Page 1

802.11n Wireless ADSL 2/2+ Router
ADN-4000
User's Manual
1
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright© 2009 by PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this
publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or
translated into any language or computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of PLANET.
PLANET makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or implied, with respect
to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness
for any particular purpose. Any software described in this manual is sold or licensed "as is".
Should the programs prove defective following their purchase, the buyer (and not this
company, its distributor, or its dealer) assumes the entire cost of all necessary servicing,
repair, and any incidental or consequential damages resulting from any defect in the
software. Further, this company reserves the right to revise this publication and to make
changes from time to time in the contents hereof without obligation to notify any person of
such revision or changes.
All brand and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks and/or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
3. Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio technician for help.
FCC Caution
To assure continued compliance (example-use only shielded interface cables when
connecting to computer or peripheral devices). Any changes or modifications not expressly
approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate
the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the Following
two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this Device must
accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
2
Page 3
Federal Communication Commission (FCC) Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. In order to avoid the possibility of exceeding the FCC radio frequency
exposure limits, human proximity to the antenna shall not be less than 20 cm (8 inches)
during normal operation.
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of DIRECTIVE 1999/5/EC OF THE
EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL OF 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and
telecommunication terminal Equipment and the mutual recognition of their conformity
(R&TTE)
The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC (Telecommunications
Terminal Equipment and Satellite Earth Station Equipment) As of April 8, 2000.
WEEE Regulation
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of
the presence of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end
users of electrical and electronic equipment should understand the meaning of the
crossed-out wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of WEEE as unsorted municipal
waste and have to collect such WEEE separately.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it.
However, special attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity
when working with electrical equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer
manufacture must therefore be allowed at all times to ensure the safe use of the equipment.
Revision
User’s Manual for 802.11n Wireless ADSL 2/2+ Router
Model: ADN-4000v2
Rev: 1.0 (Aug. 2009)
Part No. EM-ADN4000v2_v1
3
Page 4

Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION ...........................................................................................................................7
1.1 Feature ....................................................................................................................8
1.2 Package Contents..................................................................................................10
1.3 Physical Details......................................................................................................10
2. INSTALLATION...........................................................................................................................13
2.1 Choosing the Best Location for Wireless Operation...............................................13
2.2 Connecting the ADSL Router.................................................................................13
2.3 Configuring the Network Properties .......................................................................14
3. WEB CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT ............................................................................... 18
3.1 Quick Setup ...........................................................................................................19
3.1.1 WAN Interface Setup ..................................................................................................19
3.1.1.1 Setup VPI/VCI .................................................................................................19
3.1.1.2 Select Protocol and Connection ......................................................................20
3.1.1.3 Internet Connection Type - PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) ............................21
3.1.1.4 Internet Connection Type - PPP over ATM (PPPoA) .................................. 22
3.1.1.5 Internet Connection Type - Dynamic IP........................................................23
3.1.1.6 Internet Connection Type - Static IP .............................................................24
3.1.1.7 Internet Connection Type - IP over ATM (IPoA)......................................... 25
3.1.1.8 Internet Connection Type - Bridge.................................................................26
3.1.2 LAN Interface Setup....................................................................................................27
3.1.3 WAN Setup Summary ................................................................................................. 28
3.1.4 Quick Setup Completed...............................................................................................29
3.2 DSL Router Device information..............................................................................30
3.2.1 Summary of Device information .................................................................................30
3.2.2 WAN Interface information.........................................................................................31
3.2.3 Statistics.......................................................................................................................32
3.2.3.1 Statistics of LAN...............................................................................................32
3.2.3.2 Statistics of WAN Service................................................................................ 33
3.2.3.3 Statistics of xTM ..............................................................................................34
3.2.3.4 Statistics of xDSL .............................................................................................35
3.2.4 Route table information ............................................................................................... 37
3.2.5 ARP table information.................................................................................................38
3.2.6 DHCP IP Leases information ......................................................................................38
4
Page 5

3.3 Advanced Setup.....................................................................................................39
3.3.1 Layer2 INTERFACE ................................................................................................... 39
3.3.1.1 ATM Interface....................................................................................................39
3.3.1.2 ETH Interface..................................................................................................... 41
3.3.2 WAN CONFIGURATION..........................................................................................41
3.3.2.1 Add PPPoE WAN configuration ....................................................................42
3.3.1.2 Add MER (IPoE) Configuration ....................................................................45
3.3.1.3 Add PPPoA Configuration..............................................................................48
3.3.1.4 Add IPoA Configuration .................................................................................51
3.3.1.5 Add Bridge Configuration ..............................................................................54
3.3.3 LAN configuration ......................................................................................................56
3.3.4 NAT-- Network Address Translation .......................................................................... 57
3.3.4.1 DMZ Host .........................................................................................................59
3.3.4.2 Port Triggering.................................................................................................61
3.3.4.3 NAT -- Virtual Servers Setup .........................................................................62
3.3.5 Security........................................................................................................................65
3.3.5.1 Outgoing IP Filtering Setup............................................................................66
3.3.5.2 Incoming IP Filtering Setup............................................................................ 69
3.3.5.3 MAC Filtering Setup .......................................................................................72
3.3.6 Quality of Service........................................................................................................74
3.3.6.1 Enable QoS .......................................................................................................74
3.3.6.2 QoS--Queue Config..........................................................................................76
3.3.6.3 QoS -- QoS Classification ................................................................................78
3.3.7 Routing ........................................................................................................................80
3.3.7.1 Routing – Default Gateway ............................................................................. 80
3.3.7.2 Static Routes ..................................................................................................... 81
3.3.7.3 RIP..................................................................................................................... 82
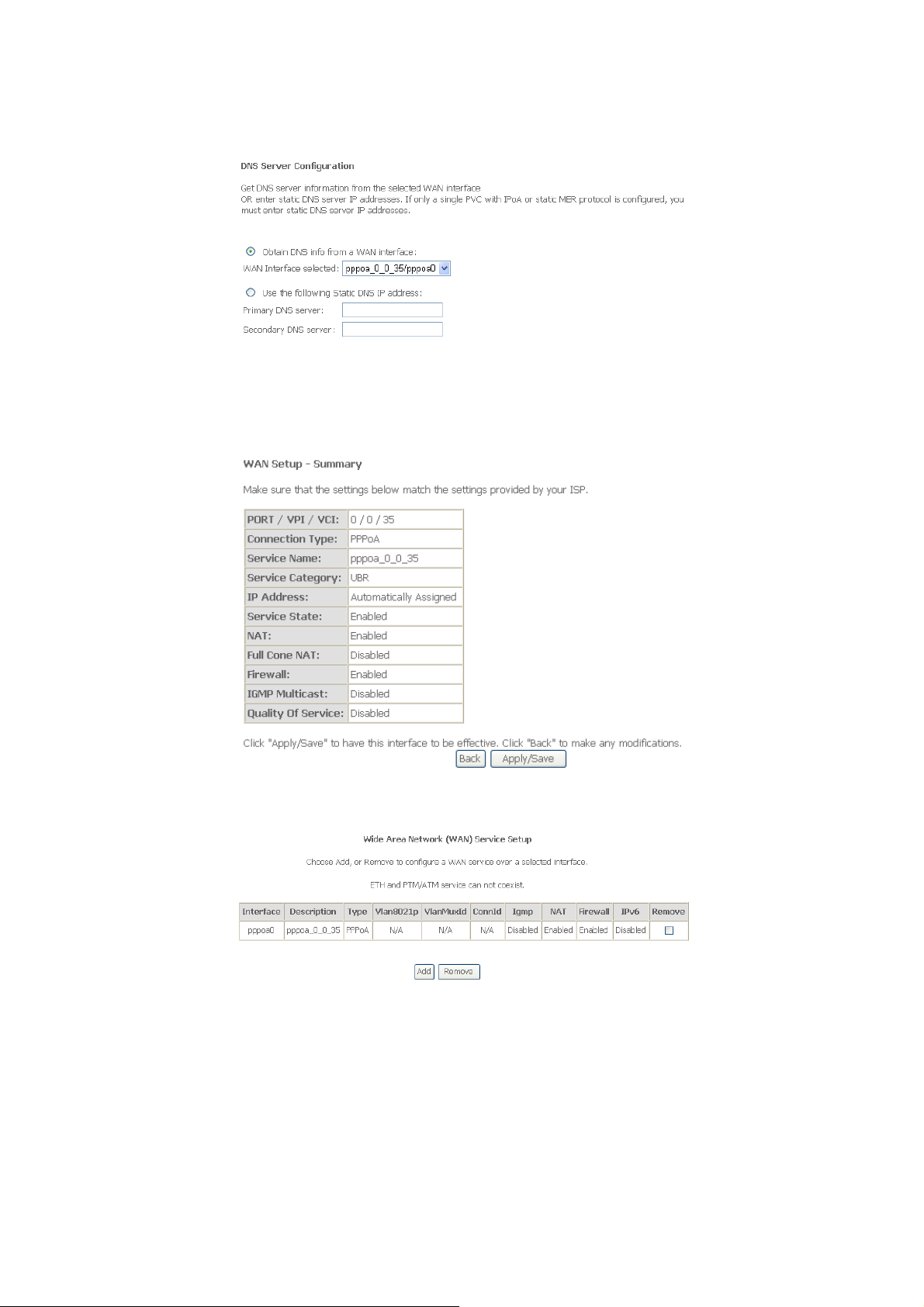
3.3.8 DNS .............................................................................................................................84
3.3.8.1 DNS Server .......................................................................................................84
3.3.8.2 Dynamic DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DDNS)............................................ 86
3.3.9 DSL.............................................................................................................................. 88
3.3.10 Interface Grouping..................................................................................................... 89
3.3.11 Certificate ..................................................................................................................90
3.3.11.1 Create New Local Certificate........................................................................ 90
5
Page 6

3.3.11.2 Import Existing Local Certificate.................................................................92
3.3.11.3 Trusted CA Certificates.................................................................................93
3.4 Wireless .................................................................................................................94
3.4.1 Wireless – Basic ..........................................................................................................94
3.4.2 Wireless – Security......................................................................................................95
3.4.3 Wireless – Advanced ................................................................................................... 96
3.5 Diagnostics ............................................................................................................98
3.6 Management..........................................................................................................99
3.6.1 Settings ........................................................................................................................99
3.6.1.1 Settings Backup................................................................................................99
3.6.1.2 Settings Update................................................................................................. 99
3.6.1.3 Settings Restore Default ..................................................................................99
3.6.2 System Log ................................................................................................................ 100
3.6.3 SNMP Client..............................................................................................................103
3.6.3.1 Configure ........................................................................................................105
3.6.4 TR-69 Client Management ........................................................................................106
3.6.5 Internet Time .............................................................................................................107
3.6.6 Access Control........................................................................................................... 108
3.6.6.1 Access Control – Services..............................................................................108
3.6.6.2 Access Control -- IP Addresses.....................................................................108
3.6.6.3 Access Control – Passwords ..........................................................................109
3.6.7 Update Software ........................................................................................................110
3.6.8 Save/Reboot...............................................................................................................110
APPENDIX A: GLOSSARY...........................................................................................................111
6
Page 7

1. Introduction
The PLANET 802.11n Wireless ADSL 2/2+ Router with 2T2R MIMO antenna technology,
ADN-4000, provides office and residential users the ideal solution for sharing a high-speed
ADSL 2/2+ broadband Internet connection and four-10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet backbone. It
can support downstream transmission rates of up to 24Mbps and upstream transmission
rates of up to 3.5Mbps. The product supports PPPoA (RFC 2364 - PPP over ATM
Adaptation Layer 5), RFC 2684 encapsulation over ATM (bridged or routed), PPP over
Ethernet (RFC 2516), and IPoA (RFC1483) to establish a connection with ISP.
With built-in IEEE 802.11b/g/n Draft 2.0 wireless network capability, all computers and
wireless-enabled network devices can connect to the ADN-4000 without additional cabling.
New 802.11n Draft 2.0 wireless capability also gives you the highest speed of wireless
experience ever. With a compatible wireless card installed in your PC, you can transfer file
up to 300Mbps (transfer data rate). The radio coverage is also doubled, so you don’t need to
worry if the size of your office or house is big.
To secure the wireless communication, the ADN-4000 supports most up-to-date encryption,
WEP, and WPA-PSK/ WPA2-PSK. In order to simplify the security settings, ADN-4000
supports WPS configuration with PBC/PIN type. Your whole wireless network can be
secured.
Via the user-friendly management interface, ADN-4000 can be managed by workstations
running standard web browsers. Furthermore, ADN-4000 provides DHCP server, NAT,
Virtual Server, DMZ, Access Control, IP Filter, PPTP/IPSec/L2TP pass-through, DDNS, and
UPnP capability.
The ADN-4000 also serves as an Internet firewall, protecting your network from being
accessed by outside users. It provides the natural firewall function (Network Address
Translation, NAT). All incoming and outgoing IPs are monitored and filtered. Moreover, it
can be configured to block internal users from accessing to the Internet.
7
Page 8

1.1 Feature
Internet Access Features
Shared Internet Access All users on the LAN can access the Internet through the
ADN-4000 using only a single external IP Address. The local (invalid) IP Addresses are
hidden from external sources. This process is called NAT (Network Address Translation).
Built-in ADSL 2/2+ Modem The ADN-4000 provides ADSL 2/2+ modem, and supports
all common ADSL connections.
PPPoE, PPPoA, Direct Connection Support Various WAN connections are supported
by ADN-4000.
Fixed or Dynamic IP Address On the Internet (WAN port) connection, the ADN-4000
supports both Dynamic IP Address (IP Address is allocated on connection) and Fixed IP
Address.
Advanced Internet Functions
Virtual Servers This feature allows Internet users to access Internet servers on your
LAN. The required setup is quick and easy.
DMZ Support The ADN-4000 can translate public IP addresses to private IP address to
allow unrestricted 2-way communication with Servers or individual users on the Internet.
This provides the most flexibility to run programs, which could be incompatible in NAT
environment.
Firewall Supports simple firewall with NAT technology and provides option for access
control from Internet, like Telnet, FTP, TFTP, HTTP, SNMP, and ICMP services. It also
supports IP/MAC /Application/URL filtering.
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) UPnP allows automatic discovery and configuration of
the Broadband Router. UPnP is supported by Windows ME, XP, or later.
Dynamic DNS Support When used with the Virtual Servers feature, the ADN-4000
allows users to connect to Servers on your LAN using a Domain Name, even if you have
a dynamic IP address which changes every time you connect.
VPN Pass through Support PCs with VPN (Virtual Private Networking) software using
PPTP, L2TP, and IPSec are transparently supported - no configuration is required.
RIP Routing It supports RIPv1/2 routing protocol for routing capability.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) It is an easy way to remotely manage
the router via SNMP.
8
Page 9

LAN Features
4-Port Switch The ADN-4000 incorporates a 4-Port 10/100Base-TX switching hub,
making it easy to create or extend your LAN.
DHCP Server Support Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol provides a dynamic IP
address to PCs and other devices upon request. The ADN-4000 can act as a DHCP
Server for devices on your local LAN and WLAN.
Wireless Features
Standards Compliant The ADN-4000 complies with IEEE 802.11n (Draft 2.0) wireless
technology capable of up to 300Mbps data rate.
Two Dipped Antennas with MIMO Technology The ADN-4000 provides farther
coverage, less dead spaces and higher throughput with 2T2R MIMO technology.
Support IEEE 802.11b, g and 802.11n Draft 2.0 Wireless Station The 802.11n
standard provides for backward compatibility with the 802.11b and 802.11g standard, so
802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n Draft 2.0 can be used simultaneously.
WEP Support WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is included. Key sizes of 64 Bit and 128
Bit are supported.
WPS Push Button Control The ADN-4000 supports WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) to
easy connect wireless network without configuring the security.
WPA-PSK Support WPA-PSK_TKIP and WAP-PSK_AES encryption are supported.
Wireless MAC Access Control The Wireless Access Control feature can check the
MAC address (hardware address) of Wireless stations to ensure that only trusted
Wireless Stations can access your LAN.
9
Page 10
1.2 Package Contents
The following items should be included:
z
ADN-4000 Unit x 1
z
Quick Installation Guide x 1
z
User’s Manual CD x 1
z
Power Adapter x 1
z
RJ-45 Cable x 1
z
RJ-11 Cable x 2
z
ADSL Splitter x 1
If any of the above items are damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
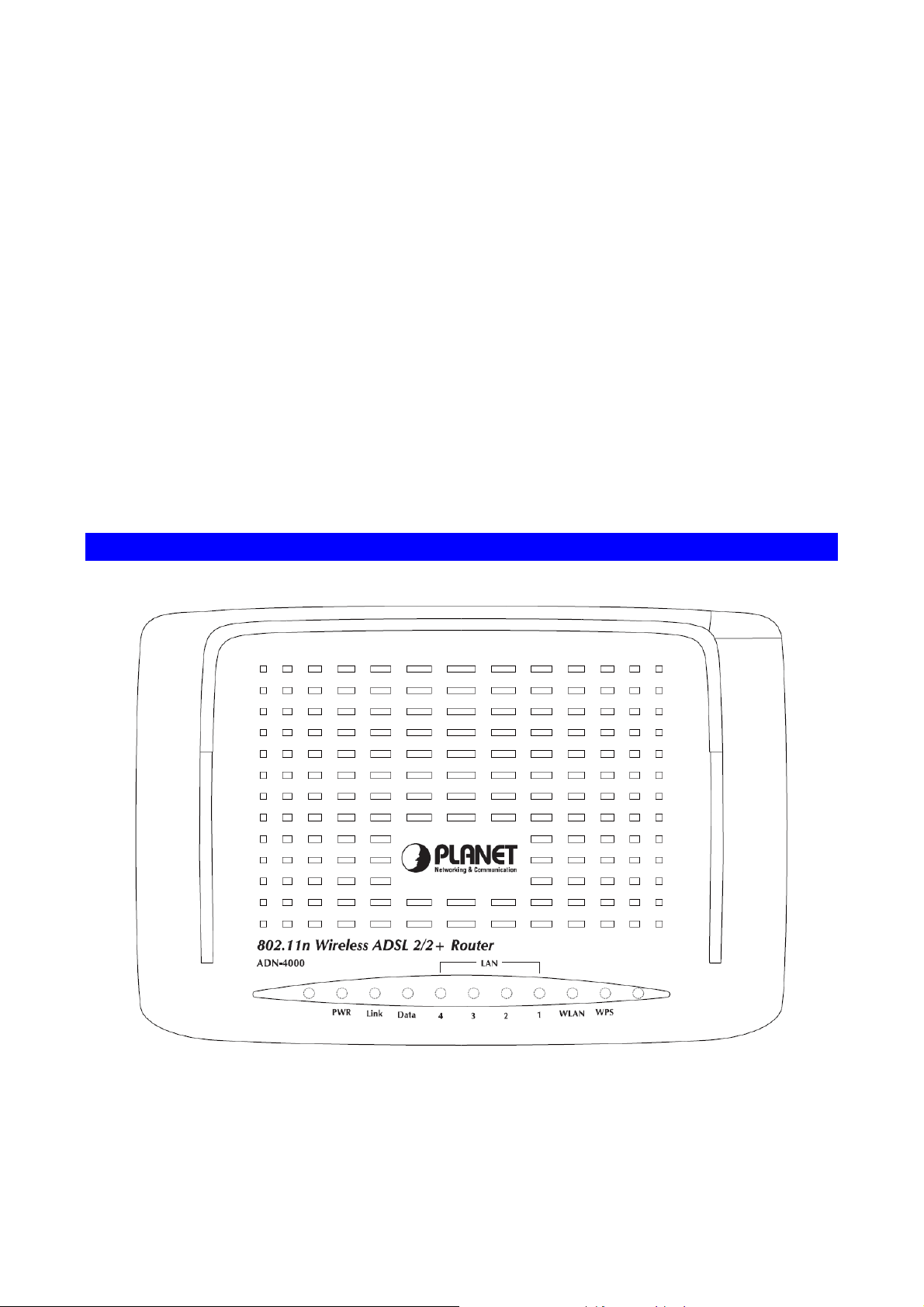
1.3 Physical Details
Front Panel
10
Page 11
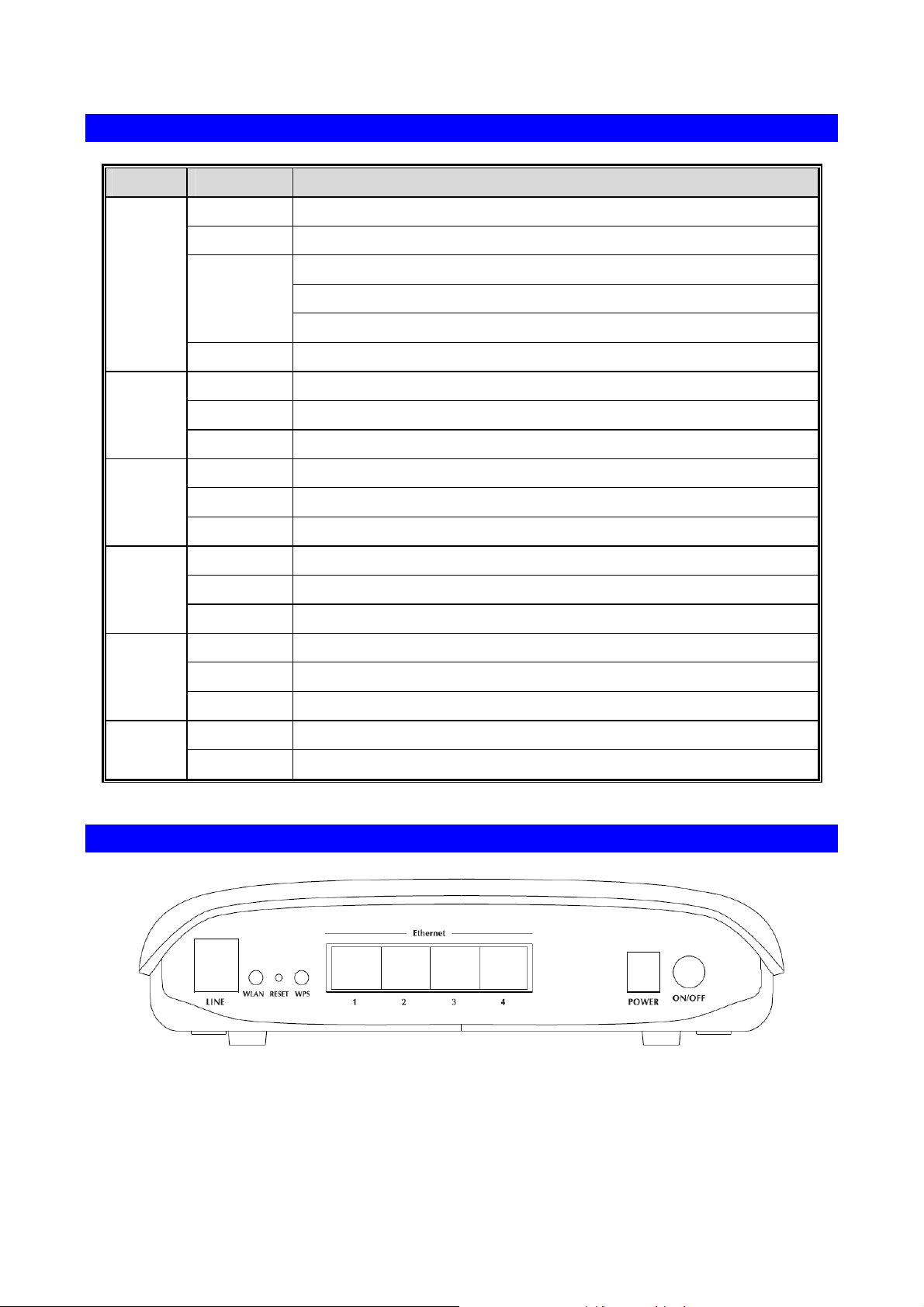
LED definition
LED State Description
Off The power is off.
Green The power is on and operating normally.
PWR
Link
Data
LAN 1-4
WLAN
The power is self-testing.
Red
Blink Red Upgrading software.
Off No signal is detected.
Blink Green The DSL line is training.
Green The DSL line connection is established.
Off No Internet connection.
Green The users can access the Internet.
Red Device attempts to become IP connected but fails.
Off No Ethernet signal is detected.
Green Ethernet interface is ready to work.
Blink Green Data is passing through Ethernet port.
Off No radio signal is detected.
Green WLAN interface is ready to work
Blink Green Data is passing through wireless.
The device enters the console mode of the boot loader.
The self-testing fails if the LED is always RED.
WPS
Rear Panel
Off WPS service is not during using, or WPS is setup successfully.
Blink Green WPS service tries to establish.
11
Page 12
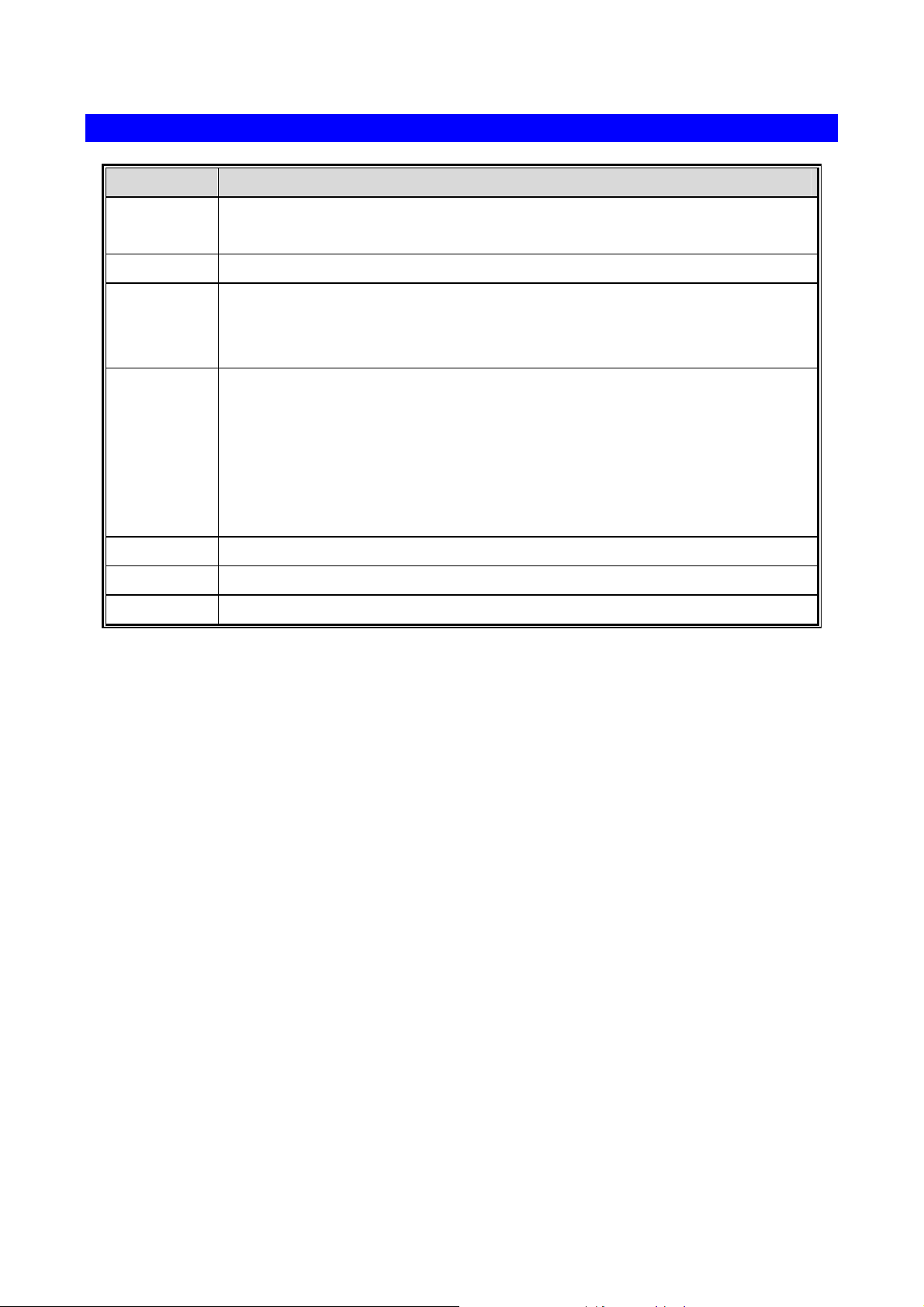
Rear Panel Port and Button Definition
Connector Description
LINE
WLAN
RESET
WPS
LAN 1~4
POWER
ON/OFF
The RJ-11 allows data communication between the modem and the ADSL
network through a twisted-pair phone wire.
The WLAN button can enable and disable the wireless function.
To restore the factory default settings of device. Keep the device powered on
and push a paper clip into the hole. Press down the button over 5 seconds and
then release.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is the simplest way to build connection between
wireless network clients and this ADSL router. Press this button on the router
and enable WPS function of the wireless clients, the router and clients will
automatically configure the security key and connect directly. Please note that
the router will wait for WPS requests from wireless clients in 2 minutes after the
WPS button is pressed.
The RJ-45 allows PC or network devices to connect by network cable.
The Power connector with 12V DC, 1A
The Power Button uses for turning on or off the device.
12
Page 13

