
Pepwave MAX HD4 MBX
User Manual
Pepwave Products:
MAX HD4 MBX / MBX / HD4 MBX / MAX-HD4-MBX-LTEA-R-T / EXM-T4-LTEA-R
Pepwave Firmware 7.1.1
February 2019
Copyright & Trademarks
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Copyright © 2019 Pepwave Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Pepwave and the
Pepwave logo are trademarks of Pepwave Ltd. Other brands or products mentioned may be trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective owners.

Table of Contents
Introduction and Scope 7
Glossary 8
Product Features 9
Supported Network Features 9
WAN 9
LAN 10
VPN 10
Firewall 10
Captive Portal 11
Outbound Policy 11
AP Controller 11
QoS 11
Other Supported Features 11
Pepwave MAX Mobile Router Overview 13
MAX HD4 MBX 13
Advanced Feature Summary 16
Drop-in Mode and LAN Bypass: Transparent Deployment 16
QoS: Clearer VoIP 16
Per-User Bandwidth Control 17
High Availability via VRRP 17
USB Modem and Android Tethering 18
Built-In Remote User VPN Support 19
SIM-card USSD support 19
Installation 21
Preparation 21
Constructing the Network 21
Configuring the Network Environment 22
Connecting to the Web Admin Interface 23
Configuring the LAN Interface(s) 25
Basic Settings 25
https://www.peplink.com 2 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Port Settings 36
Captive Portal 36
Configuring the WAN Interface(s) 39
Ethernet WAN 40
DHCP Connection 42
Static IP Connection 43
PPPoE Connection 44
L2TP Connection 46
Cellular WAN 47
Wi-Fi WAN 53
Creating Wi-Fi Connection Profiles 60
WAN Health Check 62
Dynamic DNS Settings 64
Advanced Wi-Fi Settings 66
MediaFast Configuration 71
Setting Up MediaFast Content Caching 71
Scheduling Content Prefetching 72
Viewing MediaFast Statistics 73
Bandwidth Bonding SpeedFusionTM / PepVPN 75
PepVPN 75
The Pepwave Router Behind a NAT Router 82
SpeedFusionTM Status 83
IPsec VPN 83
IPsec VPN Settings 84
Outbound Policy Management 88
Outbound Policy 89
Custom Rules for Outbound Policy 90
Algorithm: Weighted Balance 90
Algorithm: Persistence 91
Algorithm: Enforced 93
Algorithm: Priority 93
Algorithm: Overflow 94
Algorithm: Least Used 94
https://www.peplink.com 3 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Algorithm: Lowest Latency 94
Expert Mode 95
Inbound Access 95
Port Forwarding Service 95
UPnP / NAT-PMP Settings 98
NAT Mappings 98
QoS 100
User Groups 100
Bandwidth Control 101
Application 102
Application Prioritization 102
Prioritization for Custom Applications 102
DSL/Cable Optimization 103
Firewall 103
Outbound and Inbound Firewall Rules 104
Access Rules 104
Apply Firewall Rules to PepVpn Traffic 107
Intrusion Detection and DoS Prevention 107
Content Blocking 109
Application Blocking 109
Web Blocking 110
Customized Domains 110
Exempted User Groups 110
Exempted Subnets 110
URL Logging 110
OSPF & RIPv2 111
BGP 114
Remote User Access 116
Miscellaneous Settings 118
High Availability 118
PPTP Server 122
Certificate Manager 124
Service Forwarding 124
https://www.peplink.com 4 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

SMTP Forwarding 125
Web Proxy Forwarding 126
DNS Forwarding 126
Custom Service Forwarding 126
Service Passthrough 127
GPS Forwarding 128
AP Controller 129
Wireless SSID 129
Settings 134
AP Controller Status 140
Info 140
Access Point (Usage) 142
Wireless SSID 145
Wireless Client 146
Nearby Device 147
Event Log 148
Toolbox 149
System Settings 150
Admin Security 150
Firmware 154
Time 155
Schedule 155
Email Notification 157
Event Log 159
SNMP 160
InControl 163
Configuration 163
Feature Add-ons 164
Reboot 164
Tools 165
Ping 165
Traceroute Test 166
PepVPN Test 166
https://www.peplink.com 5 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Wake-on-LAN 167
CLI (Command Line Interface Support) 167
Status 169
Device 169
Active Sessions 170
Client List 172
WINS Client 173
UPnP / NAT-PMP 173
SpeedFusion Status 174
Event Log 178
Bandwidth Status 179
Real-Time 180
Hourly 180
Daily 181
Monthly 181
Appendix B: Declaration 185
https://www.peplink.com 6 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

1 Introduction and Scope
Pepwave routers provide link aggregation and load balancing across multiple WAN connections,
allowing a combination of technologies like 3G HSDPA, EVDO, 4G LTE, Wi-Fi, external WiMAX
dongle, and satellite to be utilized to connect to the Internet.
This manual covers setting up Pepwave routers and provides an introduction to their features
and usage.
Tips
Want to know more about Pepwave routers? Visit our YouTube Channel for a video introduction!
http://youtu.be/UCkVQThLKO4
https://www.peplink.com 7 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

2 Glossary
The following terms, acronyms, and abbreviations are frequently used in this manual:
Term Definition
3G 3rd generation standards for wireless communications (e.g., HSDPA)
4G 4th generation standards for wireless communications (e.g., LTE)
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DNS Domain Name System
EVDO Evolution-Data Optimized
FQDN Fully Qualified Domain Name
HSDPA High-Speed Downlink Packet Access
HTTP Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol
IP Internet Protocol
LAN Local Area Network
MAC Address Media Access Control Address
MTU Maximum Transmission Unit
MSS Maximum Segment Size
NAT Network Address Translation
PPPoE Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet
QoS Quality of Service
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
https://www.peplink.com 8 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

UDP User Datagram Protocol
VPN Virtual Private Network
VRRP Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
WAN Wide Area Network
WINS Windows Internet Name Service
WLAN Wireless Local Area Network
3 Product Features
Pepwave routers enable all LAN users to share broadband Internet connections, and they
provide advanced features to enhance Internet access. Our MAX HD series wireless routers are
embedded with multiple 4G LTE modems, and allow simultaneous wireless Internet connections
through multiple wireless networks. The wireless Internet connections can be bonded together
using our SpeedFusion technology. This allows better reliability, larger bandwidth, and
increased wireless coverage are comparing to use only one 4G LTE modem.
Below is a list of supported features on Pepwave routers. Features vary by model. For more
information, please see peplink.com/products.
3.1 Supported Network Features
3.1.1 WAN
● Ethernet WAN connection in full/half duplex
● Static IP support for PPPoE
● Built-in cellular modems
● USB mobile connection(s)
● Wi-Fi WAN connection
● Network address translation (NAT)/port address translation (PAT)
● Inbound and outbound NAT mapping
● IPsec NAT-T and PPTP packet passthrough
● MAC address clone and passthrough
● Customizable MTU and MSS values
● WAN connection health check
https://www.peplink.com 9 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

● Dynamic DNS (supported service providers: changeip.com, dyndns.org, no-ip.org,
tzo.com and DNS-O-Matic)
● Ping, DNS lookup, and HTTP-based health check
3.1.2 LAN
● Wi-Fi AP
● Ethernet LAN ports
● DHCP server on LAN
● Extended DHCP option support
● Static routing rules
● VLAN on LAN support
3.1.3 VPN
● PepVPN with SpeedFusionTM
● PepVPN performance analyzer
● X.509 certificate support
● VPN load balancing and failover among selected WAN connections
● Bandwidth bonding and failover among selected WAN connections
● IPsec VPN for network-to-network connections (works with Cisco and Juniper only)
● Ability to route Internet traffic to a remote VPN peer
● Optional pre-shared key setting
TM
● SpeedFusion
● PPTP server
● PPTP and IPsec passthrough
throughput, ping, and traceroute tests
3.1.4 Firewall
● Outbound (LAN to WAN) firewall rules
● Inbound (WAN to LAN) firewall rules per WAN connection
● Intrusion detection and prevention
● Specification of NAT mappings
● Outbound firewall rules can be defined by destination domain name
https://www.peplink.com 10 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

3.1.5 Captive Portal
● Splash screen of open networks, login page for secure networks
● Customizable built-in captive portal
● Supports linking to outside page for captive portal
3.1.6 Outbound Policy
● Link load distribution per TCP/UDP service
● Persistent routing for specified source and/or destination IP addresses per TCP/UDP
service
● Traffic prioritization and DSL optimization
● Prioritize and route traffic to VPN tunnels with Priority and Enforced algorithms
3.1.7 AP Controller
● Configure and manage Pepwave AP devices
● Review the status of connected APs
3.1.8 QoS
● Quality of service for different applications and custom protocols
● User group classification for different service levels
● Bandwidth usage control and monitoring on group- and user-level
● Application prioritization for custom protocols and DSL/cable optimization
3.2 Other Supported Features
● User-friendly web-based administration interface
● HTTP and HTTPS support for web admin interface
● Configurable web administration port and administrator password
● Firmware upgrades, configuration backups, ping, and traceroute via web admin interface
● Remote web-based configuration (via WAN and LAN interfaces)
● Time server synchronization
● SNMP
● Email notification
● Read-only user for web admin
https://www.peplink.com 11 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

● Shared IP drop-in mode
● Authentication and accounting by RADIUS server for web admin
● Built-in WINS servers*
● Syslog
● SIP passthrough
● PPTP packet passthrough
● Event log
● Active sessions
● Client list
● WINS client list
● UPnP / NAT-PMP
● Real-time, hourly, daily, and monthly bandwidth usage reports and charts
● IPv6 support
● Support USB tethering on Android 2.2+ phones
https://www.peplink.com 12 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

4 Pepwave MAX Mobile Router Overview
4.1 MAX HD4 MBX
4.1.1 Panel Appearance
https://www.peplink.com 13 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

4.1.2 LED Indicators
The statuses indicated by the front panel LEDs are as follows:
Status Indicators
https://www.peplink.com 14 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

OFF System initializing
Red Booting up or busy
Status
Blinking
red
Green Ready
Wi-Fi AP and Wi-Fi WAN Indicators
OFF Disabled Intermittent
Boot up error
Wi-Fi WAN /
Cellular 1 /
Cellular 2
Green LED ON 10 / 100 / 1000 Mbps
Orange LED
Port Type Auto MDI/MDI-X ports
Blinking slowly Connecting to wireless network(s)
onnected to wireless network(s) with traffic
Blinking
ON Connected to wireless network(s) without traffic
LAN and Ethernet WAN Ports
Blinking Data is transferring
OFF No data is being transferred or port is not connected
C
https://www.peplink.com 15 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

5 Advanced Feature Summary
5.1 Drop-in Mode and LAN Bypass: Transparent Deployment
As your organization grows, it needs more bandwidth. But modifying your network would require
effort better spent elsewhere. In Drop-in Mode, you can conveniently install your Peplink router
without making any changes to your network. And if the Peplink router loses power for any reason,
LAN Bypass will safely and automatically bypass the Peplink router to resume your original network
connection.
5.2
QoS: Clearer VoIP
VoIP and videoconferencing are highly sensitive to latency. With QoS, Peplink routers can detect
https://www.peplink.com 16 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

VoIP traffic and assign it the highest priority, giving you crystal-clear calls.
5.3 Per-User Bandwidth Control
With per-user bandwidth control, you can define bandwidth control policies for up to 3 groups of
users to prevent network congestion. Define groups by IP address and subnet, and set bandwidth
limits for every user in the group.
5.4 High Availability via VRRP
https://www.peplink.com 17 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

When your organization has a corporate requirement demanding the highest availability with no
single point of failure, you can deploy two Peplink routers in High Availability mode. With High
Availability mode, the second device will take over when needed.
5.5 USB Modem and Android Tethering
For increased WAN diversity, plug in a USB LTE modem as backup. Peplink routers are
compatible with over 200 modem types. You can also tether to smartphones running Android
4.1.X and above.
https://www.peplink.com 18 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

5.6
Built-In Remote User VPN Support
Use L2TP with IPsec to safely and conveniently connect remote clients to your private network.
L2TP with IPsec is supported by most devices, but legacy devices can also connect using PPTP.
Click here for full instructions on setting up L2TP with IPsec.
5.7 SIM-card USSD support
https://www.peplink.com 19 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Cellular-enabled routers can now use USSD to check their SIM card’s balance, process pre-paid
cards, and configure carrier-specific services.Click here for full instructions on using USSD.
https://www.peplink.com 20 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

