Page 1

ADSL Modem Router
ADE-3100 / ADE-4100
User’s Manual
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright (C) 2005 PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved.
The products and programs described in this User’s Manual are licensed products of
PLANET Technology, This User’s Manual contains proprietary information protected by
copyright, and this User’s Manual and all accompanying hardware, software, and
documentation are copyrighted.
No part of this User’s Manual may be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or
reduced to any electronic medium or machine-readable form by any means by electronic or
mechanical. Including photocopying, recording, or information storage and retrieval
systems, for any purpose other than the purchaser's personal use, and without the prior
express written permission of PLANET Technology.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all
environments and applications, and makes no warranty and representation, either implied
or expressed, with respect to the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a
particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User’s Manual is accurate; PLANET
disclaims liability for any inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not
represent a commitment on the part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for
any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User’s Manual. PLANET makes no
commitment to update or keep current the information in this User’s Manual, and reserves
the right to make improvements to this User’s Manual and/or to the products described in
this User’s Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would
appreciate your comments and suggestions.
FCC Compliance Statement
This equipment generates and uses radio frequency energy and if not installed and used
properly, that is, in strict accordance with the instructions provided with the equipment, may
cause interference to radio and TV communication. The equipment has been tested and
found to comply with the limits for a Class A computing device in accordance with the
specifications in Subpart B of Part 15 of FCC rules, which are designed to provide
reasonable protection against such interference in a residential installation. However, there
is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If you suspect this
Page 3

equipment is causing interference, turn your Ethernet Switch on and off while your radio or
TV is showing interference, if the interference disappears when you turn your Ethernet
Switch off and reappears when you turn it back on, there is interference being caused by
the Ethernet Switch.
You can try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
w Reorient the receiving radio or TV antenna where this may be done safely.
w To the extent possible, relocate the radio, TV or other receiver away from the Switch.
w Plug the Ethernet Switch into a different power outlet so that the Switch and the receiver
are on different branch circuits.
If necessary, you should consult the place of purchase or an experienced radio/television
technician for additional suggestions.
CE mark Warning
The is a class B device, In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Trademarks
The PLANET logo is a trademark of PLANET Technology. This documentation may refer to
numerous hardware and software products by their trade names. In most, if not all cases,
these designations are claimed as trademarks or registered trademarks by their respective
companies.
Revision
User’s Manual for PLANET ADSL Modem Router:
Model: ADE-3100A/B, ADE-4100A/B
Rev: 4.0 (Feb 2005)
Part No.: EM-ADE4100_3100v4
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION.............................................................................................................1
1.1 FEATURES ...................................................................................................................1
1.2 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS ..............................................................................................1
2. KNOWING YOUR ROUTER...........................................................................................2
2.1 FRONT PANEL ..............................................................................................................2
2.2 REAR PANEL................................................................................................................3
3. LOGIN.............................................................................................................................4
4. STATUS PAGES.............................................................................................................5
4.1 HOME PAGE.................................................................................................................5
4.2 PPP PAGE...................................................................................................................6
4.3 ADSL PAGE.................................................................................................................7
5. CONFIGURATION PAGES.............................................................................................9
5.1 MODES........................................................................................................................9
5.2 WAN CONFIGURATION ...............................................................................................10
5.2.1 ATM...................................................................................................................11
5.2.2 DHCP Client......................................................................................................12
5.2.3 MAC Spoofing...................................................................................................12
5.2.4 Static IP Settings...............................................................................................12
5.3 LAN CONFIGURATION.................................................................................................13
5.3.1 DHCP Server.....................................................................................................13
5.3.2 Ethernet Mode Setting.......................................................................................14
5.4 PPP CONFIGURATION.................................................................................................15
5.4.1 PPP Account Configuration...............................................................................15
5.4.2 PPP Session Configuration...............................................................................16
5.4.3 PPP Disconnect Timer Configuration................................................................17
5.4.4 PPP Miscellaneous Configuration.....................................................................19
5.5 NAT CONFIGURATION PAGES......................................................................................20
5.6 VIRTUAL SERVER CONFIGURATION...............................................................................21
5.7 BRIDGE FILTERING......................................................................................................22
5.8 DNS CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................23
5.9 DYNAMIC DNS...........................................................................................................25
5.10 USER PASSWORD CONFIGURATION............................................................................25
5.11 SAVE SETTINGS / REBOOT ........................................................................................26
6. ADMIN PRIVILEGE.......................................................................................................27
Page 5

6.1 WAN STATUS ............................................................................................................27
6.2 ATM STATUS .............................................................................................................27
6.3 ADSL CONFIGURATION...............................................................................................28
6.4 ROUTE TABLE ............................................................................................................29
6.4.1 System Default Gateway Configuration.............................................................30
6.4.2 Route Configuration..........................................................................................30
6.5 LEARNED MAC TABLE................................................................................................30
6.6 RIP CONFIGURATION..................................................................................................31
6.6.1 RIP Per Interface Configuration.........................................................................32
6.7 MISCELLANEOUS CONFIGURATION ...............................................................................33
6.8 TCP STATUS .............................................................................................................35
6.9 ADMIN PASSWORD CONFIGURATION.............................................................................35
6.10 RESET TO FACTORY DEFAULT....................................................................................36
6.11 DIAGNOSTIC TEST ....................................................................................................36
6.12 SYSTEM LOG ...........................................................................................................37
6.13 LOCAL CODE IMAGE UPDATE.....................................................................................37
APPENDIX A. COMPLIANCE STATEMENT....................................................................39
APPENDIX B. ENCAPSULATION MODE........................................................................40
APPENDIX C. TROUBLESHOOTING..............................................................................41
OVERVIEW.......................................................................................................................41
GENERAL PROBLEMS........................................................................................................41
CONFIGURATION AND INTERNET ACCESS ............................................................................41
APPENDIX D. SPECIFICATIONS.....................................................................................43
Page 6

1. Introduction
This Router is a highly integrated, cost-effective solution. All setup and provisioning is accomplished via a
simple intuitive Web interface which further enhances the user experience.
1.1 Features
l ADSL Compliance
n Compliant with ADSL standards
u Full-rate ANSI T1.413 Issue 2 and ITU G.dmt (G.992.1) standards
u Splitterless ITU G.lite (G.992.2) specification
u ADSL over POTS (Annex A) and ADSL over ISDN (Annex B)
n DMT modulation and demodulation
n Full-rate adaptive modem
u Maximum downstream rate of 8 Mbps
u Maximum upstream rate of 1 Mbps
l ATM Protocols
n WAN mode support: PPP over ATM (RFC 2364) and PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516)
n LAN mode support: bridged/routed Ethernet over ATM (RFC 1483) and Classical IP over ATM
(RFC 1577)
n ATM Forum UNI 3.1/4.0 PVC
n Up to 8 VCs (Virtual Circuits)
l Bridge Mode
n Ethernet to ADSL self-learning Transparent Bridging (IEEE 802.1D)
n Supports up to 128 MAC learning addresses
l Router Mode
n IP routing–RIPv2
n Static routing
n DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server and Client
n NAPT (Network Address and Port Translation)
n NAT (Network Address Translation)
n ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
l Security
n User authentication for PPP
n PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
n CHAP (Challenge Authentication Protocol)
n Password protected system management
1.2 System Requirements
l Pentium III 266 MHz processor minimum
l 128 MB RAM minimum
l 20 MB of free disk space minimum
l Ethernet Network Interface Controller (NIC) RJ45 Port
l Internet Browser
l Ethernet (CAT5) Cable
1
Page 7