2. Installation
This chapter offers information about installing your router. If you are not familiar with the
hardware or software parameters presented here, please consult your service provider for
the values needed.
2.1 Choosing the Best Location for Wireless Operation
Keep the numbers of walls and ceilings to the minimum:
The signal emitted from wireless LAN devices can penetrate through ceilings and
walls. However, each wall or ceiling can reduce the range of wireless LAN devices
from 1 ~ 30 miters. Position your wireless devices so that the number of walls or
ceilings obstructing the signal path is minimized.
Consider the direct line between access points and workstations:
A wall that is 0.5 meters thick, at a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 1 meter
thick. At a 2-degree angle, it appears over 14 meters thick. Be careful to position
access points and client adapters so the signal can travel straight through (90º angle)
a wall or ceiling for better reception.
Building materials make difference:
Buildings constructed using metal framing or doors can reduce effective range of the
device. If possible, position wireless devices so that their signals can pass through
drywall or open doorways. Avoid positioning them in the way that their signal must
pass through metallic materials. Poured concrete walls are reinforced with steel while
cinderblock walls generally have little or no structural steel.
Position the antenna for best reception:
Play around with the antenna position to see if signal strength improves. Some
adapters or access points allow you to judge the strength of the signal.
Keep your product away (at least 1~2 meters) from electrical devices:
Keep wireless devices away from electrical devices that generate RF noise such as
microwave ovens, monitors, electric motors, etc.
2.2 Connecting the ADSL Router
See the following figure. Connect the DSL port of the DSL Router with a telephone
cable.
Connect the Ethernet port of the DSL Router to the network card of the PC via an
Ethernet cable.
Plug one end of the power adapter to the wall outlet and connect the other end to the
PWR port of the DSL Router.
13
Page 14
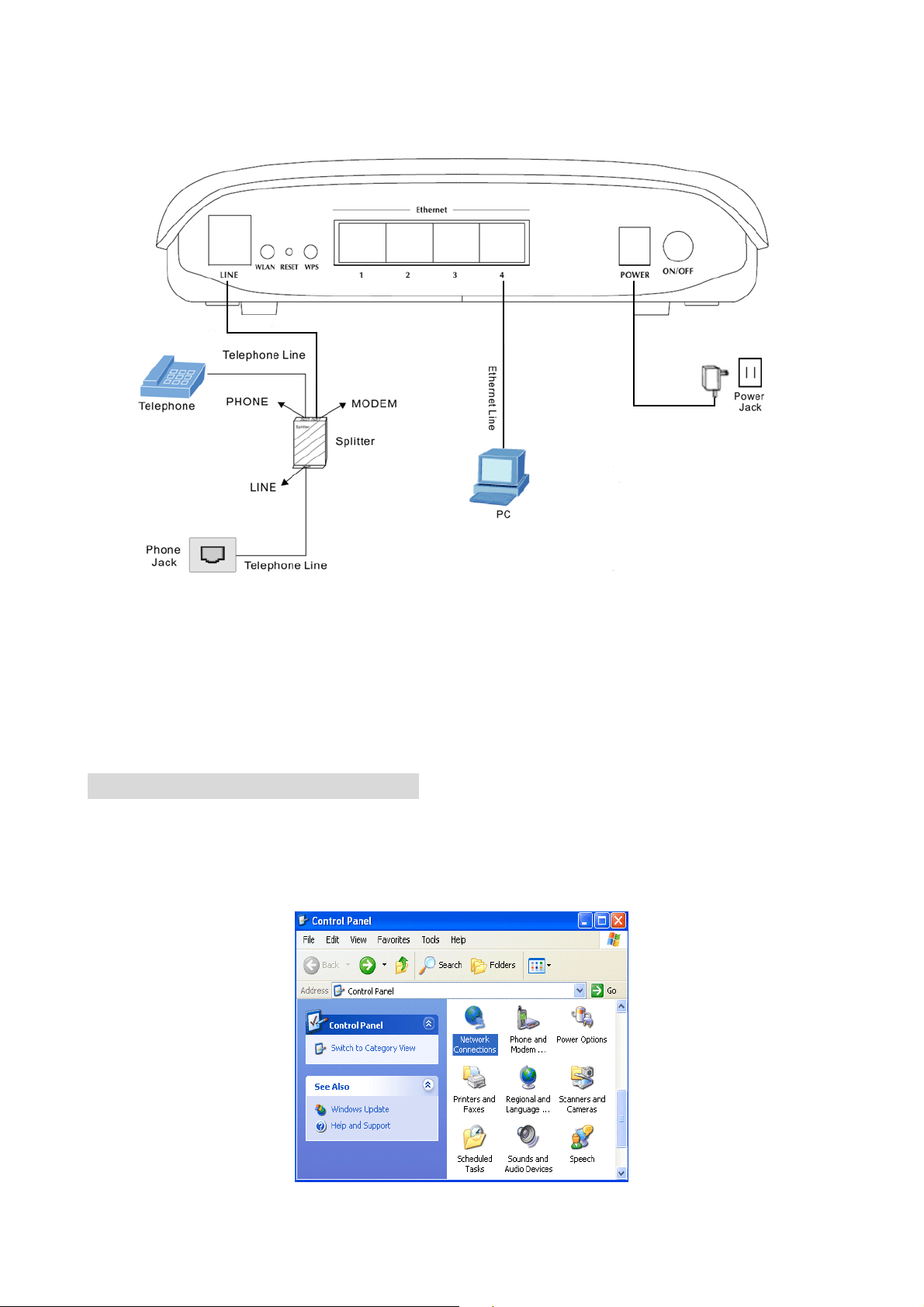
The following figure displays the connection of the DSL Router, PC, and telephones.
If do not need to connect to the splitter,
z Connect the modem to wall jack with a telephone cable directly.
z Use Ethernet cable to connect “LAN” port of the modem and network adaptor of your
computer.
2.3 Configuring the Network Properties
Configuring PC in Windows XP
1. Go to Start / Control Panel (in Classic View). In the Control Panel, double-click on
Network Connections
2. Double-click Local Area Connection.
14
Page 15
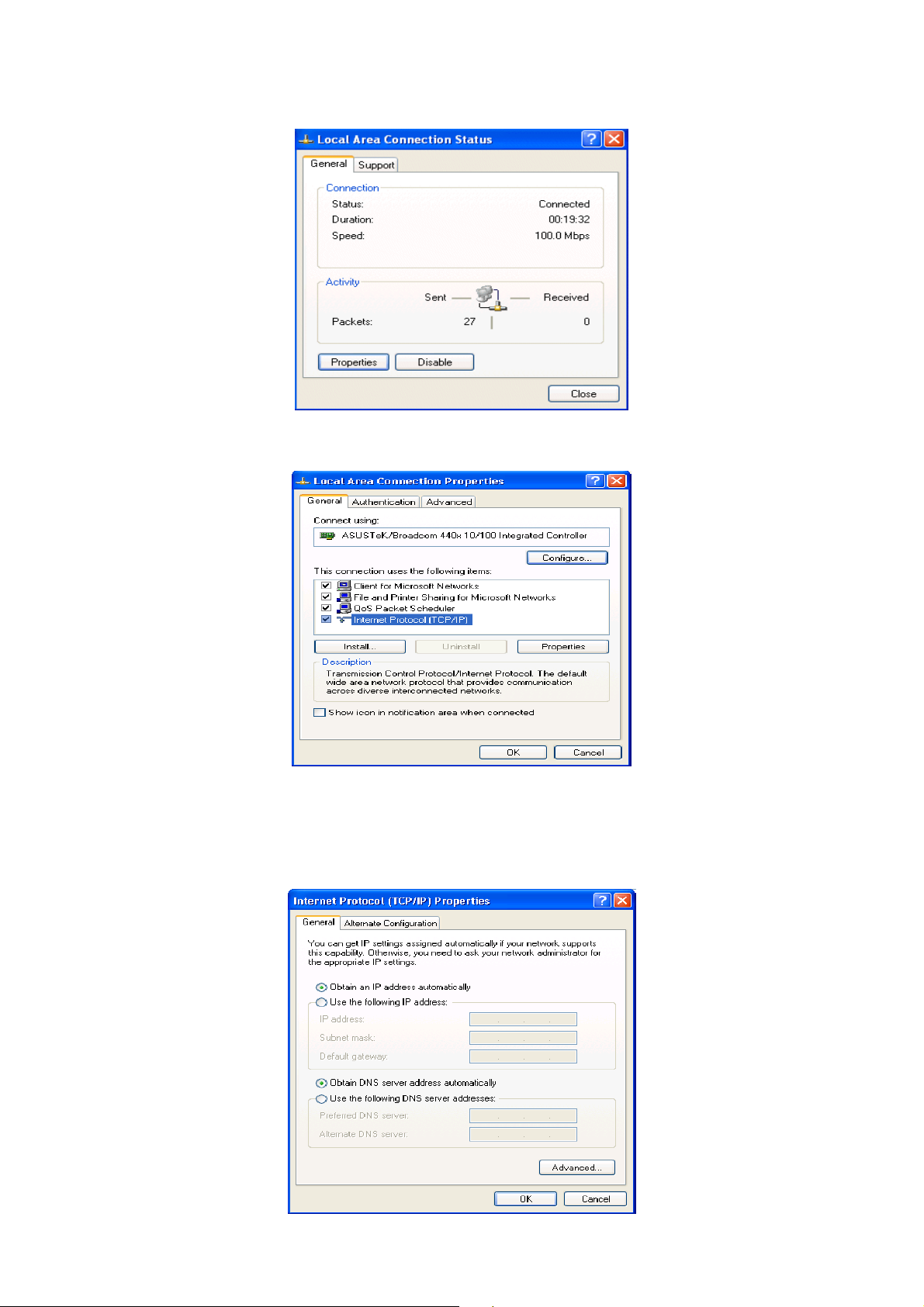
3. In the Local Area Connection Status window, click Properties.
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
5. Select the Obtain an IP address automatically and the Obtain DNS server address
automatically radio buttons.
6. Click OK to finish the configuration.
15
Page 16
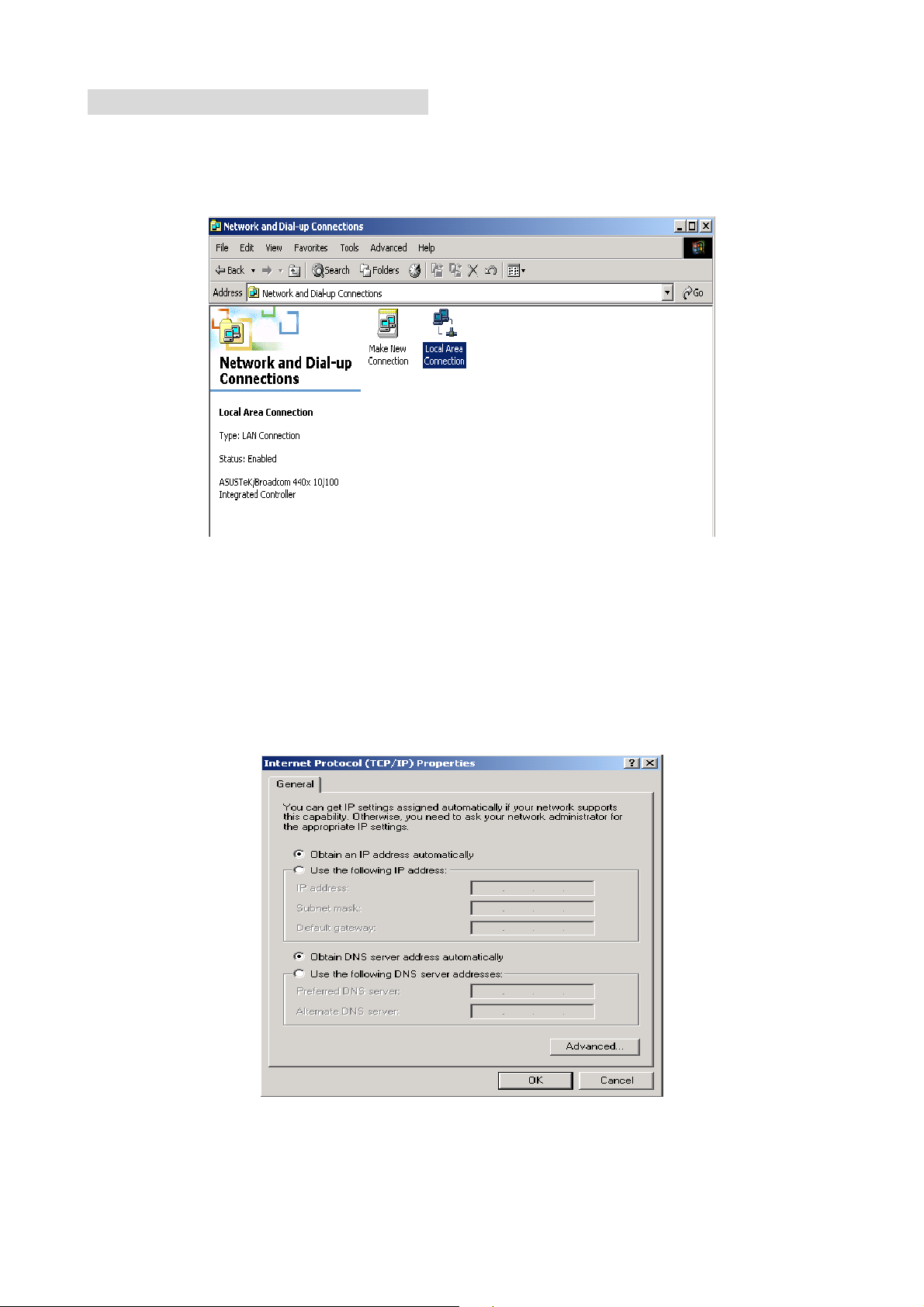
Configuring PC in Windows 2000
1. Go to Start / Settings / Control Panel. In the Control Panel, double-click on Network
and Dial-up Connections.
2. Double-click Local Area Connection.
3. In the Local Area Connection Status window click Properties.
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
5. Select the Obtain an IP address automatically and the Obtain DNS server address
automatically radio buttons.
6. Click OK to finish the configuration.
16
Page 17
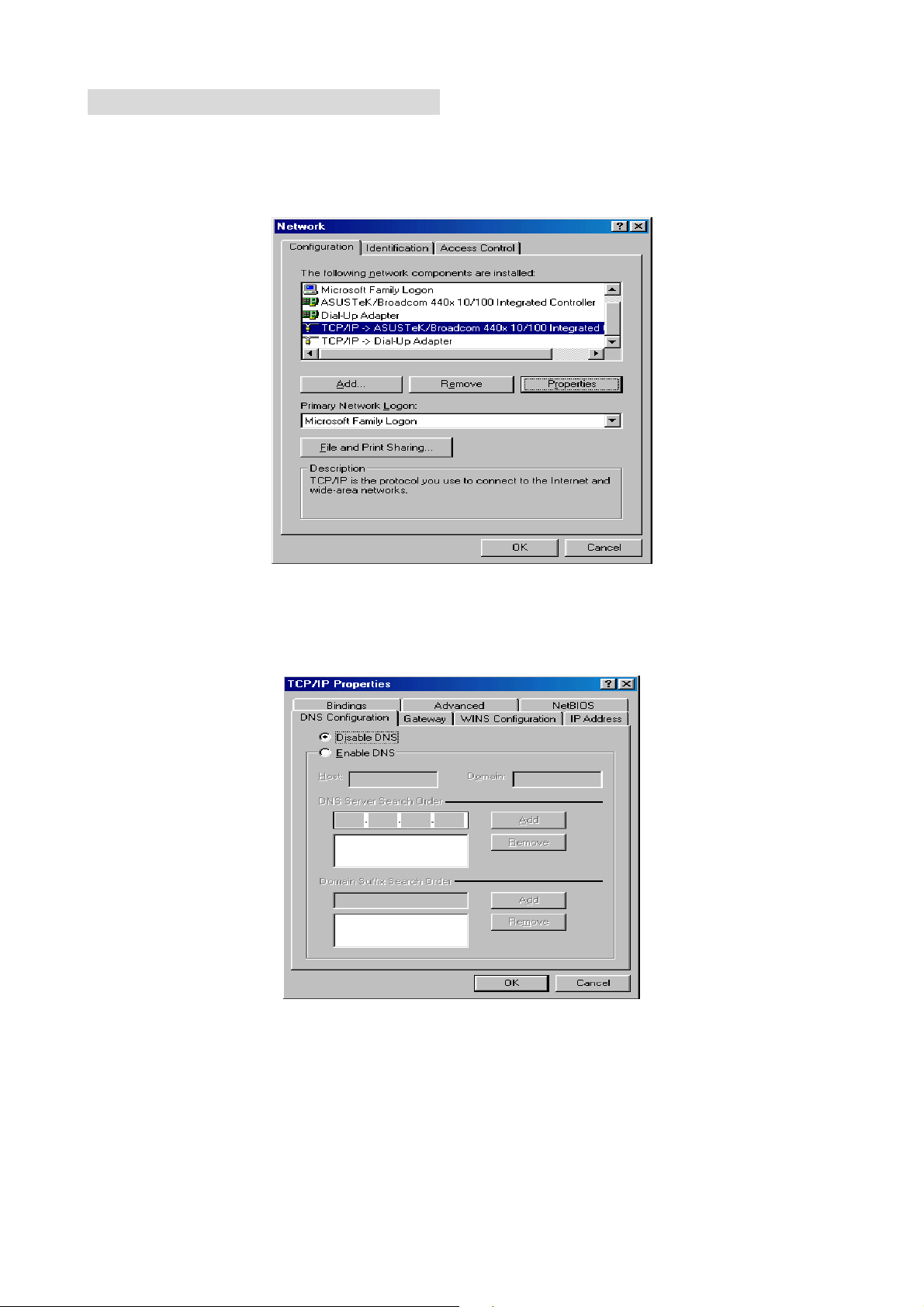
Configuring PC in Windows 98/Me
1. Go to Start / Settings / Control Panel. In the Control Panel, double-click on Network
and choose the Configuration tab.
2. Select TCP/IP Æ the name of your Network Interface Card (NIC) in your PC.
3. Select the Obtain an IP address automatically radio button.
4. Then select the DNS Configuration tab.
5. Select the Disable DNS radio button and click OK to finish the configuration.
17
Page 18
3. Web Configuration Management
Determine your connection settings
Before you configure the router, you need to know the connection information supplied by
your ADSL service provider.
Connecting the ADSL Router to your network
Unlike a simple hub or switch, the setup of the ADSL Router consists of more than simply
plugging everything together. Because the Router acts as a DHCP server, you will have to
set some values within the Router, and also configure your networked PCs to accept the IP
Addresses the Router chooses to assign them.
Generally there are several different operating modes for your applications. And you can
know which mode is necessary for your system from ISP. These modes are router, bridge,
PPPoE+NAT, and PPPoA+NAT.
Configuring with Web Browser