A PC Card/ExpressCard for the
6 Installation
The following section details connecting Pepwave routers to your network.
6.1 Preparation
Before installing your Pepwave router, please prepare the following as appropriate for your
installation:
● At least one Internet/WAN access account and/or Wi-Fi access information
● Depending on network connection type(s), one or more of the following:
○ Ethernet WAN: A 10/100/1000BaseT UTP cable with RJ45 connector
○ USB: A USB modem
○ Embedded modem: A SIM card for GSM/HSPA service
○ Wi-Fi WAN: Wi-Fi antennas
○ PC Card/Express Card WAN:
corresponding card slot
● A computer installed with the TCP/IP network protocol and a supported web browser.
Supported browsers include Microsoft Internet Explorer 8.0 or above, Mozilla Firefox
10.0 or above, Apple Safari 5.1 or above, and Google Chrome 18 or above.
6.2 Constructing the Network
At a high level, construct the network according to the following steps:
1. With an Ethernet cable, connect a computer to one of the LAN ports on the
Pepwave router. Repeat with different cables for up to 4 computers to be
connected.
2. With another Ethernet cable or a USB modem/Wi-Fi antenna/PC Card/Express
Card, connect to one of the WAN ports on the Pepwave router. Repeat the same
procedure for other WAN ports.
3. Connect the power adapter to the power connector on the rear panel of the
Pepwave router, and then plug it into a power outlet.
https://www.peplink.com 21 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

The following figure schematically illustrates the resulting configuration:
6.3 Configuring the Network Environment
To ensure that the Pepwave router works properly in the LAN environment and can access the
Internet via WAN connections, please refer to the following setup procedures:
● LAN configuration
For basic configuration, refer to Section 8, Connecting to the Web Admin Interface.
For advanced configuration, go to Section 9, Configuring the LAN Interface(s).
● WAN configuration
For basic configuration, refer to Section 8, Connecting to the Web Admin Interface.
For advanced configuration, go to Section 9.2, Captive Portal.
https://www.peplink.com 22 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

7 Connecting to the Web Admin Interface
1. Start a web browser on a computer that is connected with the Pepwave router
through the LAN.
2. To connect to the router’s web admin interface, enter the following LAN IP address
in the address field of the web browser:
http://192.168.50.1
(This is the default LAN IP address for Pepwave routers.)
3. Enter the following to access the web admin
interface.
Username: admin
Password: admin
(This is the default username and password for
Pepwave routers. The admin and read-only user
passwords can be changed at System>Admin
Security.)
4. After successful login, the Dashboard will be displayed
https://www.peplink.com 23 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

The Dashboard shows current WAN, LAN, and Wi-Fi AP statuses. Here, you can change WAN
connection priority and switch on/off the Wi-Fi AP. For further information on setting up these
connections, please refer to Sections 8 and 9.
Device Information displays details about the device, including model name, firmware version,
and uptime. For further information, please refer to Section 22.
Important Note
Configuration changes (e.g. WAN, LAN, admin settings, etc.) will take effect only after clicking the
Save button at the bottom of each page. The Apply Changes button causes the changes to be saved
and applied.
https://www.peplink.com 24 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

8 Configuring the LAN Interface(s)
8.1 Basic Settings
LAN interface settings are located at Network>LAN>Network Settings. Navigating to that
page will result in the following dashboard:
This represents the LAN interfaces that are active on your router (including VLAN). A grey “X”
means that the VLAN is used in other settings and cannot be deleted. You can find which
settings are using the VLAN by hovering over the grey “X”.
Alternatively, a red “X” means that there are no settings using the VLAN. You can delete that
VLAN by clicking the red “X”
Clicking any of the existing LAN interfaces (or creating a new one) will result in the following
IP Settings
IP Address
https://www.peplink.com 25 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave
The IP address and subnet mask of the Pepwave router on the LAN.

Network Settings
Name
VLAN ID
Inter-VLAN
routing
Captive Portal
Enter a name for the LAN.
Enter a number for your VLAN.
Check this box to enable routing between virtual LANs.
Check this box to turn on captive portals.
https://www.peplink.com 26 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Drop-in Mode Settings
Drop-in mode eases the installation of Peplink routers on a live network between
Enable
the existing firewall and router, such that no configuration changes are required
on existing equipment. Check the box to enable the drop-in mode feature, if
available on your model.
WAN for Drop-In
Mode
Share Drop-In IP
Shared IP
AddressA
WAN Default
Gateway
WAN DNS Servers
A
Advanced feature, please click the button on the top right-hand corner to activate.
-
Select the WAN port to be used for drop-in mode. If WAN 1 with LAN Bypass is
selected, the high availability feature will be disabled automatically.
When this option is enabled, the passthrough IP address will be used to connect
to WAN hosts (email notification, remote syslog, etc.). The Pepwave router will
listen for this IP address when WAN hosts access services provided by the
Pepwave router (web admin access from the WAN, DNS server requests, etc.).
A
To connect to hosts on the LAN (email notification, remote syslog, etc.), the
default gateway address will be used. The Pepwave router will listen for this IP
address when LAN hosts access services provided by the Pepwave router (web
admin access from the WAN, DNS proxy, etc.).
Access to this IP address will be passed through to the LAN port if this device is
not serving the service being accessed. The shared IP address will be used in
connecting to hosts on the WAN (email notification, remote syslog, etc.) The
device will also listen on the IP address when hosts on the WAN access services
served on this device (web admin access from the WAN, DNS server, etc.)
Enter the WAN router's IP address in this field. If there are more hosts in addition
to the router on the WAN segment, check the I have other host(s) on WAN
segment box and enter the IP address of the hosts that need to access LAN
devices or be accessed by others.
Enter the selected WAN's corresponding DNS server IP addresses.
https://www.peplink.com 27 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Layer 2 PepVPN Bridging
PepVPN Profiles
to Bridge
Spanning Tree
Protocol
Override IP
Address when
bridge
connected
The remote network of the selected PepVPN profiles will be bridged with this local
LAN, creating a Layer 2 PepVPN, they will be connected and operate like a single
LAN, and any broadcast or multicast packets will be sent over the VPN.
Click the box will enable STP for this layer 2 profile bridge.
Select "Do not override" if the LAN IP address and local DHCP server should
remain unchanged after the Layer 2 PepVPN is up.
If you choose to override IP address when the VPN is connected, the device will
not act as a router, and most Layer 3 routing functions will cease to work.
DHCP Server Settings
https://www.peplink.com 28 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

When this setting is enabled, the DHCP server automatically assigns an IP
DHCP Server
address to each computer that is connected via LAN and configured to obtain an
IP address via DHCP. The Pepwave router’s DHCP server can prevent IP
address collision on the LAN.
IP Range &
Subnet Mask
Lease Time
DNS Servers
WINS Server
BOOTP
Extended
DHCP Option
These settings allocate a range of IP addresses that will be assigned to LAN
computers by the Pepwave router’s DHCP server.
This setting specifies the length of time throughout which an IP address of a
DHCP client remains valid. Upon expiration of the lease time, the assigned IP
address will no longer be valid and renewal of the IP address assignment will be
required.
This option allows you to input the DNS server addresses to be offered to DHCP
clients. If Assign DNS server automatically is selected, the Pepwave router’s
built-in DNS server address (i.e., LAN IP address) will be offered.
This option allows you to optionally specify a Windows Internet Name Service
(WINS) server. You may choose to use the built-in WINS server or external
WINS servers.
When this unit is connected using SpeedFusionTM, other VPN peers can share
this unit's built-in WINS server by entering this unit's LAN IP address in their
DHCP WINS Server setting. Afterward, all PC clients in the VPN can resolve the
NetBIOS names of other clients in remote peers. If you have enabled this option,
a list of WINS clients will be displayed at Status>WINS Clients.
Check this box to enable BOOTP on older networks that still require it.
In addition to standard DHCP options (e.g., DNS server address, gateway
address, subnet mask), you can specify the value of additional extended DHCP
options, as defined in RFC 2132. With these extended options enabled, you can
pass additional configuration information to LAN hosts.
To define an extended DHCP option, click the Add button, choose the option to
define and enter its value. For values that are in IP address list format, you can
enter one IP address per line in the provided text area input control. Each option
can be defined once only.
This setting reserves the assignment of fixed IP addresses for a list of computers
on the LAN. The computers to be assigned fixed IP addresses on the LAN are
identified by their MAC addresses. The fixed IP address assignment is displayed
as a cross-reference list between the computers’ names, MAC addresses, and
DHCP
Reservation
fixed IP addresses.
Name (an optional field) allows you to specify a name to represent the device.
MAC addresses should be in the format of 00:AA:BB:CC:DD:EE. Press to
create a new record. Press to remove a record. Reserved client information
can be imported from the Client List, located at Status>Client List. For more
details, please refer to Section 22.3.
https://www.peplink.com 29 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

LAN Physical Settings
This is the port speed of the LAN interface. It should be set to the same speed as
the connected device to avoid port negotiation problems. When a static speed is
Speed
set, you may choose whether to advertise its speed to the peer device. Auto is
selected by default. You can choose not to advertise the port speed if the port
has difficulty negotiating with the peer device.
Static Route Settings
This table is for defining static routing rules for the LAN segment. A static route
consists of the network address, subnet mask, and gateway address. The
address and subnet mask values are in w.x.y.z format.
Static Route
The local LAN subnet and subnets behind the LAN will be advertised to the VPN.
Remote routes sent over the VPN will also be accepted. Any VPN member will be
able to route to the local subnets. Press to create a new route. Press
to remove a route.
https://www.peplink.com 30 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

WINS Server Settings
Enable
Check the box to enable the WINS server. A list of WINS clients will be displayed
at Status>WINS Clients.
DNS Proxy Settings
To enable the DNS proxy feature, check this box, and then set up the
feature at Network>LAN>DNS Proxy Settings. A DNS proxy server can
Enable
DNS Caching
be enabled to serve DNS requests originating from
LAN/PPTP/SpeedFusion
servers/resolvers defined for each WAN connection.
This field is to enable DNS caching on the built-in DNS proxy server.
When the option is enabled, queried DNS replies will be cached until the
records’ TTL has been reached. This feature can help improve DNS
lookup time. However, it cannot return the most up-to-date result for those
frequently updated DNS records. By default, DNS Caching is disabled.
TM
peers. Requests are forwarded to the DNS
https://www.peplink.com 31 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

When this option is enabled, the DNS proxy server will also forward DNS
Include Google Public
DNS Servers
Local DNS Records
DNS Resolvers A
A
- Advanced feature, please click the button on the top right hand corner to activate.
requests to Google's Public DNS Servers, in addition to the DNS servers
defined in each WAN. This could increase the DNS service's availability.
This setting is disabled by default.
This table is for defining custom local DNS records. A static local DNS
record consists of a host name and IP address. When looking up the host
name from the LAN to LAN IP of the Pepwave router, the corresponding
IP address will be returned. Press to create a new record. Press
to remove a record.
Check the box to enable the WINS server. A list of WINS clients will be
displayed at Network>LAN>DNS Proxy Settings>DNS Resolvers. This
field specifies which DNS resolvers will receive forwarded DNS requests.
If no WAN/VPN/LAN DNS resolver is selected, all of the WAN’s DNS
resolvers will be selected.
If a SpeedFusion
resolver IP address(es). Queries will be forwarded to the selected
connections’ resolvers. If all of the selected connections are down,
queries will be forwarded to all resolvers on healthy WAN connections.
TM
peer is selected, you may enter the VPN peer’s DNS
Finally, if needed, configure Bonjour forwarding, Apple’s zero configuration networking protocol.
Once VLAN configuration is complete, click Save to store your changes.
Bonjour Forwarding Settings
Enable
Bonjour Service
Check this box to turn on Bonjour forwarding.
Choose Service and Client networks from the drop-down menus, and then click
to add the networks. To delete an existing Bonjour listing, click .
To enable VLAN configuration, click the button in the IP Settings section.
https://www.peplink.com 32 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

