation Layer
5), RFC 2684 encapsulation over ATM (bridged or routed), PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516), and IPoA
(RFC1483) to establish a connection with ISP.
High-speed 802.11n Wireless Access
With built-in IEEE 802.11b/g and 802.11n wireless network capabilities, the ADN-4102 allows any computer
and wireless-enabled network device to connect it without additional cabling. S mart phones also ju mp on the
bandwagon of wireless networking. Its 802.11n wireless capability gives you a high-speed wireless
transmission up to 150Mbps. With a compatible wireless LAN card installed in your PC, any file can be
transferred at a very high speed. The radio coverage is also doubled than before, offering you the
high-speed wireless connection, even in a spacious office or house.
6
Page 7

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
One-touch Secure Wireless Connection
To secure the wireless communication, the ADN-4102 features the most up-to-date encryptions like WEP,
WP A-PSK and WPA2-PSK. The ADN-4102 also supports WPS configuration with PBC/PIN type for users to
easily connect to a secure wireless network with no need of complicated settings.
4-in-1 (4 Multiple SSIDs) Wireless Networking Infrastructures
Up to four wireless networking with management can be established by the ADN-4102. This flexibility makes
it the best choice for SOHO wireless networking in restaurants, hotels, bookstores and more.
Front Panel
7
Page 8

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
LED Indicator
LED State Description
ADN‐4102
PWR
DSL
Internet
LAN 1-4
Wi-Fi
WPS
Rear Panel
Green Indicates when the ADSL Router is powered on. The LED will remain on.
Off When the router is powered off
Green When DSL port is connected by Ethernet cable, the LED remains ON.
Flashing Modem is trying to establish a connection to telecom’s network
Off No Internet connection.
Green
Green
Flashing TX or RX activity
Green
Flashing The wireless data is transmitting.
Off The wireless Interface is disabled.
Off WPS service is not in use or WPS is set up successfully.
Green
Indicates when the router is connected to a DSLAM. The LED will blink
rapidly when Internet traffic is transmitted or received.
Indicates when a networking device is connected to a wired port on the back
of the ADN-4102. The LED will blink rapidly when wired data traffic is
transmitted or received.
Blinks rapidly when wireless data traffic is transmitted or received over the
wireless network.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup activity. When the WPS mode is activated, the Power
LED blinks as it awaits a connection
8
Page 9
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Port and Button Definition
Connector Description
POWER Button
WPS
RST
PWR
LAN 1-4
ADSL
The power button is for turning on or off the router.
Pressing for 5 seconds and then releasing it can enable the WPS function of the
wireless clients. The ADN-4102 and clients will automatically configure the security
key and connect directly.
The reset button can restore the default settings of device. To restore factory
defaults, keep the device powered on and push a paper clip into the hole. Press
down the button for over 5 seconds and then release.
Power connector with 12V DC, 0.5A
Router is successfully connected to a device through the corresponding port (1, 2, 3,
or 4). If the LED is flashing, the ADN-4102 is actively sending or receiving data over
that port.
The RJ11 connector allows data communication between the modem and the ADSL
network through a twisted-pair phone wire.
1.1 System Requirements
Make sure first that you have prepared these following items to guarantee the router can work normally.
Services subscriptions.
An 10/100Mbps Ethernet card installed on your PC.
Hub or Switch. (Attached to several PCs through one of Ethernet interfaces on the device).
Operating system: Windows 7, Windows 2000, or Windows XP.
Internet Explorer V8.0 or higher, or firefox v23 or higher.
9
Page 10
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
1.2 Features
The device supports the following features:
Internet Access Features
Shared Internet Access through a single external IP address
Supports NAT (Network Address Translation)
Built-in ADSL 2/2+ Modem for all common ADSL connections
Various WAN connections - PPPoE, PPPoA, Direct Connection Supports Fixed and Dynamic IP Address
Advanced Internet Functions
Supports Virtual Servers with quick and easy setup
DMZ Support to allow unrestricted 2-way communication with servers or individual users on the Internet
Simple firewall with NAT technology
Provides options for access control from Internet like Telnet, FTP, TFTP, HTTP, and ICMP services
Supports IP/ MAC/ Application/ URL filtering
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) to allow automatic discovery and configuration of the broadband router
Dynamic DNS Support, allowing users to connect a server to the LAN by using a Domain Name even if
you have a dynamic IP address
Supports Planet Dynamic DNS service
RIP v1/v2 Routing support
LAN Features
4-port 10/100BASE-TX switching
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server Support
Supports IPv6/IPv4
Optional NAT ALG, offering 9 items that can be selected from web UI, including VPN passthrough, SIP,
H.323, ICQ, etc
Parental Controls -- Limit specific PC with IP or MAC address to the time and programs available for
internet connection
Wireless Features
IEEE 802.11b/g/n Wireless Standard compliant
Provides data rate up to 150Mbps via 802.11n technology
10
Page 11
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) Support with key sizes of 64 bit and 128 bit
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) Push Button Control for easy wireless connection without configurations
WPA-PSK Support: WPA-PSK_TKIP and WAP-PSK_AES encryptions
Wireless MAC Access Control to ensure that only trusted wireless stations can access your LAN
1.3 Specifications
Product 802.11n Wireless ADSL 2/2+ 4-port Router
Model ADN-4102A
Hardware
Compliant with ADSL Standard
- Full-rate ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
- G.dmt (ITU G.992.1)
- G.lite (ITU G.992.2)
- G.hs,Multimode (ITU G.994.1)
Standard
Protocol
AAL and ATM Support
LAN
Ports
LED Indicators
Button
Max. Concurrent Sessions
Wireless Standard
Wireless Frequency
Wireless Channels
WLAN
WAN
Capable of ADSL2 Standard
- G.dmt.bis (ITU G.992.3)
Capable of ADSL2+ Standard
- G.dmt.bisplus (ITU G.992.5)
- Reach Extended ADSL (RE ADSL )
Supports Annex A, M, L
RFC 2364 - PPP over ATM (LLC/VCMUX)
RFC 2516 - PPP over Ethernet (LLC/VCMUX)
RFC 1483 - Classic IP over ATM (LLC/VCMUX)
RFC 2684 - Bridged IP over ATM (LLC/VCMUX)
RFC 2684 - Routed IP over ATM (LLC/VCMUX)
Supports up to 8 PVCs
ATM Forum UNI 3.1/4.0 PVC
VC and LLC Multiplexing
Integrated ATM AAL5 support (UBR,CBR,VBR-rt and VBR-nrt)
0~255 VPI plus 1~65535 VCI address range
OAM F4 & F5 Segment end-to-end loop-back, AIS, and RDI OAM cells
4 x Ethernet (10/100Mbps, auto-negotiation, auto MDI/MDI-X)
1 x 802.11b/g/n Access Point with one 2dBi dipole antenna
1 x RJ11
PWR, Link, Data, LAN 1~4, WLAN, WPS
Reset, WPS, Power
2048
IEEE 802.11b, g and 802.11n
2.4 to 2.4835GHz (Industrial Scientific Medical Band )
Maximum 14 channels, depending on regulatory authorities
11
Page 12
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Wireless Data Encryption
Wireless Data Rate
RF Modulation
Transmit Power
Receiver Sensitivity
Software
Protocols/Features
Security
Management
Environment Specifications
Dimensions (W x D x H)
ADN‐4102
64 bit/128 bit WEP, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK and WPS PBC
Maximum up to 150 Mbps
IEEE 802.11b: 1/2/5.5/11Mbps
IEEE 802.11g: 6/9/12/18/24/36/48/54Mbps
IEEE 802.11n: 14/29/43/58/87/116/130/144Mps in 20MHz
30/60/90/120/150Mbps in 40MHz
IEEE 802.11b mode: DSSS (CCK,QPSK,BPSK)
IEEE 802.11g mode: OFDM (BPSK,QPSK,16QAM,64QAM)
HT20 and HT40: 64 QAM, 16QAM, QPSK, BPSK
IEEE 802.11b: 16.5dBm ± 1.5dBm
IEEE 802.11g: 14dBm ± 1.5dBm
IEEE 802.11n HT20M:13dbm ± 1.5dBm
IEEE 802.11n HT40M: 13dbm ± 1.5dBm
IEEE 802.11b: < -80dBm
IEEE 802.11g: < -68dBm
IEEE 802.11n HT20M: < -64dbm
IEEE 802.11n HT40M: < -61dbm
NAT supports multimedia applications
NAT, St atic Routing, and RIPv1/2
Transparent Bridging
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS)
SNTP
DNS relay and IGMP proxy
DMZ and Virtual Server
Quality of Service (QoS) for Traffic Prioritization
TR-069 Ready
UPnP
PPP over PAP (Password Authentication Protocol, RFC 1334)
PPP over CHAP (Challenge Authentication Protocol, RFC 1994)
DoS Protection
Access Control
ACL (Access Control)
IP / MAC / URL Filter
Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) Firewall
Password protection for system management
Web-based configuration
Embedded Telnet server for remote and local management
Firmware upgraded and configuration data upload/download via Web
Support DHCP Server/Client/Relay
Built-in diagnostic tool
TR-069
117 x 100 x 25 mm
12
Page 13