It is advisable to change the administrator password to safeguard the security of your
network.
To configure the router, open your browser, type “http: //192.168.1.1” into the address bar
and click “Go” to get to the login page.
Save this address in your Favorites for future reference.
In login dialog, enter “admin” as user name and “admin” as default password. After log in,
you will see the following page. The default screen is Quick Setup setting screen. You can
configure the device step by step.
18
Page 19
3.1 Quick Setup
When we enter into Quick Setup page, it mainly includes functions to do.
Account setup
Time Server setup
WAN setup
Wireless setup
'Quick Setup' enables speedy and accurate configuration of your Internet connection and
other important parameters. The following sections describe these various configuration
parameters. Whether you configure these parameters or use the default ones, click 'Next' to
enable your Internet connection.
When subscribing to a broadband service, you should be aware of the method by which you
are connected to the Internet. Your physical WAN device can be either Ethernet, DSL, or
both. Technical information regarding the properties of your Internet connection should be
provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). For example, your ISP should inform you
whether you are connected to the Internet using a static or dynamic IP address, or what
protocols, such as PPPOA or PPPoE, you will be using to communicate over the Internet.
3.1.1 WAN Interface Setup
In WAN Interface Setup phase, we mainly setup PVC and the property of this PVC:
VPI
VCI
Protocol
Connection Mode
3.1.1.1 Setup VPI/VCI
After logging into the DSL router, When we were not config any PVC at privious time and we
have not default settings include PVC,you will see a “Quick Setup” web page, which will
include some basic configuration that is needed by ATM PVC. the following introductions will
guide you through the steps necessary to configure your DSL Router.
According to your Internet service providers (ISP) instructions, specify the following
parameters:
VPI (Virtual Path Identifier):
The virtual path between two points in an ATM network and its valid value is from 0 to 255.
VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier):
The virtual channel between two points in an ATM network, ranging from 32 to 65535 (1 to
31 are reserved for known protocols).
19
Page 20
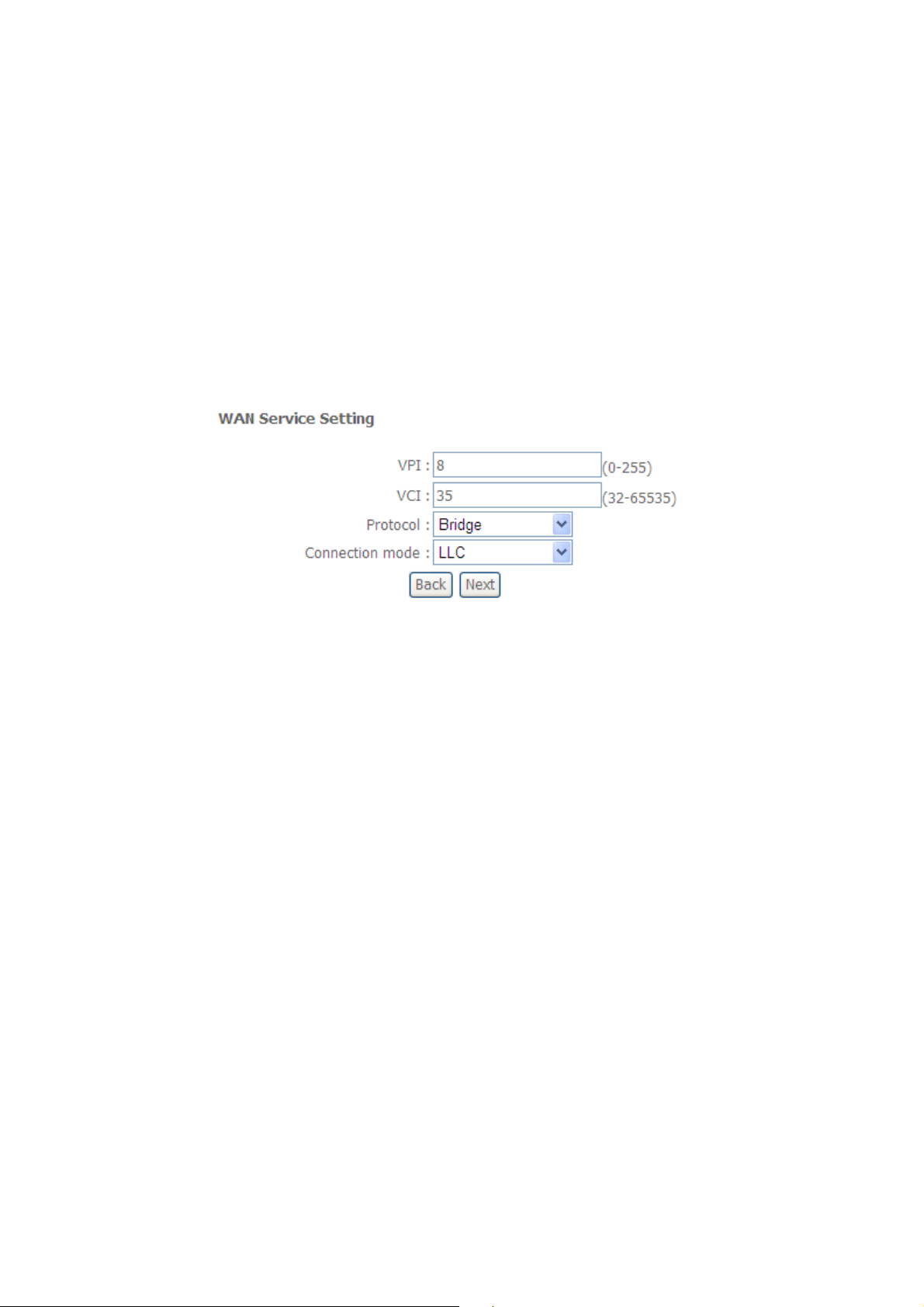
3.1.1.2 Select Protocol and Connection
You can select your protocol from the following list; each protocol has its connection mode:
PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet)
PPPoA (PPP over ATM)
Dynamic
Static IP
IPoA (IP over ATM)
Bridging
Figure: WAN Service page
For example, Change the connection type of PVC 0/35 to “bridge”. Select “bridging”, and
“LLC” (depending on the uplink equipment, generally “LLC”) as “Connect Mode”.
20
Page 21
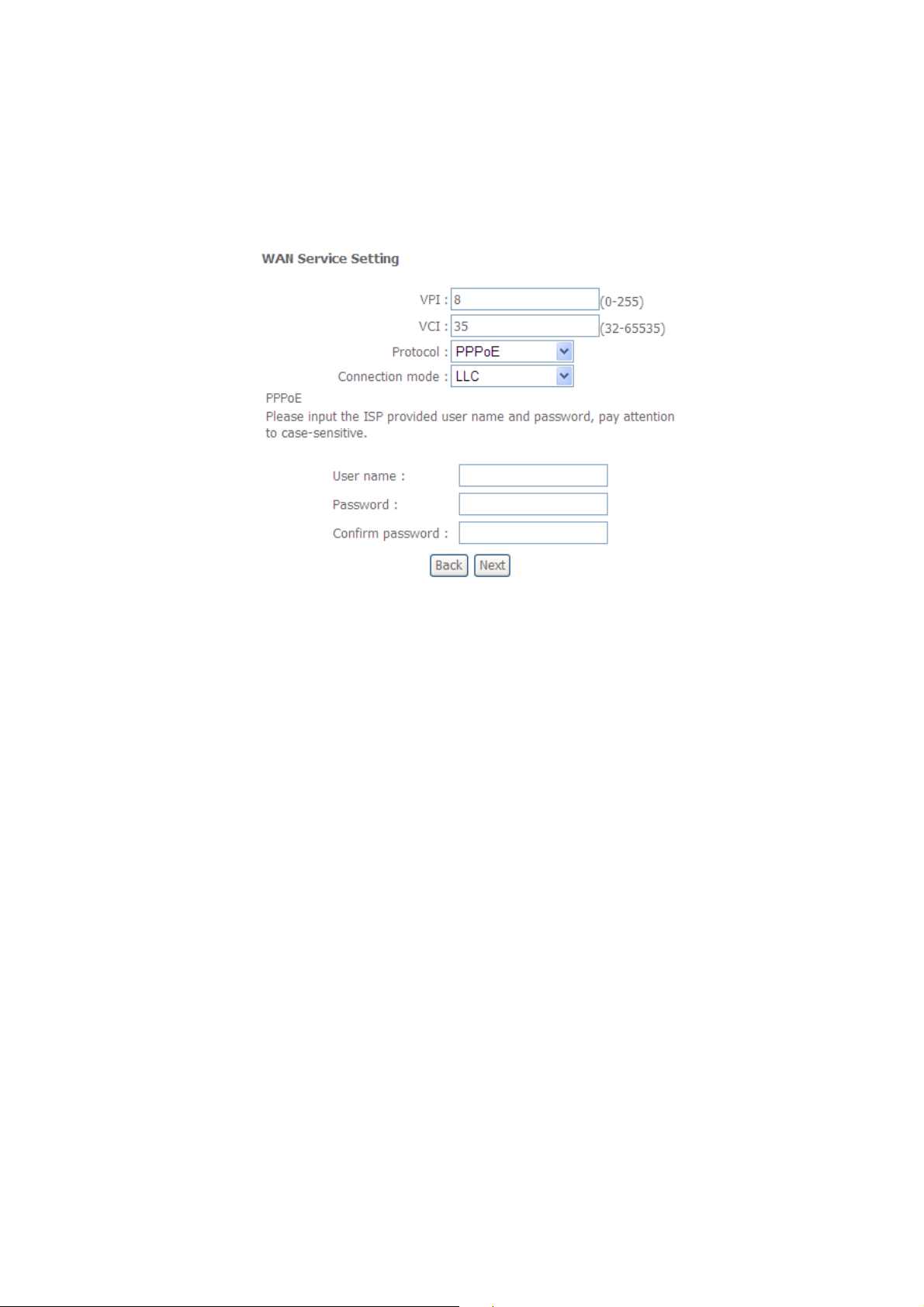
3.1.1.3 Internet Connection Type - PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
A. Setup the PVC.
B. Select PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) from the “Protocol” box and its Connection mode.
C. Enter PPP information.
Figure: PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) should provide you with the following information:
PPP Username
PPP Password
Authentication Method
21
Page 22
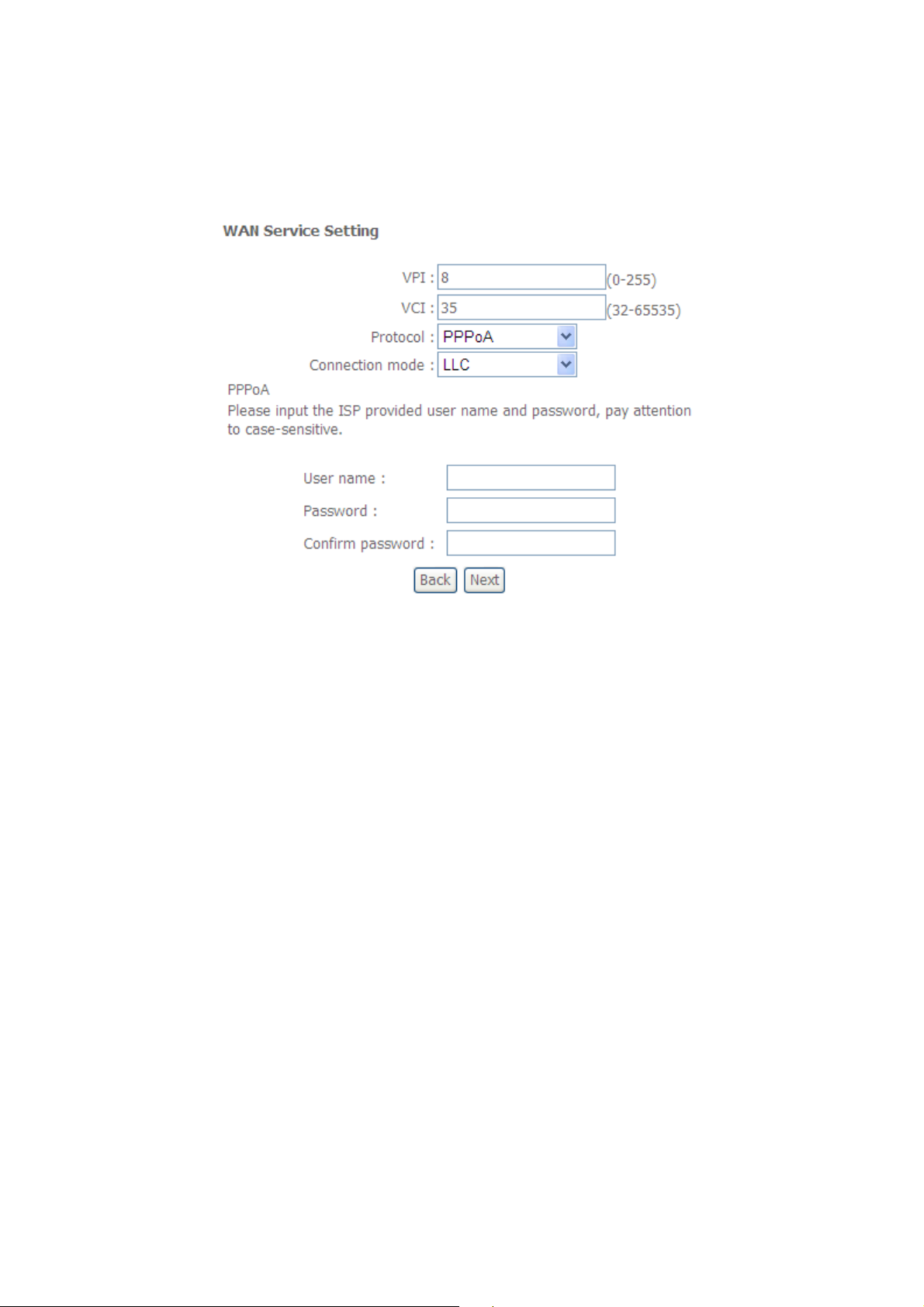
3.1.1.4 Internet Connection Type - PPP over ATM (PPPoA)
A. Setup the PVC.
B. Select PPP over ATM (PPPoA) from the ”Protocol” box and Its connection mode.
C. Enter PPP information.
Figure: PPP over ATM (PPPoA)
Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) should provide you with the following information:
PPP Username
PPP Password
Authentication Method
22
Page 23
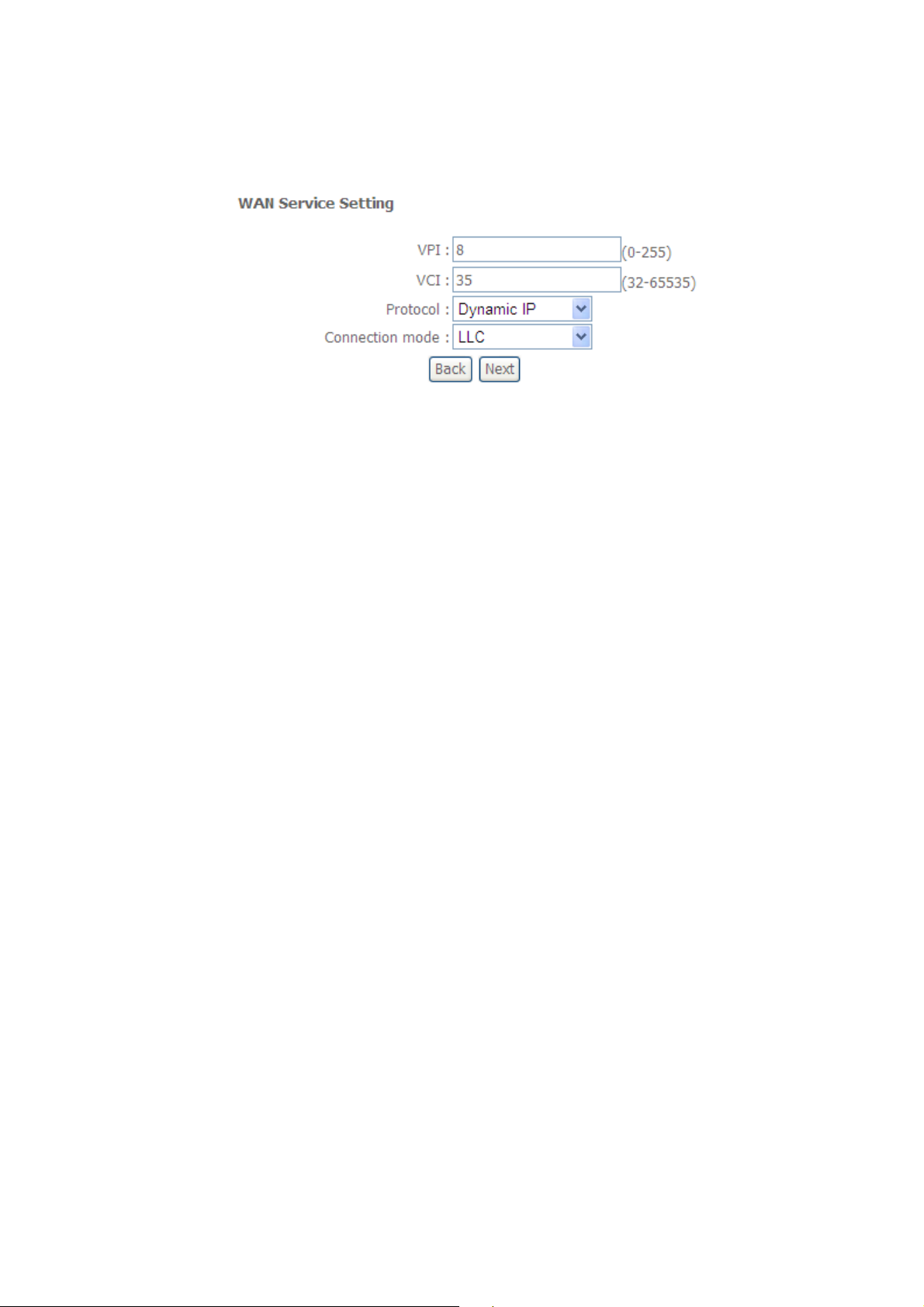
3.1.1.5 Internet Connection Type - Dynamic IP
A. Setup the PVC
B. Select Dynamic IP from the “Protocol” box and its connection type.
Figure: Dynamic IP
23
Page 24
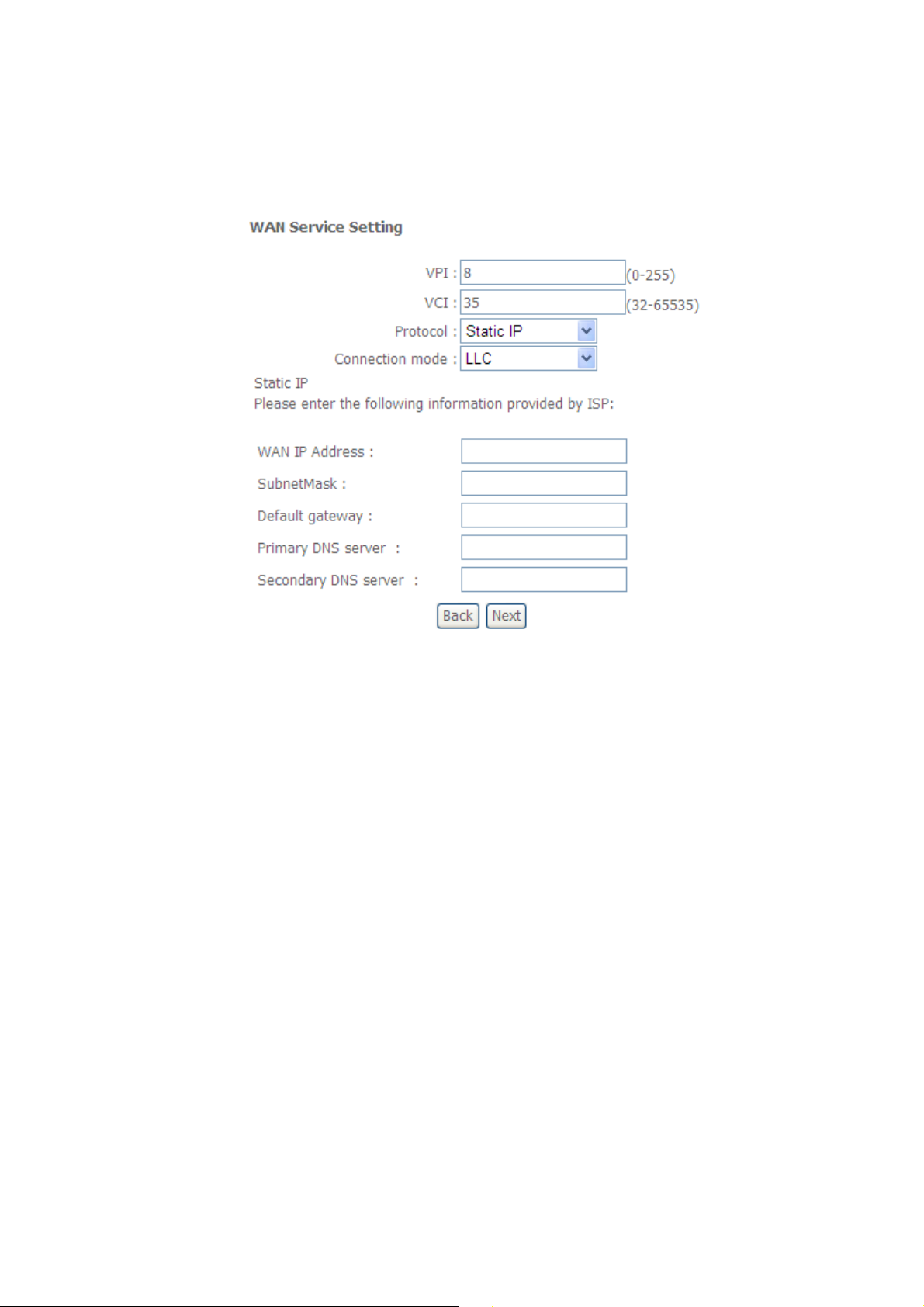
3.1.1.6 Internet Connection Type - Static IP
A. Setup the PVC.
B. Select Static IP from the “Protocol” box and its connection mode.
C. Enter the IP information.
Figure: Static IP
Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) should provide you with the following
WAN IP address and Subnet Mask information
Default gateway information
DNS server information
24
Page 25
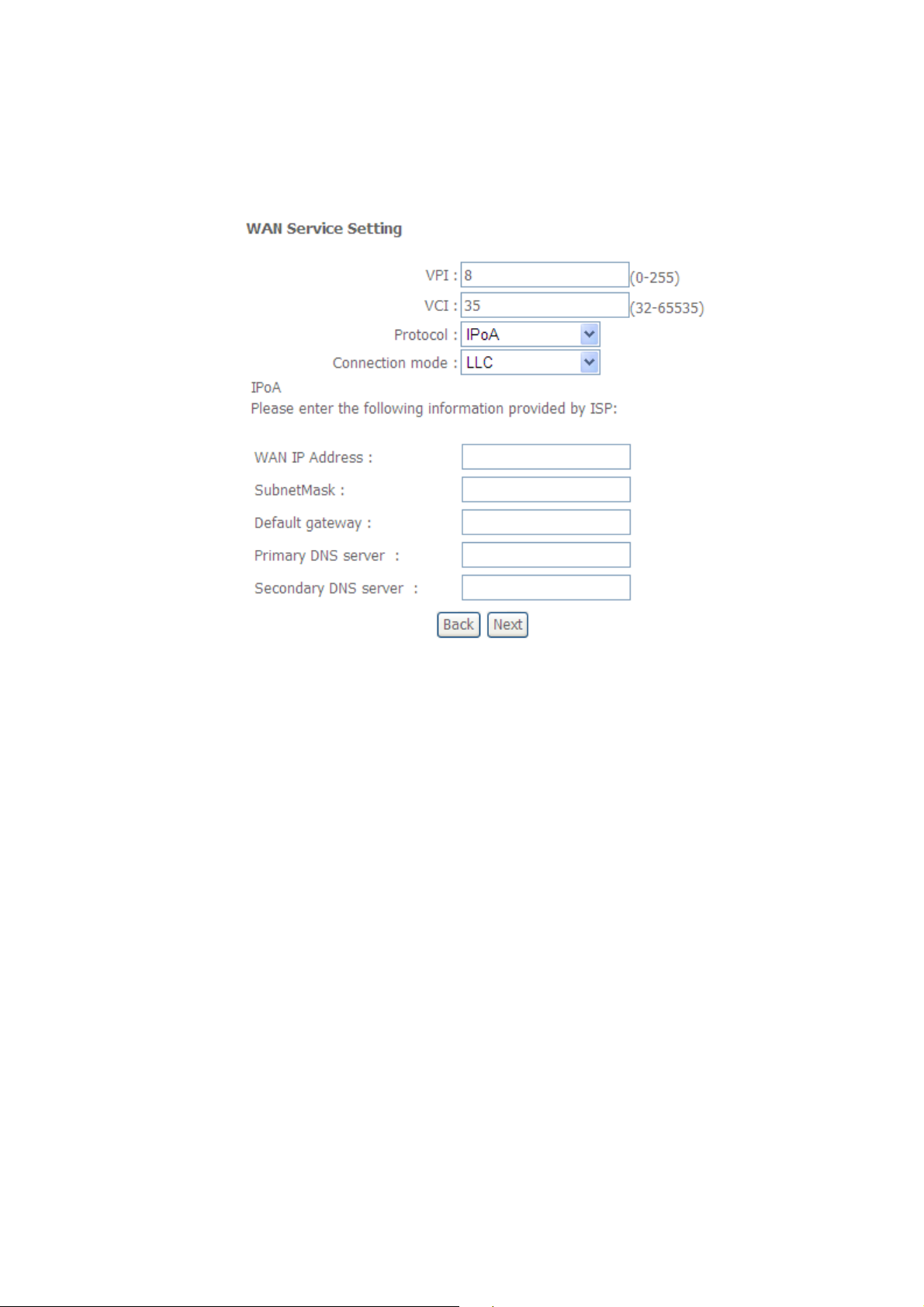
3.1.1.7 Internet Connection Type - IP over ATM (IPoA)
A. Setup the PVC.
B. Select IP over ATM (IPoA) from the “Protocol” box and its connection mode.
Figure: IP over ATM (IPoA)
Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) should provide you with the following.
WAN IP address and Subnet Mask information
Default gateway information
DNS server information
25
Page 26