To add a new LAN, click the New LAN button. To change LAN settings, click the name of the
LAN to change under the LAN heading.
The following settings are displayed when creating a new LAN or editing an existing LAN.
IP Settings
Enter the Pepwave router’s IP address and subnet mask values to be used on
IP Address &
Subnet Mask
the LAN.
Network Settings
Name
VLAN ID
Inter-VLAN
routing
Enter a name for the LAN.
Enter a number for your VLAN.
Check this box to enable routing between virtual LANs.
https://www.peplink.com 33 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Captive Portal
DHCP Server
Check this box to turn on captive portals.
DHCP Server Settings
When this setting is enabled, the Pepwave router’s DHCP server automatically
assigns an IP address to each computer that is connected via LAN and configured
to obtain an IP address via DHCP. The Pepwave router’s DHCP server can
prevent IP address collisions on the LAN.
To enable DHCP bridge relay, please click the icon on this menu item.
IP Range &
Subnet Mask
Lease Time
DNS Servers
WINS Servers
These settings allocate a range of IP address that will be assigned to LAN
computers by the Pepwave router’s DHCP server.
This setting specifies the length of time throughout which an IP address of a DHCP
client remains valid. Upon expiration of Lease Time, the assigned IP address will
no longer be valid and the IP address assignment must be renewed.
This option allows you to input the DNS server addresses to be offered to DHCP
clients. If Assign DNS server automatically is selected, the Pepwave router’s
built-in DNS server address (i.e., LAN IP address) will be offered.
This option allows you to specify the Windows Internet Name Service (WINS)
server. You may choose to use the built-in WINS server or external WINS servers.
When this unit is connected using SpeedFusionTM, other VPN peers can share this
unit's built-in WINS server by entering this unit's LAN IP address in their DHCP
WINS Servers setting. Therefore, all PC clients in the VPN can resolve the
NetBIOS names of other clients in remote peers. If you have enabled this option, a
list of WINS clients will be displayed at Status>WINS Clients.
https://www.peplink.com 34 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

BOOTP
Extended DHCP
Option
DHCP
Reservation
Check this box to enable BOOTP on older networks that still require it.
In addition to standard DHCP options (e.g. DNS server address, gateway address,
subnet mask), you can specify the value of additional extended DHCP options, as
defined in RFC 2132. With these extended options enabled, you can pass
additional configuration information to LAN hosts. To define an extended DHCP
option, click the Add button, choose the option to define, and then enter its value.
For values that are in IP address list format, you can enter one IP address per line
in the provided text area input control. Each option can be defined once only.
This setting reserves the assignment of fixed IP addresses for a list of computers
on the LAN. The computers to be assigned fixed IP addresses on the LAN are
identified by their MAC addresses. The fixed IP address assignment is displayed
as a cross-reference list between the computers’ names, MAC addresses, and
fixed IP addresses.
Name (an optional field) allows you to specify a name to represent the device.
MAC addresses should be in the format of 00:AA:BB:CC:DD:EE. Press to
create a new record. Press to remove a record. Reserved clients information
can be imported from the Client List, located at Status>Client List. For more
details, please refer to Section 22.3.
To configure DHCP relay, first click the button found next to the DHCP Server option to
display the settings.
DHCP Relay Settings
Enable
DHCP Server IP
Address
DHCP Option 82
Check this box to turn on DHCP relay. Click the icon to disable DHCP relay.
Enter the IP addresses of one or two DHCP servers in the provided fields. The
DHCP servers entered here will receive relayed DHCP requests from the LAN. For
active-passive DHCP server configurations, enter active and passive DHCP server
relay IP addresses in DHCP Server 1 and DHCP Server 2.
DHCP Option 82 includes device information as relay agent for the attached client
when forwarding DHCP requests from client to server. This option also embeds
the device’s MAC address and network name in circuit and remote IDs. Check this
box to enable DHCP Option 82.
https://www.peplink.com 35 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Once DHCP is set up, configure LAN Physical Settings, Static Route Settings, WINS Server
Settings, and DNS Proxy Settings as noted above.
8.2 Port Settings
To configure port settings, navigate to Network > Port Settings
On this screen, you can enable specific ports, as well as determine the speed of the LAN ports,
whether each port is a trunk or access port, can well as which VLAN each link belongs to, if any.
8.3 Captive Portal
The captive portal serves as gateway that clients have to pass if they wish to access the internet
using your router. To configure, navigate to Network>LAN>Captive Portal.
Captive Portal Settings
https://www.peplink.com 36 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Enable
Hostname
Access Mode
RADIUS Server
Check Enable and then, optionally, select the LANs/VLANs that will use the
captive portal.
To customize the portal’s form submission and redirection URL, enter a new
URL in this field. To reset the URL to factory settings, click Default.
Click Open Access to allow clients to freely access your router. Click User
Authentication to force your clients to authenticate before accessing your
router.
This authenticates your clients through a RADIUS server. After selecting this
option, you will see the following fields:
Fill in the necessary information to complete your connection to the server and
enable authentication.
This authenticates your clients through a LDAP server. Upon selecting this
option, you will see the following fields:
LDAP Server
Fill in the necessary information to complete your connection to the server and
enable authentication.
Access Quota
Quota Reset
Time
Allowed
Networks
Set a time and data cap to each user’s Internet usage.
This menu determines how your usage quota resets. Setting it to Daily will
reset it at a specified time every day. Setting a number of minutes after quota
reached establish a timer for each user that begins after the quota has been
reached.
To whitelist a network, enter the domain name / IP address here and click
. To delete an existing network from the list of allowed networks, click the
button next to the listing.
https://www.peplink.com 37 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Splash Page
Here, you can choose between using the Pepwave router’s built-in captive
portal and redirecting clients to a URL you define.
The Portal Customization menu has two options: and . Clicking displays
a pop-up previewing the captive portal that your clients will see. Clicking displays the
following menu:
Portal Customization
Logo Image
Message
Terms &
Conditions
Click the Choose File button to select a logo to use for the built-in portal.
If you have any additional messages for your users, enter them in this field.
If you would like to use your own set of terms and conditions, please enter them
here. If left empty, the built-in portal will display the default terms and conditions.
https://www.peplink.com 38 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Custom
Landing
Page
Fill in this field to redirect clients to an external URL.
9 Configuring the WAN Interface(s)
WAN Interface settings are located at Network>WAN. To reorder WAN priority, drag on the
appropriate WAN by holding the left mouse button, move it to the desired priority (the first one
would be the highest priority, the second one would be lower priority, and so on), and drop it by
releasing the mouse button.
To disable a particular WAN connection, drag on the appropriate WAN by holding the left mouse
button, move it the Disabled row, and drop it by releasing the mouse button.
You can also set priorities on the Dashboard. Click the Details button in the corresponding row
to modify the connection setting.
Important Note
Connection details will be changed and become effective immediately after clicking the Save and Apply button.
https://www.peplink.com 39 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

9.1 Ethernet WAN
Health Check
Method
PING Hosts
Health Check Settings
This field specifies the Health Check method to be used for this WAN connection.
● Disabled - The WAN connection is always considered to be up and will not
be treated as down for any IP routing errors.
● PING - ICMP PING packets will be issued to test connectivity with
configurable target IP addresses or host names.
● DNS Lookup - DNS lookups will be issued to test the connectivity with
configurable target DNS server IP addresses.
● HTTP - HTTP connections will be issued to test the connectivity with
configurable URLs and strings to match.
Default: DNS Lookup
These fields are for specifying the target IP addresses or host names where ICMP
Ping packets will be sent to for health check.
If the box Use first two DNS servers as PING Hosts is checked, the first two DNS
servers will be the ping targets for checking the connection healthiness. If the box
is not checked, the field Host 1 must be filled and the field Host 2 is optional.
The connection is considered to be up if ping responses are received from any one
of the ping hosts.
Timeout
If a health check test cannot be completed within the specified amount of time, the
test will be treated as failed.
https://www.peplink.com 40 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Health Check
Interval
Health Check
Retries
Recovery
Retries
This is the time interval between each health check test.
This is the number of consecutive check failures before treating a connection as
down.
This is the number of responses required after a health check failure before treating
a connection as up again.
Bandwidth Allowance Monitor Settings
Bandwidth
Allowance
Monitor
Action
Start Day
Monthly
Allowance
https://www.peplink.com 41 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave
Check the box Enable to enable bandwidth usage monitoring on this WAN
connection for each billing cycle. When this option is not enabled, bandwidth usage
of each month is still being tracked but no action will be taken.
If Email Notification is enabled, you will receive an email notification when usage
hits 75% and 95% of the monthly allowance.
If the box Disconnect when usage hits 100% of monthly allowance is checked, this
WAN connection will be disconnected automatically when the usage hits the
monthly allowance. It will not resume unless this option has been turned off or the
usage has been reset when a new billing cycle starts.
This option allows you to select which day of the month a billing cycle starts.
This field is to specify the bandwidth allowance for each billing cycle.

Additional Public IP Settings
If you have access to status public IP addresses,, you can assign them on this field.
Dynamic DNS Settings
This setting specifies the dynamic DNS service provider to be used for the WAN based
on supported dynamic DNS service providers:
● changeip.com
Dynamic DNS
Service Provider
● dyndns.org
● no-ip.org
● tzo.com
● DNS-O-Matic
Select Disabled to disable this feature. See Section 9.5 for configuration details.
9.1.1 DHCP Connection
There are four possible connection methods:
1. DHCP
2. Static IP
3. PPPoE
4. L2TP
The DHCP connection method is suitable if the ISP provides an IP address automatically using
DHCP (e.g., satellite modem, WiMAX modem, cable, Metro Ethernet, etc.).
https://www.peplink.com 42 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

DHCP Connection Settings
NAT allows substituting the real address in a packet with a mapped
Routing Mode
address that is routable on the destination network. By clicking the help
icon in this field, you can display the IP Forwarding option, if your
network requires it.
IP Address/ Subnet
Mask/ Default
This information is obtained from the ISP automatically.
Gateway
Hostname
(Optional)
DNS Servers
If your service provider's DHCP server requires you to supply a hostname
value upon acquiring an IP address, you may enter the value here. If your
service provider does not provide you with the value, you can safely
bypass this option.
Each ISP may provide a set of DNS servers for DNS lookups. This setting
specifies the DNS (Domain Name System) servers to be used when a
DNS lookup is routed through this connection.
Selecting Obtain DNS server address automatically results in the DNS
servers being assigned by the WAN DHCP server to be used for outbound
DNS lookups over the connection. (The DNS servers are obtained along
with the WAN IP address assigned from the DHCP server.)
When Use the following DNS server address(es) is selected, you may
enter custom DNS server addresses for this WAN connection into the
DNS Server 1 and DNS Server 2 fields.
9.1.2 Static IP Connection
The static IP connection method is suitable if your ISP provides a static IP address to connect
directly.
https://www.peplink.com 43 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Static IP Settings
NAT allows substituting the real address in a packet with a mapped address that
Routing Mode
is routable on the destination network. By clicking the help icon in this field, you
can display the IP Forwarding option, if your network requires it.
IP Address /
Subnet Mask /
Default
Gateway
DNS Servers
These settings allow you to specify the information required in order to
communicate on the Internet via a fixed Internet IP address. The information is
typically determined by and can be obtained from the ISP.
Each ISP may provide a set of DNS servers for DNS lookups. This setting
specifies the DNS (Domain Name System) servers to be used when a DNS
lookup is routed through this connection. Selecting Obtain DNS server address
automatically results in the DNS servers being assigned by the WAN DHCP
server to be used for outbound DNS lookups over the connection. (The DNS
servers are obtained along with the WAN IP address assigned from the DHCP
server.) When Use the following DNS server address(es) is selected, you may
enter custom DNS server addresses for this WAN connection into the DNS
Server 1 and DNS Server 2 fields.
9.1.3 PPPoE Connection
This connection method is suitable if your ISP provides a login ID/password to connect via
PPPoE.
https://www.peplink.com 44 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

PPPoE Settings
NAT allows substituting the real address in a packet with a mapped address
Routing Mode
that is routable on the destination network. By clicking the help icon in this
field, you can display the IP Forwarding option, if your network requires it.
IP Address /
Subnet Mask /
This information is obtained from the ISP automatically.
Default Gateway
PPPoE User Name
/ Password
Confirm PPPoE
Password
Service Name
(Optional)
IP Address
(Optional)
DNS Servers
Enter the required information in these fields in order to connect via PPPoE to
the ISP. The parameter values are determined by and can be obtained from
the ISP.
Verify your password by entering it again in this field.
Service name is provided by the ISP.
Note: Leave this field blank unless it is provided by your ISP.
If your ISP provides a PPPoE IP address, enter it here.
Note: Leave this field blank unless it is provided by your ISP.
Each ISP may provide a set of DNS servers for DNS lookups. This setting
specifies the DNS (Domain Name System) servers to be used when a DNS
lookup is routed through this connection. Selecting Obtain DNS server
address automatically results in the DNS servers being assigned by the
WAN DHCP server to be used for outbound DNS lookups over the
https://www.peplink.com 45 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

connection. (The DNS servers are obtained along with the WAN IP address
assigned from the DHCP server.) When Use the following DNS server
address(es) is selected, you may enter custom DNS server addresses for
this WAN connection into the DNS Server 1 and DNS Server 2 fields.
9.1.4 L2TP Connection
L2TP has all the compatibility and convenience of PPTP with greater security. Combine this with
IPsec for a good balance between ease of use and security.
L2TP Settings
L2TP Username /
Password
Confirm L2TP
Password
Server IP
Address / Host
Address Type
DNS Servers
Enter the required information in these fields in order to connect via L2TP to
your ISP.
The parameter values are determined by and can be obtained from your ISP.
Verify your password by entering it again in this field.
L2TP server address is a parameter which is provided by your ISP.
Note: Leave this field blank unless it is provided by your ISP.
Your ISP will also indicate whether the server IP address is Dynamic or Static.
Please click the appropriate value.
Each ISP may provide a set of DNS servers for DNS lookups. This setting
specifies the
https://www.peplink.com 46 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