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Power
Temperature and Humidity
Emission
ADN‐4102
12V DC, 0.5A
Operating temperature: 0 ~ 50 degrees C
Storage temperature: -10 ~ 70 degrees C
Humidity: 10 ~ 95% non-condensing
FCC, CE
13
Page 14
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Chapter 2. Hardware Installation
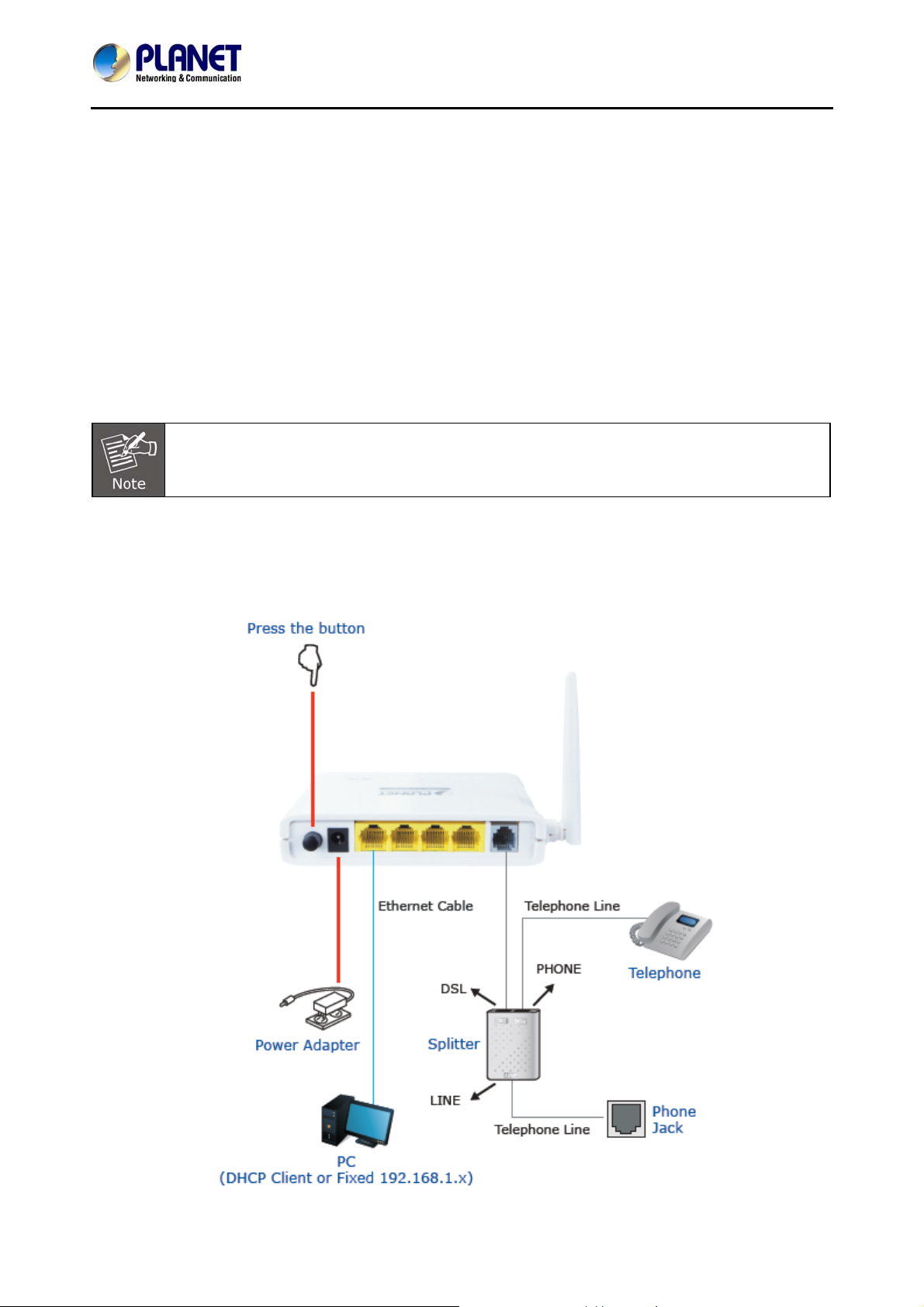
Connect the LINE interface of the device and the DSL interface of the splitter with a telephone cable.
Connect the phone set to the Phone interface of the splitter through a telephone cable. Connect the input
cable to the LINE interface of the splitter.
The splitter has three interfaces:
LINE: Connect to a wall phone interface (RJ-11 jack).
DSL: Connect to the DSL interface of the device.
Phone: Connect to a telephone set.
Connect the LAN interface of the device to the network card of the PC through an Ethernet cable
(MDI/MDIX).
Insert one end of the power adapter to the wall outlet and connect the other end to the POWER interface of
the device.
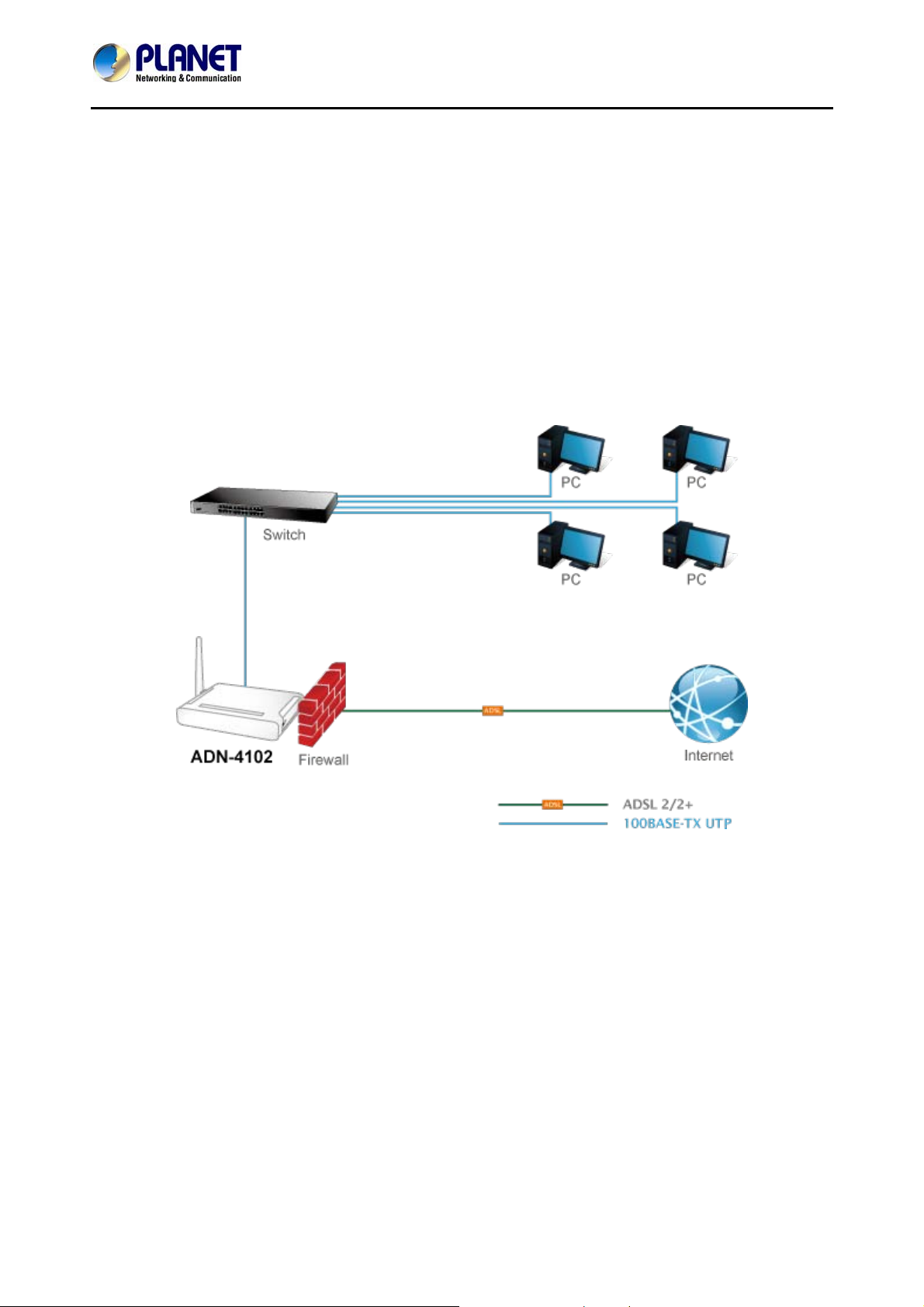
The following figure shows the application diagram for the connection of the router, PC, splitter and the
telephone sets.
Use the twisted-pair cable to connect the hub or switch.
14
Page 15