2. Knowing Your Router
k if data is being
When selecting the location for the Router, allow room to access the connections on the rear panel. You will
want to place the Router so that you will be able to see the LED indicators on the front panel. It may be
convenient for you locate the Router near the PC you intend to use for initial configuration of the Router.
2.1 Front Panel
Place the Router in a location that permits an easy view of the LED indicators shown in the front panel
diagram below.
Front panel of ADE-3100
LED Indicators of ADE-3100:
LEDs Color Active
PWR Green
READY Green Blink The system is ready to use.
ADSL Green
ACT Green Blink Transmitting data or receiving data over Ethernet link.
LAN
LNK Green
TX Green Blink Transmitting data via ADSL link.
WAN
RX Green Blink Receiving data via ADSL link.
LED Indicators of ADE-4100:
LEDs Color Active
ON The power adaptor is connected to the Modem.
ON ADSL connection is established.
ON The Ethernet connection is established.
Front panel of ADE-4100
Description
Description
WAN
LAN
2
PWR Green
READY Green Blink The system is ready to use.
ADSL Green
ACT Green
1
2
Green
3
4
ON The power adaptor is connected to the Modem.
ON ADSL connection is established.
ON If data is being transferred via ADSL link.
The Ethernet connection is established. Blin
ON
transmitted or received over Ethernet link.
Page 8
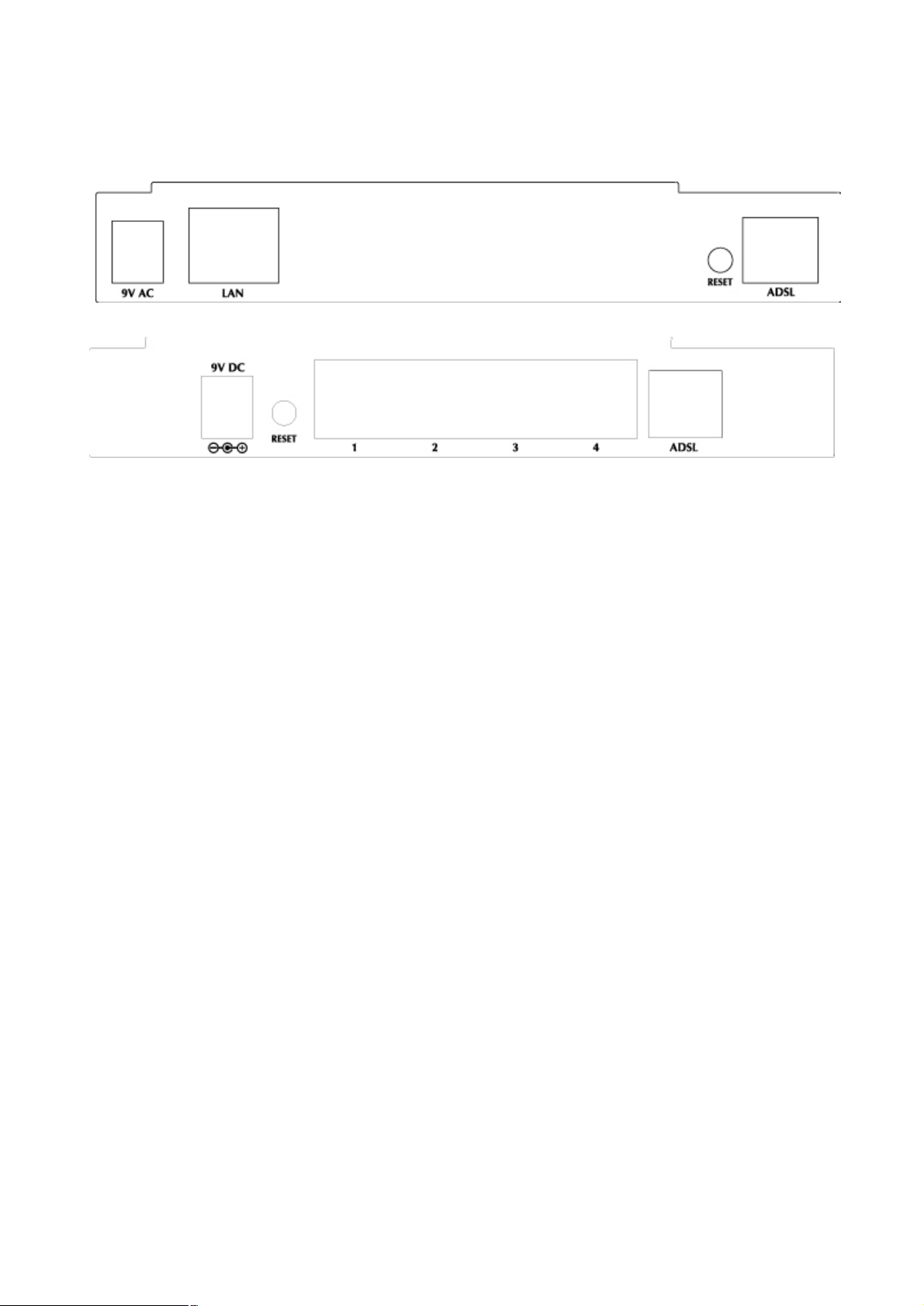
2.2 Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Router provides access to the power adapter cord connection as well as the port
connections.
RESET button: The Router comes with a reset button built into the rear panel. Use this button to restore the
factory default settings. If you need to reset the Router, press the reset button for 2-3 seconds and then
release it. The ADSL LED will stop blinking temporarily and then blink again in about 15 seconds. It means
the Router finish rebooting.
Rear panel of ADE-3100
Rear panel of ADE-4100
3
Page 9
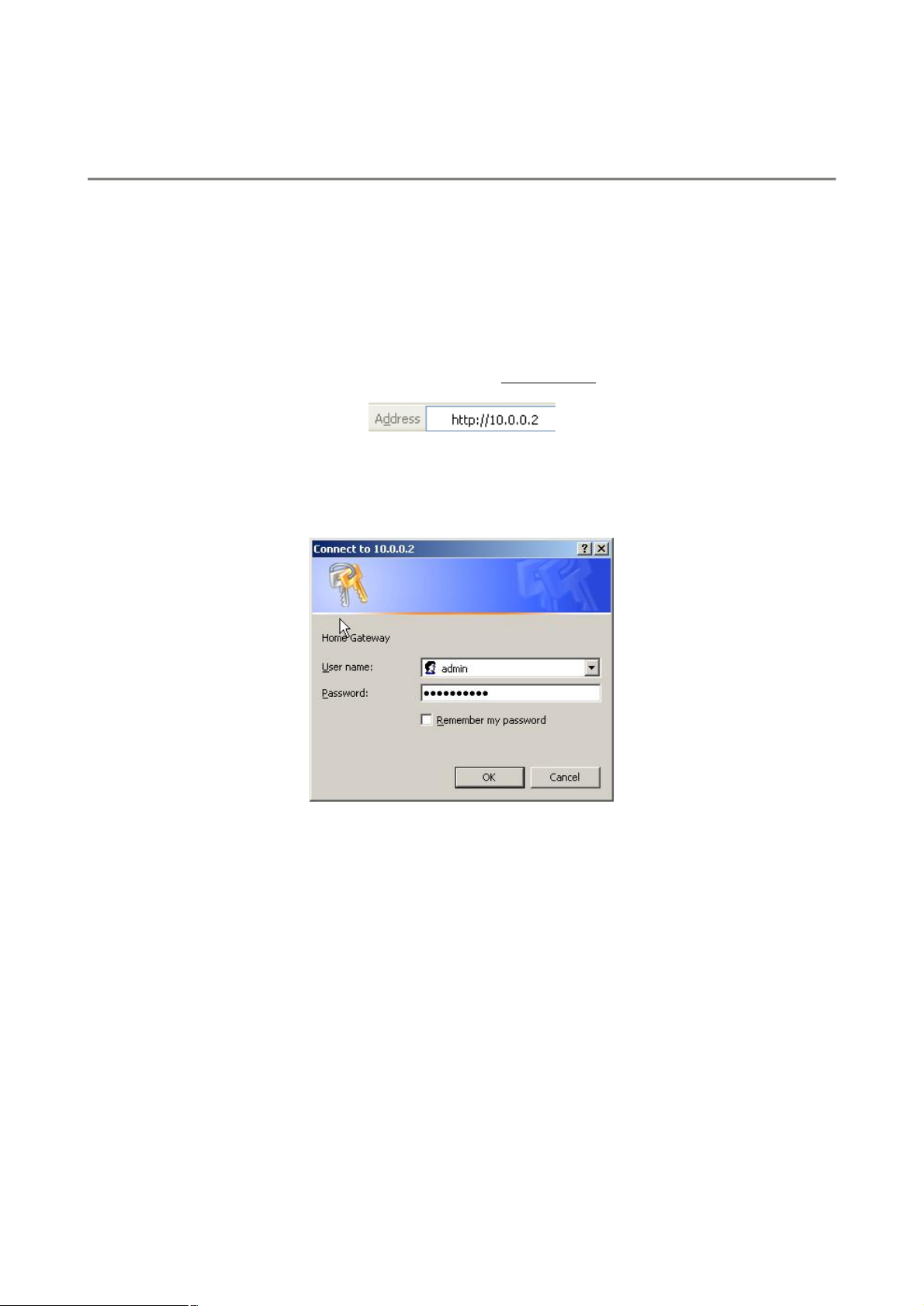
3. Login
There are two levels of access rights/privileges for the Router:
l Administrator: User name admin, the administrator account has complete read/write access on all
pages (Status, Configuration and Admin Privilege). Admin account also has FTP server access.
l User: User name user, the User account has read/write access to pages under the Status and
Configuration sections.
The following steps will enable you to log into the Router:
1. Launch the Web browser (Internet Explorer, Netscape, etc.).
2. Enter the LAN port default IP address (default gateway) http://10.0.0.2 in the address bar.
3. Entry of the username and password will be prompted. Enter the default login User Name and Password:
The default login User Name of the administrator is admin, and the default login Password is epicrouter. The
default login User Name for the non-administrator is user, and the default login Password is password.
4. Remember my password checkbox: By default, this box is not checked. Users can check this box so
that Internet Explorer will remember the User name and Password for future logins. It is recommended
to leave this box unchecked for security purposes.
Admin and User passwords can be changed after login. Refer to Section 5.10 for User Password
configuration and Section 6.9 for Admin Password configuration for further instruction.
4
Page 10
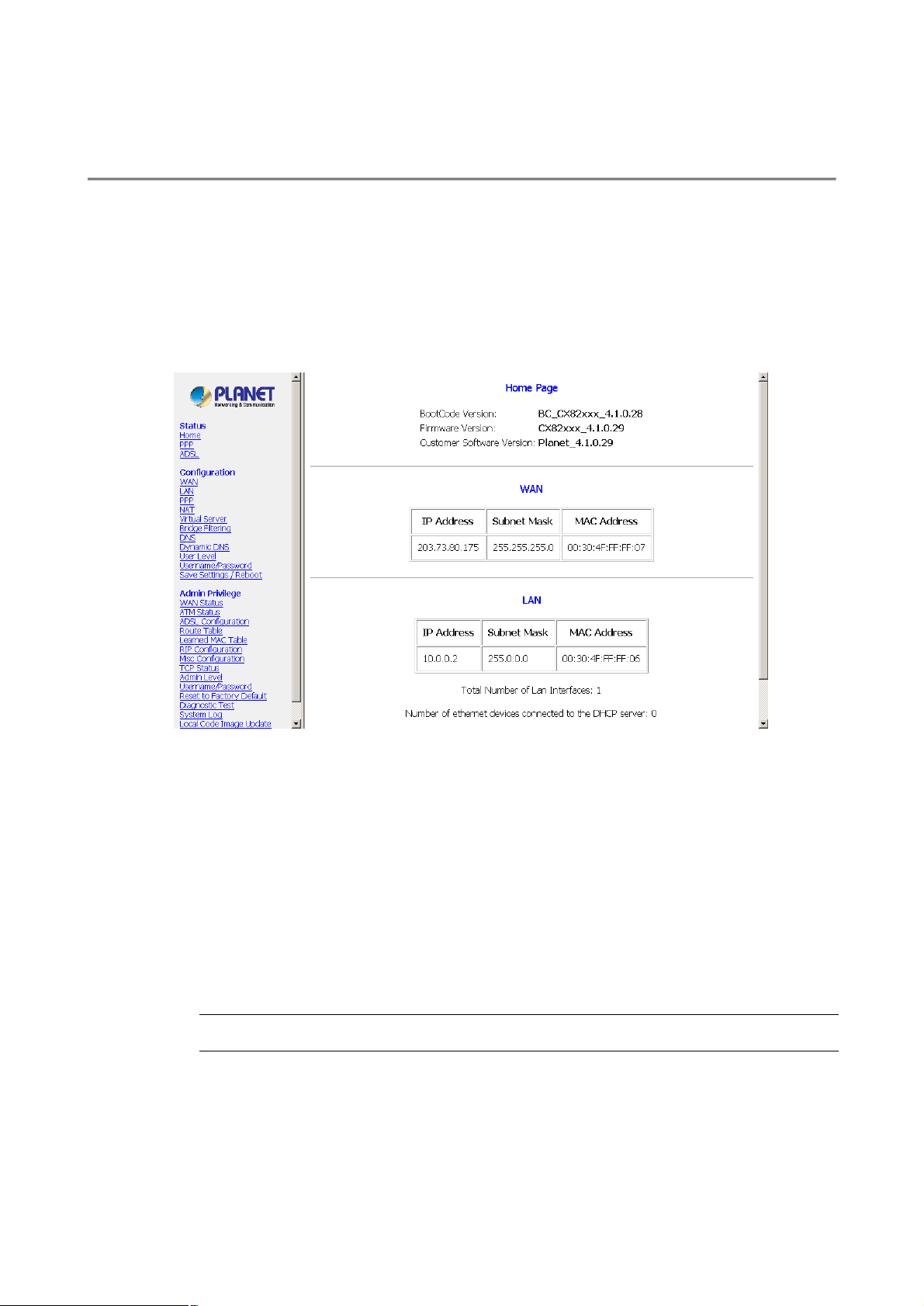
4. Status Pages
If there are no devices connected to the DHCP server, then a table will not appear, otherwise
The links under the Status column are associated with the pages that represent the status of system
(computer and Router) and interfaces (connections). This includes LAN, WAN, DHCP, PPP, and ADSL status.
These pages can be viewed and modified by both user and admin accounts.
4.1 Home Page
The Home page shows the firmware versions; LAN, WAN, and DHCP interface status; and Ethernet
connection status.
Firmware Version: It is the default version number, which is not changeable.
Customer Software Version: It is the version of the firmware that is controllable by the ADSL
Modem/Router manufacturer.
WAN and LAN: It displays the IP address, Subnet Mask and MAC address for the WAN (ADSL) and LAN
interface.
Total Number of LAN Interfaces: It displays the total number of available interfaces for the LAN interface.
The total number of available interfaces is the amount of computers that are able to hook up to the DHCP
Server.
Number of Ethernet Devices Connected to the DHCP Server: It displays the DHCP client table with the
assigned IP addresses and MAC addresses.
?Note
Ethernet Link Status: It displays the link up or down for the Ethernet connection (up if connected, down if
not connected).
USB Link Status (reserved function): It displays the link up or down for the USB connection (up if
connected, down if not connected).
a table listing all devices connected to DHCP server will appear on the bottom of the page.
5
Page 11
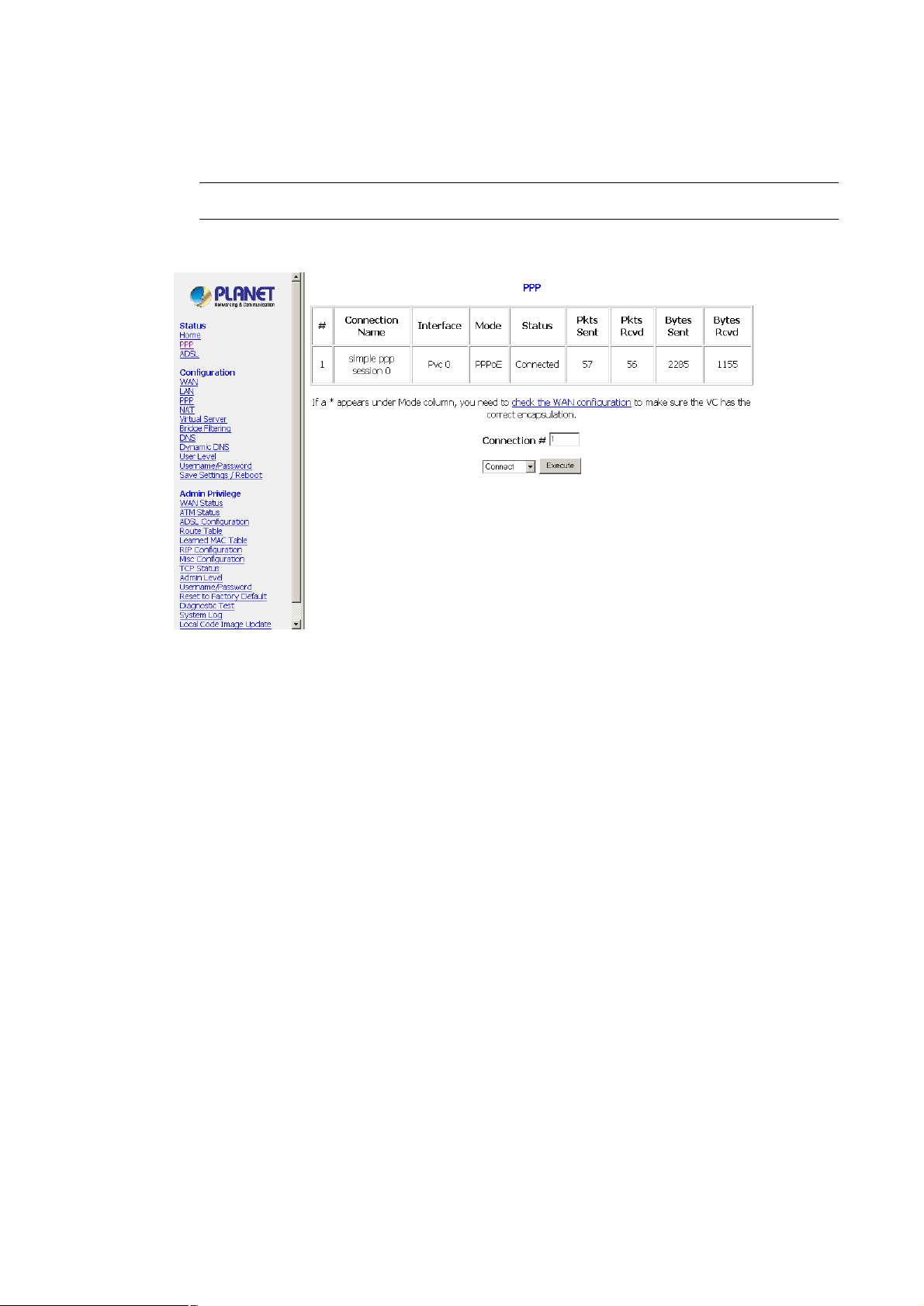
4.2 PPP Page
The PPP Status page shows the status of each PPP session for each PPP interface. This page contains
information that is dynamic and will refresh every 8 seconds.
?Note
PPP interfaces can be created, modified, and deleted in the PPP Configuration page. Refer
to Section 5.4 for further information.
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol): The table displays the following fields:
l Connection Name: This is user defined. User defined connections for PPP can be created in PPP
Configuration page.
l Interface: States the interface that is being used (PVC0 ... PVC7).
l Mode: There are two available modes for the connection:
PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
PPP over ATM (PPPoA)
l Status: States whether PPP connection is Connected or Not Connected.
l Packets Sent: Number of packets sent by a particular PPP Connection.
l Packets Received: Number of packets received by a particular PPP Connection.
l Bytes Sent: Number of bytes sent by a particular PPP Connection.
l Bytes Received: Number bytes received by a particular PPP Connection.
Connect and Disconnect: It allows you to manually connect/disconnect the PPP connection for each PPP
interface. In other words, each PPP session can be connected and disconnected individually.
l Connection #: Specifies the PPP session to be connected/disconnected.
l Connect/Disconnect Execute: Press this button to either connect or disconnect.
Connection status dialog will be displayed below the Execute button after it is pressed.
Sample dialog with explanation:
l PPP X: Connecting... This is displayed while the PPP session is attempting to connect to the ISP.
l PPP X: Connect ERROR This is displayed when a connection cannot be made due to an error.
l PPP X: is currently not connected This is displayed when a disconnect attempt is made on a
session that is not currently connected.
l PPP X: does not exist! This is displayed when a connect or disconnect attempt is made on a
session number that does not exist.
6
Page 12
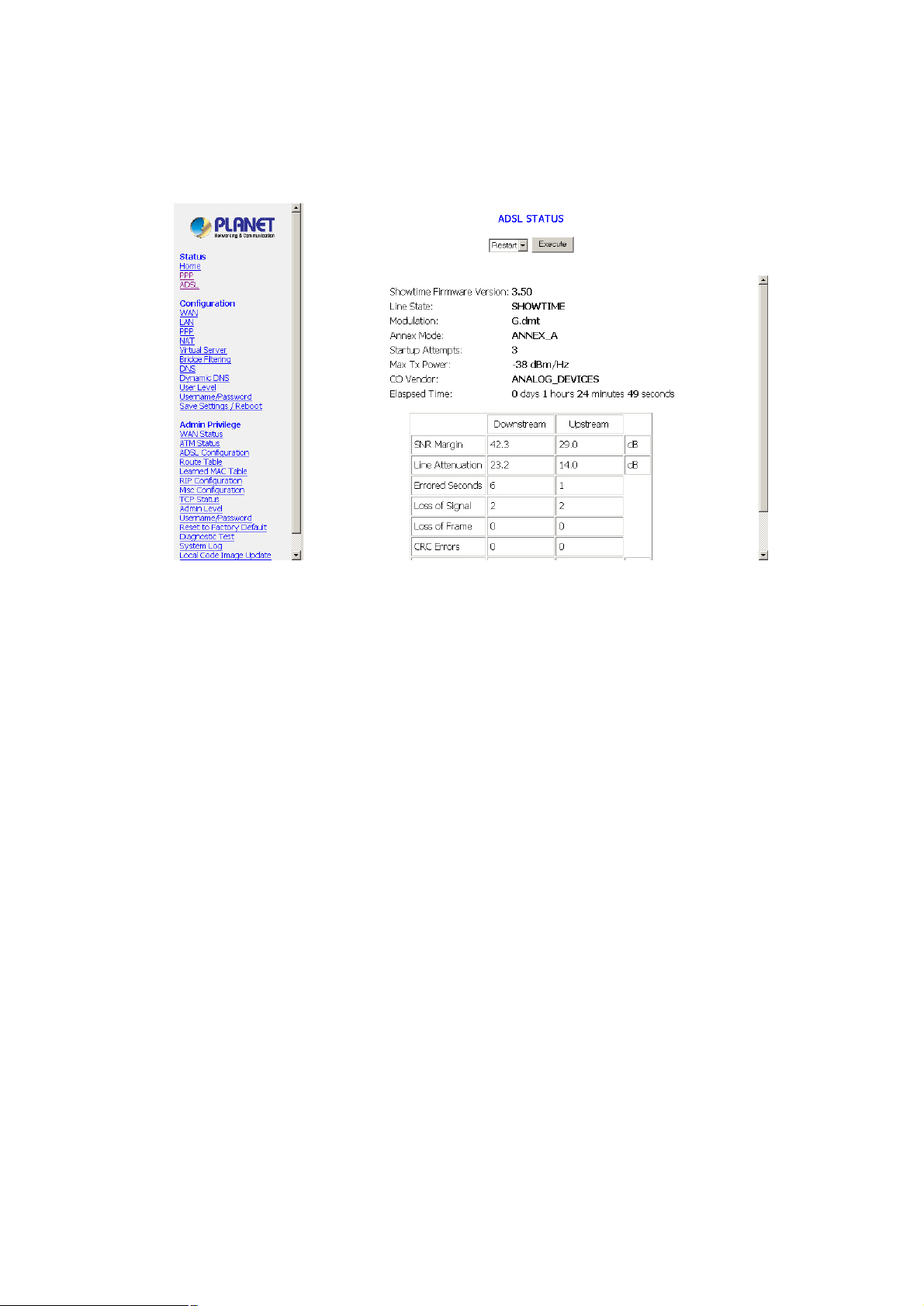
4.3 ADSL Page
The ADSL Status page shows the ADSL physical layer or link status. The information displayed on this page
is either inherent to the Router or set by the ADSL Central Office (CO) DSLAM, neither of which cannot be
changed by the user. This page contains information that is dynamic and will refresh every 2 seconds.
Restart/Stop Execute: It allows you to stop or restart the ADSL connection by selecting the appropriate
action and clicking Execute.
Showtime Firmware Version: It displays the ADSL data pump firmware version.
ADSL Line Status: It displays the ADSL connection process and status. The different states for this field
are as follows:
l Activation: The Router is in this state when it is attempting to start the activation process.
l Initialization: The Router is initializing handshake with the CO.
l Training: It is a part of the handshake process with the CO.
l Channel Analysis: It is a part of the handshake process with the CO.
l Exchange: It is a part of the handshake process with the CO.
l Down: It indicates that the ADSL connection is down.
l Showtime: It indicates that a connection has been established between the Router and the CO.
ADSL Modulation: It displays the ADSL modulation status, which can either be G.dmt or T1.413.
ADSL Annex Mode: It displays the ADSL annex mode, which can either be Annex A or Annex B.
ADSL Startup Attempts: It displays the number of ADSL connection attempts after loss of showtime. A
connection attempt is recorded only if showtime is attained.
ADSL Max TX Power: It displays the transmit output power level of the CPE (Customer Premise
Equipment), which is the transmit output power level of the Router.
ADSL CO Vendor: It displays the Central Office (CO) DSLAM vendor name, if available. If the Router is
not connected to an ADSL vendor, then ‘UNUSED_VENDOR_0’ will appear in this field.
Elapsed Time: It displays the time of the Router has been in operation. This is the amount of time the
Router is on, not the amount of time it is connected to the PC or in showtime status.
A table contained the information of SNR Margin, Line Attenuation, Errored Seconds, Loss of Signal,
Loss of Frame, CRC Errors, Data Rate, and Latency is also available.
SNR Margin: Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is the measure of signal intensity relative to the background
7
Page 13