DNS (Domain Name System) servers to be used when a DNS lookup is routed
through this
connection.
Selecting Obtain DNS server address automatically results in the DNS
servers assigned
by the PPPoE server to be used for outbound DNS lookups over the WAN
connection.
(The DNS servers are obtained along with the WAN IP address assigned from
the PPPoE
server.)
When Use the following DNS server address(es) is selected, you can enter
custom DNS server addresses for this WAN connection into the DNS server 1
and DNS server 2 fields.
9.2 Cellular WAN
To access cellular WAN settings, click Network>WAN>Details.
https://www.peplink.com 47 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Cellular Status
IMSI
MEID
ESN
IMEI
This is the International Mobile Subscriber Identity which uniquely identifies the SIM
card. This is applicable to 3G modems only.
Some Pepwave routers support both HSPA and EV-DO. For Sprint or Verizon
Wireless EV-DO users, a unique MEID identifier code (in hexadecimal format) is used
by the carrier to associate the EV-DO device with the user. This information is
presented in hex and decimal format.
This serves the same purpose as MEID HEX but uses an older format.
This is the unique ID for identifying the modem in GSM/HSPA mode.
WAN Connection Settings
WAN Connection
Name
Operating
Schedule
Enter a name to represent this WAN connection.
Click the drop-down menu to apply a time schedule to this interface if needed.
https://www.peplink.com 48 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Auto: The subnet mask will be set automatically.
Subnet Selection
Routing Mode
DNS Servers
Force /31 Subnet: The subnet mask will be set as 255.255.255.254(/31), and the
gateway IP address will be recalculated.
This option allows you to select the routing method to be used in routing IP frames via
the WAN connection. The mode can be either NAT (network address translation)
or IP Forwarding. Click the button to enable IP forwarding.
Each ISP may provide a set of DNS servers for DNS lookups. This setting specifies
the DNS (Domain Name System) servers to be used when a DNS lookup is routed
through this
connection.
Selecting Obtain DNS server address automatically results in the DNS servers
assigned
by the PPPoE server to be used for outbound DNS lookups over the WAN
connection.
(The DNS servers are obtained along with the WAN IP address assigned from the
PPPoE
server.)
When Use the following DNS server address(es) is selected, you can enter custom
DNS server addresses for this WAN connection into the DNS server 1 and DNS
server 2 fields.
https://www.peplink.com 49 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

If both cards were enabled on the above field, then you can designate the priority of
Cellular Settings
SIM Card
Indicate which SIM card this cellular WAN will use. Only applies to cellular WAN with
redundant SIM cards.
Preferred SIM
https://www.peplink.com 50 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Card
3G/2G
Authentication
Data Roaming
Operator Settings
APN / Login /
Password /
SIM PIN
the SIM card slots here.
This drop-down menu allows restricting cellular to particular band. Click the
button to enable the selection of specific bands.
Choose from PAP Only or CHAP Only to use those authentication methods
exclusively. Select Auto to automatically choose an authentication method.
This checkbox enables data roaming on this particular SIM card. Please check your
service provider’s data roaming policy before proceeding.
This setting applies to 3G/EDGE/GPRS modems only. It does not apply to
EVDO/EVDO Rev. A modems. This allows you to configure the APN settings of your
connection. If Auto is selected, the mobile operator should be detected
automatically. The connected device will be configured and connection will be made
automatically. If there is any difficulty in making connection, you may select Custom
to enter your carrier’s APN, Login, Password, and Dial Number settings manually.
The correct values can be obtained from your carrier. The default and recommended
setting is Auto.
When Auto is selected, the information in these fields will be filled automatically.
Select Custom to customize these parameters. The parameter values are
determined by and can be obtained from the ISP.
Bandwidth
Allowance
Monitor
Action
Start Day
Monthly
Allowance
Check the box Enable to enable bandwidth usage monitoring on this WAN
connection for each billing cycle. When this option is not enabled, bandwidth usage
of each month is still being tracked but no action will be taken.
If email notification is enabled, you will be notified by email when usage hits 75% and
95% of the monthly allowance. If Disconnect when usage hits 100% of monthly
allowance is checked, this WAN connection will be disconnected automatically when
the usage hits the monthly allowance. It will not resume connection unless this option
has been turned off or the usage has been reset when a new billing cycle starts.
This option allows you to define which day of the month each billing cycle begins.
This field is for defining the maximum bandwidth usage allowed for the WAN
connection each month.
https://www.peplink.com 51 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

General Settings
Independent
from Backup
WANs
Standby State
Idle Disconnect
If this is checked, the connection will be working independent from other Backup WAN
connections. Those in Backup Priority will ignore the status of this WAN connection,
and will be used when none of the other higher priority connections are available.
This option allows you to choose whether to remain connected or disconnected when
this WAN connection is no longer in the highest priority and has entered the standby
state. When Remain connected is chosen, bringing up this WAN connection to active
makes it immediately available for use.
When Internet traffic is not detected within the user-specified timeframe, the modem
will automatically disconnect. Once the traffic is resumed by the LAN host, the
connection will be re-activated.
Health Check Settings
Health Check
Method
Timeout
Health Check
Interval
This setting allows you to specify the health check method for the cellular connection.
Available options are Disabled, Ping, DNS Lookup, HTTP, and SmartCheck. The
default method is DNS Lookup. See Section 10.4 for configuration details.
If a health check test cannot be completed within the specified amount of time, the test
will be treated as failed.
This is the time interval between each health check test.
https://www.peplink.com 52 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Health Check
Retries
Recovery
Retries
Dynamic DNS
Service
Provider
This is the number of consecutive check failures before treating a connection as down.
This is the number of responses required after a health check failure before treating a
connection as up again.
Dynamic DNS Settings
This setting specifies the dynamic DNS service provider to be used for the WAN based
on supported dynamic DNS service providers:
● changeip.com
● dyndns.org
● no-ip.org
● tzo.com
● DNS-O-Matic
Select Disabled to disable this feature. See Section 9.5 for configuration details.
MTU
This field is for specifying the Maximum Transmission Unit value of the WAN
MTU
connection. An excessive MTU value can cause file downloads stall shortly after
connected. You may consult your ISP for the connection's MTU value.
9.3 Wi-Fi WAN
To access Wi-Fi WAN settings, click Network>WAN>Details.
https://www.peplink.com 53 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

WAN Connection Settings
WAN Connection
Name
Operating
Schedule
Independent from
Backup WANs
Standby State
MTU
Reply to ICMP
PING
Enter a name to represent this WAN connection.
Click the drop-down menu to apply a time schedule to this interface.
If this is checked, the connection will be working independent from other Backup
WAN connections. Those in Backup Priority will ignore the status of this WAN
connection, and will be used when none of the other higher priority connections
are available.
This setting specifies the state of the WAN connection while in standby. The
available options are Remain Connected (hot standby) and Disconnect (cold
standby).
This setting specifies the maximum transmission unit. By default, MTU is set to
Custom 1440. You may adjust the MTU value by editing the text field. Click
Default to restore the default MTU value. Select Auto and the appropriate MTU
value will be automatically detected. The auto-detection will run each time the
WAN connection establishes
If this setting is disabled, the WAN connection will not respond to ICMP ping
requests. By default, this setting is enabled.
https://www.peplink.com 54 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Wi-Fi WAN Settings
Select the channel width for this Wi-Fi WAN. 20MHz will have greater support for
Channel Width
older devices using 2.4Ghz, while 40MHz is appropriate for networks with newer
devices that connect using 5Ghz
Determine whether the channel will be automatically selected. If you select custom,
the following table will appear:
Channel
Selection
Data Rate
Output Power
Roaming
Connect to Any
Open Mode AP
Beacon Miss
Selecting Auto will enable the router to automatically determine the best data rate,
while manually selecting a rate will force devices to connect using the fixed rate.
If you are setting up a network with many Wi-Fi devices in close proximity, then you
can configure the output power here. Click the “boost” button for additional power.
However, with that option ticked, output power may exceed local regulatory limits.
Checking this box will enable Wi-Fi roaming. Click the icon for additional
options.
This option is to specify whether the Wi-Fi WAN will connect to any open mode
access points it finds.
This sets the threshold for the number of missed beacons.
https://www.peplink.com 55 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Counter
Bandwidth Allowance Monitor
If Error! Reference source not found. is enabled, you will be notified by email
when usage hits 75% and 95% of the monthly allowance.
Action
If Disconnect when usage hits 100% of monthly allowance is checked, this
WAN connection will be disconnected automatically when the usage hits the
monthly allowance. It will not resume connection unless this option has been
turned off or the usage has been reset when a new billing cycle starts.
Start Day
Monthly
Allowance
This option allows you to define which day of the month each billing cycle begins.
This field is for defining the maximum bandwidth usage allowed for the WAN
connection each month.
Health Check Settings
https://www.peplink.com 56 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

This setting specifies the health check method for the WAN connection. This value
Method
can be configured as Disabled, PING, DNS Lookup, or HTTP. The default
method is DNS Lookup. For mobile Internet connections, the value of Method
can be configured as Disabled or SmartCheck.
Health Check Disabled
When Disabled is chosen in the Method field, the WAN connection will always be considered as up.
The connection will NOT be treated as down in the event of IP routing errors.
Health Check Method: PING
ICMP ping packets will be issued to test the connectivity with a configurable target IP address or
hostname. A WAN connection is considered as up if ping responses are received from either one or
both of the ping hosts.
This setting specifies IP addresses or hostnames with which connectivity is to be
tested via ICMP ping. If Use first two DNS servers as Ping Hosts is checked,
PING Hosts
the target ping host will be the first DNS server for the corresponding WAN
connection. Reliable ping hosts with a high uptime should be considered. By
default, the first two DNS servers of the WAN connection are used as the ping
hosts.
Health Check Method: DNS Lookup
DNS lookups will be issued to test connectivity with target DNS servers. The connection will be treated
as up if DNS responses are received from one or both of the servers, regardless of whether the result
was positive or negative.
This field allows you to specify two DNS hosts’ IP addresses with which
connectivity is to be tested via DNS Lookup.
Health Check
DNS Servers
If Use first two DNS servers as Health Check DNS Servers is checked, the first
two DNS servers will be the DNS lookup targets for checking a connection's
health. If the box is not checked, Host 1 must be filled, while a value for Host 2 is
optional.
https://www.peplink.com 57 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

If Include public DNS servers is selected and no response is received from all
specified DNS servers, DNS lookups will also be issued to some public DNS
servers. A WAN connection will be treated as down only if there is also no
response received from the public DNS servers.
Connections will be considered as up if DNS responses are received from any one
of the health check DNS servers, regardless of a positive or negative result. By
default, the first two DNS servers of the WAN connection are used as the health
check DNS servers.
Health Check Method: HTTP
HTTP connections will be issued to test connectivity with configurable URLs and strings to match
WAN Settings>WAN Edit>Health Check Settings>URL1
The URL will be retrieved when performing an HTTP health check. When String
URL1
to Match is left blank, a health check will pass if the HTTP return code is between
200 and 299 (Note: HTTP redirection codes 301 or 302 are treated as failures).
When String to Match is filled, a health check will pass if the HTTP return code is
between 200 and 299 and if the HTTP response content contains the string.
.
URL 2
WAN Settings>WAN Edit>Health Check Settings>URL2
If URL2 is also provided, a health check will pass if either one of the tests passed.
Other Health Check Settings
Timeout
Health Check
This setting specifies the timeout in seconds for ping/DNS lookup requests. The
default timeout is 5 seconds.
This setting specifies the time interval in seconds between ping or DNS lookup
https://www.peplink.com 58 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Interval
Health Check
Retries
Recovery Retries
requests. The default health check interval is 5 seconds.
This setting specifies the number of consecutive ping/DNS lookup timeouts after
which the Peplink Balance will treat the corresponding WAN connection as down.
Default health retries is set to 3. Using the default Health Retries setting of 3, the
corresponding WAN connection will be treated as down after three consecutive
timeouts.
This setting specifies the number of consecutive successful ping/DNS lookup
responses that must be received before the Peplink Balance treats a previously
down WAN connection as up again. By default, Recover Retries is set to 3. Using
the default setting, a WAN connection that is treated as down will be considered
as up again upon receiving three consecutive successful ping/DNS lookup
responses.
Dynamic DNS Settings
This setting specifies the dynamic DNS service provider to be used for the
WAN. Supported providers are:
● changeip.com
Service Provider
User ID / User /
Email
Password / Pass /
● dyndns.org
● no-ip.org
● tzo.com
● DNS-O-Matic
Select Disabled to disable this feature.
This setting specifies the registered user name for the dynamic DNS service.
This setting specifies the password for the dynamic DNS service.
https://www.peplink.com 59 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