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Chapter 3. Web Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure the device by using the Web-base d configuration utility.
3.1 Accessing the Router
The following describes how to access the device for the first time in details.
Step 1 Open the Internet Explorer (IE) browser and enter http://192.168.1.1
Step 2 On the Login page that is displayed, enter the username and password, and then click OK.
z The username and password of the super user are admin and admin.
in the address bar.
After logging in, the page shown in the following figure appears. You can check, configure and modify all the
settings.
15
Page 16
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
On the Web configuration page, you can click Apply Changes to save the
settings temporarily. If you want to save the settings on this page
permanently, clicks “save” that appears at the bottom of the Web page
after the configuration.
3.2 Status
In the navigation bar , choose Status. On the Status page that is displayed contains: Device Info, ADSL and
Statistics.
3.2.1 Device Information
Choose Status > Device Info and the page displayed shows the current status and some basic settings of
the router, such as software version, DSP version, uptime, upstream speed, and downstream speed.
16
Page 17
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.2.2 ADSL
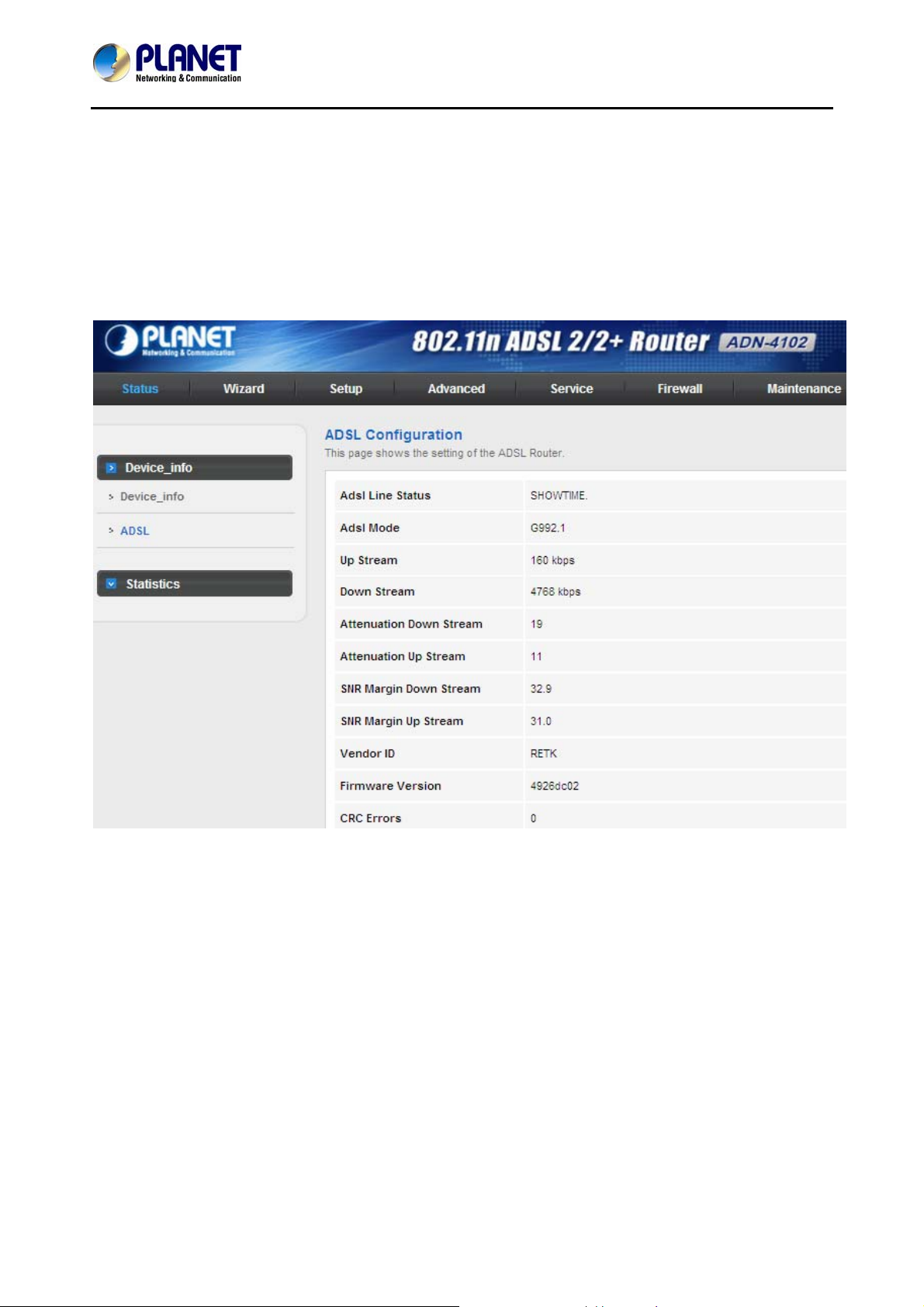
Click ADSL in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. On this page, you can view
the ADSL line status, upstream rate, downstream rate and othe r information.
Choose Status > LAN and the page displayed shows some basic LAN settings of the router. On this page,
you can view the LAN IP address, DHCP server status, MAC address, and DHCP client table.
17
Page 18
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
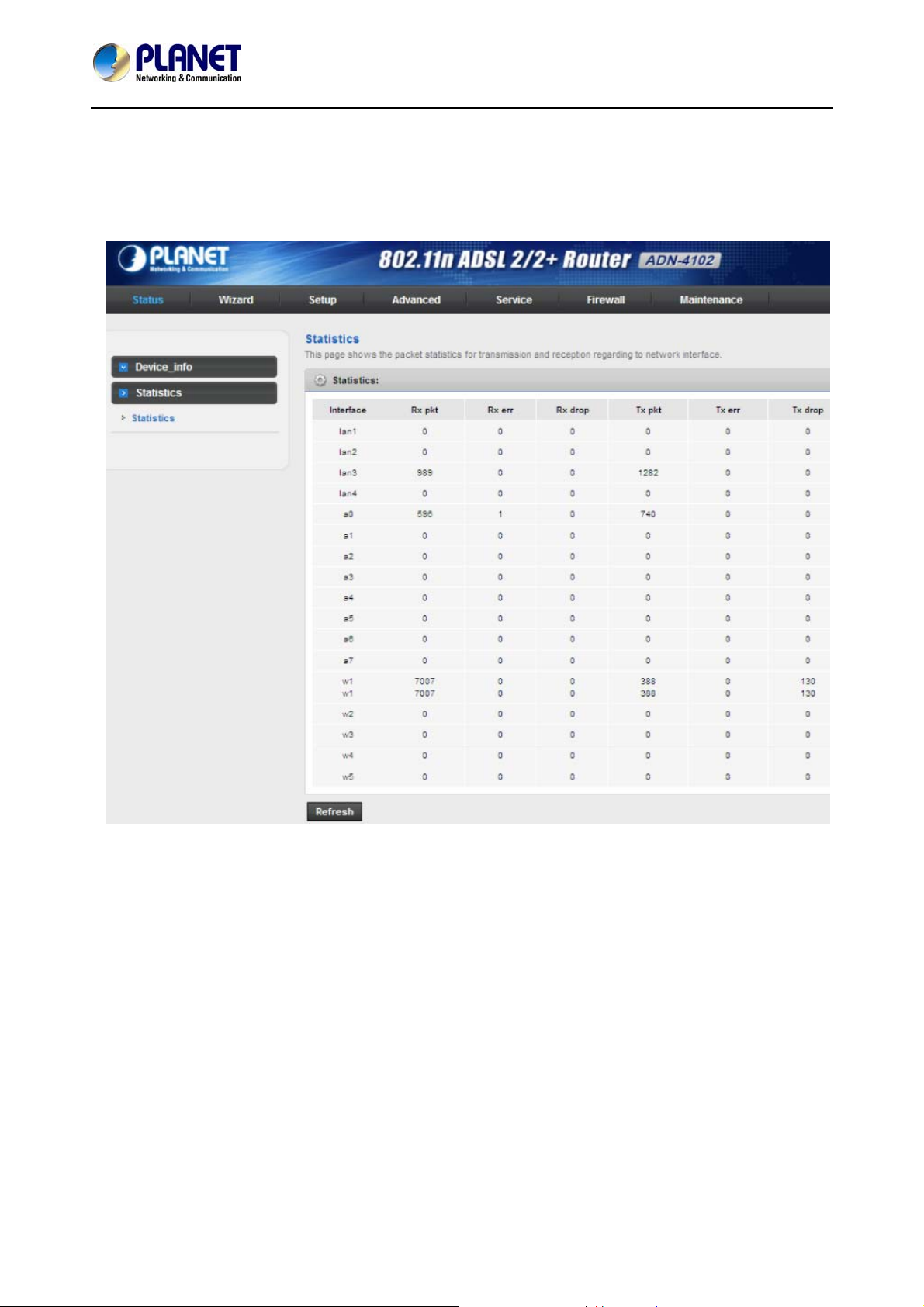
3.2.3 Statistics
Choose Status > Statistics. Click Statistics in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure
appears. On this page, you can view the statistics of each netwo rk port.
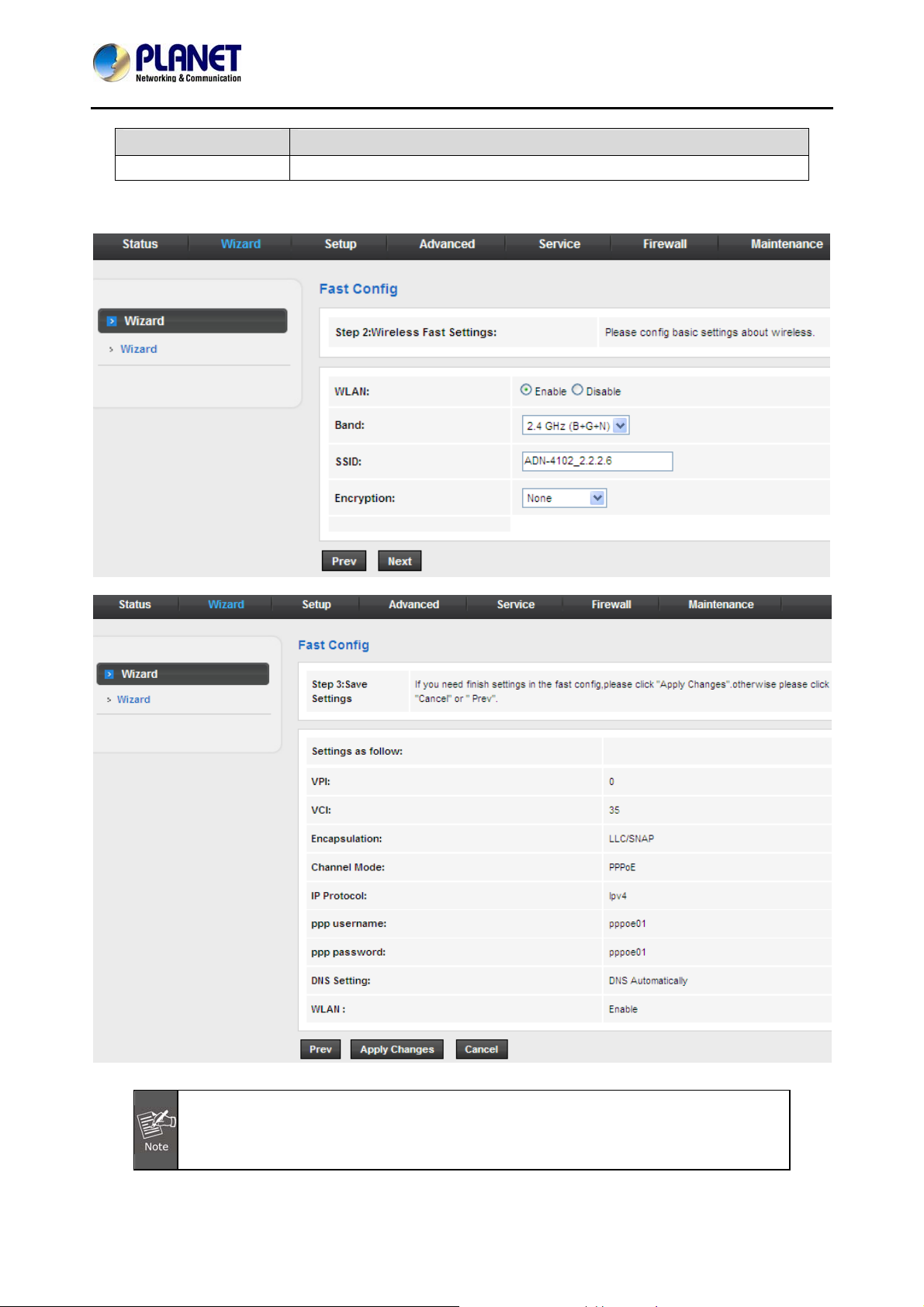
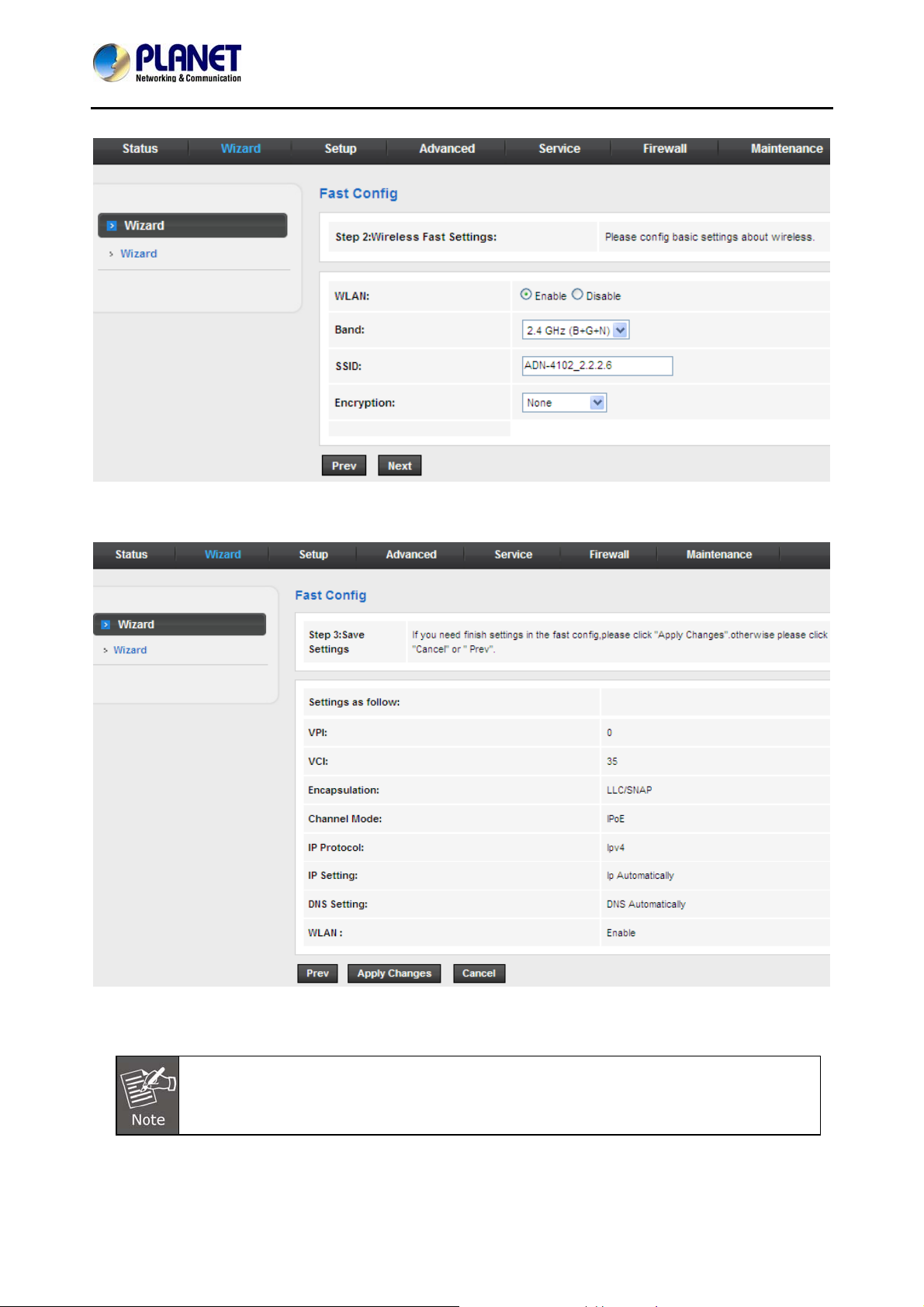
3.3 Wizard
When subscribing to a broadband service, you should be aware of the method by which you are connected
to the Internet. Y our physical WAN device can be either PPP, ADSL, or both. The technical information about
the properties of your Internet connection is provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). For example,
your ISP should inform you whether you are connected to the Internet using a static or dynamic IP address,
and the protocol that you use to communicate on the Internet.
18
Page 19
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
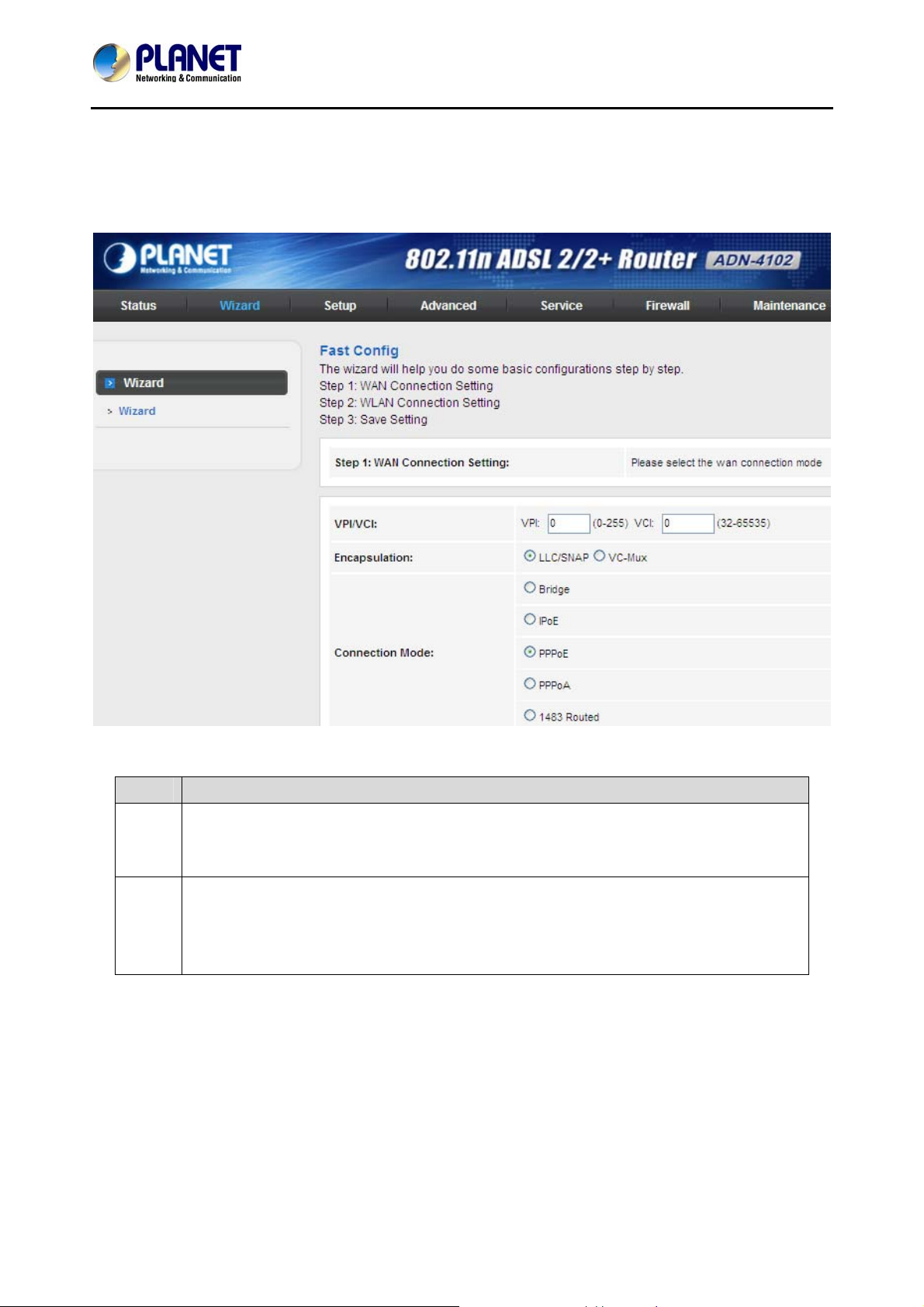
In the navigation bar, choose Wizard. The page shown in the following figure appears. The Wizard page
guides fast and accurate configuration of the Internet connection and other important parameters. The
following sections describe these various configuration parameters. Whether you configure these
parameters or use the default ones, click NEXT to enable your Internet connection.
The following table describes the parameters on this page:
Field Description
Virtual path identifier (VPI) is the virtual path between two points in an ATM network. Its
VPI
VCI
valid value is in the range of 0 to 255. Enter the correct VPI provided by your ISP. By
default, VPI is set to 0.
Virtual channel identifier (VCI) is the virtual channel between two points in an ATM
network. Its valid value is in the range of 32 to 65535. (0 to 31 is reserved for local
management of ATM traffic) Enter the correct VCI provided by your ISP. By default, VCI is
set to 0.
There are five WAN connection types: Bridged, IPoE (MER), PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE), PPP over
ATM (PPPoA), 1483 Routed, and. The following describes them respectively.
19
Page 20
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Bridge
After setting, click Next and the page as shown in the following figure appears.
ADN‐4102
20
Page 21
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
PPPoE/PPPoA
On the Connection Mode page, set the WAN connection type to PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE), and the
encapsulation mode to LLC/SNAP.
Field Description
PPP Username Enter the username for PPPoE dial-up, which is provided by your ISP.
21
Page 22
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Field Description
PPP Password Enter the password for PPPoE dial-up, which is provided by your ISP.
After setting, click Next and the page as shown in the following figure appears.
ADN‐4102
If the WAN connection type is set to PPPoA, the parameters of the WAN connection
type are the same as those of PPPoE. For the parameters on these pages, refer to the
parameter description of PPPoE.
22
Page 23
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
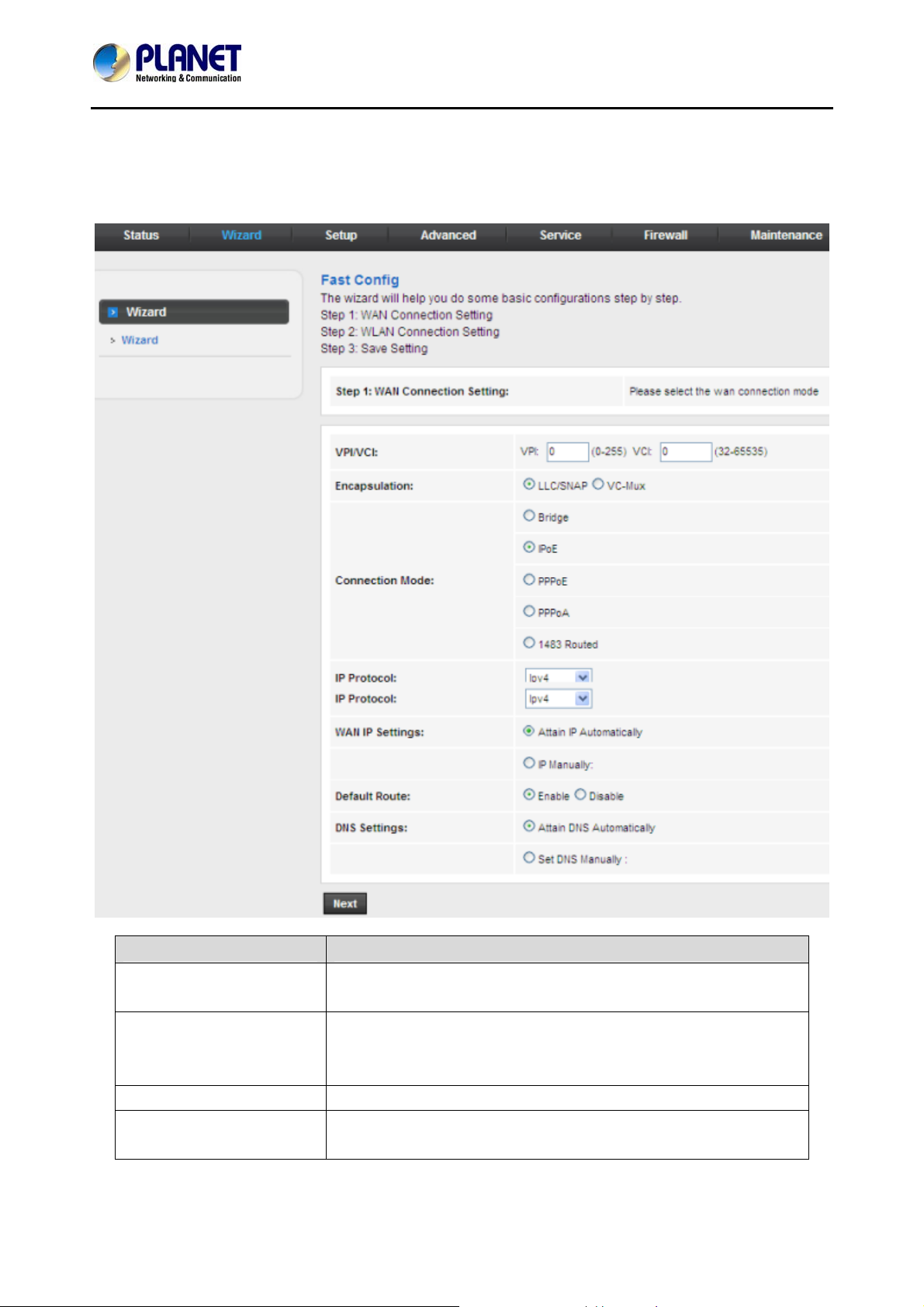
IPoE (MER)/1483 Routed
On the Connection Mode page, set the WAN connection type to IPoE, and the encapsulation mode to
LLC/SNAP.
Field Description
Attain IP Automatically
IP Manually
Attain DNS Automatically Select it and DHCP automatically assigns DNS server address.
Set DNS Manually
Select it and DHCP automatically assigns the IP address for WAN
connection.
When selecting it, you need to manually enter the IP address,
subnet mask, and default gateway for WAN connection, which are
provided by your ISP.
Select it to manually enter the primary DNS server address and
secondary DNS server address.
23
Page 24
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
After setting, click Next and the page as shown in the following figure appears.
ADN‐4102
For subsequent configuration, refer to the description in the above section PPPoE/PPPoA.
If the WAN connection type is set to 1483 Routed, the parameters of the WAN connection
type are the same as those of IPoE. For the parameters on these pages, refer to the
parameter description of IPoE.
24
Page 25
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
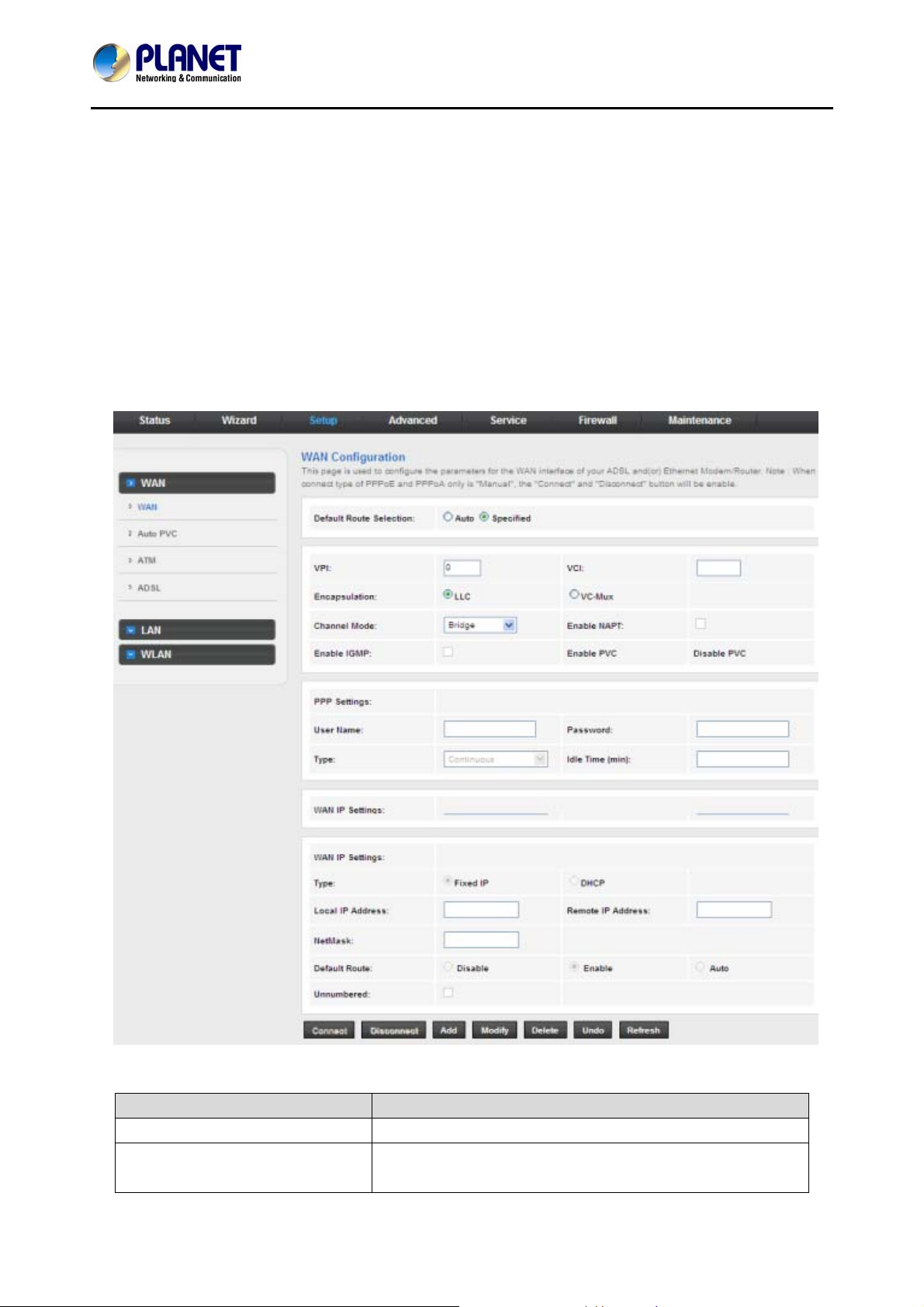
3.4 Setup
In the navigation bar, click Setup. The Setup page that is displayed contains WAN and LAN.
3.4.1 WAN
Choose Setup > WAN. The WAN page that is displayed contains WAN, Auto PVC, ATM and ADSL.
3.4.1.1 WAN Setting
Click WAN in the left pane and the page sho wn in the following figure appears.
On this page, you can configure W A N interface of your router.
ADN‐4102
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Default Route Selection
VPI
You can select Auto or Specified.
The virtual path between two points in an ATM network,
ranging from 0 to 255.
25
Page 26
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Field Description
The virtual channel between two points in an ATM network,
VCI
Encapsulation
Channel Mode
Enable NAPT
Enable IGMP
PPP Settings
User Name
Password
Type
Idle Time (min)
WAN IP Settings
Type
Local IP Address Enter the IP address of WAN interface provided by your ISP.
Netmask Enter the subnet mask of the local IP address.
Unnumbered Select this checkbox to enable IP unnumbered function.
Add
Modify
WAN Interfaces Table
ranging from 32 to 65535 (1 to 31 are reserved for known
protocols)
You can choose LLC and VC-Mux.
You can choose Bridge, IPoE, PPPoE, PPPoA, 1483
Routed or IPoA.
Select it to enable Network Address Port Translation (NAPT)
function. If you do not select it and you want to access the
Internet normally, you must add a route on the uplink
equipment. Otherwise, the access to the Internet fails.
Normally, it is enabled.
You can enable or disable Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP) function.
Enter the correct user name for PPP dial-up, which is
provided by your ISP.
Enter the correct password for PPP dial-up, which is provided
by your ISP.
You can choose Continuous, Connect on Demand, or
Manual.
If set the type to Connect on Demand, you need to enter the
idle timeout time. Within the preset minutes, if the router does
not detect the flow of the user continuously, the router
automatically disconnects the PPPoE connection.
You can choose Fixed IP or DHCP.
If select Fixed IP, you should enter the local IP address,
remote IP address and subnet mask.
If select DHCP, the router is a DHCP client, the WAN IP
address is assigned by the remote DHCP server.
After configuring the parameters of this page, click it to add
new PVC into the Current ATM VC Table.
Select PVC in the Current ATM VC Table, and modify the
parameters of this PVC. After finishing, click it to apply the
settings of this PVC.
This table shows the existed PVCs. It shows the interface
name, channel mode, VPI/VCI, encapsulation mode, local IP
address, remote IP address and other information. The
maximum item of this table is eight.
ADN‐4102
26
Page 27
802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
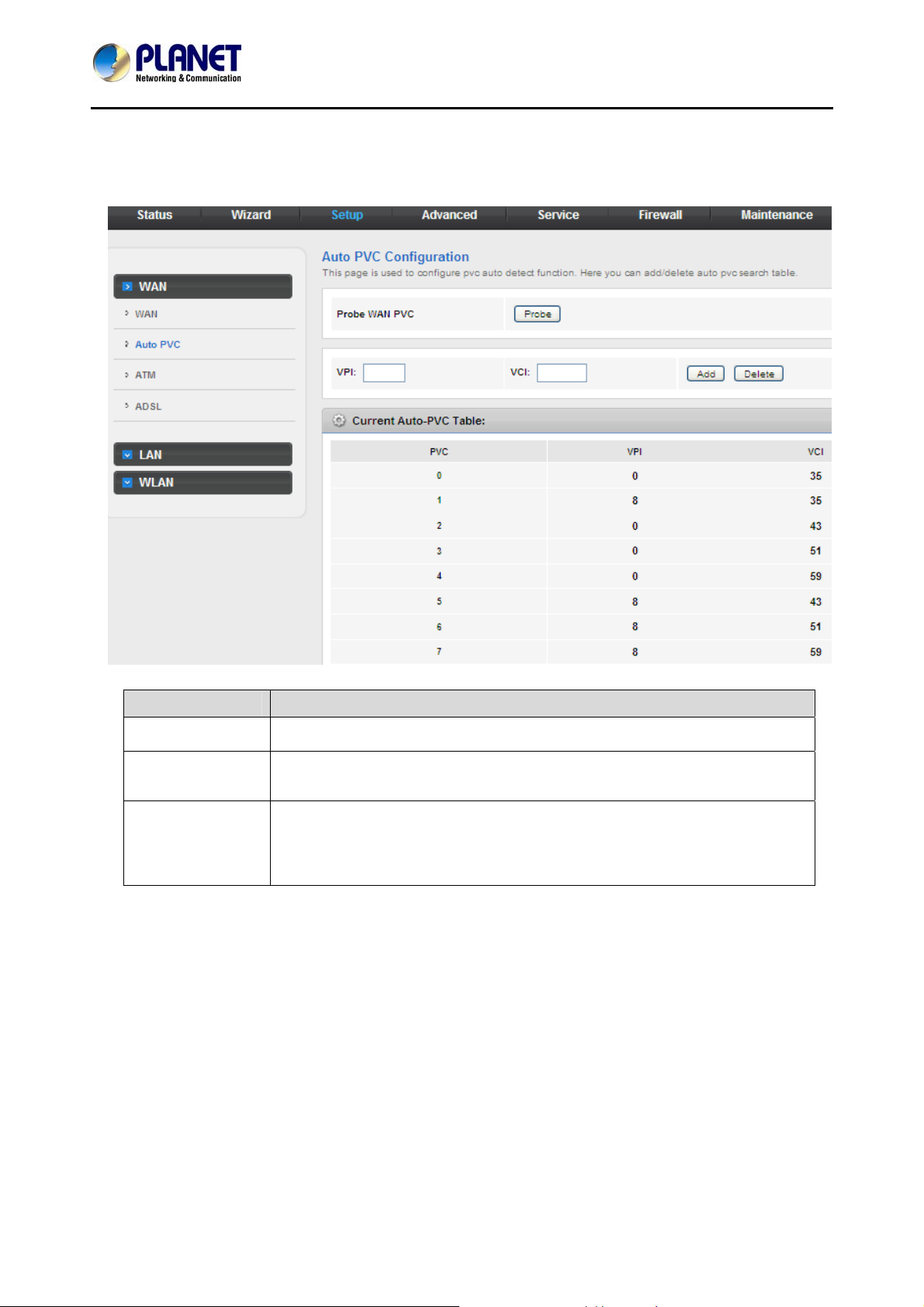
3.4.1.2 Auto PVC
Click Auto PVC in the lef t pane and the p age shown in the following figure appears. On this p age, you can
get a PVC automatically through detecting function, and add or delete the PVC that you do not want.
Field Description
Probe WAN PVC Click Probe to display WAN Permanent virtual circuit.
VPI
VCI
Virtual Path Identifier. This is read-only field and is selected on the Select
column of the Current ATM VC Table.
Virtual Channel Identifier. This is read-only field and is selected on the Select
column in the Current ATM VC Table. The VCI, together with VPI, is used to
identify the next destination of a cell as it passes through the ATM switch.
27
Page 28