3.1.1.8 Internet Connection Type - Bridge
A. Setup the PVC.
B. Select Bridge from the “Protocol” box and its connection mode.
Figure: Bridge
26
Page 27

3.1.2 LAN Interface Setup
In LAN interface setup page, you can modify your default LAN IP and DHCP Server
settings. The Default LAN IP is 192.168.1.1 and DHCP is Enable.
Figure: LAN Interface Setup
Configuring the DHCP server
The Router has a DHCP server for which the factory setting is active. Consequently, the IP
addresses of the PCs are automatically assigned by the DSL Router.
Note:
If the DHCP server for the DSL Router is activated, you can configure the network
setting on the PC so that the option Obtain an IP address automatically is set up.
Further information about this can be found in the section entitled
If you deactivate the DHCP server, you will have to assign a static IP address for the
PCs that use the network settings
¾ To activate the DHCP server, select ‘Enable’.
¾ If the DHCP server is active, you can define a Lease time. The Lease time determines
the period for which the PCs retain the IP addresses assigned to them without
changing them.
Note:
If you select Never expires, the IP addresses are never changed. Activate this option if you
want to make NAT or firewall settings using the IP addresses of the PCs; otherwise you
have to assign static IP addresses to these PCs.
27
Page 28

3.1.3 WAN Setup Summary
When In WAN setup summary phase, the property of the PVC added can view:
VPI/VCI
Connection Type:
Service Name:
Service Category:
IP Address:
Service State:
NAT
Firewall
IGMP
QoS
Figure: WAN setup summary
Click “Save/Reboot” to save these settings. And you can click “Back” to make any
modifications. After you click “Save/Reboot”, it shows the following message.
Figure: DSL Router Reboot
NOTE: You need to reboot to activate this WAN interface and further configure services
over this interface,and it will take about two minutes to done with it.
28
Page 29

3.1.4 Quick Setup Completed
DSL router does not require further configuration in order to start working. After the setup
described in this chapter, you can immediately start using your gateway to:
Share a broadband connection among multiple users (HTTP, FTP, Telnet, and
NetMeeting) and between all of the computers connected to your home network.
Build a home network by connecting additional PCs and network devices to the
gateway.
Control network parameters, including DHCP, DNS and WAN settings.
View network status, traffic statistics, system log and more.
Allow access from the Internet to games and other services provided by computers in
the home network.
Prohibit computers in the home network from accessing selected services on the
Internet.
Block access to specific Internet Web sites from your home network. To learn about
how to configure your Firewall security parameters, please refer to section 7.3. If you
wish to apply corporate-grade security to your network, please refer to section 7.3.11.
If your gateway is equipped with multiple LAN ports, you can connect additional devices
directly to the gateway. Otherwise, connect a hub or switch to the LAN port, to which you can
connect additional devices. In both cases, configure newly connected devices to
automatically obtain IP address as described above.
29
Page 30

3.2 DSL Router Device information
Click “Device Info”, It should view the information as below:
Summary
WAN
Statistics
Route
ARP
DHCP
3.2.1 Summary of Device information
This interface contains the following information:
Board ID:
Software Version:
Bootloader (CFE) Version:
Wireless Driver Version:
Upstream Line Rate
Downstream Line Rate
LAN IPv4 Address: The management IP address
Default Gateway: No gateway in a pure bridging mode; under other modes such as
PPPOE/PPPOA, it is the address of the uplink equipment.
DNS Server address: Obtained from the uplink equipment in PPPOE/PPPOA mode;
No DNS Server address in a pure bridging mode; or input them manually.
Figure: summary of Device information
30
Page 31

3.2.2 WAN Interface information
Click “WAN” to show the following interface, depend on the selected connection mode, the
Summary screen shows the status and also the connect or disconnect button.
This interface contains the following informations of every WAN connection:
Interface
Decsription
Type
VlanMuxID
Igmp
NAT
Firewall
Status
IPv4 Address
Figure: WAN interface information
31
Page 32
3.2.3 Statistics
In this page, It includes four parts information:
Statistics of LAN
Statistics of WAN Service
Statistics of xTM
Statistics of xDSL
3.2.3.1 Statistics of LAN
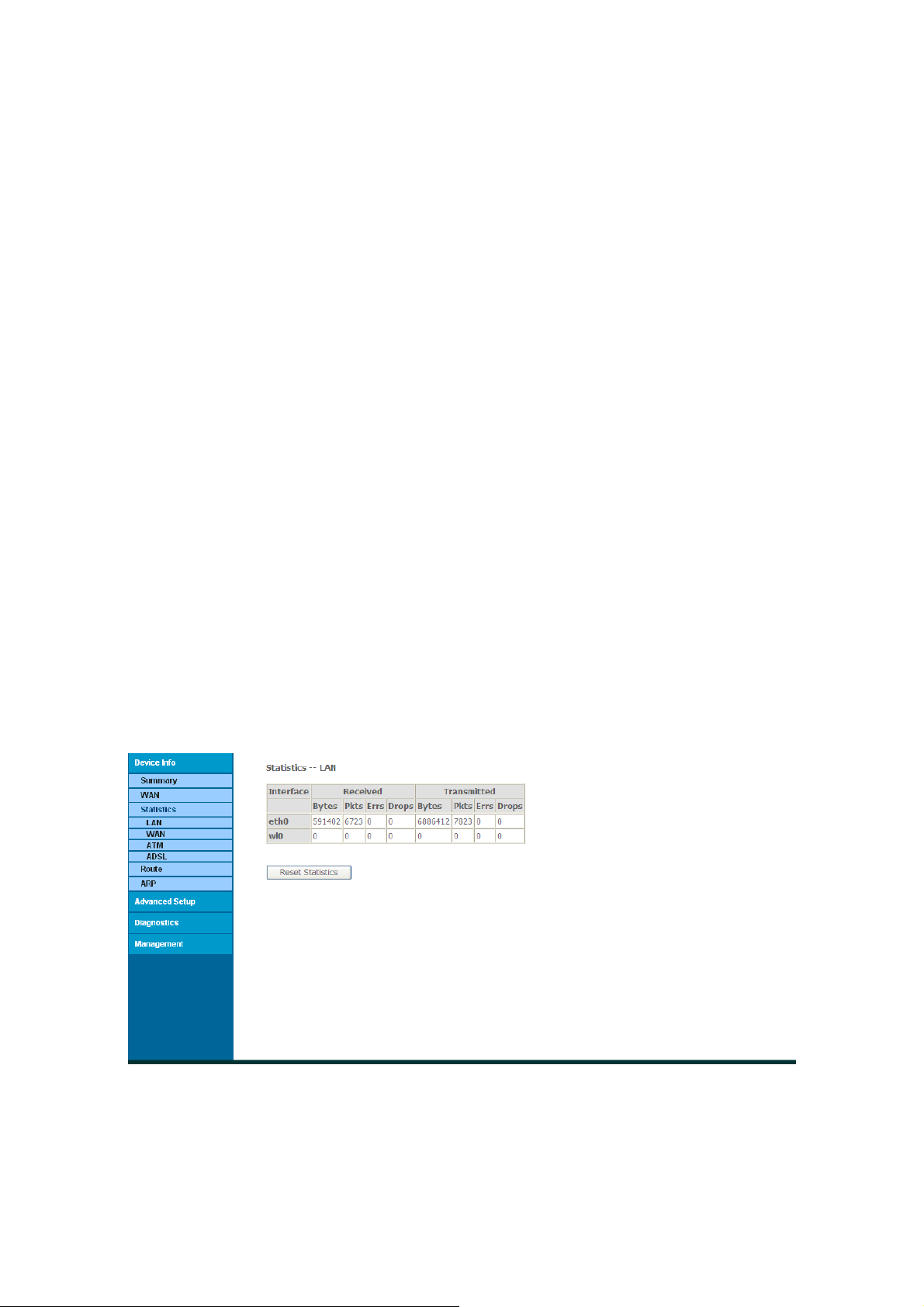
Click “Statistics” --> ”LAN” to show the following interface. You can query information on
packets recevied at the Ethernet. Click “Reset Statistics” to return the values to zero and
recount them.
You can view the info as below:
Interface
Received
Bytes: Bytes of Received
Pkts: Packets of Received
Errs: Errors packets of Received
Drops: Drops packets of Received
Transmitted
Bytes: Bytes of Received
Pkts: Packets of Received
Errs: Errors packets of Received
Drops: Drops packets of Received
Figure: Statistics of LAN
32
Page 33

3.2.3.2 Statistics of WAN Service
Click “Statistics” --> ”WAN Service” to show the following interface. You can query
information on packets recevied at the WAN interfaces. Click “Reset Statistics” to return the
values to zero and recount them.
Informations as below:
Interface
Description
Received
Bytes: Bytes of Received
Pkts: Packets of Received
Errs: Errors packets of Received
Drops: Drops packets of Received
Transmitted
Bytes: Bytes of Received
Pkts: Packets of Received
Errs: Errors packets of Received
Drops: Drops packets of Received
Figure: Statistics of WAN
33
Page 34

3.2.3.3 Statistics of xTM
Click “Statistics”-->”xTM” to show the following interface. You can query information on
packets recevied at the xTM interfaces. Click “Reset” to return the values to zero and
recount them.
There are three part info:
xTM Interface Statistics:
Port Number
In Octets
Out Octets
In Packets
Out Packets
In OAM Cells
Out OAM Cells
In ASM Cells
Out ASM Cells
In Packet Errors
In Cell Errors
Figure: Statistics of xTM
34
Page 35
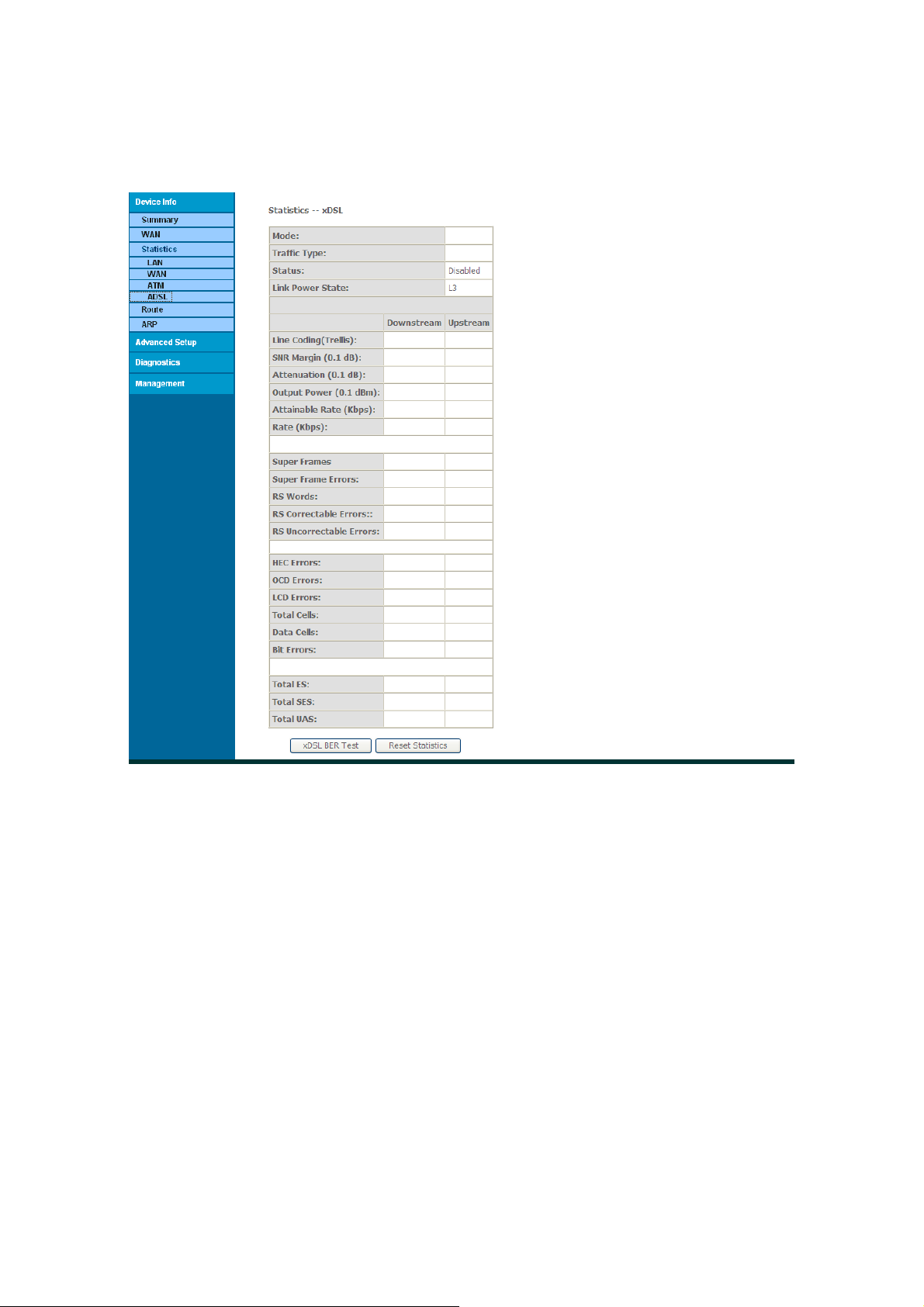
3.2.3.4 Statistics of xDSL
Click “Statistics”-->”xDSL” to show the following interface.
If the DSL line is activated, the following window will show.
Figure: Statistics of xDSL
You will see the following information pertinent to the ADSL line in the page:
Mode:
Trafic Type:
Status:
Link Power State:
Rate (Kbps): Upstream Line Rate / Downstream Line Rate.
At the lower part of this interface, there is a “Reset Statistics” button. Click it to return values
to zero and recount.
35
Page 36

ADSL BER Test
Click “ADSL BER Test” to do a “Bit Error Rate” Test on the DSL line. The test interface is as
follows:
Figure: ADSL BER Test
The Tested Time (sec) has the following choices: 1, 5, 10, 20, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300, and
360. Select a time and then click “Start” to pop up the following interfaces in sequence.
Figure: ADSL BER Test Running Page
Figure: ADSL BER Test Result
Note: If the error ratio reaches up to “e-5”, the user will not be able to access the
Internet.
36
Page 37

3.2.4 Route table information
Click “Route”. You can view the route table information,Each route item in route table has
info as below:
Destination
Gateway
Subnet Mask
Flag
Metric
Service
Interface
Figure: Route table
37
Page 38

3.2.5 ARP table information
Click “ARP” to show the following interface. You can query the MAC and IP addresses
information of the equipment attached to the Router.
Each ARP item has information as below:
IP address
Flags
HW address
Device
Figure: ARP table
3.2.6 DHCP IP Leases information
Click “DHCP” to show the following interface. You can query the IP addresses assignment to
which MAC Address in DSL router’s LAN side,Through Ethernet can obtain the IP Address
from the DHCP server on DSL router.
Each Leases item include info as below:
Hostname
MAC Address
IP Address
Expires In: How many times the Device Leases the IP Address for the MAC Address
Figure: DHCP Leases List
38
Page 39

3.3 Advanced Setup
Click “Advanced Setup” to enter the advanced system setup interface.there many items as
below:
Layer2 Interface
WAN Servic
LAN
Security
Parental control
Quality of Service
Routing
DNS
DSL
Upnp
Dns Proxy
Interface Grouping
LAN Ports
Certificate
Advance Setup is DSL Router’s config center,
3.3.1 Layer2 INTERFACE
Choose Advanced Setup > Layer2 Interface and two items may appear.
ATM Interface
ETH Interface
3.3.1.1 ATM Interface
Choose Advanced Setup > Layer2 Interface > ATM Interface . In this page, you can
add or remove to configure DSL ATM Interfaces.
Click Add to add ATM Interface and the following page appears.
39
Page 40

In this page, you can enter this PVC (VPI and VCI) value, and select DSL link type (EoA is
for PPPoE, IPoE, and Bridge.), encapsulation mode, service category, connection Mode.
VPI (Virtual Path Identifier): The virtual path between two points in an ATM network,
and its valid value is from 0 to 255.
VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier): The virtual channel between two points in an ATM
network, ranging from 32 to 65535 (1 to 31 are reserved for known protocols).
DSL Link Type: EoA (it is for PPPoE, IPoE, and Bridge), PPPoA, or IPoA
Encapsulation Mode: LLC/SNAP-BRIDGING, or VC/MUX
Service Category: UBR Without PCR, UBR With PCR, CBR, Non Realtime VBR,
Realtime VBR.
Connection Mode: Default mode, VLAN MUX mode, or MSC mode
Enable Quality Of Service: enable/disable.
In actual applications, you can modify them depending on your requirement.
You can also select the Enable Quality Of Service check box in to enable the packet
level QoS for a PVC. This improves performance for selected classes of applications.
Note: QoS cannot be set for CBR and Realtime VBR.
Click Apply/Save to save the configuration, and return the following page:
If you want to remove this Interface, please select the Remove check box and click
Remove.
40
Page 41
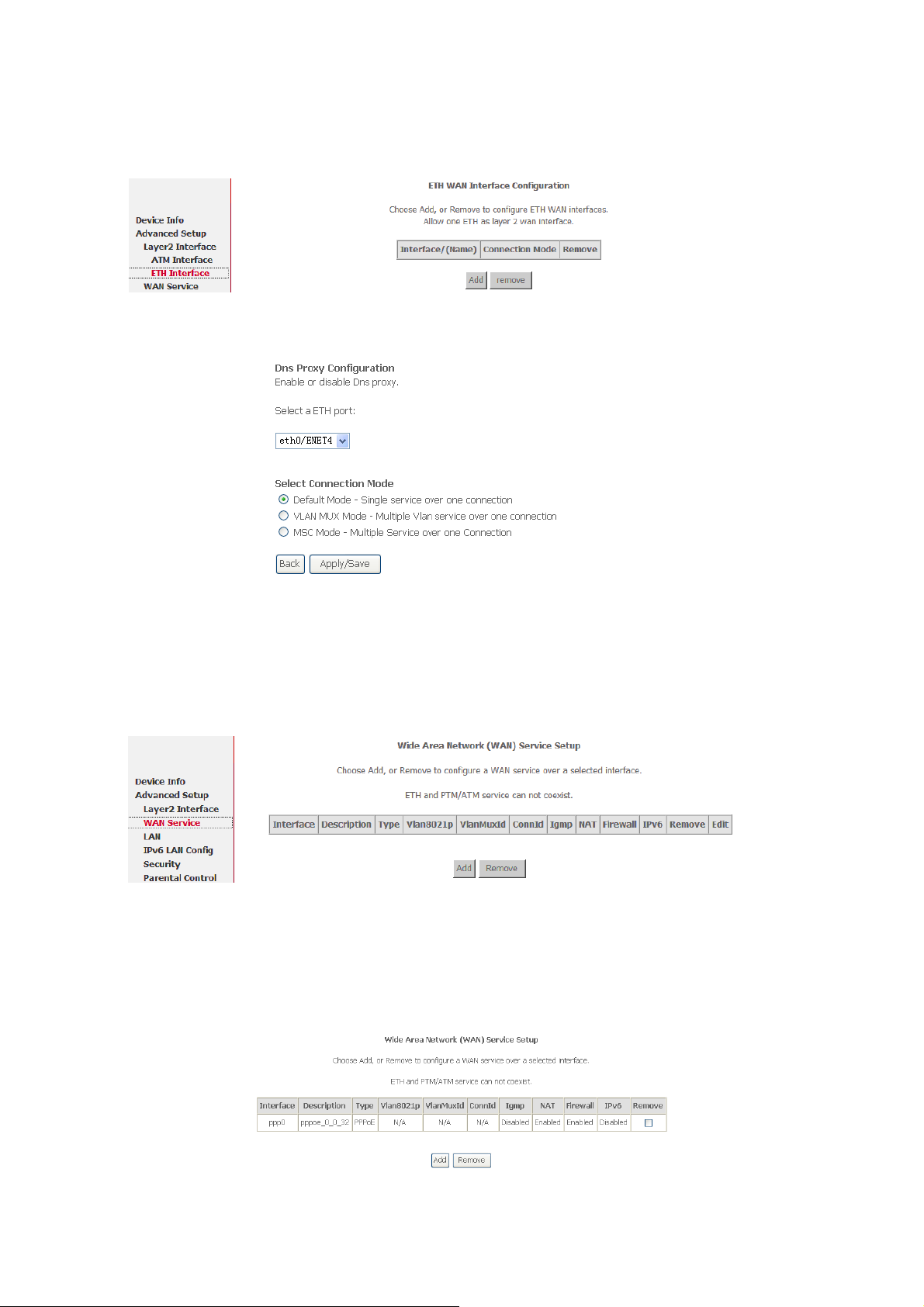
3.3.1.2 ETH Interface
Choose Advanced Setup > Layer2 Interface > ETH Interface, and the following page
appears. In this page, you can add or remove to configure ETH WAN Interfaces.
Click Add and the following page appears.
In this page, you can select a ETH port, such as eth0/ENET4, and select connection
mode. Click Apply/Save to save configuration.
3.3.2 WAN CONFIGURATION
Choose Advance Setup > WAN Service, and the following page appears.
Figure 1
WAN configuration
Click Add, it turns into the following page. You can configure PPPoE, PPPoA, Mer (IPoE),
Bridge, IPoA WAN configuration.
Note: ETH and PTM/ATM sevice can not be coexist.
Choose Remove check box, click Remove to delete the WAN configuration.
41
Page 42