TZO Key
Update All Hosts
Hosts / Domain
Check this box to automatically update all hosts.
This setting specifies a list of hostnames or domains to be associated with the
public Internet IP address of the WAN connection.
Important Note
In order to use dynamic DNS services, appropriate hostname registration(s), as well as a valid account
with a supported dynamic DNS service provider, are required.
A dynamic DNS update is performed whenever a WAN’s IP address is changed, such as when an IP is
changed after a DHCP IP refresh or reconnection.
Due to dynamic DNS service providers’ policies, a dynamic DNS host expires automatically when the
host record has not been not updated for a long time. Therefore, the Peplink Balance performs an
update every 23 days, even if a WAN’s IP address did not change.
9.3.1 Creating Wi-Fi Connection Profiles
You can manually create a profile to connect to a Wi-Fi connection. This is useful for creating a
profile for connecting to hidden-SSID access points. Click Network>WAN>Details>Create
Profile… to get started.
This will open a window similar to the one shown below
https://www.peplink.com 60 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Wi-Fi Connection Profile Settings
Type
Network Name
(SSID)
Security
Select whether the network will connect automatically or manually.
Enter a name to represent this Wi-Fi connection.
This option allows you to select which security policy is used for this wireless
network.
Available options:
● Open
● WEP
● WPA/WPA2 – Personal
● WPA/WPA2 – Enterprise
https://www.peplink.com 61 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

9.4 WAN Health Check
To ensure traffic is routed to healthy WAN connections only, the Pepwave router can
periodically check the health of each WAN connection. The health check settings for each WAN
connection can be independently configured via Network>WAN>Details.
Health Check Settings
This setting specifies the health check method for the WAN connection. This value
Method
When Disabled is chosen in the Method field, the WAN connection will always be considered as up.
The connection will NOT be treated as down in the event of IP routing errors.
can be configured as Disabled, PING, DNS Lookup, or HTTP. The default
method is DNS Lookup. For mobile Internet connections, the value of Method
can be configured as Disabled or SmartCheck.
Health Check Disabled
Health Check Method: PING
ICMP ping packets will be issued to test the connectivity with a configurable target IP address or
hostname. A WAN connection is considered as up if ping responses are received from either one or
both of the ping hosts.
This setting specifies IP addresses or hostnames with which connectivity is to be
tested via ICMP ping. If Use first two DNS servers as Ping Hosts is checked,
PING Hosts
the target ping host will be the first DNS server for the corresponding WAN
connection. Reliable ping hosts with a high uptime should be considered. By
default, the first two DNS servers of the WAN connection are used as the ping
hosts.
Health Check Method: DNS Lookup
https://www.peplink.com 62 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

DNS lookups will be issued to test connectivity with target DNS servers. The connection will be treated
as up if DNS responses are received from one or both of the servers, regardless of whether the result
was positive or negative.
This field allows you to specify two DNS hosts’ IP addresses with which
connectivity is to be tested via DNS lookup.
If Use first two DNS servers as Health Check DNS Servers is checked, the first
two DNS servers will be the DNS lookup targets for checking a connection's
health. If the box is not checked, Host 1 must be filled, while a value for Host 2 is
optional.
Health Check
DNS Servers
If Include public DNS servers is selected and no response is received from all
specified DNS servers, DNS lookups will also be issued to some public DNS
servers. A WAN connection will be treated as down only if there is also no
response received from the public DNS servers.
Connections will be considered as up if DNS responses are received from any one
of the health check DNS servers, regardless of a positive or negative result. By
default, the first two DNS servers of the WAN connection are used as the health
check DNS servers.
Health Check Method: HTTP
HTTP connections will be issued to test connectivity with configurable URLs and strings to match.
WAN Settings>WAN Edit>Health Check Settings>URL1
The URL will be retrieved when performing an HTTP health check. When String
URL1
URL 2
to Match is left blank, a health check will pass if the HTTP return code is between
200 and 299 (Note: HTTP redirection codes 301 or 302 are treated as failures).
When String to Match is filled, a health check will pass if the HTTP return code is
between 200 and 299 and if the HTTP response content contains the string.
WAN Settings>WAN Edit>Health Check Settings>URL2
If URL2 is also provided, a health check will pass if either one of the tests passed.
https://www.peplink.com 63 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Other Health Check Settings
Timeout
Health Check
Interval
Health Check
Retries
Recovery Retries
This setting specifies the timeout in seconds for ping/DNS lookup requests. The
default timeout is 5 seconds.
This setting specifies the time interval in seconds between ping or DNS lookup
requests. The default health check interval is 5 seconds.
This setting specifies the number of consecutive ping/DNS lookup timeouts after
which the Pepwave router will treat the corresponding WAN connection as down.
Default health retries is set to 3. Using the default Health Retries setting of 3, the
corresponding WAN connection will be treated as down after three consecutive
timeouts.
This setting specifies the number of consecutive successful ping/DNS lookup
responses that must be received before the Pepwave router treats a previously
down WAN connection as up again. By default, Recover Retries is set to 3. Using
the default setting, a WAN connection that is treated as down will be considered
as up again upon receiving three consecutive successful ping/DNS lookup
responses.
Automatic Public DNS Server Check on DNS Test Failure
When the health check method is set to DNS Lookup and health checks fail, the Pepwave router will
automatically perform DNS lookups on public DNS servers. If the tests are successful, the WAN may not
be down, but rather the target DNS server malfunctioned. You will see the following warning message
on the main page:
9.5 Dynamic DNS Settings
Pepwave routers are capable of registering the domain name relationships to dynamic DNS
https://www.peplink.com 64 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

service providers. Through registration with dynamic DNS service provider(s), the default public
Internet IP address of each WAN connection can be associated with a host name. With dynamic
DNS service enabled for a WAN connection, you can connect to your WAN's IP address from
the external, even if its IP address is dynamic. You must register for an account from the listed
dynamic DNS service providers before enabling this option.
If the WAN connection's IP address is a reserved private IP address (i.e., behind a NAT router),
the public IP of each WAN will be automatically reported to the DNS service provider.
Either upon a change in IP addresses or every 23 days without link reconnection, the Pepwave
router will connect to the dynamic DNS service provider to perform an IP address update within
the provider’s records.
The settings for dynamic DNS service provider(s) and the association of hostname(s) are
configured via Network>WAN>Details>Dynamic DNS Service Provider/Dynamic DNS
Settings.
Dynamic DNS Settings
This setting specifies the dynamic DNS service provider to be used for the
WAN based on supported dynamic DNS service providers:
● changeip.com
● dyndns.org
● no-ip.org
Dynamic DNS
Account Name /
Email Address
● tzo.com
● DNS-O-Matic
● Others…
Support custom Dynamic DNS servers by entering its URL.
Works with any service compatible with DynDNS API.
Select Disabled to disable this feature.
This setting specifies the registered user name for the dynamic DNS service.
https://www.peplink.com 65 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Password / TZO
Key
Hosts / Domain
This setting specifies the password for the dynamic DNS service.
This field allows you to specify a list of host names or domains to be
associated with the public Internet IP address of the WAN connection. If you
need to enter more than one host, use a carriage return to separate them.
Important Note
In order to use dynamic DNS services, appropriate host name registration(s) and a valid account with a
supported dynamic DNS service provider are required. A dynamic DNS update is performed whenever
a WAN’s IP address changes (e.g., the IP is changed after a DHCP IP refresh, reconnection, etc.). Due
to dynamic DNS service providers’ policy, a dynamic DNS host will automatically expire if the host
record has not been updated for a long time. Therefore the Pepwave router performs an update every
23 days, even if a WAN’s IP address has not changed.
10 Advanced Wi-Fi Settings
Wi-Fi settings can be configured at Advanced>Wi-Fi Settings (or AP>Settings on some
models). Note that menus displayed can vary by model.
AP Settings
SSID
Operating
Country
You can select the wireless networks for 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz seperately for each
SSID.
This drop-down menu specifies the national/regional regulations which the WiFi radio should follow.
● If a North American region is selected, RF channels 1 to 11 will be
available and the maximum transmission power will be 26 dBm (400
mW).
● If European region is selected, RF channels 1 to 13 will be available.
The maximum transmission power will be 20 dBm (100 mW).
NOTE: Users are required to choose an option suitable to local laws and
regulations.
https://www.peplink.com 66 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Preferred
Frequency
Indicate the preferred frequency to use for clients to connect.
Important Note
Per FCC regulation, the country selection is not available on all models marketed in the US.
All US models are fixed to US channels only.
AP Settings (part 2)
This option allows you to specify whether 802.11b and/or 802.11g client
Protocol
Channel Width
Channel
Auto Channel
Update
Output Power
Client Signal
Strength
association requests will be accepted. Available options are 802.11ng and
802.11na. By default, 802.11ng is selected.
Available options are 20 MHz, 40 MHz, and Auto (20/40 MHz) . Default is
Auto (20/40 MHz), which allows both widths to be used simultaneously.
This option allows you to select which 802.11 RF channel will be utilized.
Channel 1 (2.412 GHz) is selected by default.
Indicate the time of day at which update automatic channel selection.
This option is for specifying the transmission output power for the Wi-Fi AP.
There are 4 relative power levels available – Max, High, Mid, and Low. The
actual output power will be bound by the regulatory limits of the selected
country.
This setting determines the maximum strength at which the Wi-Fi AP can
broadcast
https://www.peplink.com 67 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Threshold
Maximum number
of clients
This setting determines the maximum number of clients that can connect to
this Wi-Fi frequency.
Advanced Wi-Fi AP settings can be displayed by clicking the on the top right-hand corner of
the Wi-Fi AP Settings section, which can be found at AP>Settings. Other models will display a
separate section called Wi-Fi AP Advanced Settings, which can be found at Advanced>Wi-Fi
Settings.
Advanced AP Settings
This field specifies the VLAN ID to tag to management traffic, such as
Management VLAN
ID
Operating
Schedule
Beacon Rate A
Beacon Interval A
communication traffic between the AP and the AP Controller. The value is zero
by default, which means that no VLAN tagging will be applied.
NOTE: Change this value with caution as alterations may result in loss of
connection to the AP Controller.
Choose from the schedules that you have defined in System>Schedule. Select
the schedule for the integrated AP to follow from the drop-down menu.
This option is for setting the transmit bit rate for sending a beacon. By default,
1Mbps is selected.
This option is for setting the time interval between each beacon. By default,
100ms is selected.
https://www.peplink.com 68 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

This field allows you to set the frequency for the beacon to include delivery
DTIM A
RTS Threshold A
traffic indication messages. The interval is measured in milliseconds. The
default value is set to 1 ms.
The RTS (Request to Clear) threshold determines the level of connection
required before the AP starts sending data. The recommended standard of the
RTS threshold is around 500.
Fragmentation
Threshold A
Distance / Time
Convertor
Slot Time A
ACK Timeout A
Frame Aggregation
A
A
- Advanced feature, please click the button on the top right-hand corner to activate.
This setting determines the maximum size of a packet before it gets fragmented
into multiple pieces.
Select the range you wish to cover with your Wi-Fi, and the router will make
recommendations for the Slot Time and ACK Timeout.
This field is for specifying the unit wait time before transmitting a packet. By
default, this field is set to 9 µs.
This field is for setting the wait time to receive an acknowledgement packet
before performing a retransmission. By default, this field is set to 48 µs.
This option allows you to enable frame aggregation to increase transmission
throughput.
https://www.peplink.com 69 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Boost
Web Administration Settings
Enable
Web Access
Protocol
Management Port
Admin Username
Admin Password
Ticking this box enables web admin access for APs located on the WAN.
Determines whether the web admin portal can be accessed through HTTP or
HTTPS
Determines the port at which the management UI can be accessed.
Determines the username to be used for logging into the web admin portal
Determines the password for the web admin portal on external AP.
Wi-Fi WAN settings can be configured at Advanced>Wi-Fi Settings (or Advanced>Wi-Fi
WAN or some models).
Wi-Fi WAN Settings
Channel Width
Bit Rate
Available options are 20/40 MHz and 20 MHz. Default is 20/40 MHz, which
allows both widths to be used simultaneously.
This option allows you to select a specific bit rate for data transfer over the
device’s Wi-Fi network. By default, Auto is selected.
This option is for specifying the transmission output power for the Wi-Fi AP.
Output Power
There are 4 relative power levels available – Max, High, Mid, and Low. The
actual output power will be bound by the regulatory limits of the selected
country. Note that selecting the
option may cause the MAX’s radio
https://www.peplink.com 70 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

output to exceed local regulatory limits.
11 MediaFast Configuration
MediaFast settings can be configured from the Network menu.
11.1 Setting Up MediaFast Content Caching
To access MediaFast content caching settings, select Advanced>Cache Control
Cache Control Settings
Domain
Source IP
Subnet
Content Type
https://www.peplink.com 71 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave
Choose to Cache on all domains, or enter domain names and then choose either
Cache the specified domains only or Do not cache the specified domains.
This setting allows caching to be applied to the user-specified IP subnets. If "Any"
is selected, then caching will apply to all subnets.
Check these boxes to cache the listed content types or leave boxes unchecked to
disable caching for the listed types.