noise. The SNR Margin is the amount of increased noise that can be tolerated while maintaining the
designated BER (bit error rate). The SNR Margin is set by Central Office DSLAM. If the SNR Margin is
increased, bit error rate performance will improve, but the data rate will decrease. Conversely, if the SNR
Margin is decreased, bit error rate performance will decrease, but the data rate will increase.
Line Attenuation: Attenuation is the decrease in magnitude of the ADSL line signal between the
transmitter (Central Office DSLAM) and the receiver (Client ADSL Bridge/Router), measured in dB. It is
measured by calculating the difference in dB between the signal power level received at the Client ADSL
Bridge/Router and the reference signal power level transmitted from the Central Office DSLAM.
Errored Seconds: During Showtime, if any given second contains a CRC error, then that second will be
declared and recorded as an Errored Second.
Loss of Signal: Loss of signal refers to the ADSL Bridge/Router losing an ADSL signal, not the computer
losing a signal with the modem. Loss of Signal event is only recorded if the signal is lost while the ADSL
Bridge/Router is in showtime status. This field displays the count of ADSL signal loss events.
Loss of Frame: A frame is a unit of data in ATM. This field displays the count of ADSL frame loss events. A
Loss of Frame event is only recorded if the signal is lost while the ADSL Bridge/Router is in showtime
status.
CRC Errors: Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) is a method for checking errors in data transmissions. This
field displays the number of transmit data frames containing CRC errors.
Data Rate: This field displays the ADSL data rate in kbps.
Latency: Latency, synonymously delay, is the amount of time it takes for a packet of data to get from one
designated point to another. This field displays the two mapping modes for latency (fast and interleaved).
8
Page 14
5. Configuration Pages
setting(s) and reboot the Router. Changes will not take effect until the settings are saved and
Classical IP over
The links under Configuration column are associated to the pages that represent the configurations of
system and interfaces. These pages can be viewed and modified by both user and admin accounts.
?Note
5.1 Modes
Table 5-1 lists the mode configurations.
Table 5-1 Mode Configuration
WAN
Configuration
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Gateway
Encapsulation
Bridge
PPP Service
PPP User Name
PPP Password
DHCP Client
Enable
PPP Half Bridge
DHCP Server
NAT
DNS Proxy
Bridge Mode: Bridge Mode is used when there is one PC connected to the LAN-side Ethernet port. IEEE
802.1D method of transport bridging is used to bridge between the WAN (ADSL) side and the LAN
(Ethernet) side, i.e., to store and forward.
Router Mode: Router Mode is used when there is more than one PC connected to the LAN-side Ethernet
port. This enables the ADSL WAN access to be shared with multiple nodes on the LAN. Network Address
Translation (NAT) is supported so that one WAN-side IP address can be shared among multiple LAN-side
devices. DHCP is used to serve each LAN-side device and IP address.
When any settings are changed, please go to the Save Settings page to save the new
the Router is rebooted. If power is lost before saving, all new configurations since the last
save will be lost, even if they were submitted.
Bridge Mode
N/A Automatically
N/A Automatically
N/A Automatically
1483 Bridged IP
LLC, 1483
Bridged IP
VC-Mux
Enabled Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
N/A Provided by ISP N/A N/A Provided by ISP
N/A Provided by ISP N/A N/A Provided by ISP
N/A Provided by ISP N/A N/A Provided by ISP
Unchedked Unchedked Checked Unchedked Unchedked
Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
Disabled Enabled Enabled Enabled
Disabled Enabled (Dynamic
Disabled Enabled Enabled Enabled Disabled
Router Mode
(PPPoA/PPPoE)
assigned by ISP
assigned by ISP
assigned by ISP
PPPoA
LLC/VC-Mux,
PPPoE
LLC/VC-Mux
NAPT)
Router Mode
(Dynamic IP)
Automatically
assigned by ISP
Automatically
assigned by ISP
Automatically
assigned by ISP
1483
Bridged/Routed
IP LLC, 1483
Bridged/Routed
IP VC-Mux,
Classical IP over
ATM
Enabled
(Dynamic NAPT)
Router Mode
(Static IP)
Provided by ISP Automatically
Provided by ISP Automatically
Provided by ISP Automatically
1483
Bridged/Routed
IP LLC, 1483
Bridged/Routed
IP VC-Mux,
ATM
Enabled
(Dynamic NAPT)
Half Bridge
assigned by ISP
assigned by ISP
assigned by ISP
PPPoA
LLC/VC-Mux,
PPPoE
LLC/VC-Mux
Disabled
9
Page 15
10
PPP Half Bridge: Although the Router mode is capable of terminating the PPP in the modem and hence
does not require PPPoE client software on the host PC, there are some disadvantages to Router mode
when only single-user support is required. For instance, Router mode uses NAT which requires ALG
support. PPP Half Bridge also terminates the PPP in the modem and does not require a PPPoE client on
the PC. However, PPP Half Bridge does not use NAT and is not limited by ALGs. PPP Half Bridge will work
with Ethernet interface to the PC.
Single-User Mode: Only one computer is connected at the LAN side through Ethernet.
Multi-User Mode: Multiple computers are connected at the LAN side through Ethernet.
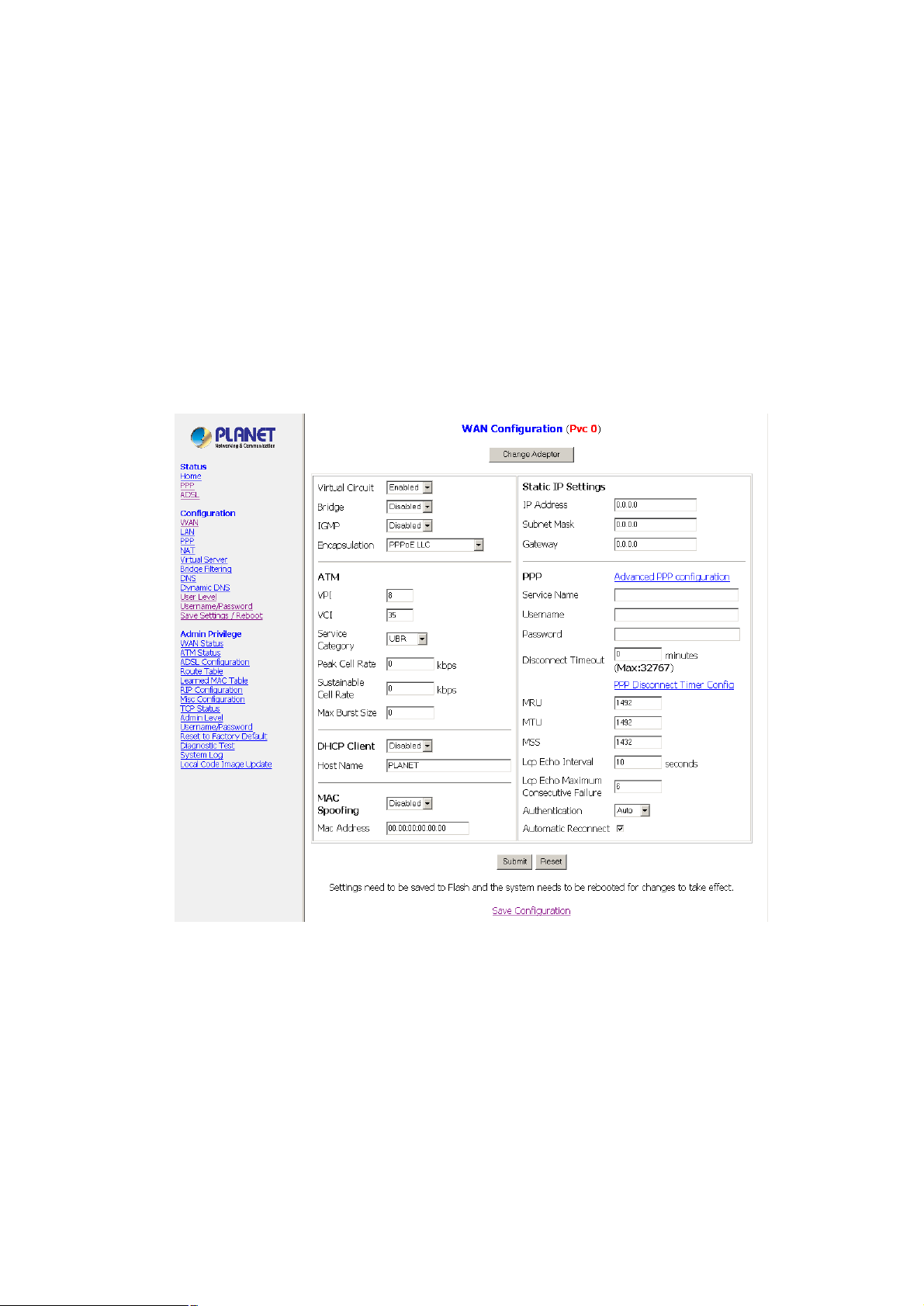
5.2 WAN Configuration
The WAN configuration page allows you to set the configuration for the WAN/ADSL ports. Before you
enter the WAN Configuration page, you will be asked to select an adapter (PVC0 through PVC7) first.
Once you select the adaptor, then following page will appear.
Virtual Circuit: Select Enable to activate the current PVC configuration. The current PVC is displayed at
the top of the page in parenthesis. Default is Enabled for PVC0 and Disabled for PVC1-PVC7.
Bridge: Enable to connect the LAN to the WAN (bridge the two connections). This is available in Bridge
Mode only (see Table 5-2). Default is Disabled.
Page 16