3.3.2.1 Add PPPoE WAN configuration
In the WAN Service Setup page, click Add to add WAN configuration. This section
describes the procedure for adding pppoe_0_0_32 (PPPoE mode).
Step 1: Click Add to turn into the following page. (At first, you must add suitable ATM
configuration for this WAN configuration.) In this page, you can select ATM
Interface .
Step 2: After proper selection, click Next, and the following page appears.
Step 3: In this page, select WAN service type PPP over Ethernet(PPPoE). Click Next,
and the following page appears.
42
Page 43

Step 4: In this page, you can modify the PPP username, PPP password, and
authentication method.
PPP Username: The correct user name that your ISP provides to you.
PPP Password: The correct password that your ISP provides to you.
PPPoE Service Name: If your ISP provides it to you, please enter it. If not, do not
enter any information.
Authentication Method: The value can be AUTO, PAP, CHAP, or MSCHAP. Usually,
you can select AUTO.
Enable Fullcone NAT: A full cone NAT is one where all requests from the same
internal IP address and port are mapped to the same external IP address and port.
Furthermore, any external host can send a packet to the internal host, by sending a
packet to the mapped external address.
Dial on demand (with idle timeout timer): If this function is enabled, you need to
enter the idle timeout time. Within the preset minutes, if the modem does not detect
the flow of the user continuously, the modem automatically stops the PPPOE
connection. Once it detects the flow (like access to a webpage), the modem restarts
the PPPoE dialup. If this function is disabled, the modem performs PPPoE dial-up all
the time. The PPPoE connnection does not stop, unless the modem is powered off
and DSLAM or uplink equipment is abnormal.
PPP IP extension: After PPP IP extension is enabled, the WAN IP address obtained
by the modem through built-in dial-up can be directly assigned to the PC being
attached with the modem (at this time, the modem has only one PC). From the view
of the PC user, this is even with that the PC dials up to obtain an IP addres. But
actually, the dial-up is done by the modem. If this function is disabled, the modem
itself obtains the WAN IP address automatically.
Advanced DMZ: Only LAN4 port supports this service. This is the virtual server
configuration option. The DMZ Host feature allows one local computer to be exposed
to the internet, to be this feature,the other computer can easily enter the DMZ Host, a
DMZ host is not protected by the firewall and may be vulnerable to attack.
Designating a DMZ host may also put other computers in the home network at risk.
When designating a DMZ host, you must consider the security implications and
protect it if necessary.
PPP IP extension: If you want to configure DMZ Host, you should enable it at first.
Non DMZ IP Address: The DMZ host IP address. You can modify it.
Non DMZ Net Mask: The DMZ Host Subnet Mask, it is build upon the DMZ Host IP
Address.
Use Static IPv4 Address: If this function is disabled, the modem obtains an IP
address assigned by an uplink equipment such as BAS, through PPPoE dial-up. If
this function is enabled, the modem uses this IP address as the WAN IP address.
IGMP Multicast: IGMP proxy. For example, if you want PPPoE mode to support IPTV,
enable it.
After enter the PPP Username and PPP Password, click Next, and the following page
appears.
43
Page 44

Step 5 e as the system default gateway.
: In this page, select a preferred WAN interfac
Click Next,
and the following page appears.
Step 6
: In this page, you can get DNS server information from the selected WAN interface
or enter static DNS server IP addresses. If only a single PVC with IPoA or static
MER protocol is configured, you must e
Next
, and the following page appears.
nter static DNS server IP addresses. Click
Step 7
: In this page, it shows all the configurations. Click Apply/Save to all the
configurations,
and the following page appears. Click Back to make any
modifications.
44
Page 45

3.3.1.2 Add MER (IPoE) Configuration
In the WAN Service Setup page, click Add to add WAN configuration. This section
describes the procedure for adding ipoe_0_0_32 (Mer mode).
Step 1: Click Add to turn into the following page. (At first, you must add suitable ATM
configuration for this WAN configuration.)
Step 2: Select an ATM Interface, such as atm1/ (0_0_32). Click Next and the following
page appears.
Step 3: In this page, you can modify the WAN service type, Service Description, and
Enable IPv6 for this service. Click Next and the following page appears.
45
Page 46

tep 4:
In this page, you can modify the IP Settings. Enter information provided by your S
ISP to configure the WAN IP settings. Click Next and the following page appears.
Not
e:
If select Obtain an IP address automatically is chosen, DHCP will be enabled for
PVC in MER mode.
If Use the following Static IP a
ask and i
m nterface gateway.
ddress is chosen, enter the WAN IP address, subnet
: In this page, you can modify the NetwStep 5 ork Address Translation Settings. Click
Next and the following page appears.
: In this page, select a preferred wan inStep 6 terface as the system default gateway. Click
Next and the following page appears.
46
Page 47

Step 7
: In this page, you can get DNS server information from the selected WAN interface
or enter static DNS server IP addresses. If only a single PVC with IPoA or static
MER protocol is configured, you must e
Next
and the following page appears.
nter static DNS server IP addresses. Click
: In this page, click Apply/Save to save all the configurations, aStep 8 nd the following
p .
age appears. If you want to make any modifications, click Back
47
Page 48
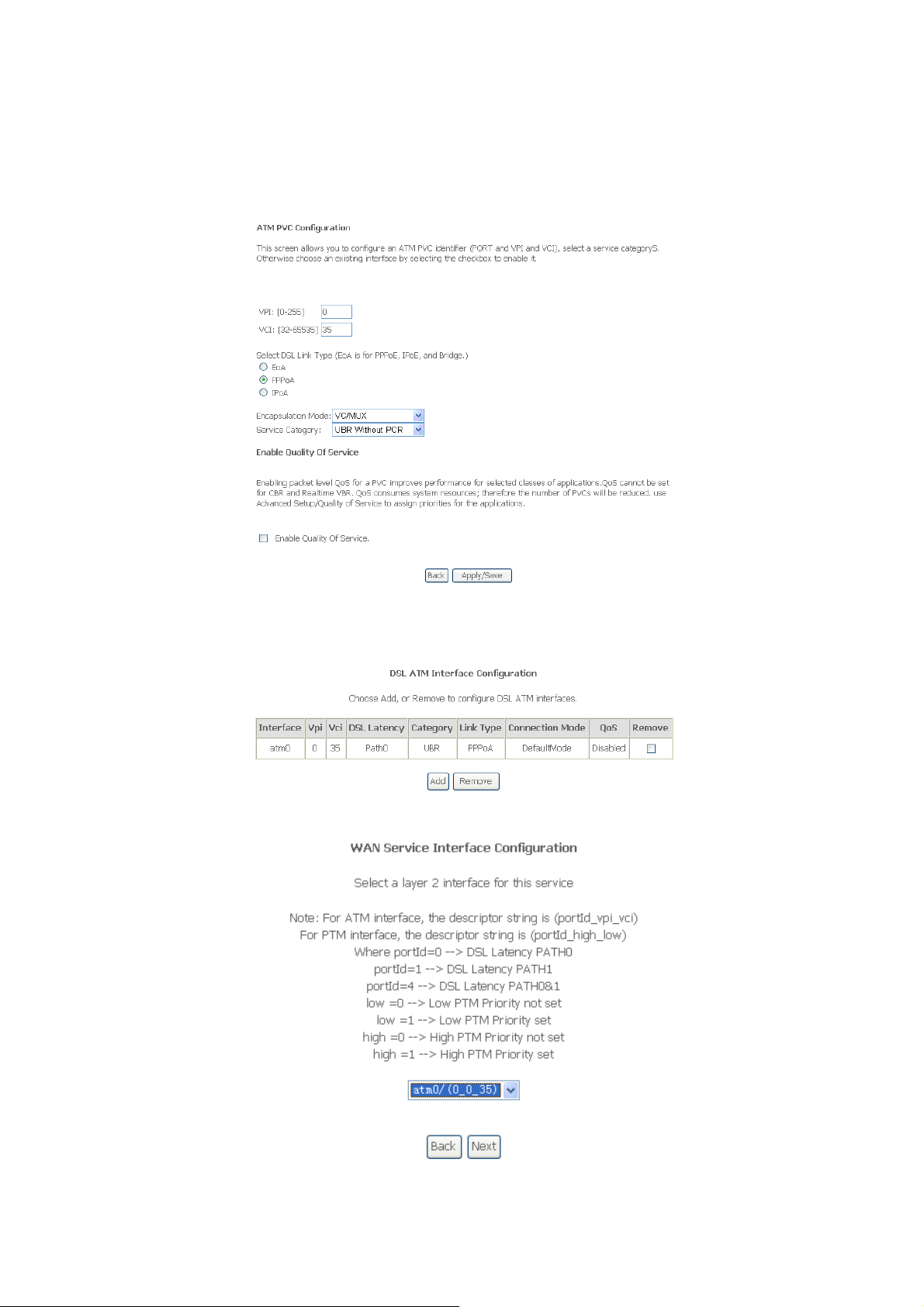
3.3.1.3 Add PPPoA Configuration
This section describes the procedure for adding pppoa_0_0_35 (PPPoA mode).
Step 1: You need to open the Layer2 Interface > ATM Interface page to add a PVC for
PPPoA mode. Click Add and the following page appears.
Step 2: Select the DSL link type to PPPoA, the Encapsulation Mode to VC/MUX
(according to the uplink equipment). Click Apply/Save, and the following page
appears.
Step 3: Return to the WAN Service page, and click Add. The following page appears.
48
Page 49

tep 4: Af ge appears.
S ter proper selection, click Next, and the following pa
: In this page, you can modify theStep 5 service description in the text box. Click Next,
and the following p age appears.
Step 6
: In this page, you can modify the PPP Username, PPP Password, Authentication
Method a
ccording to your requirement. Click Next, and the following page
appears.
49
Page 50
Step 7 . Click
: In this page, select a preferred wan interface as the system default gateway
Next
, and the following page appears.
Step 8
: In this page, you can get DNS server information from the selected WAN interface
or enter static DNS server IP addresses. If only a single PVC with IPoA or static
MER protocol is configured, you must e
Next
and the following page appears.
nter static DNS server IP
addresses. Click
: In this page, click Apply/Save to save all the configurations, aStep 9 nd the following
page appears. If you want to make any modifications, click Back.
50
Page 51

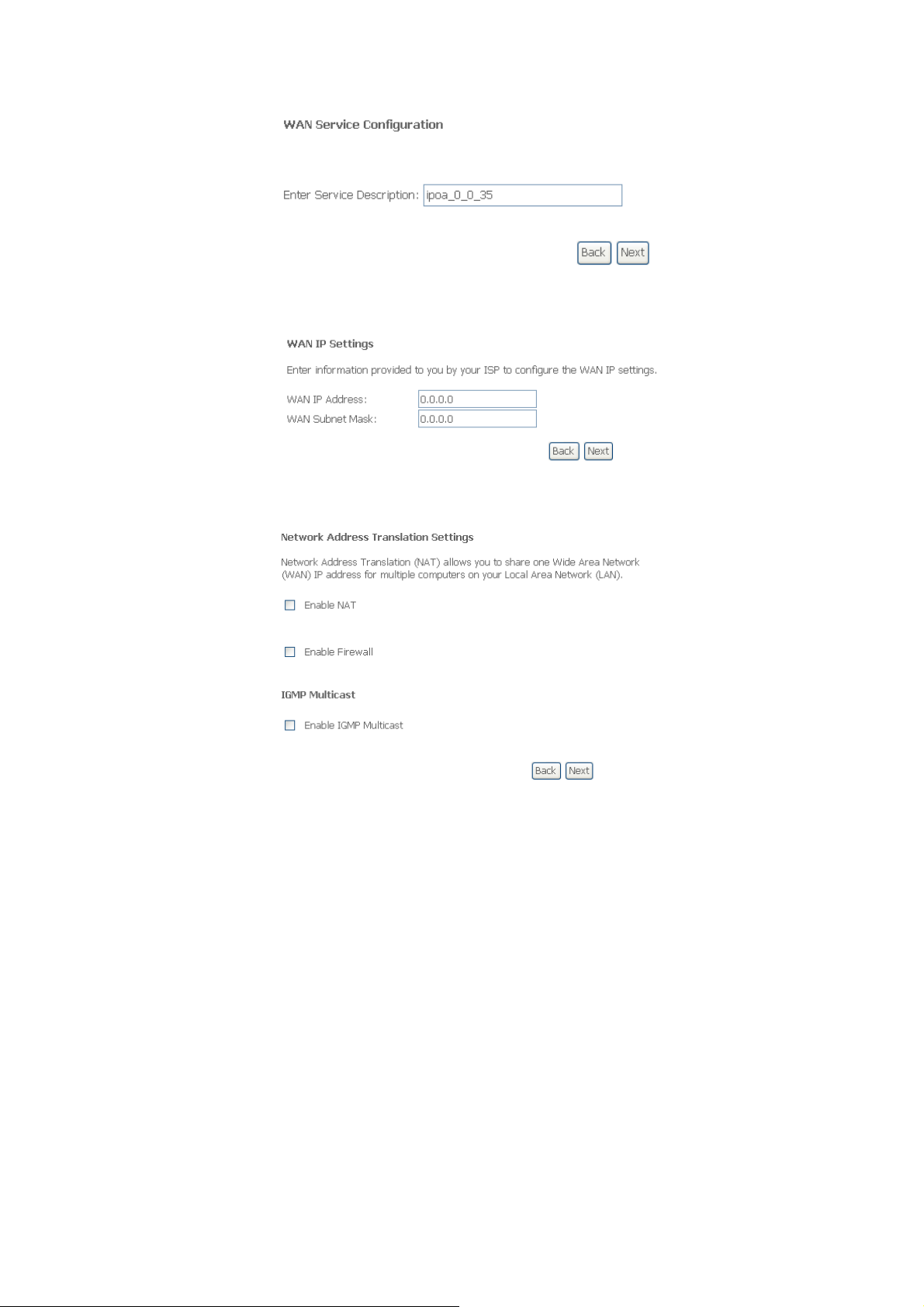
3.3.1.4 Add IPoA Configuration
This section describes the procedure for adding ipoa_0_0_35 (IPoA mode).
Step 1: You need to open the Layer2 Interface > ATM Interface page to add a PVC for
IPoA mode. Click Add and the following page appears.
Step 2: Select the DSL link type to IPoA, the Encapsulation Mode to
LLC/SNAP-ROUTING (according to the uplink equipment). Click Apply/Save, and
the following page appears.
Step 3: Return to the WAN Service page, and click Add. The following page appears.
51
Page 52
Step 4: After proper modifications, click Next, and the following page appears.
Step 5: In this page, you can modify the service description. Click Next, and the following
page appears.
Step 6: In this page, enter information provided to you by your ISP to configure the WAN
IP settings. Click Next, and the following page appears.
In this page, Network Address Translation (NAT) allows you to share one Wide Area
Network (WAN) IP address for multiple computers on your Local Area Network (LAN).
Enable NAT: Select it to enable the NAT function of the modem. If you do not want to
enable NAT, and wish the user of modem to access the Internet normally, you need to add
a route on the uplink equipment. Otherwise, the access to the Internet fails. Normally,
enable the NAT function.
52
Page 53

Step 7: Af ge appears.
ter proper selection, click Next, and the following pa
: In this page, select a preferred WAN interfacStep 8 default gateway.
Click Next,
and the following page appears.
e as the system
Step 9 imary
: In this page, you should use static DNS IP address for IPoA mode. Enter pr
DNS serv d secondary DNS server. Click Next,
er an and the following page
appears.
Click Apply/Save to save all the configurations. AnStep 10: d the following page appears.
If you want to make any modifications, click Back.
53
Page 54

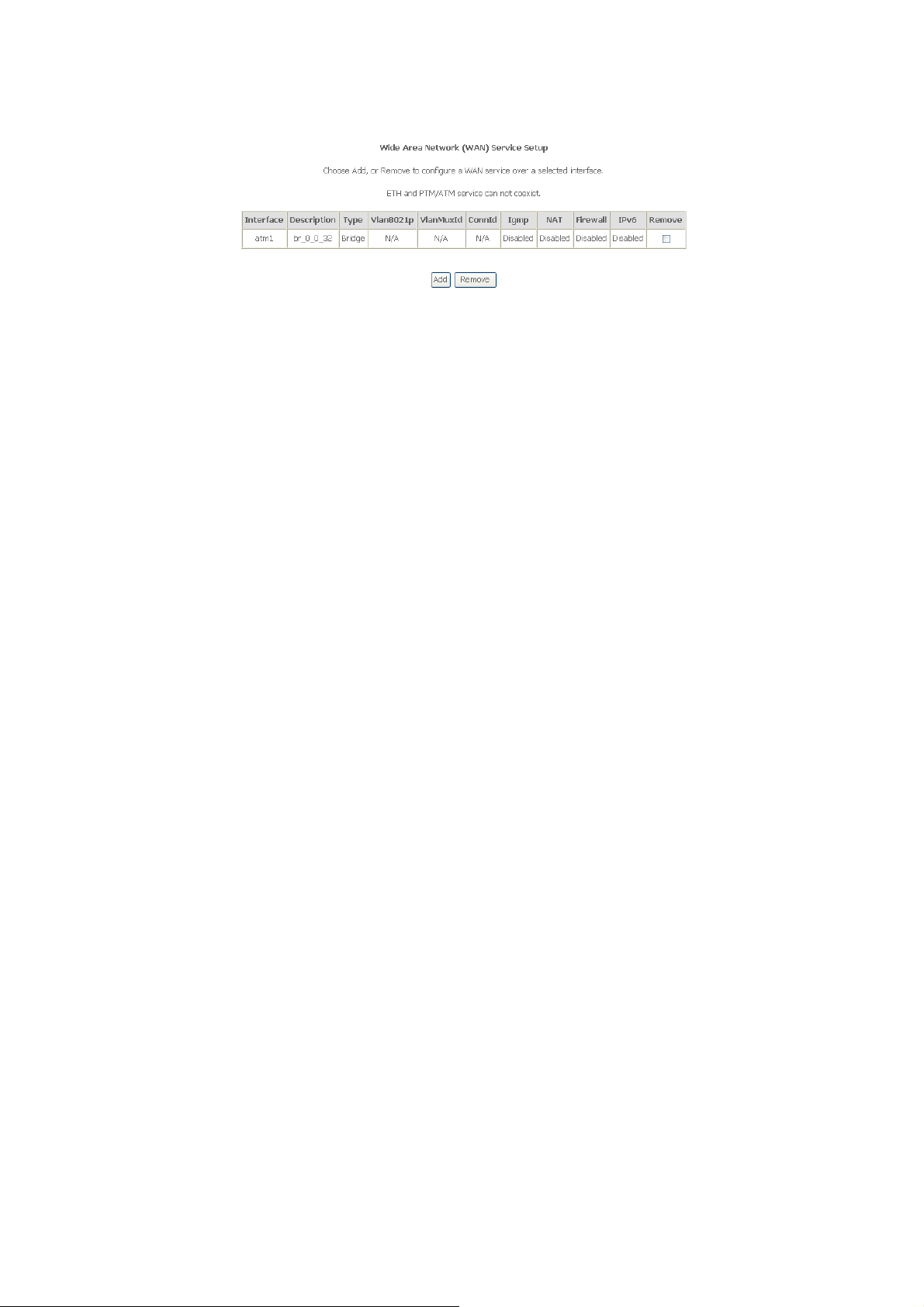
3.3.1.5 Add Bridge Configuration
In the WAN Service Setup page, click Add to add WAN configuration. This section
describes the procedure for adding br_0_0_32 (Bridge mode).
Step 1: Click Add to turn into the following page. (At first, you must add suitable ATM
configuration for this WAN configuration.) In this page, you can select ATM
Interface.
Step 2: Select an ATM Interface, such as atm1/(0_0_32). Click Next, and the following
page appears.
Step 3: In this page, you can modify the WAN service type, Service Description and
Enable IPv6 for this service. Click Next, and the following page appears.
54
Page 55
Step 4: Click Apply/Save to save all the configurations, and the following page appears.
To make any modifications, click Back.
55
Page 56

3.3.3 LAN configuration
Choose Advanced Setup > LAN, and the following page appears. In this page, you can
configure an IP address for the DSL Router or enable DHCP server.
In this page, you can modify the IP address of the device. The preset IP address is
192.168.1.1. This is the private IP address of the DSL Router, under which the device can
be reached in the local network. It can be freely assigned from the block of available
addresses. The IP address under which the Router can be reached from outside is
assigned by the ISP.
56
Page 57