Cache Lifetime
Settings
Enter a file extension, such as JPG or DOC. Then enter a lifetime in days to
specify how long files with that extension will be cached. Add or delete entries
using the controls on the right.
11.2 Scheduling Content Prefetching
Content prefetching allows you to download content on a schedule that you define, which can
help to preserve network bandwidth during busy times and keep costs down. To access
MediaFast content prefetching settings, select Advanced >Prefetch Schedule.
Prefetch Schedule Settings
Name
Status
Next Run
Time/Last Run
Time
Last Duration
Result
Last Download
This field displays the name given to the scheduled download.
Check the status of your scheduled download here.
These fields display the date and time of the next and most recent occurrences of
the scheduled download.
Check this field to ensure that the most recent download took as long as expected
to complete. A value that is too low might indicate an incomplete download or
incorrectly specified download target, while a value that is too long could mean a
download with an incorrectly specified target or stop time.
This field indicates whether downloads are in progress ( ) or complete ( ).
Check this field to ensure that the most recent download file size is within the
expected range. A value that is too low might indicate an incomplete download or
https://www.peplink.com 72 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

incorrectly specified download target, while a value that is too long could mean a
download with an incorrectly specified target or stop time. This field is also useful
for quickly seeing which downloads are consuming the most storage space.
To begin a scheduled download immediately, click .
Actions
To cancel a scheduled download, click .
To edit a scheduled download, click .
To delete a scheduled download, click .
Click to begin creating a new scheduled download. Clicking the button will cause
the following screen to appear:
New Schedule
Simply provide the requested information to create your schedule.
Clear Web Cache
Clear Statistics
To clear all cached content, click this button. Note that this action cannot be
undone.
To clear all prefetch and status page statistics, click this button.
11.3 Viewing MediaFast Statistics
To get details on storage and bandwidth usage, select Status>MediaFast.
https://www.peplink.com 73 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

https://www.peplink.com 74 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

12 Bandwidth Bonding SpeedFusion
TM
/ PepVPN
TM
Pepwave bandwidth bonding SpeedFusion
WAN routers to bond multiple Internet connections to increase site-to-site bandwidth and reliability.
SpeedFusion functionality securely connects your Pepwave router to another Pepwave or Peplink
device (Peplink Balance 210/310/380/580/710/1350 only). Data, voice, or video communications
between these locations are kept confidential across the public Internet.
TM
Bandwidth bonding SpeedFusion
of failures and network congestion at one or more WANs, other WANs can be used to continue
carrying the network traffic.
Different models of our SD-WAN routers have different numbers of site-to-site connections
allowed. End-users who need to have more site-to-site connections can purchase a
SpeedFusion license to increase the number of site-to-site connections allowed.
Pepwave routers can aggregate all WAN connections’ bandwidth for routing SpeedFusion
traffic. Unless all the WAN connections of one site are down, Pepwave routers can keep the
VPN up and running.
VPN bandwidth bonding is supported in Firmware 5.1 or above. All available bandwidth will be
utilized to establish the VPN tunnel, and all traffic will be load balanced at packet level across all
links. VPN bandwidth bonding is enabled by default.
is specifically designed for multi-WAN environments. In case
is our patented technology that enables our SD-
TM
12.1 PepVPN
To configure PepVPN and SpeedFusion, navigate to Advanced>SpeedFusion™ or
Advanced>PepVPN.
https://www.peplink.com 75 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

The local LAN subnet and subnets behind the LAN (defined under Static Route on the LAN
settings page) will be advertised to the VPN. All VPN members (branch offices and
headquarters) will be able to route to local subnets.
Note that all LAN subnets and the subnets behind them must be unique. Otherwise, VPN
members will not be able to access each other.
All data can be routed over the VPN using the 256-bit AES encryption standard. To configure,
navigate to Advanced>SpeedFusion™ or Advanced>PepVPN and click the New Profile
button to create a new VPN profile (you may have to first save the displayed default profile in
order to access the New Profile button). Each profile specifies the settings for making VPN
connection with one remote Pepwave or Peplink device. Note that available settings vary by
model.
A list of defined SpeedFusion
connection profiles and a Link Failure Detection Time option will
be shown. Click the New Profile button to create a new VPN connection profile for making a
VPN connection to a remote Peplink Balance via the available WAN connections. Each profile is
for making a VPN connection with one remote Peplink Balance.
https://www.peplink.com 76 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

PepVPN Profile Settings
This field is for specifying a name to represent this profile. The name can be any
Name
Active
Encryption
Authentication
Remote ID /
Pre-shared Key
combination of alphanumeric characters (0-9, A-Z, a-z), underscores (_), dashes
(-), and/or non-leading/trailing spaces ( ).
When this box is checked, this VPN connection profile will be enabled. Otherwise,
it will be disabled.
By default, VPN traffic is encrypted with 256-bit AES. If Off is selected on both
sides of a VPN connection, no encryption will be applied.
Select from By Remote ID Only, Preshared Key, or X.509 to specify the method
the Peplink Balance will use to authenticate peers. When selecting By Remote ID
Only, be sure to enter a unique peer ID number in the Remote ID field.
This optional field becomes available when Remote ID / Pre-shared Key is
selected as the Peplink Balance’s VPN Authentication method, as explained
above. Pre-shared Key defines the pre-shared key used for this particular VPN
connection. The VPN connection's session key will be further protected by the preshared key. The connection will be up only if the pre-shared keys on each side
match. When the peer is running firmware 5.0+, this setting will be ignored.
https://www.peplink.com 77 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Enter Remote IDs either by typing out each Remote ID and Pre-shared Key, or by
pasting a CSV. If you wish to paste a CSV, click the icon next to the “Remote
ID / Preshared Key” setting.
These optional fields become available when X.509 is selected as the Peplink
Remote
ID/Remote
Certificate
Balance’s VPN authentication method, as explained above. To authenticate VPN
connections using X.509 certificates, copy and paste certificate details into these
fields. To get more information on a listed X.509 certificate, click the Show Details
link below the field.
Allow Shared
Remote ID
NAT Mode
Remote IP
Address / Host
Names
(Optional)
Cost
Data Port
When this option is enabled, the router will allow multiple peers to run using the
same remote ID.
Check this box to allow the local DHCP server to assign an IP address to the
remote peer. When NAT Mode is enabled, all remote traffic over the VPN will be
tagged with the assigned IP address using network address translation.
If NAT Mode is not enabled, you can enter a remote peer’s WAN IP address or
hostname(s) here. If the remote uses more than one address, enter only one of
them here. Multiple hostnames are allowed and can be separated by a space
character or carriage return. Dynamic-DNS host names are also accepted.
This field is optional. With this field filled, the Peplink Balance will initiate
connection to each of the remote IP addresses until it succeeds in making a
connection. If the field is empty, the Peplink Balance will wait for connection from
the remote peer. Therefore, at least one of the two VPN peers must specify this
value. Otherwise, VPN connections cannot be established.
Define path cost for this profile.
OSPF will determine the best route through the network using the assigned cost.
Default: 10
This field is used to specify a UDP port number for transporting outgoing VPN
data. If Default is selected, UDP port 4500 will be used. Port 32015 will be used if
the remote unit uses Firmware prior to version 5.4 or if port 4500 is unavailable. If
Custom is selected, enter an outgoing port number from 1 to 65535.
Bandwidth Limit
Cost
WAN
SmoothingA
Define maximum download and upload speed to each individual peer. This
functionality requires the peer to use PepVPN version 4.0.0 or above.
Define path cost for this profile.
OSPF will determine the best route through the network using the assigned cost.
Default: 10
Select the degree to which WAN Smoothing will be implemented across your
WAN links.
https://www.peplink.com 78 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Use IP ToS
Latency
Difference Cutoff
A
- Advanced feature, please click the button on the top right-hand corner to activate.
Checking this button enables the use of IP ToS header field.
Traffic will be stopped for links that exceed the specified millisecond value with
respect to the lowest latency link. (e.g. Lowest latency is 100ms, a value of 500ms
means links with latency 600ms or more will not be used)
To enable Layer 2 Bridging between PepVPN profiles, navigate to Network>LAN>Basic
Settings>*LAN Profile Name* and refer to instructions in section 9.1
8.41
WAN Connection Priority
If your device supports it, you can specify the priority of WAN connections to be
used for making VPN connections. WAN connections set to OFF will never be
WAN Connection
Priority
used. Only available WAN connections with the highest priority will be used.
To enable asymmetric connections, connection mapping to remote WANs, cut-off
latency, and packet loss suspension time, click the button.
Send All Traffic To
This feature allows you to redirect all traffic to a specified PepVPN connection. Click the button to
select your connection and the following menu will appear:
https://www.peplink.com 79 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

You could also specify a DNS server to resolve incoming DNS requests. Click the checkbox next to
Backup Site to designate a backup SpeedFusion profile that will take over, should the main PepVPN
connection fail.
Outbound Policy/PepVPN Outbound Custom Rules
Some models allow you to set outbound policy and custom outbound rules from Advanced>PepVPN.
See Section 14 for more information on outbound policy settings.
PepVPN Local ID
The local ID is a text string to identify this local unit when establishing a VPN connection. When creating
a profile on a remote unit, this local ID must be entered in the remote unit's Remote ID field. Click the
icon to edit Local ID.
https://www.peplink.com 80 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

PepVPN Settings
To designate a custom handshake port (TCP), click the custom radio button and
Handshake Port
A
enter the port number you wish to designate.
Backward
Compatibility
Link Failure
Detection Time
A
- Advanced feature, please click the button on the top right-hand corner to activate.
Determine the level of backward compatibility needed for PepVPN tunnels. The
use of the Latest setting is recommended as it will improve the performance and
resilience of SpeedFusion connections.
The bonded VPN can detect routing failures on the path between two sites over
each WAN connection. Failed WAN connections will not be used to route VPN
traffic. Health check packets are sent to the remote unit to detect any failure. The
more frequently checks are sent, the shorter the detection time, although more
bandwidth will be consumed.
When Recommended (default) is selected, a health check packet is sent every
five seconds, and the expected detection time is 15 seconds.
When Fast is selected, a health check packet is sent every three seconds, and the
expected detection time is six seconds.
When Faster is selected, a health check packet is sent every second, and the
expected detection time is two seconds.
When Extreme is selected, a health check packet is sent every 0.1 second, and
the expected detection time is less than one second.
Important Note
Peplink proprietary SpeedFusionTM uses TCP port 32015 and UDP port 4500 for establishing VPN connections. If
you have a firewall in front of your Pepwave devices, you will need to add firewall rules for these ports and protocols
to allow inbound and outbound traffic to pass through the firewall.
Tip
Want to know more about VPN sub-second session failover? Visit our YouTube Channel for a video tutorial!
https://www.peplink.com 81 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

http://youtu.be/TLQgdpPSY88
12.2 The Pepwave Router Behind a NAT Router
Pepwave routers support establishing SpeedFusionTM over WAN connections which are behind
a NAT (network address translation) router.
To enable a WAN connection behind a NAT router to accept VPN connections, you can
configure the NAT router in front of the WAN connection to inbound port-forward TCP port
32015 to the Pepwave router.
If one or more WAN connections on Unit A can accept VPN connections (by means of port
forwarding or not), while none of the WAN connections on the peer Unit B can do so, you should
enter all of Unit A’s public IP addresses or hostnames into Unit B’s Remote IP Addresses /
Host Names field. Leave the field in Unit A blank. With this setting, a SpeedFusion
can be set up and all WAN connections on both sides will be utilized.
TM
connection
See the following diagram for an example of this setup in use:
https://www.peplink.com 82 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