IGMP: IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) relay/proxy specification and environment, default is
Disabled. IGMP is available in all modes and all encapsulations. Support IGMP proxy/relay function for
Router, based on the following requirement and cases:
l On CO side, there must be at least one IGMP querier (router) present. IGMP querier will send
IGMP query packet. The Router is responsible to relay these IGMP queries to Ethernet.
l End-user multicast application device sends IGMP report while receiving IGMP query or being
activated by the user. The Router should be responsible to proxy (that is, change source IP to
Router’s WAN IP) the IGMP report to ADSL WAN side, including all PVCs. The same case is for
IGMP leave packet.
l Not necessary to relay multicast routing between two ADSL PVCs or two interfaces in LAN side.
l Special purpose multicast packet (such as RIP 2 packet) should run without Interference.
Table 5-2. Packet Process
Rx Entity
ADSL
Ethernet
?Note
Q. Where can I download the free software to test IGMP?
Answer: Please go to this link http://manimac.itd.nrl.navy.mil/MGEN/.
Encapsulation: The different types of encapsulation include PPPoA VC-Mux, PPPoA LLC, 1483 Bridged
IP LLC, 1483 Routed IP LLC, 1483 Bridged IP VC-Mux, 1483 Routed IP VC-Mux, Classical IP over ATM,
PPPoE VC-Mux, PPPoE LLC, and PPPoENone.
Before the IGMP mode is enabled; please go to the Miscellaneous Configuration page to
enable the IGMP proxy. Otherwise, the IGMP selection will not be valid.
Packet Class TTL Action
IGMP query 1 Relay to Ethernet
IGMP report 1 Ignore
IGMP leave 1 Ignore
General Multicast IP - Relay it to Ethernet
IGMP query 1 Ignore
IGMP report 1 Relay to all ADSL PVCs
IGMP leave 1 Relay to all ADSL PVCs
General Multicast IP - Ignore
5.2.1 ATM
VPI: Virtual Path Identifier is a virtual path used for cell routing that is identified by an eight bit field in the
ATM cell header. The VPI field specifies this eight bit identifier for routing.
Range: 0-255 Default: 0
VCI: A Virtual Channel Identifier is a virtual channel that is identified by a unique numerical tag that is
defined by a 16-bit field in the ATM cell header. The purpose of the virtual channel is to identify where the
cell should travel. The VCI field specifies this 16 bit numerical tag that determines the destination.
Range: 0-65535 Default: 35
Service Category: This field allows you to select from the following service categories.
l UBR (default): When configured as UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate), traffic is delivered with best
efforts but with no guarantee. This allows for fluctuation in times of temporary increase of available
bandwidth. For example, if a PVC with CBR is temporarily inactive, the PVC(s) with UBR will utilize
that bandwidth while it is available. UBR is intended for applications that do not require any
maximum bound on the transfer delay.
l CBR: When a PVC is specified as a CBR (Constant Bit Rate), that PVC is guaranteed a certain
bandwidth, characterized by the Peak Cell Rate (PCR). The CBR does not have to transmit with a
peak cell rate, and when it does, it is only when the bandwidth specified by the PCR is guaranteed.
l VBR-nrt: An PVC enabled with VBR-nrt (Variable Bit Rate - non real time) can transmit a cell only
if the PVC has a token available. The PVC accumulates tokens at the rate of the Sustainable Cell
11
Page 17