3.3.4 NAT-- Network Address Translation
Overview
Setting up the NAT function
¾ The DSL Router comes equipped with the NAT (Network Address Translation)
function. With address mapping, several users in the local network can access the
Internet via one or more public IP addresses. All the local IP addresses are assigned
to the router's public IP address by default.
¾ One of the characteristics of NAT is that data from the Internet is not allowed into the
local network unless it has been explicitly requested by one of the PCs in the
network. Most Internet applications can run behind the NAT firewall without any
problems. For example, if you request Internet pages or send and receive e-mails,
the request for data from the Internet comes from a PC in the local network, and so
the router allows the data through. The router opens precisely one port for the
application. A port in this context is an internal PC address, via which the data is
exchanged between the Internet and a client on a PC in the local network.
Communicating via a port is subject to the rules of a particular protocol (TCP or
UDP).
¾ If an external application tries to send a call to a PC in the local network, the router
will block it. There is no open port via which the data could enter the local network.
Some applications, such as games on the Internet, require several links, i.e. several
ports so that the players can communicate with each other. In addition, these
applications must also be permitted to send requests from other users on the
Internet to users in the local network. These applications cannot be run if Network
Address Translation (NAT) has been activated.
¾ Using port forwarding (the forwarding of requests to particular ports) the router is
forced to send requests from the Internet for a certain service, e.g. a game, to the
appropriate port(s) on the PC on which the game is running. Port triggering is a
special variant of port forwarding. Unlike port forwarding, the DSL Router forwards
the data from the port block to the PC which has previously sent data to the Internet
via a certain port (trigger port). This means that approval for the data transfer is not
tied to one specific PC in the network, but rather to the port numbers of the required
Internet service. Where configuration is concerned, this means: You have to define
a so-called trigger port for the application and also the protocol (TCP or UDP) that
this port uses. You then assign the public ports that are to be opened for the
application to this trigger port. u The router checks all outgoing data for the port
number and protocol. If it identifies a match of port and protocol for a defined trigger
57
Page 58

port, then it will open the assigned public ports and notes the IP address of the PC
that sent the data. If data comes back from the Internet via one of these public ports,
the router allows it through and directs it to the appropriate PC. A trigger event
always comes from a PC within the local network. If a trigger port is addressed from
outside, the router simply ignores it.
Note:
An application that is configured for port triggering can only be run by one user in the
local network at a time.
As long as the public ports are open, they can be used by unauthorized persons to gain
access to a PC in the local network.
When the DSL Router is supplied, the NAT function (Network Address Translation) is
activated, i.e. all IP addresses of PCs in the local network are converted to the router's public
IP address when accessing the Internet. You can use the NAT settings to configure the DSL
Router to carry out the following tasks:
Note:
For the functions described below, the IP addresses of the PCs must remain unchanged. If
the IP addresses of the PCs are assigned via the DHCP server of the DSL Router, you must
select Never expires (see page79) as the settings in the Local Network menu entry for the
Lease time or assign static IP addresses for the PCs.
You can activate or deactivate the NAT function (by default the NAT function is activated).
58
Page 59
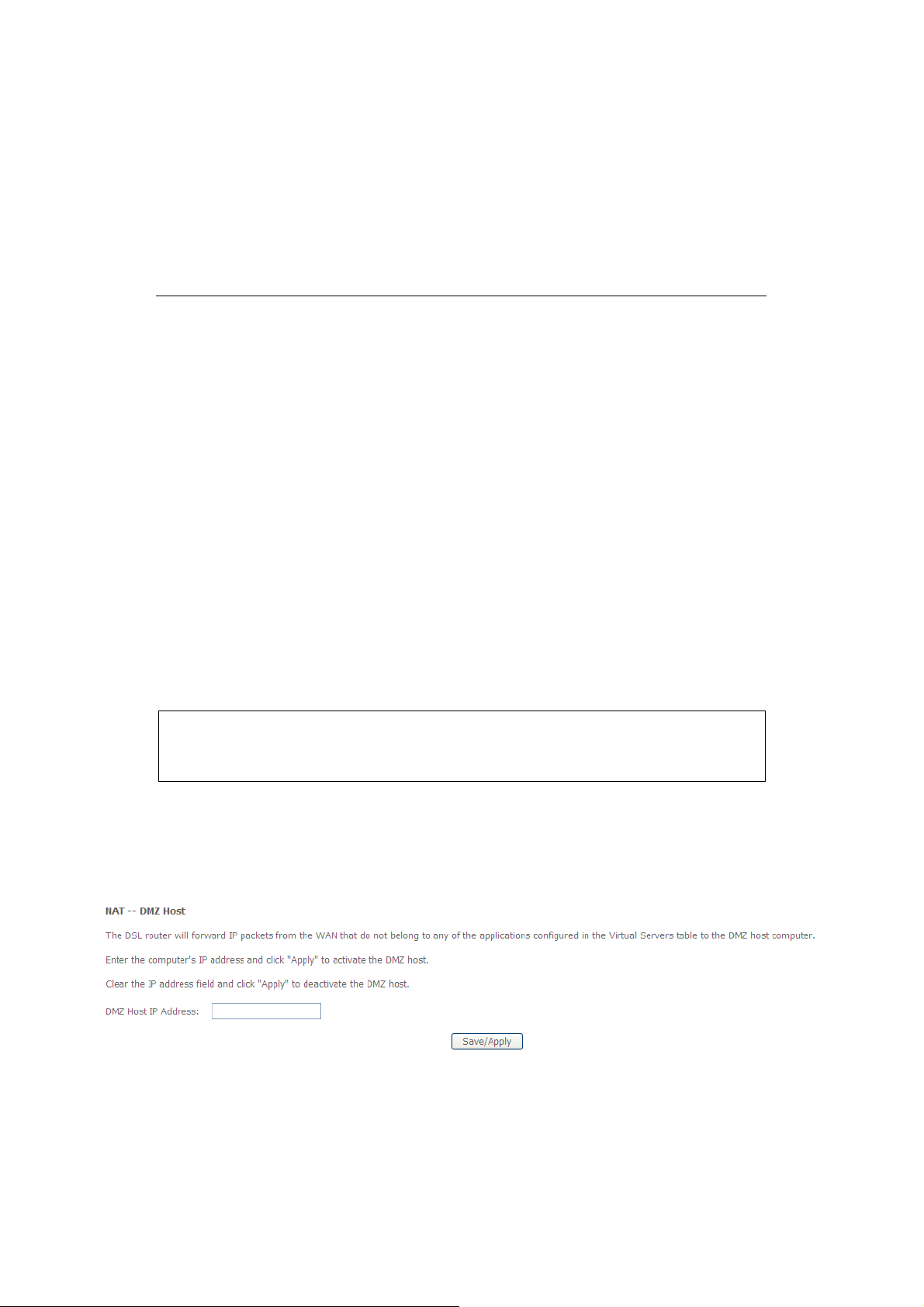
3.3.4.1 DMZ Host
The DMZ (Demilitarized) Host feature allows one local computer to be exposed to the
Internet. You wish to use a special-purpose Internet service, such as an on-line game or
video-conferencing Program, that is not present in the Port Forwarding list and for which no
port range information is available. You are not concerned with security and wish to expose
one computer to all services without restriction.
Note:
A DMZ host is not protected by the firewall and may be vulnerable to
attack. Designating a DMZ host may also put other computer sin the
home net work at risk. When using a DMZ host, you must consider the
security implications and protect it if necessary.
You can set up a client in your local network to be a so-called "DMZ host". Your device will
then forward all incoming data traffic from the Internet to this client. You can then, for
example, operate your own Web server on one of the clients in your local network and make
it accessible to Internet users. As the exposed host, the local client is directly visible to the
Internet and therefore particularly vulnerable to attacks (e.g. hacker attacks). Only activate
this function if it is absolutely necessary (e.g. to operate a Web server) and other functions
(e.g. port forwarding) are not adequate. In this case you should take appropriate measures
for the clients concerned.
Note:
Only one PC per public IP address can be set up as an Exposed Host
Add a DMZ host
¾ To set up a PC as an DMZ host, select DMZ Host from the Advanced SetupÆNATÆ
DMZ host
Figure: DMZ Host Config
¾ Enter the Local IP address of the PC that is to be enabled as an Exposed Host.
¾ Apply the settings by clicking “Save/Apply”.
59
Page 60

Remove DMZ host
Clear the DMZ Host Address
Apply setting by click Save/Apply
60
Page 61

3.3.4.2 Port Triggering
If you configure port triggering for a certain application, you need to determine a so-called
trigger port and the protocol (TCP or UDP) that this port uses. You then assign the public
ports that are to be opened for the application to this trigger port. You can select known
Internet services or assign ports or port blocks manually.
Add port Triggering
To set up port triggering for a service, select Port Triggering from the Advanced
¾ Settings Æ NAT Æ Port Triggering Æ add
Figure: Port Triggering
¾ Select the required application from the applications list.
If the application you require is not in the list, you must enter the relevant data on the
screen custom application
¾ Trigger port start and Trigger port end: Enter the port that is to be monitored for
outgoing data traffic.
¾ Trigger protocol: Select the protocol that is to be monitored for outgoing data traffic.
¾ Open Protocol: Select the protocol that is to be allowed for incoming data traffic
¾ Open port start and Open port end: Enter the port that is to be opened for incoming
traffic.
Note:
You can use a single port number, several port numbers separated by commas, port blocks
consisting of two port numbers separated by a dash, or any combination of these, for
example 80, 90-140, 180.
¾ Apply the settings by clicking “save/apply”
Remove port Triggering
Check remove box
Apply setting by click Save/Apply
61
Page 62

3.3.4.3 NAT -- Virtual Servers Setup
In its default state, DSL router blocks all external users from connecting to or communicating
with your net-work. Therefore the system is safe from hackers who may try to intrude on the
network and damage it. However, you may want to expose your network to the Internet in
certain limited and controlled ways in order to enable some applications to work from the
LAN (game, voice and chat applications, for example) and to enable Internet-access to
servers in the home network. The Port Forwarding feature supports both of these
functionalities. If you are familiar with networking terminology and concepts, you may have
encountered this topic referred to as “Local Servers” The Port Forwarding screen lets you
define the applications that require special handling by DSL router .All you have to do is
select the application protocol and the local IP address of the computer that will be using or
providing the service. If required, you may add new protocols in addition to the most
common ones provided by DSL router. For example, if you wanted to use a File Transfer
Protocol (FTP) application on one of your PCs, you would simply select FTP from the list and
enter the local IP address or host name of the designated computer. All FTP-related data
arriving at DSL router from the Internet will henceforth be forwarded to the specific computer.
Similarly, you can grant Internet users access to servers inside your home network, by
identifying each service and the PC that will provide it. This is useful, for example, if you
want to host a Web server inside your home network. When an Internet user points his/her
browser to DSL router external IP address, the gateway will forward the incoming HTTP
request to your Web server. With one external IP address (DSL router main IP address),
different applications can be assigned to your LAN computers, however each type of
application is limited to use one computer. For example, you can de net hat FTP will use
address X to reach computer A and Telnet will also use address X to reach computer A, but
attempting to define FTP to use address X to reach both computer A and B will fail. DSL
router therefore provides the ability to add additional public IP addresses to port forwarding
rules, which you must obtain from your ISP, and enter into the NT IP Addresses Pool (see
section 7.3.7). You will then be able to define FTP to use address X to reach computer A and
address Y to reach computer B. Additionally, port forwarding enables you to redirect traffic to
a different port instead of the one to which it was designated. Lets say, that you have a Web
server running on your PC on port 8080 and you want to grant access to this server to any
one who accesses DSL router via HTTP To accomplish this, do the following:
¾ Define a port forwarding rule for the HTTP service, with the PC IP or host name.
¾ Specify 8080 in the Forward to Port’ field.
All incoming HTTP traffic will now be forwarded to the PC running the Web server on port
8080 when setting a port forwarding service; you must ensure that the port is not already in
use by another application, which may stop functioning. A common example is when using
SIP signaling in Voice over IP the port used by the gateway VoIP application (5060) is the
same port on which port forwarding is set for LAN SIP agents.
62
Page 63

Note:
Some applications, such as FTP, TFTP, PPTP and H323, require the support of special
specific Application Level Gateway (ALG) modules in order to work inside the home network.
Data packets associated with these applications contain information that allows them to be
routed correctly. An ALG is needed to handle these packets and ensure that they reach their
intended destinations. DSL router is equipped with a robust list of ALG modules in order to
enable maximum functionality in the home network The ALG is automatically assigned
based on the destination port
Add Port Forwarding
¾ To set up Virtual Servers for a service, select the Advanced Setup Æ NAT Æ Virtual
Servers and click “add” to add the Virtual Server.
Figure: Add virtual Servers
¾ Select a service ,or custom your server
¾ Set Server IP address
¾ Enter the Set Server IP address of the computer that will provide the service (the
server in the Local Host field. Note that unless an additional external IP address has
been added, only one LAN computer can be assigned to provide a specific service
or application.
¾ Set External port start external port end
¾ Select protocol
¾ Set Internal port start and internal port end
¾ Entry Remote IP
¾ Click OK to apply the settings
If the application you require is not in the list, you must manually enter the relevant data on
the screen:
Select the protocol for the service you are providing from the Protocol list. Under Public port,
enter the port number of the service you are providing. In the Local port field, enter the
internal port number to which service requests are to be forwarded. In the Local IP address
field, enter the IP address of the PC that provides the service.
63
Page 64

Example: the Web server has been configured to react to requests on port 8080. However,
the requests from websites enter the Web server via port 80 (standard value). If you add the
PC to the forwarding table and define port 80 as the public port and port 8080 as an internal
port, all requests from the Internet are diverted to the service with the port number 80 on the
Web server of the PC you have defined with port 8080.
Note:
You can use a single port number, several port numbers separated by commas, port blocks
consisting of two port numbers separated by a dash, or any combination of these, for
example 80, 90-140, 180.
Del Port Forwarding
¾ Click remove box
¾ Click remove to apply the settings
64
Page 65

3.3.5 Security
Security is an important function of DSL; it protects the resources of a private network from
users from other networks. Also the item prevents unauthorized internet users form
accessing private networks connected to the internet. All messages entering or leaving the
intranet (i.e., the local network to which you are connected) must pass through the security
examines, which examines each message and blocks those that do not meet the specified
security criteria.
There are three basic types of security techniques:
z IP packet filtering: The system examines each packet entering or leaving the
network and accepts or rejects it based on user-defined rules. Packet filtering is
fairly effective and transparent to users, but it is difficult to configure.
z Circuit-level gateway implementation: This process applies security mechanisms
when a TCP or UDP connection is established. Once the connect has been made,
packets can flow between the hosts without further checking.
z MAC frame filtering: The system examines each frame entering or leaving the
network form layer 2. And accord to user-defined rules accepts and rejects frame.
A security management program can be configured one of two basic ways:
z A default-deny policy.
z A default-allow policy.
A default-deny approach to security is by far the more secure, but due to the difficulty in
configuring and managing a network in that fashion, many networks instead use the
default-allow approach. Let's assume for the moment that your security management
program utilizes a default-deny policy, and you only have certain services enabled that you
want people to be able to use from the Internet.
NOTE: The security is like a firewall.
Figure: the Security application
Click “Security” -->” IP Filtering” to show the following interface. By default, the firewall is
enabled. The firewall is used to block document transmissions between the Internet and
your PC. It serves as a safety guard and only permits authorized documents to be sent into
the LAN.
Note: If the Router configured as bridge mode, the IP Filtering will disabled and the IP
filtering interface will disappear.
And if the Router configured as Non-Bridge mode PVC, the MAC Filtering will disabled
and the MAC Filtering interface will disappear.
65
Page 66
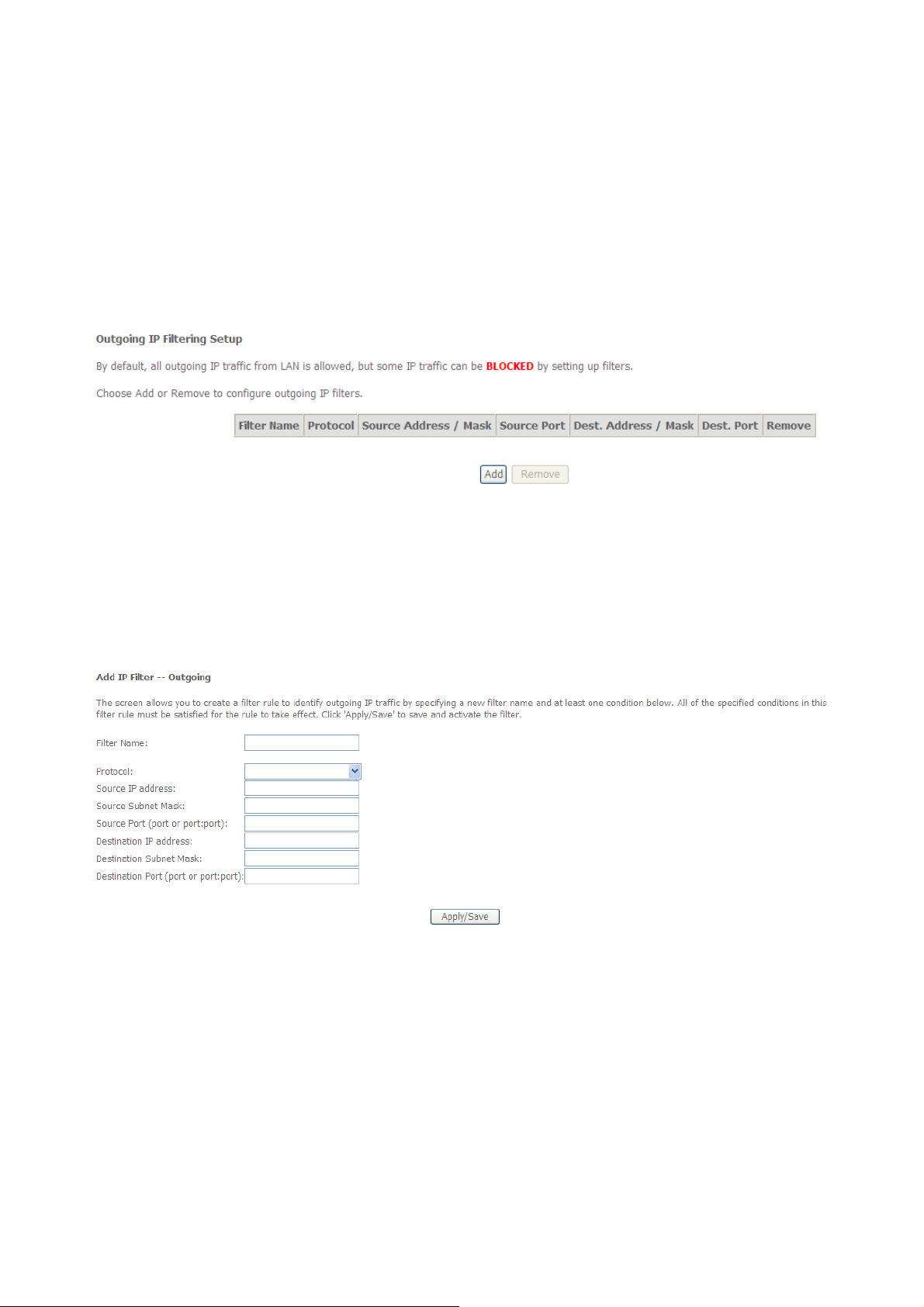
3.3.5.1 Outgoing IP Filtering Setup
When Outgoing IP Filtering rules setup being enable on the ROUTER, the various security
functions for the local network will enable at the same time .You can protect the network
against hacker attacks and block individual PC’s access to selected services or internet
sites.
Click “Security”-->” IP Filtering”-->” Outgoing” to show the following interface.
By default, all outgoing IP traffic from LAN is allowed, but some IP traffic can be BLOCKED
by setting up filters.
Figure: Outgoing IP Filtering Config
Click “Add” to enter the related interface defining the IP filtering rule as follows.
The screen allows you to create a filter rule to identify outgoing IP traffic by specifying a new
filter name and at least one condition below. All of the specified conditions in this filter rule
must be satisfied for the rule to take effect. Click 'Save/Apply' to save and activate the filter.
Figure: Outgoing IP Filtering Add Setup
66
Page 67
Filter Name: Enter the name of outgoing filter rule
Protocol: Select one among TCP/UDP TCP UDP or ICMP protocols
Source IP address: Enter an IP address. When you have set IP address, the outgoing
packet (protocol selected packet) will block.
Source subnet mask
Source port : UPD/TCP source port or a range of ports
Destination IP address: Destination IP (default no set)
Destination subnet mask:
Destination port : UPD/TCP destination port or a range of ports
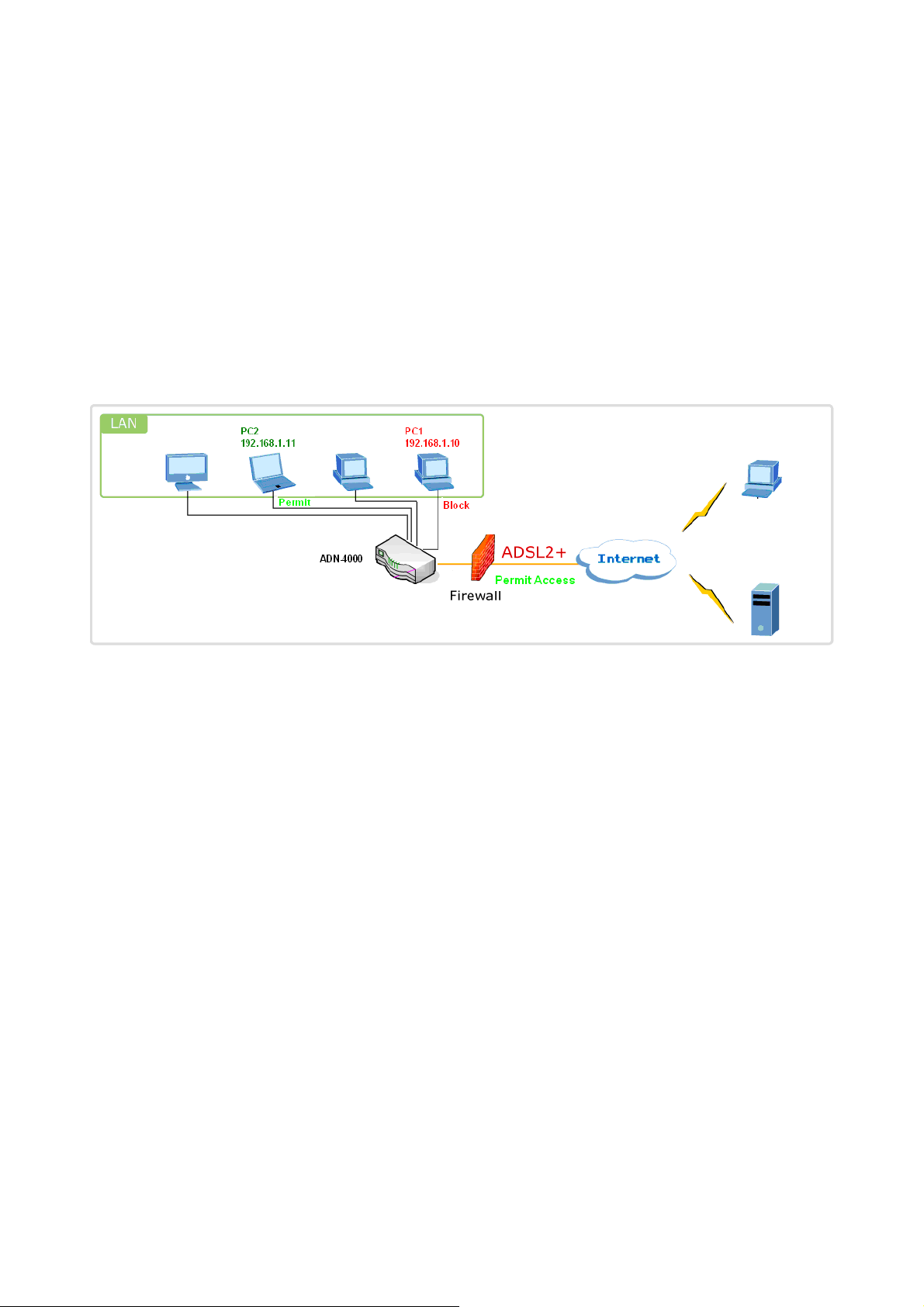
There is an example to introduce how to configure the outgoing IP Filtering.
The topology is as follows:
Figure: Outgoing IP filer application
Request:
z I need to block a whose IP address is 192.168.1.10. All outgoing UDP/TCP packet
from that PC1(192.168.1.10) is disallowed.
z Allow all outgoing traffic packet from PC2 (192.168.1.11).
67
Page 68

Configuration:
1. By default, all outgoing IP traffic from LAN is allowed, so allow all the IP packet
come for the PC2.
2. The detailed configuration steps are as follows:
Figure: Outgoing IP Filtering Add Setup example
3. Click “Save/apply” to show below.
Figure: Outgoing IP Filtering Config Complete
68
Page 69

3.3.5.2 Incoming IP Filtering Setup
The incoming IP filter is used to block and permit IP packet transmisstion from internet. By
default incoming IP filter block all incoming packet from internet. When incoming IP Filtering
rules setup being enable on the ROUTER, you can permit remote individual PC to access
various local network service .
Click “Security”-->” IP Filtering”-->” Incoming” to show the following interface.
By default, all incoming IP traffic from the WAN is blocked when the firewall is enabled.
However, some IP traffic can be ACCEPTED by setting up filters.
Figure: Incoming IP Filtering Config
Click “Add” to enter the related interface defining the IP filtering rule as follows.
The screen allows you to create a filter rule to identify incoming IP traffic by specifying a new
filter name and at least one condition below. All of the specified conditions in this filter rule
must be satisfied for the rule to take effect. Click 'Save/Apply' to save and activate the filter.
And you must select at least one or multiple WAN interfaces to apply this rule.
Figure: Incoming IP Filtering Add Setup
69
Page 70
Filter Name: Enter the name of incoming filter rule
Protocol: Select one among TCP/UDP TCP UDP or ICMP protocols
Source IP address: Enter an IP address. When you have set IP address, the incoming
packet (protocol selected packet) will allow.
Source subnet mask:
Source port : UPD/TCP source port or a range of ports
Destination IP address: Destination IP (default no set)
Destination subnet mask:
Destination port : UPD/TCP destination port or a range of ports
Wan interfaces: You can select WAN interfaces and PVC
There is an example to introduce how to configure the incoming IP Filtering:
Figure: incoming IP filer application
Request:
z I need to permit a PC whose IP address is 10.10.10.10. All Incoming TCP/UDP packet
traffic from that PC(10.10.10.10) is allowed.
z Block all IP traffic from other PC .
70
Page 71