One of the WANs connected to Router A is non-NAT’d (212.1.1.1). The rest of the WANs
connected to Router A and all WANs connected to Router B are NAT’d. In this case, the Peer IP
Addresses / Host Names field for Router B should be filled with all of Router A’s hostnames or
public IP addresses (i.e., 212.1.1.1, 212.2.2.2, and 212.3.3.3), and the field in Router A can be
left blank. The two NAT routers on WAN1 and WAN3 connected to Router A should inbound
port-forward TCP port 32015 to Router A so that all WANs will be utilized in establishing the
VPN.
12.3 SpeedFusionTM Status
SpeedFusionTM status is shown in the Dashboard. The connection status of each connection
profile is shown as below.
TM
After clicking the Status button at the top right corner of the SpeedFusion
TM
forwarded to Status>SpeedFusion
, where you can view subnet and WAN connection
information for each VPN peer. Please refer to Section 22.6 for details.
table, you will be
IP Subnets Must Be Unique Among VPN Peers
The entire interconnected SpeedFusionTM network is a single non-NAT IP network. Avoid duplicating subnets in
your sites to prevent connectivity problems when accessing those subnets.
13 IPsec VPN
IPsec VPN functionality securely connects one or more branch offices to your company's main
headquarters or to other branches. Data, voice, and video communications between these
locations are kept safe and confidential across the public Internet.
IPsec VPN on Pepwave routers is specially designed for multi-WAN environments. For
instance, if a user sets up multiple IPsec profiles for a multi-WAN environment and WAN1 is
connected and healthy, IPsec traffic will go through this link. However, should unforeseen
problems (e.g., unplugged cables or ISP problems) cause WAN1 to go down, our IPsec
implementation will make use of WAN2 and WAN3 for failover.
https://www.peplink.com 83 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

13.1 IPsec VPN Settings
Many Pepwave products can make multiple IPsec VPN connections with Peplink, Pepwave,
Cisco, and Juniper routers. Note that all LAN subnets and the subnets behind them must be
unique. Otherwise, VPN members will not be able to access each other. All data can be routed
over the VPN with a selection of encryption standards, such as 3DES, AES-128, and AES-256.
To configure IPsec VPN on Pepwave devices that support it, navigate to Advanced>IPsec
VPN.
A NAT-Traversal option and list of defined IPsec VPN profiles will be shown. NAT-Traversal
should be enabled if your system is behind a NAT router. Click the New Profile button to create
new IPsec VPN profiles that make VPN connections to remote Pepwave, Cisco, or Juniper
routers via available WAN connections. To edit any of the profiles, click on its associated
connection name in the leftmost column.
https://www.peplink.com 84 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

https://www.peplink.com 85 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

IPsec VPN Settings
Name
Active
Connect Upon
Disconnection
of
Remote
Gateway IP
Address / Host
Name
Local Networks
This field is for specifying a local name to represent this connection profile.
When this box is checked, this IPsec VPN connection profile will be enabled.
Otherwise, it will be disabled.
Check this box and select a WAN to connect to this VPN automatically when the
specified WAN is disconnected.
Enter the remote peer’s public IP address. For Aggressive Mode, this is
optional.
Enter the local LAN subnets here. If you have defined static routes, they will be
shown here.
Using NAT, you can map a specific local network / IP address to another, and
the packets received by remote gateway will appear to be coming from the
mapped network / IP address. This allow you to establish IPsec connection to a
remote site that has one or more subnets overlapped with local site.
Two types of NAT policies can be defined:
One-to-One NAT policy: if the defined subnet in Local Network and NAT Network
has the same size, for example, policy "192.168.50.0/24 > 172.16.1.0/24" will
translate the local IP address 192.168.50.10 to 172.16.1.10 and 192.168.50.20
to 172.16.1.20. This is a bidirectional mapping which means clients in remote
site can initiate connection to the local clients using the mapped address too.
Many-to-One NAT policy: if the defined NAT Network on the right hand side is an
IP address (or having a network prefix /32), for example, policy "192.168.1.0/24
> 172.168.50.1/32" will translate all clients in 192.168.1.0/24 network to
172.168.50.1. This is a unidirectional mapping which means clients in remote
site will not be able to initiate connection to the local clients.
Remote
Networks
Authentication
Enter the LAN and subnets that are located at the remote site here.
To access your VPN, clients will need to authenticate by your choice of methods.
Choose between the Preshared Key and X.509 Certificate methods of
authentication.
https://www.peplink.com 86 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Mode
Force UDP
Encapsulation
Pre-shared Key
Remote
Certificate (pem
encoded)
Local ID
Remote ID
Phase 1 (IKE)
Proposal
Choose Main Mode if both IPsec peers use static IP addresses. Choose
Aggressive Mode if one of the IPsec peers uses dynamic IP addresses.
For forced UDP encapsulation regardless of NAT-traversal, tick this checkbox.
This defines the peer authentication pre-shared key used to authenticate this
VPN connection. The connection will be up only if the pre-shared keys on each
side match.
Available only when X.509 Certificate is chosen as the Authentication method,
this field allows you to paste a valid X.509 certificate.
In Main Mode, this field can be left blank. In Aggressive Mode, if Remote
Gateway IP Address is filled on this end and the peer end, this field can be left
blank. Otherwise, this field is typically a U-FQDN.
In Main Mode, this field can be left blank. In Aggressive Mode, if Remote
Gateway IP Address is filled on this end and the peer end, this field can be left
blank. Otherwise, this field is typically a U-FQDN.
In Main Mode, this allows setting up to six encryption standards, in descending
order of priority, to be used in initial connection key negotiations. In Aggressive
Mode, only one selection is permitted.
This is the Diffie-Hellman group used within IKE. This allows two parties to
Phase 1 DH
Group
Phase 1 SA
Lifetime
Phase 2 (ESP)
Proposal
Phase 2 PFS
Group
establish a shared secret over an insecure communications channel. The larger
the group number, the higher the security.
Group 2: 1024-bit is the default value.
Group 5: 1536-bit is the alternative option.
This setting specifies the lifetime limit of this Phase 1 Security Association. By
default, it is set at 3600 seconds.
In Main Mode, this allows setting up to six encryption standards, in descending
order of priority, to be used for the IP data that is being transferred. In
Aggressive Mode, only one selection is permitted.
Perfect forward secrecy (PFS) ensures that if a key was compromised, the
attacker will be able to access only the data protected by that key.
None - Do not request for PFS when initiating connection. However, since there
is no valid reason to refuse PFS, the system will allow the connection to use PFS
if requested by the remote peer. This is the default value.
Group 2: 1024-bit Diffie-Hellman group. The larger the group number, the higher
the security.
https://www.peplink.com 87 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Group 5: 1536-bit is the third option.
Phase 2 SA
Lifetime
WAN Connection
This setting specifies the lifetime limit of this Phase 2 Security Association. By
default, it is set at 28800 seconds.
WAN Connection Priority
Select the appropriate WAN connection from the drop-down menu.
14 Outbound Policy Management
Pepwave routers can flexibly manage and load balance outbound traffic among WAN
connections.
Important Note
Outbound policy is applied only when more than one WAN connection is active
The settings for managing and load balancing outbound traffic are located at
Advanced>Outbound Policy or Advanced>PepVPN, depending on the model.
https://www.peplink.com 88 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave
.

14.1 Outbound Policy
Outbound policies for managing and load balancing outbound traffic are located at
Network>Outbound Policy> or Advanced>PepVPN>Outbound Policy.
There are three main selections for the outbound traffic policy:
● High Application Compatibility
● Normal Application Compatibility
● Custom
Note that some Pepwave routers provide only the Send All Traffic To setting here. See
Section 12.1 for details.
Outbound Policy Settings
High Application
Compatibility
Normal
Application
Compatibility
Custom
Outbound traffic from a source LAN device is routed through the same WAN
connection regardless of the destination Internet IP address and protocol. This
option provides the highest application compatibility.
Outbound traffic from a source LAN device to the same destination Internet IP
address will be routed through the same WAN connection persistently, regardless
of protocol. This option provides high compatibility to most applications, and users
still benefit from WAN link load balancing when multiple Internet servers are
accessed.
Outbound traffic behavior can be managed by defining rules in a custom rule
table. A default rule can be defined for connections that cannot be matched with
any of the rules.
The default policy is Normal Application Compatibility.
Tip
Want to know more about creating outbound rules? Visit our YouTube Channel for a video tutorial!
https://www.peplink.com 89 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

http://youtu.be/rKH4AS_bQnE
14.2 Custom Rules for Outbound Policy
Click in the Outbound Policy form. Choose Custom and press the Save button.
14.2.1 Algorithm: Weighted Balance
This setting specifies the ratio of WAN connection usage to be applied on the specified IP
protocol and port. This setting is applicable only when Algorithm is set to Weighted Balance.
https://www.peplink.com 90 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

The amount of matching traffic that is distributed to a WAN connection is proportional to the
weight of the WAN connection relative to the total weight. Use the sliders to change each
WAN’s weight.
For example, with the following weight settings:
● Ethernet WAN1: 10
● Ethernet WAN2: 10
● Wi-Fi WAN: 10
● Cellular 1: 10
● Cellular 2: 10
● USB: 10
Total weight is 60 = (10 +10 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 10).
Matching traffic distributed to Ethernet WAN1 is 16.7% = (10 / 60 x 100%.
Matching traffic distributed to Ethernet WAN2 is 16.7% = (10 / 60) x 100%.
Matching traffic distributed to Wi-Fi WAN is 16.7% = (10 / 60) x 100%.
Matching traffic distributed to Cellular 1 is 16.7% = (10 / 60) x 100%.
Matching traffic distributed to Cellular 2 is 16.7% = (10 / 60) x 100%.
Matching traffic distributed to USB is 16.7% = (10 / 60) x 100%.
14.2.2 Algorithm: Persistence
The configuration of persistent services is the solution to the few situations where link load
https://www.peplink.com 91 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave
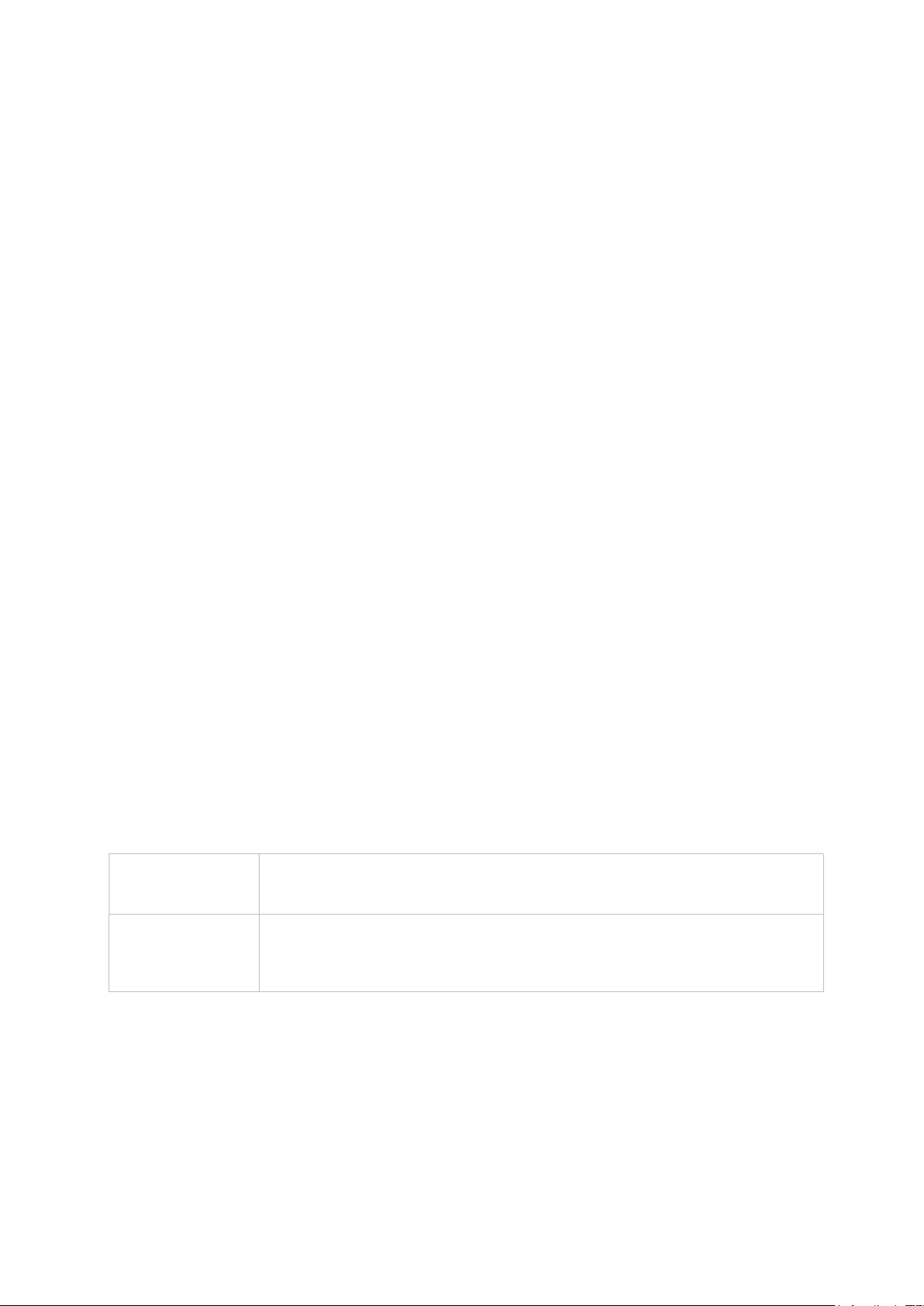
distribution for Internet services is undesirable. For example, for security reasons, many ebanking and other secure websites terminate the session when the client computer’s Internet IP
address changes mid-session.
In general, different Internet IP addresses represent different computers. The security concern
is that an IP address change during a session may be the result of an unauthorized intrusion
attempt. Therefore, to prevent damages from the potential intrusion, the session is terminated
upon the detection of an IP address change.
Pepwave routers can be configured to distribute data traffic across multiple WAN connections.
Also, the Internet IP depends on the WAN connections over which communication actually
takes place. As a result, a LAN client computer behind the Pepwave router may communicate
using multiple Internet IP addresses. For example, a LAN client computer behind a Pepwave
router with three WAN connections may communicate on the Internet using three different IP
addresses.
With the persistence feature, rules can be configured to enable client computers to persistently
utilize the same WAN connections for e-banking and other secure websites. As a result, a client
computer will communicate using one IP address, eliminating the issues mentioned above.
There are two persistent modes: By Source and By Destination.
By Source:
By Destination:
The same WAN connection will be used for traffic matching the rule and
originating from the same machine, regardless of its destination. This option will
provide the highest level of application compatibility.
The same WAN connection will be used for traffic matching the rule, originating
from the same machine, and going to the same destination. This option can
better distribute loads to WAN connections when there are only a few client
machines.
The default mode is By Source. When there are multiple client requests, they can be distributed
(persistently) to WAN connections with a weight. If you choose Auto in Load Distribution, the
weights will be automatically adjusted according to each WAN’s Downstream Bandwidth
https://www.peplink.com 92 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