12
Rate, and the PVC can only accumulate a maximum of the value specified by Maximum Burst Size
tokens.
When a PVC has a token available, it can transmit cells at the rate of PCR. After a cell is transmitted, the
PVC loses the token it has accumulated.
In the case of multiple PVCs, CBR specified PVCs will have higher priority than PVCs with UBR.
For example, the CBR PVCs will take their bandwidth and the remaining bandwidth will be split among
the UBR PVCs. In the case of total PVC CBR bandwidth exceeding ADSL upstream, the total upstream
bandwidth will be shared proportionally to the bandwidth allocated for each CBR PVC.
Peak Cell Rate: This value specifies the maximum, and in some cases guaranteed, cell rate for CBR and
VBR-nrt. Peak Cell Rates are typically measured in Cells/Second, however, the user entered value is in
kbps and is then converted by the firmware.
Range: 0-32767 Default: 0
Sustainable Cell Rate: It is the sustained rate at which a PVC enabled with VBR-nrt can transmit ATM
cells. Sustainable Cell Rate (SCR) can be considered as the true reserved bandwidth for a PVC.
Range: 0-32767 Default: 0
Max Burst Size: It is the number of cells a PVC enabled with VBR-nrt can transmit continuously at peak
cell rate (PCR).
Range: 0-32767 Default: 0
5.2.2 DHCP Client
DHCP Client: It is to enable or disable (default) the Router WAN as a DHCP client, where the ISP would be
the DHCP server. DHCP Client is generally used in the following encapsulations: 1483 Bridged IP LLC,
1483 Routed IP LLC, 1483 Bridged IP VC-MUX, 1483 Routed IP VC-Mux, and Classical IP over ATM. This
option is for non-static (dynamic) IP addresses.
Host Name: When DHCP Client is Enabled, copy the ISP recognized Host Name here. The Host Name
can be up to 19 characters.
5.2.3 MAC Spoofing
MAC Spoofing: Enable MAC Spoofing to make a different MAC Address appear on the WAN side. This is
also used to solve the scenario where the ISP only recognizes one MAC Address. System default is
Disable.
MAC Address: When MAC Spoofing is enabled, copy the ISP-recognized MAC address here. Format for
MAC address is six pairs of hexadecimal numbers (0-9, A-F) separated by colons. System default is:
00:00:00:00:00:00.
5.2.4 Static IP Settings
Static IP Settings are for users who have a Static IP Address (WAN side) from their ISP.
IP Address: It is the static IP Address given by the ISP.
Range: x.x.x.y, where 0 ≤ x≤ 255 and 1 ≤ y≤ 254 Default: 192.168.241.101
Subnet Mask: It is the subnet mask given by the ISP.
Range: x.x.x.x, where 0 ≤ x≤ 255 Default: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: It is the Gateway given by the ISP.
Page 18

13
Range: x.x.x.y, where 0 ≤ x≤ 255 and 1 ≤ y≤ 254 Default: 0.0.0.0
5.3 LAN Configuration
The LAN configuration page allows you to set the configuration for the LAN port.
LAN IP Address & Subnet Mask: The LAN IP Address is what the computer uses to identify and
communicate with the Router (this is the address you enter in the address bar of Internet Explorer to
access these pages). You can change this to another private IP address and subnet mask, such as
192.168.1.2 and 255.255.255.0.
Range: x.x.x.x, where 0 ≤ x≤ 255
Default is 10.0.0.2 and 255.0.0.0 (respectively)
5.3.1 DHCP Server
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a communications protocol that allows network
administrators to manage and assign IP addresses to computers within the network. DHCP provides a
unique address to a computer in the network which enables it to connect to the Internet through Internet
Protocol (IP). DHCP is controlled by the DHCP Server. The following settings allow you to configure the
DHCP server.
DHCP Server: Select Enabled (default) to activate DHCP Server.
DHCP Address Pool Selection: Two types of Address Pool selections are available, with System
Allocated as the default.
l System Allocated: The DHCP address pool is based on LAN port IP address plus 12 IP addresses.
For example, when the LAN IP address is 10.0.0.2; the DHCP address pool the range from 10.0.0.3
to 10.0.0.14.
l User Defined: When User Defined is selected, the DHCP address pool starts at the User Defined
Start Address and ends at the User Defined End Address. The maximum pool size can be 253 IP
addresses: 255 total IP addresses - 1 broadcast address - 1 LAN port IP address.
User Defined Start Address: It is the starting IP address of the DHCP pool for User Defined DHCP
Page 19

14
Address Pool Selection.
Range: x.x.x.x, where 0 ≤ x≤ 255 Default: 10.0.0.4
User Defined End Address: It is the last IP address in the DHCP pool for User Defined DHCP Address
Pool Selection.
Range: x.x.x.x, where 0 ≤ x≤ 255 Default: 10.0.0.15
DHCP Gateway Selection: The default setting for the DHCP Gateway Selection is Automatic. You can
select User Defined and specify User Defined Gateway Address.
The DHCP server will issue the User Defined Gateway Address to the LAN DHCP clients.
User Defined Gateway Address: The purpose for the User Defined Gateway Address is to have two
gateway addresses, as the LAN IP Address at the top of the LAN Configuration page is also a gateway
address.
Lease time: The Lease time is the amount of time a network user will be allowed to connect with DHCP
server. If all fields are 0, the allocated IP addresses will be effective forever.
Ranges for Lease Time fields: Days 0-36500, Hours 0-23, Minutes 0-59, Seconds 0-59, default value is 1
days 0 hours 0 minutes 0 seconds.
User mode: Under the Single User mode, the DHCP server only allocates one IP address to a local PC.
Under the Multiple User mode (default), the DHCP server allocates the IP addresses specified by the
DHCP address pool.
Save Configuration: Clicking this will link you to the Save Settings / Reboot page.
5.3.2 Ethernet Mode Setting
The Ethernet Mode configuration page allows you to set the LAN port into the following modes:
l AutoSense (default): The Router will automatically sense which mode to use, selecting between 100
Mbps Full Duplex, 100 Mbps Half Duplex, 10 Mbps Full Duplex, and 10 Mbps Half Duplex.
l 100 Mbps Full Duplex: Data can be transferred and received simultaneously at the transfer rate of
100 Mega-bits per second.
l 100 Mbps Half Duplex: Data cannot be transferred and received at the same time. For example,
data can be sent, and once the transmission is complete, data can be received. This is done at a
transfer rate of 100 Mega-bits per second.
l 10 Mbps Full Duplex: Data can be transferred and received simultaneously at the transfer rate of 10
Mega-bits per second.
l 10 Mbps Half Duplex: Data cannot be transferred and received at the same time. For example, data
can be sent, and once the transmission is complete, data can be received. This is done at a transfer
rate of 10 Mega-bits per second.
Page 20

15
5.4 PPP Configuration
The PPP Configuration page allows you to configure multiple PPP sessions for each PVC. Multiple PPP
sessions enables you to set up different connection settings and be able to toggle/choose those settings for
each PVC. The Router can support up to total of 16 PPP sessions, and each PVC can support up to 8 PPP
sessions. The multiple PPP sessions may be configured with any combination over 8 PVCs.
5.4.1 PPP Account Configuration
To begin PPP Session configuration, you must first go to the PPP Account Configuration page (below) to
set up an account. The link to this page can be found on the PPP Configuration page. On the PPP
Account Configuration page, you must configure the Account ID, User Name and Password.
Account ID: It allows you to create an account ID to help distinguish different accounts, up to 16 maximum.
The Account ID can be up to 31 characters.
User Name: Enter the PPP user name (provided by the ISP). The User Name can be up to 127 characters.
Page 21

16
?Note
nts with the same account name. If a different User
Password: Enter the PPP password (provided by the ISP). The Password is not needed to delete or
modify the account. The Password can be up to 127 characters.
PPP Account Configuration Status table will be displayed at the bottom of this page to show all the
accounts. The status table does not display the password.
The Number of PPP Accounts: It displays the total number of PPP Accounts entered.
You cannot have two different user accou
Name with an already existing Account ID is submitted, it will replace the previous account
with that Account ID. You can have the same User Name and Password for two different
accounts (Account ID).
5.4.2 PPP Session Configuration
Once you set up a PPP Account, you can begin PPP Session configuration either by clicking the Go back
to PPP Configuration link on the PPP Account Configuration page or clicking on PPP under the
Configuration menu on the left hand side of the browser.
Session Name: It allows you to enter a Session Name. This is user defined to help distinguish different
session for different PPP accounts and different PVCs.
PVC: It allows you to choose the specific PVC for the PPP session.
Service Name: The Service Name of the PPP session is required by some ISPs. If the ISP does not
provide the Service Name, please leave it blank.
Account to Use: You must select an account created in PPP Account Configuration page here.
Page 22