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.4.1.3 ATM
Click ATM in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. On this page, you can
configure the parameters of the A TM, including QoS, PCR, CDVT, SCR and MBS.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
VPI
VCI
QoS
PCR
SCR
MBS
CDVT
Virtual Path Identifier. This is read-only field and is selected on the Select column
in the Current ATM VC Table.
Virtual Channel Identifier. This is read-only field and is selected on the Select
column in the Current ATM VC Table. The VCI, together with VPI, is used to
identify the next destination of a cell as it passes through the ATM switch.
Quality of Server, a characteristic of data transmission that measures how
accurately and how quickly a message or data is transferred from a source host to
a destination host over a network. The four QoS options are
UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate): When UBR is selected; the SCR and MBS fields
are disabled.
CBR ( Constant Bit Rate): When CBR is sele cted; the SCR and MBS fields are
disabled.
nrt-VBR (non-real-time Variable Bit Rate): When nrt-VBR is selected, the
SCR and MBS fields are enabled.
rt-VBR (real-time Variable Bit Rate): When rt-VBR is selected, the SCR and
MBS fields are enabled.
Peak Cell Rate, measured in cells/sec., is the cell rate which the source may
never exceed.
Sustained Cell Rate, measured in cells/sec., is the average cell rate over the
duration of the connection.
Maximum Burst Size, a traffic parameter that specifies the maximum number of
cells that can be transmitted at the peak cell rate.
Cell delay variation tolerance (CDVT) is the amount of delay permitted between
ATM cells (in microseconds).
28
Page 29