Configuration:
1. By default, all incoming IP traffic from internet is blocked, so all the IP packets
come for the internet are blocked.
2. The detailed configuration steps are as follows:
Figure: Incoming IP Filtering Add Setup example
3. Click “Save/apply” to show below.
Figure: Incoming IP Filtering Config Complete
71
Page 72

3.3.5.3 MAC Filtering Setup
May be you want manage Layer 2 MAC address to block or permit a computer within the
home network .when you enable MAC filter rules ,the ROUTER serves as a firewall which
work at layer 2.
Click “Security”-->”MAC Filtering” to show the following interface.
Note: MAC Filtering is only effective on ATM PVCs configured in Bridge mode. If the ATM
PVCs is configured in other routing mode(such as PPPoE mode), the “MAC Filtering Setup”
will not appears in the “Security” option.
FORWARDED means that all MAC layer frames will be FORWARDED except those
matching with any of the specified rules in the following table. BLOCKED means that all
MAC layer frames will be BLOCKED except those matching with any of the specified rules
in the following table.
Figure: MAC Filtering Setup overview
72
Page 73

Click “add” to add MAC filter rules. The interface shows below.
Figure: MAC Filtering Add Config
Protocol Type: Select one among PPPoE IPV4 IPV6 AppleTalk IPX NETBEUI or ICMP
protocols
Destination MAC Address:
Source MAC Address :
Frame Direction: The direction of transmit frame, you can select LAN->WAN (from LAN
to WAN) WAN -> LAN (from WAN to LAN) LAN Ù WAN.
WAN Interface: Select a WAN interface.
73
Page 74
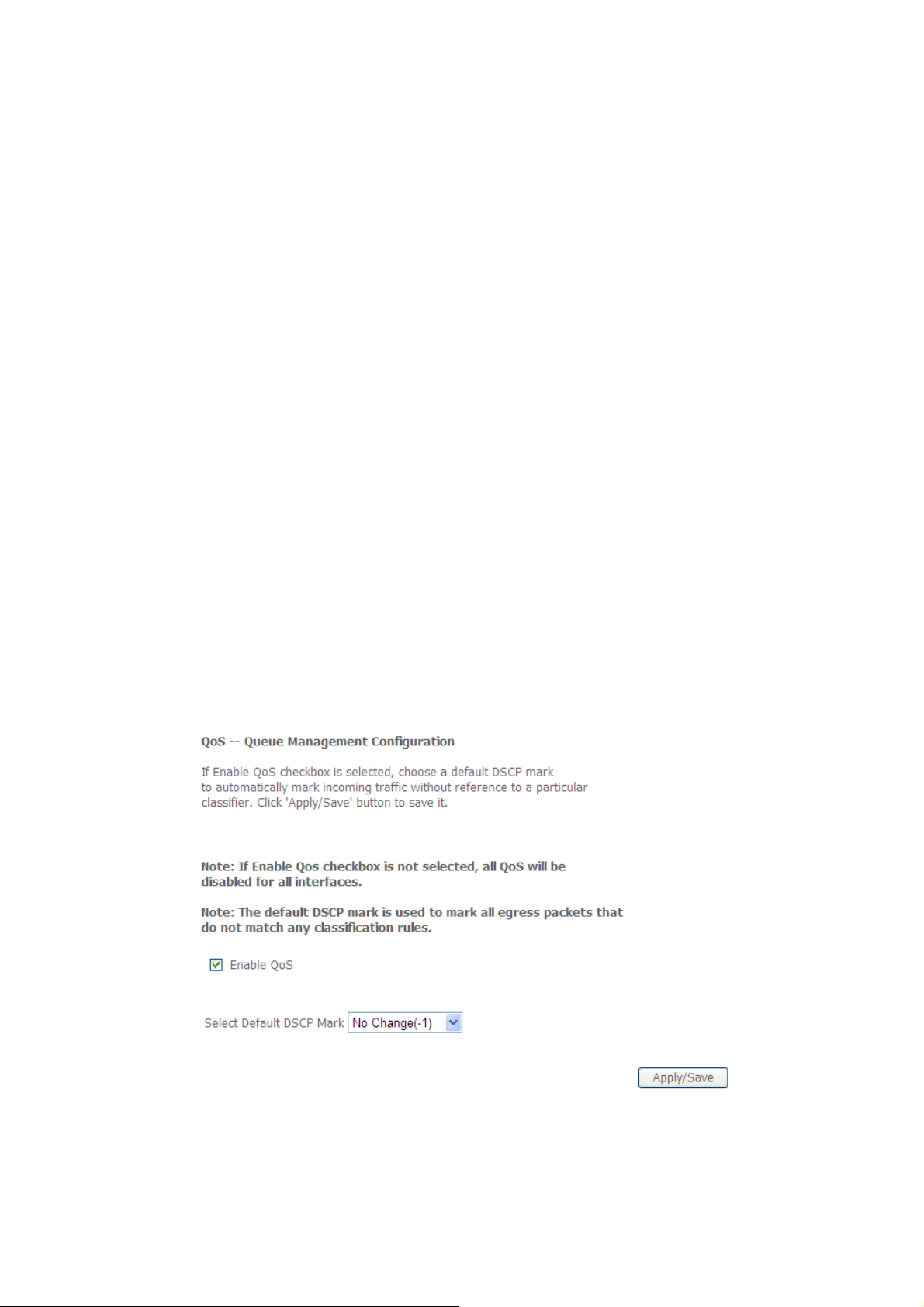
3.3.6 Quality of Service
Many communication and multimedia applications require large, high speed bandwidths to
transfer data between the local network and the internet. However, for many applications
there is often only one internet connection available with limited capacity. QoS (Quality of
Service) divides this capacity between the different applications and provides underplayed,
continuous data transfer where data packets with higher priority are given preference.
Click “Quality of Service” to show the following interface. Under “Quality of Service”, there
are two network share mode:” Queue Config”, ”QoS Classification”.
Quality of Service (QoS) for networks is an industry-wide set of standards and mechanisms
for ensuring high-quality performance for critical applications. By using QoS mechanisms,
network administrators can use existing resources efficiently and ensure the required level
of service without reactively expanding or over-provisioning their networks.
Traditionally, the concept of quality in networks meant that all network traffic was treated
equally. The result was that all network traffic received the network’s best effort, with no
guarantees for reliability, delay, variation in delay, or other performance characteristics. With
best-effort delivery service, however, a single bandwidth-intensive application can result in
poor or unacceptable performance for all applications. The QoS concept of quality is one in
which the requirements of some applications and users are more critical than others, which
means that some traffic needs preferential treatment.
3.3.6.1 Enable QoS
In this interface, you can do QoS queue management configuration. By default, the system
is enable QoS and set a default DSCP mark to automatically mark incoming traffic without
reference to particular classifier.
Click ”Advance Setup”Æ”Quality of Classification” to show following interface:
Figure: QoS queue management configuration
Choose “Enable QoS” can enable QoS and the system can set default DSCP mark
74
Page 75

oS.Click “save/Apply” to active Q
75
Page 76

3.3.6.2 QoS--Queue Config
The queuing in packet QoS will become effective only when packet is forwarded to
QoS-enabled PVC. Packet forwarding is determined by IP routing or bridging, not under
ontrol of the pac cket QoS.
Click “Queue Config” to pop up an interface as below. In this interface, you can configur
e
QoS Queue. A maximum 24 entries can be configured.
QoS Queue Configuration can allocated three queues .Each of the queues can be
configured for a precedence value (Lower integer values for precedence imply higher
priority for this queue relative to others). The queue entry configured here will be used by th
e
classifier to place ingress packets appropriately.
Figure:QoS Queue Config overview
NOTE:
Lower integer values for precedence imply higher priority for this queue relative to others.
For example: add a QoS queue entry and allocate it to a specific network interface (PVC
0/8/81) 。Set integer values for queue precedence are 2.
Step 1. Click “add ” bottom to show following interface:
Figure: QoS Queue Config
76
Page 77

Name: Fill a name for the entry.
Enable: Enable or Disable to configure a QoS queue entry.
Interface: select a specific network interface. When you have already selected a
network interface, the specific network interface selected will automatically allocate to
the queue
Precedence: select an integer value for queue precedence. When you have already
selected a integer value, the queue entry will place to ingress packets appropriate
ly.
Lower integer values for precedence imply higher priority for this queue relative to
others.
Step 2.
Add a QoS queue entry and assign it to a specific network interface, set integer
values for queue precedence is 2. Show following interface:
Step 3.
After proper modifications, click “Save/Apply”. (This configuration will take effective
at once.)
If you want to delete a certain queue, you can disable this queue and choose this queue, last
click “Remove” button to delete it.
After the queue config is already configured, you can create several traffic class rules to
classify the upstream traffic.
77
Page 78

3.3.6.3 QoS -- QoS Classification
Some application require that specific bandwidths ensure its data be forward in the time.
QoS classification can creates traffic class rule to classify the upstream traffic. Assign queue
which defines the precedence and the interface and optionally overwrite the IP
header
DSCP byte. After QoS classification, QoS divides capacity between the different
applications and provides un-delayed, continuous data transfer where data packet wit
h
higher priority are given preference. The follow diagram show how QoS classify the
Click “QoS Classification” to pop up an interface as below. In this interface, you can
configure network traffic classes.
Figure: QoS Classification Conifg overview
Click “Add” to show the following interface.
78
Page 79

Figure: QoS Classification Conifg
79
Page 80

3.3
.7 Routing
3.3.7.1 Routing – Default Gateway
In this interface, you can modify the Default Gateway settings.
If Enable Automatic Assigned Default Gateway checkbox is selected, this router will accept
the first received default gateway assignment from one of the PPPoA, PPPoE or
MER/DHCP enabled PVC(s). If the checkbox is not selected, enter the static default
gateway AND/OR a WAN interface. Click 'Save/Apply' button to save it.
NOTE:
If changin
g the Automatic Assigned Default Gateway from unselected
to selected, You must reboot the router to get the automatic assigned
default gateway.
Figure: Default Gateway
80
Page 81
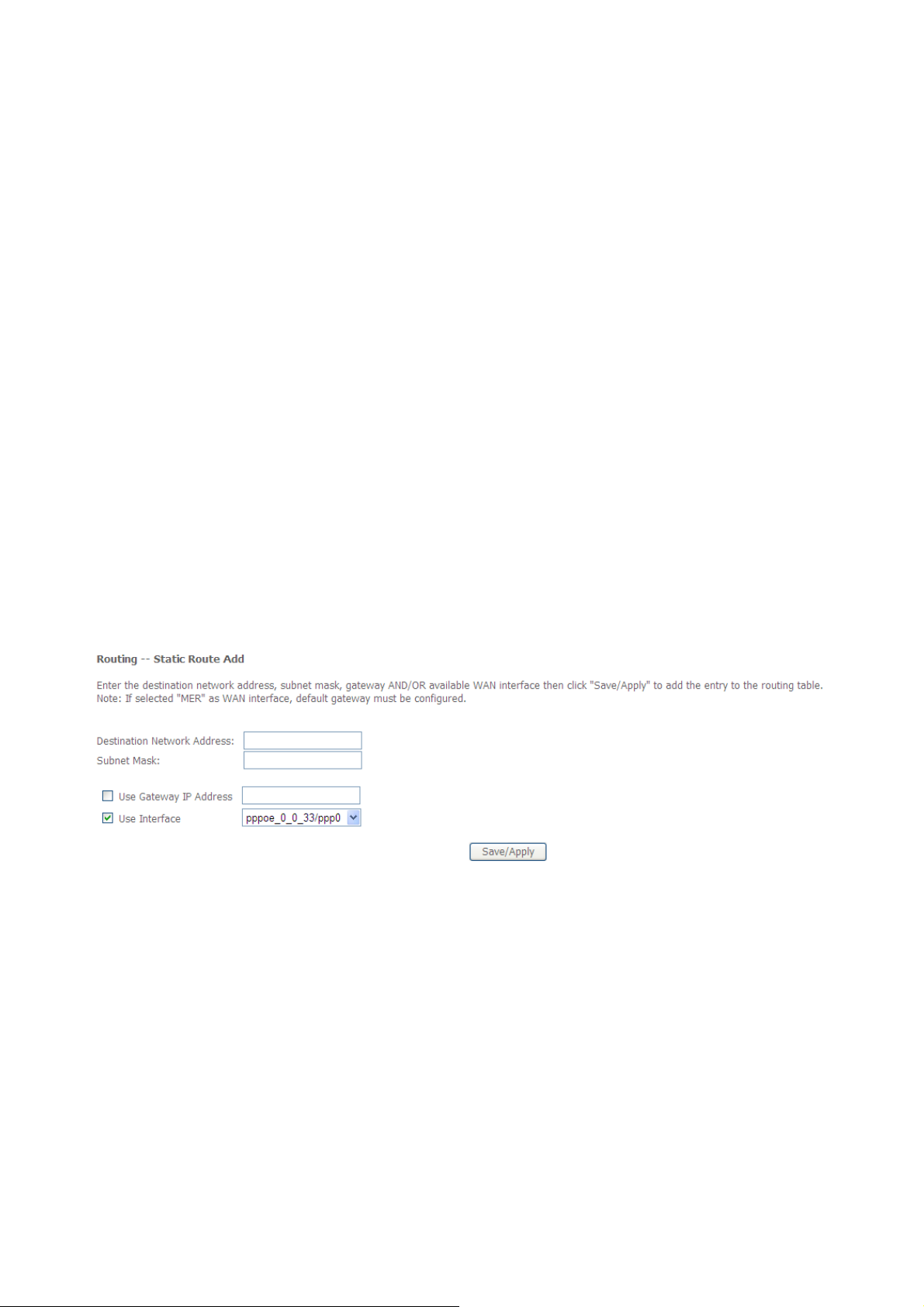
3.3.7.2 Sta
Networking d
tic Routes
evices forward packets using route information that is either manually
configured or dynamically learned using a routing protocol. Static routes are manually
configured and define an explicit path between two networking devices. Unlike a dynamic
routing protocol, static routes are not automatically updated and must be manu
ally
reconfigured if the network topology changes. The benefits of using static routes include
security and resource efficiency. Static routes use less bandwidth than dynamic routing
protocols and no CPU cycles are used to calculate and communicate routes. The main
disadvantage to using static routes is the lack of automatic reconfiguration if the network
topology changes.
Static routes can be redistributed into dynamic routing protocols but routes generated by
dynamic routing protocols cannot be redistributed into the static routing table. No algorithm
exists to prevent the configuration of routing loops that use static routes.
Static routes are useful for smaller networks with only one path to an outside network and to
provide security for a larger network for certain types of traffic or links to other networks that
need more control. In general, most networks use dynamic routing protocols to
communicate between networking devices but may have one or two static routes
configured for special cases
Figure: Static routes Add Config
Add static route
¾ Enter destination network address
¾ Enter subnet Mask
¾ Enable “Use Gateway IP Address” and enter IP address
¾ Select use interface
¾ Apply setting by click Save/Apply
81
Page 82

3.3.7.3 RIP
Background
The Routing Information Protocol, or RIP, as it is more commonly called, is one of the most
enduring of all routing protocols. RIP is also one of the more easily confused protocol
because a variety of RIP-like routing protocols proliferated, some of which even used
the same name! RIP and the myriad RIP-like protocols were based on the same set of
algorithms that us se distance vectors to mathematically compare routes to identify the best
path to any given destination address. These algorithms emerged from academic research
that dates back to 1957. Today's open standard version of RIP, sometimes referred to as IP
RIP, is formally defined in two documents: Request For Comments (RFC) 1058 and
Internet Standard (STD) 56. As IP-based networks became both more numerous and
greater in size, it became apparent to the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) that RIP
needed to be updated. Consequently, the IETF released RFC 1388 in January 1993, which
was then superseded in November 1994 by RFC 1723, which describes RIP 2 (the second
version of RIP). These RFCs described an extension of RIP's capabilities but did not
attempt to obsolete the previous version of RIP. RIP 2 enabled RIP messages to carry
more information, which permitted the use of a simple authentication mechanism to secure
table updates. More importantly, RIP 2 supported subnet masks, a critical feature that was
not available in RIP.
This chapter summa
rizes the basic capabilities and features associated with RIP. Topics
include the routing update process, RIP routing metrics, routing stability, and routing timers.
Routing Updates
RIP sends routing-update messages at regular intervals and when the network topology
changes. When a router receives a routing update that includes changes to an entry, it
updates its routing table to r
eflect the new route. The metric value for the path is increased
by 1, and the sender is indicated as the next hop. RIP routers maintain only the best route
(the route with the lowest metric value) to a destination. After updating its routing table, the
router immediately begins transmitting routing updates to inform other network routers of
the change. These updates are sent independently of the regularly scheduled updates that
RIP routers send
82
Page 83

RIP Routing Metric
RIP uses a single routing metric (hop count) to measure the distance between the source
and a destination network. Each hop in a path from source to destination is assigned a hop
count value, which is typically 1. When a router receives a routing update that contains a
new or changed destination network entry, the router adds 1 to the metric value indicated in
the update and en
as the next hop
RIP configuration
ters the network in the routing table. The IP address of the sender is used
Figure: RIP Configuration
¾
To activate RIP for the device, select the 'Enabled' radio button for Global RIP Mode.
¾
To configure an individual interface, select the desired RIP version and operation,
followed by placing a check in the 'Enabled' checkbox for the interface.
Click the 'Save/Apply' button to save the configuration, and to start or stop RIP based on the
Global RIP mode selected.
83
Page 84

3.3.8 DNS
Short for Domain Name System (or Service or Server), an Internet service that translates
domain names into IP addresses. Because domain names are alphabetic, they're easier to
remember. The Internet however, is really based on IP addresses. Every time you use a
domain name, therefore, a DNS service must translate the name into the corresponding IP
address. For example, the domain name www.example.com might translate to
198.105.232.4.
The DNS system is, in fact, its own network. If one DNS server doesn't know how t
o
translate a particular domain name, it asks another one, and so on, until the correct IP
address is returned.
3.3.8.1 DNS Server
In this interface, you can modify the DNS server settings.
Figure: DNS Server Configuration overview
If 'Enable Automatic Assigned DNS' checkbox is selected, this router will accept the first
received DNS assignment from one of the PPPoA, PPPoE or MER/DHCP enabled PVC(s)
during the connection establishment.
If the checkbox is not selected, enter the primary and optional secondary DNS server IP
addresses. The interface is below.
84
Page 85

Figure: DNS Server Add Configuration
Click 'Save' button to save the new configuration.
NOTE: You must reboot the router to make the new configuration effective.
85
Page 86

3.3.8.2 Dynamic DOMAIN NAME SERVICE (DDNS)
OVERVIEW
Dynamic DNS allows binding of domain names to hosts with dynamically assigned IP
addresses by a Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server and updates the name server
with the new information about the host or the network. This is particularly useful to
broadband users hosting internet services such as File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Hyper Text
Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) on their local hosts
connected to the broadband network at home. Dynamic DNS allows access to such hosts
connected to the broadband networks using a domain name to exchange files, send receiv
e
email with highly personalized email addresses and host a website. The primary
requirement in such case is for the domain name to be associated with the ever changing IP
address of the host or the network. For more details about dynamic DNS please refer to
RFC 2136.
To provide such support for the feature described above, a client is installed in the host
serving the internet traffic directed to the domain. The client updates the IP address of the
host whenever the host renegotiates the IP address for any reason. The system provides
support for dynamic DNS allows the users to configure the following dynamic DNS servers
for DDNS service:
¾
DynDNS.org: A free DNS service for hosts with dynamic IP addresses.
¾
TZO: A service provider providing dynamic and static DNS services for a fee.
To use one of the providers mentioned above requires the users to register with the dynamic
DNS service provider the information about the host and the install the client software on the
host which can update the nd the domain name
formation.
in
service provider with the IP address a
CONFIGURATION
The DDNS feature in Linux reference software requires to be configured in the
menu config
to include the support for this feature. Once the software support is configured to be built fo
a profile, this feature can be configured using the WEB UI as:
¾ Choose the Advanced Setup from the WEB UI, choose the DNS menu item under
Advanced
¾ Setup and select the Dynamic DNS menu item under DNS.
r
Figure: Dynamic DNS Configuration overview
86
Page 87

¾ Click the Add button to configure new host information.
Figure: Dynamic DNS Add Configuration
D-DNS provider: Dynamic DNS provider’s website.
Hostname: This is the domain name which can be modified.
Interface: The interface that the packets pass through on the ROUTER.
Username: This is the Username needed access the DDNS’s management interface.
Password: This is the Password you will be prompted to enter when you access the
DDNS’s management interface.
¾ Select the service provider for the DDNS service; provide the hostname and the
interface to use when sending the DDNS updates. Also enter the service provider
specific registration information and click Save/Apply to use the feature.
87
Page 88

3.3.9 DSL
In this interface, you can check the DSL settings. Mostly, the user just need to remain this
factory default setting. Our Router support these modulations: G.Dmt, G.lite, T1.413, ADSL2,
AnnexL, ADSL2+ and AnnexM. The ROUTER will negotiate the modulation mode with the
DSLAM.
Figure: DSL modulation settings
88
Page 89

3.3.10 Interface Gr
ouping
Interface Grouping supports multiple ports to PVC and bridging groups. Each group will
perform as an independent network. To support this feature, you must create mapping
groups with appropriate LAN and WAN interfaces using the Ad
d button. The Remove button
will remove the grouping and add the ungrouped interfaces to the Default group. Only the
default group has IP interface.
Selecting the “Enable virtual ports” button in WEB UI “Interface Grouping” page will create
three virtual interfaces within the system. Each virtual interface represents a physical
Ethernet port within the external Ethernet Switch.
89
Page 90