17
Disconnect Timeout: The Disconnect Timeout allows you to set the specific period of time, in minutes, to
disconnect from the ISP. The default is 0, which means never disconnect from the ISP.
Range: 0-32767 Default: 0
PPP Idle Timer Config: It will link you to the PPP Disconnect Timer Configuration page (see Section
5.4.3).
MRU: The MRU (Maximum Receive Unit) field indicates the maximum size IP packet that the peer of PPP
connection (this device) can receive. During the PPP negotiation, the peer of the PPP connection will
indicate its MRU and will accept any value up to that size.
Range: 0-32767 Default: 1492
MTU: Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is the largest size packet that can be sent by the modem. If the
network stack of any packet is larger than the MTU value, then the packet will be fragmented before the
transmission. During the PPP negotiation, the peer of the PPP connection will indicate its MRU and will
accept any value up to that size.
Range: 0-32767 Default: 1492
MSS: Maximum Segment Size is the largest size of data that TCP will send in a single, unfragmented IP
packet. The LAN client and the WAN host will indicate their MSS during the TCP connection handshake.
Range: 0-32767 Default: 1432
Lcp Echo Interval: It is the time interval, in seconds, between PPP session connection attempts.
Range: 0-32767 Default: 10
Lcp Echo Maximum Consecutive Failure: It is the number of times a PPP session can fail while trying to
connect before stopping. If a PPP session fails this number of times, you must manually reconnect the PPP
session.
Range: 0-32767 Default: 6
Authentication: The different types of available authentications are:
l Auto (default): When auto is selected, PAP mode will run by default. However, if PAP fails, then
CHAP will run as the secondary protocol. This is the default setting.
l PAP: Password Authentication Procedure. Authentication is done through username and password.
l CHAP: Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol. Typically more secure than PAP, CHAP uses
username and password in combination with a randomly generated challenge string which has to be
authenticated using a one-way hashing function.
Automatic Reconnect: When it is checked, the Router will reconnect a PPP session when it is terminated
by the ISP. If a PPP session is terminated under any other conditions (i.e. by Disconnect Timeout or
manual disconnect), the Automatic Reconnect will not reconnect the session. This box is unchecked by
default.
PPP Configuration Status: A table will be displayed at the bottom of this page to show all related
information of PPP configuration.
5.4.3 PPP Disconnect Timer Configuration
The PPP Disconnect Timer Configuration page enables you to configure what action will bring a PPP
Session out of the Idle state (disconnected state) and reset the Idle Timer. This is done by specifying
criteria contained in packets, namely IP Protocol and Port. The Idle Timer refers to the Disconnect Timeout,
specified on the PPP Configuration page.
The PPP Idle Timer is recommended to be disabled (Disconnect Timeout = 0 on PPP Configuration page)
if you want an always-on connection. PPP Disconnect Timer Configuration is intended for users who do
not desire an always-on connection and/or their ISP charge by connection time.
Page 23

18
5.4.3.1 Enable/Disable Idle Timer Filter
All Traffic will reset Idle Timer (ignore filter below): Selecting this option will disable the PPP Idle
Timeout filter and allow any traffic through any protocol or port to reset the idle timer. The only dependency
is that the traffic must correspond with the Filter Application (Inbound and/or Outbound). For example, if
Outbound Traffic Only is selected, only traffic in the outbound direction will reset the idle timer. When this
option is selected, all user configured criteria (displayed in the filter table) is bypassed.
Only filtered traffic will reset the Idle Timer (use filter below): Selecting this option will enable the PPP
Idle Timeout filter and only allow traffic specified in the filter table to reset the idle timer. The traffic specified
in the filter table must also correspond with the Filter Application selection. For example, outbound traffic
with criteria matching that of the filter table will only be allowed to pass if either Outbound Traffic Only or
Inbound and Outbound Traffic is selected.
?Note
PPP reconnect on WAN access must be enabled for the Idle Timer to reconnect a PPP
Session when a request is made from the LAN to the WAN.
5.4.3.2 Filter Application
The Filter Application consists of three options that determine which sources (LAN and/or WAN) will be
able to reset the Idle Timer and reconnect the PPP session.
Inbound Traffic Only: Selecting this option will allow PPP requests from the WAN side to reset the
Disconnect Timeout timer. Note that requests from the WAN side cannot bring a PPP Session out of Idle
state. This is because when a PPP Session is in Idle state, the connection is down (if they match the filter
table criteria).
Outbound Traffic Only (default): When this option is selected, PPP sessions can only be activated (Idle
Timeout) when a request is made on the LAN side to the WAN side. The disconnect timer will reset when
outbound traffic is detected (if they match the filter table criteria).
Inbound and Outbound Traffic: Selecting this will allow both WAN and LAN source packets to reset the
idle timer.
5.4.3.3 Filter Details
The table displayed in the Filter Details section of the page shows all the current Idle Filters. Traffic must
match the criteria of one of these filters in order to cause an Idle Timeout, unless All Traffic will reset Idle
Timer is selected. As a default and starting point for configuration, WWW browsing (HTTP), FTP, and
Telnet related packets are part of the filter table.
Page 24

19
IP Protocol: It is the IP Protocol name corresponding to the Protocol Number.
Protocol #: It is the IP protocol (number) through which the PPP session can be activated. The Protocol
Numbers for filters are:
l TCP Protocol Number: 6
l UDP Protocol Number: 17
l ICMP Protocol Number: 1
l IGMP Protocol Number: 2
Port #: It is the Port through which the PPP session can be activated. The default filters are:
l HTTP TCP Port: 80
l FTP TCP Port: 20 and 21
l Telnet TCP Port: 23
l DNS UDP: 53
Action: You can add a rule by entering the appropriate information, selecting Add on the Action dropdown
menu, and clicking Submit. To delete an entry, you can enter the information of an entry that already exists
on the table, select Delete on the Action dropdown menu, and click Submit.
5.4.4 PPP Miscellaneous Configuration
These options can be found on the Miscellaneous Configuration page under Admin Privilege.
PPP Half Bridge: When PPP Half Bridge is enabled, only one PC is able to access the Internet, and the
DHCP server will duplicate the WAN IP address from the ISP to the local client PC. Only the PC with the
WAN IP address can access the Internet. System default is Disabled.
PPP reconnect on WAN access: If enabled, the PPP session will automatically establish a connection
when a packet tries to access the WAN. System default is Disabled.
Connect PPP when ADSL link is up: If this option is enabled, the Router will connect the PPP session
whenever an ADSL connection is established. If this option is disabled, the PPP session will not connect
whenever the ADSL Showtime is reached. System default is Enabled.
Q. If the PPP session is disconnected after the Disconnect Timeout, how can I reconnect it?
Answer: You have to go to the PPP Status page, enter the correct connection number, select the Connect
option in the dropdown menu, and then click Execute. This will restart the PPP secession.
Q. What can I do to ensure an always-on connection with my PPP session?
Answer: There are two things you should do: 1) Make sure you have ‘0 ‘in the Disconnect Timeout field.
This will make sure that the PPP session is not disconnected from the user side. 2) Make sure the
Automatic Reconnect box is checked. This will cause the Router to automatically reconnect if the
connection is severed from either the ISP side or the user side.
Action Manual PPP
(Fee Based)
Connect PPP when ADSL link is up
Disconnect Timeout
PPP Reconnect on WAN access
Automatic Reconnect
Q. What is the difference between PPP Connect on WAN Access and the Automatic Reconnect?
Answer: For the PPP connect on WAN access, the PPP will be automatically reconnected when an URL is
entered in the browser (packet interested in going out the WAN). For the Automatic Reconnect, it will
reconnect the PPP session whenever it is terminated by ISP.
Disabled Enabled Enabled
0 Set Timeout 0
Disabled Enabled Disabled
Disabled Disabled Enabled
PPP Timeout
(Fee Based)
PPP Always-on
Page 25

20
5.5 NAT Configuration Pages
NAT allows only one entry (User IP) per session, while NAPT allows many entries (User IPs)
The NAT Configuration page allows you to set the configuration for the Network Address Translation. The
NAT module provides Dynamic Network Address and Port Translation (Dynamic NAPT) capability
between LAN and multiple WAN connections, and the LAN traffic is routed to appropriate WAN
connections based on the destination IP addresses and the Route Table. This eliminates the need for the
static NAT session configuration between multiple LAN clients and multiple WAN connections.
When Dynamic NAPT is chosen (default), there is no need to configure the NAT Session and NAT Session
Name Configuration.
Session Name: It allows you to enter a Session Name to help distinguish different NAT Sessions for
different interfaces among different PPP sessions and PVCs.
The Session Name can be up to 31 characters, and there can be up to 16 different NAT session names.
Interface: It allows you to choose specific WAN Interfaces (PVC or PPP Session) for NAT Session. The
options for this field are PVC0 ... PVC7 and any PPP session that was created by the user.
NAT Session Name Status: This table is displayed at the bottom of this page to show all the NAT Session
Names with their corresponding WAN Interfaces.
Number of NAT Configurations: It displays the total number of NAT Sessions entered.
?Note
per session.
Page 26

21
NAT: Use this field to Enable/Disable NAT. Default is Enable.
Mode: Options for the NAT dropdown menu are:
l NAT: Static peer-to-peer mode (1x1).
l NAPT: Static multiple mapping mode (1xN).
l Dynamic NAPT (default): Dynamic multiple mapping mode (NxN).
Session Name: It allows you to select the session from the configured NAT Session Name Configuration.
User’s IP: It allows you to assign the IP address to map the corresponding NAT/NAPT sessions.
Session Name Status: This table will be displayed at the middle of the page to show the Session Name
with its corresponding IP Address.
Number of NAT Configurations: It displays the total number of NAT Sessions entered.
Available Sessions: This table will be displayed at the bottom of the page to show all the available
Session Names with their corresponding WAN Interface.
Number of Sessions: It displays the total number of NAT Sessions entered.
5.6 Virtual Server Configuration
The Virtual Server Configuration page allows you to set the configuration of the Virtual Server. Virtual
Servers are used for port forwarding from the WAN to LAN networks. All UDP/TCP ports are protected from
intrusion. If any specific local PCs need to be mapped to the UDP/TCP port on WAN side, please input the
mappings here. There can be up to 20 different Virtual Server Configurations.
Page 27

22
ID: It is the ID number corresponding to the Virtual Server configuration.
Public Port - Start: It allows you to enter the port number of the Public Network (WAN or external network).
If you are entering a range of ports, this is the first port.
Public Port - End: It represents the last port number in a port range. If you only want one port number (no
port range), simply enter the same number here as in the Public Port - Start field. The maximum number
of the mapped Port is 20.
Private Port: It allows you to enter the port number of the Private Network (LAN or internal network). In
most cases, the private port number is same as public port number. This port number cannot be seen from
the WAN side.
Host IP Address: It allows you to enter the private network IP address for the particular server.
5.7 Bridge Filtering
Bridge Filtering allows packets to be forwarded or blocked, depending on the MAC address. The Bridge
Filtering configuration page allows you to set the configuration of MAC filtering. There can be up to 4
different Bridge Filtering configurations.
Page 28

23
Source MAC: This is the Source MAC to block or from which to forward. See the next page for instructions
on how to configure this. The Source MAC must consist of 12 hexadecimal characters.
Destination MAC: This is the Destination MAC to block or to forward to. See the next page for instructions
on how to configure this. The Destination MAC must consist of 12 hexadecimal characters.
Type: Enter the hexadecimal number for the Ethernet type field in Ethernet_II packets. For example, 0800
is for IP protocol. The Type must consist of 4 hexadecimal characters.
Block: When block is selected, everything from the Source MAC with destination Destination MAC will be
blocked.
Forward: When forward is selected, everything from the Source MAC will be forwarded to the Destination
MAC.
Q. How do I block packets from MAC address 000002fa6fab through IP protocol?
Answer: First go to the Bridge Filtering page under Configuration. Then type 000002fa6fab in the ID
Source MAC field and 0800 in the Type field. If bridge filtering is not already enabled, select Yes under the
Enable Bridge Filtering field. Then select Block and click Submit.
Q. How do I block incoming packets with destination MAC address 000003dc8faa through IP protocol?
Answer: First go to the Bridge Filtering page under Configuration. Then type 000003dc8faa in the
Destination MAC field, and 0800 in the Type field. If bridge filtering is not already enabled, select Yes
under the Enable Bridge Filtering field. Then select Block and click Submit.
Q. How do I forward packets with MAC address 000002fa6fab to destination MAC 000003dc8faa through
IP protocol?
Answer: First go to the Bridge Filtering page under Configuration. Then type 000002fa6fab in the ID
Source MAC field, 000003dc8faa in the Destination MAC field, and 0800 in the Type field. If bridge
filtering is not already enabled, select Yes under the Enable Bridge Filtering field. Then select Forward
and click Submit.
5.8 DNS Configuration
The DNS Configuration page allows you to set the configuration of the DNS proxy.
For the DHCP requests from local PCs, the DHCP server will set the LAN port IP as the default DNS server.
Page 29