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.4.1.4 ADSL
Click ADSL in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. On this page, you can
select the DSL modulation. This factory default setting is mostly used . The router supports these
modulations: G. Li te , G.Dmt, T1.413, ADSL2 and ADSL2+. The router negotiates the modulation modes
with the DSLAM.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Choose preferred xdsl standard protocols.
G.lite : G.992.2 Annex A
ADSL modulation
AnnexL Option Enable/Disable ADSL2/ADSL2+ Annex L capability.
AnnexM Option Enable/Disable ADSL2/ADSL2+ Annex M capability.
ADSL Capability
G.Dmt : G.992.1 Annex A
T1.413 : T1.413 issue #2
ADSL2 : G.992.3 Annex A
ADSL2+ : G.992.5 Annex A
“Bitswap Enable”: Enable/Disable bitswap capability.
“SRA Enable”: Enable/Disable SRA (seamless rate adaptation)
capability.
3.4.2 LAN
Choose Setup > LAN. The LAN page that is displayed cont ains LAN, DHCP, DHCP Static and LAN IPv6.
29
Page 30

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.4.2.1 LAN Setting
Click LAN in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. On this page, you can
change IP address of the router. The default IP address is 192.168.1.1, which is the private IP address of
the router.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
IP Address The IP address of your LAN hosts used to identify the device’s LAN port.
Subnet Mask
Secondary IP
IGMP Snooping
MAC Address Control
New MAC Address Enter MAC address and then click Add to add a new MAC address.
Enter the subnet mask of LAN interface. The range of subnet mask is from
255.255.0.0 to 255.255.255.254
Select it to enable/disable a secondary LAN IP address. The two LAN IP
addresses must be in the different network.
Enable/disable the IGMP snooping function for the multiple bridged LAN
ports.
It is the access control based on MAC address. Select LAN1, LAN2, LAN3,
LAN4, WLAN and the host whose MAC address listed in the Currently
Allowed MAC Address Table can access the device. Then click “Apply
Changes” to save the new settings.
3.4.2.2 DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows the individual PC to obtain the TCP/IP configuration
from the centralized DHCP server. You can configure this router as a DHCP server or disable it. The
DHCP server can assign IP address, IP default gatewa y, and DNS server to DHCP clients. This router can
30
Page 31

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
also act as a surrogate DHCP server (DHCP Relay) where it relays IP address assignment from an actual
real DHCP server to clients. You can enable or disable DHCP server.
Click DHCP in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
You can choose None, DHCP Relay and DHCP Server. If set to DHCP
DHCP Mode
Interface
IP Pool Range
Show Client
Server, the router can assign IP addresses, IP default gateway and DNS
Servers to the host in Windows95, Windows NT and other operating
systems that support the DHCP client.
By default, all ports are selected; click it to unselect and those ports cannot
function with the IP address.
Specify the lowest and highest addresses in the pool. It specifies the first IP
address in the IP address pool. The router assigns IP address based on the
IP pool range to the host.
Click it and the Active DHCP Client Table appears. It shows IP addresses
assigned to clients.
31
Page 32

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Field Description
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask.
Default Gateway Enter the default gateway of the IP address pool.
The Lease Time is the amount of time that a network user is allowed to
maintain a network connection to the device using the current dynamic IP
Max. Lease Time
Domain Name
DNS Servers You can configure the DNS server IP addresses for DNS Relay.
address. At the end of the Lease Time, the lease is either renewed or a new
IP is issued by the DHCP server. The amount of time is in units of seconds.
The default value is 1440 minutes (1 day).
Domain Name is the most recognized system for assigning addresses to
Internet web servers.
Click Show Client on the DHCP Mode page and the page shown in the following figure appears. You can
view the IP address assigned to each DHCP client.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
IP Address It displays the IP address assigned to the DHCP clie nt from the router.
It displays the MAC address of the DHCP client. Each Ethernet device has a
MAC Address
Expiry
Refresh Click it to refresh this page.
Close Click it to close this page.
unique MAC address. The MAC address is assigned at the factory a nd it consist s
of six pairs of hexadecimal character, for example, 00-30-4F-00-02-12.
It displays the lease time. The lease time determines the period that the host
retains the assigned IP addresses before the IP addresses change.
32
Page 33

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Click Set Vendor Class IP Range on the DHCP Mode page and the page as shown in the following figure
appears. On this page, you can configure the IP address range based on the device type.
In the DHCP Mode field, choose None and the page sho wn in the following figure appears.
33
Page 34

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
In the DHCP Mode field, choose DHCP Relay and the page shown in the following figure appears.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
If set to DHCP Relay, the router acts as a surrogate DHCP Server and
DHCP Mode
Relay Server Enter the DHCP server address provided by your ISP.
Apply Changes Click it to save the settings on this page.
Undo Click it to refresh this page.
relays the DHCP requests and responses between the remote server
and the client.
ADN‐4102
3.4.2.3 DHCP Static IP
Click DHCP Static IP in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. You can assign
the IP addresses on the LAN to the specific individual PCs based on their MAC address.
34
Page 35

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
IP Address
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of a host on the LAN.
Add
Delete Selected
Undo Click it to refresh this page.
Current ATM VC Table It shows the assigned IP address based on the MAC address.
Enter the specified IP address in the IP pool range, which is
assigned to the host.
After entering the IP address and MAC address, click it. A row will
be added in the DHCP Static IP Table.
Select a row in the DHCP Static IP Table; then click it and this row
is deleted.
3.4.2.4 LAN IPv6
On this page, you can configure the LAN IPv6. Choose Setup > LAN > LAN IPv6. The IPv6 LAN setting
page as shown in the following figure appears:
The following table describes the parameters:
LAN Global Address Setting
Field Description
Global Address Specify the LAN global IPv6 address; may be assigned by ISP.
RA Settings
Field Description
Enable Enable or disable the Router Advertisement feature.
35
Page 36