which is specified in the WAN settings page). If you choose Custom, you can customize the
weight of each WAN manually by using the sliders.
14.2.3 Algorithm: Enforced
This setting specifies the WAN connection usage to be applied on the specified IP protocol and
port. This setting is applicable only when Algorithm is set to Enforced.
Matching traffic will be routed through the specified WAN connection, regardless of the health
check status of the WAN connection. Starting from Firmware 5.2, outbound traffic can be
TM
enforced to go through a specified SpeedFusion
connection.
14.2.4 Algorithm: Priority
This setting specifies the priority of the WAN connections used to route the specified network
service. The highest priority WAN connection available will always be used for routing the
specified type of traffic. A lower priority WAN connection will be used only when all higher
priority connections have become unavailable.
Starting from Firmware 5.2, outbound traffic can be prioritized to go through SpeedFusion
TM
connection(s). By default, VPN connections are not included in the priority list.
Tip
https://www.peplink.com 93 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Configure multiple distribution rules to accommodate different kinds of services.
14.2.5 Algorithm: Overflow
The traffic matching this rule will be routed through the healthy WAN connection that has the
highest priority and is not in full load. When this connection gets saturated, new sessions will be
routed to the next healthy WAN connection that is not in full load.
Drag and drop to specify the order of WAN connections to be used for routing traffic. Only the
highest priority healthy connection that is not in full load will be used.
14.2.6 Algorithm: Least Used
The traffic matching this rule will be routed through the healthy WAN connection that is selected
in Connection and has the most available download bandwidth. The available download
bandwidth of a WAN connection is calculated from the total download bandwidth specified on
the WAN settings page and the current download usage. The available bandwidth and WAN
selection is determined every time an IP session is made.
14.2.7 Algorithm: Lowest Latency
The traffic matching this rule will be routed through the healthy WAN connection that is selected
https://www.peplink.com 94 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

in Connection and has the lowest latency. Latency checking packets are issued periodically to
a nearby router of each WAN connection to determine its latency value. The latency of a WAN
is the packet round trip time of the WAN connection. Additional network usage may be incurred
as a result.
Tip
The roundtrip time of a 6M down/640k uplink can be higher than that of a 2M down/2M up link because the overall
round trip time is lengthened by its slower upload bandwidth, despite its higher downlink speed. Therefore, this
algorithm is good for two scenarios:
● All WAN connections are symmetric; or
● A latency sensitive application must be routed through the lowest latency WAN, regardless of the WAN’s
available bandwidth.
14.2.8 Expert Mode
Expert Mode is available on some Pepwave routers for use by advanced
users. To enable the feature, click on the help icon and click turn on Expert
.
Mode
In Expert Mode, a new special rule, SpeedFusion
the Custom Rules table. This rule represents all SpeedFusion
learned from remote VPN peers. By default, this bar is on the top of all custom
rules. This position means that traffic for remote VPN subnets will be routed to
the corresponding VPN peer. You can create custom Priority or Enforced
rules and move them
above the bar to override the SpeedFusion
Upon disabling Expert Mode, all rules above the bar will be removed.
TM
TM
routes.
Routes, is displayed in
TM
routes
15 Inbound Access
15.1 Port Forwarding Service
Pepwave routers can act as a firewall that blocks, by default, all inbound access from the
Internet. By using port forwarding, Internet users can access servers behind the Pepwave
https://www.peplink.com 95 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

router. Inbound port forwarding rules can be defined at Advanced>Port Forwarding.
To define a new service, click Add Service.
Port Forwarding Settings
This setting specifies whether the inbound service takes effect. When Enable is
checked, the inbound service takes effect: traffic is matched and actions are taken by
Enable
Service Name
IP Protocol
the Pepwave router based on the other parameters of the rule. When this setting is
disabled, the inbound service does not take effect: the Pepwave router disregards the
other parameters of the rule.
This setting identifies the service to the system administrator. Valid values for this
setting consist of only alphanumeric and underscore “_” characters.
The IP Protocol setting, along with the Port setting, specifies the protocol of the
service as TCP, UDP, ICMP, or IP. Traffic that is received by the Pepwave router via
the specified protocol at the specified port(s) is forwarded to the LAN hosts specified
by the Servers setting. Please see below for details on the Port and Servers
settings. Alternatively, the Protocol Selection Tool drop-down menu can be used to
automatically fill in the protocol and a single port number of common Internet services
(e.g. HTTP, HTTPS, etc.). After selecting an item from the Protocol Selection Tool
drop-down menu, the protocol and port number remain manually modifiable.
https://www.peplink.com 96 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

The Port setting specifies the port(s) that correspond to the service, and can be
configured to behave in one of the following manners:
Any Port, Single Port, Port Range, Port Map, and Range Mapping
Any Port: all traffic that is received by the Pepwave router via the specified protocol is
forwarded to the servers specified by the Servers setting. For example, with IP
Protocol set to TCP, and Port set to Any Port, all TCP traffic is forwarded to the
configured servers.
Single Port: traffic that is received by the Pepwave router via the specified protocol at
the specified port is forwarded via the same port to the servers specified by the
Servers setting. For example, with IP Protocol set to TCP, and Port set to Single
Port and Service Port 80, TCP traffic received on port 80 is forwarded to the
configured servers via port 80.
Port Range: traffic that is received by the Pepwave router via the specified protocol at
Port
the specified port range is forwarded via the same respective ports to the LAN hosts
specified by the Servers setting. For example, with IP Protocol set to TCP, and Port
set to Port Range and Service Ports 80-88, TCP traffic received on ports 80 through
88 is forwarded to the configured servers via the respective ports.
Inbound IP
Address(es)
Server IP
Address
Port Mapping: traffic that is received by Pepwave router via the specified protocol at
the specified port is forwarded via a different port to the servers specified by the
Servers setting.
For example, with IP Protocol set to TCP, and Port set to Port Mapping, Service
Port 80, and Map to Port 88, TCP traffic on port 80 is forwarded to the configured
servers via port 88.
(Please see below for details on the Servers setting.)
Range Mapping: traffic that is received by the Pepwave router via the specified
protocol at the specified port range is forwarded via a different port to the servers
specified by the Servers setting.
This setting specifies the WAN connections and Internet IP address(es) from which
the service can be accessed.
This setting specifies the LAN IP address of the server that handles the requests for
the service.
https://www.peplink.com 97 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

15.1.1 UPnP / NAT-PMP Settings
UPnP and NAT-PMP are network protocols which allow a computer connected to the LAN port
to automatically configure the router to allow parties on the WAN port to connect to itself. That
way, the process of inbound port forwarding becomes automated.
When a computer creates a rule using these protocols, the specified TCP/UDP port of all WAN
connections' default IP address will be forwarded.
Check the corresponding box(es) to enable UPnP and/or NAT-PMP. Enable these features only
if you trust the computers connected to the LAN ports.
When the options are enabled, a table listing all the forwarded ports under these two protocols
can be found at Status>UPnP / NAT-PMP.
16 NAT Mappings
NAT mappings allow IP address mapping of all inbound and outbound NAT’d traffic to and from
an internal client IP address. Settings to configure NAT mappings are located at
Advanced>NAT Mappings.
To add a rule for NAT mappings, click Add NAT Rule.
https://www.peplink.com 98 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

Note that inbound mapping is not needed for WAN connections in drop
-
in mode
NAT Mapping Settings
LAN
Client(s)
Address
Range
Network
Inbound
Mappings
NAT mapping rules can be defined for a single LAN IP Address, an IP Range,
or an IP Network.
This refers to the LAN host’s private IP address. The system maps this address
to a number of public IP addresses (specified below) in order to facilitate
inbound and outbound traffic. This option is only available when IP Address is
selected.
The IP range is a contiguous group of private IP addresses used by the LAN
host. The system maps these addresses to a number of public IP addresses
(specified below) to facilitate outbound traffic. This option is only available when
IP Range is selected.
The IP network refers to all private IP addresses and ranges managed by the
LAN host. The system maps these addresses to a number of public IP
addresses (specified below) to facilitate outbound traffic. This option is only
available when IP Network is selected.
This setting specifies the WAN connections and corresponding WAN-specific
Internet IP addresses on which the system should bind. Any access to the
specified WAN connection(s) and IP address(es) will be forwarded to the LAN
host. This option is only available when IP Address is selected in the LAN
Client(s) field.
https://www.peplink.com 99 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave

or IP forwarding mode. Also note that each WAN IP address can be associated
to one NAT mapping only.
This setting specifies the WAN IP addresses that should be used when an IP
connection is made from a LAN host to the Internet. Each LAN host in an IP
range or IP network will be evenly mapped to one of each selected WAN's IP
addresses (for better IP address utilization) in a persistent manner (for better
Outbound
Mappings
application compatibility).
Note that if you do not want to use a specific WAN for outgoing accesses, you
should still choose default here, then customize the outbound access rule in the
Outbound Policy section. Also note that WAN connections in drop-in mode or
IP forwarding mode are not shown here.
Click Save to save the settings when configuration has been completed.
Important Note
Inbound firewall rules override the Inbound Mappings settings.
17 QoS
17.1 User Groups
LAN and PPTP clients can be categorized into three user groups: Manager, Staff, and Guest.
This menu allows you to define rules and assign client IP addresses or subnets to a user group.
You can apply different bandwidth and traffic prioritization policies on each user group in
the Bandwidth Control and Application sections (note that the options available here vary by
model).
The table is automatically sorted by rule precedence. The smaller and more specific subnets are
put towards the top of the table and have higher precedence; larger and less specific subnets
are placed towards the bottom.
Click the Add button to define clients and their user group. Click the button to remove the
defined rule. Two default rules are pre-defined and put at the bottom. They are All DHCP
reservation clients and Everyone, and they cannot be removed. The All DHCP reservation
client represents the LAN clients defined in the DHCP Reservation table on the LAN settings
page. Everyone represents all clients that are not defined in any rule above. Click on a rule to
change its group.
https://www.peplink.com 100 Copyright @ 2019 Pepwave
 Loading...
Loading...