24
Thus, all DNS query messages will come into LAN port first. The DNS proxy on the Router records the
available DNS servers and forwards DNS query messages to one of DNS servers.
DNS Proxy Enable/Disable: When the DNS Proxy is Disabled, the LAN port does not process the DNS
query message. For the DHCP requests from local PCs, the DHCP server will set the user-configured DNS
server as the DNS server. Then all DNS query messages will be directly sent to the DNS servers. DNS
Proxy is enabled by default.
Auto Discovered: When enabled (default), the DNS proxy will store the DNS server IP addresses
obtained from DHCP client or PPP into the table. All DNS query messages will be sent to the dynamically
obtained DNS server. Select this option when the DNS Server address is unknown but provided
(automatically) by the ISP.
User Configured: When enabled, the DNS proxy will use the user-configured DNS server. All DNS query
messages will be sent to the DNS server. Enter the DNS IP in the DNS Server field. Select this option when
the DNS Server address assigned by the ISP is known. User Configured is disabled by default.
Auto Discovery + User Configured: Selecting both options will cause the DNS proxy’s table to have all
the IP addresses of dynamically obtained and user configured DNS servers.
?Note
DNS Server: It is the user defined DNS server URL name and IP. Default is Disabled.
l URL Name (Add/Delete): It is the URL name for the DNS server. This can be up to 255 characters.
l Host IP (Add Only): It is the IP address of the DNS Server.
DNS Proxy Setting: It is a table of all DNS server IP addresses.
DNS Server Setting: It is a table of all DNS sever URL names.
Save Configuration: Clicking this will link the user to the Save Settings / Reboot page.
When User Configured is ticked, you have to enter the IP of DNS server(s) to make the
feature take effect.
Page 30

25
5.9 Dynamic DNS
The Dynamic DNS page allows you to set the configuration of the DDNS.
You need to apply for a DNS domain name from http://www.dyndns.org. The Router will update the WAN IP
address to DDNS’s database once a WAN port was connected to Internet if Dynamic DNS function is
enabled. And the users in Internet can find out your Router according to this domain name.
DDNS Server: Select the DDNS server from drop-down list.
Update Type: There are three types of update method.
l dyndns: Select dyndns type if your IP is dynamic.
l custom: Select custom type if you own a unique domain name.
l static: Select static type if your IP is fixed.
Username & Password: Enter the username and password of your DDNS service account.
Host Name 0-4: Enter at least one host name in the field. You need to pre-configure these host names in
your DDNS service account so that the DDNS server could map them to your IP.
For more information of DDNS service, please visit http://www.dyndns.org.
5.10 User Password Configuration
The User Password Configuration page allows the user or admin to set the password for the user account.
The User Password can be up to 65 characters (excluding ‘&’).
Page 31

26
5.11 Save Settings / Reboot
The Save Settings / Reboot page allows you to either save the new configuration to the flash and reboot
the Router or simply reboot the Router without saving changes.
Save & Reboot: Click this to apply all changes.
Reboot Only: Do this to discard all changes since last save.
After either one of these buttons are clicked, the Router will do the following:
l Save & Reboot: Two pages will appear after pressing this button. The first one states: “Your settings
are being saved and the modem being rebooted. Save-reboot in progress, please wait….”
Followed by “Your settings have been saved and the modem has rebooted. Done.”
l Reboot Only: Two pages will appear after pressing this button. The first one states: “The modem is
being rebooted. Reboot in progress, please wait….” Followed by “The modem is being rebooted.
Done.”
Page 32

27
6. Admin Privilege
The links under Admin Privilege are only accessible when user is logged in as Admin.
Regular user account does not have authorization to view or alter the content on the pages in the Admin
Privilege section.
6.1 WAN Status
The WAN Status page shows the information and status of WAN PVCs.
WAN: It displays the IP address, Subnet Mask and MAC address for the WAN (ADSL) interface. Use the
Virtual Circuit selection to select different PVCs for status display.
Virtual Circuit: Select the Virtual Circuit that you want to release/renew, select the appropriate option on
the menu dropdown and click Execute.
6.2 ATM Status
The ATM Status page shows all the statistics information of ATM cells. This page contains information that
is dynamic and will refresh every 2 seconds.
Page 33

8
Reset Counters: This button allows user to reset the ATM Status counter.
6.3 ADSL Configuration
The ADSL Configuration page allows you to set the configuration for ADSL protocols.
Annex Mode Config: It allows you to manually configure the Router for Annex A or Annex B mode by
selecting User Configured and choosing the Annex Mode in the next field.
User Selected Annex Mode: It allows you to select from Annex A and Annex B.
Please DO NOT change the default setting of Annex Mode unless you are instructed to do this
by your ISP.
Trellis: Trellis Code is an advanced method of FEC (Forward Error Correction). It allows you to enable or
disable the Trellis Code. By default, it is always enabled.
Handshake Protocol: It allows you to select from the following ADSL handshake protocols: Autosense -
2
Page 34

29
G.dmt first (default), Autosense - T1.413 first, G.dmt/G.lite, T1.413, G.dmt, and G.lite.
Wiring Selection: It allows you to enter the wiring selection for the RJ-11.
Tip/Ring is the default for the Router without the inner/outer pair relay. Available types are Auto, Tip/Ring
(default), and A/A1, where Tip/Ring is the inner-most pair of wires on the RJ11 and A/A1 is the second
inner-most pair.
Bit Swapping: It allows you to enable or disable the upstream bit swapping. Bit Swapping is disabled by
default.
6.4 Route Table
The Route Table page displays the routing table and allows you to manually enter a routing entry. The
routing table will display the routing status of Destination, Netmask, Gateway, and Interface. The interface
br0 indicates the USB interface (reserved function); lo0 indicates the loopback interface; ppp1 indicates the
PPP interface. The Gateway is the learned Gateway.
l The Gateway field of the static route entry allows users to either enter a Gateway IP address or select
a Network Interface.
l All user-defined routes retained in the CPE memory, regardless if they are already in the Routing
Table, are displayed on the same Route Table page.
l All user defined route entries kept in the CPE memory during run time are saved to flash when the
user chooses to save and reboot the CPE. When the CPE restarts, it reloads all saved user-defined
routes to the CPE memory and tries to apply to the system.
l A user-defined route entry is added to the Routing Table whenever the system provides an
environment that makes the route entry applicable. It is removed from the Routing Table whenever
the route entry becomes not applicable. e.g. If the route entry’s Gateway is associated with a dynamic
Network Interface but the connection is not established, then the route entry does not appear in the
Routing Table. When that interface comes up later, the route entry is then added.
Page 35

30
l If the selected Network Interface is static or dynamic and the connection is already up, then the route
entry appears in the Routing Table immediately. If there is a Gateway associated with the selected
Network Interface, then that Gateway’s IP address appears in the Gateway field of the route entry.
If the selected Network Interface is dynamic but the connection is not established, then the route entry
does not appear in the Routing Table. When the interface comes up later, the route entry is then
added.
6.4.1 System Default Gateway Configuration
The system-wide Default Gateway provides three options: Auto (default), User-selected
Network Interface, and None.
l None: It allows you to choose to have no Default Gateway in the CPE.
l Auto (default): It allows you to enable the Router to automatically decide the Default Gateway.
l User-selected Network Interface: It allows you to select a Network Interface from a list (PVCs, PPP
Sessions and LAN). This option allows you to associate the system-wide Default Gateway to a
Network Interface, static or dynamic, and provides a way to fix the Default Gateway to a dynamic
Network Interface before the interface is established.
?Note
l Specify IP: It allows you to specify the IP address of the default gateway.
The options for this field are IP PVC0 ... IP PVC7, IP Ethernet 0, IP BridgeMux0, and any
PPP session that was created by the user.
6.4.2 Route Configuration
Destination: It allows you to enter the remote network or host IP address for the static routing.
Netmask: It allows you to enter the Subnet Mask for the static routing.
Gateway: It allows you to enter the IP address of the gateway device that allows the router to contact the
remote network or the host for Specified IP or select an Interface for the Gateway.
Manually Configured Routes: It displays the static route entries entered by the user.
6.5 Learned MAC Table
Network bridges operate at the physical network layer. The purpose of a bridge is to connect two or more
networks and enable packet sharing between them. Bridges are different from routers because they
forward packets based on physical addresses, whereas routers use IP address to forward packets. Bridges
must learn all the physical (MAC) addresses of the devices so it can forward the packets reliably. The
purpose of the Learned MAC Table is to store and display these bridge-recognized MAC addresses.
The Learned MAC Table page shows the current learned Bridge MAC table. This page contains
information that is dynamic and will refresh every 8 seconds.
Page 36

31
Aging Timeout: It allows you to enter the update period for the MAC table.
Have this number lower if you want a more frequent refresh rate.
Range: 0 - 32767 Default: 100
6.6 RIP Configuration
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a management protocol that ensures that all hosts in a particular
network share the same information about routing paths.
The RIP Configuration page allows you to set the configuration for the system wide configuration of RIP.
The actual RIP configuration is in the RIP Per Interface Configuration.
RIP: It allows you to Enable or Disable the RIP session. The resulting RIP session will monitor all network
interfaces that are currently available for messages from other RIP routers. RIP is disabled by default.
Border Gateway: RIP implements Border Gateway as specified in RFC 1058 and RFC 1723. This limits all
subnet routes and host routes to routers within that same network.
Updates sent outside that network will only include a single entry representing the entire network, including
all subnets and host-specific routes. The Border Gateway is enabled by default.
Page 37

32
Supplier Interval: It allows you to enter the Supplier Interval timer in seconds.
This timer specifies how often the RIP sends announcements as a RIP Supplier.
Range: 0 - 2147483647 Default: 30
Expire Timeout:It allows you to enter the Expire Timeout in seconds. This timer specifies the expiration
time of a route. When a route has not been updated for more than the “expire” period of time, it is removed
from the Route Table. This route is then invalidated and remains in the internal RIP Route Table. It will be
included in the RIP announcements to let other routers know the changes.
Range: 0 - 2147483647 Default: 180
Garbage Timeout: It allows you to enter the Garbage timer in seconds. This timer specifies how long the
expired and invalidated routes are kept in the Internal RIP Route Table before they are removed from it.
Range: 0 - 2147483647 Default: 120
6.6.1 RIP Per Interface Configuration
The RIP Per Interface Configuration page allows you to set the configuration for each Interface (PVCs,
PPP Sessions and LAN).
Interface: It allows you to choose the Interface (PVCs, PPP Sessions and LAN), for the RIP to be
configured. The available selections are: IP Ethernet 0, IP USB 0, IP PVC0...IP PVC7, IP BridgeMux 0, and
any PPP user defined sessions (maximum of 16):
Enable: It allows you to Enable (Yes) or Disable (No) the specified interface for RIP.
Supplier: It allows you to select the Supplier Mode (RIP Transmit).
l Disabled: The supplier transmit is disabled.
l V1 BC: The supplier transmits in RIPv1 Broadcast.
l V2 BC: The supplier transmits in RIPv2 Broadcast.
l V2 MC: The supplier transmits in RIPv2 Multicast.
Listener: It allows you to select the Listener Mode (RIP Receive).
l V1: The listener receives the RIPv1 only.
l V2: The listener receives the RIPv2 only.
l V1+V2: This listener receives the both RIPv1 and RIPv2.
Current RIP Settings: It displays the each interface’s RIP status.
Page 38