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Field Description
M Flag Enable or disable the “Managed address configuration” flag in RA packet.
O Flag Enable or disable the “Other configuration” flag in RA packet.
Max. Interval Maximum sending time interval.
Min. Interval Minimum sending time interval.
Specify the RA feature prefix mode
Prefix Mode
ULA Unique Local Address. Enable/Di sable the feature to access.
RA DNS Enable Enable/Disable the feature to access.
Auto: The RA prefix will use WAN dhcp-pd prefix
Manual: User will specify the prefix Address, Length, Preferred time and Valid
time.
DHCPv6 Settings
Field Description
ADN‐4102
DHCPv6 Mode Select the Mode to None or Manual Mode or Auto Mode.
IPv6 Address Suffix
Pool
IPv6 DNS Mode Select the Mode to Auto or Manual.
Enter the IPv6 address.
36
Page 37

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.5 WLAN
This page contains all the wireless basic settings. Most users will be able to configure the wireless portion
and get it working properly using the setting on this screen.
The following table describes the parameters:
Fields Description
Disable Wireless
LAN Interface
Band
Mode Select AP Mode.
SSID
Channel Width Select channel width to 20MHz, 40MHz or 20/40MHz.
Control Sideband Select upper or lower sideband.
Channel Number
Radio Power
(Percent)
Enable/Disable the wireless function for ADSL modem.
Select the appropriate band from the list provided to correspond with your network
setting.
The Service Set Identifier (SSID) or network name. It is case sensitive and must not
exceed 32 characters, which may be any keyboard character. The mobile wireless
stations will select the same SSID to be able to communicate with your ADSL m odem
(or AP).
Select the appropriate channel from the list provided to correspond with your netwo r k
settings. You will assign a different channel for each AP to avoid signal interference.
100%, 80%, 50%, 25%, 10%.
Associated Click it to see the clients currently associated with the ADSL modem.
37
Page 38

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Fields Description
Clients
3.5.1 Security
This screen allows you to set up the wireless security. Turn on WEP or WPA by using encryption keys that
could prevent any unauthorized access to your WLAN.
The following table describes the parameters:
Fields Description
SSID Type Select the SSID Type.
38
Page 39

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Fields Description
There are 4 types of security to be selected. To secure your WLAN, it’s
strongly recommended to enable this feature.
WEP: Make sure that all wireless devices on your network are using the
same encryption level and key.
WPA/WPA2 (TKIP): WPA/WPA2 uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
(TKIP) for data encryption. TKIP utilizes a stronger encryption method and
Encryption
Use 802.1x Authentication
WPA Authentication Mode
Pre-Shared Key Format
incorporates Message Integrity Code (MIC) to provide protection against
hackers.
WPA/WPA2 (AES): WPA/WPA2, also known as 802.11i, uses Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES) for data encryption. AES utilizes a symmetric
128-bit block data encryption.
WPA2 Mixed: The AP supports WPA (TKIP) and WPA2 (AES) for data
encryption. The actual selection of the encryption methods will depend on
the clients.
Check it to enable 802.1x authentication. This option is selected only when
the “Encryption” is chosen to either None or WEP. If the “Encryption” is
WEP, you need to further select the WEP key length to be either WEP 64
character or WEP 128 character.
There are 2 types of authentication mode for WPA.
WPA-RADIUS: WPA RADIUS uses an external RADIUS server to perform
user authentication. To use WPA RADIUS, enter the IP address of the
RADIUS server, the RADIUS port (default is 1812) and the shared secret
from the RADIUS server.
Pre-Shared Key: Pre-Shared Key authentication is based on a shared
secret that is known only by the parties involved. To use WPA Pre-Shared
Key, select key format and enter a password in the “Pre-Shared Key
Format” and “Pre-Shared Key” setting respectively.
Passphrase: Select this to enter the Pre-Shared Key secret as
user-friendly textual secret.
Hex (64 characters): Select this to enter the Pre-Shared Key secret as
hexadecimal secret.
ADN‐4102
Pre-Shared Key
Authentication RADIUS
Server
Specify the shared secret used by this Pre-Shared Key. If the “Pre-Shared
Key Format” is specified as PassPhrase, then it indicates a passphrase of
8 to 64 character long or 64-hexadecimal number.
If the WPA-RADIUS is selected in “WPA Authentication Mode”, the port
(default is 1812), IP address and password of external RADIUS server are
specified here.
39
Page 40

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
3.5.2 MBSSIDs
This screen allows you to do the wireless multiple MBSSIDs setup.
ADN‐4102
40
Page 41

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.5.3 Access Control
This page allows administrator to have access control by entering M AC address o f client stations. Wh en this
function is enabled, MAC address can be added to access control list and only those client s whose wirele ss
MAC address are in the access control list will be able to connect to your DSL device (or AP).
Field Description
The Selections are:
Disable: Disable the wireless ACL feature.
Allow Listed: When this option is selected, no wireless clients except those whose
Wireless Access
Control Mode
MAC Address Enter client MAC address.
Apply Changes Click Apply Changes to add new settings; then it restarts.
Add Click to add MAC address to the Current Access Control List.
Reset Clear the settings.
Delete Selected Select the rows to be deleted from Current Access Control List.
Delete All Flush the list.
MAC addresses are in the current access control list will be able to connect (to this
device).
Deny Listed: When this option is selected, all wireless clients except those whose
MAC addresses are in the current access control list will not be able to connect (to
this device).
41
Page 42

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
3.5.4 Advanced Settings
ADN‐4102
This page allows advanced users who have sufficient knowl edge of wirel ess LAN. The se settings will not be
changed unless you know exactly what will happen for the changes you made on your DSL device.
42
Page 43

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
3.5.5 WPS
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is a push-button or pin to simplify a secure network set-up.
ADN‐4102
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Disable WPS Enable/Disable the WPS function.
Self-Pin Number Click Regenerate Pin to reset automatically to obtain an 8-digit number.
Push Button
Configuration
Start Pin Enter the Pin number to connect from device to Wi-Fi dongle.
Click Start PBC button to connect from Wi-Fi dongle to device automatically.
3.6 Advanced
In the navigation bar, click Advanced. On the Advanced page that is displayed contains Route, NAT,
QoS, CWMP (TR-069), Port Mappings and Others.
3.6.1 Route
The Routing page enables you to define specific route for your Internet and network data. Most users do
not need to define routes. On a typical small home or office LAN, the existing routes that set up the default
gateways for your LAN hosts and for the DSL device p rovide the most appropriate p ath for all your Internet
traffic.
¾ On your LAN hosts, a default gateway directs all Internet traffic to the LAN port(s) on the DSL
device. Your LAN hosts know their default gateway either because you assigned it to them
43
Page 44

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
when you modified your TCP/IP properties, or because you configured them to receive the
information dynamically from a server whenever they access the Internet.
¾ On the DSL device itself, a default gateway is defined to direct all outbound Internet traffic to a route
at your ISP. The default gateway is assigned either automatically by your ISP whenever the device
negotiates an Internet access, or manually by user to set up through the configuration.
You may need to define routes if your home setup includes two or more networks or subnets, if you
connect to two or more ISP services, or if you connect to a remote corporate LAN.
3.6.1.1 Static Route
Click Static Route in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page is used
to configure the routing information. You can add or delete IP routes.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Enable
Destination
Subnet Mask
Next Hop
Metric
Click it to enable/disable the selected route or route to be added.
The network IP address of the subnet. The destination can be specified as the IP
address of a subnet or a specific host in the subnet. It can also be specified as all
zeros to indicate that this route should be used for all destinations for which no other
route is defined (this is the route that creates the default gateway).
The network mask of the destination subnet. The default gateway uses a mask of
0.0.0.0.
The IP address of the next hop through which traffic will flow towards the destination
subnet.
Defines the number of hops between network nodes that data packets travel. The
44
Page 45

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Field Description
default value is 0, which means that the subnet is directly one hop away on the local
LAN network.
ADN‐4102
Interface
Add Route
Update
Delete Selected
The WAN interface to which a static routing subnet is to be applied.
Add a user-defined destination route.
Update the selected destination route on the Static Route Table.
Delete a selected destination route on the Static Route Table.
Click this button to view the DSL device’s routing table. The IP Route Table displays,
as shown in Figure.
Show Routes
Click Show Routes and the page shown in the following figure appears. The table
shows a list of destination routes commonly accessed by your network.
45
Page 46

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.1.2 IPv6 Static Route
Click IPv6 Static Route in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page is
used to configure the routing information. You can add or delete IP routes.
The following table describes the parameters:
Fields Description
Destination Enter the IPv6 address of the destinatio n device.
Prefix Length Enter the prefix length of the IPV6 address.
Next Hop
Interface The interface for the specified route.
Add Route Click it to add the new static route to the IPv6 Static Route Table.
Delete the Selected
Enter the IPv6 address of the next hop in the IPv6 route to the destination
address.
Select a row in the IPv6 Static Route Table and click it to delete the row.
3.6.1.3 RIP
RIP is an Internet protocol you can set up to share routing table information with other routing d evices on your
LAN, at your ISP’s location, or on remote networks connected to your network via the ADS L li ne. Most sm a ll
home or office networks do not need to use RIP; they have only one router, such as the ADSL Router, and
one path to an ISP. In these cases, there is no need to share routes, because all Internet data from the
network is sent to the same ISP gateway. You may want to configure RIP if any of the following
circumstances apply to your network:
¾ Your home network setup includes an additional router or RIP-enabled PC (other than the ADSL
Router). The ADSL Router and the router will need to communicate via RIP to share their routing
tables.
¾ Your network connects via the ADSL line to a remote network, such as a corporate network. In order
46
Page 47

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
for your LAN to learn the routes used within your corporate network, they should both be configured
with RIP.
¾ Your ISP requests that you run RIP for communication with devices on their network.
ADN‐4102
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
RIP
Apply Click it to save the settings on this page.
Interface Choose the router interface that uses RIP.
Recv V e rsion
Send Version
Add
Delete
You can select OFF or ON. In this example, OFF is selected.
Choose the interface version that receives RIP messages. You can choose RIP1,
RIP2, or Both.
Choose RIP1 to indicate the router receives RIP v1 messages.
Choose RIP2 to indicate the router receives RIP v2 messages.
Choose Both to indicate the router receives RIP v1 and RIP v2 messages.
The working mode for sending RIP messages. You can choose RIP1 or RIP2.
Choose RIP1 to indicate the router broadcasts RIP1 messages only.
Choose RIP2 to indicate the router multicasts RIP2 messages only.
Click it to add the RIP interface to the Rip Config List.
Select a row in the Rip Config List and click it to delete the row.
3.6.2 NAT
Choose Advanced > NAT and the page shown in the following figure appears. The page displayed
contains DMZ, Virtual Server, ALG, NAT Exclude IP, Port Trigger, FTP ALG Port, and NAT IP
Mapping.
47
Page 48

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.2.1 DMZ
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) is used to provide Internet services without sacrificing unauthorized access to
its local private network. Typically, the DMZ host contains devices accessible to Internet traffic, such as
web (HTTP) servers, FTP servers, SMTP (e-mail) servers and DNS servers.
Click DMZ in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. The following describes
how to configure manual DMZ.
Select Enable DMZ to enable this function.
Enter an IP address of the DMZ host.
Click Apply Changes to save the settings on this page temporarily.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
WAN Interface Choose a WAN Interface.
DMZ Host IP Address Enter an IP address of the DMZ host.
Current DMZ Table A list of the previously configured DMZ information.
Apply Changes Click Apply Changes to add new settings.
Reset Clear the settings.
Delete the Selected Select the number of rows from the Current DMZ Table to be deleted.
48
Page 49

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.2.2 Virtual Server
Internet users would not be able to access a server on your LAN because of native NAT protection.The
“virtual server” feature solves these problems and allows internet users to connect to your servers.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
You can select the common service type, for example, AUTH, DNS or FTP.
You can also define a service name.
Service Type
Protocol
WAN Setting
WAN Interface Choose the WAN interface that will apply virtual server.
WAN Port Choose the access port on the WAN.
LAN Open Port Enter the port number of the specified service type.
LAN IP Address
If you select Usual Service Name, the corresponding parameter has the
default settings.
If you select User-defined Service Name, you need to enter the
corresponding parameters.
Choose the transport layer protocol that the service type uses. You can
choose TCP or UDP.
You can choose Interface or IP Address.
Enter the IP address of the virtual server. It is in the same network segment
with LAN IP address of the router.
3.6.2.3 ALG
An application layer gateway (ALG) is a feature on ScreenOS gateways that enables the gateway to parse
application layer payloads and take decisions on them. ALGs are typically employed to support applications
that use the application layer payload to communicate the dynamic Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or
49
Page 50