3.3.11 Certificate
To use Cert
are two menu items under “Certificate” menu: “Local” a
ificate user interface, choose “Certificate” under “Advanced Setup” menu. There
nd “CA”. For either type of certificate,
the base screen shows a list of certificates stored in Router.
Figure:
Local
Certificate overview
In the menu, “Local” means local certificates. “Trusted CA” means trusted Certificate
Authority certificates. Local certificates preserve the identity of the Router. CA certificates
are used by the Router to very certificates from other hosts.
Local certificates can be created by two ways:
z Create a new certificate request, have it signed by a certificate authority and load
the signed certificate
z Import an existing signed certificate directly
3.3.11.1 Create New Local Certificate
Certificate name:
Creates an SSL certificate in the specified certificate repository (administrator's or domain's
repository) by using a private key file and a corresponding certificate file.
Common Name:
The common name is the "fully qualified domain name," (or FQDN) used for DNS lookups of
your server (for example, www.mydomain.com). Browsers use this information to identify
your Web site. Some browsers will refuse to establish a secure connection with your site if
the server name does not ma icate. Please do not include
tch the common name in the certif
the protocol specify "http://" or any port numbers or pathnames in the common name. Do not
use wildcard characters such as * or ? and do not use an IP address.
Organization Name:
The name of the organization to which the entity belongs (such as the name of a company).
State/Province Name:
This is the name of the state or province where your organization's head office is located.
Please enter the full name of the state or province.
90
Page 91
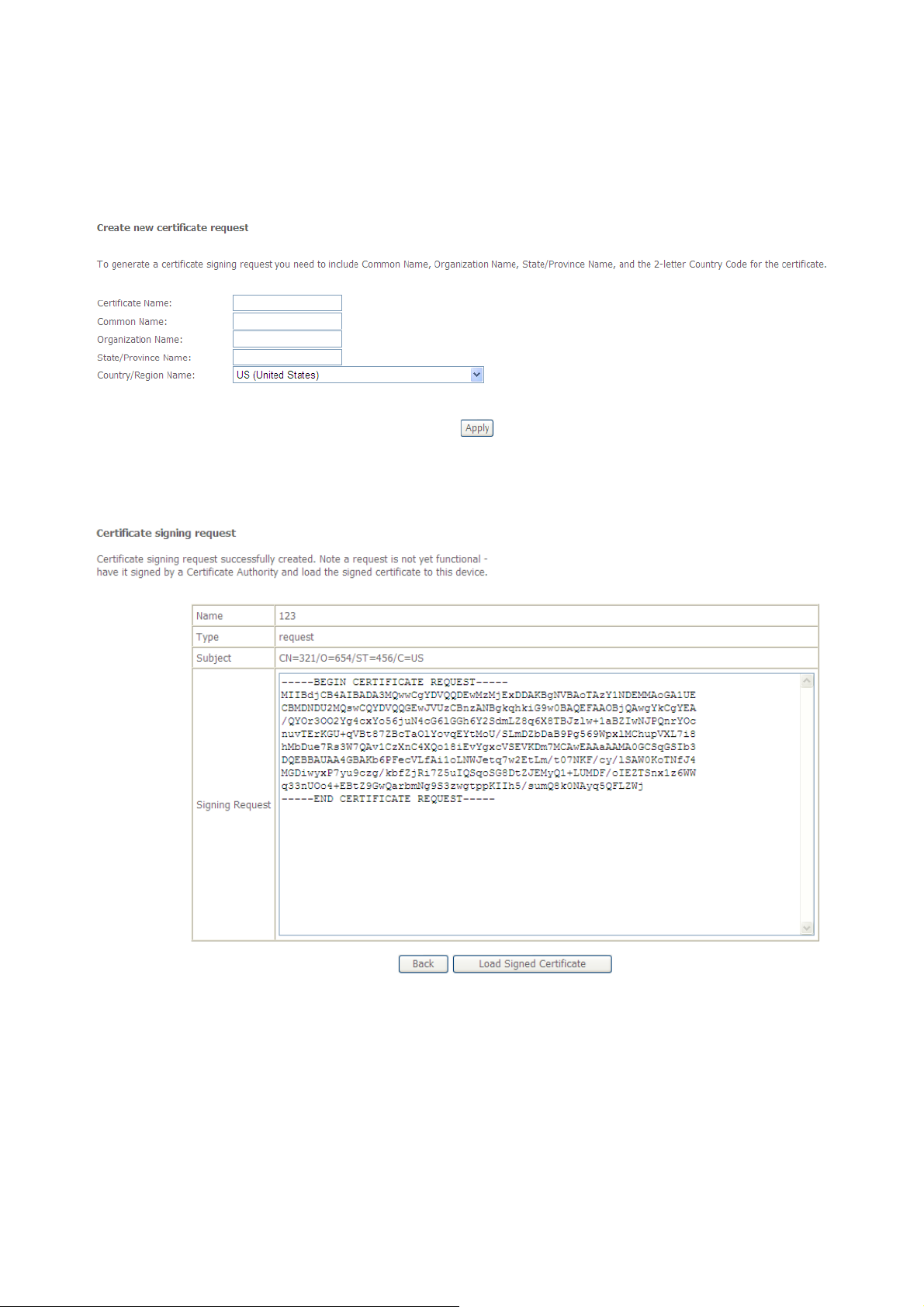
Country/Region Name:
This is the two-letter ISO abbreviation for your country (for example, GB for the United
Kingdom).
Follow the following steps to create a new certificate:
Click “Create Certificate Request”, enter necessary information:
Figure: create new certificate request
Click “Apply” and wait several seconds, the generated certificate request will be shown:
Figure: generated certificate request
91
Page 92

The certificate request needs to be submitted to a certificate authority, which would sign the
request. Then the signed certificate needs to be loaded into Router. Click “Load Certificate”
button from the previous screen or from the base screen will bring up the load certificate
page. Paste the signed certificate and click apply and a new cert
ificate is created.
Figure: Load Certificate
3.3.11.2 Import Existing Local Certificate
To import existing certificate, click “Import Certificate” button and paste both certificate and
corresponding private key:
Figure: Import Certificate
92
Page 93

3.3.11.3 Trusted CA Certificates
Click “Certificate” --> “Trusted CA” to show the interface. CA certificates are used by you to
verify peers' certificates. Maximum 4 certificates can be stored.
Figure: Trusted CA certificates
Click “Import Certificate”. CA certi mporting is
ficate can only be imported. The screen for i
shown below:
Figure: Import CA Certificate
93
Page 94
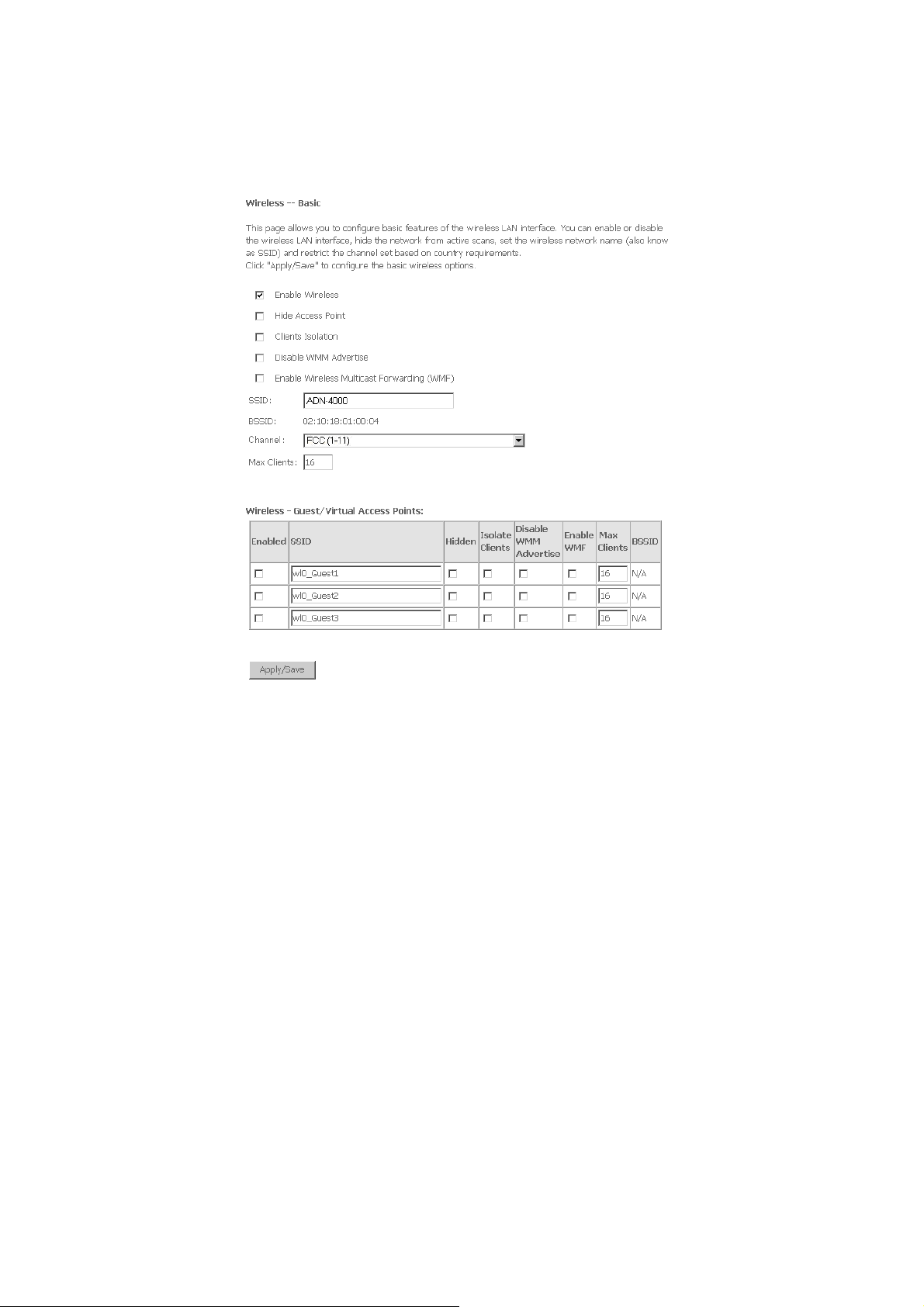
3
.4 Wireless
3.4.1 Wireless – Basic
Choose
Wireless > Basic, the following page appears.
Enable Wireless: If you want to make wireless be available, you have to check this
box first. Otherwise, the Hide Access Point SSID, Country, Enable Wireless Gues
Network, and Guest SSID boxes are not displayed.
Hide Access Point: Check this box if you want to hide any access point for y
router, so
Clients Isolation: When many clients connect to the same access point, they can
access
the same access point, you can check this box.
Disable WMM Advertise: WMM is short for wi-fi multimedia, which can provide
high-performance multimedia voice and video data transfers.
SSID: For added sec
Channel: ed. This
parameter further specifies example, the channel will
adjust according to nations to adapt to each nation's frequency provision (FCC 1~1
ETSI 1~13, JP
Max Clients: S ions to be enble to link with AP.
Once the client s are refused. The value of
maximum client
Wireless - Guest/V irtual network
function be available, you have to check those boxes in the t
soft
ware version, three virtual access points can be configured.
After setting, click
take effect.
a station cannot obtain the SSID through passive scanning.
each other. If you want to disable the access between clients which connect
urity, you should change the default SSID to a unique name.
The option of the channel with which your gateway is configur
your wireless connection. For
1~14).
pecifies maximum wireless client stat
s exceed the max vlaue, all other client
s is 16.
irtual Access Points: If you want to make Guest/V
able below. In the current
Save/Apply to save the basic wireless options and make the change
t
our
1,
94
Page 95
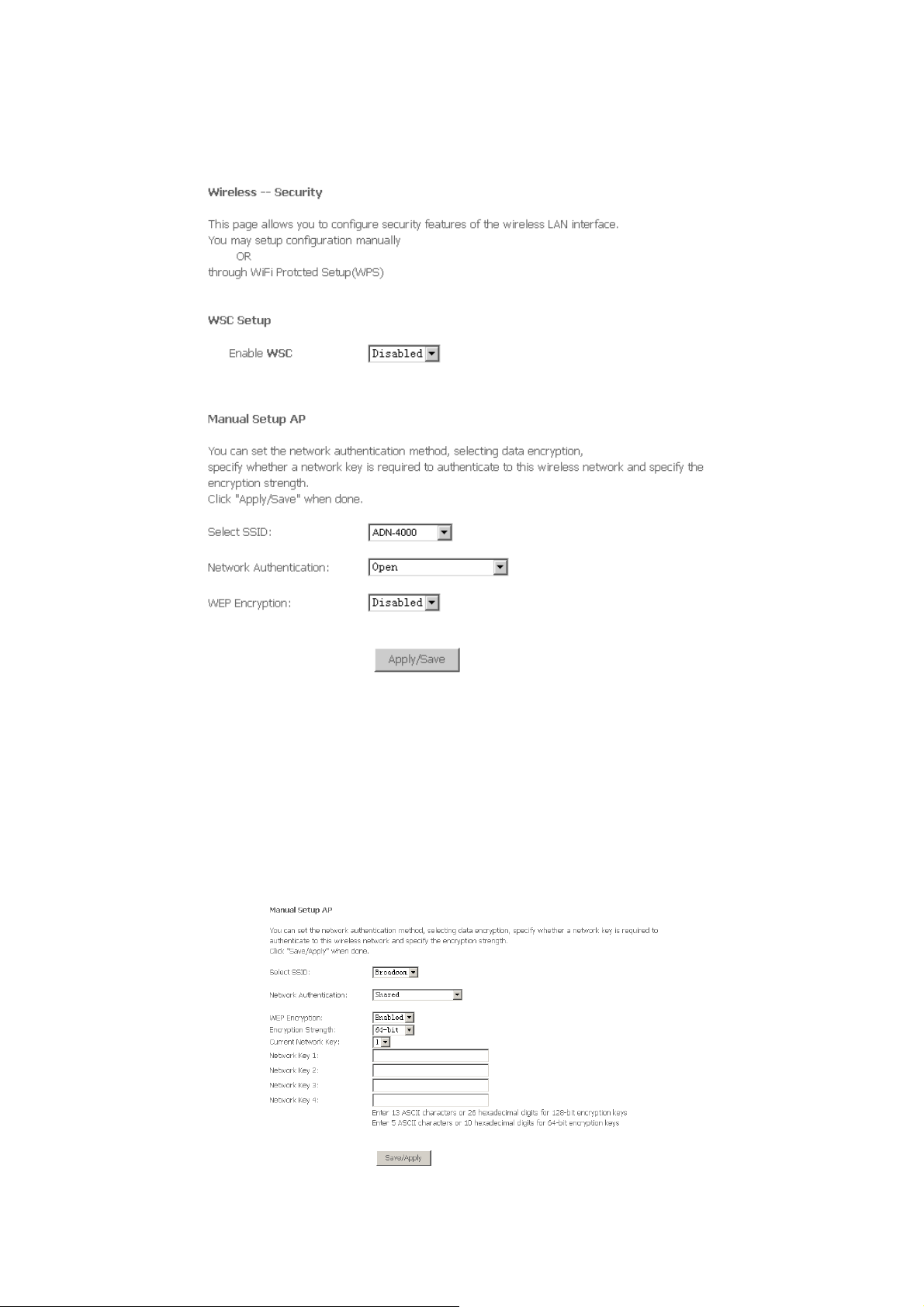
3.4.2 Wireless – Security
Choose Wireless > Security, the following page appears. In this page, the data is not
the default encrypted when it is transferred from the device to the client station. This is
option.
Enable WSC: If enable Manual Setup AP, you can not enable WSC.
Select SSID: Select the wireless LAN of SSID to configure security features.
Network Authentication: Select the authentication mode for the selected wireless
LAN of SSID to be open. That is no WEP encryption, so the WEP Encryption
disabled.
64-bit WE
P
If you select the “Shared” as the Network Authentication, you can select 64-bit or
as the Encryption Strength. In the following figure, select 64-bit as an example.
is
128-bit
95
Page 96

Network Authentication: Select the authentication mode for the selected wireless
LAN of SSID to be open or shared.
WEP Encryption: Enable WEP Encryption.
Encryption Strength: Select the desired Data Security level to be 64-bit.
Current Network Key: Select one of network key that you set on the Key boxes as
default one.
Network Key 1 to 4: Enter 5 ASCII characters or 10 hexadecimal dig
its for 64-bit
tem allows you to type in 4 kinds of encryption keys to fill out WEP keys box. The sys
the WEP key.
The authentication modes are as follows: 802.1X, WPA, WP
A-PSK,WPA2, WPA2 –PSK,
Mixed WPA2/WPA, Mixed WPA2/WPA –PSK.
After proper configuration, click Save/Apply to save the wireless security options an
make the modification effect.
3.4.3 Wireless – Advanced
Choose Wireless > Advanced, the following page appears. This page allows yo
configure advanced features of the wireless LAN interface. You can select a p
channel on which to operate, force the transmission rate to a particular speed, set the
fragmentation threshold, set the RTS threshold, set the wakeup interval for clients in
power-save mode, set t
he beacon interval for the access point, set XPress mode and set
whether short or long preambles are used.
articular
d
u to
96
Page 97

Band: Select using wireless frequency band range. The radio frequency remains a
t
2.4GHz.
Channel: Fill in the appropriate channel to correspond with your network settings. A
devices in your wireless network must use the same channel in order to work correctly
This router supports auto cha
nneling functionality.
Auto Channel Timer (min): Specifies the timer of auto channelling.
802.11n/EWC: Select disable 802.11n or Auto.
Bandwidth: Select the bandwidth for the network.
802.11n Rate/54g™ Rate: Select the transmission rate for the network. The rate of
data transmission should be set depending on the speed of your wireless network.
You can select from a range of transmission speeds, or you can select Auto to have
the Router automatically use the fastest possible data rate and enable the
Auto-Fallback feature. Auto-Fallback will negotiate the best possible connection
speed between the Router and a wireless client. The default value is Auto.
802.11n Protection: The 802.11n standards provide a protection method so
802.11b/g and 802.11n devices can co-exist in the same network without “speaking”
at the same time.
Support 802.11n Client Only: Only stations that are onfigured in 802.11n mode can
associate.
Multicast Rate: S
data transmission should be set dep
You can select from a range of trans
elect the multicast transmission rate for the network. The rate of
ending on the speed of your wireless network.
mission speeds, or you can select Auto to have
the Router automatically use the fastest possible data rate and enable the
Auto-Fallback feature. Auto-Fallback will negotiate the best possible connection
speed between the Router and a wireless client. The default value is Auto.
Basic Rate: Select the
basic transmission rate ability for the AP.
Fragmentation Threshold: Packets that are larger than this threshold are
fragmented into multiple packets. Try to increase the fragmentation threshold if you
encounter high packet error rates. Do not set the threshold too low,
since this can
result in reduced networking performance.
RTS Threshold: This value should remain at its default setting of 2347.Should you
encounter inconsistent data flow, only minor reductions are recommended. Should
you encounter inconsistent data flow, only minor reduction of the default value, 2347,
is recommended. If a network packet is smaller than the preset RT
the RT
(R a
frame. Af
S/CTS mechanism will not be enabled. The Router sends Request to Send
TS) frames to a particular receiving station and negotiates the sending of a dat
ter receiving an RTS, the wireless station responds with a Clear to Send
(CTS) frame to acknowledge the right to begin transmission. The RTS
S threshold size,
Threshold
value should remain at its default value of 2347.
DTIM Inter
255 for the Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM.) A DTIM is a count
informing client
val: (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) Enter a value between 1 and
down
s of the next window for listening to broadcast and multicast
messages.
Beacon Interval: A beacon is a packet of information that is sent from a connected
device t ss. A beacon
interval is a period of time (sent wi ng the beacon again.
o all other devices wh ailability and readinere it announces its av
th the beacon) before sendi
e
The beacon interval may be adjusted in milliseconds (ms). Default (100) is
recommended.
XPress™ Technology: Select Enable or Disable. This is a special accelerating
technology for IEEE802.11g. The defaule is Disabled.
ll
.
97
Page 98

Transmit Power: A
security purposes if you wish
WMM (Wi-Fi
Multimedia): Select whether WMM is enable or disabled. Before you
djust the transmission range here. This tool can be helpful for
to limit the transmission range.
disable WMM, you should understand that all QoS queues or traffic classes relate to
wireless do not take e
WMM No Acknowledgement: Select whether ACK in WMM p
'Ack Policy' for each access category is set to Disable, meanin
ffects.
acket. By default, the
g that an acknowledge
packet is returned for every packet received. This provides a more reliable
transmission but increases traffic load, which decreases performance. To disable the
acknowledgement can be useful for Voice, for example, where speed of transmission
is important and packet loss is tolerable to a certain degree.
WMM APSD: APSD is short for automatic power save delivery, Selecting enable will
make it has very low power consumption. WMM Power Save is an improvement to
the 802.11e amendment addi anagement functionality to WMM.
ng advanced power m
Click Save/Apply to configure the advanced wireless
options and make the changes take
effect.
3.5 Diagnostics
Click “Diagnostics” to show the interface.
Your Router is capable of testing your DSL connection. The individual tests are listed below.
If a test displays a fail status, click "Rerun Diagnostic Tests" at the bottom of this page to
make sure the fail status is consistent. If the test continues to fail, click "Help" and follow the
troubleshooting procedures.
Figure: Diagnostics page
98
Page 99

3.6 Management
3.6.1 Settings
3.6.1.1 Settings Backup
Click the “Backup Settings”, backup the DSL router configurations.
Figure: Backup Config
3.6.1.2 Settings Update
Click the “Browsing...” button, se gure settings file. Then click the
lect the correct update confi
“Update Settings” to update the Router settings.
Figure : Update Settings
3.6.1.3 Settings Restore Default
Click “Rest
ore Default Settings” to restore DSL router settings to the factory defaults.
Figure: Restore Default Settings
99
Page 100
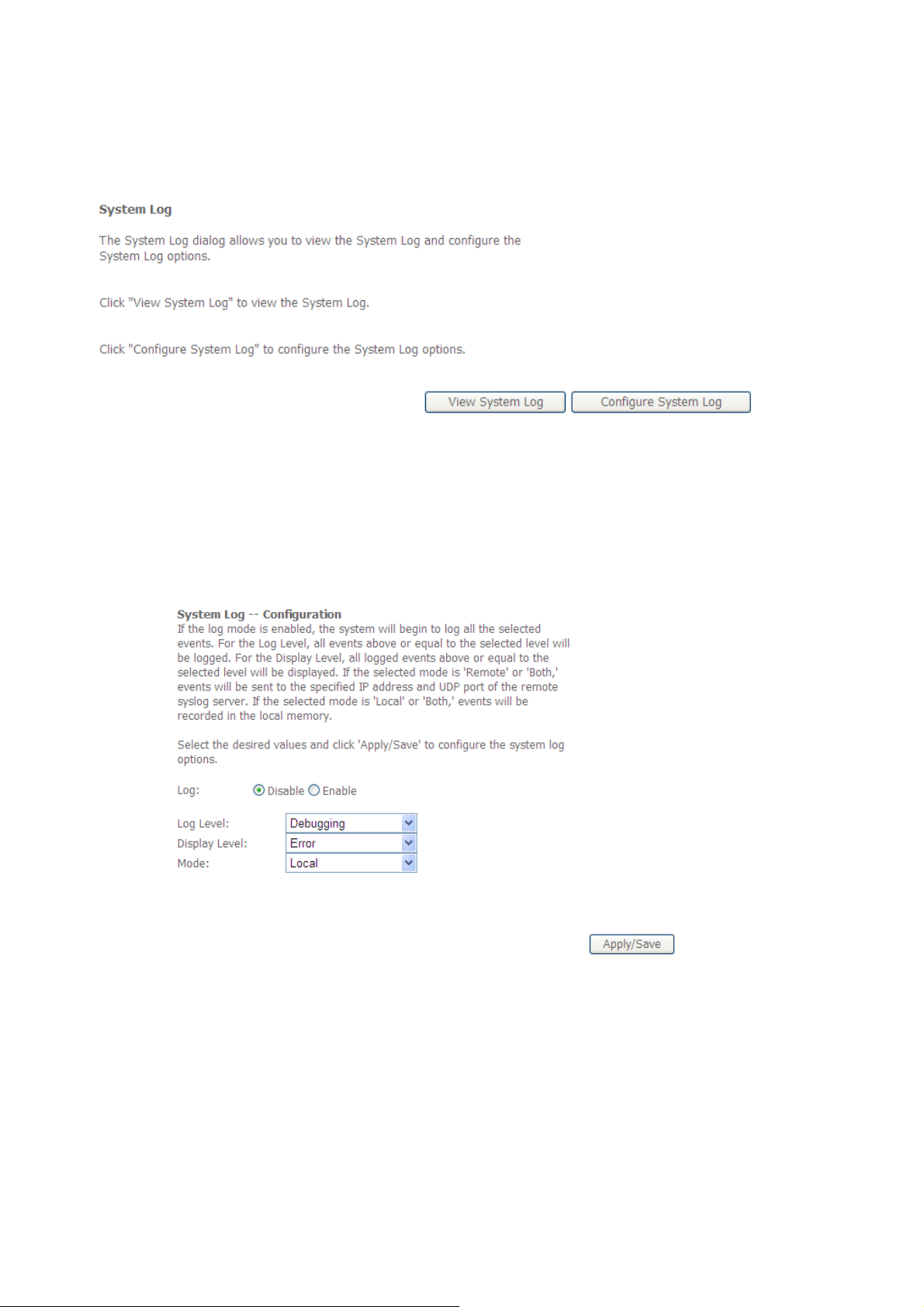
3.6.2 System Log
Click “System Log” to show the following interface. The system log dialog allows you to view
the system log and configure the system log options.
Figure: System Log overview
Click “Configure System Log” to show the following interface. You can enable or disable the
system log and then select the log level, display level and mode, and click “Apply” to end
your configurations.
Both the log level and display level have eight choices. The default log level is “Debugging”
and the default display level is “Error”.
The mode options are “Local”, “Remote”, and “Both”. The default one is “Local”.
100
 Loading...
Loading...