33
6.7 Miscellaneous Configuration
The Miscellaneous Configuration page allows you to set miscellaneous configurations for the following:
HTTP, FTP, TFTP, DMZ, Command Line Interface, DHCP, PPP, IGMP, and SNTP.
HTTP Server Access: It allows you to configure where these Web pages could be accessed from.
l All (default): When this field is checked, it allows both WAN and LAN access to the Web pages.
l Restricted LAN: It allows the Web pages access from LAN side.
l Restricted WAN Specified IP & Subnet Mask: It allows the Web access from WAN side with a
specify IP and subnet mask.
HTTP Server Port: It allows you to specify the port of the Web access. For example, when it is changed to
8080, the HTTP server address for the LAN side is http://10.0.0.2:8080.
Range: 0 - 32767 Default: 80
Page 39

34
FTP server: It allows you to enable or disable the FTP server connection.
System default is Enabled.
l Disable WAN side FTP access: This will disable WAN side access to the FTP server, default is
Disabled.
TFTP server: It allows you to enable or disable the TFTP connection. System default is Disabled.
DMZ: A DMZ (De-Militarized Zone) is added between a protected network and an external network, in
order to provide an additional layer of security. When there is a suspected packet coming from WAN, the
system will forward this packet to the DMZ host.
DMZ Host IP: The IP address of the DMZ host viewable at the WAN (external) side.
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a communications protocol that allows network
administrators to manage and assign IP addresses to computers within the network. DHCP provides a
unique address to a computer in the network which enables it to connect to the Internet through Internet
Protocol (IP).
l NONE: It will disable the DHCP server. Note that this setting will override the DHCP Server
Enable/Disable on the LAN configuration page.
l DHCP Server (default): Select this to activate the DHCP server.
l DHCP Relay: If it is enabled, the DHCP requests from local PCs will forward to the DHCP server runs
on WAN side. To have this function working properly, please disable the NAT to run on router mode
only, disable the DHCP server on the LAN port, and make sure the routing table has the correct
routing entry.
DHCP Relay Target IP: If DHCP Relay is enabled, DHCP requests are relayed to DHCP Target IP on the
WAN side.
IGMP Proxy: It is the global setting for IGMP Proxy. If it is enabled, then the enabled IGMP Proxy on WAN
PVCs will be working. Otherwise, no WAN PVC can have IGMP Proxy working on it. System default is
Disabled.
PPP Half Bridge: When PPP Half Bridge is enabled, only one PC is able to access the Internet, and the
DHCP server will duplicate the WAN IP address from the ISP to the local client PC. Only the PC with the
WAN IP address can access the Internet. System default is Disabled.
PPP reconnect on WAN access: If enabled, the PPP session will automatically establish a connection
when a packet tries to access the WAN. System default is Disabled.
Connect PPP when ADSL link is up: If this option is enabled, the Router will connect the PPP session
whenever an ADSL connection is established. If this option is disabled, the PPP session will not connect
whenever the ADSL Showtime is reached.
System default is Enabled.
?Note
SNTP: Simple Network Time Protocol is an efficient method of obtaining the time from a Time Server.
Time Zone: It specifies the time zone (geographical location).
Daylight Saving Time: You can select yes to activate Daylight Savings Time.
User defined Time server: This is the time server from which the Router retrieves the time.
For more information, please refer to Section 5.4: PPP Configuration.
Page 40

35
6.8 TCP Status
The TCP Status page shows the statistics for all TCP connections. This page contains information that is
dynamic and will refresh every 2 seconds.
6.9 Admin Password Configuration
The Admin Password Configuration page allows you to set the password for administrator. The Admin
password can be up to 65 characters (excluding ‘&’).
Page 41

36
6.10 Reset to Factory Default
The Reset to Factory Default page allows you to reset the Router to original factory default configuration.
6.11 Diagnostic Test
The Diagnostic Test page shows the test results for the connectivity of the physical layer and protocol
layer for both LAN and WAN sides. This page will continually refresh every 2 seconds until all tests are
complete.
Page 42

37
6.12 System Log
The System Log page shows the events triggered by the system. This page contains information that is
dynamic and will refresh every 5 seconds.
6.13 Local Code Image Update
The Local Code Image Update page allows you to upgrade the image code locally. Firstly, you need to
download the new code to your local drive. And then follow the description below to update your firmware.
1. Login to WEB management Interface
http://10.0.0.2 and then click Local Code Image
Update.
2. Click Image Download. After the user clicks on
"Image Download", the system will reboot with
new configuration by disabling the "SNTP",
DNSPROXY","IGMPPROXY", "FTPSERVER",
“Wireless”, "Telnet" and "ADSL" components.
Page 43

38
3. Select Bootrom.dlf and click Download to
If system doesn’t get into this page in a
n again then
Display “File successfully transferred” message
upgrade boot code. Never power off after
download start.
Note: If system doesn’t get into this page in a long
time, please power on again then click Local Code
Image Update again.
4. Display “File successfully transferred” message
when upgrade successfully. Wait system reboot.
5. Click Local Code Image Update again for
firmware code upgrade. Click Image Download.
6. Select Firmware.dlf and click download to
upgrade firmware code. Never power off after
download start.
?Note
7.
when upgrade successfully. Wait system
reboot. Power on again, system will refresh
new factory default setting. Press the reset
button at the rear panel to load factory default
setting.
long time, please power o
click Local Code Image Update again.
Page 44

39
Appendix A. Compliance Statement
FCC Warning
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1)
This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
l Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
l Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
l Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
l Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference in which case
the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Page 45

40
Appendix B. Encapsulation Mode
Bridged mode(RFC-1483)
RFC-1483 provides the simplest method of connecting end station over an ATM network. User data in the
form of Ethernet frames is encapsulated into AAL5-PDU for transport over ATM. RFC-1483 provides no
authentication and configuration such as would be provided by PPP. RFC-1483 implementation supports VC
multiplexing and LLC/SNAP encapsulation in both routed and bridged configurations.
Classical IP over ATM-IPOA(RFC1577)
User data in the form of IP packets is encapsulated into AAL-5 PDUs for transport over ATM. The fact that the
user data is routed at an IP layer instead of bridged MAC layer allows the source and destination to be on
different subnets. A notable drawback of IPoA is the lack of authentication and configuration such as would be
provided by PPP.
PPP over ATM-PPPoA(RFC-2364)
The use of PPPoA is similar to IPoA. However, a PPP session is established to the remote access server
(RAS). The PPP packets are encapsulated according to RFC-2364 for transmission over an ATM link. On the
receive side, the de-encapsulation is performed. The PPP session is terminated and the IP packets can be
delivered to the end user over Ethernet or other medium.
PPP over Ethernet-PPPoE(RFC-2516)
The PPP over Ethernet(PPPoE)encapsulation is used to transport PPP traffic from a PC to a DSL device
over Ethernet and then over the DSL link using RFC-1483 encapsulation. There may be multiple PPP
sessions, each terminated in a PC or in the CPE device and in a PPP aggregator on the CO side.
l The PPPoE Client terminates PPPoE session within the CPE device, this configuration enables PPPoE
session without a need for additional software.
l The PPP traffic for a Relay Agent is not terminated in the DSL device, rather it is relayed over the DSL
link to a PPP aggregator in the CO PPPoE relay agent determines on which session locally originated
PPPoE traffic belongs. The relay agent forwards that traffic, without any unnecessary processing to the
correct destination only. Similarly, received data is immediately relayed only to the appropriate client PC.
Not only does this approach enhance performance by eliminating additional process, it also provides a
critical security feature, so it prevents for example corporate bound data from being exposed to the
Internet.
Page 46

41
Appendix C. Troubleshooting
This Appendix covers the most likely problems and their solutions.
Overview
This chapter covers some common problems that may be encountered while using ADE-3100/4100 and some
possible solutions to them. If you follow the suggested steps and ADE-3100/4100 still does not function
properly, contact your dealer for further advice.
General Problems
Question 1 Can't connect to ADE-3100/4100 to configure it.
Answer 1
Check the following:
• ADE-3100/4100 is properly installed, LAN connections are OK, and it is powered ON.
• Ensure that your PC and ADE-3100/4100 are on the same network segment. (If you
don't have a router, this must be the case.)
• If your PC is set to "Obtain an IP Address automatically" (DHCP client), restart it.
• If your PC uses a Fixed (Static) IP address, ensure that it is using an IP Address
within the range 10.0.0.3 to 10.255.255.254 and thus compatible with
ADE-3100/4100's default IP Address of 10.0.0.2.
Also, the Network Mask should be set to 255.0.0.0 to match ADE-3100/4100. In
Windows, you can check these settings by using Control Panel-Network to check the
Properties for the TCP/IP protocol.
Configuration and Internet Access
Question 1 When I enter a URL or IP address I get a time out error.
Answer 1
A number of things could be causing this.
Question 2
Try the following troubleshooting steps.
• Check if other PCs work. If they do, ensure that your PCs IP settings are correct. If
using a Fixed IP Address, check the Network Mask, Default gateway and DNS
configured on PC.
• If the PCs are configured correctly, but still not working, check ADE-3100/4100.
Ensure that it is connected and ON. Connect to it and check its settings. (If you can't
connect to it, check the LAN and power connections.)
• If ADE-3100/4100 is configured correctly, contact your ISP to see if Internet
connection is working correctly.
If the PPP is disconnected after the Disconnect Timeout and how can I reconnect it?
Page 47

42
Answer 2 You have to go to the PPP link under Status column, choose the correct PVC and
Connect option, and then click Execute to restart a new PPP secession.
Question 3
Answer 3
Since only one PVC is mapped to one local PC IP address, why can I input more than one
IP address for one NAT session?
Even it is applicable to insert multiple IPs for NAT mapping, only the first IP address of
each session takes effect.
Page 48

43
Appendix D. Specifications
Product ADSL Modem Router
Model ADE-3100 ADE-4100
ADSL Standards Full-rate ANSI T1.413 issue 2 and ITU-T G992.1 (G.DMT), Splitterless ITU-T
G.992.2 (G.lite)
Protocol Support RFC2364 - PPP over ATM (LLC/VCMUX)
RFC2516 - PPP over Ethernet (LLCSNAP/VCMUX)
RFC1577 - Classic IP over ATM
RFC1483 - Bridged IP over ATM(LLCSNAP/VCMUX)
RFC1483 - Routed IP over ATM (LLCSNAP/VCMUX)
AAL & ATM Support Integrated ATM AAL 5 support
Data Rate UP / DOWN Stream: 1 / 8 Mbps
Power Supply 9V AC, 1.0A maximum 9V DC, 1.5A maximum
Environment Operating temperature: 0ºc to 40ºc
Operating humidity: 10% to 90%
Storage temperature: -20ºc to 70ºc(non-condensing)
Storage humidity: 10% to 90%(non-condensing)
Dimension 163mm x 124mm x 39mm (L x W x H)
ADSL Interface RJ-11 Modular Jack
Page 49

44
 Loading...
Loading...