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) ports on which the applications open data connections. Such applications
include the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and various IP telephony protocols.
ALG consists of a security component that augments a firewall or NAT employed in a computer network. It
allows customized NAT traversal filters to be plugged into the gateway to support address and port
translation for certain application layer "control/data" protocols such as FTP, SIP, RTSP, file transfer in IM
applications, etc. In order for these protocols to work through NAT or a firewall, either the application has to
know about an address/port number combination that allows incoming packets, or the NAT has to monitor
the control traffic and open up port mappings (firewall pinhole) dynamically as required. Legitimate
application data can thus be passed through the security checks of the firewall or NAT that would have
otherwise restricted the traffic for not meeting its limited filter criteria.
50
Page 51

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.2.4 NAT excluding IP
NAT improves network security in effect by hiding the private network behind one global and visible IP
address. NAT address mapping can also be used to link two IP domains via a LAN-to-LAN connection.
Network Address Translation (NAT) is the method by which the Router shares the single IP address
assigned by your ISP with the other computers on your network. This function should only be used if your
ISP assigns you multiple IP addresses or you need NAT disabled for an advanced system configuration. If
you have a single IP address and you turn NAT off, the computers on your network will not be able to
access the Internet. Other problems may also occur. Turning off NAT will disable your firewall functions.
51
Page 52

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.2.5 Port Trigger
Port triggering is a configuration option on a NAT-enabled router that allows a host machine to dynamically
and automatically forward a specific port back to itself. Port triggering opens an incoming port when your
computer is using a specified outgoing port for specific traffic. Port triggering does not require that you
know the computer’s IP address in advance. The IP address is captured automatically. Port triggering
requires specific outbound traffic to open the inbound ports, and the triggered ports are closed after a
period of no activity.
Click the Usual Application Name drop-down menu to choose the application you want to setup for port
triggering. When you have chosen an application the default Trigger settings will populate the table below.
If the application you want to set up isn’t listed, click the User-defined Application Name radio button and
type in a name for the trigger in the Custom application field. Configure the Start Match Port, End Match
Port, Trigger Protocol, Start Relate Port, End Relate Port, Open Protocol and Nat type settings for the
port trigger you want to configure.
52
Page 53

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
When you have finished, click the Apply changes button.
3.6.2.6 FTP ALG Port
FTP uses two communication channels, one for control commands and one for the actual files being
transferred. When an FTP session is opened, the FTP client establishes a TCP connection (the control
channel) to (usually) port 21 on the FTP server. What happens after this point depends on the mode of
FTP being used.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
FTP ALG port Set an FTP ALG port.
Add Dest. Ports Add a port configuration.
Delete Selected Dest. Port Delete a selected port configuration from the list.
3.6.2.7 NAT IP Mapping
NAT is short for Network Address Translation. The Network Address Translation Settings window allows
you to share one WAN IP address for multiple computers on your LAN. Click NAT IP Mapping in the left
pane and the page shown in the following figure appears.
53
Page 54

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Entries in this table allow you to configure one IP pool for specified source IP address from LAN, so one
packet whose source IP is in range of the specified address will select one IP address from the pool for
NAT.
The following table describes the parameters:
Fields Description
Type There are four types: one-to-one, Many-to-One, Many-to-Many, Many-to-one.
Local Start & End IP Enter the local IP Address you plan to map to. Local Start IP is the starting local
IP address and Local End IP is the ending local IP address. If the rule is for all
local IPs, then the Start IP is 0.0.0.0 and the End IP is 255.255.255.255
Global Start & End IP Enter the Globe IP Address you want to do NAT. Global Start IP is the starting
global IP address and Global End IP is the ending global IP address. If you
have a dynamic IP, enter 0.0.0.0 as the global Start IP.
NAT IP Mapping Table This displays the information about the Mapping addresses.
54
Page 55

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.3 QoS
The DSL device provides a control mechanism that can provide different priority to different users or data
flows. The QoS is enforced by the QoS rules in the QoS table. A QoS rule contains two configuration blocks:
Traffic Classification and Action. The Traffic Classification enables you to classify packets on the basis of
various fields in the packet and perhaps the physical ingress port. The Action enables you to assign the
strictly priority level for and mark some fields in the packet that matches the Traffic Classification rule. You
can configure any or all field as needed in these two QoS blocks for a QoS rule.
Enable QoS and click Apply to enable IP QoS function.
Click add rule to add a new IP QoS rule.
The page shown in the following figure appears.
55
Page 56

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.4 CWMP (TR-069)
Choose Advanced > CWMP and the page shown in the following page appears. On this page, you can
configure the TR-069 CPE.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
ACS
Enable Enable/Disable the function to access.
56
Page 57

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Field Description
URL The URL of the auto-configuration server to connect to.
User Name The user name for logging in to the ACS.
Password The password for logging in to the ACS.
Periodic Inform Enable
Periodic Inform Interval Specify the amount of time between connections to ACS.
Connection Request
User Name The connection username provided by TR-069 service.
Password The connection password provided by TR-069 service.
Debug
Show Message
CPE sends GetRPC
Skip MReboot
Delay Specify whether to start the TR-069 program after a short delay.
Auto-Execution
Select Enable to periodically connect to the ACS to check whether
the configuration updates.
Select Enable to display ACS SOAP messages on the serial
console.
Select Enable, the router contacts the ACS to obtain configuration
updates.
Specify whether to send an MReboot event code in the inform
message.
Specify whether to automa tically st art the TR-069 af ter the router i s
powered on.
ADN‐4102
57
Page 58

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.5 Port Mapping
The ADSL device provides multiple interface groups. Up to five interface groups are su pporte d including o ne
default group. The LAN and WAN interfaces could be included. Traffic coming from one interface of a group
can only be flowed to the interfaces in the same interface group. Thus, the DSL device can isolate traffic
from group to group for some application. By default, all the interfaces (LAN and WAN) belon g to the default
group, and the other four groups are all empty. It is possible to assign any interface to any group but only
one group.
The following table describes the parameters:
Fields Description
Enabled/Disabled
Click radio button to enable/disable the interface group feature. If disabled, all
interfaces belong to the default group.
58
Page 59

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
To manipulate a mapping group:
1. Select a group from the table.
Interface groups
2. Select interfaces from the available/grouped interface list and add it to the
grouped/available interface list using the arrow buttons to manipulate the
required mapping of the ports.
3.6.6. Others
Choose Advance > Others and the page shown in the following figure appears. The page displayed
contains Bridge Setting, Client Limit, Tunnel and Others.
3.6.6.1 Bridge Setting
Choose Advance > Others > Bridge Setting and the page shown in the following figure appears. This
page is used to configure the bridge parameters. You can change the settings or view some information on
the bridge and its attached ports.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Aging Time
802.1d Spanning Tree
Show MACs Click it to show a list of the learned MAC addresses for the bridge.
If the host is idle for 300 seconds (default value), its entry is deleted from
the bridge table.
You can select Disable or Enable.
Select Enable to provide path redundancy while preventing undesirable
loops in your network.
59
Page 60

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Click Show MACs and the page shown in the following figure appears. This table shows a list of learned
MAC addresses for this bridge.
3.6.6.2 Client Limit
Choose Advance > Others > Client Limit and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page
is used to configure the capability of forcing how many devices can access the Internet.
Fields Description
Client Limit Capability
Enable/Disable the function to access
If enabled, maximum devices would be 32; default is 4.
60
Page 61

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.6.3 Tunnel
Choose Advanced > Others > Tunnel and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page is
used to configure the IPv6 with LAN to transfer to IPv4.
The following table describes the parameters:
V6inV4 Tunnel
Field Description
Enable Enable or Disable the V6inV4 Tunnel.
Interface Name Select the current WAN interface used as tunnel interface.
Mode 6to4 Tunnel or 6rd Tunnel.
DS-Lite Tunnel
Field Description
Enable Enable or disable the DS-Lite tunnel.
Interface Select the current WAN interface used as tunnel interface.
Mode Auto or manual.
61
Page 62

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.6.6.4 Others
Choose Advanced > Others > Others in the left p ane and the p age shown in the followin g figure appears.
You can enable half bridge so that the PPPoE or PPPoA connection will set to Continuous.
3.7 Service
In the navigation bar, click Service. On the Service page that is displayed contains IGMP, UPnP, SNMP
DNS and DDNS.
62
Page 63

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.7.1 IGMP
3.7.1.1 IGMP Proxy
Choose Service > IGMP and the page shown in the following figure appears. IGMP proxy enables the
system to issue IGMP host messages on behalf of hosts that the system discovered through standard
IGMP interfaces. The system acts as a proxy for its hosts after you enable it.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
IGMP Proxy
Multicast Allowed Enable/Disab le the function to access.
Robust Count Robust factor of the IGMP Proxy Counter.
Last Member Query
Count
Query Interval
Query Response
Interval
Group Leave Delay
The Internet Group Management Protocol. Enable/Disable the function to acce ss.
The last-member query interval is the maximum amount of time between
group-specific query messages, including those sent in response to leave-group
messages. You can configure this interval to change the amount of time it takes a
routing device to detect the loss of the last member of a group.
The amount of time between IGMP General Query messages sent by the router
(if the router is a querier on this subnet).
The maximum amount of time in seconds that the IGMP router waits to receive a
response to a General Query message. The query response interval is the
Maximum Response Time field in the IGMP v2 Host Membership Query message
header. The default query response interval is 10 seconds and must be less than
the query interval.
The amount of time in seconds that the IGMP router waits to receive a response
to a Group-Specific Query message. The last member query interval is also the
amount of time in seconds between successive Group-Specific Query messages.
63
Page 64

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.7.1.2 MLD
MLD means Multicast Listener Discovery; its component of the IPv6. MLD is u s ed by IPv6 routers for discovering multicast listeners on a directly-attached link, much like IGMP being used in IPv4.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
MLD Proxy
MLD Snooping
Robust Counter Robust factor of the MLD Counter.
Query Interval
Query Response Interval
Response Interval of Last
Group Member
MLD Proxy can be used to support IPv6 multicast data. Enable/Disable the
function to access.
Snooping is an IPv6 multicast constraining mechanism that runs on Layer 2
devices to manage and control IPv6 multicast groups. By analyzing received
MLD messages, a Layer 2 device running MLD Snooping establishes
mappings between ports and multicast MAC addresses and forwards IPv6
multicast data based on these mappings.
Multicast Listener Discovery Snooping (MLD). Enable/Disable the function to
access.
The amount of time between IGMP General Query messages sent by the
router (if the router is a querier on this subnet).
The maximum amount of time in seconds that the IGMP router waits to
receive a response to a General Query message. The query response
interval is the Maximum Response Time field in the IGMP v2 Host
Membership Query message header. The default query response interval is
10 seconds and must be less than the query interval.
The amount of time in seconds that the IGMP router waits to receive a
response to a Group-Specific Query message. The last member query
interval is also the amount of time in seconds between successive
Group-Specific Query messages.
64
Page 65

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.7.2 UPNP
Choose Service > UPnP and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page is used to
configure UPnP. The system acts as a daemon after you enable it.
3.7.3 SNMP
Choose Service > SNMP, click Enable SNMP and the page shown in the following figure appears. You
can configure the SNMP parameters.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Enable SNMP
Select it to enable SNMP function. You need to enable SNMP, and
then you can configure the parameters of this page.
65
Page 66

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Field Description
Trap IP Address
Community Name
(Read-only)
Community Name
(Read-Write)
Enter the trap IP address. The trap information is sent to the
corresponding host.
The network administrators must use this password to read the
information of this router.
The network administrators must use this password to configure the
information of the router.
3.7.4 DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) is an Internet service that translates the domain name into IP address.
Because the domain name is alphabetic, it is easier to remember. The Internet, however, is based on IP
addresses. Every time you use a domain name, DNS translates the name into the corresponding IP
address. For example, the domain name www.example.com might be translated to 198.105.232.4. The
DNS has its own network. If one DNS server does not know how to translate a particular domain name, it
asks another one, and so on, until the correct IP address is returned.
Choose Service > DNS. The DNS page that is displayed contains DNS and IPv6 DNS.
3.7.4.1 DNS
Click DNS in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears.
The following table describes the parameters:
Fields Description
Select it, and the router accepts the first received DNS assignment
Attain DNS Automatically
Set DNS Manually
from one of the PPPoA, PPPoE or MER enabled PVC(s) during the
connection establishment.
Select it to enter the IP addresses of the DNS 1, DNS 2, DNS 3,
servers manually.
66
Page 67

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
3.7.4.2 IPv6 DNS
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Select it and the router accepts the first received DNS assignment from
Attain DNS Automatically
Set DNS Manually
one of the PPPoA, PPPoE or MER enabled PVC(s) during the
connection establishment.
Select it and enter the IP addresses of the primary and secondary DNS
server.
ADN‐4102
67
Page 68

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.7.5 DDNS
Click DDNS in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page is used to
configure the dynamic DNS address from DynDNS.org, TZO, PHDNS or Planet. You can add or remove
to configure dynamic DNS. The Planet DDNS is free for customers.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
DDNS provider
Host Name The DDNS identifier.
Interface The WAN interface of the router.
Enable Enable or disable DDNS function.
Username The name provided by DDNS provider.
Password The password provided by DDNS provider.
Email The email provided by DDNS provider.
Key The key provided by DDNS provider.
Choose the DDNS provider name. You can choose DynDNS.org, TZO or
Planet.
68
Page 69

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.7.6 FTP Server
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to transfer computer files from one
host to another host over a TCP-based network. It’s built on a client-server architecture and uses separate
control and data connections between the client and the server. FTP users may authenticate themselves
using a clear-text sign-in protocol, normally in the form of a username and password, but can connect
anonymously if the server is configured to allow it.
3.8 Firewall
Choose Service > Firewall and the Firewall page that is displayed contains MAC Filter, IP/Port Filter,
URL Filter, ACL, DoS and Parent Control.
69
Page 70

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.8.1 MAC Filter
Click MAC Filter in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. Entries in the table
are used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network to Internet through the gateway.
These filters are helpful in securing or rest ricting your local network.
Field Description
Outgoing Default Policy Specify the default action on the LAN to WAN bridging/forwarding path.
Incoming Default Policy Specify the default action on the WAN to LAN bridging/forwarding path.
Direction Traffic bridging/forwarding direction.
Action Deny or allow traffic when matching this rule.
Src MAC Address The source MAC address must be xxxxxxxxxxxx format.
Dst MAC Address The destination MAC address must be xxxxxxxxxxxx format.
70
Page 71

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.8.2 IP/Port Filter
3.8.2.1 IP/Port Filter
Click IP/Port Filter in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. Entries in the t able
are used to restrict certain types of data packets through the gateway. These filters are helpful in securing
or restricting your local network.
Field Description
Outgoing Default Policy Specify the default action on the LAN to WAN forwarding path.
Incoming Default Policy Specify the default action on the WAN to LAN forwarding path.
71
Page 72

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
3.8.2.2 IPv6/Port Filter
ADN‐4102
Fields on the second setting block:
Field Description
Rule Action Permit or deny traffic when matching this rule.
Direction Traffic forwarding direction.
Protocol There are 4 options available: IP, TCP, UDP and ICMP.
Src IP Address The source IP address assigned to the traffic on which filtering is applied.
Src Subnet Mask Subnet-mask of the source IP.
Src Port Starting and ending source port numbers.
Dst IP Address The destination IP address assigned to the traffic on which filtering is applied.
Dst Subnet Mask Subnet-mask of the destination IP.
Dst Port Starting and ending destination port numbers.
Enable Enable/Disable the function to access.
72
Page 73

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.8.3 URL Filter
Click URL Filter in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page is used to
block a fully qualified domain name, such as tw.yahoo.com and filtered keyword (yahoo). You can add or
delete FQDN and filtered keyword.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
You can choose Disable or Enable.
Select Disable to disable URL/KEYWORD blocking function and
URL Blocking Capability
Keyword Enter the keyword to block.
Add Keyword
Delete Selected Keyword
URL Blocking Table A list of the URLs to whi ch access is blocked.
keyword filtering function.
Select Enable to block access to the URLs and keywords specified in
the URL Blocking Table.
Click it to add a URL/keyword to the URL Blocking Table.
Select a row in the URL Blocking Table and click it to delete the row.
3.8.4 ACL
3.8.4.1 ACL
Choose Service > ACL and the page shown in the following figure appears. On this page, you can permit
the data packets from LAN or WAN to access the router. You can configure the IP address for Access
Control List (ACL). If ACL is enabled, only the effective IP address in the ACL can acce ss the router.
If you select Enable in ACL capability, ensure that your ho st IP address is in ACL list
before it takes effect.
73
Page 74

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
• When you click White List, only the devices whose IP addresses
LAN ACL Mode
WAN ACL Mode
Direction Select
LAN ACL Switch Select it to enable or disable ACL function.
IP Address
Services Allowed
are listed in the Current ACL Table can access the router.
• When you click Black List, the devices whose IP addresses are
listed in the Current ACL Table are denied to access the router.
• When you click White List, only the devices whose IP addresses
are listed in the Current ACL Table can access the router.
• When you click Black List, the devices whose IP addresses are
listed in the Current ACL Table are denied to access the router.
Select the router interface. You can select LAN or WAN. In this
example, LAN is selected.
Enter the IP address of the specified interface. Only the IP address
that is in the same network segment with the IP address of the
specified interface can access the router.
You can choose the following services from LAN: Web, Telnet , SSH,
74
Page 75

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Field Description
FTP, TFTP, SNMP, or PING. You can also choose all the services.
Add
After setting the parameters, click it to add an entry to the Current
ACL Table.
3.8.4.2 IPv6 ACL
ADN‐4102
75
Page 76

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
If WAN is sel ected in the field of Direction Select, the page is shown as the following figure.
ADN‐4102
76
Page 77

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.8.5 DoS
Denial-of-Service Att ack (DoS att ack) is a type of att ack on a net work that is de signed to brin g the network
to its knees by flooding it with useless traffic.
The following table describes the parameters:
Fields Description
Enable DoS Prevention Enable denial -of-service feature to access.
Enable Source IP Blocking Enable the function to block IP Source and set the time in seconds.
77
Page 78

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.8.6 Parental Control
Choose Advance > Parental Control and the page shown in the following figure appears. This page is
used to control children's online time. The PC with specified MAC or IP address can only surf the internet
within the specified period of time
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Select it to enable Parental Control function. You need to enable Parental
Parental Control
Date Select one or more days you want to control
Time The specified period of time you want to control
Specify PC Select IP or MAC
IP Address The IP Address of the PC you want to control
MAC Address The MAC Address of the PC you want to control
Add Rule Add the Parental Control rule
Reset Reset the page
Current Parental
Control Table
Delete All Delete all Parental Control rules
Control to configure the parameters on this page. Parental Control is used to
control children's online time. If enabled, the PC with specified MAC or IP
address can only surf the internet within the specified period of time.
Show Parental Control rules
3.9 Maintenance
In the navigation bar, click Maintenance. The Maintenance page displayed contains Update, Password,
78
Page 79

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
Reboot, Time Log and Diagnostics.
3.9.1 Update
Choose Maintenance > Update. The Update page displayed contains Upgrade Firmware and
Backup/Restore.
Do not turn off the router or press the Reset button while the procedure is in progress.
3.9.1.1 Firmware Update
Click Firmware Update in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. On this page,
you can upgrade the firmware of the router.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Select File
Upload
Reset Click it to start selecting the firmware file.
Click Browse to select the firmware file.
After selecting the firmware file, click Upload to start upgrading the firmware file.
79
Page 80

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.1.2 Backup/Restore
Click Backup/Restore in the left pane and the page shown in the following figure appears. You can back
up the current settings to a file and restore the settings from the file that was saved previously.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Save Settings to File
Load Settings from File
Upload
Click it and select the path. Then you can save the configuration file of
the router.
Click Browse to select the configuration file.
After selecting the configuration file of the router, click Upload to start
uploading the configuration file of the router.
80
Page 81

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.2 Password
Choose Maintenance > Password and the page shown in the following figure appears. By default, the
user name and password of the administrator are admin and admin respectively. The user name and
password of the common user are user and user respectively.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
User Name
Privilege Choose the privilege for the account.
Old Password Enter the old password
New Password Enter your new password to which you want to change.
Confirmed Password For confirmation, enter the new password again.
Choose the user name for accessing the router. You can choose admin
or user.
81
Page 82

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.3 Reboot
Choose Maintenance > Reboot and the page shown in the following figure appears. Y ou can set the router reset to the default settings or set the router to commit the current settings.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Reboot
Restore to Default Setting
Do not turn off your modem or press the reset button while this procedure is in p rog ress.
It takes around 30 seconds to reboot the device and then again login
User name and Password.
It helps to change to default settings. It takes around 30 seconds to
restart the device and then again login User name and Password.
82
Page 83

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.4. Time
Choose Maintenance > Time and the page shown in the following figure appears. You can configure the
system time manually or get the system time from the time server.
The following table describes the parameters:
Fields Description
System Time Configure the system time manually.
Day Light Daylight Saving Time.
State
Server Configure the primary NTP server manually.
Server2 Configure the secondary NTP server manually.
Interval NTP updating time interval.
Time Zone Choose the time zone of your country from the drop-down list.
GMT Time Greenwich Mean time.
Enable the option to update the system clock automatically.
Disable the option to update the system clock manually.
83
Page 84

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.5 Log
Choose Maintenance > Log and the page shown in the following figure appears. On this page, you can
enable or disable system log function and view the system log.
The following table describes the parameters:
Fields Description
Error Enable/Disable the functi on to display the Error.
Notice Enable/Disable the function to notify the Error.
3.9.6 Diagnostic
In the navigation bar , click Diagnostic. The Diagnostic page displayed contains Ping, Ping6, Traceroute,
Traceroute6, OAM Loopback, ADSL Statistics and Diag-Test.
84
Page 85

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
3.9.6.1 Ping
Choose Diagnostic > Ping and the page shown in the following figure appears.
ADN‐4102
The following table describes the parameter:
Field Description
Host Address Enter IP address you want to ping.
Interface Choose a WAN interface.
85
Page 86

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
3.9.6.2 Ping6
Choose Diagnostic > Ping6 and the page shown in the following figure appears.
ADN‐4102
Field Description
Host Address Enter IPv6 address you want to ping.
Interface Choose a WAN interface.
86
Page 87

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.6.3 Traceroute
Choose Diagnostic >Traceroute and the following page appears. By Traceroute Diagnostic, you can
track the route path through the information which is from your computer to the Internet other side host.
The following table describes the parameters:
Field Description
Host Enter the destination host address for diagnosis.
NumberOfTries Number of repetitions.
Timeout Put in the timeout value.
Datasize Packet size.
DSCP Differentiated Services Code Point, You should set a value between 0-63.
MaxHopCount Maximum number of routes.
Interface Select the interface.
87
Page 88

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.6.4 Traceroute6
Choose Diagnostic >Tra ceroute6 and the following page appears. By Traceroute Diagnostic, you can track the route path through the information which is from your computer to the Internet other sid e host.
Fields Description
Host The address of a destination host to be diagnosed.
Number of Tries Repeat times.
Timeout Timeout duration.
Data size Data packet size.
Max. Hop Count Maximum number of routes.
Interface Select the interface.
88
Page 89

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.6.5 OAM Loopback
Choose Diagnostic > OAM Loopback and the page shown in the followin g figure appears. On this page,
you can use VCC loopback function to check the connectivity of the VCC. The ATM loopback test is useful
for troubleshooting problems with the DSLAM and A TM network.
Click Go! to start testing.
Fields Description
Flow Type
VPI Virtual Path Identifier
VCI Virtual Circuit Identifier.
There are 4 flow types. The selection can be F5 Segment, F5 End-to-End,
F4 Segment and F4 End-to-End
89
Page 90

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.6.6 ADSL Diagnostic
Choose Diagnostic > ADSL Diagnostic and the page shown in the following figure appears. It is used for
ADSL tone diagnostics.
Click Start to start ADSL tone diagnostics.
90
Page 91

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
ADN‐4102
3.9.6.7 Diag-Test
Choose Diagnostics > Diag-Test and the page shown in the following figure appears. On this page, you
can test the DSL connection. You can also view the LAN status connection and ADSL connection.
Click Run Diagnostic Test to start testing.
91
Page 92

802.11nWirelessADSL2/2+Router
Chapter 4. Q&A
Question Answer
Why are all the indicators
off?
Why is the LAN indicator
not on?
Why is the Link indicator
not on?
Why does the Internet
access fail when the Link
indicator is on?
Why does the web
configuration page of the
device fail to be
accessed?
How to restore the
default configuration after
incorrect configuration?
Check the connection between the power adapter and the power
Check whether the power switch is turned on.
Check the following:
The connection between the device and the PC, the hub, or the
The running status of the computer, hub, or switch
Check the connection between the Line interface of the device and the
socket.
Ensure that the following information is entered correctly.
VPI and VCI
User name and password
Choose Start > Run from the desktop. Enter Ping 192.168.1.1 (the
default IP address of the device) in the DOS window.
If the web configuration page still cannot be accessed, check the
following configurations.
The connection between the device and the computer
The TCP/IP properties of the network card of the computer
Keep the device powered on and press the Reset button for 5
seconds. The device automatically reboots and is restored to the
factory default configuration.
The default configurations of the device are as follows:
IP address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0.
For an administrator user, use admin for both user name and
ADN‐4102
socket.
switch
password.
92
 Loading...
Loading...